BIOLOGY. An Introduction to Invertebrates CAMPBELL. Reece Urry Cain Wasserman Minorsky Jackson
|
|
|
- Esther Mills
- 6 years ago
- Views:
Transcription
1 CAMPBELL BIOLOGY TENTH EDITION Reece Urry Cain Wasserman Minorsky Jackson 33 An Introduction to Invertebrates Lecture Presentation by Nicole Tunbridge and Kathleen Fitzpatrick
2 Deuterostomia Metazoa Eumetazoa Bilateria Ecdysozoa Lophotrochozoa Figure 33.UN08 Phylum Porifera (sponges) Cnidaria (hydras, jellies, sea anemones, corals) Platyhelminthes (flatworms) Rotifera (rotifers) Lophophorates: Ectoprocta, Brachiopoda Mollusca (clams, snails, squids) Annelida (segmented worms) Nematoda (roundworms) Arthropoda (spiders, centipedes, crustaceans, and insects) Echinodermata (sea stars, sea urchins) Chordata (lancelets, tunicates, vertebrates) Description Lack true tissues; have choanocytes (collar cells flagellated cells that ingest bacteria and tiny food particles) Unique stinging structures (nematocytes) housed in specialized cells (cnidocytes); diploblastic; radially symmetrical; gastrovascular cavity (digestive compartment with a single opening) Dorsoventrally flattened acoelomates; gastrovascular cavity or no digestive tract Pseudocoelomates with alimentary canal (digestive tube with mouth and anus); jaws (trophi); head with ciliated crown Coelomates with lophophores (feeding structures bearing ciliated tentacles) Coelomates with three main body parts (muscular foot, visceral mass, mantle); coelom reduced; most have hard shell made of calcium carbonate Coelomates with segmented body wall and internal organs (except digestive tract, which is unsegmented) Cylindrical pseudocoelomates with tapered ends; no circulatory system; undergo ecdysis Coelomates with segmented body, jointed appendages, and exoskeleton made of protein and chitin Coelomates with bilaterally symmetrical larvae and five-part body organization as adults; unique water vascular system; endoskeleton Coelomates with notochord; dorsal, hollow nerve cord; pharyngeal slits; post-anal tail (see Chapter 34)
3 Figure 33.2 Porifera ANCESTRAL PROTIST Cnidaria Common ancestor of all animals Eumetazoa Bilateria Lophotrochozoa Ecdysozoa Deuterostomia
4 Figure 33.UN03 Porifera Cnidaria Lophotrochozoa Ecdysozoa Deuterostomia Bilateria Bilaterian animals have bilateral symmetry and triploblastic development Most have a coelom and a digestive tract with two openings
5 Concept 33.3: Lophotrochozoans, a clade identified by molecular data, have the widest range of animal body forms Some develop a lophophore for feeding, others pass through a trochophore larval stage, and a few have neither feature The clade Lophotrochozoa was identified by molecular data Lophotrochozoa includes the flatworms, rotifers, ectoprocts, brachiopods, molluscs, and annelids
6 Flatworms Members of phylum Platyhelminthes live in marine, freshwater, and damp terrestrial habitats Triploblastic, acoelomates Flatworms have a gastrovascular cavity with one opening Gas exchange takes place across the surface, and protonephridia regulate the osmotic balance Their dorsoventrally flattened shape maximizes surface area for gas exchange
7 Figure 33.9 MAKE CONNECTIONS: Maximizing Surface Area Folding Flattening SA: 6 (3 cm 3 cm) = 54 cm 2 V: 3 cm 3 cm 3 cm = 27 cm 3 1 µm Thylakoid SA: 2 (3 cm 1 cm) + 2 (9 cm 1 cm) + 2 (3 cm 9 cm) = 78 cm 2 V: 1 cm 3 cm 9 cm = 27 cm 3 Diagrams comparing surface area (SA) for two different shapes with the same volume (V) Branching Projections
8 Flatworms are divided into two lineages Rhabditophora (Planarian) Free-living Planarians live in fresh water and prey on smaller animals Planarians have light-sensitive eyespots and centralized nerve nets The planarian nervous system is more complex and centralized than the nerve nets of cnidarians
9 Parasitic rhabditophorans live in or on other animals Two important groups of parasitic rhabditophorans are the trematodes and the tapeworms parasites of vertebrates and lack a digestive system Tapeworms absorb nutrients from the host s intestine
10 Rotifers Rotifers, phylum Rotifera, are tiny animals that inhabit fresh water, the ocean, and damp soil Rotifers are smaller than many protists but are truly multicellular and have specialized organ systems
11 Ectoprocts and Brachiopods Lophophorates have a lophophore, a crown of ciliated tentacles around their mouth Lophophorates have a true coelom
12 Deuterostomia Metazoa Eumetazoa Bilateria Ecdysozoa Lophotrochozoa Figure 33.UN08 Phylum Porifera (sponges) Cnidaria (hydras, jellies, sea anemones, corals) Platyhelminthes (flatworms) Rotifera (rotifers) Lophophorates: Ectoprocta, Brachiopoda Mollusca (clams, snails, squids) Annelida (segmented worms) Nematoda (roundworms) Arthropoda (spiders, centipedes, crustaceans, and insects) Echinodermata (sea stars, sea urchins) Chordata (lancelets, tunicates, vertebrates) Description Lack true tissues; have choanocytes (collar cells flagellated cells that ingest bacteria and tiny food particles) Unique stinging structures (nematocytes) housed in specialized cells (cnidocytes); diploblastic; radially symmetrical; gastrovascular cavity (digestive compartment with a single opening) Dorsoventrally flattened acoelomates; gastrovascular cavity or no digestive tract Pseudocoelomates with alimentary canal (digestive tube with mouth and anus); jaws (trophi); head with ciliated crown Coelomates with lophophores (feeding structures bearing ciliated tentacles) Coelomates with three main body parts (muscular foot, visceral mass, mantle); coelom reduced; most have hard shell made of calcium carbonate Coelomates with segmented body wall and internal organs (except digestive tract, which is unsegmented) Cylindrical pseudocoelomates with tapered ends; no circulatory system; undergo ecdysis Coelomates with segmented body, jointed appendages, and exoskeleton made of protein and chitin Coelomates with bilaterally symmetrical larvae and five-part body organization as adults; unique water vascular system; endoskeleton Coelomates with notochord; dorsal, hollow nerve cord; pharyngeal slits; post-anal tail (see Chapter 34)
13 Molluscs Phylum Mollusca includes snails and slugs, oysters and clams, and octopuses and squids Mostly marine, soft-bodied animals but most are protected by a hard shell Four of the major classes of molluscs are Polyplacophora (chitons) Gastropoda (snails and slugs) Bivalvia (clams, oysters, and other bivalves) Cephalopoda (squids, octopuses, cuttlefish, and chambered nautiluses)
14 All molluscs have a similar body plan with three main parts Muscular foot Visceral mass Mantle Many molluscs also have a water-filled mantle cavity and feed using a rasplike radula
15 Gastropods About three-quarters of all living species of molluscs are gastropods Gastropods move slowly by a rippling motion of the foot or by cilia Most have a single, spiraled shell that functions in protection from injury, dehydration, and predation
16 Cephalopods Cephalopods are carnivores with beak-like jaws surrounded by tentacles of their modified foot Squids use their siphon to fire a jet of water, which allows them to swim very quickly
17 Annelids Annelids are coelomates with bodies composed of a series of fused rings The phylum Annelida was traditionally divided into three clades Polychaeta (polychaetes) Oligochaeta (oligochaetes) Hirundinea (leeches) two major clades - Errantia - Sedentaria
18 Sedentarians Sedentarians tend to be less mobile than errantians Some species burrow into the substrate, while others live in protective tubes
19 Concept 33.4: Ecdysozoans are the most species-rich animal group Ecdysozoans are covered by a tough coat called a cuticle The cuticle is shed or molted through a process called ecdysis The two largest phyla are nematodes and arthropods
20 Nematodes Nematodes, or roundworms, are found in most aquatic habitats, in the soil, in moist tissues of plants, and in body fluids and tissues of animals Caenorhabditis elegans is a model organism in research Trichinella spiralis can be acquired by humans from undercooked pork
21 Arthropod Two out of every three known species of animals are arthropods The arthropod body plan consists of a segmented body, hard exoskeleton, and jointed appendages trilobite
22 Arthropod evolution is characterized by a decrease in the number of segments and an increase in appendage specialization These changes may have been caused by changes in Hox gene sequence or regulation
23 Figure Experiment Origin of Ubx and abd-a Hox genes? Other ecdysozoans Arthropods Common ancestor Onychophorans Results Ant = antenna J = jaws L1 L15 = body segments
24 General Characteristics of Arthropods The appendages of some living arthropods are modified for functions such as walking, feeding, sensory reception, reproduction, and defense These modified appendages are jointed and come in pairs Arthropod evolution is characterized by a decrease in the number of segments and an increase in appendage specialization These changes may have been caused by changes in Hox gene sequence or regulation
25 Morphological and molecular evidence suggests that living arthropods consist of three major lineages that diverged early in the phylum s evolution Chelicerates (sea spiders, horseshoe crabs, scorpions, ticks, mites, and spiders) Myriapods (centipedes and millipedes) Pancrustaceans (lobsters and other crustaceans, as well as insects and their relatives)
26 Chelicerates Chelicerates, clade Chelicerata, are named for clawlike feeding appendages called chelicerae Most modern chelicerates are arachnids, which include spiders, scorpions, ticks, and mites
27 Myriapods The clade Myriapoda includes millipedes and centipedes All living myriapods are terrestrial They have a pair of antennae and three pairs of appendages modified as mouthparts
28 Pancrustaceans Together, insects and crustaceans form the clade Pancrustacea Crustaceans Crustaceans live in marine and freshwater environments, have highly specialized appendages Planktonic crustaceans copepod
29 Insects Hexapoda is an enormous clade including insects and their relatives, live in almost every terrestrial habitat and in fresh water The internal anatomy of an insect includes several complex organ systems
30 Insects diversified several times following the evolution of flight, adaptation to feeding on gymnosperms, and the expansion of angiosperms Insect and plant diversity declined during the Cretaceous extinction, but has been increasing in the 65 million years since
31 Flight is one key to the great success of insects An animal that can fly can escape predators, find food, and disperse to new habitats much faster than organisms that can only crawl Insect wings are an extension of the cuticle
32 Figure Archaeognatha (bristletails; 350 species) Zygentoma (silverfish; 450 species) Winged insects (many orders; six are shown below) Complete metamorphosis Incomplete metamorphosis Coleoptera (beetles; 350,000 species) Hemiptera (85,000 species) Diptera (151,000 species) Orthoptera (13,000 species) Hymenoptera (125,000 species) Proboscis Lepidoptera (120,000 species)
33 Insects with complete metamorphosis have larval stages known by such names as maggot, grub, or caterpillar The larval stage looks entirely different from the adult stage In incomplete metamorphosis, the young, called nymphs, resemble adults but are smaller and go through a series of molts until they reach full size
A. Porifera (sponges): B. Cnidaria (jellies, hydra, sea anemones, and corals):
 Invertebrates Notes A. Porifera (sponges): Porifera literally means. Most sponges are. They are that collect food particles from the water as they pass through flagellated cells called. These cells then
Invertebrates Notes A. Porifera (sponges): Porifera literally means. Most sponges are. They are that collect food particles from the water as they pass through flagellated cells called. These cells then
1. Animals are (diploid) with tissues arranged into organs and organ systems. 3. Animals require for aerobic respiration.
 Chapter 25 Animals: The Invertebrates I. Overview of the Animal Kingdom A. General Characteristics of Animals 1. Animals are (diploid) with tissues arranged into organs and organ systems. 2. Animals are.
Chapter 25 Animals: The Invertebrates I. Overview of the Animal Kingdom A. General Characteristics of Animals 1. Animals are (diploid) with tissues arranged into organs and organ systems. 2. Animals are.
Animal Diversity. Kingdom Animalia
 7ch11 Animal Diversity Kingdom Animalia Animal Characteristics 1. animals are eukaryotes and are multicellular 2. cells are specialized for different functions (vision,digestion,reproduction) 3. protein,
7ch11 Animal Diversity Kingdom Animalia Animal Characteristics 1. animals are eukaryotes and are multicellular 2. cells are specialized for different functions (vision,digestion,reproduction) 3. protein,
An Overview of Animal Diversity
 Fig. 32-1 An Overview of Animal Diversity Multicellular Nutrition mode: Heterotrophic (ingestion) Cell structure & specialization Tissues develop from embryonic layers Nervous & Muscle (unique) Lack cell
Fig. 32-1 An Overview of Animal Diversity Multicellular Nutrition mode: Heterotrophic (ingestion) Cell structure & specialization Tissues develop from embryonic layers Nervous & Muscle (unique) Lack cell
Phylum: Porifera (sponges)
 Phylum: Porifera (sponges) (8,761 known species) General Description: Simplest animals, multicellular No organs or body systems Skeleton composed of spongin (soft) and spicules (hard) Symmetry: Asymmetrical
Phylum: Porifera (sponges) (8,761 known species) General Description: Simplest animals, multicellular No organs or body systems Skeleton composed of spongin (soft) and spicules (hard) Symmetry: Asymmetrical
Ch17_Animals. Animals Multicellular eukaryotes. What is an animal? Animal development. Main differences with plants Main differences with fungi
 Animals Multicellular eukaryotes Domain Domain Kingdoms Main differences with plants Main differences with fungi What is an animal? Domain Nutritional mode: Heterotrophic (Ingestive) Level of organization:
Animals Multicellular eukaryotes Domain Domain Kingdoms Main differences with plants Main differences with fungi What is an animal? Domain Nutritional mode: Heterotrophic (Ingestive) Level of organization:
What is an animal? 10/22/17. Bio 242 Laboratory Module 2
 Bio 242 Laboratory Module 2 Theme: Evolution shapes the flow and pattern of information through phylogenetic lineages, evident in the linkage between form and function Objectives -we will track the effects
Bio 242 Laboratory Module 2 Theme: Evolution shapes the flow and pattern of information through phylogenetic lineages, evident in the linkage between form and function Objectives -we will track the effects
2 Mollusks and Annelid Worms
 CHAPTER 15 2 Mollusks and Annelid Worms SECTION Invertebrates BEFORE YOU READ After you read this section, you should be able to answer these questions: What are the four features of mollusks? What are
CHAPTER 15 2 Mollusks and Annelid Worms SECTION Invertebrates BEFORE YOU READ After you read this section, you should be able to answer these questions: What are the four features of mollusks? What are
Characteris*c s of Living Things 1. Chemical Uniqueness: Molecular Organization
 Characteris*c s of Living Things 1. Chemical Uniqueness: Molecular Organization 2. Hierarchical Organization: macromolecules - > Cells - >Organs - >Organ systems 3. Reproduction 4. Genetic Programs 5.
Characteris*c s of Living Things 1. Chemical Uniqueness: Molecular Organization 2. Hierarchical Organization: macromolecules - > Cells - >Organs - >Organ systems 3. Reproduction 4. Genetic Programs 5.
Ch17_Animals. Animals Multicellular eukaryotes. What is an animal? Animal development. Main differences with plants Main differences with fungi
 Animals Multicellular eukaryotes Domain Domain Kingdoms Main differences with plants Main differences with fungi What is an animal? Domain Nutritional mode: Heterotrophic (Ingestive) Level of organization:
Animals Multicellular eukaryotes Domain Domain Kingdoms Main differences with plants Main differences with fungi What is an animal? Domain Nutritional mode: Heterotrophic (Ingestive) Level of organization:
Chapter 33 - Protostome Animals
 Chapter 33 - Protostome Animals Learning Objectives: Students should be able to... Describe the major characteristics that differentiate the Ecdysozoa and the Lophotrochozoa. List and describe the basic
Chapter 33 - Protostome Animals Learning Objectives: Students should be able to... Describe the major characteristics that differentiate the Ecdysozoa and the Lophotrochozoa. List and describe the basic
The Animal Kingdom. Animal Kingdom. Characteristics of All Animals. Major Characteristics Used To Classify Animals
 The Animal Kingdom Animal Kingdom Phylums: 1. Sponges 2. Cnidaria Jelly Fish, Hydra 3. Flatworms Flukes, Tapeworms 4. Roundworms- Hookworms 5. Segmented Worms- Earthworms 6. Rotifera- Rotifers 7. Mullusca
The Animal Kingdom Animal Kingdom Phylums: 1. Sponges 2. Cnidaria Jelly Fish, Hydra 3. Flatworms Flukes, Tapeworms 4. Roundworms- Hookworms 5. Segmented Worms- Earthworms 6. Rotifera- Rotifers 7. Mullusca
Class Polychaeta: Marine Worms
 Class Polychaeta: Marine Worms Animal Phyla Phylum Mollusca (Snails, Clams, Octopods and Allies): Radula: rasping tongue Shell: 3 layers, mostly calcium carbonate Inner-most = nacre = mother of pearl Mantle:
Class Polychaeta: Marine Worms Animal Phyla Phylum Mollusca (Snails, Clams, Octopods and Allies): Radula: rasping tongue Shell: 3 layers, mostly calcium carbonate Inner-most = nacre = mother of pearl Mantle:
Chapter 35. Table of Contents. Section 1 Mollusca. Section 2 Annelida. Mollusks and Annelids
 Mollusks and Annelids Table of Contents Section 1 Mollusca Section 2 Annelida Section 1 Mollusca Objectives Describe the key characteristics of mollusks. Describe the body plan of mollusks. Name the characteristics
Mollusks and Annelids Table of Contents Section 1 Mollusca Section 2 Annelida Section 1 Mollusca Objectives Describe the key characteristics of mollusks. Describe the body plan of mollusks. Name the characteristics
Chapter 5 Marine Protozoans and Invertebrates
 Chapter 5 Marine Protozoans and Invertebrates I. The Protozoans A. Kindgom Protista a catch-all category B. Characteristics 1. Mode of nutrition 2. Single-celled or multicellular? 3. Cell structure 4.
Chapter 5 Marine Protozoans and Invertebrates I. The Protozoans A. Kindgom Protista a catch-all category B. Characteristics 1. Mode of nutrition 2. Single-celled or multicellular? 3. Cell structure 4.
What is an animal? Introduction to Animals 2. Phylum Mollusca. Phylum Mollusca 4/20/2016
 What is an animal? Introduction to Animals 2 Multicellular chemoorganoheterotrophs Eukaryotes that lack cell walls and chloroplasts Have mitochondria Are motile at some point in their lives Snails, Octopus,
What is an animal? Introduction to Animals 2 Multicellular chemoorganoheterotrophs Eukaryotes that lack cell walls and chloroplasts Have mitochondria Are motile at some point in their lives Snails, Octopus,
Kingdom Animalia: Sponges. Types of Body Symmetry Radial body parts are symmetrical around a central point (like a pie)
 Kingdom Animalia: Phylum Characteristics Types of Body Symmetry Radial body parts are symmetrical around a central point (like a pie) Bilateral right and left sides are alike and roughly equally proportional
Kingdom Animalia: Phylum Characteristics Types of Body Symmetry Radial body parts are symmetrical around a central point (like a pie) Bilateral right and left sides are alike and roughly equally proportional
Arthropods are everywhere
 Phylum Arthropoda chitin exoskeleton jointed appendages repeated segments open circulatory system more than 10 million species respiratory system varies with subphlyum Arthropods are everywhere Two out
Phylum Arthropoda chitin exoskeleton jointed appendages repeated segments open circulatory system more than 10 million species respiratory system varies with subphlyum Arthropods are everywhere Two out
Chapter 23: The Animal Kingdom
 Chapter 23: The Animal Kingdom Lecture Outline Enger, E. D., Ross, F. C., & Bailey, D. B. (2012). Concepts in biology (14th ed.). New York: McGraw- Hill. 1 23-1 What is an animal? 23-2 Eukaryotic Multicellular
Chapter 23: The Animal Kingdom Lecture Outline Enger, E. D., Ross, F. C., & Bailey, D. B. (2012). Concepts in biology (14th ed.). New York: McGraw- Hill. 1 23-1 What is an animal? 23-2 Eukaryotic Multicellular
Invertebrate Notes. Arthropoda. Subphylum: Cheliceratahorseshoe. crabs, spiders, scorpions, mites, & ticks
 Invertebrate Notes Invertebrate Phyla: Trilobita-- trilobites (extinct) Arthropoda Cheliceratahorseshoe crabs, spiders, scorpions, mites, & ticks Mandibulata-- crustaceans, insects, millipedes, centipedes
Invertebrate Notes Invertebrate Phyla: Trilobita-- trilobites (extinct) Arthropoda Cheliceratahorseshoe crabs, spiders, scorpions, mites, & ticks Mandibulata-- crustaceans, insects, millipedes, centipedes
Animals. Invertebrate Diversity & Evolution
 Animals Invertebrate Diversity & Evolution Animal Characteristics Multicellular Heterotrophic (can be classified by their feeding strategies) Classified by feeding strategies Filter feeders (suspension
Animals Invertebrate Diversity & Evolution Animal Characteristics Multicellular Heterotrophic (can be classified by their feeding strategies) Classified by feeding strategies Filter feeders (suspension
Characteristics of Animals pp Topic 7: Animal Diversity Ch Symmetry pp Characteristics of Animals
 Topic 7: Animal Diversity Ch. 32-34 Characteristics of Animals pp.704-705 Animals: Are eukaryotic Are multicellular Are ingestive heterotrophs Have no cell walls Most are motile Most have tissues organized
Topic 7: Animal Diversity Ch. 32-34 Characteristics of Animals pp.704-705 Animals: Are eukaryotic Are multicellular Are ingestive heterotrophs Have no cell walls Most are motile Most have tissues organized
Chapter 7. Marine Animals Without a Backbone
 Chapter 7 Marine Animals Without a Backbone Molluscs Characteristics of Phylum: More than 200,000 species Name means "soft body" Basic body plan head, muscular foot and visceral mass in most species Mantle-
Chapter 7 Marine Animals Without a Backbone Molluscs Characteristics of Phylum: More than 200,000 species Name means "soft body" Basic body plan head, muscular foot and visceral mass in most species Mantle-
Phylum Mollusca. Includes snails and slugs, oysters and clams, and octopuses and squids.
 Mollusks Phylum Mollusca Includes snails and slugs, oysters and clams, and octopuses and squids. Bivalves Nautilus Characteristics Soft-bodied invertebrate Covered with protective mantle that may or may
Mollusks Phylum Mollusca Includes snails and slugs, oysters and clams, and octopuses and squids. Bivalves Nautilus Characteristics Soft-bodied invertebrate Covered with protective mantle that may or may
Unit 18.2: Mollusks and Annelids
 Unit 18.2: Mollusks and Annelids Lesson Objectives Describe invertebrates in the phylum Mollusca. Summarize the characteristics of annelids. Vocabulary Annelida deposit feeder gills heart mantle Mollusca
Unit 18.2: Mollusks and Annelids Lesson Objectives Describe invertebrates in the phylum Mollusca. Summarize the characteristics of annelids. Vocabulary Annelida deposit feeder gills heart mantle Mollusca
Phylum Mollusca Snails, slugs, oysters, clams, octopuses, and squids
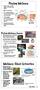 Phylum Mollusca Snails, slugs, oysters, clams, octopuses, and squids Nephridium Most are marine Visceral mass Soft-bodied animals, but most are protected by a hard shell Coelom Digestive tract Gonads Shell
Phylum Mollusca Snails, slugs, oysters, clams, octopuses, and squids Nephridium Most are marine Visceral mass Soft-bodied animals, but most are protected by a hard shell Coelom Digestive tract Gonads Shell
Chapter 36. Table of Contents. Section 1 Phylum Arthropoda. Section 2 Subphylum Crustacea. Section 3 Subphylum Chelicerata and Myriapoda.
 Arthropods Table of Contents Section 1 Phylum Arthropoda Section 2 Subphylum Crustacea Section 3 Subphylum Chelicerata and Myriapoda Section 1 Phylum Arthropoda Objectives Describe the distinguishing characteristics
Arthropods Table of Contents Section 1 Phylum Arthropoda Section 2 Subphylum Crustacea Section 3 Subphylum Chelicerata and Myriapoda Section 1 Phylum Arthropoda Objectives Describe the distinguishing characteristics
Protostomes vs Deuterostomes. Phylum Mollusca
 Protostomes vs Deuterostomes Animals that have a true coelom and complete digestive system can be divided into two main groups. This division is based on the way their embryos develop and the way in which
Protostomes vs Deuterostomes Animals that have a true coelom and complete digestive system can be divided into two main groups. This division is based on the way their embryos develop and the way in which
Mollusks Soft-bodied Invertebrates
 Mollusks Soft-bodied Invertebrates Phylum Mollusca Very diverse - more species of molluscs than any other group in the ocean. Phylum includes: Bivalves (2 shells); ex. Clam Gastropods (1 shell, coiled);
Mollusks Soft-bodied Invertebrates Phylum Mollusca Very diverse - more species of molluscs than any other group in the ocean. Phylum includes: Bivalves (2 shells); ex. Clam Gastropods (1 shell, coiled);
Phylum Mollusca. Soft-bodied animals. Internal or external shell. Include snails, slugs, clams, squids and octopi
 Phylum Mollusca Soft-bodied animals Internal or external shell Include snails, slugs, clams, squids and octopi Trochophore: free-swimming larval stage of an aquatic mollusk True coeloms Have complex organ
Phylum Mollusca Soft-bodied animals Internal or external shell Include snails, slugs, clams, squids and octopi Trochophore: free-swimming larval stage of an aquatic mollusk True coeloms Have complex organ
ARTHROPODS. Phylum Arthropoda. 08 Sept Arthropoda.ppt 1
 ARTHROPODS Phylum Arthropoda 08 Sept. 2014 Arthropoda.ppt 1 Phylum Arthropoda Phylum Arthropoda Greek: arthro = jointed, + pod = foot Huge group, > 1,000,000 species. estimate: 1,000,000 spp. arthropods
ARTHROPODS Phylum Arthropoda 08 Sept. 2014 Arthropoda.ppt 1 Phylum Arthropoda Phylum Arthropoda Greek: arthro = jointed, + pod = foot Huge group, > 1,000,000 species. estimate: 1,000,000 spp. arthropods
The Animals: Kingdom Animalia
 The Animals: Kingdom Animalia Kingdom Animalia (Animals) What is an Animal? Zoology- The study of Animals General Characteristics of 1. Animals are multicellular and eukaryotic. Animals 2. Animals consume
The Animals: Kingdom Animalia Kingdom Animalia (Animals) What is an Animal? Zoology- The study of Animals General Characteristics of 1. Animals are multicellular and eukaryotic. Animals 2. Animals consume
What are the four main characteristics of arthropods? What are two types of metamorphosis in insects?
 CHAPTER 15 3 Arthropods SECTION Invertebrates BEFORE YOU READ After you read this section, you should be able to answer these questions: What are the four main characteristics of arthropods? What are two
CHAPTER 15 3 Arthropods SECTION Invertebrates BEFORE YOU READ After you read this section, you should be able to answer these questions: What are the four main characteristics of arthropods? What are two
Basic mollusc body plan
 Phylum Mollusca Phylum Mollusca 3 embryonic germ layers true coelom complete gut second largest phylum of animals, around 100,000 species mainly aquatic, but some terrestrial species Basic mollusc body
Phylum Mollusca Phylum Mollusca 3 embryonic germ layers true coelom complete gut second largest phylum of animals, around 100,000 species mainly aquatic, but some terrestrial species Basic mollusc body
Chapter 28 Mollusks & Annelids. BIOLOGY II Miss. Loulousis
 Chapter 28 Mollusks & Annelids BIOLOGY II Miss. Loulousis Mollusks have a true coelom Snails, slugs, oysters, clams, scallops, octopuses, and squids are all mollusks Annelid earthworm next section Mollusks
Chapter 28 Mollusks & Annelids BIOLOGY II Miss. Loulousis Mollusks have a true coelom Snails, slugs, oysters, clams, scallops, octopuses, and squids are all mollusks Annelid earthworm next section Mollusks
Mollusks- soft bodied
 Mollusks- soft bodied Objectives Understand the taxonomic relationships and major features of mollusks Learn the external and internal anatomy of the clam and squid Understand the major advantages and
Mollusks- soft bodied Objectives Understand the taxonomic relationships and major features of mollusks Learn the external and internal anatomy of the clam and squid Understand the major advantages and
What Is an Annelid? Annelids are worms with segmented bodies. They have a true coelom that is lined with tissue derived from mesoderm.
 What Is an Annelid? What Is an Annelid? Phylum: Annelidae Annelids are worms with segmented bodies. They have a true coelom that is lined with tissue derived from mesoderm. Three Germ Layers of an Annelid
What Is an Annelid? What Is an Annelid? Phylum: Annelidae Annelids are worms with segmented bodies. They have a true coelom that is lined with tissue derived from mesoderm. Three Germ Layers of an Annelid
Chapter 28 Arthropods and Echinoderms. Body Terms. Evolution has led to:
 Chapter 28 Arthropods and Echinoderms Introduction to Arthropods jointed feet Most diverse and successful animals Over 750,000 species identified Segmented bodies Tough exoskeleton Jointed appendages Body
Chapter 28 Arthropods and Echinoderms Introduction to Arthropods jointed feet Most diverse and successful animals Over 750,000 species identified Segmented bodies Tough exoskeleton Jointed appendages Body
Kingdom Animalia Subkingdom Eumetazoa Bilateria Phylum Mollusca
 Kingdom Animalia Subkingdom Eumetazoa Bilateria Phylum Mollusca Professor Andrea Garrison Biology 3A Illustrations 2014 Cengage Learning unless otherwise noted Phylum Mollusca Molluscs (mollis = soft)
Kingdom Animalia Subkingdom Eumetazoa Bilateria Phylum Mollusca Professor Andrea Garrison Biology 3A Illustrations 2014 Cengage Learning unless otherwise noted Phylum Mollusca Molluscs (mollis = soft)
`Mollusks. may or may not form a hard, calcium carbonate shell. Trochophore Larva
 `Mollusks Phylum Mollusca Soft-bodied invertebrate covered with protective mantle that may or may not form a hard, calcium carbonate shell Includes chitons, snails, slugs, clams, oysters, squid, octopus,
`Mollusks Phylum Mollusca Soft-bodied invertebrate covered with protective mantle that may or may not form a hard, calcium carbonate shell Includes chitons, snails, slugs, clams, oysters, squid, octopus,
Kingdom Animalia. Lab Exercise 23. Objectives. Introduction
 Lab Exercise Kingdom Animalia Objectives - Be able to recognize and name the major groups of animals - Be able to identify key characteristics that separate animal taxa - Be able to use a dichotomous key
Lab Exercise Kingdom Animalia Objectives - Be able to recognize and name the major groups of animals - Be able to identify key characteristics that separate animal taxa - Be able to use a dichotomous key
Name Date Period. Mollusk Review TORSION HEMOLYMPH SESSILE TROCHOPHORE ADDUCTOR KIDNEY HEMOCOEL MANTLE CHROMATOPHORES VISCERAL MASS
 Name Date Period Mollusk Review MOLLUSK VOCABULARY: Match the word with its definition. TORSION HEMOLYMPH SESSILE TROCHOPHORE ADDUCTOR KIDNEY HEMOCOEL MANTLE CHROMATOPHORES VISCERAL MASS Free-swimming
Name Date Period Mollusk Review MOLLUSK VOCABULARY: Match the word with its definition. TORSION HEMOLYMPH SESSILE TROCHOPHORE ADDUCTOR KIDNEY HEMOCOEL MANTLE CHROMATOPHORES VISCERAL MASS Free-swimming
EXTRACREDIT PROJECT ANIMALS OF SOUTHERN CALIFORNIA S OCEAN
 BIO 10 FUNDAMENTALS OF BIOLOGY Instructor: K. Villatoro Student s Name: EXTRACREDIT PROJECT ANIMALS OF SOUTHERN CALIFORNIA S OCEAN WELCOME TO THE CABRILLO MARINE AQUARIUM! This site was chosen because
BIO 10 FUNDAMENTALS OF BIOLOGY Instructor: K. Villatoro Student s Name: EXTRACREDIT PROJECT ANIMALS OF SOUTHERN CALIFORNIA S OCEAN WELCOME TO THE CABRILLO MARINE AQUARIUM! This site was chosen because
Chordates 1. Biology 2
 Chordates 1 Biology 2 Kingdom Animals Eukaryotic Multicellular - Many cell types Heterotrophic Feed by ingestion No cell walls Diploid life cycle Phylogenetic Tree Deuterostome Bilateral Symmetry 3 tissues
Chordates 1 Biology 2 Kingdom Animals Eukaryotic Multicellular - Many cell types Heterotrophic Feed by ingestion No cell walls Diploid life cycle Phylogenetic Tree Deuterostome Bilateral Symmetry 3 tissues
Mollusks Are Soft and Unsegmented
 Mollusks Objectives Understand the taxonomic relationships and major features of mollusks Learn the external and internal anatomy of the clam and squid Understand the major advantages and limitations of
Mollusks Objectives Understand the taxonomic relationships and major features of mollusks Learn the external and internal anatomy of the clam and squid Understand the major advantages and limitations of
Mollusks are soft bodied animals that have an internal or external shell, a similar body plan consisting of four basic parts: a foot, mantle, shell,
 Mollusca Mollusks are soft bodied animals that have an internal or external shell, a similar body plan consisting of four basic parts: a foot, mantle, shell, and visceral mass. Mollusks also possess a
Mollusca Mollusks are soft bodied animals that have an internal or external shell, a similar body plan consisting of four basic parts: a foot, mantle, shell, and visceral mass. Mollusks also possess a
Overview of Invertebrates
 Overview of Invertebrates General Features of Animals Heterotrophic Multicellular (eukaryotic) Cells lack rigid cell walls Cells are usually quite flexible. Cells (except sponges) are organized into structural
Overview of Invertebrates General Features of Animals Heterotrophic Multicellular (eukaryotic) Cells lack rigid cell walls Cells are usually quite flexible. Cells (except sponges) are organized into structural
Page # Feeding. Animal diversity 3 - The Protostomes (Annelida, Mollusca, Arthropoda) Diversity of Annelida. But first from last time
 Animal diversity 3 - The Protostomes (Annelida, Mollusca, Arthropoda) Key concepts What are the distinguishing characters and life histories of the Annelida, Mollusca, Arthropoda? There are LOTS more species
Animal diversity 3 - The Protostomes (Annelida, Mollusca, Arthropoda) Key concepts What are the distinguishing characters and life histories of the Annelida, Mollusca, Arthropoda? There are LOTS more species
27-4 Mollusks. Slide 1 of 43. End Show. Copyright Pearson Prentice Hall
 1 of 43 What Is a Mollusk? What Is a Mollusk? Mollusks are soft-bodied animals that usually have an internal or external shell. Mollusks include snails, slugs, clams, squids, octopi... They are group together
1 of 43 What Is a Mollusk? What Is a Mollusk? Mollusks are soft-bodied animals that usually have an internal or external shell. Mollusks include snails, slugs, clams, squids, octopi... They are group together
Chapter 6 SPONGES. Invertebrates. Sponges. Pore-Bearers. Movement of Water
 Invertebrates Chapter 6 Animals Without Backbones Animals that lack a backbone are called invertebrates. It is estimated that 97% of all species of animals are invertebrates. With the exception of insects,
Invertebrates Chapter 6 Animals Without Backbones Animals that lack a backbone are called invertebrates. It is estimated that 97% of all species of animals are invertebrates. With the exception of insects,
Requirements for Animal Life. Phylum Bryozoa. Colonial Bryozoans. A lophophore is a structure used for:
 Requirements for Animal Life Animal phylogeny based on sequencing of SSU-rRNA The demands of 3 unique environments Marine, freshwater, terrestrial Gas exchange Nutrition Distribution and transport Disposal
Requirements for Animal Life Animal phylogeny based on sequencing of SSU-rRNA The demands of 3 unique environments Marine, freshwater, terrestrial Gas exchange Nutrition Distribution and transport Disposal
I n t r o d u c t i o n. A n i m a l s
 I n t r o d u c t i o n t o A n i m a l s What is an Animal? Taxonomy: Kingdom Animalia Type of Cells: Eukaryotic Cellular Organization: Multicellular Reproduction: Sexual / Asexual Feeding: Heterotrophic
I n t r o d u c t i o n t o A n i m a l s What is an Animal? Taxonomy: Kingdom Animalia Type of Cells: Eukaryotic Cellular Organization: Multicellular Reproduction: Sexual / Asexual Feeding: Heterotrophic
Course: Biology 211 Iowa State University
 Leader: Elizabeth Supplemental Instruction Course: Biology 211 Iowa State University Instructor: Dr. Deitloff Date: 2/27/14 Exam 2: Chapters 31 through 34 and information from guest lecturer 50 questions
Leader: Elizabeth Supplemental Instruction Course: Biology 211 Iowa State University Instructor: Dr. Deitloff Date: 2/27/14 Exam 2: Chapters 31 through 34 and information from guest lecturer 50 questions
Chapter 10: Mollusca
 Chapter 10: Mollusca Latin: soft 90,000 living spp. 70,000 fossil spp. marine fresh water terrestrial chitons snails nudibranchs clams oysters nautiluses tusk shells slugs sea butterflies mussels squids/cuttlefish
Chapter 10: Mollusca Latin: soft 90,000 living spp. 70,000 fossil spp. marine fresh water terrestrial chitons snails nudibranchs clams oysters nautiluses tusk shells slugs sea butterflies mussels squids/cuttlefish
Sponges are considered the oldest of the animal phyla. The name Porifera means "pore bearer" in Latin.
 Animals All animals are members of the Kingdom Animalia, also called Metazoa. This Kingdom does not contain prokaryotes (Kingdom Monera, includes bacteria, blue green algae) or protists (Kingdom Protista,
Animals All animals are members of the Kingdom Animalia, also called Metazoa. This Kingdom does not contain prokaryotes (Kingdom Monera, includes bacteria, blue green algae) or protists (Kingdom Protista,
Worm Essential Questions
 1. What are the four major phyla of marine worms? (in order from least to most complex) Worm Essential Questions Marine Biology Platyhelminthes - flatworms Nemertea ribbon worms or proboscis worms Nematoda
1. What are the four major phyla of marine worms? (in order from least to most complex) Worm Essential Questions Marine Biology Platyhelminthes - flatworms Nemertea ribbon worms or proboscis worms Nematoda
Symmetry. Asymmetrical- no shape. Radial- same in half when cut any angle. Bilateral- having a distinct right and left side
 Symmetry Asymmetrical- no shape Radial- same in half when cut any angle Bilateral- having a distinct right and left side Invertebrates 95% of Animals No Backbone The simplest animals and they do not have
Symmetry Asymmetrical- no shape Radial- same in half when cut any angle Bilateral- having a distinct right and left side Invertebrates 95% of Animals No Backbone The simplest animals and they do not have
 Kingdom: Animalia Phylum:Mollusca Classes: Bivalva, Gastropoda, Cephalopoda http://www.youtube.com/watch?v=0a7j5prl8hc&feature=related http://www2.beavercreek.k12.oh.us/videos/45/pgr45_700k.asf What is
Kingdom: Animalia Phylum:Mollusca Classes: Bivalva, Gastropoda, Cephalopoda http://www.youtube.com/watch?v=0a7j5prl8hc&feature=related http://www2.beavercreek.k12.oh.us/videos/45/pgr45_700k.asf What is
Chapter 29 Echinoderms and Invertebrate Chordates. Section Echinoderms. I. What Is An Echinoderm? 11/1/2010. Biology II Mrs.
 Chapter 29 Echinoderms and Invertebrate Chordates Section 29.1 - Echinoderms Biology II Mrs. Michaelsen I. What Is An Echinoderm? A. Move by means of hydraulic, suction cuptipped appendages. B. Skin covered
Chapter 29 Echinoderms and Invertebrate Chordates Section 29.1 - Echinoderms Biology II Mrs. Michaelsen I. What Is An Echinoderm? A. Move by means of hydraulic, suction cuptipped appendages. B. Skin covered
Biology. Slide 1 of 43. End Show. Copyright Pearson Prentice Hall
 Biology 1 of 43 2 of 43 What Is a Mollusk? What are the defining features of mollusks? 3 of 43 What Is a Mollusk? What Is a Mollusk? Mollusks are soft-bodied animals that usually have an internal or external
Biology 1 of 43 2 of 43 What Is a Mollusk? What are the defining features of mollusks? 3 of 43 What Is a Mollusk? What Is a Mollusk? Mollusks are soft-bodied animals that usually have an internal or external
Phylum Platyhelminthes. You will need: five colours of pencil crayon or pen (preferably blue, green, red, orange and purple)
 Phylum Platyhelminthes You will need: five colours of pencil crayon or pen (preferably blue, green, red, orange and purple) Phylum Platyhelminthes bilaterally symmetrical have all 3 embryonic germ layers:
Phylum Platyhelminthes You will need: five colours of pencil crayon or pen (preferably blue, green, red, orange and purple) Phylum Platyhelminthes bilaterally symmetrical have all 3 embryonic germ layers:
I. Evolutionary Perspective. Chapter 12. II. Molluscan Characteristics. A. Regions of Molluscan Body 11/2/10
 I. Evolutionary Perspective Chapter 12 Molluscan Success Some of the world s best predators Large brains Complex sensory structures Rapid locomotion Grasping tentacles Tearing mouthparts Have been around
I. Evolutionary Perspective Chapter 12 Molluscan Success Some of the world s best predators Large brains Complex sensory structures Rapid locomotion Grasping tentacles Tearing mouthparts Have been around
Mollusks and Annelids
 Mollusks and Annelids Bởi: OpenStaxCollege The mollusks are a diverse group (85,000 described species) of mostly marine species. They have a variety of forms, ranging from large predatory squid and octopus,
Mollusks and Annelids Bởi: OpenStaxCollege The mollusks are a diverse group (85,000 described species) of mostly marine species. They have a variety of forms, ranging from large predatory squid and octopus,
Kingdom: Animals. AP Biology Domain Eukarya. Domain Archaea. Domain Bacteria. Common ancestor
 Kingdom: Animals Domain Eukarya Domain Bacteria Domain Archaea Domain Eukarya 2012-2013 Common ancestor Animal Evolution On Exam 4/23/13 Porifera Cnidaria Nematoda Platyhelminthes sponges jellyfish flatworms
Kingdom: Animals Domain Eukarya Domain Bacteria Domain Archaea Domain Eukarya 2012-2013 Common ancestor Animal Evolution On Exam 4/23/13 Porifera Cnidaria Nematoda Platyhelminthes sponges jellyfish flatworms
Specimen Collection and Classification Activity
 Specimen Collection and Classification Activity Understanding the classification of animals is an important building block of science education, yet most adults cannot tell you how to group the most common
Specimen Collection and Classification Activity Understanding the classification of animals is an important building block of science education, yet most adults cannot tell you how to group the most common
Animal Evolution: Chordate and Vertebrate Evolution and Diversity (Learning Outline)
 Animal Evolution: Chordate and Vertebrate Evolution and Diversity (Learning Outline) 1. Distinguishing features of the phylum Chordata and representative organisms. 2. Highlights of evolutionary steps
Animal Evolution: Chordate and Vertebrate Evolution and Diversity (Learning Outline) 1. Distinguishing features of the phylum Chordata and representative organisms. 2. Highlights of evolutionary steps
5 Marine Biology Notes. Marine Invertebrates (Animals Without a Backbone)
 5 Marine Biology Notes Marine Invertebrates (Animals Without a Backbone) Invertebrates Animals without a backbone are known as invertebrates. Those with a backbone are called vertebrates. About 97% of
5 Marine Biology Notes Marine Invertebrates (Animals Without a Backbone) Invertebrates Animals without a backbone are known as invertebrates. Those with a backbone are called vertebrates. About 97% of
MARINE SCIENCE. Monday 16 Apr 2018
 MARINE SCIENCE Monday 16 Apr 2018 Guest Teacher Grab a copy of the How Scientists Classify Marine Life article & question worksheet from the front counter. Using the article Read the information. Answer
MARINE SCIENCE Monday 16 Apr 2018 Guest Teacher Grab a copy of the How Scientists Classify Marine Life article & question worksheet from the front counter. Using the article Read the information. Answer
Bivalved molluscs filter feeders
 Class Bivalvia Bivalved molluscs have two shells (valves). Mussels, clams, oysters, scallops, shipworms. Mostly sessile filter feeders. No head or radula. Class Bivalvia Part of the mantle is modified
Class Bivalvia Bivalved molluscs have two shells (valves). Mussels, clams, oysters, scallops, shipworms. Mostly sessile filter feeders. No head or radula. Class Bivalvia Part of the mantle is modified
Kingdom Animalia. Eukaryotic Multicellular Heterotrophs Lack Cell Walls
 Kingdom Animalia Eukaryotic Multicellular Heterotrophs Lack Cell Walls Must do: Feed, Respiration, Circulation, Excretion, Response, Movement, and Reproduction Symmetry Asymmetrical- no shape Radial- same
Kingdom Animalia Eukaryotic Multicellular Heterotrophs Lack Cell Walls Must do: Feed, Respiration, Circulation, Excretion, Response, Movement, and Reproduction Symmetry Asymmetrical- no shape Radial- same
Kingdom Animalia part 2.notebook. April 08, The fun continues... Kingdom Animalia
 The fun continues....... Kingdom Animalia 1 2 Joint legged animals (arthropoda) found from the bottom of the ocean to high above the Earth's surface included insects, arachnid, and crustacean hard external
The fun continues....... Kingdom Animalia 1 2 Joint legged animals (arthropoda) found from the bottom of the ocean to high above the Earth's surface included insects, arachnid, and crustacean hard external
Life Lecture Notes Chapter 13 Mollusca unsegmented bodied critters Valve mantle ii. Bilateral symmetry Gills foot Radula Visceral mass
 Life Lecture Notes Chapter 13 I. Phylum Mollusca a. General Characteristics i. Soft unsegmented bodied critters often covered by a shell called a Valve which is produced by the mantle. ii. Bilateral symmetry
Life Lecture Notes Chapter 13 I. Phylum Mollusca a. General Characteristics i. Soft unsegmented bodied critters often covered by a shell called a Valve which is produced by the mantle. ii. Bilateral symmetry
What is an animal? Mul.cellular heterotrophs: feed by inges&on. How does this differ from plants, fungi, pro.sts?
 What is an animal? Mul.cellular heterotrophs: feed by inges&on. How does this differ from plants, fungi, pro.sts? What is an animal? Carbohydrates stored as glycogen Polysaccharide of glucose (no, you
What is an animal? Mul.cellular heterotrophs: feed by inges&on. How does this differ from plants, fungi, pro.sts? What is an animal? Carbohydrates stored as glycogen Polysaccharide of glucose (no, you
Animal Evolution. II. Overview of Animal Phylogeny A. Parazoan 1. Lack tissue 2. Animals with tissue are classified eumetazoa 3.
 Animal Evolution I. Animal Characteristics A. Most animals share the following characteristics: 1. Multi-cellular 2. Eukaryotic 3. Heterotrophy a. Ingestion b. Carbohydrates stored as glycogen 4. No cell
Animal Evolution I. Animal Characteristics A. Most animals share the following characteristics: 1. Multi-cellular 2. Eukaryotic 3. Heterotrophy a. Ingestion b. Carbohydrates stored as glycogen 4. No cell
27/12/2012. Learning Outcome G4
 Learning Outcome G4 Learning Outcome G4 Analyse the increasing complexity of the Phylum Mollusca, the Phylum Echinodermata, and the Phylum Arthropoda Phylum Mollusca, Echinodermata & Arthropoda Students
Learning Outcome G4 Learning Outcome G4 Analyse the increasing complexity of the Phylum Mollusca, the Phylum Echinodermata, and the Phylum Arthropoda Phylum Mollusca, Echinodermata & Arthropoda Students
Phylum Platyhelminthes Phylum Nematoda Phylum Mollusca. By: Jerzylin, Beata & Jennifer
 Phylum Platyhelminthes Phylum Nematoda Phylum Mollusca By: Jerzylin, Beata & Jennifer Phylum Platyhelminthes Common Characteristics: Triploblastic Bilateral Symmetry Protostome No true stomach structure
Phylum Platyhelminthes Phylum Nematoda Phylum Mollusca By: Jerzylin, Beata & Jennifer Phylum Platyhelminthes Common Characteristics: Triploblastic Bilateral Symmetry Protostome No true stomach structure
Mollusks and Annelids. Chapter 23+
 Mollusks and Annelids Chapter 23+ 1 Annelids and Mollusks Coelomates Trochophore larvae Bilateral symmetry More complex organ systems 2 Moving On Up 3 Coelom Coelomates Evolutionary milestone True body
Mollusks and Annelids Chapter 23+ 1 Annelids and Mollusks Coelomates Trochophore larvae Bilateral symmetry More complex organ systems 2 Moving On Up 3 Coelom Coelomates Evolutionary milestone True body
Have You Wondered? College of Marine Sciences, Shanghai Ocean University
 Have You Wondered? 1. What role sponges play in marine ecosystems? 2. Why some animals are radially symmetrical? 3. If all gelatinous animals are jellyfishes? 4. What flatworms are? 5. What a lophophorate
Have You Wondered? 1. What role sponges play in marine ecosystems? 2. Why some animals are radially symmetrical? 3. If all gelatinous animals are jellyfishes? 4. What flatworms are? 5. What a lophophorate
Class XI Chapter 4 Animal Kingdom Biology
 Chapter 4 Animal Kingdom Question 1: What are the difficulties that you would face in classification of animals, if common fundamental features are not taken into account? For the classification of living
Chapter 4 Animal Kingdom Question 1: What are the difficulties that you would face in classification of animals, if common fundamental features are not taken into account? For the classification of living
5/10/2014. Most known organisms are animals. Of the 1.5 million known species, one-third are animals.
 Most known organisms are animals Of the 1.5 million known species, one-third are animals. Most animal species live on land, but the greatest diversity of animal phyla are marine. The most diverse communities
Most known organisms are animals Of the 1.5 million known species, one-third are animals. Most animal species live on land, but the greatest diversity of animal phyla are marine. The most diverse communities
Class XI Chapter 4 Animal Kingdom Biology
 Class XI Chapter 4 Animal Kingdom Biology Question 1: What are the difficulties that you would face in classification of animals, if common fundamental features are not taken into account? For the classification
Class XI Chapter 4 Animal Kingdom Biology Question 1: What are the difficulties that you would face in classification of animals, if common fundamental features are not taken into account? For the classification
Aquarium entrance stamp here
 Aquarium entrance stamp here Bio 11 - ZOOLOGY Instructor: K. Villatoro Student s Name: CLASSIFICATION OF KINGDOM ANIMALIA WELCOME TO THE CABRILLO MARINE AQUARIUM! This site was chosen because it exhibits
Aquarium entrance stamp here Bio 11 - ZOOLOGY Instructor: K. Villatoro Student s Name: CLASSIFICATION OF KINGDOM ANIMALIA WELCOME TO THE CABRILLO MARINE AQUARIUM! This site was chosen because it exhibits
Figure 32.8 Animal phylogeny based on sequencing of SSU-rRNA
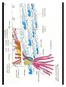 Figure 32.8 Animal phylogeny based on sequencing of SSU-rRNA Polychaetes Representative Annelids Oligochaetes Marine worms Hirudineans Terrestrial & aquatic Leeches - Aquatic & terrestrial Annelid Circulatory,
Figure 32.8 Animal phylogeny based on sequencing of SSU-rRNA Polychaetes Representative Annelids Oligochaetes Marine worms Hirudineans Terrestrial & aquatic Leeches - Aquatic & terrestrial Annelid Circulatory,
Chapter 12 Part 2. The Worms Platyhelminthes, Nematoda & Annelida
 Chapter 12 Part 2 The Worms Platyhelminthes, Nematoda & Annelida Phylum: Platyhelminthes Examples: Flatworms, Planaria sp., tapeworms and blood flukes Acoelomate, Invertebrate, Simplest critter w/ bilateral
Chapter 12 Part 2 The Worms Platyhelminthes, Nematoda & Annelida Phylum: Platyhelminthes Examples: Flatworms, Planaria sp., tapeworms and blood flukes Acoelomate, Invertebrate, Simplest critter w/ bilateral
Molluscs. Chapter 16
 Molluscs Chapter 16 Phylum Mollusca Phylum Mollusca includes snails and slugs, oysters and clams, and octopuses and squids. Phylum Mollusca Molluscs have a mesoderm lined body cavity a coelom. They are
Molluscs Chapter 16 Phylum Mollusca Phylum Mollusca includes snails and slugs, oysters and clams, and octopuses and squids. Phylum Mollusca Molluscs have a mesoderm lined body cavity a coelom. They are
28 2 Groups of Arthropods
 28 2 Groups of Arthropods 1 of 42 28 2 Groups of Arthropods Arthropods are classified based on the number and structure of their body segments and appendages particularly their mouthparts. The three major
28 2 Groups of Arthropods 1 of 42 28 2 Groups of Arthropods Arthropods are classified based on the number and structure of their body segments and appendages particularly their mouthparts. The three major
What are Arthropods? General Characteristics. General Characteristics 5/14/2013. Phylum Arthropoda Biology 11
 What are Arthropods? Phylum Arthropoda Biology 11 Segmented invertebrates Jointed appendages Exoskeleton Includes the most numerous and diverse animals on Earth They are found in virtually every habitat
What are Arthropods? Phylum Arthropoda Biology 11 Segmented invertebrates Jointed appendages Exoskeleton Includes the most numerous and diverse animals on Earth They are found in virtually every habitat
Phylum Mollusca. More than 500,000 known species. Class Polyplacophora. Class Bivalvia. Class Gastropoda. Class Cephalopoda
 Phylum Mollusca Class Polyplacophora Class Gastropoda Class Bivalvia Class Cephalopoda chitons Snails Sea slugs nudibranchs clams Squid Octopus Cuttlefish Nautilus More than 500,000 known species A bag,
Phylum Mollusca Class Polyplacophora Class Gastropoda Class Bivalvia Class Cephalopoda chitons Snails Sea slugs nudibranchs clams Squid Octopus Cuttlefish Nautilus More than 500,000 known species A bag,
Henry Guan, Akash Kashyap, and Angus Qian
 Henry Guan, Akash Kashyap, and Angus Qian http://peterbe.mobi/plog/interior-octopus/octopus.jpg Akash Kashyap Overview 85, 000 species Marine, Terrestrial, Freshwater habitats Very Diverse Classes: Chitons,
Henry Guan, Akash Kashyap, and Angus Qian http://peterbe.mobi/plog/interior-octopus/octopus.jpg Akash Kashyap Overview 85, 000 species Marine, Terrestrial, Freshwater habitats Very Diverse Classes: Chitons,
What is an animal? Heterotrophs Multicellular Eukaryotic Cells No Cell Walls Bodies contain tissues : Epithelial Muscular Connective Nervous
 Animals What is an animal? Heterotrophs Multicellular Eukaryotic Cells No Cell Walls Bodies contain tissues : Epithelial Muscular Connective Nervous Epithelial Cover body surfaces: skin, lining of lungs
Animals What is an animal? Heterotrophs Multicellular Eukaryotic Cells No Cell Walls Bodies contain tissues : Epithelial Muscular Connective Nervous Epithelial Cover body surfaces: skin, lining of lungs
Phylum Mollusca Classes
 Lecture Mollusks Phylum Mollusca Classes Aculifera with spicules Aplacophora - mollusks without shells Polyplacophora ( Amphineura) chiton, eight plates, intertidal Conchifera with shells Monoplacophora
Lecture Mollusks Phylum Mollusca Classes Aculifera with spicules Aplacophora - mollusks without shells Polyplacophora ( Amphineura) chiton, eight plates, intertidal Conchifera with shells Monoplacophora
Phylum Molluska.
 Phylum Molluska www.onacd.ca 3 Main Classes of Mollusks GASTROPODA : includes limpets, snails, slugs and whelks BIVALVIA: includes clams, oysters, muscles, scallops and shipworms CEPHALOPODA: includes
Phylum Molluska www.onacd.ca 3 Main Classes of Mollusks GASTROPODA : includes limpets, snails, slugs and whelks BIVALVIA: includes clams, oysters, muscles, scallops and shipworms CEPHALOPODA: includes
Arthropods, Echinoderms, and Chordates
 Arthropods, Echinoderms, and Chordates Bi 10 10/22/2013 Revised Schedule Friday, Nov. 22: Chapter 17, Part 2 Chapter 15, 16 Reading Quiz Due Wednesday, Nov. 27: Special Lecture: Review + World s Weirdest
Arthropods, Echinoderms, and Chordates Bi 10 10/22/2013 Revised Schedule Friday, Nov. 22: Chapter 17, Part 2 Chapter 15, 16 Reading Quiz Due Wednesday, Nov. 27: Special Lecture: Review + World s Weirdest
1) Which of the following is NOT a class in the phylum Porifera: a) Aschelminthes b) Hexactinellida c) Calcareous d) Demosponges
 Martha - Porifera: 1) Which of the following is NOT a class in the phylum Porifera: a) Aschelminthes b) Hexactinellida c) Calcareous d) Demosponges 2) What can sponges NOT be used for: a) Arts b) Bathing
Martha - Porifera: 1) Which of the following is NOT a class in the phylum Porifera: a) Aschelminthes b) Hexactinellida c) Calcareous d) Demosponges 2) What can sponges NOT be used for: a) Arts b) Bathing
Major groups of animals. I. Phylum Porifera. RADIATA II. Phylum Cnidaria. A. Class Hydrozoa. B. Class Anthozoa. C. Class Cubozoa. D.
 Major groups of animals I. Phylum Porifera A. no true tissues B. cell types 1. pinacocytes (pinacoderm - incipient tissue) 2. archaeocytes - in mesohyl 3. choanocytes C. Body forms 1. Asconoid a) water
Major groups of animals I. Phylum Porifera A. no true tissues B. cell types 1. pinacocytes (pinacoderm - incipient tissue) 2. archaeocytes - in mesohyl 3. choanocytes C. Body forms 1. Asconoid a) water
Features Used to Classify
 Features Used to Classify Animals Bởi: OpenStaxCollege Scientists have developed a classification scheme that categorizes all members of the animal kingdom, although there are exceptions to most rules
Features Used to Classify Animals Bởi: OpenStaxCollege Scientists have developed a classification scheme that categorizes all members of the animal kingdom, although there are exceptions to most rules
Biol Echinoderms & Chordates. But first a few words about Development
 Biol 1309 Echinoderms & Chordates 1 But first a few words about Development Blastula- zygote first develops into a hollow ball of cells Deuterostome - mouth second Protostome - mouth first Cleavage - describes
Biol 1309 Echinoderms & Chordates 1 But first a few words about Development Blastula- zygote first develops into a hollow ball of cells Deuterostome - mouth second Protostome - mouth first Cleavage - describes
Title: May 31 2:42 PM (1 of 23) Phylum Mollusca
 Title: May 31 2:42 PM (1 of 23) Phylum Mollusca Title: May 31 3:25 PM (2 of 23) often referred to as mollusks second largest phylum has 7 classes only looking at 4 bilateral symmetry, true body cavity
Title: May 31 2:42 PM (1 of 23) Phylum Mollusca Title: May 31 3:25 PM (2 of 23) often referred to as mollusks second largest phylum has 7 classes only looking at 4 bilateral symmetry, true body cavity
INVERTEBRATES. Cnidaria jelly, corals eumetazoa 2 radial Platyhelminthes flateworm 3 bilateral 1 a -- Nematoda roundworms 2 p --
 Diversity II ANIMAL OVERVIEW Animals: multicellular, heterotrophic eukaryotes, obtain nutrients by ingestion, and lack cell wall. Ingestion: eating other organisms or organic material. Collagen: most abundant
Diversity II ANIMAL OVERVIEW Animals: multicellular, heterotrophic eukaryotes, obtain nutrients by ingestion, and lack cell wall. Ingestion: eating other organisms or organic material. Collagen: most abundant
Introductory List to Local Marine Animals
 Introductory List to Local Marine Animals During your visit to the Huntsman you will have the opportunity to see and investigate many different types of marine animals, especially invertebrates. Below
Introductory List to Local Marine Animals During your visit to the Huntsman you will have the opportunity to see and investigate many different types of marine animals, especially invertebrates. Below
