The Stack Effect. Mat Ansari PE
|
|
|
- Chastity Greer
- 5 years ago
- Views:
Transcription
1 The Stack Effect Mat Ansari PE All young Engineers and Architects who are going to be involved with the design of tall buildings need to thoroughly understand the concept of Stack Effect. By thorough I mean not just ASHRAE formulas but solid concepts on what this phenomenon is doing to the building and how it can work against your design intent and the proper operation of the building. (Note: This post is not for experienced Engineers, but rather for beginners in the HVAC design field. However, comments of experienced Engineers are most welcome.) To begin with, when we design a tall building (and I am not defining tall on purpose) the stack effect is encountered in many different and unrelated aspects of the total building design. Here are just a few of the many situations: The main lobby doors in very cold regions can suck in outside air and drop the lobby temperature to dangerously low levels. (Freeze sprinkler pipes etc.) This can take a new designer by surprise because he thinks his design of building OSA/exhaust ratio should have kept the lobby positive and air should be going out not coming in. It might become difficult to operate exit doors due to excessive differential pressure between inside and outside. Elevator shafts that have vents can be a real problem in tall buildings. The elevators doors can stick and malfunction. Then there is this whole business of smoke management for tall buildings. You should not even go near the smoke management design if you have not mastered the stack effect. The mathematics of Stack Effect can get pretty complicated, and computer modeling is frequently used; but in this post I will just
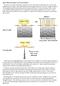
2 try to explain the Stack mechanism. Anyone interested in details should look up the ASHRAE Handbook. The first question that comes up in a new designer s m ind is: Well how significant can it be? And the answer is: Very significant! Let us try to get a feel for the magnitude of an UNCHECKED stack effect and it will be very obvious why a tall building cannot be designed without studying the stack effect very carefully. If there are two adjacent columns of air, having different temperatures, both open at the top and connected at the bottom, then you will set up a flow from the colder denser column to the warmer lighter column. That in a nutshell is the Stack Effect. To drive the concepts home with an extreme example, let us see what will happen if a high-rise in a very cold climate was not sealed to protect against the stack effect. See Figure 1. (IMPORTANT NOTE: Figure 1 does not represent what actually happens in a tall high-rise. In a real building there is leakage on every level and air is coming in on the lower levels and leaving on the upper levels. In the middle is an elevation known as the Neutral Plane. See the Chapter on Ventilation and Infiltration in ASHRAE Handbook for details. I am just trying to explain why the stack sets up and how significant it can be if only open at top and bottom like a boiler chimney.)
3 There are 2 columns, A and B. Both are exactly 1 square foot in cross-sectional area. Both are exactly 1,000 feet high. (Pretty ordinary height for a Chicago skyscraper, maybe 70 stories or so.) Column A is kept at a temperature of 75 F and column B (cold Chicago winter morning) at 0 F. Both the columns have a connection at the bottom, which I have called the Boundary Plate in the sketch. Imagine that it can be pulled out, and the 2 columns can be connected. What I want to know is: what is the force or pressure on this boundary plate applied by the cold air o utside trying to force its way into the warmer 75 F degree air if the plate were removed? And that is of course the stack effect. Luckily the answer doesn t need any complicated formulas, just some simple arithmetic. At 75 F the weight density of air is lbf/ft 3 A 1000ft high stack of this 75 F air with a 1ft 2 base will weigh: ( X 1000 = 74.2 LBF/FT 2 ). And since we have chosen the base to be exactly 1 ft 2, this is also the pressure at the base. Also, since fluids exert pressure equally in all directions, this is also the pressure on the boundary plate. At 0 F the weight density of air is lbf/ft 3. As above, the pressure at the base of the 0 F column is ( X 1000 = 86.4 LBF/FT 2 ). So the net pressure on the boundary plate from the cold side is ( ) OR 12.2 PSF. That is the stack effect. And its magnitude is such that it cannot be ignored. In well-designed high-rise structures the stack effect is never allowed unchecked. All the floor penetrations are sealed and
4 direct air paths from ground to roof blocked. But still, imagine a lobby door wide open and along comes an elevator (with roof vents in its shaft) and the elevator doors open. The cold air has a path in, and the warm air will be pushed through the elevator shaft to the top of the building and out. Some Random Observations about Figure 1: Some people may ask, what happened to the atmospheric pressure above the columns, why is that not considered? Well, it cancels out when taking a difference of the two sides. The enclosure B which is shown dotted is really not necessary. Just plain out-doors will give the same values. The densities I used were for DRY air. For air at 0 F it doesn t make much difference. For air at 75 F the density of say 50% RH air will be less (lighter) which will increase the stack effect. But the point here is just to show what is going on and not accurate calculations. Of course the reverse stack effect is also possible. This is demonstrated when you are standing outside the lobby of a Las Vegas Casino on a 110 F day and the doors open. Nice cool air comes out. Usually the magnitude of this reverse effect is not as bothersome (exce pt for extreme climates like Vegas) due to the lower value of temperature differential. Again, talking about the magnitude, unchecked (and top/bottom opening only) this 12.2 PSF equates to 2.35 WC. (In a real building it will not be this high due to infil tration on the lower floors and exfiltration on the upper floors.) But still, considering that we design lobbies to somewhere around 0.05 to 0.1 inches of positive pressure, you can foresee how hard it will be to keep the cold air out. Another way to get a feel for the magnitude of stack effect is that 12.2 PSF equates to about 67 MPH wind on a flat vertical surface! You can imagine trying to open/close a door against this pressure. As mentioned above a peculiarity of the stack effect in a real world building is that there is always a NEUTRAL plane where the air will neither go in nor come out. It is just simple logic that if air keeps coming in as you drill holes going up, and
5 keeps going out as you drill holes from top down, then at some point it will neither infiltrate nor ex -filtrate. Because the density will drop a little due to altitude, so air may be a couple of percentage points lighter at 1000 feet than at the base. To compensate for that, in ac curate work, you can take the density at mid-height, 500 feet, and then use that value in the above formula. Remember all we are trying to do is to find the pressures at the base of the two columns. This is why revolving doors are so necessary in extreme climates. Because of their rotating seal design they are always better than the double door vestibules. Ω
Chapter: Atmosphere Section 3: Air Movement
 Table of Contents Chapter: Atmosphere Section 3: Air Movement We will learn about Air Movement=Wind -Why different latitudes on Earth will receive different amounts of Solar Energy -The Coriolis Effect
Table of Contents Chapter: Atmosphere Section 3: Air Movement We will learn about Air Movement=Wind -Why different latitudes on Earth will receive different amounts of Solar Energy -The Coriolis Effect
Exercises The Atmosphere (page 383) 20.2 Atmospheric Pressure (pages )
 Exercises 20.1 The Atmosphere (page 383) 1. The energizes the molecules in Earth s atmosphere. 2. Why is gravity important to Earth s atmosphere? 3. What would happen to Earth s atmosphere without the
Exercises 20.1 The Atmosphere (page 383) 1. The energizes the molecules in Earth s atmosphere. 2. Why is gravity important to Earth s atmosphere? 3. What would happen to Earth s atmosphere without the
Static Fluids. **All simulations and videos required for this package can be found on my website, here:
 DP Physics HL Static Fluids **All simulations and videos required for this package can be found on my website, here: http://ismackinsey.weebly.com/fluids-hl.html Fluids are substances that can flow, so
DP Physics HL Static Fluids **All simulations and videos required for this package can be found on my website, here: http://ismackinsey.weebly.com/fluids-hl.html Fluids are substances that can flow, so
PROCESS ROTATING EQUIPMENT (CENTRIFUGAL PUMPS )
 PROCESS ROTATING EQUIPMENT ( ) Slide No: ١ Pumps can be divided into two main groups: Displacement pumps Dynamic pumps Slide No: ٢ Slide No: ٣ Slide No: ٤ Slide No: ٥ BASIC CENTRIFUGAL PUMP PARTS Casing
PROCESS ROTATING EQUIPMENT ( ) Slide No: ١ Pumps can be divided into two main groups: Displacement pumps Dynamic pumps Slide No: ٢ Slide No: ٣ Slide No: ٤ Slide No: ٥ BASIC CENTRIFUGAL PUMP PARTS Casing
Test Review: Geometry I Period 2,4,6. TEST DATE: All classes Wednesday April 9. Things it would be a good idea to know:
 Test Review: Geometry I Period 2,4,6 TEST DATE: All classes Wednesday April 9 Things it would be a good idea to know: 1) Special Right Triangles 2) Geometric Mean 3) SOHCAHTOA Test Outline Part I - Non-Calculator
Test Review: Geometry I Period 2,4,6 TEST DATE: All classes Wednesday April 9 Things it would be a good idea to know: 1) Special Right Triangles 2) Geometric Mean 3) SOHCAHTOA Test Outline Part I - Non-Calculator
ConcepTest PowerPoints
 ConcepTest PowerPoints Chapter 10 Physics: Principles with Applications, 6 th edition Giancoli 2005 Pearson Prentice Hall This work is protected by United States copyright laws and is provided solely for
ConcepTest PowerPoints Chapter 10 Physics: Principles with Applications, 6 th edition Giancoli 2005 Pearson Prentice Hall This work is protected by United States copyright laws and is provided solely for
Liquid level measurement using hydrostatic pressure and buoyancy
 iquid level measurement using hydrostatic pressure and buoyancy This worksheet and all related files are licensed under the Creative Commons Attribution icense, version 1.0. To view a copy of this license,
iquid level measurement using hydrostatic pressure and buoyancy This worksheet and all related files are licensed under the Creative Commons Attribution icense, version 1.0. To view a copy of this license,
Liquid Level Measurement
 Technical Article Liquid Level Measurement A pressure transmitter can be used to determine the liquid level in a tank, well, river or other body of liquid. The pressure at the bottom of a liquid filled
Technical Article Liquid Level Measurement A pressure transmitter can be used to determine the liquid level in a tank, well, river or other body of liquid. The pressure at the bottom of a liquid filled
Pressure and Density Altitude
 Pressure and Density Altitude Reference Sources Pilot s Handbook of Aeronautical Knowledge o Pages 9-1 to 9-4, Aircraft Performance o Pages 9-20 to 9-21, Density Altitude Charts Study Questions 1. Where
Pressure and Density Altitude Reference Sources Pilot s Handbook of Aeronautical Knowledge o Pages 9-1 to 9-4, Aircraft Performance o Pages 9-20 to 9-21, Density Altitude Charts Study Questions 1. Where
SIZING THE EXTROL DIAPHRAGM-TYPE HYDRO-PNEUMATIC TANK
 SIZING THE EXTROL DIAPHRAGM-TYPE HYDRO-PNEUMATIC TANK 1400 Division Road, West Warwick, RI 02893 T: 401.884.6300 F: 401.885.2567 www.amtrol.com Sizing the ExTrol Diaphragm-Type Hydro-Pneumatic Tank For
SIZING THE EXTROL DIAPHRAGM-TYPE HYDRO-PNEUMATIC TANK 1400 Division Road, West Warwick, RI 02893 T: 401.884.6300 F: 401.885.2567 www.amtrol.com Sizing the ExTrol Diaphragm-Type Hydro-Pneumatic Tank For
PREVIEW COPY. Table of Contents. Basic Pumping Concepts...3. Maintaining Packing and Seals Lesson Three Maintaining Centrifugal Pumps...
 Table of Contents Lesson One Lesson Two Basic Pumping Concepts...3 Maintaining Packing and Seals...19 Lesson Three Maintaining Centrifugal Pumps...37 Lesson Four Overhauling Centrifugal Pumps...53 Lesson
Table of Contents Lesson One Lesson Two Basic Pumping Concepts...3 Maintaining Packing and Seals...19 Lesson Three Maintaining Centrifugal Pumps...37 Lesson Four Overhauling Centrifugal Pumps...53 Lesson
Section 1. Global Wind Patterns and Weather. What Do You See? Think About It. Investigate. Learning Outcomes
 Chapter 5 Winds, Oceans, Weather, and Climate Section 1 Global Wind Patterns and Weather What Do You See? Learning Outcomes In this section, you will Determine the effects of Earth s rotation and the uneven
Chapter 5 Winds, Oceans, Weather, and Climate Section 1 Global Wind Patterns and Weather What Do You See? Learning Outcomes In this section, you will Determine the effects of Earth s rotation and the uneven
Physics General Physics. Lecture 19 - Fluids. Fall 2016 Semester Prof. Matthew Jones
 Physics 22000 General Physics Lecture 19 - Fluids Fall 2016 Semester Prof. Matthew Jones 1 2 What s New This Time? Previously, we had ignored the effect of gravity on the gas particles that were described
Physics 22000 General Physics Lecture 19 - Fluids Fall 2016 Semester Prof. Matthew Jones 1 2 What s New This Time? Previously, we had ignored the effect of gravity on the gas particles that were described
LAB 5 Pressure and Fluids
 Cabrillo College Physics 10L Full Name LAB 5 Pressure and Fluids Read Hewitt Chapters 11 and 14 What to learn and explore Physicists have found that if they visualize (or model) a gas as a collection of
Cabrillo College Physics 10L Full Name LAB 5 Pressure and Fluids Read Hewitt Chapters 11 and 14 What to learn and explore Physicists have found that if they visualize (or model) a gas as a collection of
Chapter 15 Fluids. Copyright 2010 Pearson Education, Inc.
 Chapter 15 Fluids Density Units of Chapter 15 Pressure Static Equilibrium in Fluids: Pressure and Depth Archimedes Principle and Buoyancy Applications of Archimedes Principle Fluid Flow and Continuity
Chapter 15 Fluids Density Units of Chapter 15 Pressure Static Equilibrium in Fluids: Pressure and Depth Archimedes Principle and Buoyancy Applications of Archimedes Principle Fluid Flow and Continuity
What is air track? 1 Introduction
 What is air track? 1 Introduction The SAHF model was thought up by Australian Shan Raffel in the early 2000 s. After much debate with colleagues, and under the influence of American Ed Hartin the model
What is air track? 1 Introduction The SAHF model was thought up by Australian Shan Raffel in the early 2000 s. After much debate with colleagues, and under the influence of American Ed Hartin the model
Practical Guide. By Steven T. Taylor, P.E., Member ASHRAE
 ractical Guide The following article was published in ASHRAE Journal, March 2003. Copyright 2003 American Society of Heating, Refrigerating and Air- Conditioning Engineers, Inc. It is presented for educational
ractical Guide The following article was published in ASHRAE Journal, March 2003. Copyright 2003 American Society of Heating, Refrigerating and Air- Conditioning Engineers, Inc. It is presented for educational
SAMPLE RH = P 1. where. P 1 = the partial pressure of the water vapor at the dew point temperature of the mixture of dry air and water vapor
 moisture starts to condense out of the air. The temperature at which this happens is called the dew point temperature, or the saturation temperature. What is commonly called saturation pressure or condensing
moisture starts to condense out of the air. The temperature at which this happens is called the dew point temperature, or the saturation temperature. What is commonly called saturation pressure or condensing
2 Buoyant Force. TAKE A LOOK 2. Identify What produces buoyant force?
 CHAPTER 3 2 Buoyant Force SECTION Forces in Fluids BEFORE YOU READ After you read this section, you should be able to answer these questions: What is buoyant force? What makes objects sink or float? How
CHAPTER 3 2 Buoyant Force SECTION Forces in Fluids BEFORE YOU READ After you read this section, you should be able to answer these questions: What is buoyant force? What makes objects sink or float? How
Chapter 9 Fluids CHAPTER CONTENTS
 Flowing fluids, such as the water flowing in the photograph at Coors Falls in Colorado, can make interesting patterns In this chapter, we will investigate the basic physics behind such flow Photo credit:
Flowing fluids, such as the water flowing in the photograph at Coors Falls in Colorado, can make interesting patterns In this chapter, we will investigate the basic physics behind such flow Photo credit:
A Simple Horizontal Velocity Model of a Rising Thermal Instability in the Atmospheric Boundary Layer
 A Simple Horizontal Velocity Model of a Rising Thermal Instability in the Atmospheric Boundary Layer (In other words, how to take a closer look at downwind thermal drift) Abstract This pilot, as well as
A Simple Horizontal Velocity Model of a Rising Thermal Instability in the Atmospheric Boundary Layer (In other words, how to take a closer look at downwind thermal drift) Abstract This pilot, as well as
1 Fluids and Pressure
 CHAPTER 3 1 Fluids and Pressure SECTION Forces in Fluids BEFORE YOU READ After you read this section, you should be able to answer these questions: What are fluids? What is atmospheric pressure? What is
CHAPTER 3 1 Fluids and Pressure SECTION Forces in Fluids BEFORE YOU READ After you read this section, you should be able to answer these questions: What are fluids? What is atmospheric pressure? What is
Space Pressurization: Concept and Practice ASHRAE Distinguished Lecture Series
 Space Pressurization: Concept and Practice ASHRAE Distinguished Lecture Series Jim Coogan Siemens Building Technologies ASHRAE, St. Louis Chapter November10, 2014 Agenda Introduction (concept, purpose,
Space Pressurization: Concept and Practice ASHRAE Distinguished Lecture Series Jim Coogan Siemens Building Technologies ASHRAE, St. Louis Chapter November10, 2014 Agenda Introduction (concept, purpose,
Pascal s Sinking Feeling LinkedIn Article March 8, 2016 Caoimhín P. Connell Forensic Industrial Hygienist
 Forensic Applications Consulting Technologies, Inc. Pascal s Sinking Feeling LinkedIn Article March 8, 2016 Caoimhín P. Connell Forensic Industrial Hygienist A very common myth we encounter is the issue
Forensic Applications Consulting Technologies, Inc. Pascal s Sinking Feeling LinkedIn Article March 8, 2016 Caoimhín P. Connell Forensic Industrial Hygienist A very common myth we encounter is the issue
Chapter: Atmosphere Section 3: Air Movement
 Table of Contents Chapter: Atmosphere Section 3: Air Movement We will learn about: -Air Movement=Wind -Why different latitudes on Earth will receive different amounts of Solar Energy -The Coriolis Effect
Table of Contents Chapter: Atmosphere Section 3: Air Movement We will learn about: -Air Movement=Wind -Why different latitudes on Earth will receive different amounts of Solar Energy -The Coriolis Effect
Agood tennis player knows instinctively how hard to hit a ball and at what angle to get the ball over the. Ball Trajectories
 42 Ball Trajectories Factors Influencing the Flight of the Ball Nathalie Tauziat, France By Rod Cross Introduction Agood tennis player knows instinctively how hard to hit a ball and at what angle to get
42 Ball Trajectories Factors Influencing the Flight of the Ball Nathalie Tauziat, France By Rod Cross Introduction Agood tennis player knows instinctively how hard to hit a ball and at what angle to get
Convection Current Exploration:
 Heat on Earth 8.10A RECOGNIZE THAT THE SUN PROVIDES THE ENERGY THAT DRIVES CONVECTION WITHIN THE ATMOSPHERE AND OCEANS, PRODUCING WINDS AND OCEAN CURRENTS [INCORPORATE 6.6B INTO CONVECTION] A few reminders
Heat on Earth 8.10A RECOGNIZE THAT THE SUN PROVIDES THE ENERGY THAT DRIVES CONVECTION WITHIN THE ATMOSPHERE AND OCEANS, PRODUCING WINDS AND OCEAN CURRENTS [INCORPORATE 6.6B INTO CONVECTION] A few reminders
Installation Instructions MODEL VSTI-A020 Tank Indicator Installation Model: VSTI-A020, Stainless Reverse Read System Versa Steel Inc. Guide Cables No
 Tank Indicator Installation Model: VSTI-A020, Stainless Reverse Read System Guide Cables No Guide Cables 1 August 4, 2011 Assembly Instructions: (Shown with a 2 board, 12 ft kit) ITEM NO. PART NUMBER DESCRIPTION
Tank Indicator Installation Model: VSTI-A020, Stainless Reverse Read System Guide Cables No Guide Cables 1 August 4, 2011 Assembly Instructions: (Shown with a 2 board, 12 ft kit) ITEM NO. PART NUMBER DESCRIPTION
PHYSICS. Light: Sound:
 PHYSICS Light: The speed of light changes as it passes through different things such as air, glass and water. This affects the way we see things underwater with a diving mask. As the light passes through
PHYSICS Light: The speed of light changes as it passes through different things such as air, glass and water. This affects the way we see things underwater with a diving mask. As the light passes through
VACUUM TESTING PRECAST CONCRETE MANHOLES
 1 OF 5 testing is a quick, safe and practical way to validate manhole system integrity. Manhole sections can be tested at the precast concrete plant prior to delivery or on site prior to backfilling. Here
1 OF 5 testing is a quick, safe and practical way to validate manhole system integrity. Manhole sections can be tested at the precast concrete plant prior to delivery or on site prior to backfilling. Here
Guidance on room integrity testing and its interpretation
 Guidance Note Guidance on room integrity testing and its interpretation Guidance on room integrity testing and its interpretation 1. SCOPE... 6 2. INTRODUCTION AND BACKGROUND... 6 2.1. DEVELOPMENT OF INTEGRITY
Guidance Note Guidance on room integrity testing and its interpretation Guidance on room integrity testing and its interpretation 1. SCOPE... 6 2. INTRODUCTION AND BACKGROUND... 6 2.1. DEVELOPMENT OF INTEGRITY
THE INNER WORKINGS OF A SIPHON Jacques Chaurette p. eng. January 2003
 THE INNER WORKINGS OF A SIPHON Jacques Chaurette p. eng. www.lightmypump.com January 2003 Synopsis The objective of this article is to explain how a siphon works. The difference between low pressure, atmospheric
THE INNER WORKINGS OF A SIPHON Jacques Chaurette p. eng. www.lightmypump.com January 2003 Synopsis The objective of this article is to explain how a siphon works. The difference between low pressure, atmospheric
USPA National Speed Skydiving Championships Competition Rules. Chapter 14. United States Parachute Association Copyright 2018 by USPA
 USPA National Speed Skydiving Championships Competition Rules Chapter 14 United States Parachute Association Copyright 2018 by USPA USPA AUTHORITY The competition will be conducted under the authority
USPA National Speed Skydiving Championships Competition Rules Chapter 14 United States Parachute Association Copyright 2018 by USPA USPA AUTHORITY The competition will be conducted under the authority
PLEA th Conference, Opportunities, Limits & Needs Towards an environmentally responsible architecture Lima, Perú 7-9 November 2012
 Natural Ventilation using Ventilation shafts Multiple Interconnected Openings in a Ventilation Shaft Reduce the Overall Height of the Shaft While Maintaining the Effectiveness of Natural Ventilation ABHAY
Natural Ventilation using Ventilation shafts Multiple Interconnected Openings in a Ventilation Shaft Reduce the Overall Height of the Shaft While Maintaining the Effectiveness of Natural Ventilation ABHAY
COURSE NUMBER: ME 321 Fluid Mechanics I Fluid statics. Course teacher Dr. M. Mahbubur Razzaque Professor Department of Mechanical Engineering BUET
 COURSE NUMBER: ME 321 Fluid Mechanics I Fluid statics Course teacher Dr. M. Mahbubur Razzaque Professor Department of Mechanical Engineering BUET 1 Fluid statics Fluid statics is the study of fluids in
COURSE NUMBER: ME 321 Fluid Mechanics I Fluid statics Course teacher Dr. M. Mahbubur Razzaque Professor Department of Mechanical Engineering BUET 1 Fluid statics Fluid statics is the study of fluids in
Chapter 15 Fluid. Density
 Density Chapter 15 Fluid Pressure Static Equilibrium in Fluids: Pressure and Depth Archimedes Principle and Buoyancy Applications of Archimedes Principle By Dr. Weining man 1 Units of Chapter 15 Fluid
Density Chapter 15 Fluid Pressure Static Equilibrium in Fluids: Pressure and Depth Archimedes Principle and Buoyancy Applications of Archimedes Principle By Dr. Weining man 1 Units of Chapter 15 Fluid
1 Currents. TAKE A LOOK 2. Read a Map In what direction does the Gulf Stream flow?
 CHAPTER 5 1 Currents SECTION The Movement of Ocean Water BEFORE YOU READ After you read this section, you should be able to answer these questions: What factors affect ocean currents? Why are ocean currents
CHAPTER 5 1 Currents SECTION The Movement of Ocean Water BEFORE YOU READ After you read this section, you should be able to answer these questions: What factors affect ocean currents? Why are ocean currents
Wednesday, September 20, 2017 Reminders. Week 3 Review is now available on D2L (through Friday) Exam 1, Monday, September 25, Chapters 1-4
 Wednesday, September 20, 2017 Reminders Week 3 Review is now available on D2L (through Friday) Exam 1, Monday, September 25, Chapters 1-4 PLEASE don t memorize equations, but know how to recognize them
Wednesday, September 20, 2017 Reminders Week 3 Review is now available on D2L (through Friday) Exam 1, Monday, September 25, Chapters 1-4 PLEASE don t memorize equations, but know how to recognize them
In the liquid phase, molecules can flow freely from position. another. A liquid takes the shape of its container. 19.
 In the liquid phase, molecules can flow freely from position to position by sliding over one another. A liquid takes the shape of its container. In the liquid phase, molecules can flow freely from position
In the liquid phase, molecules can flow freely from position to position by sliding over one another. A liquid takes the shape of its container. In the liquid phase, molecules can flow freely from position
In the liquid phase, molecules can flow freely from position to position by sliding over one another. A liquid takes the shape of its container.
 In the liquid phase, molecules can flow freely from position to position by sliding over one another. A liquid takes the shape of its container. In the liquid phase, molecules can flow freely from position
In the liquid phase, molecules can flow freely from position to position by sliding over one another. A liquid takes the shape of its container. In the liquid phase, molecules can flow freely from position
Controlling Cabin and Envelope Air Flows & Pressure Differentials
 Controlling Cabin and Envelope Air Flows & Pressure Differentials To control envelope moisture and related problems Douglas S. Walkinshaw and Keith F. Preston ECHO Air Inc www.indoorair.ca 1 This paper
Controlling Cabin and Envelope Air Flows & Pressure Differentials To control envelope moisture and related problems Douglas S. Walkinshaw and Keith F. Preston ECHO Air Inc www.indoorair.ca 1 This paper
The Rule of Right-Angles: Exploring the term Angle before Depth
 The Rule of Right-Angles: Exploring the term Angle before Depth I m a firm believer in playing an efficient game. Goaltenders can increase their efficiency in almost every category of their game, from
The Rule of Right-Angles: Exploring the term Angle before Depth I m a firm believer in playing an efficient game. Goaltenders can increase their efficiency in almost every category of their game, from
Lecture Outline Chapter 15. Physics, 4 th Edition James S. Walker. Copyright 2010 Pearson Education, Inc.
 Lecture Outline Chapter 15 Physics, 4 th Edition James S. Walker Chapter 15 Fluids Density Units of Chapter 15 Pressure Static Equilibrium in Fluids: Pressure and Depth Archimedes Principle and Buoyancy
Lecture Outline Chapter 15 Physics, 4 th Edition James S. Walker Chapter 15 Fluids Density Units of Chapter 15 Pressure Static Equilibrium in Fluids: Pressure and Depth Archimedes Principle and Buoyancy
T. James Noyes, El Camino College Winds Unit (Topic 8A-1) page 1
 T. James Noyes, El Camino College Winds Unit (Topic 8A-1) page 1 Name: Section: Winds Unit (3 pts) The Ocean and the Atmosphere We need to learn about the atmosphere, because the ocean and atmosphere are
T. James Noyes, El Camino College Winds Unit (Topic 8A-1) page 1 Name: Section: Winds Unit (3 pts) The Ocean and the Atmosphere We need to learn about the atmosphere, because the ocean and atmosphere are
γ water = 62.4 lb/ft 3 = 9800 N/m 3
 CEE 4 Aut 004, Exam # Work alone. Answer all questions. Total pts: 90. Always make your thought process clear; if it is not, you will not receive partial credit for incomplete or partially incorrect answers.
CEE 4 Aut 004, Exam # Work alone. Answer all questions. Total pts: 90. Always make your thought process clear; if it is not, you will not receive partial credit for incomplete or partially incorrect answers.
Full Name: Class: Period: Date:
 Topic/Objective: Essential Question: Full Name: Class: Period: Date: Tutor Use Only: Air Pressure and Wind (Chapter 19) Air Pressure the weight of the atmosphere pushing down on the Earth exerting a force
Topic/Objective: Essential Question: Full Name: Class: Period: Date: Tutor Use Only: Air Pressure and Wind (Chapter 19) Air Pressure the weight of the atmosphere pushing down on the Earth exerting a force
From and
 From http://www.school-for-champions.com/science/fluidpressure.htm and http://www.school-forchampions.com/science/fluidfloating.htm by Ron Kurtus, School for Champions Pressure in Fluids by Ron Kurtus
From http://www.school-for-champions.com/science/fluidpressure.htm and http://www.school-forchampions.com/science/fluidfloating.htm by Ron Kurtus, School for Champions Pressure in Fluids by Ron Kurtus
To connect the words of Archimedes Principle to the actual behavior of submerged objects.
 Archimedes Principle PURPOSE To connect the words of Archimedes Principle to the actual behavior of submerged objects. To examine the cause of buoyancy; that is, the variation of pressure with depth in
Archimedes Principle PURPOSE To connect the words of Archimedes Principle to the actual behavior of submerged objects. To examine the cause of buoyancy; that is, the variation of pressure with depth in
Wind Effect on Smoke Exhaust by Natural Vent
 The 2012 World Congress on Advances in Civil, Environmental, and Materials Research (ACEM 12) Seoul, Korea, August 26-30, 2012 Wind Effect on Smoke Exhaust by Natural Vent J. Li 1) and *W.K. Chow 2) 1)
The 2012 World Congress on Advances in Civil, Environmental, and Materials Research (ACEM 12) Seoul, Korea, August 26-30, 2012 Wind Effect on Smoke Exhaust by Natural Vent J. Li 1) and *W.K. Chow 2) 1)
What Causes Wind? Exploration: How Does Air Move When Pressure Builds Up? 4.2 Explore. Predict
 4.2 Explore What Causes Wind? In Learning Set 1, you built an anemometer. You used it to measure wind speed and direction in your community. In the last section, you read about how wind and ocean currents
4.2 Explore What Causes Wind? In Learning Set 1, you built an anemometer. You used it to measure wind speed and direction in your community. In the last section, you read about how wind and ocean currents
OFFICIAL POLICE REPORT
 TRAINING LAB FIREARMS AND BALLISTICS: USING BULLET TRAJECTORY TO DETERMINE THE POSITION OF A DISTANT SHOOTER NAME Background: You have been trained to locate the position of a close range shooter by using
TRAINING LAB FIREARMS AND BALLISTICS: USING BULLET TRAJECTORY TO DETERMINE THE POSITION OF A DISTANT SHOOTER NAME Background: You have been trained to locate the position of a close range shooter by using
Trigonometry Problems
 GCSE MATHEMATICS Trigonometry Problems These questions have been taken or modified from previous AQA GCSE Mathematics Papers. Instructions Use black ink or black ball-point pen. Draw diagrams in pencil.
GCSE MATHEMATICS Trigonometry Problems These questions have been taken or modified from previous AQA GCSE Mathematics Papers. Instructions Use black ink or black ball-point pen. Draw diagrams in pencil.
Meteorology 2/6/2017. Wind, and its Interaction with Particle Plumes. Variation of wind speed with elevation. Variation of wind speed during the day
 Meteorology The effect of wind, weather, and temperature conditions on the behavior of particle plumes Wind, and its Interaction with Particle Plumes Variation of wind speed with elevation Variation of
Meteorology The effect of wind, weather, and temperature conditions on the behavior of particle plumes Wind, and its Interaction with Particle Plumes Variation of wind speed with elevation Variation of
Loads on Structures. Dead Load / Fixed Load Live Load / Imposed Load Earthquake Load Wind Load Snow Load
 Loads on Structures Dead Load / Fixed Load Live Load / Imposed Load Earthquake Load Wind Load Snow Load Characteristics of Wind Load Depends upon - velocity and density of the air height above ground level
Loads on Structures Dead Load / Fixed Load Live Load / Imposed Load Earthquake Load Wind Load Snow Load Characteristics of Wind Load Depends upon - velocity and density of the air height above ground level
UNIT 2 FLUIDS PHYS:1200 LECTURE 12 FLUIDS (1)
 1 UNIT 2 FLUIDS PHYS:1200 LECTURE 12 FLUIDS (1) Lecture 12 is the first lecture on the new topic of fluids. Thus far we have been discussing the physics of ideal solid objects that do not change their
1 UNIT 2 FLUIDS PHYS:1200 LECTURE 12 FLUIDS (1) Lecture 12 is the first lecture on the new topic of fluids. Thus far we have been discussing the physics of ideal solid objects that do not change their
 ASHRAE WILL ILL GIVE Y OU THE W ORLD This ASHRAE Distinguished Lecturer is brought to you by the Society Chapter Technology Transfer Committee Complete the Distinguished Lecturer Event Summary Critique
ASHRAE WILL ILL GIVE Y OU THE W ORLD This ASHRAE Distinguished Lecturer is brought to you by the Society Chapter Technology Transfer Committee Complete the Distinguished Lecturer Event Summary Critique
Fluids. James H Dann, Ph.D. Say Thanks to the Authors Click (No sign in required)
 Fluids James H Dann, Ph.D. Say Thanks to the Authors Click http://www.ck12.org/saythanks (No sign in required) To access a customizable version of this book, as well as other interactive content, visit
Fluids James H Dann, Ph.D. Say Thanks to the Authors Click http://www.ck12.org/saythanks (No sign in required) To access a customizable version of this book, as well as other interactive content, visit
Figure 1 Figure 1 shows the involved forces that must be taken into consideration for rudder design. Among the most widely known profiles, the most su
 THE RUDDER starting from the requirements supplied by the customer, the designer must obtain the rudder's characteristics that satisfy such requirements. Subsequently, from such characteristics he must
THE RUDDER starting from the requirements supplied by the customer, the designer must obtain the rudder's characteristics that satisfy such requirements. Subsequently, from such characteristics he must
Applications of Bernoulli s principle. Principle states that areas with faster moving fluids will experience less pressure
 Applications of Bernoulli s principle Principle states that areas with faster moving fluids will experience less pressure Artery o When blood flows through narrower regions of arteries, the speed increases
Applications of Bernoulli s principle Principle states that areas with faster moving fluids will experience less pressure Artery o When blood flows through narrower regions of arteries, the speed increases
Question : What are some tips and recommendations and choices for roof venting?? Part One
 Greenhouse - Q and A TIPS AND ADVICE Agroponic Industries Ltd. Calgary, Alberta, Canada ph 403 241 8234 email: agropon@agroponic.com Ask the Experts Question : What are some tips and recommendations and
Greenhouse - Q and A TIPS AND ADVICE Agroponic Industries Ltd. Calgary, Alberta, Canada ph 403 241 8234 email: agropon@agroponic.com Ask the Experts Question : What are some tips and recommendations and
FUNDAMENTALS OF PRESSURE REGULATORS ROBERT BENNETT MANAGER OF TRAINING ELSTER AMERICAN METER
 FUNDAMENTALS OF PRESSURE REGULATORS ROBERT BENNETT MANAGER OF TRAINING ELSTER AMERICAN METER SUPPLY = DEMAND FUNCTION OF A REGULATOR A regulator may be defined as a "mechanism for controlling or governing
FUNDAMENTALS OF PRESSURE REGULATORS ROBERT BENNETT MANAGER OF TRAINING ELSTER AMERICAN METER SUPPLY = DEMAND FUNCTION OF A REGULATOR A regulator may be defined as a "mechanism for controlling or governing
The following article was authored by Jacques Chaurette of Fluide Design, Inc. ( All rights reserved. - HOW DOES A SIPHON WORK?
 The following article was authored by Jacques Chaurette of Fluide Design, Inc. (www.fluidedesign.com) All rights reserved. - HOW DOES A SIPHON WORK? - A siphon is a length of tubing that allows you to
The following article was authored by Jacques Chaurette of Fluide Design, Inc. (www.fluidedesign.com) All rights reserved. - HOW DOES A SIPHON WORK? - A siphon is a length of tubing that allows you to
How Much Pressure Can You Stand?
 How Much Pressure Can You Stand? The reason you don't end up like a human sieve on a bed of nails is that there are so many nails supporting your weight - each individual nail is only supporting a tiny
How Much Pressure Can You Stand? The reason you don't end up like a human sieve on a bed of nails is that there are so many nails supporting your weight - each individual nail is only supporting a tiny
The Fundamentals of Putting
 The Fundamentals of Putting Episode 2 Putter Face and Path Direction The putter face angle at impact and the swing path direction at impact are the critical factors which determine the initial direction
The Fundamentals of Putting Episode 2 Putter Face and Path Direction The putter face angle at impact and the swing path direction at impact are the critical factors which determine the initial direction
PHYSICS - CLUTCH CH 17: FLUID MECHANICS.
 !! www.clutchprep.com INTRO TO DENSITY LIQUIDS and GASES are types of. So we use the term to refer generally to both Liquids AND Gases. The DENSITY of a material is a measure of how tight the molecules
!! www.clutchprep.com INTRO TO DENSITY LIQUIDS and GASES are types of. So we use the term to refer generally to both Liquids AND Gases. The DENSITY of a material is a measure of how tight the molecules
Andrew Carter. Dry Ice: Sublimating underwater, Forming a Cloud of CO 2, and CO 2 gas spilling over an edge.
 Flow Visualization MCEN 5151, Spring 2011 Andrew Carter Team Project 3 5/4/11 Dry Ice: Sublimating underwater, Forming a Cloud of CO 2, and CO 2 gas spilling over an edge. Purpose: The objective of this
Flow Visualization MCEN 5151, Spring 2011 Andrew Carter Team Project 3 5/4/11 Dry Ice: Sublimating underwater, Forming a Cloud of CO 2, and CO 2 gas spilling over an edge. Purpose: The objective of this
PUMP CONSULTING & TRAINING LLC Joseph R. Askew 1811 Stonecrest Ct. Lakeland, Fl
 PUMP CONSULTING & TRAINING LLC Joseph R. Askew 1811 Stonecrest Ct. Lakeland, Fl. 33813 863-644-3118 E-mail: pmpcnslt@tampabay.rr.com June 10, 2006 Phosphate Conference Clearwater Convention June 2006 Presentation
PUMP CONSULTING & TRAINING LLC Joseph R. Askew 1811 Stonecrest Ct. Lakeland, Fl. 33813 863-644-3118 E-mail: pmpcnslt@tampabay.rr.com June 10, 2006 Phosphate Conference Clearwater Convention June 2006 Presentation
Chapter 12. Properties of Gases
 Properties of Gases Each state of matter has its own properties. Gases have unique properties because the distance between the particles of a gas is much greater than the distance between the particles
Properties of Gases Each state of matter has its own properties. Gases have unique properties because the distance between the particles of a gas is much greater than the distance between the particles
Density and Specific Gravity
 Fluids Phases of Matter Matter is anything that has mass and takes up space (volume). The three common phases of matter are solid, liquid, and gas. A solid has a definite shape and size. A liquid has a
Fluids Phases of Matter Matter is anything that has mass and takes up space (volume). The three common phases of matter are solid, liquid, and gas. A solid has a definite shape and size. A liquid has a
The Discussion of this exercise covers the following points: Range with an elevated or suppressed zero Suppressed-zero range Elevated-zero range
 Exercise 4-3 Zero Suppression and Zero Elevation EXERCISE OBJECTIVE In this exercise, you will learn the effect that mounting a pressure transmitter above or below the reference level has on the hydrostatic
Exercise 4-3 Zero Suppression and Zero Elevation EXERCISE OBJECTIVE In this exercise, you will learn the effect that mounting a pressure transmitter above or below the reference level has on the hydrostatic
ACCESSORY KIT INSTALLATION INSTRUCTIONS
 ACCESSORY KIT INSTALLATION INSTRUCTIONS PROPANE CONVERSION - INDUCED COMBUSTION FURNACES 1NP0501 FOR USE WITH 95% MODELS: TG9S, GG9S (130,000 BTU ONLY) FOR USE WITH 80% MODELS: TG(8,L)S, GG(8,L)S (130,000
ACCESSORY KIT INSTALLATION INSTRUCTIONS PROPANE CONVERSION - INDUCED COMBUSTION FURNACES 1NP0501 FOR USE WITH 95% MODELS: TG9S, GG9S (130,000 BTU ONLY) FOR USE WITH 80% MODELS: TG(8,L)S, GG(8,L)S (130,000
Worked Questions and Answers
 Worked Questions and Answers A Learning Document for prospective Candidates For the Rotary Drilling Well Control Test Programme Copyright, IWCF June 2000 Revision No.1, November 2000 IWCF 2000 page 1 of
Worked Questions and Answers A Learning Document for prospective Candidates For the Rotary Drilling Well Control Test Programme Copyright, IWCF June 2000 Revision No.1, November 2000 IWCF 2000 page 1 of
PHYS 101 Previous Exam Problems
 PHYS 101 Previous Exam Problems CHAPTER 14 Fluids Fluids at rest pressure vs. depth Pascal s principle Archimedes s principle Buoynat forces Fluids in motion: Continuity & Bernoulli equations 1. How deep
PHYS 101 Previous Exam Problems CHAPTER 14 Fluids Fluids at rest pressure vs. depth Pascal s principle Archimedes s principle Buoynat forces Fluids in motion: Continuity & Bernoulli equations 1. How deep
Density. Chapters 12-14: Phases of Matter. Example: Density. Conceptual Check. Springs 2/27/12. Mass Density vs. Weight Density
 Chapters 12-14: Phases of Matter Density Sequence of increasing molecule motion (and kinetic energy) Solid Liquid Gas The densities of most liquids and solids vary slightly with changes in temperature
Chapters 12-14: Phases of Matter Density Sequence of increasing molecule motion (and kinetic energy) Solid Liquid Gas The densities of most liquids and solids vary slightly with changes in temperature
Kinetic-Molecular Theory
 GASES Chapter Eleven Kinetic-Molecular Theory! Recall that our only previous description of gases stated that gases completely fill and take the shape of their containers.! The Kinetic-Molecular Theory
GASES Chapter Eleven Kinetic-Molecular Theory! Recall that our only previous description of gases stated that gases completely fill and take the shape of their containers.! The Kinetic-Molecular Theory
The process of measuring air
 Measuring Leakage in High-Rise Buildings By Colin Genge The process of measuring air leakage to the outside in singlefamily homes is fairly well known among home performance professionals and anyone familiar
Measuring Leakage in High-Rise Buildings By Colin Genge The process of measuring air leakage to the outside in singlefamily homes is fairly well known among home performance professionals and anyone familiar
Air Pollution Dispersion
 Air Pollution Dispersion Dispersion Processes Convective Dispersion Air Parcel Dynamics Adiabatic Process Lapse Rate Equilibrium and Stability Atmospheric Stability Stability and Dispersion Temperature
Air Pollution Dispersion Dispersion Processes Convective Dispersion Air Parcel Dynamics Adiabatic Process Lapse Rate Equilibrium and Stability Atmospheric Stability Stability and Dispersion Temperature
IWCF Equipment Sample Questions (Surface Stack)
 IWCF Equipment Sample Questions (Surface Stack) 1. During a well control operation 4000 psi was shut in below the middle pipe rams. Ram type BOP data: Model: Cameron U type Rated Working Pressure: 15000
IWCF Equipment Sample Questions (Surface Stack) 1. During a well control operation 4000 psi was shut in below the middle pipe rams. Ram type BOP data: Model: Cameron U type Rated Working Pressure: 15000
FC-CIV HIDRCANA: Channel Hydraulics Flow Mechanics Review Fluid Statics
 FC-CIV HIDRCANA: Channel Hydraulics Flow Mechanics Review Fluid Statics Civil Engineering Program, San Ignacio de Loyola University Objective Calculate the forces exerted by a fluid at rest on plane or
FC-CIV HIDRCANA: Channel Hydraulics Flow Mechanics Review Fluid Statics Civil Engineering Program, San Ignacio de Loyola University Objective Calculate the forces exerted by a fluid at rest on plane or
2 Available: 1390/08/02 Date of returning: 1390/08/17 1. A suction cup is used to support a plate of weight as shown in below Figure. For the conditio
 1. A suction cup is used to support a plate of weight as shown in below Figure. For the conditions shown, determine. 2. A tanker truck carries water, and the cross section of the truck s tank is shown
1. A suction cup is used to support a plate of weight as shown in below Figure. For the conditions shown, determine. 2. A tanker truck carries water, and the cross section of the truck s tank is shown
Notes Chapter 3. Buoyancy
 Notes Chapter 3 Buoyancy Pressure in a Fluid 3.2 Pressure and the Buoyant Forces Liquids and gases are fluids materials that can flow and have no definite shape. Objects in a fluid experience a buoyant
Notes Chapter 3 Buoyancy Pressure in a Fluid 3.2 Pressure and the Buoyant Forces Liquids and gases are fluids materials that can flow and have no definite shape. Objects in a fluid experience a buoyant
AEROSPACE MICRO-LESSON
 AIAA Easily digestible Aerospace Principles revealed for K-12 Students and Educators. These lessons will be sent on a bi-weekly basis and allow grade-level focused learning. - AIAA STEM K-12 Committee.
AIAA Easily digestible Aerospace Principles revealed for K-12 Students and Educators. These lessons will be sent on a bi-weekly basis and allow grade-level focused learning. - AIAA STEM K-12 Committee.
Chapter 6. You lift a 10 N physics book up in the air a distance of 1 meter at a constant velocity of 0.5 m/s. The work done by gravity is
 I lift a barbell with a mass of 50 kg up a distance of 0.70 m. Then I let the barbell come back down to where I started. How much net work did I do on the barbell? A) - 340 J B) 0 J C) + 35 J D) + 340
I lift a barbell with a mass of 50 kg up a distance of 0.70 m. Then I let the barbell come back down to where I started. How much net work did I do on the barbell? A) - 340 J B) 0 J C) + 35 J D) + 340
Sizing of extraction ventilation system and air leakage calculations for SR99 tunnel fire scenarios
 Sizing of extraction ventilation system and air leakage calculations for SR99 tunnel fire scenarios Yunlong (Jason) Liu, PhD, PE HNTB Corporation Sean Cassady, FPE HNTB Corporation Abstract Extraction
Sizing of extraction ventilation system and air leakage calculations for SR99 tunnel fire scenarios Yunlong (Jason) Liu, PhD, PE HNTB Corporation Sean Cassady, FPE HNTB Corporation Abstract Extraction
Chapter. Air Pressure and Wind
 Chapter Air Pressure and Wind 19.1 Understanding Air Pressure Air Pressure Defined Air pressure is the pressure exerted by the weight of air. 19.1 Understanding Air Pressure Air Pressure Defined Air pressure
Chapter Air Pressure and Wind 19.1 Understanding Air Pressure Air Pressure Defined Air pressure is the pressure exerted by the weight of air. 19.1 Understanding Air Pressure Air Pressure Defined Air pressure
Summary of Lecture 10, 04 March 2008 Introduce the Hadley circulation and examine global weather patterns. Discuss jet stream dynamics jet streams
 Summary of Lecture 10, 04 March 2008 Introduce the Hadley circulation and examine global weather patterns. Discuss jet stream dynamics jet streams arise because the Coriolis force prevents Hadley-type
Summary of Lecture 10, 04 March 2008 Introduce the Hadley circulation and examine global weather patterns. Discuss jet stream dynamics jet streams arise because the Coriolis force prevents Hadley-type
GRUNDFOS industry GRUNDFOS CR MONITOR. Intelligent warning
 GRUNDFOS industry GRUNDFOS CR MONITOR Intelligent warning Look into the future with the CR monitor Tired of having to overhaul your pumps on a regular basis only to find that they are operating flawlessly?
GRUNDFOS industry GRUNDFOS CR MONITOR Intelligent warning Look into the future with the CR monitor Tired of having to overhaul your pumps on a regular basis only to find that they are operating flawlessly?
Write important assumptions used in derivation of Bernoulli s equation. Apart from an airplane wing, give an example based on Bernoulli s principle
 HW#3 Sum07 #1. Answer in 4 to 5 lines in the space provided for each question: (a) A tank partially filled with water has a balloon well below the free surface and anchored to the bottom by a string. The
HW#3 Sum07 #1. Answer in 4 to 5 lines in the space provided for each question: (a) A tank partially filled with water has a balloon well below the free surface and anchored to the bottom by a string. The
Exam Question 9: Hydrostatics. March 6, Applied Mathematics: Lecture 8. Brendan Williamson. Introduction. Density, Weight and Volume
 Exam Question 9: Hydrostatics March 6, 2017 This lecture is on hydrostatics, which is question 9 of the exam paper. Most of the situations we will study will relate to objects partly or fully submerged
Exam Question 9: Hydrostatics March 6, 2017 This lecture is on hydrostatics, which is question 9 of the exam paper. Most of the situations we will study will relate to objects partly or fully submerged
Homework #14, due Wednesday, Nov. 28 before class. Quiz #14, Wednesday November 28 at the beginning of class
 ANNOUNCEMENTS Homework #14, due Wednesday, Nov. 28 before class Conceptual questions: Chapter 14, #8 and #16 Problems: Chapter 14, #58, #66 Study Chapter 14 by Wednesday Quiz #14, Wednesday November 28
ANNOUNCEMENTS Homework #14, due Wednesday, Nov. 28 before class Conceptual questions: Chapter 14, #8 and #16 Problems: Chapter 14, #58, #66 Study Chapter 14 by Wednesday Quiz #14, Wednesday November 28
W I L D W E L L C O N T R O L PRESSURE BASICS AND CONCEPTS
 PRESSURE BASICS AND CONCEPTS Pressure Basics and Concepts Learning Objectives You will be familiarized with the following basic pressure concepts: Defining pressure Hydrostatic pressure Pressure gradient
PRESSURE BASICS AND CONCEPTS Pressure Basics and Concepts Learning Objectives You will be familiarized with the following basic pressure concepts: Defining pressure Hydrostatic pressure Pressure gradient
4 Testing Agency Guide. 4.1 U.S. Army Corps of Engineers (USACE) Standard for Air Leakage
 10 4 Testing Agency Guide 4.1 U.S. Army Corps of Engineers (USACE) Standard for Air Leakage The USACE requires all new buildings and major renovation projects to pass an air leakage test where the results
10 4 Testing Agency Guide 4.1 U.S. Army Corps of Engineers (USACE) Standard for Air Leakage The USACE requires all new buildings and major renovation projects to pass an air leakage test where the results
EARTH SCIENCE 5.9 (WIND) WEATHER
 EARTH SCIENCE 5.9 (WIND) WEATHER Video Notes Key Points: 1. According to the video, what two factors cause wind: a. b. 2. Fill in the blanks from this quote from the video: Energy from the Sun heats the,
EARTH SCIENCE 5.9 (WIND) WEATHER Video Notes Key Points: 1. According to the video, what two factors cause wind: a. b. 2. Fill in the blanks from this quote from the video: Energy from the Sun heats the,
Understanding pressure and pressure
 CHAPTER 1 1-1 PRESSURE BASICS Remember to think downhole. The concepts provided in this section cover the foundations for good well control. Understanding pressure and pressure relationships is important
CHAPTER 1 1-1 PRESSURE BASICS Remember to think downhole. The concepts provided in this section cover the foundations for good well control. Understanding pressure and pressure relationships is important
Airtightness Testing in Large Buildings: NESEA 2016
 Airtightness Testing in Large Buildings: NESEA 2016 Dr John Straube, P.Eng. Associate Professor, University of Waterloo Principal, RDH Building Science This session: why would one invest in airtightness
Airtightness Testing in Large Buildings: NESEA 2016 Dr John Straube, P.Eng. Associate Professor, University of Waterloo Principal, RDH Building Science This session: why would one invest in airtightness
1. All fluids are: A. gases B. liquids C. gases or liquids D. non-metallic E. transparent ans: C
 Chapter 14: FLUIDS 1 All fluids are: A gases B liquids C gases or liquids D non-metallic E transparent 2 Gases may be distinguished from other forms of matter by their: A lack of color B small atomic weights
Chapter 14: FLUIDS 1 All fluids are: A gases B liquids C gases or liquids D non-metallic E transparent 2 Gases may be distinguished from other forms of matter by their: A lack of color B small atomic weights
Permeability. Darcy's Law
 Permeability Permeability is a property of the porous medium that measures the capacity and ability of the formation to transmit fluids. The rock permeability, k, is a very important rock property because
Permeability Permeability is a property of the porous medium that measures the capacity and ability of the formation to transmit fluids. The rock permeability, k, is a very important rock property because
The Discussion of this exercise covers the following points: Pumps Basic operation of a liquid pump Types of liquid pumps The centrifugal pump.
 Exercise 2-3 Centrifugal Pumps EXERCISE OBJECTIVE In this exercise, you will become familiar with the operation of a centrifugal pump and read its performance chart. You will also observe the effect that
Exercise 2-3 Centrifugal Pumps EXERCISE OBJECTIVE In this exercise, you will become familiar with the operation of a centrifugal pump and read its performance chart. You will also observe the effect that
Float a Big Stick. To investigate how objects float by analyzing forces acting on a floating stick
 Chapter 19: Liquids Flotation 53 Float a Big Stick Purpose To investigate how objects float by analyzing forces acting on a floating stick Required Equipment/Supplies Experiment vernier calipers 250-mL
Chapter 19: Liquids Flotation 53 Float a Big Stick Purpose To investigate how objects float by analyzing forces acting on a floating stick Required Equipment/Supplies Experiment vernier calipers 250-mL
Propane Conversion Kit Instruction
 Propane Conversion Kit Instruction Condensing gas boiler Required Input Rates Logamax plus GB62-80 kw 270,000 btu/hr Logamax plus GB62-00 kw 35,000 btu/hr This kit and instructions are for converting the
Propane Conversion Kit Instruction Condensing gas boiler Required Input Rates Logamax plus GB62-80 kw 270,000 btu/hr Logamax plus GB62-00 kw 35,000 btu/hr This kit and instructions are for converting the
