This document downloaded from vulcanhammer.net vulcanhammer.info Chet Aero Marine
|
|
|
- Brittney Miles
- 5 years ago
- Views:
Transcription
1 This document downloaded from vulcanhammer.net vulcanhammer.info Chet Aero Marine Don t forget to visit our companion site Use subject to the terms and conditions of the respective websites.
2 ENCE 3610 Soil Mechanics Lecture 5 Effective (Intergranular) Stress in Soils Capillary Rise in Soils
3 Stresses in Soils Geostatic and Hydrostatic Stresses Total Stress Pore Water Pressure Effective Stress and Overburden Pressure (po) Upward and Downward Seepage Stresses Lateral Earth Pressures External Load Stresses Elastic Methods (Boussinesq, etc.) Empirical Methods (2:1) Combined Stresses and Mohr s Circle Use of Mohr s Circle (principal stresses, etc.) Theory of elasticity and plasticity General Comments The principal source of soil stress is caused by the weight of the soil (adjusted usually by the pore water pressure) above the point in the soil under examination Additional stresses can and are induced by load from the soil surface, such as footings, deep foundations, embankments and other weight-bearing structures
4 Hydrostatic and Total Stress Hydrostatic Stress The stress induced by the weight of the water at a given depth Total Stress The stress produced at any point by the overburden pressure of the soil plus any applied loads (equation does not include loads) Assumes water is at rest and not experiencing forces other than static gravity Also exists in the pores of the soil as it does in free water, thus the name pore water pressure (but pore water pressure doesn t have to be hydrostatic) Generally ignores the effect of pore water pressure Applies in general to dry or unsaturated soils
5 Pore Water Pressure Pressure of water within the pores or voids of the soil Can be caused by: Hydrostatic pressure, either direct from above or from downflow of water Capillary action Water has a buoyant effect on soils under the water table For hydrostatic conditions, this includes all soils under the water table The buoyant effect of the water equals the weight of the water the soil displaces Seepage Pressure from applied loads compressing trapped water This reduces the effective unit weight of the soil for the purposes of calculating effective stress
6 Effective (Intergranular) Stress Saturated, hydrostatic conditions Homogeneous soil layer
7 Effective Stress General Expression The total stress minus the pore water pressure Equation only considers the load of the soil itself One of the most important concepts in soil mechanics As depth increases, soil stress generally increases because of increasing H Varying unit weight will vary increase in effective stress Above water table, pore water pressure is generally not considered (except for capillary condition)
8 Methods for Computation of Effective Stress Pore Water plus Total Stress Method Tabulate heights of layers and unit weights (saturated and unsaturated of each) Note location of water table Use this equation to compute effective stress: Submerged Weight Method Tabulate layer heights and unit weights as with other method Layers above water table use unsaturated (wet) unit weight Layers below water table use submerged unit weight Add as with other method
9 P o Diagram Useful tool to visualise the increase of effective stress/overburde n pressure as a function of depth and to clearly see the effect of the pore water Z pressure Can also be used in some cases to illustrate the changes that take place with applied loads and other conditions P o Inflection Points due to changes in unit weight, water table, etc.
10 Methods of Plotting P o Diagrams Manual Plotting Spreadsheet Plotting Find points of inflection (changes in unit weight, water table level, other changes in pore water pressure, etc.) Compute effective stress/overburden pressure at each point using standard equations Join points with lines In some cases, pore water pressure functions are not linear, so lines cannot accurately be used in P o diagrams Divide up soil into layers of constant effective stress function with depth Compute increase in effective stress for each layer Successively add the increments of increasing (usually) effective stress and create a set of data points at the bottom of each layer Use the data set to plot the P o diagram
11 P o Example 1
12 P o Example 2
13 P o Example 3
14 Groundwater Zones in Soil
15 Capillarity and Capillary Rise in Soils Result of surface tension in water between the water itself and a solid surface it touches (glass tube, soil particles, etc.) Capillary rise takes place when the surface tension in the water is greater than the force of gravity of the water under it Capillary rise stops when the force of the water equals the weight supporting it
16 Capillarity in Soils A more complex phenomenon in soils due to complex geometry of particles More pronounced in fine grained soils Volume changes in fine grained soils can be in part attributed to capillarity Area of soil above water table where capillary rise is taking place is called the vadose zone Compressive stresses take place in the soil in an area with capillary rise takes place
17 Capillarity and Capillary Rise in Soils Equilibrium of capillary rise force and water head in a tube (z c = height of water column) πdt s cosα = πz c d 4 2 γ w
18 Capillarity and Capillary Rise Assumptions T s = g/mm = 0 d = D 10 /5 (D 10 usually expressed in millimetres) w =.001 g/mm 3 Substituting and Solving for z c (millimetres) z c = 150 D 10
19 Capillarity Example Given Cohesive Soil D10 = mm (#200 sieve opening) Find Solution Capillary Rise in Soil zc = 150/0.074 ~ 2027 mm ~ 2 m
20 Capillary Rise and Effective Stress Note the following: Phreatic surface is where the pore water pressure is zero At the surface, since there is no surcharge, total stress is zero Thus, the pore water pressure above the phreatic surface is negative with capillary rise, with the same slope as below the phreatic surface There is thus a positive effective stress at the surface to balance the negative pore water pressure
21 Capillary Rise and Effective Stress Assume that saturated unit weight = 20 kn/m 3 At surface Pore water pressure = -(2)(9.8) = kpa Total Stress = 0 kpa Effective stress = = 19.6 kpa At 2 m below surface Pore water pressure = 0 Total Stress = (20)(2) = 40 kpa Effective Stress = 40 0 = 40 kpa At 10 m below surface Pore water pressure = (8)(9.8) = 78.4 kpa Total Stress = (20)(10) = 200 kpa Effective Stress = = kpa
22 Effective Stress without Capillary Rise Assume that saturated unit weight = 20 kn/m 3 and dry unit weight = 16 kn/m 3 At surface Pore water pressure = 0 kpa Effective stress = 0 kpa Total Stress = 0 kpa At 2 m below surface Pore water pressure = 0 Total Stress = (16)(2) = 32 kpa Effective Stress = 32 0 = 32 kpa At 10 m below surface Pore water pressure = (8)(9.8) = 78.4 kpa Total Stress = 32 + (20)(8) = 192 kpa Effective Stress = = kpa
23 Questions?
computed using Equation 3-18 by setting the 2nd term equal to 0 and K A equal to K o and using the pressure distribution as shown in Figure 3-23.
 computed using Equation 3-18 by setting the 2nd term equal to 0 and K A equal to K o and using the pressure distribution as shown in Figure 3-23. (2) For the resisting side, passive pressure theory indicates
computed using Equation 3-18 by setting the 2nd term equal to 0 and K A equal to K o and using the pressure distribution as shown in Figure 3-23. (2) For the resisting side, passive pressure theory indicates
Pore-Air Entrapment during Infiltration
 Pore-Air Entrapment during Infiltration GEO-SLOPE International Ltd. www.geo-slope.com 1200, 700-6th Ave SW, Calgary, AB, Canada T2P 0T8 Main: +1 403 269 2002 Fax: +1 888 463 2239 Introduction Infiltration
Pore-Air Entrapment during Infiltration GEO-SLOPE International Ltd. www.geo-slope.com 1200, 700-6th Ave SW, Calgary, AB, Canada T2P 0T8 Main: +1 403 269 2002 Fax: +1 888 463 2239 Introduction Infiltration
Saturated-Unsaturated Consolidation
 Introduction Saturated-Unsaturated Consolidation This example looks at the volume change behavior of a saturated-unsaturated column under loading, wetting and drying conditions. Feature Highlights GeoStudio
Introduction Saturated-Unsaturated Consolidation This example looks at the volume change behavior of a saturated-unsaturated column under loading, wetting and drying conditions. Feature Highlights GeoStudio
Physics 221, March 1. Key Concepts: Density and pressure Buoyancy Pumps and siphons Surface tension
 Physics 221, March 1 Key Concepts: Density and pressure Buoyancy Pumps and siphons Surface tension Fluids: Liquids Incompressible Gases Compressible Definitions Particle density: Density: Pressure: ρ particle
Physics 221, March 1 Key Concepts: Density and pressure Buoyancy Pumps and siphons Surface tension Fluids: Liquids Incompressible Gases Compressible Definitions Particle density: Density: Pressure: ρ particle
Submerged Slope with Excess Pore- Water Pressure
 Submerged Slope with Excess Pore- Water Pressure GEO-SLOPE International Ltd. www.geo-slope.com 1400, 633-6th Ave SW, Calgary, AB, Canada T2P 2Y Main: +1 403 269 02 Fax: +1 403 266 481 Introduction Analyzing
Submerged Slope with Excess Pore- Water Pressure GEO-SLOPE International Ltd. www.geo-slope.com 1400, 633-6th Ave SW, Calgary, AB, Canada T2P 2Y Main: +1 403 269 02 Fax: +1 403 266 481 Introduction Analyzing
γ water = 62.4 lb/ft 3 = 9800 N/m 3
 CEE 42 Aut 200, Exam #1 Work alone. Answer all questions. Always make your thought process clear; if it is not, you will not receive partial credit for incomplete or partially incorrect answers. Some data
CEE 42 Aut 200, Exam #1 Work alone. Answer all questions. Always make your thought process clear; if it is not, you will not receive partial credit for incomplete or partially incorrect answers. Some data
m v = 1.04 x 10-4 m 2 /kn, C v = 1.29 x 10-2 cm 2 /min
 2.10 Problems Example 2.1: Design of Shallow Foundation in Saturated Clay Design a square footing to support a column load of 667 kn. The base of the footing will be located 1 m below the ground level
2.10 Problems Example 2.1: Design of Shallow Foundation in Saturated Clay Design a square footing to support a column load of 667 kn. The base of the footing will be located 1 m below the ground level
For a cantilever pile wall shown in Figure 1, assess the performance of the system and answer the following questions.
 Question 1 For a cantilever pile wall shown in Figure 1, assess the performance of the system and answer the following questions. Figure 1 - Cantilever Pile Wall i. Estimate the net resulting horizontal
Question 1 For a cantilever pile wall shown in Figure 1, assess the performance of the system and answer the following questions. Figure 1 - Cantilever Pile Wall i. Estimate the net resulting horizontal
Module 7 Lecture 1. Swelling and Collapse Behavior
 Swelling and Collapse Behavior Module 7 Lecture 1 Collapse and swelling phenomena occur in unsaturated soils during the saturation process. The compacted unsaturated soils, on the dry of optimum, have
Swelling and Collapse Behavior Module 7 Lecture 1 Collapse and swelling phenomena occur in unsaturated soils during the saturation process. The compacted unsaturated soils, on the dry of optimum, have
Pressure Measurement
 Pressure Measurement Absolute and Gage Pressure P abs = P gage + P atm where P abs = Absolute pressure P abs = Gage pressure P abs = atmospheric pressure A perfect vacuum is the lowest possible pressure.
Pressure Measurement Absolute and Gage Pressure P abs = P gage + P atm where P abs = Absolute pressure P abs = Gage pressure P abs = atmospheric pressure A perfect vacuum is the lowest possible pressure.
Cubzac-les-Ponts Experimental Embankments on Soft Clay
 Cubzac-les-Ponts Experimental Embankments on Soft Clay GEO-SLOPE International Ltd. www.geo-slope.com 1, 7 - th Ave SW, Calgary, AB, Canada TP T Main: +1 3 9 Fax: +1 3 39 Introduction In the 197 s, a series
Cubzac-les-Ponts Experimental Embankments on Soft Clay GEO-SLOPE International Ltd. www.geo-slope.com 1, 7 - th Ave SW, Calgary, AB, Canada TP T Main: +1 3 9 Fax: +1 3 39 Introduction In the 197 s, a series
UNIT-I SOIL EXPLORATION
 SIDDHARTH GROUP OF INSTITUTIONS :: PUTTUR Siddharth Nagar, Narayanavanam Road 517583 QUESTION BANK (DESCRIPTIVE) Subject with Code : Geotechnical Engineering - II (16CE127) Year & Sem: III-B.Tech & II-Sem
SIDDHARTH GROUP OF INSTITUTIONS :: PUTTUR Siddharth Nagar, Narayanavanam Road 517583 QUESTION BANK (DESCRIPTIVE) Subject with Code : Geotechnical Engineering - II (16CE127) Year & Sem: III-B.Tech & II-Sem
Theory of a vertically loaded Suction Pile in CLAY
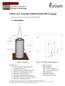 11 Theory of a vertically loaded Suction Pile in CLAY Mainly based on the et Norske Veritas NV-RP-E303 1. Convention Water COG h L Soil COG t Figure 1 Suction Pile Figure 2 Suction pile with main parameters
11 Theory of a vertically loaded Suction Pile in CLAY Mainly based on the et Norske Veritas NV-RP-E303 1. Convention Water COG h L Soil COG t Figure 1 Suction Pile Figure 2 Suction pile with main parameters
Chapter 13 Fluids. Copyright 2009 Pearson Education, Inc.
 Chapter 13 Fluids Phases of Matter Density and Specific Gravity Pressure in Fluids Atmospheric Pressure and Gauge Pressure Pascal s Principle Units of Chapter 13 Measurement of Pressure; Gauges and the
Chapter 13 Fluids Phases of Matter Density and Specific Gravity Pressure in Fluids Atmospheric Pressure and Gauge Pressure Pascal s Principle Units of Chapter 13 Measurement of Pressure; Gauges and the
Infiltration and Air Pressure Build-up
 1 Introduction Infiltration and Air Pressure Build-up This air flow example illustrates how the build-up of air pressure in advance of a wetting front can inhibit water movement. The example is based on
1 Introduction Infiltration and Air Pressure Build-up This air flow example illustrates how the build-up of air pressure in advance of a wetting front can inhibit water movement. The example is based on
Design Data 22M. Flotation of Circular Concrete Pipe. w w I = w - x 1000 (3) (SG x 1000)
 Design Data M Flotation of Circular Concrete Pipe There are several installation conditions where there is the possibility that concrete pipe may float even though the density of concrete is approximately.4
Design Data M Flotation of Circular Concrete Pipe There are several installation conditions where there is the possibility that concrete pipe may float even though the density of concrete is approximately.4
Effective stress. Chapter Total vertical stress at 5 m depth: kpa. Pore water pressure: kpa. Therefore, effective vertical stress: kpa
 Chapter 3 Effective stress 3.1 Figure Q3.1 Total vertical stress at 5 m depth: Pore water pressure: Therefore, effective vertical stress: Alternative method: Buoyant unit weight: Effective vertical stress:
Chapter 3 Effective stress 3.1 Figure Q3.1 Total vertical stress at 5 m depth: Pore water pressure: Therefore, effective vertical stress: Alternative method: Buoyant unit weight: Effective vertical stress:
Application of Expansive Soil Geotechnical Procedures
 Application of Expansive Soil Geotechnical Procedures FPA PRESENTATION John T. Bryant, Ph.D., P.G., P.E with Robert L. Lytton, Ph.D., PE. And Mr. Dean Read HOUSTON, TEXAS WEDNESDAY DECEMBER 10, 2008 2008
Application of Expansive Soil Geotechnical Procedures FPA PRESENTATION John T. Bryant, Ph.D., P.G., P.E with Robert L. Lytton, Ph.D., PE. And Mr. Dean Read HOUSTON, TEXAS WEDNESDAY DECEMBER 10, 2008 2008
Lecture Outline Chapter 15. Physics, 4 th Edition James S. Walker. Copyright 2010 Pearson Education, Inc.
 Lecture Outline Chapter 15 Physics, 4 th Edition James S. Walker Chapter 15 Fluids Density Units of Chapter 15 Pressure Static Equilibrium in Fluids: Pressure and Depth Archimedes Principle and Buoyancy
Lecture Outline Chapter 15 Physics, 4 th Edition James S. Walker Chapter 15 Fluids Density Units of Chapter 15 Pressure Static Equilibrium in Fluids: Pressure and Depth Archimedes Principle and Buoyancy
Department of Civil & Geological Engineering GEOE Engineering Geology
 Department of Civil & Geological Engineering GEOE 218.3 Engineering Geology Assignment #3, Head, Pore Pressure & Effective Stress Due 08 Oct, 2010 NOTE: Numbered subscripts indicate depth, in metres, below
Department of Civil & Geological Engineering GEOE 218.3 Engineering Geology Assignment #3, Head, Pore Pressure & Effective Stress Due 08 Oct, 2010 NOTE: Numbered subscripts indicate depth, in metres, below
Static Fluids. **All simulations and videos required for this package can be found on my website, here:
 DP Physics HL Static Fluids **All simulations and videos required for this package can be found on my website, here: http://ismackinsey.weebly.com/fluids-hl.html Fluids are substances that can flow, so
DP Physics HL Static Fluids **All simulations and videos required for this package can be found on my website, here: http://ismackinsey.weebly.com/fluids-hl.html Fluids are substances that can flow, so
Additional Information
 Buoyancy Additional Information Any object, fully or partially immersed in a fluid, is buoyed up by a force equal to the weight of the fluid displaced by the object. Archimedes of Syracuse Archimedes principle
Buoyancy Additional Information Any object, fully or partially immersed in a fluid, is buoyed up by a force equal to the weight of the fluid displaced by the object. Archimedes of Syracuse Archimedes principle
Applying Hooke s Law to Multiple Bungee Cords. Introduction
 Applying Hooke s Law to Multiple Bungee Cords Introduction Hooke s Law declares that the force exerted on a spring is proportional to the amount of stretch or compression on the spring, is always directed
Applying Hooke s Law to Multiple Bungee Cords Introduction Hooke s Law declares that the force exerted on a spring is proportional to the amount of stretch or compression on the spring, is always directed
Tension Cracks. Topics Covered. Tension crack boundaries Tension crack depth Query slice data Thrust line Sensitivity analysis.
 Tension Cracks 16-1 Tension Cracks In slope stability analyses with cohesive soils, tension forces may be observed in the upper part of the slope. In general, soils cannot support tension so the results
Tension Cracks 16-1 Tension Cracks In slope stability analyses with cohesive soils, tension forces may be observed in the upper part of the slope. In general, soils cannot support tension so the results
 Hydrostatic pressure Consider a tank of fluid which contains a very thin plate of (neutrally buoyant) material with area A. This situation is shown in Figure below. If the plate is in equilibrium (it does
Hydrostatic pressure Consider a tank of fluid which contains a very thin plate of (neutrally buoyant) material with area A. This situation is shown in Figure below. If the plate is in equilibrium (it does
INSTITUTE OF AERONAUTICAL ENGINEERING (Autonomous) Dundigal, Hyderabad
 INSTITUTE OF AERONAUTICAL ENGINEERING (Autonomous) Dundigal, Hyderabad - 500 043 CIVIL ENGINEERING Tutorial Question Bank Name : FOUNDATION ENGINEERING Code : A60126 Class : III B. Tech II Semester Branch
INSTITUTE OF AERONAUTICAL ENGINEERING (Autonomous) Dundigal, Hyderabad - 500 043 CIVIL ENGINEERING Tutorial Question Bank Name : FOUNDATION ENGINEERING Code : A60126 Class : III B. Tech II Semester Branch
INSTITUTE OF AERONAUTICAL ENGINEERING (Autonomous) Dundigal, Hyderabad CIVIL ENGINEERING TUTORIAL QUESTION BANK
 INSTITUTE OF AERONAUTICAL ENGINEERING (Autonomous) Dundigal, Hyderabad - 00 04 CIVIL ENGINEERING TUTORIAL QUESTION BANK Course Name Course Code Regulation Course Structure Course Coordinator Course Faculty
INSTITUTE OF AERONAUTICAL ENGINEERING (Autonomous) Dundigal, Hyderabad - 00 04 CIVIL ENGINEERING TUTORIAL QUESTION BANK Course Name Course Code Regulation Course Structure Course Coordinator Course Faculty
Prof. B V S Viswanadham, Department of Civil Engineering, IIT Bombay
 43 Module 3: Lecture - 5 on Compressibility and Consolidation Contents Stresses in soil from surface loads; Terzaghi s 1-D consolidation theory; Application in different boundary conditions; Ramp loading;
43 Module 3: Lecture - 5 on Compressibility and Consolidation Contents Stresses in soil from surface loads; Terzaghi s 1-D consolidation theory; Application in different boundary conditions; Ramp loading;
Reinforced Soil Retaining Walls-Design and Construction
 Lecture 32 Reinforced Soil Retaining Walls-Design and Construction Prof. G L Sivakumar Babu Department of Civil Engineering Indian Institute of Science Bangalore 560012 Example calculation An 8 m high
Lecture 32 Reinforced Soil Retaining Walls-Design and Construction Prof. G L Sivakumar Babu Department of Civil Engineering Indian Institute of Science Bangalore 560012 Example calculation An 8 m high
Vapour pressure of liquids SURFACE TENSION
 Vapour pressure of liquids A liquid in a closed container is subjected to partial vapour pressure due to the escaping molecules from the surface; it reaches a stage of equilibrium when this pressure reaches
Vapour pressure of liquids A liquid in a closed container is subjected to partial vapour pressure due to the escaping molecules from the surface; it reaches a stage of equilibrium when this pressure reaches
FC-CIV HIDRCANA: Channel Hydraulics Flow Mechanics Review Fluid Statics
 FC-CIV HIDRCANA: Channel Hydraulics Flow Mechanics Review Fluid Statics Civil Engineering Program, San Ignacio de Loyola University Objective Calculate the forces exerted by a fluid at rest on plane or
FC-CIV HIDRCANA: Channel Hydraulics Flow Mechanics Review Fluid Statics Civil Engineering Program, San Ignacio de Loyola University Objective Calculate the forces exerted by a fluid at rest on plane or
3 1 PRESSURE. This is illustrated in Fig. 3 3.
 P = 3 psi 66 FLUID MECHANICS 150 pounds A feet = 50 in P = 6 psi P = s W 150 lbf n = = 50 in = 3 psi A feet FIGURE 3 1 The normal stress (or pressure ) on the feet of a chubby person is much greater than
P = 3 psi 66 FLUID MECHANICS 150 pounds A feet = 50 in P = 6 psi P = s W 150 lbf n = = 50 in = 3 psi A feet FIGURE 3 1 The normal stress (or pressure ) on the feet of a chubby person is much greater than
Figure 5.1: molecular interaction
 Chapter 5 Surface tension 5.1 Definition If a line element be imagined on the surface of a liquid in any direction, the surface tension of the liquid, at a given temperature, is defined as the force per
Chapter 5 Surface tension 5.1 Definition If a line element be imagined on the surface of a liquid in any direction, the surface tension of the liquid, at a given temperature, is defined as the force per
Chapter 13 Fluids. Copyright 2009 Pearson Education, Inc.
 Chapter 13 Fluids Phases of Matter Density and Specific Gravity Pressure in Fluids Atmospheric Pressure and Gauge Pressure Pascal s Principle Units of Chapter 13 Measurement of Pressure; Gauges and the
Chapter 13 Fluids Phases of Matter Density and Specific Gravity Pressure in Fluids Atmospheric Pressure and Gauge Pressure Pascal s Principle Units of Chapter 13 Measurement of Pressure; Gauges and the
Fluids. James H Dann, Ph.D. Say Thanks to the Authors Click (No sign in required)
 Fluids James H Dann, Ph.D. Say Thanks to the Authors Click http://www.ck12.org/saythanks (No sign in required) To access a customizable version of this book, as well as other interactive content, visit
Fluids James H Dann, Ph.D. Say Thanks to the Authors Click http://www.ck12.org/saythanks (No sign in required) To access a customizable version of this book, as well as other interactive content, visit
Pressure Plate Drying and Wetting
 1 Introduction Pressure Plate Drying and Wetting This air flow example illustrates how the process of axis translation, which is used in pressure plates to measure the water content function, can be modeled.
1 Introduction Pressure Plate Drying and Wetting This air flow example illustrates how the process of axis translation, which is used in pressure plates to measure the water content function, can be modeled.
Objectives deals with forces applied by fluids at rest or in rigid-body motion.
 Objectives deals with forces applied by fluids at rest or in rigid-body motion. The fluid property responsible for those forces is pressure, which is a normal force exerted by a fluid per unit area. discussion
Objectives deals with forces applied by fluids at rest or in rigid-body motion. The fluid property responsible for those forces is pressure, which is a normal force exerted by a fluid per unit area. discussion
Chapter 3 PRESSURE AND FLUID STATICS
 Fluid Mechanics: Fundamentals and Applications, 2nd Edition Yunus A. Cengel, John M. Cimbala McGraw-Hill, 2010 Chapter 3 PRESSURE AND FLUID STATICS Lecture slides by Hasan Hacışevki Copyright The McGraw-Hill
Fluid Mechanics: Fundamentals and Applications, 2nd Edition Yunus A. Cengel, John M. Cimbala McGraw-Hill, 2010 Chapter 3 PRESSURE AND FLUID STATICS Lecture slides by Hasan Hacışevki Copyright The McGraw-Hill
Students measure the change in pressure by varying the volume of trapped air in a syringe while:
 How Does a Trapped Gas Behave? Teacher Information Objective Students investigate the effect of changes in the volume of a confined gas on pressure at constant temperature. Using the pressure sensor, students
How Does a Trapped Gas Behave? Teacher Information Objective Students investigate the effect of changes in the volume of a confined gas on pressure at constant temperature. Using the pressure sensor, students
A deliberation on the surface tension theory
 A deliberation on the surface tension theory Hamid V. Ansari Department of Physics, Isfahan University, Isfahan, IRAN Personal address: No. 16, Salman-Farsi Lane, Zeinabieh Street, Isfahan, Postal Code
A deliberation on the surface tension theory Hamid V. Ansari Department of Physics, Isfahan University, Isfahan, IRAN Personal address: No. 16, Salman-Farsi Lane, Zeinabieh Street, Isfahan, Postal Code
. In an elevator accelerating upward (A) both the elevator accelerating upward (B) the first is equations are valid
 IIT JEE Achiever 2014 Ist Year Physics-2: Worksheet-1 Date: 2014-06-26 Hydrostatics 1. A liquid can easily change its shape but a solid cannot because (A) the density of a liquid is smaller than that of
IIT JEE Achiever 2014 Ist Year Physics-2: Worksheet-1 Date: 2014-06-26 Hydrostatics 1. A liquid can easily change its shape but a solid cannot because (A) the density of a liquid is smaller than that of
Fluid Mechanics. Liquids and gases have the ability to flow They are called fluids There are a variety of LAWS that fluids obey
 Fluid Mechanics Fluid Mechanics Liquids and gases have the ability to flow They are called fluids There are a variety of LAWS that fluids obey Density Regardless of form (solid, liquid, gas) we can define
Fluid Mechanics Fluid Mechanics Liquids and gases have the ability to flow They are called fluids There are a variety of LAWS that fluids obey Density Regardless of form (solid, liquid, gas) we can define
Chapter 9 Fluids CHAPTER CONTENTS
 Flowing fluids, such as the water flowing in the photograph at Coors Falls in Colorado, can make interesting patterns In this chapter, we will investigate the basic physics behind such flow Photo credit:
Flowing fluids, such as the water flowing in the photograph at Coors Falls in Colorado, can make interesting patterns In this chapter, we will investigate the basic physics behind such flow Photo credit:
γ water = 62.4 lb/ft 3 = 9800 N/m 3
 CEE 4 Aut 004, Exam # Work alone. Answer all questions. Total pts: 90. Always make your thought process clear; if it is not, you will not receive partial credit for incomplete or partially incorrect answers.
CEE 4 Aut 004, Exam # Work alone. Answer all questions. Total pts: 90. Always make your thought process clear; if it is not, you will not receive partial credit for incomplete or partially incorrect answers.
Chapter 4 Surface Tension
 Chapter 4 Surface Tension Contents. Introduction 4.1 Surface tension, Angle of Contact and capillary Rise Method 4.2 Rise of Liquid in a Conical Capillary Tube 4.3 Energy Required to Raise a Liquid in
Chapter 4 Surface Tension Contents. Introduction 4.1 Surface tension, Angle of Contact and capillary Rise Method 4.2 Rise of Liquid in a Conical Capillary Tube 4.3 Energy Required to Raise a Liquid in
Vacuum P=0. h=76 cm A B C. Barometer
 Recap: Pressure Pressure = Force per unit area (P = F /A; units: Pascals) Density of object = mass / volume (ρ = m /V; units: kg / m 3 ) Pascal s Law:Pressure is transmitted equally in all directions throughout
Recap: Pressure Pressure = Force per unit area (P = F /A; units: Pascals) Density of object = mass / volume (ρ = m /V; units: kg / m 3 ) Pascal s Law:Pressure is transmitted equally in all directions throughout
Chapter 13. liquids. gases. 1) Fluids exert pressure. a) because they're made up of matter and therefore forces are applied to them
 \ Chapter 13 Fluids 1) Fluids exert pressure a) because they're made up of matter and therefore forces are applied to them liquids gases b) they are made of matter in constant motion colliding with other
\ Chapter 13 Fluids 1) Fluids exert pressure a) because they're made up of matter and therefore forces are applied to them liquids gases b) they are made of matter in constant motion colliding with other
Chapter 3 Atmospheric Thermodynamics
 Chapter 3 Atmospheric Thermodynamics Spring 2017 Partial Pressure and Dalton Dalton's law of partial pressure: total pressure exerted by a mixture of gases which do not interact chemically is equal to
Chapter 3 Atmospheric Thermodynamics Spring 2017 Partial Pressure and Dalton Dalton's law of partial pressure: total pressure exerted by a mixture of gases which do not interact chemically is equal to
Scott Denning CSU CMMAP 1
 Thermodynamics, Buoyancy, and Vertical Motion Temperature, Pressure, and Density Buoyancy and Static Stability Adiabatic Lapse Rates Dry and Moist Convective Motions Present Atmospheric Composition What
Thermodynamics, Buoyancy, and Vertical Motion Temperature, Pressure, and Density Buoyancy and Static Stability Adiabatic Lapse Rates Dry and Moist Convective Motions Present Atmospheric Composition What
Chapter 15 Fluid. Density
 Density Chapter 15 Fluid Pressure Static Equilibrium in Fluids: Pressure and Depth Archimedes Principle and Buoyancy Applications of Archimedes Principle By Dr. Weining man 1 Units of Chapter 15 Fluid
Density Chapter 15 Fluid Pressure Static Equilibrium in Fluids: Pressure and Depth Archimedes Principle and Buoyancy Applications of Archimedes Principle By Dr. Weining man 1 Units of Chapter 15 Fluid
MS.RAJA ELGADY/PRESSURE PAPER 3
 1- (a) A water tank has a rectangular base of dimensions 1.5m by 1.2m and contains 1440 kg of water. Calculate (i) the weight of the water, weight =...... [1] (ii) the pressure exerted by the water on
1- (a) A water tank has a rectangular base of dimensions 1.5m by 1.2m and contains 1440 kg of water. Calculate (i) the weight of the water, weight =...... [1] (ii) the pressure exerted by the water on
STUDY ON UPWARD MOVEMENT OF FINES FROM SANDY SEABED UNDER CYCLIC WATER PRESSURE CHANGE DUE TO WAVES
 C- Fourth International Conference on Scour and Erosion STUDY ON UPWARD MOVEMENT OF FINES FROM SANDY SEABED UNDER CYCLIC WATER PRESSURE CHANGE DUE TO WAVES Takashi TSUCHIDA, Akihiro MATSUI and Ryoichi
C- Fourth International Conference on Scour and Erosion STUDY ON UPWARD MOVEMENT OF FINES FROM SANDY SEABED UNDER CYCLIC WATER PRESSURE CHANGE DUE TO WAVES Takashi TSUCHIDA, Akihiro MATSUI and Ryoichi
Assistant Lecturer Anees Kadhum AL Saadi
 Pressure Variation with Depth Pressure in a static fluid does not change in the horizontal direction as the horizontal forces balance each other out. However, pressure in a static fluid does change with
Pressure Variation with Depth Pressure in a static fluid does not change in the horizontal direction as the horizontal forces balance each other out. However, pressure in a static fluid does change with
Atmospheric Stability/Skew-T Diagrams. Fall 2016
 Atmospheric Stability/Skew-T Diagrams Fall 2016 Air Parcel Consider a parcel of infinitesimal dimensions that is: Thermally isolated from the environment so that its temperature changes adiabatically as
Atmospheric Stability/Skew-T Diagrams Fall 2016 Air Parcel Consider a parcel of infinitesimal dimensions that is: Thermally isolated from the environment so that its temperature changes adiabatically as
When a uniform pressure acts on a flat plate of area A and a force F pushes the plate, then the pressure p is : p = F/A
 Chapter 2. Fluid Statics Fluid statics is concerned with the balance of forces which stabilize fluids at rest. In the case of a liquid, as the pressure largely changes according to its height, it is necessary
Chapter 2. Fluid Statics Fluid statics is concerned with the balance of forces which stabilize fluids at rest. In the case of a liquid, as the pressure largely changes according to its height, it is necessary
Conceptual Physics Matter Liquids Gases
 Conceptual Physics Matter Liquids Gases Lana Sheridan De Anza College July 25, 2017 Last time atomic structure forms of matter solids density elasticity liquids & pressure Overview liquids pressure surface
Conceptual Physics Matter Liquids Gases Lana Sheridan De Anza College July 25, 2017 Last time atomic structure forms of matter solids density elasticity liquids & pressure Overview liquids pressure surface
LECTURE 16: Buoyancy. Select LEARNING OBJECTIVES:
 Lectures Page 1 Select LEARNING OBJECTIVES: LECTURE 16: Buoyancy Understand that the buoyant force is a result of a pressure gradient within a fluid. Demonstrate the ability to analyze a scenario involving
Lectures Page 1 Select LEARNING OBJECTIVES: LECTURE 16: Buoyancy Understand that the buoyant force is a result of a pressure gradient within a fluid. Demonstrate the ability to analyze a scenario involving
Khosla's theory. After studying a lot of dam failure constructed based on Bligh s theory, Khosla came out with the following;
 Khosla's theory After studying a lot of dam failure constructed based on Bligh s theory, Khosla came out with the following; Following are some of the main points from Khosla's Theory From observation
Khosla's theory After studying a lot of dam failure constructed based on Bligh s theory, Khosla came out with the following; Following are some of the main points from Khosla's Theory From observation
Concept of Fluid. Density. Pressure: Pressure in a Fluid. Pascal s principle. Buoyancy. Archimede s Principle. Forces on submerged surfaces
 FLUID MECHANICS The fluid essential to all life has a beauty of its own. It also helps support the weight of this swimmer. (credit: Terren, Wikimedia Commons) Concept of Fluid Density Pressure: Pressure
FLUID MECHANICS The fluid essential to all life has a beauty of its own. It also helps support the weight of this swimmer. (credit: Terren, Wikimedia Commons) Concept of Fluid Density Pressure: Pressure
Equation 1: F spring = kx. Where F is the force of the spring, k is the spring constant and x is the displacement of the spring. Equation 2: F = mg
 1 Introduction Relationship between Spring Constant and Length of Bungee Cord In this experiment, we aimed to model the behavior of the bungee cord that will be used in the Bungee Challenge. Specifically,
1 Introduction Relationship between Spring Constant and Length of Bungee Cord In this experiment, we aimed to model the behavior of the bungee cord that will be used in the Bungee Challenge. Specifically,
The tensile capacity of suction caissons in sand under rapid loading
 Frontiers in Offshore Geotechnics: ISFOG 25 Gourvenec & Cassidy (eds) 25 Taylor & Francis Group, London, ISBN 415 3963 X The tensile capacity of suction caissons in sand under rapid loading Guy T. Houlsby,
Frontiers in Offshore Geotechnics: ISFOG 25 Gourvenec & Cassidy (eds) 25 Taylor & Francis Group, London, ISBN 415 3963 X The tensile capacity of suction caissons in sand under rapid loading Guy T. Houlsby,
Fluid Mechanics. Chapter Three: Fluid Statics. Dr. Amer Khalil Ababneh
 Fluid Mechanics Chapter Three: Fluid Statics Dr. Amer Khalil Ababneh This chapter deals with mechanics of fluids by introducing concepts related to pressure and by describing how to calculate forces associated
Fluid Mechanics Chapter Three: Fluid Statics Dr. Amer Khalil Ababneh This chapter deals with mechanics of fluids by introducing concepts related to pressure and by describing how to calculate forces associated
Tutorial 5 Relative equilibrium
 Tutorial 5 Relative equilibrium 1. n open rectangular tank 3m long and 2m wide is filled with water to a depth of 1.5m. Find the slope of the water surface when the tank moves with an acceleration of 5m/s
Tutorial 5 Relative equilibrium 1. n open rectangular tank 3m long and 2m wide is filled with water to a depth of 1.5m. Find the slope of the water surface when the tank moves with an acceleration of 5m/s
An Introduction to Deep Foundations
 An Introduction to Deep Foundations J. Paul Guyer, P.E., R.A. Paul Guyer is a registered mechanical engineer, civil engineer, fire protection engineer and architect with over 35 years experience in the
An Introduction to Deep Foundations J. Paul Guyer, P.E., R.A. Paul Guyer is a registered mechanical engineer, civil engineer, fire protection engineer and architect with over 35 years experience in the
Unit 7. Pressure in fluids
 -- Unit 7. Pressure in fluids Index 1.- Pressure...2 2.- Fluids...2 3.- Pressure in fluids...3 4.- Pascal's principle...5 5.- Archimedes principle...6 6.- Atmospheric pressure...7 6.1.- Torricelli and
-- Unit 7. Pressure in fluids Index 1.- Pressure...2 2.- Fluids...2 3.- Pressure in fluids...3 4.- Pascal's principle...5 5.- Archimedes principle...6 6.- Atmospheric pressure...7 6.1.- Torricelli and
CENGRS GEOTECHNICA PVT. LTD. Job No Sheet No. 1
 CENGRS GEOTECHNICA PVT. LTD. Job No. 214030 Sheet No. 1 INTERIM REPORT ON GEOTECHNICAL INVESTIGATION FOR PROPOSED 66 KV GRID PLOT AT G-7, DWARKA, NEW DELHI. 1.0 INTRODUCTION 1.1 Project Description M/s.
CENGRS GEOTECHNICA PVT. LTD. Job No. 214030 Sheet No. 1 INTERIM REPORT ON GEOTECHNICAL INVESTIGATION FOR PROPOSED 66 KV GRID PLOT AT G-7, DWARKA, NEW DELHI. 1.0 INTRODUCTION 1.1 Project Description M/s.
PHY131H1S - Class 23. Today: Fluids Pressure Pascal s Law Gauge Pressure Buoyancy, Archimedes Principle. A little pre-class reading quiz
 PHY131H1S - Class 23 Today: Fluids Pressure Pascal s Law Gauge Pressure Buoyancy, Archimedes Principle Archimedes (287-212 BC) was asked to check the amount of silver alloy in the king s crown. The answer
PHY131H1S - Class 23 Today: Fluids Pressure Pascal s Law Gauge Pressure Buoyancy, Archimedes Principle Archimedes (287-212 BC) was asked to check the amount of silver alloy in the king s crown. The answer
Module 3: Hydrostatic forces on submerged bodies Lecture 7: Calculation of horizontal component, buoyancy. Forces on submerged bodies (continued)
 Forces on submerged bodies (continued) Buoyancy file:///d /Web%20Course/Dr.%20Nishith%20Verma/local%20server/fluid_mechanics/lecture7/7_1.htm[5/9/2012 3:05:26 PM] Forces on submerged bodies (continued)
Forces on submerged bodies (continued) Buoyancy file:///d /Web%20Course/Dr.%20Nishith%20Verma/local%20server/fluid_mechanics/lecture7/7_1.htm[5/9/2012 3:05:26 PM] Forces on submerged bodies (continued)
COURSE NUMBER: ME 321 Fluid Mechanics I Fluid statics. Course teacher Dr. M. Mahbubur Razzaque Professor Department of Mechanical Engineering BUET
 COURSE NUMBER: ME 321 Fluid Mechanics I Fluid statics Course teacher Dr. M. Mahbubur Razzaque Professor Department of Mechanical Engineering BUET 1 Fluid statics Fluid statics is the study of fluids in
COURSE NUMBER: ME 321 Fluid Mechanics I Fluid statics Course teacher Dr. M. Mahbubur Razzaque Professor Department of Mechanical Engineering BUET 1 Fluid statics Fluid statics is the study of fluids in
OPERATING INSTRUCTIONS
 OPERATING INSTRUCTIONS Combination Permeameter ELE International Chartmoor Road, Chartwell Business Park Leighton Buzzard, Bedfordshire, LU7 4WG England phone: +44 (0) 1525 249200 fax: +44 (0) 1525 249249
OPERATING INSTRUCTIONS Combination Permeameter ELE International Chartmoor Road, Chartwell Business Park Leighton Buzzard, Bedfordshire, LU7 4WG England phone: +44 (0) 1525 249200 fax: +44 (0) 1525 249249
LAB 13: FLUIDS OBJECTIVES
 217 Name Date Partners LAB 13: FLUIDS Fluids are an important part of our body OBJECTIVES OVERVIEW Fluid Properties To learn how some fundamental physical principles apply to fluids. To understand the
217 Name Date Partners LAB 13: FLUIDS Fluids are an important part of our body OBJECTIVES OVERVIEW Fluid Properties To learn how some fundamental physical principles apply to fluids. To understand the
CHAPTER 5: VACUUM TEST WITH VERTICAL DRAINS
 CHAPTER 5: VACUUM TEST WITH VERTICAL DRAINS 5.1 Introduction Using surcharging as the sole soil consolidation mean can take a long time to reach the desired soil settlement. Soil consolidation using prefabricated
CHAPTER 5: VACUUM TEST WITH VERTICAL DRAINS 5.1 Introduction Using surcharging as the sole soil consolidation mean can take a long time to reach the desired soil settlement. Soil consolidation using prefabricated
University Curriculum Development for Decentralized Wastewater Management
 Page i University Curriculum Development for Decentralized Wastewater Management Hydraulics I: Fundamentals Module Text Paul Trotta, P.E., Ph.D. Justin Ramsey, P.E. Chad Cooper September 2004 Page ii NDWRCDP
Page i University Curriculum Development for Decentralized Wastewater Management Hydraulics I: Fundamentals Module Text Paul Trotta, P.E., Ph.D. Justin Ramsey, P.E. Chad Cooper September 2004 Page ii NDWRCDP
Phys101 Lectures Fluids I. Key points: Pressure and Pascal s Principle Buoyancy and Archimedes Principle. Ref: 10-1,2,3,4,5,6,7.
 Phys101 Lectures 21-22 Fluids I Key points: Pressure and Pascal s Principle Buoyancy and Archimedes Principle Ref: 10-1,2,3,4,5,6,7. Page 1 10-1 Phases of Matter The three common phases of matter are solid,
Phys101 Lectures 21-22 Fluids I Key points: Pressure and Pascal s Principle Buoyancy and Archimedes Principle Ref: 10-1,2,3,4,5,6,7. Page 1 10-1 Phases of Matter The three common phases of matter are solid,
UNDER DOD DIRECTIVE 5200,20 AND DISTRIBUTION STATEMENT A
 THIS REPORT HAS BEEN DELIMITED AND CLEARED FOR PUBLIC RELEASE UNDER DOD DIRECTIVE 5200,20 AND NO RESTRICTIONS ARE IMPOSED UPON ITS USE AND DISCLOSURE, DISTRIBUTION STATEMENT A APPROVED FOR PUBLIC RELEASE;
THIS REPORT HAS BEEN DELIMITED AND CLEARED FOR PUBLIC RELEASE UNDER DOD DIRECTIVE 5200,20 AND NO RESTRICTIONS ARE IMPOSED UPON ITS USE AND DISCLOSURE, DISTRIBUTION STATEMENT A APPROVED FOR PUBLIC RELEASE;
ME 200 Thermodynamics I Spring 2010 (Last) (First) Thermo Number: CIRCLE YOUR LECTURE BELOW
 ME 200 Thermodynamics I Name: Spring 2010 Thermo Number: CIRCLE YOUR LECTURE BELOW Div. 1 8:30 am Div. 2 10:30 am Div. 3 12:30 pm Naik Tree Clark Div. 4 1:30 pm Kim Div. 5 3:30 pm Mathison EXAM 2 INSTRUCTIONS
ME 200 Thermodynamics I Name: Spring 2010 Thermo Number: CIRCLE YOUR LECTURE BELOW Div. 1 8:30 am Div. 2 10:30 am Div. 3 12:30 pm Naik Tree Clark Div. 4 1:30 pm Kim Div. 5 3:30 pm Mathison EXAM 2 INSTRUCTIONS
VI. Static Stability. Consider a parcel of unsaturated air. Assume the actual lapse rate is less than the dry adiabatic lapse rate: Γ < Γ d
 VI. Static Stability Consider a parcel of unsaturated air. Assume the actual lapse rate is less than the dry adiabatic lapse rate: Γ < Γ d VI. Static Stability Consider a parcel of unsaturated air. Assume
VI. Static Stability Consider a parcel of unsaturated air. Assume the actual lapse rate is less than the dry adiabatic lapse rate: Γ < Γ d VI. Static Stability Consider a parcel of unsaturated air. Assume
Fluid Statics. AP Physics 2
 Fluid Statics AP Physics 2 States of Matter Before we begin to understand the nature of a Fluid we must understand the nature of all the states of matter: The 3 primary states of matter - solid - Definite
Fluid Statics AP Physics 2 States of Matter Before we begin to understand the nature of a Fluid we must understand the nature of all the states of matter: The 3 primary states of matter - solid - Definite
End of Chapter Exercises
 End of Chapter Exercises Exercises 1 12 are conceptual questions that are designed to see if you have understood the main concepts of the chapter. 1. While on an airplane, you take a drink from your water
End of Chapter Exercises Exercises 1 12 are conceptual questions that are designed to see if you have understood the main concepts of the chapter. 1. While on an airplane, you take a drink from your water
Notes Chapter 3. Buoyancy
 Notes Chapter 3 Buoyancy Pressure in a Fluid 3.2 Pressure and the Buoyant Forces Liquids and gases are fluids materials that can flow and have no definite shape. Objects in a fluid experience a buoyant
Notes Chapter 3 Buoyancy Pressure in a Fluid 3.2 Pressure and the Buoyant Forces Liquids and gases are fluids materials that can flow and have no definite shape. Objects in a fluid experience a buoyant
Chapter 3: Fluid Statics. 3-1 Pressure 3-2 Fluid Statics 3-3 Buoyancy and Stability 3-4 Rigid-Body Motion
 3-1 Pressure 3-2 Fluid Statics 3-3 Buoyancy and Stability 3-4 Rigid-Body Motion Chapter 3 Fluid Statics 3-1 Pressure (1) Pressure is defined as a normal force exerted by a fluid per unit area. Units of
3-1 Pressure 3-2 Fluid Statics 3-3 Buoyancy and Stability 3-4 Rigid-Body Motion Chapter 3 Fluid Statics 3-1 Pressure (1) Pressure is defined as a normal force exerted by a fluid per unit area. Units of
8. Now plot on the following grid the values of T (K) and V from the table above, and connect the points.
 Charles s Law According to Charles s law, the volume of a fixed mass of gas varies directly with its Kelvin temperature if its pressure is constant. The following table contains Celsius temperature and
Charles s Law According to Charles s law, the volume of a fixed mass of gas varies directly with its Kelvin temperature if its pressure is constant. The following table contains Celsius temperature and
ESCI 343 Atmospheric Dynamics II Lesson 10 - Topographic Waves
 ESCI 343 Atmospheric Dynamics II Lesson 10 - Topographic Waves Reference: An Introduction to Dynamic Meteorology (3 rd edition), J.R. Holton Reading: Holton, Section 7.4. STATIONARY WAVES Waves will appear
ESCI 343 Atmospheric Dynamics II Lesson 10 - Topographic Waves Reference: An Introduction to Dynamic Meteorology (3 rd edition), J.R. Holton Reading: Holton, Section 7.4. STATIONARY WAVES Waves will appear
Equilibrium. Observations
 Equilibrium Observations When you look closely at a rope you will see that it consists of several strands of twine. If you tried to hang a heavy (or massive) object on a single strand of twine it would
Equilibrium Observations When you look closely at a rope you will see that it consists of several strands of twine. If you tried to hang a heavy (or massive) object on a single strand of twine it would
Exam Question 9: Hydrostatics. March 6, Applied Mathematics: Lecture 8. Brendan Williamson. Introduction. Density, Weight and Volume
 Exam Question 9: Hydrostatics March 6, 2017 This lecture is on hydrostatics, which is question 9 of the exam paper. Most of the situations we will study will relate to objects partly or fully submerged
Exam Question 9: Hydrostatics March 6, 2017 This lecture is on hydrostatics, which is question 9 of the exam paper. Most of the situations we will study will relate to objects partly or fully submerged
Shallow foundations settlement
 References: 1. Rajapakse, Ruwan. Geotechnical Engineering Calculations and Rules of Thumb. 2. Schroeder, W.L., Dickenson, S.E, Warrington, Don, C. Soils in Construction. Fifth Edition. Upper Saddle River,
References: 1. Rajapakse, Ruwan. Geotechnical Engineering Calculations and Rules of Thumb. 2. Schroeder, W.L., Dickenson, S.E, Warrington, Don, C. Soils in Construction. Fifth Edition. Upper Saddle River,
Fluid Mechanics - Hydrostatics. Sections 11 5 and 6
 Fluid Mechanics - Hydrostatics Sections 11 5 and 6 A closed system If you take a liquid and place it in a system that is CLOSED like plumbing for example or a car s brake line, the PRESSURE is the same
Fluid Mechanics - Hydrostatics Sections 11 5 and 6 A closed system If you take a liquid and place it in a system that is CLOSED like plumbing for example or a car s brake line, the PRESSURE is the same
MET Lecture 8 Atmospheric Stability
 MET 4300 Lecture 8 Atmospheric Stability Stability Concept Stable: Ball returns to original position Neutral: Ball stays wherever it is placed Unstable: Displacement grows with time. Atmospheric Stability
MET 4300 Lecture 8 Atmospheric Stability Stability Concept Stable: Ball returns to original position Neutral: Ball stays wherever it is placed Unstable: Displacement grows with time. Atmospheric Stability
End of Chapter Exercises
 End of Chapter Exercises Exercises 1 12 are conceptual questions that are designed to see if you have understood the main concepts of the chapter. 1. While on an airplane, you take a drink from your water
End of Chapter Exercises Exercises 1 12 are conceptual questions that are designed to see if you have understood the main concepts of the chapter. 1. While on an airplane, you take a drink from your water
LAB 13: FLUIDS OBJECTIVES
 205 Name Date Partners LAB 13: FLUIDS Fluids are an important part of our body OBJECTIVES OVERVIEW Fluid Properties To learn how some fundamental physical principles apply to fluids. To understand the
205 Name Date Partners LAB 13: FLUIDS Fluids are an important part of our body OBJECTIVES OVERVIEW Fluid Properties To learn how some fundamental physical principles apply to fluids. To understand the
AP Lab 11.3 Archimedes Principle
 ame School Date AP Lab 11.3 Archimedes Principle Explore the Apparatus We ll use the Buoyancy Apparatus in this lab activity. Before starting this activity check to see if there is an introductory video
ame School Date AP Lab 11.3 Archimedes Principle Explore the Apparatus We ll use the Buoyancy Apparatus in this lab activity. Before starting this activity check to see if there is an introductory video
Hydrostatics Physics Lab XI
 Hydrostatics Physics Lab XI Objective Students will discover the basic principles of buoyancy in a fluid. Students will also quantitatively demonstrate the variance of pressure with immersion depth in
Hydrostatics Physics Lab XI Objective Students will discover the basic principles of buoyancy in a fluid. Students will also quantitatively demonstrate the variance of pressure with immersion depth in
Pros and Cons of the Analysis of Slope Stability by Various Methods of Slices or Columns
 Pros and Cons of the Analysis of Slope Stability by Various Methods of Slices or Columns by Robert Pyke Ph.D., G.E. Partially Completed Draft April 22, 2017 General Background The history of slope stability
Pros and Cons of the Analysis of Slope Stability by Various Methods of Slices or Columns by Robert Pyke Ph.D., G.E. Partially Completed Draft April 22, 2017 General Background The history of slope stability
A Resource for Free-standing Mathematics Units. Graph showing Pressure plotted against Volume for a sample of air in a Boyle s law experiment
 Data An experiment to investigate Boyle s law is carried out with the apparatus shown in the diagram. The pressure and volume of the gas (air) trapped in the closed end can be varied by raising or lowering
Data An experiment to investigate Boyle s law is carried out with the apparatus shown in the diagram. The pressure and volume of the gas (air) trapped in the closed end can be varied by raising or lowering
HW #10 posted, due Thursday, Dec 2, 11:59 p.m. (last HW that contributes to the final grade)
 HW #10 posted, due Thursday, Dec 2, 11:59 p.m. (last HW that contributes to the final grade) Last Lecture Class: States/Phases of Matter, Deformation of Solids, Density, Pressure Today: Pressure vs. Depth,
HW #10 posted, due Thursday, Dec 2, 11:59 p.m. (last HW that contributes to the final grade) Last Lecture Class: States/Phases of Matter, Deformation of Solids, Density, Pressure Today: Pressure vs. Depth,
and its weight (in newtons) when located on a planet with an acceleration of gravity equal to 4.0 ft/s 2.
 1.26. A certain object weighs 300 N at the earth's surface. Determine the mass of the object (in kilograms) and its weight (in newtons) when located on a planet with an acceleration of gravity equal to
1.26. A certain object weighs 300 N at the earth's surface. Determine the mass of the object (in kilograms) and its weight (in newtons) when located on a planet with an acceleration of gravity equal to
mass of container full of air = g mass of container with extra air = g volume of air released = cm 3
 1992 Q32 The air pressure inside the passenger cabin of an airliner is 9 x 10 4 Pa when the airliner is at its cruising height. The pressure of the outside atmosphere at this height is 4 x 10 4 Pa. Calculate
1992 Q32 The air pressure inside the passenger cabin of an airliner is 9 x 10 4 Pa when the airliner is at its cruising height. The pressure of the outside atmosphere at this height is 4 x 10 4 Pa. Calculate
Why do fish float upward when they die if their weight is slightly greater than the buoyant force?
 From Warmup That's how fish go up and down in water! But by that mechanism, would Marlin and Dory really have been able to go so deep in the ocean in search of Nemo? I doubt it but I don t know for sure.
From Warmup That's how fish go up and down in water! But by that mechanism, would Marlin and Dory really have been able to go so deep in the ocean in search of Nemo? I doubt it but I don t know for sure.
2 Available: 1390/08/02 Date of returning: 1390/08/17 1. A suction cup is used to support a plate of weight as shown in below Figure. For the conditio
 1. A suction cup is used to support a plate of weight as shown in below Figure. For the conditions shown, determine. 2. A tanker truck carries water, and the cross section of the truck s tank is shown
1. A suction cup is used to support a plate of weight as shown in below Figure. For the conditions shown, determine. 2. A tanker truck carries water, and the cross section of the truck s tank is shown
Physics 1021 Experiment 4. Buoyancy
 1 Physics 1021 Buoyancy 2 Buoyancy Apparatus and Setup Materials Force probe 1000 ml beaker Vernier Calipers Plastic cylinder String or paper clips Assorted bars and clamps Water Attach the force probe
1 Physics 1021 Buoyancy 2 Buoyancy Apparatus and Setup Materials Force probe 1000 ml beaker Vernier Calipers Plastic cylinder String or paper clips Assorted bars and clamps Water Attach the force probe
