EXPERIMENTING The Respiratory and Circulatory Systems CLIL Course University of Nottingham STUDENT S WORKSHEETS
|
|
|
- Jodie Long
- 5 years ago
- Views:
Transcription
1 EXPERIMENTING The Respiratory and Circulatory Systems CLIL Course University of Nottingham STUDENT S WORKSHEETS M. Antònia Berga Sabaté January March 2009
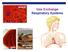
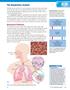
2 Worksheet 1 You breathe to take air into your body. There is a gas in the air called oxygen that your body needs to work. The air goes up your nose or into your mouth. Then it goes down a tube called the windpipe and into your lungs. Count How many seconds can you hold your breath? Answer: I can hold my breath... seconds. Ask your partner How many seconds can you hold your breath? Answer: He/She can hold his/her breath... seconds. Raise your hands, tell your score, look at the board and write down Number of SECONDS Number of children Count again How many times do we breathe in a minute? Answer: I breathe. times in a minute. Don't forget to breathe! How many times do we breathe in a minute after taking exercise? Answer: I breathe. times in a minute. Work in pairs Is there any difference?... Why do we breathe faster when we exercise? Complete the sentence using the words from the box: Oxygen - body - air - breathe We.. faster when we exercise because our. needs more from the.. to make more energy to work harder. M. Antònia Berga Sabaté CEIP FRANCESC MACIÀ (Súria) 1
3 Worksheet 2 Hi! I m Oxy, a tiny molecule of oxygen. You take me from the air. Please come along with me as I take you on a trip into your body. Take a big breath. Hold it in. Where does the air go? Why do we need it? Do you want to travel with me? You breathe to stay alive. Without air, your body would stop working in only a few minutes. Oops! Don't forget to let that air out! It's really amazing! You breathe about 20 times every minute. Imagine how much air you use in one day! I want you to breathe clean air. The air that enters your body through your nose is on its way to your lungs. Let's see how it gets there. Your nose (or nasal cavity) does many useful things for you. It smells for you. It tells you when lunch is ready to eat. As well, it sneezes (AHH CHOO!) for you when you get pepper up your nose. It warms the air on a cold day and cools the air on a hot day. I m now in your nose. It lets air in and cleans it. The next destination: your windpipe. Your windpipe (or trachea) runs down your neck. It takes the air into your lungs. Follow me! Don't confuse this with the tube that takes food to your stomach! Both your windpipe and your nose have "mucus" in them. This sticky stuff is great because it catches the dirt carried in by the air. Now I m still moving! The air you breathe goes deep down into two big spongy sacs called your lungs. Take another big breath. Do you see your chest moving? After the air goes through your nose and windpipe, it reaches your lungs. How can we get there? Through two tubes called bronchi. They divide into smaller and smaller tubes, your bronchioles. Can you still follow me? I m travelling through these tubes. You have to use a microscope to see them. M. Antònia Berga Sabaté CEIP FRANCESC MACIÀ (Súria) 2
4 Worksheet 3 Finally, I reach the end and I fall into very tiny sacs, which are like miniature balloons. You have millions of these air sacs in your lungs. They are called alveoli. Inside them, I m going to say goodbye to you, my friends. Now I m ready to begin the long trip around your body looking for a cell that needs me, the oxygen from the air. BYE! Work in pairs: After reading the story, label the parts of the respiratory system. Ask each other some questions: What are the lungs? Where is the windpipe? How many bronchi have we got? What are the alveoli? M. Antònia Berga Sabaté CEIP FRANCESC MACIÀ (Súria) 3
5 Worksheet 4 Read the sentences from the box and write the airway in the correct order. The air enters the body through goes into the lungs through small tubes called travels from the nose to goes from the trachea to two tubes called passes into the blood through arrives in two spongy organs called the lungs the trachea the bronchioles the bronchi the alveoli the nasal cavity The air travels through big big tubes into tubes narrow into tubes. narrow tubes. M. Antònia Berga Sabaté CEIP FRANCESC MACIÀ (Súria) 4
6 Worksheet 5 Find the words related to the topic: LUNGS NOSE TRACHEA BRONCHI BRONCHIOLE ALVEOLI BREATHE DIAPHRAGM OXYGEN AIR O U Z Y L D V M F F L A A B J T I Q P J L U N G S Z B R Q R V N C N K J F G F Y Q E Y E K A Q R U V D E V C I A K K D L G W I L J Y G C E T U Y D I A P H R A G M B A H B R O N C H I O L E Z R I E Q G T R A C H E A E E O R R H A G I E G S K P A V N D O R C E A C X O D V G C C Q F A L V E O L I C N V M H F Q R N H G S Y P K O Z N I D A Y R Z Y G X U K S G L Q D K Q I O X Y G E N E N D D R P M. Antònia Berga Sabaté CEIP FRANCESC MACIÀ (Súria) 5
7 Worksheet 6 Materials we need: Tweezers A tray Scissors Foil paper The Respiratory system is for breathing, which is the process which oxygen in the air is brought into the lungs and into close contact with the blood. At the same time the blood gives up carbon dioxide, which goes out of the lungs with the air when we breathe. Method: OBSERVING A RESPIRATORY SYSTEM We are going to observe the RESPIRATORY SYSTEM of a mammal: a pig. It is very similar to the human one. Try to observe all the parts carefully. We use the scissors to cut the trachea to see inside it. Is it smooth or rough? Where does it finish? Apart from the trachea and lungs, what other parts can you see? Put some foil paper around the end of the trachea and blow very hard. What happens? What are the lungs like? Amazing Facts: 1. The right lung is larger. 2. The fastest sneeze is 165 km per hour. 3. The capillaries measure 1600 km. M. Antònia Berga Sabaté CEIP FRANCESC MACIÀ (Súria) 6
8 Worksheet 7 OUR QUESTION Number 1 OUR EQUIPMENT (list and draw) To do the experiment we need: METHOD (what do we do?) Draw a picture: Worksheet 8 M. Antònia Berga Sabaté CEIP FRANCESC MACIÀ (Súria) 7
9 MY PREDICTIONS (what I think we will see) I think we will see RESULTS (what happens?) blow up - rough - spongy - reddish - smooth - trachea - lungs - bronchi bronchioles Complete: The trachea is...inside and. outside. We can see When we blow into the trachea, the lungs.... WHAT I HAVE LEARNED I have learned the parts of the Respiratory System: M. Antònia Berga Sabaté CEIP FRANCESC MACIÀ (Súria) 8
10 Worksheet 9 MAKE A MODEL OF YOUR LUNGS (Lungs Expanding and Contracting) When we breathe in our diaphragm (the muscle under our chest) moves down and our ribs move out. Air goes in from outside and the lungs fill with air. When we breathe out our diaphragm moves up and our ribs move back. The air goes out and the lungs empty. Materials we need: One plastic bottle for each group. Some balloons. Scissors Method: We are going to make a model that works in a similar way to our lungs. 1. Push one balloon into the neck of the bottle. Fold the neck of the balloon around the neck of the bottle. 2. Cut the bottom of the bottle. 3. Cut the neck of another balloon and place it over the open end of the bottle. 4. Pull on the middle of this piece of rubber. What happens to the balloon? 5. Let the piece of rubber go and then push it. What happens to the balloon? Amazing Facts: 1. About half a litre of air goes in and out of the lungs in each breath. 2. A person breathes about 21,600 times every day. M. Antònia Berga Sabaté CEIP FRANCESC MACIÀ (Súria) 9
11 Worksheet 10 Number 2 OUR QUESTION OUR EQUIPMENT (list and draw) To do the experiment we need: METHOD (what do we do?) Draw a picture: M. Antònia Berga Sabaté CEIP FRANCESC MACIÀ (Súria) 10
12 Worksheet 11 MY PREDICTIONS (what I think we will see) I think we will see RESULTS (what happens?) Complete: When we pull the rubber, the balloon When we push the rubber, the balloon. WHAT I HAVE LEARNED Write true sentences: When we breathe in When we breathe out the diaphragm the lungs moves up lungs empty moves down lungs fill with air M. Antònia Berga Sabaté CEIP FRANCESC MACIÀ (Súria) 11
13 Worksheet 12 NOSE LUNGS TRACHEA BRONCHI ALVEOLI BRONCHIOLES Label and write in order Two spongy organs where oxygen passes into the blood. Small tubes which carry air into the lungs. Air travels down this big tube into the lungs. Air comes in through this. Tiny air sacs inside the lungs. Two big branches of the trachea. M. Antònia Berga Sabaté CEIP FRANCESC MACIÀ (Súria) 12
14 Worksheet 13 Divide into groups of 3 children and try to speak with your partners for 4-5 minutes about the topic: SMOKING AND HEALTH Before starting the discussion, try to complete these sentences. They can help you to talk about the topic When people smoke, they breathe in Tobacco contains Smoking is for the lungs. The smoke eliminates the cilia from Smoking can cause M. Antònia Berga Sabaté CEIP FRANCESC MACIÀ (Súria) 13
15 Worksheet 14 Your pulse is a measure of how fast your heart is beating. It is the number of beats your heart makes in one minute. You can feel your pulse at certain points on your body. The easiest place to feel it is in your wrist, using the first two fingers of your other hand. Use a stopwatch or a watch with a second hand to count how many beats there are in one minute. Count the number of beats for 10 seconds, and then multiply this number by 6. This will give you your beat rate for a minute. Take your pulse rate How many beats did you count in a minute? Answer: My pulse is.beats a minute. Ask two friends and compare How many beats did you count in a minute? Answer: He/She has... beats per minute. Answer: He/She has.... beats per minute. Record your results in the chart Sitting quietly for ½ minute Your pulse per minute A friend s pulse per minute 1 st time 2 nd time 3 rd time 4 th time Your heart beats faster or slower depending on what you are doing. M. Antònia Berga Sabaté CEIP FRANCESC MACIÀ (Súria) 14
16 Take exercise for two minutes (walk fast, jump, hop ) Find your pulse rate after exercise. For the next two minutes, exercise vigorously. Do any exercise that you want to but be careful. Then quickly sit down. Now have your partner take your pulse rate and record it. Exercise/Activity Prediction (up or down) Time (minutes) Pulse Rate Does it go up or down? Was your prediction right? After 2 minutes of exercising After 4 minutes of exercising After 6 minutes of exercising Resting Conclusion When I exercise my pulse rate goes. When I rest it goes. My fastest pulse rate was per minute. down oxygen up My slowest pulse rate was per minute. When I exercise my heart beats faster because my body needs more. Compare your pulse rate with that of your friend. Answer this question: Where else can you feel a pulse on your body? M. Antònia Berga Sabaté CEIP FRANCESC MACIÀ (Súria) 15
17 Worksheet 15 After watching the video label the parts of the Circulatory system: Heart Arteries Veins Now write the names of the four chambers of the heart: Left ventricle Right ventricle Right atrium Left atrium M. Antònia Berga Sabaté CEIP FRANCESC MACIÀ (Súria) 16
18 Worksheet 16 MAKING A STETHOSCOPE When the valves in our heart open and close to pump blood they make a lub dub sound. With every heartbeat the heart muscles contract to pump blood around the body. Doctors use a stethoscope to listen to the heart because it is difficult to hear the heart s valves without one. Materials we need: Two pieces of plastic tubing (30 centimetres long approx.) Two small kitchen funnels. Or two plastic bottle funnels cut from the top third of plastic water bottles. Scissors. Method: We are going to make a model that works in a similar way to a doctor s stethoscope. 1. Connect the funnels to the plastic tube. 2. Place one end to your ear and the other end to a friend s chest. 3. Can you hear the sound of your friend s heartbeat better with your stethoscope or without it? 4. Can you explain why it seems louder? 5. Can you hear the heartbeat better by listening through the front of the ribcage or from the back? Amazing Facts: 1. The heart pumps about 5 litres of blood each minute. 2. Your heart is about the same size as your closed fist. Worksheet M. Antònia Berga Sabaté CEIP FRANCESC MACIÀ (Súria) 17
19 Worksheet 17 Number 3 OUR QUESTION OUR EQUIPMENT (list and draw) To do the experiment we need: METHOD (what do we do?) Draw a picture: M. Antònia Berga Sabaté CEIP FRANCESC MACIÀ (Súria) 18
20 MY PREDICTIONS (what I think we will notice) I think we are going to feel... RESULTS (what happens?) WHAT I HAVE LEARNED beats - pump - body - heart - heartbeat - blood Complete: Doctors use a stethoscope to measure the..... The pulse rate is the number of... of our Our heart works like a carrying... around our M. Antònia Berga Sabaté CEIP FRANCESC MACIÀ (Súria) 19
21 Worksheet 18 Materials we need: A piece of plasticine or blu-tack. A drinking straw. A stopwatch SEEING YOUR PULSE Method: We are going to find your pulse point on the inside of your wrist below your thumb. 1. Place a piece of plasticine (or blue-tack) on this point. 2. Push one end of a drinking straw into the plasticine so that it stands upright from your wrist. 3. Lay your arm flat on the table. Keep it very still. 4. What do you notice? 5. Count the number of times the straw moves in one minute. (Your heartbeat). (The straw moves backwards and forwards slightly as the blood pumped by your heart passes through your wrist). M. Antònia Berga Sabaté CEIP FRANCESC MACIÀ (Súria) 20
22 Worksheet 19 Read carefully the text about what the blood is like: Adults have about 5 litres of blood in their body. Blood is made of a pale liquid called plasma. Floating in it are red cells, white cells and platelets. Red cells carry oxygen to all parts of the body. White cells fight germs to protect your body from infection. Platelets help your blood to clot when you cut yourself and bleed. Read the texts from the box and write true sentences: The platelets The white cells The plasma The red cells defend the body against illnesses. clot the blood so you don t bleed. is a fluid. It transports substances. carry oxygen to all the cells of the body. M. Antònia Berga Sabaté CEIP FRANCESC MACIÀ (Súria) 21
23 Worksheet 20 Hello! I m Bly, a tiny drop of blood. I travel around your body all the time, through tubes called blood vessels. The large tubes are called arteries and veins. The small tubes are called capillaries. They are very tiny and we need a microscope to see them. Some blood vessels are bigger and you can even see them under your skin! Look at your wrist. The blue coloured tubes you see just under your skin are veins full of me (blood). If we could take out all the blood vessels in your body and place them end-to-end, how far do you think they would go? Your blood vessels would go round the world more than once. It s true! So what pumps me? I'll give you a hint! It's a big organ with strong walls of muscle that acts like a pump, which is in the middle of your chest, behind your lungs. You guessed it. It's your heart. What does a heart look like? Well, as you can see, it's not really shaped like a valentine heart. Close your hands together. That's about the size of your heart! Your heart is like a box divided into four sections. We call them chambers. The two bottom sections (the right and left ventricles) are a little bit bigger than the ones on top (the right and left atriums). These four chambers all have specific jobs to do in order to pump me through your body. Your heart pumps all day and all night. It never takes a rest. About once every second and even faster if you are running. Do you feel your heart pumping me? I m going to your lungs to collect oxygen, and then I m going to return to your heart. There I m going to be pumped to the rest of your body. I carry oxygen and food to every cell and I take away waste and carbon dioxide. The vessels that carry me away from your heart are called arteries. The main one is called Aorta. Those that carry me back to the heart are called veins. Give your heart a treat. It really likes fruit and vegetables. It works better with practice, so remember to take exercise! Take care of your body! I hope you have learned that your heart and me are very special! Bye bye my friends! Good luck! M. Antònia Berga Sabaté CEIP FRANCESC MACIÀ (Súria) 22
24 Worksheet 20 Match these words with their functions: 1. Heart a. Carries blood back to heart. 2. Blood b. Pumps blood around the body. 3. Artery c. Carries blood away from the heart. 4. Vein d. Carries food and oxygen around the body. Label the parts of the heart using the chart below: Left ventricle Right ventricle Right atrium Left atrium Aorta Pulmonary artery website and click on the answer you think is correct: Open the following M. Antònia Berga Sabaté CEIP FRANCESC MACIÀ (Súria) 23
25 Worksheet 21 Materials we need: A tray Scissors Rubber gloves Tweezers Cutter or scalpel A pig s heart for each group Method: DISSECTING A PIG S HEART We are going to look into the heart of a pig because it is very similar to the human heart in size, structure and function. EXTERNAL OBSERVATION: 1. Remove the fat that covers the heart to see it more clearly. 2. Place the flat side of the heart on the tray. COMPLETE: The more fleshy and consistent part is the There is a big crease between the left and the right. (Note that when we talk about left and right, we mean the position of the animal s body. So, your left is the right side of the heart and your right is the left part of the heart). M. Antònia Berga Sabaté CEIP FRANCESC MACIÀ (Súria) 24
26 INTERNAL OBSERVATION: 1. Cut the heart vertically, as indicated on the picture. 2. Observe the ventricles and then cut and open an atrium. COMPLETE: At the top of the heart there are two more chambers. They are the right and the left Remember that - Arteries carry blood away from the heart. They are thicker. - Veins carry blood back into the heart. Can you see an artery? Which one? A vein? Which one? Compare the thickness of the walls of both ventricles. Which one is thicker? Why do you think so? Amazing Facts: 1. Your heart beats about 100,000 times a day. 2. It pumps about 5 litres of blood per minute. M. Antònia Berga Sabaté CEIP FRANCESC MACIÀ (Súria) 25
27 Worksheet 22 Number 4 OUR QUESTION OUR EQUIPMENT (list and draw) To do the experiment we need: METHOD (what do we do?) Draw a picture: M. Antònia Berga Sabaté CEIP FRANCESC MACIÀ (Súria) 26
28 MY PREDICTIONS (what I think we will see) I think we will see The four of the heart. At the top there are two.... At the bottom there are two.. The main. and the main. RESULTS Draw the atriums and the ventricles: WHAT I HAVE LEARNED Match and then write true sentences: There are Ventricles are Arteries carry blood Veins carry blood Arteries are The Vena Cava is The Aorta is. the main vein. away from the heart. thicker than veins. bigger than atriums. back into the heart. the main artery. four chambers in the heart. M. Antònia Berga Sabaté CEIP FRANCESC MACIÀ (Súria) 27
29 Worksheet 23 The Circulatory system: The group of organs that carries nutrients, oxygen and other substances to all cells of the body. Right atrium: collects blood from the body. Right ventricle: Pumps blood to the lungs. Left atrium: Receives blood form the lungs. Left ventricle: Pushes blood to the rest of the body. Read carefully the text and number (from 1 to 8) the steps of the blood circulation : The left side of your heart sends oxygen-rich blood out to the body. The body takes the oxygen out of the blood and uses it in your body's cells. When the cells use the oxygen, they make carbon dioxide and other stuff that gets carried away by the blood. The returning blood enters the right side of the heart. The right ventricle pumps the blood to the lungs. In the lungs, carbon dioxide is removed from the blood and sent out of the body when we exhale. What's next? Of course, a fresh breath of oxygen that can enter the blood to start the process again. And remember, it all happens in about a minute! From the body To the body To the lungs From the lungs M. Antònia Berga Sabaté CEIP FRANCESC MACIÀ (Súria) 28
30 Worksheet What does your heart do? A-It pumps air around your body B-It pumps blood around your body C-It pumps blood to just your muscles 2. Which of these would make your heart beat the fastest? A-Lying down B-Sitting on a chair C-Swimming 3. What does your pulse rate tell you? A-How fast your heart is beating B-How fast you are running C-How old you are 4. Why does your heart beat faster when you exercise? A-Because it gets excited B-To get oxygen to your muscles more quickly C-To make a louder noise 5. Which of these is true? A-Eating bread or pasta gives us energy to be active B-Eating lots of chips helps us grow healthily C-Meat gives us most things we need to keep healthy milk important in a healthy diet? A-They contain lots of fibre, which is good for your heart B-They contain lots of protein, which helps your body grow C-They contain lots of sugar 7. Blood moves round your body in special tubes called blood vessels. Which of these is NOT a blood vessel? A-A vein B-An artery C-A ventricle 8. What happens to your blood when it reaches your lungs? A-It picks up oxygen B-It picks up carbon dioxide C-Nothing 9. Where is your heart? A-In the middle of your chest B-On the right side of your chest C-On the left side of your chest 10. Why is smoking cigarettes bad for you? A-Because cigarettes can burn your fingers B-Because cigarettes can harm your heart and lungs C-Because the smoke gets in your eyes 6. Why are foods like eggs, fish and M. Antònia Berga Sabaté CEIP FRANCESC MACIÀ (Súria) 29
31 Blood heart lungs - vessels It pumps the blood around the body THE HEART AND THE LUNGS CONNECT FOUR GAME They are protected by the rib cage. It is bright red when full of oxygen. Blood without oxygen is pumped back to these. Blood collects oxygen from these. They take in oxygen. We have two of these. It is dark red when it does not contain oxygen. It is a muscle. Smoking is bad for them. The pulse measures beats from this. It carries oxygen round the body. They connect all parts of the body to the heart. It has four chambers. Blood travels through these tubes. It travels to every part of the body. M. Antònia Berga Sabaté CEIP FRANCESC MACIÀ (Súria) 30
A breath of fresh air
 A breath of fresh air BIG IDEAS You are learning to: Describe the structure of the lungs Explain how the lungs clean themselves Interpret patterns in data Where are the lungs and what do they do? The lungs
A breath of fresh air BIG IDEAS You are learning to: Describe the structure of the lungs Explain how the lungs clean themselves Interpret patterns in data Where are the lungs and what do they do? The lungs
The Human Body. Everyone Needs Healthy Systems. Blood Vessels
 The Human Body Everyone Needs Healthy Systems There are several systems that make up the human body. Although their functions differ, they all work together to keep your body running smoothly. Some of
The Human Body Everyone Needs Healthy Systems There are several systems that make up the human body. Although their functions differ, they all work together to keep your body running smoothly. Some of
Components: Reader with DIGI MATERIAL cross-platform application (ios, Android, Windows, MacOSX) CLIL READERS. Level headwords.
 CirculatorySystem _6 cover.qxp_circulatorysystem _6 cover.qxp 21/9/16 6:56 PM Page 1 Level 6 Components: Reader with DIGI MATERIAL cross-platform application (ios, Android, Windows, MacOSX) Level 1 300
CirculatorySystem _6 cover.qxp_circulatorysystem _6 cover.qxp 21/9/16 6:56 PM Page 1 Level 6 Components: Reader with DIGI MATERIAL cross-platform application (ios, Android, Windows, MacOSX) Level 1 300
1.2 The structure and functions of the cardio-respiratory system Learning objectives
 1.2 The structure and functions of the cardio-respiratory system Learning objectives To understand the functions of the circulatory system. To be able to identify the differences between veins, arteries
1.2 The structure and functions of the cardio-respiratory system Learning objectives To understand the functions of the circulatory system. To be able to identify the differences between veins, arteries
Video. Respiration System. You will use 3 pages of your journal for this lesson. 1. One page for hand written notes onto a journal page
 Respiratory System Video Respiration System You will use 3 pages of your journal for this lesson. 1. One page for hand written notes onto a journal page 2. 2 nd page for diagram 3. 3 rd page for chart
Respiratory System Video Respiration System You will use 3 pages of your journal for this lesson. 1. One page for hand written notes onto a journal page 2. 2 nd page for diagram 3. 3 rd page for chart
Lesson 6 Plate Tectonics and Continental Drift PS 2.2 a,e PS 3.1i
 Table of Contents Letter to the Student...................................... 5 Letter to the Family....................................... 6 New York State Performance Standards Correlation Chart.......
Table of Contents Letter to the Student...................................... 5 Letter to the Family....................................... 6 New York State Performance Standards Correlation Chart.......
Circulation and Respiration: Vital Signs Student Version
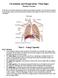 Circulation and Respiration: Vital Signs Student Version In this lab, you will learn about the circulatory and respiratory systems. You will test the capacity of your lungs, measure your blood pressure
Circulation and Respiration: Vital Signs Student Version In this lab, you will learn about the circulatory and respiratory systems. You will test the capacity of your lungs, measure your blood pressure
PARTS AND STRUCTURE OF THE RESPIRATORY SYSTEM
 PARTS AND STRUCTURE OF THE RESPIRATORY SYSTEM Parts of the Respiratory System The RS can be divided into two parts: 1. Respiratory Tract, (path that air follows). Nasal passage Pharynx Larynx Trachea Bronchi,
PARTS AND STRUCTURE OF THE RESPIRATORY SYSTEM Parts of the Respiratory System The RS can be divided into two parts: 1. Respiratory Tract, (path that air follows). Nasal passage Pharynx Larynx Trachea Bronchi,
Monday, ! Today: Respiratory system! 5/20/14! Transport of Blood! What we ve been covering! Circulatory system! Parts of blood! Heart! tubing!
 Monday, 5.19.14! What we ve been covering! Circulatory system! Parts of blood! Heart! tubing! Transport of Blood! What is transported! Nutrients! Oxygen! Carbon Dioxide! Hormones! Antibodies! What it is/does!
Monday, 5.19.14! What we ve been covering! Circulatory system! Parts of blood! Heart! tubing! Transport of Blood! What is transported! Nutrients! Oxygen! Carbon Dioxide! Hormones! Antibodies! What it is/does!
Structures of the Respiratory System include:
 Respiratory System Structures of the Respiratory System include: ü Oral Cavity ü Nasal Cavity ü Pharynx ü Epiglottis ü Larynx ü Trachea ü Diaphragm ü Lung ü Bronchus ü Bronchioles ü Alveolus ü Pulmonary
Respiratory System Structures of the Respiratory System include: ü Oral Cavity ü Nasal Cavity ü Pharynx ü Epiglottis ü Larynx ü Trachea ü Diaphragm ü Lung ü Bronchus ü Bronchioles ü Alveolus ü Pulmonary
RESPIRATION AND EXCRETION
 CHAPTER 13 RESPIRATION AND EXCRETION SECTION 13 1 The Respiratory System (pages 430-438) This section describes the parts of the respiratory system and how they work to help you breathe and speak. Introduction
CHAPTER 13 RESPIRATION AND EXCRETION SECTION 13 1 The Respiratory System (pages 430-438) This section describes the parts of the respiratory system and how they work to help you breathe and speak. Introduction
The Respiratory System
 Respiration and Excretion Name Date Class The Respiratory System This section describes the parts of the respiratory system and how they work to help you breathe and speak. Use Target Reading Skills As
Respiration and Excretion Name Date Class The Respiratory System This section describes the parts of the respiratory system and how they work to help you breathe and speak. Use Target Reading Skills As
The Respiratory System
 Name Date Class The Respiratory System This section describes the parts of the respiratory system and how they work to help you breathe and speak. Use Target Reading Skills As you read, complete the flowchart
Name Date Class The Respiratory System This section describes the parts of the respiratory system and how they work to help you breathe and speak. Use Target Reading Skills As you read, complete the flowchart
Animal Systems: The Respiratory System
 Animal Systems: The Respiratory System Tissues, Organs, and Systems of Living Things Cells, Cell Division, and Animal Systems and Plant Systems Cell Specialization Human Systems The Digestive The Circulatory
Animal Systems: The Respiratory System Tissues, Organs, and Systems of Living Things Cells, Cell Division, and Animal Systems and Plant Systems Cell Specialization Human Systems The Digestive The Circulatory
Respiration. Chapter 33
 Respiration Chapter 33 Learning Objectives: Understand the basis of gas exchange and factors that influence diffusion of gases in and out of tissues Compare and contrast different respiratory systems among
Respiration Chapter 33 Learning Objectives: Understand the basis of gas exchange and factors that influence diffusion of gases in and out of tissues Compare and contrast different respiratory systems among
OB11 Carry out qualitative tests to compare the carbon dioxide levels of inhaled and exhaled air
 Biology: 5. Respiration and Breathing Please remember to photocopy 4 pages onto one sheet by going A3 A4 and using back to back on the photocopier OB9 Syllabus Describe the process of aerobic respiration
Biology: 5. Respiration and Breathing Please remember to photocopy 4 pages onto one sheet by going A3 A4 and using back to back on the photocopier OB9 Syllabus Describe the process of aerobic respiration
The Respiratory System
 The Respiratory System (pages 112 120) Respiratory System Functions (pages 113 114) Key Concept: The respiratory system moves oxygen from the outside environment into the body. It also removes carbon dioxide
The Respiratory System (pages 112 120) Respiratory System Functions (pages 113 114) Key Concept: The respiratory system moves oxygen from the outside environment into the body. It also removes carbon dioxide
1. Label a diagram of the respiratory system. Objective sheet 3 Notes
 1. Label a diagram of the respiratory system Objective sheet 3 Notes 2. Functions of the respiratory structures Name Description Function Nasal Cavity Trachea Bronchi (Singular Bronchus) Bronchioles Lungs
1. Label a diagram of the respiratory system Objective sheet 3 Notes 2. Functions of the respiratory structures Name Description Function Nasal Cavity Trachea Bronchi (Singular Bronchus) Bronchioles Lungs
The Breathing System
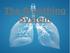 The Breathing System Learning Intentions 1. Students should Know how Breathing happens 2. Name and know the functions of the Breathing System 3. Know how the organs work and how they work with other systems
The Breathing System Learning Intentions 1. Students should Know how Breathing happens 2. Name and know the functions of the Breathing System 3. Know how the organs work and how they work with other systems
Unit 8 B: Respiration
 Unit 8 B: Respiration Respiration: Respiration is a chemical reaction that happens in all living cells. It is the way that energy is released from glucose, for our cells to use to keep us functioning.
Unit 8 B: Respiration Respiration: Respiration is a chemical reaction that happens in all living cells. It is the way that energy is released from glucose, for our cells to use to keep us functioning.
Physical Health and your Respiratory System and Circulatory System
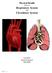 Physical Health and your Respiratory System and Circulatory System Unit Plan Emily Pritchard Fall 2008 1 P a g e Table of Contents Unit Description... 3 Unit Rationale.. 4 Unit Goals....6 Unit Objectives....7
Physical Health and your Respiratory System and Circulatory System Unit Plan Emily Pritchard Fall 2008 1 P a g e Table of Contents Unit Description... 3 Unit Rationale.. 4 Unit Goals....6 Unit Objectives....7
You Might Also Like. I look forward helping you focus your instruction while saving tons of time. Kesler Science Station Lab Activities 40%+ Savings!
 Thanks Connect Thank you for downloading my product. I truly appreciate your support and look forward to hearing your feedback. You can connect with me and find many free activities and strategies over
Thanks Connect Thank you for downloading my product. I truly appreciate your support and look forward to hearing your feedback. You can connect with me and find many free activities and strategies over
SCIENCE 8 RESPIRATION
 SCIENCE 8 RESPIRATION WHEN WE BREATHE, WHAT DO WE BREATHE IN? O2, N2, CO2, O3, NO2 (gas fumes), CO, pollutant, fragrants, toxins, etc. WHAT IS THE PURPOSE OF BREATHING IN? WHAT DOES OUR BODY WANT? O2 WHY?
SCIENCE 8 RESPIRATION WHEN WE BREATHE, WHAT DO WE BREATHE IN? O2, N2, CO2, O3, NO2 (gas fumes), CO, pollutant, fragrants, toxins, etc. WHAT IS THE PURPOSE OF BREATHING IN? WHAT DOES OUR BODY WANT? O2 WHY?
Respiratory System Homework
 Respiratory System Homework The R S is the body s breathing equipment. Similar to the D system, it takes S from outside the body (G, particularly O ), circulates them through the body to C and T, then
Respiratory System Homework The R S is the body s breathing equipment. Similar to the D system, it takes S from outside the body (G, particularly O ), circulates them through the body to C and T, then
The Respiratory System
 Name Date Class The Respiratory System (pages 564-572) Respiratory System Functions (pages 565-566) Key Concept: The respiratory system moves oxygen from the outside environment into the body. It also
Name Date Class The Respiratory System (pages 564-572) Respiratory System Functions (pages 565-566) Key Concept: The respiratory system moves oxygen from the outside environment into the body. It also
Department of Biology Work Sheet Respiratory system,9 class
 I. Name the following : Department of Biology Work Sheet Respiratory system,9 class 1. A muscular sheet separating the thoracic and abdominal cavities. 2. A respiratory tube supported by cartilaginous
I. Name the following : Department of Biology Work Sheet Respiratory system,9 class 1. A muscular sheet separating the thoracic and abdominal cavities. 2. A respiratory tube supported by cartilaginous
Anatomy and Physiology Part 11: Of Blood and Breath by: Les Sellnow
 Anatomy and Physiology Part 11: Of Blood and Breath by: Les Sellnow There are few similarities between horses and automobiles, but in a manner of speaking, the horse's circulatory and respiratory systems
Anatomy and Physiology Part 11: Of Blood and Breath by: Les Sellnow There are few similarities between horses and automobiles, but in a manner of speaking, the horse's circulatory and respiratory systems
Multicellular Organisms. Sub-Topic 2.7 Animal Transport & Exchange Systems
 Multicellular Organisms Sub-Topic 2.7 Animal Transport & Exchange Systems On completion of this sub-topic I will be able to state that: Rings of cartilage keep the main airways open Oxygen and carbon dioxide
Multicellular Organisms Sub-Topic 2.7 Animal Transport & Exchange Systems On completion of this sub-topic I will be able to state that: Rings of cartilage keep the main airways open Oxygen and carbon dioxide
The Respiratory System
 The Respiratory System Learning Outcomes Identify the following structures in the lungs: windpipe, bronchus, bronchioles and air sacs State the function of the air sacs State the path oxygen takes when
The Respiratory System Learning Outcomes Identify the following structures in the lungs: windpipe, bronchus, bronchioles and air sacs State the function of the air sacs State the path oxygen takes when
Respiration. The ins and outs
 Respiration The ins and outs Functions 1. To bring O 2 into the body and transfer it to the blood stream 2. To remove CO 2 Circulation and respiration work together to achieve these functions Why Do We
Respiration The ins and outs Functions 1. To bring O 2 into the body and transfer it to the blood stream 2. To remove CO 2 Circulation and respiration work together to achieve these functions Why Do We
The Respiratory System
 Science Unit: Lesson 4: Human Anatomy How Do We Move? The Respiratory System School year: 2007/2008 Developed for: Developed by: Grade level: Duration of lesson: Henderson Annex Elementary School, Vancouver
Science Unit: Lesson 4: Human Anatomy How Do We Move? The Respiratory System School year: 2007/2008 Developed for: Developed by: Grade level: Duration of lesson: Henderson Annex Elementary School, Vancouver
Chapter 11: Respiratory System Review Assignment
 Name: Date: Mark: / 45 Chapter 11: Respiratory System Review Assignment Multiple Choice = 45 Marks Identify the choice that best completes the statement or answers the question. 1. Which of the following
Name: Date: Mark: / 45 Chapter 11: Respiratory System Review Assignment Multiple Choice = 45 Marks Identify the choice that best completes the statement or answers the question. 1. Which of the following
Results: Complete the following table and create a bar graph of your data.
 EXPERIMENT - DOES BREATHING VOLUME CHANGE AFTER EXERCISE? Aim: To discover if breathing volume changes after exercise. Hypothesis: Make an educated guess about how your breathing rate and breath volume
EXPERIMENT - DOES BREATHING VOLUME CHANGE AFTER EXERCISE? Aim: To discover if breathing volume changes after exercise. Hypothesis: Make an educated guess about how your breathing rate and breath volume
Human Biology Respiratory System
 Human Biology Respiratory System Respiratory System Responsible for process of breathing Works in cooperation with Circulatory system Three types: 1. Internal Respiration 2. External Respiration 3. Cellular
Human Biology Respiratory System Respiratory System Responsible for process of breathing Works in cooperation with Circulatory system Three types: 1. Internal Respiration 2. External Respiration 3. Cellular
Sc ienc e 9-Biology Work sheet 8-2 A Single Breat h & Tak ing Care
 Unit 2 Your Living Body Sc ienc e 9-Biology Work sheet 8-2 A Single Breat h & Tak ing Care Name No pen or pencil No Textbook 20 Due Date Show Me Hand In Correct and Hand In Again By Read pages 159-167
Unit 2 Your Living Body Sc ienc e 9-Biology Work sheet 8-2 A Single Breat h & Tak ing Care Name No pen or pencil No Textbook 20 Due Date Show Me Hand In Correct and Hand In Again By Read pages 159-167
Q1. Which activity is most likely to use aerobic respiration for energy?
 Q1. Which activity is most likely to use aerobic respiration for energy? 10 km cross country run Vault in gymnastics Shot put Jumping to block a shot in basketball (Total 1 mark) Q. All of the following
Q1. Which activity is most likely to use aerobic respiration for energy? 10 km cross country run Vault in gymnastics Shot put Jumping to block a shot in basketball (Total 1 mark) Q. All of the following
Ollie the Oxygen Molecule s amazing adventure
 Ollie the Oxygen Molecule s amazing adventure t was a warm, summer day. Ollie is floating around a park when he felt a strange sucking feeling. It forces him back into a nasal hole. He turns around and
Ollie the Oxygen Molecule s amazing adventure t was a warm, summer day. Ollie is floating around a park when he felt a strange sucking feeling. It forces him back into a nasal hole. He turns around and
Lesson 9.1: The Importance of an Organ Delivery System
 Lesson 9.1: The Importance of an Organ Delivery System Animals require a continuous supply of oxygen (O 2 ) for cellular respiration, and they must expel carbon dioxide (CO 2 ), the waste product of this
Lesson 9.1: The Importance of an Organ Delivery System Animals require a continuous supply of oxygen (O 2 ) for cellular respiration, and they must expel carbon dioxide (CO 2 ), the waste product of this
X Marks the Blind Spot
 X Marks the Blind Spot Human Body 10 minutes In this activity, students will learn about how their eyes and brains work together to trick them. Materials Needed 3x5 index cards Black marker Ruler or straight
X Marks the Blind Spot Human Body 10 minutes In this activity, students will learn about how their eyes and brains work together to trick them. Materials Needed 3x5 index cards Black marker Ruler or straight
practices makes perfect
 Human Respiratory system Chapter 1: Respiration PMR 03, 08 1. The human respiratory system consists of: a... b... c.. d... e. Our body has.. lungs (right & left). f. Each lung consists of the, and alveoli.
Human Respiratory system Chapter 1: Respiration PMR 03, 08 1. The human respiratory system consists of: a... b... c.. d... e. Our body has.. lungs (right & left). f. Each lung consists of the, and alveoli.
Topic 13: Gas Exchange Ch. 42. Gas Exchange pp Gas Exchange. Gas Exchange in Fish pp Gas Exchange in Fish
 Topic 13: Gas Exchange Ch. 42 Fig. 42.24 Gas Exchange pp.979-989 Gas exchange involves the uptake of oxygen and the discharge of carbon dioxide (i.e. respiration or breathing). It is necessary for cellular
Topic 13: Gas Exchange Ch. 42 Fig. 42.24 Gas Exchange pp.979-989 Gas exchange involves the uptake of oxygen and the discharge of carbon dioxide (i.e. respiration or breathing). It is necessary for cellular
Outline - Respiratory System. Function of the respiratory system Parts of the respiratory system Mechanics of breathing Regulation of breathing
 Respiratory system Function Outline - Respiratory System I. II. III. IV. Respiratory System The function of the respiratory system is to bring in oxygen to the body and remove carbon dioxide. Function
Respiratory system Function Outline - Respiratory System I. II. III. IV. Respiratory System The function of the respiratory system is to bring in oxygen to the body and remove carbon dioxide. Function
Pop Quiz. What produces mucus, HCl and pepsinogen in the stomach? List a water soluable vitamin What is a ruminant stomach?
 Pop Quiz What produces mucus, HCl and pepsinogen in the stomach? List a water soluable vitamin What is a ruminant stomach? Respiratory System Review Cellular respiration: obtain glucose and oxygen, get
Pop Quiz What produces mucus, HCl and pepsinogen in the stomach? List a water soluable vitamin What is a ruminant stomach? Respiratory System Review Cellular respiration: obtain glucose and oxygen, get
Human gas exchange. Question Paper. Save My Exams! The Home of Revision. Cambridge International Examinations. 56 minutes. Time Allowed: Score: /46
 Human gas exchange Question Paper Level Subject Exam oard Topic Sub Topic ooklet O Level iology ambridge International Examinations Respiration Human gas exchange Question Paper Time llowed: 56 minutes
Human gas exchange Question Paper Level Subject Exam oard Topic Sub Topic ooklet O Level iology ambridge International Examinations Respiration Human gas exchange Question Paper Time llowed: 56 minutes
Chapter 1: Respiration
 Chapter 1: Respiration Respiration Human Breathing Mechanism Transport of oxygen Importance of a healthy respiratory system Respiratory system lungs inhalation exhalation Diffusion of oxygen by blood Transport
Chapter 1: Respiration Respiration Human Breathing Mechanism Transport of oxygen Importance of a healthy respiratory system Respiratory system lungs inhalation exhalation Diffusion of oxygen by blood Transport
Name period date assigned date due date returned
 Name period date assigned date due date returned procedure 1. Take one balloon and stretch it out 2. Take one deep breath and blow into the balloon until you cannot breath out anymore. Do Not Take A Second
Name period date assigned date due date returned procedure 1. Take one balloon and stretch it out 2. Take one deep breath and blow into the balloon until you cannot breath out anymore. Do Not Take A Second
What is breathing an respiration?
 LE SSON 15 What is breathing an respiration? You need energy to live. So do birds, trees, and bacteria. All living things need energy to carry out the life processes. And, there can be no life without
LE SSON 15 What is breathing an respiration? You need energy to live. So do birds, trees, and bacteria. All living things need energy to carry out the life processes. And, there can be no life without
The Respiratory System. Medical Terminology
 The Respiratory System Medical Terminology The respiratory system is where gas exchange occurs via respiration; inhalation/exhalation. pick up oxygen from inhaled air expels carbon dioxide and water sinus
The Respiratory System Medical Terminology The respiratory system is where gas exchange occurs via respiration; inhalation/exhalation. pick up oxygen from inhaled air expels carbon dioxide and water sinus
GOZO COLLEGE GIRLS SECONDARY Half Yearly Exams
 GOZO COLLEGE GIRLS SECONDARY Half Yearly Exams 2012-2013 Subject: Form: Time: PHYSICAL EDUCATION 4 Junior Lyceum 1 hr 30 min NAME: HY2012-13 4JL MF 1 Section A: Skill Acquisition, Movement and Physical
GOZO COLLEGE GIRLS SECONDARY Half Yearly Exams 2012-2013 Subject: Form: Time: PHYSICAL EDUCATION 4 Junior Lyceum 1 hr 30 min NAME: HY2012-13 4JL MF 1 Section A: Skill Acquisition, Movement and Physical
Circulation and Gas Exchange Chapter 42
 Circulation and Gas Exchange Chapter 42 Circulatory systems link exchange surfaces with cells throughout the body Diffusion is only efficient over small distances In small and/or thin animals, cells can
Circulation and Gas Exchange Chapter 42 Circulatory systems link exchange surfaces with cells throughout the body Diffusion is only efficient over small distances In small and/or thin animals, cells can
alveoli Chapter 42. Gas Exchange elephant seals gills AP Biology
 alveoli Chapter 42. Gas Exchange gills elephant seals Gas exchange O 2 & CO 2 exchange exchange between environment & cells provides O 2 for aerobic cellular respiration need moist membrane need high
alveoli Chapter 42. Gas Exchange gills elephant seals Gas exchange O 2 & CO 2 exchange exchange between environment & cells provides O 2 for aerobic cellular respiration need moist membrane need high
It is a product of proteins broken down in the mammal. It is exchanged for oxygen which is taken into the blood.
 5 The table shows the approximate composition of air breathed out by a mammal. Where does the nitrogen in the air breathed out come from? It is a product of proteins broken down in the mammal. It is a
5 The table shows the approximate composition of air breathed out by a mammal. Where does the nitrogen in the air breathed out come from? It is a product of proteins broken down in the mammal. It is a
Hyndland Secondary School Biology Department
 Hyndland Secondary School Biology Department Body in Action Homework and Question Booklet 1 Body in Action (a) Movement... 2 Skeleton... 2 Joints... 3 Body in Action (b) The need for Energy... 5 Heart...
Hyndland Secondary School Biology Department Body in Action Homework and Question Booklet 1 Body in Action (a) Movement... 2 Skeleton... 2 Joints... 3 Body in Action (b) The need for Energy... 5 Heart...
Breathing: The normal rate is about 14 to 20 times a minute. Taking in of air is called Inspiration and the forcing out of air is called Expiration.
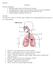 Biology 12 Respiration Divisions of Respiration Breathing: entrance and exit of air into and out of the lungs External Respiration: exchange of gases(o2 and CO2) between air (in alveoli) and blood Internal
Biology 12 Respiration Divisions of Respiration Breathing: entrance and exit of air into and out of the lungs External Respiration: exchange of gases(o2 and CO2) between air (in alveoli) and blood Internal
First Aid Exercises 1
 First Aid Exercises 1 1 A N S W E R T H E Q U E S T I O N S I N Y O U R O W N W O R D S! What are the emergency numbers you should remember? What kind of information should you give when you call for help?
First Aid Exercises 1 1 A N S W E R T H E Q U E S T I O N S I N Y O U R O W N W O R D S! What are the emergency numbers you should remember? What kind of information should you give when you call for help?
AP Biology. Chapter 42. Gas Exchange. Optimizing gas exchange. Gas exchange. Gas exchange in many forms. Evolution of gas exchange structures
 alveoli Chapter 42. Gas Exchange gills elephant seals Gas exchange & C exchange exchange between environment & cells provides for aerobic cellular respiration need moist membrane need high surface area
alveoli Chapter 42. Gas Exchange gills elephant seals Gas exchange & C exchange exchange between environment & cells provides for aerobic cellular respiration need moist membrane need high surface area
BIOLOGY 12: UNIT J - CHAPTER 15 - REVIEW WORKSHEET RESPIRATORY SYSTEM
 BIOLOGY 12: UNIT J - CHAPTER 15 - REVIEW WORKSHEET RESPIRATORY SYSTEM A. CHAPTER REVIEW 1. Define the four components of respiration. 2. What happens to the air as it moves along the air passages? What
BIOLOGY 12: UNIT J - CHAPTER 15 - REVIEW WORKSHEET RESPIRATORY SYSTEM A. CHAPTER REVIEW 1. Define the four components of respiration. 2. What happens to the air as it moves along the air passages? What
Show Me Hand In. Correct and Hand In Again By. Read pages of SP to help you answer the following questions: 1. Name 4 gases contained in air:,
 Name 20 Due Date Show Me Hand In Correct and Hand In Again By Read pages 151-157 of SP to help you answer the following questions: 1. Name 4 gases contained in air:, and. 2. What are two types of solid
Name 20 Due Date Show Me Hand In Correct and Hand In Again By Read pages 151-157 of SP to help you answer the following questions: 1. Name 4 gases contained in air:, and. 2. What are two types of solid
Respiratory System Review
 KEY THIS TEST WILL BE COMPLETED IN ONE CLASS PERIOD MONDAY, MARCH 10. 2014 Respiratory System Review Name A. Directions: Fill in the blank with the appropriate vocabulary word or words (several examples
KEY THIS TEST WILL BE COMPLETED IN ONE CLASS PERIOD MONDAY, MARCH 10. 2014 Respiratory System Review Name A. Directions: Fill in the blank with the appropriate vocabulary word or words (several examples
BIOLOGY INTERACTIVE ASSESSMENT QUESTIONS BASED ON STANDARD PRACTICAL EXERCISES... Biology Part 1 LEARNING VERSION
 INTERACTIVE ASSESSMENT QUESTIONS BASED ON STANDARD PRACTICAL EXERCISES... Biology Part 1 IN THIS ANSWERS ARE IMMEDIATELY AND VISIBLY MARKED, CORRECT ANSWERS ARE INDICATED ON REQUEST, AND END OF SECTION
INTERACTIVE ASSESSMENT QUESTIONS BASED ON STANDARD PRACTICAL EXERCISES... Biology Part 1 IN THIS ANSWERS ARE IMMEDIATELY AND VISIBLY MARKED, CORRECT ANSWERS ARE INDICATED ON REQUEST, AND END OF SECTION
S.T.E.M Part 1: Prior Knowledge: Energy and Simple Machines
 S.T.E.M. 2016-7 Part 1: Prior Knowledge: Energy and Simple Machines Prior Knowledge: What is Energy? Redefining: energy, force, work and pressure Experiment 1: Floating Ping Pong Ball You need: - Ping
S.T.E.M. 2016-7 Part 1: Prior Knowledge: Energy and Simple Machines Prior Knowledge: What is Energy? Redefining: energy, force, work and pressure Experiment 1: Floating Ping Pong Ball You need: - Ping
I. Gas Exchange Respiratory Surfaces Respiratory Surface:
 I. Gas Exchange Respiratory Surfaces Respiratory Surface: Common characteristics of respiratory surfaces: a) Moist: allows for the RAPID diffusion of dissolved gasses across its surface. Whereas the respiratory
I. Gas Exchange Respiratory Surfaces Respiratory Surface: Common characteristics of respiratory surfaces: a) Moist: allows for the RAPID diffusion of dissolved gasses across its surface. Whereas the respiratory
Respiratory System Unit
 Respiratory System Unit An integrative unit including lessons in Science, Art, Math, Health, and Literature 3rd Grade Anatomy Wegner 1 Introduction: The respiratory system allows the human body to take
Respiratory System Unit An integrative unit including lessons in Science, Art, Math, Health, and Literature 3rd Grade Anatomy Wegner 1 Introduction: The respiratory system allows the human body to take
Gas Exchange ACTIVITY OVERVIEW SUMMARY KEY CONCEPTS AND PROCESS SKILLS KEY VOCABULARY. Teacher s Guide B-75 L A B O R ATO R Y
 Gas Exchange 17 40- to 2 50-minute sessions ACTIVITY OVERVIEW L A B O R ATO R Y SUMMARY This activity explores the role of the respiratory system in the regulation of gases in the blood. Students investigate
Gas Exchange 17 40- to 2 50-minute sessions ACTIVITY OVERVIEW L A B O R ATO R Y SUMMARY This activity explores the role of the respiratory system in the regulation of gases in the blood. Students investigate
GAS EXCHANGE & CIRCULATION CHAPTER 42 ( )
 Winter 08 1 of 10 GAS EXCHANGE & CIRCULATION CHAPTER 42 (867 891) MOVEMENT OF GASES Both O 2 and CO 2 move by The movement down a If a gas produced in one location, it diffuses away But diffusion is usually
Winter 08 1 of 10 GAS EXCHANGE & CIRCULATION CHAPTER 42 (867 891) MOVEMENT OF GASES Both O 2 and CO 2 move by The movement down a If a gas produced in one location, it diffuses away But diffusion is usually
UNIFYING CONCEPTS OF ANIMAL CIRCULATION
 UNIFYING CONCEPTS OF ANIMAL CIRCULATION Every organism must exchange materials with its environment, relying upon diffusion, the spontaneous movement of molecules from an area of higher concentration to
UNIFYING CONCEPTS OF ANIMAL CIRCULATION Every organism must exchange materials with its environment, relying upon diffusion, the spontaneous movement of molecules from an area of higher concentration to
3 Respiration, Circulation and Excretion
 Respiration, Circulation and Excretion Notes LOOK AND COMPARE 1. Compare the picture and photograph above. What are the people doing? What differences do you notice? THINK AND EXPLAIN What does the astronaut
Respiration, Circulation and Excretion Notes LOOK AND COMPARE 1. Compare the picture and photograph above. What are the people doing? What differences do you notice? THINK AND EXPLAIN What does the astronaut
Glucose + Oxygen Carbon Dioxide + Water + Energy C6H12O CO2 + 6H20 + energy
 Cell Respiration - A food oxidization process in body cells to produce energy - Occurs (happens) in animal cells and plant cells Notes : Metabolic Reactions in Gaseous Exchange CELL RESPIRATION Photosynthesis
Cell Respiration - A food oxidization process in body cells to produce energy - Occurs (happens) in animal cells and plant cells Notes : Metabolic Reactions in Gaseous Exchange CELL RESPIRATION Photosynthesis
Page 1. Chapter 33: Respiration O 2 CO 2
 Chapter 33: Respiration O 2 CO 2 Features of Respiratory Systems: 1) Moist surface (to dissolve gas) 2) Thin cells lining surface 3) Large surface area contacting environment Facilitate Diffusion Methods
Chapter 33: Respiration O 2 CO 2 Features of Respiratory Systems: 1) Moist surface (to dissolve gas) 2) Thin cells lining surface 3) Large surface area contacting environment Facilitate Diffusion Methods
inquiry question How does the respiratory system contribute to energy production for movement? UNCORRECTED PAGE PROOFS
 inquiry question How does the respiratory system contribute to energy production for movement? chapter 7 Structure and functions of the respiratory system The respiratory system is the starting point for
inquiry question How does the respiratory system contribute to energy production for movement? chapter 7 Structure and functions of the respiratory system The respiratory system is the starting point for
FUNDAMENTAL CRITERIA FOR FIRST AID INTRODUCTION
 CHAPTER 1 FUNDAMENTAL CRITERIA FOR FIRST AID INTRODUCTION Soldiers may have to depend upon their first aid knowledge and skills to save themselves or other soldiers. They may be able to save a life, prevent
CHAPTER 1 FUNDAMENTAL CRITERIA FOR FIRST AID INTRODUCTION Soldiers may have to depend upon their first aid knowledge and skills to save themselves or other soldiers. They may be able to save a life, prevent
Assignments for Life Processes(Respiration)
 Assignments for Life Processes(Respiration) 1 Question 1 Why do organisms need food? Organisms need food for obtaining energy to perform the vital functions. Question 2 What is a respiratory substrate?
Assignments for Life Processes(Respiration) 1 Question 1 Why do organisms need food? Organisms need food for obtaining energy to perform the vital functions. Question 2 What is a respiratory substrate?
Gas Exchange Respiratory Systems
 alveoli gills Gas Exchange Respiratory Systems elephant seals 2008-2009 Why do we need a respiratory system? respiration for respiration Need O 2 in for aerobic cellular respiration make ATP Need CO 2
alveoli gills Gas Exchange Respiratory Systems elephant seals 2008-2009 Why do we need a respiratory system? respiration for respiration Need O 2 in for aerobic cellular respiration make ATP Need CO 2
Living with. Chronic Obstructive Pulmonary Disease COPD. Breathing and Relaxation
 Living with Chronic Obstructive Pulmonary Disease COPD Breathing and Relaxation Anatomy and Physiology of COPD Breathing Techniques Positions to Reduce Shortness of Breath Relaxation Exercise Breathing
Living with Chronic Obstructive Pulmonary Disease COPD Breathing and Relaxation Anatomy and Physiology of COPD Breathing Techniques Positions to Reduce Shortness of Breath Relaxation Exercise Breathing
Chapter 9 Airway Respirations Metabolism Oxygen Requirements Respiratory Anatomy Respiratory Anatomy Respiratory Anatomy Diaphragm
 1 Chapter 9 Airway 2 Respirations Every cell of the body requires to survive Oxygen must come in and carbon must go out 3 Metabolism Metabolism--Process where the body s cells convert food to Adequate
1 Chapter 9 Airway 2 Respirations Every cell of the body requires to survive Oxygen must come in and carbon must go out 3 Metabolism Metabolism--Process where the body s cells convert food to Adequate
L9 Frog Dissection- External Page 1 of 7 STUDENT LABORATORY PACKET. Student s Name Modified from Prentice Hall Lab. Manual Lab Instructor Date Points
 L9 Frog Dissection- External Page 1 of 7 STUDENT LABORATORY PACKET Lab 9: Bull Frog: External Examination Student s Name Modified from Prentice Hall Lab. Manual Lab Instructor Date Points Objective: 1.
L9 Frog Dissection- External Page 1 of 7 STUDENT LABORATORY PACKET Lab 9: Bull Frog: External Examination Student s Name Modified from Prentice Hall Lab. Manual Lab Instructor Date Points Objective: 1.
Part 3: Simulation Cards Reader s Page
 Reader s Page Make 1 copy for Reader. Instructions will be on the front, questions on the back. As an option, the simulation may be frozen and a discussion of information on back of card undertaken. Students
Reader s Page Make 1 copy for Reader. Instructions will be on the front, questions on the back. As an option, the simulation may be frozen and a discussion of information on back of card undertaken. Students
3.6. The Respiratory System
 The Respiratory System Whether you are aware of it or not, you breathe in and out 15 times each minute on average. This rate increases automatically if your physical activity increases. With normal breathing,
The Respiratory System Whether you are aware of it or not, you breathe in and out 15 times each minute on average. This rate increases automatically if your physical activity increases. With normal breathing,
SCIENCE- NOTES. Q1. Draw the diagram of human respiratory system and explain the function of the following parts:
 SCIENCE- NOTES NAME: RESPIRATION IN ORGANISMS STD.VII DIV: Q1. Draw the diagram of human respiratory system and explain the function of the following parts: i. Nasal cavity ii. Trachea iii. Lungs iv. Bronchioles
SCIENCE- NOTES NAME: RESPIRATION IN ORGANISMS STD.VII DIV: Q1. Draw the diagram of human respiratory system and explain the function of the following parts: i. Nasal cavity ii. Trachea iii. Lungs iv. Bronchioles
AP Biology. Gas Exchange Respiratory Systems. Gas exchange. Why do we need a respiratory system? Optimizing gas exchange. Gas exchange in many forms
 alveoli Gas Exchange Respiratory Systems gills elephant seals 2008-2009 Why do we need a respiratory system? Need O 2 in food respiration for respiration for aerobic cellular respiration make ATP Need
alveoli Gas Exchange Respiratory Systems gills elephant seals 2008-2009 Why do we need a respiratory system? Need O 2 in food respiration for respiration for aerobic cellular respiration make ATP Need
Blood Circulation Simulation Grade 5
 TEACHING LEARNING COLLABORATIVE (TLC) LIFE SCIENCE Blood Circulation Simulation Grade 5 Created by: Shelly Bell (Kelseyville Elementary School), Bart Pontoni (Riviera Elementary School), and Shane Lee
TEACHING LEARNING COLLABORATIVE (TLC) LIFE SCIENCE Blood Circulation Simulation Grade 5 Created by: Shelly Bell (Kelseyville Elementary School), Bart Pontoni (Riviera Elementary School), and Shane Lee
UNIT 9 - RESPIRATORY SYSTEM LECTURE NOTES
 UNIT 9 - RESPIRATORY SYSTEM LECTURE NOTES 9.01 GENERAL FUNCTIONS OF THE RESPIRATORY SYSTEM A. Brings oxygenated air to the alveoli B. Removes air containing carbon dioxide C. Filters, warms, and humidifies
UNIT 9 - RESPIRATORY SYSTEM LECTURE NOTES 9.01 GENERAL FUNCTIONS OF THE RESPIRATORY SYSTEM A. Brings oxygenated air to the alveoli B. Removes air containing carbon dioxide C. Filters, warms, and humidifies
G622. APPLIED SCIENCE Monitoring the Activity of the Human Body ADVANCED SUBSIDIARY GCE. Thursday 27 May 2010 Afternoon. Duration: 1 hour 30 minutes
 ADVANCED SUBSIDIARY GCE APPLIED SCIENCE Monitoring the Activity of the Human Body G622 *OCE/17533* Candidates answer on the Question Paper OCR Supplied Materials: None Other Materials Required: Electronic
ADVANCED SUBSIDIARY GCE APPLIED SCIENCE Monitoring the Activity of the Human Body G622 *OCE/17533* Candidates answer on the Question Paper OCR Supplied Materials: None Other Materials Required: Electronic
08 Respiration. #79 Respiration realeases energy from food
 08 Respiration #79 Respiration realeases energy from food Respiration is the chemical reactions that break down nutrient molecules in living cells to release energy. In humans, our cells need energy (ATP)
08 Respiration #79 Respiration realeases energy from food Respiration is the chemical reactions that break down nutrient molecules in living cells to release energy. In humans, our cells need energy (ATP)
GASEOUS EXCHANGE 17 JULY 2013
 GASEOUS EXCHANGE 17 JULY 2013 Lesson Description In this lesson we: Discuss what is gaseous exchange? Consider requirements of an efficient gaseous exchange surface. Look at diversity in gas exchange systems.
GASEOUS EXCHANGE 17 JULY 2013 Lesson Description In this lesson we: Discuss what is gaseous exchange? Consider requirements of an efficient gaseous exchange surface. Look at diversity in gas exchange systems.
Department of Biology Work Sheet Respiratory system
 Department of Biology Work Sheet Respiratory system 1. Name the following : i. A muscular sheet separating the thoracic and abdominal cavities. ii. A respiratory tube supported by cartilaginous rings.
Department of Biology Work Sheet Respiratory system 1. Name the following : i. A muscular sheet separating the thoracic and abdominal cavities. ii. A respiratory tube supported by cartilaginous rings.
A Liter a Lung Measuring Lung Capacity
 A Liter a Lung Measuring Lung Capacity OBJECTIVE In this investigation, students will compare the actual and expected vital capacities of their classmates. LEVEL Middle Grades Life Science CONNECTIONS
A Liter a Lung Measuring Lung Capacity OBJECTIVE In this investigation, students will compare the actual and expected vital capacities of their classmates. LEVEL Middle Grades Life Science CONNECTIONS
Diagram 1: The three phases of gas exchange
 1 Diagram 1: The three phases of gas exchange 1. Breathing When an animal breathes, a large, moist internal surface is exposed to air. O 2 diffuses across the cells lining the lungs and into surrounding
1 Diagram 1: The three phases of gas exchange 1. Breathing When an animal breathes, a large, moist internal surface is exposed to air. O 2 diffuses across the cells lining the lungs and into surrounding
GASEOUS EXCHANGE IN HUMANS 06 AUGUST 2014
 GASEOUS EXCHANGE IN HUMANS 06 AUGUST 2014 In this lesson we: Lesson Description Look at gaseous exchange in humans in terms of o Ventilation o Inspiration o Expiration o Transport of gases o Homeostatic
GASEOUS EXCHANGE IN HUMANS 06 AUGUST 2014 In this lesson we: Lesson Description Look at gaseous exchange in humans in terms of o Ventilation o Inspiration o Expiration o Transport of gases o Homeostatic
Frog Dissection. PreLab: 1. Where do frogs get their energy? Draw a simple food chain to illustrate.
 Name Date Frog Dissection Class # PreLab: Amphibian Reading As members of the class Amphibia, frogs may live some of their adult lives on land, but they must return to water to reproduce. Eggs are laid
Name Date Frog Dissection Class # PreLab: Amphibian Reading As members of the class Amphibia, frogs may live some of their adult lives on land, but they must return to water to reproduce. Eggs are laid
Respiratory System 1
 Respiratory System 1 Outline Respiratory structures Gills Air-Breathing Animals Amphibians and Reptiles Mammals Birds Structures and Mechanisms of Breathing 2 Copyright The McGraw-Hill Companies, Inc.
Respiratory System 1 Outline Respiratory structures Gills Air-Breathing Animals Amphibians and Reptiles Mammals Birds Structures and Mechanisms of Breathing 2 Copyright The McGraw-Hill Companies, Inc.
Chapter 16 Respiratory System
 Introduction Chapter 16 Respiratory System The respiratory system consists of tubes that filter incoming air and transport it to alveoli where gases are exchanged. Think pair share: what organs are associated
Introduction Chapter 16 Respiratory System The respiratory system consists of tubes that filter incoming air and transport it to alveoli where gases are exchanged. Think pair share: what organs are associated
Lab: The Effect of Exercise on Cellular Respiration
 Lab: The Effect of Exercise on Cellular Respiration Purpose: To analyze the effect the exercise has on breathing rate, heart rate, and carbon dioxide production Background Information: Cellular respiration
Lab: The Effect of Exercise on Cellular Respiration Purpose: To analyze the effect the exercise has on breathing rate, heart rate, and carbon dioxide production Background Information: Cellular respiration
The diagram shows an alveolus next to a blood capillary in a lung. (a) (i) Draw a ring around the correct answer to complete the sentence. diffusion.
 BREATHING / GAS EXCHANGE. NAME. Q.Gas exchange takes place in the lungs. The diagram shows an alveolus next to a blood capillary in a lung. The arrows show the movement of two gases, A and B. (a) (i) Draw
BREATHING / GAS EXCHANGE. NAME. Q.Gas exchange takes place in the lungs. The diagram shows an alveolus next to a blood capillary in a lung. The arrows show the movement of two gases, A and B. (a) (i) Draw
Clinical Respiratory System Quiz
 Quiz Description Clinical Respiratory System Quiz Q.1) Q.2) Q.3) Q.4) Q.5) Q.6) What is NOT true about Asthma? It can be triggered by air temperature and allergens. It is the inflammation of the throat.
Quiz Description Clinical Respiratory System Quiz Q.1) Q.2) Q.3) Q.4) Q.5) Q.6) What is NOT true about Asthma? It can be triggered by air temperature and allergens. It is the inflammation of the throat.
How Animals Survive (Circulation and Gas Exchange)
 How Animals Survive (Circulation and Gas Exchange) by Flourence Octaviano on February 16, 2018 lesson duration of 30 minutes under Earth and Life Science generated on February 16, 2018 at 12:45 am Tags:
How Animals Survive (Circulation and Gas Exchange) by Flourence Octaviano on February 16, 2018 lesson duration of 30 minutes under Earth and Life Science generated on February 16, 2018 at 12:45 am Tags:
SWAN CANNING RIVERPARK
 Riverpark Dolphin Junior Background information Dolphins are mammals. Unlike fish, they do not have gills and cannot stay permanently underwater, they must come to the surface to breathe air at regular
Riverpark Dolphin Junior Background information Dolphins are mammals. Unlike fish, they do not have gills and cannot stay permanently underwater, they must come to the surface to breathe air at regular
Chapter 22 Gas Exchange
 Chapter 22 Gas Exchange PowerPoint Lectures for Biology: Concepts & Connections, Sixth Edition Campbell, Reece, Taylor, Simon, and Dickey Lecture by Edward J. Zalisko Introduction: Surviving in Thin Air
Chapter 22 Gas Exchange PowerPoint Lectures for Biology: Concepts & Connections, Sixth Edition Campbell, Reece, Taylor, Simon, and Dickey Lecture by Edward J. Zalisko Introduction: Surviving in Thin Air
Gaseous exchange. Grade 11
 z Gaseous exchange Grade 11 z Terminology 1. Breathing 2. Gaseous exchange 3. Diffusion 4. Spongy mesophyll cells 5. Tracheae 6. Gills 7. Alveoli 8. Larynx 9. Diaphragm 10. Endothelium 1. Pleura 2. Squamous
z Gaseous exchange Grade 11 z Terminology 1. Breathing 2. Gaseous exchange 3. Diffusion 4. Spongy mesophyll cells 5. Tracheae 6. Gills 7. Alveoli 8. Larynx 9. Diaphragm 10. Endothelium 1. Pleura 2. Squamous
Aerobic and Anaerobic Respiration Revision 4
 Aerobic and Anaerobic Respiration Revision 4 64 minutes 64 marks Page of 0 Q. (a) The table shows an athlete s breathing rate after the end of a race. Use the information shown in the table to draw a line
Aerobic and Anaerobic Respiration Revision 4 64 minutes 64 marks Page of 0 Q. (a) The table shows an athlete s breathing rate after the end of a race. Use the information shown in the table to draw a line
