Research Paper: The Effect of Five-Toed Shoes on Electromyographic Activity of Leg Muscles During Stance Phase of Running
|
|
|
- Irene Neal
- 5 years ago
- Views:
Transcription
1 January Volume 6. Number 4 Research Paper: The Effect of Five-Toed Shoes on Electromyographic Activity of Leg Muscles During Stance Phase of Running CrossMark Maryam Razaghzadeh 1, Mehrdad Anbarian 2, Hamideh Khodaveisi 3* 1. Department of Physical Education, Borujerd Branch, Islamic Azad University, Borujerd, Iran. 2. Department of Sport Biomechanics, Faculty of Sport Sciences, Bu-Ali Sina University, Hamedan, Iran. 3. Department of Physical Education, Faculty of Human Sciences, Hamedan Branch, Islamic Azad University, Hamedan, Iran. Use your device to scan and read the article online Citation: Khodaveisi H, Razaghzadeh M, Anbarian M. The Effect of Five-Toed Shoes on Electromyographic Activity of Leg Muscles During Stance Phase of Running. Physical Treatments. 2017; 6(4): :: Article info: Received: 12 Jun Accepted: 08 Oct A B S T R A C T Purpose: The current study aimed at evaluating the effect of 5-toed shoes on electromyographic activity of leg muscles during the stance phase of running. Methods: The current semi-experimental study recorded the electromyographic activity of tibialis anterior, soleus, gastrocnemius lateralis, and medialis muscles of 15 healthy male students (mean age: 24.5±3.4 years, mean height: 177.6±5.8 cm, and mean weight: 75.7±8.9 kg) during the stance phase of running in barefoot and shod (5-toed shoes) conditions. Paired sample t test was used for statistical analysis with SPSS19. Keywords: Five-toed shoe, Electromyography, Running, Leg muscles Results: In shod running, electromyographic activity of tibialis anterior during loading response phase (P=0.001) and electromyographic activity of soleus (P=0.002) and medial gastrocnemius (P=0.004) during propulsion phase were significantly higher, compared with the barefoot running; there was no significant difference in gastrocnemius lateralis muscle between both conditions (P 0.05). Conclusion: According to the current study findings, using 5-toed shoes could increase electromyographic activity of leg muscles during the stance phase of running. 1. Introduction R unning is a basic skill of displacing and executing sports activities [1]. Leisure runners are the vulnerable groups and it is shown that 19.4% to 79.3% of individuals participating in activities including running experience chronic injuries every year [2]. Recently barefoot running is of great interest in sports clinics [3]. Some researchers reported that barefoot running results in reduction of chronic injuries in runners [4]. This can be due to the fact that in barefoot running, heel-toe pattern is used, which leads to reduction of contact forces on organs from ground or land surface [5]. Since foot is the most important tool of interaction between the ground and body, the performance structure of * Corresponding Author: Hamideh Khodaveisi, PhD Address: Department of Physical Education, Faculty of Human Sciences, Hamedan Branch, Islamic Azad University, Hamedan, Iran. Phone: +98 (918) khodaveisi_hamideh@yahoo.com 227
2 January Volume 6. Number 4 foot influences the pattern of transitional movements [6, 7]. Any deviation in feet can transfer its effect on joints and upper extremities in a chain format. Modification of forces applied to foot is one of the roles of these shoes [1]. Recently, in biomechanics studies, focus on barefoot running and the number of runners who tend to run on barefoot and 5-toed shoes were increasing, which shows that barefoot running reduces the possible damages on joints and muscles followed by the reduction of velocity and intensity of foot contact with ground by the musculoskeletal system. The study showed that running on barefoot and 5-toed shoes imposes less pressure on the body; in addition, eccentric activity of quadriceps femoris muscle in barefoot is reduced, compared with the normal shoes. There are different shoes in the market such as instable shoes; 5-toed shoes and the shoes designed for different sports such as running [8-10]. The purpose of using instable shoes is involving the muscles more, and as a result, strengthening the muscles and preventing their weaknesses in long-term that play an important role in kinematic and kinetic changes [11, 12]. Five-toed shoes are already available in the market. There are few researches to determine the merits and demerits of 5-toed shoes [3, 13]. For example, it is reported that there is no difference in the sense of joints after running between barefoot and 5-toed shoes [13]. Also, the force applied to Achilles tendon in barefoot running is greater than that of 5-toed shoes running, while the knee extension moment in running in 5-toed shoes is greater than that of barefoot running [3]. Because of the important role of the shoes in comfort and level of pressures applied to joints, it is necessary to study the role of such shoes. The current study aimed at investigating the electromyographic activity of leg muscles in loading response sub-phase and running progress in barefoot and 5-toed shoes. can record the activity of 16 muscles simultaneously. The electrodes are adhesive and disposable, and can be attached to the positive and negative electrodes of each channel in a electromyography (EMG) device. It also contains specific gel to reduce the skin resistance and receive the muscle electrical activity and transfer to EMG device. The shoes used in the current study were the 5-toed shoes (Figure 1). The procedures were followed when the subjects referred to the lab. First, the redundant hair on front foot was removed and the skin was cleaned with cotton and alcohol. Then, the adhesive AG-Agcl electrodes containing conduction gel were installed on the selected muscles based on SENIAM recommendations to reduce the skin electrical resistance and transfer the electrical impulses [14]. The earth electrode was placed on the tibia bone. Surface EMG signals were collected with sampling frequency of 1000 HZ and passed through a bypass filter 8 to 450 HZ. After installing the electrodes, the subjects were asked to move in a direct path of 15 m at the determined speed (Figure 2) to have a natural running (3 to 5 meters) and prepare themselves for the main test. Three trials were recorded for each situation (barefoot and shed). The muscles were soleus, medial, lateralis gastrocnemius, and tibialis anterior, and the moving speed (3 m/s) was controlled by a chronometer. In the current study, the stance phase of running was divided into loading and propulsion sub-phases. The values of RMS were normalized in each sub-phase by the Maximal Voluntary Isometric Contraction (MVIC) method. Statistical analysis was performed with SPSS version 19. The Shapiro-Wilk test was applied to assess the normal distribution of the data. The paired t test was used to compare the variables between different positions. P<0.05 was considered as the level of significance. 2. Materials and Methods The current quasi-experimental study was conducted in The sample constituted 15 healthy male students with the mean age of 24.5 years, mean height cm, and mean weight 75.7 kg. The inclusion criteria of the study were no history of surgery, fracture, burning, damage, or severe trauma in lower extremities, as well as no artificial organs in thigh, knee, and ankle, in addition to no medical shoes, diabetes, and specific diseases. Biomonitor ME6000 (Finland) was used to record the electromyographic activity of muscles. The device Figure 1. The shoes used in the study 228
3 January Volume 6. Number 4 4. Discussion Figure 2. Running path and EMG recording 3. Results The results of comparing tibialis anterior muscle activity between 5-toed shoes and barefoot in the sub-phase of loading response showed a significant difference in the mean activity of tibialis anterior muscle between the cases (P=0.001). The muscle activity of tibialis anterior was higher in the 5-toed shoes than barefoot (Table 1). The means of electromyographic activity of soleus muscle, medial, and lateralis gastrocnemius in barefoot and 5-toed shoes in the sub-phase of loading response of running stance showed no significant difference (Table 1). Findings showed no significant difference between muscle activity of tibialis anterior and lateralis gastrocnemius in both cases; while the activity of medial gastrocnemius and soleus muscles when using 5-toed shoes was significantly greater than that of the barefoot in the propulsion sub-phase (Table 2). The current study aimed at investigating the electromyographic activity of leg muscles in loading response and running propulsion sub-phases in barefoot and 5-toed shoes runners. The activity of tibialis anterior muscle in 5-toed shoes in loading response sub-phase was higher than that of the barefoot case. Tibialis anterior muscles are contracted extroversive in loading response in toe-heel pattern to prevent quick contact of foot with the ground [15]. Therefore, the greater activity of this muscle in this sub-phase for 5-toed shoes may cause more absorption of energy in ankle joint and reduction of contact forces in foot striking the ground. The toe-heel running pattern in shoe and barefoot runners can be the reason of greater activity of tibialis anterior muscle [16-18]. There was no significant difference in the mean electromyographic activity of soleus, medial, and lateralis gastrocnemius muscles between both cases in the loading sub-phase of running stance. The current study findings showed that in the propulsion sub-phase there was no significant difference in the mean activity of tibialis anterior and lateralis gastrocnemius muscles for the 5-toed shoes and barefoot, while the activity of medial gastrocnemius and soleus muscles in 5-toed shoes was significantly greater than that of the barefoot in the propulsion sub-phase. These results were not consistent with those of Sinclair`s research, which stated that the force applied on Achilles tendon in running with barefoot is less than that of the 5-toed shoes [3]. Table 1. Modified RMS comparison of leg muscles in the running loading response sub-phase in barefoot and five-toed shoes Muscle Barefoot Five-Toed Shoes t P Tibialis anterior 67.7± ± * Soleus 47.5± ± Medial gastrocnemius 44.5± ± Lateralis gastrocnemius 47.3± ± *:P<0.05 Table 2. Comparison of modified RMS in calf muscles in propulsion in five-toed shoes and barefoot runners Muscle Barefoot Five-Toed Shoes t P Tibialis anterior 41.9± ± Soleus 68.3± ± * Medial gastrocnemius 76.3± ± * Lateralis gastrocnemius 71.1± ± *:P<
4 January Volume 6. Number 4 The likely reason can be that the greater electromyographic activity of muscles in dynamic movements does not show the greater force produced by muscles [19] and the relationship of muscle activity domain with the produced force is linear only in isometric contraction [20, 21]. Thus, another reason can be toe-heel running pattern for greater force on Achilles tendon in barefoot running, although more research is needed to prove it. According to the results of most researches, the purpose of shoe design is to increase muscle activity and prevent muscle weaknesses in daily activities such as running and walking [12, 22]. Regarding the current study results, it can be said that 5-toed shoes can increase the leg muscles activities such as tibialis anterior, medial, and lateralis gastrocnemius in running stance, in addition to protection of foot against damage from contact with external bodies. Therefore, they are suitable to strengthen the leg muscles in daily activities. The role of medial gastrocnemius muscles such as ankle plantar flexor in running is to stabilize the ankle and knee and control tibialis bone rotation to reduce the damage. It seems that in 5-toed shoes, due to the increase of medial gastrocnemius activity, the possible damages on ankle and knee are less. Yet, the effect of these shoes on the activity of other extremities and trunk muscles as well as other kinematic and kinetic variables should be studied to explain the biomechanical features of these shoes. Using the 5-toed shoes can increase the activity of tibialis anterior muscle in loading response and also increase the activity of medial gastrocnemius and soleus muscles in the propulsion sub-phase. It seems that running in 5-toed shoes had more efficiency to activate leg muscles, compared with normal shoes. Acknowledgements This study was extracted from MSc. thesis of the first author, Maryam Razaghzadeh, in the Department of Physical Education, Borujerd Branch, Islamic Azad University, Borujerd. The authors would like to thank all the participants in the study Conflict of Interest All authors certify that this manuscript has neither been published in whole nor in part nor being considered for publication elsewhere. They have no conflicts of interest to declare. References [1] Nigg BM. Biomechanics of running shoes. Journal of Biomechanics. 1988; 21(10):887. doi: / (88) [2] Van Gent RN, Siem D, van Middelkoop M, van Os AG, Bierma-Zeinstra SMA, Koes BW, et al. Incidence and determinants of lower extremity running injuries in long distance runners: A systematic review. British Journal of Sports Medicine. 2007; 41(8): doi: /bjsm [3] Sinclair J. Effects of barefoot and barefoot inspired footwear on knee and ankle loading during running. Clinical Biomechanics. 2014; 29(4): doi: /j.clinbiomech [4] Lieberman DE, Venkadesan M, Werbel WA, Daoud AI, D Andrea S, Davis IS, et al. Foot strike patterns and collision forces in habitually barefoot versus shod runners. Nature. 2010; 463(7280): doi: /nature08723 [5] Sinclair J, Greenhalgh A, Brooks D, Edmundson CJ, Hobbs SJ. The influence of barefoot and barefoot-inspired footwear on the kinetics and kinematics of running in comparison to conventional running shoes. Footwear Science. 2013; 5(1): doi: / [6] Zifchock RA, Davis I. A comparison of semi-custom and custom foot orthotic devices in high and low arched individuals during walking. Clinical Biomechanics. 2008; 23(10): doi: /j.clinbiomech [7] Ledoux WR, Shofer JB, Ahroni JH, Smith DG, Sangeorzan BJ, Boyko EJ. Biomechanical differences among pes cavus, neutrally aligned, and pes planus feet in subjects with diabetes. Foot & Ankle International. 2003; 24(11): doi: / [8] Lussiana T, Hébert-Losier K, Mourot L. Effect of minimal shoes and slope on vertical and leg stiffness during running. Journal of Sport and Health Science. 2015; 4(2): doi: /j.jshs [9] Bonacci J, Saunders PU, Hicks A, Rantalainen T, Vicenzino B (Guglielmo) T, Spratford W. Running in a minimalist and lightweight shoe is not the same as running barefoot: A biomechanical study. British Journal of Sports Medicine. 2013; 47(6): doi: /bjsports [10] Ridge ST, Johnson AW, Mitchell UH, Hunter I, Robinson E, Rich BSE, et al. Foot bone marrow edema after a 10-week transition to minimalist running shoes. Medicine & Science in Sports & Exercise. 2013; 45(7): doi: / mss.0b013e [11] Boyer KA, Andriacchi TP. Changes in running kinematics and kinetics in response to a rockered shoe intervention. Clinical Biomechanics. 2009; 24(10): doi: /j. clinbiomech [12] Landry SC, Nigg BM, Tecante KE. Standing in an unstable shoe increases postural sway and muscle activity of selected smaller extrinsic foot muscles. Gait & Posture. 2010; 32(2): doi: /j.gaitpost [13] Squadrone R, Gallozzi C. Effect of a five-toed minimal protection shoe on static and dynamic ankle position sense. The Journal of Sports Medicine and Physical Fitness. 2011; 51(3): PMID:
5 January Volume 6. Number 4 [14] Hermens HJ, Freriks B, Merletti R, Stegeman D, Blok J, Rau G, et al. European recommendations for surface electromyography. Roessingh Research and Development. 1999; 8(2): [15] Von Tscharner V, Goepfert B, Nigg BM. Changes in EMG signals for the muscle tibialis anterior while running barefoot or with shoes resolved by non-linearly scaled wavelets. Journal of Biomechanics. 2003; 36(8): doi: / s (03) [16] De Wit B, De Clercq D, Aerts P. Biomechanical analysis of the stance phase during barefoot and shod running. Journal of Biomechanics. 2000; 33(3): doi: /s (99)00192-x [17] Divert C, Mornieux G, Baur H, Mayer F, Belli A. Mechanical comparison of barefoot and shod running. International Journal of Sports Medicine. 2005; 26(7): doi: /s [18] Squadrone R, Gallozzi C. Biomechanical and physiological comparison of barefoot and two shod conditions in experienced barefoot runners. Journal of Sports Medicine and Physical Fitness. 2009; 49(1):6-13. PMID: [19] Kamen G, Gabriel D. Essentials of electromyography: Human Kinetics. Canada: Human Kinetics; [20] Winter DA. Biomechanics and motor control of human movement. New Jersey: John Wiley & Sons; doi: / [21] Disselhorst-Klug C, Schmitz-Rode T, Rau G. Surface electromyography and muscle force: Limits in semg force relationship and new approaches for applications. Clinical Biomechanics. 2009; 24(3): doi: /j.clinbiomech [22] Romkes J, Rudmann C, Brunner R. Changes in gait and EMG when walking with the Masai Barefoot Technique. Clinical Biomechanics. 2006; 21(1): doi: /j.clinbiomech
6 January Volume 6. Number 4 232
Steffen Willwacher, Katina Fischer, Gert Peter Brüggemann Institute of Biomechanics and Orthopaedics, German Sport University, Cologne, Germany
 P01-3 ID126 SURFACE STIFFNESS AFFECTS JOINT LOADING IN RUNNING Steffen Willwacher, Katina Fischer, Gert Peter Brüggemann Institute of Biomechanics and Orthopaedics, German Sport University, Cologne, Germany
P01-3 ID126 SURFACE STIFFNESS AFFECTS JOINT LOADING IN RUNNING Steffen Willwacher, Katina Fischer, Gert Peter Brüggemann Institute of Biomechanics and Orthopaedics, German Sport University, Cologne, Germany
Research Paper: semg Characteristics of the Lower Extremity Muscles During Walking in Mentally Retarded
 PHYSICAL TREA MENTS April 2016. Volume 6. Number 1 Research Paper: semg Characteristics of the Lower Extremity Muscles During Walking in Mentally Retarded Adolescents CrossMark Mehrdad Anbarian 1*, Younes
PHYSICAL TREA MENTS April 2016. Volume 6. Number 1 Research Paper: semg Characteristics of the Lower Extremity Muscles During Walking in Mentally Retarded Adolescents CrossMark Mehrdad Anbarian 1*, Younes
The Effect of Training in Minimalist Running Shoes on Running Economy
 Brigham Young University BYU ScholarsArchive All Faculty Publications 2015-08-11 The Effect of Training in Minimalist Running Shoes on Running Economy Sarah T. Ridge Brigham Young University - Provo, sarah_ridge@byu.edu
Brigham Young University BYU ScholarsArchive All Faculty Publications 2015-08-11 The Effect of Training in Minimalist Running Shoes on Running Economy Sarah T. Ridge Brigham Young University - Provo, sarah_ridge@byu.edu
Outline. Biomechanics of Running. Biomechanics of Running 3/11/2011. Born to Run : A Biomechanical Analysis of Barefoot vs.
 Born to Run : A Biomechanical Analysis of Barefoot vs. Shod Running Linfield College Alicia Amsberry, Brooke Bekkedahl, & Michelle Weber Outline The Biomechanics of Running Barefoot vs. Shod-Running Vibram
Born to Run : A Biomechanical Analysis of Barefoot vs. Shod Running Linfield College Alicia Amsberry, Brooke Bekkedahl, & Michelle Weber Outline The Biomechanics of Running Barefoot vs. Shod-Running Vibram
A New Approach to Modeling Vertical Stiffness in Heel-Toe Distance Runners
 Brigham Young University BYU ScholarsArchive All Faculty Publications 2003-12-01 A New Approach to Modeling Vertical Stiffness in Heel-Toe Distance Runners Iain Hunter iain_hunter@byu.edu Follow this and
Brigham Young University BYU ScholarsArchive All Faculty Publications 2003-12-01 A New Approach to Modeling Vertical Stiffness in Heel-Toe Distance Runners Iain Hunter iain_hunter@byu.edu Follow this and
Impact of heel position on leg muscles during walking
 Original article Niigata Journal of Health and Welfare Vol. 14, No. 1 Impact of heel position on leg muscles during walking Koichi Akaishi Graduate School of Health and Welfare, Niigata University of Health
Original article Niigata Journal of Health and Welfare Vol. 14, No. 1 Impact of heel position on leg muscles during walking Koichi Akaishi Graduate School of Health and Welfare, Niigata University of Health
The effects of CrossFit and minimalist footwear on Achilles tendon kinetics during running
 Article The effects of CrossFit and minimalist footwear on Achilles tendon kinetics during running Sinclair, Jonathan Kenneth and Sant, Benjamin Available at http://clok.uclan.ac.uk/16748/ Sinclair, Jonathan
Article The effects of CrossFit and minimalist footwear on Achilles tendon kinetics during running Sinclair, Jonathan Kenneth and Sant, Benjamin Available at http://clok.uclan.ac.uk/16748/ Sinclair, Jonathan
Foot Biomechanics Getting Back to the Base
 Foot Biomechanics Getting Back to the Base Christopher J. Mehallo, D.O. Rothman Institute Orthopaedics Objectives Understand basic foot biomechanics during walking and running Understand common sports
Foot Biomechanics Getting Back to the Base Christopher J. Mehallo, D.O. Rothman Institute Orthopaedics Objectives Understand basic foot biomechanics during walking and running Understand common sports
MINIMALIST / BAREFOOT RUNNING
 MINIMALIST / BAREFOOT RUNNING DR GAVIN SHANG SPORTS PHYSICIAN MBBCH (WITS) MPHIL SPORTS MED (UCT/SSISA) BORN TO RUN BAREFOOT RUNNING Tarahumara Indians: Persistence hunting and thermo-regulatory advantage
MINIMALIST / BAREFOOT RUNNING DR GAVIN SHANG SPORTS PHYSICIAN MBBCH (WITS) MPHIL SPORTS MED (UCT/SSISA) BORN TO RUN BAREFOOT RUNNING Tarahumara Indians: Persistence hunting and thermo-regulatory advantage
This article appeared in a journal published by Elsevier. The attached copy is furnished to the author for internal non-commercial research and
 This article appeared in a journal published by Elsevier. The attached copy is furnished to the author for internal non-commercial research and education use, including for instruction at the authors institution
This article appeared in a journal published by Elsevier. The attached copy is furnished to the author for internal non-commercial research and education use, including for instruction at the authors institution
Running Injuries in Adolescents Jeffrey Shilt, M.D. Part 1 Page 1
 Running Injuries in Adolescents Jeffrey Shilt, M.D. Chief Surgical Officer, The Woodlands, Texas Children's Hospital Associate Professor, Orthopedic and Scoliosis Surgery, Baylor College of Medicine Part
Running Injuries in Adolescents Jeffrey Shilt, M.D. Chief Surgical Officer, The Woodlands, Texas Children's Hospital Associate Professor, Orthopedic and Scoliosis Surgery, Baylor College of Medicine Part
Normal and Abnormal Gait
 Normal and Abnormal Gait Adrielle Fry, MD EvergreenHealth, Division of Sport and Spine University of Washington Board Review Course March 6, 2017 What are we going to cover? Definitions and key concepts
Normal and Abnormal Gait Adrielle Fry, MD EvergreenHealth, Division of Sport and Spine University of Washington Board Review Course March 6, 2017 What are we going to cover? Definitions and key concepts
THE INFLUENCE OF SLOW RECOVERY INSOLE ON PLANTAR PRESSURE AND CONTACT AREA DURING WALKING
 March 12, 2015 5:39:44pm WSPC/170-JMMB 1540005 ISSN: 0219-51942nd Reading Journal of Mechanics in Medicine and Biology Vol. 15, No. 2 (2015) 1540005 (6 pages) c World Scientific Publishing Company DOI:
March 12, 2015 5:39:44pm WSPC/170-JMMB 1540005 ISSN: 0219-51942nd Reading Journal of Mechanics in Medicine and Biology Vol. 15, No. 2 (2015) 1540005 (6 pages) c World Scientific Publishing Company DOI:
Arch Height and Running Shoes: The Best Advice to Give Patients
 Arch Height and Running Shoes: The Best Advice to Give Patients by Thomas C. Michaud, DC Published May 1, 2014 by Dynamic Chiropractic Magazine Because runners with different arch heights are prone to
Arch Height and Running Shoes: The Best Advice to Give Patients by Thomas C. Michaud, DC Published May 1, 2014 by Dynamic Chiropractic Magazine Because runners with different arch heights are prone to
Footwear Science Publication details, including instructions for authors and subscription information:
 This article was downloaded by: [Songning Zhang] On: 08 November 2012, At: 01:58 Publisher: Taylor & Francis Informa Ltd Registered in England and Wales Registered Number: 1072954 Registered office: Mortimer
This article was downloaded by: [Songning Zhang] On: 08 November 2012, At: 01:58 Publisher: Taylor & Francis Informa Ltd Registered in England and Wales Registered Number: 1072954 Registered office: Mortimer
Michiel Twiss BScPT, MScPT i.a. Contact:
 Quest for the Holy Strike Contemporary considerations for the clinical management and prevention of running related injuries: kinematics and kinetics in forefoot and rearfoot strike patterns Michiel Twiss
Quest for the Holy Strike Contemporary considerations for the clinical management and prevention of running related injuries: kinematics and kinetics in forefoot and rearfoot strike patterns Michiel Twiss
Running injuries - what are the most important factors
 Created as a free resource by Clinical Edge Based on Physio Edge podcast 59 with Greg Lehman, Tom Goom and Dr Christian Barton Get your free trial of online Physio education at Why do runners get injured?
Created as a free resource by Clinical Edge Based on Physio Edge podcast 59 with Greg Lehman, Tom Goom and Dr Christian Barton Get your free trial of online Physio education at Why do runners get injured?
University of Bath DOI: / Publication date: Document Version Peer reviewed version. Link to publication
 Citation for published version: Squadrone, R, Rodano, R, Hamill, J & Preatoni, E 2015, 'Acute effect of different minimalist shoes on foot strike pattern and kinematics in rearfoot strikers during running'
Citation for published version: Squadrone, R, Rodano, R, Hamill, J & Preatoni, E 2015, 'Acute effect of different minimalist shoes on foot strike pattern and kinematics in rearfoot strikers during running'
Chapter 1 - Injury overview Chapter 2 - Fit for Running Assessment Chapter 3 - Soft Tissue Mobilization... 21
 Table of Contents Introduction Chapter 1 - Injury overview... 6 Chapter 2 - Fit for Running Assessment... 13 Chapter 3 - Soft Tissue Mobilization... 21 Chapter 4 - Dynamic Warm-up... 28 Chapter 5 - Strengthening...
Table of Contents Introduction Chapter 1 - Injury overview... 6 Chapter 2 - Fit for Running Assessment... 13 Chapter 3 - Soft Tissue Mobilization... 21 Chapter 4 - Dynamic Warm-up... 28 Chapter 5 - Strengthening...
Gait. Kinesiology RHS 341 Lecture 12 Dr. Einas Al-Eisa
 Gait Kinesiology RHS 341 Lecture 12 Dr. Einas Al-Eisa Definitions Locomotion = the act of moving from one place to the other Gait = the manner of walking Definitions Walking = a smooth, highly coordinated,
Gait Kinesiology RHS 341 Lecture 12 Dr. Einas Al-Eisa Definitions Locomotion = the act of moving from one place to the other Gait = the manner of walking Definitions Walking = a smooth, highly coordinated,
Clinical Biomechanics
 Clinical Biomechanics 25 (2010) 1047 1052 Contents lists available at ScienceDirect Clinical Biomechanics journal homepage: www.elsevier.com/locate/clinbiomech Gender differences in lower extremity gait
Clinical Biomechanics 25 (2010) 1047 1052 Contents lists available at ScienceDirect Clinical Biomechanics journal homepage: www.elsevier.com/locate/clinbiomech Gender differences in lower extremity gait
The Influence of High Heeled Shoes on Kinematics, Kinetics, and Muscle EMG of Normal Female Gait
 JOURNAL OF APPLIED BIOMECHANICS, 2000, 16, 309-319 2000 by Human Kinetics Publishers, Inc. The Influence of High Heeled Shoes on Kinematics, Kinetics, and Muscle EMG of Normal Female Gait Darren J. Stefanyshyn,
JOURNAL OF APPLIED BIOMECHANICS, 2000, 16, 309-319 2000 by Human Kinetics Publishers, Inc. The Influence of High Heeled Shoes on Kinematics, Kinetics, and Muscle EMG of Normal Female Gait Darren J. Stefanyshyn,
Footwear Science Publication details, including instructions for authors and subscription information:
 This article was downloaded by: [University of Calgary] On: 22 May 2012, At: 07:35 Publisher: Taylor & Francis Informa Ltd Registered in England and Wales Registered Number: 1072954 Registered office:
This article was downloaded by: [University of Calgary] On: 22 May 2012, At: 07:35 Publisher: Taylor & Francis Informa Ltd Registered in England and Wales Registered Number: 1072954 Registered office:
Acute Changes in Running Mechanics Across Footwear with Various Heel-to-Toe Height Differences
 Brigham Young University BYU ScholarsArchive All Theses and Dissertations 2016-03-01 Acute Changes in Running Mechanics Across Footwear with Various Heel-to-Toe Height Differences Daniel C. Moody Brigham
Brigham Young University BYU ScholarsArchive All Theses and Dissertations 2016-03-01 Acute Changes in Running Mechanics Across Footwear with Various Heel-to-Toe Height Differences Daniel C. Moody Brigham
Supplementary Figure S1
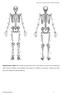 Supplementary Figure S1: Anterior and posterior views of the marker set used in the running gait trials. Forty-six markers were attached to the subject (15 markers on each leg, 4 markers on each arm, and
Supplementary Figure S1: Anterior and posterior views of the marker set used in the running gait trials. Forty-six markers were attached to the subject (15 markers on each leg, 4 markers on each arm, and
Giovanni Alfonso Borelli Father of Biomechanics
 Giovanni Alfonso Borelli Father of Biomechanics 1608-1679 Peter Guy BSc DCh Private practice Whitby and Peterborough Professor Chiropody Faculty Michener Institute of Education at UHN Advisory Board Member
Giovanni Alfonso Borelli Father of Biomechanics 1608-1679 Peter Guy BSc DCh Private practice Whitby and Peterborough Professor Chiropody Faculty Michener Institute of Education at UHN Advisory Board Member
A Pilot Study on Electromyographic Analysis of Single and Double Revolution Jumps in Figure Skating
 Journal of Exercise Science and Physiotherapy, Vol. 5, No. 1: 14-19, 2009 A Pilot Study on Electromyographic Analysis of Single and Double Revolution Jumps in Figure Skating Taylor¹, C. L. and Psycharakis²,
Journal of Exercise Science and Physiotherapy, Vol. 5, No. 1: 14-19, 2009 A Pilot Study on Electromyographic Analysis of Single and Double Revolution Jumps in Figure Skating Taylor¹, C. L. and Psycharakis²,
Gait Analysis by High School Students
 Gait Analysis by High School Students André Heck 1 and Caroline van Dongen 2 1 AMSTEL Institute, University of Amsterdam, Amsterdam, The Netherlands, heck@science.uva.nl 2 St. Antoniuscollege, Gouda, The
Gait Analysis by High School Students André Heck 1 and Caroline van Dongen 2 1 AMSTEL Institute, University of Amsterdam, Amsterdam, The Netherlands, heck@science.uva.nl 2 St. Antoniuscollege, Gouda, The
Electromyography Study on Lower Limb Muscle Synchronizations Strategies during Walking and Sitto-Stand Tasks on High-Heeled Shoes
 Electromyography Study on Lower Limb Muscle Synchronizations Strategies during Walking and Sitto-Stand Tasks on High-Heeled Shoes A Dissertation submitted for The partial fulfillment of Master of Engineering
Electromyography Study on Lower Limb Muscle Synchronizations Strategies during Walking and Sitto-Stand Tasks on High-Heeled Shoes A Dissertation submitted for The partial fulfillment of Master of Engineering
Comparison of Kinematics and Kinetics During Drop and Drop Jump Performance
 schouweiler, hess UW-L Journal of Undergraduate Research XIII (21) Comparison of Kinematics and Kinetics During Drop and Drop Jump Performance Ryan Schouweiler, Karina Hess Faculty Sponsor: Thomas Kernozek,
schouweiler, hess UW-L Journal of Undergraduate Research XIII (21) Comparison of Kinematics and Kinetics During Drop and Drop Jump Performance Ryan Schouweiler, Karina Hess Faculty Sponsor: Thomas Kernozek,
INTRODUCTION TO GAIT ANALYSIS DATA
 INTRODUCTION TO GAIT ANALYSIS DATA 1. Phases of gait a. Stance (% gc) i. Loading response (10%) ii. Mid- and terminal stance (%) iii. Pre-swing (10%) b. Swing (% gc) i. Initial swing ii. Mid-swing iii.
INTRODUCTION TO GAIT ANALYSIS DATA 1. Phases of gait a. Stance (% gc) i. Loading response (10%) ii. Mid- and terminal stance (%) iii. Pre-swing (10%) b. Swing (% gc) i. Initial swing ii. Mid-swing iii.
What is the optimal design of a rocker shoe
 What is the optimal design of a rocker shoe University of Salford School of Health, Sport and Rehabilitation Sciences Deutsche Sporthochschule Köln J Chapman, S Preece, C Nester, B Braunstein, P Bruggerman
What is the optimal design of a rocker shoe University of Salford School of Health, Sport and Rehabilitation Sciences Deutsche Sporthochschule Köln J Chapman, S Preece, C Nester, B Braunstein, P Bruggerman
Acute effect of different minimalist shoes on foot strike pattern and kinematics in rearfoot strikers during running
 University of Massachusetts Amherst From the SelectedWorks of Joseph Hamill 2014 Acute effect of different minimalist shoes on foot strike pattern and kinematics in rearfoot strikers during running Roberto
University of Massachusetts Amherst From the SelectedWorks of Joseph Hamill 2014 Acute effect of different minimalist shoes on foot strike pattern and kinematics in rearfoot strikers during running Roberto
Joint contact loading in forefoot and rearfoot strike patterns during running
 Graduate Theses and Dissertations Graduate College 211 Joint contact loading in forefoot and rearfoot strike patterns during running Brandon David Rooney Iowa State University Follow this and additional
Graduate Theses and Dissertations Graduate College 211 Joint contact loading in forefoot and rearfoot strike patterns during running Brandon David Rooney Iowa State University Follow this and additional
Assessments SIMPLY GAIT. Posture and Gait. Observing Posture and Gait. Postural Assessment. Postural Assessment 6/28/2016
 Assessments 2 SIMPLY GAIT Understanding movement Evaluations of factors that help therapist form professional judgments Include health, palpatory, range of motion, postural, and gait assessments Assessments
Assessments 2 SIMPLY GAIT Understanding movement Evaluations of factors that help therapist form professional judgments Include health, palpatory, range of motion, postural, and gait assessments Assessments
Ankle biomechanics demonstrates excessive and prolonged time to peak rearfoot eversion (see Foot Complex graph). We would not necessarily expect
 Case Study #1 The first case study is a runner presenting with bilateral shin splints with pain and tenderness along the medial aspect of the tibia. The symptoms have increased significantly over the last
Case Study #1 The first case study is a runner presenting with bilateral shin splints with pain and tenderness along the medial aspect of the tibia. The symptoms have increased significantly over the last
Comparison of gait properties during level walking and stair ascent and descent with varying loads
 Vol.2, No.12, 1372-1376 (2010) doi:10.4236/health.2010.212203 Health Comparison of gait properties during level walking and stair ascent and descent with varying loads Tomohiro Demura 1*, Shin-ich Demura
Vol.2, No.12, 1372-1376 (2010) doi:10.4236/health.2010.212203 Health Comparison of gait properties during level walking and stair ascent and descent with varying loads Tomohiro Demura 1*, Shin-ich Demura
Athlete Profiling. Injury Prevention
 Athlete Profiling Injury Prevention Fraser McKinney Physiotherapist Special interest in: Basketball Athletics Race Walking Research Performance markers (screening / HR assessments / biomechanics) Athlete
Athlete Profiling Injury Prevention Fraser McKinney Physiotherapist Special interest in: Basketball Athletics Race Walking Research Performance markers (screening / HR assessments / biomechanics) Athlete
Mike Prevost, PhD
 A Quick Guide to Transitioning to Running Sandals Mike Prevost, PhD www.shammasandals.com A Quick Guide to Transitioning to Running Sandals Mike Prevost, PhD Nothing has impacted my run gait more than
A Quick Guide to Transitioning to Running Sandals Mike Prevost, PhD www.shammasandals.com A Quick Guide to Transitioning to Running Sandals Mike Prevost, PhD Nothing has impacted my run gait more than
A bit of background. Session Schedule 3:00-3:10: Introduction & session overview. Overarching research theme: CPTA
 A Cognitive-Biomechanical Perspective for the Management of Common Chronic Musculoskeletal Conditions Skulpan Asavasopon, PT, PhD Loma Linda University Christopher M. Powers, PT, PhD, FAPTA University
A Cognitive-Biomechanical Perspective for the Management of Common Chronic Musculoskeletal Conditions Skulpan Asavasopon, PT, PhD Loma Linda University Christopher M. Powers, PT, PhD, FAPTA University
Expanded Gait Assessment and Evaluation and Validation of Minimalist Footwear
 Expanded Gait Assessment and Evaluation and Validation of Minimalist Footwear Abstract Stephen C. Gangemi, DC, DIBAK 213 Providence Rd, Chapel Hill, NC 27514 919-419-9099(phone); 919-419-9049(fax); drgangemi@drgangemi.com
Expanded Gait Assessment and Evaluation and Validation of Minimalist Footwear Abstract Stephen C. Gangemi, DC, DIBAK 213 Providence Rd, Chapel Hill, NC 27514 919-419-9099(phone); 919-419-9049(fax); drgangemi@drgangemi.com
The Problem. An Innovative Approach to the Injured Runner. Dosage. Mechanics. Structure! Postural Observations. Lower Quarter Assessment
 The Problem An Innovative Approach to the Injured Runner Irene S. Davis, PhD, PT, FAPTA, FACSM Director, Spaulding National Running Center Harvard Medical School Healthy People 2020 Initiative 76% runners
The Problem An Innovative Approach to the Injured Runner Irene S. Davis, PhD, PT, FAPTA, FACSM Director, Spaulding National Running Center Harvard Medical School Healthy People 2020 Initiative 76% runners
PERFORMANCE, STRIDE CHARACTERISTICS, AND MUSCLE ACTIVITY WHILE RUNNING WITH A TRADITIONAL COMPARED TO A NEWLY DEVELOPED RUNNING SHOE
 PERFORMANCE, STRIDE CHARACTERISTICS, AND MUSCLE ACTIVITY WHILE RUNNING WITH A TRADITIONAL COMPARED TO A NEWLY DEVELOPED RUNNING SHOE Eric Lichtenstein 1, Lars Donath 1,2, Aislinn Oeri 1, Ralf Roth 1, Roland
PERFORMANCE, STRIDE CHARACTERISTICS, AND MUSCLE ACTIVITY WHILE RUNNING WITH A TRADITIONAL COMPARED TO A NEWLY DEVELOPED RUNNING SHOE Eric Lichtenstein 1, Lars Donath 1,2, Aislinn Oeri 1, Ralf Roth 1, Roland
THE EFFECT OF BINDING POSITION ON KINETIC VARIABLES IN ALPINE SKIING
 THE EFFECT OF BINDING POSITION ON KINETIC VARIABLES IN ALPINE SKIING H. SCHWAMEDER 1, B. M. NIGG 2, V. v. TSCHARNER 2, D. STEFANYSHYN 2 1 Institute of Sports Sciences, University of Salzburg 2 Human Performance
THE EFFECT OF BINDING POSITION ON KINETIC VARIABLES IN ALPINE SKIING H. SCHWAMEDER 1, B. M. NIGG 2, V. v. TSCHARNER 2, D. STEFANYSHYN 2 1 Institute of Sports Sciences, University of Salzburg 2 Human Performance
Barefoot Running. Ed Mulligan, PT, DPT, OCS, SCS, ATC. Clinical Orthopedic Rehabilitation Education
 Barefoot Running Ed Mulligan, PT, DPT, OCS, SCS, ATC Clinical Orthopedic Rehabilitation Education Not a new concept Nov 1958 1984 Olympics Interesting Trivia Abebe Bilika won the 1960 Olympic marathon
Barefoot Running Ed Mulligan, PT, DPT, OCS, SCS, ATC Clinical Orthopedic Rehabilitation Education Not a new concept Nov 1958 1984 Olympics Interesting Trivia Abebe Bilika won the 1960 Olympic marathon
COMPARISON STUDY BETWEEN THE EFFICIENY OF THE START TECHNIQUES IN THE ROMANIAN COMPETITIVE SWIMMING
 Bulletin of the Transilvania University of Braşov Series IX: Sciences of Human Kinetics Vol. 6 (55) No. 1 2013 COMPARISON STUDY BETWEEN THE EFFICIENY OF THE START TECHNIQUES IN THE ROMANIAN COMPETITIVE
Bulletin of the Transilvania University of Braşov Series IX: Sciences of Human Kinetics Vol. 6 (55) No. 1 2013 COMPARISON STUDY BETWEEN THE EFFICIENY OF THE START TECHNIQUES IN THE ROMANIAN COMPETITIVE
12/4/2010 3:10 / 3:40
 Running Assessment Workshop Anthony Luke MD, MPH, CAQ (Sport Med) UCSF PCSM Conference 2010 Running boom in the 70 s and 90 s Men then women % of women runners Wheelchair Evolution 26.2 miles 42.195 km
Running Assessment Workshop Anthony Luke MD, MPH, CAQ (Sport Med) UCSF PCSM Conference 2010 Running boom in the 70 s and 90 s Men then women % of women runners Wheelchair Evolution 26.2 miles 42.195 km
Acute Differences in Foot Strike and Spatiotemporal Variables for Shod, Barefoot or Minimalist Male Runners
 Journal of Sports Science and Medicine (2014) 13, 280-286 http://www.jssm.org Research article Acute Differences in Foot Strike and Spatiotemporal Variables for Shod, Barefoot or Minimalist Male Runners
Journal of Sports Science and Medicine (2014) 13, 280-286 http://www.jssm.org Research article Acute Differences in Foot Strike and Spatiotemporal Variables for Shod, Barefoot or Minimalist Male Runners
video Purpose Pathological Gait Objectives: Primary, Secondary and Compensatory Gait Deviations in CP AACPDM IC #3 1
 s in CP Disclosure Information AACPDM 71st Annual Meeting September 13-16, 2017 Speaker Names: Sylvia Ounpuu, MSc and Kristan Pierz, MD Differentiating Between, Secondary and Compensatory Mechanisms in
s in CP Disclosure Information AACPDM 71st Annual Meeting September 13-16, 2017 Speaker Names: Sylvia Ounpuu, MSc and Kristan Pierz, MD Differentiating Between, Secondary and Compensatory Mechanisms in
GROUND REACTION FORCE DOMINANT VERSUS NON-DOMINANT SINGLE LEG STEP OFF
 GROUND REACTION FORCE DOMINANT VERSUS NON-DOMINANT SINGLE LEG STEP OFF Sara Gharabaghli, Rebecca Krogstad, Sara Lynch, Sofia Saavedra, and Tamara Wright California State University, San Marcos, San Marcos,
GROUND REACTION FORCE DOMINANT VERSUS NON-DOMINANT SINGLE LEG STEP OFF Sara Gharabaghli, Rebecca Krogstad, Sara Lynch, Sofia Saavedra, and Tamara Wright California State University, San Marcos, San Marcos,
empower Reclaim your power. Information for technicians empower Ottobock 1
 empower Reclaim your power. Information for technicians empower Ottobock 1 empower Powered propulsion for more freedom in life The empower Ankle is an innovation in the field of prosthetic feet. It is
empower Reclaim your power. Information for technicians empower Ottobock 1 empower Powered propulsion for more freedom in life The empower Ankle is an innovation in the field of prosthetic feet. It is
Journal of Advanced Sport Technology 1(1):22-29
 Journal of Advanced Sport Technology 1(1):22-29 Original Research The effectiveness of a novel Kinesio Taping technique on the ground reaction force components during bilateral drop landing in athletes
Journal of Advanced Sport Technology 1(1):22-29 Original Research The effectiveness of a novel Kinesio Taping technique on the ground reaction force components during bilateral drop landing in athletes
Diabetes and Orthoses. Rob Bradbury Talar Made
 Diabetes and Orthoses Rob Bradbury Talar Made Diabetes High prevalence disease 4-6% in UK (over 2.5 mill diagnosed and a further 0.5 ) 6+% in USA 40% in some parts of Middle East (may be higher in Indian
Diabetes and Orthoses Rob Bradbury Talar Made Diabetes High prevalence disease 4-6% in UK (over 2.5 mill diagnosed and a further 0.5 ) 6+% in USA 40% in some parts of Middle East (may be higher in Indian
My pa;ents are ocen keen to quiz me about it, I expect yours are as well.
 Wed 11am T12 This summer I'm publishing a book on lower limb tendinopathy and this presenta;on is essen;ally a spin-off from my research for the book and my clinical work with novice runners. 1 My pa;ents
Wed 11am T12 This summer I'm publishing a book on lower limb tendinopathy and this presenta;on is essen;ally a spin-off from my research for the book and my clinical work with novice runners. 1 My pa;ents
Relationship between Ground Reaction Force and Stability Level of the Lower Extremity in Runners Background: Objective: Design and Setting:
 Relationship between Ground Reaction Force and Stability Level of the Lower Extremity in Runners Kimitake Sato, Monique Butcher-Mokha Barry University Miami Shores, FL Background: Neuromuscular control
Relationship between Ground Reaction Force and Stability Level of the Lower Extremity in Runners Kimitake Sato, Monique Butcher-Mokha Barry University Miami Shores, FL Background: Neuromuscular control
Effects of minimalist and maximalist footwear on Achilles tendon load in recreational runners
 Article Effects of minimalist and maximalist footwear on Achilles tendon load in recreational runners Sinclair, Jonathan Kenneth, Richards, Jim and Shore, Hannah Available at http://clok.uclan.ac.uk/12531/
Article Effects of minimalist and maximalist footwear on Achilles tendon load in recreational runners Sinclair, Jonathan Kenneth, Richards, Jim and Shore, Hannah Available at http://clok.uclan.ac.uk/12531/
INTERACTION OF STEP LENGTH AND STEP RATE DURING SPRINT RUNNING
 INTERACTION OF STEP LENGTH AND STEP RATE DURING SPRINT RUNNING Joseph P. Hunter 1, Robert N. Marshall 1,, and Peter J. McNair 3 1 Department of Sport and Exercise Science, The University of Auckland, Auckland,
INTERACTION OF STEP LENGTH AND STEP RATE DURING SPRINT RUNNING Joseph P. Hunter 1, Robert N. Marshall 1,, and Peter J. McNair 3 1 Department of Sport and Exercise Science, The University of Auckland, Auckland,
Expanded Gait Assessment and Evaluation and Validation of Minimalist Footwear
 Expanded Gait Assessment and Evaluation and Validation of Minimalist Footwear Abstract Stephen C. Gangemi, DC, DIBAK 213 Providence Rd, Chapel Hill, NC 27514 919-419-9099(phone); 919-419-9049(fax); drgangemi@drgangemi.com
Expanded Gait Assessment and Evaluation and Validation of Minimalist Footwear Abstract Stephen C. Gangemi, DC, DIBAK 213 Providence Rd, Chapel Hill, NC 27514 919-419-9099(phone); 919-419-9049(fax); drgangemi@drgangemi.com
Customized rocker sole constructions
 Customized rocker sole constructions German guidelines to improve results in daily practice Stief, Thomas Registered Association for the Encouragement of Research and Education Management in Orthopedic
Customized rocker sole constructions German guidelines to improve results in daily practice Stief, Thomas Registered Association for the Encouragement of Research and Education Management in Orthopedic
An investigation of kinematic and kinetic variables for the description of prosthetic gait using the ENOCH system
 An investigation of kinematic and kinetic variables for the description of prosthetic gait using the ENOCH system K. OBERG and H. LANSHAMMAR* Amputee Training and Research Unit, University Hospital, Fack,
An investigation of kinematic and kinetic variables for the description of prosthetic gait using the ENOCH system K. OBERG and H. LANSHAMMAR* Amputee Training and Research Unit, University Hospital, Fack,
Empower. Reclaim your power. Information for technicians. Empower Ottobock 1
 Empower Reclaim your power. Information for technicians Empower Ottobock 1 Empower Powered propulsion for more freedom in life The Empower is an innovation in the field of prosthetic feet. It is equipped
Empower Reclaim your power. Information for technicians Empower Ottobock 1 Empower Powered propulsion for more freedom in life The Empower is an innovation in the field of prosthetic feet. It is equipped
HPW Biomechanics
 HPW Biomechanics hpw@mail.com www.hpwbiomechanics.com ~ via e-mail ~ January 31, 213 To: Attn: From: Subject: I-Roc Debbie Chapman Janet S. Dufek, Ph.D. Research Scientist Additional Footwear Evaluation
HPW Biomechanics hpw@mail.com www.hpwbiomechanics.com ~ via e-mail ~ January 31, 213 To: Attn: From: Subject: I-Roc Debbie Chapman Janet S. Dufek, Ph.D. Research Scientist Additional Footwear Evaluation
The Starting Point. Prosthetic Alignment in the Transtibial Amputee. Outline. COM Motion in the Coronal Plane
 Prosthetic Alignment in the Transtibial Amputee The Starting Point David C. Morgenroth, MD, Department of Rehabilitation Medicine University of Washington VAPSHCS Outline COM Motion in the Coronal Plane
Prosthetic Alignment in the Transtibial Amputee The Starting Point David C. Morgenroth, MD, Department of Rehabilitation Medicine University of Washington VAPSHCS Outline COM Motion in the Coronal Plane
Six Weeks Habituation of Simulated Barefoot Running Induces Neuromuscular Adaptations and Changes in Foot Strike Patterns in Female Runners
 e-issn 1643-3750 DOI: 10.12659/MSM.893518 Received: 2015.01.08 Accepted: 2015.02.13 Published: 2015.07.13 Six Weeks Habituation of Simulated Barefoot Running Induces Neuromuscular Adaptations and Changes
e-issn 1643-3750 DOI: 10.12659/MSM.893518 Received: 2015.01.08 Accepted: 2015.02.13 Published: 2015.07.13 Six Weeks Habituation of Simulated Barefoot Running Induces Neuromuscular Adaptations and Changes
Redistribution of Mechanical Work at the Knee and Ankle Joints During Fast Running in Minimalist Shoes
 Journal of Athletic Training 2016;51(10):806 812 doi: 10.4085/1062-6050-51.12.05 Ó by the National Athletic Trainers Association, Inc www.natajournals.org original research Redistribution of Mechanical
Journal of Athletic Training 2016;51(10):806 812 doi: 10.4085/1062-6050-51.12.05 Ó by the National Athletic Trainers Association, Inc www.natajournals.org original research Redistribution of Mechanical
Posture influences ground reaction force: implications for crouch gait
 University of Tennessee, Knoxville From the SelectedWorks of Jeffrey A. Reinbolt July 14, 2010 Posture influences ground reaction force: implications for crouch gait H. X. Hoang Jeffrey A. Reinbolt, University
University of Tennessee, Knoxville From the SelectedWorks of Jeffrey A. Reinbolt July 14, 2010 Posture influences ground reaction force: implications for crouch gait H. X. Hoang Jeffrey A. Reinbolt, University
Positive running posture sums up the right technique for top speed
 Positive running, a model for high speed running Frans Bosch positive running posture sums up the right technique for top speed building blocks in running: Pelvic rotation for- and backward and hamstring
Positive running, a model for high speed running Frans Bosch positive running posture sums up the right technique for top speed building blocks in running: Pelvic rotation for- and backward and hamstring
CHAPTER IV FINITE ELEMENT ANALYSIS OF THE KNEE JOINT WITHOUT A MEDICAL IMPLANT
 39 CHAPTER IV FINITE ELEMENT ANALYSIS OF THE KNEE JOINT WITHOUT A MEDICAL IMPLANT 4.1 Modeling in Biomechanics The human body, apart of all its other functions is a mechanical mechanism and a structure,
39 CHAPTER IV FINITE ELEMENT ANALYSIS OF THE KNEE JOINT WITHOUT A MEDICAL IMPLANT 4.1 Modeling in Biomechanics The human body, apart of all its other functions is a mechanical mechanism and a structure,
Effects of unstable shoes on energy cost during treadmill walking at various speeds
 Journal of Sports Science and Medicine (2012) 11, 632-637 http://www.jssm.org Research article Effects of unstable shoes on energy cost during treadmill walking at various speeds Keiji Koyama 1, Hisashi
Journal of Sports Science and Medicine (2012) 11, 632-637 http://www.jssm.org Research article Effects of unstable shoes on energy cost during treadmill walking at various speeds Keiji Koyama 1, Hisashi
Does Ski Width Influence Muscle Action in an Elite Skier? A Case Study. Montana State University Movement Science Laboratory Bozeman, MT 59717
 Does Ski Width Influence Muscle Action in an Elite Skier? A Case Study John G. Seifert 1, Heidi Nunnikhoven 1, Cory Snyder 1, Ronald Kipp 2 1 Montana State University Movement Science Laboratory Bozeman,
Does Ski Width Influence Muscle Action in an Elite Skier? A Case Study John G. Seifert 1, Heidi Nunnikhoven 1, Cory Snyder 1, Ronald Kipp 2 1 Montana State University Movement Science Laboratory Bozeman,
Lower Extremity Joint Kinematics of Shod, Barefoot, and Simulated Barefoot Treadmill Running
 Original Research Lower Extremity Joint Kinematics of Shod, Barefoot, and Simulated Barefoot Treadmill Running MICHELE LEBLANC and HEIDI FERKRANUS* Exercise Science Department, California Lutheran University,
Original Research Lower Extremity Joint Kinematics of Shod, Barefoot, and Simulated Barefoot Treadmill Running MICHELE LEBLANC and HEIDI FERKRANUS* Exercise Science Department, California Lutheran University,
NO IMMEDIATE EFFECTS OF HIGHLY CUSHIONED SHOES ON BASIC RUNNING BIOMECHANICS
 NO IMMEDIATE EFFECTS OF HIGHLY CUSHIONED SHOES ON BASIC RUNNING BIOMECHANICS Naoko Aminaka, Kevin Arthur, John P. Porcari, Carl Foster, Maria Cress, and Chelsea Hahn University of Wisconsin - La Crosse,
NO IMMEDIATE EFFECTS OF HIGHLY CUSHIONED SHOES ON BASIC RUNNING BIOMECHANICS Naoko Aminaka, Kevin Arthur, John P. Porcari, Carl Foster, Maria Cress, and Chelsea Hahn University of Wisconsin - La Crosse,
Neurorehabil Neural Repair Oct 23. [Epub ahead of print]
![Neurorehabil Neural Repair Oct 23. [Epub ahead of print] Neurorehabil Neural Repair Oct 23. [Epub ahead of print]](/thumbs/86/94477916.jpg) APPENDICE Neurorehabil Neural Repair. 2009 Oct 23. [Epub ahead of print] Segmental Muscle Vibration Improves Walking in Chronic Stroke Patients With Foot Drop: A Randomized Controlled Trial. Paoloni M,
APPENDICE Neurorehabil Neural Repair. 2009 Oct 23. [Epub ahead of print] Segmental Muscle Vibration Improves Walking in Chronic Stroke Patients With Foot Drop: A Randomized Controlled Trial. Paoloni M,
In-Shoe Loading in Rearfoot and Non-Rearfoot Strikers during Running Using Minimalist Footwear
 Orthopedics & Biomechanics 1 In-Shoe Loading in Rearfoot and Non-Rearfoot Strikers during Running Using Minimalist Footwear Authors T. W. Kernozek 1, S. Meardon 2, C. N. Vannatta 1 Affiliation 1 Department
Orthopedics & Biomechanics 1 In-Shoe Loading in Rearfoot and Non-Rearfoot Strikers during Running Using Minimalist Footwear Authors T. W. Kernozek 1, S. Meardon 2, C. N. Vannatta 1 Affiliation 1 Department
Dynamic/Static Foot. Tissues. Static Foot. Dynamic Foot
 Dynamic/Static Tissues Static Plantar fascia biomechanical windlass mechanism intrinsic muscles stabilize metatarsophalangeal (MP) toe joints Weight on whole foot - MP toe joints straight Plantar fascia
Dynamic/Static Tissues Static Plantar fascia biomechanical windlass mechanism intrinsic muscles stabilize metatarsophalangeal (MP) toe joints Weight on whole foot - MP toe joints straight Plantar fascia
Formthotics Case Study Medial Tibial Stress Syndrome
 Formthotics Case Study Medial Tibial Stress Syndrome In association with 1 Medial Tibial Stress Syndrome Practitioner Practice Patient Rebecca Gifford PodiatryMed, Christchurch, NZ Chelsea Hewson Page
Formthotics Case Study Medial Tibial Stress Syndrome In association with 1 Medial Tibial Stress Syndrome Practitioner Practice Patient Rebecca Gifford PodiatryMed, Christchurch, NZ Chelsea Hewson Page
ATHLETES AND ORTHOTICS. January 29, 2014
 ATHLETES AND ORTHOTICS January 29, 2014 TOPICS TO COVER TODAY Why use an orthotic? What athlete would benefit from wearing orthotics? What device should I use: Custom versus off of the shelf orthotics?
ATHLETES AND ORTHOTICS January 29, 2014 TOPICS TO COVER TODAY Why use an orthotic? What athlete would benefit from wearing orthotics? What device should I use: Custom versus off of the shelf orthotics?
THE ANKLE-HIP TRANSVERSE PLANE COUPLING DURING THE STANCE PHASE OF NORMAL WALKING
 THE ANKLE-HIP TRANSVERSE PLANE COUPLING DURING THE STANCE PHASE OF NORMAL WALKING Thales R. Souza, Rafael Z. Pinto, Renato G. Trede, Nadja C. Pereira, Renata N. Kirkwood and Sérgio T. Fonseca. Movement
THE ANKLE-HIP TRANSVERSE PLANE COUPLING DURING THE STANCE PHASE OF NORMAL WALKING Thales R. Souza, Rafael Z. Pinto, Renato G. Trede, Nadja C. Pereira, Renata N. Kirkwood and Sérgio T. Fonseca. Movement
SHUFFLE TURN OF HUMANOID ROBOT SIMULATION BASED ON EMG MEASUREMENT
 SHUFFLE TURN OF HUMANOID ROBOT SIMULATION BASED ON EMG MEASUREMENT MASANAO KOEDA, TAKAYUKI SERIZAWA, AND YUTA MATSUI Osaka Electro-Communication University, Faculty of Information Science and Arts, Department
SHUFFLE TURN OF HUMANOID ROBOT SIMULATION BASED ON EMG MEASUREMENT MASANAO KOEDA, TAKAYUKI SERIZAWA, AND YUTA MATSUI Osaka Electro-Communication University, Faculty of Information Science and Arts, Department
BIOMECHANICAL ASSESSMENT & ORTHOTIC SALES SCRIPTS
 BIOMECHANICAL ASSESSMENT & ORTHOTIC SALES SCRIPTS 1 Categories the client Categorise who the potential client actually is, as this will guide how you present the sale. a) Current patient of yours pre-existing
BIOMECHANICAL ASSESSMENT & ORTHOTIC SALES SCRIPTS 1 Categories the client Categorise who the potential client actually is, as this will guide how you present the sale. a) Current patient of yours pre-existing
The study on exercise effects by the change of elastics and angle of the Insole
 The study on exercise effects by the change of elastics and angle of the Insole Lee, Chang-Min, Oh, Yeon-ju, Kim, Jin-Hoon Department of Industrial and Management Engineering Dong-Eui University Gaya-Dong
The study on exercise effects by the change of elastics and angle of the Insole Lee, Chang-Min, Oh, Yeon-ju, Kim, Jin-Hoon Department of Industrial and Management Engineering Dong-Eui University Gaya-Dong
Biomechanical Analysis of Race Walking Compared to Normal Walking and Running Gait
 University of Kentucky UKnowledge Theses and Dissertations--Kinesiology and Health Promotion Kinesiology and Health Promotion 2015 Biomechanical Analysis of Race Walking Compared to Normal Walking and
University of Kentucky UKnowledge Theses and Dissertations--Kinesiology and Health Promotion Kinesiology and Health Promotion 2015 Biomechanical Analysis of Race Walking Compared to Normal Walking and
Why Running shoes do not work: Looking at Pronation, Cushioning, Motion Control and Barefoot running. by Steve Magness
 Why Running shoes do not work: Looking at Pronation, Cushioning, Motion Control and Barefoot running. by Steve Magness The running shoe model needs to be fixed. Pronation, Motion Control, Cushioning, and
Why Running shoes do not work: Looking at Pronation, Cushioning, Motion Control and Barefoot running. by Steve Magness The running shoe model needs to be fixed. Pronation, Motion Control, Cushioning, and
It has been observed that 20-30% of children never form the arches or curves in both the feet or in just one foot.
 Introduction Flat feet, also known as Pes Planus or fallen arches, are a medical condition in which the arch of the foot is prone to suboptimal development. Normally, in this condition, the bottom of the
Introduction Flat feet, also known as Pes Planus or fallen arches, are a medical condition in which the arch of the foot is prone to suboptimal development. Normally, in this condition, the bottom of the
Transformation of nonfunctional spinal circuits into functional states after the loss of brain input
 Transformation of nonfunctional spinal circuits into functional states after the loss of brain input G. Courtine, Y. P. Gerasimenko, R. van den Brand, A. Yew, P. Musienko, H. Zhong, B. Song, Y. Ao, R.
Transformation of nonfunctional spinal circuits into functional states after the loss of brain input G. Courtine, Y. P. Gerasimenko, R. van den Brand, A. Yew, P. Musienko, H. Zhong, B. Song, Y. Ao, R.
Formthotics Case Study Severs Disease
 Formthotics Case Study Severs Disease In association with Severs Disease Practitioner Practice Patient Rebecca Gifford PodiatryMed, Christchurch, NZ Dominic Buyers Severs disease or calcaneal apophysitis
Formthotics Case Study Severs Disease In association with Severs Disease Practitioner Practice Patient Rebecca Gifford PodiatryMed, Christchurch, NZ Dominic Buyers Severs disease or calcaneal apophysitis
Serve the only stroke in which the player has full control over its outcome. Bahamonde (2000) The higher the velocity, the smaller the margin of
 Lower Extremity Performance of Tennis Serve Reporter: Chin-Fu Hsu Adviser: Lin-Hwa Wang OUTLINE Introduction Kinetic Chain Serve Types Lower Extremity Movement Summary Future Work INTRODUCTION Serve the
Lower Extremity Performance of Tennis Serve Reporter: Chin-Fu Hsu Adviser: Lin-Hwa Wang OUTLINE Introduction Kinetic Chain Serve Types Lower Extremity Movement Summary Future Work INTRODUCTION Serve the
-Elastic strain energy (duty factor decreases at higher speeds). Higher forces act on feet. More tendon stretch. More energy stored in tendon.
 As velocity increases ( ) (i.e. increasing Froude number v 2 / gl) the component of the energy cost of transport associated with: -Internal kinetic energy (limbs accelerated to higher angular velocity).
As velocity increases ( ) (i.e. increasing Froude number v 2 / gl) the component of the energy cost of transport associated with: -Internal kinetic energy (limbs accelerated to higher angular velocity).
Changes of gait pattern, muscle activity, and perceived comfort in response to variations of height-elevating insoles in young adults
 Original Article Journal of Exercise Rehabilitation 218;14(1):1-15 Changes of gait pattern, muscle activity, and perceived comfort in response to variations of height-elevating insoles in young adults
Original Article Journal of Exercise Rehabilitation 218;14(1):1-15 Changes of gait pattern, muscle activity, and perceived comfort in response to variations of height-elevating insoles in young adults
Physical Therapy Solutions Quarterly Newsletter Spring 2017
 SOLUTIONS Physical Therapy Solutions Quarterly Newsletter Spring 2017 Visit us at www.ptsiowa.com for links to physical therapy resources, dynamic stretching videos, past newsletters and more! Quick Links...
SOLUTIONS Physical Therapy Solutions Quarterly Newsletter Spring 2017 Visit us at www.ptsiowa.com for links to physical therapy resources, dynamic stretching videos, past newsletters and more! Quick Links...
KOTARO SASAKI Curriculum Vitae
 KOTARO SASAKI Curriculum Vitae Department of Mechanical & Biomedical Engineering Boise State University 1910 University Dr. Boise ID 83725-2075 Phone: (208) 426-4027 Email: kosasaki@boisestate.edu EDUCATION
KOTARO SASAKI Curriculum Vitae Department of Mechanical & Biomedical Engineering Boise State University 1910 University Dr. Boise ID 83725-2075 Phone: (208) 426-4027 Email: kosasaki@boisestate.edu EDUCATION
Identify and explain how specific kinematic and kinetic elements relate to the absolute speed technical model
 LINEAR SPEED: ABSOLUTE SPEED THEORY AND APPLICATION LEARNING OBJECTIVES Identify and explain how specific kinematic and kinetic elements relate to the absolute speed technical model Recognize the coaching
LINEAR SPEED: ABSOLUTE SPEED THEORY AND APPLICATION LEARNING OBJECTIVES Identify and explain how specific kinematic and kinetic elements relate to the absolute speed technical model Recognize the coaching
The Effect of Military Load Carriage on Ground Reaction Forces. Technical Note. Stewart A Birrell 1 Robin H Hooper 1 Roger A Haslam 1
 The Effect of Military Load Carriage on Ground Reaction Forces Technical Note Stewart A Birrell 1 Robin H Hooper 1 Roger A Haslam 1 1 Department of Human Sciences, Loughborough University, Leicestershire,
The Effect of Military Load Carriage on Ground Reaction Forces Technical Note Stewart A Birrell 1 Robin H Hooper 1 Roger A Haslam 1 1 Department of Human Sciences, Loughborough University, Leicestershire,
JAPMA Article In Press
 JAPMA Article In Press This article has undergone peer review, copyediting, and author review but is not a final version and may differ from the published version. DOI: http://dx.doi.org/10.7547/15-051
JAPMA Article In Press This article has undergone peer review, copyediting, and author review but is not a final version and may differ from the published version. DOI: http://dx.doi.org/10.7547/15-051
Differences in Joint Moments at the Hip, Knee, and Ankle While Wearing Running Shoes and Distance Spikes
 Brigham Young University BYU ScholarsArchive All Theses and Dissertations 2009-07-15 Differences in Joint Moments at the Hip, Knee, and Ankle While Wearing Running Shoes and Distance Spikes Aared D. Sampson
Brigham Young University BYU ScholarsArchive All Theses and Dissertations 2009-07-15 Differences in Joint Moments at the Hip, Knee, and Ankle While Wearing Running Shoes and Distance Spikes Aared D. Sampson
Modelling the stance leg in 2D analyses of sprinting: inclusion of the MTP joint affects joint
 1 Technical Note 2 3 4 5 Title: Modelling the stance leg in 2D analyses of sprinting: inclusion of the MTP joint affects joint kinetics (corrected version) 6 7 8 9 10 11 Authors: Neil E. Bezodis a,b, Aki
1 Technical Note 2 3 4 5 Title: Modelling the stance leg in 2D analyses of sprinting: inclusion of the MTP joint affects joint kinetics (corrected version) 6 7 8 9 10 11 Authors: Neil E. Bezodis a,b, Aki
Running Form Modification: When Self-selected is Not Preferred
 Running Form Modification: When Self-selected is Not Preferred Bryan Heiderscheit, PT, PhD Department of Orthopedics and Rehabilitation Department of Biomedical Engineering University of Wisconsin-Madison
Running Form Modification: When Self-selected is Not Preferred Bryan Heiderscheit, PT, PhD Department of Orthopedics and Rehabilitation Department of Biomedical Engineering University of Wisconsin-Madison
A7HLE71CO PHYSICAL THERAPY
 I A7HLE71CO Runner's Video Gait Analysis Matthew Wolin, 12/4/2018 Footwear: Altra Torin 3.0 Treadmill speed: 7.0 mph VGA Analyst: Chris Jensen, PT, MPT, OCS, CKPT POSTERIOR VIEW FINDINGS: (mid-stance)..
I A7HLE71CO Runner's Video Gait Analysis Matthew Wolin, 12/4/2018 Footwear: Altra Torin 3.0 Treadmill speed: 7.0 mph VGA Analyst: Chris Jensen, PT, MPT, OCS, CKPT POSTERIOR VIEW FINDINGS: (mid-stance)..
RUNNING SHOE STIFFNESS: THE EFFECT ON WALKING GAIT
 RUNNING SHOE STIFFNESS: THE EFFECT ON WALKING GAIT Stephen N Stanley, Peter J M c Nair, Angela G Walker, & Robert N Marshall Auckland Institute of Technology, Auckland, New Zealand University of Auckland,
RUNNING SHOE STIFFNESS: THE EFFECT ON WALKING GAIT Stephen N Stanley, Peter J M c Nair, Angela G Walker, & Robert N Marshall Auckland Institute of Technology, Auckland, New Zealand University of Auckland,
The effects of various running inclines on three-segment foot mechanics and plantar fascia strain
 2014, vol. 15 (4), 209 215 The effects of various running inclines on three-segment foot mechanics and plantar fascia strain doi: 10.1515/humo-2015-0013 Jonathan Sinclair*, Stephen Atkins, Hayley Vincent
2014, vol. 15 (4), 209 215 The effects of various running inclines on three-segment foot mechanics and plantar fascia strain doi: 10.1515/humo-2015-0013 Jonathan Sinclair*, Stephen Atkins, Hayley Vincent
