WAVE BREAKING OVER LOCAL TOPOGRAPHY DURING THE MAP IOP 15 MISTRAL EVENT: OBSERVATIONS AND HIGH-RESOLUTION NUMERICAL SIMULATIONS
|
|
|
- Candice Mason
- 6 years ago
- Views:
Transcription
1 WAVE BREAKING OVER LOCAL TOPOGRAPHY DURING THE MAP IOP 15 MISTRAL EVENT: OBSERVATIONS AND HIGH-RESOLUTION NUMERICAL SIMULATIONS Vincent Guénard 1, Gilles Tedeschi 1, Philippe Drobinski 2, Jean Luc Caccia 1 1 LSEET-LEPI, CNRS, Université du Sud Toulon-Var, Avenue de l université, BP 20132, La Garde Cedex, France. 2 SA, CNRS, Institut Pierre Simon Laplace, Ecole Polytechnique, Palaiseau Cedex, France. guenard@lseet.univ-tln.fr Abstract: This study investigates the fundamental processes involved in the severe Mistral s windstorm occurring during the MAP IOP 15 (from 06 to 09 November 1999). It is based on numerical high-resolution simulations performed with the RAMS non-hydrostatic model at 3 km resolution. The simulation is found able to capture the flow complexity both upstream of the Alps and in coastal regions affected by the Mistral. The simulations accurately reproduce dynamical and thermodynamical fields observed by the observational network consisting of two UHF wind profilers set up near Marseille and Toulon and two radiosoundings at Lyon and Nîmes. The model indicates that the Mistral is mainly governed by flow splitting and downslope accelerations occurring at different scales. Wave breaking are triggered above local topography resulting in hydraulic jumps that in turn induce two mountain wakes trailing from the Alps and the Massif Central. The flow is accelerated by channelling effects between these two wakes. The simulations therefore evidence that channelling effects by the Rhône valley do not explain the Mistral s dynamics, which are fundamentally three-dimensional, multi-scaled and formed by a multitude of orographic processes. Keywords - Flow splitting, Low-level jet, Mountain wakes, RAMS 1. INTRODUCTION A severe Mistral event has been documented by two UHF wind profilers during the Mesoscale Alpine Program IOP 15 from the 6 to the 8 November 1999 (Guénard et al. 2005). The two wind profilers have been set up at the Rhône valley exit (STC), near Marseille, and downstream of the Alps (TLN) at Toulon (Fig. 1). This study aims at interpreting the time evolution of the wind profiles measured from the ground to 3 km AGL (above sea level) by means of high-resolution numerical simulations (3 km horizontal resolution) provided by the RAMS non-hydrostatic model. Figure 1. Target area in southeastern France and model grid divisions (from 27 to 3 km). Lyon and Nîmes are the radiosoundings locations. STC and TLN are the UHF wind profiler locations. 280
2 2. THE MISTRAL OBSERVATIONS The synoptic environment is typical of a Mistral event. The Genoa cyclogenesis (1004 hpa) is initiated after the passage of a cold front from the Atlantic toward the Alps on 06 Nov. at 12 UTC. The Azores ridge (1028 hpa) over Spain strengthens the surface pressure gradient and the cyclone moves southeastward resulting in a strong northwesterly flow. The two wind profilers show that a deep Mistral is triggered at the same time on 06 Nov. at 12 UTC (Fig. 2). Radiosondes at Nîmes (not shown), located farther on west from STC (Fig. 1b), indicate that the Mistral is 6 km deep. It evolves into a low-level jet on the 06 Nov. at 21 UTC at TLN (Fig. 2b) and on the 07 Nov. at 04 UTC at STC (Fig. 3a). The Mistral ends on 07 Nov. at 12 UTC at TLN and on 09 Nov. at 00 UTC at STC. The maximum wind speeds have reached 40 m s -1 at STC and 30 ms -1 at TLN. Time-height diagrams of vertical velocity are presented for STC (Fig. 2c) and TLN (Fig. 2d). It can be first noted that w is contaminated by a rainfall occurring above the two sites on 06 Nov. at 09 UTC, visible by the large patch of intense negative w. The end of the rainfall coincides with the Mistral s onset. The w vertical profiles reveal that the air masses are globally subsident during the Mistral s activity. w is stronger above TLN (from -1 to - 2 m s -1 ) than above STC (from -0.5 to -1 m s -1 ). A patch of relatively strong positive w values (around + 1 m s -1 ) is nevertheless observed on 07 Nov. at 03 UTC above 0.75 km AGL at STC (Fig. 2c). After the Mistral s breakdown at TLN on 07 Nov. at 12 UTC, positive w values (around m s -1 ) are also observed. Figure 2. Time-height diagrams observed from 06 to 09 Nov. at 00 UTC. WS (m s -1 ) and WD ( ) at (a) STC and (b) TLN. w (m s -1 ) at (c) STC and (d) TLN: bold lines contour the surface w = 0 m s THE RAMS SIMULATIONS High-resolution numerical simulations have been performed with the non-hydrostatic RAMS model (Pielke et al. 1992). The simulations use three nested grids with 27, 9 and 3 km horizontal resolutions (see Fig. 1 for the model coverage). RAMS is nested into the ECMWF analyses giving its initial and boundary conditions every 6 hours. The simulation has been initialized on 05 Nov. at 00 UTC and has been integrated over 96 h. 281
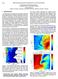
3 The numerical results have been validated through direct comparisons against the UHF and radiosonde (RS) available observations. The comparisons involve the horizontal wind speed WS and direction WD (RS+UHF), the vertical velocity w (UHF), the relative humidity RH and the virtual potential temperature v (RS) vertical profiles. The validation is not detailed here. The model simulations are in good agreement with observations in retrieving the transition from a deep to a shallow Mistral. The simulation correctly reproduces the intensity of the wind (maximum wind speed at STC ~ 35 m s -1, ~ 30 m s -1 at TLN) as well as the vertical velocity fields (maximum vertical velocity are underestimated by 0.5 m s -1 at TLN). RH and v have been also well reproduced with a bias of 15 % and 2 K respectively. The early Mistral s breakdown at TLN after a shallow phase is accurately simulated by the model. The persistence of the Mistral s low-level jet at STC is successfully captured by RAMS. At this step, it can be assumed that the RAMS simulations capture the dynamics of this Mistral event. The early cessation of the Mistral at TLN and the wind persistence of the STC low-level jet are now examined with the numerical simulations. 4. WAKE BREAKING DOWNSTREAM OF THE ALPS The vertical cross-section of the WS and v upstream of TLN on 07 Nov. at 00 UTC (Fig. 3c), clearly shows descending isentropes over the lee slopes of the Sainte Baume. A hydraulic jump occurs near the wind profiler associated with TKE ~ 3 m 2 s -2 (Fig. 3d) suggesting a gravity-wave breaking occurrence. The w cross-section (Fig. 3d) evidences the existence of mountain wave by the alternation of patches of upward and downward motions. w reaches 1.5 m s -1 in agreement with the observations (Fig. 2d). Upward motions are simulated by the model after the wave breaking that likely explains the positive w values observed at TLN after the Mistral s breakdown (Fig. 2d). The breaking wave induces a mountain wake generating potential vorticity clearly visible on the surface wind fields at 0.5 km ASL (above sea level) on Fig. 3a and 3b. In fact, TLN is located at the exact position of the PV source. Farther downstream of TLN, positive and negative PV banners trail from the Sainte Baume with + 4 pvu and -2 pvu respectively. Figure 3. Simulated flow on 07 Nov. at 00 UTC. (a) Horizontal wind, in m s-1, and (b) PV, in pvu, surface fields at 500 m AGL. South-North vertical sections crossing the TLN location in terms of (c) WS (colour scale) in m s-1 and v (solid lines) in K and (d) w (colour scale)in m s-1 and TKE (sold lines) in m2 s
4 5. FLOW SEPARATION AT THE EXIT OF THE RHONE VALLEY The cross-section of the WS and v upstream of STC on 08 Nov. at 00 UTC (Fig. 4c) shows descending isentropes over the lee slopes of the Alpilles without hydraulic jump triggering. w values confirm lower vertical motions at STC (~ -0.5 ms -1 ) as observed by the wind profiler (Fig. 2c). The PV surface field at 0.5 km ASL (Fig. 4b) reveals that PV banners trail from the Massif du Lubéron and the Mont Ventoux. These PV filaments are generated by the flow separation mechanism. Their intensities are related to the primary PV banner induced by the Alps and to the incident flow as suggested by Aebischer and Schär (1998). Throughout the Mistral event, northwesterly to northeasterly incident flows prevail with a descending thermal inversion (from 3 km AGL on 07 Nov. at 00 UTC to 1 km AGL on 08 Nov. at 12 UTC, see Guénard et al. 2005). Thus, flow splitting occurs around the Alps during the deep Mistral phase leading to a large horizontal extension of the Mistral. As the incident thermal inversion height decreases, the flow splits around the less elevated peaks bordering the Rhône valley. It induces a flow confinement between the Alps wake and the Massif Central wake detailed by Jiang et al. (2003). The MAP IOP 15 Alps wake is not steady contrary to the wake documented during the MAP IOP 4 (Schär et al. 2003). The wake is induced by flow splitting around the Alps but also by wave breaking over local topography (for instance over the Sainte Baume). Figure 4. Simulated flow on 08 Nov. at 00 UTC. (a) Horizontal wind, in m s -1, and (b) PV, in pvu, surface fields at 500 m AGL. South-North vertical sections crossing the STC location in terms of (c) WS (colour scale) in m s -1 and v (solid lines) in K and (d) w (colour scale) in m s -1 and TKE (solid lines) in m 2 s CONCLUSIONS The study has shown that the low-level jets observed at Saint Chamas and Toulon result from different mechanisms. The transient low-level jet observed at Toulon is induced by wave breaking over the Sainte Baume in response to a downslope flow. The low-level jet observed at Saint Chamas is mainly due to flow splitting around the Massif du Lubéron and the Mont Ventoux. This process involves channelling low-level accelerations between two wakes trailing from the Massif Central and the Alps. Downslope flows are also triggered over the Alpilles without gravity-wave breaking. The study highlights the flow 283
5 complexity mainly attributed to multi-scale interactive processes that make difficult the forecasting of the fine-scale dynamics of the Mistral. Acknowledgement: This work is supported by the Université du Sud Toulon-Var. The authors have appreciated the logistical support of Météo-France, Degréane Horizon and EDF during the MAP experiment. The authors are also thankful for all the efforts made by the MAP, the RAMS and the ECMWF communities. REFERENCES Aebischer, U. and C. Schär, 1998: Low-level potential vorticity and cyclogenesis to the lee of the Alps. J. Atmos. Sci., 55, Guénard V., P. Drobinski, J. L. Caccia, B. Campistron, and B. Bénech, 2005: An observational study of the Mistral mesoscale dynamics. Bound.-Layer Meteor., 115, Jiang, Q., R. B. Smith and J. D. Doyle, 2003: The nature of the Mistral: Observations and modelling of two MAP events. Quart. J. Roy. Meteor. Soc., 129, Pielke, R.A., and Coauthors 1992: A comprehensive meteorological modelling system - RAMS. Meteor. Atmos. Phys., 49, Schär, C., M. Sprenger, D. Luthi, Q. Jiang, R. B. Smith, and R. Benoit, 2003: Structure and dynamics of an Alpine potential vorticity banner. Quart. J. Roy. Meteor. Soc., 129,
THE GAP AND KATABATIC CONTRIBUTIONS FOR THE MAP IOP 15 MISTRAL WINDSTORM. Université Sud Toulon-Var, LSEET-LEPI-CNRS, Toulon, France
 P7.1 THE GAP AND KATABATIC CONTRIBUTIONS FOR THE MAP IOP 15 MISTRAL WINDSTORM Vincent Guénard * 1, Philippe Drobinski 2, Jean Luc Caccia 1 1 Université Sud Toulon-Var, LSEET-LEPI-CNRS, Toulon, France 2
P7.1 THE GAP AND KATABATIC CONTRIBUTIONS FOR THE MAP IOP 15 MISTRAL WINDSTORM Vincent Guénard * 1, Philippe Drobinski 2, Jean Luc Caccia 1 1 Université Sud Toulon-Var, LSEET-LEPI-CNRS, Toulon, France 2
10.6 The Dynamics of Drainage Flows Developed on a Low Angle Slope in a Large Valley Sharon Zhong 1 and C. David Whiteman 2
 10.6 The Dynamics of Drainage Flows Developed on a Low Angle Slope in a Large Valley Sharon Zhong 1 and C. David Whiteman 2 1Department of Geosciences, University of Houston, Houston, TX 2Pacific Northwest
10.6 The Dynamics of Drainage Flows Developed on a Low Angle Slope in a Large Valley Sharon Zhong 1 and C. David Whiteman 2 1Department of Geosciences, University of Houston, Houston, TX 2Pacific Northwest
Sophie Bastin (*), Philippe Drobinski IPSL, Paris, France;
 1.7 TEMPERATURE AND WIND VELOCITY OSCILLATIONS ALONG A GENTLE SLOPE DURING SEA-BREEZE EVENTS. Sophie Bastin (), Philippe Drobinski IPSL, Paris, France; 1. INTRODUCTION The flow structure at Vallon d Ol
1.7 TEMPERATURE AND WIND VELOCITY OSCILLATIONS ALONG A GENTLE SLOPE DURING SEA-BREEZE EVENTS. Sophie Bastin (), Philippe Drobinski IPSL, Paris, France; 1. INTRODUCTION The flow structure at Vallon d Ol
Polar storms and polar jets: Mesoscale weather systems in the Arctic & Antarctic
 Polar storms and polar jets: Mesoscale weather systems in the Arctic & Antarctic Ian Renfrew School of Environmental Sciences, University of East Anglia ECMWF-WWRP/Thorpex Polar Prediction Workshop 24-27
Polar storms and polar jets: Mesoscale weather systems in the Arctic & Antarctic Ian Renfrew School of Environmental Sciences, University of East Anglia ECMWF-WWRP/Thorpex Polar Prediction Workshop 24-27
Atmospheric Waves James Cayer, Wesley Rondinelli, Kayla Schuster. Abstract
 Atmospheric Waves James Cayer, Wesley Rondinelli, Kayla Schuster Abstract It is important for meteorologists to have an understanding of the synoptic scale waves that propagate thorough the atmosphere
Atmospheric Waves James Cayer, Wesley Rondinelli, Kayla Schuster Abstract It is important for meteorologists to have an understanding of the synoptic scale waves that propagate thorough the atmosphere
Gravity waves in stable atmospheric boundary layers
 Gravity waves in stable atmospheric boundary layers Carmen J. Nappo CJN Research Meteorology Knoxville, Tennessee 37919, USA Abstract Gravity waves permeate the stable atmospheric planetary boundary layer,
Gravity waves in stable atmospheric boundary layers Carmen J. Nappo CJN Research Meteorology Knoxville, Tennessee 37919, USA Abstract Gravity waves permeate the stable atmospheric planetary boundary layer,
and vertical mass fluxes are quantitatively evaluated thanks to the numerical simulation. 1. INTRODUCTION
 P.1 SEA-BREEZE CASE STUDY USING A COMBINATION OF OBSERVATIONAL AND NUMERICAL SIMULATION IN COMPLEX TERRAIN IN SOUTHERN FRANCE: CONTRIBUTION TO MATTER TRANSPORT; S. Bastin (1,*), P. Drobinski (1), A.M.
P.1 SEA-BREEZE CASE STUDY USING A COMBINATION OF OBSERVATIONAL AND NUMERICAL SIMULATION IN COMPLEX TERRAIN IN SOUTHERN FRANCE: CONTRIBUTION TO MATTER TRANSPORT; S. Bastin (1,*), P. Drobinski (1), A.M.
BUF PIT SLO HTS AHN 10.0 CHS CKL AYS
 Cold-air damming When a cold anticyclone is located to the north of an approximately north-south oriented mountain range in winter, a pool of cold air may become entrenched along the eastern slope and
Cold-air damming When a cold anticyclone is located to the north of an approximately north-south oriented mountain range in winter, a pool of cold air may become entrenched along the eastern slope and
The total precipitation (P) is determined by the average rainfall rate (R) and the duration (D),
 Orographic precipitation Common ingredients of heavy orographic precipitation The total precipitation (P) is determined by the average rainfall rate (R) and the duration (D), P = RD. (1) The rainfall rate
Orographic precipitation Common ingredients of heavy orographic precipitation The total precipitation (P) is determined by the average rainfall rate (R) and the duration (D), P = RD. (1) The rainfall rate
Vortex-vortex interaction between Hurricane Nadine (2012) and an Atlantic cutoff dropping the predictability over the Mediterranean
 Vortex-vortex interaction between Hurricane (2012) and an Atlantic dropping the predictability over the Mediterranean Florian Pantillon 1,2 Jean-Pierre Chaboureau 2 and Evelyne Richard 2 1 IMK-TRO, Karlsruhe
Vortex-vortex interaction between Hurricane (2012) and an Atlantic dropping the predictability over the Mediterranean Florian Pantillon 1,2 Jean-Pierre Chaboureau 2 and Evelyne Richard 2 1 IMK-TRO, Karlsruhe
6.28 PREDICTION OF FOG EPISODES AT THE AIRPORT OF MADRID- BARAJAS USING DIFFERENT MODELING APPROACHES
 6.28 PREDICTION OF FOG EPISODES AT THE AIRPORT OF MADRID- BARAJAS USING DIFFERENT MODELING APPROACHES Cecilia Soriano 1, Darío Cano 2, Enric Terradellas 3 and Bill Physick 4 1 Universitat Politècnica de
6.28 PREDICTION OF FOG EPISODES AT THE AIRPORT OF MADRID- BARAJAS USING DIFFERENT MODELING APPROACHES Cecilia Soriano 1, Darío Cano 2, Enric Terradellas 3 and Bill Physick 4 1 Universitat Politècnica de
Summer mistral at the exit of the Rhône valley
 Q. J. R. Meteorol. Soc. (),, pp. 7 doi:.6/qj..6 Summer mistral at the exit of the Rhône valley By P. DROBINSKI,S.BASTIN,V.GUENARD, J.-L. CACCIA,A.M.DABAS, P. DELVILLE, A. PROTAT, O. REITEBUCH 6 and C.
Q. J. R. Meteorol. Soc. (),, pp. 7 doi:.6/qj..6 Summer mistral at the exit of the Rhône valley By P. DROBINSKI,S.BASTIN,V.GUENARD, J.-L. CACCIA,A.M.DABAS, P. DELVILLE, A. PROTAT, O. REITEBUCH 6 and C.
Mountain Forced Flows
 Mountain Forced Flows Jeremy A. Gibbs University of Oklahoma gibbz@ou.edu February 3, 2015 1 / 45 Overview Orographic Precipitation Common Ingredients of Heavy Orographic Precipitation Formation and Enhancement
Mountain Forced Flows Jeremy A. Gibbs University of Oklahoma gibbz@ou.edu February 3, 2015 1 / 45 Overview Orographic Precipitation Common Ingredients of Heavy Orographic Precipitation Formation and Enhancement
Mesoscale Meteorology
 Mesoscale Meteorology METR 4433 Spring 2015 3.4 Drylines The dryline is a mesoscale phenomena whose development and evaluation is strongly linked to the PBL. In this section, we will consider its general
Mesoscale Meteorology METR 4433 Spring 2015 3.4 Drylines The dryline is a mesoscale phenomena whose development and evaluation is strongly linked to the PBL. In this section, we will consider its general
10.2 ATMOSPHERIC ROTORS: AIRCRAFT IN SITU AND CLOUD RADAR MEASUREMENTS IN T-REX
 10.2 ATMOSPHERIC ROTORS: AIRCRAFT IN SITU AND CLOUD RADAR MEASUREMENTS IN T-REX Vanda Grubišić 1, Larry Armi 2, Joachim Kuettner 3, Samuel Haimov 4, Larry Oolman 4, Rick Damiani 4, and Brian Billings 1
10.2 ATMOSPHERIC ROTORS: AIRCRAFT IN SITU AND CLOUD RADAR MEASUREMENTS IN T-REX Vanda Grubišić 1, Larry Armi 2, Joachim Kuettner 3, Samuel Haimov 4, Larry Oolman 4, Rick Damiani 4, and Brian Billings 1
Strengthening of the tropopause inversion layer during the 2009 sudden stratospheric warming in the MERRA-2 analysis
 Strengthening of the tropopause inversion layer during the 009 sudden stratospheric warming in the MERRA- analysis K. Wargan and L. Coy Global Modeling and Assimilation Office Outline We use the MERRA-
Strengthening of the tropopause inversion layer during the 009 sudden stratospheric warming in the MERRA- analysis K. Wargan and L. Coy Global Modeling and Assimilation Office Outline We use the MERRA-
DUE TO EXTERNAL FORCES
 17B.6 DNS ON GROWTH OF A VERTICAL VORTEX IN CONVECTION DUE TO EXTERNAL FORCES Ryota Iijima* and Tetsuro Tamura Tokyo Institute of Technology, Yokohama, Japan 1. INTRODUCTION Various types of vertical vortices,
17B.6 DNS ON GROWTH OF A VERTICAL VORTEX IN CONVECTION DUE TO EXTERNAL FORCES Ryota Iijima* and Tetsuro Tamura Tokyo Institute of Technology, Yokohama, Japan 1. INTRODUCTION Various types of vertical vortices,
Abrupt marine boundary layer changes revealed by airborne in situ and lidar measurements
 Abrupt marine boundary layer changes revealed by airborne in situ and lidar measurements David A. Rahn 1, Thomas R. Parish 2, and David Leon 2 1 Univeristy of Kansas 2 Univeristy of Wyoming Precision Atmospheric
Abrupt marine boundary layer changes revealed by airborne in situ and lidar measurements David A. Rahn 1, Thomas R. Parish 2, and David Leon 2 1 Univeristy of Kansas 2 Univeristy of Wyoming Precision Atmospheric
1 INTRODUCTION. Figure 2: Synoptical situation at the beginning of the simulation: 5th January 1999 at 12UTC.
 2.2 NOCTURNAL CIRCULATIONS UNDER WEAK PRESSURE GRADIENTS IN THE ISLAND OF MALLORCA J. Cuxart and M.A. Jiménez Universitat de les Illes Balears, Spain 1 INTRODUCTION To study the local nocturnal circulations
2.2 NOCTURNAL CIRCULATIONS UNDER WEAK PRESSURE GRADIENTS IN THE ISLAND OF MALLORCA J. Cuxart and M.A. Jiménez Universitat de les Illes Balears, Spain 1 INTRODUCTION To study the local nocturnal circulations
EVOLUTION AND STRUCTURE OF TWO SEVERE CYCLONIC BORA EVENTS: CONTRAST BETWEEN THE NORTHERN AND SOUTHERN ADRIATIC
 EVOLUTION AND STRUCTURE OF TWO SEVERE CYCLONIC BORA EVENTS: CONTRAST BETWEEN THE NORTHERN AND SOUTHERN ADRIATIC Kristian Horvath 1, Stjepan Ivatek Šahdan 1, Branka Ivančan-Picek 1 and Vanda Grubišić 2
EVOLUTION AND STRUCTURE OF TWO SEVERE CYCLONIC BORA EVENTS: CONTRAST BETWEEN THE NORTHERN AND SOUTHERN ADRIATIC Kristian Horvath 1, Stjepan Ivatek Šahdan 1, Branka Ivančan-Picek 1 and Vanda Grubišić 2
Hong Kong International Airport North Runway South Runway
 P.1 Atmospheric Waves Associated with a Valley of Lantau Island: Observation, Theory and Numerical Simulation P.W. Chan * Hong Kong Observatory, Hong Kong, China 1. INTRODUCTION The Hong Kong Observatory
P.1 Atmospheric Waves Associated with a Valley of Lantau Island: Observation, Theory and Numerical Simulation P.W. Chan * Hong Kong Observatory, Hong Kong, China 1. INTRODUCTION The Hong Kong Observatory
Effects of Moist Froude Number and CAPE on a Conditionally Unstable Flow over a Mesoscale Mountain Ridge
 FEBRUARY 2005 C H E N A N D L I N 331 Effects of Moist Froude Number and CAPE on a Conditionally Unstable Flow over a Mesoscale Mountain Ridge SHU-HUA CHEN Department of Land, Air, and Water Resources,
FEBRUARY 2005 C H E N A N D L I N 331 Effects of Moist Froude Number and CAPE on a Conditionally Unstable Flow over a Mesoscale Mountain Ridge SHU-HUA CHEN Department of Land, Air, and Water Resources,
August 1990 H. Kondo 435. A Numerical Experiment on the Interaction between Sea Breeze and
 August 1990 H. Kondo 435 A Numerical Experiment on the Interaction between Sea Breeze and Valley Wind to Generate the so-called "Extended Sea Breeze" By Hiroaki Kondo National Research Institute for Pollution
August 1990 H. Kondo 435 A Numerical Experiment on the Interaction between Sea Breeze and Valley Wind to Generate the so-called "Extended Sea Breeze" By Hiroaki Kondo National Research Institute for Pollution
1.6 HIGH RESOLUTION SIMULATIONS OF THE ISLAND-INDUCED CIRCULATIONS FOR THE ISLAND OF HAWAII DURING HaRP. Yang Yang and Yi-Leng Chen*
 1.6 HIGH RESOLUTION SIMULATIONS OF THE ISLAND-INDUCED CIRCULATIONS FOR THE ISLAND OF HAWAII DURING HaRP Yang Yang and Yi-Leng Chen* Department of Meteorology University of Hawaii at Manoa Honolulu, Hawaii
1.6 HIGH RESOLUTION SIMULATIONS OF THE ISLAND-INDUCED CIRCULATIONS FOR THE ISLAND OF HAWAII DURING HaRP Yang Yang and Yi-Leng Chen* Department of Meteorology University of Hawaii at Manoa Honolulu, Hawaii
Climatology of the 10-m wind along the west coast of South American from 30 years of high-resolution reanalysis
 Climatology of the 10-m wind along the west coast of South American from 30 years of high-resolution reanalysis David A. Rahn and René D. Garreaud Departamento de Geofísica, Facultad de Ciencias Físicas
Climatology of the 10-m wind along the west coast of South American from 30 years of high-resolution reanalysis David A. Rahn and René D. Garreaud Departamento de Geofísica, Facultad de Ciencias Físicas
A Numerical Simulation of Convectively Induced Turbulence (CIT) above Deep Convection
 A Numerical Simulation of Convectively Induced Turbulence (CIT) above Deep Convection Jung-Hoon Kim and Hye-Yeong Chun Department of Atmospheric Sciences Yonsei University, Seoul, Korea 1. Introduction
A Numerical Simulation of Convectively Induced Turbulence (CIT) above Deep Convection Jung-Hoon Kim and Hye-Yeong Chun Department of Atmospheric Sciences Yonsei University, Seoul, Korea 1. Introduction
P2.17 OBSERVATIONS OF STRONG MOUNTAIN WAVES IN THE LEE OF THE MEDICINE BOW MOUNTAINS OF SOUTHEAST WYOMING
 P2.17 OBSERVATIONS OF STRONG MOUNTAIN WAVES IN THE LEE OF THE MEDICINE BOW MOUNTAINS OF SOUTHEAST WYOMING Larry D. Oolman 1, Jeffrey R. French 1, Samuel Haimov 1, David Leon 1, and Vanda Grubišić 2 1 University
P2.17 OBSERVATIONS OF STRONG MOUNTAIN WAVES IN THE LEE OF THE MEDICINE BOW MOUNTAINS OF SOUTHEAST WYOMING Larry D. Oolman 1, Jeffrey R. French 1, Samuel Haimov 1, David Leon 1, and Vanda Grubišić 2 1 University
A flow regime diagram for forecasting lee waves, rotors and downslope winds
 Meteorol. Appl. 13, 179 195 (2006) doi:10.1017/s1350482706002088 A flow regime diagram for forecasting lee waves, rotors and downslope winds P. F. Sheridan & S. B. Vosper Met Office, FitzRoy Road, Exeter
Meteorol. Appl. 13, 179 195 (2006) doi:10.1017/s1350482706002088 A flow regime diagram for forecasting lee waves, rotors and downslope winds P. F. Sheridan & S. B. Vosper Met Office, FitzRoy Road, Exeter
2.4. Applications of Boundary Layer Meteorology
 2.4. Applications of Boundary Layer Meteorology 2.4.1. Temporal Evolution & Prediction of the PBL Earlier, we saw the following figure showing the diurnal evolution of PBL. With a typical diurnal cycle,
2.4. Applications of Boundary Layer Meteorology 2.4.1. Temporal Evolution & Prediction of the PBL Earlier, we saw the following figure showing the diurnal evolution of PBL. With a typical diurnal cycle,
Super-parameterization of boundary layer roll vortices in tropical cyclone models
 DISTRIBUTION STATEMENT A. Approved for public release; distribution is unlimited. Super-parameterization of boundary layer roll vortices in tropical cyclone models PI Isaac Ginis Graduate School of Oceanography
DISTRIBUTION STATEMENT A. Approved for public release; distribution is unlimited. Super-parameterization of boundary layer roll vortices in tropical cyclone models PI Isaac Ginis Graduate School of Oceanography
13.1 EFFECTS OF DIABATIC COOLING ON THE FORMATION OF CONVECTIVE SYSTEMS UPSTREAM OF THE APENNINES DURING MAP IOP-8
 13.1 EFFECTS OF DIABATIC COOLING ON THE FORMATION OF CONVECTIVE SYSTEMS UPSTREAM OF THE APENNINES DURING MAP IOP-8 Heather Dawn Reeves and Yuh-Lang Lin North Carolina State University Raleigh, NC 1. Introduction
13.1 EFFECTS OF DIABATIC COOLING ON THE FORMATION OF CONVECTIVE SYSTEMS UPSTREAM OF THE APENNINES DURING MAP IOP-8 Heather Dawn Reeves and Yuh-Lang Lin North Carolina State University Raleigh, NC 1. Introduction
ASSESSMENT OF SEA BREEZE CHARACTERISTICS FROM SODAR ECHOGRAMS
 ASSESSMENT OF SEA BREEZE CHARACTERISTICS FROM SODAR ECHOGRAMS SUNEETHA RANI. JUPUDI Prof. M. PURNACHANDRA RAO Department of Physics, Andhra University, Visakhapatnam, India. ABSTRACT The SODAR echograms
ASSESSMENT OF SEA BREEZE CHARACTERISTICS FROM SODAR ECHOGRAMS SUNEETHA RANI. JUPUDI Prof. M. PURNACHANDRA RAO Department of Physics, Andhra University, Visakhapatnam, India. ABSTRACT The SODAR echograms
Numerical Approach on the Mechanism of Precipitation-Topography Relationship in Mountainous Complex Terrain
 Numerical Approach on the Mechanism of Precipitation-Topography Relationship in Mountainous Complex Terrain Yoshiharu, S. 1, S. Miyata 2, E. Nakakita 3 and M. Hasebe 4 1 Faculty of Engineering, Utsunomiya
Numerical Approach on the Mechanism of Precipitation-Topography Relationship in Mountainous Complex Terrain Yoshiharu, S. 1, S. Miyata 2, E. Nakakita 3 and M. Hasebe 4 1 Faculty of Engineering, Utsunomiya
AIRFLOW GENERATION IN A TUNNEL USING A SACCARDO VENTILATION SYSTEM AGAINST THE BUOYANCY EFFECT PRODUCED BY A FIRE
 - 247 - AIRFLOW GENERATION IN A TUNNEL USING A SACCARDO VENTILATION SYSTEM AGAINST THE BUOYANCY EFFECT PRODUCED BY A FIRE J D Castro a, C W Pope a and R D Matthews b a Mott MacDonald Ltd, St Anne House,
- 247 - AIRFLOW GENERATION IN A TUNNEL USING A SACCARDO VENTILATION SYSTEM AGAINST THE BUOYANCY EFFECT PRODUCED BY A FIRE J D Castro a, C W Pope a and R D Matthews b a Mott MacDonald Ltd, St Anne House,
The dryline is a mesoscale phenomena whose development and evaluation is strongly linked to the PBL.
 2.2. Development and Evolution of Drylines The dryline is a mesoscale phenomena whose development and evaluation is strongly linked to the PBL. Text books containing sections on dryline: The Dry Line.
2.2. Development and Evolution of Drylines The dryline is a mesoscale phenomena whose development and evaluation is strongly linked to the PBL. Text books containing sections on dryline: The Dry Line.
Darwin s mid-evening surge
 Darwin s mid-evening surge Gerald L. Thomsen and Roger K. Smith Meteorological Institute, University of Munich, Germany November 11, 2009 Corresponding author: Gerald Thomsen, gerald@meteo.physik.uni-muenchen.de
Darwin s mid-evening surge Gerald L. Thomsen and Roger K. Smith Meteorological Institute, University of Munich, Germany November 11, 2009 Corresponding author: Gerald Thomsen, gerald@meteo.physik.uni-muenchen.de
Role of the Hoggar massif in the West African monsoon onset
 GEOPHYSICAL RESEARCH LETTERS, VOL. 32, L01705, doi:10.1029/2004gl020710, 2005 Role of the Hoggar massif in the West African monsoon onset Philippe Drobinski, 1 Benjamin Sultan, 2 and Serge Janicot 2 Received
GEOPHYSICAL RESEARCH LETTERS, VOL. 32, L01705, doi:10.1029/2004gl020710, 2005 Role of the Hoggar massif in the West African monsoon onset Philippe Drobinski, 1 Benjamin Sultan, 2 and Serge Janicot 2 Received
A R e R v e iew e w on o n th t e h e Us U e s s e s of o Clou o d u - (S ( y S s y t s e t m e )-Re R sol o ving n Mod o e d ls Jeff Duda
 A Review on the Uses of Cloud- (System)-Resolving Models Jeff Duda What is a Cloud-Resolving-Model (CRM)? General definition: A model with the following properties Resolution high enough to be able to
A Review on the Uses of Cloud- (System)-Resolving Models Jeff Duda What is a Cloud-Resolving-Model (CRM)? General definition: A model with the following properties Resolution high enough to be able to
WSRC-MS mdf r An Observational Study of Turbulence in the SPBL
 WSRC-MS-97-0385 mdf- 770760--r An Observational Study of Turbulence in the SPBL by R. Kurzeja Westinghouse Savannah River Company Savannah River Site Aiken, South Carolina 29808 A document prepared for
WSRC-MS-97-0385 mdf- 770760--r An Observational Study of Turbulence in the SPBL by R. Kurzeja Westinghouse Savannah River Company Savannah River Site Aiken, South Carolina 29808 A document prepared for
Impact of the thermal stratification on the atmospheric flow over a topography
 Impact of the thermal stratification on the atmospheric flow over a topography A. Butet METEO-FRANCE CNRM/GMEI42 av. Coriolis 31057 Toulouse Cedex, France Email: alain.butet@meteo.fr Abstract Chemical
Impact of the thermal stratification on the atmospheric flow over a topography A. Butet METEO-FRANCE CNRM/GMEI42 av. Coriolis 31057 Toulouse Cedex, France Email: alain.butet@meteo.fr Abstract Chemical
Mesoscale air-sea interaction and feedback in the western Arabian Sea
 Mesoscale air-sea interaction and feedback in the western Arabian Sea Hyodae Seo (Univ. of Hawaii) Raghu Murtugudde (UMD) Markus Jochum (NCAR) Art Miller (SIO) AMS Air-Sea Interaction Workshop Phoenix,
Mesoscale air-sea interaction and feedback in the western Arabian Sea Hyodae Seo (Univ. of Hawaii) Raghu Murtugudde (UMD) Markus Jochum (NCAR) Art Miller (SIO) AMS Air-Sea Interaction Workshop Phoenix,
Observations of the Temporal Evolution and Spatial Structure of the Gap Flow in the Wipp Valley on 2 and 3 October 1999
 2684 MONTHLY WEATHER REVIEW VOLUME 132 Observations of the Temporal Evolution and Spatial Structure of the Gap Flow in the Wipp Valley on 2 and 3 October 1999 MARTIN D. WEISSMANN Department of Meteorology
2684 MONTHLY WEATHER REVIEW VOLUME 132 Observations of the Temporal Evolution and Spatial Structure of the Gap Flow in the Wipp Valley on 2 and 3 October 1999 MARTIN D. WEISSMANN Department of Meteorology
Dynamics and variability of surface wind speed and divergence over mid-latitude ocean fronts
 Dynamics and variability of surface wind speed and divergence over mid-latitude ocean fronts Larry O Neill 1, Tracy Haack 2, and Simon de Szoeke 1 1 Oregon State University, Corvallis, OR 2 Naval Research
Dynamics and variability of surface wind speed and divergence over mid-latitude ocean fronts Larry O Neill 1, Tracy Haack 2, and Simon de Szoeke 1 1 Oregon State University, Corvallis, OR 2 Naval Research
Estimating Topographic Blocking Using a Froude Number When the Static Stability Is Nonuniform
 MARCH 2008 R E I N E C K E A N D D U R R A N 1035 Estimating Topographic Blocking Using a Froude Number When the Static Stability Is Nonuniform PATRICK A. REINECKE AND DALE R. DURRAN Department of Atmospheric
MARCH 2008 R E I N E C K E A N D D U R R A N 1035 Estimating Topographic Blocking Using a Froude Number When the Static Stability Is Nonuniform PATRICK A. REINECKE AND DALE R. DURRAN Department of Atmospheric
Orographic influences on the Adriatic sirocco wind
 European Geosciences Union 2007 Annales Geophysicae Orographic influences on the Adriatic sirocco wind Z. Pasarić, D. Belušić, and Z. B. Klaić Department of Geophysics, Faculty of Science, University of
European Geosciences Union 2007 Annales Geophysicae Orographic influences on the Adriatic sirocco wind Z. Pasarić, D. Belušić, and Z. B. Klaić Department of Geophysics, Faculty of Science, University of
9.2 Mesoscale Eddy Formation and Shock Features Associated with a Coastally Trapped Disturbance
 9.2 Mesoscale Eddy Formation and Shock Features Associated with a Coastally Trapped Disturbance Stephen D. Burk and William T. Thompson Naval Research Laboratory Monterey, California 1. Introduction On
9.2 Mesoscale Eddy Formation and Shock Features Associated with a Coastally Trapped Disturbance Stephen D. Burk and William T. Thompson Naval Research Laboratory Monterey, California 1. Introduction On
MET 200 Lecture 11 Local Winds. Last Lecture: Forces. Review of Forces. Balance of Forces
 MET 200 Lecture 11 Local Winds Last Lecture: Forces Scales of Motion Eddies Sea Breeze Mountain-Valley Circulations Chinook - Snow Eater Drainage Wind - Katabatic Wind 1 2 Review of Forces 1. Pressure
MET 200 Lecture 11 Local Winds Last Lecture: Forces Scales of Motion Eddies Sea Breeze Mountain-Valley Circulations Chinook - Snow Eater Drainage Wind - Katabatic Wind 1 2 Review of Forces 1. Pressure
High-resolution simulations of mountain weather improved with observations from small unmanned aircraft
 High-resolution simulations of mountain weather improved with observations from small unmanned aircraft Hálfdán Ágústsson, Haraldur Ólafsson, Marius O. Johannessen, Joachim Reuder, Dubravka Rasol and Ólafur
High-resolution simulations of mountain weather improved with observations from small unmanned aircraft Hálfdán Ágústsson, Haraldur Ólafsson, Marius O. Johannessen, Joachim Reuder, Dubravka Rasol and Ólafur
Sea and Land Breezes METR 4433, Mesoscale Meteorology Spring 2006 (some of the material in this section came from ZMAG)
 Sea and Land Breezes METR 4433, Mesoscale Meteorology Spring 2006 (some of the material in this section came from ZMAG) 1 Definitions: The sea breeze is a local, thermally direct circulation arising from
Sea and Land Breezes METR 4433, Mesoscale Meteorology Spring 2006 (some of the material in this section came from ZMAG) 1 Definitions: The sea breeze is a local, thermally direct circulation arising from
The impact of step orography on flow in the Eta Model: Two contrasting examples
 Geological and Atmospheric Sciences Publications Geological and Atmospheric Sciences 2000 The impact of step orography on flow in the Eta Model: Two contrasting examples William A. Gallus Jr. Iowa State
Geological and Atmospheric Sciences Publications Geological and Atmospheric Sciences 2000 The impact of step orography on flow in the Eta Model: Two contrasting examples William A. Gallus Jr. Iowa State
Modelling atmospheric stability with CFD: The importance of tall profiles
 ENERGY Modelling atmospheric stability with CFD: The importance of tall profiles VindKraftNet Seminar on Profiles Jean-François Corbett, Global Head of CFD Service 1 SAFER, SMARTER, GREENER DNV GL CFD
ENERGY Modelling atmospheric stability with CFD: The importance of tall profiles VindKraftNet Seminar on Profiles Jean-François Corbett, Global Head of CFD Service 1 SAFER, SMARTER, GREENER DNV GL CFD
Evolution and Structure of Two Severe Cyclonic Bora Events: Contrast between the Northern and Southern Adriatic
 946 W E A T H E R A N D F O R E C A S T I N G VOLUME 24 Evolution and Structure of Two Severe Cyclonic Bora Events: Contrast between the Northern and Southern Adriatic KRISTIAN HORVATH, STJEPAN IVATEK-ŠAHDAN,
946 W E A T H E R A N D F O R E C A S T I N G VOLUME 24 Evolution and Structure of Two Severe Cyclonic Bora Events: Contrast between the Northern and Southern Adriatic KRISTIAN HORVATH, STJEPAN IVATEK-ŠAHDAN,
Impact of fine-scale wind stress curl structures on coastal upwelling dynamics : The Benguela system as a case of study.
 IOVWST Meeting May 21, 2015, Portland (OR) Impact of fine-scale wind stress curl structures on coastal upwelling dynamics : The Benguela system as a case of study. Fabien Desbiolles1,2, Bruno Blanke1,
IOVWST Meeting May 21, 2015, Portland (OR) Impact of fine-scale wind stress curl structures on coastal upwelling dynamics : The Benguela system as a case of study. Fabien Desbiolles1,2, Bruno Blanke1,
Characterization of Boundary-Layer Meteorology During DISCOVER-AQ
 Characterization of Boundary-Layer Meteorology During DISCOVER-AQ Daniel M. Alrick and Clinton P. MacDonald Sonoma Technology, Inc. Gary A. Morris St. Edward s University for Texas Air Quality Research
Characterization of Boundary-Layer Meteorology During DISCOVER-AQ Daniel M. Alrick and Clinton P. MacDonald Sonoma Technology, Inc. Gary A. Morris St. Edward s University for Texas Air Quality Research
10.6 Eddy Formation and Shock Features Associated with a Coastally Trapped Disturbance
 10.6 Eddy Formation and Shock Features Associated with a Coastally Trapped Disturbance William T. Thompson and Stephen D. Burk Naval Research Laboratory Monterey, California 1. Introduction On 28 August
10.6 Eddy Formation and Shock Features Associated with a Coastally Trapped Disturbance William T. Thompson and Stephen D. Burk Naval Research Laboratory Monterey, California 1. Introduction On 28 August
A Theory for Strong Long-Lived Squall Lines Revisited
 A Theory for Strong Long-Lived Squall Lines Revisited MORRIS L. WEISMAN AND RICHARD ROTUNNO National Center for Atmospheric Research,* Boulder, Colorado (Manuscript received 29 April 2002, in final form
A Theory for Strong Long-Lived Squall Lines Revisited MORRIS L. WEISMAN AND RICHARD ROTUNNO National Center for Atmospheric Research,* Boulder, Colorado (Manuscript received 29 April 2002, in final form
Lecture 14. Heat lows and the TCZ
 Lecture 14 Heat lows and the TCZ ITCZ/TCZ and heat lows While the ITCZ/TCZ is associated with a trough at low levels, it must be noted that a low pressure at the surface and cyclonic vorticity at 850 hpa
Lecture 14 Heat lows and the TCZ ITCZ/TCZ and heat lows While the ITCZ/TCZ is associated with a trough at low levels, it must be noted that a low pressure at the surface and cyclonic vorticity at 850 hpa
Modeling of Mountain Waves in T-REX
 10.6 Modeling of Mountain Waves in T-REX Steven E. Koch 1,2, Ligia R. Bernardet 1,2, Brian D. Jamison 1,3, and John M. Brown 1 1 NOAA / Earth Systems Research Laboratory (ESRL), Boulder, Colorado 2 Developmental
10.6 Modeling of Mountain Waves in T-REX Steven E. Koch 1,2, Ligia R. Bernardet 1,2, Brian D. Jamison 1,3, and John M. Brown 1 1 NOAA / Earth Systems Research Laboratory (ESRL), Boulder, Colorado 2 Developmental
2. THE NEW ENGLAND AIR QUALITY STUDY
 P2.4 NEW ENGLAND COASTAL AIR POLLUTION DISPERSION MODELING Michael Tjernström * and Mark Žagar Stockholm University, Stockholm, Sweden Wayne Angevine CIRES, University of Colorado, and NOAA Aeronomy Laboratory,
P2.4 NEW ENGLAND COASTAL AIR POLLUTION DISPERSION MODELING Michael Tjernström * and Mark Žagar Stockholm University, Stockholm, Sweden Wayne Angevine CIRES, University of Colorado, and NOAA Aeronomy Laboratory,
RELATIONSHIP BETWEEN CROSS-EQUATORIAL FLOW, TRADE WIND FLOW AND FAVOURABLE CONDITIONS OF THE CYCLOGENESIS OVER THE MOZAMBICA CHANNEL
 RELATIONSHIP BETWEEN CROSS-EQUATORIAL FLOW, TRADE WIND FLOW AND FAVOURABLE CONDITIONS OF THE CYCLOGENESIS OVER THE MOZAMBICA CHANNEL Olga Ramiarinjanahary a), Bessafi Miloud b), Adolphe A. Ratiarison c)
RELATIONSHIP BETWEEN CROSS-EQUATORIAL FLOW, TRADE WIND FLOW AND FAVOURABLE CONDITIONS OF THE CYCLOGENESIS OVER THE MOZAMBICA CHANNEL Olga Ramiarinjanahary a), Bessafi Miloud b), Adolphe A. Ratiarison c)
High fidelity gust simulations around a transonic airfoil
 High fidelity gust simulations around a transonic airfoil AEROGUST Workshop 27 th - 28 th April 2017, University of Liverpool Presented by B. Tartinville (Numeca) Outline of the presentation 1Objectives
High fidelity gust simulations around a transonic airfoil AEROGUST Workshop 27 th - 28 th April 2017, University of Liverpool Presented by B. Tartinville (Numeca) Outline of the presentation 1Objectives
Local Winds. Please read Ahrens Chapter 10
 Local Winds Please read Ahrens Chapter 10 Scales of Motion Microscale: meters Turbulent eddies Formed by mechanical disturbance or convection Lifetimes of minutes Mesoscale: km s to 100 s of km s Local
Local Winds Please read Ahrens Chapter 10 Scales of Motion Microscale: meters Turbulent eddies Formed by mechanical disturbance or convection Lifetimes of minutes Mesoscale: km s to 100 s of km s Local
Non orographic and orographic gravity waves above Antarctica and the Southern Ocean
 Non orographic and orographic gravity waves above Antarctica and the Southern Ocean Riwal Plougonven Laboratoire de Météorologie Dynamique, IPSL Ecole Normale Supérieure Work involving: Albert Hertzog,
Non orographic and orographic gravity waves above Antarctica and the Southern Ocean Riwal Plougonven Laboratoire de Météorologie Dynamique, IPSL Ecole Normale Supérieure Work involving: Albert Hertzog,
Gravity waves and bores. Material kindly provided by Dr. Steven Koch GSD NOAA (Boulder, CO)
 Gravity waves and bores Material kindly provided by Dr. Steven Koch GSD NOAA (Boulder, CO) Presented at Iowa State University 11 April 2005 What is a gravity wave? An oscillation caused by the displacement
Gravity waves and bores Material kindly provided by Dr. Steven Koch GSD NOAA (Boulder, CO) Presented at Iowa State University 11 April 2005 What is a gravity wave? An oscillation caused by the displacement
Partitioning of snowy and rainy precipitation in a case of a north Adriatic frontal passage
 Advances in Geosciences, 7, 279 284, 26 SRef-ID: 168-7359/adgeo/26-7-279 European Geosciences Union 26 Author(s). This work is licensed under a Creative Commons License. Advances in Geosciences Partitioning
Advances in Geosciences, 7, 279 284, 26 SRef-ID: 168-7359/adgeo/26-7-279 European Geosciences Union 26 Author(s). This work is licensed under a Creative Commons License. Advances in Geosciences Partitioning
P2.20 ANTICIPATING DAMAGING FOEHN WINDSTORMS EAST OF THE CENTRAL APPALACHIANS
 P2.20 ANTICIPATING DAMAGING FOEHN WINDSTORMS EAST OF THE CENTRAL APPALACHIANS Phillip Manuel* and Stephen Keighton NOAA/National Weather Service, Blacksburg, VA 1. INTRODUCTION Lower tropospheric flow
P2.20 ANTICIPATING DAMAGING FOEHN WINDSTORMS EAST OF THE CENTRAL APPALACHIANS Phillip Manuel* and Stephen Keighton NOAA/National Weather Service, Blacksburg, VA 1. INTRODUCTION Lower tropospheric flow
INTRODUCTION * Corresponding author address: Michael Tjernström, Stockholm University, Department of Meteorology, SE-
 4.12 NEW ENGLAND COASTAL BOUNDARY LAYER MODELING Mark Žagar and Michael Tjernström * Stockholm University, Stockholm, Sweden Wayne Angevine CIRES, University of Colorado, and NOAA Aeronomy Laboratory,
4.12 NEW ENGLAND COASTAL BOUNDARY LAYER MODELING Mark Žagar and Michael Tjernström * Stockholm University, Stockholm, Sweden Wayne Angevine CIRES, University of Colorado, and NOAA Aeronomy Laboratory,
The Effects of Gap Wind Induced Vorticity, the ITCZ, and Monsoon Trough on Tropical Cyclogenesis
 The Effects of Gap Wind Induced Vorticity, the ITCZ, and Monsoon Trough on Tropical Cyclogenesis Heather M. Holbach and Mark A. Bourassa Center for Ocean-Atmospheric Prediction Studies Department of Earth,
The Effects of Gap Wind Induced Vorticity, the ITCZ, and Monsoon Trough on Tropical Cyclogenesis Heather M. Holbach and Mark A. Bourassa Center for Ocean-Atmospheric Prediction Studies Department of Earth,
Thorsten Mauritsen *, Gunilla Svensson Stockholm University, Stockholm, Sweden
 J.1 WAVE FLOW SIMULATIONS OVER ARCTIC LEADS Thorsten Mauritsen *, Gunilla Svensson Stockholm University, Stockholm, Sweden Branko Grisogono Department of Geophysics, Faculty of Science, Zagreb, Croatia
J.1 WAVE FLOW SIMULATIONS OVER ARCTIC LEADS Thorsten Mauritsen *, Gunilla Svensson Stockholm University, Stockholm, Sweden Branko Grisogono Department of Geophysics, Faculty of Science, Zagreb, Croatia
Atomspheric Waves at the 500hPa Level
 Atomspheric Waves at the 5hPa Level Justin Deal, Eswar Iyer, and Bryce Link ABSTRACT Our study observes and examines large scale motions of the atmosphere. More specifically it examines wave motions at
Atomspheric Waves at the 5hPa Level Justin Deal, Eswar Iyer, and Bryce Link ABSTRACT Our study observes and examines large scale motions of the atmosphere. More specifically it examines wave motions at
2. External nfluences
 2. External nfluences Vertical wind shear Dry air (saharan) Upper tropospheric features Tropical cyclone motion Landfall Extra-tropical transition Risks 1 Gafilo 2004 EXTERNAL INFLUENCES 2 VERTICAL WIND
2. External nfluences Vertical wind shear Dry air (saharan) Upper tropospheric features Tropical cyclone motion Landfall Extra-tropical transition Risks 1 Gafilo 2004 EXTERNAL INFLUENCES 2 VERTICAL WIND
Precipitation over concave terrain
 Precipitation over concave terrain Qingfang Jiang, UCAR visiting scientist Naval Research Laboratory, Monterey, CA 1. INTRODUCTION The motivation of this model-based idealized study can be illustrated
Precipitation over concave terrain Qingfang Jiang, UCAR visiting scientist Naval Research Laboratory, Monterey, CA 1. INTRODUCTION The motivation of this model-based idealized study can be illustrated
Observations and Modeling of Coupled Ocean-Atmosphere Interaction over the California Current System
 Observations and Modeling of Coupled Ocean-Atmosphere Interaction over the California Current System Cape Blanco Dudley Chelton 1, Xin Jin 2, Jim McWilliams 2 & Tracy Haack 3 1 Oregon State University
Observations and Modeling of Coupled Ocean-Atmosphere Interaction over the California Current System Cape Blanco Dudley Chelton 1, Xin Jin 2, Jim McWilliams 2 & Tracy Haack 3 1 Oregon State University
Large-Scale Flow Response to the Breaking of Mountain Gravity Waves François Lott, LMD, Ecole Normale Supérieure;
 Large-Scale Flow Response to the Breaking of Mountain Gravity Waves François Lott, LMD, Ecole Normale Supérieure; flott@lmd.ens.fr 1) General: gravity waves and their impact on climate 2) Regional and
Large-Scale Flow Response to the Breaking of Mountain Gravity Waves François Lott, LMD, Ecole Normale Supérieure; flott@lmd.ens.fr 1) General: gravity waves and their impact on climate 2) Regional and
Blocking, descent and gravity waves: Observations and modelling of a MAP northerly föhn event
 Q. J. R. Meteorol. Soc. (2005), 131, pp. 675 701 doi: 10.1256/qj.03.176 Blocking, descent and gravity waves: Observations and modelling of a MAP northerly föhn event By QINGFANG JIANG 1, JAMES D. DOYLE
Q. J. R. Meteorol. Soc. (2005), 131, pp. 675 701 doi: 10.1256/qj.03.176 Blocking, descent and gravity waves: Observations and modelling of a MAP northerly föhn event By QINGFANG JIANG 1, JAMES D. DOYLE
Lecture 20. Active-weak spells and breaks in the monsoon: Part 1
 Lecture 20 Active-weak spells and breaks in the monsoon: Part 1 Although the summer monsoon season is the rainy season over most of the Indian region, it does not rain every day, at any place, during the
Lecture 20 Active-weak spells and breaks in the monsoon: Part 1 Although the summer monsoon season is the rainy season over most of the Indian region, it does not rain every day, at any place, during the
Synoptic features of orographically enhanced heavy rainfall on the east coast of Korea associated with Typhoon Rusa (2002)
 Click Here for Full Article GEOPHYSICAL RESEARCH LETTERS, VOL. 34, L02803, doi:10.1029/2006gl028592, 2007 Synoptic features of orographically enhanced heavy rainfall on the east coast of Korea associated
Click Here for Full Article GEOPHYSICAL RESEARCH LETTERS, VOL. 34, L02803, doi:10.1029/2006gl028592, 2007 Synoptic features of orographically enhanced heavy rainfall on the east coast of Korea associated
Effect of Orography on Land and Ocean Surface Temperature
 Present and Future of Modeling Global Environmental Change: Toward Integrated Modeling, Eds., T. Matsuno and H. Kida, pp. 427 431. by TERRAPUB, 2001. Effect of Orography on Land and Ocean Surface Temperature
Present and Future of Modeling Global Environmental Change: Toward Integrated Modeling, Eds., T. Matsuno and H. Kida, pp. 427 431. by TERRAPUB, 2001. Effect of Orography on Land and Ocean Surface Temperature
Idealized Numerical Modeling of a Land/Sea Breeze
 Idealized Numerical Modeling of a Land/Sea Breeze Jeremy A. Gibbs School of Meteorology, University of Oklahoma 3 December 2008 1 Introduction With references in the Bible, the land and sea breeze is one
Idealized Numerical Modeling of a Land/Sea Breeze Jeremy A. Gibbs School of Meteorology, University of Oklahoma 3 December 2008 1 Introduction With references in the Bible, the land and sea breeze is one
Xiaoli Guo Larsén,* Søren Larsen and Andrea N. Hahmann Risø National Laboratory for Sustainable Energy, Roskilde, Denmark
 Quarterly Journal of the Royal Meteorological Society Q. J. R. Meteorol. Soc. 138: 274 279, January 2012 A Notes and Correspondence Origin of the waves in A case-study of mesoscale spectra of wind and
Quarterly Journal of the Royal Meteorological Society Q. J. R. Meteorol. Soc. 138: 274 279, January 2012 A Notes and Correspondence Origin of the waves in A case-study of mesoscale spectra of wind and
Wind Power. Kevin Clifford METR 112 April 19, 2011
 Wind Power Kevin Clifford METR 112 April 19, 2011 Outline Introduction Wind Turbines Determining Wind Power Output The Price of Wind Power Wind Power Availability across the World and US California Wind
Wind Power Kevin Clifford METR 112 April 19, 2011 Outline Introduction Wind Turbines Determining Wind Power Output The Price of Wind Power Wind Power Availability across the World and US California Wind
NUMERICAL INVESTIGATION OF THE FLOW BEHAVIOUR IN A MODERN TRAFFIC TUNNEL IN CASE OF FIRE INCIDENT
 - 277 - NUMERICAL INVESTIGATION OF THE FLOW BEHAVIOUR IN A MODERN TRAFFIC TUNNEL IN CASE OF FIRE INCIDENT Iseler J., Heiser W. EAS GmbH, Karlsruhe, Germany ABSTRACT A numerical study of the flow behaviour
- 277 - NUMERICAL INVESTIGATION OF THE FLOW BEHAVIOUR IN A MODERN TRAFFIC TUNNEL IN CASE OF FIRE INCIDENT Iseler J., Heiser W. EAS GmbH, Karlsruhe, Germany ABSTRACT A numerical study of the flow behaviour
Standard atmosphere Typical height (m) Pressure (mb)
 Standard atmosphere Pressure (mb) Typical height (ft) Typical height (m) 1013.25 0 0 1000 370 110 850 4780 1460 700 9880 3010 500 18280 5570 300 30050 9160 Whiteman 2000 Pressure decreases exponentially
Standard atmosphere Pressure (mb) Typical height (ft) Typical height (m) 1013.25 0 0 1000 370 110 850 4780 1460 700 9880 3010 500 18280 5570 300 30050 9160 Whiteman 2000 Pressure decreases exponentially
P3.3 BOUNDARY LAYER STRUCTURE IN THE INN VALLEY DURING HIGH AIR POLLUTION (INNAP)
 P. BOUNDARY LAYER STRUCTURE IN THE INN VALLEY DURING HIGH AIR POLLUTION (INNAP) Alexander Gohm, Florian Harnisch, Andreas Fix University of Innsbruck, Austria DLR, Oberpfaffenhofen, Germany. INTRODUCTION
P. BOUNDARY LAYER STRUCTURE IN THE INN VALLEY DURING HIGH AIR POLLUTION (INNAP) Alexander Gohm, Florian Harnisch, Andreas Fix University of Innsbruck, Austria DLR, Oberpfaffenhofen, Germany. INTRODUCTION
Darwin s mid-evening surge
 Australian Meteorological and Oceanographic Journal 60 (2010) 25-36 Darwin s mid-evening surge Gerald L. Thomsen and Roger K. Smith Meteorological Institute, University of Munich, Germany (Manuscript received
Australian Meteorological and Oceanographic Journal 60 (2010) 25-36 Darwin s mid-evening surge Gerald L. Thomsen and Roger K. Smith Meteorological Institute, University of Munich, Germany (Manuscript received
13.6 AIRBORNE RADAR OBSERVATIONS OF BREAKING WAVES/ROTORS IN THE LEE OF THE MEDICINE BOW MOUNTAINS IN SE WYOMING, USA
 13.6 AIRBORNE RADAR OBSERVATIONS OF BREAKING WAVES/ROTORS IN THE LEE OF THE MEDICINE BOW MOUNTAINS IN SE WYOMING, USA Jeffrey R. French 1 *, Samuel Haimov 1, Larry Oolman 1, Vanda Grubišić 2, and Dave
13.6 AIRBORNE RADAR OBSERVATIONS OF BREAKING WAVES/ROTORS IN THE LEE OF THE MEDICINE BOW MOUNTAINS IN SE WYOMING, USA Jeffrey R. French 1 *, Samuel Haimov 1, Larry Oolman 1, Vanda Grubišić 2, and Dave
An Undular Bore and Gravity Waves Illustrated by Dramatic Time-Lapse Photography
 AUGUST 2010 C O L E M A N E T A L. 1355 An Undular Bore and Gravity Waves Illustrated by Dramatic Time-Lapse Photography TIMOTHY A. COLEMAN AND KEVIN R. KNUPP Department of Atmospheric Science, University
AUGUST 2010 C O L E M A N E T A L. 1355 An Undular Bore and Gravity Waves Illustrated by Dramatic Time-Lapse Photography TIMOTHY A. COLEMAN AND KEVIN R. KNUPP Department of Atmospheric Science, University
EFFECTS OF WAVE, TIDAL CURRENT AND OCEAN CURRENT COEXISTENCE ON THE WAVE AND CURRENT PREDICTIONS IN THE TSUGARU STRAIT
 EFFECTS OF WAVE, TIDAL CURRENT AND OCEAN CURRENT COEXISTENCE ON THE WAVE AND CURRENT PREDICTIONS IN THE TSUGARU STRAIT Ayumi Saruwatari 1, Yoshihiro Yoneko 2 and Yu Tajima 3 The Tsugaru Strait between
EFFECTS OF WAVE, TIDAL CURRENT AND OCEAN CURRENT COEXISTENCE ON THE WAVE AND CURRENT PREDICTIONS IN THE TSUGARU STRAIT Ayumi Saruwatari 1, Yoshihiro Yoneko 2 and Yu Tajima 3 The Tsugaru Strait between
THE EFFECT OF THE OCEAN EDDY ON TROPICAL CYCLONE INTENSITY
 TE EFFECT OF TE OCEAN ON TROPICAL CYCLONE INTENSITY 3C.1 Chia-Ying Lee and Chun-Chieh Wu* Department of Atmospheric Sciences, National Taiwan University, Taipei, Taiwan 1. INTRODUCTION It has been widely
TE EFFECT OF TE OCEAN ON TROPICAL CYCLONE INTENSITY 3C.1 Chia-Ying Lee and Chun-Chieh Wu* Department of Atmospheric Sciences, National Taiwan University, Taipei, Taiwan 1. INTRODUCTION It has been widely
Prof. Geraint Vaughan. Centre for Atmospheric Science School of Earth, Atmospheric and Environmental Sciences. Bogdan Antonescu
 Upper-level fronts tropopause disturbances and convection Prof. Geraint Vaughan Centre for Atmospheric Science School of Earth, Atmospheric and Environmental Sciences Bogdan Antonescu the meteorological
Upper-level fronts tropopause disturbances and convection Prof. Geraint Vaughan Centre for Atmospheric Science School of Earth, Atmospheric and Environmental Sciences Bogdan Antonescu the meteorological
Meteorology Lecture 17
 Meteorology Lecture 17 Robert Fovell rfovell@albany.edu 1 Important notes These slides show some figures and videos prepared by Robert G. Fovell (RGF) for his Meteorology course, published by The Great
Meteorology Lecture 17 Robert Fovell rfovell@albany.edu 1 Important notes These slides show some figures and videos prepared by Robert G. Fovell (RGF) for his Meteorology course, published by The Great
18 Flight Hazards over High Ground
 18 Flight Hazards over High Ground meteorology 18.1 Mountain Effect on Fronts When a warm front passes a mountain range, the air, is lifted over the mountain and will strengthen the formation of cloud
18 Flight Hazards over High Ground meteorology 18.1 Mountain Effect on Fronts When a warm front passes a mountain range, the air, is lifted over the mountain and will strengthen the formation of cloud
Blocking, descent and gravity waves: Observations and modelling of a MAP northerly föhn event
 Q. J. R. Meteorol. Soc. (2005), 131, pp. 675 701 doi: 10.1256/qj.03.176 Blocking, descent and gravity waves: Observations and modelling of a MAP northerly föhn event By QINGFANG JIANG 1, JAMES D. DOYLE
Q. J. R. Meteorol. Soc. (2005), 131, pp. 675 701 doi: 10.1256/qj.03.176 Blocking, descent and gravity waves: Observations and modelling of a MAP northerly föhn event By QINGFANG JIANG 1, JAMES D. DOYLE
Investigation of the atmospheric boundary layer dynamics during the ESCOMPTE campaign
 Ann. Geophys., 25, 597 622, 2007 European Geosciences Union 2007 Annales Geophysicae Investigation of the atmospheric boundary layer dynamics during the ESCOMPTE campaign F. Saïd 1, A. Brut 2, B. Campistron
Ann. Geophys., 25, 597 622, 2007 European Geosciences Union 2007 Annales Geophysicae Investigation of the atmospheric boundary layer dynamics during the ESCOMPTE campaign F. Saïd 1, A. Brut 2, B. Campistron
Transport and mixing in the extratropical tropopause region in a high vertical resolution GCM
 Transport and mixing in the extratropical tropopause region in a high vertical resolution GCM (Miyazaki et al. JAS 2010a,2010b) Kazuyuki Miyazaki Royal Netherlands Meteorological Institute (KNMI) Japan
Transport and mixing in the extratropical tropopause region in a high vertical resolution GCM (Miyazaki et al. JAS 2010a,2010b) Kazuyuki Miyazaki Royal Netherlands Meteorological Institute (KNMI) Japan
Effects of Trade-Wind Strength and Direction on the Leeside Circulations and Rainfall of the Island of Hawaii
 DECEMBER 2008 YANG ET AL. 4799 Effects of Trade-Wind Strength and Direction on the Leeside Circulations and Rainfall of the Island of Hawaii YANG YANG AND YI-LENG CHEN Department of Meteorology, School
DECEMBER 2008 YANG ET AL. 4799 Effects of Trade-Wind Strength and Direction on the Leeside Circulations and Rainfall of the Island of Hawaii YANG YANG AND YI-LENG CHEN Department of Meteorology, School
DYNAMICAL PROCESSES IN UNDISTURBED KATABATIC FLOWS
 DYNAMCAL PROCESSES N UNDSTURBED KATABATC FLOWS Gregory S Poulosl, Thomas B McKee2, James E Bossed and Roger A Pielke2 'Los Alamos National Laboratory, Los Alamos, NM Colorado State University, Fort Collins,
DYNAMCAL PROCESSES N UNDSTURBED KATABATC FLOWS Gregory S Poulosl, Thomas B McKee2, James E Bossed and Roger A Pielke2 'Los Alamos National Laboratory, Los Alamos, NM Colorado State University, Fort Collins,
OPTIMIZING THE LENGTH OF AIR SUPPLY DUCT IN CROSS CONNECTIONS OF GOTTHARD BASE TUNNEL. Rehan Yousaf 1, Oliver Scherer 1
 OPTIMIZING THE LENGTH OF AIR SUPPLY DUCT IN CROSS CONNECTIONS OF GOTTHARD BASE TUNNEL Rehan Yousaf 1, Oliver Scherer 1 1 Pöyry Infra Ltd, Zürich, Switzerland ABSTRACT Gotthard Base Tunnel with its 57 km
OPTIMIZING THE LENGTH OF AIR SUPPLY DUCT IN CROSS CONNECTIONS OF GOTTHARD BASE TUNNEL Rehan Yousaf 1, Oliver Scherer 1 1 Pöyry Infra Ltd, Zürich, Switzerland ABSTRACT Gotthard Base Tunnel with its 57 km
Isaac Newton ( )
 Introduction to Climatology GEOGRAPHY 300 Isaac Newton (1642-1727) Tom Giambelluca University of Hawai i at Mānoa Atmospheric Pressure, Wind, and The General Circulation Philosophiæ Naturalis Principia
Introduction to Climatology GEOGRAPHY 300 Isaac Newton (1642-1727) Tom Giambelluca University of Hawai i at Mānoa Atmospheric Pressure, Wind, and The General Circulation Philosophiæ Naturalis Principia
ABSTRACT INTRODUCTION
 Numerical investigation of the formation of elevated pollution layers over the Los Angeles air basin Rong Lu, R.P. Turco Department of Atmospheric Sciences, University of California, Los Angeles, 405 Hilgard
Numerical investigation of the formation of elevated pollution layers over the Los Angeles air basin Rong Lu, R.P. Turco Department of Atmospheric Sciences, University of California, Los Angeles, 405 Hilgard
