full papers Strong and Conductive Dry Carbon Nanotube Films by Microcombing
|
|
|
- Posy Judith Byrd
- 6 years ago
- Views:
Transcription
1 Carbon Nanotubes Strong and Conductive Dry Carbon Nanotube Films by Microcombing Liwen Zhang, Xin Wang, Weizong Xu, Yongyi Zhang, Qingwen Li, Philip D. Bradford, and Yuntian Zhu * I n order to maximize the carbon nanotube (CNT) buckypaper properties, it is critical to improve their alignment and reduce their waviness. In this paper, a novel approach, microcombing, is reported to fabricate aligned CNT films with a uniform structure. High level of nanotube alignment and straightness was achieved using sharp surgical blades with microsized features at the blade edges to comb single layer of CNT sheet. These microcombs also reduced structural defects within the film and enhanced the nanotube packing density. Following the microcombing approach, the as-produced CNT films demonstrated a tensile strength of up to 3.2 GPa, Young s modulus of up to 172 GPa, and electrical conductivity of up to S m 1, which are much superior to previously reported CNT films or buckypapers. More importantly, this novel technique requires less rigorous process control and can construct CNT films with reproducible properties. 1. Introduction Carbon nanotubes (CNTs), with superior mechanical properties, high thermal, and electrical conductivities, have been the focus of extensive research for structural composites, [1,2 ] thermal interface materials, [3 5 ] and electrical conductors. [6 8 ] Researchers have devoted great effort to exploring high strength and lightweight CNT reinforcements for composites, by designing novel structures of CNT assemblies at the microand nano-scales. [9 14 ] CNTs, as reinforcements for composites, L. W. Zhang, Dr. X. Wang, Dr. W. Z. Xu, Prof. Y. T. Zhu Department of Materials Science and Engineering North Carolina State University NC 27695, USA ytzhu@ncsu.edu Dr. Y. Y. Zhang, Prof. Q. W. Li Suzhou Institute of Nano-Science and Nano-Biotics Suzhou , China Prof. P. D. Bradford College of Textile North Carolina State University NC 27695, USA DOI: /smll have been developed in the forms of fibers and films (also named buckypapers, sheets, where buckypaper often specifically refers to randomly oriented CNT paper). Among these, CNT films and buckypapers have drawn increasing interest due to their outstanding 2D or 3D properties, easy fabrication, and amenability for scaled-up production. In solution-based or melt-processing fabrication of CNT films and buckypapers, the large surface area and high aspect ratio of CNTs make them extremely difficult to disperse in solution or melt, and thus gives rise to nonuniform structures. [14 ] Short CNTs (<10 µm), although easier to disperse, usually render inefficient load transfer across the weakly bonded interfaces in resultant composites, [11 ] as the short nanotubes are only held by weak van der Waals forces. Consequently, the mechanical properties of CNT buckypapers produced by short-cnt dispersion have very low strengths of only about 10 MPa and low Young s moduli of less than 1 GPa. [15 20 ] These are far below the properties of individual CNTs and would limit their potential for envisioned applications. Many attempts have been made to improve the mechanical and electrical properties of buckypapers through promoting nanotube dispersion [16,17,21,22 ] or increasing intertube bonding to construct a 2D or 3D CNT network within the buckypaper. [18,23 ] However, no significant progress has been made in achieving the predicted properties Wiley-VCH Verlag GmbH & Co. KGaA, Weinheim
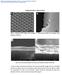
2 Figure 1. Microfeatures of the edge of the microcombing blade. Recently, it has been found that the CNT alignment has a profound impact on the mechanical and electrical properties of CNT films and buckypapers. [20,24 27 ] Domino pushing and shear pressing approaches have been developed to fabricate aligned CNT buckypapers directly from vertically aligned CNT arrays. [24,26 ] The long and aligned CNTs have effective contacts against each other along their alignment direction, and thus contributing to efficient load and electron transfer. However, the size of the as-produced buckpaper is usually limited by the size of the array substrate because of the nature of domino pushing and shear pressing approaches. In another work, CNT buckypapers produced by the floating catalyst chemical vapor deposition (FCCVD) method were processed by a stretching pressing approach and resulted in a high degree of CNT alignment and thus increased the tensile strength by 200% [27 ] compared with the nonstretched ones. [28,29 ] In 2002, Fan and co-workers developed drawable CNTs, which allow a vertically super-aligned CNT array to convert into a horizontally aligned 2D CNT sheet. [10 ] Rather than the 3D CNT array, this 2D CNT sheet has a high degree of CNT alignment in the horizontal direction, which maximizes the potentials of the CNTs while constructing them into multiple forms, such as CNT yarns and layered CNT films. Inoue et al. took advantage of this drawable feature of the super-aligned CNTs, used a winding method to fabricate anisotropic CNT films from multi-walled CNT arrays, and achieved a tensile strength of 75.6 MPa and an electrical conductivity of S m 1. [30 ] In 2012, Di et al. used few-walled CNT arrays to produce aligned CNT films by a similar winding method coupled with ethanol-densification, and achieved a tensile strength up to 2 GPa and Young s modulus up to 90 GPa. [31 ] More recently, they renewed their record to 2.96 and 124 GPa for the tensile strength and Young s modulus by densification using ethanol and acetone, respectively. [32 ] Apart from CNT alignment, another critical issue that limits the CNT film property is CNT waviness, as pointed out in our previous work. [33,34 ] In approaches of fabricating CNT/ Polymer composite films, stretching was proved effective in reducing CNT waviness and improving composite properties. However, stretching of a single layer of aligned CNT sheet is extremely difficult. It requires exceptionally careful control of stretching rate and very high quality of drawable CNT arrays. In this work, we present a simple and effective approach, called microcombing, to reduce CNT waviness directly at their single-layer level before the potential formation of large CNT bundles. Principally based on the previously reported winding technique, this method, for the first time, utilizes a microscale rough surface to locally mitigate entangled bundles and straighten the wavy CNTs. The as-combed single layer of CNT sheet exhibits high level of nanotube alignment and straightness, which leads to a uniform structure of CNT film with a tensile strength of up to 3.2 GPa, Young s modulus of up to 172 GPa, and electrical conductivity of up to S m 1. More importantly, the microcombing approach is not restricted to high quality of drawable arrays, requires less rigorous process control, and can construct CNT films with reproducible properties. 2. Experimental Section Figure 2. Microcombing process: a) schematic overview; b) schematic side view. Materials : The drawable CNT arrays used in the experiment were synthesized using a chemical vapor deposition method. [31 ] The CNT arrays were approximately 200 µm in height, with individual nanotubes having 2 5 walls and 5 7 nm in diameters. Microcombing Process : The key component of the process, microcombing of individual layer of CNT sheets, is accomplished by using two oppositely positioned 2015 Wiley-VCH Verlag GmbH & Co. KGaA, Weinheim
3 (a) Tensile strength (MPa) Short-CNT buckypapers Floating-CNT buckypapers Aligned CNT films Un-combed CNT films Combed CNT films This work Tensile strength (MPa) Un-combed Combed Combed dry CNT films Un-combed dry CNT films (b) Tensile strength (MPa) Young's modulus (GPa) Short-CNT buckypapers Young's modulus (GPa) Figure 3. Mechanical properties of CNT films: a) comparison of combed CNT films with previously reported buckypapers and other aligned CNT films; b) enlargement of the data area for buckypapers produced by short CNT dispersion. surgical blades. Scanning electron microscopy (SEM) images ( Figure 1 ) of the blade edge show microfeatures (teeth width: 2 µm, teeth depth: 0.5 µm), which can act as microcombs to disentangle and straighten the wavy CNTs. The experimental setup is shown by the schematics in Figure 2, when a layer of CNT sheet was drawn out from the CNT array, it passed two surgical blades, then wound to a rotating mandrel with a diameter of 3 cm at a speed of 20 r min 1. The contact angle between the CNT sheet and the blade was controlled at A metal needle with a diameter of 0.65 mm bent into 90 was placed on the mandrel at 1 o clock position, coating the densifying solution on the CNT sheet layer by layer during the winding process, as shown in Figure 2 b. The densifying solution consists of deionized water and ethanol with a mixing ratio of 1:1 by volume. 200 revolutions produced a film with a thickness of about 3 µm. The CNT film was then peeled off from the mandrel and hot-pressed at 80 C for 2 h under a pressure of 10 MPa. Under high pressure, the film was condensed to about 2 µm Figure 4. Typical tensile stress strain curves of the uncombed and combed dry CNT films. Since the coating solution was H 2 O and ethanol, they evaporated during the process, leaving a pure dry CNT film with aligned long CNTs. Characterization Methods : Tensile test specimens were cut from both the uncombed and combed dry CNT films. The test coupons are typically 1-mm wide and a gauge length of 10 mm. The width was measured using a calibrated scale bar in an optical micrometer. The sample thickness was measured by a micrometer and further confirmed by SEM (HITACHI S-4800). Tensile tests were conducted using an Instron 3365 tensile testing machine with a load cell of 10 N and a strain rate of 0.5 mm min 1. The weight of each specimen was measured at University of Delaware using a MX5 microbalance by Mettler-Toledo, Inc., which had an accuracy of 1 mg. Specimen density was calculated based on the measured dimension and weight. Surface morphology of both the combing blades and the as-produced dry films were analyzed by SEM (Verio 460L) and transmission electron microscope (TEM, Tecnai G2 F20 S-TWIN). A 4-probe Agilent 34410A 6.5 digit multimeter was used to test the electrical conductivity of the films along the CNT direction. Silver electrodes were produced by magnetron sputtering. 3. Results and Discussion 3.1. Mechanical Properties Strain Table 1 and Figure 3 compare the mechanical properties of the dry CNT films produced by microcombing with previously reported data. The CNT buckypapers made of short CNTs are named as short-cnt buckypapers; the buckypapers produced by FCCVD method are called floating- CNT buckypapers; and the CNT films made by winding 2D CNT sheet from the drawable arrays are called aligned CNT films. The tensile strength of the as-produced uncombed dry CNT films of (1.56 ± 0.19) GPa agrees well with the previously reported data for aligned CNT films ( GPa). By microcombing, the tensile strength of the CNT film was Wiley-VCH Verlag GmbH & Co. KGaA, Weinheim
4 Table 1. Mechanical property comparison for buckypapers and dry CNT films. Type Material Treatment Young s modulus [GPa] Tensile strength [MPa] Ref. Short-CNT buckypapers SWCNT [15] SWCNT [16] HNO SWCNT [17] SOCl SWCNT [18] Irradiation MWCNT [19] SWCNT [20] SWCNT Oleum + heat 8 30 [21] MWCNT Chemicals [22] Floating-CNT buckypapers MWCNT [25] 30% stretch % stretch % stretch Few-walled CNT 3.2 ± ± 19 [27] Stretch 11.9 ± ± 28 Stretch+press once 13.4 ± ± 25 Stretch+press twice 15.4 ± ± 36 SWCNT [28] Purification SWCNT [29] Aligned CNT films Few-walled CNT [31] Few-walled CNT 40 ± ± 0.07 (GPa) [32] Ethanol-densified 124 ± ± 0.31 (GPa) Acetone-densified 99 ± ± 0.29 (GPa) Few-walled CNT Uncombed 151 ± ± 188 This work Combed 172 ± ± 212 Table 2. Electrical conductivity values of the CNT films produced in our work and the data from the literatures. Type Material Treatment Electrical conductivity [S m 1 ] Ref. Short-CNT buckypapers SWCNT [16] HNO SWCNT [17] SOCl MWCNT to [19] SWCNT Oleum [21] Oleum + heat MWCNT Chemicals to [22] MWCNT [24] Oriented Floating-CNT buckypapers MWCNT [25] 40% stretch SWCNT [29] Aligned CNT films MWCNT [30] Few-walled CNT [31] Few-walled CNT [32] Ethanol-densified Acetone-densified Few-walled CNT Uncombed ± 1156 This work Combed ± Wiley-VCH Verlag GmbH & Co. KGaA, Weinheim
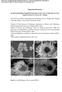
5 Figure 5. a,d) Optical photos and b,c,e,f) SEM images showing the differences between the uncombed and combed dry CNT sheets. improved by 105% from (1.56 ± 0.19) GPa to (3.21 ± 0.21) GPa, which surpasses the mechanical properties of CNT films or buckypapers reported earlier. Also, the Young s modulus has a 14% increase to (172 ± 13) GPa compared with the uncombed films. The density of the uncombed dry films is 0.84 g cm 3, whereas the density of the combed dry films is 1.04 g cm 3. Thus, the specific tensile strength of the combed dry CNT films is calculated to be 3.08 GPa g cm 3. The higher density of the combed dry CNT films indicates enhanced nanotube packing resulted from microcombing. In comparison, the reported density of the aligned CNT films is typically 0.9 g cm 3, [31 ] which is lower than our combed films. With a higher packing density, the aligned CNTs have a stronger inter-tube interaction, which in turn results in a more effective load transfer in the structure. Figure 4 displays typical tensile stress strain curves for the uncombed and combed dry CNT films. The slopes of the combed films show an apparent change compared with the uncombed ones. The Young s modulus is significantly improved by the microcombing. This is a direct evidence of the reduction of the CNT waviness and the improvement in the CNT alignment. In addition, the combed CNT films exhibit a higher tensile strain than that of the uncombed films, suggesting a reduction of structural defects induced by microcombing. The microcombing is simple, effective, and does not require a narrow window of controlled parameters, which greatly promotes the reproducibility and repeatability of the film properties Electrical Properties Table 2 compares the electrical conductivity of the combed- CNT films and other CNT buckypaprs and films. In our work, the uncombed CNT films exhibit a high electrical conductivity of S m 1, which is among the highest reported values. After microcombing, the electrical conductivity is further improved by 80% to S m 1. This substantial increase in electrical conductivity is also a direct result from better inter-tube contact to facilitate electron transfer due to the improved CNT straightness, enhanced CNT alignment, and higher nanotube packing density Wiley-VCH Verlag GmbH & Co. KGaA, Weinheim
6 3.3. Effect of Microcombing on the CNT Structure Combing, which has been used for centuries in the textile industry, is a process to disentangle and straighten staple fibers in order to achieve higher level of fiber alignment in the fiber web. [35 ] In this work, sharp surgical blades with microscale features at the blade edges were used to disentangle and straighten the wavy CNTs in the as-drawn CNT sheet. One pair of the blades was used to comb both the topside and bottom-side of the CNT sheet, giving a uniform microcombing (Figure 2 ). Coming with more blades was found to break CNT sheets or to group CNTs into nonuniform bundles, which is not desired. Additionally, the rotating speed and the contact angle between the CNT sheet and the combing blades are important. It was found fast drawing/rotating speed of the CNT sheet could benefit the CNT alignment. But when the speed was too fast, weak van der Waals forces could not hold the CNTs together any more, leading to the breakage of the CNT sheet. 20 r min 1 was the fastest speed that we found to operate successfully. In our experiment, the contact angle between the CNT sheet and the combing blades was controlled at (Figure 2 b), which was the optimum angle that we found to allow CNT sheet to be fully combed without breakage. When using smaller contact angles (less than ), the contact surface between the CNT sheet and the blade became larger. The increased friction made the nanotubes accumulate onto the edge of the blade, and break the CNT sheet at the blade. When using larger contact angles, the effect of microcombing was less effective in improving the packing and alignment of CNTs. Figure 5 shows both the optical photos and SEM images of the dry CNT sheets before and after microcombing, and before and after solution treatment, respectively. After the microcombing process, it is evident that the CNT sheets become shiny due to their smoothened surfaces (Figure 5 a,b). As shown in the SEM images (Figure 5 b,c,e,f), the microcombing process reduced the waviness of CNTs and enhanced the structural uniformity. This is also demonstrated by the TEM images of a single layer of CNT sheet before and after microcombing, as shown in Figure 6. After solution treatment (Figure 5 e,f), the nanotubes formed larger bundles and the sheets became denser. This was caused by the shrinking and densification effect of the ethanol in the coating solution. 4. Conclusion A novel microcombing approach is developed in this study to fabricate dry CNT films with ultrahigh mechanical properties and exceptional electrical performances. The approach Figure 6. TEM images of one single layer of CNT sheet a,b) before and c,d) after microcombing. has been shown to be effective in mitigating CNT waviness, reducing film defects, and improving CNT alignment and packing. The dry CNT films produced by microcombing exhibited very high Young s modulus of 172 GPa, excellent tensile strength of 3.2 GPa, and unprecedented electrical conductivity of S m 1. This approach is simple and effective, and can greatly improve the reproducibility and repeatability of the CNT film properties. Acknowledgements The authors are grateful to Suzhou Institute of Nano-Science and Nano-Biotics for providing the CNT arrays. The authors also thank Jiali Yu, a student in the University of Delaware, for her help with the sample weight measurement. This work was funded by the US Air Force Office of Scientific Research (Grant No. FA ). [1] L. Wei, X. H. Zhang, G. Xu, P. D. Bradford, X. Wang, H. B. Zhao, Y. Y. Zhang, Q. X. Jia, F. G. Yuan, Q. W. Li, Y. P. Qiu, Y. T. Zhu, Carbon 2011, 49, [2] X. F. Zhang, Q. W. Li, T. G. Holesinger, P. N. Arendt, J. Y. Huang, P. D. Kirven, T. G. Clapp, R. F. DePaula, X. Z. Liao, Y. H. Zhao, L. X. Zheng, D. E. Perterson, Y. T. Zhu, Adv. Mater. 2007, 19, [3] R. S. Ruoff, D. C. Lorents, Carbon 1995, 33 (7 ), Wiley-VCH Verlag GmbH & Co. KGaA, Weinheim
7 [4] M. J. Biercuk, M. C. Llaguno, M. Radosavljevic, J. K. Hyun, A. T. Johnson, J. E. Fischer, Appl. Phys. Lett. 2002, 75 (15 ), [5] J. Wang, J. S. Wang. Appl. Phys. Lett. 2006, 75 (11 ), [6] C. Niu, E. K. Sichel, R. Hoch, D. Moy, H. Tennent, Appl. Phys. Lett. 1997, 75 (11 ), [7] K. H. An, W. S. Kim, Y. S. Park, Y. C. Choi, S. M. Lee, D. C. Chung, D. J. Bae, S. C. Lim, Y. H. Lee, Adv. Mater. 2001, 13 (7 ), [8] S. Rosenblatt, Y. Yaish, J. Park, J. Gore, V. Sazonova, P. L. McEuen, Nano Lett. 2002, 2 (8 ), [9] E. T. Thostenson, Z. Ren, T. Chou, Composites Sci. Technol. 2001, 61 (13 ), [10] K. L. Jiang, Q. Q. Li, S. S. Fan, Nature 2002, 419 (6909 ), 801. [11] P. M. Ajayan, T. M. James, Nature 2007, 447 (7148 ), [12] H. D. Wagner, Nature Nanotechnol. 2007, 2 (12 ), [13] W. J. Ma, L. Q. Liu, Z. Zhang, R. Yang, G. Liu, T. H. Zhang, X. F. An, X. S. Yi, Y. Ren, Z. Q. Niu, J. Z. Li, H. B. Dong, W. Y. Zhou, P. M. Ajayan, S. S. Xie, Nano Lett. 2009, 9 (8 ), [14] J. T. Di, X. Wang, Y. Y. Xing, Y. Y. Zhang, X. H. Zhang, W. B. Lu, Q. W. Li, Y. T. Zhu, Small 2014, 10 (22 ), [15] R. H. Baughman, C. Cui, A. A. Zakhidov, Z. Iqbal, J. N. Barisci, G. M. Spinks, G. G. Wallace, A. Mazzoldi, D. D. Rossi, A. G. Rinzler, O. Jaschinski, S. Roth, M. Kertesz, Science 1999, 284 (5418 ), [16] X. F. Zhang, T. V. Sreekumar, T. Liu, S. Kumar. J. Phys. Chem. B 2004, 108 (42 ), [17] U. Dettlaff-Weglikowska, D. Tománek, S. Roth, V. Skákalová, R. Graupner, S. H. Jhang, B. H. Kim, H. J. Lee, L. Ley, Y. W. Park, J. Am. Chem. Soc. 2005, 127 (14 ), [18] S. R. Wang, Z. Y. Liang, B. Wang, C. Zhang, Adv. Mater. 2007, 19 (9 ), [19] G. H. Xu, Q. Zhang, W. P. Zhou, J. Q. Huang, F. Wei, Appl. Phys. A 2008, 92 (3 ), [20] J. G. Park, J. Smithyman, C. Y. Lin, A. Cooke, A. W. Kismarahardja, S. Li, R. Liang, J. S. Brooks, C. Zhang, B. Wang, J. Appl. Phys. 2009, 106 (10 ), [21] T. V. Sreekumar, T. Liu, S. Kumar, L. M. Ericson, R. H. Hauge, R. E. Smalley, Chem. Mater. 2003, 15 (1 ), [22] Z. Špitalský, C. Galiotis, C. Aggelopoulos, G. Tsoukleri, C. Tsakiroglou, J. Parthenios, S. Georga, C. Krontiras, D. Tasis, K. Papagelis, Mater. Sci. Eng. B 2009, 165 (3 ), [23] A. Kis, G. Csanyi, J. P. Salvetat, T. N. Lee, E. Couteau, A. J. Kulik, W. Benoit, J. Brugger, L. Forro, Nat. Mater. 2004, 3 (3 ), [24] D. Wang, P. C. Song, C. H. Liu, W. Wu, S. S. Fan, Nanotechnology 2008, 19 (7 ), [25] Q. F. Cheng, J. W. Bao, J. Park, Z. Y. Liang, C. Zhang, B. Wang, Adv. Funct. Mater. 2009, 19 (20 ), [26] P. D. Bradford, X. Wang, H. B. Zhao, J. P. Maria, Q. X. Jia, Y. T. Zhu, Composites Sci. Technol. 2010, 70 (13 ), [27] Q. L. Liu, M. Li, Y. Z. Gu, Y. Y. Zhang, S. K. Wang, Q. W. Li, Z. G. Zhang, Nanoscale 2014, 6 (8 ), [28] L. Song, L. Ci, L. Lv, Z. P. Zhou, X. Q. Yan, D. F. Liu, H. J. Yuan, Y. Gao, J. X. Wang, L. F. Liu, X. W. Zhao, Z. X. Zhang, X. Y. Dou, W. Y. Zhou, G. Wang, C. Y. Wang, S. S. Xie, Adv. Mater. 2004, 16 (17 ), [29] W. J. Ma, L. Song, R. Yang, T. H. Zhang, Y. C. Zhao, L. F. Sun, Y. Ren, D. F. Liu, L. F. Liu, J. Shen, Z. X. Zhang, Y. J. Xiang, W. Y. Zhou, S. S. Xie, Nano Lett. 2007, 7 (8 ), [30] Y. Inoue, Y. Suzuki, Y. Minami, J. Muramatsu, Y. Shimamura, K. Suzuki, A. Ghemes, M. Okada, S. Sakakibara, H. Mimura, K. Naito, Carbon 2011, 49 (7 ), [31] J. T. Di, D. M. Hu, H. Y. Chen, Z. Z. Yong, M. H. Chen, Z. H. Feng, Y. T. Zhu, Q. W. Li, ACS Nano 2012, 6 (6 ), [32] Y. J. Wang, M. Li, Y. Z. Gu, X. H. Zhang, S. K. Wang, Q. W. Li, Z. G. Zhang, Nanoscale 2015, 7 (7 ), [33] X. Wang, P. D. Bradford, W. Liu, H. B. Zhao, Y. Inoue, J. P. Maria, Q. W. Li, F. G. Yuan, Y. T. Zhu, Composites Sci. Technol. 2011, 71 (14 ), [34] X. Wang, Y. T. Zhu, Z. Z. Yong, Q. W. Li, P. D. Bradford, W. Liu, D. S. Tucker, W. Cai, H. Wang, F. G. Yuan, Mater. Res. Lett. 2013, 1 (1 ), [35] C. A. Lawrence, Scitech. Book News 2003, 27, 238. Received: January 14, 2015 Revised: March 10, 2015 Published online: May 4, Wiley-VCH Verlag GmbH & Co. KGaA, Weinheim
Electronic Supplementary Information (ESI)
 Electronic Supplementary Material (ESI) for Energy & Environmental Science. This journal is The Royal Society of Chemistry 2018 Electronic Supplementary Information (ESI) Nanomat Li-S batteries based on
Electronic Supplementary Material (ESI) for Energy & Environmental Science. This journal is The Royal Society of Chemistry 2018 Electronic Supplementary Information (ESI) Nanomat Li-S batteries based on
Fabrication of Novel Lamellar Alternating Nitrogen-Doped
 Electronic Supplementary Material (ESI) for Journal of Materials Chemistry A. This journal is The Royal Society of Chemistry 2017 Fabrication of Novel Lamellar Alternating Nitrogen-Doped Microporous Carbon
Electronic Supplementary Material (ESI) for Journal of Materials Chemistry A. This journal is The Royal Society of Chemistry 2017 Fabrication of Novel Lamellar Alternating Nitrogen-Doped Microporous Carbon
Layered polyaniline/graphene film from sandwich-structured polyaniline/graphene/polyaniline nanosheets for high-performance pseudosupercapacitors
 Supporting Information for: Layered polyaniline/graphene film from sandwich-structured polyaniline/graphene/polyaniline nanosheets for high-performance pseudosupercapacitors Zhongqiu Tong a, Yongning Yang
Supporting Information for: Layered polyaniline/graphene film from sandwich-structured polyaniline/graphene/polyaniline nanosheets for high-performance pseudosupercapacitors Zhongqiu Tong a, Yongning Yang
Hierachical Nickel-Carbon Structure Templated by Metal-Organic Frameworks for Efficient Overall Water Splitting
 Electronic Supplementary Material (ESI) for Energy & Environmental Science. This journal is The Royal Society of Chemistry 2018 Electronic Supplementary Information Hierachical Nickel-Carbon Structure
Electronic Supplementary Material (ESI) for Energy & Environmental Science. This journal is The Royal Society of Chemistry 2018 Electronic Supplementary Information Hierachical Nickel-Carbon Structure
High performance carbon nanotube based fiber-shaped. supercapacitors using redox additives of polypyrrole and. hydroquinone
 Electronic Supplementary Material (ESI) for Journal of Materials Chemistry A. This journal is The Royal Society of Chemistry 2015 Supporting information High performance carbon nanotube based fiber-shaped
Electronic Supplementary Material (ESI) for Journal of Materials Chemistry A. This journal is The Royal Society of Chemistry 2015 Supporting information High performance carbon nanotube based fiber-shaped
Supporting Information
 Copyright WILEY VCH Verlag GmbH & Co. KGaA, 69469 Weinheim, Germany, 2016. Supporting Information for Adv. Energy Mater., DOI: 10.1002/aenm.201502539 From Hollow Carbon Spheres to N-Doped Hollow Porous
Copyright WILEY VCH Verlag GmbH & Co. KGaA, 69469 Weinheim, Germany, 2016. Supporting Information for Adv. Energy Mater., DOI: 10.1002/aenm.201502539 From Hollow Carbon Spheres to N-Doped Hollow Porous
Supporting Information
 Electronic Supplementary Material (ESI) for Journal of Materials Chemistry A. This journal is The Royal Society of Chemistry 2017 Supporting Information Metal-organic framework-derived CoSe2/(NiCo)Se2
Electronic Supplementary Material (ESI) for Journal of Materials Chemistry A. This journal is The Royal Society of Chemistry 2017 Supporting Information Metal-organic framework-derived CoSe2/(NiCo)Se2
Supporting Information. Metal organic framework-derived Fe/C Nanocubes toward efficient microwave absorption
 Electronic Supplementary Material (ESI) for Journal of Materials Chemistry A. This journal is The Royal Society of Chemistry 2015 Supporting Information Metal organic framework-derived Fe/C Nanocubes toward
Electronic Supplementary Material (ESI) for Journal of Materials Chemistry A. This journal is The Royal Society of Chemistry 2015 Supporting Information Metal organic framework-derived Fe/C Nanocubes toward
Supplementary Material
 Electronic Supplementary Material (ESI) for Journal of Materials Chemistry A. This journal is The Royal Society of Chemistry 2018 Supplementary Material Biomass Chitosan Derived Cobalt/Nitrogen Doped Carbon
Electronic Supplementary Material (ESI) for Journal of Materials Chemistry A. This journal is The Royal Society of Chemistry 2018 Supplementary Material Biomass Chitosan Derived Cobalt/Nitrogen Doped Carbon
Supplementary Information. High areal capacity lithium sulfur battery cathode by. site-selective vapor infiltration of hierarchical
 Electronic Supplementary Material (ESI) for Nanoscale. This journal is The Royal Society of Chemistry 2017 Supplementary Information High areal capacity lithium sulfur battery cathode by site-selective
Electronic Supplementary Material (ESI) for Nanoscale. This journal is The Royal Society of Chemistry 2017 Supplementary Information High areal capacity lithium sulfur battery cathode by site-selective
Supporting Information
 Electronic Supplementary Material (ESI) for Journal of Materials Chemistry A. This journal is The Royal Society of Chemistry 2017 Supporting Information Fe 3 O 4 Quantum Dots Decorated MoS 2 Nanosheet
Electronic Supplementary Material (ESI) for Journal of Materials Chemistry A. This journal is The Royal Society of Chemistry 2017 Supporting Information Fe 3 O 4 Quantum Dots Decorated MoS 2 Nanosheet
Supplementary Information. O-vacancy Enriched NiO Hexagonal Platelets Fabricated on Ni. Foam as Self-supported Electrode for Extraordinary
 Electronic Supplementary Material (ESI) for Journal of Materials Chemistry A. This journal is The Royal Society of Chemistry 2018 Supplementary Information O-vacancy Enriched NiO Hexagonal Platelets Fabricated
Electronic Supplementary Material (ESI) for Journal of Materials Chemistry A. This journal is The Royal Society of Chemistry 2018 Supplementary Information O-vacancy Enriched NiO Hexagonal Platelets Fabricated
Supporting Information
 Electronic Supplementary Material (ESI) for Journal of Materials Chemistry A. This journal is The Royal Society of Chemistry 2016 Supporting Information Branched polyethylenimine grafted electrospun polyacrylonitrile
Electronic Supplementary Material (ESI) for Journal of Materials Chemistry A. This journal is The Royal Society of Chemistry 2016 Supporting Information Branched polyethylenimine grafted electrospun polyacrylonitrile
Electronic Supplementary Information. Hierarchically porous Fe-N-C nanospindles derived from. porphyrinic coordination network for Oxygen Reduction
 Electronic Supplementary Material (ESI) for Catalysis Science & Technology. This journal is The Royal Society of Chemistry 2018 Electronic Supplementary Information Hierarchically porous Fe-N-C nanospindles
Electronic Supplementary Material (ESI) for Catalysis Science & Technology. This journal is The Royal Society of Chemistry 2018 Electronic Supplementary Information Hierarchically porous Fe-N-C nanospindles
state asymmetric supercapacitors
 Electronic Supplementary Material (ESI) for Journal of Materials Chemistry A. This journal is The Royal Society of Chemistry 2016 3D hierarchical CoO@MnO 2 core-shell nanohybrid for high-energy solid state
Electronic Supplementary Material (ESI) for Journal of Materials Chemistry A. This journal is The Royal Society of Chemistry 2016 3D hierarchical CoO@MnO 2 core-shell nanohybrid for high-energy solid state
Interconnected hierarchical NiCo 2 O 4 microspheres as high performance. electrode material for supercapacitor
 Electronic Supplementary Material (ESI) for Dalton Transactions. This journal is The Royal Society of Chemistry 2017 Interconnected hierarchical microspheres as high performance electrode material for
Electronic Supplementary Material (ESI) for Dalton Transactions. This journal is The Royal Society of Chemistry 2017 Interconnected hierarchical microspheres as high performance electrode material for
Supporting Information
 Electronic Supplementary Material (ESI) for Journal of Materials Chemistry A. This journal is The Royal Society of Chemistry 2017 Supporting Information 3D-composite structure of FeP nanorods supported
Electronic Supplementary Material (ESI) for Journal of Materials Chemistry A. This journal is The Royal Society of Chemistry 2017 Supporting Information 3D-composite structure of FeP nanorods supported
Supporting Information
 Electronic Supplementary Material (ESI) for Nanoscale. This journal is The Royal Society of Chemistry 2017 Supporting Information Dual active nitrogen doped hierarchical porous hollow carbon nanospheres
Electronic Supplementary Material (ESI) for Nanoscale. This journal is The Royal Society of Chemistry 2017 Supporting Information Dual active nitrogen doped hierarchical porous hollow carbon nanospheres
Supporting information
 Electronic Supplementary Material (ESI) for Journal of Materials Chemistry A. This journal is The Royal Society of Chemistry Please do 2018 not adjust margins Supporting information Self-assembled 3D flower-like
Electronic Supplementary Material (ESI) for Journal of Materials Chemistry A. This journal is The Royal Society of Chemistry Please do 2018 not adjust margins Supporting information Self-assembled 3D flower-like
Facile fabrication of well-defined polyaniline microtubes derived. from natural kapok fiber for supercapacitor with long-term.
 Electronic Supplementary Material (ESI) for RSC Advances. This journal is The Royal Society of Chemistry 2016 Facile fabrication of well-defined polyaniline microtubes derived from natural kapok fiber
Electronic Supplementary Material (ESI) for RSC Advances. This journal is The Royal Society of Chemistry 2016 Facile fabrication of well-defined polyaniline microtubes derived from natural kapok fiber
Silver Nanowires Coated on Cotton for Flexible Pressure Sensors. College of Materials Science and Engineering, Key Lab of Guangdong Province for
 Electronic Supplementary Material (ESI) for Journal of Materials Chemistry C. This journal is The Royal Society of Chemistry 2015 Supporting Information Silver Nanowires Coated on Cotton for Flexible Pressure
Electronic Supplementary Material (ESI) for Journal of Materials Chemistry C. This journal is The Royal Society of Chemistry 2015 Supporting Information Silver Nanowires Coated on Cotton for Flexible Pressure
Facile synthesis of N-rich carbon quantum dots by spontaneous. polymerization and incision of solvents as efficient bioimaging probes
 Electronic Supplementary Material (ESI) for Nanoscale. This journal is The Royal Society of Chemistry 2015 Supporting Information Facile synthesis of N-rich carbon quantum dots by spontaneous polymerization
Electronic Supplementary Material (ESI) for Nanoscale. This journal is The Royal Society of Chemistry 2015 Supporting Information Facile synthesis of N-rich carbon quantum dots by spontaneous polymerization
Ultrathin Co-Fe Hydroxide Nanosheet Arrays for Improved
 Electronic Supplementary Material (ESI) for RSC Advances. This journal is The Royal Society of Chemistry 2017 Supplementary Information Ultrathin Co-Fe Hydroxide Nanosheet Arrays for Improved Oxygen Evolution
Electronic Supplementary Material (ESI) for RSC Advances. This journal is The Royal Society of Chemistry 2017 Supplementary Information Ultrathin Co-Fe Hydroxide Nanosheet Arrays for Improved Oxygen Evolution
Electronic Supplementary Information (ESI)
 Electronic Supplementary Material (ESI) for Journal of Materials Chemistry A. This journal is The Royal Society of Chemistry 2018 Electronic Supplementary Information (ESI) Hierarchically porous Mo-doped
Electronic Supplementary Material (ESI) for Journal of Materials Chemistry A. This journal is The Royal Society of Chemistry 2018 Electronic Supplementary Information (ESI) Hierarchically porous Mo-doped
Supplementary Information
 Electronic Supplementary Material (ESI) for RSC Advances. This journal is The Royal Society of Chemistry 2018 Supplementary Information Core@Shell Structured Co-CoO@NC Nanoparticles Supported on Nitrogen
Electronic Supplementary Material (ESI) for RSC Advances. This journal is The Royal Society of Chemistry 2018 Supplementary Information Core@Shell Structured Co-CoO@NC Nanoparticles Supported on Nitrogen
Supporting Information
 Electronic Supplementary Material (ESI) for Journal of Materials Chemistry A. This journal is The Royal Society of Chemistry 2018 Supporting Information Paragenesis BN/CNTs Hybrid as a Monoclinic Sulfur
Electronic Supplementary Material (ESI) for Journal of Materials Chemistry A. This journal is The Royal Society of Chemistry 2018 Supporting Information Paragenesis BN/CNTs Hybrid as a Monoclinic Sulfur
Supplementary Information
 Supplementary Information Fig S1 a top-down SEM image of PS template. b. cross-sectional SEM of PS template (with diameter of 440 nm). Fig. S2 The cross-sectional SEM of the dense Ge film(a) and 3DOM Ge
Supplementary Information Fig S1 a top-down SEM image of PS template. b. cross-sectional SEM of PS template (with diameter of 440 nm). Fig. S2 The cross-sectional SEM of the dense Ge film(a) and 3DOM Ge
Nitrogen-Doped Core-Sheath Carbon Nanotube Array for Highly Stretchable Supercapacitor
 www.advancedsciencenews.com Nitrogen-Doped Core-Sheath Carbon Nanotube Array for Highly Stretchable Supercapacitor Zhitao Zhang, Lie Wang, Yiming Li, Yuhang Wang, Jing Zhang, Guozhen Guan, Zhiyong Pan,
www.advancedsciencenews.com Nitrogen-Doped Core-Sheath Carbon Nanotube Array for Highly Stretchable Supercapacitor Zhitao Zhang, Lie Wang, Yiming Li, Yuhang Wang, Jing Zhang, Guozhen Guan, Zhiyong Pan,
Supporting Information
 Copyright WILEY-VCH Verlag GmbH & Co. KGaA, 69469 Weinheim, Germany, 2016. Supporting Information for Adv. Energy Mater., DOI: 10.1002/aenm.201600322 Integrated Intercalation-Based and Interfacial Sodium
Copyright WILEY-VCH Verlag GmbH & Co. KGaA, 69469 Weinheim, Germany, 2016. Supporting Information for Adv. Energy Mater., DOI: 10.1002/aenm.201600322 Integrated Intercalation-Based and Interfacial Sodium
Supplementary Information
 Electronic Supplementary Material (ESI) for Journal of Materials Chemistry A. This journal is The Royal Society of Chemistry 2018 Supplementary Information Scalable and Ascendant Synthesis of Coated Carbon
Electronic Supplementary Material (ESI) for Journal of Materials Chemistry A. This journal is The Royal Society of Chemistry 2018 Supplementary Information Scalable and Ascendant Synthesis of Coated Carbon
Supporting Information
 Electronic Supplementary Material (ESI) for Journal of Materials Chemistry A. This journal is The Royal Society of Chemistry 2019 Supporting Information Bioinspired Pomegranate-like Microflowers Confining
Electronic Supplementary Material (ESI) for Journal of Materials Chemistry A. This journal is The Royal Society of Chemistry 2019 Supporting Information Bioinspired Pomegranate-like Microflowers Confining
Pingping zhao, Xing Hua, Wei Xu, Wei Luo,* Shengli Chen,* and Gongzhen Cheng
 Electronic Supplementary Material (ESI) for Catalysis Science & Technology. This journal is The Royal Society of Chemistry 2016 Electronic Supplementary Information Metal-Organic Framework-Derived Hybrid
Electronic Supplementary Material (ESI) for Catalysis Science & Technology. This journal is The Royal Society of Chemistry 2016 Electronic Supplementary Information Metal-Organic Framework-Derived Hybrid
Flexible and Printable Paper Based Strain Sensors for Wearable and Large Area Green Electronics
 Electronic Supplementary Material (ESI) for Nanoscale. This journal is The Royal Society of Chemistry 2016 Supporting Information Flexible and Printable Paper Based Strain Sensors for Wearable and Large
Electronic Supplementary Material (ESI) for Nanoscale. This journal is The Royal Society of Chemistry 2016 Supporting Information Flexible and Printable Paper Based Strain Sensors for Wearable and Large
MXene/Graphene Hybrid Fibers for High. Performance Flexible Supercapacitors
 Electronic Supplementary Material (ESI) for Journal of Materials Chemistry A. This journal is The Royal Society of Chemistry 2017 Supporting Information for MXene/Graphene Hybrid Fibers for High Performance
Electronic Supplementary Material (ESI) for Journal of Materials Chemistry A. This journal is The Royal Society of Chemistry 2017 Supporting Information for MXene/Graphene Hybrid Fibers for High Performance
Electronic Supplementary Information
 Electronic Supplementary Material (ESI) for Nanoscale. This journal is The Royal Society of Chemistry 2014 Electronic Supplementary Information Flexible 3D Porous CuO Nanowire Arrays for Enzymeless Glucose
Electronic Supplementary Material (ESI) for Nanoscale. This journal is The Royal Society of Chemistry 2014 Electronic Supplementary Information Flexible 3D Porous CuO Nanowire Arrays for Enzymeless Glucose
noble-metal-free hetero-structural photocatalyst for efficient H 2
 Electronic Supplementary Material (ESI) for Journal of Materials Chemistry A. This journal is The Royal Society of Chemistry 2017 Ni 12 P 5 nanoparticles embedded into porous g-c 3 N 4 nanosheets as a
Electronic Supplementary Material (ESI) for Journal of Materials Chemistry A. This journal is The Royal Society of Chemistry 2017 Ni 12 P 5 nanoparticles embedded into porous g-c 3 N 4 nanosheets as a
Supporting Information. In-Situ Facile Bubble-Templated Fabrication of New-Type Urchin-Like (Li, Mo)- Doped Lix(Mo0.3V0.7)2O5 for Zn 2+ Storage
 Electronic Supplementary Material (ESI) for Journal of Materials Chemistry A. This journal is The Royal Society of Chemistry 2017 Supporting Information In-Situ Facile Bubble-Templated Fabrication of New-Type
Electronic Supplementary Material (ESI) for Journal of Materials Chemistry A. This journal is The Royal Society of Chemistry 2017 Supporting Information In-Situ Facile Bubble-Templated Fabrication of New-Type
Tunable CoFe-Based Active Sites on 3D Heteroatom Doped. Graphene Aerogel Electrocatalysts via Annealing Gas Regulation for
 Electronic Supplementary Material (ESI) for Journal of Materials Chemistry A. This journal is The Royal Society of Chemistry 2018 Tunable CoFe-Based Active Sites on 3D Heteroatom Doped Graphene Aerogel
Electronic Supplementary Material (ESI) for Journal of Materials Chemistry A. This journal is The Royal Society of Chemistry 2018 Tunable CoFe-Based Active Sites on 3D Heteroatom Doped Graphene Aerogel
Supporting Information for
 Electronic Supplementary Material (ESI) for Journal of Materials Chemistry A. This journal is The Royal Society of Chemistry 2016 Supporting Information for 3D Hierarchical Ni(PO 3 ) 2 Nanosheet Arrays
Electronic Supplementary Material (ESI) for Journal of Materials Chemistry A. This journal is The Royal Society of Chemistry 2016 Supporting Information for 3D Hierarchical Ni(PO 3 ) 2 Nanosheet Arrays
Supplementary Information
 Electronic Supplementary Material (ESI) for Journal of Materials Chemistry A. This journal is The Royal Society of Chemistry 2019 Supplementary Information Mo modulation effect on the hydrogen binding
Electronic Supplementary Material (ESI) for Journal of Materials Chemistry A. This journal is The Royal Society of Chemistry 2019 Supplementary Information Mo modulation effect on the hydrogen binding
Electronic Supplementary Information
 Electronic Supplementary Material (ESI) for Journal of Materials Chemistry A. This journal is The Royal Society of Chemistry 018 Electronic Supplementary Information Superhydrophilic amorphous Co-B-P nanosheet
Electronic Supplementary Material (ESI) for Journal of Materials Chemistry A. This journal is The Royal Society of Chemistry 018 Electronic Supplementary Information Superhydrophilic amorphous Co-B-P nanosheet
Porous and High-strength Graphitic Carbon/SiC Three-Dimensional Electrode for Capacitive Deionization and Fuel Cell Applications
 Electronic Supplementary Material (ESI) for Journal of Materials Chemistry A. This journal is The Royal Society of Chemistry 2018 Supporting Information Porous and High-strength Graphitic Carbon/SiC Three-Dimensional
Electronic Supplementary Material (ESI) for Journal of Materials Chemistry A. This journal is The Royal Society of Chemistry 2018 Supporting Information Porous and High-strength Graphitic Carbon/SiC Three-Dimensional
Supporting Information. Mitigating the P2 O2 phase transition of high-voltage
 Electronic Supplementary Material (ESI) for Journal of Materials Chemistry A. This journal is The Royal Society of Chemistry 2019 Supporting Information Mitigating the P2 O2 phase transition of high-voltage
Electronic Supplementary Material (ESI) for Journal of Materials Chemistry A. This journal is The Royal Society of Chemistry 2019 Supporting Information Mitigating the P2 O2 phase transition of high-voltage
Supporting Information for
 Electronic Supplementary Material (ESI) for Journal of Materials Chemistry A. This journal is The Royal Society of Chemistry 2015 Supporting Information for Core-shell ZnO/ZnFe 2 O 4 @C Mesoporous Nanospheres
Electronic Supplementary Material (ESI) for Journal of Materials Chemistry A. This journal is The Royal Society of Chemistry 2015 Supporting Information for Core-shell ZnO/ZnFe 2 O 4 @C Mesoporous Nanospheres
Electronic Supporting Information (ESI)
 Electronic Supplementary Material (ESI) for Journal of Materials Chemistry A. This journal is The Royal Society of Chemistry 2018 Electronic Supporting Information (ESI) Designing a Carbon Nanotubes Interconnected
Electronic Supplementary Material (ESI) for Journal of Materials Chemistry A. This journal is The Royal Society of Chemistry 2018 Electronic Supporting Information (ESI) Designing a Carbon Nanotubes Interconnected
Octahedral Pd Nanocages with Porous Shells Converted by Co(OH) 2 Nanocages with Nanosheet surface as Robust Electrocatalysts for Ethanol Oxidation
 Electronic Supplementary Material (ESI) for Journal of Materials Chemistry A. This journal is The Royal Society of Chemistry 2018 Octahedral Pd Nanocages with Porous Shells Converted by Co(OH) 2 Nanocages
Electronic Supplementary Material (ESI) for Journal of Materials Chemistry A. This journal is The Royal Society of Chemistry 2018 Octahedral Pd Nanocages with Porous Shells Converted by Co(OH) 2 Nanocages
Supporting Information
 Supporting Information A General Strategy to Fabricate P as Highly Efficient Cocatalyst via Photo-Reduction Deposition for Hydrogen Evolution Yuming Dong a, *, Linggang Kong a, Pingping Jiang a, Guangli
Supporting Information A General Strategy to Fabricate P as Highly Efficient Cocatalyst via Photo-Reduction Deposition for Hydrogen Evolution Yuming Dong a, *, Linggang Kong a, Pingping Jiang a, Guangli
Supporting Information. High cycling stable supercapacitor through electrochemical. deposition of metal-organic frameworks/polypyrrole positive
 Electronic Supplementary Material (ESI) for Dalton Transactions. This journal is The Royal Society of Chemistry 2018 Supporting Information High cycling stable supercapacitor through electrochemical deposition
Electronic Supplementary Material (ESI) for Dalton Transactions. This journal is The Royal Society of Chemistry 2018 Supporting Information High cycling stable supercapacitor through electrochemical deposition
Electronic Supplementary Information
 Electronic Supplementary Material (ESI) for Journal of Materials Chemistry A. This journal is The Royal Society of Chemistry 2017 Electronic Supplementary Information High-performance LiTi 2 (PO 4 ) 3
Electronic Supplementary Material (ESI) for Journal of Materials Chemistry A. This journal is The Royal Society of Chemistry 2017 Electronic Supplementary Information High-performance LiTi 2 (PO 4 ) 3
Highly enhanced performance of spongy graphene as oil sorbent
 Supporting Information Highly enhanced performance of spongy graphene as oil sorbent Hengchang Bi, a Xiao Xie, a Kuibo Yin, a Yilong Zhou, a Shu Wan, a Rodney S. Ruoff b and Litao Sun* a a SEU-FEI Nano-Pico
Supporting Information Highly enhanced performance of spongy graphene as oil sorbent Hengchang Bi, a Xiao Xie, a Kuibo Yin, a Yilong Zhou, a Shu Wan, a Rodney S. Ruoff b and Litao Sun* a a SEU-FEI Nano-Pico
Key Laboratory of Material Chemistry for Energy Conversion and Storage (Ministry
 Electronic Supplementary Material (ESI) for Dalton Transactions. This journal is The Royal Society of Chemistry 2018 Supporting Information for Dramatically enhanced visible-light driven H 2 evolution
Electronic Supplementary Material (ESI) for Dalton Transactions. This journal is The Royal Society of Chemistry 2018 Supporting Information for Dramatically enhanced visible-light driven H 2 evolution
Supporting Information
 Electronic Supplementary Material (ESI) for Materials Horizons. This journal is The Royal Society of Chemistry 2017 Supporting Information Co/CoP Embedded in Hairy Nitrogen-Doped Carbon Polyhedron as an
Electronic Supplementary Material (ESI) for Materials Horizons. This journal is The Royal Society of Chemistry 2017 Supporting Information Co/CoP Embedded in Hairy Nitrogen-Doped Carbon Polyhedron as an
catalytically deposited Cu current collector patterns for high-performance flexible in-plane micro-size energy
 Electronic Supplementary Material (ESI) for Energy & Environmental Science. This journal is The Royal Society of Chemistry 018 Electronic Supplementary Information (ESI) In-situ growth of Cu(OH) @FeOOH
Electronic Supplementary Material (ESI) for Energy & Environmental Science. This journal is The Royal Society of Chemistry 018 Electronic Supplementary Information (ESI) In-situ growth of Cu(OH) @FeOOH
A reformative oxidation strategy using high concentration nitric acid for. enhancing emission performance of graphene quantum dots
 Electronic Supplementary Material (ESI) for RSC Advances. This journal is The Royal Society of Chemistry 2014 A reformative oxidation strategy using high concentration nitric acid for enhancing emission
Electronic Supplementary Material (ESI) for RSC Advances. This journal is The Royal Society of Chemistry 2014 A reformative oxidation strategy using high concentration nitric acid for enhancing emission
Curriculum Vitae. Yu (Will) Wang
 Curriculum Vitae Yu (Will) Wang Assistant Research Professor yu.wang3@wsu.edu School of Mechanical and Materials Engineering Washington State University, Pullman, 99164, WA, USA EDUCATION B.S. Sichuan
Curriculum Vitae Yu (Will) Wang Assistant Research Professor yu.wang3@wsu.edu School of Mechanical and Materials Engineering Washington State University, Pullman, 99164, WA, USA EDUCATION B.S. Sichuan
Supplementary Information. Indole-Based Conjugated Macromolecule as Redox- Mediated Electrolyte for Ultrahigh Power Supercapacitor
 Electronic Supplementary Material (ESI) for Energy & Environmental Science. This journal is The Royal Society of Chemistry 2017 Supplementary Information Indole-Based Conjugated Macromolecule as Redox-
Electronic Supplementary Material (ESI) for Energy & Environmental Science. This journal is The Royal Society of Chemistry 2017 Supplementary Information Indole-Based Conjugated Macromolecule as Redox-
Supplementary Information. A synergistic interaction between isolated Au nanoparticles with oxygen vacancies in
 Electronic Supplementary Material (ESI) for Journal of Materials Chemistry A. This journal is The Royal Society of Chemistry 2018 Supplementary Information A synergistic interaction between isolated Au
Electronic Supplementary Material (ESI) for Journal of Materials Chemistry A. This journal is The Royal Society of Chemistry 2018 Supplementary Information A synergistic interaction between isolated Au
Electronic Supplementary Information (ESI)
 Electronic Supplementary Material (ESI) for Nanoscale. This journal is The Royal Society of Chemistry 2019 Electronic Supplementary Information (ESI) FeP@C Nanoarray Vertically Grown on Graphene Nanosheets:
Electronic Supplementary Material (ESI) for Nanoscale. This journal is The Royal Society of Chemistry 2019 Electronic Supplementary Information (ESI) FeP@C Nanoarray Vertically Grown on Graphene Nanosheets:
Supporting Information
 Electronic Supplementary Material (ESI) for Journal of Materials Chemistry A. This journal is The Royal Society of Chemistry 2015 Supporting Information Template-Preparation of Three-Dimensional Molybdenum
Electronic Supplementary Material (ESI) for Journal of Materials Chemistry A. This journal is The Royal Society of Chemistry 2015 Supporting Information Template-Preparation of Three-Dimensional Molybdenum
High performing AgNWs transparent conducting electrodes with 2.5Ω/Sq based upon Roll-to- Roll compatible post processing technique
 Electronic Supplementary Material (ESI) for Nanoscale. This journal is The Royal Society of Chemistry 2019 High performing AgNWs transparent conducting electrodes with 2.5Ω/Sq based upon Roll-to- Roll
Electronic Supplementary Material (ESI) for Nanoscale. This journal is The Royal Society of Chemistry 2019 High performing AgNWs transparent conducting electrodes with 2.5Ω/Sq based upon Roll-to- Roll
Supporting information
 Electronic Supplementary Material (ESI) for Inorganic Chemistry Frontiers. This journal is the Partner Organisations 2018 Supporting information Cube-Like CuCoO Nanostructures on Reduced Graphene Oxide
Electronic Supplementary Material (ESI) for Inorganic Chemistry Frontiers. This journal is the Partner Organisations 2018 Supporting information Cube-Like CuCoO Nanostructures on Reduced Graphene Oxide
Supporting Information
 Electronic Supplementary Material (ESI) for Journal of Materials Chemistry A. This journal is The Royal Society of Chemistry 2018 Supporting Information Electronic coupling-tunable of cobalt sulfide/carbon
Electronic Supplementary Material (ESI) for Journal of Materials Chemistry A. This journal is The Royal Society of Chemistry 2018 Supporting Information Electronic coupling-tunable of cobalt sulfide/carbon
Electronic Supplementary Information for. Highly Stable Mesoporous Silica Nanospheres Embedded with
 Electronic Supplementary Material (ESI) for RSC Advances. This journal is The Royal Society of Chemistry 17 Electronic Supplementary Information for Highly Stable Mesoporous Silica Nanospheres Embedded
Electronic Supplementary Material (ESI) for RSC Advances. This journal is The Royal Society of Chemistry 17 Electronic Supplementary Information for Highly Stable Mesoporous Silica Nanospheres Embedded
A Ni 3 N-Co 3 N hybrid nanowire array electrode for high-performance nonenzymatic glucose detection
 Electronic Supplementary Material (ESI) for Analytical Methods. This journal is The Royal Society of Chemistry 2018 Electronic Supplementary Information A Ni 3 N-Co 3 N hybrid nanowire array electrode
Electronic Supplementary Material (ESI) for Analytical Methods. This journal is The Royal Society of Chemistry 2018 Electronic Supplementary Information A Ni 3 N-Co 3 N hybrid nanowire array electrode
A Flexible, Lightweight, and Wearable Triboelectric Nanogenerator for Energy Harvesting and Self- Powered Sensing
 FULL PAPER Triboelectric Nanogenerators A Flexible, Lightweight, and Wearable Triboelectric Nanogenerator for Energy Harvesting and Self- Powered Sensing Fan Wu, Congju Li,* Yingying Yin, Ran Cao, Hui
FULL PAPER Triboelectric Nanogenerators A Flexible, Lightweight, and Wearable Triboelectric Nanogenerator for Energy Harvesting and Self- Powered Sensing Fan Wu, Congju Li,* Yingying Yin, Ran Cao, Hui
The study of 3-strand PP/PE composite monofilament Rope
 International Conference on Manufacturing Science and Engineering (ICMSE 2015) The study of 3-strand PP/PE composite monofilament Rope Jian-gao Shi1 *, Wenwen Yu1, Yongli Liu1, Lei Wang1, Xiaoxue Chen1,
International Conference on Manufacturing Science and Engineering (ICMSE 2015) The study of 3-strand PP/PE composite monofilament Rope Jian-gao Shi1 *, Wenwen Yu1, Yongli Liu1, Lei Wang1, Xiaoxue Chen1,
Supporting Information
 Electronic Supplementary Material (ESI) for Nanoscale. This journal is The Royal Society of Chemistry 2017 Supporting Information Phytic acid-derivative transition metal phosphides encapsulated in N,P-codoped
Electronic Supplementary Material (ESI) for Nanoscale. This journal is The Royal Society of Chemistry 2017 Supporting Information Phytic acid-derivative transition metal phosphides encapsulated in N,P-codoped
Hydrophilic/Hydrophobic Interphase-Mediated. Bubble-Like Stretchable Janus Ultrathin Films. Towards Self-Adaptive and Pneumatic
 1 Supporting Information for Hydrophilic/Hydrophobic Interphase-Mediated Bubble-Like Stretchable Janus Ultrathin Films Towards Self-Adaptive and Pneumatic Multifunctional Electronics Peng Xiao,, Yun Liang,,
1 Supporting Information for Hydrophilic/Hydrophobic Interphase-Mediated Bubble-Like Stretchable Janus Ultrathin Films Towards Self-Adaptive and Pneumatic Multifunctional Electronics Peng Xiao,, Yun Liang,,
Optical measurement in carbon nanotubes formation by pulsed laser ablation
 Thin Solid Films 457 (004) 7 11 Optical measurement in carbon nanotubes formation by pulsed laser ablation Tomoaki Ikegami, Futoshi Nakanishi*, Makoto Uchiyama, Kenji Ebihara Graduate School of Science
Thin Solid Films 457 (004) 7 11 Optical measurement in carbon nanotubes formation by pulsed laser ablation Tomoaki Ikegami, Futoshi Nakanishi*, Makoto Uchiyama, Kenji Ebihara Graduate School of Science
Recent advances in energy transfer in bulk and nanoscale. luminescent materials: From spectroscopy to applications
 Electronic Supplementary Material (ESI) for Chemical Society Reviews. This journal is The Royal Society of Chemistry 215 Electronic supplementary information Recent advances in energy transfer in ulk and
Electronic Supplementary Material (ESI) for Chemical Society Reviews. This journal is The Royal Society of Chemistry 215 Electronic supplementary information Recent advances in energy transfer in ulk and
Journal of Materials Chemistry A. Supporting Information. Cobalt Nickel Boride as an Active Electrocatalyst for Water Splitting
 Electronic Supplementary Material (ESI) for. This journal is The Royal Society of Chemistry Please do 2017 not adjust margins Supporting Information Cobalt Nickel Boride as an Active Electrocatalyst for
Electronic Supplementary Material (ESI) for. This journal is The Royal Society of Chemistry Please do 2017 not adjust margins Supporting Information Cobalt Nickel Boride as an Active Electrocatalyst for
3D Yolk-Shelled NiGa 2 S 4 Microspheres Confined with Nanosheets for High Performance Supercapacitors
 Electronic Supplementary Material (ESI) for Journal of Materials Chemistry A. This journal is The Royal Society of Chemistry 2017 Electronic Supplementary Information (ESI) 3D Yolk-Shelled NiGa 2 S 4 Microspheres
Electronic Supplementary Material (ESI) for Journal of Materials Chemistry A. This journal is The Royal Society of Chemistry 2017 Electronic Supplementary Information (ESI) 3D Yolk-Shelled NiGa 2 S 4 Microspheres
Electronic Supplementary Information (ESI) for Analyst. A Facile Graphene Oxide-Based Fluorescent Nanosensor for in Situ
 Electronic Supplementary Material (ESI) for Analyst. This journal is The Royal Society of Chemistry 2018 Electronic Supplementary Information (ESI) for Analyst A Facile Graphene Oxide-Based Fluorescent
Electronic Supplementary Material (ESI) for Analyst. This journal is The Royal Society of Chemistry 2018 Electronic Supplementary Information (ESI) for Analyst A Facile Graphene Oxide-Based Fluorescent
Supplementary Information. Flexible crystalline silicon radial junction photovoltaics with vertically aligned tapered microwires
 Electronic Supplementary Material (ESI) for Energy & Environmental Science. This journal is The Royal Society of Chemistry 2018 Supplementary Information Flexible crystalline silicon radial junction photovoltaics
Electronic Supplementary Material (ESI) for Energy & Environmental Science. This journal is The Royal Society of Chemistry 2018 Supplementary Information Flexible crystalline silicon radial junction photovoltaics
Supporting Information
 Electronic Supplementary Material (ESI) for Journal of Materials Chemistry A. This journal is The Royal Society of Chemistry 2018 Supporting Information From ZIF-8 Polyhedron to Three-Dimensional Nitrogen
Electronic Supplementary Material (ESI) for Journal of Materials Chemistry A. This journal is The Royal Society of Chemistry 2018 Supporting Information From ZIF-8 Polyhedron to Three-Dimensional Nitrogen
Supporting Information
 Electronic Supplementary Material (ESI) for Journal of Materials Chemistry A. This journal is The Royal Society of Chemistry 2017 Supporting Information Continuous fabrication of graphene-confined polypyrrole
Electronic Supplementary Material (ESI) for Journal of Materials Chemistry A. This journal is The Royal Society of Chemistry 2017 Supporting Information Continuous fabrication of graphene-confined polypyrrole
Transformation Optics and Experiments
 Forum for Electromagnetic Research Methods and Application Technologies (FERMAT) Transformation Optics and Experiments Tie Jun Cui and Wei Xiang Jiang State Key Laboratory of Millimeter Waves Southeast
Forum for Electromagnetic Research Methods and Application Technologies (FERMAT) Transformation Optics and Experiments Tie Jun Cui and Wei Xiang Jiang State Key Laboratory of Millimeter Waves Southeast
Abrasive wear of UHMWPE yarns against ceramic pins
 Abrasive wear of UHMWPE yarns against ceramic pins Juan Pu Ph.D student Mechanical Engineering, UC Berkeley Outline 1. Introduction 2. Experimental setup 3. Surface characterization of UHMWPE fibers and
Abrasive wear of UHMWPE yarns against ceramic pins Juan Pu Ph.D student Mechanical Engineering, UC Berkeley Outline 1. Introduction 2. Experimental setup 3. Surface characterization of UHMWPE fibers and
ANALYSIS OF THE POSITIVE FORCES EXHIBITING ON THE MOORING LINE OF COMPOSITE-TYPE SEA CAGE
 194 He, W., Li, C.: Analysis of the positive forces exhibiting on ANALYSIS OF THE POSITIVE FORCES EXHIBITING ON THE MOORING LINE OF COMPOSITE-TYPE SEA CAGE Wei He 1* Chunliu Li 2 1 Ocean College, Agricultural
194 He, W., Li, C.: Analysis of the positive forces exhibiting on ANALYSIS OF THE POSITIVE FORCES EXHIBITING ON THE MOORING LINE OF COMPOSITE-TYPE SEA CAGE Wei He 1* Chunliu Li 2 1 Ocean College, Agricultural
Sodium Borohydride Stabilizes Very Active Gold Nanoparticle Catalyst ELECTRONIC SUPPLEMENTARY INFORMATIONS. I. General data..p2
 Electronic Supplementary Material (ESI) for ChemComm. This journal is The Royal Society of Chemistry 2014 Sodium Borohydride Stabilizes Very Active Gold Nanoparticle Catalyst Christophe Deraedt, Lionel
Electronic Supplementary Material (ESI) for ChemComm. This journal is The Royal Society of Chemistry 2014 Sodium Borohydride Stabilizes Very Active Gold Nanoparticle Catalyst Christophe Deraedt, Lionel
Numerical simulation of three-dimensional flow field in three-line rollers and four-line rollers compact spinning systems using finite element method
 Indian Journal of Fibre & Textile Research Vol. 42, March 2017, pp. 77-82 Numerical simulation of three-dimensional flow field in three-line rollers and four-line rollers compact spinning systems using
Indian Journal of Fibre & Textile Research Vol. 42, March 2017, pp. 77-82 Numerical simulation of three-dimensional flow field in three-line rollers and four-line rollers compact spinning systems using
Improved Sputter Depth Resolution in Auger Thin Film Analysis Using In Situ Low Angle Cross-Sections
 Improved Sputter Depth Resolution in Auger Thin Film Analysis Using In Situ Low Angle Cross-Sections Uwe Scheithauer SIEMENS AG, ZT MF 7, Otto-Hahn-Ring 6, 81730 München, Germany Phone: + 49 89 636-44143,
Improved Sputter Depth Resolution in Auger Thin Film Analysis Using In Situ Low Angle Cross-Sections Uwe Scheithauer SIEMENS AG, ZT MF 7, Otto-Hahn-Ring 6, 81730 München, Germany Phone: + 49 89 636-44143,
RELATIONSHIP BETWEEN STRUCTURE AND MECHANICAL PROPERTIES OF BRAIDING GOLF SHAFTS AND KANSEI
 RELATIONSHIP BETWEEN STRUCTURE AND MECHANICAL PROPERTIES OF BRAIDING GOLF SHAFTS AND KANSEI M. OHARA, A. OHTANI, A. NAKAI, H. HAMADA, M. SAKATA, T. TANAKA, M. KUME, Y. YOSHIDA, T. YOSHIDA Kyoto Institute
RELATIONSHIP BETWEEN STRUCTURE AND MECHANICAL PROPERTIES OF BRAIDING GOLF SHAFTS AND KANSEI M. OHARA, A. OHTANI, A. NAKAI, H. HAMADA, M. SAKATA, T. TANAKA, M. KUME, Y. YOSHIDA, T. YOSHIDA Kyoto Institute
Stress Analysis of The West -East gas pipeline with Defects Under Thermal Load
 Stress Analysis of The West -East gas pipeline with Defects Under Thermal Load Abstract Xu Lei School of Petroleum Engineering, Yangtze University, Wuhan 430000, China 13071247220@163.com Natural gas is
Stress Analysis of The West -East gas pipeline with Defects Under Thermal Load Abstract Xu Lei School of Petroleum Engineering, Yangtze University, Wuhan 430000, China 13071247220@163.com Natural gas is
Carbon nanotube yarns
 Korean J. Chem. Eng., 29(3), 277-287 (2012) DOI: 10.1007/s11814-012-0016-1 INVITED REVIEW PAPER Carbon nanotube yarns Junbeom Park and Kun-Hong Lee Department of Chemical Engineering, Pohang University
Korean J. Chem. Eng., 29(3), 277-287 (2012) DOI: 10.1007/s11814-012-0016-1 INVITED REVIEW PAPER Carbon nanotube yarns Junbeom Park and Kun-Hong Lee Department of Chemical Engineering, Pohang University
KNOTLESS SCREEN PRINTING FOR CRYSTALLINE SILICON SOLAR CELLS
 KNOTLESS SCREEN PRINTING FOR CRYSTALLINE SILICON SOLAR CELLS 7th Workshop on Metallization Konstanz - October 23, 2017 Y. Zhang 1, L. Zhang 2, L. Jiang 1, L. Song 1, C. Guo 1, V. Dua 1, H. Yang 1, E. Kim
KNOTLESS SCREEN PRINTING FOR CRYSTALLINE SILICON SOLAR CELLS 7th Workshop on Metallization Konstanz - October 23, 2017 Y. Zhang 1, L. Zhang 2, L. Jiang 1, L. Song 1, C. Guo 1, V. Dua 1, H. Yang 1, E. Kim
Supporting Information
 Electronic Supplementary Material (ESI) for Sustainable Energy & Fuels. This journal is The Royal Society of Chemistry 2018 Supporting Information Electrospray Synthesis of Si Encapsulated in Graphite/carbon
Electronic Supplementary Material (ESI) for Sustainable Energy & Fuels. This journal is The Royal Society of Chemistry 2018 Supporting Information Electrospray Synthesis of Si Encapsulated in Graphite/carbon
An Ultrathin Flexible 2D Membrane Based on Single-Walled Nanotube MoS 2 Hybrid Film for High-Performance Solar Steam Generation
 FULL PAPER Solar Steam Generation An Ultrathin Flexible 2D Membrane Based on Single-Walled Nanotube MoS 2 Hybrid Film for High-Performance Solar Steam Generation Xiangdong Yang, Yanbing Yang, Linna Fu,
FULL PAPER Solar Steam Generation An Ultrathin Flexible 2D Membrane Based on Single-Walled Nanotube MoS 2 Hybrid Film for High-Performance Solar Steam Generation Xiangdong Yang, Yanbing Yang, Linna Fu,
3D CNTs/Graphene-S-Al 3 Ni 2 Cathodes for High-Sulfur-Loading and Long-Life Lithium Sulfur Batteries
 FULL PAPER Lithium-Sulfur Batteries 3D CNTs/Graphene-S-Al 3 Ni 2 Cathodes for High-Sulfur-Loading and Long-Life Lithium Sulfur Batteries Zeqing Guo, Huagui Nie,* Zhi Yang,* Wuxing Hua, Chunping Ruan, Dan
FULL PAPER Lithium-Sulfur Batteries 3D CNTs/Graphene-S-Al 3 Ni 2 Cathodes for High-Sulfur-Loading and Long-Life Lithium Sulfur Batteries Zeqing Guo, Huagui Nie,* Zhi Yang,* Wuxing Hua, Chunping Ruan, Dan
Identification of a Large Amount of Excess Fe in Superconducting Single- Layer FeSe/SrTiO 3 Films
 Identification of a Large Amount of Excess Fe in Superconducting Single- Layer FeSe/SrTiO 3 Films Yong Hu 1,2,#, Yu Xu 1,2,, Qingyan Wang 1,, Lin Zhao 1, Shaolong He 1, Jianwei Huang 1,2, Cong Li 1,2,
Identification of a Large Amount of Excess Fe in Superconducting Single- Layer FeSe/SrTiO 3 Films Yong Hu 1,2,#, Yu Xu 1,2,, Qingyan Wang 1,, Lin Zhao 1, Shaolong He 1, Jianwei Huang 1,2, Cong Li 1,2,
Supporting information
 Electronic Supplementary Material (ESI) for Journal of Materials Chemistry A. This journal is The Royal Society of Chemistry 2017 Please note this document replaces the version originally published on
Electronic Supplementary Material (ESI) for Journal of Materials Chemistry A. This journal is The Royal Society of Chemistry 2017 Please note this document replaces the version originally published on
Plasma Sources and Feedback Control in Pretreatment Web Coating Applications
 Plasma Sources and Feedback Control in Pretreatment Web Coating Applications Joseph Brindley, Benoit Daniel, Victor Bellido-Gonzalez, Dermot Monaghan Gencoa Ltd., Physics Rd, L24 9HP Liverpool, UK (+44)
Plasma Sources and Feedback Control in Pretreatment Web Coating Applications Joseph Brindley, Benoit Daniel, Victor Bellido-Gonzalez, Dermot Monaghan Gencoa Ltd., Physics Rd, L24 9HP Liverpool, UK (+44)
Electronic Supplementary Information
 Electronic Supplementary Material (ESI) for Journal of Materials Chemistry B. This journal is The Royal Society of Chemistry 2018 Electronic Supplementary Information Experimental 2.1 Chemicals and Materials
Electronic Supplementary Material (ESI) for Journal of Materials Chemistry B. This journal is The Royal Society of Chemistry 2018 Electronic Supplementary Information Experimental 2.1 Chemicals and Materials
Hydrophilic Sponges for Leaf-Inspired Continuous Pumping of Liquids
 Communication Elastic Sponges Hydrophilic Sponges for Leaf-Inspired Continuous Pumping of Liquids Tingjiao Zhou, Jinbin Yang, Deyong Zhu, Jieyao Zheng, Stephan Handschuh-Wang, Xiaohu Zhou, Junmin Zhang,
Communication Elastic Sponges Hydrophilic Sponges for Leaf-Inspired Continuous Pumping of Liquids Tingjiao Zhou, Jinbin Yang, Deyong Zhu, Jieyao Zheng, Stephan Handschuh-Wang, Xiaohu Zhou, Junmin Zhang,
HYDROGEN FAST FILLING TO A TYPE IV TANK DEVELOPED FOR MOTORCYCLES
 HYDROGEN FAST FILLING TO A TYPE IV TANK DEVELOPED FOR MOTORCYCLES Yamada, E. 1, Hiraki, W. 2, and Muramatsu, H. 3 1 FC-EV Research Division, Japan Automobile Research Institute, 1328-23 Takaheta, Osaka,
HYDROGEN FAST FILLING TO A TYPE IV TANK DEVELOPED FOR MOTORCYCLES Yamada, E. 1, Hiraki, W. 2, and Muramatsu, H. 3 1 FC-EV Research Division, Japan Automobile Research Institute, 1328-23 Takaheta, Osaka,
Precision punching of hole on composite panels
 Indian Journal of Engineering & Materials Sciences Vol. 22, December 2015, pp. 641-651 Precision punching of hole on composite panels H Y Chan, A B Abdullah* & Z Samad School of Mechanical Engineering,
Indian Journal of Engineering & Materials Sciences Vol. 22, December 2015, pp. 641-651 Precision punching of hole on composite panels H Y Chan, A B Abdullah* & Z Samad School of Mechanical Engineering,
The scope of fracture zone measure and high drill gas drainage technology research
 Available online www.jocpr.com Journal of Chemical and Pharmaceutical Research, 214, 6(1):45-457 Research Article ISSN : 975-7384 CODEN(USA) : JCPRC5 The scope of fracture zone measure and high drill gas
Available online www.jocpr.com Journal of Chemical and Pharmaceutical Research, 214, 6(1):45-457 Research Article ISSN : 975-7384 CODEN(USA) : JCPRC5 The scope of fracture zone measure and high drill gas
Nickel Hexacyanoferrate/Carbon Composite as a High-Rate and. Long-Life Cathode Material for Aqueous Hybrid Energy
 Electronic Supplementary Material (ESI) for ChemComm. This journal is The Royal Society of Chemistry 2017 Nickel Hexacyanoferrate/Carbon Composite as a High-Rate and Long-Life Cathode Material for Aqueous
Electronic Supplementary Material (ESI) for ChemComm. This journal is The Royal Society of Chemistry 2017 Nickel Hexacyanoferrate/Carbon Composite as a High-Rate and Long-Life Cathode Material for Aqueous
Influence of Ventilation Tube Rupture from Fires on Gas Distribution in Tunnel
 Available online at www.sciencedirect.com Procedia Engineering 26 (211) 144 1446 First International Symposium on Mine Safety Science and Engineering Influence of Ventilation Tube Rupture from Fires on
Available online at www.sciencedirect.com Procedia Engineering 26 (211) 144 1446 First International Symposium on Mine Safety Science and Engineering Influence of Ventilation Tube Rupture from Fires on
Numerical simulation on down-hole cone bit seals
 Numerical simulation on down-hole cone bit seals Yi Zhang, Wenbo Cai School of Mechatronic Engineering, Southwest Petroleum University Chengdu, 610500, China dream5568@126.com Abstract Seals are a critical
Numerical simulation on down-hole cone bit seals Yi Zhang, Wenbo Cai School of Mechatronic Engineering, Southwest Petroleum University Chengdu, 610500, China dream5568@126.com Abstract Seals are a critical
