Exercise: Satellite Imagery Analysis. 29 June 2016 Japan Meteorological Agency
|
|
|
- Hector Willis
- 6 years ago
- Views:
Transcription
1 Exercise: Satellite Imagery Analysis 29 June 2016 Japan Meteorological Agency
2 Contents 1. Fog/Stratiform Cloud 2. Cb (Cumulonimbus)/Cg (Cumulus congestus) 3. Upper-level Flow Jet stream, upper trough, upper level vortex 4. Lower-level Flow 5. Tropical Cyclones 6. Mountain Waves 7. Volcanic Ash 8. Forest Fires 9. Yellow Sand
3 Determination of Cloud Types
4 Visible and Infrared Imagery Visible imagery Used to determine intensity of reflected solar radiation Used to measure optical thickness of cloud Thin Darker Thick (or dense) Brighter Infrared imagery Used to determine brightness temperature of target objects Used to measure cloud height Low Level Darker High Level Brighter
5 Determination Using Visible and Infrared Imagery Dark Infrared image Bright Dark Visible image Bright Ci Cm Cb,Cg,Cu Sc St
6 Fog/Stratiform Cloud
7 Identification of Fog/Stratiform Cloud Fog/stratiform cloud is dense and forms at very low levels. It appears darker in infrared imagery and brighter in visible imagery. The surface of a fog area is also smooth in visible imagery because it is located immediately below a stable layer. Infrared Visible
8 At Nighttime I4 IR I4 IR 3.9 μm 10.4 μm 3.9 μm 10.4 μm S2 (I4 - IR) Water Cloud Surface Infrared difference imagery S2: I4 (3.9 μm) IR (10.4 μm) 0 <0 Gray White
9 S2 (I4-IR); Fog
10 Cb (Cumulonimbus)/ Cg (Cumulus congestus)
11 Differentiation between Cb and Cg Cb Whiter than Cg in infrared imagery Accompanied by anvil Ci Cg Dotted appearance Anvil Ci Use animation to see movement.
12 Cb/Cg Infrared imagery (The F wedge points to Cb, while the G wedges indicate Cg.) Visible imagery
13 Examples of Cu and significantly developed Cb IR VS A A B B
14 Examples of Cu and significantly developed Cb IR VS A A is Cb A B B is Cu B
15 Anvil Ci Cb Ci Cb Ci Infrared imagery Both taken at 09 UTC on August 3, Visible imagery The distinction of Cb/Ci is important. Cb: heavy rain Ci: NO heavy rain Ci/Cb differentiation is based on texture, movement and location.
16 Differentiation between Cb and Ci All available information from satellite imagery should be utilized in addition to color. Point 1 Form and texture Cb: The windward side is usually clear and distinct. Ci: This is stratiform cloud with a feathering pattern, and appears very white in IR. Cb and dense Ci cannot be differentiated on the basis of form alone. Point 2 Movement and lifetime Cb: Develops/decays rapidly. Cb is stationary or slow-moving. Ci: Flows rapidly to the leeward side due to fast flow of upper air. The lifetime of convective cloud (Cb) is generally shorter than that of stratiform cloud (Ci). Point 3 Location Cb: Develops due to atmospheric instability. Ci: Prevails in connection with upper-layer jets, areas north of cloud bands, the northern side of cyclones and other locations.
17 Upper-level Flow
18 Use of Water Vapor Imagery WV Height [km] Tropopause H 2 O Mixing ratio
19 Purpose of Water Vapor Imagery Analysis Positional estimation for troughs, vortexes, ridges and jet streams in upper or middle air based on the rate of change in bright and dark regions Water vapor imagery, 00 UTC, 17 October 2007
20 Upper troughs are low-pressure areas in the upper layer. They are characterized by downdraft at the back and updraft at the front. In descendent atmospheric conditions: The atmosphere is warmed by adiabatic compressive heating. Relatively dry air comes down from the stratosphere. This makes upper troughs warm and dry, giving them a black appearance in water vapor imagery. height Upper Troughs gray black gray trough Upper trough moist dry Water Vapor imagery, 12UTC, 4 October 2007
21 Boundaries Related to Jet Streams Water Vapor imagery, 00UTC, 8 October 2007 In some cases, jet frontal zones are relatively dry and jet stream zones are relatively moist. This causes the appearance of a boundary in water vapor imagery. Dry = Dark appearance moist moist jet axis
22 Transverse Line Infrared imagery of a transverse line 03UTC, 30 August hpa analysis, 00UTC, 30 August 1998.
23 Jet streams, Upper Troughs, Upper vortices
24 Jet streams, Upper Troughs, Upper vortices Jet stream Upper vortex Upper trough
25 Lower-level Flow
26 Comparison of Visible Imagery and Infrared Imagery Low level = Darker in infrared imagery Middle density = Relatively bright in visible imagery
27 Tropical Cyclones
28 Tropical Cyclones Convective clouds with cyclonic rotation
29 Tropical Cyclone Structure Surface L Coriolis force (Northern Hemisphere) L Cyclonic rotation
30 Mountain Waves
31 Lee Wave Clouds Lee wave clouds are wave-like lower clouds generated along mountain ranges. The wave length is typically km. Lee wave clouds indicate the presence of a stable layer around the mountain-top height and relatively strong winds at this level. visible image at 03UTC, Oct 21, 2007 visible image at 02UTC, Nov 3, 1998 water vapor image at 03UTC, Oct 21, 2007
32 Example of a Lee Wave Cloud visible image at 03UTC, Oct 21, 2007 Lee wave clouds are sometimes accompanied by clear air turbulence in the lower layer. Emagram from observation at Sapporo 12UTC, 21 October 2007 Sapporo stability is neutral under the reverse layer Pilot reports (PIREPs) of turbulence severe moderate plus moderate
33 Orographic Ci Infrared imagery at 03 UTC on Jan 1, Orographic Ci is cirrus generated along mountain ranges. Its upstream edge is sharp and its downstream edge is indistinct. Orographic Ci indicates relatively strong winds in the lower layer (around the mountain-top height) and relatively high humidity in the upper layer. Visible imagery at 03 UTC on Jan 1, 2007.
34 Volcanic Ash
35 Infrared Difference Imagery (IR I2) SP μm (IR) 12.3 μm (I2) Cloud free area SiO 2 Thin Ci Dry Wet Thick cloud Radiation characteristics of quartz (SiO 2 ) Blackbody Volcanic ash and Yellow sand IR1: cleaner window Different transmissivity characteristics IR - I2 ( μm) is 0 Positive =0 Negative Positive ( Gray Black Light gray White Black )
36 Volcanic Ash from Kuchinoerabujima Difference imagery ( μm)
37 Fire Detection with I4 (3.9μm) T fire = 500K Temperature T(3.9μm) T(11μm) Response functions to fire differ between IR1 and IR4 T surface = 300K 0.05 Fire Fraction When 5% of a 300 K pixel is 500 K, 320 K is detected in IR1 (11 μm) 360 K is detected in IR4 (3.9 μm) 320K 300K Less affected IR1 11μm Sub-pixel Effect IR4 3.9μm 1 pixel 360K more affected
38 Volcanic Ash from Mt. Raung in Indonesia Difference imagery ( μm)
39 Forest Fire
40 Forest Fire Hot Spot in Indonesia Difference imagery ( μm)
41 Forest Fires and Smoke in Indonesia Visible imagery
42 Yellow Sand
43 Infrared Difference Imagery (IR I2) SP μm (IR) 12.3 μm (I2) Cloud free area SiO 2 Thin Ci Dry Wet Thick cloud Radiation characteristics of quartz (SiO 2 ) Blackbody Volcanic ash and Yellow sand IR1: cleaner window Different transmissivity characteristics IR - I2 ( μm) is 0 Positive =0 Negative Positive ( Gray Black Light gray White Black )
44 Yellow Sand (Difference imagery) 10.5 μm (IR)-12.3 μm (I2) Yellow sand forecast
45 Exercise
46 Answer the questions. Check Text Questions
47 Drawing
48 Fog/St (1)
49 Fog/St (2) Drag on to the image Select L
50 Cb/Cg
51 Lower-level Flow
52 Drag onto the image Tropical Cyclone
53 Upper-level Flow
54 Upper vortex, trough
DIRECCION DE PERSONAL AERONAUTICO DPTO. DE INSTRUCCION PREGUNTAS Y OPCIONES POR TEMA
 MT DIREION DE PERSONL ERONUTIO DPTO. DE INSTRUION PREGUNTS Y OPIONES POR TEM 1 TEM: 0643 OM-RT - Weather - hap. 6 OD_PREG: PREG20098600 (5301) PREGUNT: Every physical process of weather is accompanied
MT DIREION DE PERSONL ERONUTIO DPTO. DE INSTRUION PREGUNTS Y OPIONES POR TEM 1 TEM: 0643 OM-RT - Weather - hap. 6 OD_PREG: PREG20098600 (5301) PREGUNT: Every physical process of weather is accompanied
18 Flight Hazards over High Ground
 18 Flight Hazards over High Ground meteorology 18.1 Mountain Effect on Fronts When a warm front passes a mountain range, the air, is lifted over the mountain and will strengthen the formation of cloud
18 Flight Hazards over High Ground meteorology 18.1 Mountain Effect on Fronts When a warm front passes a mountain range, the air, is lifted over the mountain and will strengthen the formation of cloud
PHSC 3033: Meteorology Stability
 PHSC 3033: Meteorology Stability Equilibrium and Stability Equilibrium s 2 States: Stable Unstable Perturbed from its initial state, an object can either tend to return to equilibrium (A. stable) or deviate
PHSC 3033: Meteorology Stability Equilibrium and Stability Equilibrium s 2 States: Stable Unstable Perturbed from its initial state, an object can either tend to return to equilibrium (A. stable) or deviate
Earth s Atmosphere. Earth s atmosphere is a key factor in allowing life to survive here.
 Chapter 10.2 Earth s Atmosphere Earth s atmosphere is a key factor in allowing life to survive here. This narrow band of air has the right ingredients and maintains the correct temperature, to allow life
Chapter 10.2 Earth s Atmosphere Earth s atmosphere is a key factor in allowing life to survive here. This narrow band of air has the right ingredients and maintains the correct temperature, to allow life
10.2 Energy Transfer in the Atmosphere
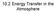 10.2 Energy Transfer in the Atmosphere Learning Outcomes Understand the different layers of the atmosphere Understand how energy moves in, out, and around our atmosphere er Composi
10.2 Energy Transfer in the Atmosphere Learning Outcomes Understand the different layers of the atmosphere Understand how energy moves in, out, and around our atmosphere er Composi
ATS 351 Lecture 6. Air Parcel. Air Parcel Movement: Why does rising air expand and cool? Stability & Skew-T Diagrams
 ATS 351 Lecture 6 Stability & Skew-T Diagrams To demonstrate stability, a parcel of air is used Expands and contracts freely Always has uniform properties throughout Air Parcel Air Parcel Movement: Why
ATS 351 Lecture 6 Stability & Skew-T Diagrams To demonstrate stability, a parcel of air is used Expands and contracts freely Always has uniform properties throughout Air Parcel Air Parcel Movement: Why
A Guide To Aviation Weather
 A Guide To Aviation Weather Richard D. Clark, Ph.D. Professor of Meteorology Student Assistants: Keith Liddick and Sam DeAlba Department of Earth Sciences Millersville University 16 NOV 2005 Outline Icing
A Guide To Aviation Weather Richard D. Clark, Ph.D. Professor of Meteorology Student Assistants: Keith Liddick and Sam DeAlba Department of Earth Sciences Millersville University 16 NOV 2005 Outline Icing
Wind is caused by differences in air pressure created by changes in temperature and water vapor content.
 Topic 8: Weather Notes, Continued Workbook Chapter 8 Wind is caused by differences in air pressure created by changes in temperature and water vapor content. Wind blows from high pressure areas to low
Topic 8: Weather Notes, Continued Workbook Chapter 8 Wind is caused by differences in air pressure created by changes in temperature and water vapor content. Wind blows from high pressure areas to low
Local Winds. Please read Ahrens Chapter 10
 Local Winds Please read Ahrens Chapter 10 Scales of Motion Microscale: meters Turbulent eddies Formed by mechanical disturbance or convection Lifetimes of minutes Mesoscale: km s to 100 s of km s Local
Local Winds Please read Ahrens Chapter 10 Scales of Motion Microscale: meters Turbulent eddies Formed by mechanical disturbance or convection Lifetimes of minutes Mesoscale: km s to 100 s of km s Local
Civil Air Patrol Auxiliary of the United States Air Force
 Mountain Flying Qualification Course Civil Air Patrol Auxiliary of the United States Air Force Mountain Weather Slopes Most U.S. mountain ranges are oriented north-south, while the prevailing winds are
Mountain Flying Qualification Course Civil Air Patrol Auxiliary of the United States Air Force Mountain Weather Slopes Most U.S. mountain ranges are oriented north-south, while the prevailing winds are
Envs, Geol, Phys 112: Global Climate. Energy-Atmosphere System Review Aguado & Bert, Ch. 1, 2, 3, 4, 5, 6, 9, 10
 Exam 1 Review Energy-Atmosphere System Review Aguado & Bert, Ch. 1, 2, 3, 4, 5, 6, 9, 10 Location on Earth (L04) Latitude & Longitude great circles, prime meridian, time zones, cardinal points, azimuth
Exam 1 Review Energy-Atmosphere System Review Aguado & Bert, Ch. 1, 2, 3, 4, 5, 6, 9, 10 Location on Earth (L04) Latitude & Longitude great circles, prime meridian, time zones, cardinal points, azimuth
ENVIRONMENTAL PHYSICS
 ENVIRONMENTAL PHYSICS Atmospheric Stability An understanding of why and how air moves in the atmosphere is fundamental to the prediction of weather and climate. What happens to air as it moves up and down
ENVIRONMENTAL PHYSICS Atmospheric Stability An understanding of why and how air moves in the atmosphere is fundamental to the prediction of weather and climate. What happens to air as it moves up and down
DIRECCION DE PERSONAL AERONAUTICO DPTO. DE INSTRUCCION PREGUNTAS Y OPCIONES POR TEMA
 MT DIREION DE PERSONL ERONUTIO DPTO. DE INSTRUION PREGUNTS Y OPIONES POR TEM Pag.: 1 TEM: 0159 OMMERIL PILOT - (H. 6) WETHER OD_PREG: PREGUNT: RPT: 5301 Every physical process of weather is accompanied
MT DIREION DE PERSONL ERONUTIO DPTO. DE INSTRUION PREGUNTS Y OPIONES POR TEM Pag.: 1 TEM: 0159 OMMERIL PILOT - (H. 6) WETHER OD_PREG: PREGUNT: RPT: 5301 Every physical process of weather is accompanied
APPI PPG LECTURE 5: FURTHER METEOROLOGY
 LECTURE 5: FURTHER METEOROLOGY Introduction: This lecture covers Further Meteorology and aims to give you more of an understanding of advanced weather conditions and patterns. However Meteorology is a
LECTURE 5: FURTHER METEOROLOGY Introduction: This lecture covers Further Meteorology and aims to give you more of an understanding of advanced weather conditions and patterns. However Meteorology is a
Notepack 41. Aim: What factors determine the climate of a certain area? Do Now: What is the difference between weather and climate?
 Notepack 41 Aim: What factors determine the climate of a certain area? Do Now: What is the difference between weather and climate? WEATHER VS. CLIMATE Weather atmospheric conditions at a certain location
Notepack 41 Aim: What factors determine the climate of a certain area? Do Now: What is the difference between weather and climate? WEATHER VS. CLIMATE Weather atmospheric conditions at a certain location
Sea and Land Breezes METR 4433, Mesoscale Meteorology Spring 2006 (some of the material in this section came from ZMAG)
 Sea and Land Breezes METR 4433, Mesoscale Meteorology Spring 2006 (some of the material in this section came from ZMAG) 1 Definitions: The sea breeze is a local, thermally direct circulation arising from
Sea and Land Breezes METR 4433, Mesoscale Meteorology Spring 2006 (some of the material in this section came from ZMAG) 1 Definitions: The sea breeze is a local, thermally direct circulation arising from
8 th Grade Science Meteorology Review
 8 th Grade Science Meteorology Review #1 Where does Earth get the energy that produces global weather patterns? A: The sun B: Humidity C: Air masses D: Cyclones A. The Sun #2 Do all of the areas on Earth
8 th Grade Science Meteorology Review #1 Where does Earth get the energy that produces global weather patterns? A: The sun B: Humidity C: Air masses D: Cyclones A. The Sun #2 Do all of the areas on Earth
Unit Test Study Guide:
 Name: Homeroom: Date: Unit 6: Meteorology Study Guide Unit Test Study Guide: Atmosphere & Weather Use the summary points below as a resource to help you study for our unit test Monday! EARTH S ATMOSPHERE:
Name: Homeroom: Date: Unit 6: Meteorology Study Guide Unit Test Study Guide: Atmosphere & Weather Use the summary points below as a resource to help you study for our unit test Monday! EARTH S ATMOSPHERE:
Trade winds Prevailing westerlies east
 Warm-up Page: 528, 1. What is the major wind belt that is nearest the equator? Trade winds Page: 528, 2. What is the major wind belt that the most of the USA belongs to: Prevailing westerlies Page: 528,
Warm-up Page: 528, 1. What is the major wind belt that is nearest the equator? Trade winds Page: 528, 2. What is the major wind belt that the most of the USA belongs to: Prevailing westerlies Page: 528,
Atmospheric & Ocean Circulation-
 Atmospheric & Ocean Circulation- Overview: Atmosphere & Climate Atmospheric layers Heating at different latitudes Atmospheric convection cells (Hadley, Ferrel, Polar) Coriolis Force Generation of winds
Atmospheric & Ocean Circulation- Overview: Atmosphere & Climate Atmospheric layers Heating at different latitudes Atmospheric convection cells (Hadley, Ferrel, Polar) Coriolis Force Generation of winds
Meteorology I Pre test for the Second Examination
 Meteorology I Pre test for the Second Examination MULTIPLE CHOICE 1. A primary reason why land areas warm up more rapidly than water areas is that a) on land, all solar energy is absorbed in a shallow
Meteorology I Pre test for the Second Examination MULTIPLE CHOICE 1. A primary reason why land areas warm up more rapidly than water areas is that a) on land, all solar energy is absorbed in a shallow
WINDS Understand the cause of wind and how it affects climate Chapter 4 Pages 59-67
 WINDS Understand the cause of wind and how it affects climate Chapter 4 Pages 59-67 What is Wind? A wind is a horizontal movement of air across a surface. Vertical movements are currents or updrafts and
WINDS Understand the cause of wind and how it affects climate Chapter 4 Pages 59-67 What is Wind? A wind is a horizontal movement of air across a surface. Vertical movements are currents or updrafts and
Weather & Atmosphere Study Guide
 Weather & Atmosphere Study Guide 1. Draw a simple water cycle diagram using the following words: Precipitation, Evaporation, Condensation, Transpiration 2. In your own words, explain the difference between
Weather & Atmosphere Study Guide 1. Draw a simple water cycle diagram using the following words: Precipitation, Evaporation, Condensation, Transpiration 2. In your own words, explain the difference between
Length of day for a full year. Ocean Gyres. Wet. Adiabatic. lapse rate, starts at. dewpoint Dry Adiabatic lapse rate
 Vernal Equinox March 20, 11:57 AM, CDT Sun will rise exactly in the east and set exactly in the west. All latitudes get 12 hours of day and 12 hours of dark. Length of day for a full year Wet Adiabatic
Vernal Equinox March 20, 11:57 AM, CDT Sun will rise exactly in the east and set exactly in the west. All latitudes get 12 hours of day and 12 hours of dark. Length of day for a full year Wet Adiabatic
Goals for today: continuing Ch 8: Atmospheric Circulation and Pressure Distributions. 26 Oct., 2011
 Goals for today: 26 Oct., 2011 continuing Ch 8: Atmospheric Circulation and Pressure Distributions Examples of synoptic scale and mesoscale circulation systems that are driven by geographic diversity in
Goals for today: 26 Oct., 2011 continuing Ch 8: Atmospheric Circulation and Pressure Distributions Examples of synoptic scale and mesoscale circulation systems that are driven by geographic diversity in
1.3: CLIMATE GEOGRAPHY. pgs
 1.3: CLIMATE GEOGRAPHY pgs. 76-89 INTRODUCTION WEATHER: Is the combination of temperature, precipitation, cloud cover and wind that we experience EACH DAY. Example: 22 0 C and clear skies. CLIMATE: The
1.3: CLIMATE GEOGRAPHY pgs. 76-89 INTRODUCTION WEATHER: Is the combination of temperature, precipitation, cloud cover and wind that we experience EACH DAY. Example: 22 0 C and clear skies. CLIMATE: The
DIRECCION DE PERSONAL AERONAUTICO DPTO. DE INSTRUCCION PREGUNTAS Y OPCIONES POR TEMA
 DIREION DE PERSONL ERONUTIO DPTO. DE INSTRUION PREGUNTS Y OPIONES POR TEM MT 28/04/2006 T E M : 0159 OMMERIL PILOT - (H. 6) WETHER OD_PREG: P R E G U N T : RPT: 5301 Every physical process of weather is
DIREION DE PERSONL ERONUTIO DPTO. DE INSTRUION PREGUNTS Y OPIONES POR TEM MT 28/04/2006 T E M : 0159 OMMERIL PILOT - (H. 6) WETHER OD_PREG: P R E G U N T : RPT: 5301 Every physical process of weather is
Warm-up. color mass. albedo. mirage
 Warm-up Page: 523, 1. The amount of solar energy reflected or absorbed depends on the, texture, composition, volume,, transparency and other properties. color mass Page: 523, 2. The fraction of solar radiation
Warm-up Page: 523, 1. The amount of solar energy reflected or absorbed depends on the, texture, composition, volume,, transparency and other properties. color mass Page: 523, 2. The fraction of solar radiation
CHAPTER 9. More on meteorology
 CHAPTER 9 More on meteorology 1). Atmospheric Pressure Atmospheric pressure is the pressure with which the atmosphere acts downwards due to its weight. Pressure decreases with altitude because the column
CHAPTER 9 More on meteorology 1). Atmospheric Pressure Atmospheric pressure is the pressure with which the atmosphere acts downwards due to its weight. Pressure decreases with altitude because the column
Chapter 8 Air Masses
 Chapter 8 Air Masses Air Masses - 1 1. An Air Mass is a large body of air usually about 1500 km across and several km thick, that has homogeneous physical properties. 2. The important physical properties
Chapter 8 Air Masses Air Masses - 1 1. An Air Mass is a large body of air usually about 1500 km across and several km thick, that has homogeneous physical properties. 2. The important physical properties
Chapter 4: Moisture and Atmospheric Stability The hydrologic cycle
 Chapter 4: Moisture and Atmospheric Stability The hydrologic cycle from: USGS http://water.usgs.gov/edu/watercycle.html Evaporation: enough water to cover the entire surface of Earth to 1 meter cycles
Chapter 4: Moisture and Atmospheric Stability The hydrologic cycle from: USGS http://water.usgs.gov/edu/watercycle.html Evaporation: enough water to cover the entire surface of Earth to 1 meter cycles
Vertical Motion and Atmospheric Stability
 Lesson 4 Vertical Motion and Atmospheric Stability This lesson describes the vertical structure of the atmosphere, atmospheric stability and the corresponding vertical motion. Adiabatic diagrams are introduced
Lesson 4 Vertical Motion and Atmospheric Stability This lesson describes the vertical structure of the atmosphere, atmospheric stability and the corresponding vertical motion. Adiabatic diagrams are introduced
Global Wind and Pressure Belts as a Response to the Unequal Heating of the Atmosphere
 GRADE 11 GEOGRAPHY SESSION 3: GLOBAL AIR CIRCULATION Key Concepts In this lesson we will focus on summarising what you need to know about: The mechanics present to create global wind and pressure belts
GRADE 11 GEOGRAPHY SESSION 3: GLOBAL AIR CIRCULATION Key Concepts In this lesson we will focus on summarising what you need to know about: The mechanics present to create global wind and pressure belts
REMINDERS: Problem Set 2: Due Monday (Feb 3)
 REMINDERS: Problem Set 2: Due Monday (Feb 3) Midterm 1: Next Wednesday, Feb 5 - Lecture material covering chapters 1-5 - Multiple Choice, Short Answers, Definitions - Practice midterm will be on course
REMINDERS: Problem Set 2: Due Monday (Feb 3) Midterm 1: Next Wednesday, Feb 5 - Lecture material covering chapters 1-5 - Multiple Choice, Short Answers, Definitions - Practice midterm will be on course
SIO20 - Midterm Examination 2 v1 Winter Section A. Circle the letter corresponding to the best answer. (1 point each)
 NAME: Section A. Circle the letter corresponding to the best answer. (1 point each) 1. Rainbows result from: a. refraction and reflection of sunlight by water droplets b. reflection of sunlight by oceans
NAME: Section A. Circle the letter corresponding to the best answer. (1 point each) 1. Rainbows result from: a. refraction and reflection of sunlight by water droplets b. reflection of sunlight by oceans
Prof. Geraint Vaughan. Centre for Atmospheric Science School of Earth, Atmospheric and Environmental Sciences. Bogdan Antonescu
 Upper-level fronts tropopause disturbances and convection Prof. Geraint Vaughan Centre for Atmospheric Science School of Earth, Atmospheric and Environmental Sciences Bogdan Antonescu the meteorological
Upper-level fronts tropopause disturbances and convection Prof. Geraint Vaughan Centre for Atmospheric Science School of Earth, Atmospheric and Environmental Sciences Bogdan Antonescu the meteorological
Atmospheric & Ocean Circulation- I
 Atmospheric & Ocean Circulation- I First: need to understand basic Earth s Energy Balance 1) Incoming radiation 2) Albedo (reflectivity) 3) Blackbody Radiation Atm/ Ocean movement ultimately derives from
Atmospheric & Ocean Circulation- I First: need to understand basic Earth s Energy Balance 1) Incoming radiation 2) Albedo (reflectivity) 3) Blackbody Radiation Atm/ Ocean movement ultimately derives from
Water Budget I: Precipitation Inputs
 Water Budget I: Precipitation Inputs Forest Cover Global Mean Annual Precipitation (MAP) Biomes and Rainfall Forests won t grow where P < 15 / yr Forest type depends strongly on rainfall quantity, type
Water Budget I: Precipitation Inputs Forest Cover Global Mean Annual Precipitation (MAP) Biomes and Rainfall Forests won t grow where P < 15 / yr Forest type depends strongly on rainfall quantity, type
Atmospheric Circulation
 Atmospheric Circulation Why do we say Earth's temperature is moderate? It may not look like it, but various processes work to moderate Earth's temperature across the latitudes. Atmospheric circulation
Atmospheric Circulation Why do we say Earth's temperature is moderate? It may not look like it, but various processes work to moderate Earth's temperature across the latitudes. Atmospheric circulation
Chapter 2. Turbulence and the Planetary Boundary Layer
 Chapter 2. Turbulence and the Planetary Boundary Layer In the chapter we will first have a qualitative overview of the PBL then learn the concept of Reynolds averaging and derive the Reynolds averaged
Chapter 2. Turbulence and the Planetary Boundary Layer In the chapter we will first have a qualitative overview of the PBL then learn the concept of Reynolds averaging and derive the Reynolds averaged
Water Budget I: Precipitation Inputs
 Water Budget I: Precipitation Inputs Forest Cover Forests and Rainfall Forests won t grow where P < 15 / yr Forest type depends strongly on rainfall quantity, type (snow, rain) and timing (summer, winter)
Water Budget I: Precipitation Inputs Forest Cover Forests and Rainfall Forests won t grow where P < 15 / yr Forest type depends strongly on rainfall quantity, type (snow, rain) and timing (summer, winter)
CHAPTER 6 Air-Sea Interaction
 CHAPTER 6 Air-Sea Interaction What causes Earth s seasons? Tilt (23.5 ) responsible for seasons 2011 Pearson Education, Inc. Distribution of Solar Energy Distribution of Solar Energy Atmosphere absorbs
CHAPTER 6 Air-Sea Interaction What causes Earth s seasons? Tilt (23.5 ) responsible for seasons 2011 Pearson Education, Inc. Distribution of Solar Energy Distribution of Solar Energy Atmosphere absorbs
Meteorology. Circle the letter that corresponds to the correct answer
 Chapter 4 Worksheet 3 Meteorology Name: Circle the letter that corresponds to the correct answer 1) Natural convection and turbulence are most likely to occur when: a) temperature decreases rapidly with
Chapter 4 Worksheet 3 Meteorology Name: Circle the letter that corresponds to the correct answer 1) Natural convection and turbulence are most likely to occur when: a) temperature decreases rapidly with
Understanding Weather
 Understanding Weather Images Graphic of the atmosphere. Enlarge Cirrus clouds. Enlarge Air masses Air masses are parcels of air that bring distinctive weather features to the country. An air mass is a
Understanding Weather Images Graphic of the atmosphere. Enlarge Cirrus clouds. Enlarge Air masses Air masses are parcels of air that bring distinctive weather features to the country. An air mass is a
NATS 101, Section 4, Spring 2009 Midterm Examination #2 March 13, 2009
 EXAM NUMBER NATS 101, Section 4, Spring 2009 Midterm Examination #2 March 13, 2009 Name: SID: S Instructions: Write your name and student ID on ALL pages of the exam. In the multiple-choice/fill in the
EXAM NUMBER NATS 101, Section 4, Spring 2009 Midterm Examination #2 March 13, 2009 Name: SID: S Instructions: Write your name and student ID on ALL pages of the exam. In the multiple-choice/fill in the
Meteorology. Circle the letter that corresponds to the correct answer
 Chapter 4 Worksheet 2 Meteorology Name: Circle the letter that corresponds to the correct answer 1) If the air temperature remains constant, evaporating water into the air will the dew point and the relative
Chapter 4 Worksheet 2 Meteorology Name: Circle the letter that corresponds to the correct answer 1) If the air temperature remains constant, evaporating water into the air will the dew point and the relative
Lecture 13 March 24, 2010, Wednesday. Atmospheric Pressure & Wind: Part 4
 Lecture 13 March 24, 2010, Wednesday Atmospheric Pressure & Wind: Part 4 Synoptic scale winds Mesoscale winds Microscale winds Air-sea interactions The largest synoptic scale wind. Monsoon: Arabic for
Lecture 13 March 24, 2010, Wednesday Atmospheric Pressure & Wind: Part 4 Synoptic scale winds Mesoscale winds Microscale winds Air-sea interactions The largest synoptic scale wind. Monsoon: Arabic for
Write answers on your own paper. A. the Sun B. the Moon C. Earth s gravity D. Earth s rotation
 The tmosphere Write answers on your own paper 1. What is the primary energy source that drives all weather events, including precipitation, hurricanes, and tornados?. the Sun. the Moon C. Earth s gravity
The tmosphere Write answers on your own paper 1. What is the primary energy source that drives all weather events, including precipitation, hurricanes, and tornados?. the Sun. the Moon C. Earth s gravity
The atmospheric circulation system
 The atmospheric circulation system Key questions Why does the air move? Are the movements of the winds random across the surface of the Earth, or do they follow regular patterns? What implications do these
The atmospheric circulation system Key questions Why does the air move? Are the movements of the winds random across the surface of the Earth, or do they follow regular patterns? What implications do these
Class Notes: Week 10. April 9 th,2019. Topics: Front and Mid-Latitude Wave Cyclones El Niño / La Niña Mid-term 2 review
 Class Notes: Week 10 April 9 th,2019 Topics: Front and Mid-Latitude Wave Cyclones El Niño / La Niña Mid-term 2 review Front- is a boundary between 2 different types of air masses Air masses with different
Class Notes: Week 10 April 9 th,2019 Topics: Front and Mid-Latitude Wave Cyclones El Niño / La Niña Mid-term 2 review Front- is a boundary between 2 different types of air masses Air masses with different
Adiabatic Lapse Rates and Atmospheric Stability
 8 Adiabatic Lapse Rates and Atmospheric Stability Learning Goals After studying this chapter, students should be able to: 1. describe adiabatic processes as they apply to the atmosphere (p. 174); 2. apply
8 Adiabatic Lapse Rates and Atmospheric Stability Learning Goals After studying this chapter, students should be able to: 1. describe adiabatic processes as they apply to the atmosphere (p. 174); 2. apply
3 Global Winds and Local Winds
 CHAPTER 1 3 Global Winds and Local Winds SECTION The Atmosphere BEFORE YOU READ After you read this section, you should be able to answer these questions: What causes wind? What is the Coriolis effect?
CHAPTER 1 3 Global Winds and Local Winds SECTION The Atmosphere BEFORE YOU READ After you read this section, you should be able to answer these questions: What causes wind? What is the Coriolis effect?
Canada s vast size creates a diverse range of weather conditions and climatic conditions. Warming trend for last 10 years Wet Spring Dry five summers
 Chapter 4 Weather and Climate Canada s vast size creates a diverse range of weather conditions and climatic conditions. Weather examples: Rainy today Snow tomorrow Fog on Wednesday 23 degree C today High
Chapter 4 Weather and Climate Canada s vast size creates a diverse range of weather conditions and climatic conditions. Weather examples: Rainy today Snow tomorrow Fog on Wednesday 23 degree C today High
Lesson: Atmospheric Dynamics
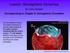 Lesson: Atmospheric Dynamics By Keith Meldahl Corresponding to Chapter 8: Atmospheric Circulation Our atmosphere moves (circulates) because of uneven solar heating of the earth s surface, combined with
Lesson: Atmospheric Dynamics By Keith Meldahl Corresponding to Chapter 8: Atmospheric Circulation Our atmosphere moves (circulates) because of uneven solar heating of the earth s surface, combined with
(a) Deflection to the left, slower velocity means greater deflection, greatest deflection at the south pole
 1 Test 2 Aid Sheet Exam: A single 8.5 by 11 inch aid sheet (both sides) and Type 2 nonprogrammable calculators are permitted. The time allowed for this Test (Part A plus Part B combined) is 90 minutes.
1 Test 2 Aid Sheet Exam: A single 8.5 by 11 inch aid sheet (both sides) and Type 2 nonprogrammable calculators are permitted. The time allowed for this Test (Part A plus Part B combined) is 90 minutes.
Atmosphere & Weather. Earth Science
 Atmosphere & Weather Earth Science Energy Transfer in the Atmosphere Earth s energy is provided by the SUN! Energy is important to us because it 1. Drives winds and ocean currents. 2. Allows plants to
Atmosphere & Weather Earth Science Energy Transfer in the Atmosphere Earth s energy is provided by the SUN! Energy is important to us because it 1. Drives winds and ocean currents. 2. Allows plants to
WEATHER SYSTEMS OF MIDDLE LATITUDES
 CHAPTER 10 WEATHER SYSTEMS OF MIDDLE LATITUDES MULTIPLE CHOICE QUESTIONS 1. In equal volumes, which one of the following air masses exerts the highest surface air pressure? a. cp *b. A c. mp d. ct e. mt
CHAPTER 10 WEATHER SYSTEMS OF MIDDLE LATITUDES MULTIPLE CHOICE QUESTIONS 1. In equal volumes, which one of the following air masses exerts the highest surface air pressure? a. cp *b. A c. mp d. ct e. mt
Winds and Ocean Circulations
 Winds and Ocean Circulations AT 351 Lab 5 February 20, 2008 Sea Surface Temperatures 1 Temperature Structure of the Ocean Ocean Currents 2 What causes ocean circulation? The direction of most ocean currents
Winds and Ocean Circulations AT 351 Lab 5 February 20, 2008 Sea Surface Temperatures 1 Temperature Structure of the Ocean Ocean Currents 2 What causes ocean circulation? The direction of most ocean currents
>>>>>>>>WHEN YOU FINISH <<<<<<<< Hand in the answer sheet separately.
 Instructor: Prof. Seiberling PHYSICS DEPARTMENT MET 1010 2nd Midterm Exam October 28, 2002 Name (print, last rst): Signature: On my honor, I have neither given nor received unauthorized aid on this examination.
Instructor: Prof. Seiberling PHYSICS DEPARTMENT MET 1010 2nd Midterm Exam October 28, 2002 Name (print, last rst): Signature: On my honor, I have neither given nor received unauthorized aid on this examination.
ATMS 310 Tropical Dynamics
 ATMS 310 Tropical Dynamics Introduction Throughout the semester we have focused on mid-latitude dynamics. This is not to say that the dynamics of other parts of the world, such as the tropics, are any
ATMS 310 Tropical Dynamics Introduction Throughout the semester we have focused on mid-latitude dynamics. This is not to say that the dynamics of other parts of the world, such as the tropics, are any
MET 200 Lecture 11 Local Winds. Last Lecture: Forces. Review of Forces. Balance of Forces
 MET 200 Lecture 11 Local Winds Last Lecture: Forces Scales of Motion Eddies Sea Breeze Mountain-Valley Circulations Chinook - Snow Eater Drainage Wind - Katabatic Wind 1 2 Review of Forces 1. Pressure
MET 200 Lecture 11 Local Winds Last Lecture: Forces Scales of Motion Eddies Sea Breeze Mountain-Valley Circulations Chinook - Snow Eater Drainage Wind - Katabatic Wind 1 2 Review of Forces 1. Pressure
ATMOSPHERIC CIRCULATION. WIND = The horizontal movement of air. Results from the differences in air pressure. Always moves from HIGH to LOW.
 ATMOSPHERIC CIRCULATION WIND = The horizontal movement of air. Results from the differences in air pressure. Always moves from HIGH to LOW. Pressure differences result from variations in temperature. AIR
ATMOSPHERIC CIRCULATION WIND = The horizontal movement of air. Results from the differences in air pressure. Always moves from HIGH to LOW. Pressure differences result from variations in temperature. AIR
Cloud Development and Forms
 Chapter 6 Lecture Understanding Weather and Climate Seventh Edition Cloud Development and Forms Redina L. Herman Western Illinois University Mechanisms That Lift Air When air lifts, clouds develop and
Chapter 6 Lecture Understanding Weather and Climate Seventh Edition Cloud Development and Forms Redina L. Herman Western Illinois University Mechanisms That Lift Air When air lifts, clouds develop and
Air Pressure and Wind
 Air Pressure and Wind 19.1 Understanding Air Pressure Air Pressure Defined Air pressure is the pressure exerted by the weight of air. Air pressure is exerted in all directions down, up, and sideways. The
Air Pressure and Wind 19.1 Understanding Air Pressure Air Pressure Defined Air pressure is the pressure exerted by the weight of air. Air pressure is exerted in all directions down, up, and sideways. The
Scales of Atmospheric Motion
 Lecture 12 Local Wind Systems Scales of Atmospheric Motion Small turbulent eddies (swirls) A synoptic eddy 1 Coriolis Effect The larger the scale, the longer the life time. Wind shear and turbulent eddy
Lecture 12 Local Wind Systems Scales of Atmospheric Motion Small turbulent eddies (swirls) A synoptic eddy 1 Coriolis Effect The larger the scale, the longer the life time. Wind shear and turbulent eddy
Pilot Rating Exam Meteorology
 Pilot Rating Exam Meteorology Derived from material originally assembled by Kenny Eaton (Dunstable Hang-Gliding and Paragliding Club), Nigel Page and Pat Dower (DSC) The 3 levels of understanding Will
Pilot Rating Exam Meteorology Derived from material originally assembled by Kenny Eaton (Dunstable Hang-Gliding and Paragliding Club), Nigel Page and Pat Dower (DSC) The 3 levels of understanding Will
Global Weather Patterns
 Global Weather Patterns AZ State Standards Concept 2: Energy in the Earth System (Both Internal and External) Understand the relationships between the Earth s land masses, oceans, and atmosphere. PO 2.
Global Weather Patterns AZ State Standards Concept 2: Energy in the Earth System (Both Internal and External) Understand the relationships between the Earth s land masses, oceans, and atmosphere. PO 2.
Chapter. Air Pressure and Wind
 Chapter Air Pressure and Wind 19.1 Understanding Air Pressure Air Pressure Defined Air pressure is the pressure exerted by the weight of air. 19.1 Understanding Air Pressure Air Pressure Defined Air pressure
Chapter Air Pressure and Wind 19.1 Understanding Air Pressure Air Pressure Defined Air pressure is the pressure exerted by the weight of air. 19.1 Understanding Air Pressure Air Pressure Defined Air pressure
Lornshill Academy. Geography Department Higher Revision Physical Environments - Atmosphere
 Lornshill Academy Geography Department Higher Revision Physical Environments - Atmosphere Physical Environments Atmosphere Global heat budget The earth s energy comes from solar radiation, this incoming
Lornshill Academy Geography Department Higher Revision Physical Environments - Atmosphere Physical Environments Atmosphere Global heat budget The earth s energy comes from solar radiation, this incoming
Weather Unit Study Guide
 Weather Unit Study Guide - 2018 Weather vs Climate What does weather measure? The condition of the earth's atmosphere at a particular time and place. How are climate and weather different? Climate is the
Weather Unit Study Guide - 2018 Weather vs Climate What does weather measure? The condition of the earth's atmosphere at a particular time and place. How are climate and weather different? Climate is the
14 Oct., Dr. Wilson will post Quiz 2 correct answers and scores over the weekend. Today we begin Ch. 6 Cloud Development and Forms
 14 Oct., 2011 Dr. Wilson will post Quiz 2 correct answers and scores over the weekend Today we begin Ch. 6 Cloud Development and Forms Vertical motion is key in relation to cloud development, and vertical
14 Oct., 2011 Dr. Wilson will post Quiz 2 correct answers and scores over the weekend Today we begin Ch. 6 Cloud Development and Forms Vertical motion is key in relation to cloud development, and vertical
Section 3: Atmospheric Circulation
 Section 3: Atmospheric Circulation Preview Key Ideas The Coriolis Effect Global Winds Local Winds Maps in Action Key Ideas Explain the Coriolis effect. Describe the global patterns of air circulation,
Section 3: Atmospheric Circulation Preview Key Ideas The Coriolis Effect Global Winds Local Winds Maps in Action Key Ideas Explain the Coriolis effect. Describe the global patterns of air circulation,
The total precipitation (P) is determined by the average rainfall rate (R) and the duration (D),
 Orographic precipitation Common ingredients of heavy orographic precipitation The total precipitation (P) is determined by the average rainfall rate (R) and the duration (D), P = RD. (1) The rainfall rate
Orographic precipitation Common ingredients of heavy orographic precipitation The total precipitation (P) is determined by the average rainfall rate (R) and the duration (D), P = RD. (1) The rainfall rate
Atmosphere Circulation
 Atmosphere Circulation Winds What Causes Winds? Difference in air pressure due to unequal heating of the atmosphere. Temperatures vary according to the amount of sun it gets. Uneven heating of the Earth
Atmosphere Circulation Winds What Causes Winds? Difference in air pressure due to unequal heating of the atmosphere. Temperatures vary according to the amount of sun it gets. Uneven heating of the Earth
Lecture 7. The Indian monsoon: is it a gigantic land-sea breeze?
 Lecture 7 The Indian monsoon: is it a gigantic land-sea breeze? In the next set of lectures I am going to discuss the different hypotheses put forth for the basic system responsible for the monsoon. I
Lecture 7 The Indian monsoon: is it a gigantic land-sea breeze? In the next set of lectures I am going to discuss the different hypotheses put forth for the basic system responsible for the monsoon. I
Meteorology. Iain Darby NAPC/PH-NSIL IAEA. International Atomic Energy Agency
 Meteorology Iain Darby NAPC/PH-NSIL International Atomic Energy Agency Good Weather Information Accurate weather forecasts play a vital role in all aviation activity It is required by law in many countries
Meteorology Iain Darby NAPC/PH-NSIL International Atomic Energy Agency Good Weather Information Accurate weather forecasts play a vital role in all aviation activity It is required by law in many countries
In comparison to depressions, these can be quite boring, at least in terms of the weather they bring.
 Anticyclones In comparison to depressions, these can be quite boring, at least in terms of the weather they bring. In summary, anticyclones; Are larger than low pressure systems, Last longer than low pressure
Anticyclones In comparison to depressions, these can be quite boring, at least in terms of the weather they bring. In summary, anticyclones; Are larger than low pressure systems, Last longer than low pressure
P2.17 OBSERVATIONS OF STRONG MOUNTAIN WAVES IN THE LEE OF THE MEDICINE BOW MOUNTAINS OF SOUTHEAST WYOMING
 P2.17 OBSERVATIONS OF STRONG MOUNTAIN WAVES IN THE LEE OF THE MEDICINE BOW MOUNTAINS OF SOUTHEAST WYOMING Larry D. Oolman 1, Jeffrey R. French 1, Samuel Haimov 1, David Leon 1, and Vanda Grubišić 2 1 University
P2.17 OBSERVATIONS OF STRONG MOUNTAIN WAVES IN THE LEE OF THE MEDICINE BOW MOUNTAINS OF SOUTHEAST WYOMING Larry D. Oolman 1, Jeffrey R. French 1, Samuel Haimov 1, David Leon 1, and Vanda Grubišić 2 1 University
Clouds and More Clouds AOSC 200 Tim Canty. Class Web Site: Lecture 12 Oct Hot air rises!
 Clouds and More Clouds AOSC 200 Tim Canty Class Web Site: http://www.atmos.umd.edu/~tcanty/aosc200 Topics for today: How to make clouds pt 1. Lecture 12 Oct 4 2018 1 Hot air rises! What happens then? 2
Clouds and More Clouds AOSC 200 Tim Canty Class Web Site: http://www.atmos.umd.edu/~tcanty/aosc200 Topics for today: How to make clouds pt 1. Lecture 12 Oct 4 2018 1 Hot air rises! What happens then? 2
Exit Ticket: Coriolis Effect
 Exit Ticket: Coriolis Effect 1. How does the Coriolis Effect influence the path of projectiles or wind traveling through the atmosphere? Causes them to curve 2. In which direction does the Coriolis Effect
Exit Ticket: Coriolis Effect 1. How does the Coriolis Effect influence the path of projectiles or wind traveling through the atmosphere? Causes them to curve 2. In which direction does the Coriolis Effect
Local Winds & Microclimates. Unit 2- Module 1
 Local Winds & Microclimates Unit 2- Module 1 Objectives Overview of local winds (sea & land breezes, valley winds) Overview of microclimates (valley, urban, woodland) Local Winds Local Winds Local winds
Local Winds & Microclimates Unit 2- Module 1 Objectives Overview of local winds (sea & land breezes, valley winds) Overview of microclimates (valley, urban, woodland) Local Winds Local Winds Local winds
Weather EOG Review Questions
 Weather EOG Review Questions 1. Which statement best describes runoff? A Water vapor cools off and changes into water droplets. B Water in the form of rain, snow, sleet, or hail falls from clouds. C Precipitation
Weather EOG Review Questions 1. Which statement best describes runoff? A Water vapor cools off and changes into water droplets. B Water in the form of rain, snow, sleet, or hail falls from clouds. C Precipitation
ASAP Satellite-based tropopause fold and mountain wave detection and validation
 ASAP Satellite-based tropopause fold and mountain wave detection and validation Tony Wimmers, Kristopher M. Bedka, Wayne Feltz, Nathan Uhlenbrock Cooperative Institute for Meteorological Satellite Studies
ASAP Satellite-based tropopause fold and mountain wave detection and validation Tony Wimmers, Kristopher M. Bedka, Wayne Feltz, Nathan Uhlenbrock Cooperative Institute for Meteorological Satellite Studies
Chapter 7 Weather and Climate
 Chapter 7 Weather and Climate *Describe what weather is, what affects it, and where it occurs. *Explain the connection between air pressure and wind. * *Many factors affect a region s weather. * *atmosphere
Chapter 7 Weather and Climate *Describe what weather is, what affects it, and where it occurs. *Explain the connection between air pressure and wind. * *Many factors affect a region s weather. * *atmosphere
Water in the Atmosphere
 Water in the Atmosphere Chapter 24 Solid to Liquid The process of changing state, such as melting ice, requires that energy be transferred in the form of heat. Latent heat is the energy absorbed or released
Water in the Atmosphere Chapter 24 Solid to Liquid The process of changing state, such as melting ice, requires that energy be transferred in the form of heat. Latent heat is the energy absorbed or released
Social Studies CHAPTER 2: PART 2 CLIMATE AND WEATHER
 Social Studies CHAPTER 2: PART 2 CLIMATE AND WEATHER Climate Weather and Identity Climate and weather have a large influence on how Canadians build their identity. We will study the factors that contribute
Social Studies CHAPTER 2: PART 2 CLIMATE AND WEATHER Climate Weather and Identity Climate and weather have a large influence on how Canadians build their identity. We will study the factors that contribute
2.2 Southwest Monsoon
 2.2 Southwest Monsoon While many manuals place their discussion of the northeast monsoon first-since it can be associated with January, the first month of the year-the southwest monsoon is presented first
2.2 Southwest Monsoon While many manuals place their discussion of the northeast monsoon first-since it can be associated with January, the first month of the year-the southwest monsoon is presented first
Chapter 7: Circulation And The Atmosphere
 Chapter 7: Circulation And The Atmosphere Highly integrated wind system Main Circulation Currents: series of deep rivers of air encircling the planet Various perturbations or vortices (hurricanes, tornados,
Chapter 7: Circulation And The Atmosphere Highly integrated wind system Main Circulation Currents: series of deep rivers of air encircling the planet Various perturbations or vortices (hurricanes, tornados,
MET Lecture 8 Atmospheric Stability
 MET 4300 Lecture 8 Atmospheric Stability Stability Concept Stable: Ball returns to original position Neutral: Ball stays wherever it is placed Unstable: Displacement grows with time. Atmospheric Stability
MET 4300 Lecture 8 Atmospheric Stability Stability Concept Stable: Ball returns to original position Neutral: Ball stays wherever it is placed Unstable: Displacement grows with time. Atmospheric Stability
Horizontal movement of air between cooler and warmer regions. - horizontal movement of air Convection over areas where is
 Winds and Water Chapter 9 continued... Uneven Heating The various materials of the earth absorb and emit energy at different rates Convection Heated air expands; density reduced; air rises Upward movement
Winds and Water Chapter 9 continued... Uneven Heating The various materials of the earth absorb and emit energy at different rates Convection Heated air expands; density reduced; air rises Upward movement
Turbulence forecasts based on upper-air soundings
 OC3570 Turbulence forecasts based on upper-air soundings By Greg Ireton Introduction The objective of this paper is to make turbulence forecasts from upper-air data by making Richardson s number calculations
OC3570 Turbulence forecasts based on upper-air soundings By Greg Ireton Introduction The objective of this paper is to make turbulence forecasts from upper-air data by making Richardson s number calculations
MET 101 Introduction to Meteorology
 MET 101 Introduction to Meteorology MET 101 Griswold 1 MIDTERM EXAM Spring Semester 2015 Thursday, March 12, 2015 Name: Student ID #: Instructions: Closed Book. Time limit is 50 minutes. Total Points Attainable:
MET 101 Introduction to Meteorology MET 101 Griswold 1 MIDTERM EXAM Spring Semester 2015 Thursday, March 12, 2015 Name: Student ID #: Instructions: Closed Book. Time limit is 50 minutes. Total Points Attainable:
Weather questions. Question 1 (1 Mark) State what information is included in a cyclone warning.
 Question 1 (1 Mark) Weather questions State what information is included in a cyclone warning. Question 2 (1 Mark) In which direction do winds travel around a high pressure system in the southern hemisphere?
Question 1 (1 Mark) Weather questions State what information is included in a cyclone warning. Question 2 (1 Mark) In which direction do winds travel around a high pressure system in the southern hemisphere?
Announcements. Why does the wind blow? What makes the ocean flow? Pressure gradients and Coriolis. First assignment (deep-sea sediments)
 Announcements First assignment (deep-sea sediments) I expect to be finished grading exams in two weeks. Second problem set due November 7th New topic: Physics of atmospheric and oceanic circulation Atmospheric
Announcements First assignment (deep-sea sediments) I expect to be finished grading exams in two weeks. Second problem set due November 7th New topic: Physics of atmospheric and oceanic circulation Atmospheric
Shop No.89, 1 st floor, Old Rajinder Nagar, New Delhi DAY REVISION PROGRAM DAY-23
 IAS BEE Shop No.89, 1 st floor, Old Rajinder Nagar, New Delhi 110060 91-7330833391 40- DAY REVISION PROGRAM DAY-23 1. Consider the following statements with reference to structure and composition of atmosphere:
IAS BEE Shop No.89, 1 st floor, Old Rajinder Nagar, New Delhi 110060 91-7330833391 40- DAY REVISION PROGRAM DAY-23 1. Consider the following statements with reference to structure and composition of atmosphere:
Section 1. Global Wind Patterns and Weather. What Do You See? Think About It. Investigate. Learning Outcomes
 Chapter 5 Winds, Oceans, Weather, and Climate Section 1 Global Wind Patterns and Weather What Do You See? Learning Outcomes In this section, you will Determine the effects of Earth s rotation and the uneven
Chapter 5 Winds, Oceans, Weather, and Climate Section 1 Global Wind Patterns and Weather What Do You See? Learning Outcomes In this section, you will Determine the effects of Earth s rotation and the uneven
Questionnaire for the theoretical part of education in skydiving. Meteorology
 1. At which approximately altitude is the atmospheric pressure ½ of the pressure at MSL (mean sea level)? a) 1.500m MSL b) 2.000m MSL c) 5.500m MSL d) 7.000m MSL 2. The rate of oxygen in the air is 21%.
1. At which approximately altitude is the atmospheric pressure ½ of the pressure at MSL (mean sea level)? a) 1.500m MSL b) 2.000m MSL c) 5.500m MSL d) 7.000m MSL 2. The rate of oxygen in the air is 21%.
3 Global Winds and Local Winds
 CHAPTER 15 3 Global Winds and Local Winds SECTION The Atmosphere BEFORE YOU READ After you read this section, you should be able to answer these questions: What causes wind? What is the Coriolis effect?
CHAPTER 15 3 Global Winds and Local Winds SECTION The Atmosphere BEFORE YOU READ After you read this section, you should be able to answer these questions: What causes wind? What is the Coriolis effect?
4/29/2011. Concept of Stability Lapse Rates Determine Stability and Stability Indices. Air pressure decreases with elevation.
 Chapter 6: Stability Concept of Stability Concept of Stability Lapse Rates Determine Stability and Stability Indices Air Parcel Expands as It Rises Air Parcel Expands As It Rises Air pressure decreases
Chapter 6: Stability Concept of Stability Concept of Stability Lapse Rates Determine Stability and Stability Indices Air Parcel Expands as It Rises Air Parcel Expands As It Rises Air pressure decreases
Heart of England Offshore Cruising Association HOEOCA
 Sailing Weather Penny Tranter 19 January 2017 Heart of England Offshore Cruising Association HOEOCA Weather and climate The difference between weather and climate? Weather is the state of the atmosphere
Sailing Weather Penny Tranter 19 January 2017 Heart of England Offshore Cruising Association HOEOCA Weather and climate The difference between weather and climate? Weather is the state of the atmosphere
