Asia contributes more than 90 percent of the world aquaculture. production, like other farming system. Aquaculture and fisheries is
|
|
|
- Kory Morton
- 6 years ago
- Views:
Transcription
1 CHAPTER-7 Fish Diseases 7.1. Introduction Asia contributes more than 90 percent of the world aquaculture production, like other farming system. Aquaculture and fisheries is plagued with disease problems resulting from its intensification and commercialization. Parallel conditions occur among infections to different kinds of culture facilities and different regions. These conditions affect host-parasite relationships as well as influencing methods of control or more properly management and they promote the development and execution of involving approaches to solve culture problems involving disease. Fish diseases have been classified according to their cause and general aspects of their etiology, epizootology and epidemiology. The physiological conditions of fish and their entire environment play an important role is connected with the course of diseases. Fish diseases are broadly classified into pathogenic and nonpathogenic diseases. Pathogenic diseases are virus, bacteria, fungi, protozoans, parasitic, crustaceans, helminthes and other parasites, Non-pathogenic diseases are hereditary, ecological, tumors, environmental and vitamin disturbances. The highest important is given to fish diseases which are highly contagious (Pathogenic). The host pathogen relationship generally undergoes several stages of development. The incubation period is when the pathogen multiplies, but the host does not yet show any signs of diseases. The incubation 178
2 period may range from a day or two for virulent pathogens, to prolonged periods of several months. After this asymptomatic period, specific and non-specific signs of disease become evident. Whether the host dies or survive will depend on its ability to resist the infection. During the epidemic, some of the infected fishes may not exhibit clinical signs at all and become carriers capable of transmitting the disease agent or initiating a future epizootic (Pilly, 1992). Disease is now a primary constraint to the culture of many aquatic species, impeding both economic and social development in many areas. This situation can be attributed to a variety of multifaceted and high interconnected factors such as the increased globalization of trade in live aquatic animals and their products; the intensification of aquaculture through the translocation of larvae and broodstock; the development and expansion of the fish trade (Subhasinghe et al., 2001). The increasing of production in culture system causes increases the potential for disease. The fishes are usually more physically and behaviorally stressed they have easier access to infectious agents that have interfered the system and the margin of error for maintaining good water quality is decreased. In each progressive type of system the stocking rate increases and the predicted production rate increases. At each step, new components added to achieve the production increase the risk for acquiring certain infectious and non-infectious conditions. The number and intensity of infectious disease agents occurring in the above types of grow out depend and on a number of factors. These 179
3 factors involve the type of facility, the source of quality of food, water, stock and the group of species of parasites. Some parasites requiring intermediate hosts are most common in a extensive ponds. Undrainable ponds in particular offer hardly scope for change of water, waste removal and aeration, thus gradually reaching a state which may be stressful for fishes. Stressful environment predispose fish to infectious diseases and thus understanding the process involved in fish diseases out breaks in vital for fish health management. In polyculture systems where several species of carps, catfishes and other species are also raised together, artificial feed acceptability is not uniform among all the species drug administration through feed to a particular species is not ensures. India is one of the best producers among the world freshwater fish producers with Indian major carp s viz. catla, rohu, mrigal and pangas is being the most preferred species (FAO, 2003). Pangas is a fast growing fish, which recently become a very popular food fish and valuable species in the South East Asia. In the present observations, major carps along with pangas in the experimental ponds taken for disease observations. Many workers have investigated on the fish diseases for the past decades. Gopalakrishnan (1961) reported that mass mortalities in India in major carp s catla, rohu and mrigala due to motile Aeromonods infections. Snieszko (1974) reported that disease signs caused by Aeromonas, in tropical fish, motile Aeromonas infections manifesting in all these forms have been studied by Gopalakrishnan, 180
4 (1961); Karunasagar et al., (1989); Carnahan, (1993); Joseph and Carnahan, (1994); Karunasagar et al., (1995). Motile Aeromonas are also the most commonly associated bacteria in case of epizootic ulcerative syndromes (Pal and Pradhan, 1990; Torreset et al., 1990; Lio-Po et al., 1991; Karunasagar and Karunasagar, 1994 and Karunasagar et al., 1995). Some of the workers have reported the epizootic ulcerative syndrome (EUS) is fungal associated syndrome with an invasive fungus, Aphonomyces invagis, the predominant species (Roberts et al., 1992, 1993; Willoughby et al., 1995). Further worked on the bacterial diseases of the fish by Leung et al., (1995), (1996); Karunasagar et al., (1995); Henderson et al., (1999); Austin and Austin, (1999). Viral diseases of fishes have been reported by Freiches et al., (1986), (1989); Kasoranchandra et al, (1991); Roberts et al., (1994) and Kanchanakhan, (1997). Fungal diseases are also described by Limsuwan and Chinabut, (1983); Srivastava, (1979); Roberts et al., (1993); Willoughby et al., (1995) and Chinabut et al., (1995). Further various types of diseases were studied by Qureshi et al., (1995); Rottwell et al., (1997); Watson et al., (1998); Bullard et al., (2000); Chang et al., (2002); Freyer and Hedrick, (2003); Wahli, (2005); Ogawa et al., (2006). In order for a disease to spread from either cultured fish to wild fish or vice-versa, certain criteria as reported by Olivier (2002) are essential; presence of pathogen both fish and water sources; presence of susceptible host; viability, in terms of number and longevity of 181
5 pathogen in the environment; viable infection route. However once the pathogen or disease agent is introduced and becomes established into the natural environment, there is little or no possibility for either treatment or eradication. Crustacean parasites are Argulus and Lernea, helminthes parasites are the dangerous parasites in the culture system. Protozoans are also cusses the most significant problems in the culture systems Materials and Methods The fishes were collected from weekly once in the experimental ponds of Devapudi village, Mudenepalli Mondal, Krishna district, Andhra Pradesh, India. The collected fishes were brought to the laboratory, external diseased characters were observed carefully by using magnify lens. Skin scarping and gill rashes observations were done to observe the external signs. The gill lamellae were mounted immediately with glycerin and observe diseased conditions. The skin was carefully observed for identification of ulcers and differentiation is done at the rate of superficial or deep ulcerations. Caudal, pelvic and pectoral fins were observed for colour, deformity and any other necroses. The stomach was observed any abnormal conditions were observed carefully by opening the fish by giving an incision through the vent. The internal organs like spleen, liver, intestine, gallbladder and gonads were carefully observed for any deformities or diseases. The weight of the fish was noted both diseased and normal healthy fish. After observation and identification of the disease, the diseased fish was fixed in 5% formalin and stored 182
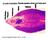
6 in laboratory for further study and water quality conditions observed regularly Observations: The infectious fish showed exopthalmic conditions of eyes (Fig. 7.1-A). The eyes are protruded out and external covering of the eye is damaged (Fig. 7.1-B, C). This condition is also known as pop eye in fish. Myxobolus infected fishes were found to be week, lethargic and crowding and they moves near to the water inlet and comes to the surface of the water. Gill filaments were covered with large number of cysts (Fig. 7.2-A, B, C, D and E). Hemorrhage was seen on the body surface as bluish red marks where several necrotic patches and skeletal deformities observed with Bacterial Hemorrhagic septicemia. Further catla, pangas also observed bacterial hemorrhagic septicemia (Fig 7.3 A, B). The skin is lost its original pink coloration, the characteristic features of pathogen and showed pale coloration of gills. The skin is exposed directly due to loss of scales. It showed multiple superficial ulcers. These ulcers at an advanced stage developed into deep scratches. The ulcers are surrounded by a ring of inflammatory necrotizing patricidal hemorrhage exceeds which often seen on the skin (Fig: 7.4-A, B). 183
7 Table: 7.1. Important bacterial diseases reported from Tropical fish Causative Agent Fish affected References Catla, Rohu, Mrigala Gopalakrishan, (1961) Karunasagar et al., (1986, 1989) Aeromonas hydrophila Aeromonas salmonicida Cat fish Djajadiredja et al., (1982) Crucian carp Miyazaki and Kage, (1985) Ornamental fish Hettiarchi and Cheng, (1994) Murrels, barbs, Pearl spot Common carp Tilapia Karunasagar and Karunasagar,(1994) Reddy et al., (1994) Commom carp Bootsma et al., (1977) Citrobacter fruendii Common carp Karunasagar et al.,(1992) Edwardsilella trada Flexibacter columnaris Flexibacter maritimus Flavovacterium spp. Eels Miyazaki and Egusa, (1976) Lia-Po et al., 91982) Seabass Chong and Cho, (1986) Red Sea Bream Wakabayashi et al., (1984) Salmonids Wakabayashi et al., (1980) Mycobacterium spp. Snakehead Adams et al., (1996) Pseudomonas spp. Eels Lia-Po et al., (1982) Staphylococcus aureus Silver fish Shaha and Tyagi, (1986) Seabass Kasorchandra and Boonyaratpalin, (1984) Chang and Chao, (1986) Grouper Chua and Teng, (1987) Vibrio spp. Chong and Chao, (1986) Milkfish Muroga et al., (1986) Snapper Leung et al., (1950) Eles Miyazaki et al., (1977) Rainbow trouts Sharma et al., (1995) Source: Karunasagar et al.,
8 Operculum and jaws are hyperemic, the fish are fins are frayed showing delicate, opaque, pale fin edge (Fig: 7.5-A). The base of the fins is inflamated. Hemorrhages at the base of pectoral, pelvic, dorsal and caudal fins (Fig: 7.5- B, C) are observed with inflammation. Hemorrhages at the base of pectoral fins with ulceration were observed. The gills showed paleness with pectoral hemorrhages. Gill lamellae are frayed and fragmented (Fig: 7.6-A, B, C).The entire brachial apertures are swollen with entire mucous secretions. The stomach is bulged with distended edematous abdomen (Fig: 7.7-A, B, C). Sometimes spine is abnormally curved due to which the fish lost its original shape. Infected fish showed a large polypodial mass in the buccal cavity which interfered and obstruct the respiratory movements due to which fish die of anoxia condition (Fig: 7.8-A). Red mouth disease was also observed in pangas (Fig 7.8 B). The infected fish showed less body weight than the normal in some cases; if the fish was cut ventrally and open for observation of viscera and edematous. Infected fish liver is pale yellowish in color. The stomach is totally destroyed with bacterial capsulation. The gall bladder is blackish colour and become enlarged (Fig 7.11 A). This fish are also showed deformed calcified gonads. Crustacean diseases like Argulus observed in rohu (Fig: 7.9-A, B, C), Lernea infection (Fig: 7.9-D, E) observed in fingerlings of mrigala. Important bacterial disease were reported from tropical fishes are shown in Table
9 7.4. Discussion Diseases of fish are one of the major constraints resulting from intensification of culture and may eventually become a limiting factor to the economics of a successful and sustainable culture. In the present study investigations, Myxobolous were seen in the gills of the mrigala (Fig. 7.2) and in the connective tissue with the ruptured cysts in the secondary lamellae of the gills of the rohu. As the gill lamellar surface was covered by ruptured cyst with necrotic tissues, the normal respiratory functions of the gill appeared to be impaired. Similar conditions observed by several workers. Sanullah and Ahmed (1980) described that the presence of Myxobolous cysts in the different locations of secondary lamellae with hyperplasic gill epithelial cells. Myxobolus infection in common carp is reported to results in lesions, inflammations, congestion and hyperplasia of the gills (Rukyani, 1990). Several damage of to the gills has been observed histological studies during Myxobolous infection of catla, common carp and gible carp (Dykova and Lom, 1988; Wang et al., 2003). Skeletal muscles have been reported to be a location for Myxobolus infection on the fishes is also reported to damage of spleen and gall bladder (Molnar et al., 2002). In the present study enlarged gall bladder observed in catla (Fig 7.11-A). The feeding behavior of the fishes and possibly very close contact of the spores with the fishes appear to be responsible for the infection. Further, these ponds were fertilized with organic manured before stocking of the fishes. Heavy organic loading and different 186
10 anthropogenic activities in the ponds may cause likely to be responsible for these infections (Chavda et al., 2010). Muscles also exhibited the destruction of Myxobolus, necrosis of connective tissues and presence of spores in the infected fishes. Myxozoan infection in gills, muscles and kidney in cyprinids were observed by Longshaw et al., (2005). In muscles spores were seen in the Coelozoic stage. The damage caused to muscle is also seen as necrotic patches and hemorrhages on the body surface. Enlargement of liver, spleen, stomach and gall bladder (Fig: 7.10 A, B) together with loss of cell structure are damage to the fibrilar connective tissue. Further indicates the response of spleen to invading organisms. The spleen is reported to be an integral component of the lymph reticular system playing a crucial role in generating a response to invading pathogens. A severe infection of Myxobolus hypothalamus was reported by Molnar et al., (2006). Myxobolus infection and its effect on catla were studied by Chavda et al., (2010). They concluded that anthropogenic activities in the pond, feeding behavior of the fishes and very close contact of spored with fishes appear to be responsible for Myxobolous infection. Tail rot and fin rot disease is a bacterial diseases of fresh water fish. It is widely distributed in tropical and temperate countries. The disease is characterized by grayish white spots on the body, skin erosion and fin or tail becomes ruptured. Most of the species are susceptible to those diseases and it may cause large mortalities (Frerichs and Roberts, 1989; Noga, 2000). In the present study, the 187
11 infection of tail and fin rot disease was observed in the catla (Fig 7.5- A), rohu (Fig. 7.5-C) and Pangas (Fig 7.4-A). Flavobacterium columnaris is recognised as etiological agent of tail and fin rot disease. It was formerly called Flavobacterium columnaris, but in 1996 it was transferred to the genus Flavobacterium (Decostere et al., 1997). Rahman et al., (2010) worked on the tail rot and fin rot disease occurred in catla (Catla catla) and koi (Anabus testudineus) concluded that the effect of fish shoed lesion and erosion on the tail and fins of fishes. Kubilay et al., (2008) observed and isolated of Flavobacterium columnaris from cultured rainbow trout (Oncorhynchus mysitus) fry in Turkey. Aas et al., (2001) worked in the ulcers and fin erosions of Gadus morhua due to pollution. Prearo et al., (2002) reported typical skin lesion and coetaneous ridding at the base of the fins and abdomen by Vibriosis in cultured brown trout. Stephen Smith (2005) observed localized skin fin lesions along with deep ulcerations and skin cysts. A relationship between fish pathogens or parasites and pollution that fish parasites could be used as environmental factors (Sures, 2004). In the present study revealed that an acute gill erosion with frayed gill lamellae with pale coloration observed in the pangas. Similar observations are followed by Voronin and Chernysheva (1998) observed acute Epitheliocystis infection in the gills of common carp with undifferentiated epithelial cells, chloride and mucous cells with necrotic gill tissue. Xu-Kuidong et al., (2000) observed that Trichodinosis in marine fish for caused serious physiological damage 188
12 of the gills in Lateolabrase japonicus. Epithelial damage of gills with mixed infection was caused by bronchial monogenea in Cachoma fish (Aragort et al., 2005). In the crustacean parasites, Lernea and Argulus causing considerable damage to culture and fishery in the Andhra Pradesh as well as India. Once fishes attached with Lernea are found aberrantly swimming with gliding movement against bottom or submerged substratum with marked emaciation and loss of weight. In severe infection fish appears sick, found floating on the surface of water with belly or abdomen facing up. Argulus are wide spread and harmful ectoparasite on a culture fishes; they damage the directly extracting tissue fluid and haemolymph. Ultimately lesions are formed in the body surface, fins, gills where secondary infection persists. Argulus often cause mortality of fish in culture ponds by puncturing the skin of the host and injecting a cytolytic toxin through their oral string. Further, Argulus signs of extreme irritation on the body, swim at high speed often jump out of the water and rub body surface against submerged objectives. Injuries due to Argulus infection are not only by attachment of parasites on the fish body but extensively by its feeding activities, which involves secretions and injection of digestive fluid and tearing tissue by buccal apparatus and appendages. A circular depression and red coloration on skin epithelium appears is prolonged attachment of parasites. The area of feeding becomes ulcerated and epithelial mucus cells increase in number and copious 189
13 mucus is prolonged. The toxic sections of buccal glands create severe irritation in the skin, scales loosen and ultimately they are lost. The present observations showed a distended edematous with inflamated vent. These results also similar with following observations; the abdominal distention due to liquid presence in the coelom with ulcers and eye loss due to Aeromonas infection in Sea bream (Bovo et al., 1995). Bacterial infection along with external signs of gold fish results abdominal swelling syndrome (Chansue et al., 1999). Acosta et al., (2000) observed that the swollen abdomen in brown trout due to Hofnio alvei infection. Rutilus nautilus heavily infected with Ligula intestinalis showing deformation of abdomen and fin displacement (Loot et al., 2001). Athanassopaulou et al., (2004) reported that the skeletal abnormalities in fish infected with nodovirus. Roberts and Peerson (2005) observed that the abdominal swelling and oedema of ventin Atlantic salmon, Salmo salar with Infectious Pancreatic Necrosis (IPN). In the present study, in pangas swellings on abdomen cause of Abdominal dropsy (Fig 7.7-A) In the present study identified a range of clinical signs of diseases and condition of Pangasius hypophthalmus culture along with major carp s catla, rohu and mrigala. The most prevalent symptom disease ws red spots, anal protrusion, diffused liver, spleen, gall bladder, tail and fin rot, pop eye, abdominal dropsy, gill rot and ulcerations (Fig: 7.7-A, B). Similar type of results was also observed by the following authors (Amin, 2000; Mazid, 2001 Faruk et al., 2004 a, b). 190
14 Fish culture is a significant socio-economic activity, especially rural communities, contribute to livelihood, food security and poverty alleviation through such mechanism as income generation, employment, services, use of local resources, diversified farming practices, domestic and international trade and other economic investment serving the sector (NACA/FAO, 2001; Edwards et al., 2002). Prevalence of fish disease has negative economy impact on fisheries and aquaculture by Worldbank in 1997 was in the range of $US 3 billion per annum (Subasinghe et al., 2001 a, 2001b). Infectious disease are constraining the development and sustainability of the fishes and aquaculture sector through direct production losses and increased operating costs and indirectly, through restriction on trade and impact on biodiversity. In adequate or poorly implemented bio-security measures have led to significant losses due to aquatic animal diseases in many countries around the world. Epizootic ulcerative syndrome is one of the dangerous diseases in culture ponds in costal districts of Andhra Pradesh. The disease occurs more than two decades in South, South-East Asia (Lilley et al., 1992; Roberts et al., 1994 and Das, 1997). In India the first outbreak of EUS occurred in the north-eastern state of Tripura during the monsoon months of September, 1988 following floods from Bangladesh since then it has spread to almost all the other states. By May, 1988, the disease had spread in to the northeastern states of India in channa species and by 1990 out breaks had occurred 191
15 throughout much of the country (Das, 1994). In Kerala also showed that EUS had completely distributed the inland fish market and the economic situation of small scale fishermen and fish vendors. It also affected small scale of aquaculturist. West Bengal also due to EUS, 73 percent of aquaculture operations were adversely affected in the form of mortalities in the ponds. Similar scenarios have been played out in many of the developing countries in South and South East Asia (Lilley et al., 1992; Roberts et al., 1994). In Andhra Pradesh EUS was first reported during October 1990 from Lake Kolleru of West Godavari and Krishna districts of all water areas including irrigation canals, drains, swamps and ponds. The outbreaks usually occurred between Octobers to December, predominantly during the post-monsoon months. The incidence was more in confined water (10-55%) than in river water (4-15%) (ACIAR 1997). Indian major carp rohu, suffer high mortalities as fingerlings (Roberts et al., 1989). In the present study pangas (Fig 7.4 A) also affected Epizootic ulcerative syndrome. Studies on the role of the various groups of pathogens associated with the disease have emphasized particularly the role of Aphanomyces spp. It was shown that a specific slow growing temperature sensitive species. Aphanomyces invaderis is the primary pathogen (Willoughby et al., 1995), later the species name was referred to A. invadans. Aphanomyces invadans is the causative fungus of EUS (Callinan et al., 1997; Lilley et al., 1997). Experimental injection challenges have shown that the pathogenic fungus, A. 192
16 invadans, is capable of causing lesions in rainbow trout at 18 0 C. But is less infective in stickleback, Gasterosteus aculeatus and roach, Rutilus rutilus at C (Khan et al., 1998). Tilapia, Oreochromis niloticus, milkfish (Chanos chanos), chines major carps and European carps are reported to be unaffected by EUS. It hs been shown that fungal growth was suppressed by an intensive inflammatory response in experimentally injected common carp, Cyprinus carpio with zoospores of Aphanomyces from MG and EUS out breaks respectively (Wada et al., 1996; Sharifpour, 1997). Economic losses from diseases are likely to increase as culture expands and intensifies. Assessing the impact of disease in culture systems is not easy, as acute losses are recognised and quantified. Chronic mortalities and poor growth caused by disease are generally not recognised. In order to quantify disease losses, and should be able to indentify disease as the reason for crop loss, slow growth or poor harvest (Mohan and Bhatta, 2002). For sustainable farming, the health management programme should focus on two main approaches like Ecosystem management: environmental management with optimum water, soil quality maintenance, with proper stocking density, devoid of stress to animals and Disease management. The main principles of fish disease control should be based on all-round prophylaxis and prevention is better than treatment approach as the treatment in such systems becomes impractical and uneconomic. 193
17 Disease have been a major constraint to sustainable management practices of the fishery sector, impeding both economic and socio-economic progress in many countries, fish health programme are, therefore, of primary importance for sustainable aquaculture development, production and trade for many countries. The risk of major diseases incursions newly emerging diseases will keep on threatening the sector, and unless appropriate health management measures are maintained and effectively implemented, the government and private sector will be faced with more costs in terms of production losses and the effors needed to contain and eradicate diseases, funds that would have been better spent in preventing their entry into the system. 194
Introduction. Case study 4 - Koi herpes virus. Major impact on commercial food carp production. History. KHV and other species
 Introduction Case study 4 - Koi herpes virus Dr. David Huchzermeyer Sterkspruit Veterinary Clinic Lydenburg Koi Herpesvirus is a recently emerged viral disease of carp (Cyprinus carpio) in all of its varieties
Introduction Case study 4 - Koi herpes virus Dr. David Huchzermeyer Sterkspruit Veterinary Clinic Lydenburg Koi Herpesvirus is a recently emerged viral disease of carp (Cyprinus carpio) in all of its varieties
EPIZOTIC ULCERATIVE SYNDROME K.D.A. HUCHZERMEYER Sterkspruit Veterinary Clinic, Lydenburg South Africa B.C.W. van der Waal University of Venda
 EPIZOTIC ULCERATIVE SYNDROME K.D.A. HUCHZERMEYER Sterkspruit Veterinary Clinic, Lydenburg South Africa B.C.W. van der Waal University of Venda Aphanomyces invadans Primary fish pathogen An invasive aquatic
EPIZOTIC ULCERATIVE SYNDROME K.D.A. HUCHZERMEYER Sterkspruit Veterinary Clinic, Lydenburg South Africa B.C.W. van der Waal University of Venda Aphanomyces invadans Primary fish pathogen An invasive aquatic
BACTERIAL CAUSES OF FIN ROT IN SOME FRESH WATER FISHES.
 BACTERIAL CAUSES OF FIN ROT IN SOME FRESH WATER FISHES. Enany,, M. E., El Sayed,, M. E., Diab.. A. S., Hassan,, S. M., and El Gamal,, R.M.** *Department of Microbiology, Faculty of Vet. Medicine, Suez
BACTERIAL CAUSES OF FIN ROT IN SOME FRESH WATER FISHES. Enany,, M. E., El Sayed,, M. E., Diab.. A. S., Hassan,, S. M., and El Gamal,, R.M.** *Department of Microbiology, Faculty of Vet. Medicine, Suez
Introduction. Major impact on commercial food carp production. Worldwide distribution. History. Spring viraemia of carp (SVC)
 Introduction KOI HERPESVIRUS: USING BIOSECURITY AND SURVEILLANCE TO PRODUCE DISEASE FREE FISH David Huchzermeyer Sterkspruit Veterinary Clinic Lydenburg Koi herpesvirus is a recently emerged viral disease
Introduction KOI HERPESVIRUS: USING BIOSECURITY AND SURVEILLANCE TO PRODUCE DISEASE FREE FISH David Huchzermeyer Sterkspruit Veterinary Clinic Lydenburg Koi herpesvirus is a recently emerged viral disease
Significant exotic diseases IHN 2011/09/23 EPIZOOTIC HAEMATOPOIETIC NECROSIS. David Huchzermeyer Sterkspruit Veterinary Clinic
 Significant exotic diseases EPIZOOTIC HAEMATOPOIETIC NECROSIS David Huchzermeyer Sterkspruit Veterinary Clinic Iridovirus. South eastern Australia. Apart from salmonids and redfin perch, guppies and mosquito
Significant exotic diseases EPIZOOTIC HAEMATOPOIETIC NECROSIS David Huchzermeyer Sterkspruit Veterinary Clinic Iridovirus. South eastern Australia. Apart from salmonids and redfin perch, guppies and mosquito
Pathogenicity of the bacterial isolate Aeromonas hydrophila to catfishes, carps and perch
 J. Bangladesh Agril. Univ. 10(1): 157 161, 2012 ISSN 1810-3030 Pathogenicity of the bacterial isolate Aeromonas hydrophila to catfishes, carps and perch M. J. A. Sarkar and M. M. Rashid Department of Aquaculture,
J. Bangladesh Agril. Univ. 10(1): 157 161, 2012 ISSN 1810-3030 Pathogenicity of the bacterial isolate Aeromonas hydrophila to catfishes, carps and perch M. J. A. Sarkar and M. M. Rashid Department of Aquaculture,
PHASE I - The Effect of PrimaLac on Disease Resistance of Common Carp (Cyprinus carpio) Dr. Ra anan Ariav, Aqua-Vet Technologies Ltd.
 . PHASE I - The Effect of PrimaLac on Disease Resistance of Common Carp (Cyprinus carpio) Dr. Ra anan Ariav, Aqua-Vet Technologies Ltd. EXPERIMENTAL GOALS I GENERAL HEALTH: 1) Presence of disease causing
. PHASE I - The Effect of PrimaLac on Disease Resistance of Common Carp (Cyprinus carpio) Dr. Ra anan Ariav, Aqua-Vet Technologies Ltd. EXPERIMENTAL GOALS I GENERAL HEALTH: 1) Presence of disease causing
Key words: Seed, Inbreeding, Diseases and Brood Stock
 Present status of Parasitic and Bacterial diseases in Fresh Water Fish Seed Farms in East Godavari District, Andhra Pradesh P.Sandeep 1 *, B.Chamundeswari Devi 2 and K.Phaneendra Kumar 3 1 Scientist, Fisheries
Present status of Parasitic and Bacterial diseases in Fresh Water Fish Seed Farms in East Godavari District, Andhra Pradesh P.Sandeep 1 *, B.Chamundeswari Devi 2 and K.Phaneendra Kumar 3 1 Scientist, Fisheries
AQUATIC ANIMAL BIOSECURITY: CHALLENGES AND SOLUTIONS. THE CASE OF KOI HERPESVIRUS
 AQUATIC ANIMAL BIOSECURITY: CHALLENGES AND SOLUTIONS. THE CASE OF KOI HERPESVIRUS David Huchzermeyer and Philippa Colly Sterkspruit Veterinary Clinic Introduction Koi herpesvirus is a recently emerged
AQUATIC ANIMAL BIOSECURITY: CHALLENGES AND SOLUTIONS. THE CASE OF KOI HERPESVIRUS David Huchzermeyer and Philippa Colly Sterkspruit Veterinary Clinic Introduction Koi herpesvirus is a recently emerged
Gill pathology of juvenile carps in nursery ponds
 Bangladesh}. Fish. Res., 2 (1 ), 1998 : 63-67 Gill pathology of juvenile carps in nursery ponds G.U. Ahmed, M.M. Haque and M.j. Hoque Faculty of Fisheries, Bangladesh Agricultural University Mymensing
Bangladesh}. Fish. Res., 2 (1 ), 1998 : 63-67 Gill pathology of juvenile carps in nursery ponds G.U. Ahmed, M.M. Haque and M.j. Hoque Faculty of Fisheries, Bangladesh Agricultural University Mymensing
Crayfish plague. White spot disease of shrimp. Withering disease of abalone. Infectious haematopoietic necrosis (IHN)
 Aquatic Animal Diseases and Biological Standards Dr. David Huchzermeyer Impact and consequences of fish translocations are reflected in the criteria for Aquatic Animal Disease listing Significant production
Aquatic Animal Diseases and Biological Standards Dr. David Huchzermeyer Impact and consequences of fish translocations are reflected in the criteria for Aquatic Animal Disease listing Significant production
Management and surveillance of fish diseases Fish disease is-the culmination of an interaction between the susceptible fish, the pathogen and the
 Management and surveillance of fish diseases Fish disease is-the culmination of an interaction between the susceptible fish, the pathogen and the environment. An optimum environment always helps in the
Management and surveillance of fish diseases Fish disease is-the culmination of an interaction between the susceptible fish, the pathogen and the environment. An optimum environment always helps in the
SUMMARY AND CONCLUSION. The main aim of the fish culture on commercial basis is to get
 CHAPTER-8 SUMMARY AND CONCLUSION The main aim of the fish culture on commercial basis is to get high and profitable fish yields. This can only be possible through sustainable management practices without
CHAPTER-8 SUMMARY AND CONCLUSION The main aim of the fish culture on commercial basis is to get high and profitable fish yields. This can only be possible through sustainable management practices without
Experimental infection of Aeromonas hydrophila in pangasius
 Progressive Agriculture 27 (3): 392-399, 2016 ISSN: 1017-8139 Experimental infection of Aeromonas hydrophila in pangasius J Sarker 1, MAR Faruk* Department of Aquaculture, Bangladesh Agricultural University,
Progressive Agriculture 27 (3): 392-399, 2016 ISSN: 1017-8139 Experimental infection of Aeromonas hydrophila in pangasius J Sarker 1, MAR Faruk* Department of Aquaculture, Bangladesh Agricultural University,
Common Diseases of Cultured Fish. Stephen Reichley, DVM, PhD, CertAqV Director of Fish Health
 Common Diseases of Cultured Fish Stephen Reichley, DVM, PhD, CertAqV Director of Fish Health Bacterial Diseases Edwardsiella ictaluri Enteric Septicemia of Catfish (ESC) Hole-in-the-head Gram-negative
Common Diseases of Cultured Fish Stephen Reichley, DVM, PhD, CertAqV Director of Fish Health Bacterial Diseases Edwardsiella ictaluri Enteric Septicemia of Catfish (ESC) Hole-in-the-head Gram-negative
Why is Aquaculture and Aquatic Animal Health so Important?
 OIE Workshop for Aquatic Animal Focal Points Dubrovnik, Croatia 16-18 November 2010 Why is Aquaculture and Aquatic Animal Health so Important? Barry Hill President OIE Aquatic Animal Health Standards Commission
OIE Workshop for Aquatic Animal Focal Points Dubrovnik, Croatia 16-18 November 2010 Why is Aquaculture and Aquatic Animal Health so Important? Barry Hill President OIE Aquatic Animal Health Standards Commission
Infection Experiments with Aphanomyces invadans in Advanced Fingerlings of Four Different Carp Species
 Infection Experiments with Aphanomyces invadans in Advanced Fingerlings of Four Different Carp Species P. K.PRADHAN 1, C.V. MOHAN 2, K. M. SHANKAR 3 and B. MOHANA KUMAR 4 1 College of Fisheries, Central
Infection Experiments with Aphanomyces invadans in Advanced Fingerlings of Four Different Carp Species P. K.PRADHAN 1, C.V. MOHAN 2, K. M. SHANKAR 3 and B. MOHANA KUMAR 4 1 College of Fisheries, Central
fish diseases in the European
 Survey & Diagnosis of listed fish diseases in the European Community 2009 Niels Jørgen Olesen, Nicole Nicolajsen 14 th Annual Meeting of the National Reference Laboratories for Fish Diseases Aarhus, Denmark,
Survey & Diagnosis of listed fish diseases in the European Community 2009 Niels Jørgen Olesen, Nicole Nicolajsen 14 th Annual Meeting of the National Reference Laboratories for Fish Diseases Aarhus, Denmark,
Appendix F: Ecology F-5C Pile Installation Demonstration Project Analysis of Tissues of Fish Exposed to Pile Driving
 Appendix F: Ecology F-5C Pile Installation Demonstration Project Analysis of Tissues of Fish Exposed to Pile Driving Pile Installation Demonstration Project Analysis of Tissues of Fish Exposed to Pile
Appendix F: Ecology F-5C Pile Installation Demonstration Project Analysis of Tissues of Fish Exposed to Pile Driving Pile Installation Demonstration Project Analysis of Tissues of Fish Exposed to Pile
Fish Dissection. 1. Place the preserved perch on the dissecting tray. Locate the head region. Examine the eyes. 6. What is the name of these flaps?
 Name: Date: Per: Introduction: Fish Dissection In this lab students will work within a group to learn from the dissection of a Perch. Dissection gives the student the opportunity to observe the location
Name: Date: Per: Introduction: Fish Dissection In this lab students will work within a group to learn from the dissection of a Perch. Dissection gives the student the opportunity to observe the location
AROWANA DISEASES AND CURES
 AROWANA DISEASES AND CURES IN NATURE, ALL CREATURES ARE CARRIERS OF DISEASES TO SOME EXTENT. SOME ARE INFECTIOUS, WHILE OTHERS ARE NOT. IT DEPENDS ON VARIOUS FACTORS AND ACTIVITIES. DIFFERENCES STILL EXIST
AROWANA DISEASES AND CURES IN NATURE, ALL CREATURES ARE CARRIERS OF DISEASES TO SOME EXTENT. SOME ARE INFECTIOUS, WHILE OTHERS ARE NOT. IT DEPENDS ON VARIOUS FACTORS AND ACTIVITIES. DIFFERENCES STILL EXIST
Managing a Quality Pond
 Managing a Quality Pond Gary Burtle The University of Georgia Successful Pond Management Set your GOAL Pond design Stocking Strategy Proper Nutrients Fish Growth and Harvest Successful Fish Reproduction
Managing a Quality Pond Gary Burtle The University of Georgia Successful Pond Management Set your GOAL Pond design Stocking Strategy Proper Nutrients Fish Growth and Harvest Successful Fish Reproduction
FISH ANATOMY DIAGRAM AND QUESTIONS
 Name Block FISH ANATOMY DIAGRAM AND QUESTIONS External: 1. What percentage of fish are bony fish? 2. What is the operculum s function? 3. The nostrils are used for, not. 4. Which fins keeps the fish level
Name Block FISH ANATOMY DIAGRAM AND QUESTIONS External: 1. What percentage of fish are bony fish? 2. What is the operculum s function? 3. The nostrils are used for, not. 4. Which fins keeps the fish level
Epizootic Ulcerative Syndrome
 Epizootic Ulcerative Syndrome Scientific Opinion adopted 15/9/11 http://www.efsa.europa.eu/en/scdocs/scdoc/2387.htm Ana Afonso - Animal Health and Welfare (AHAW) Background EUS Legislation EUS epidemiology:
Epizootic Ulcerative Syndrome Scientific Opinion adopted 15/9/11 http://www.efsa.europa.eu/en/scdocs/scdoc/2387.htm Ana Afonso - Animal Health and Welfare (AHAW) Background EUS Legislation EUS epidemiology:
1.2.7 Furunculosis. Emmett B. Shotts, Jr. College of Veterinary Medicine University of Georgia Athens, GA /
 1.2.7 Furunculosis - 1 1.2.7 Furunculosis Emmett B. Shotts, Jr. College of Veterinary Medicine University of Georgia Athens, GA 30602 404/542-5811 emshotts@alltel.net A. Name of Disease and Etiological
1.2.7 Furunculosis - 1 1.2.7 Furunculosis Emmett B. Shotts, Jr. College of Veterinary Medicine University of Georgia Athens, GA 30602 404/542-5811 emshotts@alltel.net A. Name of Disease and Etiological
Booklet translated by SREJ at CSDC 1
 Name: Gr. : Booklet translated by SREJ at CSDC 1 This is the beginning of a new project about Aquaculture. Before we start, I would like to see what you already know about the subject. Write all the words
Name: Gr. : Booklet translated by SREJ at CSDC 1 This is the beginning of a new project about Aquaculture. Before we start, I would like to see what you already know about the subject. Write all the words
Exploring the Aquaculture Industry
 Lesson B2 12 Exploring the Aquaculture Industry Unit B. Animal Science and the Industry Problem Area 2. Identifying and Understanding the Segments of the Animal Science Industry Lesson 12. Exploring the
Lesson B2 12 Exploring the Aquaculture Industry Unit B. Animal Science and the Industry Problem Area 2. Identifying and Understanding the Segments of the Animal Science Industry Lesson 12. Exploring the
Disease emergence and spread related to wildlife trade: aquatic species
 Disease emergence and spread related to wildlife trade: aquatic species Barry Hill President, OIE Aquatic Animal Health Standards Commission Centre for Environment, Fisheries and Aquaculture Science (Cefas)
Disease emergence and spread related to wildlife trade: aquatic species Barry Hill President, OIE Aquatic Animal Health Standards Commission Centre for Environment, Fisheries and Aquaculture Science (Cefas)
Distribution, prevalence and intensity of protozoan and monogenean parasites of carp fingerlings in selected nursery ponds
 Bangladesh J. Fish. Res., 11(1), 2007: 37-44 BFRI Distribution, prevalence and intensity of protozoan and monogenean of carp fingerlings in selected nursery ponds M.K. Hossain, A.T.A. Ahmed, M.H. Khan*J,
Bangladesh J. Fish. Res., 11(1), 2007: 37-44 BFRI Distribution, prevalence and intensity of protozoan and monogenean of carp fingerlings in selected nursery ponds M.K. Hossain, A.T.A. Ahmed, M.H. Khan*J,
Department of Aquaculture, Faculty of Fisheries, Bangladesh Agricultural University, Mymensingh-2202, Bangladesh
 Asian J. Med. Biol. Res. 2015, 1 (1), 95-102 Asian Journal of Medical and Biological Research ISSN 2411-4472 www.ebupress.com/journal/ajmbr Article Seasonal variation of water quality parameters, clinical
Asian J. Med. Biol. Res. 2015, 1 (1), 95-102 Asian Journal of Medical and Biological Research ISSN 2411-4472 www.ebupress.com/journal/ajmbr Article Seasonal variation of water quality parameters, clinical
AQUACULTURE STATUS OF VIETNAM Han Mai Huong, Cairo, November 2011
 AQUACULTURE STATUS OF VIETNAM Han Mai Huong, Cairo, November 2011 VIETNAM Mainland Territory: 331,211.6 sq. km. Lying on the eastern part of the Indochinese peninsula, Vietnam is a strip of land shaped
AQUACULTURE STATUS OF VIETNAM Han Mai Huong, Cairo, November 2011 VIETNAM Mainland Territory: 331,211.6 sq. km. Lying on the eastern part of the Indochinese peninsula, Vietnam is a strip of land shaped
INTENSIVE MONOCULTURE OF STRIPED CATFISH, (Pangasianodon
 INTENSIVE MONOCULTURE OF STRIPED CATFISH, (Pangasianodon hypophthalmus) IN THE MEKONG DELTA, VIETNAM This project is the outcome of a group efforts to whom credit and technical responsibility goes. The
INTENSIVE MONOCULTURE OF STRIPED CATFISH, (Pangasianodon hypophthalmus) IN THE MEKONG DELTA, VIETNAM This project is the outcome of a group efforts to whom credit and technical responsibility goes. The
Fish. Water Dwelling Animals
 Fish Water Dwelling Animals Class Agnatha (Jawless fish) They are believed to be the most primitive and oldest vertebrates. Lamprey and hagfish are the only 2 living members of this class and are placed
Fish Water Dwelling Animals Class Agnatha (Jawless fish) They are believed to be the most primitive and oldest vertebrates. Lamprey and hagfish are the only 2 living members of this class and are placed
PROTEC GILL. The fine art of gill protection
 The fine art of gill protection PROTEC GILL Protec Gill - designed to support gill health and recovery during disease, environmental and treatment challenges. GILLS AN IMPORTANT MULTI-FUNCTIONING ORGAN
The fine art of gill protection PROTEC GILL Protec Gill - designed to support gill health and recovery during disease, environmental and treatment challenges. GILLS AN IMPORTANT MULTI-FUNCTIONING ORGAN
6/2/2014. Carps. Common Carp. Silver Carp. Rohu. Bighead Carp. Other introductions: Gourami Dojo Golden apple snail Pacu Mosquito fish
 The Philippine aquaculture has been enhanced by species introduction. Major aquaculture commodities are exotics Exotic species are organisms transported outside their natural habitats Oreochromis niloticus
The Philippine aquaculture has been enhanced by species introduction. Major aquaculture commodities are exotics Exotic species are organisms transported outside their natural habitats Oreochromis niloticus
Ecological interactions between parasites and wildlife
 Ecological interactions between parasites and wildlife Case study: salmon farms, wild salmon, and sea lice Sean Godwin November 21, 2018 Guest lecture #3 Introduction to Ecology Outline 1. Pathogens and
Ecological interactions between parasites and wildlife Case study: salmon farms, wild salmon, and sea lice Sean Godwin November 21, 2018 Guest lecture #3 Introduction to Ecology Outline 1. Pathogens and
Interactions Between Wild and Farmed Salmonids in Southern British Columbia: Pathogen Transfer
 Interactions Between Wild and Farmed Salmonids in Southern British Columbia: Pathogen Transfer Stewart Johnson, Michael Foreman, Kyle Garver Brent Hargreaves, Simon R.M. Jones and Chrys Neville PICES AGM
Interactions Between Wild and Farmed Salmonids in Southern British Columbia: Pathogen Transfer Stewart Johnson, Michael Foreman, Kyle Garver Brent Hargreaves, Simon R.M. Jones and Chrys Neville PICES AGM
PATHOGENICITY OF MYXOBOLUS INFECTION AND ITS EFFECT ON PROTEIN EXPRESSION IN CATLA CATLA IN CENTRAL GUJARAT REGION
 Journal of Cell and Tissue Research Vol. 10(1) 2157-2164 (2010) ISSN: 0974-0910(Available online at www.tcrjournals.com) Original Article PATHOGENICITY OF MYXOBOLUS INFECTION AND ITS EFFECT ON PROTEIN
Journal of Cell and Tissue Research Vol. 10(1) 2157-2164 (2010) ISSN: 0974-0910(Available online at www.tcrjournals.com) Original Article PATHOGENICITY OF MYXOBOLUS INFECTION AND ITS EFFECT ON PROTEIN
Aquatic Animal Health export requirements
 Aquatic Animal Health export requirements Aquatic State Veterinarian Sasha Saugh Tel: 021 430 7052 Email: SashaS@daff.gov.za FISH DISEASES: Diseases Epizootic haematopoietic necrosis (EHN)- Rainbow trout
Aquatic Animal Health export requirements Aquatic State Veterinarian Sasha Saugh Tel: 021 430 7052 Email: SashaS@daff.gov.za FISH DISEASES: Diseases Epizootic haematopoietic necrosis (EHN)- Rainbow trout
Growth performance evaluation of genetically improved silver barb (Barbonymus gonionotus Bleeker) in different agro-ecological zones in Bangladesh
 Bangladesh]. Fish. Res., 12 (2), 2008: 129-134 Growth performance evaluation of genetically improved silver barb (Barbonymus gonionotus Bleeker) in different agro-ecological zones in Bangladesh A.H.M.
Bangladesh]. Fish. Res., 12 (2), 2008: 129-134 Growth performance evaluation of genetically improved silver barb (Barbonymus gonionotus Bleeker) in different agro-ecological zones in Bangladesh A.H.M.
Impact of introduction of culture based fisheries on fish production in two perennial reservoirs in Sri Lanka
 2015; 2(4S): 05-09 ISSN: 2347-5129 IJFAS 2015; 2(4S): 05-09 2015 IJFAS www.fisheriesjournal.com Received: 07-01-2015 Accepted: 02-02-2015 Pushpalatha K.B.C Fernando W.A.J.R Chandrasoma J. Correspondence
2015; 2(4S): 05-09 ISSN: 2347-5129 IJFAS 2015; 2(4S): 05-09 2015 IJFAS www.fisheriesjournal.com Received: 07-01-2015 Accepted: 02-02-2015 Pushpalatha K.B.C Fernando W.A.J.R Chandrasoma J. Correspondence
HATCHERY QUALITY ASSURANCE PROGRAM
 HATCHERY QUALITY ASSURANCE PROGRAM for MURRAY COD, GOLDEN PERCH and SILVER PERCH Stuart J. Rowland and Patrick Tully Murray cod Maccullochella peelii peelii Golden perch Macquaria ambigua Silver perch
HATCHERY QUALITY ASSURANCE PROGRAM for MURRAY COD, GOLDEN PERCH and SILVER PERCH Stuart J. Rowland and Patrick Tully Murray cod Maccullochella peelii peelii Golden perch Macquaria ambigua Silver perch
Perch Dissection Lab
 Perch Dissection Lab Introduction: The fish in the class Osteichthyes have bony skeletons. There are three groups of the bony fish - -- ray-finned fish, lobe-finned fish, and the lung fish. The perch is
Perch Dissection Lab Introduction: The fish in the class Osteichthyes have bony skeletons. There are three groups of the bony fish - -- ray-finned fish, lobe-finned fish, and the lung fish. The perch is
Branchiuran Fish Louse Disease
 3.2.15 Branchiuran Fish Louse Disease - 1 3.2.15 Branchiuran Fish Louse Disease Bill Hogans Atlantic Reference Center Huntsman Marine Science Center St. Andrews, New Brunswick E0C 2X0 Canada 506/529-8895
3.2.15 Branchiuran Fish Louse Disease - 1 3.2.15 Branchiuran Fish Louse Disease Bill Hogans Atlantic Reference Center Huntsman Marine Science Center St. Andrews, New Brunswick E0C 2X0 Canada 506/529-8895
COMMON CARP. Welcome to Expert Topic. Each issue will take an in-depth look at a particular species and how its feed is managed.
 COMMON CARP Welcome to Expert Topic. Each issue will take an in-depth look at a particular species and how its feed is managed. 40 March April 2016 - International Aquafeed 2 1 Israel Czech Republic 1
COMMON CARP Welcome to Expert Topic. Each issue will take an in-depth look at a particular species and how its feed is managed. 40 March April 2016 - International Aquafeed 2 1 Israel Czech Republic 1
Chapter 30 Nonvertebrate Chordates, Fishes, and Amphibians Name
 Chapter 30 Nonvertebrate Chordates, Fishes, and Amphibians Name Lab Dissecting a Perch Background Information Fish are the largest group of vertebrates found in fresh and salt water. In fact, over 25,000
Chapter 30 Nonvertebrate Chordates, Fishes, and Amphibians Name Lab Dissecting a Perch Background Information Fish are the largest group of vertebrates found in fresh and salt water. In fact, over 25,000
STUDY PERFORMANCE REPORT
 STUDY PERFORMANCE REPORT State: Michigan Project No.: F-80-R-7 Study No.: 230654 Title: Evaluation of brown trout and steelhead competitive interactions in Hunt Creek, Michigan. Period Covered: October
STUDY PERFORMANCE REPORT State: Michigan Project No.: F-80-R-7 Study No.: 230654 Title: Evaluation of brown trout and steelhead competitive interactions in Hunt Creek, Michigan. Period Covered: October
EFFECT OF AFLATOXIN-CONTAMINATED FEEDS IN NILE TILAPIA OREOCHROMIS NILOTICUS L.
 EFFECT OF AFLATOXIN-CONTAMINATED FEEDS IN NILE TILAPIA OREOCHROMIS NILOTICUS L. A. G. Cagauan, R. H. Tayaban and R. M. Bartolome College of Fisheries/Freshwater Aquaculture Center Central Luzon State University
EFFECT OF AFLATOXIN-CONTAMINATED FEEDS IN NILE TILAPIA OREOCHROMIS NILOTICUS L. A. G. Cagauan, R. H. Tayaban and R. M. Bartolome College of Fisheries/Freshwater Aquaculture Center Central Luzon State University
Thailand s Current Quarantine Status on Aquatic Animal Diseases
 水研センター研報, 別冊第 2 号,4-4, 平成 17 年 Bull. Fish. Res. Agen. Supplement No. 2, 41-45, 2005 Thailand s Current Quarantine Status on Aquatic Animal Diseases Somkiat KANCHANAKHAN Inland Aquatic Animal Health Research
水研センター研報, 別冊第 2 号,4-4, 平成 17 年 Bull. Fish. Res. Agen. Supplement No. 2, 41-45, 2005 Thailand s Current Quarantine Status on Aquatic Animal Diseases Somkiat KANCHANAKHAN Inland Aquatic Animal Health Research
Internal Anatomy of Fish
 Internal Anatomy of Fish The Systems of a Fish Skeletal System Muscular System Respiratory System Digestive System Circulatory System Nervous System Reproductive System Special Organs Skeletal System
Internal Anatomy of Fish The Systems of a Fish Skeletal System Muscular System Respiratory System Digestive System Circulatory System Nervous System Reproductive System Special Organs Skeletal System
ORGANIC REFORM- IMPLEMENTATION PLANNING FOR AQUACULTURE. Lorella de la Cruz Iglesias Unit A2 DG Maritime Affairs and Fisheries
 ORGANIC REFORM- IMPLEMENTATION PLANNING FOR AQUACULTURE Lorella de la Cruz Iglesias Unit A2 DG Maritime Affairs and Fisheries 1 Article 15(3) of new Regulation Production rules for algae and aquaculture
ORGANIC REFORM- IMPLEMENTATION PLANNING FOR AQUACULTURE Lorella de la Cruz Iglesias Unit A2 DG Maritime Affairs and Fisheries 1 Article 15(3) of new Regulation Production rules for algae and aquaculture
TOWARDS ECOSYSTEM BASED MANAGEMENT OF FISHERIES: WHAT ROLE CAN ECONOMICS (AQUACULTURE) PLAY? PRESENTER: MR. ALAGIE SILLAH THE GAMBIA
 TOWARDS ECOSYSTEM BASED MANAGEMENT OF FISHERIES: WHAT ROLE CAN ECONOMICS (AQUACULTURE) PLAY? PRESENTER: MR. ALAGIE SILLAH THE GAMBIA HOW WOULD AQUACULTURE INCREASE FISH CONSUMPTION IN THE GAMBIA Capture
TOWARDS ECOSYSTEM BASED MANAGEMENT OF FISHERIES: WHAT ROLE CAN ECONOMICS (AQUACULTURE) PLAY? PRESENTER: MR. ALAGIE SILLAH THE GAMBIA HOW WOULD AQUACULTURE INCREASE FISH CONSUMPTION IN THE GAMBIA Capture
What is Saprolegnia? Saprolegnia is ubiquitous in fresh water ecosystems and is the main genus of water molds responsible for significant
 Aquatic fungi Nuvee Prapasarakul, D.V.M., Ph.D. Department of Veterinary Microbiology, Faculty of Veterinary Science, Chulalongkorn University Fungal Diseases of Fish, Shellfish and Amphibians Saprolegnia
Aquatic fungi Nuvee Prapasarakul, D.V.M., Ph.D. Department of Veterinary Microbiology, Faculty of Veterinary Science, Chulalongkorn University Fungal Diseases of Fish, Shellfish and Amphibians Saprolegnia
Focus Fish anatomy and acoustic technology
 NOAA Gray s Reef National Marine Sanctuary Acoustic Fish Tagging Project Activity: Make and Implant a tag (transmitter) into a Snapper or Grouper Species Then Dissect Fish Grades 9-12 Developed by C.J.
NOAA Gray s Reef National Marine Sanctuary Acoustic Fish Tagging Project Activity: Make and Implant a tag (transmitter) into a Snapper or Grouper Species Then Dissect Fish Grades 9-12 Developed by C.J.
Current status of transboundary fish diseases in Myanmar: Occurrence, surveillance, research and training
 Current status of transboundary fish diseases in Myanmar: Occurrence, surveillance, research and training Saw, New Year Date published: 2004 To cite this document : Saw, N. Y. (2004). Current status of
Current status of transboundary fish diseases in Myanmar: Occurrence, surveillance, research and training Saw, New Year Date published: 2004 To cite this document : Saw, N. Y. (2004). Current status of
Perch Dissection Lab
 Name: Block: Due Date: Perch Dissection Lab Background The fish in the class Osteichthyes have bony skeletons. There are three groups of the bony fish: ray-finned, lobe-finned, and the lungfish. The perch
Name: Block: Due Date: Perch Dissection Lab Background The fish in the class Osteichthyes have bony skeletons. There are three groups of the bony fish: ray-finned, lobe-finned, and the lungfish. The perch
PROVINCIAL AQUACULTURE DEVELOPMENT PROJECT LAO PDR SUPPORT FOR TECHNICAL SERVICES. Guidelines for Broodstock and Hatchery Management
 FI:DP/LAO/97/007 STS - Field Document No. 5 PROVINCIAL AQUACULTURE DEVELOPMENT PROJECT LAO PDR SUPPORT FOR TECHNICAL SERVICES Guidelines for Broodstock and Hatchery Management Based on the work of Francois
FI:DP/LAO/97/007 STS - Field Document No. 5 PROVINCIAL AQUACULTURE DEVELOPMENT PROJECT LAO PDR SUPPORT FOR TECHNICAL SERVICES Guidelines for Broodstock and Hatchery Management Based on the work of Francois
Brackishwater Culture of Tilapia in the Philippines: An Assessment
 Brackishwater Culture of Tilapia in the Philippines: An Assessment Rafael D. Guerrero III Philippine Council for Aquatic and Marine Research and Development Los Baños,, Laguna 4030 Luzviminda A. Guerrero
Brackishwater Culture of Tilapia in the Philippines: An Assessment Rafael D. Guerrero III Philippine Council for Aquatic and Marine Research and Development Los Baños,, Laguna 4030 Luzviminda A. Guerrero
Jerri Bartholomew and Sarah Bjork*
 The Effects of Flow on the Salmon Parasite Ceratomyxa shasta : Establishing Baseline Information For Assessment of Flow Management Alternatives For Mitigating Effects of Myxozoan Pathogens in the Klamath
The Effects of Flow on the Salmon Parasite Ceratomyxa shasta : Establishing Baseline Information For Assessment of Flow Management Alternatives For Mitigating Effects of Myxozoan Pathogens in the Klamath
Fish Anatomy (male) Handout 3.1a. Body cavity lining. Air bladder. Pyloric caeca. Muscle tissue. Kidney. Dorsal fin. Adipose fin.
 65 Fish Anatomy (male) Handout 3.1a Body cavity lining Air bladder Gill cover Kidney Pyloric caeca Dorsal fin Muscle tissue Adipose fin Nostril Gall bladder Intestine Lateral line Mandible Maxilla Gill
65 Fish Anatomy (male) Handout 3.1a Body cavity lining Air bladder Gill cover Kidney Pyloric caeca Dorsal fin Muscle tissue Adipose fin Nostril Gall bladder Intestine Lateral line Mandible Maxilla Gill
Pop Quiz. What produces mucus, HCl and pepsinogen in the stomach? List a water soluable vitamin What is a ruminant stomach?
 Pop Quiz What produces mucus, HCl and pepsinogen in the stomach? List a water soluable vitamin What is a ruminant stomach? Respiratory System Review Cellular respiration: obtain glucose and oxygen, get
Pop Quiz What produces mucus, HCl and pepsinogen in the stomach? List a water soluable vitamin What is a ruminant stomach? Respiratory System Review Cellular respiration: obtain glucose and oxygen, get
Dead Perch Parts. ACADEMIC STANDARDS: 4 th Grade B. Know that living things are made up of parts that have specific functions.
 Dead Perch Parts Fish Anatomy Adapted from: An original Creek Connections activity created from the Fish Anatomy model. Grade Level: Intermediate or advanced Duration: 30 minutes Setting: classroom Summary:
Dead Perch Parts Fish Anatomy Adapted from: An original Creek Connections activity created from the Fish Anatomy model. Grade Level: Intermediate or advanced Duration: 30 minutes Setting: classroom Summary:
One of largest flukes: 30 x 13 mm
 One of largest flukes: 30 x 13 mm The adult parasites reside in the intra-hepatic bile ducts, produce eggs, and the eggs are passed in the host's feces. After passing through the first intermediate host
One of largest flukes: 30 x 13 mm The adult parasites reside in the intra-hepatic bile ducts, produce eggs, and the eggs are passed in the host's feces. After passing through the first intermediate host
Killingly Public Schools
 Grade 11 Draft: Jan. 2005 Killingly Public Schools Aquaculture/Natural Resources III Tilapia Production CONTENT STANDARD 11 AQ III 1: The students will understand the origin of Tilapia culture, the worldwide
Grade 11 Draft: Jan. 2005 Killingly Public Schools Aquaculture/Natural Resources III Tilapia Production CONTENT STANDARD 11 AQ III 1: The students will understand the origin of Tilapia culture, the worldwide
Regional Approach to Risk Assessment for Aquaculture in the Pacific Islands
 Regional Approach to Risk Assessment for Aquaculture in the Pacific Islands Ben Ponia, Aquaculture Adviser Secretariat of the Pacific Community New Caledonia SPC Region & Organization 22 Pacific Island
Regional Approach to Risk Assessment for Aquaculture in the Pacific Islands Ben Ponia, Aquaculture Adviser Secretariat of the Pacific Community New Caledonia SPC Region & Organization 22 Pacific Island
Polyculture of the freshwater prawn Macrobrachium malcolmsonii (H.M. Edwards) in Koilsagar reservoir of Mahabubnagar district (TS), India
 2015; 2(4): 147-152 ISSN: 2347-5129 IJFAS 2015; 2(4): 147-152 2015 IJFAS www.fisheriesjournal.com Received: 12-01-2015 Accepted: 04-03-2015 B. Laxmappa Fisheries Development Officer, Mahabubnagar-509001,
2015; 2(4): 147-152 ISSN: 2347-5129 IJFAS 2015; 2(4): 147-152 2015 IJFAS www.fisheriesjournal.com Received: 12-01-2015 Accepted: 04-03-2015 B. Laxmappa Fisheries Development Officer, Mahabubnagar-509001,
During the 2750 wild and cultured young salmonids fish (Oncorhynchus nerka, O. tschawytscha, O. keta, O. kisutch) and trout (Salvelinus
 uring 2000-2010 the 2750 wild and cultured young salmonids fish (Oncorhynchus nerka, O. tschawytscha, O. keta, O. kisutch) and trout (Salvelinus malma) from Kamchatka were examined by histological and
uring 2000-2010 the 2750 wild and cultured young salmonids fish (Oncorhynchus nerka, O. tschawytscha, O. keta, O. kisutch) and trout (Salvelinus malma) from Kamchatka were examined by histological and
AN OVERVIEW OF FISH SEED SUPPLY IN THREE PROVINCES OF THE MEKONG DELTA REGION OF CAMBODIA
 Page 1 of 7 AN OVERVIEW OF FISH SEED SUPPLY IN THREE PROVINCES OF THE MEKONG DELTA REGION OF CAMBODIA by Sem Viriyak, Thay Somony, Keo Sovannary, Chhoun Von, Setboonsarng and Jeney 1. Abstract Fish and
Page 1 of 7 AN OVERVIEW OF FISH SEED SUPPLY IN THREE PROVINCES OF THE MEKONG DELTA REGION OF CAMBODIA by Sem Viriyak, Thay Somony, Keo Sovannary, Chhoun Von, Setboonsarng and Jeney 1. Abstract Fish and
Schistosomiasis. World Health Day 2014 SMALL BITE: Fact sheet. Key facts
 Fact sheet Key facts is an acute and chronic disease caused by parasitic worms. At least 249 million people required preventive treatment for schistosomiasis in 2012. The number of people reported to have
Fact sheet Key facts is an acute and chronic disease caused by parasitic worms. At least 249 million people required preventive treatment for schistosomiasis in 2012. The number of people reported to have
From water to land. Why closed containment is the future of international salmon farming
 From water to land Why closed containment is the future of international salmon farming by Sue Scott Taking the high road in the controversy over ocean net pen salmon aquaculture is pretty challenging,
From water to land Why closed containment is the future of international salmon farming by Sue Scott Taking the high road in the controversy over ocean net pen salmon aquaculture is pretty challenging,
Preparation of this document
 iii Preparation of this document This document reviews and analyses published literature, grey literature, and personal communications on the social, economic and environmental impacts of tilapias in the
iii Preparation of this document This document reviews and analyses published literature, grey literature, and personal communications on the social, economic and environmental impacts of tilapias in the
Healthy Calves for 4-H Calf Club Projects and Ontario Calf Shows
 Healthy Calves for 4-H Calf Club Projects and Ontario Calf Shows Information compiled by the Ontario Association of Bovine Practitioners Calf Health Team including: Dr s Tim Henshaw (Eastgen), Christie
Healthy Calves for 4-H Calf Club Projects and Ontario Calf Shows Information compiled by the Ontario Association of Bovine Practitioners Calf Health Team including: Dr s Tim Henshaw (Eastgen), Christie
/20 Lab #5 The Dissection of the Perch
 /20 Lab #5 The Dissection of the Perch Perch are members of the class Osterichthyes, or bony fishes. They are found in many Canadian waters and are an excellent specimen of boney fish. Food enters the
/20 Lab #5 The Dissection of the Perch Perch are members of the class Osterichthyes, or bony fishes. They are found in many Canadian waters and are an excellent specimen of boney fish. Food enters the
Fish Dissection Background
 Fish Dissection Background Introduction Living things are similar to and different from each other. For example, when we look at the inside of a fish, we learn that the organ systems of fish are similar
Fish Dissection Background Introduction Living things are similar to and different from each other. For example, when we look at the inside of a fish, we learn that the organ systems of fish are similar
Proposal for the translocation of trout from the Kromrivier (Cederberg) to the Jan Du Toit s River (Waaihoek, Greater Hex River mountain range)
 Proposal for the translocation of trout from the Kromrivier (Cederberg) to the Jan Du Toit s River (Waaihoek, Greater Hex River mountain range) 1 Prepared for Cape Nature (CN) Prepared by Dr. Leonard Flemming
Proposal for the translocation of trout from the Kromrivier (Cederberg) to the Jan Du Toit s River (Waaihoek, Greater Hex River mountain range) 1 Prepared for Cape Nature (CN) Prepared by Dr. Leonard Flemming
Animal welfare in farmed fish
 Animal welfare in farmed fish Martin Cooke MRCVS martin@ocatra.com 31 March 2017 Image: Salmon Farm Science Source: FAO (2016) The State of World Fisheries and Aquaculture 2016 Finfish aquaculture (2015)
Animal welfare in farmed fish Martin Cooke MRCVS martin@ocatra.com 31 March 2017 Image: Salmon Farm Science Source: FAO (2016) The State of World Fisheries and Aquaculture 2016 Finfish aquaculture (2015)
Possibility of disease control by ambient dissolved oxygen level. Masashi Maita Tokyo University of Marine Science and Technology Japan
 Possibility of disease control by ambient dissolved oxygen level Masashi Maita Tokyo University of Marine Science and Technology Japan Counter measures against infectious diseases in Aquaculture Food safety
Possibility of disease control by ambient dissolved oxygen level Masashi Maita Tokyo University of Marine Science and Technology Japan Counter measures against infectious diseases in Aquaculture Food safety
Risk of spread after introduction of the virus in to wild boar population
 Available tools for the prevention and control of diseases in wildlife, with focus on ASF in wild boar in infected country: hunting biosecurity and wild boar carcass disposal Marius Masiulis FAO international
Available tools for the prevention and control of diseases in wildlife, with focus on ASF in wild boar in infected country: hunting biosecurity and wild boar carcass disposal Marius Masiulis FAO international
Animal Systems: The Respiratory System
 Animal Systems: The Respiratory System Tissues, Organs, and Systems of Living Things Cells, Cell Division, and Animal Systems and Plant Systems Cell Specialization Human Systems The Digestive The Circulatory
Animal Systems: The Respiratory System Tissues, Organs, and Systems of Living Things Cells, Cell Division, and Animal Systems and Plant Systems Cell Specialization Human Systems The Digestive The Circulatory
The Situation of Main Commercial Fishing in Lake Biwa
 The Situation of Main Commercial Fishing in Lake Biwa Then, I would like to explain the fisheries situation change in Lake Biwa for these 60 years by comparing with fluctuation of some fishing yields recorded
The Situation of Main Commercial Fishing in Lake Biwa Then, I would like to explain the fisheries situation change in Lake Biwa for these 60 years by comparing with fluctuation of some fishing yields recorded
Common Freshwater Fish Diseases, Their Symptoms and Control Measures : Types Symptoms Control measures A. Parasitic diseases
 Common Freshwater Fish Diseases, Their Symptoms and Control Measures : Types Symptoms Control measures A. Parasitic diseases 1. Whirling disease Excessive secretion of mucus and weakness, rapid tail chasing
Common Freshwater Fish Diseases, Their Symptoms and Control Measures : Types Symptoms Control measures A. Parasitic diseases 1. Whirling disease Excessive secretion of mucus and weakness, rapid tail chasing
Notes Dermocystidium sp. in Scottish Atlantic salmon, Salmo salar: Evidence for impact on fish in marine fish farms
 Bull. Eur. Ass. Fish Pathol., 21(5) 2001, 209 Notes Dermocystidium sp. in Scottish Atlantic salmon, Salmo salar: Evidence for impact on fish in marine fish farms Bruno, D.W. FRS Marine Laboratory, Victoria
Bull. Eur. Ass. Fish Pathol., 21(5) 2001, 209 Notes Dermocystidium sp. in Scottish Atlantic salmon, Salmo salar: Evidence for impact on fish in marine fish farms Bruno, D.W. FRS Marine Laboratory, Victoria
Supporting a world class Tasmanian fisheries and seafood sector. The Plan to build a modern economy, to create jobs
 Supporting a world class Tasmanian fisheries and seafood sector The Plan to build a modern economy, to The Plan to make build a Tasmania modern economy, attractive to for create investment jobs and to
Supporting a world class Tasmanian fisheries and seafood sector The Plan to build a modern economy, to The Plan to make build a Tasmania modern economy, attractive to for create investment jobs and to
ACUTE TEMPERATURE TOLERANCE OF JUVENILE CHINOOK SALMON FROM THE MOKELUMNE RIVER
 ACUTE TEMPERATURE TOLERANCE OF JUVENILE CHINOOK SALMON FROM THE MOKELUMNE RIVER Charles H. Hanson, Ph.D. Hanson Environmental, Inc. SUMMARY A series of static acute tests were performed to determine the
ACUTE TEMPERATURE TOLERANCE OF JUVENILE CHINOOK SALMON FROM THE MOKELUMNE RIVER Charles H. Hanson, Ph.D. Hanson Environmental, Inc. SUMMARY A series of static acute tests were performed to determine the
Fish Dissection. Background
 Fish Dissection The Fish Dissection program at Hatfield Marine Science Center is a 50-minute hands-on program for 4th through 12th grade students. Students will work in small groups as they examine a variety
Fish Dissection The Fish Dissection program at Hatfield Marine Science Center is a 50-minute hands-on program for 4th through 12th grade students. Students will work in small groups as they examine a variety
18000 RIMSTAD INDEPENDENT CONTINENTAL COMPARTMENT
 18000 RIMSTAD INDEPENDENT CONTINENTAL COMPARTMENT The new compartment Rimstad The compartment consists of a single, closed farm located in Tingvoll municipality, Møre og Romsdal County. Type of facility:
18000 RIMSTAD INDEPENDENT CONTINENTAL COMPARTMENT The new compartment Rimstad The compartment consists of a single, closed farm located in Tingvoll municipality, Møre og Romsdal County. Type of facility:
Historical developments and current issues in fish nutrition
 Historical developments and current issues in fish nutrition EAAP 2016 29 th of August, Johan Schrama & Sachi Kaushik Content presentation Historical development of aquaculture Trends in fish nutrition/fish
Historical developments and current issues in fish nutrition EAAP 2016 29 th of August, Johan Schrama & Sachi Kaushik Content presentation Historical development of aquaculture Trends in fish nutrition/fish
Compound Aqua feeds in a More Competitive Market: Alternative protein sources for a more sustainable future
 Compound Aqua feeds in a More Competitive Market: Alternative protein sources for a more sustainable future Abstract Albert G.J. Tacon Aquatic Farms Ltd 49-139 Kamehameha Hwy Kaneohe, Hawaii 96744 USA
Compound Aqua feeds in a More Competitive Market: Alternative protein sources for a more sustainable future Abstract Albert G.J. Tacon Aquatic Farms Ltd 49-139 Kamehameha Hwy Kaneohe, Hawaii 96744 USA
PREVALENCE OF PARASITIC INFECTIONS OF FARMED TILAPIA (Oreochromis niloticus) AND CATFISH (Clarias gariepinus) IN NYERI COUNTY, KENYA
 PREVALENCE OF PARASITIC INFECTIONS OF FARMED TILAPIA (Oreochromis niloticus) AND CATFISH (Clarias gariepinus) IN NYERI COUNTY, KENYA KVA ANNUAL SCIENTIFIC CONFERENCE 27TH-29 TH APRIL, 2016 PRESENTER: Dr
PREVALENCE OF PARASITIC INFECTIONS OF FARMED TILAPIA (Oreochromis niloticus) AND CATFISH (Clarias gariepinus) IN NYERI COUNTY, KENYA KVA ANNUAL SCIENTIFIC CONFERENCE 27TH-29 TH APRIL, 2016 PRESENTER: Dr
Augmentation of fish and prawn production from Koilsagar reservoir of Mahabubnagar: A success story
 2014; 2(1): 197-206 ISSN: 2347-5129 IJFAS 2014; 2(1): 197-206 2013 IJFAS www.fisheriesjournal.com Received: 14-08-2014 Accepted: 29-08-2014 B. Laxmappa Fisheries Development Officer, Department of Fisheries,
2014; 2(1): 197-206 ISSN: 2347-5129 IJFAS 2014; 2(1): 197-206 2013 IJFAS www.fisheriesjournal.com Received: 14-08-2014 Accepted: 29-08-2014 B. Laxmappa Fisheries Development Officer, Department of Fisheries,
JERZY ANTYCHOWICZ 1 AND MICHAŁ REICHERT 2. Abstract. Material and Methods. Key words: carp, Myxobolus encephalicus, parasitoses, symptoms.
 Bull Vet Inst Pulawy 49, 35-39, 2005 OCCURRENCE OF MYXOBOLUS ENCEPHALICUS (MUSLOW 1911) IN POLAND: POSSIBLE RELATIONSHIP BETWEEN THE PARASITE INFECTION AND CLINICAL SYMPTOMS IN COMMON CARP (CYPRINUS CARPIO)
Bull Vet Inst Pulawy 49, 35-39, 2005 OCCURRENCE OF MYXOBOLUS ENCEPHALICUS (MUSLOW 1911) IN POLAND: POSSIBLE RELATIONSHIP BETWEEN THE PARASITE INFECTION AND CLINICAL SYMPTOMS IN COMMON CARP (CYPRINUS CARPIO)
Volume: 1; Issue: 1; June-2015; pp ISSN
 Volume: 1; Issue: 1; June-2015; pp 08-13. ISSN 2454-5422 Effect of Garlic Allium Sativum (L.) Extract on Disease Induced Common Carp, Cyprinus Carpio (L.) S. Rajeshwari 1*, V. Balasubramanian 1, M.K. Rajan
Volume: 1; Issue: 1; June-2015; pp 08-13. ISSN 2454-5422 Effect of Garlic Allium Sativum (L.) Extract on Disease Induced Common Carp, Cyprinus Carpio (L.) S. Rajeshwari 1*, V. Balasubramanian 1, M.K. Rajan
Feeding Tilapia in Intensive Recirculating Systems
 NCRAC Extension Fact Sheets North Central Regional Aquaculture Center 8-2003 Feeding Tilapia in Intensive Recirculating Systems Marty Riche United States Department of Agriculture Donald Garling Michigan
NCRAC Extension Fact Sheets North Central Regional Aquaculture Center 8-2003 Feeding Tilapia in Intensive Recirculating Systems Marty Riche United States Department of Agriculture Donald Garling Michigan
Reducing Disease Risks Caused by Pathogens Associated with Columbia
 Reducing Disease Risks Caused by Pathogens Associated with Columbia River Hatcheries Jerri Bartholomew Department of Microbiology Oregon State University, Corvallis, OR Pathogen Transmission and Hatchery
Reducing Disease Risks Caused by Pathogens Associated with Columbia River Hatcheries Jerri Bartholomew Department of Microbiology Oregon State University, Corvallis, OR Pathogen Transmission and Hatchery
Traditional Aquaculture
 Traditional Aquaculture Prehistoric origins of both agriculture and aquaculture as crafts Oxbow lakes Neolithic hunter-gatherers in the Nile seasonal collection of catfish from oxbow lakes Egyptian bas-relief
Traditional Aquaculture Prehistoric origins of both agriculture and aquaculture as crafts Oxbow lakes Neolithic hunter-gatherers in the Nile seasonal collection of catfish from oxbow lakes Egyptian bas-relief
What is a Fish? Fishes are aquatic vertebrates. Most fishes have paired fins, scales, and gills.
 What is a Fish? Fishes are aquatic vertebrates. Most fishes have paired fins, scales, and gills. Feeding and Digestion Every mode of feeding is seen in fish herbivores, carnivores, parasites, filter feeders,
What is a Fish? Fishes are aquatic vertebrates. Most fishes have paired fins, scales, and gills. Feeding and Digestion Every mode of feeding is seen in fish herbivores, carnivores, parasites, filter feeders,
Gill Health in Finfish Aquaculture. Dr. Hamish Rodger
 Gill Health in Finfish Aquaculture Dr. Hamish Rodger Gill Health in Finfish Aquaculture Outline Gill disease background Aetiologies of gill disease Pathologies Control & treatments Gill Health in Finfish
Gill Health in Finfish Aquaculture Dr. Hamish Rodger Gill Health in Finfish Aquaculture Outline Gill disease background Aetiologies of gill disease Pathologies Control & treatments Gill Health in Finfish
Conservation aquaculture: a critical tool for recovery of burbot in the Kootenai River
 Conservation aquaculture: a critical tool for recovery of burbot in the Kootenai River Northwest Fish Culture Conference December 6-8, 2011 Ken Cain et al. Department of Fish and Wildlife and the Aquaculture
Conservation aquaculture: a critical tool for recovery of burbot in the Kootenai River Northwest Fish Culture Conference December 6-8, 2011 Ken Cain et al. Department of Fish and Wildlife and the Aquaculture
Effect of formalin treatment on saltwater tolerance in Caspian roach (Rutilus rutilus caspicus)
 International Research Journal of Applied and Basic Sciences. Vol., 3 (5), 1027-1031, 2012 Available online at http:// www. irjabs.com ISSN 2251-838X 2012 Effect of formalin treatment on saltwater tolerance
International Research Journal of Applied and Basic Sciences. Vol., 3 (5), 1027-1031, 2012 Available online at http:// www. irjabs.com ISSN 2251-838X 2012 Effect of formalin treatment on saltwater tolerance
Proceedings of the Autumn Symposium on Aquaculture, '97
 Proceedings of the Autumn Symposium on Aquaculture, '97 1. Aquaculture in Hiroshima Prefecture Yasuyoshi MURAKAMI (Hiroshima Fisheries Experimental Station) 2. The Present Situation and Some Problems of
Proceedings of the Autumn Symposium on Aquaculture, '97 1. Aquaculture in Hiroshima Prefecture Yasuyoshi MURAKAMI (Hiroshima Fisheries Experimental Station) 2. The Present Situation and Some Problems of
