Army Lists ITALY. Contents
|
|
|
- Warren McCarthy
- 5 years ago
- Views:
Transcription
1
2 Army Lists ITALY Contents Early Roman, Latin or Etruscan 500 to 300 BCE Italian Hill Tribes 500 to 290 BCE Umbrian 500 to 290 BCE Early Campanian 500 to 275 BCE Magna Graecia 500 to 267 BCE Apulian 500 to 203 BCE Bruttian 500 to 203 BCE Lucanian 500 to 203 BCE Camillan Roman 400 to 275 BCE Samnite 396 to 272 BCE Later Campanian 335 to 211 BCE MidRepublican Roman 275 to 100 BCE Later Republican Roman 105 to 20 BCE Spartacus Slave Revolt 73 to 71 BCE Early Imperial Roman 20 BCE to 268 CE Imperial Roman 269 to 407 CE Foederate Roman 408 to 460 CE Later Foederate Roman 461 to 476 CE
3 Creating an army with the Mortem et Gloriam Army Lists Use the army lists to create your own customised armies using the Mortem et Gloriam Army Builder. There are few general rules to follow: 1. An army must have at least 2 generals and can have no more than You must take at least the minimum of any troops noted, and may not go beyond the maximum of any. 3. No army may have more than two generals who are Talented or better. 4. Unless specified otherwise, all elements in a UG must be classified identically. Unless specified otherwise, if an optional characteristic is taken, it must be taken by all the elements in the UG for which that optional characteristic is available. 5. Any UGs can be downgraded by one quality grade and/or by one shooting skill representing less strong, tired or understrength troops. If any bases are downgraded all in the UG must be downgraded. So Experienced skirmishers can always be downgraded to PoorUnskilled. Where allies are allowed they must conform to the following rules: 1. They must be a minimum of 2 and a maximum of 4 UGs. 2. They must take UGs sufficient to get them to at least 50% of the minimums in the list being used. 3. They can thereafter take any troops up to the maximum to create the rest of the allied contingent. 4. Unless specified in the notes, the general must be the same type as the army commander in the main list but cannot be legendary. Usually this results in 13 UGs being compulsory and you having full flexibility on the rest. Where an internal ally is allowed, and no contingent is specified they must conform to the following rules: 1. They must be a minimum of 2 and a maximum of 4 UGs. 2. The total number of troops taken of each type in the entire army must not exceed the maxima for that troop type. 3. They must take UGs sufficient to get them to at least 50% of the minimums in the list if there is sufficient allowance for a UG after the core army itself has taken the minimum. 4. They can thereafter take any troops up to the maximum to create the rest of the allied contingent. Usually this results in 13 UGs being compulsory and you having full flexibility on the rest.
4 Historical Introduction At the start of the 5 th century BCE Italy was dominated by several different groups. The Celts were expanding from Gaul and Germany and coming into contact with the Etruscans in northern Italy. South of the Etruscans were the Latin tribes and amongst them an insignificant city called Rome. In the south of Italy the Greeks had founded a number of cities along the coast. Running through the spine of Italy were various tribes including Oscans and tribes which shared their heritage with Illyrians on the other side of the Adriatic. The Celtic invasions of northern Italy led to the ultimate collapse of the Etruscan civilisation. In around 390 BCE the Gauls sacked Rome. The city survived and from this point on started a process that ultimately would lead to the Roman Empire. The Romans were a military state and all citizens were obliged to perform military service. Uniquely the Romans would offer a form of citizenship to many of the cities and nations that they would conquer. This led to a vast increase in man power available for military service. During the 4 th century BCE Rome expanded, absorbed both Etruria and the Latin tribes and fought three bitter wars against the Samnites. In 282 BCE the Greek city of Tarentum, alarmed by Roman expansion, invited Pyrrhus of Epirus to lead their war against Rome. This was the first contact by Rome against the successors of Alexander the Great and the first contact with Elephants. In three brutal but indecisive battles (leading to the term Pyrrhic victory) the Romans fought this new opponent. Losing interest, Pyrrhus sought other opportunities and Rome quickly came to dominate southern Italy. As the 3 rd century BCE progressed the Romans came increasingly into conflict with the Celts of northern Italy. In 218 BCE a new opponent appeared as Hannibal led his Carthaginian army over the Alps. In his first few years in Italy, he won three dramatic victories the Trebia, Lake Trasimene, and Cannae and won over many allies of Rome. Hannibal was however unable to take Rome itself and the Romans used scorch earth tactics, refused battle and gradually wore down the Carthaginians. Carthaginian attempts to reinforce Hannibal were intercepted and defeated. Rome beat the Carthaginians in Spain and invaded Africa. The Carthaginian defeat at Zama signalled the end of the Carthaginian threat to Italy. During the 2 nd century BCE Rome expanded into Greece, Macedon and Asia Minor. The sacks of Carthage and Corinth in 146 BCE demonstrated Rome was the most powerful state in the Mediterranean. The expansion in the Mediterranean drove divisions between Rome and her allies in Italy. The Italians demanded equal treatment with Roman citizens, united and formed a state, Italia. The Social War (from socii, the term for allies ) was fought between 90 and 88 BCE Rome quickly offered citizenship to undermine the revolt and from this point on Italy can be regarded as a unified state. The expansion of Rome led to wealthy landowners obtaining vast numbers of slaves to man their farms and mines. The escape of a small group of Gladiators led to a slave revolt that devastated large parts of Italy. The initial Roman response was inadequate and the arms of the defeated forces only help to equip the slaves. It would require an army of eight legions to defeat Spartacus and end the slave revolt.
5 From this point for nearly 400 years the threats to Italy were to come from Roman civil wars. The key to power was military control. First Sulla, then Julius Caesar ruled Rome through military conquest. Caesar s adopted greatnephew, Octavian, won power after defeating Antony and Cleopatra and converted the Republic into an Empire around 25 BCE. The year of the four Emperors, 69 CE, saw the next threat of civil war in Italy. Vespasian emerged the ultimate victor and a period of relative stability followed. Roman expansion was intermittent, and with the conquest of Britain (started in 46 CE) and Dacia (101 to 106 CE) the Roman empire reached its largest extent. In 192 CE, with the assassination of Commodus, the period of stability ended. Things went from bad to worse and the period 235 to 284 CE saw at least 26 claimants to be emperor. This ended with the reign of Diocletian. He introduced reforms that led to the division of the empire into Eastern and Western portions. In 306 CE, Constantine the Great was declared emperor by his troops on the death of his father. He defeated his opponents and was to rule until 337 CE. He put an end to the persecution of Christians and established a second capital at Constantinople. Theodosius was the last Emperor who ruled over the whole Empire. After his death in 395 CE the Roman state would continue to have two different emperors with different seats of power. Rome had already come under pressure from Goths and Germans. Triggered by the migration of the Huns, the borders of the Empire were collapsing. Italy was invaded, and Rome was sacked in 410 CE and again in 455 CE. The Emperor s seat was moved to Ravenna. The deposition of the emperor, Romulus Augustulus, in 476 CE by Odoacer, is generally accepted to mark the end of the Roman empire in the west.
6 Army Commander 1 Any Instinctive Dates 500 BCE to 330 BCE SubGenerals 03 Any Instinctive Terrain Coastal, Mountains Internal Allied Generals 02 Any Instinctive Camp Unfortified; Poor or Name Cavalry Infantry of 1st class Infantry of 2nd or 3rd class Slingers of 4th or 5th class Javelinmen of 4th or 5th class Allies Formed Close Tribal Close Italian Hill Tribe allies Samnite allies (only Etruscan from 396 BCE) Gallic allies Lowland Gallic (only Etruscan from 396 BCE) Campanian allies Early Campanian (only Latin from 340 to 338 BCE) Early Roman, Latin or Etruscan Type Training and Quality Protection Shooting Skill Melee Characteristics Min Mandatory Optional Max 4 4,6 Short Spear Melee Expert 12 Shove, Shield 8 6,8 Long Spear Orb/Square Cover ,8 Long Spear Orb/Square 80 Combat Shy Sling 9 Combat Shy Javelin 27 UG Size
7 Historical Notes Early Roman, Latin or Etruscan This list includes Etruscan, Roman and Latin armies. The Etruscan League was established in the 7th century BCE It expanded from modern Tuscany into the Po valley, Latium and Campania. In the 6th century BCE they were allied with Carthage against the Greek cities in Italy (Magna Graecia). In 474 BCE the combined fleets of the Syracusans and Cumae defeated the Etruscan fleet and the Etruscans lost control of the Tyrrhenian Sea. This led to their decline at the hands of the Romans and the Gauls. Around 282 BCE an army of Etruscans and Gauls was decisively beaten near Lake Vadimo by the Romans. Thereafter the Etruscans came firmly under Roman control. Early Rome was dominated by the Etruscans. After the Etruscans failed to reestablish the monarchy in Rome (traditionally overthrown in 509 BCE) Rome established its primacy in Latium. In the early 4th century Rome captured the Etruscan city of Veii and subjugated the Volsci and Aequi. In 387 BCE Rome was sacked by a Gallic army under Brennos but they were subsequently driven off by M Furius Camillus. Following the First Samnite War (343 BCE to 341 BCE) the Latins revolted. The Latin War (340 BCE to 338 BCE) saw the Latin League dissolved, increased control by Rome and the Latins being granted some rights and varying degrees of citizenship. Troop Notes Cavalry: Etruscan and early Roman cavalry seem to have been armed only with a thrusting spear. Infantry of the 1st class: The Etruscans had adopted Hoplite panoply from the Greeks. The 1st class (wealthiest individuals) could possess the full panoply. Infantry of the 2nd, 3rd class: These were less well equipped than the 1st class. Infantry of the 4th class: There is debate whether these were less well equipped spearmen or skirmishers. Infantry of the 5th class: These were skirmishers. Some may have been slingers, the remainder were javelinmen. Changes from last version Updated territory types.
8 Army Commander 1 Any Instinctive Dates 500 BCE to 290 BCE SubGenerals 03 Any Instinctive Terrain Mountains Internal Allied Generals 02 Any Instinctive Camp Unfortified; Poor or Name Characteristics Min Mandatory Optional Max 0 4,6 Cavalry Short Spear Melee Expert 8 Unskilled 0 6 Picked warriors Superior Short Spear Shoot & Charge Javelin 18 Unskilled 16 6,8,9 Warriors Short Spear Shoot & Charge Javelin 120 s Combat Shy Javelin 27 Notes A command may not have more than one UG of picked warriors. Historical Notes Central Italy was controlled by a number of tribes including the Aequi, Aurunci, Hernici, Picentes, Sabines, Sidicini and Volsci. They were conquered by Rome between the 5th century BCE and 3rd century BCE. Troop Notes Cavalry: The Italian Hill Tribes had a small amount of cavalry. Infantry: The core of the army were javelinmen equipped with a shield and javelins. The wealthiest individuals might acquire some armour. Changes from last version Added Shoot & Charge option. Type Training and Quality Italian Hill Tribes Protection Shooting Skill Melee UG Size
9 Army Commander 1 Any Instinctive Dates 500 BCE to 290 BCE SubGenerals 13 Any Instinctive Terrain Mountains Internal Allied Generals Camp Unfortified; Poor or Name Characteristics Min Mandatory Optional Max 4 4,6 Cavalry Short Spear Melee Expert 12 Shove, Shield 8 6,8 Hoplites Long Spear Orb/Square Formed Close Cover 24 Unskilled 8 6,8,9 Javelinmen Short Spear Shoot & Charge Javelin 80 Slingers Combat Shy Sling 9 Skirmishing javelinmen Combat Shy Javelin 27 Historical Notes The Umbrians were driven into the Appenines by the Etruscans. After the downfall of the Etruscans, Umbrians aided the Samnites in their struggle against Rome. When Rome fought the Gauls in 295 BCE, allied Umbrians and Etruscans had to return to their territories to defend against simultaneous Roman attacks. They were unable to help the Samnites and their Gallic allies in the battle of Sentinum. The Roman victory at Sentinum started a period of integration under Rome. Troop Notes Little evidence exists for the Umbrian army, but it may have been a mix of Latin and Oscan influences. Changes from last version Added Shoot & Charge option. Type Training and Quality Protection Umbrian Shooting Skill Melee UG Size
10 Army Commander 1 Any Instinctive Dates 500 BCE to 275 BCE SubGenerals 03 Any Instinctive Terrain Standard, Coastal Internal Allied Generals Camp Unfortified; Poor or Name Characteristics Min Mandatory Optional Max Unskilled 4 4,6 Cavalry Superior Short Spear Shoot & Charge Javelin 12 Experienced 0 4,6 Light cavalry Formed Flexible Javelin 6 Shove, Shield 8 6,8 Hoplites Long Spear Orb/Square Formed Close Cover 40 Unskilled 8 6,8,9 Javelinmen Short Spear Shoot & Charge Javelin 60 s Combat Shy Javelin 27 Allies Roman allies Early Roman, Latin or Etruscan (343 BCE) Roman allies Camillan Roman (343 BCE) Latin allies Early Roman, Latin or Etruscan (from 342 to 338 BCE) Notes The Roman ally must either be taken from the Early Roman, Latin or Etruscan list or from the Camillan Roman list. Historical Notes The Campani, an Oscan people, gained control of the Greek and Etruscan cities of the northern Campanian plain. In 343 BCE threatened by Samnite incursions the Campanians invited Roman intervention, resulting in the first Samnite war. When a peace treaty threatened to carve up Italy between the Romans and Samnites, many Campanians joined the Latins in revolting against Rome. At the end of the war the Campanians were granted Roman citizenship without voting rights. In 327 BCE the Campanians once again sought Roman aid after the Samnites established a garrison at Neapolis. This led to the Second Samnite War. Thereafter Campania remained loyal to Rome until the Second Punic War. Troop Notes Type Training and Quality Early Campanian Protection Shooting Skill Cavalry: The Campanians had some of the best cavalry in Italy. Hoplites: The Campanians adopted hoplite panoply and tactics from their Greek subjects and neighbours. Javelinmen: The Campanians could also draw on infantry using traditional Oscan tactics. Melee UG Size
11 Early Campanian Changes from last version Added Shoot & Charge option.
12 Army Commander 1 Any Instinctive Dates 500 BCE to 267 BCE SubGenerals 02 Any Instinctive Terrain Coastal Internal Allied Generals 01 Any Instinctive Camp Unfortified or Flexible; Poor or Name Greek cavalry Tyrant's bodyguard Citizen hoplites Mercenary hoplites (from 400 BCE) Italian mercenaries Levied citizens Light horse Upgrade light horse as "Tarentine" (from 350 BCE) Archers Slingers Javelinmen Type Training and Drilled Close Formed Close Drilled Close Formed Close Quality Magna Graecia Protection Shooting Skill Melee Characteristics Min Mandatory Optional Max UG Size Superior Poor Unskilled 4 4,6 Short Spear Shoot & Charge Javelin 12 Shove, Shield 0 6 Long Spear Orb/Square Cover 6 Shove, Shield 12 6,8 Long Spear Orb/Square Cover 48 Shove, Shield 0 6,8 Long Spear Orb/Square Cover 18 Unskilled 0 6,8,9 Short Spear Shoot & Charge Javelin ,8,9 Long Spear Shove Orb/Square 36 Experienced Cantabrian, 0 4,6 Javelin Combat Shy 12 Experienced 4,6 Cantabrian Javelin Any Combat Shy Bow 9 Combat Shy Sling 9 Combat Shy Javelin 18
13 Magna Graecia Allies Spartan allies Later Spartan (Tarentum from 343 to 338 BCE) Apulian allies (Tarentum from 290 to 282 BCE ) Lucanian allies (Tarentum from 290 to 282 BCE ) Notes Apulian allies may not be taken with Lucanian allies. Historical Notes Magna Graecia was the name given by the Romans to the coastal areas of Southern Italy in the presentday regions of Campania, Apulia, Basilicata, Calabria and Sicily that were extensively populated by Greek settlers. It included over 25 cities including Capua, Neapolis, Tarentum, Thurii and Rhegium. Most of the cities fell either to Oscan or Roman control during the 4th and 3rd centuries BCE. The last cities were captured after the Pyrrhic War including Tarentum in 272 BCE. This list excludes the armies led by Pyrrhus against the Romans. Troop Notes The cities fought in typical Greek style. Italian mercenaries were readily available. "Tarentine" cavalry were equipped with shields and javelins. Changes from last version New list.
14 Army Commander 1 Any Instinctive Dates 500 BCE to 203 BCE SubGenerals 13 Any Instinctive Terrain Mountains Internal Allied Generals Camp Unfortified; Poor or Name Type Training and Quality Protection Apulian Shooting Skill Melee Characteristics Min Mandatory Optional Max Unskilled 4 4,6 Armoured cavalry Superior Short Spear Shoot & Charge Javelin 8 Experienced 8 4,6 Light cavalry Formed Flexible Javelin 16 Unskilled 0 6 Picked warriors Superior Short Spear Shoot & Charge Javelin 18 Unskilled 12 6,8,9 Javelinmen Short Spear Shoot & Charge Javelin 96 s Combat Shy Javelin 27 Notes A command may not have more than one UG of picked warriors. Historical Notes Apulia in southeast Italy was occupied by tribes of mixed Illyrian and Oscan origin. Different tribes allied with both the Romans, the Samnites and with Pyrrhus. Troop Notes Cavalry: The Apulians had plenty of cavalry, many of whom were unarmoured. Shields were not carried before the 4th century BCE. Javelinmen: The infantry were javelinmen. Round shields were carried. Some wore Greek style helmets. Armour was rare. Changes from last version Reclassified infantry with Shoot & Charge option. UG Size
15 Army Commander 1 Any Instinctive Dates 500 BCE to 203 BCE SubGenerals 03 Any Instinctive Terrain Mountains Internal Allied Generals Camp Unfortified; Poor or Name Armoured cavalry Light cavalry Formed Flexible Picked warriors Javelinmen s Allies Lucanian allies (from 334 to 326 BCE) Notes A command may not have more than one UG of picked warriors. Historical Notes Troop Notes Type Training and Cavalry: The Bruttians had less cavalry than the Apulians and proportionately more were armoured. Javelinmen: The infantry were javelinemen. Round shields were carried. Some wore Greek style helmets. Changes from last version Reclassified infantry with Shoot & Charge option. Quality Protection Bruttian Shooting Skill Melee Characteristics Min Mandatory Optional Max Superior Superior Unskilled 0 4,6 Short Spear Shoot & Charge Javelin 8 Experienced 4 4,6 Javelin 8 Unskilled 0 6 Short Spear Shoot & Charge Javelin 18 Unskilled 18 6,8,9 Short Spear Shoot & Charge Javelin 108 Combat Shy Javelin 27 The Bruttii were located in the toe of Italy. They arose as a revolt of the former inhabitants against the Lucanians in the mid4th century BCE. In 326 BCE a combined Lucanian and Bruttian army defeated and killed the army of Alexander of Epirus (grandfather of Pyrrhus). Around 300 BCE the Bruttii were attacked by Agathocles of Syracuse. They then allied with Pyrrhus and later Hannibal against the Romans. UG Size
16 Army Commander 1 Any Instinctive Dates 500 BCE to 203 BCE SubGenerals 03 Any Instinctive Terrain Mountains Internal Allied Generals Camp Unfortified; Poor or Name Type Training and Quality Protection Lucanian Shooting Skill Melee Characteristics Min Mandatory Optional Max Unskilled 4 4,6 Armoured cavalry Superior Short Spear Shoot & Charge Javelin 8 Experienced 8 4,6 Light cavalry Formed Flexible Javelin 12 Unskilled 0 6 Picked warriors Superior Short Spear Shield Cover Shoot & Charge Javelin 18 Unskilled 12 6,8,9 Javelinmen Short Spear Shoot & Charge Javelin 96 Upgrade javelinmen as Unskilled 6,8,9 Short Spear Shield Cover Shoot & Charge armoured Javelin Up to half s Combat Shy Javelin 27 Allies Bruttian allies Roman allies Camillan Roman (298 to 290 BCE) Notes A command may not have more than one UG of picked warriors. Historical Notes The Lucanians were an Oscan tribe who conquered the areas of Italy south of Samnium. In 326 BCE a combined Lucanian and Bruttian army defeated and killed the army of Alexander of Epirus (grandfather of Pyrrhus). In 298 BCE they made alliance with Rome but on the landing of Pyrrhus in Italy (281 BCE) they were among the first to declare in his favour. After the departure of Pyrrhus they were exposed to the resentment of Rome and reduced to subjection in 272 BCE Some Lucanians supported Hannibal during the Second Punic War. UG Size
17 Troop Notes Reclassified infantry with Shoot & Charge option. Lucanian Cavalry: The Lucanians had less cavalry than the Apulians and proportionately more were armoured. Javelinmen: The infantry were javelinemen. Round shields were carried. Armour is more common in images of Lucanian warriors. Changes from last version
18 Army Commander 1 Any Instinctive Dates 400 BCE to 275 BCE SubGenerals 03 Any Instinctive Terrain Standard, Coastal Internal Allied Generals 01 Any Instinctive Camp Unfortified; Poor or Name Characteristics Min Mandatory Optional Max 4 4,6 Cavalry Short Spear Melee Expert 12 Legions comprising 1/3 Front rank Hastati and 2/3 Rear ranks Principes and Triarii with associated leves Hastati Charge Only 18 6,9 Long Spear Shield Cover Orb/Square Formed Close Javelin 90 Principes and triarii Long Spear Shield Cover Orb/Square Formed Close See note Leves Combat Shy Javelin 30 Pedites extraordinarii Italian infantry Accensi Rorarii Allies Italian Hill Tribe allies Samnite allies (only in 340 BCE) Notes Type Training and Formed Close Quality Camillan Roman Protection Shooting Skill Melee Superior Poor Poor Unskilled Shoot & Charge, 0 4 Short Spear Javelin Orb/Square 4 Unskilled 0 6,8,9 Short Spear Shoot & Charge Javelin ,8 Long Spear Shove 12 Combat Shy Javelin See note SPECIAL RULE: Legions must deploy in 3 ranks. Hastati must be easily distinguished from principes and triarii. The numbers in the list reflect the total number of hastati, principes and triarii. The number of rorarii cannot exceed the number of leves. UG Size
19 Historical Notes Changes from last version Regraded legions. Added Shoot & Charge option. Leves no longer mandatory. Camillan Roman The development of the Republican Roman army is a controversial topic. This list represents an intermediate stage between the Etruscan system and the later system described by Polybius. The reforms are attributed to Camillus around 400 BCE but may date much later. Accordingly, Roman armies between 400 and 341 BCE may use either the Early Roman list or this list. Troop Notes Cavalry: Roman cavalry at this stage still seems to have been relatively ineffective. Infantry: The infantry were organised into three lines with Hastati, armed with throwing spears in the front line, Principes, armed with the Long Spear in the second line and Triarii armed with long spear in the third line. The Accensi were reserves. s: Leves, javelin armed skirmishers formed a quarter of each legion. Rorarii may have been additional skirmishers that could be called upon if required.
20 Army Commander 1 Any Professional Dates 396 BCE to 272 BCE SubGenerals 03 Any Professional Terrain Mountains Internal Allied Generals Camp Unfortified or Flexible; Poor or Name Armoured cavalry Light cavalry Linen Legion or equivalent Type Training and Formed Flexible Quality Protection Samnite Shooting Skill Melee Characteristics Min Mandatory Optional Max Superior Unskilled 0 4,6 Short Spear Shoot & Charge Javelin 6 Experienced 4 4,6 Javelin 8 Unskilled Melee Expert, 0 6,8 Superior Short Spear Shoot & Charge, Javelin Orb/Square 24 Unskilled Shoot & Charge, 12 6,8 Samnite foot Short Spear Javelin Orb/Square 90 Unskilled Melee Expert, 0 6,8 Upgrade Samnite foot Short Spear Shoot & Charge, Javelin Orb/Square 32 Javelinmen Short Spear Javelin 27 Allies Roman allies Camillan Roman (only in 340 BCE) Campanian allies Early Campanian (from 326 to 304 BCE) Campanian allies Later Campanian (from 326 to 304 BCE) Apulian allies (before 281 BCE) Volsci and/or Hernici allies Italian Hill Tribes (before 281 BCE) Etruscan allies Early Roman, Latin or Etruscan (from 311 to 295 BCE) Umbrian allies (from 296 to 295 BCE) Gallic allies Lowland Gallic (from 296 to 295 BCE) UG Size
21 Notes Changes from last version Reclassified Samnite infantry. Added Shoot & Charge option. Adjusted maximums. Samnite A Samnite army in 296 BCE may have Gallic, Etruscan and Umbrian allies. In 295 BCE two commands of Gallic allies (up to 4 UG in each) may be chosen (representing the army at Sentinum). Otherwise only one ally is permitted. The Campanian ally must be chosen from either the Early Campanian or Later Campanian list. Historical Notes The Samnites were an Oscan people living in south central Italy. They allied with Rome against the Gauls in 354 BCE, but later became enemies of the Romans and were soon involved in a series of three wars against the Romans. Despite a spectacular victory over the Romans at the Battle of the Caudine Forks (321 BCE), the Samnites were eventually subjugated. Although weakened, the Samnites later helped Pyrrhus and Hannibal in their wars against Rome. Troop Notes Cavalry: Samnite cavalry were similar to other Oscan cavalry. Livy records them throwing javelins. Infantry: The Samnites operated units of picked troops, the best known being the Linen legion.
22 Army Commander 1 Any Dates 335 BCE to 211 BCE SubGenerals 13 Any Terrain Standard, Coastal Internal Allied Generals Camp Unfortified; Poor or Name Cavalry Characteristics Min Mandatory Optional Max Unskilled 4 4,6 Superior Short Spear Shoot & Charge Javelin 12 Hastati Charge Only 9 6,9 Long Spear Shield Cover Orb/Square Formed Close Javelin 120 Principes and triarii Long Spear Shield Cover Orb/Square Formed Close See note From 275 BCE Legions comprising 2/5 hastati, 2/5 principes and 1/5 triarii Hastati and principes Triarii in a combined unit with hastati & principes Triarii Melee Expert, 8 4,8 Impact Weapon Shield Cover Orb/Square 120 Melee Expert, Shield Cover Orb/Square See note Shove, Shield 2,4 Long Spear Orb/Square Cover See note s Combat Shy Javelin 27 Notes Before 275 BCE SPECIAL RULE: Legions must deploy in 3 ranks, with hastati in the front rank. The ranks may be redressed as a prompted action after deployment. From 275 BCE a maximum of 1 triarii may be taken for each 4 hastati and principes. Instead of deploying separately, 1 triarii may be combined with 4 hastati and principes into a TuG of 5. The numbers in the list reflect the total number of hastati, principes and triarii. Historical Notes Type Training and Before 275 BCE Legions comprising 1/3 front rank hastati and 2/3 rear ranks principes and triarii Drilled Close Drilled Close Drilled Close Quality Later Campanian Protection Shooting Skill Melee This list reflects Campanian armies after the integration with Rome and that adopted Roman fighting techniques. The exact date is uncertain, hence the overlap with the Early Campanian list. In 216 BCE the Campanian city of Capua joined Hannibal. In contrast the city of Nola remained defiant. Capua fell to the Romans in 211 BCE after a long siege. UG Size
23 Troop Notes Campanian troops adopted Roman fighting techniques and methods. Changes from last version Added Shoot & Charge option. Triarii no longer mandatory. Later Campanian
24 Army Commander 1 Any Dates 275 BCE to 100 BCE SubGenerals 03 Any Terrain Standard, Coastal Internal Allied Generals 01 Any (represents uncooperative consul) Camp Unfortified or Fortified; Poor, or Name Elephants (from 200 BCE) Cavalry Legions Characteristics Min Mandatory Optional Max Unskilled Melee Expert, 0 4,6 Short Spear Javelin Shoot & Charge 8 Melee Expert, 16 4,6,8 Hastati & principes Impact Weapon Shield Cover Drilled Close Orb/Square 80 Triarii in a combined with Melee Expert, Shield Cover hastati & principes Drilled Close Orb/Square See note Upgrade legions as veteran Veteran hastati & principes Veteran triarii in a combined unit Type Training and ELEPHANTS Tribal Loose Drilled Close Drilled Close Mid Republican Roman Quality Protection Shooting Skill Melee Superior Melee Expert, 0 4,6,8 Impact Weapon Shield Cover Orb/Square 16 Superior Melee Expert, Shield Cover Orb/Square See note Shove, Shield 4 Triarii Superior Long Spear Orb/Square Drilled Close Cover See note Unskilled Shoot & Charge, 0 4 Pedites extraordinarii Superior Short Spear Javelin Orb/Square 4 Unskilled Shoot & Charge, 0 6,8,9 Italian infantry Short Spear Javelin Orb/Square 12 Spanish scutarii (from ,8,9 Impact Weapon BCE) 9 Devastating 0 6,8,9 Gallic foot Formed Flexible Chargers 9 UG Size
25 Mid Republican Roman Unskilled 0 6,8,9 Illyrian foot Short Spear Shoot & Charge Tribal Flexible Javelin 9 0 6,8 Thureophoroi Long Spear Shove Orb/Square Drilled Close 8 Numidian cavalry (from 202 Skilled 0 4,6 Combat Shy BCE) Javelin 6 Experienced Cantabrian, 0 4,6 Illyrian or Spanish cavalry Javelin Combat Shy 6 Experienced 6 Leves Combat Shy Javelin See note Upgrade leves to velites Experienced 6 Short Spear Shoot & Charge (from 209 BCE) Javelin All or none Skilled 0 6,9 Cretan archers Combat Shy Bow 9 Slingers Combat Shy Sling 9 Allies Celtiberian, Iberian or Lusitanian allies (in Spain from 212 BCE) Numidian allies Numidian or Moorish (in Africa from 204 to 202 BCE) Aitolian allies Hellenistic Greek (in Greece from 198 to 189 BCE) Attalid Pergamene allies (in Asia from 190 to 189 BCE) Notes The number of triarii cannot exceed 1/4 of the number of hastati and principes. The army cannot have more leves or velites than hastati and principes. Triarii may be deployed separately or combined with the hastati and principes. If combined, the hastati, principes and triarii form a TuG of 5. Hastati, principes and triarii may be downgraded to represent unenthusiastic allied, raw, slave or penal legions. Armies must be chosen as Italy, Gaul, Spain, Africa, Greece (from 200BC) or Asia (from 190BC), reflecting their campaign history. Spanish and Gauls can only be used in Italy, Gaul, Spain or Africa. Elephants can be used Greece or Asia at any date, but only from 153BCE in Spain, Gaul, Italy or Africa. Cretans, Thureophoroi and Illyrians can only be used in Greece or Asia.
26 Changes from last version Mid Republican Roman Historical Notes This list reflects the Roman army described by Polybius. The reforms that led to the Polybian system appear to have started after the First Samnite War. During this period Rome conquered all of Italy. In the three Punic wars Rome destroyed Carthage and created a Roman province in Africa. It also created provinces in Spain and later in southern Gaul. At the end of the Punic war Rome became engaged in a war with Philip V of Macedon who they defeated at the battle of Cynoscephalae in 197 BCE. Thereafter Rome was constantly invited to interfere in Greek affairs leading to wars with the Seleucid kingdom (defeated at Magnesia in 189 BCE), Macedon and Greece. In 146 BCE Greece and Macedon were incoporated as Roman provinces. The Attalid Kingdom of Pergamene was bequeathed to Rome and incorporated in 129 BCE. The Roman system of government and large manpower led to a continual series of aggressive wars. Troop Notes Elephants: The Romans captured Elephants from the Carthaginians at Zama and then used them regularly in the east and occasionally in the west. Cavalry: Roman cavalry improved compared to earlier times, possibly due to contact with Greek cavalry in the army of Pyrrhus. Numidian cavalry: Numidian cavalry were available to the Romans after Masinissa joined the Romans before Zama. Numidian cavalry were used regularly throughout the 2nd century BCE. Hastati, principes and triarii: The principes changed from using a thrusting spear to the pilum. Only the triarii, retained the long spear. Pedites Extraordinarii: Italian picked troops who were used to lead the army on the march, or if threatened from the rear might form the rearguard. Italian infantry: Troops were obtained from Rome's Italian allies who hadn't converted to the manipular system. Spanish scutarii: Troops obtained from Spanish tribes friendly to Rome. Gallic foot: Rome was allied with various Gallic tribes from the middle of the 3rd century BCE although most Gallic tribes were hostile to Rome and fought a series of wars against Rome through this period. Illyrian foot: Rome was allied to various Illyrian tribes from the first expedition to Greece in 200 BCE. As with the Gauls, Rome also fought a series of wars against Illyrian tribes during this period. Thureophoroi: In the east Rome would use Thureophoroi supplied by allied Greek states. Light horse: Roman armies would obtain light horse from local allied states. Velites: After 210 BCE the existing leves were replaced by velites. These were protected by larger shields and were much more prepared to fight and chase off other skirmishers. Cretan archers: Cretan archers were available to armies in the east. Slingers: Slingers were recruited in both east and west. The Balearic islands and Rhodes were particularly known for their slingers. Slingers also came from Tralles (in Asia Minor) and Syracuse. Clarified notes. Added optional Shoot & Charge. Triarii and Leves no longer mandatory. Combat Shy option for light horse.
27 Army Commander 1 Any Professional Dates 105 BCE to 20 BCE SubGenerals 03 Any Professional Terrain Standard, Coastal Internal Allied Generals 01 Any Professional Camp Fortified; Poor, or Superior Name Heavy cavalry Legionaries Upgrade legionaries to veteran Caesar's Xth Legion (from 59 to 45 BCE) Downgrade raw legions Spanish scutarii (only western armies) Thracian foot (only eastern armies) Gallic foot (only Italy or western armies) Archers (only eastern armies) Bolt shooters Light cavalry Numidian cavalry (only Italy or western armies) Type Training and Formed Flexible Tribal Loose ARTILLERY Later Republican Roman Quality Protection Shooting Skill Melee Characteristics Min Mandatory Optional Max UG Size Superior Exceptional Poor Unskilled Melee Expert, 0 4,6 Short Spear Javelin Shoot & Charge 8 Melee Expert, 18 4,6,8 Impact Weapon Shield Cover Orb/Square 40 Melee Expert, 0 4,6,8 Impact Weapon Shield Cover Orb/Square 24 Melee Expert, 0 4,6,8 Impact Weapon Shield Cover Orb/Square 8 Melee Expert, 0 4,6,8 Impact Weapon Shield Cover Orb/Square ,8,9 Impact Weapon 9 Devastating 0 6,8,9 Melee Expert Chargers 9 Devastating 0 6,8,9 Chargers 18 Experienced 0 6,8 Combat Shy Bow 8 Experienced 0 2,3,4 Barricades Light Art 4 Experienced Cantabrian, 0 4,6 Javelin Combat Shy 8 Skilled 0 4,6 Combat Shy Javelin 8
28 Later Republican Roman Syrian horse archers (only Experienced 0 4,6 Combat Shy eastern armies from 42 BCE) Bow 18 Experienced 4,6 Upgrade horse archers Cantabrian Combat Shy Bow All or none Velites (before 80 BCE) Short Spear Shoot & Charge Javelin 9 Javelinmen Combat Shy Javelin 9 Archers Combat Shy Bow 9 Slingers Combat Shy Sling 9 Cretan archers (only Italy or Skilled 0 6,9 Combat Shy eastern armies) Bow 9 Allies Numidian allies Numidian or Moorish (in Italy in 90 BCE or Africa from 49 to 46 BCE or in Africa or Spain from 45 to 33 BCE) Bithynian allies (in Asia from 88 to 75 BCE) Galatian allies (in Asia from 74 to 31 BCE) Nomadic Arab allies PreIslamic Arab (in Syria from 64 to 53 BCE) Jewish allies (in Syria and Egypt from 63 to 38 BCE) Aeduan allies Lowland Gallic (Caesar in Gaul in 52 BCE) Armenian allies (in Asia from 53 to 36 BCE) Notes Western armies campaigned in Gaul, Italy, Spain and Africa. Eastern armies campaigned in Greece, Asia or Syria. Marius, Sulla and Caesar must be either Talented or Legendary generals. Numidian allies outside Africa cannot include elephants. At this date, bolt shooters must be deployed separately and may not be attached to legions.
29 Historical Notes Changes from last version Later Republican Roman This list reflects the Roman army after the reforms of Marius. The Social War from 91 to 88 BCE was fought between Rome and a number of Italian regions who allied together. The result led to the unification of Italy under Roman leadership. The wars of conquest from the previous century continued with Rome coming into contact with Parthia, creating the Roman province of Syria and Caesar's conquest of Gaul. The closer ties between armies and their commanders starting with Sulla led to the civil wars which eventually led to Octavian becoming the first Roman emperor. Troop Notes Cavalry: The Romans relied increasingly on their allies for cavalry during this period. This included Spanish and Gallic cavalry in the west. Caesar also used German cavalry. Legionaries: The manipular system was abandoned and replaced by cohorts. All legionaries were equipped with two pilum, a lighter pilum which could be thrown and a heavier pilum that could be thrown or used as a thrusting spear. The main weapon was the Gladius. Caesar's veterans: The loyalty of legionaries was now to their general rather than the state. Caesar's veterans, recruited for the Gallic wars, were by the time of the war with Pompey probably amongst the most experienced soldiers in the ancient world. Spanish scutarii: Rome continued to obtain troops from friendly tribes in Spain. Thracian foot: In the east Rome obtained troops from Thrace. Archers: Archers were obtained from allied states in Syria. Velites: Velites are last mentioned in 80 BCE. After this date, skirmishers were supplied by allied states or mercenaries. Bolt Shooters: Caesar appears to have been one of the earlier Roman generals to adopt artillery in field situations. Restricted number of Cantabrian. Added Shoot & Charge option. Combat Shy option for light horse.
30 Army Commander 1 Crixus = Instinctive Talented; Spartacus = Instinctive Legendary Dates 73 BCE to 71 BCE SubGenerals 13 Any Instictive Terrain Coastal, Mountains Internal Allied Generals Camp Unfortified; Poor Name Characteristics Min Mandatory Optional Max Only if CinC is Spartacus 0 4 Cavalry Short Spear Melee Expert 4 Exgladiator slaves Slaves equipped with Roman arms Only if CinC is Crixus Upgrade slaves equipped with Roman arms as Gauls or Germans Poorly equipped slaves Women, children and old men Slingers Javelinmen Notes Type Training and Tribal Loose Tribal Loose Tribal Flexible Tribal Loose Tribal Loose Spartacus Slave Revolt Quality Protection Shooting Skill Melee Superior Fanatic, Melee 0 4 Expert 8 Devastating 16 6,8 Chargers 64 Devastating 16 6,8 Chargers 24 Poor Poor Poor Poor Devastating 27 8,9,10 Chargers ,12 Combat Shy 24 Combat Shy Sling 18 Combat Shy Javelin 27 SPECIAL RULE: Any unit that Spartacus joins, fights in the front rank and remains with becomes fanatic which must be proactively pointed out to opponents at the beginning of setting up. UG Size
31 Historical Notes Spartacus Slave Revolt In 73 BCE Spartacus was amongst a group of 70 gladiators who broke out of a gladiatorial school. They defeated a series of Roman forces gathering more support and equipment each time. By the end of 73 BCE the force had collected up to 70,000 escaped slaves including woman and children. In 72 BCE they moved north, and although a smaller slave force under Crixus was defeated, the threat to Rome was such that several legions were hastily raised. Spartacus outmanouvred the Roman forces and defeated them in turn. At this point the slaves turned south. The Romans raised eight legions under M. Licinius Crassus.. Two legions under Mummius were defeated but Crassus attached the main slave force and inflicted several thousand casualties. Unable to escape to Sicily, the slaves were penned into the toe of Italy. Short of supplies they made a desparate break out but were defeated in detail by Crassus in two further battles. Pompey returning from fighting in Spain with his forces captured and killed 5,000 slaves. Troop Notes Cavalry: The slave revolt army had a small amount of cavalry. Infantry: The slaves started with gladiatorial equipment but captured Roman equipment from the early victories they inflicted on the hastily raised Roman forces that were initially sent against them. The rapid increase in numbers meant there was a shortage of arms. Many of the slaves were Gauls and Germans and a proportion would have been familiar with handling weapons. They are recorded as forming their own units. It is also possible that the slaves were joined by a few disaffected Samnites who had been defeated by Sulla in the Social War some 15 years earlier. Changes from last version Ally generals replaced as subgenerals. Updated territory types.
32 Army Commander 1 Any Professional Dates 20 BCE to 268 CE SubGenerals 03 Any Professional Terrain Standard, Coastal Internal Allied Generals Camp Fortified; Poor, or Superior Name Cavalry Upgrade cavalry Equites catafractarii (from 100 CE) Legionaries Upgrade legionaries to veteran Upgrade legionaries to Praetorian Guard Auxilia Auxilary archers Bolt shooters (see note) Light horse Type Training and Drilled Loose Drilled Loose Drilled Loose Drilled Loose ARTILLERY Early Imperial Roman Quality Protection Shooting Skill Melee Characteristics Min Mandatory Optional Max UG Size Unskilled Melee Expert, 0 4,6 Short Spear Shoot & Charge, Javelin Dismountable 18 Unskilled Melee Expert, 0 4,6 Superior Short Spear Shoot & Charge, Javelin Dismountable 8 Charging 0 4,6 Melee Expert Lancer 6 Melee Expert, 16 4,6,8 Impact Weapon Shield Cover Orb/Square, Integral Shooters 48 Melee Expert, 0 4,6,8 Superior Impact Weapon Shield Cover Orb/Square, Integral Shooters 24 Melee Expert, 0 4,6,8 Exceptional Impact Weapon Shield Cover Orb/Square, Integral Shooters 8 Unskilled Melee Expert, 12 4,6,8 Short Spear Shoot & Charge, Javelin Orb/Square 32 Experienced 0 6,8 Combat Shy Bow 8 Experienced 0 2,3,4 Barricades Light Art 4 Experienced Cantabrian, 0 4,6 Javelin Combat Shy 12
33 Early Imperial Roman Experienced Cantabrian, 0 4,6 Equites sagittarii Bow Combat Shy 12 Experienced 0 6,8,9 Archers Combat Shy Bow 18 Experienced 0 6,8,9 Slingers Combat Shy Sling 9 Experienced 0 6,8,9 Javelinmen Combat Shy Javelin 9 Allies Jewish client allies Jewish (in Syria to 6 CE) Nabatean allies (in Syria to 106 CE) Edessan or Emessan allies Parthian Vassal States (in Syria) Commagene allies (in Syria) Armenian allies (in Syria) Batavian or other German allies Early German (in Germany from 16 BCE to 16 CE) Notes Cavalry dismount as, Drilled Loose, Unskilled Javelin, Short Spear (and Melee Expert if this characteristic has been chosen). SPECIAL RULE. Instead of being deployed separately, bolt shooters may be attached to a unit of legionaries. Add "ExperiencedLight Artillery shooting to the normal characteristics of one base of a legionary TuG, and use a ballistae base for this (e.g. 5 legionaries and 1 ballistae as a TuG of 6). Note that this base is still a legionary: an infantry base not an artillery base. The TuG moves at BWg speeds (but may double move) and with any move the TuG may abandon the bolt shooters, in which case replace the artillery base with a normal legionary base and revert to infantry speeds for movement thereafter. This special rule should be explained to opponents as soon as the first TuG of this type is deployed. Any legionary or auxilia units may be equipped with Caltrops. Integral shooters may only be chosen after 138 CE.
34 Historical Notes Early Imperial Roman At some point after 30 BCE the emperor Augustus started to reform the Roman army. The core of the army remained the legions who were recruited from Roman citizens. The Auxilia were established to complement the legions. They were recruited from the peregrini or noncitizens of the empire. By the end of Augustus's reign the imperial army consisted of about 250,000 men in 25 legions and approximately 250 units of auxilia. With the exception of the Praetorian Guard all legions were stationed on the frontiers of the empire. Apart from the conquests of Britain and Dacia the frontier remained largely unchanged. The main threats were the Germans and Sarmatians to the north and east of the Rhine and Danube and the Parthians to the east of Syria. A period of increasing trouble and decline began with the reign of Commodus. Commodus' assassination in 192 triggered the Year of the Five Emperors, of which Septimius Severus emerged victorious. The assassination of Alexander Severus in 235 CE led to the Crisis of the Third Century in which 26 men were declared emperor by the Roman Senate over a fiftyyear period. Troop Notes Cavalry: Cavalry were supplied by the Auxilia. In the east, units of horse archers were raised. Cataphracts were apparently first adopted around 100 CE. Infantry: The core of the army were the legions. All legionaries used pilum and sword as in late republican times, but lorica segmentata replaced the chain mail as body armour. Auxilary equipment was standardised using lighter spears or javelins instead of the pilum Units of auxilary archers were raised, particularly in the east. Changes from last version Reclassified cavalry. Reduced minimum number of auxilia. Added Shoot & Charge option. Combat Shy option for light horse. Adjusted list end date.
35 Army Commander 1 Any Professional Dates 269 CE to 407 CE SubGenerals 03 Any Professional Terrain Standard, Coastal, Mountains Internal Allied Generals Camp Fortified; Poor, or Superior Name Equites Upgrade equites Equites Illyricani, Dalmatae or similar Equites catafractarii or clibinarii (western armies) Equites catafractarii or clibinarii (eastern armies) Hun mercenaries (from 388 CE) Legionaries or auxilia Upgrade legionaries to veteran Guard legionaries Regrade legionaries or auxilia Type Training and Drilled Loose Drilled Loose Drilled Close Drilled Close Formed Flexible Quality Imperial Roman Protection Shooting Skill Melee Characteristics Min Mandatory Optional Max UG Size Unskilled Melee Expert, 4 4,6 Short Spear Shoot & Charge, Javelin Dismountable 16 Unskilled Melee Expert, 0 4,6 Superior Short Spear Shoot & Charge, Javelin Dismountable 8 Experienced 0 4,6 Short Spear Shoot & Charge Javelin 6 ArmHrs/Fully Devastating 0 4,6 Long Spear Armoured Chargers, Shove 6 ArmHrs/Fully Devastating 0 4,6 Long Spear Armoured Chargers, Shove 8 Experienced 0 4,6 Melee Expert Shoot & Charge Bow 6 Melee Expert, 24 4,6,8 Impact Weapon Shield Cover Orb/Square, Integral Shooters 64 Melee Expert, 0 4,6,8 Superior Impact Weapon Shield Cover Orb/Square, Integral Shooters 16 Melee Expert, 0 4,6,8 Exceptional Impact Weapon Shield Cover Orb/Square, Integral Shooters 8 Unskilled Melee Expert, 6,8 Short Spear Shoot & Charge, Javelin Orb/Square Any
36 From 298 CE in western armies, 324 CE in eastern armies Upgrade auxilia to auxilia palatina Reequip legionaries or auxilia Reequip guard legionaries or auxilia palatina Armoured auxilia sagittarii (eastern armies) Auxilia sagittarii Gothic foot (eastern armies from 360 CE) Bolt shooters (see note) Equites mauri or similar Equites sagittarii (western armies) Equites sagittarii (eastern armies) Archers s with javelins Drilled Loose Drilled Loose Tribal Close ARTILLERY Imperial Roman Unskilled Melee Expert, 0 6,8 Superior Short Spear Shoot & Charge, Javelin Orb/Square 24 Superior Experienced 6,8 Short Spear Shield Cover Orb/Square Darts See note Experienced 6,8 Short Spear Shield Cover Orb/Square Darts See note Experienced 0 6,8 Combat Shy Bow 8 Experienced 0 6,8 Combat Shy Bow 8 Devastating 0 6,8,9 Chargers 12 Experienced 0 2,3,4 Barricades Light Art 4 Experienced Cantabrian, 0 4,6 Javelin Combat Shy 8 Experienced Cantabrian, 0 4,6 Bow Combat Shy 6 Experienced Cantabrian, 0 4,6 Bow Combat Shy 12 Combat Shy Bow 18 Combat Shy Javelin 9
37 Allies Armenian allies (in Syria or Asia from 296 to 298 CE) Nomadic Arab allies PreIslamic Arab (in Syria or Asia from 305 CE) Tervingi allies (Western army in Illyricum in 324 CE) Armenian allies (in Syria from 325 to 363 CE) Notes Imperial Roman Western armies were based in Britain, Gaul, Spain, Africa, Italy and Illyricum. The army of Licinius in 324 CE is treated as a Western army in Illyricum although it was defeated at Adrianople. Eastern armies were based in Thrace, Macedonia/Greece, Pontus, Asia, Syria or Egypt. No more than half the TuGs may be Superior or Exceptional. Cavalry dismount as, Drilled Loose, Unskilled Javelin, Short Spear (and Melee Expert if this characteristic has been chosen). The introduction of darts was gradual and started with guard or palatina units. As a result from 307 to 350 CE only two TuGs of guard legionaries or palatina may be regraded. From 351 to 380 CE up to half TuGs may be regraded. From 381 CE any TuGs may be regraded. SPECIAL RULE BOLT SHOOTERS. Instead of being deployed separately, bolt shooters may be attached to a unit of legionaries. Add "ExperiencedLight Artillery shooting to the normal characteristics of one base of a legionary TuG, and use a ballistae base for this (e.g. 5 legionaries and 1 ballistae as a TuG of 6). Note that this base is still a legionary: an infantry base not an artillery base. The TuG moves at BWg speeds (but may double move) and with any move the TuG may abandon the bolt shooters, in which case replace the artillery base with a normal legionary base and revert to infantry speeds for movement thereafter. This special rule should be explained to opponents as soon as the first TuG of this type is deployed. Any legionary or auxilia units may be equipped with Caltrops. SPECIAL RULE CLUBMEN (from 269 to 350 CE): If the enemy army could have any cavalry with ArmHrs/Fully Armoured; one Impact Weapon, Melee Expert legionary base per TuG can be converted to 2Handed Cut & Crush at no additional cost. The base must be clearly distinguished from other legionaries. Historical Notes The assassination of Alexander Severus in 235 CE led to the Crisis of the Third Century in which 26 men were declared emperor by the Roman Senate over a fiftyyear period. It was not until the reign of Diocletian (from 284) that the empire was fully stabilized with the introduction of the Tetrarchy, which saw four emperors rule the empire at once. This arrangement was ultimately unsuccessful, leading to a civil war that was finally ended by Constantine I, who defeated his rivals and became the sole ruler of the empire. Constantine subsequently shifted the capital to Byzantium, which was renamed "Constantinople" in his honour. It remained the capital of the east until its demise. In 357 CE the Emperor Julian defeated 30,000 Alamanni. In 378 CE Gothic rebels defeated and killed the Emperor Valens. The Empire fell under increasing pressure from Goths, Huns and Alans. Troop Notes Alterations to the Roman army continued throughout the Empire. In the 260s the cavalry arm of the army may have been expanded. The Roman army was reformed by Constantine I. The main innovation was the creation of field armies in rear of the frontier defences. The field armies originally contained "palatina" units but they were later joined by "comitatensis" units. Lighter throwing spears were introduced to supplement the pilum. The shorter gladius was replaced by the longer spatha.
Army Lists ITALY. Contents
 Army Lists ITALY Contents Creating an army with the Mortem et Gloriam Army Lists Historical Introduction Army Commander 1 Any Instinctive Dates 500 BC to 330 BC SubGenerals 03 Any Instinctive Terrain
Army Lists ITALY Contents Creating an army with the Mortem et Gloriam Army Lists Historical Introduction Army Commander 1 Any Instinctive Dates 500 BC to 330 BC SubGenerals 03 Any Instinctive Terrain
Western Mediterranean Sea BC
 Western Mediterranean Sea 231 218 BC By the terms of the peace treaty that ended the First Punic War in 241, Carthage was forced to cede Sicily, which became Rome s first province. Three years later, Rome
Western Mediterranean Sea 231 218 BC By the terms of the peace treaty that ended the First Punic War in 241, Carthage was forced to cede Sicily, which became Rome s first province. Three years later, Rome
Spain, Sicily and Africa. Contents. Army Lists
 Spain, Sicily and Africa Contents Army Lists Creating an army with the Mortem et Gloriam Army Lists Historical Introduction Army Commander 1 Any Instinctive Dates 650 BC to 202 AD SubGenerals 13 Any
Spain, Sicily and Africa Contents Army Lists Creating an army with the Mortem et Gloriam Army Lists Historical Introduction Army Commander 1 Any Instinctive Dates 650 BC to 202 AD SubGenerals 13 Any
SunTzuGames presents
 SunTzuGames presents Ancient battles a game by Emil Larsen (4) -0 min 4+ version - Omega.4 Ancient Battles Introduction In ancient battles you get to play out some of ancient history s most iconic battles.
SunTzuGames presents Ancient battles a game by Emil Larsen (4) -0 min 4+ version - Omega.4 Ancient Battles Introduction In ancient battles you get to play out some of ancient history s most iconic battles.
Spain, Sicily and Africa. Contents. Army Lists
 Spain, Sicily and Africa Contents Army Lists Creating an army with the Mortem et Gloriam Army Lists Historical Introduction Army Commander 1 Any Instinctive Dates 550 B.C. to 380 B.C. SubGenerals 13
Spain, Sicily and Africa Contents Army Lists Creating an army with the Mortem et Gloriam Army Lists Historical Introduction Army Commander 1 Any Instinctive Dates 550 B.C. to 380 B.C. SubGenerals 13
CHARIOT MINIATURES. PRICING 15mm Historical packs $6.60 All have 8 foot, 4 mounted, single elephant or chariot or 2 artillery pieces.
 CHARIOT MINIATURES PRICING 15mm Historical packs $6.60 All have 8 foot, 4 mounted, single elephant or chariot or 2 artillery pieces. ASS22, ABR1 $6.60 ASS21 $8.25 Chariots 2 Horse 2 Crew $5.50 2 Horse
CHARIOT MINIATURES PRICING 15mm Historical packs $6.60 All have 8 foot, 4 mounted, single elephant or chariot or 2 artillery pieces. ASS22, ABR1 $6.60 ASS21 $8.25 Chariots 2 Horse 2 Crew $5.50 2 Horse
Army Lists. Persia. Contents
 Army Lists Contents Early Achaemenid n Later Achaemenid n Parthian Parthian Vassal States Early Sassanid n Middle Sassanid n Version: 1.01 Published: 16 th July 2016 Creating an army with the Mortem et
Army Lists Contents Early Achaemenid n Later Achaemenid n Parthian Parthian Vassal States Early Sassanid n Middle Sassanid n Version: 1.01 Published: 16 th July 2016 Creating an army with the Mortem et
Rise of Rome through the Punic Wars. Based on the map above, who do you think would be Rome s main opponent?
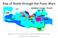 Rise of Rome through the Punic Wars Based on the map above, who do you think would be Rome s main opponent? 753 BC: Rome begins as one of many city states on the Italian Peninsula. 509 BC: Roman Republic
Rise of Rome through the Punic Wars Based on the map above, who do you think would be Rome s main opponent? 753 BC: Rome begins as one of many city states on the Italian Peninsula. 509 BC: Roman Republic
2 nd and 3 rd Punic War
 nd and rd Punic War These are the armies of the second and third Punic war. The armies are based upon those found in DBA. and Might of s. They have been modified based on research and gut instinct. Tables
nd and rd Punic War These are the armies of the second and third Punic war. The armies are based upon those found in DBA. and Might of s. They have been modified based on research and gut instinct. Tables
BATTLE OF IBERA Part of the Second Punic War Spring 215 BC
 BATTLE OF IBERA Part of the Second Punic War Spring 215 BC This is a small scenario for Hail Caesar based on the Battle of Ibera. The Troops are not according to any historical account but the unit we
BATTLE OF IBERA Part of the Second Punic War Spring 215 BC This is a small scenario for Hail Caesar based on the Battle of Ibera. The Troops are not according to any historical account but the unit we
Creating a campaign game of the Teutoburg Forest Disaster in 9AD,
 Creating a campaign game of the Teutoburg Forest Disaster in 9AD, The Ancient Warfare series launched its latest game Roman Civil Wars in December 2011 but did not include a scenario for this famous event.
Creating a campaign game of the Teutoburg Forest Disaster in 9AD, The Ancient Warfare series launched its latest game Roman Civil Wars in December 2011 but did not include a scenario for this famous event.
Army Lists. North America and Oceania. Contents
 Army Lists North America and Oceania Contents Eastern Woodland Culture 900 to 1500 CE Mound-Builder Culture 900 to 1500 CE Plains Culture 900 to 1500 CE Pueblo Culture 900 to 1500 CE Tu i Empire 950 to
Army Lists North America and Oceania Contents Eastern Woodland Culture 900 to 1500 CE Mound-Builder Culture 900 to 1500 CE Plains Culture 900 to 1500 CE Pueblo Culture 900 to 1500 CE Tu i Empire 950 to
Army Lists. Gaul, Germany and Britain. Contents
 Army Lists Gaul, Germany and Britain Contents Creating an army with the Mortem et Gloriam Army Lists Historical Introduction Army Commander 1 Any Instinctive Dates 350 BC to 50 BC SubGenerals 03 Any Instinctive
Army Lists Gaul, Germany and Britain Contents Creating an army with the Mortem et Gloriam Army Lists Historical Introduction Army Commander 1 Any Instinctive Dates 350 BC to 50 BC SubGenerals 03 Any Instinctive
Syria and Asia Minor. Contents. Army Lists
 Syria and Asia Minor Contents Army Lists Creating an army with the Mortem et Gloriam Army Lists Historical Introduction Army Commander 1 Any Instinctive Dates 525 BC to 300 BC SubGenerals 13 Any Instinctive
Syria and Asia Minor Contents Army Lists Creating an army with the Mortem et Gloriam Army Lists Historical Introduction Army Commander 1 Any Instinctive Dates 525 BC to 300 BC SubGenerals 13 Any Instinctive
Hambone Barca vs. Miles Gloriousus GAME RULES By George Sivess
 Hambone Barca vs. Miles Gloriousus GAME RULES By George Sivess Two of my favorite Ancient Generals, Hambone Barca (the illegitimate and slightly less capable son of Hamilcar), and Miles, the star of A
Hambone Barca vs. Miles Gloriousus GAME RULES By George Sivess Two of my favorite Ancient Generals, Hambone Barca (the illegitimate and slightly less capable son of Hamilcar), and Miles, the star of A
Kings of War Historical Ancient Combat Rome s Rise and Fall!
 Kings of War Historical Ancient Combat Rome s Rise and Fall! This supplement is designed for use with Mantic Games Kings of War rules, but it is not an official Mantic Games publication. Kings of War and
Kings of War Historical Ancient Combat Rome s Rise and Fall! This supplement is designed for use with Mantic Games Kings of War rules, but it is not an official Mantic Games publication. Kings of War and
Army Lists. Gaul, Germany and Britain. Contents
 Army Lists Gaul, Germany and Britain Contents Creating an army with the Mortem et Gloriam Army Lists Historical Introduction Army Commander 1 Any Instinctive Dates 350 B.C. to 50 B.C. SubGenerals 13
Army Lists Gaul, Germany and Britain Contents Creating an army with the Mortem et Gloriam Army Lists Historical Introduction Army Commander 1 Any Instinctive Dates 350 B.C. to 50 B.C. SubGenerals 13
Army Lists. Syria and Asia Minor. Contents
 Syria and Asia Minor Contents Army Lists Asiatic Greek 670 to 129 BCE Lycian 525 to 300 BCE Bithynian 434 to 74 BCE Armenian 330 BCE to 252 CE Asiatic Successor 323 to 280 BCE Cappadocian 300 BCE to 17
Syria and Asia Minor Contents Army Lists Asiatic Greek 670 to 129 BCE Lycian 525 to 300 BCE Bithynian 434 to 74 BCE Armenian 330 BCE to 252 CE Asiatic Successor 323 to 280 BCE Cappadocian 300 BCE to 17
Which Fun facts do you find out in Roman soldiers life?
 Group 1 What was a legion? What other soldiers did the Romans have? What armour and weapons did the Romans have? How well-trained were Roman soldiers? Which Fun facts do you find out in Roman soldiers
Group 1 What was a legion? What other soldiers did the Romans have? What armour and weapons did the Romans have? How well-trained were Roman soldiers? Which Fun facts do you find out in Roman soldiers
Army Lists. Spain, Sicily and Africa. Contents
 Spain, Sicily and Africa Contents Army Lists Libyan 650 BCE to 202 CE Sicel 550 to 380 BCE Early Carthaginian (02) 550 to 275 BCE Sardinian 550 to 215 BCE Siciliot Greek 550 to 241 BCE Syracusan 411 to
Spain, Sicily and Africa Contents Army Lists Libyan 650 BCE to 202 CE Sicel 550 to 380 BCE Early Carthaginian (02) 550 to 275 BCE Sardinian 550 to 215 BCE Siciliot Greek 550 to 241 BCE Syracusan 411 to
PROCONSUL RULES FOR ANCIENT BATTLES
 Index Section Subject Page 1.0 Basic Concepts 2 1.1 Command Groups 2 1.2 Stands and Basing 2 1.3 Strength Points [SP] 2 1.4 Game Play 2 2.0 Command and Control 3 2.1 Moving Commanders 3 2.2 Losing a Commander
Index Section Subject Page 1.0 Basic Concepts 2 1.1 Command Groups 2 1.2 Stands and Basing 2 1.3 Strength Points [SP] 2 1.4 Game Play 2 2.0 Command and Control 3 2.1 Moving Commanders 3 2.2 Losing a Commander
1. MELEE EXPERT Melee Expert covers troops who were especially good at hand-to-hand combat for their quality grade. So an AVERAGE Melee Expert is
 1. MELEE EXPERT Melee Expert covers troops who were especially good at hand-to-hand combat for their quality grade. So an AVERAGE Melee Expert is good at melee for average troops; a SUPERIOR non-melee
1. MELEE EXPERT Melee Expert covers troops who were especially good at hand-to-hand combat for their quality grade. So an AVERAGE Melee Expert is good at melee for average troops; a SUPERIOR non-melee
Army Lists. Egypt and Judaea. Contents
 Army Lists Egypt and Judaea Contents Cyrenean Greek 630 to 74 BCE Meroitic Kushite 592 BCE to 350 CE Late Period Egyptian 405 to 343 BCE Nabatean 312 BCE to 106 CE PreIslamic Arab 300 BCE to 400 CE Ptolemaic
Army Lists Egypt and Judaea Contents Cyrenean Greek 630 to 74 BCE Meroitic Kushite 592 BCE to 350 CE Late Period Egyptian 405 to 343 BCE Nabatean 312 BCE to 106 CE PreIslamic Arab 300 BCE to 400 CE Ptolemaic
This is directly commanded by Leonidas, the Army General, and consists of 5 Divisions.
 Spartan Army The Spartans are perhaps the most well-known of all the Greek armies. Hopefully my version of their army is more historically accurate than some of the portrayals in films and books. The Spartans
Spartan Army The Spartans are perhaps the most well-known of all the Greek armies. Hopefully my version of their army is more historically accurate than some of the portrayals in films and books. The Spartans
IMPERIAL WARRIOR ARMY LIST ERRATA To November 2011
 IMPERIAL WARRIOR ARMY LIST ERRATA To November 2011 Any updates or corrections are shown under the specific list. Lines refer to the line starting underneath the list or from the top of the page if the
IMPERIAL WARRIOR ARMY LIST ERRATA To November 2011 Any updates or corrections are shown under the specific list. Lines refer to the line starting underneath the list or from the top of the page if the
Army Lists. House of Valois. Contents
 Army Lists House of Valois Contents Creating an army with the Mortem et Gloriam Army Lists Historical Introduction Army Commander 1 Any Professional except Legendary Dates 1291 AD to 1405 AD SubGenerals
Army Lists House of Valois Contents Creating an army with the Mortem et Gloriam Army Lists Historical Introduction Army Commander 1 Any Professional except Legendary Dates 1291 AD to 1405 AD SubGenerals
Mortem et Gloriam Magna
 16/10/2018 Mortem et Gloriam Magna Small Table Variant for.. 28mm figures on a 6'x4' or 15mm figures on a 4' x 3' table Introduction Mortem et Gloriam Magna is a simple adaptation of the main MeG game
16/10/2018 Mortem et Gloriam Magna Small Table Variant for.. 28mm figures on a 6'x4' or 15mm figures on a 4' x 3' table Introduction Mortem et Gloriam Magna is a simple adaptation of the main MeG game
Army Lists. France. Contents
 Army Lists France Contents Creating an army with the Mortem et Gloriam Army Lists Historical Introduction Army Commander 1 Any Professional except Legendary Dates 1291 A.D. to 1405 A.D. SubGenerals
Army Lists France Contents Creating an army with the Mortem et Gloriam Army Lists Historical Introduction Army Commander 1 Any Professional except Legendary Dates 1291 A.D. to 1405 A.D. SubGenerals
Army Lists. France. Contents
 Army Lists France Contents Creating an army with the Mortem et Gloriam Army Lists Historical Introduction Army Commander 1 Any Professional except Legendary Dates 1291 A.D. to 1405 A.D. SubGenerals
Army Lists France Contents Creating an army with the Mortem et Gloriam Army Lists Historical Introduction Army Commander 1 Any Professional except Legendary Dates 1291 A.D. to 1405 A.D. SubGenerals
Official amendements for L Art de la Guerre Rules
 Official amendements for L Art de la Guerre Rules This document regroups and assembles the official amendments and corrections to L Art de la Guerre V3. They are presented in the chronological order of
Official amendements for L Art de la Guerre Rules This document regroups and assembles the official amendments and corrections to L Art de la Guerre V3. They are presented in the chronological order of
Army Lists. Germany, Gaul and Britain. Contents
 Army Lists Germany, Gaul and Britain Contents Highland Gallic 350 to 50 BCE Lowland Gallic 350 to 40 BCE Early German 180 BCE to 219 CE Ancient British 60 BCE to 90 CE Scots Irish 50 BCE to 450 CE Batavian
Army Lists Germany, Gaul and Britain Contents Highland Gallic 350 to 50 BCE Lowland Gallic 350 to 40 BCE Early German 180 BCE to 219 CE Ancient British 60 BCE to 90 CE Scots Irish 50 BCE to 450 CE Batavian
Appendix A: Army Lists
 Appendix A: Army Lists BAR includes a set of 6 Army List as part of the core rules which allow you to play with 6 common armies. They will also be revised in future army list supplements. By looking at
Appendix A: Army Lists BAR includes a set of 6 Army List as part of the core rules which allow you to play with 6 common armies. They will also be revised in future army list supplements. By looking at
PROCONSUL SCENARIO Dacia 87CE
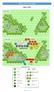 Dacia 87CE Page 1 of 5 Dacia 87CE The Kingdom of Dacia [present day Romania] frequently launched raids across the Danube into Roman territory. On several occasions the Romans tried to bring them to heel.
Dacia 87CE Page 1 of 5 Dacia 87CE The Kingdom of Dacia [present day Romania] frequently launched raids across the Danube into Roman territory. On several occasions the Romans tried to bring them to heel.
IMPETVS ANCIENTS BETA LISTS
 IMPETVS ANCIENTS BETA LISTS Version 2.2 December2017 Since last version: Early Franks list added. Dadi&Piombo PAGE ARMY 2 Early Sumerians 2 Nubians 2 Akkadian Empire 3 Minoans and Early Mycaeneans 3 Achaians
IMPETVS ANCIENTS BETA LISTS Version 2.2 December2017 Since last version: Early Franks list added. Dadi&Piombo PAGE ARMY 2 Early Sumerians 2 Nubians 2 Akkadian Empire 3 Minoans and Early Mycaeneans 3 Achaians
Army Lists. Sumer and Akkad. Contents
 Army Lists Sumer and Akkad Contents Creating an army with the Mortem et Gloriam Army Lists Historical Introduction A note on chronology Early Sumerian Army Commander 1 Any Instinctive Dates 3000 BC to
Army Lists Sumer and Akkad Contents Creating an army with the Mortem et Gloriam Army Lists Historical Introduction A note on chronology Early Sumerian Army Commander 1 Any Instinctive Dates 3000 BC to
The Gladiator s Present:
 The Gladiator s Present: Here are the Troop Types in the Roman legion The Roman Legionnaire Only Roman citizens could sign up for the army. They had to be fit and able to fight. These lower soldiers were
The Gladiator s Present: Here are the Troop Types in the Roman legion The Roman Legionnaire Only Roman citizens could sign up for the army. They had to be fit and able to fight. These lower soldiers were
Army Lists. India. Contents
 Army Lists India Contents Creating an army with the Mortem et Gloriam Army Lists Historical Introduction Army Commander SubGenerals Internal Allied Generals Name Type Training and Anuradhapura Kingdom
Army Lists India Contents Creating an army with the Mortem et Gloriam Army Lists Historical Introduction Army Commander SubGenerals Internal Allied Generals Name Type Training and Anuradhapura Kingdom
Kings in the North. Contents. Army Lists
 Kings in the North Contents Army Lists Creating an army with the Mortem et Gloriam Army Lists Historical Introduction ŵ Wales ŵ Scotland Ireland Jarls of Orkney Kingdom of the Isles and the Isle of Man
Kings in the North Contents Army Lists Creating an army with the Mortem et Gloriam Army Lists Historical Introduction ŵ Wales ŵ Scotland Ireland Jarls of Orkney Kingdom of the Isles and the Isle of Man
LAKE TRASIMENUS 217 BC
 KE TRSIMENUS 217 BC Command & Colors: ncients 1 CRTGININ C annibal M M C W W W C C S S Flaminius Steep ills Impassable M M M M ake Trasimenus ake Trasimenus ROMN istorical Background Much of annibal s
KE TRSIMENUS 217 BC Command & Colors: ncients 1 CRTGININ C annibal M M C W W W C C S S Flaminius Steep ills Impassable M M M M ake Trasimenus ake Trasimenus ROMN istorical Background Much of annibal s
CIVITATES BELLANTES. Rules for Ancient Wargames with Miniatures 500 BC to AD 200 by Simon MacDowall & Caoimhín Boru
 CIVITATES BELLANTES Rules for Ancient Wargames with Miniatures 500 BC to AD 200 by Simon MacDowall & Caoimhín Boru O n the fourth day both generals lead out their forces and drew them up for battle. Scipio
CIVITATES BELLANTES Rules for Ancient Wargames with Miniatures 500 BC to AD 200 by Simon MacDowall & Caoimhín Boru O n the fourth day both generals lead out their forces and drew them up for battle. Scipio
Land of the Samurai. Contents. Army Lists
 Land of the Samurai Contents Army Lists Creating an army with the Mortem et Gloriam Army Lists Historical Introduction ō ō ō ō ō ō ō ō ō ū ō Ō ō Army Commander 1 Any Instinctive Dates 500 BCE. to 250
Land of the Samurai Contents Army Lists Creating an army with the Mortem et Gloriam Army Lists Historical Introduction ō ō ō ō ō ō ō ō ō ū ō Ō ō Army Commander 1 Any Instinctive Dates 500 BCE. to 250
Kings of War Historical Ancient Combat Hoplon, Pike & Arrow!
 Kings of War Historical Ancient Combat Hoplon, Pike & Arrow! This Supplement is not published by Mantic Games. Kings of War and all associated logos are property of Mantic Games and are used without permission.
Kings of War Historical Ancient Combat Hoplon, Pike & Arrow! This Supplement is not published by Mantic Games. Kings of War and all associated logos are property of Mantic Games and are used without permission.
Mandate of Heaven. Contents. Army Lists
 Mandate of Heaven Contents Army Lists Creating an army with the Mortem et Gloriam Army Lists Historical Introduction ō Chinese names and terms Erlitou Chinese Army Commander 1 Any Instinctive Dates 1700
Mandate of Heaven Contents Army Lists Creating an army with the Mortem et Gloriam Army Lists Historical Introduction ō Chinese names and terms Erlitou Chinese Army Commander 1 Any Instinctive Dates 1700
The Roman Army. Some soldiers had special skills. They shot bows and arrows, flung stones from slingshots, or could swim rivers to surprise an enemy.
 The Roman Army The Roman army was the largest and meanest fighting force in the ancient world and is one of the main reasons Rome became so powerful. It conquered a vast empire across the world and was
The Roman Army The Roman army was the largest and meanest fighting force in the ancient world and is one of the main reasons Rome became so powerful. It conquered a vast empire across the world and was
Basic Impetus Chinese Army Lists
 Basic Impetus Chinese Army Lists Chinese history can be seen as a succession of barbarian peoples held at bay by a powerful Chinese dynasty which would eventually fail. The resulting invading barbarians
Basic Impetus Chinese Army Lists Chinese history can be seen as a succession of barbarian peoples held at bay by a powerful Chinese dynasty which would eventually fail. The resulting invading barbarians
Kings of War Historical Ancient Combat Hoplon, Pike & Arrow!
 Kings of War Historical Ancient Combat Hoplon, Pike & Arrow! This Supplement is not published by Mantic Games. Kings of War and all associated logos are property of Mantic Games and are used without permission.
Kings of War Historical Ancient Combat Hoplon, Pike & Arrow! This Supplement is not published by Mantic Games. Kings of War and all associated logos are property of Mantic Games and are used without permission.
Stephan Hess Compiled by Ken Demyen
 By Stephan Hess Compiled by Ken Demyen CONTENTS Introduction... Rules... Characters & Mounts... s... s... Shamans... Mount... Elephant Mount... Unit s... Skirmishers... Warband... Phalanx... Testudo...
By Stephan Hess Compiled by Ken Demyen CONTENTS Introduction... Rules... Characters & Mounts... s... s... Shamans... Mount... Elephant Mount... Unit s... Skirmishers... Warband... Phalanx... Testudo...
Rome at War Hannibal at Bay Errata and FAQ
 First Edition Rules Rome at War Hannibal at Bay Errata and FAQ Pg 3: Light Cavalry description has a depiction of Light Infantry. 2.21: Change "enemy units" to "any non-leader units". 6.1: After Example,
First Edition Rules Rome at War Hannibal at Bay Errata and FAQ Pg 3: Light Cavalry description has a depiction of Light Infantry. 2.21: Change "enemy units" to "any non-leader units". 6.1: After Example,
Great Battles of History Forum: Macedonians vs. Romans
 C3i Magazine, Nr.1 (1992) Great Battles of History Forum: Macedonians vs. Romans by Richard H. Berg The design and development of SPQR was a task highlighted by the need to recreate the remarkable military
C3i Magazine, Nr.1 (1992) Great Battles of History Forum: Macedonians vs. Romans by Richard H. Berg The design and development of SPQR was a task highlighted by the need to recreate the remarkable military
Athenian Army. The Army is commanded by the Athenian Polemarch, Perikles, who is an Elected, Reliable and Strong commander.
 Athenian Army My Athenian Army was one of the first I completed and as such has had to suffer fighting through considerable rule changes. It has also undergone several expansion and configuration changes.
Athenian Army My Athenian Army was one of the first I completed and as such has had to suffer fighting through considerable rule changes. It has also undergone several expansion and configuration changes.
Time of Day Display. DBA 3.0 doesn t have any kind of time limit, and this can seriously distort the re-creation of many historical battles.
 Time of Day Display...by Super Stevie, Jan 10th 2017 DBA 3.0 doesn t have any kind of time limit, and this can seriously distort the re-creation of many historical battles. Take Hastings for example. Why
Time of Day Display...by Super Stevie, Jan 10th 2017 DBA 3.0 doesn t have any kind of time limit, and this can seriously distort the re-creation of many historical battles. Take Hastings for example. Why
The Battle of Chalons 20 th June 451 AD
 Introduction The Battle of Chalons This project has been designed as a Kings of War battle supplement for use with Rome's Rise and Fall from www.hourofwolves.org This battle, fought from mid-afternoon
Introduction The Battle of Chalons This project has been designed as a Kings of War battle supplement for use with Rome's Rise and Fall from www.hourofwolves.org This battle, fought from mid-afternoon
IDEAS AND RESOURCES FOR USING
 IDEAS AND RESOURCES FOR USING THE FIRST IN A NEW SERIES SET IN ANCIENT ROME BY WITH PUPILS IN YEARS 7/P7 9/S1 C o n t e n t s I Synopsis About the author II Behind the story 1: The real Capua school; The
IDEAS AND RESOURCES FOR USING THE FIRST IN A NEW SERIES SET IN ANCIENT ROME BY WITH PUPILS IN YEARS 7/P7 9/S1 C o n t e n t s I Synopsis About the author II Behind the story 1: The real Capua school; The
Army Lists BYZANTIUM. Contents
 Army Lists BYZANTIUM Contents Creating an army with the Mortem et Gloriam Army Lists Historical Introduction Later PreIslamic Bedouin Army Commander 1 Any Instinctive Dates 400 A.D. to 636 A.D. SubGenerals
Army Lists BYZANTIUM Contents Creating an army with the Mortem et Gloriam Army Lists Historical Introduction Later PreIslamic Bedouin Army Commander 1 Any Instinctive Dates 400 A.D. to 636 A.D. SubGenerals
COMITATUS Warfare in the Dark Ages AD
 COMITATUS Warfare in the Dark Ages AD 250-1100 Scenario 1 The Battle of Daras AD 50 Historical Background The young East Roman General Belisarius, in his first major command, was sent to defend the city
COMITATUS Warfare in the Dark Ages AD 250-1100 Scenario 1 The Battle of Daras AD 50 Historical Background The young East Roman General Belisarius, in his first major command, was sent to defend the city
Rules Update for Warmaster Ancients
 Rules Update for Warmaster Ancients P25 Skirmishers Evading a Charge delete all four paragraphs and replace as follows. Note that this new rule replaces the rules addition Evades from close range become
Rules Update for Warmaster Ancients P25 Skirmishers Evading a Charge delete all four paragraphs and replace as follows. Note that this new rule replaces the rules addition Evades from close range become
Alexander the Great. Tables Explained Each list has an outline of a number of units. The following is an example unit:
 Alexander the Great These are the armies of Alexander the Great and his Enemies. The armies are based upon those found in DBA. and Might of s. They have been modified based on research and gut instinct.
Alexander the Great These are the armies of Alexander the Great and his Enemies. The armies are based upon those found in DBA. and Might of s. They have been modified based on research and gut instinct.
The Persian, Macedonian and Punic Wars.
 The Persian, Macedonian and Punic Wars. 600BC to 200BC For use with Historicon 1.2 Introduction The Persian, Macedonian and Punic Wars. 600BC to 200BC Welcome to our first edition of army lists for Historicon,
The Persian, Macedonian and Punic Wars. 600BC to 200BC For use with Historicon 1.2 Introduction The Persian, Macedonian and Punic Wars. 600BC to 200BC Welcome to our first edition of army lists for Historicon,
Dark Age Britain. Tables Explained Each list has an outline of a number of units. The following is an example unit:
 Dark Age Britain These are the armies of Post Roman Britain and the Age of Arthur. The armies are based upon those found in DBA. and Might of s. They have been modified based on research and gut instinct.
Dark Age Britain These are the armies of Post Roman Britain and the Age of Arthur. The armies are based upon those found in DBA. and Might of s. They have been modified based on research and gut instinct.
Army Lists. Britain after the Romans to the Norman conquest. Contents
 Army Lists Britain after the Romans to the Norman conquest Contents Creating an army with the Mortem et Gloriam Army Lists Historical Introduction Army Commander 1 Any Instinctive Dates 407 AD to 468
Army Lists Britain after the Romans to the Norman conquest Contents Creating an army with the Mortem et Gloriam Army Lists Historical Introduction Army Commander 1 Any Instinctive Dates 407 AD to 468
Military History Review
 Military History Review How is chess different from the game of go? A. Chess is attrition based while Go is resource efficient. B. Chess forces the opponent to defend territory and high ranking pieces.
Military History Review How is chess different from the game of go? A. Chess is attrition based while Go is resource efficient. B. Chess forces the opponent to defend territory and high ranking pieces.
Army Lists. Arabia. Contents
 Army Lists Arabia Contents Creating an army with the Mortem et Gloriam Army Lists Historical Introduction Early Arab Conquest Army Commander 1 Any Instinctive Dates 629 AD to 637 AD SubGenerals 13 Any
Army Lists Arabia Contents Creating an army with the Mortem et Gloriam Army Lists Historical Introduction Early Arab Conquest Army Commander 1 Any Instinctive Dates 629 AD to 637 AD SubGenerals 13 Any
Kings of War Historical Ancient Combat Hoplon, Pike & Arrow!
 Kings of War Historical Ancient Combat Hoplon, Pike & Arrow! This Supplement is not published by Mantic Games. Kings of War and all associated logos are property of Mantic Games and are used without permission.
Kings of War Historical Ancient Combat Hoplon, Pike & Arrow! This Supplement is not published by Mantic Games. Kings of War and all associated logos are property of Mantic Games and are used without permission.
Introduction:... 4 Character Classes;... 4 Weapons:... 4 Organisation:... 4 Actions:... 5 Movement:... 5 Shooting:... 5 To Hit:...
 State of war A.C.W. Skirmish Wargame Rules Tyneside Wargames club Version 1a 1 2 Table of contents Introduction:... 4 Character Classes;... 4 Weapons:... 4 Organisation:... 4 Actions:... 5 Movement:...
State of war A.C.W. Skirmish Wargame Rules Tyneside Wargames club Version 1a 1 2 Table of contents Introduction:... 4 Character Classes;... 4 Weapons:... 4 Organisation:... 4 Actions:... 5 Movement:...
COMMON CORE Lessons & Activities SAMPLE
 COMMON CORE Lessons & Activities TEACH IT TODAY! About this Book This Common Core Lessons and Activities Book allows you to immediately meet new Common Core State Standards for English Language Arts, as
COMMON CORE Lessons & Activities TEACH IT TODAY! About this Book This Common Core Lessons and Activities Book allows you to immediately meet new Common Core State Standards for English Language Arts, as
Page. Blades (Bd) classed as foot troop description figures per base recoil interpenetration combat factors flank support
 Aggression defender selection in the army lists Allies can t garrison can t guard a camp moving in groups in tournaments BBDBA allies BBDBA allied camps BBDBA allied PIPs allied contingents Arable Homeland
Aggression defender selection in the army lists Allies can t garrison can t guard a camp moving in groups in tournaments BBDBA allies BBDBA allied camps BBDBA allied PIPs allied contingents Arable Homeland
Army Lists. Mandate of Heaven. Contents
 Mandate of Heaven Contents Army Lists Erlitoi Chinese 1700 to 1301 BCE Chinese Northern Barbarians 1700 to 500 BCE Later Shang Chinese 1300 to 1017 BCE Chinese Nomadic Barbarians 1300 to 314 BCE Early
Mandate of Heaven Contents Army Lists Erlitoi Chinese 1700 to 1301 BCE Chinese Northern Barbarians 1700 to 500 BCE Later Shang Chinese 1300 to 1017 BCE Chinese Nomadic Barbarians 1300 to 314 BCE Early
Rise and Fall of the Roman Empire: Strategic Decision Series Copyright (c) 2016, Two Generals Games LLC Version: 4.9.
 Rise and Fall of the Roman Empire: Strategic Decision Series Copyright (c) 2016, Two Generals Games LLC Version: 4.9 "Dulce et decorum est pro patria mori." -Horace Table of Contents Turns...2 Units and
Rise and Fall of the Roman Empire: Strategic Decision Series Copyright (c) 2016, Two Generals Games LLC Version: 4.9 "Dulce et decorum est pro patria mori." -Horace Table of Contents Turns...2 Units and
The Battle Of Cannae: The History And Legacy Of Ancient Rome's Most Decisive Military Defeat By Charles River Editors READ ONLINE
 The Battle Of Cannae: The History And Legacy Of Ancient Rome's Most Decisive Military Defeat By Charles River Editors READ ONLINE If you are searching for a book by Charles River Editors The Battle of
The Battle Of Cannae: The History And Legacy Of Ancient Rome's Most Decisive Military Defeat By Charles River Editors READ ONLINE If you are searching for a book by Charles River Editors The Battle of
Year 7 History Key Terms Homework. How England Began
 Year 7 History Key Terms Homework How England Began New Words: How England Began #1 New Words: How England Began #2 Migration Invasion Chronology Huguenots The movement of people from one place, usually
Year 7 History Key Terms Homework How England Began New Words: How England Began #1 New Words: How England Began #2 Migration Invasion Chronology Huguenots The movement of people from one place, usually
Why are the Roman Army successful?
 Why are the Roman Army successful? Discipline Centurions were in charge of discipline. They carried a stick of very hard wood and they used it to beat their soldiers. They used to punish even small things
Why are the Roman Army successful? Discipline Centurions were in charge of discipline. They carried a stick of very hard wood and they used it to beat their soldiers. They used to punish even small things
Part1 Setting up the Game. Sample file
 Part1 Setting up the Game Setting up the game Necessary equipment All you need to play Polemos American Civil War is: A number of ordinary six-sided dice, numbered 1-6, known hereafter as D6. A ten-sided
Part1 Setting up the Game Setting up the game Necessary equipment All you need to play Polemos American Civil War is: A number of ordinary six-sided dice, numbered 1-6, known hereafter as D6. A ten-sided
PERSIA, IRAN AND INDIA. Contents. Army Lists
 PERSIA, IRAN AND INDIA Contents Army Lists Creating an army with the Mortem et Gloriam Army Lists Historical Introduction ā Army Commander 1 Any Instinctive Dates 550 BC to 424 BC SubGenerals 03 Any Instinctive
PERSIA, IRAN AND INDIA Contents Army Lists Creating an army with the Mortem et Gloriam Army Lists Historical Introduction ā Army Commander 1 Any Instinctive Dates 550 BC to 424 BC SubGenerals 03 Any Instinctive
"Chopping Wood " Battle on the Raate Road, Dec39-Jan40. by Steve Keyer of Two Tin Soldiers
 "Chopping Wood " Battle on the Raate Road, Dec39-Jan40 by Steve Keyer of Two Tin Soldiers Historical perspective This scenario represents the reduction of a small Russian "motti". In old Finnish, the term
"Chopping Wood " Battle on the Raate Road, Dec39-Jan40 by Steve Keyer of Two Tin Soldiers Historical perspective This scenario represents the reduction of a small Russian "motti". In old Finnish, the term
Tournament Report ITC This one needs to be in English to be used also for the DBMM group please ignore any wrong spelling and expressions...
 This one needs to be in English to be used also for the DBMM group please ignore any wrong spelling and expressions... Thanks to Lorenzo and all his helpers for the organization of the ITC since 2012!
This one needs to be in English to be used also for the DBMM group please ignore any wrong spelling and expressions... Thanks to Lorenzo and all his helpers for the organization of the ITC since 2012!
Mercenary: Land Warfare in the First Punic War, BC
 SPQR Scenario Battles Agrigentum and Adys Mercenary: Land Warfare in the First Punic War, 262-256 BC BY DAN FOURNIE Background The First Punic War was decided at sea. After four years of war, Rome found
SPQR Scenario Battles Agrigentum and Adys Mercenary: Land Warfare in the First Punic War, 262-256 BC BY DAN FOURNIE Background The First Punic War was decided at sea. After four years of war, Rome found
ONE IF BY LAND" - AMERICAN 1:10 SCALE WAR OF INDEPENDENCE RULES by Bob Bergman. Infantry/Cavalry figure 10 men Artillery crew figure 5 men
 ONE IF BY LAND" - AMERICAN 1:10 SCALE WAR OF INDEPENDENCE RULES by Bob Bergman Ground Scale 1 inch = 15 yards One Turn About five minutes Infantry/Cavalry figure 10 men Artillery crew figure 5 men Artillery
ONE IF BY LAND" - AMERICAN 1:10 SCALE WAR OF INDEPENDENCE RULES by Bob Bergman Ground Scale 1 inch = 15 yards One Turn About five minutes Infantry/Cavalry figure 10 men Artillery crew figure 5 men Artillery
Order Code. Test reaction if:
 Move Sequence in each period 1. Dice for arrivals and returns 2. Test reaction for first time in charge reach or shot at 3. Declare and Test for charges. Test Reaction for all other causes 5. Charge Response,
Move Sequence in each period 1. Dice for arrivals and returns 2. Test reaction for first time in charge reach or shot at 3. Declare and Test for charges. Test Reaction for all other causes 5. Charge Response,
Kings of War Historical Ancient Combat Viking Age!
 Kings of War Historical Ancient Combat Viking Age! This Supplement is not published by Mantic Games. Kings of War and all associated logos are property of Mantic Games and are used without permission.
Kings of War Historical Ancient Combat Viking Age! This Supplement is not published by Mantic Games. Kings of War and all associated logos are property of Mantic Games and are used without permission.
The Maximilian Adventure
 The Maximilian Adventure FRENCH FORCES The French forces sent to Mexico by the Emperor Napoleon III were tasked with defeating what was seen as the ineffective government of Mexico and establishing a client
The Maximilian Adventure FRENCH FORCES The French forces sent to Mexico by the Emperor Napoleon III were tasked with defeating what was seen as the ineffective government of Mexico and establishing a client
Introduction. The conqueror takes over the possessions of the conquered
 Introduction The careers of these men embrace such a multitude of events that my preamble shall consist of nothing more than one plea: if I do not record all of their most celebrated achievements or describe
Introduction The careers of these men embrace such a multitude of events that my preamble shall consist of nothing more than one plea: if I do not record all of their most celebrated achievements or describe
ARE YE FOR KING OR PARLIAMENT?
 ARE YE FOR KING OR PARLIAMENT? A Warmaster Ancients Variant For The Period 1641-52 Written by Jimi Tubman Assisted by the members of the Washington Wargames Club ( http://www.washingtonwargames.co.uk ).
ARE YE FOR KING OR PARLIAMENT? A Warmaster Ancients Variant For The Period 1641-52 Written by Jimi Tubman Assisted by the members of the Washington Wargames Club ( http://www.washingtonwargames.co.uk ).
Army Lists. The Franks. Contents
 Army Lists The Franks Contents Creating an army with the Mortem et Gloriam Army Lists Historical Introduction Army Commander 1 Any Instinctive Dates 419 AD to 621 AD Sub-Generals 0-3 Any Instinctive
Army Lists The Franks Contents Creating an army with the Mortem et Gloriam Army Lists Historical Introduction Army Commander 1 Any Instinctive Dates 419 AD to 621 AD Sub-Generals 0-3 Any Instinctive
Army Lists. Mandate of Heaven. Contents
 Mandate of Heaven Contents Army Lists Erlitoi Chinese 1700 to 1301 BCE Chinese Northern Barbarians 1700 to 500 BCE Later Shang Chinese 1300 to 1017 BCE Chinese Nomadic Barbarians 1300 to 314 BCE Early
Mandate of Heaven Contents Army Lists Erlitoi Chinese 1700 to 1301 BCE Chinese Northern Barbarians 1700 to 500 BCE Later Shang Chinese 1300 to 1017 BCE Chinese Nomadic Barbarians 1300 to 314 BCE Early
COMMON TRAINING PROFICIENCY LEVEL FOUR INSTRUCTIONAL GUIDE SECTION 5 EO C DISCUSS THE HISTORY OF DRILL PREPARATION
 COMMON TRAINING PROFICIENCY LEVEL FOUR INSTRUCTIONAL GUIDE SECTION 5 EO C408.01 DISCUSS THE HISTORY OF DRILL Total Time: 30 min PREPARATION PRE-LESSON INSTRUCTIONS Resources needed for the delivery of
COMMON TRAINING PROFICIENCY LEVEL FOUR INSTRUCTIONAL GUIDE SECTION 5 EO C408.01 DISCUSS THE HISTORY OF DRILL Total Time: 30 min PREPARATION PRE-LESSON INSTRUCTIONS Resources needed for the delivery of
Cannae The Experience Of Battle In The Second Punic War
 We have made it easy for you to find a PDF Ebooks without any digging. And by having access to our ebooks online or by storing it on your computer, you have convenient answers with cannae the experience
We have made it easy for you to find a PDF Ebooks without any digging. And by having access to our ebooks online or by storing it on your computer, you have convenient answers with cannae the experience
King George Commands and We Obey
 King George Commands and We Obey Basing Army Commanders 80mm dia base with a vignette on it, min 3 figures. Divisional Commanders 80mm dia base with a vignette on it, max 2 figures. Brigade Commanders
King George Commands and We Obey Basing Army Commanders 80mm dia base with a vignette on it, min 3 figures. Divisional Commanders 80mm dia base with a vignette on it, max 2 figures. Brigade Commanders
TOURNAMENTS AT COLD WARS 2014
 TOURNAMENTS AT COLD WARS 2014 NASAMW Ancient and Medieval Events Below is a short description of tournaments being put on by the North American Society of Ancient and Medieval Wargamers, the Renaissance
TOURNAMENTS AT COLD WARS 2014 NASAMW Ancient and Medieval Events Below is a short description of tournaments being put on by the North American Society of Ancient and Medieval Wargamers, the Renaissance
2/10/2016. In the ancient world, massed infantry phalanxes constituted the core of many armies. 1. Swiss pikemen (the return of the phalanx)
 Decline of Roman Empire in Europe Mounted warriors from the east Feudal order replaces Imperial order Protection in exchange for military service Land tenure based on this obligation Feudal levee = temporary
Decline of Roman Empire in Europe Mounted warriors from the east Feudal order replaces Imperial order Protection in exchange for military service Land tenure based on this obligation Feudal levee = temporary
No charges, but Ar0llery shoot.
 No charges, but Ar0llery shoot. Heavy Ar7llery are in range of anything 12 BW range. Can shoot overhead at any enemy 2BW from friends, but cannot shoot over one target to shoot another à has to shoot the
No charges, but Ar0llery shoot. Heavy Ar7llery are in range of anything 12 BW range. Can shoot overhead at any enemy 2BW from friends, but cannot shoot over one target to shoot another à has to shoot the
Weapons and Tactics of Alexander the Great. James Cunningham, Sam O'Connell and Marshall Pease
 Weapons and Tactics of Alexander the Great James Cunningham, Sam O'Connell and Marshall Pease Alexander s Army How was the Macedonian Army able to become so powerful? -The discovery of gold in Amphipolis
Weapons and Tactics of Alexander the Great James Cunningham, Sam O'Connell and Marshall Pease Alexander s Army How was the Macedonian Army able to become so powerful? -The discovery of gold in Amphipolis
The Scottish Wars against England
 The Scottish Wars against England Male lust and a mole can be blamed for the opening of the Scottish Wars of Independence. The male lust was in the breast of Alexander the Third, The King of Scots. (Note
The Scottish Wars against England Male lust and a mole can be blamed for the opening of the Scottish Wars of Independence. The male lust was in the breast of Alexander the Third, The King of Scots. (Note
DBA-RRR. Renaissance, Reformation and Restoration Extension Rules v By Tony Aguilar
 DBA-RRR Renaissance, Reformation and Restoration 1500-1700 Extension Rules v. 1.21 By Tony Aguilar DBA-RRR Renaissance, Reformation and Restoration Rules v. 1.21 (January 2012) Page 1 DESIGNER NOTES This
DBA-RRR Renaissance, Reformation and Restoration 1500-1700 Extension Rules v. 1.21 By Tony Aguilar DBA-RRR Renaissance, Reformation and Restoration Rules v. 1.21 (January 2012) Page 1 DESIGNER NOTES This
Pavia: Climax of the Italian Wars
 Pavia: Climax of the Italian Wars by E.R. Bickford Production: Lise Patterson & Chris Dickson 2013 Decision Games Bakersfield, CA. AAR of Pavia: Climax of the Italian Wars Pavia is a little village in
Pavia: Climax of the Italian Wars by E.R. Bickford Production: Lise Patterson & Chris Dickson 2013 Decision Games Bakersfield, CA. AAR of Pavia: Climax of the Italian Wars Pavia is a little village in
Chapter 12 Section 2 The Spanish-American War. Click on a hyperlink to view the corresponding slides.
 Chapter 12 Section 2 The Spanish-American War Click on a hyperlink to view the corresponding slides. Guide to Reading Main Idea The United States defeated Spain in a war, acquired new overseas territories,
Chapter 12 Section 2 The Spanish-American War Click on a hyperlink to view the corresponding slides. Guide to Reading Main Idea The United States defeated Spain in a war, acquired new overseas territories,
SNAPHANCE SCENARIO Franco-Dutch War - Battle of Seneffe 11 August 1674
 Franco-Dutch War - Battle of Seneffe 11 August 1674 Note: the woods on the hilltop are orchards. Page 1 of 5 Franco-Dutch War - Battle of Seneffe 11 August 1674 William of Orange invaded Northern France
Franco-Dutch War - Battle of Seneffe 11 August 1674 Note: the woods on the hilltop are orchards. Page 1 of 5 Franco-Dutch War - Battle of Seneffe 11 August 1674 William of Orange invaded Northern France
Army Lists. Britain after the Romans to the Norman conquest. Contents
 Army Lists Britain after the Romans to the Norman conquest Contents Creating an army with the Mortem et Gloriam Army Lists Historical Introduction Early Post-Roman British Army Commander 1 Any Instinctive
Army Lists Britain after the Romans to the Norman conquest Contents Creating an army with the Mortem et Gloriam Army Lists Historical Introduction Early Post-Roman British Army Commander 1 Any Instinctive
Army Lists. Land of the Samurai. Contents
 Land of the Samurai Contents Army Lists Yayoi Japanese 500 BCE to 250 CE Yamoto Era Japanese 251 to 790 CE Emishi 400 to 802 CE Heian Japanese 794 to 1179 CE Sohei Monks (02) 980 to 1550 CE Kamakura Samurai
Land of the Samurai Contents Army Lists Yayoi Japanese 500 BCE to 250 CE Yamoto Era Japanese 251 to 790 CE Emishi 400 to 802 CE Heian Japanese 794 to 1179 CE Sohei Monks (02) 980 to 1550 CE Kamakura Samurai
Conquest of the Palatinate A Thirty Years War Campaign
 Conquest of the Palatinate A Thirty Years War Campaign Frederick V of the Palatinate By GAJO Games 10-May-13 TYW Palatinate / GAJO Games 1 Historical Background: The Thirty Years' War began in 1618 with
Conquest of the Palatinate A Thirty Years War Campaign Frederick V of the Palatinate By GAJO Games 10-May-13 TYW Palatinate / GAJO Games 1 Historical Background: The Thirty Years' War began in 1618 with
PART 2 TEACHERS NOTES GO ROMAN THEME 1: THE LEGIONARY SOLDIER LET S INVESTIGATE NOTES AND OBJECT CHECKLIST
 PART 2 TEACHERS NOTES GO ROMAN THEME 1: THE LEGIONARY SOLDIER LET S INVESTIGATE NOTES AND OBJECT CHECKLIST GO ROMAN THEME 1: THE LEGIONARY SOLDIER Men from three legions of Roman soldiers were stationed
PART 2 TEACHERS NOTES GO ROMAN THEME 1: THE LEGIONARY SOLDIER LET S INVESTIGATE NOTES AND OBJECT CHECKLIST GO ROMAN THEME 1: THE LEGIONARY SOLDIER Men from three legions of Roman soldiers were stationed
