NORDIC AND BALTIC GRID DISTURBANCE STATISTICS 2014
|
|
|
- Austin Curtis
- 6 years ago
- Views:
Transcription
1 NORDIC AND BALTIC GRID DISTURBANCE STATISTICS REGIONAL GROUP NORDIC
2 1 INTRODUCTION DESCRIPTION OF THE REPORT CONTACT PERSONS VOLTAGE LEVELS IN THE NORDIC AND BALTIC NETWORKS THE SCOPE AND LIMITATIONS OF THE STATISTICS SUMMARY OVERVIEW OF THE NORDIC AND BALTIC COUNTRIES SUMMARY OF DENMARK SUMMARY OF FINLAND SUMMARY OF ESTONIA SUMMARY OF ICELAND SUMMARY OF LATVIA SUMMARY OF LITHUANIA SUMMARY OF NORWAY SUMMARY OF SWEDEN DISTURBANCES ANNUAL NUMBER OF DISTURBANCES DURING THE PERIOD DISTURBANCES DISTRIBUTED ACCORDING TO MONTH DISTURBANCES DISTRIBUTED ACCORDING TO CAUSE ENERGY NOT SUPPLIED (ENS) ENERGY NOT SUPPLIED DISTRIBUTED ACCORDING TO VOLTAGE LEVEL ENERGY NOT SUPPLIED (ENS) AND TOTAL CONSUMPTION ENERGY NOT SUPPLIED (ENS) DISTRIBUTED ACCORDING TO MONTH ENERGY NOT SUPPLIED (ENS) DISTRIBUTED ACCORDING TO CAUSE ENERGY NOT SUPPLIED (ENS) DISTRIBUTED ACCORDING TO COMPONENT FAULTS IN POWER SYSTEM COMPONENTS DEFINITIONS AND SCOPE OVERVIEW OF THE FAULTS RELATED TO DISTURBANCES FAULTS ON OVERHEAD LINES KV OVERHEAD LINES KV OVERHEAD LINES KV OVERHEAD LINES OVERHEAD LINE FAULT TRENDS FAULTS IN CABLES FAULTS IN POWER TRANSFORMERS FAULTS IN INSTRUMENT TRANSFORMERS FAULTS IN CIRCUIT BREAKERS FAULTS IN CONTROL EQUIPMENT FAULTS IN COMPENSATION DEVICES OUTAGES CAUSED BY DISTURBANCES OUTAGES IN POWER SYSTEM UNITS DURATION OF OUTAGES IN DIFFERENT POWER SYSTEM UNITS CUMULATIVE DURATION OF OUTAGES IN SOME POWER SYSTEM UNITS RELIABILITY TRENDS FOR SOME POWER SYSTEM UNITS REFERENCES APPENDIX 1 THE CALCULATION OF ENERGY NOT SUPPLIED APPENDIX 2 POLICIES FOR EXAMINING THE CAUSE FOR LINE FAULTS APPENDIX 3 CONTACT PERSONS IN THE NORDIC AND BALTIC COUNTRIES Page 2 of 79
3 APPENDIX 4 CONTACT PERSONS FOR THE DISTRIBUTION NETWORK STATISTICS Page 3 of 79
4 1 INTRODUCTION 1.1 DESCRIPTION OF THE REPORT This report is an overview of the Nordic and Baltic HVAC transmission grid disturbance statistics for the year providing the statistical data are Energinet.dk in Denmark, Elering in Estonia, Fingrid Oyj in Finland, Landsnet in Iceland, Augstsprieguma tīkls in Latvia, Litgrid in Lithuania, Statnett SF in Norway and Svenska kraftnät in Sweden. The statistics can be found at ENTSO-E website, The disturbance data of the whole Denmark is included in this report, although only the grid of eastern Denmark belongs to the synchronous Nordic grid. Figure presents the grids of the statistics. Although this summary originates from the Nordic and Baltic co-operation that aims to use the combined experience of the eight countries regarding the design and operation of their respective power systems, other ENTSO-E countries are encouraged to participate in the statistics as well. The report is made according to the Nordel Guidelines for Classification of Grid Disturbances [1] and includes the faults causing disturbances in the kv grids. The guidelines for the Classification of Grid Disturbances were prepared by Nordel 1 during the years and have been in use since Most charts include data for the ten-year period In some cases where older data has been available, even longer periods have been used. The material in the statistics covers the main systems and associated network devices with the 100 kv voltage level as the imum. Control equipment and installations for reactive compensation are also included in the statistics. The guidelines and disturbance statistics were in the Scandinavian language until In 2007, however, the guidelines were translated into English and the report of the statistical year 2006 was the first set of statistics written in English. The structure of these statistics is similar to the 2006 statistics. Despite common guidelines, there are slight differences in the interpretations between different countries and companies. These differences may have a or effect on the statistical material and are considered being of little significance. Nevertheless, users should partly because of these differences, but also because of the different countries or transmission and power companies maintenance and general policies use the appropriate published average values. Values concerning control equipment and unspecified faults or causes should be used with wider margins than other values. 1 Nordel was the co-operation organization of the Nordic until Page 4 of 79
5 The report is organised as follows. Chapter 2 summarises the statistics, covering the consequences of disturbances in the form of energy not supplied (ENS) and covering the total number of disturbances in the Nordic and Baltic power system. In addition, each Transmission System Operator has presented the most important issues of the year Chapter 3 discusses the disturbances and focuses on the analysis and allocation of the causes of disturbances. The distribution of disturbances during the year 2014 for each country is presented; for example, the consequences of the disturbances in the form of energy not supplied. Chapter 4 presents the tables and figures of energy not supplied for each country and Chapter 5 discusses the faults in different components. A summary of all the faults is followed by the presentation of more detailed statistics. Chapter 6 covers outages in the various power system units. This part of the statistics starts from the year CONTACT PERSONS Each country is represented by at least one contact person, responsible for his/her country s statistical information. The contact person can provide additional information concerning the ENTSO- E Nordic and Baltic disturbance statistics. The relevant contact information is given in Appendix 3. There are no common Nordic and Baltic disturbance statistics for voltage levels lower than 100 kv. However, Appendix 4 presents the relevant contact persons for these statistics. Page 5 of 79
6 FIGURE THE NORDIC AND BALTIC MAIN GRIDS [2] Page 6 of 79
7 1.3 VOLTAGE LEVELS IN THE NORDIC AND BALTIC NETWORKS Table presents the transmission system voltage levels of the networks in the Nordic and Baltic countries. In the statistics, voltage levels are grouped as statistical voltages according to the table. TABLE NOMINAL VOLTAGE LEVELS (U N) IN THE NORDIC AND BALTIC NETWORKS, THE RESPECTIVE STATISTICAL VOLTAGES AND THE PERCENTAGE OF THE GRID AT THE RESPECTIVE NOMINAL VOLTAGE LEVEL (P) Denmark Finland Iceland Norway Sweden Estonia Latvia Lithuania Statistical voltage range, kv kv kv kv kv kv U N P % U N P % U N P % U N P % U N P % U N P % U N P % U N P % THE SCOPE AND LIMITATIONS OF THE STATISTICS Table presents the coverage of the statistics in each country. The percentage of the grid is estimated according to the length of lines included in the statistics material divided by the actual length of lines in the grid. The data, which the collect from the grid owners, is not necessarily one hundred percent accurate because the collected values are not fully consistent. Page 7 of 79
8 TABLE PERCENTAGE OF NATIONAL NETWORKS INCLUDED IN THE STATISTICS Voltage level kv kv kv Denmark 100 % 100 % 100 % Estonia % 100 % Finland 1) 100 % 100 % 96 % Iceland % 100 % Latvia % 100 % Lithuania % 100 % Norway 100 % 100 % 100 % Sweden 100 % 100 % 100 % 1) Percentage for Finland is reduced due to some small regional grids not delivering complete data. The network statistics of each country cover data from several grid owners, and the representation of their statistics is not fully consistent. Finland: The data includes approximately 96 % of Finnish 110 kv lines and approximately 90 % of 110/20 kv transformers. Iceland: The network statistics cover the whole 220 kv and 132 kv voltage levels. Norway: A large part of the 110 and 132 kv network is resonant earthed. This category is combined with the kv solid earthed network in these statistics. The ten-year average values for the Baltic countries are not available in this report because they only have data from the year Hence, the Baltic countries are presented with statistics from the year 2014 and the average values are only calculated with the data from the Nordic countries. Page 8 of 79
9 2 SUMMARY 2.1 OVERVIEW OF THE NORDIC AND BALTIC COUNTRIES In 2014, the energy not supplied (ENS) due to faults in the Nordic and Baltic main grids was 4.86 GWh. The ENS for the Nordic main grid totalled 4.76 GWh, which is below the ten-year average 6.66 GWh. The energy not supplied and corresponding ten-year average values for the period in each country are presented in the following sections. The sections also present the number of disturbances for each country as well as the number of disturbances that caused energy not supplied in In addition, the summaries present the most important issues in 2014 defined by each Transmission System Operator. 2.2 SUMMARY OF DENMARK In Denmark, the energy not supplied in 2014 was 23.9 MWh (ten-year average 19.1 MWh). The number of grid disturbances was 77 (ten-year average 64) and 7 of them caused ENS. On average, 7 disturbances per year caused ENS in In 2014, 42 % of ENS was caused by faults during operation and maintenance and 48 % of ENS was caused by faults in adjoining statistical areas (statistical category 'Other'). 2.3 SUMMARY OF FINLAND In Finland, the energy not supplied in 2014 was 499 MWh (ten-year average 356 MWh). The number of grid disturbances was 513 (ten-year average 397) and 90 of them caused ENS. On average, 74 disturbances per year caused ENS in In 2014, 58 % of ENS was caused by overhead lines faults and 13 % by substation faults. The most significant reasons for ENS were Other causes 54 % and Technical equipment 23 %. Most of the disturbances were caused by Lightning and occurred during the summer months. 2.4 SUMMARY OF ESTONIA In Estonia, the energy not supplied in 2014 was 29.7 MWh (ten-year average 161 MWh). The number of grid disturbances was 225 (ten-year average 260) of which 11 caused ENS. On average, 20 disturbances per year caused ENS in In 2014, 65 % of ENS was caused by a fault in the adjoining network of a big customer connected to the 110 kv transmission grid. In the transmission grid, the most influential fault for Page 9 of 79
10 customers occurred in June 6th: after line tripping the transformers automatic reserve switching failed to connect a replacement transformer after a transformer disconnected. This resulted in 5.5 MWh ENS for customers. More than half of the disturbances were caused by environmental causes (stork contaation and lightning) on the 110 kv overhead lines and they occurred during the summer months. However, these were only insulator flashovers and did not cause any ENS. 2.5 SUMMARY OF ICELAND In Iceland, the energy not supplied in 2014 was MWh (ten-year average 1179 MWh). The total number of disturbances was 40 (ten-year average 31) of which 23 caused ENS. On average, 18 disturbances per year caused ENS in Registered grid disturbances increased in 2014 compared with the previous year. The weather played a central role in most cases. During the wintertime in January, February and October, the weather related disturbances caused some ENS. In May August, three large disturbances resulted in the trip of power intensive industry causing the major part of ENS this year, total of 654 MWh. On June 18th, an unusual disturbance in the transmission system occurred and it was the largest disturbance this year. It was caused by an upgrade of the EMS system in the control centre. The automatic generation control AGC received wrong parameters that resulted in units receiving wrong set points. This caused an under frequency and a trip of load. The total ENS of this event was 335 MWh 2.6 SUMMARY OF LATVIA In Latvia the energy not supplied (ENS) in 2014 was 35.6 MWh. The number of grid disturbances was 151 of which 19 caused ENS. There was one grid disturbance, caused by a fire in the overhead line corridor ( external influence ) that caused 43 % of 2014 ENS. According to the overall disturbance origins, 78 % of the ENS was caused by faults in overhead lines and 22 % in substations. 73 (48 %) disturbances were cleared with a successful high-speed reclosing. 2.7 SUMMARY OF LITHUANIA In Lithuania, the energy not supplied in 2014 was 39.2 MWh and originated from the 110 kv voltage grid. The total number of grid disturbances was 160 and 25 of them caused ENS. In 2014, 77 % of ENS was caused by substation faults and 13 % by overhead line faults. 124 disturbances were cleared with a successful auto-reclosing. Page 10 of 79
11 On February 2nd, one of two power transformers was taken out of service at the 110/10/10kV substation Amaliai since the 110 kv inlet circuit breaker of the transformer needed maintenance. During the maintenance, incorrect protections of the active inlet circuit breaker by the telecommand disconnected the line circuit breaker at the supplying Kaunas substation. This fault resulted in 26 MWh ENS. The largest number of the disturbances were caused by External influences and occurred during the summer months. 2.8 SUMMARY OF NORWAY In Norway, the energy not supplied in 2014 was 2165 MWh (ten-year average 3316 MWh). The number of grid disturbances was 461 (ten-year average 293) and 146 of them caused ENS. On average, 95 disturbances per year caused ENS in Compared to the ten-year average, there was an increase of faults in two categories: weather related and reactive components. In 2014 there were three major disturbances in the 420 kv network. They resulted all in outages of a gas pipeline teral and it caused approximately 1/3 of the total ENS. 2.9 SUMMARY OF SWEDEN In Sweden, the energy not supplied in 2014 was MWh (ten-year average MWh). There were 759 grid disturbances (ten-year average 546) of which 202 caused ENS. On average, 157 disturbances per year caused ENS in This year MWh of ENS was caused by faults on the 400kV grid. 70 % of all disturbances during 2014 occurred during the summer months, from June to August. (Ten-year average 50 % for the same time period.) In 2014, 41.7 % of ENS was caused by line faults and 54.5 % by substation faults. The main cause for ENS during 2014 was technical equipment 51 %, followed by lightning and unknown, 20 % and 23 % respectively. There were 134 faults with an unknown cause, many of those probably caused by lightning but not confirmed. 759 disturbances is an extremely high compared with a normal year. In 2014 there were 429 faults caused by lightning. This can be explained by an unusual number of thunderstorms during the summer. Sweden had some very unusual events during one week of July when seven instrument transformers exploded. It was during an unusually long warm period, but still on a temperature below 40 C. Page 11 of 79
12 3 DISTURBANCES This chapter includes an overview of disturbances in the Nordic and Baltic countries. It also presents the connection between disturbances, energy not supplied, causes of faults, and distribution during the year 2014, together with the development of the number of disturbances over the ten-year period It is important to note the difference between a disturbance and a fault. A disturbance may consist of a single fault, but it can also contain many faults, typically consisting of an initial fault followed by some secondary faults. Grid disturbances are defined as: Outages, forced or unintended disconnection or failed reconnection as a result of faults in the power grid [1, 3]. 3.1 ANNUAL NUMBER OF DISTURBANCES DURING THE PERIOD The number of disturbances during the year 2014 in the Nordic and Baltic main grids was The number for the Nordic main grids was 1850, which is above the ten-year average of The number of grid disturbances cannot directly be used for comparative purposes between countries because of the large differences between external conditions in the transmission networks of the Nordic and Baltic countries. Table presents the sum of disturbances during the year 2014 for the Nordic and Baltic countries and the annual average for the period for the Nordic countries for the complete kv grids. Figure shows the development of the number of disturbances in each Nordic country during the period TABLE THE NUMBER OF GRID DISTURBANCES IN EACH NORDIC AND BALTIC COUNTRY IN 2014 AND THE ANNUAL AVERAGE FOR THE PERIOD Number of disturbances Number of disturbances causing ENS 1) Denmark Estonia Finland Iceland Latvia Lithuania Norway Sweden Total ) The time period is because every country does not have complete data before Page 12 of 79
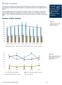
13 FIGURE NUMBER OF GRID DISTURBANCES IN EACH NORDIC COUNTRY DURING THE PERIOD DISTURBANCES DISTRIBUTED ACCORDING TO MONTH Figure and presents the percentage distribution of grid disturbances for all voltage levels according to month for the Nordic and Baltic countries, respectively. Figure presents the respective ten-year average values for the Nordic countries. Page 13 of 79
14 FIGURE PERCENTAGE DISTRIBUTION OF GRID DISTURBANCES ACCORDING TO MONTH IN EACH NORDIC COUNTRY IN 2014 FIGURE PERCENTAGE DISTRIBUTION OF GRID DISTURBANCES ACCORDING TO MONTH IN EACH BALTIC COUNTRY IN 2014 Page 14 of 79
15 FIGURE AVERAGE PERCENTAGE DISTRIBUTION OF GRID DISTURBANCES ACCORDING TO MONTH IN EACH NORDIC COUNTRY FOR THE PERIOD Table and Table present the numerical values behind Figure and Figure The numbers in the tables are sums of all the disturbances in the kv networks. For all countries, except Iceland, the number of disturbances is usually largest during the summer period. This is caused by lightning strokes during the summer. TABLE NUMBER OF GRID DISTURBANCES PER MONTH IN EACH NORDIC AND BALTIC COUNTRY IN 2014 Jan Feb Mar Apr May Jun Jul Aug Sep Oct Nov Dec Denmark Estonia Finland Iceland Latvia Lithuania Norway Sweden Total TABLE AVERAGE NUMBER OF GRID DISTURBANCES PER MONTH IN EACH NORDIC COUNTRY DURING THE YEARS Jan Feb Mar Apr May Jun Jul Aug Sep Oct Nov Dec Denmark Finland Iceland Norway Sweden Total Page 15 of 79
16 3.3 DISTURBANCES DISTRIBUTED ACCORDING TO CAUSE There are some or scale differences in the definitions of fault causes and disturbances between countries. Some countries use up to 40 different options, and others differentiate between primary and underlying causes. The exact definitions are listed in section in the Nordel Guidelines [1]. The Nordic and Baltic statistics use seven different options for fault causes and list the primary cause of the event as the starting point. Table and Table present an overview of the causes of grid disturbances and energy not supplied in each Nordic and Baltic country, respectively. Each country in this statistics has its own detailed way of gathering data according to fault cause as is explained in Appendix 2. The guidelines [1] describe the relations between the detailed fault causes and the common Nordic cause allocation. Page 16 of 79
17 TABLE GROUPING OF GRID DISTURBANCES AND ENERGY NOT SUPPLIED (ENS) BY CAUSE IN EACH NORDIC COUNTRY Cause Lightning Other environmental causes External influence Operation and maintenance Technical equipment Other Unkown Percentage distribution of disturbance Percentual distribution of disturbances that Percentual distribution of ENS caused ENS 1) ) Denmark Finland Iceland Norway Sweden Denmark Finland Iceland Norway Sweden Denmark Finland Iceland Norway Sweden Denmark Finland Iceland Norway Sweden Denmark Finland Iceland Norway Sweden Denmark Finland Iceland Norway Sweden Denmark Finland Iceland Norway Sweden ) The way to calculate the ENS varies between the countries and is presented in Appendix 1. 2) The time span is because there is not enough data available. Page 17 of 79
18 TABLE GROUPING OF GRID DISTURBANCES AND ENERGY NOT SUPPLIED (ENS) BY CAUSE IN EACH BALTIC COUNTRY Cause Lightning Other environmental causes External influence Operation and maintenance Technical equipment Other Unkown Percentage distribution of disturbance Percentual distribution of disturbances that caused Percentual distribution of ENS ENS 1) Estonia Latvia Lithuania Estonia Latvia Lithuania Estonia Latvia Lithuania Estonia Latvia Lithuania Estonia Latvia Lithuania Estonia Latvia Lithuania Estonia Latvia Lithuania ) The way to calculate the ENS varies between the countries and is presented in Appendix 1. Figure and Figure identify disturbances for all voltage levels in terms of the initial fault for the Nordic and Baltic countries, respectively. Figure presents the respective tenyear average values for the Nordic countries. Page 18 of 79
19 FIGURE PERCENTAGE DISTRIBUTION OF GRID DISTURBANCES ACCORDING TO CAUSE IN EACH NORDIC COUNTRY IN 2014 FIGURE PERCENTAGE DISTRIBUTION OF GRID DISTURBANCES ACCORDING TO CAUSE IN EACH BALTIC COUNTRY IN 2014 Page 19 of 79
20 FIGURE AVERAGE PERCENTAGE DISTRIBUTION OF GRID DISTURBANCES ACCORDING TO CAUSE IN EACH NORDIC COUNTRY DURING THE PERIOD A large number of disturbances with unknown cause probably have their real cause in the categories other environmental cause and lightning. Page 20 of 79
21 4 ENERGY NOT SUPPLIED (ENS) This chapter presents an overview of energy not supplied (ENS) in the Nordic and Baltic countries. One should remember that the amount of ENS is always an estimation. The accuracy of the estimation varies between companies in different countries and so does the calculation method for energy not supplied, as can be seen in Appendix 1. Energy not supplied is defined as: The estimated energy, which would have been supplied to end users if no interruption and no transmission restrictions had occurred [1] [3]. 4.1 ENERGY NOT SUPPLIED DISTRIBUTED ACCORDING TO VOLTAGE LEVEL Table shows the amount of energy not supplied in the five Nordic and three Baltic countries and its distribution according to voltage level. TABLE ENERGY NOT SUPPLIED (ENS) ACCORDING TO THE VOLTAGE LEVEL OF THE PRIMARY FAULT IN EACH NORDIC AND BALTIC COUNTRY Energy not supplied (MWh) Average ENS ENS divided into different voltage levels, (%) 2014 (MWh) kv kv kv Other 1) Denmark Finland Iceland Norway Sweden ENS (%) divided into different voltage levels, 2014 Estonia Latvia Lithuania Total ) The category other contains energy not supplied from system faults, auxiliary equipment, lower voltage level networks and the connections to foreign countries, etc. This is described further in the guidelines [1]. Page 21 of 79
22 Figure presents the energy not supplied according to the different voltage levels for the year 2014 in the Nordic and Baltic countries and Figure summarises the energy not supplied according to the different voltage levels for the period for the Nordic countries. A voltage level refers to the primary fault of the respective disturbance. FIGURE PERCENTAGE DISTRIBUTION OF ENERGY NOT SUPPLIED (ENS) IN TERMS OF THE VOLTAGE LEVEL OF THE PRIMARY FAULT IN EACH NORDIC AND BALTIC COUNTRY IN 2014 Page 22 of 79
23 FIGURE PERCENTAGE DISTRIBUTION OF ENERGY NOT SUPPLIED IN TERMS OF THE VOLTAGE LEVEL OF THE PRIMARY FAULT IN EACH NORDIC COUNTRY DURING THE PERIOD ENERGY NOT SUPPLIED (ENS) AND TOTAL CONSUMPTION Table shows the energy not supplied in relation to the total consumption of energy in each respective country and its distribution according to installation. TABLE ENERGY NOT SUPPLIED (ENS) AND ITS DISTRIBUTION ACCORDING TO INSTALLATION IN EACH NORDIC AND BALTIC COUNTRY Consumption GWh ENS MWh ENS / consumption ppm ppm ENS divided according to installation Overhead lines Cable Station Other during the period Denmark Finland Iceland Norway Sweden during the year 2014 Estonia Latvia Lithuania Total Page 23 of 79
24 Ppm (parts per million) represents ENS as a proportional value of the consumed energy, which is calculated: ENS (MWh) 10 6 / consumption (MWh). The sum of the ENS divided according to installation may not be exactly 100 % because all the ENS is not always connected with a cause. Figure presents the progression of ENS during the period for the Nordic countries. One should note that there is a considerable difference from year to year depending on occasional events, such as storms. These events have a significant effect on each country s yearly statistics. FIGURE ENERGY NOT SUPPLIED (ENS) DIVIDED BY CONSUMPTION (PPM) IN EACH NORDIC COUNTRY 1) An unusual number of disturbances, which had an influence on the power intensive industry, caused the high value of energy not supplied in Iceland during 2007 and ) The unusually high ENS divided by the consumption in 2011 in Norway was caused by extreme weather conditions in December (aka the storm named Dagmar). 4.3 ENERGY NOT SUPPLIED (ENS) DISTRIBUTED ACCORDING TO MONTH Figure and Figure present the distribution of energy not supplied according to month in the Nordic and Baltic countries, respectively. Figure presents the percentage distribution of the energy not supplied in the Nordic countries according to month for the period Page 24 of 79
25 FIGURE PERCENTAGE DISTRIBUTION OF ENERGY NOT SUPPLIED (ENS) ACCORDING TO MONTH IN EACH NORDIC COUNTRY IN 2014 FIGURE PERCENTAGE DISTRIBUTION OF ENERGY NOT SUPPLIED (ENS) ACCORDING TO MONTH IN EACH BALTIC COUNTRY IN 2014 Page 25 of 79
26 FIGURE AVERAGE PERCENTAGE DISTRIBUTION OF GRID DISTURBANCES ACCORDING TO MONTH IN EACH NORDIC COUNTRY DURING THE PERIOD ENERGY NOT SUPPLIED (ENS) DISTRIBUTED ACCORDING TO CAUSE Figure and Figure present the distribution of energy not supplied in 2014 according to cause in the Nordic and Baltic countries, respectively. Figure presents the percentage distribution of the energy not supplied in the Nordic countries according to cause for the period Appendix 2 provides more details about how each country investigates line faults. Page 26 of 79
27 FIGURE PERCENTAGE DISTRIBUTION OF ENERGY NOT SUPPLIED ACCORDING TO THE CAUSE OF THE PRIMARY FAULT IN EACH NORDIC COUNTRY IN 2014 FIGURE PERCENTAGE DISTRIBUTION OF ENERGY NOT SUPPLIED ACCORDING TO THE CAUSE OF THE PRIMARY FAULT IN EACH BALTIC COUNTRY IN 2014 In Lithuania, one disturbance caused 81 % ENS in the category external influences. More details are in Section 2.7. Page 27 of 79
28 FIGURE AVERAGE PERCENTAGE DISTRIBUTION OF ENS ACCORDING TO THE CAUSE OF THE PRIMARY FAULT IN EACH NORDIC COUNTRY DURING PERIOD Energy not supplied (ENS) distributed according to component Table shows the amount of energy not supplied in 2014 and the annual average for the period Table and Table show the distribution of energy not supplied according to component in the Nordic and Baltic countries, respectively. TABLE ENERGY NOT SUPPLIED (ENS) IN EACH NORDIC AND BALTIC COUNTRY IN 2014 AND THE ANNUAL AVERAGE FOR THE PERIOD ENS (MWh) Denmark Finland Iceland Norway Sweden Estonia 30 - Latvia 36 - Lithuania 39 - Total ) One Swedish regional grid delivered incomplete data in The details of the origin of the fault were not reported and therefore 750 MWh of ENS is not included from that year. Page 28 of 79
29 TABLE PERCENTAGE DISTRIBUTION OF ENERGY NOT SUPPLIED IN TERMS OF COMPONENT IN EACH NORDIC COUNTRY Denmark Finland Iceland Norway Sweden Fault location Overhead line Cable Line faults Power transformers Instrument transformers Circuit breakers Busbar Control equipment Disconnectors and earth connectors Surge arresters and spark gap Common ancillary equipment Other substation faults Substation faults Shunt capacitor Series capacitor Reactor Synchronous compensator SVC and statcom Compensation faults System fault Faults in adjoining statistical area Unknown Other faults Total Page 29 of 79
30 TABLE PERCENTAGE DISTRIBUTION OF ENERGY NOT SUPPLIED IN TERMS OF COMPONENT IN EACH BALTIC COUNTRY IN 2014 Estonia Latvia Lithuania Total Fault location Overhead line Cable Line faults Power transformers Instrument transformers Circuit breakers Busbar Control equipment Disconnectors and earth connectors Surge arresters and spark gap Common ancillary equipment Other substation faults Substation faults Shunt capacitor Series capacitor Reactor Synchronous compensator SVC and statcom Compensation faults System fault Faults in adjoining statistical area Unknown Other faults It should be noted that some countries register the total amount of energy not supplied in a disturbance in terms of the primary fault. Therefore, the data is not necessarily comparable. Page 30 of 79
31 5 FAULTS IN POWER SYSTEM COMPONENTS 5.1 DEFINITIONS AND SCOPE A fault in a component implies that it is not able to perform its function properly. Faults can have many causes, for example manufacturing defects or insufficient maintenance. This chapter presents the fault statistics for different grid components. One should take note of both the causes and consequences of the fault when analysing the fault frequencies of different devices. Overhead lines, for example, normally have more faults than cables. On the other hand, cables normally have considerably longer repair times than overhead lines. A component fault is defined as: The inability of a component to perform its required function [4]. The scope of the statistics, according to the guidelines [1], is the following: "The statistics comprise: Grid disturbances Faults causing or aggravating a grid disturbance Disconnection of end users in connection with grid disturbances Outage in parts of the electricity system in conjunction with grid disturbance The statistics do not comprise: Faults in production units Faults detected during maintenance Planned operational interruptions in parts of the electricity system Behaviour of circuit breakers and relay protection if they do not result in or extend a grid disturbance" This chapter gives an overview of all faults registered in the component groups used in these statistics, followed by more detailed statistics relating to each specific component group. Tenyear average values have been calculated for most components. For overhead lines, even a longer period has been used due to their long lifetime. The averages are calculated on the basis of the number of components with the number of faults for each time period, which takes into consideration the annual variation in the number of components. This chapter also presents fault trend curves for some components. The trend curves show the variation in the fault frequencies of consecutive five-year periods. These curves are grouped into kv, kv and kv voltage levels for most of the components. Readers who need more detailed data should use the national statistics published by the national regulators. Page 31 of 79
32 5.2 OVERVIEW OF THE FAULTS RELATED TO DISTURBANCES Table presents the number of faults and disturbances during TABLE NUMBER OF FAULTS AND GRID DISTURBANCES IN EACH NORDIC AND BALTIC COUNTRY IN Number of Number of disturbances Fault / disturbance Fault / disturbance ratio faults in 2014 in 2014 ratio in 2014 during Denmark Estonia Finland Iceland Latvia Lithuania Norway Sweden Table presents the distribution of faults and energy not supplied in terms of voltage level and country. In addition, the table shows the overhead line length and the number of power transformers in order to give a view of the grid size in each country. One should note that the number of faults includes all faults; not just faults on lines and in power transformers. TABLE FAULTS IN DIFFERENT COUNTRIES IN TERMS OF VOLTAGE LEVEL IN EACH NORDIC AND BALTIC COUNTRY Voltage kv kv kv Size of the grid Number of faults ENS (MWh) Number of power transformers Length of lines in km 1) Denmark Estonia Finland Iceland Latvia Lithuania Norway Sweden Denmark Estonia Finland Iceland Latvia Lithuania Norway Sweden Denmark Estonia Finland Iceland Latvia Lithuania Norway Sweden ) The length of lines is the sum of the length of cables and overhead lines. Page 32 of 79
33 Table and Table show the number of faults classified according to the component groups used in this statistics. One should note that not all countries have every type of equipment in their network. For example static var compensators (SVCs) or STATCOM installations do not exist in every country. The distribution of the number of components can also vary from country to country, so one should be careful when comparing countries. Note that statistics also include faults that begin outside the voltage range of the statistics (typically from networks with voltages lower than 100 kv) but still influence statistic area. TABLE PERCENTAGE DISTRIBUTION OF FAULTS ACCORDING TO COMPONENT TYPE IN EACH NORDIC COUNTRY Denmark Finland Iceland Norway Sweden Average Component type Overhead line Cable Line faults Power transformers Instrument transformers Circuit breakers Busbar Control equipment Disconnectors and earth connectors Surge arresters and spark gap Common ancillary equipment Other substation faults Substation faults Shunt capacitor Series capacitor Reactor Synchronous compensator SVC and statcom Compensation faults System fault Faults in adjoining statistical area Unknown Other faults ) The category control equipment includes also protection. Page 33 of 79
34 TABLE PERCENTAGE DISTRIBUTION OF FAULTS ACCORDING TO COMPONENT TYPE IN EACH BALTIC COUNTRY Estonia Latvia Lithuania Average Component type Overhead line Cable Line faults Power transformers Instrument transformers Circuit breakers Busbar Control equipment Disconnectors and earth connectors Surge arresters and spark gap Common ancillary equipment Other substation faults Substation faults Shunt capacitor Series capacitor Reactor Synchronous compensator SVC and statcom Compensation faults System fault Faults in adjoining statistical area Unknown Other faults FAULTS ON OVERHEAD LINES Overhead lines are a large part of the Nordic and Baltic transmission grids. Therefore, the tables in this section show the distribution of faults in 2014 as well as the average values for the period The tables also give the faults distributed by cause during the period Along with the tables, the annual distribution of faults and the number of permanent faults during the period is presented graphically for all voltage levels. The section also presents the trend curves for overhead line faults. With the help of the trend curve, it may be possible to detere the trend of faults also in the future KV OVERHEAD LINES Table shows the line lengths, faults of kv overhead lines, the causes of faults and the percentage values of 1-phase faults and permanent faults for the countries that have this voltage level. The data consists of the values for the year 2014 and for the 19-year period Figure presents the annual line fault values per line length during the tenyear period and the average value of period Figure presents the annual distribution of permanent line faults during the same period. Page 34 of 79
35 TABLE KV OVERHEAD LINES FAULTS AND THE DISTRIBUTION ACCORDING TO CAUSE IN NORDIC COUNTRIES Lines (km) Number of faults Number of faults per 100 km Other environmental causes 1- phase faults Faults divided by cause (%) during the period Lightning Unknown Permanent faults Denmark Finland Norway Sweden Total External influences Operation and maintenance Technical equipment Other FIGURE ANNUAL DISTRIBUTION OF FAULTS FOR KV OVERHEAD LINES IN NORDIC COUNTRIES DURING THE PERIOD Page 35 of 79
36 FIGURE ANNUAL DISTRIBUTION OF PERMANENT FAULTS FOR KV OVERHEAD LINES IN NORDIC COUNTRIES DURING THE PERIOD KV OVERHEAD LINES Table shows the line lengths, faults of kv overhead lines, the causes of faults and the percentage values of 1-phase faults and permanent faults. The data consists of the values for the year 2014 and for the 19-year period Figure presents the annual line fault values per line length during the ten-year period and the average value of period Figure presents the annual distribution of permanent line faults during the same period. Page 36 of 79
37 TABLE KV OVERHEAD LINES FAULTS AND THE DISTRIBUTION ACCORDING TO CAUSE IN EACH NORDIC AND BALTIC COUNTRY Lines (km) Number of faults Number of faults per 100 km Lightning Other environmental causes Operation and maintenance Technical equipment Other Unknown 1- phase faults External influences Permanent faults Faults divided by cause (%) during the period Denmark Finland Iceland Norway Sweden Faults divided by cause (%) during year 2014 Estonia Latvia Lithuania Total FIGURE ANNUAL DISTRIBUTION OF FAULTS FOR KV OVERHEAD LINES IN EACH NORDIC COUNTRY DURING THE PERIOD AND THE AVERAGE FOR IN EACH NORDIC COUNTRY Page 37 of 79
38 FIGURE ANNUAL DISTRIBUTION OF PERMANENT FAULTS FOR KV OVERHEAD LINES DURING THE PERIOD AND THE AVERAGE FOR IN EACH NORDIC COUNTRY KV OVERHEAD LINES Table shows the line lengths, faults of kv overhead lines, the causes of faults and the percentage values of 1-phase faults and permanent faults. The data consists of the values for the year 2014 and for the 19-year period Figure presents the annual line fault values per line length during the ten-year period and the average value of period Figure presents the annual distribution of permanent line faults during the same period. Page 38 of 79
39 TABLE KV OVERHEAD LINES FAULTS AND THE DISTRIBUTION ACCORDING TO CAUSE IN EACH NORDIC AND BALTIC COUNTRY Lines (km) Number of faults Number of faults per 100 km Lightning Other environmental causes External influences Operation and maintenance Technical equipment Other Unknown 1- phase faults Permanent faults Faults divided by cause (%) during the period Denmark Finland Iceland Norway Sweden Faults divided by cause (%) during year 2014 Estonia Latvia Lithuania Total ) The Norwegian grid includes a resonant earthed system, which has an effect on the low number of single-phase earth faults in Norway. FIGURE ANNUAL DISTRIBUTION OF LINE FAULTS FOR KV OVERHEAD LINES DURING THE PERIOD AND THE AVERAGE FOR IN EACH NORDIC COUNTRY Page 39 of 79
40 FIGURE ANNUAL DISTRIBUTION OF PERMANENT LINE FAULTS FOR KV OVERHEAD LINES DURING THE PERIOD AND THE AVERAGE FOR IN EACH NORDIC COUNTRY OVERHEAD LINE FAULT TRENDS Figure 5.3.7, Figure and Figure present trend curves of overhead line faults in the Nordic countries as of 1995 for kv, kv and kv lines, respectively. The five-year average is calculated by dividing the sum of the faults by the total overhead line length for each five-year period. The trend curves are proportioned to overhead line length in order to get comparable results between countries. Page 40 of 79
41 FIGURE FAULT TRENDS AS FIVE-YEAR AVERAGES FOR OVERHEAD LINES AT THE VOLTAGE LEVEL KV IN NORDIC COUNTRIES FIGURE FAULT TRENDS AS FIVE-YEAR AVERAGES FOR OVERHEAD LINES AT THE VOLTAGE LEVEL KV IN EACH NORDIC COUNTRY Page 41 of 79
42 FIGURE FAULT TRENDS AS FIVE-YEAR AVERAGES FOR OVERHEAD LINES AT THE VOLTAGE LEVEL KV IN EACH NORDIC COUNTRY 5.4 FAULTS IN CABLES Figure presents the cable distributions in the Nordic countries to voltage levels in each year from 2005 to Table 5.4.1, Table 5.4.2, and Table present cable faults and fault distribution at each statistical voltage level for the year 2014 and for the period In addition, the distribution of faults according to cause is given for the whole ten-year period. The annual distribution of faults during the period is presented graphically for kv cables only in the Nordic countries in Figure Fault trends for all the voltage levels in the Nordic countries are presented in Figure Page 42 of 79
43 FIGURE DISTRIBUTION OF CABLES LENGTHS ACCORDING TO VOLTAGE LEVEL IN EACH NORDIC COUNTRY FROM 2005 TO 2014 Page 43 of 79
44 TABLE KV CABLES FAULTS AND THE DISTRIBUTION ACCORDING TO CAUSE IN NORDIC COUNTRIES Lines (km) Number of faults Number of faults per 100 km Operation and maintenance Lightning Other environmental causes External influence Technical equipment Other Unknown Faults divided by cause (%) during the period Denmark Norway Sweden Total TABLE DISTRIBUTION OF FAULTS ACCORDING TO CAUSE FOR KV CABLES IN NORDIC AND BALTIC COUNTRIES Lines (km) Number of faults Number of faults per 100 km Lightning Other environmental causes External influence Operation and maintenance Technical equipment Other Unknown Faults divided by cause (%) during the period Denmark Iceland Norway Sweden Faults divided by cause (%) during year 2014 Latvia Total TABLE KV CABLES FAULTS AND THE DISTRIBUTION ACCORDING TO CAUSE IN EACH NORDIC AND BALTIC COUNTRY Lines (km) Number of faults Number of faults per 100 km Lightning Other environmental causes External influence Operation and maintenance Technical equipment Other Unknown Faults divided by cause (%) during the period Denmark Finland Iceland Norway Sweden Faults divided by cause (%) during year 2014 Estonia Latvia Lithuania Total ) Cables in Norway include cables in resonant earthed grids. Figure presents the annual cable fault values per cable length faults during the ten-year period for kv cables. Page 44 of 79
45 FIGURE ANNUAL DISTRIBUTION OF CABLE FAULTS DURING THE PERIOD AND THE AVERAGE FOR THE PERIOD IN EACH NORDIC COUNTRY FOR KV CABLES FIGURE FAULT TRENDS AS FIVE-YEAR AVERAGES FOR CABLES AT ALL VOLTAGE LEVELS IN EACH NORDIC COUNTRY Page 45 of 79
46 The main explanation for the high values in the fault trend for Sweden during the years is that there were several cable faults in 2008, as seen in Figure FAULTS IN POWER TRANSFORMERS The tables in this section present the distribution of faults for the year 2014 and for the period in power transformers at each respective voltage level. In addition, the tables present the distribution of faults according to cause during the ten-year period The annual distribution of faults during the period is presented graphically for all voltage levels. Fault trends for the Nordic power transformers are presented in Figure 5.5.4, Figure and Figure For power transformers, the statistics state the rated voltage of the winding with the highest voltage, as stated in Section 6.2 in the guidelines [1]. TABLE KV POWER TRANSFORMERS FAULTS AND THE DISTRIBUTION ACCORDING TO CAUSE IN NORDIC COUNTRIES Number of devices Number of faults Number of faults per 100 devices Lightning Other environmental causes External influence Operation and maintenance Technical equipment Other Unknown Faults divided by cause (%) during the period Denmark Finland Norway Sweden Total TABLE KV POWER TRANSFORMERS FAULTS AND THE DISTRIBUTION ACCORDING TO CAUSE IN EACH NORDIC AND BALTIC COUNTRY Number of devices Number of faults Number of faults per 100 devices Lightning Other environmental causes External influence Operation and maintenance Technical equipment Other Unknown Faults divided by cause (%) during the period Denmark Finland Iceland Norway Sweden Faults divided by cause (%) during year 2014 Estonia Latvia Lithuania Total Page 46 of 79
47 TABLE KV POWER TRANSFORMERS FAULTS AND THE DISTRIBUTION ACCORDING TO CAUSE IN EACH NORDIC AND BALTIC COUNTRY Number of devices Number of faults Number of faults per 100 devices Lightning Other environmental causes External influence Operation and maintenance Technical equipment Other Unknown Faults divided by cause (%) during the period Denmark Finland Iceland Norway Sweden Faults divided by cause (%) during year 2014 Estonia Latvia Lithuania Total FIGURE ANNUAL DISTRIBUTION OF FAULTS FOR KV POWER TRANSFORMERS IN NORDIC COUNTRIES DURING THE PERIOD Page 47 of 79
48 FIGURE ANNUAL DISTRIBUTION OF FAULTS FOR KV POWER TRANSFORMERS IN EACH NORDIC COUNTRY DURING THE PERIOD FIGURE ANNUAL DISTRIBUTION OF FAULTS FOR KV POWER TRANSFORMERS IN EACH NORDIC COUNTRY DURING THE PERIOD Due to a misinterpretation of the guidelines Sweden reported a high number of faults since This has been noted and Sweden will change this from 2015 and onward. Page 48 of 79
49 FIGURE FAULT TRENDS AS FIVE-YEAR AVERAGES FOR KV POWER TRANSFORMERS IN NORDIC COUNTRIES FIGURE FAULT TRENDS AS FIVE-YEAR AVERAGES FOR KV POWER TRANSFORMERS IN EACH NORDIC COUNTRY Page 49 of 79
50 FIGURE FAULT TRENDS AS FIVE-YEAR AVERAGES FOR KV POWER TRANSFORMERS IN EACH NORDIC COUNTRY Due to a misinterpretation of the guidelines Sweden reported a high number of faults since This has been noted and Sweden will change this from 2015 and onward. 5.6 FAULTS IN INSTRUMENT TRANSFORMERS Tables in this section present the faults in instrument transformers for the year 2014 and for the period at each respective voltage level. In addition, the tables present the distribution of faults according to cause during the ten-year period. Both current and voltage transformers are included among instrument transformers. A three-phase instrument transformer is treated as one unit. If a single-phase transformer is installed, it is also treated as a single unit. The figures in this section present the fault trends for instrument transformers at each statistical voltage level in the Nordic countries. Page 50 of 79
51 TABLE KV INSTRUMENT TRANSFORMERS FAULTS AND THE DISTRIBUTION ACCORDING TO CAUSE IN NORDIC COUNTRIES Number of devices Number of Number faults per 100 of faults devices Lightning Other environmental causes External influence Operation and maintenance Technical equipment Other Unknown Faults divided by cause (%) during the period Denmark Finland Norway Sweden Total TABLE KV INSTRUMENT TRANSFORMERS FAULTS AND THE DISTRIBUTION ACCORDING TO CAUSE IN EACH NORDIC AND BALTIC COUNTRY Number of devices Number of faults Number of faults per 100 devices Lightning Other environmental causes External influence Operation and maintenance Technical equipment Other Unknown Faults divided by cause (%) during the period Denmark Finland Iceland Norway Sweden Faults divided by cause (%) during year 2014 Estonia Latvia Lithuania Total Page 51 of 79
52 TABLE KV INSTRUMENT TRANSFORMERS FAULTS AND THE DISTRIBUTION ACCORDING TO CAUSE IN EACH NORDIC AND BALTIC COUNTRY Number of devices Number of faults Number of faults per 100 devices Lightning Other environmental causes External influence Operation and maintenance Technical equipment Other Unknown Faults divided by cause (%) during the period Denmark Finland Iceland Norway Sweden Faults divided by cause (%) during year 2014 Estonia Latvia Lithuania Total FIGURE FAULT TRENDS AS FIVE-YEAR AVERAGES FOR KV INSTRUMENT TRANSFORMERS IN NORDIC COUNTRIES The change in the Swedish trend curve in Figure is because in 2014, seven instrument transformers exploded in Sweden. All of the transformers that exploded were from the same manufacturer, of the same type and were manufactured the same year and they exploded during the same week after a long and warm summer period. Page 52 of 79
53 FIGURE FAULT TRENDS AS FIVE-YEAR AVERAGES FOR INSTRUMENT TRANSFORMERS AT THE VOLTAGE LEVEL KV IN EACH NORDIC COUNTRY The high value for the Danish fault trend during is caused by the transformer failures during years 2008 and Another reason is due to the fact that the number of instrument transformers is significantly smaller in Denmark than the other countries. Page 53 of 79
54 FIGURE FAULT TRENDS AS FIVE-YEAR AVERAGES FOR INSTRUMENT TRANSFORMERS AT THE VOLTAGE LEVEL KV IN EACH NORDIC COUNTRY 5.7 FAULTS IN CIRCUIT BREAKERS The tables in this section present circuit breaker faults at each respective voltage level for the year 2014 and for the ten-year period The tables also present the distribution of faults according to cause during the ten-year period. The figures in this section present the fault trends for circuit breakers at each statistical voltage level in the Nordic countries. Page 54 of 79
55 TABLE KV CIRCUIT BREAKER FAULTS AND THE DISTRIBUTION ACCORDING TO CAUSE IN NORDIC COUNTRIES Number of devices Number of faults Number of faults per 100 devices Lightning Other environmental causes External influence Operation and maintenance 2) Technical equipment Other Unknown Faults divided by cause (%) during the period Denmark Finland Norway Sweden 1) Total ) For Sweden, the breaker failures at the kv level most often occurred in breakers that are used to switch the reactors. This is the reason for the high number of circuit breaker faults in Sweden, because a reactor breaker is operated significantly more often than a line breaker. 2) One should note that a high number of operation and maintenance is because erroneous circuit breaker operations are registered as faults with operation and maintenance as the cause. These are caused by kv shunt reactor circuit breakers, which usually operate very often compared to other circuit breakers. TABLE KV CIRCUIT BREAKER FAULTS AND THE DISTRIBUTION ACCORDING TO CAUSE IN EACH NORDIC AND BALTIC COUNTRY Number of devices Number of faults Number of faults per 100 devices Lightning Other environmental causes External influence Operation and maintenance Technical equipment Other Unknown Faults divided by cause (%) during the period Denmark Finland Iceland Norway Sweden Faults divided by cause (%) during year 2014 Estonia Latvia Lithuania Total Page 55 of 79
56 TABLE KV CIRCUIT BREAKER FAULTS AND THE DISTRIBUTION ACCORDING TO CAUSE IN EACH NORDIC AND BALTIC COUNTRY Number of devices Number of faults Number of faults per 100 devices Lightning Other environmental causes External influence Operation and maintenance Technical equipment Other Unknown Faults divided by cause (%) during the period Denmark Finland Iceland Norway Sweden Faults divided by cause (%) during year 2014 Estonia Latvia Lithuania Total FIGURE FAULT TRENDS AS FIVE-YEAR AVERAGES FOR CIRCUIT BREAKERS AT THE VOLTAGE LEVEL KV IN NORDIC COUNTRIES Page 56 of 79
57 FIGURE FAULT TRENDS AS FIVE-YEAR AVERAGES FOR CIRCUIT BREAKERS AT THE VOLTAGE LEVEL KV IN NORDIC COUNTRIES The explanation for the remarkable improvement on the fault trend of Iceland is that most of the faults on circuit breakers up to 2003 in the 220 kv network occurred at one substation. These breakers caused problems due to gas leaks and were repaired in Page 57 of 79
58 FIGURE FAULT TRENDS AS FIVE-YEAR AVERAGES FOR CIRCUIT BREAKERS IN EACH NORDIC COUNTRY AT THE VOLTAGE LEVEL KV 5.8 FAULTS IN CONTROL EQUIPMENT The tables in this section present faults in control equipment at each respective voltage level for the year 2014 and for the period In addition, the tables present the distribution of faults according to cause during the ten-year period. Figure 5.8.1, Figure and Figure present the annual distribution of control equipment faults in the Nordic countries during the period at each statistical voltage level. For control equipment it is important to distinguish between faults in technical equipment and faults made by human errors. Human errors include for example erroneous settings in an IED. In the statistics human errors is registered under operation and maintenance, separated from the category technical equipment. In apparatus where the control equipment is integrated, (typical for SVC s) there is an uncertainty whether faults are registered in the control equipment or in the actual apparatus. When the control equipment is integrated in another installation it shall normally be categorized as faults in the installation and not in the control equipment. However, this definition is not yet fully applied in all countries. Page 58 of 79
59 TABLE KV CONTROL EQUIPMENT FAULTS AND THE DISTRIBUTION ACCORDING TO CAUSE IN NORDIC COUNTRIES Number of devices Number of faults Number of faults per 100 devices Lightning Other environmental causes External influence Operation and maintenance Technical equipment Other Unknown Faults divided by cause (%) during the period Denmark Finland Norway Sweden Total TABLE KV CONTROL EQUIPMENT FAULTS AND THE DISTRIBUTION ACCORDING TO CAUSE IN EACH NORDIC AND BALTIC COUNTRY Number of devices Number of faults Number of faults per 100 devices Lightning Other environmental causes External influence Operation and maintenance Technical equipment Other Unknown Faults divided by cause (%) during the period Denmark Finland Iceland Norway Sweden Faults divided by cause (%) during year 2014 Estonia Latvia Lithuania Total Page 59 of 79
60 TABLE KV CONTROL EQUIPMENT FAULTS AND THE DISTRIBUTION ACCORDING TO CAUSE IN EACH NORDIC AND BALTIC COUNTRY Number of devices Number of faults Number of faults per 100 devices Lightning Other environmental causes External influence Operation and maintenance Technical equipment Other Unknown Faults divided by cause (%) during the period Denmark Finland Iceland Norway Sweden Faults divided by cause (%) during year 2014 Estonia Latvia Lithuania Total FIGURE ANNUAL DISTRIBUTION OF KV CONTROL EQUIPMENT FAULTS IN NORDIC COUNTRIES DURING THE PERIOD Page 60 of 79
Nordel GRID DISTURBANCE AND FAULT STATISTICS
 Nordel GRID DISTURBANCE AND FAULT STATISTICS Table contents Table contents Page 1 Introduction... 3 1.1 Contact persons... 4 1.2 Guidelines the statistics... 4 1.3 Voltage levels in the Nordel network...
Nordel GRID DISTURBANCE AND FAULT STATISTICS Table contents Table contents Page 1 Introduction... 3 1.1 Contact persons... 4 1.2 Guidelines the statistics... 4 1.3 Voltage levels in the Nordel network...
It is essential that the maintenance staff is qualified for electrical works and follows safety procedures.
 MAINTENANCE OF POWER FACTOR CORRECTION EQUIPMENTS Procedures, suggestions and traceability The purpose of this document is to propose a maintenance method that allows to identify the elements to be maintained
MAINTENANCE OF POWER FACTOR CORRECTION EQUIPMENTS Procedures, suggestions and traceability The purpose of this document is to propose a maintenance method that allows to identify the elements to be maintained
Infrared Thermography Inspection Guidelines. Date Issued:
 Infrared Thermography Inspection Guidelines Date Issued: 2002 01 29 Created By: Approved By: L. Henderson G. Durnford Table Of Contents Table Of Contents...i POLICY STATEMENT...1 APPLICABLE INTERNATIONAL
Infrared Thermography Inspection Guidelines Date Issued: 2002 01 29 Created By: Approved By: L. Henderson G. Durnford Table Of Contents Table Of Contents...i POLICY STATEMENT...1 APPLICABLE INTERNATIONAL
sdfghjklzxcvbnmqwertyuiopasdfghjklzxcvbnmqw ertyuiopasdfghjklzxcvbnmqwertyuiopasdfghjklzx
 qwertyuiopasdfghjklzxcvbnmqwertyuiopasdfghjkl DRAFT zxcvbnmqwertyuiopasdfghjklzxcvbnmqwertyuiop asdfghjklzxcvbnmqwertyuiopasdfghjklzxcvbnmq wertyuiopasdfghjklzxcvbnmqwertyuiopasdfghjklz xcvbnmqwertyuiopasdfghjklzxcvbnmqwertyuiopa
qwertyuiopasdfghjklzxcvbnmqwertyuiopasdfghjkl DRAFT zxcvbnmqwertyuiopasdfghjklzxcvbnmqwertyuiop asdfghjklzxcvbnmqwertyuiopasdfghjklzxcvbnmq wertyuiopasdfghjklzxcvbnmqwertyuiopasdfghjklz xcvbnmqwertyuiopasdfghjklzxcvbnmqwertyuiopa
CEER Benchmarking Report 6.1 on the Continuity of Electricity and Gas Supply Data update 2015/2016
 Energy Quality of Supply Work Stream (EQS WS) CEER Benchmarking Report 6.1 on the Continuity of Electricity and Gas Supply Data update 2015/2016 Ref: C18-EQS-86-03 26-July-2018 Council of European Energy
Energy Quality of Supply Work Stream (EQS WS) CEER Benchmarking Report 6.1 on the Continuity of Electricity and Gas Supply Data update 2015/2016 Ref: C18-EQS-86-03 26-July-2018 Council of European Energy
WIND DATA REPORT. Paxton, MA
 WIND DATA REPORT Paxton, MA July 1, 2011 September 30, 2011 Prepared for Massachusetts Clean Energy Center 55 Summer Street, 9th Floor Boston, MA 02110 by Eric Morgan James F. Manwell Anthony F. Ellis
WIND DATA REPORT Paxton, MA July 1, 2011 September 30, 2011 Prepared for Massachusetts Clean Energy Center 55 Summer Street, 9th Floor Boston, MA 02110 by Eric Morgan James F. Manwell Anthony F. Ellis
Axpo Power Ltd. 2) GE Grid Solutions
 PS 3 SF6-free 123 kv Substation Solution to meet Axpo s sustainability strategy C. LINDNDER 1), D. GAUTSCHI 2) 1) Axpo Power Ltd. 2) GE Grid Solutions SUMMARY As it is the strategic goal of Axpo Power
PS 3 SF6-free 123 kv Substation Solution to meet Axpo s sustainability strategy C. LINDNDER 1), D. GAUTSCHI 2) 1) Axpo Power Ltd. 2) GE Grid Solutions SUMMARY As it is the strategic goal of Axpo Power
Danish gambling market statistics Third quarter, 2017
 Danish gambling market statistics Third quarter, Third Quarter, 7. december Third Quarter, Danish gambling market statistics 1 Indhold A. Introduction... 2 B. Quarterly market statistics for the Danish
Danish gambling market statistics Third quarter, Third Quarter, 7. december Third Quarter, Danish gambling market statistics 1 Indhold A. Introduction... 2 B. Quarterly market statistics for the Danish
Emilie Nelson Wes Yeomans New York Independent System Operator Market Issues Working Group NYISO Krey Corporate Center May 13, 2010
 Operations Updates Emilie Nelson Wes Yeomans New York Independent System Operator Market Issues Working Group NYISO Krey Corporate Center May 13, 21 Wind Forecast Performance 2 Overview of Wind Forecast
Operations Updates Emilie Nelson Wes Yeomans New York Independent System Operator Market Issues Working Group NYISO Krey Corporate Center May 13, 21 Wind Forecast Performance 2 Overview of Wind Forecast
ANNUAL RELIABILITY AND POWER QUALITY REPORT for the year ended 30 June 2017
 ELECTRICITY INDUSTRY (NETWORK QUALITY AND RELIABILITY OF SUPPLY) CODE 2005 ANNUAL RELIABILITY AND POWER QUALITY REPORT for the year ended 30 June 2017 SEPTEMBER 2017 Page 1 of 81 Contents 1 Purpose...
ELECTRICITY INDUSTRY (NETWORK QUALITY AND RELIABILITY OF SUPPLY) CODE 2005 ANNUAL RELIABILITY AND POWER QUALITY REPORT for the year ended 30 June 2017 SEPTEMBER 2017 Page 1 of 81 Contents 1 Purpose...
These Instructions apply to all high-voltage installations where Statnett has operational responsibility.
 Based on the Norwegian document number 1169509 rev. 10 Page: 1 of 7 1 Governing policy and legislation These Instructions for the Switching Supervisor are subject to Statnett s Funksjonspolicy for elsikkerhet
Based on the Norwegian document number 1169509 rev. 10 Page: 1 of 7 1 Governing policy and legislation These Instructions for the Switching Supervisor are subject to Statnett s Funksjonspolicy for elsikkerhet
These Instructions apply to all high-voltage installations where Statnett has operational responsibility.
 Based on the Norwegian document number 1169509 rev. 9 Page: 1 of 7 1 Governing policy and legislation These Instructions for the Switching Supervisor are subject to Statnett s Funksjonspolicy for elsikkerhet
Based on the Norwegian document number 1169509 rev. 9 Page: 1 of 7 1 Governing policy and legislation These Instructions for the Switching Supervisor are subject to Statnett s Funksjonspolicy for elsikkerhet
Power Unit 075. Maintain Substation Circuit Breakers
 Power Unit 075 Maintain Substation Circuit Breakers The specification details the required skills, knowledge and behaviours to establish competence to carry out the maintenance of high voltage power circuit
Power Unit 075 Maintain Substation Circuit Breakers The specification details the required skills, knowledge and behaviours to establish competence to carry out the maintenance of high voltage power circuit
2 nd Road Safety PIN Conference 23 June 2008 Countdown to only two more years to act!
 2 nd Road Safety PIN Conference 23 June 2008 Countdown to 2010 - only two more years to act! EU ambition EU target to cut by 50% yearly road deaths between 2001 and 2010 Countries have similar national
2 nd Road Safety PIN Conference 23 June 2008 Countdown to 2010 - only two more years to act! EU ambition EU target to cut by 50% yearly road deaths between 2001 and 2010 Countries have similar national
STCP 01-1 Issue 008 Operational Switching
 STCP 01-1 Issue 008 Operational Switching STC Procedure Document Authorisation Party Name of Party Representative Signature Date National Grid Electricity Transmission plc SP Transmission plc Scottish
STCP 01-1 Issue 008 Operational Switching STC Procedure Document Authorisation Party Name of Party Representative Signature Date National Grid Electricity Transmission plc SP Transmission plc Scottish
African swine fever in domestic pigs and wild boar (ASF)
 African swine fever in domestic pigs and wild boar (ASF) Analysis of ADNS data since 01/2018 Reporting period: 2018-01-01 2018-12-09 Data query: 2018-12-10 AGES DSR Austrian Agency for Health and Food
African swine fever in domestic pigs and wild boar (ASF) Analysis of ADNS data since 01/2018 Reporting period: 2018-01-01 2018-12-09 Data query: 2018-12-10 AGES DSR Austrian Agency for Health and Food
Bird strikes Swedish Airspace
 Bird strikes Swedish Airspace 1998-2005 Nordic Birdstrike Committee Arlanda 2006-09-21 Jörgen Andersson Jörgen Andersson, Swedish CAA 1 Objective Occurrence reports Bird population Birdstrikes between
Bird strikes Swedish Airspace 1998-2005 Nordic Birdstrike Committee Arlanda 2006-09-21 Jörgen Andersson Jörgen Andersson, Swedish CAA 1 Objective Occurrence reports Bird population Birdstrikes between
THE HORNS REV WIND FARM AND THE OPERATIONAL EXPERIENCE WITH THE WIND FARM MAIN CONTROLLER
 Copenhagen Offshore Wind 25, 26-28 October 25 1 THE HORNS REV WIND FARM AND THE OPERATIONAL EXPERIENCE WITH THE WIND FARM MAIN CONTROLLER Jesper Runge Kristoffersen M.Sc.EE Elsam Engineering A/S, Kraftværksvej
Copenhagen Offshore Wind 25, 26-28 October 25 1 THE HORNS REV WIND FARM AND THE OPERATIONAL EXPERIENCE WITH THE WIND FARM MAIN CONTROLLER Jesper Runge Kristoffersen M.Sc.EE Elsam Engineering A/S, Kraftværksvej
New developed Insulator Selection Tool (IST) software: results of application using known Russian service experience
 Proceedings of the 12th Asian Conference on Electrical Discharge, Graduate School of Shenzhen, Tsinghua University Shenzhen, China, November 19-22, 2004, p.p. 10-15 New developed Insulator Selection Tool
Proceedings of the 12th Asian Conference on Electrical Discharge, Graduate School of Shenzhen, Tsinghua University Shenzhen, China, November 19-22, 2004, p.p. 10-15 New developed Insulator Selection Tool
COMPARISON OF FIXED & VARIABLE RATES (25 YEARS) CHARTERED BANK ADMINISTERED INTEREST RATES - PRIME BUSINESS*
 COMPARISON OF FIXED & VARIABLE RATES (25 YEARS) Fixed Rates Variable Rates FIXED RATES OF THE PAST 25 YEARS AVERAGE RESIDENTIAL MORTGAGE LENDING RATE - 5 YEAR* (Per cent) Year Jan Feb Mar Apr May Jun Jul
COMPARISON OF FIXED & VARIABLE RATES (25 YEARS) Fixed Rates Variable Rates FIXED RATES OF THE PAST 25 YEARS AVERAGE RESIDENTIAL MORTGAGE LENDING RATE - 5 YEAR* (Per cent) Year Jan Feb Mar Apr May Jun Jul
System Flexibility Indicators
 System Flexibility Indicators Place your chosen image here. The four corners must just cover the arrow tips. For covers, the three pictures should be the same size and in a straight line. Operational Forum
System Flexibility Indicators Place your chosen image here. The four corners must just cover the arrow tips. For covers, the three pictures should be the same size and in a straight line. Operational Forum
You Just Experienced an Electrical Failure, What Should You Do Next? By Don Genutis Hampton Tedder Technical Services
 You Just Experienced an Electrical Failure, What Should You Do Next? By Don Genutis Hampton Tedder Technical Services Why Failures Occur Insulation Failure - Every electrical component is comprised of
You Just Experienced an Electrical Failure, What Should You Do Next? By Don Genutis Hampton Tedder Technical Services Why Failures Occur Insulation Failure - Every electrical component is comprised of
Electrical Shore Connections
 RULES FOR CLASSIFICATION OF Ships / High Speed, Light Craft and Naval Surface Craft PART 6 CHAPTER 29 NEWBUILDINGS SPECIAL EQUIPMENT AND SYSTEMS ADDITIONAL CLASS Electrical Shore Connections JULY 2014
RULES FOR CLASSIFICATION OF Ships / High Speed, Light Craft and Naval Surface Craft PART 6 CHAPTER 29 NEWBUILDINGS SPECIAL EQUIPMENT AND SYSTEMS ADDITIONAL CLASS Electrical Shore Connections JULY 2014
STCP 01-1 Issue 005 Operational Switching
 STCP 01-1 Issue 005 Operational Switching STC Procedure Document Authorisation Party National Grid Electricity Transmission plc Name of Party Representative Signature Date Formatted: Font: Arial Bold,
STCP 01-1 Issue 005 Operational Switching STC Procedure Document Authorisation Party National Grid Electricity Transmission plc Name of Party Representative Signature Date Formatted: Font: Arial Bold,
NY Wind Overview and 2016 Operation
 NY Wind Overview and 216 Operation Tolu Dina Supervisor, Operations Analysis & Services MIWG October 16, 217, Rensselaer, NY DRAFT FOR DISCUSSION PURPOSES ONLY Agenda Overview of NY Wind Wind Curtailment
NY Wind Overview and 216 Operation Tolu Dina Supervisor, Operations Analysis & Services MIWG October 16, 217, Rensselaer, NY DRAFT FOR DISCUSSION PURPOSES ONLY Agenda Overview of NY Wind Wind Curtailment
Key findings from a survey
 Key findings from a survey Golf course irrigation management practices in four Nordic countries By Carlos Gómez-Armayones and Jerry Knox, Cranfield Water Science Institute, Cranfield University, UK, February
Key findings from a survey Golf course irrigation management practices in four Nordic countries By Carlos Gómez-Armayones and Jerry Knox, Cranfield Water Science Institute, Cranfield University, UK, February
SERTP - 1 st Quarter Meeting
 2018 SERTP SERTP - 1 st Quarter Meeting First RPSG Meeting & Interactive Training Session March 29 th, 2018 Associated Electric Cooperative, Inc. Corporate Headquarters Springfield, MO 1 2018 SERTP Process
2018 SERTP SERTP - 1 st Quarter Meeting First RPSG Meeting & Interactive Training Session March 29 th, 2018 Associated Electric Cooperative, Inc. Corporate Headquarters Springfield, MO 1 2018 SERTP Process
OCEAN2012 Fish Dependence Day - UK
 OCEAN2012 Fish Dependence Day - UK Europeans are now so dependent on fish products originating from external waters that half the fish they consume are sourced outside the EU Fish dependence: The EU s
OCEAN2012 Fish Dependence Day - UK Europeans are now so dependent on fish products originating from external waters that half the fish they consume are sourced outside the EU Fish dependence: The EU s
July 2015 Sept Cork City Pedestrian Counter Report
 July 2015 Sept 2015 Cork City Pedestrian Counter Report Disclaimer Cork City Council has produced this report based on information extracted from our Pedestrian Counter Monitoring System. Although care
July 2015 Sept 2015 Cork City Pedestrian Counter Report Disclaimer Cork City Council has produced this report based on information extracted from our Pedestrian Counter Monitoring System. Although care
Compiled by Uwe Dornbusch. Edited by Cherith Moses
 REPORT ON WAVE AND TIDE MEASUREMENTS Compiled by Uwe Dornbusch. Edited by Cherith Moses 1 Aims...1 2 Summary...1 3 Introduction...1 4 Site selection...1 5 Wave recorder settings...2 6 Results...2 6.1 Water
REPORT ON WAVE AND TIDE MEASUREMENTS Compiled by Uwe Dornbusch. Edited by Cherith Moses 1 Aims...1 2 Summary...1 3 Introduction...1 4 Site selection...1 5 Wave recorder settings...2 6 Results...2 6.1 Water
RELIABILITY OF ENERGY SYSTEMS
 RELIABILITY OF ENERGY SYSTEMS Dubitsky M.A. Introduction. Depending on the goals of studies, the object of studies may be either an energy complex as a whole, or individual energy systems it includes,
RELIABILITY OF ENERGY SYSTEMS Dubitsky M.A. Introduction. Depending on the goals of studies, the object of studies may be either an energy complex as a whole, or individual energy systems it includes,
Connection Engineering Study Report for AUC Application: Fortis Okotoks 678S and High River 65S Upgrades
 Connection Engineering Study Report for AUC Application: Fortis Okotoks 678S and High River 65S Upgrades Executive Summary Project Overview FortisAlberta Inc. (FortisAlberta), in its capacity as the legal
Connection Engineering Study Report for AUC Application: Fortis Okotoks 678S and High River 65S Upgrades Executive Summary Project Overview FortisAlberta Inc. (FortisAlberta), in its capacity as the legal
Danish gambling market statistics Third quarter 2018
 Danish gambling market statistics Third quarter, Third quarter 5. december Content A. Introduction... 1 B. Overview over market developments in third quarter of... 2 C. Online casinos... 5 Developments
Danish gambling market statistics Third quarter, Third quarter 5. december Content A. Introduction... 1 B. Overview over market developments in third quarter of... 2 C. Online casinos... 5 Developments
TEGMA Fall Transportation Symposium
 TEGMA 2017 Fall Transportation Symposium John Wilson Senior Vice President Dairy industry trends 1997 1998 1999 2000 2001 2002 2003 2004 2005 2006 2007 2008 2009 2010 2011 2012 2013 2014 2015 2016 Million
TEGMA 2017 Fall Transportation Symposium John Wilson Senior Vice President Dairy industry trends 1997 1998 1999 2000 2001 2002 2003 2004 2005 2006 2007 2008 2009 2010 2011 2012 2013 2014 2015 2016 Million
Foreign overnight stays 31% Domestic overnight stays 69% 8.3 MILLION FOREIGN VISITORS IN FINLAND IN 2017
 TOURISM IS A GROWING SOURCE OF EXPORT REVENUE AND A SIGNIFICANT EMPLOYMENT PROVIDER IN FINLAND TOURISM HAS A MULTIPLIER EFFECT ON OTHER SECTORS. 1 EURO IN TOURISM ADDS 56 CENTS VALUE TO THE OTHER SECTORS.
TOURISM IS A GROWING SOURCE OF EXPORT REVENUE AND A SIGNIFICANT EMPLOYMENT PROVIDER IN FINLAND TOURISM HAS A MULTIPLIER EFFECT ON OTHER SECTORS. 1 EURO IN TOURISM ADDS 56 CENTS VALUE TO THE OTHER SECTORS.
Public data underlying the figures of Annual Report on the Results of Monitoring the Internal Electricity and Natural Gas Markets in 2016
 Public data underlying the figures of Annual Report on the Results of Monitoring the Internal Electricity and Natural Gas Markets in 2016 December 2017 Legal notice This document is a joint publication
Public data underlying the figures of Annual Report on the Results of Monitoring the Internal Electricity and Natural Gas Markets in 2016 December 2017 Legal notice This document is a joint publication
Danish gambling market statistics First quarter 2017
 Danish gambling market statistics First quarter 2017 6. juni 2017 Danish gambling market statistics 1 Introduction The Danish gambling market underwent a partial liberalisation in 2012, with the markets
Danish gambling market statistics First quarter 2017 6. juni 2017 Danish gambling market statistics 1 Introduction The Danish gambling market underwent a partial liberalisation in 2012, with the markets
New Zealand Fisheries Assessment Research Document 98/21. Not to be cited without permission of the authork) Malcolm Clark
 Not to be cited without permission of the authork) New Zealand Fisheries Assessment Research Document 98/21 A summary of commercial catch and effort information for orange roughy (Hoplostethus atlanticus)
Not to be cited without permission of the authork) New Zealand Fisheries Assessment Research Document 98/21 A summary of commercial catch and effort information for orange roughy (Hoplostethus atlanticus)
Danish gambling market statistics First quarter 2018
 Danish gambling market statistics First quarter, 2018 First quarter 2018 28. juni 2018 Indhold A. Introduction... 1 B. Overview over market developments in first quarter of 2018... 2 C. Online casinos...
Danish gambling market statistics First quarter, 2018 First quarter 2018 28. juni 2018 Indhold A. Introduction... 1 B. Overview over market developments in first quarter of 2018... 2 C. Online casinos...
Traffic Safety Basic Facts 2011
 Urban areas Fatalities on urban roads were reduced by 32% between 2000 and 2009. In 2009, about 12.300 people died in traffic accidents on urban roads in the EU-19. This corresponds to 38% of all road
Urban areas Fatalities on urban roads were reduced by 32% between 2000 and 2009. In 2009, about 12.300 people died in traffic accidents on urban roads in the EU-19. This corresponds to 38% of all road
Appendix ELP El Paso, Texas 2003 Annual Report on Freeway Mobility and Reliability
 (http://mobility.tamu.edu/mmp) Office of Operations, Federal Highway Administration Appendix ELP El Paso, Texas 2003 Annual Report on Freeway Mobility and Reliability This report is a supplement to: Monitoring
(http://mobility.tamu.edu/mmp) Office of Operations, Federal Highway Administration Appendix ELP El Paso, Texas 2003 Annual Report on Freeway Mobility and Reliability This report is a supplement to: Monitoring
Advanced Test Equipment Rentals ATEC (2832) OMS 600
 Established 1981 Advanced Test Equipment Rentals www.atecorp.com 800-404-ATEC (2832) OMS 600 Continuous partial discharge monitoring system for power generators and electrical motors Condition monitoring
Established 1981 Advanced Test Equipment Rentals www.atecorp.com 800-404-ATEC (2832) OMS 600 Continuous partial discharge monitoring system for power generators and electrical motors Condition monitoring
251 engaging and releasing club. 625 only releasing club. 236 all sides. 9,757 only player. 12,604 transfers
 1 This report offers a summary of the involvement of intermediaries in international 1 transfers completed in FIFA s International Transfer Matching System (ITMS) since 1 January 2013. Typically, three
1 This report offers a summary of the involvement of intermediaries in international 1 transfers completed in FIFA s International Transfer Matching System (ITMS) since 1 January 2013. Typically, three
Bicycle Crashes. Number of Bike Crashes. Total Bike Crashes. are down 21% and severe bike crashes down 8% since 2013 (5 years).
 Bicycle Crashes The City of Fort Collins is well known for its bike culture, and there is a strong focus on encouraging increased riding. Bike safety is an important component of supporting these efforts.
Bicycle Crashes The City of Fort Collins is well known for its bike culture, and there is a strong focus on encouraging increased riding. Bike safety is an important component of supporting these efforts.
Wind Data Verification Report Arriga 50m
 Page 1 of 11 Site Name Site Details 9531 - Arriga 5m Arriga 5m Date/Time of report generation 27/11/212 4:22 PM Site Number 9531 Mast Height 5m Mast Location 32568 E 811256 N Coordinate System UTM 55K
Page 1 of 11 Site Name Site Details 9531 - Arriga 5m Arriga 5m Date/Time of report generation 27/11/212 4:22 PM Site Number 9531 Mast Height 5m Mast Location 32568 E 811256 N Coordinate System UTM 55K
Heavy Goods Vehicles and Buses
 Traffic Safety Basic Facts 2013 - Main Figures Traffic Safety Basic Facts 2015 Heavy Goods Vehicles and Buses General More than 4.000 people died in road accidents involving HGVs in 2013. Heavy Goods Vehicles
Traffic Safety Basic Facts 2013 - Main Figures Traffic Safety Basic Facts 2015 Heavy Goods Vehicles and Buses General More than 4.000 people died in road accidents involving HGVs in 2013. Heavy Goods Vehicles
Utility Debt Securitization Authority 2013 T/TE Billed Revenues Tracking Report
 Utility Debt Securitization Authority 2013 T/TE Billed Revenues Tracking Report Billing Budgeted Billed Dollar Percent Month Revenues Revenues Variance Variance Jan 2018 11,943,180.68 12,697,662.47 754,481.79
Utility Debt Securitization Authority 2013 T/TE Billed Revenues Tracking Report Billing Budgeted Billed Dollar Percent Month Revenues Revenues Variance Variance Jan 2018 11,943,180.68 12,697,662.47 754,481.79
Cargo Theft IN ASIA 2013 SUPPLY CHAIN INTELLIGENCE CENTER:
 SUPPLY CHAIN INTELLIGENCE CENTER: Cargo Theft IN ASIA 213 FreightWatch International 51 Capital of Texas Hwy, Suite A2 Austin, Texas 78731 512.225.649 www.freightwatchintl.com INTRODUCTION FreightWatch
SUPPLY CHAIN INTELLIGENCE CENTER: Cargo Theft IN ASIA 213 FreightWatch International 51 Capital of Texas Hwy, Suite A2 Austin, Texas 78731 512.225.649 www.freightwatchintl.com INTRODUCTION FreightWatch
Engineering Technical Report 128. Risk Assessment for BT Operators Working In a ROEP Zone. Draft for Approval
 Engineering Technical Report 128 2006 Risk Assessment for BT Operators Working In a ROEP Zone Draft for Approval 2006 Energy Networks Association All rights reserved. No part of this publication may be
Engineering Technical Report 128 2006 Risk Assessment for BT Operators Working In a ROEP Zone Draft for Approval 2006 Energy Networks Association All rights reserved. No part of this publication may be
Reliability of Safety-Critical Systems Chapter 4. Testing and Maintenance
 Reliability of Safety-Critical Systems Chapter 4. Testing and Maintenance Mary Ann Lundteigen and Marvin Rausand mary.a.lundteigen@ntnu.no RAMS Group Department of Production and Quality Engineering NTNU
Reliability of Safety-Critical Systems Chapter 4. Testing and Maintenance Mary Ann Lundteigen and Marvin Rausand mary.a.lundteigen@ntnu.no RAMS Group Department of Production and Quality Engineering NTNU
C I R E D 18 th International Conference on Electricity Distribution Turin, 6 th to 9 th June 2005
 RELIABILITY AND LONG TIME BEHAVIOUR OF MV-DISTRIBUTION SWITCHGEAR IN SEVERE ENVIRONMENTAL CONDITIONS - EXAMINATION OF SF 6 -INSULATED RING MAIN UNITS (RMU) UP TO 20 YEARS IN SERVICE. B. I. Oftedal, Siemens
RELIABILITY AND LONG TIME BEHAVIOUR OF MV-DISTRIBUTION SWITCHGEAR IN SEVERE ENVIRONMENTAL CONDITIONS - EXAMINATION OF SF 6 -INSULATED RING MAIN UNITS (RMU) UP TO 20 YEARS IN SERVICE. B. I. Oftedal, Siemens
M A N I T O B A ) Order No. 123/13 ) THE PUBLIC UTILITIES BOARD ACT ) October 22, 2013
 M A N I T O B A ) Order No. 123/13 ) THE PUBLIC UTILITIES BOARD ACT ) BEFORE: Régis Gosselin, B ès Arts, MBA, CGA, Chair Larry Soldier, Member Marilyn Kapitany, B.Sc. (Hon), M.Sc., Member CENTRA GAS MANITOBA
M A N I T O B A ) Order No. 123/13 ) THE PUBLIC UTILITIES BOARD ACT ) BEFORE: Régis Gosselin, B ès Arts, MBA, CGA, Chair Larry Soldier, Member Marilyn Kapitany, B.Sc. (Hon), M.Sc., Member CENTRA GAS MANITOBA
Optimized Maintenance Planning for Transmission Power Systems.
 Optimized aintenance Planning for Transmission Power Systems. Improvement of the condition indexing process Name : - Adesh Soemeer Thesis committee: - Prof. dr. Johan Smit - Ing. Peter Oomens (Joulz) -
Optimized aintenance Planning for Transmission Power Systems. Improvement of the condition indexing process Name : - Adesh Soemeer Thesis committee: - Prof. dr. Johan Smit - Ing. Peter Oomens (Joulz) -
Traffic Safety Basic Facts 2008
 Urban road fatalities were reduced by more than 29% between 1997 and 2006. In 2006, more than 8.100 persons died in road accidents inside urban areas in the EU-14. This corresponds to 33,2% of all the
Urban road fatalities were reduced by more than 29% between 1997 and 2006. In 2006, more than 8.100 persons died in road accidents inside urban areas in the EU-14. This corresponds to 33,2% of all the
Country report. Swedish bathing water quality in Sweden. May Photo: Peter Kristensen/EEA
 Country report Swedish bathing water quality in 2017 Sweden May 2018 Photo: Peter Kristensen/EEA BWD Report For the Bathing Season 2017 Sweden The report gives a general overview of information acquired
Country report Swedish bathing water quality in 2017 Sweden May 2018 Photo: Peter Kristensen/EEA BWD Report For the Bathing Season 2017 Sweden The report gives a general overview of information acquired
Traffic Safety Basic Facts 2008
 In 2006 1, more than 4.700 seniors died in road traffic accidents in 14 European countries. Fatalities of elderly people in road traffic accidents reduced by over 3 between 1997 and 2006. Traffic Safety
In 2006 1, more than 4.700 seniors died in road traffic accidents in 14 European countries. Fatalities of elderly people in road traffic accidents reduced by over 3 between 1997 and 2006. Traffic Safety
The Statkraft Way. Switching Supervisor
 Innhold 1 PURPOSE... 1 2 SCOPE... 1 3 RESPONSIBILITY... 1 4 PROCEDURE... 1 4.1 Permanently appointed s.... 2 4.2 Emergency preparedness and locally connection authority for highvoltage equipment... 2 4.3
Innhold 1 PURPOSE... 1 2 SCOPE... 1 3 RESPONSIBILITY... 1 4 PROCEDURE... 1 4.1 Permanently appointed s.... 2 4.2 Emergency preparedness and locally connection authority for highvoltage equipment... 2 4.3
Order No. 55/18 CENTRA GAS MANITOBA INC.: PRIMARY GAS RATE APPLICATION, EFFECTIVE MAY 1, April 26, 2018
 CENTRA GAS MANITOBA INC.: PRIMARY GAS RATE APPLICATION, EFFECTIVE MAY 1, 2018 BEFORE: Larry Ring, Q.C., Panel Chair Marilyn Kapitany, B.Sc.(Hon), M.Sc., Vice Chair Carol Hainsworth, C.B.A., Member Susan
CENTRA GAS MANITOBA INC.: PRIMARY GAS RATE APPLICATION, EFFECTIVE MAY 1, 2018 BEFORE: Larry Ring, Q.C., Panel Chair Marilyn Kapitany, B.Sc.(Hon), M.Sc., Vice Chair Carol Hainsworth, C.B.A., Member Susan
Guidelines to the standard IEC60601
 EUROPEAN POWER SUPPLY MANUFACTURERS ASSOCIATION (Visit the EPSMA website at www.epsma.org) Medical Approvals for Power Supplies Guidelines to the standard IEC60601 Revision Date: 2009-09-12 This document
EUROPEAN POWER SUPPLY MANUFACTURERS ASSOCIATION (Visit the EPSMA website at www.epsma.org) Medical Approvals for Power Supplies Guidelines to the standard IEC60601 Revision Date: 2009-09-12 This document
Wisconsin 511 Traveler Information Annual Usage Summary January 3, Wisconsin 511 Phone Usage ( )
 Wisconsin 511 Traveler Information 211 Annual Usage Summary January 3, 212 Overall to-date Summary 36 months of operation 1,16,63 total calls the 1 Million mark was passed on December 3, 212 3,627,527
Wisconsin 511 Traveler Information 211 Annual Usage Summary January 3, 212 Overall to-date Summary 36 months of operation 1,16,63 total calls the 1 Million mark was passed on December 3, 212 3,627,527
EFICA 2017 Sommarøy Nordic Coastal & Fishing vessel trends
 EFICA 2017 Sommarøy Nordic Coastal & Fishing vessel trends Astrid Seltmann Analyst/Actuary, The Nordic Association of Marine Insurers (Cefor) astrid.seltmann@cefor.no NORWAY THE OUTSIDE PERSPECTIVE Cold
EFICA 2017 Sommarøy Nordic Coastal & Fishing vessel trends Astrid Seltmann Analyst/Actuary, The Nordic Association of Marine Insurers (Cefor) astrid.seltmann@cefor.no NORWAY THE OUTSIDE PERSPECTIVE Cold
To Loughborough University (LU) Facilities Management (FM) Health and Safety Policy
 Annex I To Loughborough University (LU) Facilities Management (FM) Health and Safety Policy High Voltage (HV) Electricity System Safety Rules and Associated Safety Guidance 1. Introduction a. These Safety
Annex I To Loughborough University (LU) Facilities Management (FM) Health and Safety Policy High Voltage (HV) Electricity System Safety Rules and Associated Safety Guidance 1. Introduction a. These Safety
Minimum Approach Distances (MAD)
 Minimum Approach Distances (MAD) The final rule updated OSHA s default values for transient over voltages (TOV), selecting far more conservative values. As TOV is one of the major factors for calculating
Minimum Approach Distances (MAD) The final rule updated OSHA s default values for transient over voltages (TOV), selecting far more conservative values. As TOV is one of the major factors for calculating
This test shall be carried out on all vehicles equipped with open type traction batteries.
 5.4. Determination of hydrogen emissions page 1 RESS-6-15 5.4.1. This test shall be carried out on all vehicles equipped with open type traction batteries. 5.4.2. The test shall be conducted following
5.4. Determination of hydrogen emissions page 1 RESS-6-15 5.4.1. This test shall be carried out on all vehicles equipped with open type traction batteries. 5.4.2. The test shall be conducted following
Traffic Safety Basic Facts 2012
 Urban areas Fatalities on urban roads were reduced by 39% between 2001 and 2010. In 2010, about 10.830 people died in traffic accidents on urban roads in the EU-19. This corresponds to 38% of all road
Urban areas Fatalities on urban roads were reduced by 39% between 2001 and 2010. In 2010, about 10.830 people died in traffic accidents on urban roads in the EU-19. This corresponds to 38% of all road
FINAL REPORT for Sports Tourism Report For the Year 2013
 FINAL REPORT for Sports Tourism Report For the Year 2013 Prepared for The Cyprus Tourism Orgaization September 201 CONTENTS Page 1. Main Findings 2 2. Appointment and Methodology 3. General Indicators:
FINAL REPORT for Sports Tourism Report For the Year 2013 Prepared for The Cyprus Tourism Orgaization September 201 CONTENTS Page 1. Main Findings 2 2. Appointment and Methodology 3. General Indicators:
95 Express Annual Operations Report: Fiscal Year
 95 Express Annual Operations Report: Fiscal Year 2014-2015 General The 95 Express Program completed its sixth full Fiscal Year of operations in June 2015. For the FDOT, its Fiscal Year (FY) is from July
95 Express Annual Operations Report: Fiscal Year 2014-2015 General The 95 Express Program completed its sixth full Fiscal Year of operations in June 2015. For the FDOT, its Fiscal Year (FY) is from July
Broadcasting International P7S1 Nordics Henrik Ravn, October 10, 2012
 Broadcasting International P7S1 Nordics Henrik Ravn, October 10, 2012 October 10, 2012 Page 1 Overview of P7S1 Nordics The #1 Nordic entertainment house Trailer October 10, 2012 Page 2 Highlights of P7S1
Broadcasting International P7S1 Nordics Henrik Ravn, October 10, 2012 October 10, 2012 Page 1 Overview of P7S1 Nordics The #1 Nordic entertainment house Trailer October 10, 2012 Page 2 Highlights of P7S1
Bluetongue Disease (BT)
 Bluetongue Disease (BT) Analysis of ADNS data since 01/2018 Reporting period: 2018-01-01 2018-12-09 Data query: 2018-12-10 AGES DSR Austrian Agency for Health and Food Safety www.ages.at Parameters Data
Bluetongue Disease (BT) Analysis of ADNS data since 01/2018 Reporting period: 2018-01-01 2018-12-09 Data query: 2018-12-10 AGES DSR Austrian Agency for Health and Food Safety www.ages.at Parameters Data
to both period for which data are available has been How Big is the Problem? 19 in Of these killed car occupants,
 Car Occupants Introduction This fact sheet explores some of the characteristics of car occupant fatalities. Cars comprise a considerable share of the vehicle fleet in the EU. Therefore, better understanding
Car Occupants Introduction This fact sheet explores some of the characteristics of car occupant fatalities. Cars comprise a considerable share of the vehicle fleet in the EU. Therefore, better understanding
OECD employment rate increases to 68.4% in the third quarter of 2018
 Paris, 17th January 2019 News Release: 3rd Quarter 2018 OECD employment rate increases to 68.4% in the third quarter of 2018 The OECD area employment rate the share of the working-age population with jobs
Paris, 17th January 2019 News Release: 3rd Quarter 2018 OECD employment rate increases to 68.4% in the third quarter of 2018 The OECD area employment rate the share of the working-age population with jobs
Safe Schools: A Health and Safety Check
 Name of School: Optional Information Date of Inspection: Vocational Program/Course/Room: Signature of Inspector: Use of Electrical Equipment Self-Inspection Checklist Guidelines: This checklist covers
Name of School: Optional Information Date of Inspection: Vocational Program/Course/Room: Signature of Inspector: Use of Electrical Equipment Self-Inspection Checklist Guidelines: This checklist covers
Assessment of Guide Reporting & Preliminary Results of Lion Monitoring
 Assessment of Guide Reporting & Preliminary Results of Lion Monitoring Mara Predator Project December 21 Sara Blackburn Laurence Frank maralions@gmail.com lgfrank@berkeley.edu SUMMARY The Mara Predator
Assessment of Guide Reporting & Preliminary Results of Lion Monitoring Mara Predator Project December 21 Sara Blackburn Laurence Frank maralions@gmail.com lgfrank@berkeley.edu SUMMARY The Mara Predator
WIND DATA REPORT. Bourne Water District
 WIND DATA REPORT Bourne Water District July to September 2010 Prepared for Massachusetts Clean Energy Center 55 Summer Street, 9th Floor Boston, MA 02110 by Dylan Chase James F. Manwell Utama Abdulwahid
WIND DATA REPORT Bourne Water District July to September 2010 Prepared for Massachusetts Clean Energy Center 55 Summer Street, 9th Floor Boston, MA 02110 by Dylan Chase James F. Manwell Utama Abdulwahid
UNIVERSITY OF CALIFORNIA Economics 134 DEPARTMENT OF ECONOMICS Spring 2018 Professor David Romer
 UNIVERSITY OF CALIFORNIA Economics 134 DEPARTMENT OF ECONOMICS Spring 2018 Professor David Romer LECTURE 2 OVERVIEW OF THE GREAT DEPRESSION January 22, 2018 I. THE 1920S A. GDP growth and inflation B.
UNIVERSITY OF CALIFORNIA Economics 134 DEPARTMENT OF ECONOMICS Spring 2018 Professor David Romer LECTURE 2 OVERVIEW OF THE GREAT DEPRESSION January 22, 2018 I. THE 1920S A. GDP growth and inflation B.
Country fact sheet South Korea
 ESRA results Country fact sheet South Korea The ESRA project is a joint initiative of research institutes in 25 countries aiming at collecting comparable national data on road users opinions, attitudes
ESRA results Country fact sheet South Korea The ESRA project is a joint initiative of research institutes in 25 countries aiming at collecting comparable national data on road users opinions, attitudes
Foreign overnights in the Nordic countries 2015
 Foreign overnights in the Nordic countries 2015 Sources: Statistics Statistics Statistics Statistics July 2016 VISIT FINLAND STATISTICS Contents Foreign overnights in the Nordic countries.4 Overnights
Foreign overnights in the Nordic countries 2015 Sources: Statistics Statistics Statistics Statistics July 2016 VISIT FINLAND STATISTICS Contents Foreign overnights in the Nordic countries.4 Overnights
Gas Network Craftsperson
 Gas Network Craftsperson Unit EIAU016 Carrying out Fault Diagnosis on Electrical Equipment and Circuits This assessment specification has been developed as part of the network maintenance craftsperson
Gas Network Craftsperson Unit EIAU016 Carrying out Fault Diagnosis on Electrical Equipment and Circuits This assessment specification has been developed as part of the network maintenance craftsperson
Stock Market Handbook
 Stock Market Handbook May 11, 212 Dr. Edward Yardeni 516-972-7683 eyardeni@ Sailesh S Radha 83-786-1368 jabbott@ Please visit our sites at www. blog. thinking outside the box Table Of Contents Table Of
Stock Market Handbook May 11, 212 Dr. Edward Yardeni 516-972-7683 eyardeni@ Sailesh S Radha 83-786-1368 jabbott@ Please visit our sites at www. blog. thinking outside the box Table Of Contents Table Of
PSSI 1 High Voltage Switching
 1. SCOPE This Safety Instruction sets down the procedures to be adopted when carrying out High Voltage (HV) Switching operations on The Company s System and other System(s) operated by the Company other
1. SCOPE This Safety Instruction sets down the procedures to be adopted when carrying out High Voltage (HV) Switching operations on The Company s System and other System(s) operated by the Company other
Talent ID and Development Camps
 Cycling South Africa, Raats Drive, Tableview, 7 PO Box 7, Tableview, 79, Republic of South Africa TEL: +7 557 FAX: +7 55755 EMAIL: info@cyclingsa.com WEB: www.cyclingsa.com Talent ID and Development Camps
Cycling South Africa, Raats Drive, Tableview, 7 PO Box 7, Tableview, 79, Republic of South Africa TEL: +7 557 FAX: +7 55755 EMAIL: info@cyclingsa.com WEB: www.cyclingsa.com Talent ID and Development Camps
Capacity of transport infrastructure networks
 Most infrastructure extension work is concentrated on roads. The total length of the motorway network has increased dramatically during the past two decades (about 3 % per year). Construction of the high-speed
Most infrastructure extension work is concentrated on roads. The total length of the motorway network has increased dramatically during the past two decades (about 3 % per year). Construction of the high-speed
WIM #37 I-94, MP OTSEGO, MN APRIL 2012 MONTHLY REPORT
 WIM #37 I-94, MP 200.1 OTSEGO, MN APRIL 2012 MONTHLY REPORT In order to understand the vehicle classes and groupings the Mn/DOT Vehicle Classification Scheme and the Vehicle Classification Groupings for
WIM #37 I-94, MP 200.1 OTSEGO, MN APRIL 2012 MONTHLY REPORT In order to understand the vehicle classes and groupings the Mn/DOT Vehicle Classification Scheme and the Vehicle Classification Groupings for
Manufacturers continue capacity expansion as technology orders grow
 Contact: Penny Brown, AMT, 703-827-5275 pbrown@amtonline.org For Release: September 10, 2018 Manufacturers continue capacity expansion as technology orders grow Manufacturing technology orders for July
Contact: Penny Brown, AMT, 703-827-5275 pbrown@amtonline.org For Release: September 10, 2018 Manufacturers continue capacity expansion as technology orders grow Manufacturing technology orders for July
Pressure independent control valve (PICV) FLOWMATIC
 Pressure independent control valve (PICV) FLOWMATIC 145 series FM 21654 003 01262/19 GB replaces dp 01262/17 GB Function The pressure independent control valve is a device composed of an automatic flow
Pressure independent control valve (PICV) FLOWMATIC 145 series FM 21654 003 01262/19 GB replaces dp 01262/17 GB Function The pressure independent control valve is a device composed of an automatic flow
Maintaining electrical equipment/systems
 Unit 037 Maintaining electrical equipment/systems Level: 2 Credit value: 15 NDAQ number: 500/9514/6 Unit aim This unit covers the skills and knowledge needed to prove the competences required to cover
Unit 037 Maintaining electrical equipment/systems Level: 2 Credit value: 15 NDAQ number: 500/9514/6 Unit aim This unit covers the skills and knowledge needed to prove the competences required to cover
January 2019 FY Key Performance Report
 January 2019 FY 2019 - Key Performance Report Management Notes: The information in this report is based on the FY 2019 Operating Budget, adopted by the Board on June 11, 20. RT s farebox recovery ratio
January 2019 FY 2019 - Key Performance Report Management Notes: The information in this report is based on the FY 2019 Operating Budget, adopted by the Board on June 11, 20. RT s farebox recovery ratio
2018 HR & PAYROLL Deadlines
 th (by payment date) EPAF 3rd PARTY FEEDS WTE Approval 2018 HR & PAYROLL s Normal Payroll day s 2017 B1-26 3 * 13-Dec-17 15-Dec-17 n/a n/a n/a 28-Dec-17 29-Dec-17 11:00 AM 16-Dec-2017 29-Dec-2017 JAN 2018
th (by payment date) EPAF 3rd PARTY FEEDS WTE Approval 2018 HR & PAYROLL s Normal Payroll day s 2017 B1-26 3 * 13-Dec-17 15-Dec-17 n/a n/a n/a 28-Dec-17 29-Dec-17 11:00 AM 16-Dec-2017 29-Dec-2017 JAN 2018
ASDX Series Silicon Pressure Sensors
 ASDX Series Silicon Pressure Sensors DESCRIPTION The ASDX Series is a Silicon Pressure Sensor offering a ratiometric analog interface for reading pressure over the specified full scale pressure span and
ASDX Series Silicon Pressure Sensors DESCRIPTION The ASDX Series is a Silicon Pressure Sensor offering a ratiometric analog interface for reading pressure over the specified full scale pressure span and
The Golf Related Products Produced by IAR Team Focus Technology Co., Ltd.
 The Golf Related Products 2012.12 Produced by IAR Team Focus Technology Co., Ltd. Contents 1. The Current Export Situation of China Golf Related Products At 2012...3 1.1. The Export Analysis of Chinese
The Golf Related Products 2012.12 Produced by IAR Team Focus Technology Co., Ltd. Contents 1. The Current Export Situation of China Golf Related Products At 2012...3 1.1. The Export Analysis of Chinese
23.1 Functions, Basic Configuration, and Interfaces
 23 (6.6.D) SF 6 and Other Special Gases 23.1 Functions, Basic Configuration, and Interfaces 23.1.1 Functions The primary function performed by the SF 6 and other special gases system is to provide SF 6
23 (6.6.D) SF 6 and Other Special Gases 23.1 Functions, Basic Configuration, and Interfaces 23.1.1 Functions The primary function performed by the SF 6 and other special gases system is to provide SF 6
Road Safety Vademecum
 Road Safety Vademecum Road safety trends, statistics and challenges in the EU 2010-2013 March, 2014 European Commission DG for Mobility and Transport Unit C.4 Road Safety Contents Summary of findings...
Road Safety Vademecum Road safety trends, statistics and challenges in the EU 2010-2013 March, 2014 European Commission DG for Mobility and Transport Unit C.4 Road Safety Contents Summary of findings...
GAS PIPELINE SAFETY GUIDE.
 GAS PIPELINE SAFETY GUIDE. Date of issue 27/02/2017 Date of next review 27/02/2018 Page 1 Vector Limited 2017 Gas Pipeline Safety Guide February 2017 CONTENTS CONTENTS...2 WORKING SAFELY... 3 Your Legal
GAS PIPELINE SAFETY GUIDE. Date of issue 27/02/2017 Date of next review 27/02/2018 Page 1 Vector Limited 2017 Gas Pipeline Safety Guide February 2017 CONTENTS CONTENTS...2 WORKING SAFELY... 3 Your Legal
LONG TERM SITE WIND DATA ANNUAL REPORT. Mass Turnpike Authority Blandford, MA
 LONG TERM SITE WIND DATA ANNUAL REPORT Mass Turnpike Authority Blandford, MA July 1, 2012 June 30, 2013 Prepared for Massachusetts Clean Energy Center 55 Summer Street, 9th Floor Boston, MA 02110 by Dylan
LONG TERM SITE WIND DATA ANNUAL REPORT Mass Turnpike Authority Blandford, MA July 1, 2012 June 30, 2013 Prepared for Massachusetts Clean Energy Center 55 Summer Street, 9th Floor Boston, MA 02110 by Dylan
DISSOLVED GAS ANALYSIS OF NATURAL ESTER FLUIDS UNDER ELECTRICAL AND THERMAL STRESS
 DISSOLVED GAS ANALYSIS OF NATURAL ESTER FLUIDS UNDER ELECTRICAL AND THERMAL STRESS M. Jovalekic 1*, D. Vukovic 1 and S. Tenbohlen 1 1 Institute of Power Transmission and High Voltage Technology (IEH) University
DISSOLVED GAS ANALYSIS OF NATURAL ESTER FLUIDS UNDER ELECTRICAL AND THERMAL STRESS M. Jovalekic 1*, D. Vukovic 1 and S. Tenbohlen 1 1 Institute of Power Transmission and High Voltage Technology (IEH) University
LONG TERM SITE WIND DATA ANNUAL REPORT. Paxton, MA
 LONG TERM SITE WIND DATA ANNUAL REPORT Paxton, MA July 1, 2012 June 30, 2013 Prepared for Massachusetts Clean Energy Center Summer Street, 9th Floor Boston, MA 021 by Dylan D. Chase James F. Manwell Anthony
LONG TERM SITE WIND DATA ANNUAL REPORT Paxton, MA July 1, 2012 June 30, 2013 Prepared for Massachusetts Clean Energy Center Summer Street, 9th Floor Boston, MA 021 by Dylan D. Chase James F. Manwell Anthony
THE ICELANDIC ECONOMY AN IMPRESSIVE RECOVERY BUT WHAT CHALLENGES LIE AHEAD?
 THE ICELANDIC ECONOMY AN IMPRESSIVE RECOVERY BUT WHAT CHALLENGES LIE AHEAD? FROM BUST TO BOOM. AN EPIC BUST After 16 years of growth with a short pause for breath in 2002, the Icelandic economy entered
THE ICELANDIC ECONOMY AN IMPRESSIVE RECOVERY BUT WHAT CHALLENGES LIE AHEAD? FROM BUST TO BOOM. AN EPIC BUST After 16 years of growth with a short pause for breath in 2002, the Icelandic economy entered
Development and Evolution of an Asset Management Organization
 Development and Evolution of an Asset Management Organization Art Kruppenbacher Manager Asset Management October 21, 2015 About the Iberdrola Group Headquartered in Spain 109-year history 28,000 employees
Development and Evolution of an Asset Management Organization Art Kruppenbacher Manager Asset Management October 21, 2015 About the Iberdrola Group Headquartered in Spain 109-year history 28,000 employees
08 / Industriveien 18 Phone: N Kristiansund Fax:
 Aquaculture Bulletin HEADLINES 08 / 2006 - a guideline for investors in the aquaculture business * Still high prices on the wholesale markets in the EU, with total supply of Atlantic salmon up with 4.6
Aquaculture Bulletin HEADLINES 08 / 2006 - a guideline for investors in the aquaculture business * Still high prices on the wholesale markets in the EU, with total supply of Atlantic salmon up with 4.6
Status Date Prepared Reviewed Endorsed Approved
 Discipline Engineering Standard NSW Category Signalling Title Rerailing Precautions to be Taken Reference Number SMP 26 (RIC Standard: SC 00 52 00 26 SI) Document Control Status Date Prepared Reviewed
Discipline Engineering Standard NSW Category Signalling Title Rerailing Precautions to be Taken Reference Number SMP 26 (RIC Standard: SC 00 52 00 26 SI) Document Control Status Date Prepared Reviewed
