Common Freshwater Fish Diseases, Their Symptoms and Control Measures : Types Symptoms Control measures A. Parasitic diseases
|
|
|
- Jayson McKinney
- 6 years ago
- Views:
Transcription
1 Common Freshwater Fish Diseases, Their Symptoms and Control Measures : Types Symptoms Control measures A. Parasitic diseases 1. Whirling disease Excessive secretion of mucus and weakness, rapid tail chasing & in advanced stages head, gill, etc. may be deformed. 2. Trypanosomasis (Piscine sleeping sickness) Infected fish suffers from slack, sickness. Fishes are sluggish, anemic with pale gill & skin. 3. Costiasis Costia causes dullness of skin & gills. Infected fish become restless, secrete excessive mucus & shows comparatively big head. 4. Ich. Disease (White spot disease) White spot seen on the skin, gill, fins, and cornea of the infected fish. If the infection is heavy then fish become restless and gasping air at the water surface. Infected fish reacts by rubbing their body against pond bottom and side. 5. Trichodiniasis Infected fish becomes restless, lethargic, loss body weight and body colour becomes dull with excessive mucus secretion. 6. Chillodonella infection Infected fish becomes irritable, Jump clear of the Application of Calcium Cyanamide (NCNCa) jaw, at the rate of 0.2 kg/ m 2 at the infected pond bottom and side after dewatering is required. If draining is possible, after draining the pond water remove the pond bottom mud then lime at the rate of kg/ha area can be applied to the drained pond bottom and the allowed to dry for 2 weeks to eradicate the parasites completely. After eradication of the parasite restocking is in the pond is done. Prevention is by controlling the intermediate host the leech etc into the pond. Leech can be controlled by dipping fishes into common salt (NaCl) or copper sulphate (CuSO 4 ) solution. To avoid the incidence of costiasis proper feeding & maintenance of water quality is required. Therapeutic bath with formaline ml/lit and combination of 0.1 mg/lit of malachite green with 15 mg/ lit. formaline is found effective. Pond treatment with malachite green at a concentration of 0.1mg/ lit. or with formalin at a concentration of 15 mg/lit for once or twice or thrice on need basis. Maintenance of water P H above 6.5 and dissolved oxygen level at 5 ppm or above automatically save the fish stock from infection. Short bath in formalin at a concentration of ml/ m 3 for half an hour. (or) Apply common salt (NaCl) at a concentration of % for 1-2 days to the infected pond. (or) Apply lime to the infected fish pond at the rate of kg/ ha with repetition at an interval of 7 days. Give short bath with potassium permanganate (KMnO 4 )for 10-
2 7. White scale spot disease water, slowly becomes week and unresponsive. Bluish green mucus occurs on the skin. Scale and body surface are covered with white cysts, effected fish become lethargic. 8. Dactylogyrosis Infected fish shows erratic swimming, appearance of local lesions, pale gill colour, excessive mucus secretion, falling of scales, rubbing of body against any submerged objects, etc. 9. Gyrodactylus The skin of fish becomes spotted dark and covered with bluish gray mucus layer. When it attacks on the fin the fin rays are left. In case of gill infection the fish swim listlessly below the water surface or they gather on the side, where they slowly suffocate, gills are spotted and filled with 10. Black spot disease (Digenea) 11. Strap worm disease (Lingulinosis) blood. Numerous small black nodules or cysts are found all over the body. The infected fish show sluggishness, slight distension of abdomen, surfacing, reluctant to accept feed etc. 12. Blood fluke Infected fish shows lethargic movement, reluctant to accept feed, surfacing and gasping air, etc. Infected fish gill become pale. 13. Namatods & Acanthocephalosis Infected fish shows yellowish white granules on lip, skin and fins. Adult worm are detected in the intestine or the body cavity of diseased fish. 14. Leech infection Blood spots over the body surface, loose scale, sunken eyes, pale gills, etc. (It also act as a vector). 15. Ergasilosis (Gill lice) Mechanical damage to gill lamina, gill colour faded, can be seen through microscope under low magnification. 15 (KMnO 4 )for of 50 mg/lit. Apply lime at the rate of kg/ ha. Along with liming give bath treatment with common salt(nacl) at the concentration of 3-5%. Apply lime at the rate of kg/ ha. Apart from liming give dip treatment in common salt (NaCl) solution at the concentration of 5%. Draining and drying the pond for about a week is an effective method of killing gyrodactylus. Formalin bath at the concentration of mg/lit. of water for 30 minutes may also be given. Drain & dry the infected pond followed by application of lime at the rate of kg/ ha can eradicate the parasite. Removing the infected fish as far as practicable is one way to control. Trichlorophon at the rate of mg/ lit. of water can also be applied to the infected pond. Remove the severely infected fish. Give the dip treatment with trichlorophon at a concentration of 1% for 2-3 minutes. Drain & dry the infected pond followed by application of lime at the rate of kg/ ha can eradicate the parasite. Apply lime at the rate of kg/ ha. (1) Give dip treatment with trichlorophron in a concentration of 5 mg/lit. of water for minutes; (2) If the infection is heavy -
3 16. Lernaeosis (Commonly known as Anchor worm disease ) Hook like attachment on the nostril/ head regions, fish become restless and rub against any hard substrate found in the pond due to irritation. 17. Argulosis (Carp lice) Infected fish shows- erratic swimming behaviour & reluctant to accept feed. Parasite is visible with naked eye and ulceration is seen at the attachment site. 18. Isopod infection Infected fish showslethargic movement & reluctant to accept feed, etc. remove the whole fish stock from the pond then dewater and dry the pond, after that remove a layer of soil of 20cm thickness from the pond bottom and then apply lime at the rate of kg/ ha, then refilled the pond with water and introduce a new stock of fish for culture. (1) Apply potash(kmno 4 ) to the infected fish pond at the rate of 4 mg/lit. of water. (or) (2) Give short bath treatment to the infected fish in common salt (NaCl) solution at a concentration of 2.5-3% for 5 10 minutes. Treated fish should be released to the pond immediately after the treatment. (1) Apply potash(kmno 4 ) to the infected fish pond at the rate of 4 mg/lit. of water. (or) (2) Give short bath treatment to the infected fish in common salt (NaCl) solution at a concentration of 2.5-3% for 5 10 minutes. Treated fish should be released to the pond immediately after the treatment. (or) (3) Apply cleaner solution to the infected fish pond at the rate of ml/ bigha water spread area. If draining is possible then lime at the rate of kg/ ha area can be applied to the drained pond bottom and the allowed to dry for 2 weeks to eradicate the parasites completely. After eradication of the parasite restocking is in the pond is done. Same with argulosis. B. Bacterial diseases 19. Furanculosis On the skin local erosion surrounded by inflammated reddish zone which gradually turns into a large deep ulcer. In acute cases protruding eyes and accumulation body fluids in the body cavity is seen. 20. Dropsy Accumulation of body fluid/ water in the body cavity or in Fed the infected fish with tetracycline with feed at the rate of 0.07 gm/ kg body weight of fish daily till the cure. Maintenance of hygienic environment helps in keeping the fish free from this disease. Apply KMnO 4 (Potash) at the rate of 4-5 mg/ Lit. of water to
4 scale pockets, scales become loose, abdomen bulge largely and pressing on it water comes out through the mouth etc. 21. Columnaris Lesions occur in the skin of the head region and back as well as gills. 22. Tail and fin rot Erosion and disintegration of fin and tails. As the lesion develops the outer fin margin becomes frayed and disintegration of soft tissues between fin rays starts. 23. Bacterial gill disease Infected fish shows pale swelling gill with excessive secretion of mucus. Sluggish movement, sign of asphyxiation and surfacing 24. Vibrio disease (Red boil disease) 25. Mycobacterial Disease are other symptoms. Affected fish become swollen, dark in colour with skin lesions. Mostly seen in aquarium fish. Infected fish shows loss of appetite, loss of colour scales, destruction of fins, etc. 26. Hemophilosis Lesion is found in the infected fish on the fin between the fin rays and edges of jaw or roof of the mouth. 27. Ulcer disease Infected fish shows small pimple like reddish areas on the body surface and letter develop into ulcers. 28. Re pest of freshwater eels Infected fish body shows red blotches, later on the lesions of the skin become whitish blotches and form ulcer. the infected fish pond. Give dip treatment to the infected fish with copper sulphate (CuSO 4 ) for 1-2 minutes at a concentration of 2 mg/ lit. This may be followed by feeding tetracycline to the infected fish along with feed at a concentration of mg/ kg body weight of fish. Same with columnaris disease. Bath in Potassium permanganate (KMnO 4 ) at a conc. of 1-2 mg/lit. for 7 days. Fed the infected fish with Sulphamerazin 0.2 gm/kg body weight mixed with feed for 3 consecutive days and after an interval of 2 days repetition of same dose. (or) Fed the infected fish with Furazolidone mg/ kg body weight mixed with feed for 10 consecutive days. Fed the infected fish with Kanamycin sulphate at the rate of 10 mg/ kg body weight for 4-7 days. Fed the infected fish with Oxytetracycline at the rate of mg/ body weight/ day for days. Apply KMnO 4 (Potash) at the rate of 5 mg/ lit. of water in pond water. Along with potash treatment the sulphadiazine can be fed to the infected fish along with feed at the rate of 100 mg/ kg of feed for 100 mg/ kg of feed for days. It is difficult treat, effected fish should be remove immediately and buried them. This is followed by disinfections of the effected pond after draining and
5 29. Re pest of freshwater fish 30. Coldwater disease (Peduncle disease) 31. Bacterial kidney disease C. Viral diseases Infected fish body shows cutaneous blotches which may be round, oval or elongated in shape, of whitish colouration and in some cases loss of epithelium and scales. Affected fish shows typical lesion start as a small whitish or bluish spot behind the dorsal fin. From this, erosion occurs until a crater is present in the muscle. Externally it is difficult to detect, but in some cases there will be ill defined lesions on side of the body. Effected fish kidney shows grayish- white necrotic zones filled with purulent material. drying. Same with red pest of freshwater eels. Fed the infected fish with sulphamethazine at the rate of 100 mg/kg feed/day along with feed for days. It is difficult to control But erothromycin may be fed to the fish at the rate of 100 mg/ kg feed for days. 32. Infectious pancreatic Affected fish are darker in necrosis (IPN Virus) colour, tail chasing, exophthalmia, abdomen and hemorrhages in ventral areas, etc. 33. Viral haemorrhagic The infected fish is Septicaemia (VHS) characterized by high mortality, fishes are dark in colour, lethargic and exhibits hemorrhages in fin sockets, etc. 34. Infectious Clinical symptoms shows haematopoietic necrosis lethargy, weakness, dark (IHN) colouration, anaemia, swelling of abdomen, pale gill, etc. 35. Swimbladder Infected fish swim restlessly Infection (SBI) in dorsal and lateral position at the water surface, body colour becomes dark & abdomen distended. 36. Pike fry virus The infected fish swim slowly, gills become pale, haemorrhages on the trunk and above the anal fin, etc. 37. Channel catfish Virus Affected fish- loss (CCV) equilibrium, swim erratically, shows haemorrhages of 38. Lymphocystis Disease gills, skin and fin base, etc. Affected fish develop small pear- like tumefacious either singly or in groups in skin, fin, tail, intestinal wall, liver, No control effective control measures. As prophylaxis providing optimum feed and maintenance of hygienic environment. Isolation of healthy fish is the main prophylactic measure as there are no control measures. There are no control measures. But by raising water temperature above 15 o c this can be controlled. Same with viral haemorrhagic septicemia (VHS). No control measures. Avoidance of virus is the only prophylaxis. No control measures, Avoidance of stress is the only prophylactic measure. As there is no cure, so the whole effected stock should destroyed. Then disinfect the affected Pond by draining
6 39. Papillomatosis (Cauliflower disease) D. Fungal diseases spleen, ovary, etc. Skin may develop sand papers. The cauliflower like papillomonous may be white, light red or dark gray that affect fin, body, tail etc. Lesion is also seen in the skin and jaws of affected fish. followed by drying and applying lime at the rate of kg/ha. After disinfections fish culture should start newly. Bath in soluble quinine sulphate at the rate of 60 mg/ lit. for about days. 40. Saprolegniasis (Cotton wool disease) Infected fish shows whitish fungal mesh which looks like cotton wools appears in the infected parts of fish body. Sometimes lesions appear as gray white patches on various parts of the body like- skin, fins, eyes, mouth, and gill Common salt (NaCl) at 41. Achlyasis Erosion of tail and body parts. 42. Branchiomycosis Affected fish congregate near the inlet of water & refuse to take feed. Infected fish gill becomes grayish white and finally drop off. 43. Ichthyophonus disease Infected organs shows roughness, often-necrotic lesions and hyper pigmentation. Give bath treatment to the infected fish with KMnO 4 (Potash) at the conc. of 1 gm/ 100lit. of water for 1 hr. (or) Give bath treatment to the infected fish with the conc. of 10 gm/ lit. of water for minutes. (or) Give bath treatment to the infected fish with Copper sulphate (CuSO 4 ) at the conc. of 5 gm/ 10 lit. of water for minutes. Give long bath with malachite green at the rate of mg/ lit of water minutes. (or) Give bath treatment to the infected fish with methylene blue at the concentration of mg/lit. of water for 15 minutes. Draining the pond Bottom & disinfecting with quick lime (CaO) at the rate of kg/ ha. should be done at the end of each culture practice. CuSO 4 at the rate of 8 kg/ ha may be used in 4 monthly installments of 2-3 kg/ ha each. Bath in CuSO 4 at the rate of 1 gm/10 lit. of water for minutes. Disinfect the affected fish pond with lime as Mentioned in the branchiomycosis. Remove & destroy the infected fish stock & water can be purify by applying chlorine at the rate of 200 mg/ lit. of water. E. Environmental diseases 44. Changes in water depth (If the water depth becomes less than 1 m and more than 2 m) Sun Loss of appetite, reduction in growth and fish becomes lethargic. Sudden mortality may be occur due to Maintain the water depth in the pond in an around 2 meters. If the water depth is less than 2 m Then fill up the required
7 burn disease increase of stress by pollutants. 45. Changes in water Affected fish shows temperature Thermal surfacing, loss of appetite, shock less growth and fish becomes lethargic. Effect of other factors of disease will increase and fish may die. 46. Changes in water P H Acidosis & alkalosis 47. Reduction in dissolved oxygen (D.O.) concentration (Anoxia) 48. Increase in dissolved oxygen (D.O.) concentration (Gas Bubble Disease) 49. Increase in dissolved carbon dioxide (CO 2 ) concentration 50. Increase in hydrogen sulphide(h 2 S) concentration in water 51. Increase of turbidity of pond water 52. Red or green or brown coloured layer over the pond water surface (Algal toxicosis disease) Pond water become acidic or alkaline. Affected fish shows- growth retardation, excessive mucus secretion, fraying of fins, etc. Fish will be susceptible to the infection of other diseases. Affected fish showssurfacing. Died fish mouth remains open and gill colour become pale. Fish fry & fingerlings are mostly affected. Due to entry of gas bubble in the arteries of fish body fish may die. Normally it is seen in the noon and afternoon hours of a day. Affected fish secrete excessive mucus and suffers from asphyxiation. Effected fish pond mud will smell like rotten egg and bottom dwellers like- mirika, common carp, etc. will die first. Small fish and eggs are effected first. Growth of fish retarded, dissolved oxygen concentration is reduced and fish dies from asphyxiation. Bad smell of effected fish pond water. The thickness of layer may increase from morning to noon hours. Surfacing of fish in the effected pond is seen from late night to dawn and fish may die. quantity from the nearby source. Supply water from a nearby source. Cut the quantity of feed supply. Turbulent the water with the help of a split bamboo. Harvest the table size fish and reduce the density of fish in the pond. Apply lime according to P H of water. Apply lime at the rate of 270, 140, 70 and 25 kg/ ha for P H values ranges between , , & respectively. Apart from taking the control measures cited incase of changes in water temperature cut application of feed & fertilizer temporarily. Reduce the stocking density of fish by harvesting the table size fish. Repeated netting may be done. KMnO 4 (Potash) may apply at the rate of 1-2 mg/ lit. of water in the pond. Liming can be done at rate of 27 kg/ ha water spread area. Supply water from the nearby source. If there is any mechanical aeration instruments then that should be stopped. Affected fish should transfer to a nearby pond. Take the corrective measures given in case of reduction in dissolved oxygen concentration Remove the died fish and take the corrective measures give in case of changes in water P H. Apply aluminium (filter alum) sulphate i.e. Al 2 (SO 4 ) 3 14 H 2 O at the rate of mg/ lit. of water. Actual quantity can be determined by putting alum in a glass of turbid water. After applying alum liming should be done as per the water P H as mentioned in corrective measure of water P H. Supply of feed & fertilizer to the pond should be stopped temporarily. If possible remove the coloured layer with the help of free hand or by using a split bamboo. Copper sulphate (CuSO 4 ) at the rate of mg/ lit. of water can also be
8 53. Increase in the concentration of unionized ammonia Affected fish gill become reddish and effected fish may die also. 54. Tarumatic injuries Effected fish shows biting sign of predators on body surface and other external organs like- fins. In acute cases some lesions may be seen on the body surface. 55. Acute anaphylaxis Effected fish shows extreme rigor with all fins erect, body colour become very dark & body become very rigid and 56.Deterioration of water quality by pollutants Nowadays pollutants are also taking leading role in the disease of fishes. Sources of this pollutants are- Chemical waste, industrial waste, sewage, agricultural waste, oil pollution, etc. twitching. Affected fish showshaemorrhagic eyes, pectoral fins may drop off, surfacing, loss of balance, sudden mass mortality, etc. apply. Control the water temperature, P H and also the concentration of phytoplankton in the pond and for that purpose take the renovative measures given in case of changes of water P H & temperature. Remove predators from the pond. Apply KMnO 4 (Potash) at the rate of 4-5 mg/lit of water to the effected pond. Effected fish should not be disturbed and they usually recover automatically before the next meal. Fish from the effected pond should be removed and buried under soil. Water of the effected pond should be drained out and pond bed should be dried. After that pond bottom mud up to 1 ft. depth (minimum) should be removed. Then pond should be disinfected with lime depending on P H as mentioned in the case of change in water P H. Afterwards the pond should be refilled with water and a new stock of fish can be cultured. F. Genetical diseases Genetical diseases of fishes are originated due to the - hereditary factors, shock received by fish in its early stage i.e. egg, spawn, fry, etc. This shock may be natural (like-oxygen deficiency, temperature variation, variations in light concentration, water flow variation, etc. in the spawning & cultured environment), or artificial (like- effect of chemicals and others in the spawning & cultured environment). There is no control measure of this disease. Removal of affected fishes from the stocking pond, not using the effected fish for the production of fish seed, introduction of healthy fish seed to the culture system from known sources, maintenance of congenial environment for the cultured stock, etc. are the only preventive measures. Some of the commonly found genetical fish diseases are- Types Symptoms Control measures 57. Kyphosis Affected fish shows hum formation in between the head and dorsal fin. 58. Vertebral column abnormality Affected fish shows marked dropping of back, shortening of vertebral column and fusion of vertebra. 59. Lordosis Concavity before the dorsal fin or at the dorsal fin. 60. Scoliosis Bending of caudal fin 61. Caudal peduncle Downward & upward bending of
9 abnormality caudal peduncle, absence of caudal fin, etc. 62. Mouth abnormality Downward displacement of the mouth, distortion of he mouth because of abnormalities in jaws etc. 63. Pectoral fin Large growth of pectoral fins. abnormality 64. Atrophy of pelvic fin Absence of one or both the pelvic fins. 65. Scale abnormality Changes in scales number, size, shape, etc. 66. Genetically or hereditary modifications of colour I) Xanthorism Gold colouration of fish due to gene mutation e.g. gold fish II) Albinism Whitish colouration of fish body. III) Melanism Black colouration of fish IV) Alampy Blue colouration of fish 67.Genetical or hereditary modifications due to disturbances in the embryonic stages of fish I) Over ripening or immature eggs Deformity in jaws, eyes, vertebral columns, etc. II) Oxygen deficiency Distortion of the pectoral fins, shortening of flesh in adult fish, etc. III) Temperature variation IV) Variations in light V) Effect of flow rate of water, Chemicals, etc. 68. Deformity in organs conformation Abnormality in fins. Lordosis & scoliosis may be caused. Number of dorsal and anal fin rays get reduced. Deformity in vertebral column, body colour, fins, scales, etc. Position of internal organs in other than its actual places e.g. liver on 69. Tumours Effected fish shows tumours on the body surface, enlargement of abdomen, loss of appetite, softening of bones, etc G. Nutritional diseases Nutritional deficiency Symptoms of nutritional deficiencycauses Scoliosis, blindness, eye cataract, blindness, swelling of throat, liver degeneration, damage goiter, seakoke, etc. of kidney, poor wound healing, poor growth, loss of appetite, susceptibility to infection by other pathogens, etc. Severely infected fish should be remove from the culture system. Proper quality & quantity feed supply to the cultured fishes is the only prophylactic measure.
10 H. Epizootic Ulcerative Syndrome (Locally known as Machar Gha Laga Bemar ). Species Infected: Indian Major Carps: Exotic Carps: Minor Carps: Murrels: Airbreathing fish: Eels: Weed fish: Clinical Signs: Bhakua/ Dhekera/ Bahu (Catla), Rohu and Mirika. Silver Carp, Grass Carp and Common Carp. Kurhi, Mali and Java Puthi. Goroi, Cheng, Sal and Sol. Magur, Singi, Ari, Tengra, etc. Kuchia. Puthi, Darikana, Moa, Khalihana, Botia, Tora, etc. Tiny red spot on the body surface initially. This spot later develop ulcer. After few days loosing its scales and muscles exposes body. Infected fish dies within a short period. Photo:EUS infected Common Carp treated at College of Fisheries, AAU, Raha. Prophylaxis: To prevent the infection of EUS in the cultured fish this is required. This helps in maintaining the health of cultured fish and also helps in getting a good production. The following prophylactive measures are needed for EUS: 1. Apply lime at the rate of kg/bigha of water spread area depending on P H of water before the onset of winter. This is followed by application of KMnO 4 (Potash) to the pond water at the rate of 4-5 ppm (4-5 mg/lit. of water). (OR) 2. Apply lime as mentioned in the 1 st prophylactive measure. After 1-2 days of application of lime to the pond water spraying of Sukrena W.S. over the pond water surface at the rate of 500ml/ bigha water spread area give encouraging result. Treatment measures: 1. Apply lime at the rate of kg/bigha of water spread area depending on P H of water. After 1-2 days of application of lime to the pond water spraying of Sukrena W.S. over the pond water surface at the rate of 500ml/ bigha water spread area. Repeat the application of Sukrena W.S. to the infected pond for 2 nd or 3 rd times depending on the need basis at days interval. (OR)
11 2. Dip the infected fish at 3-4% common salt (NaCl) solution and released the treated fish immediately to the pond water. (OR) 3. Apply common salt (NaCl) to the pond water at the rate of kg/ bigha water spread area. (OR) 4. Apply lime at the rate of kg/bigha of water spread area depending on P H of water. This is followed by application of KMnO 4 (Potash) to the pond water at the rate of 4-5 ppm (4-5 mg/lit. of water). (OR) 5. Give bath treatment to the infected fish at 4-6 ppm (4-6 mg/lit. of water) potash (KMnO 4 ) solution for a short period and then released the treated fish immediately to the pond water. Apart from the any of the above treatment measures antibiotic Oxytetracycline treatment may be given along with any one of the above cited treatment measures. Oxytetracycline are fed to the infected fish along with feed at the rate of mg/ kg feed for 7-10 days on need basis.
AROWANA DISEASES AND CURES
 AROWANA DISEASES AND CURES IN NATURE, ALL CREATURES ARE CARRIERS OF DISEASES TO SOME EXTENT. SOME ARE INFECTIOUS, WHILE OTHERS ARE NOT. IT DEPENDS ON VARIOUS FACTORS AND ACTIVITIES. DIFFERENCES STILL EXIST
AROWANA DISEASES AND CURES IN NATURE, ALL CREATURES ARE CARRIERS OF DISEASES TO SOME EXTENT. SOME ARE INFECTIOUS, WHILE OTHERS ARE NOT. IT DEPENDS ON VARIOUS FACTORS AND ACTIVITIES. DIFFERENCES STILL EXIST
Introduction. Case study 4 - Koi herpes virus. Major impact on commercial food carp production. History. KHV and other species
 Introduction Case study 4 - Koi herpes virus Dr. David Huchzermeyer Sterkspruit Veterinary Clinic Lydenburg Koi Herpesvirus is a recently emerged viral disease of carp (Cyprinus carpio) in all of its varieties
Introduction Case study 4 - Koi herpes virus Dr. David Huchzermeyer Sterkspruit Veterinary Clinic Lydenburg Koi Herpesvirus is a recently emerged viral disease of carp (Cyprinus carpio) in all of its varieties
Management and surveillance of fish diseases Fish disease is-the culmination of an interaction between the susceptible fish, the pathogen and the
 Management and surveillance of fish diseases Fish disease is-the culmination of an interaction between the susceptible fish, the pathogen and the environment. An optimum environment always helps in the
Management and surveillance of fish diseases Fish disease is-the culmination of an interaction between the susceptible fish, the pathogen and the environment. An optimum environment always helps in the
Introduction. Major impact on commercial food carp production. Worldwide distribution. History. Spring viraemia of carp (SVC)
 Introduction KOI HERPESVIRUS: USING BIOSECURITY AND SURVEILLANCE TO PRODUCE DISEASE FREE FISH David Huchzermeyer Sterkspruit Veterinary Clinic Lydenburg Koi herpesvirus is a recently emerged viral disease
Introduction KOI HERPESVIRUS: USING BIOSECURITY AND SURVEILLANCE TO PRODUCE DISEASE FREE FISH David Huchzermeyer Sterkspruit Veterinary Clinic Lydenburg Koi herpesvirus is a recently emerged viral disease
Managing a Quality Pond
 Managing a Quality Pond Gary Burtle The University of Georgia Successful Pond Management Set your GOAL Pond design Stocking Strategy Proper Nutrients Fish Growth and Harvest Successful Fish Reproduction
Managing a Quality Pond Gary Burtle The University of Georgia Successful Pond Management Set your GOAL Pond design Stocking Strategy Proper Nutrients Fish Growth and Harvest Successful Fish Reproduction
AQUATIC ANIMAL BIOSECURITY: CHALLENGES AND SOLUTIONS. THE CASE OF KOI HERPESVIRUS
 AQUATIC ANIMAL BIOSECURITY: CHALLENGES AND SOLUTIONS. THE CASE OF KOI HERPESVIRUS David Huchzermeyer and Philippa Colly Sterkspruit Veterinary Clinic Introduction Koi herpesvirus is a recently emerged
AQUATIC ANIMAL BIOSECURITY: CHALLENGES AND SOLUTIONS. THE CASE OF KOI HERPESVIRUS David Huchzermeyer and Philippa Colly Sterkspruit Veterinary Clinic Introduction Koi herpesvirus is a recently emerged
Fish. Water Dwelling Animals
 Fish Water Dwelling Animals Class Agnatha (Jawless fish) They are believed to be the most primitive and oldest vertebrates. Lamprey and hagfish are the only 2 living members of this class and are placed
Fish Water Dwelling Animals Class Agnatha (Jawless fish) They are believed to be the most primitive and oldest vertebrates. Lamprey and hagfish are the only 2 living members of this class and are placed
Internal Anatomy of Fish
 Internal Anatomy of Fish The Systems of a Fish Skeletal System Muscular System Respiratory System Digestive System Circulatory System Nervous System Reproductive System Special Organs Skeletal System
Internal Anatomy of Fish The Systems of a Fish Skeletal System Muscular System Respiratory System Digestive System Circulatory System Nervous System Reproductive System Special Organs Skeletal System
Significant exotic diseases IHN 2011/09/23 EPIZOOTIC HAEMATOPOIETIC NECROSIS. David Huchzermeyer Sterkspruit Veterinary Clinic
 Significant exotic diseases EPIZOOTIC HAEMATOPOIETIC NECROSIS David Huchzermeyer Sterkspruit Veterinary Clinic Iridovirus. South eastern Australia. Apart from salmonids and redfin perch, guppies and mosquito
Significant exotic diseases EPIZOOTIC HAEMATOPOIETIC NECROSIS David Huchzermeyer Sterkspruit Veterinary Clinic Iridovirus. South eastern Australia. Apart from salmonids and redfin perch, guppies and mosquito
BACTERIAL CAUSES OF FIN ROT IN SOME FRESH WATER FISHES.
 BACTERIAL CAUSES OF FIN ROT IN SOME FRESH WATER FISHES. Enany,, M. E., El Sayed,, M. E., Diab.. A. S., Hassan,, S. M., and El Gamal,, R.M.** *Department of Microbiology, Faculty of Vet. Medicine, Suez
BACTERIAL CAUSES OF FIN ROT IN SOME FRESH WATER FISHES. Enany,, M. E., El Sayed,, M. E., Diab.. A. S., Hassan,, S. M., and El Gamal,, R.M.** *Department of Microbiology, Faculty of Vet. Medicine, Suez
Fish Dissection Background
 Fish Dissection Background Introduction Living things are similar to and different from each other. For example, when we look at the inside of a fish, we learn that the organ systems of fish are similar
Fish Dissection Background Introduction Living things are similar to and different from each other. For example, when we look at the inside of a fish, we learn that the organ systems of fish are similar
Perch Dissection Lab
 Perch Dissection Lab Introduction: The fish in the class Osteichthyes have bony skeletons. There are three groups of the bony fish - -- ray-finned fish, lobe-finned fish, and the lung fish. The perch is
Perch Dissection Lab Introduction: The fish in the class Osteichthyes have bony skeletons. There are three groups of the bony fish - -- ray-finned fish, lobe-finned fish, and the lung fish. The perch is
FISH ANATOMY DIAGRAM AND QUESTIONS
 Name Block FISH ANATOMY DIAGRAM AND QUESTIONS External: 1. What percentage of fish are bony fish? 2. What is the operculum s function? 3. The nostrils are used for, not. 4. Which fins keeps the fish level
Name Block FISH ANATOMY DIAGRAM AND QUESTIONS External: 1. What percentage of fish are bony fish? 2. What is the operculum s function? 3. The nostrils are used for, not. 4. Which fins keeps the fish level
Trout Production at the Bobby N. Setzer Fish Hatchery
 Trout Production at the Bobby N. Setzer Fish Hatchery A informational slide show on how trout are reared. Prepared by NCWRC staff for the Trout in the Classroom program. NC Wildlife Resources Commission
Trout Production at the Bobby N. Setzer Fish Hatchery A informational slide show on how trout are reared. Prepared by NCWRC staff for the Trout in the Classroom program. NC Wildlife Resources Commission
MUDSKIPPER STANDARD OPERATING PROCEDURES
 MUDSKIPPER STANDARD OPERATING PROCEDURES April 1, 2003 - Revised Dec. 2005 HOUSING: Mudskippers may be held in a variety of tanks as long as they meet the following criteria: 1) The tank size is suitable
MUDSKIPPER STANDARD OPERATING PROCEDURES April 1, 2003 - Revised Dec. 2005 HOUSING: Mudskippers may be held in a variety of tanks as long as they meet the following criteria: 1) The tank size is suitable
548 Cyprinus carpio Koi Bacterial infection: Koi with many small white patches spread out over body caused by Columnaris Disease. (Photo M.
 547 Carassius auratus Goldfish Bacterial + Parasitic + Fungal: Goldfish with Ichthyobodo and also Columnaris Disease and Fungal infection on caudal area. c. Swollen belly/dropsy: see p. 148 (Ill. 551-558)
547 Carassius auratus Goldfish Bacterial + Parasitic + Fungal: Goldfish with Ichthyobodo and also Columnaris Disease and Fungal infection on caudal area. c. Swollen belly/dropsy: see p. 148 (Ill. 551-558)
Perch Dissection Lab
 Name: Block: Due Date: Perch Dissection Lab Background The fish in the class Osteichthyes have bony skeletons. There are three groups of the bony fish: ray-finned, lobe-finned, and the lungfish. The perch
Name: Block: Due Date: Perch Dissection Lab Background The fish in the class Osteichthyes have bony skeletons. There are three groups of the bony fish: ray-finned, lobe-finned, and the lungfish. The perch
PHASE I - The Effect of PrimaLac on Disease Resistance of Common Carp (Cyprinus carpio) Dr. Ra anan Ariav, Aqua-Vet Technologies Ltd.
 . PHASE I - The Effect of PrimaLac on Disease Resistance of Common Carp (Cyprinus carpio) Dr. Ra anan Ariav, Aqua-Vet Technologies Ltd. EXPERIMENTAL GOALS I GENERAL HEALTH: 1) Presence of disease causing
. PHASE I - The Effect of PrimaLac on Disease Resistance of Common Carp (Cyprinus carpio) Dr. Ra anan Ariav, Aqua-Vet Technologies Ltd. EXPERIMENTAL GOALS I GENERAL HEALTH: 1) Presence of disease causing
Invertebrate Chordates
 Invertebrate Chordates Chapter 11.2 - Fishes And Invertebrate Chordates... Invertebrate Chordates Lancelets Filter feed and spend most of their time buried in the sand. Only 2 invertebrate chordates Tunicates
Invertebrate Chordates Chapter 11.2 - Fishes And Invertebrate Chordates... Invertebrate Chordates Lancelets Filter feed and spend most of their time buried in the sand. Only 2 invertebrate chordates Tunicates
Point Rating: 3 Size: 10 mm Description: Caddisfly larvae are builders. They make sticky silk from their spit and use it to spin webs for trapping
 Point Rating: 3 Size: 10 mm Description: Caddisfly larvae are builders. They make sticky silk from their spit and use it to spin webs for trapping other insects. Other species use the silk as glue that
Point Rating: 3 Size: 10 mm Description: Caddisfly larvae are builders. They make sticky silk from their spit and use it to spin webs for trapping other insects. Other species use the silk as glue that
Environmental Engineering-I By Prof S S JAHAGIRDAR
 L- 28 Disinfection Part- I Environmental Engineering-I By Prof S S JAHAGIRDAR Contents Disinfection techniques- Ozonation, u/v radiation. Chemistry of chlorination, chlorine demand curve. Types of chlorination,
L- 28 Disinfection Part- I Environmental Engineering-I By Prof S S JAHAGIRDAR Contents Disinfection techniques- Ozonation, u/v radiation. Chemistry of chlorination, chlorine demand curve. Types of chlorination,
1 of 5 1/8/2017 8:09 PM
 Three s: Pools Aquariums[2] Ponds[4] Water that is especially cloudy or turbid can be unhealthy, regardless of whether that water is in a pool, aquarium, or pond. Different problems can cause high turbidity,
Three s: Pools Aquariums[2] Ponds[4] Water that is especially cloudy or turbid can be unhealthy, regardless of whether that water is in a pool, aquarium, or pond. Different problems can cause high turbidity,
Chapter 12 Marine Fishes
 Chapter 12 Marine Fishes Marine Protochordates Phylum: Chordata (nerve cord) Subphylum: Protochordata first chordates/primitive Primitive species of marine vertebrates Do not have advanced features (backbone)
Chapter 12 Marine Fishes Marine Protochordates Phylum: Chordata (nerve cord) Subphylum: Protochordata first chordates/primitive Primitive species of marine vertebrates Do not have advanced features (backbone)
EFFECT OF AFLATOXIN-CONTAMINATED FEEDS IN NILE TILAPIA OREOCHROMIS NILOTICUS L.
 EFFECT OF AFLATOXIN-CONTAMINATED FEEDS IN NILE TILAPIA OREOCHROMIS NILOTICUS L. A. G. Cagauan, R. H. Tayaban and R. M. Bartolome College of Fisheries/Freshwater Aquaculture Center Central Luzon State University
EFFECT OF AFLATOXIN-CONTAMINATED FEEDS IN NILE TILAPIA OREOCHROMIS NILOTICUS L. A. G. Cagauan, R. H. Tayaban and R. M. Bartolome College of Fisheries/Freshwater Aquaculture Center Central Luzon State University
Animal Systems: The Respiratory System
 Animal Systems: The Respiratory System Tissues, Organs, and Systems of Living Things Cells, Cell Division, and Animal Systems and Plant Systems Cell Specialization Human Systems The Digestive The Circulatory
Animal Systems: The Respiratory System Tissues, Organs, and Systems of Living Things Cells, Cell Division, and Animal Systems and Plant Systems Cell Specialization Human Systems The Digestive The Circulatory
Exploring the Aquaculture Industry
 Lesson B2 12 Exploring the Aquaculture Industry Unit B. Animal Science and the Industry Problem Area 2. Identifying and Understanding the Segments of the Animal Science Industry Lesson 12. Exploring the
Lesson B2 12 Exploring the Aquaculture Industry Unit B. Animal Science and the Industry Problem Area 2. Identifying and Understanding the Segments of the Animal Science Industry Lesson 12. Exploring the
Booklet translated by SREJ at CSDC 1
 Name: Gr. : Booklet translated by SREJ at CSDC 1 This is the beginning of a new project about Aquaculture. Before we start, I would like to see what you already know about the subject. Write all the words
Name: Gr. : Booklet translated by SREJ at CSDC 1 This is the beginning of a new project about Aquaculture. Before we start, I would like to see what you already know about the subject. Write all the words
Dead Perch Parts. ACADEMIC STANDARDS: 4 th Grade B. Know that living things are made up of parts that have specific functions.
 Dead Perch Parts Fish Anatomy Adapted from: An original Creek Connections activity created from the Fish Anatomy model. Grade Level: Intermediate or advanced Duration: 30 minutes Setting: classroom Summary:
Dead Perch Parts Fish Anatomy Adapted from: An original Creek Connections activity created from the Fish Anatomy model. Grade Level: Intermediate or advanced Duration: 30 minutes Setting: classroom Summary:
/20 Lab #5 The Dissection of the Perch
 /20 Lab #5 The Dissection of the Perch Perch are members of the class Osterichthyes, or bony fishes. They are found in many Canadian waters and are an excellent specimen of boney fish. Food enters the
/20 Lab #5 The Dissection of the Perch Perch are members of the class Osterichthyes, or bony fishes. They are found in many Canadian waters and are an excellent specimen of boney fish. Food enters the
Fish Dissection. 1. Place the preserved perch on the dissecting tray. Locate the head region. Examine the eyes. 6. What is the name of these flaps?
 Name: Date: Per: Introduction: Fish Dissection In this lab students will work within a group to learn from the dissection of a Perch. Dissection gives the student the opportunity to observe the location
Name: Date: Per: Introduction: Fish Dissection In this lab students will work within a group to learn from the dissection of a Perch. Dissection gives the student the opportunity to observe the location
What is a Fish? Fishes are aquatic vertebrates. Most fishes have paired fins, scales, and gills.
 What is a Fish? Fishes are aquatic vertebrates. Most fishes have paired fins, scales, and gills. Feeding and Digestion Every mode of feeding is seen in fish herbivores, carnivores, parasites, filter feeders,
What is a Fish? Fishes are aquatic vertebrates. Most fishes have paired fins, scales, and gills. Feeding and Digestion Every mode of feeding is seen in fish herbivores, carnivores, parasites, filter feeders,
What does the % represent on the beakers?
 DISSOLVED OXYGEN VIDEO FAQs What does the % represent on the beakers? What are the glass tubes to beakers for? How is the temperature being kept the same (at 5 o then 35 o )? What is salinity in parts
DISSOLVED OXYGEN VIDEO FAQs What does the % represent on the beakers? What are the glass tubes to beakers for? How is the temperature being kept the same (at 5 o then 35 o )? What is salinity in parts
FI F SH A ND F I F SHES E SUBPHYLUM VERTEBRATA
 FISH AND FISHES SUBPHYLUM VERTEBRATA 24,600 LIVING SPECIES FUN FACTS THAT S MORE THAN TERRESTRIAL ANIMALS! EARTH IS 70% WATER BUT LESS THAN.1% OF THE WATER ON THE PLANET IS FRESHWATER 41% OF FISH SPECIES
FISH AND FISHES SUBPHYLUM VERTEBRATA 24,600 LIVING SPECIES FUN FACTS THAT S MORE THAN TERRESTRIAL ANIMALS! EARTH IS 70% WATER BUT LESS THAN.1% OF THE WATER ON THE PLANET IS FRESHWATER 41% OF FISH SPECIES
Chapter 30 Nonvertebrate Chordates, Fishes, and Amphibians Name
 Chapter 30 Nonvertebrate Chordates, Fishes, and Amphibians Name Lab Dissecting a Perch Background Information Fish are the largest group of vertebrates found in fresh and salt water. In fact, over 25,000
Chapter 30 Nonvertebrate Chordates, Fishes, and Amphibians Name Lab Dissecting a Perch Background Information Fish are the largest group of vertebrates found in fresh and salt water. In fact, over 25,000
Overview of Recreational Pond Management
 Overview of Recreational Pond Management extension November 13 th 2013 Forrest Wynne State Extension Specialist for Aquaculture Kentucky State University Ponds are built for some of the following purposes:
Overview of Recreational Pond Management extension November 13 th 2013 Forrest Wynne State Extension Specialist for Aquaculture Kentucky State University Ponds are built for some of the following purposes:
Trout in the Classroom Open-Note Test
 Trout in the Classroom Open-Note Test DO NOT WRITE ON THIS PAPER: Please answer the following questions by marking your answers on the scantron 1. Pennsylvania s State Fish is A. Rainbow Trout C. Channel
Trout in the Classroom Open-Note Test DO NOT WRITE ON THIS PAPER: Please answer the following questions by marking your answers on the scantron 1. Pennsylvania s State Fish is A. Rainbow Trout C. Channel
Pool Water Chemistry Guide
 Pool Water Chemistry Guide water test The water chemistry information in this guide will help you keep your pool water clean and clear, swimmer safe, and plaster friendly. the clear choice in pool care
Pool Water Chemistry Guide water test The water chemistry information in this guide will help you keep your pool water clean and clear, swimmer safe, and plaster friendly. the clear choice in pool care
Chicken Farmers of Canada ANIMAL CARE PROGRAM UPDATE
 Chicken Farmers of Canada ANIMAL CARE PROGRAM January 2017 Animal Care Program (2009) Update New Highly Recommended Items The new Code of Practice for the Care and Handling of Hatching Eggs, Breeders,
Chicken Farmers of Canada ANIMAL CARE PROGRAM January 2017 Animal Care Program (2009) Update New Highly Recommended Items The new Code of Practice for the Care and Handling of Hatching Eggs, Breeders,
Unit 19.2: Fish. Vocabulary fish spawning swim bladder
 Unit 19.2: Fish Lesson Objectives Describe structure and function in fish. Explain how fish reproduce and develop. Give an overview of the five living classes of fish. Summarize the evolution of fish.
Unit 19.2: Fish Lesson Objectives Describe structure and function in fish. Explain how fish reproduce and develop. Give an overview of the five living classes of fish. Summarize the evolution of fish.
PROVINCIAL AQUACULTURE DEVELOPMENT PROJECT LAO PDR SUPPORT FOR TECHNICAL SERVICES. Guidelines for Broodstock and Hatchery Management
 FI:DP/LAO/97/007 STS - Field Document No. 5 PROVINCIAL AQUACULTURE DEVELOPMENT PROJECT LAO PDR SUPPORT FOR TECHNICAL SERVICES Guidelines for Broodstock and Hatchery Management Based on the work of Francois
FI:DP/LAO/97/007 STS - Field Document No. 5 PROVINCIAL AQUACULTURE DEVELOPMENT PROJECT LAO PDR SUPPORT FOR TECHNICAL SERVICES Guidelines for Broodstock and Hatchery Management Based on the work of Francois
AquaSPArkle Hot Tub and Spa Guide
 AquaSPArkle Hot Tub and Spa Guide Water Treatment Chemicals ESSENTIAL INFORMATION ON... Starting up Circulation and filtration Water testing Chemical water treatment Draining and refilling Working out
AquaSPArkle Hot Tub and Spa Guide Water Treatment Chemicals ESSENTIAL INFORMATION ON... Starting up Circulation and filtration Water testing Chemical water treatment Draining and refilling Working out
Key words: Seed, Inbreeding, Diseases and Brood Stock
 Present status of Parasitic and Bacterial diseases in Fresh Water Fish Seed Farms in East Godavari District, Andhra Pradesh P.Sandeep 1 *, B.Chamundeswari Devi 2 and K.Phaneendra Kumar 3 1 Scientist, Fisheries
Present status of Parasitic and Bacterial diseases in Fresh Water Fish Seed Farms in East Godavari District, Andhra Pradesh P.Sandeep 1 *, B.Chamundeswari Devi 2 and K.Phaneendra Kumar 3 1 Scientist, Fisheries
Platte River State Fish Hatchery Summary of 2012 Production and Operational Activities
 Platte River State Fish Hatchery Summary of 2012 Production and Operational Activities Antibiotic Use The antibiotic use at the Platte River State Fish Hatchery (Hatchery) in 2012 only focused on disease
Platte River State Fish Hatchery Summary of 2012 Production and Operational Activities Antibiotic Use The antibiotic use at the Platte River State Fish Hatchery (Hatchery) in 2012 only focused on disease
Section 15. Well Disinfection
 Section 15 Well Disinfection After constructing or repairing a well or pump, the entire well and pumping system must be disinfected in order to kill harmful microorganisms (germs and bacteria) that may
Section 15 Well Disinfection After constructing or repairing a well or pump, the entire well and pumping system must be disinfected in order to kill harmful microorganisms (germs and bacteria) that may
FIRST AID. Study Topics. At a minimum, the following topics are to be studied for the first aid exam.
 FIRST AID Study Topics At a minimum, the following topics are to be studied for the first aid exam. TOPIC Avoid getting air in stomach during rescue breathing Burns Kinds of Burns & Care Calling for Help
FIRST AID Study Topics At a minimum, the following topics are to be studied for the first aid exam. TOPIC Avoid getting air in stomach during rescue breathing Burns Kinds of Burns & Care Calling for Help
Dogfish Shark Dissection
 Dogfish Shark Dissection Name Date Period Fun Facts: Materials: The teeth of sharks are modified scales embedded in the skin of its mouth Sharks have pits on their face used to detect electric fields Sharks
Dogfish Shark Dissection Name Date Period Fun Facts: Materials: The teeth of sharks are modified scales embedded in the skin of its mouth Sharks have pits on their face used to detect electric fields Sharks
What is Saprolegnia? Saprolegnia is ubiquitous in fresh water ecosystems and is the main genus of water molds responsible for significant
 Aquatic fungi Nuvee Prapasarakul, D.V.M., Ph.D. Department of Veterinary Microbiology, Faculty of Veterinary Science, Chulalongkorn University Fungal Diseases of Fish, Shellfish and Amphibians Saprolegnia
Aquatic fungi Nuvee Prapasarakul, D.V.M., Ph.D. Department of Veterinary Microbiology, Faculty of Veterinary Science, Chulalongkorn University Fungal Diseases of Fish, Shellfish and Amphibians Saprolegnia
RECREATIONAL PONDS AND LAKES
 RECREATIONAL PONDS AND LAKES POND ECOLOGY AQUATIC PLANTS & FISH F.S. Conte Department of Animal Science University of California Davis Photos By Flickr AQUATIC PLANTS POND HEALTH Chemical Recycling Oxygen
RECREATIONAL PONDS AND LAKES POND ECOLOGY AQUATIC PLANTS & FISH F.S. Conte Department of Animal Science University of California Davis Photos By Flickr AQUATIC PLANTS POND HEALTH Chemical Recycling Oxygen
Fish Dissection. Background
 Fish Dissection The Fish Dissection program at Hatfield Marine Science Center is a 50-minute hands-on program for 4th through 12th grade students. Students will work in small groups as they examine a variety
Fish Dissection The Fish Dissection program at Hatfield Marine Science Center is a 50-minute hands-on program for 4th through 12th grade students. Students will work in small groups as they examine a variety
Fish Anatomy (male) Handout 3.1a. Body cavity lining. Air bladder. Pyloric caeca. Muscle tissue. Kidney. Dorsal fin. Adipose fin.
 65 Fish Anatomy (male) Handout 3.1a Body cavity lining Air bladder Gill cover Kidney Pyloric caeca Dorsal fin Muscle tissue Adipose fin Nostril Gall bladder Intestine Lateral line Mandible Maxilla Gill
65 Fish Anatomy (male) Handout 3.1a Body cavity lining Air bladder Gill cover Kidney Pyloric caeca Dorsal fin Muscle tissue Adipose fin Nostril Gall bladder Intestine Lateral line Mandible Maxilla Gill
Agnatha. Osteichthyes. Chordates: animals WITH a backbone. three classes of fish. Osteichthyes Boney fishes. Chondrichthyes Sharks
 Chordates: animals WITH a backbone three classes of fish Chondrichthyes Sharks Osteichthyes Boney fishes Agnathids Jawless fish Agnatha -Most primitive -Lack jaws -Round row of teeth Osteichthyes -Bony
Chordates: animals WITH a backbone three classes of fish Chondrichthyes Sharks Osteichthyes Boney fishes Agnathids Jawless fish Agnatha -Most primitive -Lack jaws -Round row of teeth Osteichthyes -Bony
For this assignment, use the Chapter about Fish that is found on me website, NOT YOUR BOOK.
 Name: For this assignment, use the Chapter about Fish that is found on me website, NOT YOUR BOOK. 1. Lampreys and hagfish lack (JAWS) and instead, have many rows of (TEETH ) 2. 3. The lamprey is a problem
Name: For this assignment, use the Chapter about Fish that is found on me website, NOT YOUR BOOK. 1. Lampreys and hagfish lack (JAWS) and instead, have many rows of (TEETH ) 2. 3. The lamprey is a problem
weber.cote Pool Paint
 weber.cote Pool Paint weber.cote Pool Paint weber.cote Pool Paint is a cement-based, integrally coloured, waterproof finish, specifically formulated for the revamping of marble plastered pools. Applied
weber.cote Pool Paint weber.cote Pool Paint weber.cote Pool Paint is a cement-based, integrally coloured, waterproof finish, specifically formulated for the revamping of marble plastered pools. Applied
males, but they are less susceptible to infectious diseases and
 General information- In nature, this specie's males have shorter fins that those we usually see in shops,these are called by the Thai "Plakad" (meaning- "Fighter"), and are used in Thailand for show-fights
General information- In nature, this specie's males have shorter fins that those we usually see in shops,these are called by the Thai "Plakad" (meaning- "Fighter"), and are used in Thailand for show-fights
Common Carp. Common Carp
 Common Carp This is one of the largest members of the minnow family, The carps closest look-alikes may be the bigmouth and smallmouth buffalos, which despite their resemblance to the carp, belong to an
Common Carp This is one of the largest members of the minnow family, The carps closest look-alikes may be the bigmouth and smallmouth buffalos, which despite their resemblance to the carp, belong to an
Taxonomy of Fishes. Chapter 18. I. SuperClass Agnatha. A. Class Myxini. Kingdom Animalia. The Fishes
 Taxonomy of Fishes Chapter 18 The Fishes Kingdom Animalia Phylum Chordata SuperClass Agnatha - jawless fish Class Chondrichthyes - cartilagenous fish Class Osteichthyes - bony fish I. SuperClass Agnatha
Taxonomy of Fishes Chapter 18 The Fishes Kingdom Animalia Phylum Chordata SuperClass Agnatha - jawless fish Class Chondrichthyes - cartilagenous fish Class Osteichthyes - bony fish I. SuperClass Agnatha
Fish Reproductive Biology
 Fish Reproductive Biology OSU South Centers Piketon, Ohio Maxwell.411@osu.edu Fish Facts 32,500 estimated species of fish in the world More than 15,000 freshwater fish species Freshwater may constitute
Fish Reproductive Biology OSU South Centers Piketon, Ohio Maxwell.411@osu.edu Fish Facts 32,500 estimated species of fish in the world More than 15,000 freshwater fish species Freshwater may constitute
PROTEC GILL. The fine art of gill protection
 The fine art of gill protection PROTEC GILL Protec Gill - designed to support gill health and recovery during disease, environmental and treatment challenges. GILLS AN IMPORTANT MULTI-FUNCTIONING ORGAN
The fine art of gill protection PROTEC GILL Protec Gill - designed to support gill health and recovery during disease, environmental and treatment challenges. GILLS AN IMPORTANT MULTI-FUNCTIONING ORGAN
Lecture Notes Chapter 14
 Lecture Notes Chapter 14 I. Chordata- phylum A. 3 subphyla 1. Urochordata 2. Cephalochordata 3. Vertebrata II. Characteristics of all Chordates (found during some part of the life cycle) A. All have a
Lecture Notes Chapter 14 I. Chordata- phylum A. 3 subphyla 1. Urochordata 2. Cephalochordata 3. Vertebrata II. Characteristics of all Chordates (found during some part of the life cycle) A. All have a
Chapter 25: Fishes 1
 Chapter 25: Fishes 1 2 Jawless Fishes (Agnatha) Cartilaginous Fishes (Chondrichthyes) Bony Fishes (Osteichthyes) Lamprey Whale shark Scorpion fish 3 Gills Single-loop Blood Circulation Vertebral column
Chapter 25: Fishes 1 2 Jawless Fishes (Agnatha) Cartilaginous Fishes (Chondrichthyes) Bony Fishes (Osteichthyes) Lamprey Whale shark Scorpion fish 3 Gills Single-loop Blood Circulation Vertebral column
Universal Precautions
 First Aid Safety First Aid is a matter of Personal Choice. The Company does not require employees to provide first aid for fellow employees. We have a medical provider close by to provide these services.
First Aid Safety First Aid is a matter of Personal Choice. The Company does not require employees to provide first aid for fellow employees. We have a medical provider close by to provide these services.
FOR LESS! The Secret to a Sparkling Pool and Patio. Enjoy a crystal clear pool with ARM & HAMMER Baking Soda
 The Secret to a Sparkling Pool and Patio FOR LESS! Enjoy a crystal clear pool with ARM & HAMMER Baking Soda ARM & HAMMER Pool Care and Outdoor Cleaning Guide 1 Pool Care: Made Easy Crystal Clear Opening
The Secret to a Sparkling Pool and Patio FOR LESS! Enjoy a crystal clear pool with ARM & HAMMER Baking Soda ARM & HAMMER Pool Care and Outdoor Cleaning Guide 1 Pool Care: Made Easy Crystal Clear Opening
1. Label a diagram of the respiratory system. Objective sheet 3 Notes
 1. Label a diagram of the respiratory system Objective sheet 3 Notes 2. Functions of the respiratory structures Name Description Function Nasal Cavity Trachea Bronchi (Singular Bronchus) Bronchioles Lungs
1. Label a diagram of the respiratory system Objective sheet 3 Notes 2. Functions of the respiratory structures Name Description Function Nasal Cavity Trachea Bronchi (Singular Bronchus) Bronchioles Lungs
5. Swimming pool season start Clean Up Procedure. 6. What is the condition of the pool water? 7. Season Start Clean Up Dose Chart.
 CONTENTS: 2. Introduction 3. How does the Aquatick 1 minute poolcare system work? 5. Swimming pool season start Clean Up Procedure. 6. What is the condition of the pool water? 7. Season Start Clean Up
CONTENTS: 2. Introduction 3. How does the Aquatick 1 minute poolcare system work? 5. Swimming pool season start Clean Up Procedure. 6. What is the condition of the pool water? 7. Season Start Clean Up
NEWS: 20% discount on service agreements signed before 1st March 2010
 Swimming Pool Maintenance Routine and charges Regular maintenance and consistent pool care is the best way to ensure a safe and healthy swimming environment. Although every pool is unique and has its own
Swimming Pool Maintenance Routine and charges Regular maintenance and consistent pool care is the best way to ensure a safe and healthy swimming environment. Although every pool is unique and has its own
Origin and Importance! ! Fish were the first vertebrates to appear on Earth about 500 million years ago.
 2/9/14 Origin and Importance Evolution Marine Fish Fish were the first vertebrates to appear on Earth about 500 million years ago. Fish are the most economically important organism and are a vital source
2/9/14 Origin and Importance Evolution Marine Fish Fish were the first vertebrates to appear on Earth about 500 million years ago. Fish are the most economically important organism and are a vital source
Fishes are vertebrates that have characteristics allowing them to live and reproduce in water.
 Section 1: are vertebrates that have characteristics allowing them to live and reproduce in water. K What I Know W What I Want to Find Out L What I Learned Essential Questions What are the features of
Section 1: are vertebrates that have characteristics allowing them to live and reproduce in water. K What I Know W What I Want to Find Out L What I Learned Essential Questions What are the features of
Paulding Soil & Water Conservation District Fish Sale Guide
 2018 Fish Sale Guide Phone: 419-399-4771 Patrick Troyer Education Specialist, Paulding SWCD Email: patrick.troyer@pauldingswcd.org Bluegill The bluegill is small freshwater fish normally measuring around
2018 Fish Sale Guide Phone: 419-399-4771 Patrick Troyer Education Specialist, Paulding SWCD Email: patrick.troyer@pauldingswcd.org Bluegill The bluegill is small freshwater fish normally measuring around
WHAT TO DO WITH ILL OR DEAD FROGS
 WHAT TO DO WITH ILL OR DEAD FROGS Lee Berger and Rick Speare School of Public Health, Tropical Medicine & Rehabilitation Sciences, James Cook University, Townsville, Qld, 4811 CONTENTS 1. Introduction...
WHAT TO DO WITH ILL OR DEAD FROGS Lee Berger and Rick Speare School of Public Health, Tropical Medicine & Rehabilitation Sciences, James Cook University, Townsville, Qld, 4811 CONTENTS 1. Introduction...
Stonefly. Gilled Snails
 Mid-Michigan Macroinvertebrates Identification Guide & Descriptions Mayfly Nymphs have 3 tail filaments occasionally 2 tail filaments never paddle or fan-like Feathery gills line the sides of the abdomen
Mid-Michigan Macroinvertebrates Identification Guide & Descriptions Mayfly Nymphs have 3 tail filaments occasionally 2 tail filaments never paddle or fan-like Feathery gills line the sides of the abdomen
Winter Culture of Caged Rainbow Trout in the South.
 Winter Culture of Caged Rainbow Trout in the South. Forrest Wynne, State Extension Specialist for Aquaculture, Kentucky State University Cooperative Extension Program, Graves County Extension Office, 251
Winter Culture of Caged Rainbow Trout in the South. Forrest Wynne, State Extension Specialist for Aquaculture, Kentucky State University Cooperative Extension Program, Graves County Extension Office, 251
Traditional Aquaculture
 Traditional Aquaculture Prehistoric origins of both agriculture and aquaculture as crafts Oxbow lakes Neolithic hunter-gatherers in the Nile seasonal collection of catfish from oxbow lakes Egyptian bas-relief
Traditional Aquaculture Prehistoric origins of both agriculture and aquaculture as crafts Oxbow lakes Neolithic hunter-gatherers in the Nile seasonal collection of catfish from oxbow lakes Egyptian bas-relief
Your guide to Pond Fish
 Full of advice for caring for your pet Your guide to Pond Fish Jollyes, only the best for you and your pets www.jollyes.co.uk Are you ready? Fish make great pets. They will add plenty of vibrant colour
Full of advice for caring for your pet Your guide to Pond Fish Jollyes, only the best for you and your pets www.jollyes.co.uk Are you ready? Fish make great pets. They will add plenty of vibrant colour
Are chloramines new? Why is my water supplier making the change to chloramines?
 In order to maintain quality water, the Central Coast Water Authority uses chloramines as disinfectant. Chloramines are a combination of chlorine and a small amount of ammonia. This web page provides answers
In order to maintain quality water, the Central Coast Water Authority uses chloramines as disinfectant. Chloramines are a combination of chlorine and a small amount of ammonia. This web page provides answers
Before we can understand what dropsy is we must first understand two natural occurring scientific processes namely, Osmosis and Diffusion.
 Dropsy (Ascites) By Duncan Griffiths Before we can understand what dropsy is we must first understand two natural occurring scientific processes namely, Osmosis and Diffusion. Osmosis is the movement of
Dropsy (Ascites) By Duncan Griffiths Before we can understand what dropsy is we must first understand two natural occurring scientific processes namely, Osmosis and Diffusion. Osmosis is the movement of
1 out of every 5,555 of drivers dies in car accidents 1 out of every 7692 pregnant women die from complications 1 out of every 116,666 skydives ended
 1 out of every 5,555 of drivers dies in car accidents 1 out of every 7692 pregnant women die from complications 1 out of every 116,666 skydives ended in a fatality in 2000 1 out of every 126,626 marathon
1 out of every 5,555 of drivers dies in car accidents 1 out of every 7692 pregnant women die from complications 1 out of every 116,666 skydives ended in a fatality in 2000 1 out of every 126,626 marathon
Focus Fish anatomy and acoustic technology
 NOAA Gray s Reef National Marine Sanctuary Acoustic Fish Tagging Project Activity: Make and Implant a tag (transmitter) into a Snapper or Grouper Species Then Dissect Fish Grades 9-12 Developed by C.J.
NOAA Gray s Reef National Marine Sanctuary Acoustic Fish Tagging Project Activity: Make and Implant a tag (transmitter) into a Snapper or Grouper Species Then Dissect Fish Grades 9-12 Developed by C.J.
Is a seahorse a fish, amphibian, or reptile? FISH
 Ch. 30 Loulousis Is a seahorse a fish, amphibian, or reptile? FISH Vertebral Column (Endoskeleton) Gills Single-loop circulation Kidneys Also share all the characteristics of chordates such as notochord,
Ch. 30 Loulousis Is a seahorse a fish, amphibian, or reptile? FISH Vertebral Column (Endoskeleton) Gills Single-loop circulation Kidneys Also share all the characteristics of chordates such as notochord,
FISHES. Agnatha Chondrichthyes Osteichthyes
 FISHES Agnatha Chondrichthyes Osteichthyes General Characteristics! Ectothermic! Vertebrates! Have scales! Swim with fins! Almost all exclusively aquatic! Filter oxygen from water over gills Classes of
FISHES Agnatha Chondrichthyes Osteichthyes General Characteristics! Ectothermic! Vertebrates! Have scales! Swim with fins! Almost all exclusively aquatic! Filter oxygen from water over gills Classes of
One of largest flukes: 30 x 13 mm
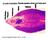 One of largest flukes: 30 x 13 mm The adult parasites reside in the intra-hepatic bile ducts, produce eggs, and the eggs are passed in the host's feces. After passing through the first intermediate host
One of largest flukes: 30 x 13 mm The adult parasites reside in the intra-hepatic bile ducts, produce eggs, and the eggs are passed in the host's feces. After passing through the first intermediate host
For pure and gentle pool and spa water
 Introducing the Aquablanc - Non Chlorine Range For pure and gentle pool and spa water Aquablanc Non Chlorine In conjunction with the Chemoform Group, Complete Pool Controls Limited offer an extensive range
Introducing the Aquablanc - Non Chlorine Range For pure and gentle pool and spa water Aquablanc Non Chlorine In conjunction with the Chemoform Group, Complete Pool Controls Limited offer an extensive range
Chapter 10 First Aid and Field Sanitation
 Review Questions Chapter 10 First Aid and Field Sanitation 1. True or False. The three reasons for performing first aid are to save lives, prevent further injuries, and prevent infection? 1. True 2. False
Review Questions Chapter 10 First Aid and Field Sanitation 1. True or False. The three reasons for performing first aid are to save lives, prevent further injuries, and prevent infection? 1. True 2. False
For this assignment, use the Chapter about Fish that is found on my website, NOT YOUR BOOK.
 Name: For this assignment, use the Chapter about Fish that is found on my website, NOT YOUR BOOK. 1. Lampreys and hagfish lack (1) and instead, have many rows of (2) 2. 3. The lamprey is a problem because
Name: For this assignment, use the Chapter about Fish that is found on my website, NOT YOUR BOOK. 1. Lampreys and hagfish lack (1) and instead, have many rows of (2) 2. 3. The lamprey is a problem because
2012 New York State Senior 4-H Horse Bowl Round 6
 One-On-One 1. C1 Q. What specific type of bacteria causes Tetanus? A. Clostridium tetani S. HIH 445-2 820/3 2. C2 Q. What is the common term for the deformity of the jaw referred to as prognathia? A. Monkey
One-On-One 1. C1 Q. What specific type of bacteria causes Tetanus? A. Clostridium tetani S. HIH 445-2 820/3 2. C2 Q. What is the common term for the deformity of the jaw referred to as prognathia? A. Monkey
Appendix F: Ecology F-5C Pile Installation Demonstration Project Analysis of Tissues of Fish Exposed to Pile Driving
 Appendix F: Ecology F-5C Pile Installation Demonstration Project Analysis of Tissues of Fish Exposed to Pile Driving Pile Installation Demonstration Project Analysis of Tissues of Fish Exposed to Pile
Appendix F: Ecology F-5C Pile Installation Demonstration Project Analysis of Tissues of Fish Exposed to Pile Driving Pile Installation Demonstration Project Analysis of Tissues of Fish Exposed to Pile
Examples of estuaries include bays, sounds, salt marshes, mangrove forests, mud flats, swamps, inlets, and sloughs.
 An estuary is a partially enclosed body of water where incoming seawater is mixed with fresh water coming from the land. Examples of estuaries include bays, sounds, salt marshes, mangrove forests, mud
An estuary is a partially enclosed body of water where incoming seawater is mixed with fresh water coming from the land. Examples of estuaries include bays, sounds, salt marshes, mangrove forests, mud
STRANGLES. What are the dangers?
 STRANGLES What is it? Strangles is caused by a bacteria. The full name of this bacteria is Streptococcus Equi subsp Equi. The bacteria infects the upper respiratory tract (e.g. around the head). It causes
STRANGLES What is it? Strangles is caused by a bacteria. The full name of this bacteria is Streptococcus Equi subsp Equi. The bacteria infects the upper respiratory tract (e.g. around the head). It causes
Importance of TOD. 1st question at most murder scenes: "How long has this person been dead?
 Death Importance of TOD 1st question at most murder scenes: "How long has this person been dead? It's crucial to know when the crime was committed. it can help narrow the search for a suspect or it can
Death Importance of TOD 1st question at most murder scenes: "How long has this person been dead? It's crucial to know when the crime was committed. it can help narrow the search for a suspect or it can
Teacher Background Information:
 Outcome: 6-1-03: Develop a system to classify common objects or living things into groups and subgroups, and explain the reasoning used in the system s development. Materials: highlighter or writing utensil
Outcome: 6-1-03: Develop a system to classify common objects or living things into groups and subgroups, and explain the reasoning used in the system s development. Materials: highlighter or writing utensil
Healthy Calves for 4-H Calf Club Projects and Ontario Calf Shows
 Healthy Calves for 4-H Calf Club Projects and Ontario Calf Shows Information compiled by the Ontario Association of Bovine Practitioners Calf Health Team including: Dr s Tim Henshaw (Eastgen), Christie
Healthy Calves for 4-H Calf Club Projects and Ontario Calf Shows Information compiled by the Ontario Association of Bovine Practitioners Calf Health Team including: Dr s Tim Henshaw (Eastgen), Christie
NO CHLORINE NO ODOUR NO SALT. The revolutionary chlorine and bromine free system for spas, swim spas and hot tubs USER GUIDE
 NO SALT NO CHLORINE NO ODOUR The revolutionary chlorine and bromine free system for spas, swim spas and hot tubs USER GUIDE CONGRATULATIONS for selecting the AQUASPA chlorine and bromine free sanitising
NO SALT NO CHLORINE NO ODOUR The revolutionary chlorine and bromine free system for spas, swim spas and hot tubs USER GUIDE CONGRATULATIONS for selecting the AQUASPA chlorine and bromine free sanitising
This workbook forms part of your assessment for this subject and MUST be completed and returned to your subject teacher.
 Name: Form: Date: Teacher: INSTRUCTIONS This workbook forms part of your assessment for this subject and MUST be completed and returned to your subject teacher. AQUACULTURE SKILLS CHECKLIST Clean and maintain
Name: Form: Date: Teacher: INSTRUCTIONS This workbook forms part of your assessment for this subject and MUST be completed and returned to your subject teacher. AQUACULTURE SKILLS CHECKLIST Clean and maintain
My Key to Manitoba Fish
 My Key to Manitoba Fish Outcome: 6-1-03: Develop a system to classify common objects or living things into groups and subgroups, and explain the reasoning used in the system s development. Materials: large
My Key to Manitoba Fish Outcome: 6-1-03: Develop a system to classify common objects or living things into groups and subgroups, and explain the reasoning used in the system s development. Materials: large
Farmed salmon/wild salmon Health interactions and challenges. Trygve T. Poppe, Norwegian University of Life Sciences NMBU
 Farmed salmon/wild salmon Health interactions and challenges Trygve T. Poppe, Norwegian University of Life Sciences NMBU Reykjavik, March 14 2014 About myself: Veterinarian from The Norwegian School of
Farmed salmon/wild salmon Health interactions and challenges Trygve T. Poppe, Norwegian University of Life Sciences NMBU Reykjavik, March 14 2014 About myself: Veterinarian from The Norwegian School of
Lake Butte des Morts Commercial Seining Project Report
 Lake Butte des Morts Commercial Seining Project Report Adam Nickel, Winnebago Gamefish (excluding sturgeon) Biologist, 22 December 2014 Conducting comprehensive fish surveys on the Upriver Lakes, including
Lake Butte des Morts Commercial Seining Project Report Adam Nickel, Winnebago Gamefish (excluding sturgeon) Biologist, 22 December 2014 Conducting comprehensive fish surveys on the Upriver Lakes, including
SNAIL MANAGEMENT IN CULTURE PONDS ROLE IN LIMITING GRUB ISSUES
 SNAIL MANAGEMENT IN CULTURE PONDS ROLE IN LIMITING GRUB ISSUES BIOLOGICAL PROFILE Internal parasites (endoparasites) Varying size, shape, and habitat Complex life cycles involving several hosts both sexual
SNAIL MANAGEMENT IN CULTURE PONDS ROLE IN LIMITING GRUB ISSUES BIOLOGICAL PROFILE Internal parasites (endoparasites) Varying size, shape, and habitat Complex life cycles involving several hosts both sexual
FAO SPECIES IDENTIFICATION SHEETS CONGIOPODIDAE* Horsefishes
 click for previous page CONGIO 1983 FAO SPECIES IDENTIFICATION SHEETS FISHING AREA 51 (W. Indian Ocean) CONGIOPODIDAE* Horsefishes Bottom fishes, with large heads and strongly compressed bodies. Snout
click for previous page CONGIO 1983 FAO SPECIES IDENTIFICATION SHEETS FISHING AREA 51 (W. Indian Ocean) CONGIOPODIDAE* Horsefishes Bottom fishes, with large heads and strongly compressed bodies. Snout
ANS 18 Test Yourself Sample Test Questions. 1. With respect to relative GLOBAL production tonnage, correctly order the following on the pyramid below:
 ANS 18 Test Yourself Sample Test Questions 1. With respect to relative GLOBAL production tonnage, correctly order the following on the pyramid below: a) Basa b) grass carp c) U.S. channel catfish d) abalone
ANS 18 Test Yourself Sample Test Questions 1. With respect to relative GLOBAL production tonnage, correctly order the following on the pyramid below: a) Basa b) grass carp c) U.S. channel catfish d) abalone
LESSON 8: COLD WEATHER INJURIES
 LESSON 8: COLD WEATHER INJURIES dehydration frostbite hypothermia insulate precipitation subcutaneous superficial CLOTHING When in cold weather, you should wear several layers of loose clothing and dress
LESSON 8: COLD WEATHER INJURIES dehydration frostbite hypothermia insulate precipitation subcutaneous superficial CLOTHING When in cold weather, you should wear several layers of loose clothing and dress
Oceans Humans both depend on it and threaten it with their activities
 Oceans Humans both depend on it and threaten it with their activities Oceans Water covers nearly ¾ of the Earth s surface More than 50% of the world s population lives within an hour of the coast Oceans
Oceans Humans both depend on it and threaten it with their activities Oceans Water covers nearly ¾ of the Earth s surface More than 50% of the world s population lives within an hour of the coast Oceans
