Computational evaluation of pedestrian wind comfort and wind safety around a high-rise building in an urban area
|
|
|
- Rosanna Hill
- 6 years ago
- Views:
Transcription
1 International Environmental Modelling and Software Society (iemss) 7th Intl. Congress on Env. Modelling and Software, San Diego, CA, USA, Daniel P. Ames, Nigel W.T. Quinn and Andrea E. Rizzoli (Eds.) Start title 4.5cm down from top of the page, Margins: left 40mm, right 40mm, top 25mm, bottom 30mm, and text flowing in one column of 13mm) Computational evaluation of pedestrian wind comfort and wind safety around a high-rise building in an W.D. Janssen a, B. Blocken a,b and T. van Hooff a a Building Physics and Services, Eindhoven University of Technology, The Netherlands b Building Physics Section, Department of Civil Engineering, Leuven University, Belgium Abstract: Pedestrian wind comfort is analyzed for a new shopping street area in Eindhoven city center. Wind nuisance is especially perceived around a tower of 105 m high, at an intersection of two streets. The Dutch wind nuisance standard NEN 8100 combined with CFD (Computational Fluid Dynamics) simulations is used to assess the pedestrian wind comfort. Special care is given to the grid generation and comparison of the CFD simulations with on-site wind speed measurements. The effectiveness of a series of incremental remedial measures is analyzed. A large canopy is shown to be successful in bringing the wind comfort to an acceptable level. Keywords: Computational Fluid Dynamics (CFD); Wind flow; Built environment; Comfort; Validation. 1 INTRODUCTION In a new shopping street in the Dutch city of Eindhoven, which also contains restaurants and accompanying terraces, a large degree of wind nuisance is experienced. The aim of this study is to determine the contribution of a main tower building in this area and of surrounding streets to the pedestrian wind climate and to present a solution for the perceived wind nuisance. For this purpose a Computational Fluid Dynamics (CFD) model is created to determine wind speed amplification factors in the pedestrian area, which are combined with the local wind statistics and the Dutch wind nuisance standard NEN 8100 to assess the wind climate. To improve the wind climate in the shopping area the effectiveness of a variety of remedial measures in the vicinity of the tower is studied. Although the use of CFD for the study of pedestrian wind conditions in complex urban configurations is still an issue of debate, CFD has been employed on a few occasions in the past as part of wind comfort assessment studies (e.g. Richards et al. 2002, Blocken et al. 2012, Janssen et al. 2013). The Dutch standard itself specifically mentions that studies can be performed by either wind tunnel testing or CFD. The CFD simulations in this study are conducted according to the Best Practice Guidelines (e.g. Franke et al. 2007, Tominaga et al. 2008) and are compared with experimental data. 2 GEOMETRY AND CFD SIMULATIONS Figure 1a shows the area of interest in this study, which is the Nieuwe Emmasingel, indicated with the orange lines. The Nieuwe Emmasingel consists of a rather long shopping street with mid-rise building blocks on the sides and an intersecting street at the foot of a high-rise building the Admirant tower (105 m). Southwest of the Admirant Tower, another high-rise building is located, which is the 96 m high Regent Tower. A large computational model containing all the high-rise buildings in the neighborhood was created, consisting of about 9.2 million cells. The area with explicitly modelled buildings was 1274 m by 1312 m and according to the Best Practice Guidelines (Franke et al., 2007, Tominaga et al. 2008) an upstream domain extension of 5H and a downstream domain extension of 15H were included in the domain. Figure 1b shows the grid with the area of interest in the center of the domain. The center part is modelled in more detail and contains smaller cells than the building blocks at the borders of the explicitly modelled area. Special care was given to the development of a high-quality and high-
2 resolution grid that consists of only hexahedral cells to gain fast convergence even with the requested second order discretization schemes. The grid was constructed using the grid generation technique by van Hooff and Blocken (2010), which allows a large degree of control over the quality of the grid and its individual cells. At the inlet of the domain a logarithmic mean wind speed profile, representing a neutral atmospheric boundary layer, is imposed with an aerodynamic roughness length z 0 of 0.5 or 1.0 m depending on the wind direction, and a reference wind speed U 10 of 5 m/s. The aerodynamic roughness length is determined based on the classification of terrain roughness by Davenport, updated by Wieringa (1992). Turbulent kinetic energy k is calculated from I U using k = 1.5(I U U) 2. For z 0 = 0.5 m, the inlet longitudinal turbulence intensity (I U ) ranges from 29 % at pedestrian height (z = 1.75 m) to 5 % at gradient height. For z 0 = 1.0 m, I U ranges from 39 % (z = 1.75 m) to 8 % at gradient height. The turbulence dissipation rate ε = u* 3 /(κ(z + z 0 )), where z is the height coordinate, κ the von Karman constant (κ = 0.42) and u* the friction velocity. Zero static pressure is imposed at the outlet of the domain and the sides and top of the domain are modeled as slip walls (zero normal velocity and zero normal gradients of all variables). At the walls, the standard wall functions by Launder and Spalding (1974) are used, with the sand-grain roughness modification by Cebeci and Bradshaw (1977). The roughness is taken into account by modification of standard wall functions with appropriate values for the equivalent sand-grain roughness height k S and the roughness constant C S (Blocken et al., 2007). The 3D Reynolds-Averaged Navier-Stokes (RANS) equations are solved with the commercial CFD code Ansys Fluent 14 (Ansys Inc, 2009). The realizable k-ε model (Shih et al., 1995) is used to provide closure. This choice is based on earlier successful validation studies with this model (e.g. Blocken and Carmeliet 2008, Blocken et al. 2012). In addition, the use of this model will be validated further in this paper. Second-order discretization schemes are used for both the convective and viscous terms of the governing equations. The SIMPLE algorithm is used for pressure-velocity coupling and second order pressure interpolation is used. 3 ON-SITE WIND SPEED MEASUREMENTS On-site measurements were performed with 3D ultrasonic anemometers during two summer months at three measurement positions in the shopping street (at 4 m height) plus a reference position at the nearby Eindhoven University campus (at 44.6 m height). The measurement frequency at all positions is at least 1 Hz, and measurement data are averaged over 10 minutes to provide values of mean wind speed and wind direction. Only data with a mean wind speed at the reference position that exceeds 5 m/s is retained to exclude measurement values affected by thermal effects. In the CFD simulations these thermal effects are also not taken into account (as required by the Dutch Standard NEN 8100). Data sets of eight wind directions (φ ref ) were used for the comparison with the CFD simulations, these are 30, 180, 210, 240, 270, 300, 330 and 360 (degrees clockwise from North). For these wind directions, at least 10 measurement intervals could be used for the comparison, while for the other wind directions (e.g. 60, 90, 120 and 150 ) less than 10 measurement intervals remained. Only data within the interval [φ ref - 5 ; φ ref + 5 ] were attributed to a given wind direction φ ref. Figure 1. The area of interest in this study is the new shopping street Nieuwe Emmasingel (indicated in orange) in the city of Eindhoven.
3 4 COMPARISON OF CFD SIMULATIONS WITH ON-SITE MEASUREMENTS A comparison is made between simulated and measured wind speed amplification factors U mp /U ref,aud, where U mp is the wind speed at one of the measurement locations and U ref,aud is the wind speed at the reference location. Results for two of the eight selected wind directions are shown in Figure 2. For these two prevailing wind directions (240 and 270 degrees from north) the average difference between measured and simulated amplification factors is For all eight studied wind directions, the amplification factors show an average deviation of 0.15, which is considered a good agreement and which justifies the use of this computational model for the wind comfort study. Figure 2. Comparison of measured (γ m ) and simulated (γ sim ) amplification factors in the area of interest. 5 WIND COMFORT ASSESSMENT WITH THE DUTCH WIND NUISANCE STANDARD NEN8100 The Dutch wind nuisance standard (NEN 8100) applies a discomfort threshold for the hourly mean wind speed (U THR ) of 5 m/s for all types of activities. Depending on the exceedance probability P of the threshold wind speed, the code defines five quality classes of wind comfort A E (Table 1). These quality classes define a good, moderate or poor wind climate for the activities traversing, strolling and sitting (Willemsen and Wisse, 2007). To determine the exceedance probability in a practical case study, three steps have to be taken for each of the 12 wind directions: 1) Obtain pedestrian level wind speed amplification factors (γ = U/U ref,60m ) from the CFD simulations (see Figure 3 for wind directions 60 and 240 ). Note that these amplification factors differ from the amplification factors described in the section on comparing CFD simulations with measurements. 2) Convert threshold wind speed at pedestrian level to a threshold wind speed at a height of 60 m (U THR,60m = U THR /γ). In the Dutch standard, the comfort criterion has a threshold of U THR = 5 m/s. 3) Determine the percentage of time that the threshold value for the hourly mean wind speed at 60 m is exceeded according to the wind statistics of the location of interest. In this study, the wind statistics for the twelve wind directions are provided by the Dutch Practice Guideline NPR Table 1: Criteria for wind comfort according to the Dutch wind nuisance standard NEN 8100 (2006) P(U THR > 5 m/s Quality Class Activity (in % hours per year) Traversing Strolling Sitting < 2.5 A Good Good Good 2.5 5,0 B Good Good Moderate 5,0 10 C Good Moderate Poor D Moderate Poor Poor > 20 E Poor Poor Poor
4 Figure 3. Simulated pedestrian level (z=1.75 m) wind speed amplification factors (γ = U/U ref,60m ) for the wind direction 240 (left) and 60 (right) from North. 6 RESULTS Summing the percentage exceedances for all 12 wind directions, results in Figure 4a for the current situation. Here the annual exceedance probabilities for wind nuisance and the accompanying quality classes according to the Dutch Standard NEN 8100 are given. The map with wind classes at pedestrian level in the current situation (Figure 4b) shows rather large areas with quality class D around the corners of the tower. These areas have a moderate wind climate for traversing and a poor wind climate for both strolling and sitting. Because a shopping street is typically a place for strolling, measures should be taken to change the wind climate in these areas to be at least moderate for strolling (= quality class C or better). Figure 5 shows the simulated air volume flow rates (m 3 /s) in the current situation for a southwest wind. The circled values give the downstream air volume flow rate caused by the Admirant Tower. It can clearly be seen that most of the wind at street level at the foot of the Admirant is deviated down from the tower and is further directed through the adjacent streets. Because the Admirant Tower is clearly the main cause of the wind nuisance problem, a possible solution would be to attach a canopy to the tower. Therefore, as a remedial measure, different sizes of canopies attached to the tower on both the south-southwest and the east-southeast side are studied. Four different canopies ascending in size are shown in Figure 6. The figures also show the effect of these canopies to the exceedance probabilities of wind nuisance for wind direction 240. Note that since the exceedance probability is shown for just one wind direction, the color scale in Figure 6 (0 7%) differs from the color scale in Figure 4 (0 20%). Simulations show that pedestrian wind comfort will be improved very effectively with an 11.4 m high canopy on both sides of the tower that overlaps the whole distance from the Admirant Tower to the buildings on the opposite sides of the shopping streets. The wind is directed over the canopy and onwards over building rooftops, as illustrated in Figure 7. In addition, the wind is not directed to the north part of the shopping street because the canopy provides a short-circuit between the overpressure zone on the windward side of the tower and the underpressure zone at the leeward side. Another part of the solution is closing a pedestrian level opening at the northeast corner of the Admirant Tower to decrease local wind velocities at northeast wind directions.
5 With these solutions the wind quality classes in the walking area around the Admirant Tower become A and B (see Figure 8) while quality class C was foreseen as an already appropriate solution for this area. The wind climate is now expected to be good for traversing and strolling. Figure 4. Annual exceedance probabilities for wind nuisance and the accompanying quality class according to the Dutch Standard NEN 8100, in the current situation. Figure 5. Simulated volume flow rate (m 3 /s) at wind direction 240 around the Admirant Tower. Vertical circled volume flow rates at 4.5 m height and the horizontal volume flow rates through the streets are given. 7 DISCUSSION As mentioned in section 2, the choice of turbulence model was based on earlier validation studies and on the validation study in this paper. This paper did not include studies with other turbulence models, but further research could focus on the effects of the turbulence model on the resulting comfort classes. The same holds for the selection of the aerodynamic roughness lengths for the inlet profiles and the roughness height for the ground surface in the domain. Although it should be mentioned that the computational model in this study is very extensive, with many buildings surrounding the area of interest. This way, the surrounding buildings will have the largest impact on the flow approaching the area of interest, rather than the upstream aerodynamic roughness lengths. Although it is known that thermal effects are also important for wind comfort (e.g. Stathopoulos 2006, Metje et al. 2008), wind comfort and safety generally only refer to the mechanical effects of wind on
6 people (e.g., Lawson and Penwarden 1975, Willemsen and Wisse 2007). Also in the Dutch wind nuisance standard, only mechanical effects are considered. Further research and elaboration of the standard will be needed to include thermal effects into the comfort assessment procedure. 8 SUMMARY AND CONCLUSIONS CFD simulations in combination with the Dutch wind nuisance standard proved to be a useful approach in improving pedestrian wind comfort around a high-rise building in an. Firstly the whole-flow field data provided by CFD showed that the tower was the main cause of the wind nuisance problem, and secondly the use of CFD made it possible to implement different measures to prevent wind nuisance while keeping the boundary conditions the same. The quality of the simulations is ensured by: 1) a successful comparison with on-site measurements. The average difference between measured and simulated amplification factors (=U 4m /U ref,aud ) for two prevailing wind directions (240 and 270 ) is only 0.04 (see Figure 2). 2) the special care that is given to creating a high-quality and high-resolution grid, according to best practice guidelines, and to the assignment of boundary conditions. Simulations combined with local wind statistics show that the southwest wind directions contribute most to the annual wind nuisance at pedestrian level. For these wind directions the Admirant Tower deviates the wind down to pedestrian level, where the wind is further directed through the adjacent streets. Because the Admirant Tower is the main cause of the wind nuisance problem, a possible solution would be to attach a canopy to the tower above the shopping street area. Different tower canopy sizes and orientations are studied. This resulted in the advice to create an 11.4 m high canopy on both sides of the tower that overlaps the whole distance from the Admirant Tower to the buildings on the opposite sides of the shopping streets. Simulations show that the wind is directed over the canopy and onwards over building rooftops. For southwest wind the canopy provides a short-circuit between the overpressure zone on the windward side of the tower and the underpressure zone at the leeward side. Another part of the solution is closing a pedestrian level opening at the northeast corner of the Admirant Tower to decrease local wind velocities at northeast wind directions. With these solutions the wind quality classes in the walking area around the Admirant Tower become A and B (see Figure 8) while quality class C was foreseen as an already appropriate solution for this area. The wind climate is now expected to be good for traversing and strolling. REFERENCES Blocken, B., Stathopoulos, T., & Carmeliet, J CFD simulation of the atmospheric boundary layer: wall function problems. Atmospheric Environment, 41(2), Blocken, B., Carmeliet, J Pedestrian wind conditions at outdoor platforms in a high-rise apartment building: generic sub-configuration validation, wind comfort assessment and uncertainty issues. Wind and Structures, 11(1), Blocken, B., Janssen, W.D., & van Hooff, T CFD simulation for pedestrian wind comfort and wind safety in s: General decision framework and case study for the Eindhoven University campus. Environmental Modelling & Software, 30, Cebeci, T., & Bradshaw, P Momentum transfer in boundary layers, Hemisphere Publishing Corporation, New York. Ansys Inc., Ansys Fluent 12.0 User s Guide. Ansys Inc., Franke, J., Hellsten, A., Schlünzen, H., & Carissimo, B Best practice guideline for the CFD simulation of flows in the urban environment. COST 732: Quality Assurance and Improvement of Microscale Meteorological Models. Janssen, W.D., Blocken, B., & van Hooff T Pedestrian wind comfort around buildings: comparison of wind comfort criteria based on whole-flow field data for a complex case study. Building and Environment 59(1),
7 Figure 6. Percentage of hours per year that a threshold wind speed of 5 m/s is exceeded for four canopies attached to the Admirant Tower for a wind direction of 240. Figure 7. Pathlines of wind flow from a wind direction of 240. a) In the current situation the tower deviates the wind down to pedestrian level while b) in the new situation the wind is directed over the building rooftops.
8 Figure 8. Wind climate quality classes NEN 8100 (A=good, E=poor) in a) the current situation and b) the new situation with a large canopy. Launder, B.E., & Spalding D.B The numerical computation of turbulent flows. Computer Methods in Applied Mechanics and Engineering, 3, Lawson, T.V., Penwarden, A.D., The effects of wind on people in the vicinity of buildings, Proceedings 4th International Conference on Wind Effects on Buildings and Structures, Cambridge University Press, Heathrow, pp Metje, N., Sterling, M., Baker, C.J., Pedestrian comfort using clothing values and body temperatures. Journal of Wind Engineering and Industrial Aerodynamics, 96(4), NEN Application of mean hourly wind speed statistics for the Netherlands. NPR 6097:2006. Dutch Practice Guideline. NEN Wind comfort and wind danger in the built environment. NEN Dutch Standard. Richards, P.J., Mallison G.D., McMillan D., & Li Y.F Pedestrian level wind speeds in downtown Auckland. Wind and Structures, 5(2 4), Shih, T.H., Liou, W.W., Shabbir, A., & Zhu, J A new k- eddy-viscosity model for high Reynolds number turbulent flows model development and validation. Computers & Fluids, 24 (3), Stathopoulos, T., Pedestrian level winds and outdoor human comfort. Journal of Wind Engineering and Industrial Aerodynamics, 94(11), Tominaga, Y., Mochida, A., Yoshie, R., Kataoka, H., Nozu, T., Yoshikawa, M., & Shirasawa, T AIJ guidelines for practical applications of CFD to pedestrian wind environment around buildings. Journal of Wind Engineering and Industrial Aerodynamics, 96(10-11), van Hooff, T., & Blocken, B Coupled urban wind flow and indoor natural ventilation modeling on a high-resolution grid: A case study for the Amsterdam ArenA stadium. Environmental Modeling & Software, 25(1), Wieringa, J Updating the Davenport roughness classification. Journal of Wind Engineering and. Industrial Aerodynamics, 41 44, Willemsen, E., & Wisse, J.A Design for wind comfort in The Netherlands: Procedures, criteria and open research issues. Journal of Wind Engineering and Industrial Aerodynamics, 95 (9-11),
Improving pedestrian wind comfort around a high rise building in an urban area: a case study by CFD simulations and on-site measurements
 Improving pedestrian wind comfort around a high rise building in an urban area: a case study by CFD simulations and on-site measurements WD Janssen, B Blocken, and T van Hooff Unit Building Physics and
Improving pedestrian wind comfort around a high rise building in an urban area: a case study by CFD simulations and on-site measurements WD Janssen, B Blocken, and T van Hooff Unit Building Physics and
a high-rise (78 m) building in the city of Antwerp. CFD simulations are performed for the building with and without second-skin facade concept impleme
 The Seventh International Colloquium on Bluff Body Aerodynamics and Applications (BBAA7) Shanghai, China; September 2-6, 2012 CFD analysis of wind comfort on high-rise building balconies: validation and
The Seventh International Colloquium on Bluff Body Aerodynamics and Applications (BBAA7) Shanghai, China; September 2-6, 2012 CFD analysis of wind comfort on high-rise building balconies: validation and
Numerical analysis of surface pressure coefficients for a building with balconies
 Numerical analysis of surface pressure coefficients for a building with balconies Montazeri H., Blocken B. Building Physics and Services, Eindhoven University of Technology, P.O. box 513, 5600 MB Eindhoven,
Numerical analysis of surface pressure coefficients for a building with balconies Montazeri H., Blocken B. Building Physics and Services, Eindhoven University of Technology, P.O. box 513, 5600 MB Eindhoven,
Pedestrian wind comfort around buildings: comparison of wind comfort criteria based on whole-flow field data for a complex case study
 Accepted for publication in Building and Environment, October 25, 2012 Pedestrian wind comfort around buildings: comparison of wind comfort criteria based on whole-flow field data for a complex case study
Accepted for publication in Building and Environment, October 25, 2012 Pedestrian wind comfort around buildings: comparison of wind comfort criteria based on whole-flow field data for a complex case study
Windsimulaties op de meteorologische microschaal
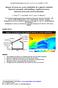
 Windsimulaties op de meteorologische microschaal dr.ir. Twan van Hooff prof.dr.ir. Bert Blocken Building Physics Section KU Leuven Unit Building Physics and Services TU/e 2015 Twan van Hooff All Rights
Windsimulaties op de meteorologische microschaal dr.ir. Twan van Hooff prof.dr.ir. Bert Blocken Building Physics Section KU Leuven Unit Building Physics and Services TU/e 2015 Twan van Hooff All Rights
Accepted for publication in Journal of Wind Engineering and Industrial Aerodynamics, 20 June 2009
 Accepted for publication in Journal of Wind Engineering and Industrial Aerodynamics, 20 June 2009 Pedestrian wind comfort around a large football stadium in an urban environment: CFD simulation, validation
Accepted for publication in Journal of Wind Engineering and Industrial Aerodynamics, 20 June 2009 Pedestrian wind comfort around a large football stadium in an urban environment: CFD simulation, validation
The evolution of the application of CFD on pedestrian wind comfort in engineering practice, a validation study
 EACWE 5 Florence, Italy 19 th 23 rd July 2009 Flying Sphere image Museo Ideale L. Da Vinci The evolution of the application of CFD on pedestrian wind comfort in engineering practice, a validation study
EACWE 5 Florence, Italy 19 th 23 rd July 2009 Flying Sphere image Museo Ideale L. Da Vinci The evolution of the application of CFD on pedestrian wind comfort in engineering practice, a validation study
COMPARISONS OF COMPUTATIONAL FLUID DYNAMICS AND
 The Seventh Asia-Pacific Conference on Wind Engineering, November 8-12, 2009, Taipei, Taiwan COMPARISONS OF COMPUTATIONAL FLUID DYNAMICS AND WIND TUNNEL EXPERIMENTS FOR PEDESTRIAN WIND ENVIRONMENTS Chin-Hsien
The Seventh Asia-Pacific Conference on Wind Engineering, November 8-12, 2009, Taipei, Taiwan COMPARISONS OF COMPUTATIONAL FLUID DYNAMICS AND WIND TUNNEL EXPERIMENTS FOR PEDESTRIAN WIND ENVIRONMENTS Chin-Hsien
Surrounding buildings and wind pressure distribution on a high rise building
 Surrounding buildings and wind pressure distribution on a high rise building Conference or Workshop Item Accepted Version Luo, Z. (2008) Surrounding buildings and wind pressure distribution on a high rise
Surrounding buildings and wind pressure distribution on a high rise building Conference or Workshop Item Accepted Version Luo, Z. (2008) Surrounding buildings and wind pressure distribution on a high rise
Building Physics and Systems, Technische Universiteit Eindhoven, P.O. box 513, 5600 MB Eindhoven, the Netherlands
 PRE-PRINT of the article: Blocken B, Carmeliet J. 2008. Pedestrian wind conditions at outdoor platforms in a high-rise apartment building: generic sub-configuration validation, wind comfort assessment
PRE-PRINT of the article: Blocken B, Carmeliet J. 2008. Pedestrian wind conditions at outdoor platforms in a high-rise apartment building: generic sub-configuration validation, wind comfort assessment
Assessment of pedestrian wind environment of high-rise complex using CFD simulation
 Assessment of pedestrian wind environment of high-rise complex using CFD simulation Hyungkeun Kim Researcher Department of architectural engineering, Yonsei University vickim@yonsei.ac.kr Taeyeon Kim Professor
Assessment of pedestrian wind environment of high-rise complex using CFD simulation Hyungkeun Kim Researcher Department of architectural engineering, Yonsei University vickim@yonsei.ac.kr Taeyeon Kim Professor
Many elite cyclists therefore try to optimise their position for drag by means of field tests or wind tunnel tests. More recently, also Computational
 The Seventh International Colloquium on Bluff Body Aerodynamics and Applications (BBAA7) Shanghai, China; September 2-6, 2012 RANS and LES simulations of the interference drag of two cyclists B. Blocken
The Seventh International Colloquium on Bluff Body Aerodynamics and Applications (BBAA7) Shanghai, China; September 2-6, 2012 RANS and LES simulations of the interference drag of two cyclists B. Blocken
APPLICATION OF COMPUTATIONAL FLUID DYNAMICS (CFD) IN WIND ANALYSIS OF TALL BUILDINGS. Damith Mohotti, Priyan Mendis, Tuan Ngo
 APPLICATION OF COMPUTATIONAL FLUID DYNAMICS (CFD) IN WIND ANALYSIS OF TALL BUILDINGS Damith Mohotti, Priyan Mendis, Tuan Ngo Department of Infrastructures Engineering, The University of Melbourne, Victoria,
APPLICATION OF COMPUTATIONAL FLUID DYNAMICS (CFD) IN WIND ANALYSIS OF TALL BUILDINGS Damith Mohotti, Priyan Mendis, Tuan Ngo Department of Infrastructures Engineering, The University of Melbourne, Victoria,
Wind tunnel test and numerical simulation of wind pressure on a high-rise building
 Journal of Chongqing University (English Edition) [ISSN 1671-8224] Vol. 9 No. 1 March 2010 Article ID: 1671-8224(2010)01-0047-07 To cite this article: AL ZOUBI Feras, LI Zheng-liang, WEI Qi-ke, SUN Yi.
Journal of Chongqing University (English Edition) [ISSN 1671-8224] Vol. 9 No. 1 March 2010 Article ID: 1671-8224(2010)01-0047-07 To cite this article: AL ZOUBI Feras, LI Zheng-liang, WEI Qi-ke, SUN Yi.
Impact of eaves on cross-ventilation of a generic isolated leeward sawtooth roof building: windward eaves, leeward eaves and eaves inclination
 Accepted for publication in Building and Environment on May 11, 2015 Impact of eaves on cross-ventilation of a generic isolated leeward sawtooth roof building: windward eaves, leeward eaves and eaves inclination
Accepted for publication in Building and Environment on May 11, 2015 Impact of eaves on cross-ventilation of a generic isolated leeward sawtooth roof building: windward eaves, leeward eaves and eaves inclination
WIND FLOW CHARACTERISTICS AROUND ROOFTOP SOLAR ARRAY - A NUMERICAL STUDY
 The Eighth Asia-Pacific Conference on Wind Engineering, December 10 14, 2013, Chennai, India WIND FLOW CHARACTERISTICS AROUND ROOFTOP SOLAR ARRAY - A NUMERICAL STUDY D.Ghosh 1, A. K. Mittal 2, S. Behera
The Eighth Asia-Pacific Conference on Wind Engineering, December 10 14, 2013, Chennai, India WIND FLOW CHARACTERISTICS AROUND ROOFTOP SOLAR ARRAY - A NUMERICAL STUDY D.Ghosh 1, A. K. Mittal 2, S. Behera
RESEARCH ON MEASUREMENT AND SIMULATION OF THE WIND ENVIRON- MENT AROUND BUILDINGS IN CAMPUS
 Eleventh International IBPSA Conference Glasgow, Scotland July 27-30, 2009 RESEARCH ON MEASUREMENT AND SIMULATION OF THE WIND ENVIRON- MENT AROUND BUILDINGS IN CAMPUS Bing Wang 1, Borong Lin 1,* 1Deparment
Eleventh International IBPSA Conference Glasgow, Scotland July 27-30, 2009 RESEARCH ON MEASUREMENT AND SIMULATION OF THE WIND ENVIRON- MENT AROUND BUILDINGS IN CAMPUS Bing Wang 1, Borong Lin 1,* 1Deparment
Validating CFD Simulation Results: Wind flow around a surface mounted cube in a turbulent channel flow
 Validating CFD Simulation Results: Wind flow around a surface mounted cube in a turbulent channel flow ISLAM ABOHELA 1, NEVEEN HAMZA 1, STEVEN DUDEK 1 1 School of Architecture, Planning and Landscape,
Validating CFD Simulation Results: Wind flow around a surface mounted cube in a turbulent channel flow ISLAM ABOHELA 1, NEVEEN HAMZA 1, STEVEN DUDEK 1 1 School of Architecture, Planning and Landscape,
Effect of Diameter on the Aerodynamics of Sepaktakraw Balls, A Computational Study
 ISSN 1750-9823 (print) International Journal of Sports Science and Engineering Vol. 03 (2009) No. 01, pp. 017-021 Effect of Diameter on the Aerodynamics of Sepaktakraw Balls, A Computational Study Zahari
ISSN 1750-9823 (print) International Journal of Sports Science and Engineering Vol. 03 (2009) No. 01, pp. 017-021 Effect of Diameter on the Aerodynamics of Sepaktakraw Balls, A Computational Study Zahari
Full scale measurements and simulations of the wind speed in the close proximity of the building skin
 Full scale measurements and simulations of the wind speed in the close proximity of the building skin Radoslav Ponechal 1,* and Peter Juras 1 1 University of Zilina, Faculty of Civil Engineering, Department
Full scale measurements and simulations of the wind speed in the close proximity of the building skin Radoslav Ponechal 1,* and Peter Juras 1 1 University of Zilina, Faculty of Civil Engineering, Department
Modelling the Output of a Flat-Roof Mounted Wind Turbine with an Edge Mounted Lip
 Modelling the Output of a Flat-Roof Mounted Wind Turbine with an Edge Mounted Lip S. J. Wylie 1, S. J. Watson 1, D. G. Infield 2 1 Centre for Renewable Energy Systems Technology, Department of Electronic
Modelling the Output of a Flat-Roof Mounted Wind Turbine with an Edge Mounted Lip S. J. Wylie 1, S. J. Watson 1, D. G. Infield 2 1 Centre for Renewable Energy Systems Technology, Department of Electronic
Wind pressure coefficient determination for greenhouses built in a reclaimed land using CFD technique
 Ref: 1064 Wind pressure coefficient determination for greenhouses built in a reclaimed land using CFD technique Hyun-seob Hwang and In-bok Lee, Department of Rural Systems Engineering, Research Institute
Ref: 1064 Wind pressure coefficient determination for greenhouses built in a reclaimed land using CFD technique Hyun-seob Hwang and In-bok Lee, Department of Rural Systems Engineering, Research Institute
Wind Flow Model of Area Surrounding the Case Western Reserve University Wind Turbine
 Wind Flow Model of Area Surrounding the Case Western Reserve University Wind Turbine Matheus C. Fernandes 1, David H. Matthiesen PhD *2 1 Case Western Reserve University Dept. of Mechanical Engineering,
Wind Flow Model of Area Surrounding the Case Western Reserve University Wind Turbine Matheus C. Fernandes 1, David H. Matthiesen PhD *2 1 Case Western Reserve University Dept. of Mechanical Engineering,
Measurement and simulation of the flow field around a triangular lattice meteorological mast
 Measurement and simulation of the flow field around a triangular lattice meteorological mast Matthew Stickland 1, Thomas Scanlon 1, Sylvie Fabre 1, Andrew Oldroyd 2 and Detlef Kindler 3 1. Department of
Measurement and simulation of the flow field around a triangular lattice meteorological mast Matthew Stickland 1, Thomas Scanlon 1, Sylvie Fabre 1, Andrew Oldroyd 2 and Detlef Kindler 3 1. Department of
AIRFLOW GENERATION IN A TUNNEL USING A SACCARDO VENTILATION SYSTEM AGAINST THE BUOYANCY EFFECT PRODUCED BY A FIRE
 - 247 - AIRFLOW GENERATION IN A TUNNEL USING A SACCARDO VENTILATION SYSTEM AGAINST THE BUOYANCY EFFECT PRODUCED BY A FIRE J D Castro a, C W Pope a and R D Matthews b a Mott MacDonald Ltd, St Anne House,
- 247 - AIRFLOW GENERATION IN A TUNNEL USING A SACCARDO VENTILATION SYSTEM AGAINST THE BUOYANCY EFFECT PRODUCED BY A FIRE J D Castro a, C W Pope a and R D Matthews b a Mott MacDonald Ltd, St Anne House,
AERODYNAMIC FEATURES AS AUXILIARY ARCHITECTURE
 N. Gu, S. Watanabe, H. Erhan, M. Hank Haeusler, W. Huang, R. Sosa (eds.), Rethinking Comprehensive Design: Speculative Counterculture, Proceedings of the 19th International Conference on Computer- Aided
N. Gu, S. Watanabe, H. Erhan, M. Hank Haeusler, W. Huang, R. Sosa (eds.), Rethinking Comprehensive Design: Speculative Counterculture, Proceedings of the 19th International Conference on Computer- Aided
Wind Microclimate Assessment
 Australian Catholic University Pedestrian comfort at 115B Victoria Parade Pedestrian comfort at 115B Victoria Parade Quality Information Document 60519200 Client: Australian Catholic University ABN: 15050192660
Australian Catholic University Pedestrian comfort at 115B Victoria Parade Pedestrian comfort at 115B Victoria Parade Quality Information Document 60519200 Client: Australian Catholic University ABN: 15050192660
OPTIMIZING THE LENGTH OF AIR SUPPLY DUCT IN CROSS CONNECTIONS OF GOTTHARD BASE TUNNEL. Rehan Yousaf 1, Oliver Scherer 1
 OPTIMIZING THE LENGTH OF AIR SUPPLY DUCT IN CROSS CONNECTIONS OF GOTTHARD BASE TUNNEL Rehan Yousaf 1, Oliver Scherer 1 1 Pöyry Infra Ltd, Zürich, Switzerland ABSTRACT Gotthard Base Tunnel with its 57 km
OPTIMIZING THE LENGTH OF AIR SUPPLY DUCT IN CROSS CONNECTIONS OF GOTTHARD BASE TUNNEL Rehan Yousaf 1, Oliver Scherer 1 1 Pöyry Infra Ltd, Zürich, Switzerland ABSTRACT Gotthard Base Tunnel with its 57 km
CFD simulation of wind-induced pressure coefficients on buildings with and without balconies: validation and sensitivity analysis
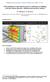 Building and Environment, Volume 60, February 2013, Pages 137-149 CFD simulation of wind-induced pressure coefficients on buildings with and without balconies: validation and sensitivity analysis H. Montazeri,
Building and Environment, Volume 60, February 2013, Pages 137-149 CFD simulation of wind-induced pressure coefficients on buildings with and without balconies: validation and sensitivity analysis H. Montazeri,
Available online at ScienceDirect. Procedia Engineering 161 (2016 )
 Available online at www.sciencedirect.com ScienceDirect Procedia Engineering 161 (216 ) 1845 1851 World Multidisciplinary Civil Engineering-Architecture-Urban Planning Symposium 216, WMCAUS 216 Experimental
Available online at www.sciencedirect.com ScienceDirect Procedia Engineering 161 (216 ) 1845 1851 World Multidisciplinary Civil Engineering-Architecture-Urban Planning Symposium 216, WMCAUS 216 Experimental
Aspects of Using CFD for Wind Comfort Modeling Around Tall Buildings
 8 th International Congress on Advances in Civil Engineering, 15-17 September 2008 Eastern Mediterranean University, Famagusta, North Cyprus Aspects of Using CFD for Wind Comfort Modeling Around Tall Buildings
8 th International Congress on Advances in Civil Engineering, 15-17 September 2008 Eastern Mediterranean University, Famagusta, North Cyprus Aspects of Using CFD for Wind Comfort Modeling Around Tall Buildings
Centre for Offshore Renewable Energy Engineering, School of Energy, Environment and Agrifood, Cranfield University, Cranfield, MK43 0AL, UK 2
 Fluid Structure Interaction Modelling of A Novel 10MW Vertical-Axis Wind Turbine Rotor Based on Computational Fluid Dynamics and Finite Element Analysis Lin Wang 1*, Athanasios Kolios 1, Pierre-Luc Delafin
Fluid Structure Interaction Modelling of A Novel 10MW Vertical-Axis Wind Turbine Rotor Based on Computational Fluid Dynamics and Finite Element Analysis Lin Wang 1*, Athanasios Kolios 1, Pierre-Luc Delafin
CFD Analysis ofwind Turbine Airfoil at Various Angles of Attack
 IOSR Journal of Mechanical and Civil Engineering (IOSR-JMCE) e-issn: 2278-1684,p-ISSN: 2320-334X, Volume 13, Issue 4 Ver. II (Jul. - Aug. 2016), PP 18-24 www.iosrjournals.org CFD Analysis ofwind Turbine
IOSR Journal of Mechanical and Civil Engineering (IOSR-JMCE) e-issn: 2278-1684,p-ISSN: 2320-334X, Volume 13, Issue 4 Ver. II (Jul. - Aug. 2016), PP 18-24 www.iosrjournals.org CFD Analysis ofwind Turbine
AIRFLOW AND TEMPERATURE FIELD CALCULATIONS FOR WINTER SPORTS FACILITIES
 AIRFLOW AND TEMPERATURE FIELD CALCULATIONS FOR WINTER SPORTS FACILITIES Andrea Frisque* Stantec Consulting, Vancouver BC V6B6A3, Canada Rowan, Williams, Davies & Irwin (RWDI), Vancouver, BC, V5Z 1K5, Canada**
AIRFLOW AND TEMPERATURE FIELD CALCULATIONS FOR WINTER SPORTS FACILITIES Andrea Frisque* Stantec Consulting, Vancouver BC V6B6A3, Canada Rowan, Williams, Davies & Irwin (RWDI), Vancouver, BC, V5Z 1K5, Canada**
Numerical Simulation of Wind Effect on a Rooftop Solar Array
 J. Energy Power Sources Vol. 2, No. 8, 2015, pp. 317-322 Received: July 1, 2015, Published: August 30, 2015 Journal of Energy and Power Sources www.ethanpublishing.com Numerical Simulation of Wind Effect
J. Energy Power Sources Vol. 2, No. 8, 2015, pp. 317-322 Received: July 1, 2015, Published: August 30, 2015 Journal of Energy and Power Sources www.ethanpublishing.com Numerical Simulation of Wind Effect
The Performance-based Wind Environment Analysis in Campus -Taking University of Shanghai for Science and Technology as an Example
 Journal of Civil Engineering and Construction 2:2 (2013) The Performance-based Wind Environment Analysis in Campus -Taking University of Shanghai for Science and Technology as an Example Miao Ye 1,a, Li
Journal of Civil Engineering and Construction 2:2 (2013) The Performance-based Wind Environment Analysis in Campus -Taking University of Shanghai for Science and Technology as an Example Miao Ye 1,a, Li
A study of heat transfer effects on air pollution dispersion in street canyons by numerical simulations
 A study of heat transfer effects on air pollution dispersion in street canyons by numerical simulations N. Moussiopoulos, I. Ossanlis and Ph. Barmpas Aristotle University Thessaloniki, Greece MIMO 3D,
A study of heat transfer effects on air pollution dispersion in street canyons by numerical simulations N. Moussiopoulos, I. Ossanlis and Ph. Barmpas Aristotle University Thessaloniki, Greece MIMO 3D,
Windcube FCR measurements
 Windcube FCR measurements Principles, performance and recommendations for use of the Flow Complexity Recognition (FCR) algorithm for the Windcube ground-based Lidar Summary: As with any remote sensor,
Windcube FCR measurements Principles, performance and recommendations for use of the Flow Complexity Recognition (FCR) algorithm for the Windcube ground-based Lidar Summary: As with any remote sensor,
Determination of the wind pressure distribution on the facade of the triangularly shaped high-rise building structure
 Determination of the wind pressure distribution on the facade of the triangularly shaped high-rise building structure Norbert Jendzelovsky 1,*, Roland Antal 1 and Lenka Konecna 1 1 STU in Bratislava, Faculty
Determination of the wind pressure distribution on the facade of the triangularly shaped high-rise building structure Norbert Jendzelovsky 1,*, Roland Antal 1 and Lenka Konecna 1 1 STU in Bratislava, Faculty
NUMERICAL SIMULATION OF STATIC INTERFERENCE EFFECTS FOR SINGLE BUILDINGS GROUP
 NUMERICAL SIMULATION OF STATIC INTERFERENCE EFFECTS FOR SINGLE BUILDINGS GROUP Xing-qian Peng, Chun-hui Zhang 2 and Chang-gui Qiao 2 Professor, College of Civil Engineering, Huaqiao University, Quanzhou,
NUMERICAL SIMULATION OF STATIC INTERFERENCE EFFECTS FOR SINGLE BUILDINGS GROUP Xing-qian Peng, Chun-hui Zhang 2 and Chang-gui Qiao 2 Professor, College of Civil Engineering, Huaqiao University, Quanzhou,
Numerical Analysis of Wind loads on Tapered Shape Tall Buildings
 IJSTE - International Journal of Science Technology & Engineering Volume 1 Issue 11 May 2015 ISSN (online): 2349-784X Numerical Analysis of Wind loads on Tapered Shape Tall Buildings Ashwin G Hansora Assistant
IJSTE - International Journal of Science Technology & Engineering Volume 1 Issue 11 May 2015 ISSN (online): 2349-784X Numerical Analysis of Wind loads on Tapered Shape Tall Buildings Ashwin G Hansora Assistant
Cross Comparisons of CFD Prediction for Wind Environment at Pedestrian Level around Buildings
 Cross Comparisons of CFD Prediction for Wind Environment at Pedestrian Level around Buildings Part Comparison of Results for Flow-field around a High-rise Building Located in Surrounding City Blocks Ryuichiro
Cross Comparisons of CFD Prediction for Wind Environment at Pedestrian Level around Buildings Part Comparison of Results for Flow-field around a High-rise Building Located in Surrounding City Blocks Ryuichiro
Smooth hill validation in FUROW s wind resource module using OpenFOAM
 in for Wind flow Numerical Smooth hill validation in s wind resource module using 5 th Symposium on in Wind Energy (SOWE 2017), Javier Magdalena Saiz, José Marín Palacios, Jesús Matesanz García and Laura
in for Wind flow Numerical Smooth hill validation in s wind resource module using 5 th Symposium on in Wind Energy (SOWE 2017), Javier Magdalena Saiz, José Marín Palacios, Jesús Matesanz García and Laura
Pedestrian Wind Environment around Buildings: Literature Review and Practical Examples
 Pedestrian Wind Environment around Buildings: Literature Review and Practical Examples BERT BLOCKEN 1, * AND JAN CARMELIET 1,2 1 Laboratory of Building Physics Department of Civil Engineering Katholieke
Pedestrian Wind Environment around Buildings: Literature Review and Practical Examples BERT BLOCKEN 1, * AND JAN CARMELIET 1,2 1 Laboratory of Building Physics Department of Civil Engineering Katholieke
CFD SIMULATIONS OF GAS DISPERSION IN VENTILATED ROOMS
 CFD SIMULATIONS OF GAS DISPERSION IN VENTILATED ROOMS T. Gélain, C. Prévost Institut de Radioprotection et de Sûreté Nucléaire (IRSN), Saclay, France Abstract In order to better understand the risks due
CFD SIMULATIONS OF GAS DISPERSION IN VENTILATED ROOMS T. Gélain, C. Prévost Institut de Radioprotection et de Sûreté Nucléaire (IRSN), Saclay, France Abstract In order to better understand the risks due
Numerical investigation on the effect of overhang roof around rural house
 Numerical investigation on the effect of overhang roof around rural house *Taksiah A. Majid 1), Shaharudin Shah Zaini 2), Mohd Azmi Ismail 3), Siti Noratikah Che Deraman 4) and Jing Lin Poon 5) 1), 2),
Numerical investigation on the effect of overhang roof around rural house *Taksiah A. Majid 1), Shaharudin Shah Zaini 2), Mohd Azmi Ismail 3), Siti Noratikah Che Deraman 4) and Jing Lin Poon 5) 1), 2),
Influence of rounding corners on unsteady flow and heat transfer around a square cylinder
 Influence of rounding corners on unsteady flow and heat transfer around a square cylinder S. K. Singh Deptt. of Mech. Engg., M. B. M. Engg. College / J. N. V. University, Jodhpur, Rajasthan, India Abstract
Influence of rounding corners on unsteady flow and heat transfer around a square cylinder S. K. Singh Deptt. of Mech. Engg., M. B. M. Engg. College / J. N. V. University, Jodhpur, Rajasthan, India Abstract
Wind effects on air-cooled condenser performance
 Wind effects on air-cooled condenser performance LEILA BORGHEI RAMIN HAGHIGHI KHOSHKHOO R&D department Mechanical engineering department Monenco Iran Consultant Engineers Power and Water University of
Wind effects on air-cooled condenser performance LEILA BORGHEI RAMIN HAGHIGHI KHOSHKHOO R&D department Mechanical engineering department Monenco Iran Consultant Engineers Power and Water University of
COMPUTATIONAL FLOW MODEL OF WESTFALL'S LEADING TAB FLOW CONDITIONER AGM-09-R-08 Rev. B. By Kimbal A. Hall, PE
 COMPUTATIONAL FLOW MODEL OF WESTFALL'S LEADING TAB FLOW CONDITIONER AGM-09-R-08 Rev. B By Kimbal A. Hall, PE Submitted to: WESTFALL MANUFACTURING COMPANY September 2009 ALDEN RESEARCH LABORATORY, INC.
COMPUTATIONAL FLOW MODEL OF WESTFALL'S LEADING TAB FLOW CONDITIONER AGM-09-R-08 Rev. B By Kimbal A. Hall, PE Submitted to: WESTFALL MANUFACTURING COMPANY September 2009 ALDEN RESEARCH LABORATORY, INC.
Welke daalhouding is het meest aerodynamisch?
 Welke daalhouding is het meest aerodynamisch? Bert Blocken a,b a Faculteit Bouwkunde, Technische Universiteit Eindhoven, Nederland b Departement Burgerlijke Bouwkunde, KU Leuven, België Welke daalhouding
Welke daalhouding is het meest aerodynamisch? Bert Blocken a,b a Faculteit Bouwkunde, Technische Universiteit Eindhoven, Nederland b Departement Burgerlijke Bouwkunde, KU Leuven, België Welke daalhouding
Wind tunnel tests of a non-typical stadium roof
 Wind tunnel tests of a non-typical stadium roof G. Bosak 1, A. Flaga 1, R. Kłaput 1 and Ł. Flaga 1 1 Wind Engineering Laboratory, Cracow University of Technology, 31-864 Cracow, Poland. liwpk@windlab.pl
Wind tunnel tests of a non-typical stadium roof G. Bosak 1, A. Flaga 1, R. Kłaput 1 and Ł. Flaga 1 1 Wind Engineering Laboratory, Cracow University of Technology, 31-864 Cracow, Poland. liwpk@windlab.pl
SCIENCE & TECHNOLOGY
 Pertanika J. Sci. & Technol. 25 (S): 227-238 (2017) SCIENCE & TECHNOLOGY Journal homepage: http://www.pertanika.upm.edu.my/ CFD Analysis on Indoor Temperature and Velocity: Effects of Incident Wind Angle
Pertanika J. Sci. & Technol. 25 (S): 227-238 (2017) SCIENCE & TECHNOLOGY Journal homepage: http://www.pertanika.upm.edu.my/ CFD Analysis on Indoor Temperature and Velocity: Effects of Incident Wind Angle
Numerical Tools Dedicated to Wind Engineering in Large Urban Area
 World Journal of Engineering and Technology, 2016, 4, 22-29 http://www.scirp.org/journal/wjet ISSN Online: 2331-4249 ISSN Print: 2331-4222 Numerical Tools Dedicated to Wind Engineering in Large Urban Area
World Journal of Engineering and Technology, 2016, 4, 22-29 http://www.scirp.org/journal/wjet ISSN Online: 2331-4249 ISSN Print: 2331-4222 Numerical Tools Dedicated to Wind Engineering in Large Urban Area
Wind resource assessment over a complex terrain covered by forest using CFD simulations of neutral atmospheric boundary layer with OpenFOAM
 Wind resource assessment over a complex terrain covered by forest using CFD simulations of neutral atmospheric boundary layer with OpenFOAM Nikolaos Stergiannis nstergiannis.com nikolaos.stergiannis@vub.ac.be
Wind resource assessment over a complex terrain covered by forest using CFD simulations of neutral atmospheric boundary layer with OpenFOAM Nikolaos Stergiannis nstergiannis.com nikolaos.stergiannis@vub.ac.be
CFD Study of Solid Wind Tunnel Wall Effects on Wing Characteristics
 Indian Journal of Science and Technology, Vol 9(45), DOI :10.17485/ijst/2016/v9i45/104585, December 2016 ISSN (Print) : 0974-6846 ISSN (Online) : 0974-5645 CFD Study of Solid Wind Tunnel Wall Effects on
Indian Journal of Science and Technology, Vol 9(45), DOI :10.17485/ijst/2016/v9i45/104585, December 2016 ISSN (Print) : 0974-6846 ISSN (Online) : 0974-5645 CFD Study of Solid Wind Tunnel Wall Effects on
Wind pressure on a single building immersed in a low jet wind profile
 Wind pressure on a single building immersed in a low jet wind profile Conference or Workshop Item Accepted Version Luo, Z. and Hang, J. (2013) Wind pressure on a single building immersed in a low jet wind
Wind pressure on a single building immersed in a low jet wind profile Conference or Workshop Item Accepted Version Luo, Z. and Hang, J. (2013) Wind pressure on a single building immersed in a low jet wind
Numerical simulation of topographic effects on wind flow fields over complex terrain
 The Eighth Asia-Pacific Conference on Wind Engineering, December 10 14, 2013, Chennai, India Numerical simulation of topographic effects on wind flow fields over complex terrain B.W. Yan 1, Q.S. LI 2,
The Eighth Asia-Pacific Conference on Wind Engineering, December 10 14, 2013, Chennai, India Numerical simulation of topographic effects on wind flow fields over complex terrain B.W. Yan 1, Q.S. LI 2,
CFD ANALYSIS AND COMPARISON USING ANSYS AND STAR-CCM+ OF MODEL AEROFOIL SELIG 1223
 International Journal of Mechanical Engineering and Technology (IJMET) Volume 8, Issue 11, November 2017, pp. 312 318, Article ID: IJMET_08_11_034 Available online at http://www.iaeme.com/ijmet/issues.asp?jtype=ijmet&vtype=8&itype=11
International Journal of Mechanical Engineering and Technology (IJMET) Volume 8, Issue 11, November 2017, pp. 312 318, Article ID: IJMET_08_11_034 Available online at http://www.iaeme.com/ijmet/issues.asp?jtype=ijmet&vtype=8&itype=11
Ermenek Dam and HEPP: Spillway Test & 3D Numeric-Hydraulic Analysis of Jet Collision
 Ermenek Dam and HEPP: Spillway Test & 3D Numeric-Hydraulic Analysis of Jet Collision J.Linortner & R.Faber Pöyry Energy GmbH, Turkey-Austria E.Üzücek & T.Dinçergök General Directorate of State Hydraulic
Ermenek Dam and HEPP: Spillway Test & 3D Numeric-Hydraulic Analysis of Jet Collision J.Linortner & R.Faber Pöyry Energy GmbH, Turkey-Austria E.Üzücek & T.Dinçergök General Directorate of State Hydraulic
FLOW CONSIDERATIONS IN INDUSTRIAL SILENCER DESIGN
 FLOW CONSIDERATIONS IN INDUSTRIAL SILENCER DESIGN George Feng, Kinetics Noise Control, Inc., 3570 Nashua Drive, Mississauga, Ontario Vadim Akishin, Kinetics Noise Control, Inc., 3570 Nashua Drive, Mississauga,
FLOW CONSIDERATIONS IN INDUSTRIAL SILENCER DESIGN George Feng, Kinetics Noise Control, Inc., 3570 Nashua Drive, Mississauga, Ontario Vadim Akishin, Kinetics Noise Control, Inc., 3570 Nashua Drive, Mississauga,
Forest Winds in Complex Terrain
 Forest Winds in Complex Terrain Ilda Albuquerque 1 Contents Project Description Motivation Forest Complex Terrain Forested Complex Terrain 2 Project Description WAUDIT (Wind Resource Assessment Audit and
Forest Winds in Complex Terrain Ilda Albuquerque 1 Contents Project Description Motivation Forest Complex Terrain Forested Complex Terrain 2 Project Description WAUDIT (Wind Resource Assessment Audit and
Observed Roughness Lengths for Momentum and Temperature on a Melting Glacier Surface
 5 Observed Roughness Lengths for Momentum and Temperature on a Melting Glacier Surface The roughness lengths for momentum and temperature are calculated on a melting glacier surface. Data from a five level
5 Observed Roughness Lengths for Momentum and Temperature on a Melting Glacier Surface The roughness lengths for momentum and temperature are calculated on a melting glacier surface. Data from a five level
COMPARISON BETWEEN THE WIND TUNNEL EXPERIMANT AND CFD ANALYSIS INTENDED FOR APARTMENT HOUSE STUDY OF STUNDARD K-E MODEL AND DURBIN MODEL
 Proceedings of B25: 4th Conference of International Building Performance imulation Association, Hyderabad, India, Dec. 7-9, 25. COMPARION BETWEEN THE WIND TUNNEL EXPERIMANT AND CFD ANALYI INTENDED FOR
Proceedings of B25: 4th Conference of International Building Performance imulation Association, Hyderabad, India, Dec. 7-9, 25. COMPARION BETWEEN THE WIND TUNNEL EXPERIMANT AND CFD ANALYI INTENDED FOR
Numerical Simulation And Aerodynamic Performance Comparison Between Seagull Aerofoil and NACA 4412 Aerofoil under Low-Reynolds 1
 Advances in Natural Science Vol. 3, No. 2, 2010, pp. 244-20 www.cscanada.net ISSN 171-7862 [PRINT] ISSN 171-7870 [ONLINE] www.cscanada.org *The 3rd International Conference of Bionic Engineering* Numerical
Advances in Natural Science Vol. 3, No. 2, 2010, pp. 244-20 www.cscanada.net ISSN 171-7862 [PRINT] ISSN 171-7870 [ONLINE] www.cscanada.org *The 3rd International Conference of Bionic Engineering* Numerical
MODELING AND SIMULATION OF VALVE COEFFICIENTS AND CAVITATION CHARACTERISTICS IN A BALL VALVE
 Proceedings of the 37 th International & 4 th National Conference on Fluid Mechanics and Fluid Power FMFP2010 December 16-18, 2010, IIT Madras, Chennai, India FMFP2010 341 MODELING AND SIMULATION OF VALVE
Proceedings of the 37 th International & 4 th National Conference on Fluid Mechanics and Fluid Power FMFP2010 December 16-18, 2010, IIT Madras, Chennai, India FMFP2010 341 MODELING AND SIMULATION OF VALVE
How an extreme wind atlas is made
 How an extreme wind atlas is made AC Kruger South African Weather Service X Larsén DTU Wind Energy Wind 1 Atlas for South Africa (WASA) Why do we need extreme wind statistics? Statistical background for
How an extreme wind atlas is made AC Kruger South African Weather Service X Larsén DTU Wind Energy Wind 1 Atlas for South Africa (WASA) Why do we need extreme wind statistics? Statistical background for
EMPIRICAL EVALUATION OF THREE WIND ANALYSIS TOOLS FOR CONCEPT DESIGN OF AN URBAN WIND SHELTER
 Y. Ikeda, C. M. Herr, D. Holzer, S. Kaijima, M. J. Kim. M, A, Schnabel (eds.), Emerging Experience in Past, Present and Future of Digital Architecture, Proceedings of the 20th International Conference
Y. Ikeda, C. M. Herr, D. Holzer, S. Kaijima, M. J. Kim. M, A, Schnabel (eds.), Emerging Experience in Past, Present and Future of Digital Architecture, Proceedings of the 20th International Conference
Performance Evaluation of Four-Sided Square Wind Catchers with Different Geometries by Numerical Method
 Article Performance Evaluation of Four-Sided Square Wind Catchers with Different Geometries by Numerical Method Maryam Hossein Ghadiri 1,a, Nik Lukman Nik Ibrahim 1,b, and Mohd Farid Mohamed 2,c 1, 2 Department
Article Performance Evaluation of Four-Sided Square Wind Catchers with Different Geometries by Numerical Method Maryam Hossein Ghadiri 1,a, Nik Lukman Nik Ibrahim 1,b, and Mohd Farid Mohamed 2,c 1, 2 Department
Study on Fire Plume in Large Spaces Using Ground Heating
 Available online at www.sciencedirect.com Procedia Engineering 11 (2011) 226 232 The 5 th Conference on Performance-based Fire and Fire Protection Engineering Study on Fire Plume in Large Spaces Using
Available online at www.sciencedirect.com Procedia Engineering 11 (2011) 226 232 The 5 th Conference on Performance-based Fire and Fire Protection Engineering Study on Fire Plume in Large Spaces Using
3D-simulation of the turbulent wake behind a wind turbine
 Journal of Physics: Conference Series 3D-simulation of the turbulent wake behind a wind turbine To cite this article: Steffen Wußow et al 2007 J. Phys.: Conf. Ser. 75 012033 View the article online for
Journal of Physics: Conference Series 3D-simulation of the turbulent wake behind a wind turbine To cite this article: Steffen Wußow et al 2007 J. Phys.: Conf. Ser. 75 012033 View the article online for
31/10/17. October 31, HIP Developments Inc. 700 Rupert Street Waterloo, ON N2V 2B5
 University of Guelph Research Park 150 Research Lane, Suite 105 Guelph, ON, N1G 4T2 226.706.8080 www.novusenv.com 31/10/17 Date: To: HIP Developments Inc. 700 Rupert Street N2V 2B5 Re: Cambridge, Ontario
University of Guelph Research Park 150 Research Lane, Suite 105 Guelph, ON, N1G 4T2 226.706.8080 www.novusenv.com 31/10/17 Date: To: HIP Developments Inc. 700 Rupert Street N2V 2B5 Re: Cambridge, Ontario
Computational Analysis of the S Airfoil Aerodynamic Performance
 Computational Analysis of the 245-3S Airfoil Aerodynamic Performance Luis Velazquez-Araque and Jiří Nožička 2 Department of Mechanical Engineering National University of Táchira, San Cristóbal 5, Venezuela
Computational Analysis of the 245-3S Airfoil Aerodynamic Performance Luis Velazquez-Araque and Jiří Nožička 2 Department of Mechanical Engineering National University of Táchira, San Cristóbal 5, Venezuela
Wind Flow Modeling: Are computationally intensive models more accurate?
 June 23 rd, 2015 Wind Flow Modeling: Are computationally intensive models more accurate? Philippe Beaucage, PhD Lead Research Scientist Michael C. Brower, PhD President & Chief Technical Officer Jose Vidal,
June 23 rd, 2015 Wind Flow Modeling: Are computationally intensive models more accurate? Philippe Beaucage, PhD Lead Research Scientist Michael C. Brower, PhD President & Chief Technical Officer Jose Vidal,
1700 Webster Street Oakland, CA. Final Report. Pedestrian Wind Conditions Consultation Wind Tunnel Tests RWDI # July 16, 2015
 Tel: 519.823.1311 Fax: 519.823.1316 Rowan Williams Davies & Irwin Inc. 650 Woodlawn Road West Guelph, Ontario, Canada N1K 1B8 1700 Webster Street Oakland, CA Final Report Pedestrian Wind Conditions Consultation
Tel: 519.823.1311 Fax: 519.823.1316 Rowan Williams Davies & Irwin Inc. 650 Woodlawn Road West Guelph, Ontario, Canada N1K 1B8 1700 Webster Street Oakland, CA Final Report Pedestrian Wind Conditions Consultation
An Impeller Blade Analysis of Centrifugal Gas Compressor Using CFD
 An Impeller Blade Analysis of Centrifugal Gas Compressor Using CFD Vivek V. Kulkarni Department of Mechanical Engineering KLS Gogte Institute of Technology, Belagavi, Karnataka Dr. Anil T.R. Department
An Impeller Blade Analysis of Centrifugal Gas Compressor Using CFD Vivek V. Kulkarni Department of Mechanical Engineering KLS Gogte Institute of Technology, Belagavi, Karnataka Dr. Anil T.R. Department
CFD simulations of the aerodynamic drag of two drafting cyclists
 Accepted for publication in Computers & Fluids on November 21, 2012 CFD simulations of the aerodynamic drag of two drafting cyclists Bert Blocken a,, Thijs Defraeye b, Erwin Koninckx c, Jan Carmeliet d,e,
Accepted for publication in Computers & Fluids on November 21, 2012 CFD simulations of the aerodynamic drag of two drafting cyclists Bert Blocken a,, Thijs Defraeye b, Erwin Koninckx c, Jan Carmeliet d,e,
OPTIMIZATION OF SINGLE STAGE AXIAL FLOW COMPRESSOR FOR DIFFERENT ROTATIONAL SPEED USING CFD
 http:// OPTIMIZATION OF SINGLE STAGE AXIAL FLOW COMPRESSOR FOR DIFFERENT ROTATIONAL SPEED USING CFD Anand Kumar S malipatil 1, Anantharaja M.H 2 1,2 Department of Thermal Power Engineering, VTU-RO Gulbarga,
http:// OPTIMIZATION OF SINGLE STAGE AXIAL FLOW COMPRESSOR FOR DIFFERENT ROTATIONAL SPEED USING CFD Anand Kumar S malipatil 1, Anantharaja M.H 2 1,2 Department of Thermal Power Engineering, VTU-RO Gulbarga,
Generation of an Annual Typical Daily Wind Speed for Heights Equal and Less than 10 meters for Urban Armidale NSW, Australia
 IOSR Journal of Engineering (IOSRJEN) ISSN (e): 2250-3021, ISSN (p): 2278-8719 Vol. 04, Issue 08 (August. 2014), VX PP 31-42 www.iosrjen.org Generation of an Annual Typical Daily Wind Speed for Heights
IOSR Journal of Engineering (IOSRJEN) ISSN (e): 2250-3021, ISSN (p): 2278-8719 Vol. 04, Issue 08 (August. 2014), VX PP 31-42 www.iosrjen.org Generation of an Annual Typical Daily Wind Speed for Heights
Transitional Steps Zone in Steeply Sloping Stepped Spillways
 Transitional Steps Zone in Steeply Sloping Stepped Spillways Jalal Attari 1 and Mohammad Sarfaraz 2 1- Assistant Professor, Power and Water University of Technology, Iran 2- Graduate Student, Department
Transitional Steps Zone in Steeply Sloping Stepped Spillways Jalal Attari 1 and Mohammad Sarfaraz 2 1- Assistant Professor, Power and Water University of Technology, Iran 2- Graduate Student, Department
Workshop 1: Bubbly Flow in a Rectangular Bubble Column. Multiphase Flow Modeling In ANSYS CFX Release ANSYS, Inc. WS1-1 Release 14.
 Workshop 1: Bubbly Flow in a Rectangular Bubble Column 14. 5 Release Multiphase Flow Modeling In ANSYS CFX 2013 ANSYS, Inc. WS1-1 Release 14.5 Introduction This workshop models the dispersion of air bubbles
Workshop 1: Bubbly Flow in a Rectangular Bubble Column 14. 5 Release Multiphase Flow Modeling In ANSYS CFX 2013 ANSYS, Inc. WS1-1 Release 14.5 Introduction This workshop models the dispersion of air bubbles
Aerodynamic Performance of Trains with Different Longitudinal Section Lines under Crosswind
 2017 2nd International Conference on Industrial Aerodynamics (ICIA 2017) ISBN: 978-1-60595-481-3 Aerodynamic Performance of Trains with Different Longitudinal Section Lines under Crosswind Taizhong Xie
2017 2nd International Conference on Industrial Aerodynamics (ICIA 2017) ISBN: 978-1-60595-481-3 Aerodynamic Performance of Trains with Different Longitudinal Section Lines under Crosswind Taizhong Xie
NUMERICAL INVESTIGATION OF THE FLOW BEHAVIOUR IN A MODERN TRAFFIC TUNNEL IN CASE OF FIRE INCIDENT
 - 277 - NUMERICAL INVESTIGATION OF THE FLOW BEHAVIOUR IN A MODERN TRAFFIC TUNNEL IN CASE OF FIRE INCIDENT Iseler J., Heiser W. EAS GmbH, Karlsruhe, Germany ABSTRACT A numerical study of the flow behaviour
- 277 - NUMERICAL INVESTIGATION OF THE FLOW BEHAVIOUR IN A MODERN TRAFFIC TUNNEL IN CASE OF FIRE INCIDENT Iseler J., Heiser W. EAS GmbH, Karlsruhe, Germany ABSTRACT A numerical study of the flow behaviour
URBAN ENERGY AND MICROCLIMATE: WIND TUNNEL EXPERIMENTS AND MULTISCALE MODELING
 URBAN ENERGY AND MICROCLIMATE: WIND TUNNEL EXPERIMENTS AND MULTISCALE MODELING Jan Carmeliet 1,2, Jonas Allegrini 1,2, Peter Moonen 1,2, Saba Saneinejad 1, Viktor Dorer 2 1 ETHZ, Chair of Building Physics,
URBAN ENERGY AND MICROCLIMATE: WIND TUNNEL EXPERIMENTS AND MULTISCALE MODELING Jan Carmeliet 1,2, Jonas Allegrini 1,2, Peter Moonen 1,2, Saba Saneinejad 1, Viktor Dorer 2 1 ETHZ, Chair of Building Physics,
Urban Design Terms of Reference. Pedestrian. Wind Comfort and Safety Studies. June 2014
 Urban Design Terms of Reference Pedestrian June 2014 Wind Comfort and Safety Studies Table of contents 1 Introduction 1.1 Purpose 1.2 Who can conduct a wind study? 1.3 Consultation with Planning and Building
Urban Design Terms of Reference Pedestrian June 2014 Wind Comfort and Safety Studies Table of contents 1 Introduction 1.1 Purpose 1.2 Who can conduct a wind study? 1.3 Consultation with Planning and Building
Pressure distribution of rotating small wind turbine blades with winglet using wind tunnel
 Journal of Scientific SARAVANAN & Industrial et al: Research PRESSURE DISTRIBUTION OF SMALL WIND TURBINE BLADES WITH WINGLET Vol. 71, June 01, pp. 45-49 45 Pressure distribution of rotating small wind
Journal of Scientific SARAVANAN & Industrial et al: Research PRESSURE DISTRIBUTION OF SMALL WIND TURBINE BLADES WITH WINGLET Vol. 71, June 01, pp. 45-49 45 Pressure distribution of rotating small wind
Flow modelling hills complex terrain and other issues
 Flow modelling hills, complex terrain and other issues Modelling approaches sorted after complexity Rules of thumbs Codes and standards Linear model, 1 st order turbulence closure LINCOM/Wasp Reynolds-averaged
Flow modelling hills, complex terrain and other issues Modelling approaches sorted after complexity Rules of thumbs Codes and standards Linear model, 1 st order turbulence closure LINCOM/Wasp Reynolds-averaged
Atmospheric Boundary Layer Simulation Using Wall Function Approach in OpenFoam CFD Software
 Atmospheric Boundary Layer Simulation Using Wall Function Approach in OpenFoam CFD Software Okafor C. Vincent, Ogunoh E. Peter, Ezeokonkwo U. John and Obodoh D. Anosike Abstract The significant development
Atmospheric Boundary Layer Simulation Using Wall Function Approach in OpenFoam CFD Software Okafor C. Vincent, Ogunoh E. Peter, Ezeokonkwo U. John and Obodoh D. Anosike Abstract The significant development
Numerical prediction of air flow within street canyons based on different two-equation k-ε models
 IOP Conference Series: Materials Science and Engineering OPEN ACCESS Numerical prediction of air flow within street canyons based on different two-equation k-ε models To cite this article: Afiq Witri Muhammad
IOP Conference Series: Materials Science and Engineering OPEN ACCESS Numerical prediction of air flow within street canyons based on different two-equation k-ε models To cite this article: Afiq Witri Muhammad
Aerodynamic Measures for the Vortex-induced Vibration of π-shape Composite Girder in Cable-stayed Bridge
 Aerodynamic Measures for the Vortex-induced Vibration of π-shape Composite Girder in Cable-stayed Bridge *Feng Wang 1), Jialing Song 2), Tuo Wu 3), and Muxiong Wei 4) 1), 2, 3), 4) Highway School, Chang
Aerodynamic Measures for the Vortex-induced Vibration of π-shape Composite Girder in Cable-stayed Bridge *Feng Wang 1), Jialing Song 2), Tuo Wu 3), and Muxiong Wei 4) 1), 2, 3), 4) Highway School, Chang
Cooperative roject for CFD rediction of edestrian ind nvironment in the Architectural Institute of Japan
 EACWE4 The Fourth European & African Conference on Wind Engineering J. Náprstek & C. Fischer (eds); ITAM AS CR, Prague, 11-15 July, 2005, Paper #292 Cooperative roject for CFD rediction of edestrian ind
EACWE4 The Fourth European & African Conference on Wind Engineering J. Náprstek & C. Fischer (eds); ITAM AS CR, Prague, 11-15 July, 2005, Paper #292 Cooperative roject for CFD rediction of edestrian ind
Large-eddy simulation study of effects of clearing in forest on wind turbines
 Large-eddy simulation study of effects of clearing in forest on wind turbines J. Matsfelt 1 and L. Davidson 1 1 Chalmers University of Technology, Dep. of Mechanics and Maritime Sciences, Div. of Fluid
Large-eddy simulation study of effects of clearing in forest on wind turbines J. Matsfelt 1 and L. Davidson 1 1 Chalmers University of Technology, Dep. of Mechanics and Maritime Sciences, Div. of Fluid
REVIEW Effects of Side Vents and Span Numbers on Wind-Induced Natural Ventilation of a Gothic Multi-Span Greenhouse
 JARQ 38 (4), 7 33 (004) http://www.jircas.affrc.go.jp REVIEW Effects of Side Vents and Span Numbers on Wind-Induced Natural Ventilation of a Gothic Multi-Span Greenhouse Murat KACIRA 1,, Sadanori SASE
JARQ 38 (4), 7 33 (004) http://www.jircas.affrc.go.jp REVIEW Effects of Side Vents and Span Numbers on Wind-Induced Natural Ventilation of a Gothic Multi-Span Greenhouse Murat KACIRA 1,, Sadanori SASE
REVIEW OF METHODS AND TECHNIQUES FOR THE ASSESMENT OF WINDS AT PEDESTRIAN LEVEL
 REVIEW OF METHODS AND TECHNIQUES FOR THE ASSESMENT OF WINDS AT PEDESTRIAN LEVEL K.Mohan 1 1 Senior Professor, Gitam School of Architecture, Gitam University, Visakhapatnam, Andhra Pradesh, India Abstract
REVIEW OF METHODS AND TECHNIQUES FOR THE ASSESMENT OF WINDS AT PEDESTRIAN LEVEL K.Mohan 1 1 Senior Professor, Gitam School of Architecture, Gitam University, Visakhapatnam, Andhra Pradesh, India Abstract
Wind Flow Validation Summary
 IBHS Research Center Validation of Wind Capabilities The Insurance Institute for Business & Home Safety (IBHS) Research Center full-scale test facility provides opportunities to simulate natural wind conditions
IBHS Research Center Validation of Wind Capabilities The Insurance Institute for Business & Home Safety (IBHS) Research Center full-scale test facility provides opportunities to simulate natural wind conditions
Numerical Computations of Wind Turbine Wakes Using Full Rotor Modeling
 2012 2nd International Conference on Power and Energy Systems (ICPES 2012) IPCSIT vol. 56 (2012) (2012) IACSIT Press, Singapore DOI: 10.7763/IPCSIT.2012.V56.21 Numerical Computations of Wind Turbine Wakes
2012 2nd International Conference on Power and Energy Systems (ICPES 2012) IPCSIT vol. 56 (2012) (2012) IACSIT Press, Singapore DOI: 10.7763/IPCSIT.2012.V56.21 Numerical Computations of Wind Turbine Wakes
Development of virtual 3D human manikin with integrated breathing functionality
 SAT-9.2-2-HT-06 Development of virtual 3D human manikin with integrated breathing functionality Martin Ivanov Development of virtual 3D human manikin with integrated breathing functionality: The presented
SAT-9.2-2-HT-06 Development of virtual 3D human manikin with integrated breathing functionality Martin Ivanov Development of virtual 3D human manikin with integrated breathing functionality: The presented
Quantification of the Effects of Turbulence in Wind on the Flutter Stability of Suspension Bridges
 Quantification of the Effects of Turbulence in Wind on the Flutter Stability of Suspension Bridges T. Abbas 1 and G. Morgenthal 2 1 PhD candidate, Graduate College 1462, Department of Civil Engineering,
Quantification of the Effects of Turbulence in Wind on the Flutter Stability of Suspension Bridges T. Abbas 1 and G. Morgenthal 2 1 PhD candidate, Graduate College 1462, Department of Civil Engineering,
A Study on the Effects of Wind on the Drift Loss of a Cooling Tower
 A Study on the Effects of Wind on the Drift Loss of a Cooling Tower Wanchai Asvapoositkul 1* 1 Department of Mechanical Engineering, Faculty of Engineering, King Mongkut s University of Technology Thonburi
A Study on the Effects of Wind on the Drift Loss of a Cooling Tower Wanchai Asvapoositkul 1* 1 Department of Mechanical Engineering, Faculty of Engineering, King Mongkut s University of Technology Thonburi
Numerical simulation and analysis of aerodynamic drag on a subsonic train in evacuated tube transportation
 Journal of Modern Transportation Volume 20, Number 1, March 2012, Page 44-48 Journal homepage: jmt.swjtu.edu.cn DOI: 10.1007/BF03325776 1 Numerical simulation and analysis of aerodynamic drag on a subsonic
Journal of Modern Transportation Volume 20, Number 1, March 2012, Page 44-48 Journal homepage: jmt.swjtu.edu.cn DOI: 10.1007/BF03325776 1 Numerical simulation and analysis of aerodynamic drag on a subsonic
PRESSURE DISTRIBUTION OF SMALL WIND TURBINE BLADE WITH WINGLETS ON ROTATING CONDITION USING WIND TUNNEL
 International Journal of Mechanical and Production Engineering Research and Development (IJMPERD ) ISSN 2249-6890 Vol.2, Issue 2 June 2012 1-10 TJPRC Pvt. Ltd., PRESSURE DISTRIBUTION OF SMALL WIND TURBINE
International Journal of Mechanical and Production Engineering Research and Development (IJMPERD ) ISSN 2249-6890 Vol.2, Issue 2 June 2012 1-10 TJPRC Pvt. Ltd., PRESSURE DISTRIBUTION OF SMALL WIND TURBINE
