Unit Five The Muscular System
|
|
|
- Felicia Cummings
- 6 years ago
- Views:
Transcription
1 Unit Five The Muscular System I. Introduction A. Definition: the muscular system is composed of all the muscles of the body including the movements of the total body, as well as movements the body. B. Properties of Muscle Tissue 1. the ability of muscle tissue to shorten or contract. 2. the ability of muscle tissue to be extended or stretched within limits. 3. the ability of muscle tissue to return to its original state after being stretched. 4. the susceptibility of muscle tissue to react to external stimuli. 5. the state in which muscle is partially contracted allowing it to react instantly when stimulated. C. Classification of Muscle Based on Nervous Control 1. muscle is muscle not subject to conscious control A. and muscle are of this type 2. muscle is muscle subject to conscious control B. is of this type
2 D. Terminology 1. Special terms for cellular parts of the muscle: A. - muscle cell membrane B. - muscle cell cytoplasm C. - muscle cell SARKOS FLESH LEMMA HUSK PLASM - JELLY 2. - connect muscle to bone, tough tissue fibers. 3. Origin- point of muscle attachment. 4. Insertion- point of muscle attachment. 5. Action- movement a particular muscle produces. 6. Innervation- supply to a muscle. 7. Muscle belly- that part of the muscle the origin and the insertion. Diagram of a muscle and its attachments:
3 II. Physiology of Skeletal Muscle Cells (or Muscle Fibers) A. Diagram of a muscle fiber: B. Enormous, large diameter and up to long. C. Multinucleated 1. Hundreds of just below the sarcolemma. The many nuclei are needed because of the high metabolic rate and protein needed for muscle. D. Myoblasts (myo = muscle, blast = precursor) 1. During development, groups of called myoblasts fuse together to create individual skeletal muscle fibers. 2. Each in a skeletal muscle fiber is the result of a single myoblasts. E. Myofibril 1. A cylindrical structure as long as the entire muscle cell. 2. Each skeletal muscle cell contains hundreds to thousands of. 3. Myofibrils can actively due to their structure.
4 F. Sarcomere (sarkos = flesh, meros= part) 1. Myofibrils are divided into sections called sarcomeres. 2. The sarcomere is the functional unit of a myofibril. 3. The sarcomere contains sections of the actin and myosin microfilaments. A. filaments are thin and made up of the protein actin B. filaments are thick and made up of the protein myosin 4. The interactions between actin and myosin result in contraction. 5. Schematic of a sarcomere: The Sliding Filament Theory
5 III. Types of Muscle Tissue A. muscle (striated, voluntary) 1. Connected to and responsible for the movement of bones. 2. Has a band-like appearance (striated) because of alternating light and dark areas due to the arrangement of actin and myosin microfilaments. 3. Is controlled by the nervous system. 4. Has multinucleated cells due to their enormous size. B. muscle (striated, involuntary) 1. Is only in heart. 2. Striations visible because the actin and myosin microfilaments are Arranged the same way in both skeletal and cardiac fibers. 3. Cardiac muscle fibers do not require nerve activity to stimulate contraction, pacemaker cells establish a regular rate of contraction. C. muscle (nonstriated, involuntary) 1. Is found in many places (ex-blood vessels, digestive organs). 2. Can contract on their own or from nerve activity but the nerve control would still be involuntary. 3. A smooth muscle fiber is a small, spindle-shaped cell with tapering ends, containing a single nucleus. D. Microscopic appearance of muscle fibers: 1. Smooth muscle 2. Cardiac muscle 3. Skeletal muscle
6 What is muscle type: I? How did you know? II? How did you know? III? How did you know? Add as many more characteristics to the Venn Diagram as possible.
7 IV. Functions of Muscles A. Allows 1. Movement of - skeletal muscles move the body by on bones of skeleton. 2. Movement of : A. muscle tissues pushes blood through the circulatory system. B. muscle tissue regulates the diameters of arteries. 3. Movement of - muscle pushes fluids and solids along the digestive tract (alimentary canal). V. Structure of Skeletal Muscle A. Muscle fiber- multinucleated and surrounded by a connective sheath, called. B. Fasciculus- groups of muscle fibers surrounded by a connective tissue called. C. Muscle belly- groups of fasciculi come together and are surrounded by connective tissue called. C. Diagram of the cross section of a muscle belly: a. Layers of the muscle (perimysium, epimysium, endomysium)
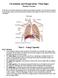
8 VI. Skeletal Muscles A. Physiology 1. Must work in 2. Muscles bones (Biceps pull forearm up, triceps pull forearm down.) 3. Muscles can only ; they cannot stretch themselves (they relax and allow themselves to be stretched). B. Muscle growth and loss 1. Muscles hypertrophy: 2. Muscle hyperplasia: 3. Muscle atrophy: C. Match the following muscles to the diagram: 1. Biceps brachii 6. Pectoralis major 11. Sartorius 2. Rectus femoris 7. gluteus maximus 12. Deltoid 3. Latissimus dorsi 8. Sternocleidomastoid 13. Biceps femoris 4. Rectus abdominous 9. Triceps brachii 14. Trapezius 5. Gastrocnemius 10. Frontalis 15. Achilles tendon
The Muscular System. Biology 105 Lecture 12 Chapter 6
 The Muscular System Biology 105 Lecture 12 Chapter 6 Outline I. Characteristics of muscles II. Three types of muscles III. Functions of muscles IV. Structure of skeletal muscles V. Mechanics of muscle
The Muscular System Biology 105 Lecture 12 Chapter 6 Outline I. Characteristics of muscles II. Three types of muscles III. Functions of muscles IV. Structure of skeletal muscles V. Mechanics of muscle
NOTES: The Muscular System (Ch 6, part 1)
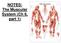 NOTES: The Muscular System (Ch 6, part 1) The muscular system consists of three types of muscle tissue: Skeletal Smooth Cardiac STRUCTURE OF A SKELETAL MUSCLE: *Individual muscles are the organs of the
NOTES: The Muscular System (Ch 6, part 1) The muscular system consists of three types of muscle tissue: Skeletal Smooth Cardiac STRUCTURE OF A SKELETAL MUSCLE: *Individual muscles are the organs of the
KeyPoint Muscle Physiology
 KeyPoint Muscle Physiology Muscle, what it s for and how it works, with mention of skeleton and adipose tissue BAB L7 Food Animal Biotechnology 3 types of muscle Skeletal. Striated, tubular, multinucleated
KeyPoint Muscle Physiology Muscle, what it s for and how it works, with mention of skeleton and adipose tissue BAB L7 Food Animal Biotechnology 3 types of muscle Skeletal. Striated, tubular, multinucleated
Muscular System Functions
 BMI 04 Skeletal Muscle & Force Generator J F Grosset BMI 04 2014 J F GROSSET 1 Muscular System Functions Body movement (Locomotion) Maintenance of posture Respiration Diaphragm and intercostal contractions
BMI 04 Skeletal Muscle & Force Generator J F Grosset BMI 04 2014 J F GROSSET 1 Muscular System Functions Body movement (Locomotion) Maintenance of posture Respiration Diaphragm and intercostal contractions
*The plasma membrane of a muscle fiber
 Skeletal Muscle Contraction: Histology: Sarcolemma: *The plasma membrane of a muscle fiber -T- tubules - Terminal Cisternae - Sarcoplasmic Reticulum *Transverse tubules- tube like invaginations or inward
Skeletal Muscle Contraction: Histology: Sarcolemma: *The plasma membrane of a muscle fiber -T- tubules - Terminal Cisternae - Sarcoplasmic Reticulum *Transverse tubules- tube like invaginations or inward
SHORT ANSWER. Write the word or phrase that best completes each statement or answers the question.
 Exam Name SHORT ANSWER. Write the word or phrase that best completes each statement or answers the question. Figure 9.1 Using Figure 9.1, match the following: 1) Endomysium. 2) Fascicle. 3) The tissue
Exam Name SHORT ANSWER. Write the word or phrase that best completes each statement or answers the question. Figure 9.1 Using Figure 9.1, match the following: 1) Endomysium. 2) Fascicle. 3) The tissue
Composition of Skeletal Muscle. Unit 6 Muscular System. 8.2 Structure of Skeletal Muscle. Functions of the Muscular System 12/7/2009
 Unit 6 Muscular System Mrs. Michaelsen Chetek High School Composition of Skeletal Muscle A. Skeletal muscle is an composed of several tissue types. 1. muscle tissue 2. tissue 3. vessels 4. tissues http://www.eicsd.k12.ny.us/schools/ems/sjf/spring2006/kelly-
Unit 6 Muscular System Mrs. Michaelsen Chetek High School Composition of Skeletal Muscle A. Skeletal muscle is an composed of several tissue types. 1. muscle tissue 2. tissue 3. vessels 4. tissues http://www.eicsd.k12.ny.us/schools/ems/sjf/spring2006/kelly-
Station 3. Appendicular and Axial skeleton
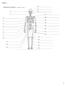 Station 1 1 Station 2 2 Station 3 Appendicular and Axial skeleton AXIAL SKELETON APPENDICULAR SKELETON 3 Station 4 4 Station 5 5 Station 5 6 Station 6 1. How many vertebrae make up the spine? 2. How many
Station 1 1 Station 2 2 Station 3 Appendicular and Axial skeleton AXIAL SKELETON APPENDICULAR SKELETON 3 Station 4 4 Station 5 5 Station 5 6 Station 6 1. How many vertebrae make up the spine? 2. How many
1. A.- 2. B.- 3. C.- 4. D.- 5. E.- Anatomy & Physiology 2A Name: FALL 2015 (Take Home) MINI-EXAM #4. Figure 11.2
 Anatomy & Physiology 2A Name: FALL 2015 (Take Home) MINI-EXAM #4 _ Figure 11.2 Using Figure 11.2: Completely define and describe letters A-E in the spaces provided below: 1. A.- 2. B.- 3. C.- 4. D.- 5.
Anatomy & Physiology 2A Name: FALL 2015 (Take Home) MINI-EXAM #4 _ Figure 11.2 Using Figure 11.2: Completely define and describe letters A-E in the spaces provided below: 1. A.- 2. B.- 3. C.- 4. D.- 5.
Meat proteins. Levels of complexity. Levels of complexity Myofibrils C, H, O, N. Amino acids. Myofibrils. Muscle fiber.
 Meat proteins Levels of complexity C, H, O, N Amino acids Actin Myosin Thin filaments Thick filaments Myofibrils Levels of complexity Myofibrils Muscle fiber Primary bundle Secondary bundle Muscle Changes
Meat proteins Levels of complexity C, H, O, N Amino acids Actin Myosin Thin filaments Thick filaments Myofibrils Levels of complexity Myofibrils Muscle fiber Primary bundle Secondary bundle Muscle Changes
ANSC/FSTC 607 Physiology & Biochemistry of Muscle as a Food Muscle Ultrastructure
 Muscle ultrastructure ANSC/FSTC 607 Physiology & Biochemistry of Muscle as a Food Muscle Ultrastructure I. Sarcomeres A. Sarcomeres are the functional units of myofibrils. B. Resting length is 2-3 µm (from
Muscle ultrastructure ANSC/FSTC 607 Physiology & Biochemistry of Muscle as a Food Muscle Ultrastructure I. Sarcomeres A. Sarcomeres are the functional units of myofibrils. B. Resting length is 2-3 µm (from
Nelson Pages
 Nelson Pages 280 309 Biology 20 Unit D: Respiratory and Motor Systems Earth s atmosphere is about: 78 % N2 21 % O2 1 % remaining gases Aerobic organisms require O 2 for cellular respiration Breathing (ventilation).
Nelson Pages 280 309 Biology 20 Unit D: Respiratory and Motor Systems Earth s atmosphere is about: 78 % N2 21 % O2 1 % remaining gases Aerobic organisms require O 2 for cellular respiration Breathing (ventilation).
Sport Biomechanical Project The Golf Swing! Noah Gibson
 Sport Biomechanical Project The Golf Swing! Noah Gibson Table&of&Contents&! Page # 1. Title Page 2. Table of Contents 3. A Gold Swing: Introduction and Analysis 4. Preliminary Movement of the Golf Swing
Sport Biomechanical Project The Golf Swing! Noah Gibson Table&of&Contents&! Page # 1. Title Page 2. Table of Contents 3. A Gold Swing: Introduction and Analysis 4. Preliminary Movement of the Golf Swing
NROSCI/BIOSC 1070 and MSNBIO 2070 September 1, 2017 Mechanisms of Skeletal Muscle Contraction
 NROSCI/BIOSC 1070 and MSNBIO 2070 September 1, 2017 Mechanisms of Skeletal Muscle Contraction Anatomy of Skeletal Muscle Fibers Most skeletal muscle fibers extend the entire length of a muscle, and are
NROSCI/BIOSC 1070 and MSNBIO 2070 September 1, 2017 Mechanisms of Skeletal Muscle Contraction Anatomy of Skeletal Muscle Fibers Most skeletal muscle fibers extend the entire length of a muscle, and are
The process that involves air entering and exiting the lungs is called VENTILATION
 Bio 067: Review sections 10-12 Respiration, skeletal, muscular Functions of the respiratory system: The process that involves air entering and exiting the lungs is called VENTILATION Involves: Inhalation
Bio 067: Review sections 10-12 Respiration, skeletal, muscular Functions of the respiratory system: The process that involves air entering and exiting the lungs is called VENTILATION Involves: Inhalation
Monday, ! Today: Respiratory system! 5/20/14! Transport of Blood! What we ve been covering! Circulatory system! Parts of blood! Heart! tubing!
 Monday, 5.19.14! What we ve been covering! Circulatory system! Parts of blood! Heart! tubing! Transport of Blood! What is transported! Nutrients! Oxygen! Carbon Dioxide! Hormones! Antibodies! What it is/does!
Monday, 5.19.14! What we ve been covering! Circulatory system! Parts of blood! Heart! tubing! Transport of Blood! What is transported! Nutrients! Oxygen! Carbon Dioxide! Hormones! Antibodies! What it is/does!
Mammalian systems. Chapter 3 Pages
 Mammalian systems Chapter 3 Pages 75-103 Learning intentions To know that multicellular organisms exist from specialized cells To know how the respiratory system is specialized and organized and how a
Mammalian systems Chapter 3 Pages 75-103 Learning intentions To know that multicellular organisms exist from specialized cells To know how the respiratory system is specialized and organized and how a
Neuroanatomy of a Kick
 Victor Da Costa Introduction A kick is a staple fighting technique that is included in many martial arts. A kick may vary in appearance from a straightforward front kick to a complicated jump spin heel
Victor Da Costa Introduction A kick is a staple fighting technique that is included in many martial arts. A kick may vary in appearance from a straightforward front kick to a complicated jump spin heel
Respiration. The ins and outs
 Respiration The ins and outs Functions 1. To bring O 2 into the body and transfer it to the blood stream 2. To remove CO 2 Circulation and respiration work together to achieve these functions Why Do We
Respiration The ins and outs Functions 1. To bring O 2 into the body and transfer it to the blood stream 2. To remove CO 2 Circulation and respiration work together to achieve these functions Why Do We
Wilderness First Responder Course Peak 7 Adventures
 Wilderness First Responder Course Peak 7 Adventures The practice of the healing arts (including Wilderness First Responder) does not lend itself well to a cook book approach. There are endless variations
Wilderness First Responder Course Peak 7 Adventures The practice of the healing arts (including Wilderness First Responder) does not lend itself well to a cook book approach. There are endless variations
BBSA/IFBBSA CRITERIA MEN S BODYBUILDING
 BBSA/IFBBSA CRITERIA MEN S BODYBUILDING 2019 MEN S BODYBUILDING General The following divisions are available for the junior men: Junior men There are the following categories in junior men s World-level
BBSA/IFBBSA CRITERIA MEN S BODYBUILDING 2019 MEN S BODYBUILDING General The following divisions are available for the junior men: Junior men There are the following categories in junior men s World-level
Internal Anatomy of Fish
 Internal Anatomy of Fish The Systems of a Fish Skeletal System Muscular System Respiratory System Digestive System Circulatory System Nervous System Reproductive System Special Organs Skeletal System
Internal Anatomy of Fish The Systems of a Fish Skeletal System Muscular System Respiratory System Digestive System Circulatory System Nervous System Reproductive System Special Organs Skeletal System
Breathing: The normal rate is about 14 to 20 times a minute. Taking in of air is called Inspiration and the forcing out of air is called Expiration.
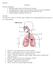 Biology 12 Respiration Divisions of Respiration Breathing: entrance and exit of air into and out of the lungs External Respiration: exchange of gases(o2 and CO2) between air (in alveoli) and blood Internal
Biology 12 Respiration Divisions of Respiration Breathing: entrance and exit of air into and out of the lungs External Respiration: exchange of gases(o2 and CO2) between air (in alveoli) and blood Internal
Slide 1 of 64. End Show Copyright Pearson Prentice Hall. End Show Copyright Pearson Prentice Hall. Respiration. Slide 5 of 64
 33-3 Form and Function in Chordates Chordates Vertebrate organ systems exhibit a wide range of complexity. This is seen in the different ways that vertebrates feed, breathe, respond, move, and reproduce.
33-3 Form and Function in Chordates Chordates Vertebrate organ systems exhibit a wide range of complexity. This is seen in the different ways that vertebrates feed, breathe, respond, move, and reproduce.
Exercise 1/Microscopy Dr. Marvin E. Holtz Human Anatomy and Physiology Lab I
 Exercise 1/Microscopy Parts of the Microscope (page 1) Each student will locate, identify and familiarize themselves with all of the parts and associated functions for each microscope part listed in the
Exercise 1/Microscopy Parts of the Microscope (page 1) Each student will locate, identify and familiarize themselves with all of the parts and associated functions for each microscope part listed in the
MICROSCOPIC STUDY OF SKELETAL MUSCLE IN EMBALMED CADAVERS
 Original Research Article MICROSCOPIC STUDY OF SKELETAL MUSCLE IN EMBALMED CADAVERS Archana Kalyankar * 1, Shivaji Sukre 2, Santoshkumar Dope 1, Sanjog Pahade 3. India. ABSTRACT Introduction: Histology
Original Research Article MICROSCOPIC STUDY OF SKELETAL MUSCLE IN EMBALMED CADAVERS Archana Kalyankar * 1, Shivaji Sukre 2, Santoshkumar Dope 1, Sanjog Pahade 3. India. ABSTRACT Introduction: Histology
Physiology of Respiration
 Physiology of Respiration External Respiration = pulmonary ventilation breathing involves 2 processes: inspiration expiration Inspiration an active process involves contraction of diaphragm innervated
Physiology of Respiration External Respiration = pulmonary ventilation breathing involves 2 processes: inspiration expiration Inspiration an active process involves contraction of diaphragm innervated
Structures of the Respiratory System include:
 Respiratory System Structures of the Respiratory System include: ü Oral Cavity ü Nasal Cavity ü Pharynx ü Epiglottis ü Larynx ü Trachea ü Diaphragm ü Lung ü Bronchus ü Bronchioles ü Alveolus ü Pulmonary
Respiratory System Structures of the Respiratory System include: ü Oral Cavity ü Nasal Cavity ü Pharynx ü Epiglottis ü Larynx ü Trachea ü Diaphragm ü Lung ü Bronchus ü Bronchioles ü Alveolus ü Pulmonary
Team Sports. Review for Final
 Team Sports Review for Final Warm up/flexibility * Flexibility is the ability to move the body's joints through a full range of motion. * Benefits of a regular flexibility program include: reduce injuries,
Team Sports Review for Final Warm up/flexibility * Flexibility is the ability to move the body's joints through a full range of motion. * Benefits of a regular flexibility program include: reduce injuries,
Human Biology Respiratory System
 Human Biology Respiratory System Respiratory System Responsible for process of breathing Works in cooperation with Circulatory system Three types: 1. Internal Respiration 2. External Respiration 3. Cellular
Human Biology Respiratory System Respiratory System Responsible for process of breathing Works in cooperation with Circulatory system Three types: 1. Internal Respiration 2. External Respiration 3. Cellular
2012 New York State Junior 4-H Horse Bowl Round 8
 One-On-One 1. C1 Q. A lack of what basic nutrient may increase the risk of impaction colic? A. Water S. ES p. 116 2. C2 Q. What is the name of the saddle on which the rider sits forward with both legs
One-On-One 1. C1 Q. A lack of what basic nutrient may increase the risk of impaction colic? A. Water S. ES p. 116 2. C2 Q. What is the name of the saddle on which the rider sits forward with both legs
S.T.E.M Part 1: Prior Knowledge: Energy and Simple Machines
 S.T.E.M. 2016-7 Part 1: Prior Knowledge: Energy and Simple Machines Prior Knowledge: What is Energy? Redefining: energy, force, work and pressure Experiment 1: Floating Ping Pong Ball You need: - Ping
S.T.E.M. 2016-7 Part 1: Prior Knowledge: Energy and Simple Machines Prior Knowledge: What is Energy? Redefining: energy, force, work and pressure Experiment 1: Floating Ping Pong Ball You need: - Ping
Kinetic chain checkpoints
 Kinetic chain checkpoints Observations: Foot/ankle Knee Lumbo-Pelvic-Hip-Complex (LPHC) Shoulder and Cervical Spine (upper body) Each joint region has a specific and optimal motion based on its structure
Kinetic chain checkpoints Observations: Foot/ankle Knee Lumbo-Pelvic-Hip-Complex (LPHC) Shoulder and Cervical Spine (upper body) Each joint region has a specific and optimal motion based on its structure
Name period date assigned date due date returned
 Name period date assigned date due date returned procedure 1. Take one balloon and stretch it out 2. Take one deep breath and blow into the balloon until you cannot breath out anymore. Do Not Take A Second
Name period date assigned date due date returned procedure 1. Take one balloon and stretch it out 2. Take one deep breath and blow into the balloon until you cannot breath out anymore. Do Not Take A Second
Lesson 6 Plate Tectonics and Continental Drift PS 2.2 a,e PS 3.1i
 Table of Contents Letter to the Student...................................... 5 Letter to the Family....................................... 6 New York State Performance Standards Correlation Chart.......
Table of Contents Letter to the Student...................................... 5 Letter to the Family....................................... 6 New York State Performance Standards Correlation Chart.......
GASEOUS EXCHANGE 17 JULY 2013
 GASEOUS EXCHANGE 17 JULY 2013 Lesson Description In this lesson we: Discuss what is gaseous exchange? Consider requirements of an efficient gaseous exchange surface. Look at diversity in gas exchange systems.
GASEOUS EXCHANGE 17 JULY 2013 Lesson Description In this lesson we: Discuss what is gaseous exchange? Consider requirements of an efficient gaseous exchange surface. Look at diversity in gas exchange systems.
What needs to be done to support muscle building in horses? Engage in effective
 marstall feeding knowledge Helping your horse build muscles What needs to be done to support muscle building in horses? Engage in effective training, aid your horse with proper feeding, train up and watch
marstall feeding knowledge Helping your horse build muscles What needs to be done to support muscle building in horses? Engage in effective training, aid your horse with proper feeding, train up and watch
BBSA/IFBBSA CRITERIA MEN S CLASSIC BODYBUILDING
 BBSA/IFBBSA CRITERIA MEN S CLASSIC BODYBUILDING 2019 MEN S CLASSIC BODYBUILDING This discipline recognized by the IFBB to be included into the Senior Men World Championship Internationally. Classic Bodybuilding
BBSA/IFBBSA CRITERIA MEN S CLASSIC BODYBUILDING 2019 MEN S CLASSIC BODYBUILDING This discipline recognized by the IFBB to be included into the Senior Men World Championship Internationally. Classic Bodybuilding
Frog Dissection. PreLab: 1. Where do frogs get their energy? Draw a simple food chain to illustrate.
 Name Date Frog Dissection Class # PreLab: Amphibian Reading As members of the class Amphibia, frogs may live some of their adult lives on land, but they must return to water to reproduce. Eggs are laid
Name Date Frog Dissection Class # PreLab: Amphibian Reading As members of the class Amphibia, frogs may live some of their adult lives on land, but they must return to water to reproduce. Eggs are laid
Lesson 9.1: The Importance of an Organ Delivery System
 Lesson 9.1: The Importance of an Organ Delivery System Animals require a continuous supply of oxygen (O 2 ) for cellular respiration, and they must expel carbon dioxide (CO 2 ), the waste product of this
Lesson 9.1: The Importance of an Organ Delivery System Animals require a continuous supply of oxygen (O 2 ) for cellular respiration, and they must expel carbon dioxide (CO 2 ), the waste product of this
Recitation question # 05
 Recitation and Lab # 05 The goal of this recitations / labs is to review material related to the CV and respiratory lectures for the second test of this course. Info required to answer this recitation
Recitation and Lab # 05 The goal of this recitations / labs is to review material related to the CV and respiratory lectures for the second test of this course. Info required to answer this recitation
How Animals Survive (Circulation and Gas Exchange)
 How Animals Survive (Circulation and Gas Exchange) by Flourence Octaviano on February 16, 2018 lesson duration of 30 minutes under Earth and Life Science generated on February 16, 2018 at 12:45 am Tags:
How Animals Survive (Circulation and Gas Exchange) by Flourence Octaviano on February 16, 2018 lesson duration of 30 minutes under Earth and Life Science generated on February 16, 2018 at 12:45 am Tags:
Animal Systems: The Respiratory System
 Animal Systems: The Respiratory System Tissues, Organs, and Systems of Living Things Cells, Cell Division, and Animal Systems and Plant Systems Cell Specialization Human Systems The Digestive The Circulatory
Animal Systems: The Respiratory System Tissues, Organs, and Systems of Living Things Cells, Cell Division, and Animal Systems and Plant Systems Cell Specialization Human Systems The Digestive The Circulatory
Respiratory Pulmonary Ventilation
 Respiratory Pulmonary Ventilation Pulmonary Ventilation Pulmonary ventilation is the act of breathing and the first step in the respiratory process. Pulmonary ventilation brings in air with a new supply
Respiratory Pulmonary Ventilation Pulmonary Ventilation Pulmonary ventilation is the act of breathing and the first step in the respiratory process. Pulmonary ventilation brings in air with a new supply
REVISION: GASEOUS EXCHANGE & EXCRETION 11 SEPTEMBER 2013
 REVISION: GASEOUS EXCHANGE & EXCRETION 11 SEPTEMBER 2013 Lesson Description In this lesson we: Revise gaseous exchange in different animals and examine the structure of the kidney Key Concepts Important
REVISION: GASEOUS EXCHANGE & EXCRETION 11 SEPTEMBER 2013 Lesson Description In this lesson we: Revise gaseous exchange in different animals and examine the structure of the kidney Key Concepts Important
Gait. Kinesiology RHS 341 Lecture 12 Dr. Einas Al-Eisa
 Gait Kinesiology RHS 341 Lecture 12 Dr. Einas Al-Eisa Definitions Locomotion = the act of moving from one place to the other Gait = the manner of walking Definitions Walking = a smooth, highly coordinated,
Gait Kinesiology RHS 341 Lecture 12 Dr. Einas Al-Eisa Definitions Locomotion = the act of moving from one place to the other Gait = the manner of walking Definitions Walking = a smooth, highly coordinated,
Chapter 28 Arthropods and Echinoderms. Body Terms. Evolution has led to:
 Chapter 28 Arthropods and Echinoderms Introduction to Arthropods jointed feet Most diverse and successful animals Over 750,000 species identified Segmented bodies Tough exoskeleton Jointed appendages Body
Chapter 28 Arthropods and Echinoderms Introduction to Arthropods jointed feet Most diverse and successful animals Over 750,000 species identified Segmented bodies Tough exoskeleton Jointed appendages Body
tapah svadhyaya ishvara pranidhana kriya yogaha
 UNIT 2: The Breath In this unit we ll look at the breath from many perspectives, including: Mechanics of breathing Language of teaching about breathing Ujjayi Bandhas 2.1 GETTING TO KNOW YOU Knowing a
UNIT 2: The Breath In this unit we ll look at the breath from many perspectives, including: Mechanics of breathing Language of teaching about breathing Ujjayi Bandhas 2.1 GETTING TO KNOW YOU Knowing a
2/28/18. Respiratory System. 1 Copyright 2016 by Elsevier Inc. All rights reserved. Introduction. Anatomy. Physiology. Respiratory System
 Introduction Respiratory System Chapter 28 Respiration: We inhale air, extract oxygen from it, exhale air Cardiovascular and respiratory systems work together Failure of either system: - Disruption of
Introduction Respiratory System Chapter 28 Respiration: We inhale air, extract oxygen from it, exhale air Cardiovascular and respiratory systems work together Failure of either system: - Disruption of
25/4/2016. Physiology #01 Respiratory system Nayef Garaibeh Rawan Alwaten
 25/4/2016 Physiology #01 Respiratory system Nayef Garaibeh Rawan Alwaten Respiratory System Introduction: - We breath while we are sleeping, talking, working and resting. - Respiratory diseases are abundant
25/4/2016 Physiology #01 Respiratory system Nayef Garaibeh Rawan Alwaten Respiratory System Introduction: - We breath while we are sleeping, talking, working and resting. - Respiratory diseases are abundant
#10 Work Physiology. By : Dewi Hardiningtyas, ST., MT., MBA. Industrial Engineering Dept. University of Brawijaya
 #10 Work Physiology By : Dewi Hardiningtyas, ST., MT., MBA. Industrial Engineering Dept. University of Brawijaya This topic is a discussion of the energy side of using muscles rather than the mechanics/force
#10 Work Physiology By : Dewi Hardiningtyas, ST., MT., MBA. Industrial Engineering Dept. University of Brawijaya This topic is a discussion of the energy side of using muscles rather than the mechanics/force
I. Gas Exchange Respiratory Surfaces Respiratory Surface:
 I. Gas Exchange Respiratory Surfaces Respiratory Surface: Common characteristics of respiratory surfaces: a) Moist: allows for the RAPID diffusion of dissolved gasses across its surface. Whereas the respiratory
I. Gas Exchange Respiratory Surfaces Respiratory Surface: Common characteristics of respiratory surfaces: a) Moist: allows for the RAPID diffusion of dissolved gasses across its surface. Whereas the respiratory
95b Deep Massage:! Technique Review and Practice - Anterior"
 95b Deep Massage:! Technique Review and Practice - Anterior" 95b Deep Massage: Technique Review and Practice - Anterior! Class Outline" 5 minutes" "Attendance, Breath of Arrival, and Reminders " 10 minutes
95b Deep Massage:! Technique Review and Practice - Anterior" 95b Deep Massage: Technique Review and Practice - Anterior! Class Outline" 5 minutes" "Attendance, Breath of Arrival, and Reminders " 10 minutes
PARTS AND STRUCTURE OF THE RESPIRATORY SYSTEM
 PARTS AND STRUCTURE OF THE RESPIRATORY SYSTEM Parts of the Respiratory System The RS can be divided into two parts: 1. Respiratory Tract, (path that air follows). Nasal passage Pharynx Larynx Trachea Bronchi,
PARTS AND STRUCTURE OF THE RESPIRATORY SYSTEM Parts of the Respiratory System The RS can be divided into two parts: 1. Respiratory Tract, (path that air follows). Nasal passage Pharynx Larynx Trachea Bronchi,
28 2 Groups of Arthropods
 28 2 Groups of Arthropods 1 of 42 28 2 Groups of Arthropods Arthropods are classified based on the number and structure of their body segments and appendages particularly their mouthparts. The three major
28 2 Groups of Arthropods 1 of 42 28 2 Groups of Arthropods Arthropods are classified based on the number and structure of their body segments and appendages particularly their mouthparts. The three major
KICKBIKE Your key to optimum sports performance
 KICKBIKE Your key to optimum sports performance Efficient Running is essential to optimum performance of most sports we play. Whether we want to maximize our speed, maximize our endurance, or both, an
KICKBIKE Your key to optimum sports performance Efficient Running is essential to optimum performance of most sports we play. Whether we want to maximize our speed, maximize our endurance, or both, an
Chapter 16 Respiratory System
 Introduction Chapter 16 Respiratory System The respiratory system consists of tubes that filter incoming air and transport it to alveoli where gases are exchanged. Think pair share: what organs are associated
Introduction Chapter 16 Respiratory System The respiratory system consists of tubes that filter incoming air and transport it to alveoli where gases are exchanged. Think pair share: what organs are associated
LUNA V. User Manual. Warning
 LUNA V User Manual Warning Dear user Thanks for using our company's products, in order to fully make use of the products, we sincerely suggests follow: Please read this instructionin detail, and keep it
LUNA V User Manual Warning Dear user Thanks for using our company's products, in order to fully make use of the products, we sincerely suggests follow: Please read this instructionin detail, and keep it
Respiratory System Homework
 Respiratory System Homework The R S is the body s breathing equipment. Similar to the D system, it takes S from outside the body (G, particularly O ), circulates them through the body to C and T, then
Respiratory System Homework The R S is the body s breathing equipment. Similar to the D system, it takes S from outside the body (G, particularly O ), circulates them through the body to C and T, then
Chapter 15. Lecture and Animation Outline
 Chapter 15 Lecture and Animation Outline To run the animations you must be in Slideshow View. Use the buttons on the animation to play, pause, and turn audio/text on or off. Please Note: Once you have
Chapter 15 Lecture and Animation Outline To run the animations you must be in Slideshow View. Use the buttons on the animation to play, pause, and turn audio/text on or off. Please Note: Once you have
GAS EXCHANGE & CIRCULATION CHAPTER 42 ( )
 Winter 08 1 of 10 GAS EXCHANGE & CIRCULATION CHAPTER 42 (867 891) MOVEMENT OF GASES Both O 2 and CO 2 move by The movement down a If a gas produced in one location, it diffuses away But diffusion is usually
Winter 08 1 of 10 GAS EXCHANGE & CIRCULATION CHAPTER 42 (867 891) MOVEMENT OF GASES Both O 2 and CO 2 move by The movement down a If a gas produced in one location, it diffuses away But diffusion is usually
COPYRIGHT 2004 SCIENTIFIC AMERICAN, INC.
 Gene therapy for restoring muscle lost to age or disease is poised to enter the clinic, but elite athletes are eyeing it to enhance performance. Can it be long before gene doping changes the nature of
Gene therapy for restoring muscle lost to age or disease is poised to enter the clinic, but elite athletes are eyeing it to enhance performance. Can it be long before gene doping changes the nature of
Respiration - Human 1
 Respiration - Human 1 At the end of the lectures on respiration you should be able to, 1. Describe events in the respiratory processes 2. Discuss the mechanism of lung ventilation in human 3. Discuss the
Respiration - Human 1 At the end of the lectures on respiration you should be able to, 1. Describe events in the respiratory processes 2. Discuss the mechanism of lung ventilation in human 3. Discuss the
Catabolism in Skeletal Muscle The Phosphagen System
 Catabolism in Skeletal Muscle The Phosphagen System Overview of ATP Regeneration Anaerobic vs Aerobic Metabolism Creatine Kinase Reaction Adenylate Kinase Reaction Purine Nucleotide Cycle Creatine Phosphate
Catabolism in Skeletal Muscle The Phosphagen System Overview of ATP Regeneration Anaerobic vs Aerobic Metabolism Creatine Kinase Reaction Adenylate Kinase Reaction Purine Nucleotide Cycle Creatine Phosphate
Chromataphores. contains. Epidermis. Epidermis contains:
 Skin of Koi Scales Chromataphores and Fukarin Three layers, plus cuticle Cuticle slime coat Epidermis outermost cellular layer Dermis contains the scales Hypodermis fatty layer Presented by: Diana Lynn
Skin of Koi Scales Chromataphores and Fukarin Three layers, plus cuticle Cuticle slime coat Epidermis outermost cellular layer Dermis contains the scales Hypodermis fatty layer Presented by: Diana Lynn
Circulation and Respiration: Vital Signs Student Version
 Circulation and Respiration: Vital Signs Student Version In this lab, you will learn about the circulatory and respiratory systems. You will test the capacity of your lungs, measure your blood pressure
Circulation and Respiration: Vital Signs Student Version In this lab, you will learn about the circulatory and respiratory systems. You will test the capacity of your lungs, measure your blood pressure
2015 JUNIOR ANATOMY EASY. 502 (easy) TH91/HIH230-2 Q: What is the largest bone in the horse's head? A: Mandible (lower jaw)
 2015 JUNIOR ANATOMY EASY 502 (easy) TH91/HIH230-2 Q: What is the largest bone in the horse's head? A: Mandible (lower jaw) 503 (easy) HIH525-1 Q: What part of a horse's foot provides traction & absorbs
2015 JUNIOR ANATOMY EASY 502 (easy) TH91/HIH230-2 Q: What is the largest bone in the horse's head? A: Mandible (lower jaw) 503 (easy) HIH525-1 Q: What part of a horse's foot provides traction & absorbs
HemoCue Training and Education Program. Capillary Sampling. Hemoglobin. USPRO1 Rev 1 3/03. Training and Education Program 2003 HemoCue, Inc.
 HemoCue Training and Education Program Capillary Sampling Hemoglobin 1 The Circulation Blood leaves the heart through the aorta and travels through a system of muscular arteries. These branch off into
HemoCue Training and Education Program Capillary Sampling Hemoglobin 1 The Circulation Blood leaves the heart through the aorta and travels through a system of muscular arteries. These branch off into
CHAPTER 3: The cardio-respiratory system
 : The cardio-respiratory system Exam style questions - text book pages 44-45 1) Describe the structures involved in gaseous exchange in the lungs and explain how gaseous exchange occurs within this tissue.
: The cardio-respiratory system Exam style questions - text book pages 44-45 1) Describe the structures involved in gaseous exchange in the lungs and explain how gaseous exchange occurs within this tissue.
Frog Dissection Pre-Lab
 Name: Class: Date: Why are we dissecting a frog? Frog Dissection Pre-Lab Frogs and humans are vertebrates and they have very similar organ systems. Although all of the internal organs are not exactly the
Name: Class: Date: Why are we dissecting a frog? Frog Dissection Pre-Lab Frogs and humans are vertebrates and they have very similar organ systems. Although all of the internal organs are not exactly the
Diagram 1: The three phases of gas exchange
 1 Diagram 1: The three phases of gas exchange 1. Breathing When an animal breathes, a large, moist internal surface is exposed to air. O 2 diffuses across the cells lining the lungs and into surrounding
1 Diagram 1: The three phases of gas exchange 1. Breathing When an animal breathes, a large, moist internal surface is exposed to air. O 2 diffuses across the cells lining the lungs and into surrounding
Sparing dystrophic muscle
 Sparing dystrophic muscle Research at NMDRC Skeletal muscle Development and Hypertrophy Dystrophic Pathology Skeletal Muscle Regeneration Stem cells and Cell Transplantation Identification and manipulation
Sparing dystrophic muscle Research at NMDRC Skeletal muscle Development and Hypertrophy Dystrophic Pathology Skeletal Muscle Regeneration Stem cells and Cell Transplantation Identification and manipulation
found that stretching increased the oxygen usage within limits but
 v 1 -. 1 qa,.x.- U I di i - -10 1. 1 4 INFLUENCE OF RESTING LENGTH ON THE OXYGEN USE OF PLAIN MUSCLE. By J. CHRISTODoss DAVID. From the Department of Pharmacology, Edinburgh University. (Received for publication
v 1 -. 1 qa,.x.- U I di i - -10 1. 1 4 INFLUENCE OF RESTING LENGTH ON THE OXYGEN USE OF PLAIN MUSCLE. By J. CHRISTODoss DAVID. From the Department of Pharmacology, Edinburgh University. (Received for publication
CHAPTER 3: The respiratory system
 CHAPTER 3: The respiratory system Practice questions - text book pages 56-58 1) When the inspiratory muscles contract, which one of the following statements is true? a. the size of the thoracic cavity
CHAPTER 3: The respiratory system Practice questions - text book pages 56-58 1) When the inspiratory muscles contract, which one of the following statements is true? a. the size of the thoracic cavity
ARE YOU A SLOW- OR A FAST-TWITCH RUNNER?
 ARE YOU A SLOW- OR A FAST-TWITCH RUNNER? How can we individualize our training towards our different goals based on our muscular makeup? In this article you will learn how to decide if you are a Fast-twitch,
ARE YOU A SLOW- OR A FAST-TWITCH RUNNER? How can we individualize our training towards our different goals based on our muscular makeup? In this article you will learn how to decide if you are a Fast-twitch,
Introduction. Respiration. Chapter 10. Objectives. Objectives. The Respiratory System
 Introduction Respiration Chapter 10 The Respiratory System Provides a means of gas exchange between the environment and the body Plays a role in the regulation of acidbase balance during exercise Objectives
Introduction Respiration Chapter 10 The Respiratory System Provides a means of gas exchange between the environment and the body Plays a role in the regulation of acidbase balance during exercise Objectives
L9 Frog Dissection- External Page 1 of 7 STUDENT LABORATORY PACKET. Student s Name Modified from Prentice Hall Lab. Manual Lab Instructor Date Points
 L9 Frog Dissection- External Page 1 of 7 STUDENT LABORATORY PACKET Lab 9: Bull Frog: External Examination Student s Name Modified from Prentice Hall Lab. Manual Lab Instructor Date Points Objective: 1.
L9 Frog Dissection- External Page 1 of 7 STUDENT LABORATORY PACKET Lab 9: Bull Frog: External Examination Student s Name Modified from Prentice Hall Lab. Manual Lab Instructor Date Points Objective: 1.
BIOLOGY 12: UNIT J - CHAPTER 15 - REVIEW WORKSHEET RESPIRATORY SYSTEM
 BIOLOGY 12: UNIT J - CHAPTER 15 - REVIEW WORKSHEET RESPIRATORY SYSTEM A. CHAPTER REVIEW 1. Define the four components of respiration. 2. What happens to the air as it moves along the air passages? What
BIOLOGY 12: UNIT J - CHAPTER 15 - REVIEW WORKSHEET RESPIRATORY SYSTEM A. CHAPTER REVIEW 1. Define the four components of respiration. 2. What happens to the air as it moves along the air passages? What
Marine Fishes. Chapter 8
 Marine Fishes Chapter 8 Fish Gills The construction of the gill is the same in all fish gill arch supports the entire structure, gill rakers are on the forward surface of the gill arch and gill filaments
Marine Fishes Chapter 8 Fish Gills The construction of the gill is the same in all fish gill arch supports the entire structure, gill rakers are on the forward surface of the gill arch and gill filaments
NORTHERN ILLINOIS UNIVERSITY. Androgenic-Anabolic Alternatives. A Thesis Submitted to the. University Honors Program. In Partial Fulfillment o f the
 NORTHERN ILLINOIS UNIVERSITY Androgenic-Anabolic Alternatives A Thesis Submitted to the University Honors Program In Partial Fulfillment o f the Requirements o f the Baccalaureate Degree With Upper D ivision
NORTHERN ILLINOIS UNIVERSITY Androgenic-Anabolic Alternatives A Thesis Submitted to the University Honors Program In Partial Fulfillment o f the Requirements o f the Baccalaureate Degree With Upper D ivision
Use scientific principles to explain how the sprayer works. You may use diagrams to support your answer.
 4.3 Marking Key This guide includes sample answers, task-specific observable elements, (Appendices 1 and 2), descriptive evaluation rubrics for each competency (Appendices 3 and 4), and non-descriptive
4.3 Marking Key This guide includes sample answers, task-specific observable elements, (Appendices 1 and 2), descriptive evaluation rubrics for each competency (Appendices 3 and 4), and non-descriptive
 Subject: Transport Code: 2803/01 Session: June Year: 2002 Mark Scheme MAXIMUM MARK 45 ADVICE TO EXAMINERS ON THE ANNOTATION OF SCRIPTS 1. Please ensure that you use the final version of the Mark Scheme.
Subject: Transport Code: 2803/01 Session: June Year: 2002 Mark Scheme MAXIMUM MARK 45 ADVICE TO EXAMINERS ON THE ANNOTATION OF SCRIPTS 1. Please ensure that you use the final version of the Mark Scheme.
Subject: Transport Code: 2803/01. Session: June Year: Mark Scheme
 Subject: Transport Code: 2803/01 Session: June Year: 2002 MAXIMUM MARK 45 ADVICE TO EXAMINERS ON THE ANNOTATION OF SCRIPTS 1. Please ensure that you use the final version of the. You are advised to destroy
Subject: Transport Code: 2803/01 Session: June Year: 2002 MAXIMUM MARK 45 ADVICE TO EXAMINERS ON THE ANNOTATION OF SCRIPTS 1. Please ensure that you use the final version of the. You are advised to destroy
An analysis is a separation of a whole into its component parts, according to
 JD Welch Anna Reponen PE 483 Final Project 3/14/2009 Introduction An analysis is a separation of a whole into its component parts, according to the Merrian Webster dictionary. So the analysis of a sprint
JD Welch Anna Reponen PE 483 Final Project 3/14/2009 Introduction An analysis is a separation of a whole into its component parts, according to the Merrian Webster dictionary. So the analysis of a sprint
2010 New York State Junior 4-H Horse Bowl Round 7
 One-On-One 1. C1 Q. In a ranch operation, what is the purpose of a boundary rider? A. To ride the fence of the property and repair any problems S. DET p. 36 2. C2 Q. Aniridia is a genetic disease that
One-On-One 1. C1 Q. In a ranch operation, what is the purpose of a boundary rider? A. To ride the fence of the property and repair any problems S. DET p. 36 2. C2 Q. Aniridia is a genetic disease that
Physiological Considerations for Compression Bandaging. Harvey N. Mayrovitz, Ph.D.
 Physiological Considerations for Compression Bandaging Harvey N. Mayrovitz, Ph.D. Objectives Therapeutic Compression Principles and Definitions Physiological Effects Mechanisms of Action Differential Features
Physiological Considerations for Compression Bandaging Harvey N. Mayrovitz, Ph.D. Objectives Therapeutic Compression Principles and Definitions Physiological Effects Mechanisms of Action Differential Features
Circulation and Gas Exchange Chapter 42
 Circulation and Gas Exchange Chapter 42 Circulatory systems link exchange surfaces with cells throughout the body Diffusion is only efficient over small distances In small and/or thin animals, cells can
Circulation and Gas Exchange Chapter 42 Circulatory systems link exchange surfaces with cells throughout the body Diffusion is only efficient over small distances In small and/or thin animals, cells can
Chapter 11: Respiratory System Review Assignment
 Name: Date: Mark: / 45 Chapter 11: Respiratory System Review Assignment Multiple Choice = 45 Marks Identify the choice that best completes the statement or answers the question. 1. Which of the following
Name: Date: Mark: / 45 Chapter 11: Respiratory System Review Assignment Multiple Choice = 45 Marks Identify the choice that best completes the statement or answers the question. 1. Which of the following
Hyndland Secondary School Biology Department
 Hyndland Secondary School Biology Department Body in Action Homework and Question Booklet 1 Body in Action (a) Movement... 2 Skeleton... 2 Joints... 3 Body in Action (b) The need for Energy... 5 Heart...
Hyndland Secondary School Biology Department Body in Action Homework and Question Booklet 1 Body in Action (a) Movement... 2 Skeleton... 2 Joints... 3 Body in Action (b) The need for Energy... 5 Heart...
Frog Dissection. External Observation
 Frog Dissection External Observation Use the diagram below to locate and identify the external features of the head. Find the mouth, external nares, tympani (ear drum), eyes, and nictitating membranes
Frog Dissection External Observation Use the diagram below to locate and identify the external features of the head. Find the mouth, external nares, tympani (ear drum), eyes, and nictitating membranes
Respiratory System. Part 2
 Respiratory System Part 2 Respiration Exchange of gases between air and body cells Three steps 1. Ventilation 2. External respiration 3. Internal respiration Ventilation Pulmonary ventilation consists
Respiratory System Part 2 Respiration Exchange of gases between air and body cells Three steps 1. Ventilation 2. External respiration 3. Internal respiration Ventilation Pulmonary ventilation consists
1. Hip flexion Muscles: Iliopsoas (psoas major + iliacus)
 Chap. 5 Testing the muscles of the Lower Extremity Part I. Manual Muscle Testing of the hip joint muscles 1. Hip flexion Muscles: Iliopsoas (psoas major + iliacus) Rectus femoris Sartorius Tensor fascia
Chap. 5 Testing the muscles of the Lower Extremity Part I. Manual Muscle Testing of the hip joint muscles 1. Hip flexion Muscles: Iliopsoas (psoas major + iliacus) Rectus femoris Sartorius Tensor fascia
What are Arthropods? General Characteristics. General Characteristics 5/14/2013. Phylum Arthropoda Biology 11
 What are Arthropods? Phylum Arthropoda Biology 11 Segmented invertebrates Jointed appendages Exoskeleton Includes the most numerous and diverse animals on Earth They are found in virtually every habitat
What are Arthropods? Phylum Arthropoda Biology 11 Segmented invertebrates Jointed appendages Exoskeleton Includes the most numerous and diverse animals on Earth They are found in virtually every habitat
Characteristics of Animals pp Topic 7: Animal Diversity Ch Symmetry pp Characteristics of Animals
 Topic 7: Animal Diversity Ch. 32-34 Characteristics of Animals pp.704-705 Animals: Are eukaryotic Are multicellular Are ingestive heterotrophs Have no cell walls Most are motile Most have tissues organized
Topic 7: Animal Diversity Ch. 32-34 Characteristics of Animals pp.704-705 Animals: Are eukaryotic Are multicellular Are ingestive heterotrophs Have no cell walls Most are motile Most have tissues organized
Invertebrate Chordates
 Invertebrate Chordates Chapter 11.2 - Fishes And Invertebrate Chordates... Invertebrate Chordates Lancelets Filter feed and spend most of their time buried in the sand. Only 2 invertebrate chordates Tunicates
Invertebrate Chordates Chapter 11.2 - Fishes And Invertebrate Chordates... Invertebrate Chordates Lancelets Filter feed and spend most of their time buried in the sand. Only 2 invertebrate chordates Tunicates
Chapter 12 Part 2. The Worms Platyhelminthes, Nematoda & Annelida
 Chapter 12 Part 2 The Worms Platyhelminthes, Nematoda & Annelida Phylum: Platyhelminthes Examples: Flatworms, Planaria sp., tapeworms and blood flukes Acoelomate, Invertebrate, Simplest critter w/ bilateral
Chapter 12 Part 2 The Worms Platyhelminthes, Nematoda & Annelida Phylum: Platyhelminthes Examples: Flatworms, Planaria sp., tapeworms and blood flukes Acoelomate, Invertebrate, Simplest critter w/ bilateral
Positive running posture sums up the right technique for top speed
 Positive running, a model for high speed running Frans Bosch positive running posture sums up the right technique for top speed building blocks in running: Pelvic rotation for- and backward and hamstring
Positive running, a model for high speed running Frans Bosch positive running posture sums up the right technique for top speed building blocks in running: Pelvic rotation for- and backward and hamstring
Tennis Stretches and Flexibility Exercises
 43 Thames Street, St Albans, Christchurch 8013 Phone: (03) 356 1353. Website: philip-bayliss.com Tennis Stretches and Flexibility Exercises The origins of tennis date back at least to the Middle Ages,
43 Thames Street, St Albans, Christchurch 8013 Phone: (03) 356 1353. Website: philip-bayliss.com Tennis Stretches and Flexibility Exercises The origins of tennis date back at least to the Middle Ages,
1. Label a diagram of the respiratory system. Objective sheet 3 Notes
 1. Label a diagram of the respiratory system Objective sheet 3 Notes 2. Functions of the respiratory structures Name Description Function Nasal Cavity Trachea Bronchi (Singular Bronchus) Bronchioles Lungs
1. Label a diagram of the respiratory system Objective sheet 3 Notes 2. Functions of the respiratory structures Name Description Function Nasal Cavity Trachea Bronchi (Singular Bronchus) Bronchioles Lungs
