Major groups of animals. I. Phylum Porifera. RADIATA II. Phylum Cnidaria. A. Class Hydrozoa. B. Class Anthozoa. C. Class Cubozoa. D.
|
|
|
- Ashlie Craig
- 6 years ago
- Views:
Transcription
1 Major groups of animals I. Phylum Porifera A. no true tissues B. cell types 1. pinacocytes (pinacoderm - incipient tissue) 2. archaeocytes - in mesohyl 3. choanocytes C. Body forms 1. Asconoid a) water flow > ostia - spongocoel - osculum b) choanocytes line spongocoel 2. Syconoid a) water flow > ostia - radial chamber - spongocoel - osculum b) choanocytes line radial chambers in body wall 3. Leuconoid a) water flow > ostia - inhalant canal - choanocyte chamber - exhalant canal - osculum b) no real spongocoel c) choanocytes in chambers dispersed throughout body D. asexual or sexual reproduction 1. budding / gemmules 2. mostly monoecious RADIATA II. Phylum Cnidaria A. Class Hydrozoa 1. solitary or colonial 2. e.g. hydra, Obelia, portuguese man o war B. Class Anthozoa 1. Corals and Anemones 2. colonial C. Class Cubozoa 1. box jellies D. Class Scyphozoa 1. true jellies E. general characteristics 1. cnidocytes (with nematocyst) 2. radial symmetry 3. tissue-level development - diploblastic a) body two cell layers thick b) epidermis - mesoglea - gastrodermis
2 4. gastrovascular cavity 5. two body forms: polyp / medusa III. Phylum Ctenophora 1. move with cilia - comb plates 2. biradial symmetry 3. diploblastic 4. collenchyme 5. monoecious - sexual reproduction 6. paired tentacles with colloblasts IV. Phylum Acoelomorpha 1. some with gastrovascular cavity (many with no gut) 2. monoecious - sexual reproduction 3. radially arranged nerve cords 4. most commensalist or mutualist BILATERIA LOPHOTROCHOZOA V. Phylum Rotifera 1. wheel organ / corona 2. mastax 3. eutely VI. Phylum Acanthocephala 1. vertebrate endoparasites 2. spiny proboscis 3. syncytial outer surface 4. dioecious 5. protonephridia VII.Phylum Platyhelminthes A. Class Turbellaria 1. mostly free living 2. planaria 3. regeneration B. Class Trematoda 1. flukes 2. diverse life cycles related to parasitism / hosts a) egg - miracidium (larva) - sporocyst (adult) - redia (adult) - cercaria (larva) - metacercaria - fluke (adult)
3 b) intermediate host often a gastropod C. Class Monogenea 1. monogenic flukes 2. attachment organs: prothaptor - opisthaptor 3. ectoparasites 4. oncomiracidium larva D. Class Cestoda 1. tapeworms 2. scolex - proglottids 3. scolex homologous to opisthaptor 4. no gut - microtriches 5. monoecious E. general characteristics 1. free-living or parasitic (many) 2. acoelomate 3. bilateral symmetry 4. organ-level development 5. syncytial tegument 6. gastrovascular cavity (or none) VIII.Phylum Mollusca 1. eucoelomate 2. bilateral symmetry 3. open or closed (in cephalopods) circulatory system 4. ctenidial gills 5. huge, diverse group - probably 3rd largest phylum B. Class Gastropoda 1. subclass Prosobranchia a) marine snails b) gills in front (torsion) 2. subclass Opisthobranchia a) sea slugs b) gills in back (detorsion) 3. subclass Pulmonata a) lung or gill b) terrestrial or freshwater snails and slugs C. Class Bivalvia 1. two halves to shell 2. suspension feeders 3. 3 chambered heart (open circulatory) 4. very specialized for filter feeding D. Class Cephalopoda 1. squid, octopus, cuttlefish
4 2. closed circulatory 3. little or no shell (except chambered nautilus) a) if shell is present, mainly used for buoyancy IX. Phylum Annelida 1. closed circulatory 2. eucoelomate 3. gills or epithelial gas exchange 4. setae / chaetae - chitinous bristles 5. proteinaceous cuticle B. Class Polychaeta 1. lots of setae (chaetae) 2. parapodia 3. gills or parapodia used for gas exchange 4. very diverse (10,000+ species) 5. strong cephalization (prostomium, peristomium, eversible pharynx, jaws) CLITELLATA C. Class Oligachaeta (paraphyletic) 1. earthworms and others. 2. mostly terrestrial, some aquatic 3. no parapodia 4. few setae (chaetae) 5. deposit feeders 6. epithelial gas exchange 7. monoecious D. Class Hirudinea 1. leeches - often ectoparasites 2. reduced or lost septa 3. no setae or parapodia 4. anterior and posterior suckers 5. mostly freshwater, some marine, some terrestrial ECDYSOZOA X. Phylum Nemata 1. some parasitic, but many free-living 2. probably second biggest phylum (probably at least 500,000 species) 3. eutely 4. collagenous cuticle 5. pseudocoelomate 6. only longitudinal muscles XI. Phylum Tardigrada
5 1. water bears 2. cryptobiosis 3. somewhat similar to arthropods 4. fluid feeders 5. open circulatory 6. eucoelomate XII.Phylum Onychophora 1. velvet worms 2. somewhat similar to arthropods 3. open circulatory 4. eucoelomate XIII.Phylum Arthropoda 1. chitinous exoskeleton - molting (ecdysis) 2. metamorphosis 3. metamerism 4. tagmatization 5. jointed limbs B. Subphylum Chelicerata 1. general characteristics a) chelicerae b) 2 tagmata c) no antennae, no mandibles d) 6 pairs of limbs on prosoma e) diverse and commonly encountered group 2. Class Arachnida a) spiders, scorpions, mites, ticks, opilionids, etc. C. Subphylum Myriapoda 1. Class Chilopoda a) centipedes 2. Class Diplopoda a) millipedes D. Subphylum Pancrustacea / Crustacea (paraphyletic) 1. general characteristics a) 3 tagmata, 2 pairs of antennae b) heavily calcified exoskeleton c) biramous appendages d) generally aquatic (some somewhat terrestrial) E. Subphylum Hexapoda 1. Class Insecta
6 a) general characteristics (1) 3 tagmata (2) 4 (or 2) wings (3) 6 legs (4) uniramous appendages (5) metamorphosis (6) tracheal system (7) malphigian tubules DEUTEROSTOMIA XIV.Phylum Echinodermata A. Class Asteriodea 1. sea stars 2. pentaradial symmetry 3. gastric eversion B. Class Ophiuroidea 1. brittle stars 2. pentaradial symmetry 3. closed ambulacrum 4. excellent regeneration 5. highly motile 6. articulated ossicles C. Class Echinoidea 1. sea urchins, sand dollars, sea biscuits 2. Aristotle s lantern 3. test D. Class Holothuroidea 1. reduced ossicles 2. soft bodied 3. bilateral symmetry E. Class Crinoidea 1. filter feeders, somewhat sessile 2. many arms, ciliated ambulacrum XV.Phylum Hemichordata 1. burrowing or tube-dwelling 2. pharyngeal slits 3. dorsal nerve cord 4. acorn worms and pterobranchs 5. probably sister to echinoderms
7 XVI.Phylum Chordata 1. dorsal hollow nerve cord 2. notochord 3. post-anal tail 4. pharyngeal slits 5. endostyle B. Subphylum Urochordata 1. general characteristics a) sea squirts, tunicates b) filter feeders, sessile adult c) cellulose tunic C. Subphylum Cephalochordata 1. general characteristics a) Amphioxus b) all chordate characteristics in adult c) dioecious d) burrowing filter-feeders D. Subphylum Craniata 1. Class Myxini a) hagfish 2. Class Petromyzontes a) lampreys 3. Class Chondrichthyes a) cartilage fish b) sharks, skates, rays, chimera c) no swim bladder or lungs 4. Class Actinopterygii a) ray-finned fish (most fish) b) operculum covering gills c) dermal scales d) with swim bladder or lungs 5. Class Sarcopterygii (polyphyletic) a) lobe-finned fish (needs to include the Amphibia, Mammalia, Reptilia, and Aves) b) dermal scales 6. Class Amphibia (polyphyletic) a) monophyletic if just the modern ones (lissamphibia) b) usually no scales 7. Class Mammalia a) hair, mammary glands 8. Class Reptilia (paraphyletic)
8 a) crocodilians, squamates, tuatara, turtles b) need to include the birds c) epidermal scales 9. Class Aves a) birds b) actually dinosaurs
Major groups of animals. I. Phylum Porifera. RADIATA II. Phylum Cnidaria. A. Class Hydrozoa. B. Class Anthozoa. C. Class Cubozoa. D.
 Major groups of animals I. Phylum Porifera A. no true tissues B. cell types 1. pinacocytes (pinacoderm - incipient tissue) 2. archaeocytes - in mesohyl 3. choanocytes C. Body forms 1. Asconoid a) water
Major groups of animals I. Phylum Porifera A. no true tissues B. cell types 1. pinacocytes (pinacoderm - incipient tissue) 2. archaeocytes - in mesohyl 3. choanocytes C. Body forms 1. Asconoid a) water
Major groups of animals. I. Phylum Porifera. RADIATA II. Phylum Cnidaria. A. Class Hydrozoa
 Major groups of animals I. Phylum Porifera A. no true tissues B. cell types 1. pinacocytes (pinacoderm - incipient tissue) 2. archaeocytes - in mesohyl 3. choanocytes C. Body forms 1. Asconoid a) water
Major groups of animals I. Phylum Porifera A. no true tissues B. cell types 1. pinacocytes (pinacoderm - incipient tissue) 2. archaeocytes - in mesohyl 3. choanocytes C. Body forms 1. Asconoid a) water
Kingdom Animalia. Lab Exercise 23. Objectives. Introduction
 Lab Exercise Kingdom Animalia Objectives - Be able to recognize and name the major groups of animals - Be able to identify key characteristics that separate animal taxa - Be able to use a dichotomous key
Lab Exercise Kingdom Animalia Objectives - Be able to recognize and name the major groups of animals - Be able to identify key characteristics that separate animal taxa - Be able to use a dichotomous key
Chapter 5 Marine Protozoans and Invertebrates
 Chapter 5 Marine Protozoans and Invertebrates I. The Protozoans A. Kindgom Protista a catch-all category B. Characteristics 1. Mode of nutrition 2. Single-celled or multicellular? 3. Cell structure 4.
Chapter 5 Marine Protozoans and Invertebrates I. The Protozoans A. Kindgom Protista a catch-all category B. Characteristics 1. Mode of nutrition 2. Single-celled or multicellular? 3. Cell structure 4.
Animals. Invertebrate Diversity & Evolution
 Animals Invertebrate Diversity & Evolution Animal Characteristics Multicellular Heterotrophic (can be classified by their feeding strategies) Classified by feeding strategies Filter feeders (suspension
Animals Invertebrate Diversity & Evolution Animal Characteristics Multicellular Heterotrophic (can be classified by their feeding strategies) Classified by feeding strategies Filter feeders (suspension
Kingdom Animalia: Sponges. Types of Body Symmetry Radial body parts are symmetrical around a central point (like a pie)
 Kingdom Animalia: Phylum Characteristics Types of Body Symmetry Radial body parts are symmetrical around a central point (like a pie) Bilateral right and left sides are alike and roughly equally proportional
Kingdom Animalia: Phylum Characteristics Types of Body Symmetry Radial body parts are symmetrical around a central point (like a pie) Bilateral right and left sides are alike and roughly equally proportional
Animal Evolution. II. Overview of Animal Phylogeny A. Parazoan 1. Lack tissue 2. Animals with tissue are classified eumetazoa 3.
 Animal Evolution I. Animal Characteristics A. Most animals share the following characteristics: 1. Multi-cellular 2. Eukaryotic 3. Heterotrophy a. Ingestion b. Carbohydrates stored as glycogen 4. No cell
Animal Evolution I. Animal Characteristics A. Most animals share the following characteristics: 1. Multi-cellular 2. Eukaryotic 3. Heterotrophy a. Ingestion b. Carbohydrates stored as glycogen 4. No cell
Chordates 1. Biology 2
 Chordates 1 Biology 2 Kingdom Animals Eukaryotic Multicellular - Many cell types Heterotrophic Feed by ingestion No cell walls Diploid life cycle Phylogenetic Tree Deuterostome Bilateral Symmetry 3 tissues
Chordates 1 Biology 2 Kingdom Animals Eukaryotic Multicellular - Many cell types Heterotrophic Feed by ingestion No cell walls Diploid life cycle Phylogenetic Tree Deuterostome Bilateral Symmetry 3 tissues
Animal Diversity. Kingdom Animalia
 7ch11 Animal Diversity Kingdom Animalia Animal Characteristics 1. animals are eukaryotes and are multicellular 2. cells are specialized for different functions (vision,digestion,reproduction) 3. protein,
7ch11 Animal Diversity Kingdom Animalia Animal Characteristics 1. animals are eukaryotes and are multicellular 2. cells are specialized for different functions (vision,digestion,reproduction) 3. protein,
Aquarium entrance stamp here
 Aquarium entrance stamp here Bio 11 - ZOOLOGY Instructor: K. Villatoro Student s Name: CLASSIFICATION OF KINGDOM ANIMALIA WELCOME TO THE CABRILLO MARINE AQUARIUM! This site was chosen because it exhibits
Aquarium entrance stamp here Bio 11 - ZOOLOGY Instructor: K. Villatoro Student s Name: CLASSIFICATION OF KINGDOM ANIMALIA WELCOME TO THE CABRILLO MARINE AQUARIUM! This site was chosen because it exhibits
Phylum: Porifera (sponges)
 Phylum: Porifera (sponges) (8,761 known species) General Description: Simplest animals, multicellular No organs or body systems Skeleton composed of spongin (soft) and spicules (hard) Symmetry: Asymmetrical
Phylum: Porifera (sponges) (8,761 known species) General Description: Simplest animals, multicellular No organs or body systems Skeleton composed of spongin (soft) and spicules (hard) Symmetry: Asymmetrical
Symmetry. Asymmetrical- no shape. Radial- same in half when cut any angle. Bilateral- having a distinct right and left side
 Symmetry Asymmetrical- no shape Radial- same in half when cut any angle Bilateral- having a distinct right and left side Invertebrates 95% of Animals No Backbone The simplest animals and they do not have
Symmetry Asymmetrical- no shape Radial- same in half when cut any angle Bilateral- having a distinct right and left side Invertebrates 95% of Animals No Backbone The simplest animals and they do not have
I n t r o d u c t i o n. A n i m a l s
 I n t r o d u c t i o n t o A n i m a l s What is an Animal? Taxonomy: Kingdom Animalia Type of Cells: Eukaryotic Cellular Organization: Multicellular Reproduction: Sexual / Asexual Feeding: Heterotrophic
I n t r o d u c t i o n t o A n i m a l s What is an Animal? Taxonomy: Kingdom Animalia Type of Cells: Eukaryotic Cellular Organization: Multicellular Reproduction: Sexual / Asexual Feeding: Heterotrophic
The Animals: Kingdom Animalia
 The Animals: Kingdom Animalia Kingdom Animalia (Animals) What is an Animal? Zoology- The study of Animals General Characteristics of 1. Animals are multicellular and eukaryotic. Animals 2. Animals consume
The Animals: Kingdom Animalia Kingdom Animalia (Animals) What is an Animal? Zoology- The study of Animals General Characteristics of 1. Animals are multicellular and eukaryotic. Animals 2. Animals consume
Class Polychaeta: Marine Worms
 Class Polychaeta: Marine Worms Animal Phyla Phylum Mollusca (Snails, Clams, Octopods and Allies): Radula: rasping tongue Shell: 3 layers, mostly calcium carbonate Inner-most = nacre = mother of pearl Mantle:
Class Polychaeta: Marine Worms Animal Phyla Phylum Mollusca (Snails, Clams, Octopods and Allies): Radula: rasping tongue Shell: 3 layers, mostly calcium carbonate Inner-most = nacre = mother of pearl Mantle:
Ch17_Animals. Animals Multicellular eukaryotes. What is an animal? Animal development. Main differences with plants Main differences with fungi
 Animals Multicellular eukaryotes Domain Domain Kingdoms Main differences with plants Main differences with fungi What is an animal? Domain Nutritional mode: Heterotrophic (Ingestive) Level of organization:
Animals Multicellular eukaryotes Domain Domain Kingdoms Main differences with plants Main differences with fungi What is an animal? Domain Nutritional mode: Heterotrophic (Ingestive) Level of organization:
EXTRACREDIT PROJECT ANIMALS OF SOUTHERN CALIFORNIA S OCEAN
 BIO 10 FUNDAMENTALS OF BIOLOGY Instructor: K. Villatoro Student s Name: EXTRACREDIT PROJECT ANIMALS OF SOUTHERN CALIFORNIA S OCEAN WELCOME TO THE CABRILLO MARINE AQUARIUM! This site was chosen because
BIO 10 FUNDAMENTALS OF BIOLOGY Instructor: K. Villatoro Student s Name: EXTRACREDIT PROJECT ANIMALS OF SOUTHERN CALIFORNIA S OCEAN WELCOME TO THE CABRILLO MARINE AQUARIUM! This site was chosen because
A. Porifera (sponges): B. Cnidaria (jellies, hydra, sea anemones, and corals):
 Invertebrates Notes A. Porifera (sponges): Porifera literally means. Most sponges are. They are that collect food particles from the water as they pass through flagellated cells called. These cells then
Invertebrates Notes A. Porifera (sponges): Porifera literally means. Most sponges are. They are that collect food particles from the water as they pass through flagellated cells called. These cells then
ANIMAL KINGDOM CHAPTER 4 14 BIOLOGY, EXEMPLAR PROBLEMS MULTIPLE CHOICE QUESTIONS
 14 BIOLOGY, EXEMPLAR PROBLEMS CHAPTER 4 ANIMAL KINGDOM MULTIPLE CHOICE QUESTIONS 1. In some animal groups, the body is found divided into compartments with at least some organs/ organ repeated. This characteristic
14 BIOLOGY, EXEMPLAR PROBLEMS CHAPTER 4 ANIMAL KINGDOM MULTIPLE CHOICE QUESTIONS 1. In some animal groups, the body is found divided into compartments with at least some organs/ organ repeated. This characteristic
BIOLOGY. An Introduction to Invertebrates CAMPBELL. Reece Urry Cain Wasserman Minorsky Jackson
 CAMPBELL BIOLOGY TENTH EDITION Reece Urry Cain Wasserman Minorsky Jackson 33 An Introduction to Invertebrates Lecture Presentation by Nicole Tunbridge and Kathleen Fitzpatrick Deuterostomia Metazoa Eumetazoa
CAMPBELL BIOLOGY TENTH EDITION Reece Urry Cain Wasserman Minorsky Jackson 33 An Introduction to Invertebrates Lecture Presentation by Nicole Tunbridge and Kathleen Fitzpatrick Deuterostomia Metazoa Eumetazoa
Kingdom Animalia. Eukaryotic Multicellular Heterotrophs Lack Cell Walls
 Kingdom Animalia Eukaryotic Multicellular Heterotrophs Lack Cell Walls Must do: Feed, Respiration, Circulation, Excretion, Response, Movement, and Reproduction Symmetry Asymmetrical- no shape Radial- same
Kingdom Animalia Eukaryotic Multicellular Heterotrophs Lack Cell Walls Must do: Feed, Respiration, Circulation, Excretion, Response, Movement, and Reproduction Symmetry Asymmetrical- no shape Radial- same
Ch17_Animals. Animals Multicellular eukaryotes. What is an animal? Animal development. Main differences with plants Main differences with fungi
 Animals Multicellular eukaryotes Domain Domain Kingdoms Main differences with plants Main differences with fungi What is an animal? Domain Nutritional mode: Heterotrophic (Ingestive) Level of organization:
Animals Multicellular eukaryotes Domain Domain Kingdoms Main differences with plants Main differences with fungi What is an animal? Domain Nutritional mode: Heterotrophic (Ingestive) Level of organization:
Characteris*c s of Living Things 1. Chemical Uniqueness: Molecular Organization
 Characteris*c s of Living Things 1. Chemical Uniqueness: Molecular Organization 2. Hierarchical Organization: macromolecules - > Cells - >Organs - >Organ systems 3. Reproduction 4. Genetic Programs 5.
Characteris*c s of Living Things 1. Chemical Uniqueness: Molecular Organization 2. Hierarchical Organization: macromolecules - > Cells - >Organs - >Organ systems 3. Reproduction 4. Genetic Programs 5.
Kingdom Animalia part 2.notebook. April 08, The fun continues... Kingdom Animalia
 The fun continues....... Kingdom Animalia 1 2 Joint legged animals (arthropoda) found from the bottom of the ocean to high above the Earth's surface included insects, arachnid, and crustacean hard external
The fun continues....... Kingdom Animalia 1 2 Joint legged animals (arthropoda) found from the bottom of the ocean to high above the Earth's surface included insects, arachnid, and crustacean hard external
Overview of Invertebrates
 Overview of Invertebrates General Features of Animals Heterotrophic Multicellular (eukaryotic) Cells lack rigid cell walls Cells are usually quite flexible. Cells (except sponges) are organized into structural
Overview of Invertebrates General Features of Animals Heterotrophic Multicellular (eukaryotic) Cells lack rigid cell walls Cells are usually quite flexible. Cells (except sponges) are organized into structural
Requirements for Animal Life. Phylum Bryozoa. Colonial Bryozoans. A lophophore is a structure used for:
 Requirements for Animal Life Animal phylogeny based on sequencing of SSU-rRNA The demands of 3 unique environments Marine, freshwater, terrestrial Gas exchange Nutrition Distribution and transport Disposal
Requirements for Animal Life Animal phylogeny based on sequencing of SSU-rRNA The demands of 3 unique environments Marine, freshwater, terrestrial Gas exchange Nutrition Distribution and transport Disposal
Class XI Chapter 4 Animal Kingdom Biology
 Chapter 4 Animal Kingdom Question 1: What are the difficulties that you would face in classification of animals, if common fundamental features are not taken into account? For the classification of living
Chapter 4 Animal Kingdom Question 1: What are the difficulties that you would face in classification of animals, if common fundamental features are not taken into account? For the classification of living
Chapter 23: The Animal Kingdom
 Chapter 23: The Animal Kingdom Lecture Outline Enger, E. D., Ross, F. C., & Bailey, D. B. (2012). Concepts in biology (14th ed.). New York: McGraw- Hill. 1 23-1 What is an animal? 23-2 Eukaryotic Multicellular
Chapter 23: The Animal Kingdom Lecture Outline Enger, E. D., Ross, F. C., & Bailey, D. B. (2012). Concepts in biology (14th ed.). New York: McGraw- Hill. 1 23-1 What is an animal? 23-2 Eukaryotic Multicellular
Class XI Chapter 4 Animal Kingdom Biology
 Class XI Chapter 4 Animal Kingdom Biology Question 1: What are the difficulties that you would face in classification of animals, if common fundamental features are not taken into account? For the classification
Class XI Chapter 4 Animal Kingdom Biology Question 1: What are the difficulties that you would face in classification of animals, if common fundamental features are not taken into account? For the classification
The Animal Kingdom: The Deuterostomes. Deuterostomes. Phylum Echinodermata 4/23/2012. Chapter 31. (bilateral ciliated larvae)
 Porifera Porifera Cnidaria Cnidaria Ctenophora Ctenophora Platyhelminthes Platyhelminthes Nemerteans Nemerteans Nematoda Nematoda Rotifera Rotifera Tardigrada Tardigrada Onychophora Onychophora Arthropoda
Porifera Porifera Cnidaria Cnidaria Ctenophora Ctenophora Platyhelminthes Platyhelminthes Nemerteans Nemerteans Nematoda Nematoda Rotifera Rotifera Tardigrada Tardigrada Onychophora Onychophora Arthropoda
Monterey Bay Aquarium Fieldtrip Worksheet
 Attach ticket stub here. Name: Class: B11 or B3A Lab day & time: Monterey Bay Aquarium Fieldtrip Worksheet General Information Address: 886 Cannery Row Monterey, California 93940 Hours: 10am 6pm (May vary
Attach ticket stub here. Name: Class: B11 or B3A Lab day & time: Monterey Bay Aquarium Fieldtrip Worksheet General Information Address: 886 Cannery Row Monterey, California 93940 Hours: 10am 6pm (May vary
1. Animals are (diploid) with tissues arranged into organs and organ systems. 3. Animals require for aerobic respiration.
 Chapter 25 Animals: The Invertebrates I. Overview of the Animal Kingdom A. General Characteristics of Animals 1. Animals are (diploid) with tissues arranged into organs and organ systems. 2. Animals are.
Chapter 25 Animals: The Invertebrates I. Overview of the Animal Kingdom A. General Characteristics of Animals 1. Animals are (diploid) with tissues arranged into organs and organ systems. 2. Animals are.
deuterostomes eucoelomates pseudocoelomates acoelomate
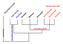 deuterostomes Mollusca Arthropoda Echinodermata Hemichordata Chordata eucoelomates Annelida Rotifera Platyhelminthes Nematoda acoelomate pseudocoelomates Phylum Hemichordata Share characteristics with
deuterostomes Mollusca Arthropoda Echinodermata Hemichordata Chordata eucoelomates Annelida Rotifera Platyhelminthes Nematoda acoelomate pseudocoelomates Phylum Hemichordata Share characteristics with
The Animal Kingdom. Animal Kingdom. Characteristics of All Animals. Major Characteristics Used To Classify Animals
 The Animal Kingdom Animal Kingdom Phylums: 1. Sponges 2. Cnidaria Jelly Fish, Hydra 3. Flatworms Flukes, Tapeworms 4. Roundworms- Hookworms 5. Segmented Worms- Earthworms 6. Rotifera- Rotifers 7. Mullusca
The Animal Kingdom Animal Kingdom Phylums: 1. Sponges 2. Cnidaria Jelly Fish, Hydra 3. Flatworms Flukes, Tapeworms 4. Roundworms- Hookworms 5. Segmented Worms- Earthworms 6. Rotifera- Rotifers 7. Mullusca
The Animal Kingdom. The Chordates
 The Animal Kingdom The Chordates Phylum Hemichordata Hemichordata (hemi = half; chordata= cord) acorn worm entirely marine adults show 3 of 4 basic characteristics: 1) pharyngial pouches 2) dorsal tubular
The Animal Kingdom The Chordates Phylum Hemichordata Hemichordata (hemi = half; chordata= cord) acorn worm entirely marine adults show 3 of 4 basic characteristics: 1) pharyngial pouches 2) dorsal tubular
ARTHROPODS. Phylum Arthropoda. 08 Sept Arthropoda.ppt 1
 ARTHROPODS Phylum Arthropoda 08 Sept. 2014 Arthropoda.ppt 1 Phylum Arthropoda Phylum Arthropoda Greek: arthro = jointed, + pod = foot Huge group, > 1,000,000 species. estimate: 1,000,000 spp. arthropods
ARTHROPODS Phylum Arthropoda 08 Sept. 2014 Arthropoda.ppt 1 Phylum Arthropoda Phylum Arthropoda Greek: arthro = jointed, + pod = foot Huge group, > 1,000,000 species. estimate: 1,000,000 spp. arthropods
Animal Evolution: Chordate and Vertebrate Evolution and Diversity (Learning Outline)
 Animal Evolution: Chordate and Vertebrate Evolution and Diversity (Learning Outline) 1. Distinguishing features of the phylum Chordata and representative organisms. 2. Highlights of evolutionary steps
Animal Evolution: Chordate and Vertebrate Evolution and Diversity (Learning Outline) 1. Distinguishing features of the phylum Chordata and representative organisms. 2. Highlights of evolutionary steps
CBSE Quick Revision Notes (Class-11 Biology) CHAPTER-04 ANIMAL KINGDOM
 CBSE Quick Revision Notes (-11 Biology) CHAPTER-04 ANIMAL KINGDOM Millions of species of animals have been described and it becomes more necessary to classify them to assign a systematic position. Animals
CBSE Quick Revision Notes (-11 Biology) CHAPTER-04 ANIMAL KINGDOM Millions of species of animals have been described and it becomes more necessary to classify them to assign a systematic position. Animals
Basic mollusc body plan
 Phylum Mollusca Phylum Mollusca 3 embryonic germ layers true coelom complete gut second largest phylum of animals, around 100,000 species mainly aquatic, but some terrestrial species Basic mollusc body
Phylum Mollusca Phylum Mollusca 3 embryonic germ layers true coelom complete gut second largest phylum of animals, around 100,000 species mainly aquatic, but some terrestrial species Basic mollusc body
February 17, Unit 2. Biodiversity. Chordata, the vertebrates
 Unit 2 Biodiversity Chordata, the vertebrates Phylum Chordata Examples: Sea squirts, fish, birds, dinosaurs, humans. General characteristics: 1. Bilaterally symmetrical 2. Coelomate 3. One way digestive
Unit 2 Biodiversity Chordata, the vertebrates Phylum Chordata Examples: Sea squirts, fish, birds, dinosaurs, humans. General characteristics: 1. Bilaterally symmetrical 2. Coelomate 3. One way digestive
 http://bio.fsu.edu/~bsc2011l/ Click on Course Documents, then Lab Review & select phyla of choice This presentation is also available: Click on Lab Review, then Spring 2005 Midterm Practical Review Practical
http://bio.fsu.edu/~bsc2011l/ Click on Course Documents, then Lab Review & select phyla of choice This presentation is also available: Click on Lab Review, then Spring 2005 Midterm Practical Review Practical
Chapter 28 Arthropods and Echinoderms. Body Terms. Evolution has led to:
 Chapter 28 Arthropods and Echinoderms Introduction to Arthropods jointed feet Most diverse and successful animals Over 750,000 species identified Segmented bodies Tough exoskeleton Jointed appendages Body
Chapter 28 Arthropods and Echinoderms Introduction to Arthropods jointed feet Most diverse and successful animals Over 750,000 species identified Segmented bodies Tough exoskeleton Jointed appendages Body
Lecture Notes Chapter 14
 Lecture Notes Chapter 14 I. Chordata- phylum A. 3 subphyla 1. Urochordata 2. Cephalochordata 3. Vertebrata II. Characteristics of all Chordates (found during some part of the life cycle) A. All have a
Lecture Notes Chapter 14 I. Chordata- phylum A. 3 subphyla 1. Urochordata 2. Cephalochordata 3. Vertebrata II. Characteristics of all Chordates (found during some part of the life cycle) A. All have a
What is an animal? Introduction to Animals 2. Phylum Mollusca. Phylum Mollusca 4/20/2016
 What is an animal? Introduction to Animals 2 Multicellular chemoorganoheterotrophs Eukaryotes that lack cell walls and chloroplasts Have mitochondria Are motile at some point in their lives Snails, Octopus,
What is an animal? Introduction to Animals 2 Multicellular chemoorganoheterotrophs Eukaryotes that lack cell walls and chloroplasts Have mitochondria Are motile at some point in their lives Snails, Octopus,
Dichotomous Key to the Animal Kingdom
 Dichotomous Key to the Animal Kingdom Purpose: To learn to use a dichotomous classification key. Materials: Pictures representing all the classes of the subphylum Vertebrata Pictures representing the different
Dichotomous Key to the Animal Kingdom Purpose: To learn to use a dichotomous classification key. Materials: Pictures representing all the classes of the subphylum Vertebrata Pictures representing the different
Classification. Phylum Chordata
 AP Biology Chapter 23 Exercise #17: Chordates: Urochordata & Cephalochordata Lab Guide Chordates show remarkable diversity. Most are vertebrates. All animals that belong to this phylum MUST, at some point
AP Biology Chapter 23 Exercise #17: Chordates: Urochordata & Cephalochordata Lab Guide Chordates show remarkable diversity. Most are vertebrates. All animals that belong to this phylum MUST, at some point
1) Which of the following is NOT a class in the phylum Porifera: a) Aschelminthes b) Hexactinellida c) Calcareous d) Demosponges
 Martha - Porifera: 1) Which of the following is NOT a class in the phylum Porifera: a) Aschelminthes b) Hexactinellida c) Calcareous d) Demosponges 2) What can sponges NOT be used for: a) Arts b) Bathing
Martha - Porifera: 1) Which of the following is NOT a class in the phylum Porifera: a) Aschelminthes b) Hexactinellida c) Calcareous d) Demosponges 2) What can sponges NOT be used for: a) Arts b) Bathing
 http://bio.fsu.edu/~bsc2011l/ Click on Course Documents, then Lab Documents Look at each lab (1 or more phyla) and the images posted. This presentation is also available: Click on Course Documents, then
http://bio.fsu.edu/~bsc2011l/ Click on Course Documents, then Lab Documents Look at each lab (1 or more phyla) and the images posted. This presentation is also available: Click on Course Documents, then
Sponges are considered the oldest of the animal phyla. The name Porifera means "pore bearer" in Latin.
 Animals All animals are members of the Kingdom Animalia, also called Metazoa. This Kingdom does not contain prokaryotes (Kingdom Monera, includes bacteria, blue green algae) or protists (Kingdom Protista,
Animals All animals are members of the Kingdom Animalia, also called Metazoa. This Kingdom does not contain prokaryotes (Kingdom Monera, includes bacteria, blue green algae) or protists (Kingdom Protista,
Invertebrate Notes. Arthropoda. Subphylum: Cheliceratahorseshoe. crabs, spiders, scorpions, mites, & ticks
 Invertebrate Notes Invertebrate Phyla: Trilobita-- trilobites (extinct) Arthropoda Cheliceratahorseshoe crabs, spiders, scorpions, mites, & ticks Mandibulata-- crustaceans, insects, millipedes, centipedes
Invertebrate Notes Invertebrate Phyla: Trilobita-- trilobites (extinct) Arthropoda Cheliceratahorseshoe crabs, spiders, scorpions, mites, & ticks Mandibulata-- crustaceans, insects, millipedes, centipedes
What is an animal? Heterotrophs Multicellular Eukaryotic Cells No Cell Walls Bodies contain tissues : Epithelial Muscular Connective Nervous
 Animals What is an animal? Heterotrophs Multicellular Eukaryotic Cells No Cell Walls Bodies contain tissues : Epithelial Muscular Connective Nervous Epithelial Cover body surfaces: skin, lining of lungs
Animals What is an animal? Heterotrophs Multicellular Eukaryotic Cells No Cell Walls Bodies contain tissues : Epithelial Muscular Connective Nervous Epithelial Cover body surfaces: skin, lining of lungs
Biol Echinoderms & Chordates. But first a few words about Development
 Biol 1309 Echinoderms & Chordates 1 But first a few words about Development Blastula- zygote first develops into a hollow ball of cells Deuterostome - mouth second Protostome - mouth first Cleavage - describes
Biol 1309 Echinoderms & Chordates 1 But first a few words about Development Blastula- zygote first develops into a hollow ball of cells Deuterostome - mouth second Protostome - mouth first Cleavage - describes
Characteristics of Animals pp Topic 7: Animal Diversity Ch Symmetry pp Characteristics of Animals
 Topic 7: Animal Diversity Ch. 32-34 Characteristics of Animals pp.704-705 Animals: Are eukaryotic Are multicellular Are ingestive heterotrophs Have no cell walls Most are motile Most have tissues organized
Topic 7: Animal Diversity Ch. 32-34 Characteristics of Animals pp.704-705 Animals: Are eukaryotic Are multicellular Are ingestive heterotrophs Have no cell walls Most are motile Most have tissues organized
Copyright 2011 Pearson Education, Inc.
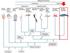 Urochordata (tunicates) Cephalochordata (lancelets) Myxini (hagfishes) Petromyzontiformes (lampreys) Chondrichthyes (sharks, rays) Actinopterygii (ray-finned fish) Actinistia (coelacanths) Dipnoi (lungfishes)
Urochordata (tunicates) Cephalochordata (lancelets) Myxini (hagfishes) Petromyzontiformes (lampreys) Chondrichthyes (sharks, rays) Actinopterygii (ray-finned fish) Actinistia (coelacanths) Dipnoi (lungfishes)
Downloaded from
 POINTS TO REMEMBER : 4. Animal Kingdom Levels of organization : Cellular level Tissue level Organ level Organ system level Circulatory System : Open type: Blood pumped out through heart. Cells and tissues
POINTS TO REMEMBER : 4. Animal Kingdom Levels of organization : Cellular level Tissue level Organ level Organ system level Circulatory System : Open type: Blood pumped out through heart. Cells and tissues
Phylum Mollusca Snails, slugs, oysters, clams, octopuses, and squids
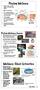 Phylum Mollusca Snails, slugs, oysters, clams, octopuses, and squids Nephridium Most are marine Visceral mass Soft-bodied animals, but most are protected by a hard shell Coelom Digestive tract Gonads Shell
Phylum Mollusca Snails, slugs, oysters, clams, octopuses, and squids Nephridium Most are marine Visceral mass Soft-bodied animals, but most are protected by a hard shell Coelom Digestive tract Gonads Shell
The Deuterostomes and the rise of the Vertebrates: from Echinoderms to Man
 The Deuterostomes and the rise of the Vertebrates: from Echinoderms to Man 1 The Deuterostomes Calcarea and Silicea Cnidaria Lophotrochozoa Ecdysozoa Deuterostomia 2 The Ancestral Deuterostome Bilateral
The Deuterostomes and the rise of the Vertebrates: from Echinoderms to Man 1 The Deuterostomes Calcarea and Silicea Cnidaria Lophotrochozoa Ecdysozoa Deuterostomia 2 The Ancestral Deuterostome Bilateral
5 Marine Biology Notes. Marine Invertebrates (Animals Without a Backbone)
 5 Marine Biology Notes Marine Invertebrates (Animals Without a Backbone) Invertebrates Animals without a backbone are known as invertebrates. Those with a backbone are called vertebrates. About 97% of
5 Marine Biology Notes Marine Invertebrates (Animals Without a Backbone) Invertebrates Animals without a backbone are known as invertebrates. Those with a backbone are called vertebrates. About 97% of
Chapter 33 - Protostome Animals
 Chapter 33 - Protostome Animals Learning Objectives: Students should be able to... Describe the major characteristics that differentiate the Ecdysozoa and the Lophotrochozoa. List and describe the basic
Chapter 33 - Protostome Animals Learning Objectives: Students should be able to... Describe the major characteristics that differentiate the Ecdysozoa and the Lophotrochozoa. List and describe the basic
Course: Biology 211 Iowa State University
 Leader: Elizabeth Supplemental Instruction Course: Biology 211 Iowa State University Instructor: Dr. Deitloff Date: 2/27/14 Exam 2: Chapters 31 through 34 and information from guest lecturer 50 questions
Leader: Elizabeth Supplemental Instruction Course: Biology 211 Iowa State University Instructor: Dr. Deitloff Date: 2/27/14 Exam 2: Chapters 31 through 34 and information from guest lecturer 50 questions
What are the four main characteristics of arthropods? What are two types of metamorphosis in insects?
 CHAPTER 15 3 Arthropods SECTION Invertebrates BEFORE YOU READ After you read this section, you should be able to answer these questions: What are the four main characteristics of arthropods? What are two
CHAPTER 15 3 Arthropods SECTION Invertebrates BEFORE YOU READ After you read this section, you should be able to answer these questions: What are the four main characteristics of arthropods? What are two
Chapter 35. Table of Contents. Section 1 Mollusca. Section 2 Annelida. Mollusks and Annelids
 Mollusks and Annelids Table of Contents Section 1 Mollusca Section 2 Annelida Section 1 Mollusca Objectives Describe the key characteristics of mollusks. Describe the body plan of mollusks. Name the characteristics
Mollusks and Annelids Table of Contents Section 1 Mollusca Section 2 Annelida Section 1 Mollusca Objectives Describe the key characteristics of mollusks. Describe the body plan of mollusks. Name the characteristics
Edible, and. Coral Reefs! Photo: CEDixon
 Spreadable, Edible, and Incredible Coral Reefs! Carrie Dixon Discovery Hall Programs Dauphin Island Sea Lab, AL Photo: CEDixon National Science Content Standards Life Science Content Standard, Grades K-4:
Spreadable, Edible, and Incredible Coral Reefs! Carrie Dixon Discovery Hall Programs Dauphin Island Sea Lab, AL Photo: CEDixon National Science Content Standards Life Science Content Standard, Grades K-4:
Invertebrates. Sponges: Porifera pore bearer 10/8/09
 Animals without backbones We ll cover characteristics of major phyla and some to class level (KPCOFGS) We ll also cover some natural history Refer to your notes that I posted on-line! Invertebrates Levels
Animals without backbones We ll cover characteristics of major phyla and some to class level (KPCOFGS) We ll also cover some natural history Refer to your notes that I posted on-line! Invertebrates Levels
Chapter 36. Table of Contents. Section 1 Phylum Arthropoda. Section 2 Subphylum Crustacea. Section 3 Subphylum Chelicerata and Myriapoda.
 Arthropods Table of Contents Section 1 Phylum Arthropoda Section 2 Subphylum Crustacea Section 3 Subphylum Chelicerata and Myriapoda Section 1 Phylum Arthropoda Objectives Describe the distinguishing characteristics
Arthropods Table of Contents Section 1 Phylum Arthropoda Section 2 Subphylum Crustacea Section 3 Subphylum Chelicerata and Myriapoda Section 1 Phylum Arthropoda Objectives Describe the distinguishing characteristics
What Is an Annelid? Annelids are worms with segmented bodies. They have a true coelom that is lined with tissue derived from mesoderm.
 What Is an Annelid? What Is an Annelid? Phylum: Annelidae Annelids are worms with segmented bodies. They have a true coelom that is lined with tissue derived from mesoderm. Three Germ Layers of an Annelid
What Is an Annelid? What Is an Annelid? Phylum: Annelidae Annelids are worms with segmented bodies. They have a true coelom that is lined with tissue derived from mesoderm. Three Germ Layers of an Annelid
`Mollusks. may or may not form a hard, calcium carbonate shell. Trochophore Larva
 `Mollusks Phylum Mollusca Soft-bodied invertebrate covered with protective mantle that may or may not form a hard, calcium carbonate shell Includes chitons, snails, slugs, clams, oysters, squid, octopus,
`Mollusks Phylum Mollusca Soft-bodied invertebrate covered with protective mantle that may or may not form a hard, calcium carbonate shell Includes chitons, snails, slugs, clams, oysters, squid, octopus,
26-3 Cnidarians Slide 1 of 47
 1 of 47 What Is a Cnidarian? What is a cnidarian? 2 of 47 What Is a Cnidarian? What Is a Cnidarian? Cnidarians are soft-bodied, carnivorous animals that have stinging tentacles arranged in circles around
1 of 47 What Is a Cnidarian? What is a cnidarian? 2 of 47 What Is a Cnidarian? What Is a Cnidarian? Cnidarians are soft-bodied, carnivorous animals that have stinging tentacles arranged in circles around
 Kingdom: Animalia Phylum:Mollusca Classes: Bivalva, Gastropoda, Cephalopoda http://www.youtube.com/watch?v=0a7j5prl8hc&feature=related http://www2.beavercreek.k12.oh.us/videos/45/pgr45_700k.asf What is
Kingdom: Animalia Phylum:Mollusca Classes: Bivalva, Gastropoda, Cephalopoda http://www.youtube.com/watch?v=0a7j5prl8hc&feature=related http://www2.beavercreek.k12.oh.us/videos/45/pgr45_700k.asf What is
PHYLUM CHORDATA: Subphylum vertebrata
 PHYLUM CHORDATA: Subphylum vertebrata There are three basic characteristics that distinguish Phylum Chordata from all other animal phyla: The presence of a flexible, rod-like, internal supporting structure
PHYLUM CHORDATA: Subphylum vertebrata There are three basic characteristics that distinguish Phylum Chordata from all other animal phyla: The presence of a flexible, rod-like, internal supporting structure
Chordates. Bởi: OpenStaxCollege
 Chordates Bởi: OpenStaxCollege Vertebrates are members of the kingdom Animalia and the phylum Chordata ([link]). Recall that animals that possess bilateral symmetry can be divided into two groups protostomes
Chordates Bởi: OpenStaxCollege Vertebrates are members of the kingdom Animalia and the phylum Chordata ([link]). Recall that animals that possess bilateral symmetry can be divided into two groups protostomes
What is an animal? 10/22/17. Bio 242 Laboratory Module 2
 Bio 242 Laboratory Module 2 Theme: Evolution shapes the flow and pattern of information through phylogenetic lineages, evident in the linkage between form and function Objectives -we will track the effects
Bio 242 Laboratory Module 2 Theme: Evolution shapes the flow and pattern of information through phylogenetic lineages, evident in the linkage between form and function Objectives -we will track the effects
Name Date Period. Mollusk Review TORSION HEMOLYMPH SESSILE TROCHOPHORE ADDUCTOR KIDNEY HEMOCOEL MANTLE CHROMATOPHORES VISCERAL MASS
 Name Date Period Mollusk Review MOLLUSK VOCABULARY: Match the word with its definition. TORSION HEMOLYMPH SESSILE TROCHOPHORE ADDUCTOR KIDNEY HEMOCOEL MANTLE CHROMATOPHORES VISCERAL MASS Free-swimming
Name Date Period Mollusk Review MOLLUSK VOCABULARY: Match the word with its definition. TORSION HEMOLYMPH SESSILE TROCHOPHORE ADDUCTOR KIDNEY HEMOCOEL MANTLE CHROMATOPHORES VISCERAL MASS Free-swimming
Protostome: Embryonic blastopore becomes mouth
 Classical hypothesis Molecular hypothesis Adoutte 2000 PNAS Protostome: Embryonic blastopore becomes mouth Schizocoelous development (typical of the protostome coelomates) 1 Deuterostome: Embryonic blastopore
Classical hypothesis Molecular hypothesis Adoutte 2000 PNAS Protostome: Embryonic blastopore becomes mouth Schizocoelous development (typical of the protostome coelomates) 1 Deuterostome: Embryonic blastopore
Phylum Platyhelminthes. You will need: five colours of pencil crayon or pen (preferably blue, green, red, orange and purple)
 Phylum Platyhelminthes You will need: five colours of pencil crayon or pen (preferably blue, green, red, orange and purple) Phylum Platyhelminthes bilaterally symmetrical have all 3 embryonic germ layers:
Phylum Platyhelminthes You will need: five colours of pencil crayon or pen (preferably blue, green, red, orange and purple) Phylum Platyhelminthes bilaterally symmetrical have all 3 embryonic germ layers:
Animal Evolution The Invertebrates
 Animal Evolution The Invertebrates More than 500 predatory mollusks live in the sea Use conotoxins to paralyze their prey Conotoxins interest biologists as potential sources for new drugs C. geographicus
Animal Evolution The Invertebrates More than 500 predatory mollusks live in the sea Use conotoxins to paralyze their prey Conotoxins interest biologists as potential sources for new drugs C. geographicus
 Echinoderms Name Means: Echino- Spiny Derm- Skin About 7,000 species No Head! No Brain! No ventral, dorsal, posterior, or anterior sides! Do have oral (mouth) and aboral sides. Symmetry: Larvae are
Echinoderms Name Means: Echino- Spiny Derm- Skin About 7,000 species No Head! No Brain! No ventral, dorsal, posterior, or anterior sides! Do have oral (mouth) and aboral sides. Symmetry: Larvae are
2 Mollusks and Annelid Worms
 CHAPTER 15 2 Mollusks and Annelid Worms SECTION Invertebrates BEFORE YOU READ After you read this section, you should be able to answer these questions: What are the four features of mollusks? What are
CHAPTER 15 2 Mollusks and Annelid Worms SECTION Invertebrates BEFORE YOU READ After you read this section, you should be able to answer these questions: What are the four features of mollusks? What are
Tropical Marine Invertebrates. Phylum Arthropoda. Phylum ARTHROPODA CAS BI 569
 Tropical Marine Invertebrates CAS BI 569 Phylum ARTHROPODA by John R. Finnerty Phylum Arthropoda Well over 1 million described extant species Four critical bodyplan features. Chitinous exoskeleton Segmented
Tropical Marine Invertebrates CAS BI 569 Phylum ARTHROPODA by John R. Finnerty Phylum Arthropoda Well over 1 million described extant species Four critical bodyplan features. Chitinous exoskeleton Segmented
Arthropods, Echinoderms, and Chordates
 Arthropods, Echinoderms, and Chordates Bi 10 10/22/2013 Revised Schedule Friday, Nov. 22: Chapter 17, Part 2 Chapter 15, 16 Reading Quiz Due Wednesday, Nov. 27: Special Lecture: Review + World s Weirdest
Arthropods, Echinoderms, and Chordates Bi 10 10/22/2013 Revised Schedule Friday, Nov. 22: Chapter 17, Part 2 Chapter 15, 16 Reading Quiz Due Wednesday, Nov. 27: Special Lecture: Review + World s Weirdest
Figure 33.25a Free-living nematode
 Figure 33.25a Free-living nematode Bilateraly symmetrical Pseudocoelomates Body covered with secreated, flexible cuticle. No cilia Only longitudinal muscles. No protonephridia Muscular pharynx Gonochoristic
Figure 33.25a Free-living nematode Bilateraly symmetrical Pseudocoelomates Body covered with secreated, flexible cuticle. No cilia Only longitudinal muscles. No protonephridia Muscular pharynx Gonochoristic
Philosophy and objectives of the course Overview of the Phylum Arthropoda D. L. A. Underwood Biology General Entomology
 Philosophy and objectives of the course Overview of the Phylum Arthropoda D. L. A. Underwood Biology 316 - General Entomology A. Course format 1. Assignment of teams a. Pass out cards with numbers and
Philosophy and objectives of the course Overview of the Phylum Arthropoda D. L. A. Underwood Biology 316 - General Entomology A. Course format 1. Assignment of teams a. Pass out cards with numbers and
Specimen Collection and Classification Activity
 Specimen Collection and Classification Activity Understanding the classification of animals is an important building block of science education, yet most adults cannot tell you how to group the most common
Specimen Collection and Classification Activity Understanding the classification of animals is an important building block of science education, yet most adults cannot tell you how to group the most common
Chapter 12 Part 2. The Worms Platyhelminthes, Nematoda & Annelida
 Chapter 12 Part 2 The Worms Platyhelminthes, Nematoda & Annelida Phylum: Platyhelminthes Examples: Flatworms, Planaria sp., tapeworms and blood flukes Acoelomate, Invertebrate, Simplest critter w/ bilateral
Chapter 12 Part 2 The Worms Platyhelminthes, Nematoda & Annelida Phylum: Platyhelminthes Examples: Flatworms, Planaria sp., tapeworms and blood flukes Acoelomate, Invertebrate, Simplest critter w/ bilateral
Phylum Platyhelminthes Phylum Nematoda Phylum Mollusca. By: Jerzylin, Beata & Jennifer
 Phylum Platyhelminthes Phylum Nematoda Phylum Mollusca By: Jerzylin, Beata & Jennifer Phylum Platyhelminthes Common Characteristics: Triploblastic Bilateral Symmetry Protostome No true stomach structure
Phylum Platyhelminthes Phylum Nematoda Phylum Mollusca By: Jerzylin, Beata & Jennifer Phylum Platyhelminthes Common Characteristics: Triploblastic Bilateral Symmetry Protostome No true stomach structure
Invertebrates. Sponges: Porifera pore bearer 10/3/13
 Animals without backbones We ll cover characteristics of major phyla and some to class level (KPCOFGS) We ll also cover some natural history Refer to your notes that I posted on-line! Invertebrates Levels
Animals without backbones We ll cover characteristics of major phyla and some to class level (KPCOFGS) We ll also cover some natural history Refer to your notes that I posted on-line! Invertebrates Levels
Chapter 6 SPONGES. Invertebrates. Sponges. Pore-Bearers. Movement of Water
 Invertebrates Chapter 6 Animals Without Backbones Animals that lack a backbone are called invertebrates. It is estimated that 97% of all species of animals are invertebrates. With the exception of insects,
Invertebrates Chapter 6 Animals Without Backbones Animals that lack a backbone are called invertebrates. It is estimated that 97% of all species of animals are invertebrates. With the exception of insects,
Chapter 29 Echinoderms and Invertebrate Chordates. Section Echinoderms. I. What Is An Echinoderm? 11/1/2010. Biology II Mrs.
 Chapter 29 Echinoderms and Invertebrate Chordates Section 29.1 - Echinoderms Biology II Mrs. Michaelsen I. What Is An Echinoderm? A. Move by means of hydraulic, suction cuptipped appendages. B. Skin covered
Chapter 29 Echinoderms and Invertebrate Chordates Section 29.1 - Echinoderms Biology II Mrs. Michaelsen I. What Is An Echinoderm? A. Move by means of hydraulic, suction cuptipped appendages. B. Skin covered
"Protochordates" BIO3334 Invertebrate Zoology. Page 1. Hemichordates and Invertebrate chordates. Protochordate taxa 2 8:30 AM
 Hemichordates and Invertebrate chordates 1 Protochordate taxa Phylum. Hemichordata Class. Enteropneusta Class. Pterobranchia Phylum. Chordata Subphylum. Urochordata Subphylum. Cephalochordata Subphylum.
Hemichordates and Invertebrate chordates 1 Protochordate taxa Phylum. Hemichordata Class. Enteropneusta Class. Pterobranchia Phylum. Chordata Subphylum. Urochordata Subphylum. Cephalochordata Subphylum.
Chordates. Chapter 23
 Chordates Chapter 23 Phylum Chordata By the end of the Cambrian period, 540 million years ago, an astonishing variety of animals inhabited Earth s oceans. One of these types of animals gave rise to vertebrates,
Chordates Chapter 23 Phylum Chordata By the end of the Cambrian period, 540 million years ago, an astonishing variety of animals inhabited Earth s oceans. One of these types of animals gave rise to vertebrates,
Hemichordates and Invert chordates
 Hemichordates and Invertebrate chordates 1 Animal innovations (Symplesiomorphies) Pharyngeal gill slits Dorsal hollow nerve cord Porifera Placozoa Cnidaria Ctenophora Platyhelminthes Gastrotricha Gnathostomulida
Hemichordates and Invertebrate chordates 1 Animal innovations (Symplesiomorphies) Pharyngeal gill slits Dorsal hollow nerve cord Porifera Placozoa Cnidaria Ctenophora Platyhelminthes Gastrotricha Gnathostomulida
BIO 221 Invertebrate Zoology I Spring Larval Development. Larval Development. Lecture 18
 BIO 221 Invertebrate Zoology I Spring 2010 Stephen M. Shuster Northern Arizona University http://www4.nau.edu/isopod Lecture 18 Larval Development 1. Often presented as a progression of stages a. Representative
BIO 221 Invertebrate Zoology I Spring 2010 Stephen M. Shuster Northern Arizona University http://www4.nau.edu/isopod Lecture 18 Larval Development 1. Often presented as a progression of stages a. Representative
ADVANCED INVERTEBRATES HAVE COMPLEX BODIES AND INTERNAL SYSTEMS
 ADVANCED INVERTEBRATES HAVE COMPLEX BODIES AND INTERNAL SYSTEMS Arthropoda Most successful phylum on Earth Exoskeleton chitin Striated muscle Articulation Crayfish, lobsters, shrimp, crabs Echinodermata
ADVANCED INVERTEBRATES HAVE COMPLEX BODIES AND INTERNAL SYSTEMS Arthropoda Most successful phylum on Earth Exoskeleton chitin Striated muscle Articulation Crayfish, lobsters, shrimp, crabs Echinodermata
Chapter 34A: The Origin & Evolution of Vertebrates I. 1. Overview of the Chordates 2. Invertebrate Chordates
 Chapter 34A: The Origin & Evolution of Vertebrates I 1. Overview of the Chordates 2. Invertebrate Chordates 1. Overview of Chordates Echinodermata Phylogeny of ANCESTRAL DEUTEROSTOME NOTOCHORD Common ancestor
Chapter 34A: The Origin & Evolution of Vertebrates I 1. Overview of the Chordates 2. Invertebrate Chordates 1. Overview of Chordates Echinodermata Phylogeny of ANCESTRAL DEUTEROSTOME NOTOCHORD Common ancestor
27/12/2012. Learning Outcome G4
 Learning Outcome G4 Learning Outcome G4 Analyse the increasing complexity of the Phylum Mollusca, the Phylum Echinodermata, and the Phylum Arthropoda Phylum Mollusca, Echinodermata & Arthropoda Students
Learning Outcome G4 Learning Outcome G4 Analyse the increasing complexity of the Phylum Mollusca, the Phylum Echinodermata, and the Phylum Arthropoda Phylum Mollusca, Echinodermata & Arthropoda Students
Readings in Chapter 2, 3, and 7.
 Early Vertebrates Readings in Chapter 2, 3, and 7. Using the Tree of Life Web Project www.tolweb.org org A project to put the entire tree of life, a phylogeny of all life, on the web. Biologists world-wide
Early Vertebrates Readings in Chapter 2, 3, and 7. Using the Tree of Life Web Project www.tolweb.org org A project to put the entire tree of life, a phylogeny of all life, on the web. Biologists world-wide
Unit 18.2: Mollusks and Annelids
 Unit 18.2: Mollusks and Annelids Lesson Objectives Describe invertebrates in the phylum Mollusca. Summarize the characteristics of annelids. Vocabulary Annelida deposit feeder gills heart mantle Mollusca
Unit 18.2: Mollusks and Annelids Lesson Objectives Describe invertebrates in the phylum Mollusca. Summarize the characteristics of annelids. Vocabulary Annelida deposit feeder gills heart mantle Mollusca
Body Plan of the Chordates. Notochord, dorsal hollow nerve cord, pharyngeal gill slits, blocks of muscle, post-anal tail
 Chordata The Major Groups Invertebrate Chordates Fishes Class: Agnatha Class Condrichthyes Class Osteichthyes Class: Amphibia Class: Reptilia Class: Aves Class: Mammalia Body Plan of the Chordates Notochord,
Chordata The Major Groups Invertebrate Chordates Fishes Class: Agnatha Class Condrichthyes Class Osteichthyes Class: Amphibia Class: Reptilia Class: Aves Class: Mammalia Body Plan of the Chordates Notochord,
Chapter 28 Mollusks & Annelids. BIOLOGY II Miss. Loulousis
 Chapter 28 Mollusks & Annelids BIOLOGY II Miss. Loulousis Mollusks have a true coelom Snails, slugs, oysters, clams, scallops, octopuses, and squids are all mollusks Annelid earthworm next section Mollusks
Chapter 28 Mollusks & Annelids BIOLOGY II Miss. Loulousis Mollusks have a true coelom Snails, slugs, oysters, clams, scallops, octopuses, and squids are all mollusks Annelid earthworm next section Mollusks
Annelida and other worms
 Phylum Annelida 1 Trochozoa (autapomorphie) Presence of the trochophore larval stage Porifera Placozoa Cnidaria Ctenophora Platyhelminthes Gastrotricha Gnathostomulida Cycliophora Rotifera Annelida Mollusca
Phylum Annelida 1 Trochozoa (autapomorphie) Presence of the trochophore larval stage Porifera Placozoa Cnidaria Ctenophora Platyhelminthes Gastrotricha Gnathostomulida Cycliophora Rotifera Annelida Mollusca
