Overview. 70.8% of Earth covered by ocean 97.2% of surface water Interconnected global or world ocean
|
|
|
- Bruno Heath
- 6 years ago
- Views:
Transcription
1 Overview 70.8% of Earth covered by ocean 97.2% of surface water Interconnected global or world ocean
2 Principal oceans Pacific Largest, deepest Atlantic Second largest Indian Mainly in Southern Hemisphere
3 Arctic Smallest, shallowest, Northern Hemisphere Antarctic Connects Pacific, Atlantic, and Indian
4 Comparison of land and depth Average depth of ocean 3729 m Average elevation of land 840 m Deepest ocean Mariana Trench 11,022 m Highest mountain Mt. Everest 8850 m
5 History of Oceanography 1. Principles of Marine Science emerge gradually over time, constrained by 2. religion, sociology, technology. Polynesian voyages in the Pacific Arabs/Indians sail the Indian Ocean Chinese ships explore African coast Europeans explore the world oceans 3. Motivations: riches, food and war
6 Why do we speak languages from Europe? Indigenous people lived here right? The Chinese had huge ships with lots of supplies right? The Polynesians explored the Pacific first right?
7 Polynesia: the first voyagers 1. By 2,500 years [BP] almost all Pacific Islands except Hawaii were colonized. 2. Outrigger canoes can tack into wind but narrow hulls hold little cargo and hulls rack in strong seas. 3. Navigated by stars, but no written language, so knowledge of stars was memory dependent. Stick charts in some cultures 4. Voyaging limited by number of coconuts/boat. Coconuts supplied food, water and vitamin C.
8 Voyaging Outrigger
9 Arab/Indian dhows, the Indian Ocean and the seasonal monsoon 1. Large lateen rigged ships; large cargoes for trading. 2. Shallow draft ships with huge center boards don t tack well, but fast down wind. 3. Monsoon winds in Indian Ocean blow from east for 6 months and from west for 6 months. 4. Indian Dhows into South Atlantic, probably to South America, in 1420.
10 Chinese ocean voyaging 1. Chinese junks have full battened sails; tack easily into the wind. 2. Big hulls, large holds, lots of water, good provisions. 3. From Chinese built superjunks, up to 440 ft long for coastal trade (no navigation). 4. Chinese invented the Compass! 4. Found no new markets; Admiral Cheng Ho was beheaded; ships were burned.
11
12 European voyaging 1. Belief in a flat earth constrained exploration. 2. Square rigged ships have big hulls with large cargoes, but only sail down wind. 3. Navigation: sextant gives azimuth of sun for latitude, but longitude was measured by dead reckoning because 4. pendulum clocks won t work on a rolling ship. Needed new clocks. 5. No coconuts! Scurvy kills after few months of no vitamin C (ascorbic acid).
13 HMS Resolution
14 Who wins the exploration sweepstakes? 1. Polynesians? No. No written language; limited cargo space constrained warfare and trade. 2. Arabs? No. Only one east west trade route. 3. Chinese? No. Rigid autocracy not healthy for ambitious Admirals. 4. Europeans? Yes!!! Boat design was dumb but big. Discovered clocks and limes, then raped and pillaged new world with Guns, Germs, and Steel in the Discovery of the new world.
15 Motives for European Exploration: food, riches, war 1. New lands: Norse explorations but native Americans were too feisty. 2. New fish stocks: Basques fished for cod off Newfoundland 1200 AD), but no one told! 3. Spices and gold: Columbus (1492) sails downwind via trades to Caribbean. Spanish begin to plunder new world. Magellan sails down wind around the world (1522), and Spanish pillage Philippines for 250 years. 4. Exploration: British (1768) send Captain James Cook with Harrison s chronometers on 3 round the world voyages all cruises down wind.
16 Fig Columbus, Magellan, Cabot
17 Ship track of Cook s voyages ( )
18 Darwin and the Voyage of the Beagle ( )
19
20 Matthew Maury (1885)
21 Voyage of the Challenger ( )
22 First Marine Laboratories 1872 Statione Zoologica (Naples) 1888 Woods Hole 1892 Hopkins Marine Station 1905 Scripps
23 Significant discoveries and dates in oceanography 1. Alfred Wegner poses continental drift in William Beebe and Otis Barton build Bathysphere in 1928; dive off Bermuda. Half mile Down World War II boosts submarine design and construction. Echo soundings used by military to map Atlantic and Pacific Oceans. Deep scattering layer. 4. Jacques Cousteau and Emile Gagnan invent the aqualung Plate tectonics re discovered 1960 s. 6. SeaSat 1978; First ocean observing satellite.
24 Russian submersible Mir
25 Wasp submersible
26 Diving in blue water
27 ROV Ventana
28 SeaSatellite view of Gulf stream: warm core and cold core rings
Unit 1 Learning Goal: I will understand the history, technology, and scientific processes involved in Marine Science.
 Unit 1: Unit 1 Learning Goal: I will understand the history, technology, and scientific processes involved in Marine Science. Lesson 1.1: *Refer to Chapter 2 in your Textbook Lesson 1.1 Learning Targets:
Unit 1: Unit 1 Learning Goal: I will understand the history, technology, and scientific processes involved in Marine Science. Lesson 1.1: *Refer to Chapter 2 in your Textbook Lesson 1.1 Learning Targets:
Chapter 1. The Science of Marine Biology - Why is it important? Marine Biology. The scientific study of the organisms that live in the sea
 Chapter 1 The Science of Marine Biology - Why is it important? Marine Biology Marine Biology - The scientific study of the organisms that live in the sea 1 Practical Reasons to study marine biology Vast
Chapter 1 The Science of Marine Biology - Why is it important? Marine Biology Marine Biology - The scientific study of the organisms that live in the sea 1 Practical Reasons to study marine biology Vast
OCN 201. History of Oceanography and Polynesian voyaging
 OCN 201 History of Oceanography and Polynesian voyaging History of Settlement: Fiji by ~ 1300 BC Tonga by ~1100 BC Samoa and Marquesas by 500 BC By now there is a distinct Polynesian culture. Easter Island
OCN 201 History of Oceanography and Polynesian voyaging History of Settlement: Fiji by ~ 1300 BC Tonga by ~1100 BC Samoa and Marquesas by 500 BC By now there is a distinct Polynesian culture. Easter Island
OCN 201. History of Oceanography and Polynesian voyaging
 OCN 201 History of Oceanography and Polynesian voyaging History of Settlement: Fiji by ~ 1300 BC Tonga by ~1100 BC Samoa and Marquesas by 500 BC By now there is a distinct Polynesian culture. Easter Island
OCN 201 History of Oceanography and Polynesian voyaging History of Settlement: Fiji by ~ 1300 BC Tonga by ~1100 BC Samoa and Marquesas by 500 BC By now there is a distinct Polynesian culture. Easter Island
OCN 201. History of Oceanography and Polynesian voyaging
 OCN 201 History of Oceanography and Polynesian voyaging History of Settlement: Fiji by ~ 1300 BC Tonga by ~1100 BC Samoa and Marquesas by 500 BC By now there is a distinct Polynesian culture. Easter Island
OCN 201 History of Oceanography and Polynesian voyaging History of Settlement: Fiji by ~ 1300 BC Tonga by ~1100 BC Samoa and Marquesas by 500 BC By now there is a distinct Polynesian culture. Easter Island
Your web browser (Safari 7) is out of date. For more security, comfort and the best experience on this site: Update your browser Ignore
 Your web browser (Safari 7) is out of date. For more security, comfort and the best experience on this site: Update your browser Ignore O CEAN EXPLO RATIO N: TIMEL INE Important s in Ocean Underwater Exploration
Your web browser (Safari 7) is out of date. For more security, comfort and the best experience on this site: Update your browser Ignore O CEAN EXPLO RATIO N: TIMEL INE Important s in Ocean Underwater Exploration
Have homework out for me to check Need notes from yesterday Teaching Point: Understanding the terms of MAIN IDEA
 1. Unpack/ Use the Restroom 2. Sharpen 2 pencils 3. Write down homework 4. Show me your agenda 5. GET ALL READING MATERIALS 6. Work on Math Muscle 7. Work on i-ready when finished 8. Global Read Aloud
1. Unpack/ Use the Restroom 2. Sharpen 2 pencils 3. Write down homework 4. Show me your agenda 5. GET ALL READING MATERIALS 6. Work on Math Muscle 7. Work on i-ready when finished 8. Global Read Aloud
AMERIGO VESPUCCI ( )
 AMERIGO VESPUCCI (1451-1512) Amerigo Vespucci was born in Italy in 1451. Vespucci went on several expeditions to South America. In 1501, he sailed in service to the King of Portugal. This was his third
AMERIGO VESPUCCI (1451-1512) Amerigo Vespucci was born in Italy in 1451. Vespucci went on several expeditions to South America. In 1501, he sailed in service to the King of Portugal. This was his third
History/Explorers/Expeditions/Technology Webquest!
 Name Block History/Explorers/Expeditions/Technology Webquest! http://www.divediscover.whoi.edu/history-ocean/21st.html Click on: History of Oceanography (on the left side of the page) 1. Oceanography may
Name Block History/Explorers/Expeditions/Technology Webquest! http://www.divediscover.whoi.edu/history-ocean/21st.html Click on: History of Oceanography (on the left side of the page) 1. Oceanography may
Background: If people did not explore the world, we would not know as much as we do now. Background evidence #1 Back then, spices were very important.
 Student D CBEAR Outline ***(Hint: your claim should be able to be proved with research, evidence, and academic thinking.) Claim: During the 1400s people liked to explore the world. ***(Hint: What do you
Student D CBEAR Outline ***(Hint: your claim should be able to be proved with research, evidence, and academic thinking.) Claim: During the 1400s people liked to explore the world. ***(Hint: What do you
Marine Science. Monday 17 September 2018
 Marine Science Monday 17 September 2018 Entry Task(s) What were the routes taken by the early explorers & navigators? Complete the map from last week. Draw lines to show the approximate paths sailed by
Marine Science Monday 17 September 2018 Entry Task(s) What were the routes taken by the early explorers & navigators? Complete the map from last week. Draw lines to show the approximate paths sailed by
Ocean Layers. Based on sunlight penetration: Based on water density: Sunlight (photosynthesis is possible) Twilight Midnight
 PART 3 Ocean Layers Based on sunlight penetration: Sunlight (photosynthesis is possible) Twilight Midnight Based on water density: Mixed layer Pycnocline (rapid change of themperature/salinity) Deep ocean
PART 3 Ocean Layers Based on sunlight penetration: Sunlight (photosynthesis is possible) Twilight Midnight Based on water density: Mixed layer Pycnocline (rapid change of themperature/salinity) Deep ocean
Ocean Exploration. Copyright 2012 LessonSnips
 Ocean Exploration Approximately 71 percent of the surface of the earth is covered by the ocean yet very little of the ocean has been explored. Once sailing ships capable of traversing the ocean were built,
Ocean Exploration Approximately 71 percent of the surface of the earth is covered by the ocean yet very little of the ocean has been explored. Once sailing ships capable of traversing the ocean were built,
VASCO NUNEZ BALBOA. Reason for Sailing. Route Taken and Obstacles Faced
 Reason for Sailing VASCO NUNEZ BALBOA Vasco Balboa was a Spanish explorer who admired Christopher Columbus. Like Christopher Columbus he wanted to sail to the New World. However, unlike Christopher Columbus
Reason for Sailing VASCO NUNEZ BALBOA Vasco Balboa was a Spanish explorer who admired Christopher Columbus. Like Christopher Columbus he wanted to sail to the New World. However, unlike Christopher Columbus
Tools of Oceanography Ocean Currents. Drift Bottles and Dyes: measures speed and direction of ocean currents.
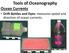 Tools of Oceanography Ocean Currents Drift Bottles and Dyes: measures speed and direction of ocean currents. Ekman Current Meters: measures speed and direction of currents in deep water. Ocean Water Sampling
Tools of Oceanography Ocean Currents Drift Bottles and Dyes: measures speed and direction of ocean currents. Ekman Current Meters: measures speed and direction of currents in deep water. Ocean Water Sampling
Magellan crosses the Atlantic Ocean
 Name: Date: Module 1, Lesson 1 Magellan crosses the Atlantic Ocean After Christopher Columbus found the New World in 1492, Spain and Portugal were eager to conquer and claim new lands. The two world powers
Name: Date: Module 1, Lesson 1 Magellan crosses the Atlantic Ocean After Christopher Columbus found the New World in 1492, Spain and Portugal were eager to conquer and claim new lands. The two world powers
Ch19&21 Test. Multiple Choice Identify the choice that best completes the statement or answers the question.
 Ch19&21 Test Multiple Choice Identify the choice that best completes the statement or answers the question. 1. A large body of saline water that may be surrounded by land is a(n) a. submersible. c. global
Ch19&21 Test Multiple Choice Identify the choice that best completes the statement or answers the question. 1. A large body of saline water that may be surrounded by land is a(n) a. submersible. c. global
OCEANOGRAPHY STUDY GUIDE
 OCEANOGRAPHY STUDY GUIDE Chapter 2 Section 1 1. Most abundant salt in ocean. Sodium chloride; NaCl 2. Amount of Earth covered by Water 71% 3. Four oceans: What are they? Atlantic, Pacific, Arctic, Indian
OCEANOGRAPHY STUDY GUIDE Chapter 2 Section 1 1. Most abundant salt in ocean. Sodium chloride; NaCl 2. Amount of Earth covered by Water 71% 3. Four oceans: What are they? Atlantic, Pacific, Arctic, Indian
Library founded at Alexandria 300 B.C.E
 Phonecians 1200 BC Origins begin as a mystery Located in western, costal part of fertile crescent Known for ships and manufacture of luxury and common goods Library founded at Alexandria 300 B.C.E *The
Phonecians 1200 BC Origins begin as a mystery Located in western, costal part of fertile crescent Known for ships and manufacture of luxury and common goods Library founded at Alexandria 300 B.C.E *The
170 points. 38 points In your textbook, read about modern oceanography. For each item write the word that meets the description.
 Ch 15 Earth s Oceans SECTION 15.1 An Overview of Oceans 38 points In your textbook, read about modern oceanography. For each item write the word that meets the description. (5 points) 1. German research
Ch 15 Earth s Oceans SECTION 15.1 An Overview of Oceans 38 points In your textbook, read about modern oceanography. For each item write the word that meets the description. (5 points) 1. German research
Maritime Exploration THE EARLY MODERN WORLD ( )
 Maritime Exploration THE EARLY MODERN WORLD (1450 1750) An important theme of 1450 1750 (The Early Modern World) will be the effects of European exploration on the world. However, there were maritime expansions
Maritime Exploration THE EARLY MODERN WORLD (1450 1750) An important theme of 1450 1750 (The Early Modern World) will be the effects of European exploration on the world. However, there were maritime expansions
Introduction to Marine Science
 Chapter 1 Introduction to Marine Science Marine Science and Oceanography Marine Science: the process of discovering i the facts, processes, and unifying principals that explain the nature of the oceans
Chapter 1 Introduction to Marine Science Marine Science and Oceanography Marine Science: the process of discovering i the facts, processes, and unifying principals that explain the nature of the oceans
Europeans borrowed and developed several tools that allowed them to:
 Europeans borrowed and developed several tools that allowed them to: 1. make long sea voyages out of sight of land 2. to know where they are without any landmarks (navigation) astrolabe Predicts location
Europeans borrowed and developed several tools that allowed them to: 1. make long sea voyages out of sight of land 2. to know where they are without any landmarks (navigation) astrolabe Predicts location
Caribbean Sea And Gulf Of Mexico (Oceans And Seas) By Jen Green READ ONLINE
 Caribbean Sea And Gulf Of Mexico (Oceans And Seas) By Jen Green READ ONLINE If you are searched for a book by Jen Green Caribbean Sea And Gulf of Mexico (Oceans and Seas) in pdf format, in that case you
Caribbean Sea And Gulf Of Mexico (Oceans And Seas) By Jen Green READ ONLINE If you are searched for a book by Jen Green Caribbean Sea And Gulf of Mexico (Oceans and Seas) in pdf format, in that case you
Currents & Gyres Notes
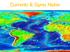 Currents & Gyres Notes Current A river of water flowing in the ocean. 2 Types of Currents Surface Currents wind-driven currents that occur in the top 100m or less Deep Currents density-driven currents
Currents & Gyres Notes Current A river of water flowing in the ocean. 2 Types of Currents Surface Currents wind-driven currents that occur in the top 100m or less Deep Currents density-driven currents
Section 6. The Surface Circulation of the Ocean. What Do You See? Think About It. Investigate. Learning Outcomes
 Chapter 5 Winds, Oceans, Weather, and Climate Section 6 The Surface Circulation of the Ocean What Do You See? Learning Outcomes In this section, you will Understand the general paths of surface ocean currents.
Chapter 5 Winds, Oceans, Weather, and Climate Section 6 The Surface Circulation of the Ocean What Do You See? Learning Outcomes In this section, you will Understand the general paths of surface ocean currents.
Nautical Chart Challenge
 Discover Your World With NOAA Nautical Chart Challenge For as long as anyone in his family could remember, Francis Beaufort wanted to make scientific observations from the deck of a ship. In 1789 at the
Discover Your World With NOAA Nautical Chart Challenge For as long as anyone in his family could remember, Francis Beaufort wanted to make scientific observations from the deck of a ship. In 1789 at the
Ocean Currents Lecture Notes
 Ocean Currents Lecture Notes (Topic 9A) page 1 Ocean Currents Lecture Notes Surface Currents Ocean Currents (What is an ocean current? How is a current different from a wave?) The water in an travels from
Ocean Currents Lecture Notes (Topic 9A) page 1 Ocean Currents Lecture Notes Surface Currents Ocean Currents (What is an ocean current? How is a current different from a wave?) The water in an travels from
Role of the oceans in the climate system
 Role of the oceans in the climate system heat exchange and transport hydrological cycle and air-sea exchange of moisture wind, currents, and upwelling gas exchange and carbon cycle Heat transport Two Primary
Role of the oceans in the climate system heat exchange and transport hydrological cycle and air-sea exchange of moisture wind, currents, and upwelling gas exchange and carbon cycle Heat transport Two Primary
TO GO TO ANY OF THE PAGES LISTED BELOW, CLICK ON ITS TITLE
 TO GO TO ANY OF THE PAGES LISTED BELOW, CLICK ON ITS TITLE CHAPTER 10 The Oceans 1 10-1 What is the world ocean? 2 10-2 How are the oceans explored? 3 Measuring Ocean Properties Enrichment Activity for
TO GO TO ANY OF THE PAGES LISTED BELOW, CLICK ON ITS TITLE CHAPTER 10 The Oceans 1 10-1 What is the world ocean? 2 10-2 How are the oceans explored? 3 Measuring Ocean Properties Enrichment Activity for
10% water in the world is tied up in the surface ocean currents. (above the pycnocline) Primary source is wind: Westerlies, Trades, Polar Easterlies
 Oceanography Chapter 9 10% water in the world is tied up in the surface ocean currents. (above the pycnocline) Primary source is wind: Westerlies, Trades, Polar Easterlies Coriolis deflects winds (and
Oceanography Chapter 9 10% water in the world is tied up in the surface ocean currents. (above the pycnocline) Primary source is wind: Westerlies, Trades, Polar Easterlies Coriolis deflects winds (and
COASTAL UPWELLING - MONTEREY BAY CALIFORNIA (modified from The Maury Project, AMS)
 Name: Date: Per: COASTAL UPWELLING - MONTEREY BAY CALIFORNIA (modified from The Maury Project, AMS) The ocean is composed of 3 distinct layers: the shallow surface mixed zone, the transition zone, and
Name: Date: Per: COASTAL UPWELLING - MONTEREY BAY CALIFORNIA (modified from The Maury Project, AMS) The ocean is composed of 3 distinct layers: the shallow surface mixed zone, the transition zone, and
SCI-5 MES_Lamb_Oceans Exam not valid for Paper Pencil Test Sessions
 SCI-5 MES_Lamb_Oceans Exam not valid for Paper Pencil Test Sessions [Exam ID:53S2JF 1 Two children are swimming and jumping in the waves at the beach. On which part of the ocean are they standing? A Abyssal
SCI-5 MES_Lamb_Oceans Exam not valid for Paper Pencil Test Sessions [Exam ID:53S2JF 1 Two children are swimming and jumping in the waves at the beach. On which part of the ocean are they standing? A Abyssal
CHAPTER 7 Ocean Circulation
 1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 13 14 CHAPTER 7 Ocean Circulation Words Ocean currents Moving seawater Surface ocean currents Transfer heat from warmer to cooler areas Similar to pattern of major wind belts
1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 13 14 CHAPTER 7 Ocean Circulation Words Ocean currents Moving seawater Surface ocean currents Transfer heat from warmer to cooler areas Similar to pattern of major wind belts
2. Have students do a pre-test (Test your Marianas Knowledge quiz) and post-test.
 Lesson Plan: Navigating Change Unit 1: The Voyage 1.2 Island Investigations Emphasis: History (island facts), geology (island formation), geography (relative location of the islands.) Description: Introducing
Lesson Plan: Navigating Change Unit 1: The Voyage 1.2 Island Investigations Emphasis: History (island facts), geology (island formation), geography (relative location of the islands.) Description: Introducing
Literacy Lab #24 - Mariana Trench Dive Earth Science - Breed /2013
 Name Date Literacy Lab #24 - Mariana Trench Dive Earth Science - Breed - 2012/2013 Directions: Take a few minutes to read the article below either online (or on the back of this page.) Write responses
Name Date Literacy Lab #24 - Mariana Trench Dive Earth Science - Breed - 2012/2013 Directions: Take a few minutes to read the article below either online (or on the back of this page.) Write responses
Navigation & Orienteering: Pre- Test
 Name: Class: Answer Key Date: Page 1 of 7 Navigation & Orienteering: Pre- Test There are three sections: Multiple Choice, True/False, and Short Answer. For the multiple choice, please select the BEST answer
Name: Class: Answer Key Date: Page 1 of 7 Navigation & Orienteering: Pre- Test There are three sections: Multiple Choice, True/False, and Short Answer. For the multiple choice, please select the BEST answer
Chapter 8 Air Masses
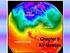 Chapter 8 Air Masses Air Masses - 1 1. An Air Mass is a large body of air usually about 1500 km across and several km thick, that has homogeneous physical properties. 2. The important physical properties
Chapter 8 Air Masses Air Masses - 1 1. An Air Mass is a large body of air usually about 1500 km across and several km thick, that has homogeneous physical properties. 2. The important physical properties
Analyzing the Japanese Sailing Ship Model. museum was founded) and 1932 (the year the models were discovered and categorized)
 Miles McCollum Anthro 1218 Professor Damian 11 March 2016 Analyzing the Japanese Sailing Ship Model Arriving at the Peabody Museum at Harvard University between 1867 (the year the museum was founded) and
Miles McCollum Anthro 1218 Professor Damian 11 March 2016 Analyzing the Japanese Sailing Ship Model Arriving at the Peabody Museum at Harvard University between 1867 (the year the museum was founded) and
Canada s Natural Systems. Canadian Geography 1202
 Canada s Natural Systems Canadian Geography 1202 Canada s Natural Systems Natural System: A system found in nature Here are the four natural systems that we will explore in the next few weeks 1. Canada
Canada s Natural Systems Canadian Geography 1202 Canada s Natural Systems Natural System: A system found in nature Here are the four natural systems that we will explore in the next few weeks 1. Canada
Sailing Blind: The Challenges of a Submarine's Navigator
 Sailing Blind: The Challenges of a Submarine's Navigator John Clark, Physics Teacher and Military Historian, Deltona HS, Deltona 2012 Naval Historical Foundation STEM-H Teacher Fellowship Instructional
Sailing Blind: The Challenges of a Submarine's Navigator John Clark, Physics Teacher and Military Historian, Deltona HS, Deltona 2012 Naval Historical Foundation STEM-H Teacher Fellowship Instructional
Lesson 2: Sailing. A league is three nautical miles. (A nautical mile is about 800 feet longer than a mile on land.)
 Early Explorers -> 2: Sailing Lesson 2: Sailing Getting Started? Big Ideas What methods did sailors have for survival on the seas? & Facts and Definitions 8 Skills " Materials Introduction Navigation is
Early Explorers -> 2: Sailing Lesson 2: Sailing Getting Started? Big Ideas What methods did sailors have for survival on the seas? & Facts and Definitions 8 Skills " Materials Introduction Navigation is
Ocean Currents Unit (4 pts)
 Name: Section: Ocean Currents Unit (Topic 9A-1) page 1 Ocean Currents Unit (4 pts) Ocean Currents An ocean current is like a river in the ocean: water is flowing traveling from place to place. Historically,
Name: Section: Ocean Currents Unit (Topic 9A-1) page 1 Ocean Currents Unit (4 pts) Ocean Currents An ocean current is like a river in the ocean: water is flowing traveling from place to place. Historically,
Ocean Currents Shortcut method by to learn faster
 Ocean Currents Shortcut method by to learn faster In our geography notes on the hydrosphere, we have seen the major movements of the ocean water. They are waves, tides and ocean currents. Having covered
Ocean Currents Shortcut method by to learn faster In our geography notes on the hydrosphere, we have seen the major movements of the ocean water. They are waves, tides and ocean currents. Having covered
Ocean Currents Shortcut method by to learn faster
 Ocean Currents Shortcut method by to learn faster In our geography notes on the hydrosphere, we have seen the major movements of the ocean water. They are waves, tides and ocean currents. Having covered
Ocean Currents Shortcut method by to learn faster In our geography notes on the hydrosphere, we have seen the major movements of the ocean water. They are waves, tides and ocean currents. Having covered
Introduction to Oceanography OCE 1001
 Introduction to Oceanography OCE 1001 Lecture Notes Chantale Bégin & Jessica Fry Version 2.1 10. Ocean Circulation (Trujillo, Chapter 7) Major ocean currents are stable and predictable; they have been
Introduction to Oceanography OCE 1001 Lecture Notes Chantale Bégin & Jessica Fry Version 2.1 10. Ocean Circulation (Trujillo, Chapter 7) Major ocean currents are stable and predictable; they have been
Don t Drink the Water
 UNIT 6 WEEK 3 Read the article Don t Drink the Water before answering Numbers 1 through 5. Don t Drink the Water Cholera is a swift and terrible disease that infects the intestines. It is caused by bacteria.
UNIT 6 WEEK 3 Read the article Don t Drink the Water before answering Numbers 1 through 5. Don t Drink the Water Cholera is a swift and terrible disease that infects the intestines. It is caused by bacteria.
Climate and Climate Change
 Climate and Climate Change Chapter Test A Multiple Choice Write the letter of the correct answer on the line at the left. 1. Climates are classified according to two major factors: a. elevation and precipitation.
Climate and Climate Change Chapter Test A Multiple Choice Write the letter of the correct answer on the line at the left. 1. Climates are classified according to two major factors: a. elevation and precipitation.
SURFACE CURRENTS AND TIDES
 NAME SURFACE CURRENTS AND TIDES I. Origin of surface currents Surface currents arise due to the interaction of the prevailing wis a the ocean surface. Hence the surface wi pattern (Figure 1) plays a key
NAME SURFACE CURRENTS AND TIDES I. Origin of surface currents Surface currents arise due to the interaction of the prevailing wis a the ocean surface. Hence the surface wi pattern (Figure 1) plays a key
Name Date L.O: SWBAT explain what breezes, planetary winds, ocean currents & monsoons are.
 Name Date L.O: SWBAT explain what breezes, planetary winds, ocean currents & monsoons are. 1. A cool breeze is blowing toward the land from the ocean on a warm, cloudless summer day. This condition is
Name Date L.O: SWBAT explain what breezes, planetary winds, ocean currents & monsoons are. 1. A cool breeze is blowing toward the land from the ocean on a warm, cloudless summer day. This condition is
SAUSD Common Core First Grade Unit of Study. Student Learning Journal. Exploring Our World. Name
 Exploring Our World Student Learning Journal Name SAUSD Common Core First Grade Unit of Study Songs of Higher Learning www.songsofhigherlearning.com Lesson 1 2 Continents and Ocean Song In this world,
Exploring Our World Student Learning Journal Name SAUSD Common Core First Grade Unit of Study Songs of Higher Learning www.songsofhigherlearning.com Lesson 1 2 Continents and Ocean Song In this world,
OPERATIONS SEAFARER CERTIFICATION GUIDANCE NOTE SA MARITIME QUALIFICATIONS CODE. Deck: Chart Work
 Page 1 of 6 Compiled by Approved by Chief Examiner Syllabus Committee: 26 February 2013 OPERATIONS SEAFARER CERTIFICATION GUIDANCE NOTE SA MARITIME QUALIFICATIONS CODE Deck: Chart Work Page 2 of 6 COLUMN
Page 1 of 6 Compiled by Approved by Chief Examiner Syllabus Committee: 26 February 2013 OPERATIONS SEAFARER CERTIFICATION GUIDANCE NOTE SA MARITIME QUALIFICATIONS CODE Deck: Chart Work Page 2 of 6 COLUMN
THE ATMOSPHERE. WEATHER and CLIMATE. The Atmosphere 10/12/2018 R E M I N D E R S. PART II: People and their. weather. climate?
 R E M I N D E R S Two required essays are due by Oct. 30, 2018. (A third may be used for extra credit in place of a Think Geographically essay.) ESSAY TOPICS (choose any two): Contributions of a noted
R E M I N D E R S Two required essays are due by Oct. 30, 2018. (A third may be used for extra credit in place of a Think Geographically essay.) ESSAY TOPICS (choose any two): Contributions of a noted
EARTH, PLANETARY, & SPACE SCIENCES 15 INTRODUCTION TO OCEANOGRAPHY. LABORATORY SESSION #6 Fall Ocean Circulation
 EARTH, PLANETARY, & SPACE SCIENCES 15 INTRODUCTION TO OCEANOGRAPHY LABORATORY SESSION #6 Fall 2017 Ocean Circulation The focus of the Lab this week is circulation of the ocean and atmosphere. Here, you
EARTH, PLANETARY, & SPACE SCIENCES 15 INTRODUCTION TO OCEANOGRAPHY LABORATORY SESSION #6 Fall 2017 Ocean Circulation The focus of the Lab this week is circulation of the ocean and atmosphere. Here, you
staying around 37 F. The water pressure in this zone can be up to one thousand times as great as the pressure on the surface.
 The Last Frontier The area of the Earth is over 197,000,000 square miles. Of that, less than one-third is land while 71% of the planet is covered by water, most of which is salt water. Only 3% of the total
The Last Frontier The area of the Earth is over 197,000,000 square miles. Of that, less than one-third is land while 71% of the planet is covered by water, most of which is salt water. Only 3% of the total
Sailing the Seas: Wind Driven Ocean Circulation Ocean Gyres
 Sailing the Seas: Wind Driven Ocean Circulation Ocean Gyres Ocean Currents What Happens at the Coast? Readings: Ch 9: 9.2-9.6, 9.8-9.13 Graphic: America's Cup sailboat race off Newport, Rhode Island. J.
Sailing the Seas: Wind Driven Ocean Circulation Ocean Gyres Ocean Currents What Happens at the Coast? Readings: Ch 9: 9.2-9.6, 9.8-9.13 Graphic: America's Cup sailboat race off Newport, Rhode Island. J.
World Explorers. By Sandy Tasker SAMPLE
 Ebook Code REAU 5053 World Explorers By Sandy Tasker Contents How the World Was Discovered... 4 Paths of Exploration... 5 The Vikings 793-1050... 6 Viking Navigation... 7 The Mongols: Early to Mid 1200s...
Ebook Code REAU 5053 World Explorers By Sandy Tasker Contents How the World Was Discovered... 4 Paths of Exploration... 5 The Vikings 793-1050... 6 Viking Navigation... 7 The Mongols: Early to Mid 1200s...
HYDROSPHERE, OCEANS AND TIDES
 HYDROSPHERE, OCEANS AND TIDES Revision 10x10learning.com 1 Chapter 12. In the Earth s Atmosphere On surface of the Earth Under the ground Hydrosphere comprises of ALL WATER Water Vapour = 0.001% Is very
HYDROSPHERE, OCEANS AND TIDES Revision 10x10learning.com 1 Chapter 12. In the Earth s Atmosphere On surface of the Earth Under the ground Hydrosphere comprises of ALL WATER Water Vapour = 0.001% Is very
OCEAN NAVIGATOR. Premium Worksheets For Children. Illustrations: Swathi Content: Marwah. For 8-12 Year olds
 OCEAN NAVIGATOR Premium Worksheets For Children For 8-12 Year olds Illustrations: Swathi Content: Marwah Index Activity Name Skills Acquired World Oceans Ocean Zones Where Are They Found? Trash Navigator
OCEAN NAVIGATOR Premium Worksheets For Children For 8-12 Year olds Illustrations: Swathi Content: Marwah Index Activity Name Skills Acquired World Oceans Ocean Zones Where Are They Found? Trash Navigator
The first man to circumnavigate the world?
 The first man to circumnavigate the world? Born 1480 in Portugal First known expedition: 1505 Sent to India on a mission for the King of Portugal 1513: A Spanish explorer, Balboa, claims to have seen a
The first man to circumnavigate the world? Born 1480 in Portugal First known expedition: 1505 Sent to India on a mission for the King of Portugal 1513: A Spanish explorer, Balboa, claims to have seen a
Sebastian Cermeno ( )
 Sebastian Cermeno (1560-1602) Sebastian Rodriguez Cermeno was a Portuguese adventurer who explored the coast of California for Spain. He was a skilled navigator and had lots of experience sailing across
Sebastian Cermeno (1560-1602) Sebastian Rodriguez Cermeno was a Portuguese adventurer who explored the coast of California for Spain. He was a skilled navigator and had lots of experience sailing across
UNIT 1: WATER SYSTEMS ON EARTH CHAPTER 3
 UNIT 1: WATER SYSTEMS ON EARTH CHAPTER 3 HEAT CAPACITY HEAT CAPACITY (SPECIFIC HEAT CAPACITY) IS THE AMOUNT OF HEAT THAT A SUBSTANCE CAN HOLD WATER HAS A HIGH HEAT CAPACITY IT CAN TAKE IN A LARGE AMOUNT
UNIT 1: WATER SYSTEMS ON EARTH CHAPTER 3 HEAT CAPACITY HEAT CAPACITY (SPECIFIC HEAT CAPACITY) IS THE AMOUNT OF HEAT THAT A SUBSTANCE CAN HOLD WATER HAS A HIGH HEAT CAPACITY IT CAN TAKE IN A LARGE AMOUNT
Chapter 10 Lecture Outline. The Restless Oceans
 Chapter 10 Lecture Outline The Restless Oceans Focus Question 10.1 How does the Coriolis effect influence ocean currents? The Ocean s Surface Circulation Ocean currents Masses of water that flow from one
Chapter 10 Lecture Outline The Restless Oceans Focus Question 10.1 How does the Coriolis effect influence ocean currents? The Ocean s Surface Circulation Ocean currents Masses of water that flow from one
Ocean Observing Systems Summer Teacher Institute August 10 August 14, 2009
 OOS? What s that?? COSEE-West 2008 Ocean Observing Systems Summer Teacher Institute Resources/Lesson Plans http://www.usc.edu/org/cosee-west/resources.html#aug08 Teacher created lesson plans from 2008
OOS? What s that?? COSEE-West 2008 Ocean Observing Systems Summer Teacher Institute Resources/Lesson Plans http://www.usc.edu/org/cosee-west/resources.html#aug08 Teacher created lesson plans from 2008
Chapter 9: Circulation of the Ocean
 Chapter 9: Circulation of the Ocean Tropical gardens on Britain s Scilly Isles. Only 48 kilometers (30 miles) off the coast of Cornwall at 50 N, these scenic islands lie in the path of the warm waters
Chapter 9: Circulation of the Ocean Tropical gardens on Britain s Scilly Isles. Only 48 kilometers (30 miles) off the coast of Cornwall at 50 N, these scenic islands lie in the path of the warm waters
General Oceanography Geology 105 Expedition #19 The Ocean and Climate
 General Oceanography Geology 105 Expedition #19 The Ocean and Climate Name Not attempting to answer questions on expeditions will result in point deductions on course workbook (two or more blank answers
General Oceanography Geology 105 Expedition #19 The Ocean and Climate Name Not attempting to answer questions on expeditions will result in point deductions on course workbook (two or more blank answers
Earth s oceans covers 71 % _ of the planet s surface. In reality, Earth s ocean waters are all. interconnected as part of a single large global ocean.
 Ocean Motion Met 101: Introduction to the World's Oceans Produced by The COMET Program Geography: Name Pd. Earth s oceans covers 71 % _ of the planet s surface. In reality, Earth s ocean waters are all
Ocean Motion Met 101: Introduction to the World's Oceans Produced by The COMET Program Geography: Name Pd. Earth s oceans covers 71 % _ of the planet s surface. In reality, Earth s ocean waters are all
Grade 8 Science: Unit 1 Water Systems Chapter 3
 Heat Capacity Grade 8 Science: Unit 1 Water Systems Chapter 3 Heat capacity ( ) is the amount of heat that a substance can hold. has a high heat capacity it can take in a large amount of heat before its
Heat Capacity Grade 8 Science: Unit 1 Water Systems Chapter 3 Heat capacity ( ) is the amount of heat that a substance can hold. has a high heat capacity it can take in a large amount of heat before its
Chinese War Junk Model: A Representation of the Not-So-Triumphant War Junks
 Storer 1 Norman R. Storer March 11, 2016 Anthro 1218 Chinese War Junk Model: A Representation of the Not-So-Triumphant War Junks of the Opium War Era While Western vessels are thought to have evolved from
Storer 1 Norman R. Storer March 11, 2016 Anthro 1218 Chinese War Junk Model: A Representation of the Not-So-Triumphant War Junks of the Opium War Era While Western vessels are thought to have evolved from
Chapter 22, Section 1 - Ocean Currents. Section Objectives
 Chapter 22, Section 1 - Ocean Currents Section Objectives Intro Surface Currents Factors Affecting Ocean Currents Global Wind Belts (you should draw and label a diagram of the global wind belts) The Coriolis
Chapter 22, Section 1 - Ocean Currents Section Objectives Intro Surface Currents Factors Affecting Ocean Currents Global Wind Belts (you should draw and label a diagram of the global wind belts) The Coriolis
OCN 201 Surface Circulation
 OCN 201 Surface Circulation Excess heat in equatorial regions requires redistribution toward the poles 1 In the Northern hemisphere, Coriolis force deflects movement to the right In the Southern hemisphere,
OCN 201 Surface Circulation Excess heat in equatorial regions requires redistribution toward the poles 1 In the Northern hemisphere, Coriolis force deflects movement to the right In the Southern hemisphere,
Wednesday, September 15, 2010 Coriolis force, 3 dimensions (p 65)
 Wednesday, September 15, 2010 Coriolis force, 3 dimensions (p 65) Weather fronts (p 63) General circulation on a rotating Earth (p 65) Geostrophy force balance (p 66) Local effects (no coriolis force)
Wednesday, September 15, 2010 Coriolis force, 3 dimensions (p 65) Weather fronts (p 63) General circulation on a rotating Earth (p 65) Geostrophy force balance (p 66) Local effects (no coriolis force)
Imagine that you can see a side view of a wave as it approaches a beach. Describe how the wave changes as the wave approaches the beach.
 Geology 101 Name Reading Guide for Ch. 19: Shores and Coastal Processes (p. 612) Waves, Currents, and Tides (p. 614) Waves and Currents (p. 614) Imagine that you can see a side view of a wave as it approaches
Geology 101 Name Reading Guide for Ch. 19: Shores and Coastal Processes (p. 612) Waves, Currents, and Tides (p. 614) Waves and Currents (p. 614) Imagine that you can see a side view of a wave as it approaches
Discovery Channel capturing expedition for documentary series
 Contact: Stephanie Fitzherbert FiveDeepsPress@richards.com Explorer makes history as first human to successfully dive to the deepest point in the Southern Ocean, in the South Sandwich Trench Victor Vescovo
Contact: Stephanie Fitzherbert FiveDeepsPress@richards.com Explorer makes history as first human to successfully dive to the deepest point in the Southern Ocean, in the South Sandwich Trench Victor Vescovo
6 th Meeting of the Scientific Committee Puerto Varas, Chile, 9-14 September SC6-Doc15 The Russian Federation s Annual Report
 6 th Meeting of the Scientific Committee Puerto Varas, Chile, 9-14 September 2018 SC6-Doc15 The Russian Federation s Annual Report National report of the Russian Federation to the SPRFMO Science Working
6 th Meeting of the Scientific Committee Puerto Varas, Chile, 9-14 September 2018 SC6-Doc15 The Russian Federation s Annual Report National report of the Russian Federation to the SPRFMO Science Working
GEOGRAPHY - STD 8 [ ] Q1.
![GEOGRAPHY - STD 8 [ ] Q1. GEOGRAPHY - STD 8 [ ] Q1.](/thumbs/84/90631870.jpg) GEOGRAPHY - STD 8 Movements of Oceans [2016-2017] Q1. Name the two types of regular movements in the oceans. Ans. The regular movements in the ocean are of two types: 1. Horizontal Ocean currents 2. Vertical
GEOGRAPHY - STD 8 Movements of Oceans [2016-2017] Q1. Name the two types of regular movements in the oceans. Ans. The regular movements in the ocean are of two types: 1. Horizontal Ocean currents 2. Vertical
Review for the second quarter. Mechanisms for cloud formation
 Review for the second quarter Mechanisms for cloud formation 1 Rising air expands and cools; Sinking air compresses and warms. (18) (24) Dry adiabatic lapse rate (10 o C/km): the rate of temperature decrease
Review for the second quarter Mechanisms for cloud formation 1 Rising air expands and cools; Sinking air compresses and warms. (18) (24) Dry adiabatic lapse rate (10 o C/km): the rate of temperature decrease
Directed Reading. Section: Ocean Currents. a(n). FACTORS THAT AFFECT SURFACE CURRENTS
 Skills Worksheet Directed Reading Section: Ocean Currents 1. A horizontal movement of water in a well-defined pattern is called a(n). 2. What are two ways that oceanographers identify ocean currents? 3.
Skills Worksheet Directed Reading Section: Ocean Currents 1. A horizontal movement of water in a well-defined pattern is called a(n). 2. What are two ways that oceanographers identify ocean currents? 3.
Finish Characteristics of Climate
 Bell Ringer Finish Characteristics of Climate Wind Coriolis Effect Newton s second law: a body in motion will continue in motion (unchanged) unless acted upon by an outside force. Liquid (water) and gas
Bell Ringer Finish Characteristics of Climate Wind Coriolis Effect Newton s second law: a body in motion will continue in motion (unchanged) unless acted upon by an outside force. Liquid (water) and gas
A COMPARISON OF EVIDENCE BETWEEN TWO LANDING SITE THEORIES
 A COMPARISON OF EVIDENCE BETWEEN TWO LANDING SITE THEORIES I ve always preferred to let the evidence of my cove location hypothesis speak for itself. I would like to address, however, the long-held theory
A COMPARISON OF EVIDENCE BETWEEN TWO LANDING SITE THEORIES I ve always preferred to let the evidence of my cove location hypothesis speak for itself. I would like to address, however, the long-held theory
Greenhouse Effect Activity
 Greenhouse Effect Activity Objectives: The student will: 1. Read and use weather instruments. 2. Collect and record temperature readings. 3. Describe the concept of the greenhouse effect. Materials: Fish
Greenhouse Effect Activity Objectives: The student will: 1. Read and use weather instruments. 2. Collect and record temperature readings. 3. Describe the concept of the greenhouse effect. Materials: Fish
UNDERWATER DRONES CONTROL TOWER UNDERWATER DRONES CONTROL TOWER
 UNDERWATER DRONES CONTROL TOWER UNDERWATER DRONES CONTROL TOWER Adnan Tahirovic - Kemal Delic ARCHITECTURE, DESIGN, ENGINEERING Talk outline - why and how uwr is important? Underwater World Explained Technology
UNDERWATER DRONES CONTROL TOWER UNDERWATER DRONES CONTROL TOWER Adnan Tahirovic - Kemal Delic ARCHITECTURE, DESIGN, ENGINEERING Talk outline - why and how uwr is important? Underwater World Explained Technology
Binder Page Name Per Exploring New York
 Binder Page Name Per Exploring New York Date This map shows the modern state of New York, and other surrounding states. 1. Put a dot on the map where Buffalo is located. Label it Buffalo. 2. Label the
Binder Page Name Per Exploring New York Date This map shows the modern state of New York, and other surrounding states. 1. Put a dot on the map where Buffalo is located. Label it Buffalo. 2. Label the
Zonal (East-West) Currents. Wind-Driven Ocean Currents. Zonal (East-West) Currents. Meridional (N-S) Currents
 Wind-Driven Ocean Currents Similarities between winds & surface currents Zonal (East-West) Currents Trade winds push currents westward north & south of the equator Equatorial currents. Up to 100 cm/sec.
Wind-Driven Ocean Currents Similarities between winds & surface currents Zonal (East-West) Currents Trade winds push currents westward north & south of the equator Equatorial currents. Up to 100 cm/sec.
3/22/11. General Circulation of the Atmosphere. General Circulation of the Atmosphere
 Chapter 10 General refers to the average air flow, actual winds will vary considerably. Average conditions help identify driving forces. The basic cause of the general circulation is unequal heating of
Chapter 10 General refers to the average air flow, actual winds will vary considerably. Average conditions help identify driving forces. The basic cause of the general circulation is unequal heating of
Nautical Navigation: Final Quiz
 Name: Nautical Navigation Final Quiz Class: (ver. 03/09/15) Date: Page 1 of 9 Nautical Navigation: Final Quiz There are three sections: Multiple Choice, True/False, and Short Answer. For the multiple choice,
Name: Nautical Navigation Final Quiz Class: (ver. 03/09/15) Date: Page 1 of 9 Nautical Navigation: Final Quiz There are three sections: Multiple Choice, True/False, and Short Answer. For the multiple choice,
A Suggested Route Large Print
 National Maritime Museum Cornwall A Suggested Route Large Print This Large Print Guide was produced by the Heritage Ability team, part of Living Options Devon (charity number 1102489) www.heritageability.org
National Maritime Museum Cornwall A Suggested Route Large Print This Large Print Guide was produced by the Heritage Ability team, part of Living Options Devon (charity number 1102489) www.heritageability.org
Friday, February 8 th. Winds/Coriolis Worksheet: Due Today Lab Worksheet: Finish Questions
 Ocean Currents Friday, February 8 th Winds/Coriolis Worksheet: Due Today Lab Worksheet: Finish Questions Non-rotating Earth Convection cell model Add rotation and add landmasses unequal heating and cooling
Ocean Currents Friday, February 8 th Winds/Coriolis Worksheet: Due Today Lab Worksheet: Finish Questions Non-rotating Earth Convection cell model Add rotation and add landmasses unequal heating and cooling
3.9 FROM ISLANDS TO ATOLLS
 3.9 1 3.9 FROM ISLANDS TO ATOLLS OBJECTIVES The students Listen to a description of the formation of volcanic islands, fringing reefs, barrier reefs, and atolls. Observe and participate in a simulation
3.9 1 3.9 FROM ISLANDS TO ATOLLS OBJECTIVES The students Listen to a description of the formation of volcanic islands, fringing reefs, barrier reefs, and atolls. Observe and participate in a simulation
IN THE TABLE OF CONTENTS AND ON THE NEXT CLEAN PAGE, TITLE IT: WIND NOTES WIND!
 IN THE TABLE OF CONTENTS AND ON THE NEXT CLEAN PAGE, TITLE IT: WIND NOTES WIND! Wind 8.10A recognize that the Sun provides the energy that drives convection within the atmosphere and oceans, producing
IN THE TABLE OF CONTENTS AND ON THE NEXT CLEAN PAGE, TITLE IT: WIND NOTES WIND! Wind 8.10A recognize that the Sun provides the energy that drives convection within the atmosphere and oceans, producing
Exit Ticket: Coriolis Effect
 Exit Ticket: Coriolis Effect 1. How does the Coriolis Effect influence the path of projectiles or wind traveling through the atmosphere? Causes them to curve 2. In which direction does the Coriolis Effect
Exit Ticket: Coriolis Effect 1. How does the Coriolis Effect influence the path of projectiles or wind traveling through the atmosphere? Causes them to curve 2. In which direction does the Coriolis Effect
MOTION IN THE OCEAN. For the student. Martine Kervran
 For the student Martine KERVRAN 1. THE OCEANS IN THE WORLD WORKSHEET 1 Grouping 1- Fill in the chart below after discussing the items with your friends and your teacher (use the language you know best
For the student Martine KERVRAN 1. THE OCEANS IN THE WORLD WORKSHEET 1 Grouping 1- Fill in the chart below after discussing the items with your friends and your teacher (use the language you know best
Lecture 13. Global Wind Patterns and the Oceans EOM
 Lecture 13. Global Wind Patterns and the Oceans EOM Global Wind Patterns and the Oceans Drag from wind exerts a force called wind stress on the ocean surface in the direction of the wind. The currents
Lecture 13. Global Wind Patterns and the Oceans EOM Global Wind Patterns and the Oceans Drag from wind exerts a force called wind stress on the ocean surface in the direction of the wind. The currents
VOL XXX SEPTEMBER 2012 ISSUE 1
 VOL XXX SEPTEMBER 2012 ISSUE 1 THE ARCTIC OCEAN IS PICTURED ABOVE SHOWING IN RED BOTH MAJOR NAVIGATION ROUTES BETWEEN THE ATLANTIC AND PACIFIC OCEANS- THE NORTHWEST PASSAGE AND THE NORTHERN SEA ROUTE OR
VOL XXX SEPTEMBER 2012 ISSUE 1 THE ARCTIC OCEAN IS PICTURED ABOVE SHOWING IN RED BOTH MAJOR NAVIGATION ROUTES BETWEEN THE ATLANTIC AND PACIFIC OCEANS- THE NORTHWEST PASSAGE AND THE NORTHERN SEA ROUTE OR
W3 Global Circulation Systems
 W3 Global Circulation Systems Which regions of Earth receive the most energy from the Sun? If not for global circulation systems There would only be two narrow regions that would support life What
W3 Global Circulation Systems Which regions of Earth receive the most energy from the Sun? If not for global circulation systems There would only be two narrow regions that would support life What
Physical Features, Where People Live, & How They Trade
 Physical Features, Where People Live, & How They Trade 5 large freshwater lakes in central North America HOMES (Huron, Ontario, Michigan, Erie, Superior) Serve as the industrial heartland of the continent
Physical Features, Where People Live, & How They Trade 5 large freshwater lakes in central North America HOMES (Huron, Ontario, Michigan, Erie, Superior) Serve as the industrial heartland of the continent
9/25/2014. Scales of Atmospheric Motion. Scales of Atmospheric Motion. Chapter 7: Circulation of the Atmosphere
 Chapter 7: Circulation of the Atmosphere The Atmosphere: An Introduction to Meteorology, 12 th Lutgens Tarbuck Lectures by: Heather Gallacher, Cleveland State University Scales of Atmospheric Motion Small-
Chapter 7: Circulation of the Atmosphere The Atmosphere: An Introduction to Meteorology, 12 th Lutgens Tarbuck Lectures by: Heather Gallacher, Cleveland State University Scales of Atmospheric Motion Small-
Canada s vast size creates a diverse range of weather conditions and climatic conditions. Warming trend for last 10 years Wet Spring Dry five summers
 Chapter 4 Weather and Climate Canada s vast size creates a diverse range of weather conditions and climatic conditions. Weather examples: Rainy today Snow tomorrow Fog on Wednesday 23 degree C today High
Chapter 4 Weather and Climate Canada s vast size creates a diverse range of weather conditions and climatic conditions. Weather examples: Rainy today Snow tomorrow Fog on Wednesday 23 degree C today High
6.9B verify through investigations that thermal energy moves in a predictable pattern from warmer to cooler 6.5B recognize that a limited number of
 6.9B verify through investigations that thermal energy moves in a predictable pattern from warmer to cooler 6.5B recognize that a limited number of elements comprise the largest portion of oceans and atmosphere
6.9B verify through investigations that thermal energy moves in a predictable pattern from warmer to cooler 6.5B recognize that a limited number of elements comprise the largest portion of oceans and atmosphere
Draw a picture of a water source. Don t forget to include yourself in the picture!
 Name Date Draw a picture of a water source. Don t forget to include yourself in the picture! My water source is Students describe the characteristics of a water source: stream, river, lake, pond, ocean,
Name Date Draw a picture of a water source. Don t forget to include yourself in the picture! My water source is Students describe the characteristics of a water source: stream, river, lake, pond, ocean,
