Q1. Which activity is most likely to use aerobic respiration for energy?
|
|
|
- Grace Bradley
- 5 years ago
- Views:
Transcription
1 Q1. Which activity is most likely to use aerobic respiration for energy? 10 km cross country run Vault in gymnastics Shot put Jumping to block a shot in basketball (Total 1 mark) Q. All of the following are functions of the blood except: Transport Protection Energy production Temperature control (Total 1 mark) Q3. In order for respiration to take place air must be taken in. (i) Name two of the air passages which allow air to enter the body. One... Two... Describe what gaseous exchange is and clearly state where it takes place. (3) (Total 5 marks) Page 1 of 13
2 Q4. The circulatory system contributes to the efficient performance of a sports performer. (i) State two different functions or roles of the blood. Function/role one... Function/role two... Explain how the heart acts as a pump in a double circulatory system. (3) (Total 5 marks) Q5. The pulse rate can be used to monitor the effects of exercise on the body. (i) Describe two places on the body where the pulse can be found. Place 1... Place... Explain why it is important to monitor and record the pulse rate when exercising or training. (3) (Total 5 marks) Page of 13
3 Q6. Sporting situations may be considered to be aerobic or anaerobic. (i) What is meant by the term 'aerobic'? (1) Describe a situation in which a performer would be working aerobically. (iii) What is meant by the term 'anaerobic'? (1) (iv) Describe a situation in which a performer would be working anaerobically. (Total 6 marks) Page 3 of 13
4 Q7. The circulatory system helps the body to work efficiently. Describe the role of the blood in the following functions. (i) Transport Control of body temperature (Total 4 marks) Q8. Name two body systems involved in providing energy for movement and physical activity (Total marks) Page 4 of 13
5 Q9. The effective working of the breathing and respiratory system is important for all performers. (i) The air passages are one part of the breathing system. Name three other parts. Part 1... Part... Part 3... (3) Describe how respiration takes place. (3) (Total 6 marks) Q10. (i) What is blood pressure? How does physical activity affect blood pressure during activity?... in the long term?... (Total 4 marks) Page 5 of 13
6 Q11. Many factors are important in determining how successful a performer may be. How do breathing rate, heart rate and metabolic rate affect the possibility of success in physical activity? (Total 7 marks) Page 6 of 13
7 M1. 10 km cross country run [1] M. Energy production [1] M3. (i) Award one mark for each of the correctly named air passages mouth nose pharynx epiglottis larynx trachea bronchi bronchioles Award up to three marks for a correct answer. award up to two marks for correctly describing it as the oxygen being taken in / being exchanged for the carbon dioxide which is to be breathed out award one mark for stating that gaseous exchange occurs in the lungs / alveoli 3 [5] M4. (i) Award up to two marks for correctly stating two different functions or roles of the blood. transport of oxygen / carbon dioxide transport of glucose / waste products body temperature control protection Page 7 of 13
8 Award up to three marks for correctly explaining the double pump function: blood enters the right atrium / dark red in colour with little oxygen right atrium pumps blood / into the right ventricle the right ventricle pumps through the pulmonary artery / to the lungs from the lungs the blood returns / to the left atrium the left atrium pumps the blood / into the left ventricle the left ventricle pumps the blood / into the aorta/ to the body Accept the above plus other suitable examples. In order to obtain the maximum marks candidates must clearly identify at least three of the stages identified above. 3 [5] M5. (i) Award one mark for each correctly described pulse point. Note that some might be correctly named and for others a description of their exact location may be accepted. Radial pulse/at the base of the thumb on the inside of the wrist Temporal pulse/just over the temple at the side of the forehead Carotid pulse/on either side of the neck Femoral pulse-in the groin. Page 8 of 13
9 Award up to three marks for a correct explanation. Examples: The heart rate lets you know how quickly the blood is being pumped around the body This is effectively providing the energy to allow the body to exercise There are certain zones or areas which the heart rate can be increased to or worked in The speed of your recovery rate is a general indicator of your fitness levels The quicker you are able to return your pulse to its resting rate the fitter you are Monitoring the rate can be used as a training indicator to make sure you are working at the correct levels Varying the pulse rate can be used relative to the principle of overload Safety aspects can be considered to ensure you are not working at too high a level. Accept the above plus any other suitable examples. 3 [5] M6. (i) Award one mark for a correct definition. An equation is acceptable. Aerobic respiration in the presence of oxygen Glucose + oxygen = energy + carbon dioxide + water 1 Award up to two marks for an accurate description. For maximum marks reference should be made to the intensity and length of time of the situation. e.g. activities that need long term energy systems, such as cross country running or long distance cycling Page 9 of 13
10 (iii) Award one mark for a correct definition. An equation is acceptable. Anaerobic respiration in the absence of oxygen glucose energy + lactic acid 1 (iv) Award up to two marks for an accurate description. For maximum marks reference should be made to the intensity and length of time of the situation. Activities that need short term energy systems such as 100m sprinting or weightlifting. [6] M7. (i) Award up to two marks for describing the transport function: It carries glycogen/, water/, oxygen/ or nutrients throughout the body/to the working muscle/and helps with the transport and removal of waste/carbon dioxide/lactic acid/away from the working muscle. Award up to two marks for describing the control of body temperature function. The blood absorbs body heat/then carries it to the skin and lungs/where it is released/veins dilate/to cool you down. [4] M8. Two systems from. circulatory respiratory digestive accept cardiovascular [] Page 10 of 13
11 M9. (i) Award one mark for each correctly identified part of the breathing system other than the air passages which were included in the question. Examples: trachea alveoli bronchioles lungs diaphragm mouth nasal cavity or nose larynx pharynx intercostal muscles bronchus, bronchi. 3 Award up to three marks for a correct description of how respiration takes place. Examples: the process by which the body / takes in oxygen / and gives out carbon dioxide the process of the lungs / inspiring / and expiring reference to aerobic and anaerobic respiration is also acceptable. Accept the above plus any other suitable examples. 3 [6] M10. (i) Resistance in the cardio-vascular system (one mark) to the flow of blood round the body (one mark). force of the blood (one mark) passing through an artery (one mark) accept a measure of blood flow/ease at which blood flows around the body. a measure of the blood flow through an artery = marks. do not accept the speed at which blood travels/how fast blood travels. Page 11 of 13
12 blood pressure goes up during physical activity; blood pressure stays low/is lowered in the long term. [4] M11. When breathing rate is low the potential for success is greater in stamina-based activities because the body works within the aerobic (breathing) system (amplification possible for extracmarks) as the body utilises O (greater VO uptake) As breathing rate gets higher and shallow it can indicate an O debt and performance will be reduced. When resting heart rate is low the potential for success is greater in stamina-based activities because of increased volume of blood circulating to muscles and oxygen supply meets demand together with. the slower the production of waste products When heart rate gets higher as demand for O increases removal of wastes (CO and lactic acid) is urgent/necessary and performance will be reduced/stopped. NB There will be facts stated which seem to contradict this line but which may be correct. The higher the metabolic rate the greater the potential for success in stamina-based activities because of the quicker breakdown of food and creation of ATP With a lower metabolic rate less energy is converted and weight is increased Performance is reduced. [7] Page 1 of 13
13 Page 13 of 13
1.2 The structure and functions of the cardio-respiratory system Learning objectives
 1.2 The structure and functions of the cardio-respiratory system Learning objectives To understand the functions of the circulatory system. To be able to identify the differences between veins, arteries
1.2 The structure and functions of the cardio-respiratory system Learning objectives To understand the functions of the circulatory system. To be able to identify the differences between veins, arteries
Monday, ! Today: Respiratory system! 5/20/14! Transport of Blood! What we ve been covering! Circulatory system! Parts of blood! Heart! tubing!
 Monday, 5.19.14! What we ve been covering! Circulatory system! Parts of blood! Heart! tubing! Transport of Blood! What is transported! Nutrients! Oxygen! Carbon Dioxide! Hormones! Antibodies! What it is/does!
Monday, 5.19.14! What we ve been covering! Circulatory system! Parts of blood! Heart! tubing! Transport of Blood! What is transported! Nutrients! Oxygen! Carbon Dioxide! Hormones! Antibodies! What it is/does!
Video. Respiration System. You will use 3 pages of your journal for this lesson. 1. One page for hand written notes onto a journal page
 Respiratory System Video Respiration System You will use 3 pages of your journal for this lesson. 1. One page for hand written notes onto a journal page 2. 2 nd page for diagram 3. 3 rd page for chart
Respiratory System Video Respiration System You will use 3 pages of your journal for this lesson. 1. One page for hand written notes onto a journal page 2. 2 nd page for diagram 3. 3 rd page for chart
The Respiratory System. Medical Terminology
 The Respiratory System Medical Terminology The respiratory system is where gas exchange occurs via respiration; inhalation/exhalation. pick up oxygen from inhaled air expels carbon dioxide and water sinus
The Respiratory System Medical Terminology The respiratory system is where gas exchange occurs via respiration; inhalation/exhalation. pick up oxygen from inhaled air expels carbon dioxide and water sinus
SCIENCE- NOTES. Q1. Draw the diagram of human respiratory system and explain the function of the following parts:
 SCIENCE- NOTES NAME: RESPIRATION IN ORGANISMS STD.VII DIV: Q1. Draw the diagram of human respiratory system and explain the function of the following parts: i. Nasal cavity ii. Trachea iii. Lungs iv. Bronchioles
SCIENCE- NOTES NAME: RESPIRATION IN ORGANISMS STD.VII DIV: Q1. Draw the diagram of human respiratory system and explain the function of the following parts: i. Nasal cavity ii. Trachea iii. Lungs iv. Bronchioles
PARTS AND STRUCTURE OF THE RESPIRATORY SYSTEM
 PARTS AND STRUCTURE OF THE RESPIRATORY SYSTEM Parts of the Respiratory System The RS can be divided into two parts: 1. Respiratory Tract, (path that air follows). Nasal passage Pharynx Larynx Trachea Bronchi,
PARTS AND STRUCTURE OF THE RESPIRATORY SYSTEM Parts of the Respiratory System The RS can be divided into two parts: 1. Respiratory Tract, (path that air follows). Nasal passage Pharynx Larynx Trachea Bronchi,
Chapter 11: Respiratory System Review Assignment
 Name: Date: Mark: / 45 Chapter 11: Respiratory System Review Assignment Multiple Choice = 45 Marks Identify the choice that best completes the statement or answers the question. 1. Which of the following
Name: Date: Mark: / 45 Chapter 11: Respiratory System Review Assignment Multiple Choice = 45 Marks Identify the choice that best completes the statement or answers the question. 1. Which of the following
Anatomy and Physiology Part 11: Of Blood and Breath by: Les Sellnow
 Anatomy and Physiology Part 11: Of Blood and Breath by: Les Sellnow There are few similarities between horses and automobiles, but in a manner of speaking, the horse's circulatory and respiratory systems
Anatomy and Physiology Part 11: Of Blood and Breath by: Les Sellnow There are few similarities between horses and automobiles, but in a manner of speaking, the horse's circulatory and respiratory systems
The diagram shows an alveolus next to a blood capillary in a lung. (a) (i) Draw a ring around the correct answer to complete the sentence. diffusion.
 BREATHING / GAS EXCHANGE. NAME. Q.Gas exchange takes place in the lungs. The diagram shows an alveolus next to a blood capillary in a lung. The arrows show the movement of two gases, A and B. (a) (i) Draw
BREATHING / GAS EXCHANGE. NAME. Q.Gas exchange takes place in the lungs. The diagram shows an alveolus next to a blood capillary in a lung. The arrows show the movement of two gases, A and B. (a) (i) Draw
Human Biology Respiratory System
 Human Biology Respiratory System Respiratory System Responsible for process of breathing Works in cooperation with Circulatory system Three types: 1. Internal Respiration 2. External Respiration 3. Cellular
Human Biology Respiratory System Respiratory System Responsible for process of breathing Works in cooperation with Circulatory system Three types: 1. Internal Respiration 2. External Respiration 3. Cellular
Assignments for Life Processes(Respiration)
 Assignments for Life Processes(Respiration) 1 Question 1 Why do organisms need food? Organisms need food for obtaining energy to perform the vital functions. Question 2 What is a respiratory substrate?
Assignments for Life Processes(Respiration) 1 Question 1 Why do organisms need food? Organisms need food for obtaining energy to perform the vital functions. Question 2 What is a respiratory substrate?
SCIENCE 8 RESPIRATION
 SCIENCE 8 RESPIRATION WHEN WE BREATHE, WHAT DO WE BREATHE IN? O2, N2, CO2, O3, NO2 (gas fumes), CO, pollutant, fragrants, toxins, etc. WHAT IS THE PURPOSE OF BREATHING IN? WHAT DOES OUR BODY WANT? O2 WHY?
SCIENCE 8 RESPIRATION WHEN WE BREATHE, WHAT DO WE BREATHE IN? O2, N2, CO2, O3, NO2 (gas fumes), CO, pollutant, fragrants, toxins, etc. WHAT IS THE PURPOSE OF BREATHING IN? WHAT DOES OUR BODY WANT? O2 WHY?
Breathing: The normal rate is about 14 to 20 times a minute. Taking in of air is called Inspiration and the forcing out of air is called Expiration.
 Biology 12 Respiration Divisions of Respiration Breathing: entrance and exit of air into and out of the lungs External Respiration: exchange of gases(o2 and CO2) between air (in alveoli) and blood Internal
Biology 12 Respiration Divisions of Respiration Breathing: entrance and exit of air into and out of the lungs External Respiration: exchange of gases(o2 and CO2) between air (in alveoli) and blood Internal
Structures of the Respiratory System include:
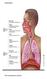
 Respiratory System Structures of the Respiratory System include: ü Oral Cavity ü Nasal Cavity ü Pharynx ü Epiglottis ü Larynx ü Trachea ü Diaphragm ü Lung ü Bronchus ü Bronchioles ü Alveolus ü Pulmonary
Respiratory System Structures of the Respiratory System include: ü Oral Cavity ü Nasal Cavity ü Pharynx ü Epiglottis ü Larynx ü Trachea ü Diaphragm ü Lung ü Bronchus ü Bronchioles ü Alveolus ü Pulmonary
08 Respiration. #79 Respiration realeases energy from food
 08 Respiration #79 Respiration realeases energy from food Respiration is the chemical reactions that break down nutrient molecules in living cells to release energy. In humans, our cells need energy (ATP)
08 Respiration #79 Respiration realeases energy from food Respiration is the chemical reactions that break down nutrient molecules in living cells to release energy. In humans, our cells need energy (ATP)
Respiratory System Homework
 Respiratory System Homework The R S is the body s breathing equipment. Similar to the D system, it takes S from outside the body (G, particularly O ), circulates them through the body to C and T, then
Respiratory System Homework The R S is the body s breathing equipment. Similar to the D system, it takes S from outside the body (G, particularly O ), circulates them through the body to C and T, then
Respiration. The ins and outs
 Respiration The ins and outs Functions 1. To bring O 2 into the body and transfer it to the blood stream 2. To remove CO 2 Circulation and respiration work together to achieve these functions Why Do We
Respiration The ins and outs Functions 1. To bring O 2 into the body and transfer it to the blood stream 2. To remove CO 2 Circulation and respiration work together to achieve these functions Why Do We
The Respiratory System
 Name Date Class The Respiratory System This section describes the parts of the respiratory system and how they work to help you breathe and speak. Use Target Reading Skills As you read, complete the flowchart
Name Date Class The Respiratory System This section describes the parts of the respiratory system and how they work to help you breathe and speak. Use Target Reading Skills As you read, complete the flowchart
OB11 Carry out qualitative tests to compare the carbon dioxide levels of inhaled and exhaled air
 Biology: 5. Respiration and Breathing Please remember to photocopy 4 pages onto one sheet by going A3 A4 and using back to back on the photocopier OB9 Syllabus Describe the process of aerobic respiration
Biology: 5. Respiration and Breathing Please remember to photocopy 4 pages onto one sheet by going A3 A4 and using back to back on the photocopier OB9 Syllabus Describe the process of aerobic respiration
Animal Systems: The Respiratory System
 Animal Systems: The Respiratory System Tissues, Organs, and Systems of Living Things Cells, Cell Division, and Animal Systems and Plant Systems Cell Specialization Human Systems The Digestive The Circulatory
Animal Systems: The Respiratory System Tissues, Organs, and Systems of Living Things Cells, Cell Division, and Animal Systems and Plant Systems Cell Specialization Human Systems The Digestive The Circulatory
Aerobic and Anaerobic Respiration Revision 4
 Aerobic and Anaerobic Respiration Revision 4 64 minutes 64 marks Page of 0 Q. (a) The table shows an athlete s breathing rate after the end of a race. Use the information shown in the table to draw a line
Aerobic and Anaerobic Respiration Revision 4 64 minutes 64 marks Page of 0 Q. (a) The table shows an athlete s breathing rate after the end of a race. Use the information shown in the table to draw a line
Topic 13: Gas Exchange Ch. 42. Gas Exchange pp Gas Exchange. Gas Exchange in Fish pp Gas Exchange in Fish
 Topic 13: Gas Exchange Ch. 42 Fig. 42.24 Gas Exchange pp.979-989 Gas exchange involves the uptake of oxygen and the discharge of carbon dioxide (i.e. respiration or breathing). It is necessary for cellular
Topic 13: Gas Exchange Ch. 42 Fig. 42.24 Gas Exchange pp.979-989 Gas exchange involves the uptake of oxygen and the discharge of carbon dioxide (i.e. respiration or breathing). It is necessary for cellular
RESPIRATION AND EXCRETION
 CHAPTER 13 RESPIRATION AND EXCRETION SECTION 13 1 The Respiratory System (pages 430-438) This section describes the parts of the respiratory system and how they work to help you breathe and speak. Introduction
CHAPTER 13 RESPIRATION AND EXCRETION SECTION 13 1 The Respiratory System (pages 430-438) This section describes the parts of the respiratory system and how they work to help you breathe and speak. Introduction
CHAPTER 3: The cardio-respiratory system
 : The cardio-respiratory system Exam style questions - text book pages 44-45 1) Describe the structures involved in gaseous exchange in the lungs and explain how gaseous exchange occurs within this tissue.
: The cardio-respiratory system Exam style questions - text book pages 44-45 1) Describe the structures involved in gaseous exchange in the lungs and explain how gaseous exchange occurs within this tissue.
The Human Body. Everyone Needs Healthy Systems. Blood Vessels
 The Human Body Everyone Needs Healthy Systems There are several systems that make up the human body. Although their functions differ, they all work together to keep your body running smoothly. Some of
The Human Body Everyone Needs Healthy Systems There are several systems that make up the human body. Although their functions differ, they all work together to keep your body running smoothly. Some of
Department of Biology Work Sheet Respiratory system,9 class
 I. Name the following : Department of Biology Work Sheet Respiratory system,9 class 1. A muscular sheet separating the thoracic and abdominal cavities. 2. A respiratory tube supported by cartilaginous
I. Name the following : Department of Biology Work Sheet Respiratory system,9 class 1. A muscular sheet separating the thoracic and abdominal cavities. 2. A respiratory tube supported by cartilaginous
inquiry question How does the respiratory system contribute to energy production for movement? UNCORRECTED PAGE PROOFS
 inquiry question How does the respiratory system contribute to energy production for movement? chapter 7 Structure and functions of the respiratory system The respiratory system is the starting point for
inquiry question How does the respiratory system contribute to energy production for movement? chapter 7 Structure and functions of the respiratory system The respiratory system is the starting point for
Lesson 9.1: The Importance of an Organ Delivery System
 Lesson 9.1: The Importance of an Organ Delivery System Animals require a continuous supply of oxygen (O 2 ) for cellular respiration, and they must expel carbon dioxide (CO 2 ), the waste product of this
Lesson 9.1: The Importance of an Organ Delivery System Animals require a continuous supply of oxygen (O 2 ) for cellular respiration, and they must expel carbon dioxide (CO 2 ), the waste product of this
Respiratory System Review
 KEY THIS TEST WILL BE COMPLETED IN ONE CLASS PERIOD MONDAY, MARCH 10. 2014 Respiratory System Review Name A. Directions: Fill in the blank with the appropriate vocabulary word or words (several examples
KEY THIS TEST WILL BE COMPLETED IN ONE CLASS PERIOD MONDAY, MARCH 10. 2014 Respiratory System Review Name A. Directions: Fill in the blank with the appropriate vocabulary word or words (several examples
1. Label a diagram of the respiratory system. Objective sheet 3 Notes
 1. Label a diagram of the respiratory system Objective sheet 3 Notes 2. Functions of the respiratory structures Name Description Function Nasal Cavity Trachea Bronchi (Singular Bronchus) Bronchioles Lungs
1. Label a diagram of the respiratory system Objective sheet 3 Notes 2. Functions of the respiratory structures Name Description Function Nasal Cavity Trachea Bronchi (Singular Bronchus) Bronchioles Lungs
The Respiratory System
 Respiration and Excretion Name Date Class The Respiratory System This section describes the parts of the respiratory system and how they work to help you breathe and speak. Use Target Reading Skills As
Respiration and Excretion Name Date Class The Respiratory System This section describes the parts of the respiratory system and how they work to help you breathe and speak. Use Target Reading Skills As
A breath of fresh air
 A breath of fresh air BIG IDEAS You are learning to: Describe the structure of the lungs Explain how the lungs clean themselves Interpret patterns in data Where are the lungs and what do they do? The lungs
A breath of fresh air BIG IDEAS You are learning to: Describe the structure of the lungs Explain how the lungs clean themselves Interpret patterns in data Where are the lungs and what do they do? The lungs
The Breathing System
 The Breathing System Learning Intentions 1. Students should Know how Breathing happens 2. Name and know the functions of the Breathing System 3. Know how the organs work and how they work with other systems
The Breathing System Learning Intentions 1. Students should Know how Breathing happens 2. Name and know the functions of the Breathing System 3. Know how the organs work and how they work with other systems
Respiration. Chapter 33
 Respiration Chapter 33 Learning Objectives: Understand the basis of gas exchange and factors that influence diffusion of gases in and out of tissues Compare and contrast different respiratory systems among
Respiration Chapter 33 Learning Objectives: Understand the basis of gas exchange and factors that influence diffusion of gases in and out of tissues Compare and contrast different respiratory systems among
Unit 8 B: Respiration
 Unit 8 B: Respiration Respiration: Respiration is a chemical reaction that happens in all living cells. It is the way that energy is released from glucose, for our cells to use to keep us functioning.
Unit 8 B: Respiration Respiration: Respiration is a chemical reaction that happens in all living cells. It is the way that energy is released from glucose, for our cells to use to keep us functioning.
The Respiratory System
 Name Date Class The Respiratory System (pages 564-572) Respiratory System Functions (pages 565-566) Key Concept: The respiratory system moves oxygen from the outside environment into the body. It also
Name Date Class The Respiratory System (pages 564-572) Respiratory System Functions (pages 565-566) Key Concept: The respiratory system moves oxygen from the outside environment into the body. It also
Lesson 6 Plate Tectonics and Continental Drift PS 2.2 a,e PS 3.1i
 Table of Contents Letter to the Student...................................... 5 Letter to the Family....................................... 6 New York State Performance Standards Correlation Chart.......
Table of Contents Letter to the Student...................................... 5 Letter to the Family....................................... 6 New York State Performance Standards Correlation Chart.......
Human gas exchange. Question Paper. Save My Exams! The Home of Revision. Cambridge International Examinations. 56 minutes. Time Allowed: Score: /46
 Human gas exchange Question Paper Level Subject Exam oard Topic Sub Topic ooklet O Level iology ambridge International Examinations Respiration Human gas exchange Question Paper Time llowed: 56 minutes
Human gas exchange Question Paper Level Subject Exam oard Topic Sub Topic ooklet O Level iology ambridge International Examinations Respiration Human gas exchange Question Paper Time llowed: 56 minutes
system. and then into the tissues. Diffusion of wastes such as Carbon Dioxide from tissues into blood and out of blood into the lungs.
 Respiratory System 1.Exchange Why do of we gases breathe? into the Think blood of all and the tissues. reasons Diffusion why we of Oxygen need a respiratory into blood from the lungs system. and then into
Respiratory System 1.Exchange Why do of we gases breathe? into the Think blood of all and the tissues. reasons Diffusion why we of Oxygen need a respiratory into blood from the lungs system. and then into
INTERNATIONAL TURKISH HOPE SCHOOL
 INTERNATIONAL TURKISH HOPE SCHOOL 2014 2015 ACADEMIC YEAR CHITTAGONG SENIOR SECTION RESPIRATION and GAS EXCHANGE CLASS IX and X Name :... Date :... SYLLABUS CONTENT Section 2: Structures and functions
INTERNATIONAL TURKISH HOPE SCHOOL 2014 2015 ACADEMIC YEAR CHITTAGONG SENIOR SECTION RESPIRATION and GAS EXCHANGE CLASS IX and X Name :... Date :... SYLLABUS CONTENT Section 2: Structures and functions
Then the partial pressure of oxygen is. b) Gases will diffuse down a pressure gradient across a respiratory surface if it is: i) permeable ii) moist
 1 AP Biology March 2008 Respiration Chapter 42 Gas exchange occurs across specialized respiratory surfaces. 1) Gas exchange: Relies on the diffusion of gases down pressure gradients. At sea level, atmosphere
1 AP Biology March 2008 Respiration Chapter 42 Gas exchange occurs across specialized respiratory surfaces. 1) Gas exchange: Relies on the diffusion of gases down pressure gradients. At sea level, atmosphere
It is a product of proteins broken down in the mammal. It is exchanged for oxygen which is taken into the blood.
 5 The table shows the approximate composition of air breathed out by a mammal. Where does the nitrogen in the air breathed out come from? It is a product of proteins broken down in the mammal. It is a
5 The table shows the approximate composition of air breathed out by a mammal. Where does the nitrogen in the air breathed out come from? It is a product of proteins broken down in the mammal. It is a
BIOLOGY 12: UNIT J - CHAPTER 15 - REVIEW WORKSHEET RESPIRATORY SYSTEM
 BIOLOGY 12: UNIT J - CHAPTER 15 - REVIEW WORKSHEET RESPIRATORY SYSTEM A. CHAPTER REVIEW 1. Define the four components of respiration. 2. What happens to the air as it moves along the air passages? What
BIOLOGY 12: UNIT J - CHAPTER 15 - REVIEW WORKSHEET RESPIRATORY SYSTEM A. CHAPTER REVIEW 1. Define the four components of respiration. 2. What happens to the air as it moves along the air passages? What
practices makes perfect
 Human Respiratory system Chapter 1: Respiration PMR 03, 08 1. The human respiratory system consists of: a... b... c.. d... e. Our body has.. lungs (right & left). f. Each lung consists of the, and alveoli.
Human Respiratory system Chapter 1: Respiration PMR 03, 08 1. The human respiratory system consists of: a... b... c.. d... e. Our body has.. lungs (right & left). f. Each lung consists of the, and alveoli.
UNIFYING CONCEPTS OF ANIMAL CIRCULATION
 UNIFYING CONCEPTS OF ANIMAL CIRCULATION Every organism must exchange materials with its environment, relying upon diffusion, the spontaneous movement of molecules from an area of higher concentration to
UNIFYING CONCEPTS OF ANIMAL CIRCULATION Every organism must exchange materials with its environment, relying upon diffusion, the spontaneous movement of molecules from an area of higher concentration to
Respiration. The resspiratory system
 Respiration The resspiratory system The Alveoli The lungs have about 300 million alveoli, with a total crosssec onal area of 50 70 m2.. Each alveolar sac is surrounded by blood capillaries. The walls of
Respiration The resspiratory system The Alveoli The lungs have about 300 million alveoli, with a total crosssec onal area of 50 70 m2.. Each alveolar sac is surrounded by blood capillaries. The walls of
The bar chart shows the amount of water lost from the body of a student on two different days.
 RESPIRATION (2nd PART) Q1. The bar chart shows the amount of water lost from the body of a student on two different days. The student ate the same amount of food and drank the same amount of liquid on
RESPIRATION (2nd PART) Q1. The bar chart shows the amount of water lost from the body of a student on two different days. The student ate the same amount of food and drank the same amount of liquid on
Chapter 1: Respiration
 Chapter 1: Respiration Respiration Human Breathing Mechanism Transport of oxygen Importance of a healthy respiratory system Respiratory system lungs inhalation exhalation Diffusion of oxygen by blood Transport
Chapter 1: Respiration Respiration Human Breathing Mechanism Transport of oxygen Importance of a healthy respiratory system Respiratory system lungs inhalation exhalation Diffusion of oxygen by blood Transport
2) During exhalation Air is cooled due to condensation and loses its moisture, depositing it on lining in trachea and nose
 Section 10: The Respiratory System A. Functions of the respiratory system: The organs of the respiratory system make sure oxygen enters the body and carbon dioxide leaves the body. 2 stages: Inhalation
Section 10: The Respiratory System A. Functions of the respiratory system: The organs of the respiratory system make sure oxygen enters the body and carbon dioxide leaves the body. 2 stages: Inhalation
EXPERIMENTING The Respiratory and Circulatory Systems CLIL Course University of Nottingham STUDENT S WORKSHEETS
 EXPERIMENTING The Respiratory and Circulatory Systems CLIL Course University of Nottingham STUDENT S WORKSHEETS M. Antònia Berga Sabaté January March 2009 Worksheet 1 You breathe to take air into your
EXPERIMENTING The Respiratory and Circulatory Systems CLIL Course University of Nottingham STUDENT S WORKSHEETS M. Antònia Berga Sabaté January March 2009 Worksheet 1 You breathe to take air into your
You Might Also Like. I look forward helping you focus your instruction while saving tons of time. Kesler Science Station Lab Activities 40%+ Savings!
 Thanks Connect Thank you for downloading my product. I truly appreciate your support and look forward to hearing your feedback. You can connect with me and find many free activities and strategies over
Thanks Connect Thank you for downloading my product. I truly appreciate your support and look forward to hearing your feedback. You can connect with me and find many free activities and strategies over
Breathing oxygenates the blood to allow food to be respired
 Chapter 6 Breathing oxygenates the blood to allow food to be respired This chapter covers: the structure of the human gas exchange system the mechanism of breathing gas exchange in the alveoli the concept
Chapter 6 Breathing oxygenates the blood to allow food to be respired This chapter covers: the structure of the human gas exchange system the mechanism of breathing gas exchange in the alveoli the concept
3/24/2009 LAB D.HAMMOUDI.MD. 1. Trachea 2. Thoracic wall 3. Lungs 4. Primary bronchi 5. Diaphragm
 RESPIRATORY PHYSIOLOGY LAB D.HAMMOUDI.MD 1. Trachea 2. Thoracic wall 3. Lungs 4. Primary bronchi 5. Diaphragm 1 KEY WORDS TO KNOW BOYLE S LAW INTERCOSTAL NERVES PHRENIC NERVE DIAPHRAGM EXTERNAL INTERCOSTAL
RESPIRATORY PHYSIOLOGY LAB D.HAMMOUDI.MD 1. Trachea 2. Thoracic wall 3. Lungs 4. Primary bronchi 5. Diaphragm 1 KEY WORDS TO KNOW BOYLE S LAW INTERCOSTAL NERVES PHRENIC NERVE DIAPHRAGM EXTERNAL INTERCOSTAL
Outline - Respiratory System. Function of the respiratory system Parts of the respiratory system Mechanics of breathing Regulation of breathing
 Respiratory system Function Outline - Respiratory System I. II. III. IV. Respiratory System The function of the respiratory system is to bring in oxygen to the body and remove carbon dioxide. Function
Respiratory system Function Outline - Respiratory System I. II. III. IV. Respiratory System The function of the respiratory system is to bring in oxygen to the body and remove carbon dioxide. Function
The Respiratory System
 The Respiratory System (pages 112 120) Respiratory System Functions (pages 113 114) Key Concept: The respiratory system moves oxygen from the outside environment into the body. It also removes carbon dioxide
The Respiratory System (pages 112 120) Respiratory System Functions (pages 113 114) Key Concept: The respiratory system moves oxygen from the outside environment into the body. It also removes carbon dioxide
Then the partial pressure of oxygen is x 760 = 160 mm Hg
 1 AP Biology March 2008 Respiration Chapter 42 Gas exchange occurs across specialized respiratory surfaces. 1) Gas exchange: the uptake of molecular oxygen (O2) from the environment and the discharge of
1 AP Biology March 2008 Respiration Chapter 42 Gas exchange occurs across specialized respiratory surfaces. 1) Gas exchange: the uptake of molecular oxygen (O2) from the environment and the discharge of
Chapter 16 Respiratory System
 Introduction Chapter 16 Respiratory System The respiratory system consists of tubes that filter incoming air and transport it to alveoli where gases are exchanged. Think pair share: what organs are associated
Introduction Chapter 16 Respiratory System The respiratory system consists of tubes that filter incoming air and transport it to alveoli where gases are exchanged. Think pair share: what organs are associated
Ollie the Oxygen Molecule s amazing adventure
 Ollie the Oxygen Molecule s amazing adventure t was a warm, summer day. Ollie is floating around a park when he felt a strange sucking feeling. It forces him back into a nasal hole. He turns around and
Ollie the Oxygen Molecule s amazing adventure t was a warm, summer day. Ollie is floating around a park when he felt a strange sucking feeling. It forces him back into a nasal hole. He turns around and
Page 1. Chapter 33: Respiration O 2 CO 2
 Chapter 33: Respiration O 2 CO 2 Features of Respiratory Systems: 1) Moist surface (to dissolve gas) 2) Thin cells lining surface 3) Large surface area contacting environment Facilitate Diffusion Methods
Chapter 33: Respiration O 2 CO 2 Features of Respiratory Systems: 1) Moist surface (to dissolve gas) 2) Thin cells lining surface 3) Large surface area contacting environment Facilitate Diffusion Methods
Gas Exchange Respiratory Systems
 alveoli gills Gas Exchange Respiratory Systems elephant seals 2008-2009 Why do we need a respiratory system? respiration for respiration Need O 2 in for aerobic cellular respiration make ATP Need CO 2
alveoli gills Gas Exchange Respiratory Systems elephant seals 2008-2009 Why do we need a respiratory system? respiration for respiration Need O 2 in for aerobic cellular respiration make ATP Need CO 2
2.1.1 List the principal structures of the
 physiology 2.1.1 List the principal structures of the The principle structures of the respiratory are: Nose/Mouth used for inhalation of oxygen-rich air and expelling carbon dioxide rich air Pharynx -
physiology 2.1.1 List the principal structures of the The principle structures of the respiratory are: Nose/Mouth used for inhalation of oxygen-rich air and expelling carbon dioxide rich air Pharynx -
Respiratory System 1
 Respiratory System 1 Outline Respiratory structures Gills Air-Breathing Animals Amphibians and Reptiles Mammals Birds Structures and Mechanisms of Breathing 2 Copyright The McGraw-Hill Companies, Inc.
Respiratory System 1 Outline Respiratory structures Gills Air-Breathing Animals Amphibians and Reptiles Mammals Birds Structures and Mechanisms of Breathing 2 Copyright The McGraw-Hill Companies, Inc.
UNIT 9 - RESPIRATORY SYSTEM LECTURE NOTES
 UNIT 9 - RESPIRATORY SYSTEM LECTURE NOTES 9.01 GENERAL FUNCTIONS OF THE RESPIRATORY SYSTEM A. Brings oxygenated air to the alveoli B. Removes air containing carbon dioxide C. Filters, warms, and humidifies
UNIT 9 - RESPIRATORY SYSTEM LECTURE NOTES 9.01 GENERAL FUNCTIONS OF THE RESPIRATORY SYSTEM A. Brings oxygenated air to the alveoli B. Removes air containing carbon dioxide C. Filters, warms, and humidifies
Living with. Chronic Obstructive Pulmonary Disease COPD. Breathing and Relaxation
 Living with Chronic Obstructive Pulmonary Disease COPD Breathing and Relaxation Anatomy and Physiology of COPD Breathing Techniques Positions to Reduce Shortness of Breath Relaxation Exercise Breathing
Living with Chronic Obstructive Pulmonary Disease COPD Breathing and Relaxation Anatomy and Physiology of COPD Breathing Techniques Positions to Reduce Shortness of Breath Relaxation Exercise Breathing
Pop Quiz. What produces mucus, HCl and pepsinogen in the stomach? List a water soluable vitamin What is a ruminant stomach?
 Pop Quiz What produces mucus, HCl and pepsinogen in the stomach? List a water soluable vitamin What is a ruminant stomach? Respiratory System Review Cellular respiration: obtain glucose and oxygen, get
Pop Quiz What produces mucus, HCl and pepsinogen in the stomach? List a water soluable vitamin What is a ruminant stomach? Respiratory System Review Cellular respiration: obtain glucose and oxygen, get
--- Respiration in Organisms. Lesson at a Glance
 --- Respiration in Organisms Lesson at a Glance. Respiration is essential for survival of every living organism whether it is an animal or a plant. It is a process by which living organisms produce energy
--- Respiration in Organisms Lesson at a Glance. Respiration is essential for survival of every living organism whether it is an animal or a plant. It is a process by which living organisms produce energy
I. Gas Exchange Respiratory Surfaces Respiratory Surface:
 I. Gas Exchange Respiratory Surfaces Respiratory Surface: Common characteristics of respiratory surfaces: a) Moist: allows for the RAPID diffusion of dissolved gasses across its surface. Whereas the respiratory
I. Gas Exchange Respiratory Surfaces Respiratory Surface: Common characteristics of respiratory surfaces: a) Moist: allows for the RAPID diffusion of dissolved gasses across its surface. Whereas the respiratory
(Slide 1) Lecture Notes: Respiratory System
 (Slide 1) Lecture Notes: Respiratory System I. (Slide 2) The Respiratory Tract A) Major structures and regions of the respiratory Tract/Route INTO body 1) nose 2) nasal cavity 3) pharynx 4) glottis 5)
(Slide 1) Lecture Notes: Respiratory System I. (Slide 2) The Respiratory Tract A) Major structures and regions of the respiratory Tract/Route INTO body 1) nose 2) nasal cavity 3) pharynx 4) glottis 5)
Lab 17. The Respiratory System. Laboratory Objectives
 Lab 17 The Respiratory System Laboratory Objectives Identify and describe the anatomical structures of the respiratory system. Describe the relationship between volume and pressure. Describe changes in
Lab 17 The Respiratory System Laboratory Objectives Identify and describe the anatomical structures of the respiratory system. Describe the relationship between volume and pressure. Describe changes in
AP Biology. Gas Exchange Respiratory Systems. Gas exchange. Why do we need a respiratory system? Optimizing gas exchange. Gas exchange in many forms
 alveoli Gas Exchange Respiratory Systems gills elephant seals 2008-2009 Why do we need a respiratory system? Need O 2 in food respiration for respiration for aerobic cellular respiration make ATP Need
alveoli Gas Exchange Respiratory Systems gills elephant seals 2008-2009 Why do we need a respiratory system? Need O 2 in food respiration for respiration for aerobic cellular respiration make ATP Need
GASEOUS EXCHANGE 17 JULY 2013
 GASEOUS EXCHANGE 17 JULY 2013 Lesson Description In this lesson we: Discuss what is gaseous exchange? Consider requirements of an efficient gaseous exchange surface. Look at diversity in gas exchange systems.
GASEOUS EXCHANGE 17 JULY 2013 Lesson Description In this lesson we: Discuss what is gaseous exchange? Consider requirements of an efficient gaseous exchange surface. Look at diversity in gas exchange systems.
Circulation and Gas Exchange Chapter 42
 Circulation and Gas Exchange Chapter 42 Circulatory systems link exchange surfaces with cells throughout the body Diffusion is only efficient over small distances In small and/or thin animals, cells can
Circulation and Gas Exchange Chapter 42 Circulatory systems link exchange surfaces with cells throughout the body Diffusion is only efficient over small distances In small and/or thin animals, cells can
Chapter 35: Respiratory Systems
 Chapter 35: Respiratory Systems AP Curriculum Alignment Cells are restricted in size by the necessity of maintain a large surface area to volume. The cells of the alveoli, which are the functioning units
Chapter 35: Respiratory Systems AP Curriculum Alignment Cells are restricted in size by the necessity of maintain a large surface area to volume. The cells of the alveoli, which are the functioning units
Name period date assigned date due date returned
 Name period date assigned date due date returned procedure 1. Take one balloon and stretch it out 2. Take one deep breath and blow into the balloon until you cannot breath out anymore. Do Not Take A Second
Name period date assigned date due date returned procedure 1. Take one balloon and stretch it out 2. Take one deep breath and blow into the balloon until you cannot breath out anymore. Do Not Take A Second
alveoli Chapter 42. Gas Exchange elephant seals gills AP Biology
 alveoli Chapter 42. Gas Exchange gills elephant seals Gas exchange O 2 & CO 2 exchange exchange between environment & cells provides O 2 for aerobic cellular respiration need moist membrane need high
alveoli Chapter 42. Gas Exchange gills elephant seals Gas exchange O 2 & CO 2 exchange exchange between environment & cells provides O 2 for aerobic cellular respiration need moist membrane need high
Use scientific principles to explain how the sprayer works. You may use diagrams to support your answer.
 4.3 Marking Key This guide includes sample answers, task-specific observable elements, (Appendices 1 and 2), descriptive evaluation rubrics for each competency (Appendices 3 and 4), and non-descriptive
4.3 Marking Key This guide includes sample answers, task-specific observable elements, (Appendices 1 and 2), descriptive evaluation rubrics for each competency (Appendices 3 and 4), and non-descriptive
3.3.2 Gas Exchange SPECIFICATION
 alevelbiology.co.uk 3.3.2 Gas Exchange SPECIFICATION Adaptations of gas exchange surfaces, shown by gas exchange: Across the body surface of a single-celled organism In the tracheal system of an insect
alevelbiology.co.uk 3.3.2 Gas Exchange SPECIFICATION Adaptations of gas exchange surfaces, shown by gas exchange: Across the body surface of a single-celled organism In the tracheal system of an insect
Chapter 13 The Respiratory System
 Chapter 13 The Respiratory System by Dr. Jay M. Templin Brooks/Cole - Thomson Learning Atmosphere Tissue cell External respiration Alveoli of lungs 1 Ventilation or gas exchange between the atmosphere
Chapter 13 The Respiratory System by Dr. Jay M. Templin Brooks/Cole - Thomson Learning Atmosphere Tissue cell External respiration Alveoli of lungs 1 Ventilation or gas exchange between the atmosphere
UNIT 2 Getting energy from food
 Biology Form 4 Page 16 Ms. R. Buttigieg UNIT 2 Getting energy from food 2.1 Aerobic and anaerobic respiration (see GSCE Biology pg. 19-20) RESPIRATIO the process by which energy is produced from food Energy
Biology Form 4 Page 16 Ms. R. Buttigieg UNIT 2 Getting energy from food 2.1 Aerobic and anaerobic respiration (see GSCE Biology pg. 19-20) RESPIRATIO the process by which energy is produced from food Energy
The table shows the effect of exercise on the action of one person s heart. Heart rate in beats per minute
 ## (a) The table shows the effect of exercise on the action of one person s heart. At rest During exercise Heart rate in beats per minute 7 165 Volume of blood leaving the heart in each beat in cm 3 Heart
## (a) The table shows the effect of exercise on the action of one person s heart. At rest During exercise Heart rate in beats per minute 7 165 Volume of blood leaving the heart in each beat in cm 3 Heart
Department of Biology Work Sheet Respiratory system
 Department of Biology Work Sheet Respiratory system 1. Name the following : i. A muscular sheet separating the thoracic and abdominal cavities. ii. A respiratory tube supported by cartilaginous rings.
Department of Biology Work Sheet Respiratory system 1. Name the following : i. A muscular sheet separating the thoracic and abdominal cavities. ii. A respiratory tube supported by cartilaginous rings.
Gaseous exchange. Grade 11
 z Gaseous exchange Grade 11 z Terminology 1. Breathing 2. Gaseous exchange 3. Diffusion 4. Spongy mesophyll cells 5. Tracheae 6. Gills 7. Alveoli 8. Larynx 9. Diaphragm 10. Endothelium 1. Pleura 2. Squamous
z Gaseous exchange Grade 11 z Terminology 1. Breathing 2. Gaseous exchange 3. Diffusion 4. Spongy mesophyll cells 5. Tracheae 6. Gills 7. Alveoli 8. Larynx 9. Diaphragm 10. Endothelium 1. Pleura 2. Squamous
AP Biology. Chapter 42. Gas Exchange. Optimizing gas exchange. Gas exchange. Gas exchange in many forms. Evolution of gas exchange structures
 alveoli Chapter 42. Gas Exchange gills elephant seals Gas exchange & C exchange exchange between environment & cells provides for aerobic cellular respiration need moist membrane need high surface area
alveoli Chapter 42. Gas Exchange gills elephant seals Gas exchange & C exchange exchange between environment & cells provides for aerobic cellular respiration need moist membrane need high surface area
GASEOUS EXCHANGE IN HUMANS 06 AUGUST 2014
 GASEOUS EXCHANGE IN HUMANS 06 AUGUST 2014 In this lesson we: Lesson Description Look at gaseous exchange in humans in terms of o Ventilation o Inspiration o Expiration o Transport of gases o Homeostatic
GASEOUS EXCHANGE IN HUMANS 06 AUGUST 2014 In this lesson we: Lesson Description Look at gaseous exchange in humans in terms of o Ventilation o Inspiration o Expiration o Transport of gases o Homeostatic
Vertebrate Respiration
 Vertebrate Respiration Functions Gas Exchange we animals require oxygen and get rid of Carbon dioxide when too much of it makes the blood acidic, when lowering the ph of the blood it will interfere with
Vertebrate Respiration Functions Gas Exchange we animals require oxygen and get rid of Carbon dioxide when too much of it makes the blood acidic, when lowering the ph of the blood it will interfere with
Chapter 22 Gas Exchange
 Chapter 22 Gas Exchange PowerPoint Lectures for Biology: Concepts & Connections, Sixth Edition Campbell, Reece, Taylor, Simon, and Dickey Lecture by Edward J. Zalisko Introduction: Surviving in Thin Air
Chapter 22 Gas Exchange PowerPoint Lectures for Biology: Concepts & Connections, Sixth Edition Campbell, Reece, Taylor, Simon, and Dickey Lecture by Edward J. Zalisko Introduction: Surviving in Thin Air
Be sure you understand these four functions of the respiratory system before you begin this lab.
 Biology 212: Human Anatomy and Physiology II ************************************************************************************************************* RESPIRATORY ANATOMY & VENTILATION *************************************************************************************************************
Biology 212: Human Anatomy and Physiology II ************************************************************************************************************* RESPIRATORY ANATOMY & VENTILATION *************************************************************************************************************
ADVANCED SUBSIDIARY GCE G622 APPLIED SCIENCE
 ADVANCED SUBSIDIARY GCE APPLIED SCIENCE Unit 3: Monitoring the activity of the human body TUESDAY 5 JUNE 2007 G622 Afternoon *CUP/T21601* Additional materials: Electronic calculator Ruler (cm/mm) Time:
ADVANCED SUBSIDIARY GCE APPLIED SCIENCE Unit 3: Monitoring the activity of the human body TUESDAY 5 JUNE 2007 G622 Afternoon *CUP/T21601* Additional materials: Electronic calculator Ruler (cm/mm) Time:
CHAPTER 17 BREATHING AND EXCHANGE OF GASES
 268 BIOLOGY CHAPTER 17 BREATHING AND EXCHANGE OF GASES 17.1 Respiratory Organs 17.2 Mechanism of Breathing 17.3 Exchange of Gases 17.4 Transport of Gases 17.5 Regulation of Respiration 17.6 Disorders of
268 BIOLOGY CHAPTER 17 BREATHING AND EXCHANGE OF GASES 17.1 Respiratory Organs 17.2 Mechanism of Breathing 17.3 Exchange of Gases 17.4 Transport of Gases 17.5 Regulation of Respiration 17.6 Disorders of
Hyndland Secondary School Biology Department
 Hyndland Secondary School Biology Department Body in Action Homework and Question Booklet 1 Body in Action (a) Movement... 2 Skeleton... 2 Joints... 3 Body in Action (b) The need for Energy... 5 Heart...
Hyndland Secondary School Biology Department Body in Action Homework and Question Booklet 1 Body in Action (a) Movement... 2 Skeleton... 2 Joints... 3 Body in Action (b) The need for Energy... 5 Heart...
Method of measuring bodytemperature. Temperature: Body temperature is the degree of heat maintained by the body. Heat is lost
 VITAL SIGNS What do you mean by VITAL SIGNS? Ms. Esther Jennifer STAFF NURSE - ICU World largest thermometer Vital signs include 1. body temperature, 2. pulse, 3. respiration and 4. blood pressure. IMPORTANCE:
VITAL SIGNS What do you mean by VITAL SIGNS? Ms. Esther Jennifer STAFF NURSE - ICU World largest thermometer Vital signs include 1. body temperature, 2. pulse, 3. respiration and 4. blood pressure. IMPORTANCE:
 Question 1: Define vital capacity. What is its significance? Vital capacity is the maximum volume of air that can be exhaled after a maximum inspiration. It is about 3.5 4.5 litres in the human body. It
Question 1: Define vital capacity. What is its significance? Vital capacity is the maximum volume of air that can be exhaled after a maximum inspiration. It is about 3.5 4.5 litres in the human body. It
Energy Systems and Growth
 Energy Systems and Growth Understanding Energy Systems and Growth Understanding how your body produces energy is vital to understanding why you train in certain ways to enhance your energy systems and
Energy Systems and Growth Understanding Energy Systems and Growth Understanding how your body produces energy is vital to understanding why you train in certain ways to enhance your energy systems and
Respiration in Organisms MULTIPLE CHOICE QUESTIONS NCERT
 10 Respiration in Organisms MULTIPLE CHOICE QUESTIONS 1. Sometimes when we do heavy exercise, anaerobic respiration takes place in our muscle cells. What is produced during this process? alcohol and lactic
10 Respiration in Organisms MULTIPLE CHOICE QUESTIONS 1. Sometimes when we do heavy exercise, anaerobic respiration takes place in our muscle cells. What is produced during this process? alcohol and lactic
Unit II Problem 4 Physiology: Diffusion of Gases and Pulmonary Circulation
 Unit II Problem 4 Physiology: Diffusion of Gases and Pulmonary Circulation - Physical principles of gases: Pressure of a gas is caused by the movement of its molecules against a surface (more concentration
Unit II Problem 4 Physiology: Diffusion of Gases and Pulmonary Circulation - Physical principles of gases: Pressure of a gas is caused by the movement of its molecules against a surface (more concentration
Cardiovascular and respiratory adjustments to exercise
 Cardiovascular and respiratory adjustments to exercise Additional notes on breathing and use of respiratory belt and pulse transducers Notes on breathing The metabolic activities of tissues use up oxygen
Cardiovascular and respiratory adjustments to exercise Additional notes on breathing and use of respiratory belt and pulse transducers Notes on breathing The metabolic activities of tissues use up oxygen
CHAPTER 3: The respiratory system
 CHAPTER 3: The respiratory system Practice questions - text book pages 56-58 1) When the inspiratory muscles contract, which one of the following statements is true? a. the size of the thoracic cavity
CHAPTER 3: The respiratory system Practice questions - text book pages 56-58 1) When the inspiratory muscles contract, which one of the following statements is true? a. the size of the thoracic cavity
Respiratory system & exercise. Dr. Rehab F Gwada
 Respiratory system & exercise Dr. Rehab F Gwada Objectives of lecture Outline the major anatomical components & important functions of the respiratory system. Describe the mechanics of ventilation. List
Respiratory system & exercise Dr. Rehab F Gwada Objectives of lecture Outline the major anatomical components & important functions of the respiratory system. Describe the mechanics of ventilation. List
The equation describes anaerobic respiration in muscle cells. How can you tell from the equation that this process is anaerobic?
 Respiration. Name.. Q.Anaerobic respiration happens in muscle cells and yeast cells. The equation describes anaerobic respiration in muscle cells. glucose lactic acid (a) How can you tell from the equation
Respiration. Name.. Q.Anaerobic respiration happens in muscle cells and yeast cells. The equation describes anaerobic respiration in muscle cells. glucose lactic acid (a) How can you tell from the equation
Breathing and Exchange of Gases
 183 Breathing and Exchange of Gases 1. Skin is an accessory organ of respiration in (a) humans (b) frog (c) rabbit (d) lizard Frog has lungs as its main respiratory organs but during hibernation & aestivation
183 Breathing and Exchange of Gases 1. Skin is an accessory organ of respiration in (a) humans (b) frog (c) rabbit (d) lizard Frog has lungs as its main respiratory organs but during hibernation & aestivation
