In my left hand I hold 15 Argentine pesos. In my right, I hold 100 Chilean
|
|
|
- Louise Merritt
- 5 years ago
- Views:
Transcription
1 Chapter 6 Meeting Standards and Standings In This Chapter How to standardize scores Making comparisons Ranks in files Rolling in the percentiles In my left hand I hold 15 Argentine pesos. In my right, I hold 100 Chilean pesos. Which is worth more? Both currencies are called pesos, right? So shouldn t the 100 be greater than the 15? Not necessarily. Peso is just word magic a coincidence of names. Each one comes out of a different country, and each country has its own economy. To compare the two amounts of money, you have to convert each currency into a standard unit. The most intuitive standard for us is our own currency. How much is each amount worth in dollars and cents? As I write this, 15 Argentine pesos are worth more than $4. One hundred Chilean pesos are worth about 15 cents. In this chapter, I show you how to use statistics to create standard units. Standard units show you where a score stands in relation to other scores in a group, and I show you additional ways to determine a score s standing within a group. Catching Some Zs As the previous paragraph shows, a number in isolation doesn t really tell a story. In order to fully understand what a number means, you have to consider the process that produced it. In order to compare one number to another, they both have to be on the same scale. In some cases, like currency conversion, it s easy to figure out a standard. In others, like temperature conversion or conversion into the metric system, a formula guides you.
2 112 Part II: Describing Data When it s not all laid out for you, you can use the mean and the standard deviation to standardize scores that come from different processes. The idea is to take a set of scores and use its mean as a zero-point and its standard deviation as a unit of measure. Then you compare the deviation of each score from the mean to the standard deviation. You re asking how big is a particular deviation relative to (something like) an average of all the deviations? To do this, you divide the score s deviation by the standard deviation. In effect, you transform the score into another kind of score. The transformed score is called a standard score, or a z-score. The formula for this is if you re dealing with a sample, and if you re dealing with a population. In either case, x represents the score you re transforming into a z-score. Characteristics of z-scores A z-score can be positive, negative, or zero. A negative z-score represents a score that s less than the mean and a positive z-score represents a score that s greater than the mean. When the score is equal to the mean, its z-score is zero. When you calculate the z-score for every score in the set, the mean of the z-scores is 0, and the standard deviation of the z-scores is 1. After you do this for several sets of scores, you can legitimately compare a score from one set to a score from another. If the two sets have different means and different standard deviations, comparing without standardizing is like comparing apples with kumquats. In the examples that follow, I show how to use z-scores to make comparisons. Bonds versus The Bambino Here s an important question that often comes up in the context of serious metaphysical discussions: Who is the greatest home run hitter of all time,
3 Chapter 6: Meeting Standards and Standings 113 Barry Bonds or Babe Ruth? Although this is a difficult question to answer, one way to get your hands around it is to look at each player s best season and compare the two. Bonds hit 73 home runs in 2001, and Ruth hit 60 in On the surface, Bonds appears to be the more productive hitter. The year 1927 was very different from 2001, however. Baseball (and everything else) went through huge changes in the intervening years, and player statistics reflect those changes. A home run was harder to hit in the 20s than in the 00s. Still, 73 versus 60? Hmmm... Standard scores can help us decide whose best season was better. To standardize, I took the top 50 home run hitters of 1927 and the top 50 from I calculated the mean and standard deviation of each group, and then turned Ruth s 60 and Bonds s 73 into z-scores. The average from 1927 is homers with a standard deviation of The average from 2001 is homers with a standard deviation of Although the means differ greatly, the standard deviations are pretty close. And the z-scores? Ruth s is Bonds s is The clear winner in the z-score best-season home run derby is Babe Ruth. Period. Just to show you how times have changed, Lou Gehrig hit 47 home runs in 1927 (finishing second to Ruth) for a z-score of In 2001, 47 home runs amounted to a z-score of Exam scores Getting away from sports debates, one practical application of z-scores is the assignment of grades to exam scores. Based on percentage scoring, instructors traditionally evaluate a score of 90 points or higher (out of 100) as an A, points as a B, points as a C, points as a D, and less than 60 points as an F. Then they average scores from several exams together to assign a course grade.
4 114 Part II: Describing Data Is that fair? Just as a peso from Argentina is worth more than a peso from Chile, and a home run was harder to hit in 1927 than in 2001, is a point on one exam worth the same as a point on another? Like peso, isn t that just word magic? Indeed it is. A point on a difficult exam is, by definition, harder to come by than a point on an easy exam. Because points might not mean the same thing from one exam to another, the fairest thing to do is convert scores from each exam into z-scores before averaging them. That way, you re averaging numbers on a level playing field. In the courses I teach, I do just that. I often find that a lower numerical score on one exam results in a higher z-score than a higher numerical score from another exam. For example, on an exam where the mean is 65 and the standard deviation is 12, a score of 71 results in a z-score of.5. On another exam, with a mean of 69 and a standard deviation of 14, a score of 75 is equivalent to a z-score of.429. (Yes, it s like Ruth s 60 home runs versus Bonds s 73.) Moral of the story: Numbers in isolation tell you very little. You have to understand the process that produces them. STANDARDIZE Excel s STANDARDIZE worksheet function calculates z-scores. Figure 6-1 shows a set of exam scores along with their mean and standard deviation. I used AVERAGE and STDEVP to calculate the statistics. The Function Arguments dialog box for STANDARDIZE is also in the figure. Figure 6-1: Exam scores and the Function Arguments dialog box for STANDARD- IZE.
5 Chapter 6: Meeting Standards and Standings 115 Because negative z-scores might have connotations that are, well, negative, educators sometimes change the z-score when they evaluate students. In effect, they re hiding the z-score, but the concept is the same standardization with the standard deviation as the unit of measure. One popular transformation is called the T-score. The T-score eliminates negative scores because a set of T-scores has a mean of 50 and a standard deviation of 10. The idea is to give an exam, grade all the tests, and calculate the mean and standard deviation. Next, turn each score into a z-score. Then follow this formula: People who use the T-score often like to round to the nearest whole number. SAT scores are another transformation of the z-score. (Some refer to the SAT as a C-score.) Caching some z s The SAT has a mean of 500 and a standard deviation of 100. After the exams are graded, and their mean and standard deviation calculated, each exam score becomes a z-score in the usual way. This formula converts the z-score into a SAT score: Rounding to the nearest whole number is part of the procedure here, too. The IQ score is still another transformed z. Its mean is 100 and (in the Stanford-Binet version) its standard deviation is 16. What s the procedure for computing an IQ score? You guessed it. In a group of IQ scores, calculate the mean and standard deviation, and then calculate the z-score. Then it s As with the other two, IQ scores are rounded to the nearest whole number. Here are the steps: 1. Enter the data into an array and select a cell. The data are in C2:C32. I selected D2 to hold the z-score for the score in C2. Ultimately, I ll autofill column D and line up all the z-scores next to the corresponding exam scores. 2. From the Statistical Functions menu, select STANDARDIZE to open the Function Arguments dialog box for STANDARDIZE. 3. In the Function Arguments dialog box, enter the appropriate values for the arguments. First, I entered the cell that holds the first exam score into the X box. In this example, that s D2. In the Mean box, I entered the cell that holds the mean C33 for this example. It has to be in absolute reference format, so the entry is $C$33.
6 116 Part II: Describing Data You can type it that way, or you select C33 and then highlight the Mean box and press the F4 key. In the Standard_dev box, I entered the cell that holds the standard deviation. The appropriate cell in this example is C34. This also has to be in absolute reference format, so the entry is $C$ Click OK to close the Function Arguments dialog box and put the z-score for the first exam score into the selected cell. To finish up, I positioned the cursor on the selected cell s autofill handle, hold the left mouse button down, and drag the cursor to autofill the remaining z-scores. Figure 6-2 shows the autofilled array of z-scores. Figure 6-2: The autofilled array of z-scores. Where Do You Stand? Standard scores are designed to show you how a score stands in relation to other scores in the same group. To do this, they use the standard deviation as a unit of measure.
7 Chapter 6: Meeting Standards and Standings 117 If you don t want to use the standard deviation, you can show a score s relative standing in a simpler way. You can determine the score s rank within the group: The highest score has a rank of 1, the second highest has a rank of 2, and so on. RANK With Excel s RANK function you can quickly determine the ranks of all the scores in a group. Figure 6-3 shows the Function Arguments dialog box for RANK along with a group of scores. I ve also set up a column for the ranks. Figure 6-3: Working with RANK. Here are the steps for using RANK: 1. Enter the data into an array and select a cell. For this example, I entered the scores into cells C2 through C16, and selected cell D2. 2. From the Statistical Functions menu select RANK to open the Function Arguments dialog box for RANK. 3. In the Function Arguments dialog box, type the appropriate values for the arguments. In the Number box, I entered the cell that holds the score whose rank I want to insert into the selected cell. For this example, that s C2. In the Ref box, I entered the array that contains the scores. I enter C2:C16 into the Ref box. This part is important. After I insert RANK into D2 I m going to drag the cursor through column D and autofill the ranks of the remaining scores. To set up for this, I have to let Excel know I want C2 through C16 to be the array for every score, not just the first one.
8 118 Part II: Describing Data That means the array in the Ref box has to look like this: $C$2:$C$16. I can either add the $-signs manually, or highlight the Ref box and then press the F4 key. In the Order box, I indicate the order for sorting the scores. To rank the scores in descending order, I can either leave the Order box alone or type 0 (zero) into that box. To rank the scores in ascending order, I type a non-zero value into the Order box. I left this box alone. 4. Click OK to put the rank into the selected cell. I then position the cursor on the selected cell s autofill handle, hold the left mouse button down, and drag the cursor to autofill the ranks of the remaining scores. (See Figure 6-4.) Figure 6-4: The autofilled ranks. LARGE and SMALL You can turn the ranking process inside out by supplying a rank and asking which score has that rank. The worksheet functions LARGE and SMALL handle this from either end. They tell you the fifth largest score or the third smallest score, or any other rank you re interested in. Figure 6-5 shows the Function Arguments dialog box for LARGE. In the Array box you enter the array of cells that holds the group of scores. In the K box you enter the position whose value you want to find. To find the seventh largest score in the array, for example, type 7 into the K box. SMALL does the same thing, except it finds score positions from the lower end of the group. The Function Arguments dialog box for SMALL also has an Array box and a K box. Entering 7 in this K box returns the seventh lowest score in the array.
9 Chapter 6: Meeting Standards and Standings 119 Figure 6-5: The Function Arguments dialog box for LARGE. PERCENTILE and PERCENTRANK Closely related to rank is the percentile, which represents a score s standing in the group as the percent of scores below it. If you ve taken standardized tests like the SAT, you ve encountered percentiles. An SAT score in the 80th percentile is higher than 80 percent of the other SAT scores. Excel s PERCENTILE function enables you to find the value at any percentile. Figure 6-6 shows the Function Arguments dialog box PERCENTILE. The dialog box shows the 75th percentile (the value that s greater than 75 percent of the scores) for the numbers in cells C2 through C16. In this example, the 75th percentile is Figure 6-6: The Function Arguments dialog box for PERCENT- ILE. In the PERCENTILE dialog box, you enter the percentile into the K box. Enter it as a decimal, so that the 75th percentile is.75.
10 120 Part II: Describing Data A few specific percentiles are often used to summarize a group of scores. The median the 50th percentile (because it s higher than 50 percent of the scores) is one of them. Three others are the 25th percentile, the 75th and the 100th percentile (the maximum score). Because Drawn and quartiled they divide a group of scores into fourths, these particular four percentiles are called quartiles. Excel s QUARTILE function calculates them. Selecting QUARTILE from the Insert Function dialog box opens the QUARTILE dialog box shown in the figure. The trick is to enter the right kind of numbers into the Quart box 1 for the 25th percentile, 2 for the 50th, 3 for the 75th, and 4 for the 100th. Entering 0 into the Quart box gives you the lowest score in the group. In contrast to percentiles, you might be interested in the flip side: Given a value, what percent of scores falls below it? PERCENTRANK handles this. In Figure 6-7 the Function Arguments dialog box for PERCENTRANK shows the percent rank of 65 for the scores in cells C2 through C16. (It s 0.642, or 64.2 percent.) The Array box holds the array of cells and the X box holds the score (65). The Significance box is optional: You can enter the amount of significant figures in which you would like the answer to appear, or you can leave it blank. Figure 6-7: The Function Arguments dialog box for PERCENT- RANK.
11 Chapter 6: Meeting Standards and Standings 121 For the X box, you can enter either the value of a score or the label of the cell in which it appears. In this example, C10 in the X box gives you the same result as putting 65 in the X box. Data analysis tool: Rank and Percentile As the name of this section indicates, Excel provides a data analysis tool that calculates ranks and percentiles of each score in a group. The Rank and Percentiles tool calculates both at the same time, so it saves you some steps versus using the separate worksheet functions. (See Chapter 2 to install Excel s data analysis tools.) In Figure 6-8, I take the exam scores from the z-score example and open the Rank and Percentile dialog box. Figure 6-8: The Rank and Percentile analysis tool. Here are the steps for using Rank and Percentile: 1. Type your data into an array. In this example, the data are in cells C2 through C In the Tools menu, choose Data Analysis to open the Data Analysis dialog box. 3. In the Data Analysis dialog box, select Rank and Percentile. 4. Click OK to open the Rank and Percentile dialog box.
12 122 Part II: Describing Data 5. In the Rank and Percentile dialog box, enter the data array into the Input Range box. Make sure that it s in absolute reference format. In this example, a label is in the first row (in cell C1). I want the label included in the output, so I enter $C$1:$C$32 in the Input Range box, and I check the Labels in First Row checkbox. 6. Click the Columns radio button to indicate that the data are organized by columns. 7. Click the New Ply radio button to create a new tabbed page in the worksheet, and to send the results to the newly created page. 8. Click OK to close the dialog box. Open the newly created page to see the results. Figure 6-9 shows the new page with the results. The table orders the scores from highest to lowest, as the Score column shows along with the Rank column. The Point column tells you the score s position in the original grouping. For example, the 98 in cell B2 is the 12th score in the original data. The Percent column gives the percentile for each score. Figure 6-9: The Output of the Rank and Percentile analysis tool.
How are the values related to each other? Are there values that are General Education Statistics
 How are the values related to each other? Are there values that are General Education Statistics far away from the others? Class Notes Measures of Position and Outliers: Z-scores, Percentiles, Quartiles,
How are the values related to each other? Are there values that are General Education Statistics far away from the others? Class Notes Measures of Position and Outliers: Z-scores, Percentiles, Quartiles,
CHAPTER 2 Modeling Distributions of Data
 CHAPTER 2 Modeling Distributions of Data 2.1 Describing Location in a Distribution The Practice of Statistics, 5th Edition Starnes, Tabor, Yates, Moore Bedford Freeman Worth Publishers Describing Location
CHAPTER 2 Modeling Distributions of Data 2.1 Describing Location in a Distribution The Practice of Statistics, 5th Edition Starnes, Tabor, Yates, Moore Bedford Freeman Worth Publishers Describing Location
Chapter 2: Modeling Distributions of Data
 Chapter 2: Modeling Distributions of Data Section 2.1 The Practice of Statistics, 4 th edition - For AP* STARNES, YATES, MOORE Chapter 2 Modeling Distributions of Data 2.1 2.2 Normal Distributions Section
Chapter 2: Modeling Distributions of Data Section 2.1 The Practice of Statistics, 4 th edition - For AP* STARNES, YATES, MOORE Chapter 2 Modeling Distributions of Data 2.1 2.2 Normal Distributions Section
NCSS Statistical Software
 Chapter 256 Introduction This procedure computes summary statistics and common non-parametric, single-sample runs tests for a series of n numeric, binary, or categorical data values. For numeric data,
Chapter 256 Introduction This procedure computes summary statistics and common non-parametric, single-sample runs tests for a series of n numeric, binary, or categorical data values. For numeric data,
The pth percentile of a distribution is the value with p percent of the observations less than it.
 Describing Location in a Distribution (2.1) Measuring Position: Percentiles One way to describe the location of a value in a distribution is to tell what percent of observations are less than it. De#inition:
Describing Location in a Distribution (2.1) Measuring Position: Percentiles One way to describe the location of a value in a distribution is to tell what percent of observations are less than it. De#inition:
Lab 5: Descriptive Statistics
 Page 1 Technical Math II Lab 5: Descriptive Stats Lab 5: Descriptive Statistics Purpose: To gain experience in the descriptive statistical analysis of a large (173 scores) data set. You should do most
Page 1 Technical Math II Lab 5: Descriptive Stats Lab 5: Descriptive Statistics Purpose: To gain experience in the descriptive statistical analysis of a large (173 scores) data set. You should do most
MIS0855: Data Science In-Class Exercise: Working with Pivot Tables in Tableau
 MIS0855: Data Science In-Class Exercise: Working with Pivot Tables in Tableau Objective: Work with dimensional data to navigate a data set Learning Outcomes: Summarize a table of data organized along dimensions
MIS0855: Data Science In-Class Exercise: Working with Pivot Tables in Tableau Objective: Work with dimensional data to navigate a data set Learning Outcomes: Summarize a table of data organized along dimensions
AP Stats Chapter 2 Notes
 AP Stats Chapter 2 Notes 2.1 Measures of Relative Standing & Density Curves What is a percentile? On a test, is a student s percentile the same as the percent correct? Example: Test Scores Suppose the
AP Stats Chapter 2 Notes 2.1 Measures of Relative Standing & Density Curves What is a percentile? On a test, is a student s percentile the same as the percent correct? Example: Test Scores Suppose the
BIOL 101L: Principles of Biology Laboratory
 BIOL 101L: Principles of Biology Laboratory Sampling populations To understand how the world works, scientists collect, record, and analyze data. In this lab, you will learn concepts that pertain to these
BIOL 101L: Principles of Biology Laboratory Sampling populations To understand how the world works, scientists collect, record, and analyze data. In this lab, you will learn concepts that pertain to these
Background Information. Project Instructions. Problem Statement. EXAM REVIEW PROJECT Microsoft Excel Review Baseball Hall of Fame Problem
 Background Information Every year, the National Baseball Hall of Fame conducts an election to select new inductees from candidates nationally recognized for their talent or association with the sport of
Background Information Every year, the National Baseball Hall of Fame conducts an election to select new inductees from candidates nationally recognized for their talent or association with the sport of
DESCRIBE the effect of adding, subtracting, multiplying by, or dividing by a constant on the shape, center, and spread of a distribution of data.
 Today's Objectives: FIND and INTERPRET the standardized score (z-score) of an individual value within a distribution of data. DESCRIBE the effect of adding, subtracting, multiplying by, or dividing by
Today's Objectives: FIND and INTERPRET the standardized score (z-score) of an individual value within a distribution of data. DESCRIBE the effect of adding, subtracting, multiplying by, or dividing by
INSTRUCTION FOR FILLING OUT THE JUDGES SPREADSHEET
 INSTRUCTION FOR FILLING OUT THE JUDGES SPREADSHEET One Judge Spreadsheet must be distributed to each Judge for each competitor. This document is the only one that the Judge completes. There are no additional
INSTRUCTION FOR FILLING OUT THE JUDGES SPREADSHEET One Judge Spreadsheet must be distributed to each Judge for each competitor. This document is the only one that the Judge completes. There are no additional
Measuring Relative Achievements: Percentile rank and Percentile point
 Measuring Relative Achievements: Percentile rank and Percentile point Consider an example where you receive the same grade on a test in two different classes. In which class did you do better? Why do we
Measuring Relative Achievements: Percentile rank and Percentile point Consider an example where you receive the same grade on a test in two different classes. In which class did you do better? Why do we
Internet Technology Fundamentals. To use a passing score at the percentiles listed below:
 Internet Technology Fundamentals To use a passing score at the percentiles listed below: PASS candidates with this score or HIGHER: 2.90 High Scores Medium Scores Low Scores Percentile Rank Proficiency
Internet Technology Fundamentals To use a passing score at the percentiles listed below: PASS candidates with this score or HIGHER: 2.90 High Scores Medium Scores Low Scores Percentile Rank Proficiency
Descriptive Statistics Project Is there a home field advantage in major league baseball?
 Descriptive Statistics Project Is there a home field advantage in major league baseball? DUE at the start of class on date posted on website (in the first 5 minutes of class) There may be other due dates
Descriptive Statistics Project Is there a home field advantage in major league baseball? DUE at the start of class on date posted on website (in the first 5 minutes of class) There may be other due dates
Averages. October 19, Discussion item: When we talk about an average, what exactly do we mean? When are they useful?
 Averages October 19, 2005 Discussion item: When we talk about an average, what exactly do we mean? When are they useful? 1 The Arithmetic Mean When we talk about an average, we can mean different things
Averages October 19, 2005 Discussion item: When we talk about an average, what exactly do we mean? When are they useful? 1 The Arithmetic Mean When we talk about an average, we can mean different things
STANDARD SCORES AND THE NORMAL DISTRIBUTION
 STANDARD SCORES AND THE NORMAL DISTRIBUTION REVIEW 1.MEASURES OF CENTRAL TENDENCY A.MEAN B.MEDIAN C.MODE 2.MEASURES OF DISPERSIONS OR VARIABILITY A.RANGE B.DEVIATION FROM THE MEAN C.VARIANCE D.STANDARD
STANDARD SCORES AND THE NORMAL DISTRIBUTION REVIEW 1.MEASURES OF CENTRAL TENDENCY A.MEAN B.MEDIAN C.MODE 2.MEASURES OF DISPERSIONS OR VARIABILITY A.RANGE B.DEVIATION FROM THE MEAN C.VARIANCE D.STANDARD
HOW TO SETUP ROUND ROBIN IN DARTS FOR WINDOWS
 Edition: 1p2 06-Aug-2008 Previous editions: 05-Aug-2008 Author : RB Appr. : RB All pages in this document shall have the same edition number 3AQ 20080805 AAAD Ed. 1p2 Page 1 of 7 TABLE OF CONTENTS 1.SCOPE...3
Edition: 1p2 06-Aug-2008 Previous editions: 05-Aug-2008 Author : RB Appr. : RB All pages in this document shall have the same edition number 3AQ 20080805 AAAD Ed. 1p2 Page 1 of 7 TABLE OF CONTENTS 1.SCOPE...3
Name Date Period. E) Lowest score: 67, mean: 104, median: 112, range: 83, IQR: 102, Q1: 46, SD: 17
 Chapter 6 Review Standards: 4, 7, 8, and 11 Name Date Period Write complete answers, using complete sentences where necessary. Show your work when possible. MULTIPLE CHOICE. Choose the one alternative
Chapter 6 Review Standards: 4, 7, 8, and 11 Name Date Period Write complete answers, using complete sentences where necessary. Show your work when possible. MULTIPLE CHOICE. Choose the one alternative
Fun with M&M s. By: Cassandra Gucciardo. Sorting
 Fun with M&M s Sorting Fractions Objectives: The students will be able to review the measures of central tendency by determining mean, median, mode and range. They will review their understanding of estimation,
Fun with M&M s Sorting Fractions Objectives: The students will be able to review the measures of central tendency by determining mean, median, mode and range. They will review their understanding of estimation,
Tension Cracks. Topics Covered. Tension crack boundaries Tension crack depth Query slice data Thrust line Sensitivity analysis.
 Tension Cracks 16-1 Tension Cracks In slope stability analyses with cohesive soils, tension forces may be observed in the upper part of the slope. In general, soils cannot support tension so the results
Tension Cracks 16-1 Tension Cracks In slope stability analyses with cohesive soils, tension forces may be observed in the upper part of the slope. In general, soils cannot support tension so the results
March Madness Basketball Tournament
 March Madness Basketball Tournament Math Project COMMON Core Aligned Decimals, Fractions, Percents, Probability, Rates, Algebra, Word Problems, and more! To Use: -Print out all the worksheets. -Introduce
March Madness Basketball Tournament Math Project COMMON Core Aligned Decimals, Fractions, Percents, Probability, Rates, Algebra, Word Problems, and more! To Use: -Print out all the worksheets. -Introduce
Excel Solver Case: Beach Town Lifeguard Scheduling
 130 Gebauer/Matthews: MIS 213 Hands-on Tutorials and Cases, Spring 2015 Excel Solver Case: Beach Town Lifeguard Scheduling Purpose: Optimization under constraints. A. GETTING STARTED All Excel projects
130 Gebauer/Matthews: MIS 213 Hands-on Tutorials and Cases, Spring 2015 Excel Solver Case: Beach Town Lifeguard Scheduling Purpose: Optimization under constraints. A. GETTING STARTED All Excel projects
Descriptive Statistics. Dr. Tom Pierce Department of Psychology Radford University
 Descriptive Statistics Dr. Tom Pierce Department of Psychology Radford University Descriptive statistics comprise a collection of techniques for better understanding what the people in a group look like
Descriptive Statistics Dr. Tom Pierce Department of Psychology Radford University Descriptive statistics comprise a collection of techniques for better understanding what the people in a group look like
Multi Class Event Results Calculator User Guide Updated Nov Resource
 Multi Class Event Results Calculator User Guide Updated Nov 2011 The Multi Class Point Score has been developed as part of Swimming Australia Ltd. s commitment to creating opportunities for people with
Multi Class Event Results Calculator User Guide Updated Nov 2011 The Multi Class Point Score has been developed as part of Swimming Australia Ltd. s commitment to creating opportunities for people with
North Point - Advance Placement Statistics Summer Assignment
 North Point - Advance Placement Statistics This assignment is due during the first week of class. It is considered an exam grade, which that category is worth approximately 60% of your total grade. All
North Point - Advance Placement Statistics This assignment is due during the first week of class. It is considered an exam grade, which that category is worth approximately 60% of your total grade. All
5th Grade Decimal Concepts
 Slide 1 / 192 Slide 2 / 192 5th Grade Decimal Concepts 2015-11-16 www.njctl.org Slide 3 / 192 Table of Contents What is a Decimal? Click on a topic to go to that section. Identify Place Values Read and
Slide 1 / 192 Slide 2 / 192 5th Grade Decimal Concepts 2015-11-16 www.njctl.org Slide 3 / 192 Table of Contents What is a Decimal? Click on a topic to go to that section. Identify Place Values Read and
5th Grade. Slide 1 / 192. Slide 2 / 192. Slide 3 / 192. Decimal Concepts. Table of Contents
 Slide 1 / 192 Slide 2 / 192 5th Grade Decimal Concepts 2015-11-16 www.njctl.org Table of Contents Slide 3 / 192 What is a Decimal? Click on a topic to go to that section. Identify Place Values Read and
Slide 1 / 192 Slide 2 / 192 5th Grade Decimal Concepts 2015-11-16 www.njctl.org Table of Contents Slide 3 / 192 What is a Decimal? Click on a topic to go to that section. Identify Place Values Read and
3. EXCEL FORMULAS & TABLES
 Winter 2017 CS130 - Excel Formulas & Tables 1 3. EXCEL FORMULAS & TABLES Winter 2017 Winter 2017 CS130 - Excel Formulas & Tables 2 Cell References Absolute reference - refer to cells by their fixed position.
Winter 2017 CS130 - Excel Formulas & Tables 1 3. EXCEL FORMULAS & TABLES Winter 2017 Winter 2017 CS130 - Excel Formulas & Tables 2 Cell References Absolute reference - refer to cells by their fixed position.
March Madness Basketball Tournament
 March Madness Basketball Tournament Math Project COMMON Core Aligned Decimals, Fractions, Percents, Probability, Rates, Algebra, Word Problems, and more! To Use: -Print out all the worksheets. -Introduce
March Madness Basketball Tournament Math Project COMMON Core Aligned Decimals, Fractions, Percents, Probability, Rates, Algebra, Word Problems, and more! To Use: -Print out all the worksheets. -Introduce
b) (2 pts.) Does the study show that drinking 4 or more cups of coffee a day caused the higher death rate?
 Question 1 (10 pts) A study published in the August 15, 2017 issue of Mayo Clinic Proceedings tracked 44,000 people aged 20 to 87 for an average of about 16 years and found that those who drank 4 or more
Question 1 (10 pts) A study published in the August 15, 2017 issue of Mayo Clinic Proceedings tracked 44,000 people aged 20 to 87 for an average of about 16 years and found that those who drank 4 or more
Frequency Distributions
 Descriptive Statistics Dr. Tom Pierce Department of Psychology Radford University Descriptive statistics comprise a collection of techniques for better understanding what the people in a group look like
Descriptive Statistics Dr. Tom Pierce Department of Psychology Radford University Descriptive statistics comprise a collection of techniques for better understanding what the people in a group look like
Student Exploration: Estimating Population Size
 Name: Date: Student Exploration: Estimating Population Size Vocabulary: percent,, sample Prior Knowledge Questions (Do these BEFORE using the Gizmo.) 1. A jar contains 0 marbles total. Some are black.
Name: Date: Student Exploration: Estimating Population Size Vocabulary: percent,, sample Prior Knowledge Questions (Do these BEFORE using the Gizmo.) 1. A jar contains 0 marbles total. Some are black.
Mac Software Manual for FITstep Pro Version 2
 Thank you for purchasing this product from Gopher. If you are not satisfied with any Gopher purchase for any reason at any time, contact us and we will replace the product, credit your account, or refund
Thank you for purchasing this product from Gopher. If you are not satisfied with any Gopher purchase for any reason at any time, contact us and we will replace the product, credit your account, or refund
Introducing Version 7R2
 Introducing Version 7R2 CircuitCAM - A Tutorial Manufacturing OperationsSoftware [Type text] COPYRIGHTS AND TRADEMARKS Information in this document is subject to change without notice. Copyright 2009 Aegis
Introducing Version 7R2 CircuitCAM - A Tutorial Manufacturing OperationsSoftware [Type text] COPYRIGHTS AND TRADEMARKS Information in this document is subject to change without notice. Copyright 2009 Aegis
Combination Analysis Tutorial
 Combination Analysis Tutorial 3-1 Combination Analysis Tutorial It is inherent in the Swedge analysis (when the Block Shape = Wedge), that tetrahedral wedges can only be formed by the intersection of 2
Combination Analysis Tutorial 3-1 Combination Analysis Tutorial It is inherent in the Swedge analysis (when the Block Shape = Wedge), that tetrahedral wedges can only be formed by the intersection of 2
Chapter 3.4. Measures of position and outliers. Julian Chan. September 11, Department of Mathematics Weber State University
 Chapter 3.4 Measures of position and outliers Julian Chan Department of Mathematics Weber State University September 11, 2011 Intro 1 We will talk about how to measure the position of an observation which
Chapter 3.4 Measures of position and outliers Julian Chan Department of Mathematics Weber State University September 11, 2011 Intro 1 We will talk about how to measure the position of an observation which
SOLUBILITY OF A SOLID IN WATER
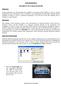 1516L Experiment 2 SOLUBILITY OF A SOLID IN WATER Objectives In this experiment you will determine the solubility of potassium nitrate (KNO 3 ) in water at various temperatures. You will prepare a plot
1516L Experiment 2 SOLUBILITY OF A SOLID IN WATER Objectives In this experiment you will determine the solubility of potassium nitrate (KNO 3 ) in water at various temperatures. You will prepare a plot
Homework Exercises Problem Set 1 (chapter 2)
 1 Name: Homework Exercises Problem Set 1 (chapter 2) Exercise 2.5.1 The 10 third-grade students at Lake Wobegone elementary school took a spelling test with 10 words, each worth one point. Given that the
1 Name: Homework Exercises Problem Set 1 (chapter 2) Exercise 2.5.1 The 10 third-grade students at Lake Wobegone elementary school took a spelling test with 10 words, each worth one point. Given that the
3. EXCEL FORMULAS & TABLES
 Fall 2017 CS130 - Excel Formulas & Tables 1 3. EXCEL FORMULAS & TABLES Fall 2017 Fall 2017 CS130 - Excel Formulas & Tables 2 Cell References Absolute reference - refer to cells by their fixed position.
Fall 2017 CS130 - Excel Formulas & Tables 1 3. EXCEL FORMULAS & TABLES Fall 2017 Fall 2017 CS130 - Excel Formulas & Tables 2 Cell References Absolute reference - refer to cells by their fixed position.
PSY201: Chapter 5: The Normal Curve and Standard Scores
 PSY201: Chapter 5: The Normal Curve and Standard Scores Introduction: Normal curve + a very important distribution in behavior sciences + three principal reasons why... - 1. many of the variables measured
PSY201: Chapter 5: The Normal Curve and Standard Scores Introduction: Normal curve + a very important distribution in behavior sciences + three principal reasons why... - 1. many of the variables measured
Microsoft Windows Software Manual for FITstep Stream Version 4
 Thank you for purchasing this product from Gopher. If you are not satisfied with any Gopher purchase for any reason at any time, contact us and we will replace the product, credit your account, or refund
Thank you for purchasing this product from Gopher. If you are not satisfied with any Gopher purchase for any reason at any time, contact us and we will replace the product, credit your account, or refund
Horse Farm Management s Report Writer. User Guide Version 1.1.xx
 Horse Farm Management s Report Writer User Guide Version 1.1.xx August 30, 2001 Before you start 3 Using the Report Writer 4 General Concepts 4 Running the report writer 6 Creating a new Report 7 Opening
Horse Farm Management s Report Writer User Guide Version 1.1.xx August 30, 2001 Before you start 3 Using the Report Writer 4 General Concepts 4 Running the report writer 6 Creating a new Report 7 Opening
EUROPEAN BRIDGE LEAGUE. 4 t h EBL TOURNAMENT DIRECTORS COURSE 31 st August 5 th September 2001 Tabiano di Salsomaggiore Terme, Italy
 EUROPEAN BRIDGE LEAGUE 4 t h EBL TOURNAMENT DIRECTORS COURSE 31 st August 5 th September 2001 Tabiano di Salsomaggiore Terme, Italy Scoring and Results Even in the computer era, with powerful machines
EUROPEAN BRIDGE LEAGUE 4 t h EBL TOURNAMENT DIRECTORS COURSE 31 st August 5 th September 2001 Tabiano di Salsomaggiore Terme, Italy Scoring and Results Even in the computer era, with powerful machines
THE NORMAL DISTRIBUTION COMMON CORE ALGEBRA II
 Name: Date: THE NORMAL DISTRIBUTION COMMON CORE ALGEBRA II Many populations have a distribution that can be well described with what is known as The Normal Distribution or the Bell Curve. This curve, as
Name: Date: THE NORMAL DISTRIBUTION COMMON CORE ALGEBRA II Many populations have a distribution that can be well described with what is known as The Normal Distribution or the Bell Curve. This curve, as
East Bay Swim League. Training Guide and Reporting Manual. For EBSL Team Computer Directors Version 1.2
 East Bay Swim League For EBSL Version 1.2 1 Table of Contents Purpose! 3 Credits! 3 Teams Initials! 4 Groups and Sub Groups! 4 Event Numbers and Descriptions! 5 Team Rosters! 9 EBSL - Team Roster Format!
East Bay Swim League For EBSL Version 1.2 1 Table of Contents Purpose! 3 Credits! 3 Teams Initials! 4 Groups and Sub Groups! 4 Event Numbers and Descriptions! 5 Team Rosters! 9 EBSL - Team Roster Format!
Lab 2: Probability. Hot Hands. Template for lab report. Saving your code
 Lab 2: Probability Hot Hands Basketball players who make several baskets in succession are described as having a hot hand. Fans and players have long believed in the hot hand phenomenon, which refutes
Lab 2: Probability Hot Hands Basketball players who make several baskets in succession are described as having a hot hand. Fans and players have long believed in the hot hand phenomenon, which refutes
The Five Magic Numbers
 The Five Magic Numbers Objective: Students will review the five numbers needed to construct a box and whisker plot. Students will also answer questions using a box and whisker plot they created. Background
The Five Magic Numbers Objective: Students will review the five numbers needed to construct a box and whisker plot. Students will also answer questions using a box and whisker plot they created. Background
Section 5 Critiquing Data Presentation - Teachers Notes
 Topics from GCE AS and A Level Mathematics covered in Sections 5: Interpret histograms and other diagrams for single-variable data Select or critique data presentation techniques in the context of a statistical
Topics from GCE AS and A Level Mathematics covered in Sections 5: Interpret histograms and other diagrams for single-variable data Select or critique data presentation techniques in the context of a statistical
Scaled vs. Original Socre Mean = 77 Median = 77.1
 Have out... - notebook - colors - calculator (phone calc will work fine) Tests back as you come in! vocab example Tests Scaled vs. Original Socre Mean = 77 Median = 77.1 + Δ vocab example 1 2.1 Describing
Have out... - notebook - colors - calculator (phone calc will work fine) Tests back as you come in! vocab example Tests Scaled vs. Original Socre Mean = 77 Median = 77.1 + Δ vocab example 1 2.1 Describing
CHAPTER 4: DECIMALS. Image from Microsoft Office Clip Art CHAPTER 4 CONTENTS
 CHAPTER 4: DECIMALS Image from Microsoft Office Clip Art CHAPTER 4 CONTENTS 4.1 Introduction to Decimals 4.2 Converting between Decimals and Fractions 4.3 Addition and Subtraction of Decimals 4.4 Multiplication
CHAPTER 4: DECIMALS Image from Microsoft Office Clip Art CHAPTER 4 CONTENTS 4.1 Introduction to Decimals 4.2 Converting between Decimals and Fractions 4.3 Addition and Subtraction of Decimals 4.4 Multiplication
Table of Contents. 1 Command Summary...1
 Table of Contents 1 Command Summary....1 1.1 General Commands.... 1 1.1.1 Operating Modes.... 1 1.1.2 In a Menu or List.... 2 1.1.3 Options Available at Any Point.... 2 1.1.4 Switch Programs.... 4 1.1.5
Table of Contents 1 Command Summary....1 1.1 General Commands.... 1 1.1.1 Operating Modes.... 1 1.1.2 In a Menu or List.... 2 1.1.3 Options Available at Any Point.... 2 1.1.4 Switch Programs.... 4 1.1.5
The ICC Duckworth-Lewis-Stern calculator. DLS Edition 2016
 The ICC Duckworth-Lewis-Stern calculator DLS Edition 2016 (DLS2-2016) Installation and operating instructions Queries about program operation should be sent to: Steven.Stern@qut.edu.au 2016 International
The ICC Duckworth-Lewis-Stern calculator DLS Edition 2016 (DLS2-2016) Installation and operating instructions Queries about program operation should be sent to: Steven.Stern@qut.edu.au 2016 International
Understood, Inc. User Guide SCUBA Solutions Version 1.7
 Understood, Inc. User Guide SCUBA Solutions Version 1.7 Table of Contents Revision History... 4 Introduction... 5 Purpose... 5 Scope... 5 Home... 5 Today s Dive Trips [Display]:... 6 Next Dive Trip [Display]:...
Understood, Inc. User Guide SCUBA Solutions Version 1.7 Table of Contents Revision History... 4 Introduction... 5 Purpose... 5 Scope... 5 Home... 5 Today s Dive Trips [Display]:... 6 Next Dive Trip [Display]:...
INSTRUCTIONS FOR USING HMS 2016 Scoring (v1)
 INSTRUCTIONS FOR USING HMS 2016 Scoring (v1) HMS 2016 Scoring (v1).xlsm is an Excel Workbook saved as a Read Only file. Intended for scoring multi-heat events run under HMS 2016, it can also be used for
INSTRUCTIONS FOR USING HMS 2016 Scoring (v1) HMS 2016 Scoring (v1).xlsm is an Excel Workbook saved as a Read Only file. Intended for scoring multi-heat events run under HMS 2016, it can also be used for
Analysis of Variance. Copyright 2014 Pearson Education, Inc.
 Analysis of Variance 12-1 Learning Outcomes Outcome 1. Understand the basic logic of analysis of variance. Outcome 2. Perform a hypothesis test for a single-factor design using analysis of variance manually
Analysis of Variance 12-1 Learning Outcomes Outcome 1. Understand the basic logic of analysis of variance. Outcome 2. Perform a hypothesis test for a single-factor design using analysis of variance manually
IHS AP Statistics Chapter 2 Modeling Distributions of Data MP1
 IHS AP Statistics Chapter 2 Modeling Distributions of Data MP1 Monday Tuesday Wednesday Thursday Friday August 22 A Day 23 B Day 24 A Day 25 B Day 26 A Day Ch1 Exploring Data Class Introduction Getting
IHS AP Statistics Chapter 2 Modeling Distributions of Data MP1 Monday Tuesday Wednesday Thursday Friday August 22 A Day 23 B Day 24 A Day 25 B Day 26 A Day Ch1 Exploring Data Class Introduction Getting
AP STATISTICS Name Chapter 6 Applications Period: Use summary statistics to answer the question. Solve the problem.
 AP STATISTICS Chapter 6 Applications Name Period: Use summary statistics to answer the question. 1) The speed vehicles travelled on a local highway was recorded for one month. The speeds ranged from 48
AP STATISTICS Chapter 6 Applications Name Period: Use summary statistics to answer the question. 1) The speed vehicles travelled on a local highway was recorded for one month. The speeds ranged from 48
Look again at the election of the student council president used in the previous activities.
 Activity III: Pairwise Comparisons (Grades 8-11) NCTM Standards: Number and Operation Data Analysis, Statistics, and Probability Problem Solving Reasoning and Proof Communication Connections Representation
Activity III: Pairwise Comparisons (Grades 8-11) NCTM Standards: Number and Operation Data Analysis, Statistics, and Probability Problem Solving Reasoning and Proof Communication Connections Representation
NUMB3RS Activity: Is It for Real? Episode: Hardball
 Teacher Page 1 NUMB3RS Activity: Is It for Real? Topic: Data analysis Grade Level: 9-10 Objective: Use formulas to generate data points. Produce line graphs of which inferences are made. Time: 20 minutes
Teacher Page 1 NUMB3RS Activity: Is It for Real? Topic: Data analysis Grade Level: 9-10 Objective: Use formulas to generate data points. Produce line graphs of which inferences are made. Time: 20 minutes
Practice Test Unit 6B/11A/11B: Probability and Logic
 Note to CCSD Pre-Algebra Teachers: 3 rd quarter benchmarks begin with the last 2 sections of Chapter 6, and then address Chapter 11 benchmarks; logic concepts are also included. We have combined probability
Note to CCSD Pre-Algebra Teachers: 3 rd quarter benchmarks begin with the last 2 sections of Chapter 6, and then address Chapter 11 benchmarks; logic concepts are also included. We have combined probability
MJA Rev 10/17/2011 1:53:00 PM
 Problem 8-2 (as stated in RSM Simplified) Leonard Lye, Professor of Engineering and Applied Science at Memorial University of Newfoundland contributed the following case study. It is based on the DOE Golfer,
Problem 8-2 (as stated in RSM Simplified) Leonard Lye, Professor of Engineering and Applied Science at Memorial University of Newfoundland contributed the following case study. It is based on the DOE Golfer,
[CROSS COUNTRY SCORING]
![[CROSS COUNTRY SCORING] [CROSS COUNTRY SCORING]](/thumbs/84/89721527.jpg) 2015 The Race Director Guide [CROSS COUNTRY SCORING] This document describes the setup and scoring processes employed when scoring a cross country race with Race Director. Contents Intro... 3 Division
2015 The Race Director Guide [CROSS COUNTRY SCORING] This document describes the setup and scoring processes employed when scoring a cross country race with Race Director. Contents Intro... 3 Division
An average pitcher's PG = 50. Higher numbers are worse, and lower are better. Great seasons will have negative PG ratings.
 Fastball 1-2-3! This simple game gives quick results on the outcome of a baseball game in under 5 minutes. You roll 3 ten-sided dice (10d) of different colors. If the die has a 10 on it, count it as 0.
Fastball 1-2-3! This simple game gives quick results on the outcome of a baseball game in under 5 minutes. You roll 3 ten-sided dice (10d) of different colors. If the die has a 10 on it, count it as 0.
SafeSeaNet Norway PEC Administration Guide
 SafeSeaNet Norway PEC Administration Guide Kystverket Vest Flathauggata 12 5525 Haugesund Telephone: +47 52 73 32 00 Telefax: +47 52 73 32 01 E-post: vest@kystverket.no Web: http://www.kystverket.no Table
SafeSeaNet Norway PEC Administration Guide Kystverket Vest Flathauggata 12 5525 Haugesund Telephone: +47 52 73 32 00 Telefax: +47 52 73 32 01 E-post: vest@kystverket.no Web: http://www.kystverket.no Table
Practice Test Unit 06B 11A: Probability, Permutations and Combinations. Practice Test Unit 11B: Data Analysis
 Note to CCSD HS Pre-Algebra Teachers: 3 rd quarter benchmarks begin with the last 2 sections of Chapter 6 (probability, which we will refer to as 6B), and then address Chapter 11 benchmarks (which will
Note to CCSD HS Pre-Algebra Teachers: 3 rd quarter benchmarks begin with the last 2 sections of Chapter 6 (probability, which we will refer to as 6B), and then address Chapter 11 benchmarks (which will
Money Lost or Won -$5 +$3 +$7
 Math 137 Unit 7 Review 1. The numbers of endangered species for several groups are listed here. Location Mammals Birds Reptiles Amphibians Total USA 63 78 14 10 Foreign 251 175 64 8 Total If one endangered
Math 137 Unit 7 Review 1. The numbers of endangered species for several groups are listed here. Location Mammals Birds Reptiles Amphibians Total USA 63 78 14 10 Foreign 251 175 64 8 Total If one endangered
Full file at
 Chapter 2 1. Describe the distribution. survival times of persons diagnosed with terminal lymphoma A) approximately normal B) skewed left C) skewed right D) roughly uniform Ans: C Difficulty: low 2. Without
Chapter 2 1. Describe the distribution. survival times of persons diagnosed with terminal lymphoma A) approximately normal B) skewed left C) skewed right D) roughly uniform Ans: C Difficulty: low 2. Without
SHIMADZU LC-10/20 PUMP
 SHIMADZU LC-10/20 PUMP Clarity Control Module ENG Code/Rev.: M091/70C Date: 24.10.2017 Phone: +420 251 013 400 DataApex Ltd. Fax: +420 251 013 401 Petrzilkova 2583/13 clarity@dataapex.com 158 00 Prague
SHIMADZU LC-10/20 PUMP Clarity Control Module ENG Code/Rev.: M091/70C Date: 24.10.2017 Phone: +420 251 013 400 DataApex Ltd. Fax: +420 251 013 401 Petrzilkova 2583/13 clarity@dataapex.com 158 00 Prague
Aim: Normal Distribution and Bell Curve
 Aim: Normal Distribution and Bell Curve HW: Complete (1-10) last 3 slides Do Now: If the variance of a set of data is 9, the standard deviation is: (1) 9 (2) 81 (3) 3 (4) 1 Normal Distribution and Bell
Aim: Normal Distribution and Bell Curve HW: Complete (1-10) last 3 slides Do Now: If the variance of a set of data is 9, the standard deviation is: (1) 9 (2) 81 (3) 3 (4) 1 Normal Distribution and Bell
Chapter. 1 Who s the Best Hitter? Averages
 Chapter 1 Who s the Best Hitter? Averages The box score, being modestly arcane, is a matter of intense indifference, if not irritation, to the non-fan. To the baseball-bitten, it is not only informative,
Chapter 1 Who s the Best Hitter? Averages The box score, being modestly arcane, is a matter of intense indifference, if not irritation, to the non-fan. To the baseball-bitten, it is not only informative,
The ICC Duckworth-Lewis Calculator. Professional Edition 2008
 The ICC Duckworth-Lewis Calculator Professional Edition 2008 (Version 1.1) Installation and operating instructions Any queries about operating the program should be sent to steven.stern@anu.edu.au 2008
The ICC Duckworth-Lewis Calculator Professional Edition 2008 (Version 1.1) Installation and operating instructions Any queries about operating the program should be sent to steven.stern@anu.edu.au 2008
CHAPTER 2 Modeling Distributions of Data
 CHAPTER 2 Modeling Distributions of Data 2.2 Density Curves and Normal Distributions The Practice of Statistics, 5th Edition Starnes, Tabor, Yates, Moore Bedford Freeman Worth Publishers Density Curves
CHAPTER 2 Modeling Distributions of Data 2.2 Density Curves and Normal Distributions The Practice of Statistics, 5th Edition Starnes, Tabor, Yates, Moore Bedford Freeman Worth Publishers Density Curves
download.file("http://www.openintro.org/stat/data/kobe.rdata", destfile = "kobe.rdata")
 Lab 2: Probability Hot Hands Basketball players who make several baskets in succession are described as having a hot hand. Fans and players have long believed in the hot hand phenomenon, which refutes
Lab 2: Probability Hot Hands Basketball players who make several baskets in succession are described as having a hot hand. Fans and players have long believed in the hot hand phenomenon, which refutes
USA Jump Rope Tournament Software User Guide 2014 Edition
 USA Jump Rope Tournament Software User Guide www.usajumprope.org Table of Contents Contents System Requirements... 3 System Conventions... 4 Phase 1 Tournament Pre registration Preparation... 5 Name Your
USA Jump Rope Tournament Software User Guide www.usajumprope.org Table of Contents Contents System Requirements... 3 System Conventions... 4 Phase 1 Tournament Pre registration Preparation... 5 Name Your
Math 227 Test 1 (Ch2 and 3) Name
 Math 227 Test 1 (Ch2 and 3) Name 1) In a survey, 20 people were asked how many magazines they had purchased during the previous year. The results are shown below. Construct a histogram to represent the
Math 227 Test 1 (Ch2 and 3) Name 1) In a survey, 20 people were asked how many magazines they had purchased during the previous year. The results are shown below. Construct a histogram to represent the
Managing Timecard Exceptions
 Managing Timecard Exceptions 1. General Exception Information Exceptions are flags in timecards, reports and Genies that identify when information on the timecard deviates from the employee s schedule.
Managing Timecard Exceptions 1. General Exception Information Exceptions are flags in timecards, reports and Genies that identify when information on the timecard deviates from the employee s schedule.
Complete Wristband System Tutorial PITCHING
 Complete Wristband System Tutorial PITCHING Type Of Wristband Brands Cutter Nike Under Armour Neumann Specifications: 5 inch by 3 inch window Youth - Durable 2.25 x 4.50 Vinyl Windows X100 Youth X200 Adult
Complete Wristband System Tutorial PITCHING Type Of Wristband Brands Cutter Nike Under Armour Neumann Specifications: 5 inch by 3 inch window Youth - Durable 2.25 x 4.50 Vinyl Windows X100 Youth X200 Adult
Overview 1. Handicap Overview 12. Types of Handicapping...12 The Handicap Cycle...12 Calculating handicaps...13 Handicap Nomenclature...
 Handicap System Overview 1 The Handicap System...1 Creating a Roster...1 Entering Courses...2 Entering Golfers...3 Entering Scores...4 Viewing Scores...7 Combing two nine holes scores to form an 18 hole
Handicap System Overview 1 The Handicap System...1 Creating a Roster...1 Entering Courses...2 Entering Golfers...3 Entering Scores...4 Viewing Scores...7 Combing two nine holes scores to form an 18 hole
Vapor Pressure of Liquids
 Vapor Pressure of Liquids In this experiment, you will investigate the relationship between the vapor pressure of a liquid and its temperature. When a liquid is added to the Erlenmeyer flask shown in Figure
Vapor Pressure of Liquids In this experiment, you will investigate the relationship between the vapor pressure of a liquid and its temperature. When a liquid is added to the Erlenmeyer flask shown in Figure
CHAPTER 2 Modeling Distributions of Data
 CHAPTER 2 Modeling Distributions of Data 2.1 Describing Location in a Distribution The Practice of Statistics, 5th Edition Starnes, Tabor, Yates, Moore Bedford Freeman Worth Publishers 2.1 Reading Quiz
CHAPTER 2 Modeling Distributions of Data 2.1 Describing Location in a Distribution The Practice of Statistics, 5th Edition Starnes, Tabor, Yates, Moore Bedford Freeman Worth Publishers 2.1 Reading Quiz
(c) The hospital decided to collect the data from the first 50 patients admitted on July 4, 2010.
 Math 155, Test 1, 18 October 2011 Name: Instructions. This is a closed-book test. You may use a calculator (but not a cell phone). Make sure all cell-phones are put away and that the ringer is off. Show
Math 155, Test 1, 18 October 2011 Name: Instructions. This is a closed-book test. You may use a calculator (but not a cell phone). Make sure all cell-phones are put away and that the ringer is off. Show
Part 1: Decimals. The decimal point separates the whole numbers from the fractional part of a
 Part 1: Decimals Decimal Place Values The decimal point separates the whole numbers from the fractional part of a number. 1328. 1095 In a whole number the decimal point is all the way to the right, even
Part 1: Decimals Decimal Place Values The decimal point separates the whole numbers from the fractional part of a number. 1328. 1095 In a whole number the decimal point is all the way to the right, even
Lesson 2 Pre-Visit Slugging Percentage
 Lesson 2 Pre-Visit Slugging Percentage Objective: Students will be able to: Set up and solve equations for batting average and slugging percentage. Review prior knowledge of conversion between fractions,
Lesson 2 Pre-Visit Slugging Percentage Objective: Students will be able to: Set up and solve equations for batting average and slugging percentage. Review prior knowledge of conversion between fractions,
THE 2018 ROSENTHAL PRIZE for Innovation in Math Teaching. Geometry Project: DARTBOARD
 THE 2018 ROSENTHAL PRIZE for Innovation in Math Teaching Geometry Project: DARTBOARD Geometric Probability Theoretical Probability and Experimental Probability Elizabeth Masslich Geometry grades 6-12 Table
THE 2018 ROSENTHAL PRIZE for Innovation in Math Teaching Geometry Project: DARTBOARD Geometric Probability Theoretical Probability and Experimental Probability Elizabeth Masslich Geometry grades 6-12 Table
[CROSS COUNTRY SCORING]
![[CROSS COUNTRY SCORING] [CROSS COUNTRY SCORING]](/thumbs/89/99405973.jpg) 2018 The Race Director Guide [CROSS COUNTRY SCORING] This document describes the setup and scoring processes employed when scoring a cross country race with Race Director. Contents Intro... 3 Division
2018 The Race Director Guide [CROSS COUNTRY SCORING] This document describes the setup and scoring processes employed when scoring a cross country race with Race Director. Contents Intro... 3 Division
Inventor Hole Notes: How to Annotate with Drill Numbers Not Diameters Author: David Ponka, Senior Applications Expert Manufacturing
 Inventor Hole Notes: How to Annotate with Drill Numbers Not Diameters Author: David Ponka, Senior Applications Expert Manufacturing Introduction Hole notes in Inventor are a great drawing aid that can
Inventor Hole Notes: How to Annotate with Drill Numbers Not Diameters Author: David Ponka, Senior Applications Expert Manufacturing Introduction Hole notes in Inventor are a great drawing aid that can
Smoothing the histogram: The Normal Curve (Chapter 8)
 Sept. 3 Statistic for the day: Compared to same month the previous year, average monthly drop in U.S. traffic fatalities from May 27 to Feb. 28:.2% Drop in March 28: 22.1% Drop in April 28: 17.9% Smoothing
Sept. 3 Statistic for the day: Compared to same month the previous year, average monthly drop in U.S. traffic fatalities from May 27 to Feb. 28:.2% Drop in March 28: 22.1% Drop in April 28: 17.9% Smoothing
MATH STUDENT BOOK. 7th Grade Unit 3
 MATH STUDENT BOOK 7th Grade Unit 3 Unit 3 Decimals Math 703 Decimals Introduction 3 1. Decimals and Their Operations 5 Comparing and Ordering Decimals 5 Rounding and Estimating Decimals 11 Adding and Subtracting
MATH STUDENT BOOK 7th Grade Unit 3 Unit 3 Decimals Math 703 Decimals Introduction 3 1. Decimals and Their Operations 5 Comparing and Ordering Decimals 5 Rounding and Estimating Decimals 11 Adding and Subtracting
Organizing Quantitative Data
 Organizing Quantitative Data MATH 130, Elements of Statistics I J. Robert Buchanan Department of Mathematics Fall 2018 Objectives At the end of this lesson we will be able to: organize discrete data in
Organizing Quantitative Data MATH 130, Elements of Statistics I J. Robert Buchanan Department of Mathematics Fall 2018 Objectives At the end of this lesson we will be able to: organize discrete data in
Healthcare Analytics Anticoagulation Time in Therapeutic Range Calculation Documentation September 4, 2015
 Healthcare Analytics Anticoagulation Time in Therapeutic Range Calculation Documentation September 4, 2015 Reference #1: Percent of Days in Range (Rosendaal Method) Article: http://www.inrpro.com/article.asp?id=1
Healthcare Analytics Anticoagulation Time in Therapeutic Range Calculation Documentation September 4, 2015 Reference #1: Percent of Days in Range (Rosendaal Method) Article: http://www.inrpro.com/article.asp?id=1
APPROVED FACILITY SCHOOLS CURRICULUM DOCUMENT SUBJECT: Mathematics GRADE: 6. TIMELINE: Quarter 1. Student Friendly Learning Objective
 TIMELINE: Quarter 1 i-ready lesson: Rational Numbers and Absolute Value i-ready lesson: Numerical Expressions and Order of Operations 6/16/15 1 i-ready lesson (2a, 2b and 2c): Algebraic Expressions 6/16/15
TIMELINE: Quarter 1 i-ready lesson: Rational Numbers and Absolute Value i-ready lesson: Numerical Expressions and Order of Operations 6/16/15 1 i-ready lesson (2a, 2b and 2c): Algebraic Expressions 6/16/15
A GUIDE TO THE LOOSE ENDS HOCKEY LEAGUE WEBSITE PAGE
 A GUIDE TO THE LOOSE ENDS HOCKEY LEAGUE WEBSITE PAGE 1 What Can Be Done Using The League Website: MAIN PAGE: From the main page, click on the man with the newspaper beneath the label News and Archives
A GUIDE TO THE LOOSE ENDS HOCKEY LEAGUE WEBSITE PAGE 1 What Can Be Done Using The League Website: MAIN PAGE: From the main page, click on the man with the newspaper beneath the label News and Archives
MATH 118 Chapter 5 Sample Exam By: Maan Omran
 MATH 118 Chapter 5 Sample Exam By: Maan Omran Problem 1-4 refer to the following table: X P Product a 0.2 d 0 0.1 e 1 b 0.4 2 c? 5 0.2? E(X) = 1.7 1. The value of a in the above table is [A] 0.1 [B] 0.2
MATH 118 Chapter 5 Sample Exam By: Maan Omran Problem 1-4 refer to the following table: X P Product a 0.2 d 0 0.1 e 1 b 0.4 2 c? 5 0.2? E(X) = 1.7 1. The value of a in the above table is [A] 0.1 [B] 0.2
Overview. Learning Goals. Prior Knowledge. UWHS Climate Science. Grade Level Time Required Part I 30 minutes Part II 2+ hours Part III
 Draft 2/2014 UWHS Climate Science Unit 3: Natural Variability Chapter 5 in Kump et al Nancy Flowers Overview This module provides a hands-on learning experience where students will analyze sea surface
Draft 2/2014 UWHS Climate Science Unit 3: Natural Variability Chapter 5 in Kump et al Nancy Flowers Overview This module provides a hands-on learning experience where students will analyze sea surface
AKTA pure 25 New Owner s Intro
 AKTA pure 25 New Owner s Intro The exercise below will give a quick demonstration of how easy and intuitive the AKTA pure 25 will be for you in demonstrating downstream processing to your students. Steps
AKTA pure 25 New Owner s Intro The exercise below will give a quick demonstration of how easy and intuitive the AKTA pure 25 will be for you in demonstrating downstream processing to your students. Steps
Lesson 1: Decimal Place Value. Concept/Topic to Teach: Students use Bruins statistical data to order and compare decimals to the thousandths.
 Math Lesson 1: Decimal Place Value Concept/Topic to Teach: Students use Bruins statistical data to order and compare decimals to the thousandths. Standards Addressed: Standard 1: 5.NBT.3 Read, write, and
Math Lesson 1: Decimal Place Value Concept/Topic to Teach: Students use Bruins statistical data to order and compare decimals to the thousandths. Standards Addressed: Standard 1: 5.NBT.3 Read, write, and
1. The data below gives the eye colors of 20 students in a Statistics class. Make a frequency table for the data.
 1. The data below gives the eye colors of 20 students in a Statistics class. Make a frequency table for the data. Green Blue Brown Blue Blue Brown Blue Blue Blue Green Blue Brown Blue Brown Brown Blue
1. The data below gives the eye colors of 20 students in a Statistics class. Make a frequency table for the data. Green Blue Brown Blue Blue Brown Blue Blue Blue Green Blue Brown Blue Brown Brown Blue
FireWorks NFIRS BI User Manual
 FireWorks NFIRS BI User Manual Last Updated: March 2018 Introduction FireWorks Business Intelligence BI and analytics tool is used to analyze NFIRS (National Fire Incident Reporting System) data in an
FireWorks NFIRS BI User Manual Last Updated: March 2018 Introduction FireWorks Business Intelligence BI and analytics tool is used to analyze NFIRS (National Fire Incident Reporting System) data in an
Trial # # of F.T. Made:
 OPEN SPINNER APPLICATION APPS Prob Sim ENTER (Spin Spinner) SET UP SPINNER. TABL (graph) the blank graph disappears & will later become a table. SET (zoom) Change Sections to ENTER. ADV (window) Change
OPEN SPINNER APPLICATION APPS Prob Sim ENTER (Spin Spinner) SET UP SPINNER. TABL (graph) the blank graph disappears & will later become a table. SET (zoom) Change Sections to ENTER. ADV (window) Change
