Influence of Settlement on Bearing Capacity Analysis of Shallow Foundations on Sandy Clays in the Niger Delta, Nigeria
|
|
|
- Adelia Bruce
- 6 years ago
- Views:
Transcription
1 Available online at European Journal of Applied Engineering and Scientific Research, 201, 2 (4):20-27 ( ISSN: Influence of Settlement on Bearing Capacity Analysis of Shallow Foundations on Sandy Clays in the Niger Delta, Nigeria S. B. Akpila and I. W. Omunguye Department of Civil Engineering, Rivers State University of Science and Technology, P. M. B. 50, Port Harcourt, Nigeria ABSTRACT The influence of foundation settlement on appropriation of bearing capacity of shallow footings on sandy clays has been studied through deep subsurface borings, laboratory tests and analysis. Generally, allowable bearing capacity values vary from -86kN/m 2 for raft foundation breadth of 19.m and 29.5m up to m depth below ground level. Values of immediate settlement, S i, for foundation breadths of 19.m and 2.m were 6mm and 7.2mm respectively for a bearing pressure of 50kN/m 2, while immediate settlement of 9.6mm and 11.7mm were respectively obtained for a bearing pressure of kn/m 2. Total settlement values ranged from 64-91mm under a bearing pressure of 50kN/m 2 as foundation depth decreases. For higher bearing pressure of kn/m 2, total settlement values ranged from mm with decrease in foundation depth. For satisfactory deformation requirement, a bearing pressure of 50kN/m 2 gave settlement values satisfying the maximum allowable limits for mat foundations on clays, while kn/m 2 gave excessive settlement values. Keywords:. Deformation, Bearing Pressure, Shear failure, Poisson Ratio. INTRODUCTION Shallow foundations placed on compressible soil formation are required to satisfy both stability and deformation criteria in foundation analysis and design. Stability criterion ensures that the anticipated induced bearing pressure from the foundations do not cause shear failure of supporting soil under loading, while deformation requirement ensures that the generated vertical volume change on the soil is within the tolerance limit of the superstructure. Three types of shear failures have been identified to occur under foundation induced loading; general shear failure, punching shear failure and local shear failure. Details of their failure mechanisms are available in literatures [1, 2,, 4, 5]. The deformation response in cohesive soils is both immediate and time dependent. In the process of dissipation of excess pore water pressure in the cohesive soil structure, soil voids decreases resulting in vertical deformation; hence foundation displacement occurs. Recent studies on the area of stability and deformation of shallow foundations in the Niger Delta of Nigeria reported the case of shallow foundation on sand overlying soft clay, having allowable bearing pressure q a, values ranging from 126-1kN/m 2, but kN/m 2 at soft clay-sand interface. For an induced bearing pressure of 95kN/m 2 and m v of 0.26m 2 /MN generated a total settlement of 12mm on m thick sand underlain by 4m thick clay [6, 7]. In the case of studies on two crude oil tank reservoirs in the Niger Delta with dimensions of 20m height and 18.8m diameter, gave a total settlement of 11mm and 148mm. At full capacity, it generated a net bearing capacity of 1kN/m 2 through metal plate placed on compacted sand [8, 9]. The methods of Perry, Meyerhof and modified Meyerhof on evaluation of bearing capacity of shallow foundation based on standard penetration test gave three bounds limits; upper, middle and lower bounds of net allowable bearing capacity for pad foundations on sand. The three bound limits occurred in the descending order of Perry, Meyerhof and Modified Meyerhof s method [10]. Shallow foundations placed on heterogeneous soil formations, gave deformation in excess of maximum allowable 20
2 values for raft foundations on clays in the Niger Delta [11]. Also, specified limiting values for allowable settlement of raft foundations founded on either clay or sand formation have been presented by scholars in literatures [12, 1, 14]. This paper attempts to report on the role of shallow foundation deformation requirement in the adoption of an appropriate bearing pressure of a superstructure. MATERIALS AND METHODS Field Exploration/ Laboratory Analysis Information about the subsurface conditions at the site was studied through ground borings to depths of 24m each using a light cable percussion boring rig. Both disturbed and undisturbed soil samples were collected for visual examination, laboratory testing and classification. Also, Standard Penetration Tests (SPT) was conducted to determine the penetration resistance of cohesionless strata at specific depths within the boreholes as borings advances. Requisite laboratory tests on soil samples were conducted to obtain input parameters for bearing capacity and settlement analysis. The water table was observed to vary from about -.m below the existing ground level at the period of investigation. Bearing Capacity Analysis A bearing capacity analysis of shallow foundation placed on soil formation consisting of soft, brown, low plasticity Sandy CLAY, overlying loose to medium-dense, slightly silty SAND formation was carried out. The proposed foundations were to be placed at one metre (1m) below ground level. The net ultimate bearing capacity, (), is given by the expression[]; () = (1+0. ) (1 0.2 ) (1) Where is undrained cohesion, B is foundation breadth, L is foundation length, is unit weight of soil, is foundation depth, and are dimensionless bearing capacity factors [5]. The net allowable, q n(a), bearing capacity of the soil has been evaluated for a factor of safety (F.S) of being applied on the net ultimate bearing capacity while the submerged unit weight is used to account for the effect of water table on bearing capacity. A comprehensive discussion on the use of bearing capacity factors has been presented [15]. Settlement Analysis: Stress Analysis An induced vertical stress analysis was based on a stress distribution of 2:1, spread at either the centre of the compressible stratum [16]. The induced vertical stress was analysed from the expression; =! "#$ (%&')((&') (2) Where, )* induced vertical stress at centre of consolidating layer, + is initial stress, B, L are footing dimension, and z is depth of interest Immediate Settlement Immediate foundation settlement at a corner of a rigid raft foundation can be obtained from the expression [17] being reported in Braja [18] as follows; *, = -$. / (1 0 1 )2 () Where; S ί is immediate settlement, B is breadth of foundation at a corner, q n is net foundation pressure, E o is modulus of elasticity, µ is Poisson ratio, I p is influence factor for rigid foundation. To obtain the settlement at the centre of the foundation, the principle of superposition was adopted and settlement value is usually four times the settlement at any corner. For saturated clays, 0=0.5 and 2 =4 +. Modulus of elasticity is computed from the expression [19];. 5 6 = 400 (4) 21
3 Consolidation Settlement Consolidation settlement was carried out on the raft foundation using expression presented in the form [20]: ρ c = 8 +&8 / 9 + : ; = 8 +&8 / 9 + : -$# (%&')((&') ; (5) Where; ρ c is consolidation settlement, q n is net foundation pressure, B is foundation breadth, p is change in pressure, e is change in void ratio, e o is initial void ratio, σ z is induced vertical stress, H is height of compressible layer, z is depth to point of induced vertical stress of interest and the term, compressibility &8 / Total Settlement Total foundation settlement can then be expressed as the summation of Equation () and Equation (5); ρ < = -$. / (1 0 1 ) : -$# ; (6) +&8 / (%&')((&') : is coefficient of volume The limiting specification for mat foundations on soils forms the basis for assessment of vertical deformation on the foundation. RESULTS AND DISCUSSION Soil Classification / Stratification Classification tests revealed the plastic soils as generally consisting of soft, brown, sandy CLAY of low to intermediate plasticity, underlain by loose to medium-dense, Slightly silty SAND as illustrated in Figure 1. Mat foundation 1m.m Soft, brown, low plasticity Sandy CLAY Average c u =0kN/m 2, ϕ av = 7m Loose to medium-dense, slightly silty SAND 24m Figure 1: Mat foundation on typical soil lithology Bearing Capacity The allowable bearing capacity, q a, for raft foundations with breadths of 19.m and 29.5m, placed at different foundation depth, D f are shown in Table 1. Generally, q a, values vary from -kn/m 2 and -86kN/m 2 for raft foundation breadth of 19.m and 29.5m respectively up to m depth below ground level. The variation of allowable bearing capacity with varying foundation depths for foundation dimensions of B =19.m and B = 2.m are presented in Figures 2 and, while a typical mat foundation placed at 1m depth within the compressible soil formation is presented in Figure 1. A slight lateral variability in bearing capacity of soil is observed in the compressible soil lithology, while variability in bearing capacity values with depth at investigated points is almost 22
4 reproducible. However, for BH2, q a, reasonably increased in value from 1.7m to 2.5m depth, beyond which the q a values on BH1 and BH2 converged to kn/m 2 at m depth. Settlement Analysis: Vertical Stress The induced vertical stress within a compressible soil thickness of 7m below ground was analyzed at varying foundation depth below ground level. A 2:1 stress distribution on the mat foundations were adopted under a bearing pressure of 50kN/m 2 and kn/m 2 on foundation dimensions of B 1 = 19. m, L 1 = 25.2 m and B 2 = 2. m, L 2 = 29.5 m. Details on the variation of induced vertical stress with foundation depth are presented in Figures 4 and 5. Settlement on Mat foundation The results of immediate settlement were analyzed for net foundation pressure of 50kN/m 2 and kn/m 2 from Equation (). The modulus of elasticity was obtained from Equation (4) as 12000MPa, Values of immediate settlement, S i, for foundation breadths of 19.m and 2.m were evaluated as 6mm and 7.2mm respectively for a bearing pressure of 50kN/m 2, while immediate settlement of 9.6mm and 11.7mm were respectively obtained for a bearing pressure of kn/m 2. Allowable Bearing Capacity (kn/m 2 ) BH1 BH2 BH BH Figure 2: Variation of Allowable Bearing Capacity with Depth (B = 19. m, L= 25.2 m) 88 Allowable Bearing Capacity (kn/m 2 ) BH1 BH2 BH BH Figure : Variation of Allowable Bearing Capacity with Depth (B = 2. m, L= 29.5 m) 2
5 46 Induced vertical stress (kn/m 2 ) Δσ (B1,L1) Δσ (B2, L2) Figure 4: Induced vertical stress (2:1spread) with foundation depth for qn= 50kN/m 2 Induced vertical stress (kn/m 2 ) Δσ (B1,L1) 64 Δσ (B2, L2) Figure 5: Induced vertical stress (2:1spread) with foundation depth for q n = kn/m 2 The various response graphs of consolidation and total settlement are portrayed in Figures 6-9. Variation in consolidation settlement with increase in foundation depth showed a decreasing trend with lower values on B 1, L 1 as against B 2, L 2. Increase in foundation depth results in reduction on thickness of compressible clay thickness (H) which ultimately causes increase in induced vertical stress and subsequently a decrease in consolidation settlement. Foundations under higher bearing pressure (kn/m 2 ) generated higher values of consolidation settlement and total settlement; 94-15mm and mm respectively, with decreasing foundation depth while for a bearing pressure of 50kN/m 2, consolidation settlement and total settlement had values of 58-mm and 64-91mm respectively, with decreasing foundation depth. Details of these are presented in Tables 2. For deformation requirement, the foundations subjected to a bearing pressure of 50kN/m 2 generally gave settlement values satisfying the maximum allowable limits for mat foundations on clays, while a bearing pressure of kn/m 2 gave excessive settlement values. 24
6 Consolidation Settlement(mm) 90 B1,l1 B2,l Figure 6: Variation of consolidation settlement with foundation depth for q n = 50kN/m 2 95 Total Settlement (mm) 90 B1,l1 B2,l Figure 7: Variation of total settlement with foundation depth for q n = 50kN/m 2 Consolidation Settlement (mm) B1,l1 120 B2,l Figure 8: Variation of consolidation settlement with foundation depth for q n = kn/m 2 25
7 Total Settlement (mm) B1,l1 B2,l Figure 9: Variation of total settlement with foundation depth for q n = kn/m 2 Table 1: Bearing Capacity BH No Depth of Foundation (m) Unit Weight γ (kn/m ) Undrained Cohesion c u (kn/m 2 ) Angle of friction φ (degrees) Allowable bearing capacity qa, ( kn/m 2 ) B = 19.m B = 2.m Table 2: Settlement Analysis of Mat Foundation Foundation Depth(m) B 1=19.mm, L 1=25.2mm q n(a) = kn/m 2 Consolidation settlement ρ c (mm) Total Settlement, ρ t, (mm) B 1=19.mm, L 1=25.2mm q n(a) = 50kN/m 2 Consolidation settlement ρ c (mm) Total Settlement, ρ t, (mm) , B 2=2.mm, L 2=29.2mm q n(a) = kn/m 2 Consolidation settlement ρ c (mm) Total Settlement, ρ t, (mm) B 2=2.mm, L 2=29.2mm q n(a) = 50kN/m 2 Consolidation settlement ρ c (mm) Total Settlement, ρ t, (mm)
8 CONCLUSION The following conclusions can be drawn from the study; i. A slight lateral variability in bearing capacity of soil is noticeable in the compressible soil lithology, while variability in bearing capacity values with depth at investigated points is almost reproducible. The variation in foundation dimensions (i.e. B and L) has no significant effect on the allowable bearing capacity. ii. Induced vertical stress, σ, depicts an increasing trend with increase in foundation depth. Larger σ were associated with larger foundation dimension under the same given bearing pressure. iii. Consolidation settlement on mat foundation was found to decrease with increase in foundation depth and size. iv. Total settlement decreased with increase in foundation depth and foundation dimension. v. Evaluated bearing capacity values did not satisfy the maximum allowable settlement requirement for mat foundation on clays. vi. Mat foundations satisfied both bearing capacity and settlement requirements under a bearing pressure of 50kN/m 2, which is lower than evaluated bearing capacity for the site. Consequently, settlement consideration determined the choice of bearing capacity needed for the foundation analysis and design in Sandy CLAY formation. REFERENCES [1]Singh, A., A Modern Geotechnical Engineering, rd Edition, CBS Publishers Delhi, [2]Caquot, A., Equilibrium des Massifs a Frottement Interne, Gauthier Villars, Paris, France, 194, []Terzaghi, K., Theoretical Soil Mechanics, John Wiley and Sons Inc. New York, 194. [4]DeBeer, E. E. and Vesic, A., Etude Experimental de la Capacitie Portante du sable sous des Foundations Directesetablies en Surface Annale des Travaux Publics de Belqique, 59(), 1958, pp [5]Vesic, A. S., A study of Bearing Capacity of Deep Foundations, Final Report, Project B-119, Georgia Inst. Techn., Atlanta Georgia, [6]Akpila, S. B., Inter-World Journal of Science and Technology, (), 2007, [7] Akpila, S. B., ThankGod, O., and Igwe, A., Journal of Scientific and Industrial Studies, 6(9), 2008, -89. [8]Akpila, S. B., Inter-World Journal of Science and Technology, (4), 2007, [9]Akpila, S. B., and ThankGod, O., International Journal of Physical Sciences, (1), 2008, [10] Akpila, S. B., Scientific Journal of Pure and Applied Sciences, 2(2), 201, 72-. [11] Akpila, S.B., and Eluozu, S., International Journal of Applied Science and Technology, 2(6), 2012, -88. [12] Skempton, A.W. and MacDonald. Institute of Civil Engineers, 5(), 1956, [1] Polshin, D. E. and Tokar, R. A., Maximum Non Uniform Settlement of Structures, Proc. of the 4 th International Conference of Soil Mechanics and Foundation Engineering, London, 1, 1957, [14] Wahls, H. E., Journal of the Geotechnical Division, ASCE, 107(GT11), 19, [15] Matawal, D. S., Journal of Engineering Research, 1991, (1), 1-9. [16] Bowles, J. E., Foundation Analysis and Design, 5 th Edition, McGraw-Hill, New York, 1997, pp [17] Harr, M. E., Fundamentals of Theoretical Soil Mechanics, McGraw-Hill, New York, [18] Braja, M. D., Principle of Foundation Engineering, 4 th Edition, PWE Publishing Company, USA, 1999, p 24. [19] Butler, F. G., Review Paper: Heavily Over-Consolidated Clays, in Proceedings of the Conference on Settlement of Structures, Pentech Press, Cambridge, 19, [20]Skempton, A. W., and Bjeruum, L., Geotechnique, 7, 1957,
Bearing Capacity and Settlement Response of PMS Tanks on Cohesionless Soil Lithology in Lekki, Lagos of Nigeria
 Available online at www.scholarsresearchlibrary.com European Journal of Applied Engineering and Scientific Research,, ():- (http://scholarsresearchlibrary.com/archive.html) ISSN: 8 Bearing Capacity and
Available online at www.scholarsresearchlibrary.com European Journal of Applied Engineering and Scientific Research,, ():- (http://scholarsresearchlibrary.com/archive.html) ISSN: 8 Bearing Capacity and
CENGRS GEOTECHNICA PVT. LTD. Job No Sheet No. 1
 CENGRS GEOTECHNICA PVT. LTD. Job No. 214030 Sheet No. 1 INTERIM REPORT ON GEOTECHNICAL INVESTIGATION FOR PROPOSED 66 KV GRID PLOT AT G-7, DWARKA, NEW DELHI. 1.0 INTRODUCTION 1.1 Project Description M/s.
CENGRS GEOTECHNICA PVT. LTD. Job No. 214030 Sheet No. 1 INTERIM REPORT ON GEOTECHNICAL INVESTIGATION FOR PROPOSED 66 KV GRID PLOT AT G-7, DWARKA, NEW DELHI. 1.0 INTRODUCTION 1.1 Project Description M/s.
REPORT GEO-TECHNICAL INVESTIGATION FOR THE PROPOSED BLOCK-1 SUB-STATION SY NO-44, NEAR KYATAGANACHERLU VILLAGE
 REPORT ON GEO-TECHNICAL INVESTIGATION FOR THE PROPOSED BLOCK-1 SUB-STATION SY NO-44, NEAR KYATAGANACHERLU VILLAGE CLIENT: KARNATAKA SOLAR POWER DEVELOPMENT CORPORATION BANGALORE 0 GEO-TECHNICAL INVESTIGATION
REPORT ON GEO-TECHNICAL INVESTIGATION FOR THE PROPOSED BLOCK-1 SUB-STATION SY NO-44, NEAR KYATAGANACHERLU VILLAGE CLIENT: KARNATAKA SOLAR POWER DEVELOPMENT CORPORATION BANGALORE 0 GEO-TECHNICAL INVESTIGATION
REPORT GEO-TECHNICAL INVESTIGATION FOR THE PROPOSED BLOCK-7 SUB-STATION SY NO-225, NEAR RAYACHERLU VILLAGE
 REPORT ON GEO-TECHNICAL INVESTIGATION FOR THE PROPOSED BLOCK-7 SUB-STATION SY NO-225, NEAR RAYACHERLU VILLAGE CLIENT: KARNATAKA SOLAR POWER DEVELOPMENT CORPORATION BANGALORE 0 GEO-TECHNICAL INVESTIGATION
REPORT ON GEO-TECHNICAL INVESTIGATION FOR THE PROPOSED BLOCK-7 SUB-STATION SY NO-225, NEAR RAYACHERLU VILLAGE CLIENT: KARNATAKA SOLAR POWER DEVELOPMENT CORPORATION BANGALORE 0 GEO-TECHNICAL INVESTIGATION
UNIT-I SOIL EXPLORATION
 SIDDHARTH GROUP OF INSTITUTIONS :: PUTTUR Siddharth Nagar, Narayanavanam Road 517583 QUESTION BANK (DESCRIPTIVE) Subject with Code : Geotechnical Engineering - II (16CE127) Year & Sem: III-B.Tech & II-Sem
SIDDHARTH GROUP OF INSTITUTIONS :: PUTTUR Siddharth Nagar, Narayanavanam Road 517583 QUESTION BANK (DESCRIPTIVE) Subject with Code : Geotechnical Engineering - II (16CE127) Year & Sem: III-B.Tech & II-Sem
m v = 1.04 x 10-4 m 2 /kn, C v = 1.29 x 10-2 cm 2 /min
 2.10 Problems Example 2.1: Design of Shallow Foundation in Saturated Clay Design a square footing to support a column load of 667 kn. The base of the footing will be located 1 m below the ground level
2.10 Problems Example 2.1: Design of Shallow Foundation in Saturated Clay Design a square footing to support a column load of 667 kn. The base of the footing will be located 1 m below the ground level
SOIL IMPROVEMENT BY VACUUM PRELOADING FOR A POWER PLANT PROJECT IN VIETNAM
 18 th Southeast Asian Geotechnical & Inaugural AGSSEA Conference 29-31 May 213, Singapore Leung, Goh & Shen (eds) SOIL IMPROVEMENT BY VACUUM PRELOADING FOR A POWER PLANT PROJECT IN VIETNAM GOUW TJIE-LIONG
18 th Southeast Asian Geotechnical & Inaugural AGSSEA Conference 29-31 May 213, Singapore Leung, Goh & Shen (eds) SOIL IMPROVEMENT BY VACUUM PRELOADING FOR A POWER PLANT PROJECT IN VIETNAM GOUW TJIE-LIONG
THE EFFECT OF EMBEDMENT DEPTH ON BEARING CAPACITY OF STRIP FOOTING IN COHESIVE FRICTIONAL MEDIUM
 Proceedings of the 4 th International Conference on Civil Engineering for Sustainable Development (ICCESD 2018), 9~11 February 2018, KUET, Khulna, Bangladesh (ISBN-978-984-34-3502-6) THE EFFECT OF EMBEDMENT
Proceedings of the 4 th International Conference on Civil Engineering for Sustainable Development (ICCESD 2018), 9~11 February 2018, KUET, Khulna, Bangladesh (ISBN-978-984-34-3502-6) THE EFFECT OF EMBEDMENT
Vertical Uplift Capacity of a Group of Equally Spaced Helical Screw Anchors in Sand
 SECM/15/080 Vertical Uplift Capacity of a Group of Equally Spaced Helical Screw Anchors in Sand S. Mukherjee 1* and Dr. S. Mittal 2 1 Amity University, Noida, India 2 Indian Institute of Technology, Roorkee,
SECM/15/080 Vertical Uplift Capacity of a Group of Equally Spaced Helical Screw Anchors in Sand S. Mukherjee 1* and Dr. S. Mittal 2 1 Amity University, Noida, India 2 Indian Institute of Technology, Roorkee,
Prof. B V S Viswanadham, Department of Civil Engineering, IIT Bombay
 43 Module 3: Lecture - 5 on Compressibility and Consolidation Contents Stresses in soil from surface loads; Terzaghi s 1-D consolidation theory; Application in different boundary conditions; Ramp loading;
43 Module 3: Lecture - 5 on Compressibility and Consolidation Contents Stresses in soil from surface loads; Terzaghi s 1-D consolidation theory; Application in different boundary conditions; Ramp loading;
Desaturating sand deposit by air injection for reducing liquefaction potential
 Desaturating sand deposit by air injection for reducing liquefaction potential M. Ishihara, M. Okamura & T. Oshita Public Works Research Institute, Tsukuba City, Japan. ABSTRACT: It has been known that
Desaturating sand deposit by air injection for reducing liquefaction potential M. Ishihara, M. Okamura & T. Oshita Public Works Research Institute, Tsukuba City, Japan. ABSTRACT: It has been known that
INSTITUTE OF AERONAUTICAL ENGINEERING (Autonomous) Dundigal, Hyderabad CIVIL ENGINEERING TUTORIAL QUESTION BANK
 INSTITUTE OF AERONAUTICAL ENGINEERING (Autonomous) Dundigal, Hyderabad - 00 04 CIVIL ENGINEERING TUTORIAL QUESTION BANK Course Name Course Code Regulation Course Structure Course Coordinator Course Faculty
INSTITUTE OF AERONAUTICAL ENGINEERING (Autonomous) Dundigal, Hyderabad - 00 04 CIVIL ENGINEERING TUTORIAL QUESTION BANK Course Name Course Code Regulation Course Structure Course Coordinator Course Faculty
Theory of a vertically loaded Suction Pile in CLAY
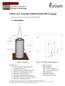 11 Theory of a vertically loaded Suction Pile in CLAY Mainly based on the et Norske Veritas NV-RP-E303 1. Convention Water COG h L Soil COG t Figure 1 Suction Pile Figure 2 Suction pile with main parameters
11 Theory of a vertically loaded Suction Pile in CLAY Mainly based on the et Norske Veritas NV-RP-E303 1. Convention Water COG h L Soil COG t Figure 1 Suction Pile Figure 2 Suction pile with main parameters
Typical factors of safety for bearing capacity calculation in different situations
 Typical factors of safety for bearing capacity calculation in different situations Density of soil: In geotechnical engineering, one deals with several densities such as dry density, bulk density, saturated
Typical factors of safety for bearing capacity calculation in different situations Density of soil: In geotechnical engineering, one deals with several densities such as dry density, bulk density, saturated
INSTITUTE OF AERONAUTICAL ENGINEERING (Autonomous) Dundigal, Hyderabad
 INSTITUTE OF AERONAUTICAL ENGINEERING (Autonomous) Dundigal, Hyderabad - 500 043 CIVIL ENGINEERING Tutorial Question Bank Name : FOUNDATION ENGINEERING Code : A60126 Class : III B. Tech II Semester Branch
INSTITUTE OF AERONAUTICAL ENGINEERING (Autonomous) Dundigal, Hyderabad - 500 043 CIVIL ENGINEERING Tutorial Question Bank Name : FOUNDATION ENGINEERING Code : A60126 Class : III B. Tech II Semester Branch
EXPERIMENTAL INVESTIGATION ON OPTIMUM INSTALLATION DEPTH OF PVD UNDER VACUUM CONSOLIDATION ABSTRACT
 EXPERIMENTAL INVESTIGATION ON OPTIMUM INSTALLATION DEPTH OF PVD UNDER VACUUM CONSOLIDATION EXPERIMENTAL INVESTIGATION ON OPTIMUM INSTALLATION DEPTH OF PVD UNDER VACUUM CONSOLIDATION J.-C CHAI i), N. MIURA
EXPERIMENTAL INVESTIGATION ON OPTIMUM INSTALLATION DEPTH OF PVD UNDER VACUUM CONSOLIDATION EXPERIMENTAL INVESTIGATION ON OPTIMUM INSTALLATION DEPTH OF PVD UNDER VACUUM CONSOLIDATION J.-C CHAI i), N. MIURA
Department of Civil & Geological Engineering GEOE Engineering Geology
 Department of Civil & Geological Engineering GEOE 218.3 Engineering Geology Assignment #3, Head, Pore Pressure & Effective Stress Due 08 Oct, 2010 NOTE: Numbered subscripts indicate depth, in metres, below
Department of Civil & Geological Engineering GEOE 218.3 Engineering Geology Assignment #3, Head, Pore Pressure & Effective Stress Due 08 Oct, 2010 NOTE: Numbered subscripts indicate depth, in metres, below
Pressuremeters in Geotechnical Design
 Pressuremeters in Geotechnical Design B.G. CLARKE Department of Civil Engineering University of Newcastle upon Tyne BLACK1E ACADEMIC & PROFESSIONAL An Imprint of Chapman & Hall London Glasgow Weinheim
Pressuremeters in Geotechnical Design B.G. CLARKE Department of Civil Engineering University of Newcastle upon Tyne BLACK1E ACADEMIC & PROFESSIONAL An Imprint of Chapman & Hall London Glasgow Weinheim
Cubzac-les-Ponts Experimental Embankments on Soft Clay
 Cubzac-les-Ponts Experimental Embankments on Soft Clay GEO-SLOPE International Ltd. www.geo-slope.com 1, 7 - th Ave SW, Calgary, AB, Canada TP T Main: +1 3 9 Fax: +1 3 39 Introduction In the 197 s, a series
Cubzac-les-Ponts Experimental Embankments on Soft Clay GEO-SLOPE International Ltd. www.geo-slope.com 1, 7 - th Ave SW, Calgary, AB, Canada TP T Main: +1 3 9 Fax: +1 3 39 Introduction In the 197 s, a series
Analysis of dilatometer test in calibration chamber
 Analysis of dilatometer test in calibration chamber Lech Bałachowski Gdańsk University of Technology, Poland Keywords: calibration chamber, DMT, quartz sand, FEM ABSTRACT: Because DMT in calibration test
Analysis of dilatometer test in calibration chamber Lech Bałachowski Gdańsk University of Technology, Poland Keywords: calibration chamber, DMT, quartz sand, FEM ABSTRACT: Because DMT in calibration test
computed using Equation 3-18 by setting the 2nd term equal to 0 and K A equal to K o and using the pressure distribution as shown in Figure 3-23.
 computed using Equation 3-18 by setting the 2nd term equal to 0 and K A equal to K o and using the pressure distribution as shown in Figure 3-23. (2) For the resisting side, passive pressure theory indicates
computed using Equation 3-18 by setting the 2nd term equal to 0 and K A equal to K o and using the pressure distribution as shown in Figure 3-23. (2) For the resisting side, passive pressure theory indicates
A REPORT ON SUB SOIL INVESTIGATION WORK NEW HAJ TOWER COMPLEX HOOGHLY RIVER BRIDGE COMMISSIONERS
 A REPORT ON SUB SOIL INVESTIGATION WORK PROJECT : NEW HAJ TOWER COMPLEX LOCATION : REVISED CHANGED SITE ON PLOT NO. IIA/26, OF RAJARHAT NEW TOWN, KOLKATA Project Implementation Authority : HOOGHLY RIVER
A REPORT ON SUB SOIL INVESTIGATION WORK PROJECT : NEW HAJ TOWER COMPLEX LOCATION : REVISED CHANGED SITE ON PLOT NO. IIA/26, OF RAJARHAT NEW TOWN, KOLKATA Project Implementation Authority : HOOGHLY RIVER
CONE PENETRATION TESTS
 February 25, 2015 John Doe, P.E. Acme Engineering and Testing 1234 Test Avenue, Suite 204 Lake Wales, FL 33853 Re: Sample CPT Soundings Dear Mr. Doe, Direct Push Services, LLC (DPS) was retained by Acme
February 25, 2015 John Doe, P.E. Acme Engineering and Testing 1234 Test Avenue, Suite 204 Lake Wales, FL 33853 Re: Sample CPT Soundings Dear Mr. Doe, Direct Push Services, LLC (DPS) was retained by Acme
1 CHAPTER 1. Standard Penetration Test: Corrections and Correlations. 1.1 General. 1.2 Standard Penetration Test (SPT)
 Page1 1 CHAPTER 1 Standard Penetration Test: Corrections and Correlations 1.1 General This chapter mainly focuses on the Standard Penetration Test, its correction and correlations with different soil properties.
Page1 1 CHAPTER 1 Standard Penetration Test: Corrections and Correlations 1.1 General This chapter mainly focuses on the Standard Penetration Test, its correction and correlations with different soil properties.
CHAPTER 5: VACUUM TEST WITH VERTICAL DRAINS
 CHAPTER 5: VACUUM TEST WITH VERTICAL DRAINS 5.1 Introduction Using surcharging as the sole soil consolidation mean can take a long time to reach the desired soil settlement. Soil consolidation using prefabricated
CHAPTER 5: VACUUM TEST WITH VERTICAL DRAINS 5.1 Introduction Using surcharging as the sole soil consolidation mean can take a long time to reach the desired soil settlement. Soil consolidation using prefabricated
An Introduction to Deep Foundations
 An Introduction to Deep Foundations J. Paul Guyer, P.E., R.A. Paul Guyer is a registered mechanical engineer, civil engineer, fire protection engineer and architect with over 35 years experience in the
An Introduction to Deep Foundations J. Paul Guyer, P.E., R.A. Paul Guyer is a registered mechanical engineer, civil engineer, fire protection engineer and architect with over 35 years experience in the
Critical face pressure and backfill pressure in shield TBM tunneling on soft ground
 Critical face pressure and backfill pressure in shield TBM tunneling on soft ground Kiseok Kim 1), Juyoung Oh 2), Hyobum Lee 3) and Hangseok Choi 4) 1), 3), 4) Department of civil engineering, Korea University,
Critical face pressure and backfill pressure in shield TBM tunneling on soft ground Kiseok Kim 1), Juyoung Oh 2), Hyobum Lee 3) and Hangseok Choi 4) 1), 3), 4) Department of civil engineering, Korea University,
Tutorial 2 Time-Dependent Consolidation. Staging Groundwater Time-dependent consolidation Point query Line query Graph Query
 Tutorial 2 Time-Dependent Consolidation Staging Groundwater Time-dependent consolidation Point query Line query Graph Query Model Set-up For this tutorial we will start with the model from Tutorial 1 Quick
Tutorial 2 Time-Dependent Consolidation Staging Groundwater Time-dependent consolidation Point query Line query Graph Query Model Set-up For this tutorial we will start with the model from Tutorial 1 Quick
APPENDIX G SCA BASIN CALCULATIONS
 ONONDAGA LAKE SEDIMENT MANAGEMENT FINAL DESIGN APPENDIX G SCA BASIN CALCULATIONS p:\honeywell -syr\444853 - lake detail design\09 reports\9.22 sediment management final design\110930 submittal\110906 onon
ONONDAGA LAKE SEDIMENT MANAGEMENT FINAL DESIGN APPENDIX G SCA BASIN CALCULATIONS p:\honeywell -syr\444853 - lake detail design\09 reports\9.22 sediment management final design\110930 submittal\110906 onon
FINAL REPORT ON: GEOTECHNICAL INVESTIGATION FOR ENVIRONMENTAL REGULATORY TRAINING INSTITUTE AT NIMLI VILLAGE, TIJARA ALWAR, RAJASTHAN.
 FINAL REPORT ON: GEOTECHNICAL INVESTIGATION FOR ENVIRONMENTAL REGULATORY TRAINING INSTITUTE AT NIMLI VILLAGE, TIJARA ALWAR, RAJASTHAN Submitted to: M/s. Nilayam Housing Pvt. Ltd. 4, Windmill Place Aya
FINAL REPORT ON: GEOTECHNICAL INVESTIGATION FOR ENVIRONMENTAL REGULATORY TRAINING INSTITUTE AT NIMLI VILLAGE, TIJARA ALWAR, RAJASTHAN Submitted to: M/s. Nilayam Housing Pvt. Ltd. 4, Windmill Place Aya
Sample Project with EPB TBM according to DIN 4085
 1 General The aim of the document is to provide information about the required input parameters and the necessary steps for the calculation of a face support pressure. This calculation is carried out under
1 General The aim of the document is to provide information about the required input parameters and the necessary steps for the calculation of a face support pressure. This calculation is carried out under
Ground control for slurry TBM tunnelling GEO Report 249
 Cutter head Slurry feed line Excavation chamber Submerged wall Plenum air cushion Pressure bulkhead Opening at base of submerged wall Slurry suction line Nick Shirlaw Ground control for slurry TBM tunnelling
Cutter head Slurry feed line Excavation chamber Submerged wall Plenum air cushion Pressure bulkhead Opening at base of submerged wall Slurry suction line Nick Shirlaw Ground control for slurry TBM tunnelling
SUMMARY OF SUBSURFACE STRATIGRAPHY AND MATERIAL PROPERTIES
 Page 1 of 101 Written by: Ming Zhu Date: 08/20/2008 Reviewed by: R. Kulasingam/J. Beech Date: 08/20/2008 SUMMARY OF SUBSURFACE STRATIGRAPHY AND MATERIAL PROPERTIES 1. INTRODUCTION This Summary of Subsurface
Page 1 of 101 Written by: Ming Zhu Date: 08/20/2008 Reviewed by: R. Kulasingam/J. Beech Date: 08/20/2008 SUMMARY OF SUBSURFACE STRATIGRAPHY AND MATERIAL PROPERTIES 1. INTRODUCTION This Summary of Subsurface
Behavior of Square Footing Resting on Reinforced Sand Subjected to Static Load
 IJIRST International Journal for Innovative Research in Science & Technology Volume 3 Issue 02 July 2016 ISSN (online): 2349-6010 Behavior of Square Footing Resting on Reinforced Sand Subjected to Static
IJIRST International Journal for Innovative Research in Science & Technology Volume 3 Issue 02 July 2016 ISSN (online): 2349-6010 Behavior of Square Footing Resting on Reinforced Sand Subjected to Static
Stability of slopes of municipal solid waste landfills with co-disposal of biosolids
 Geo-Environment and Landscape Evolution II 215 Stability of slopes of municipal solid waste landfills with co-disposal of biosolids M. Chopra, D. Reinhart, M. Vajirkar & B. Koodhathinkal University of
Geo-Environment and Landscape Evolution II 215 Stability of slopes of municipal solid waste landfills with co-disposal of biosolids M. Chopra, D. Reinhart, M. Vajirkar & B. Koodhathinkal University of
For a cantilever pile wall shown in Figure 1, assess the performance of the system and answer the following questions.
 Question 1 For a cantilever pile wall shown in Figure 1, assess the performance of the system and answer the following questions. Figure 1 - Cantilever Pile Wall i. Estimate the net resulting horizontal
Question 1 For a cantilever pile wall shown in Figure 1, assess the performance of the system and answer the following questions. Figure 1 - Cantilever Pile Wall i. Estimate the net resulting horizontal
Ground Failure Mechanism of Micoropiled-raft
 Ground Failure Mechanism of Micoropiled-raft T. H. Hwang 1), H. J. Kim 2), and * J.H. Shin 3) 1), 2), 3) Department of Civil Engineering, Konkuk University, Seoul 143-701, Korea 3) jhshin@konkuk.ac.kr
Ground Failure Mechanism of Micoropiled-raft T. H. Hwang 1), H. J. Kim 2), and * J.H. Shin 3) 1), 2), 3) Department of Civil Engineering, Konkuk University, Seoul 143-701, Korea 3) jhshin@konkuk.ac.kr
E.2 CAP SETTLEMENT RA D AND OUTBOARD
 DRAFT ONONDAGA LAKE CAPPING, DREDGING AND HABITAT INTERMEDIATE DESIGN E.2 CAP SETTLEMENT RA D AND OUTBOARD Parsons P;\Honeywell-SYR\444576 2008 Capping\09 Reports\9.1 Capping and Dredge Area & Depth IDS\Appendices\Appendix
DRAFT ONONDAGA LAKE CAPPING, DREDGING AND HABITAT INTERMEDIATE DESIGN E.2 CAP SETTLEMENT RA D AND OUTBOARD Parsons P;\Honeywell-SYR\444576 2008 Capping\09 Reports\9.1 Capping and Dredge Area & Depth IDS\Appendices\Appendix
BURIED PIPE RESPONSE SUBJECTED TO TRAFFIC LOAD EXPERIMENTAL AND NUMERICAL INVESTIGATIONS
 Geotec., Const. Mat. & Env., ISSN:2186-2990, Japan, DOI: https://doi.org/10.21660/2017.39.91957 BURIED PIPE RESPONSE SUBJECTED TO TRAFFIC LOAD EXPERIMENTAL AND NUMERICAL INVESTIGATIONS *Ahdyeh Mosadegh
Geotec., Const. Mat. & Env., ISSN:2186-2990, Japan, DOI: https://doi.org/10.21660/2017.39.91957 BURIED PIPE RESPONSE SUBJECTED TO TRAFFIC LOAD EXPERIMENTAL AND NUMERICAL INVESTIGATIONS *Ahdyeh Mosadegh
This file is part of the following reference: Access to this file is available from:
 ResearchOnline@JCU This file is part of the following reference: Shahriar, Mohammad Abu Naser (2014) Settlement of shallow foundations due to rise of water table in granular soils. PhD thesis, James Cook
ResearchOnline@JCU This file is part of the following reference: Shahriar, Mohammad Abu Naser (2014) Settlement of shallow foundations due to rise of water table in granular soils. PhD thesis, James Cook
Investigation of Stresses in Ring Stiffened Circular Cylinder
 International Journal of Engineering and Technical Research (IJETR) ISSN: 2321-869, Volume-2, Issue-9, September 214 Investigation of Stresses in Ring Stiffened Circular Cylinder Neetesh N. Thakre, Dr.
International Journal of Engineering and Technical Research (IJETR) ISSN: 2321-869, Volume-2, Issue-9, September 214 Investigation of Stresses in Ring Stiffened Circular Cylinder Neetesh N. Thakre, Dr.
Analysis of Shear Lag in Steel Angle Connectors
 University of New Hampshire University of New Hampshire Scholars' Repository Honors Theses and Capstones Student Scholarship Spring 2013 Analysis of Shear Lag in Steel Angle Connectors Benjamin Sawyer
University of New Hampshire University of New Hampshire Scholars' Repository Honors Theses and Capstones Student Scholarship Spring 2013 Analysis of Shear Lag in Steel Angle Connectors Benjamin Sawyer
Module 7 Lecture 1. Swelling and Collapse Behavior
 Swelling and Collapse Behavior Module 7 Lecture 1 Collapse and swelling phenomena occur in unsaturated soils during the saturation process. The compacted unsaturated soils, on the dry of optimum, have
Swelling and Collapse Behavior Module 7 Lecture 1 Collapse and swelling phenomena occur in unsaturated soils during the saturation process. The compacted unsaturated soils, on the dry of optimum, have
Shallow foundations settlement
 References: 1. Rajapakse, Ruwan. Geotechnical Engineering Calculations and Rules of Thumb. 2. Schroeder, W.L., Dickenson, S.E, Warrington, Don, C. Soils in Construction. Fifth Edition. Upper Saddle River,
References: 1. Rajapakse, Ruwan. Geotechnical Engineering Calculations and Rules of Thumb. 2. Schroeder, W.L., Dickenson, S.E, Warrington, Don, C. Soils in Construction. Fifth Edition. Upper Saddle River,
Reinforced Soil Retaining Walls-Design and Construction
 Lecture 32 Reinforced Soil Retaining Walls-Design and Construction Prof. G L Sivakumar Babu Department of Civil Engineering Indian Institute of Science Bangalore 560012 Example calculation An 8 m high
Lecture 32 Reinforced Soil Retaining Walls-Design and Construction Prof. G L Sivakumar Babu Department of Civil Engineering Indian Institute of Science Bangalore 560012 Example calculation An 8 m high
OTC Copyright 2008, Offshore Technology Conference
 OTC 19545 Comparison of Jackup Rig Spudcan Penetration Methods in Clay David Menzies, Fugro-McClelland Marine Geosciences, Inc., and Richard Roper, ENSCO International, Inc. Copyright 2008, Offshore Technology
OTC 19545 Comparison of Jackup Rig Spudcan Penetration Methods in Clay David Menzies, Fugro-McClelland Marine Geosciences, Inc., and Richard Roper, ENSCO International, Inc. Copyright 2008, Offshore Technology
Strength Reduction Stability
 1 Introduction Reduction Stability Stability by strength reduction is a procedure where the factor of safety is obtained by weakening the soil in steps in an elastic-plastic finite element analysis until
1 Introduction Reduction Stability Stability by strength reduction is a procedure where the factor of safety is obtained by weakening the soil in steps in an elastic-plastic finite element analysis until
An experimental study of inflatable offshore anchors in soft clay
 An experimental study of inflatable offshore anchors in soft clay T.A. Newson and F.W. Smith Department of Civil Engineering, University of Dundee P. Brunning Stolt Offshore MS Ltd., Aberdeen Introduction
An experimental study of inflatable offshore anchors in soft clay T.A. Newson and F.W. Smith Department of Civil Engineering, University of Dundee P. Brunning Stolt Offshore MS Ltd., Aberdeen Introduction
Submerged Slope with Excess Pore- Water Pressure
 Submerged Slope with Excess Pore- Water Pressure GEO-SLOPE International Ltd. www.geo-slope.com 1400, 633-6th Ave SW, Calgary, AB, Canada T2P 2Y Main: +1 403 269 02 Fax: +1 403 266 481 Introduction Analyzing
Submerged Slope with Excess Pore- Water Pressure GEO-SLOPE International Ltd. www.geo-slope.com 1400, 633-6th Ave SW, Calgary, AB, Canada T2P 2Y Main: +1 403 269 02 Fax: +1 403 266 481 Introduction Analyzing
A STUDY ON LIQUEFIED GROUND DISRUPTION EFFECTS ON LIQUID STORAGE TANK BEHAVIOR
 143 A STUDY ON LIQUEFIED GROUND DISRUPTION EFFECTS ON LIQUID STORAGE EHAVIOR Mutsuhiro YOSHIZAWA 1, Sadatomo ONIMARU 2, Akihiko UCHIDA 3 And Munenori HATANAKA 4 SUMMARY Three liquid storage tanks located
143 A STUDY ON LIQUEFIED GROUND DISRUPTION EFFECTS ON LIQUID STORAGE EHAVIOR Mutsuhiro YOSHIZAWA 1, Sadatomo ONIMARU 2, Akihiko UCHIDA 3 And Munenori HATANAKA 4 SUMMARY Three liquid storage tanks located
An integrated three-dimensional model of wave-induced pore pressure and effective stresses in a porous seabed: II. Breaking waves
 An integrated three-dimensional model of wave-induced pore pressure and effective stresses in a porous seabed: II. Breaking waves Author Jeng, D., Zhang, Hong Published 2005 Journal Title Ocean Engineering
An integrated three-dimensional model of wave-induced pore pressure and effective stresses in a porous seabed: II. Breaking waves Author Jeng, D., Zhang, Hong Published 2005 Journal Title Ocean Engineering
3. Types of foundation
 Foundation Engineering CE 48. Types of foundation & foundation materials Contents Introduction Shallow Foundations Deep Foundations Introduction Why different types of? General types of Introduction Why
Foundation Engineering CE 48. Types of foundation & foundation materials Contents Introduction Shallow Foundations Deep Foundations Introduction Why different types of? General types of Introduction Why
Critical Gust Pressures on Tall Building Frames-Review of Codal Provisions
 Dr. B.Dean Kumar Dept. of Civil Engineering JNTUH College of Engineering Hyderabad, INDIA bdeankumar@gmail.com Dr. B.L.P Swami Dept. of Civil Engineering Vasavi College of Engineering Hyderabad, INDIA
Dr. B.Dean Kumar Dept. of Civil Engineering JNTUH College of Engineering Hyderabad, INDIA bdeankumar@gmail.com Dr. B.L.P Swami Dept. of Civil Engineering Vasavi College of Engineering Hyderabad, INDIA
THE STABILITY OF THE PIPELINE LAID ON A PORO-ELASTIC SEABED
 www.arpapress.com/volumes/vol17issue1/ijrras_17_1_04.pdf THE STABILITY OF THE PIPELINE LAID ON A PORO-ELASTIC SEABED Ren Yanrong Science School, Beijing Institute of Civil Engineering and Architecture,
www.arpapress.com/volumes/vol17issue1/ijrras_17_1_04.pdf THE STABILITY OF THE PIPELINE LAID ON A PORO-ELASTIC SEABED Ren Yanrong Science School, Beijing Institute of Civil Engineering and Architecture,
An Innovative Solution for Water Bottling Using PET
 An Innovative Solution for Water Bottling Using PET A. Castellano, P. Foti, A. Fraddosio, S. Marzano, M.D. Piccioni, D. Scardigno* DICAR Politecnico di Bari, Italy *Via Orabona 4, 70125 Bari, Italy, scardigno@imedado.poliba.it
An Innovative Solution for Water Bottling Using PET A. Castellano, P. Foti, A. Fraddosio, S. Marzano, M.D. Piccioni, D. Scardigno* DICAR Politecnico di Bari, Italy *Via Orabona 4, 70125 Bari, Italy, scardigno@imedado.poliba.it
Influence of Fly Ash Content on Compaction Characteristics of Fly Ash Clay Mixture
 Jordan Journal of Civil Engineering, Volume, No. 1, 16 Influence of Fly Ash Content on Compaction Characteristics of Fly Ash Clay Mixture Ashis Kumar Bera 1)* and Sayan Kundu 2) 1) Associate Professor
Jordan Journal of Civil Engineering, Volume, No. 1, 16 Influence of Fly Ash Content on Compaction Characteristics of Fly Ash Clay Mixture Ashis Kumar Bera 1)* and Sayan Kundu 2) 1) Associate Professor
Behavior of Dry Dense Sand-Foundation System Acted upon by Impact Loads
 Journal of Civil Engineering Research 6, 6(4): 86-3 DOI:.593/j.jce.664. ehavior of Dry Dense Sand-Foundation System Acted upon by Impact Loads Adnan F. Ali, Mohammed Y. Fattah,*, alqees A. Ahmed Civil
Journal of Civil Engineering Research 6, 6(4): 86-3 DOI:.593/j.jce.664. ehavior of Dry Dense Sand-Foundation System Acted upon by Impact Loads Adnan F. Ali, Mohammed Y. Fattah,*, alqees A. Ahmed Civil
Saturated-Unsaturated Consolidation
 Introduction Saturated-Unsaturated Consolidation This example looks at the volume change behavior of a saturated-unsaturated column under loading, wetting and drying conditions. Feature Highlights GeoStudio
Introduction Saturated-Unsaturated Consolidation This example looks at the volume change behavior of a saturated-unsaturated column under loading, wetting and drying conditions. Feature Highlights GeoStudio
Numerical and Experimental Investigation of the Possibility of Forming the Wake Flow of Large Ships by Using the Vortex Generators
 Second International Symposium on Marine Propulsors smp 11, Hamburg, Germany, June 2011 Numerical and Experimental Investigation of the Possibility of Forming the Wake Flow of Large Ships by Using the
Second International Symposium on Marine Propulsors smp 11, Hamburg, Germany, June 2011 Numerical and Experimental Investigation of the Possibility of Forming the Wake Flow of Large Ships by Using the
CHAPTER 3 PROJECT DESCRIPTION AND SITE CONDITION
 19 CHAPTER 3 PROJECT DESCRIPTION AND SITE CONDITION 3.1 OVERVIEW This chapter describes Route 44 relocation project. General project information is provided along with details related to the subsurface
19 CHAPTER 3 PROJECT DESCRIPTION AND SITE CONDITION 3.1 OVERVIEW This chapter describes Route 44 relocation project. General project information is provided along with details related to the subsurface
The tensile capacity of suction caissons in sand under rapid loading
 Frontiers in Offshore Geotechnics: ISFOG 25 Gourvenec & Cassidy (eds) 25 Taylor & Francis Group, London, ISBN 415 3963 X The tensile capacity of suction caissons in sand under rapid loading Guy T. Houlsby,
Frontiers in Offshore Geotechnics: ISFOG 25 Gourvenec & Cassidy (eds) 25 Taylor & Francis Group, London, ISBN 415 3963 X The tensile capacity of suction caissons in sand under rapid loading Guy T. Houlsby,
ESTIMATION OF LATERAL SPREAD OF A CAISSON TYPE QUAY CAUSED BY BACK FILL LIQUEFACTION
 ESTIMATION OF LATERAL SPREAD OF A CAISSON TYPE QUAY CAUSED BY BACK FILL LIQUEFACTION Kunio MIZUMOTO 1, Tetsuya TSURUMI 2, Hidekatsu NAKAJIMA 3 And Susumu OKADA 4 SUMMARY It is said on the lateral spread
ESTIMATION OF LATERAL SPREAD OF A CAISSON TYPE QUAY CAUSED BY BACK FILL LIQUEFACTION Kunio MIZUMOTO 1, Tetsuya TSURUMI 2, Hidekatsu NAKAJIMA 3 And Susumu OKADA 4 SUMMARY It is said on the lateral spread
using Strength Ratios
 Shear Strength of Liquefied Soil using Strength Ratios Prof. Scott M. Olson, PhD, PE 86 th Annual Meeting Transportation Research Board January 22, 2007 Liquefaction Problems Photos from eeri.org Undrained
Shear Strength of Liquefied Soil using Strength Ratios Prof. Scott M. Olson, PhD, PE 86 th Annual Meeting Transportation Research Board January 22, 2007 Liquefaction Problems Photos from eeri.org Undrained
TYPES OF FOUNDATION. Superstructure. Substructure. Foundation
 TYPES OF FOUNDATION Introduction: The lowest artificially built part of a structure which transmits the load of the structure to the soil lying underneath is called foundation. The supporting part of a
TYPES OF FOUNDATION Introduction: The lowest artificially built part of a structure which transmits the load of the structure to the soil lying underneath is called foundation. The supporting part of a
Tension Cracks. Topics Covered. Tension crack boundaries Tension crack depth Query slice data Thrust line Sensitivity analysis.
 Tension Cracks 16-1 Tension Cracks In slope stability analyses with cohesive soils, tension forces may be observed in the upper part of the slope. In general, soils cannot support tension so the results
Tension Cracks 16-1 Tension Cracks In slope stability analyses with cohesive soils, tension forces may be observed in the upper part of the slope. In general, soils cannot support tension so the results
STUDY ON UPWARD MOVEMENT OF FINES FROM SANDY SEABED UNDER CYCLIC WATER PRESSURE CHANGE DUE TO WAVES
 C- Fourth International Conference on Scour and Erosion STUDY ON UPWARD MOVEMENT OF FINES FROM SANDY SEABED UNDER CYCLIC WATER PRESSURE CHANGE DUE TO WAVES Takashi TSUCHIDA, Akihiro MATSUI and Ryoichi
C- Fourth International Conference on Scour and Erosion STUDY ON UPWARD MOVEMENT OF FINES FROM SANDY SEABED UNDER CYCLIC WATER PRESSURE CHANGE DUE TO WAVES Takashi TSUCHIDA, Akihiro MATSUI and Ryoichi
Effect of Fluid Density and Temperature on Discharge Coefficient of Ogee Spillways Using Physical Models
 RESEARCH ARTICLE Effect of Fluid Density and Temperature on Discharge Coefficient of Ogee Spillways Using Physical Models M. SREENIVASULU REDDY 1 DR Y. RAMALINGA REDDY 2 Assistant Professor, School of
RESEARCH ARTICLE Effect of Fluid Density and Temperature on Discharge Coefficient of Ogee Spillways Using Physical Models M. SREENIVASULU REDDY 1 DR Y. RAMALINGA REDDY 2 Assistant Professor, School of
Critical Pool Level and Stability of Slopes in Granular Soils
 TECHNICAL NOTES Critical Pool Level and Stability of Slopes in Granular Soils Radoslaw L. Michalowski, F.ASCE 1 Abstract: The influence of pore-water pressure and the pool water pressure on stability of
TECHNICAL NOTES Critical Pool Level and Stability of Slopes in Granular Soils Radoslaw L. Michalowski, F.ASCE 1 Abstract: The influence of pore-water pressure and the pool water pressure on stability of
I. CHEM. E. SYMPOSIUM SERIES NO. 85
 FIRE SURVIVAL OF PROCESS VESSELS CONTAINING GAS J. Nylund * The present work is a theoretical evaluation of the ability of process vessels to survive hydrocarbon fires when the vessels are designed and
FIRE SURVIVAL OF PROCESS VESSELS CONTAINING GAS J. Nylund * The present work is a theoretical evaluation of the ability of process vessels to survive hydrocarbon fires when the vessels are designed and
Evaluating the Design Safety of Highway Structural Supports
 Evaluating the Design Safety of Highway Structural Supports by Fouad H. Fouad and Elizabeth A. Calvert Department of Civil and Environmental Engineering The University of Alabama at Birmingham Birmingham,
Evaluating the Design Safety of Highway Structural Supports by Fouad H. Fouad and Elizabeth A. Calvert Department of Civil and Environmental Engineering The University of Alabama at Birmingham Birmingham,
Mat-Supported Jack-Up Foundation On Soft Clay Overturning Storm Stability
 Mat-Supported Jack-Up Foundation On Soft Clay Overturning Storm Stability W.P. Stewart, with support from various companies and consultants. Stewart Technology Associates Abstract The Maleo Producer is
Mat-Supported Jack-Up Foundation On Soft Clay Overturning Storm Stability W.P. Stewart, with support from various companies and consultants. Stewart Technology Associates Abstract The Maleo Producer is
TACKLING JACK-UP RIG NO-GO LOCATIONS. Prakasha Kuppalli ABSTRACT
 TACKLING JACK-UP RIG NO-GO LOCATIONS Prakasha Kuppalli ABSTRACT Jack-up rigs are deployed for drilling and work-over (maintenance) of offshore oil and gas wells for producing hydrocarbons. Rigs drill through
TACKLING JACK-UP RIG NO-GO LOCATIONS Prakasha Kuppalli ABSTRACT Jack-up rigs are deployed for drilling and work-over (maintenance) of offshore oil and gas wells for producing hydrocarbons. Rigs drill through
Construction Dewatering
 Construction Dewatering Introduction The control of groundwater is one of the most common and complicated problems encountered on a construction site. Construction dewatering can become a costly issue
Construction Dewatering Introduction The control of groundwater is one of the most common and complicated problems encountered on a construction site. Construction dewatering can become a costly issue
Pore-Air Entrapment during Infiltration
 Pore-Air Entrapment during Infiltration GEO-SLOPE International Ltd. www.geo-slope.com 1200, 700-6th Ave SW, Calgary, AB, Canada T2P 0T8 Main: +1 403 269 2002 Fax: +1 888 463 2239 Introduction Infiltration
Pore-Air Entrapment during Infiltration GEO-SLOPE International Ltd. www.geo-slope.com 1200, 700-6th Ave SW, Calgary, AB, Canada T2P 0T8 Main: +1 403 269 2002 Fax: +1 888 463 2239 Introduction Infiltration
Experimental Determination of Temperature and Pressure Profile of Oil Film of Elliptical Journal Bearing
 International Journal of Advanced Mechanical Engineering. ISSN 2250-3234 Volume 4, Number 5 (2014), pp. 469-474 Research India Publications http://www.ripublication.com Experimental Determination of Temperature
International Journal of Advanced Mechanical Engineering. ISSN 2250-3234 Volume 4, Number 5 (2014), pp. 469-474 Research India Publications http://www.ripublication.com Experimental Determination of Temperature
Risk Assessment and Mitigating Measures Regarding Pile Installation at EBS Biohub Jetty
 Geotechnical Safety and Risk V T. Schweckendiek et al. (Eds.) 2015 The authors and IOS Press. This article is published online with Open Access by IOS Press and distributed under the terms of the Creative
Geotechnical Safety and Risk V T. Schweckendiek et al. (Eds.) 2015 The authors and IOS Press. This article is published online with Open Access by IOS Press and distributed under the terms of the Creative
SCHEDULE OF RATES FOR GEO-TECHNICAL INVESTIGATION WORKS FOR FAGMIL GRANULATED SINGLE SUPER PHOSPHATE PLANT AT CHITTORGARH, RAJASTHAN
 PC107-PNCV-SOR-202 0 DOC. REV. 1 OF 6 (ANNEXURE-VII) FOR FAGMIL GRANULATED SINGLE SUPER PHOSPHATE PLANT AT CHITTORGARH, RAJASTHAN 0 11.04.16 ISSUED FOR TENDER GC GC BRIJESH REV REV DATE PURPOSE PREPD REVWD
PC107-PNCV-SOR-202 0 DOC. REV. 1 OF 6 (ANNEXURE-VII) FOR FAGMIL GRANULATED SINGLE SUPER PHOSPHATE PLANT AT CHITTORGARH, RAJASTHAN 0 11.04.16 ISSUED FOR TENDER GC GC BRIJESH REV REV DATE PURPOSE PREPD REVWD
PUSH PIER SYSTEMS STABILITY. SECURITY. INTEGRITY. Push Pier Systems PN #MBPPT
 PUSH PIER SYSTEMS STABILITY. SECURITY. INTEGRITY. PN #MBPPT Push Pier Systems About Foundation Supportworks is a network of the most experienced and knowledgeable foundation repair and new construction
PUSH PIER SYSTEMS STABILITY. SECURITY. INTEGRITY. PN #MBPPT Push Pier Systems About Foundation Supportworks is a network of the most experienced and knowledgeable foundation repair and new construction
Effect of Depth of Periphery Beams on Behavior of Grid Beams on Grid Floor
 International Journal of Current Engineering and Technology E-ISSN 2277 4106, P-ISSN 2347 5161 2015 INPRESSCO, All Rights Reserved Available at http://inpressco.com/category/ijcet Research Article Effect
International Journal of Current Engineering and Technology E-ISSN 2277 4106, P-ISSN 2347 5161 2015 INPRESSCO, All Rights Reserved Available at http://inpressco.com/category/ijcet Research Article Effect
Deformation parameters of soils determined by the cone penetration test
 MATEC Web of Conferences 117, 0002 (2017) DOI: 10.101/ matecconf/20171170002 Deformation parameters of soils determined by the cone penetration test Roman Bulko 1*, Filip Gago 2 1 University of Žilina,
MATEC Web of Conferences 117, 0002 (2017) DOI: 10.101/ matecconf/20171170002 Deformation parameters of soils determined by the cone penetration test Roman Bulko 1*, Filip Gago 2 1 University of Žilina,
Displacement-based calculation method on soil-pile interaction of PHC pipe-piles
 Seattle, WA Displacement-based calculation method on soil-pile interaction of PHC pipe-piles Dr. Huang Fuyun Fuzhou University 31 st May, 217 Outline Background ing introduction ing results Simple calculation
Seattle, WA Displacement-based calculation method on soil-pile interaction of PHC pipe-piles Dr. Huang Fuyun Fuzhou University 31 st May, 217 Outline Background ing introduction ing results Simple calculation
GROUND IMPROVEMENT USING RAPID IMPACT COMPACTION
 13 th World Conference on Earthquake Engineering Vancouver, B.C., Canada August 1-, Paper No. 9 GROUND IMPROVEMENT USING RAPID IMPACT COMPACTION Henrik KRISTIANSEN 1, Michael DAVIES SUMMARY Geotechnical
13 th World Conference on Earthquake Engineering Vancouver, B.C., Canada August 1-, Paper No. 9 GROUND IMPROVEMENT USING RAPID IMPACT COMPACTION Henrik KRISTIANSEN 1, Michael DAVIES SUMMARY Geotechnical
Comparison and Sensitivity Investigations of a CALM and SALM Type Mooring System for Wave Energy Converters
 J. Mar. Sci. Eng. 214, 2, 93-122; doi:1.339/jmse2193 Article OPEN ACCESS Journal of Marine Science and Engineering ISSN 277-1312 www.mdpi.com/journal/jmse Comparison and Sensitivity Investigations of a
J. Mar. Sci. Eng. 214, 2, 93-122; doi:1.339/jmse2193 Article OPEN ACCESS Journal of Marine Science and Engineering ISSN 277-1312 www.mdpi.com/journal/jmse Comparison and Sensitivity Investigations of a
PHASE 1 WIND STUDIES REPORT
 PHASE 1 WIND STUDIES REPORT ENVIRONMENTAL STUDIES AND PRELIMINARY DESIGN FOR A SUICIDE DETERRENT SYSTEM Contract 2006-B-17 24 MAY 2007 Golden Gate Bridge Highway and Transportation District Introduction
PHASE 1 WIND STUDIES REPORT ENVIRONMENTAL STUDIES AND PRELIMINARY DESIGN FOR A SUICIDE DETERRENT SYSTEM Contract 2006-B-17 24 MAY 2007 Golden Gate Bridge Highway and Transportation District Introduction
Quantitative Risk of Linear Infrastructure on Permafrost Heather Brooks, PE. Arquluk Committee Meeting November 2015
 Slide 1 Quantitative Risk of Linear Infrastructure on Permafrost Heather Brooks, PE Arquluk Committee Meeting November 2015 Welcome to the meeting of the committee for Arquluk s Quantitative Risk of Linear
Slide 1 Quantitative Risk of Linear Infrastructure on Permafrost Heather Brooks, PE Arquluk Committee Meeting November 2015 Welcome to the meeting of the committee for Arquluk s Quantitative Risk of Linear
Learn more at
 Full scale model tests of a steel catenary riser C. Bridge 1, H. Howells 1, N. Toy 2, G. Parke 2, R. Woods 2 1 2H Offshore Engineering Ltd, Woking, Surrey, UK 2 School of Engineering, University of Surrey,
Full scale model tests of a steel catenary riser C. Bridge 1, H. Howells 1, N. Toy 2, G. Parke 2, R. Woods 2 1 2H Offshore Engineering Ltd, Woking, Surrey, UK 2 School of Engineering, University of Surrey,
The single bore multiple anchor system
 A D Barley 1 The single bore multiple anchor system Eur.Ing. A D BARLEY, Director of Engineering, Keller Ground Engineering, Wetherby, UK INTRODUCTION An anchor tendon with a 10m fixed length in soil or
A D Barley 1 The single bore multiple anchor system Eur.Ing. A D BARLEY, Director of Engineering, Keller Ground Engineering, Wetherby, UK INTRODUCTION An anchor tendon with a 10m fixed length in soil or
DIRECTIONAL DRILLING
 DIRECTIONAL DRILLING 1. General. Installation of pipelines through the levee embankment using directional drilling technology is prohibited. Installation of pipelines through a flood control project foundation
DIRECTIONAL DRILLING 1. General. Installation of pipelines through the levee embankment using directional drilling technology is prohibited. Installation of pipelines through a flood control project foundation
Mechanical Stabilisation for Permanent Roads
 Mechanical Stabilisation for Permanent Roads Tim Oliver VP Global Applications Technology Tensar International toliver@tensar.co.uk Effect of geogrid on particle movement SmartRock Effect of geogrid on
Mechanical Stabilisation for Permanent Roads Tim Oliver VP Global Applications Technology Tensar International toliver@tensar.co.uk Effect of geogrid on particle movement SmartRock Effect of geogrid on
Application of Expansive Soil Geotechnical Procedures
 Application of Expansive Soil Geotechnical Procedures FPA PRESENTATION John T. Bryant, Ph.D., P.G., P.E with Robert L. Lytton, Ph.D., PE. And Mr. Dean Read HOUSTON, TEXAS WEDNESDAY DECEMBER 10, 2008 2008
Application of Expansive Soil Geotechnical Procedures FPA PRESENTATION John T. Bryant, Ph.D., P.G., P.E with Robert L. Lytton, Ph.D., PE. And Mr. Dean Read HOUSTON, TEXAS WEDNESDAY DECEMBER 10, 2008 2008
INFLUENCE OF FLY ASH IN STRENGTH CHARACTERISTICS OF COHESIVE SOILS
 International Journal of Civil Engineering and Technology (IJCIET) Volume 7, Issue 6, November-December 2016, pp. 67 72, Article ID: IJCIET_07_06_008 Available online at http://www.iaeme.com/ijciet/issues.asp?jtype=ijciet&vtype=7&itype=6
International Journal of Civil Engineering and Technology (IJCIET) Volume 7, Issue 6, November-December 2016, pp. 67 72, Article ID: IJCIET_07_06_008 Available online at http://www.iaeme.com/ijciet/issues.asp?jtype=ijciet&vtype=7&itype=6
CIVE 554/650. Geotechnical Engineering. Rock. Soil. Water. Site Investigation Techniques. CIVE Knight 1. 1/8/2006 CIVE Knight 1
 CIVE 554/650 Site Investigation Techniques 1/8/2006 CIVE 554 - Knight 1 Geotechnical Engineering Soil Rock Water 1/8/2006 CIVE 554 - Knight 2 CIVE 554 - Knight 1 Key Soil Engineering Properties Compressibility
CIVE 554/650 Site Investigation Techniques 1/8/2006 CIVE 554 - Knight 1 Geotechnical Engineering Soil Rock Water 1/8/2006 CIVE 554 - Knight 2 CIVE 554 - Knight 1 Key Soil Engineering Properties Compressibility
SUPPORTING NOTES FOR THE EVALUATION OF UNBOUND ROAD BASE AND SUB-BASE AGGREGATES
 SUPPORTING NOTES FOR THE EVALUATION OF UNBOUND ROAD BASE AND SUB-BASE AGGREGATES (These notes are guidelines only and must not be included in the Contract Documents). 1. SCOPE These Notes are guidelines
SUPPORTING NOTES FOR THE EVALUATION OF UNBOUND ROAD BASE AND SUB-BASE AGGREGATES (These notes are guidelines only and must not be included in the Contract Documents). 1. SCOPE These Notes are guidelines
[Barve, 4(7): July, 2015] ISSN: (I2OR), Publication Impact Factor: 3.785
![[Barve, 4(7): July, 2015] ISSN: (I2OR), Publication Impact Factor: 3.785 [Barve, 4(7): July, 2015] ISSN: (I2OR), Publication Impact Factor: 3.785](/thumbs/96/128298826.jpg) IJESRT INTERNATIONAL JOURNAL OF ENGINEERING SCIENCES & RESEARCH TECHNOLOGY PARAMETRIC STUDY TO UNDERSTAND THE SEISMIC BEHAVIOUR OF INTZE TANK SUPPORTED ON SHAFT Prasad S. Barve *, Ruchi P. Barve * Civil
IJESRT INTERNATIONAL JOURNAL OF ENGINEERING SCIENCES & RESEARCH TECHNOLOGY PARAMETRIC STUDY TO UNDERSTAND THE SEISMIC BEHAVIOUR OF INTZE TANK SUPPORTED ON SHAFT Prasad S. Barve *, Ruchi P. Barve * Civil
Elastic-Plastic Finite Element Analysis for Zhongwei--guiyang Natural Gas Pipeline Endangered by Collapse
 Abstract Elastic-Plastic Finite Element Analysis for Zhongwei--guiyang Natural Gas Pipeline Endangered by Collapse Gengxin Wu,Peng Zhang,Zhixiang Li,Zunhai Ke,Guizhi Li,Anmin Jiang 2 School of Civil Engineering
Abstract Elastic-Plastic Finite Element Analysis for Zhongwei--guiyang Natural Gas Pipeline Endangered by Collapse Gengxin Wu,Peng Zhang,Zhixiang Li,Zunhai Ke,Guizhi Li,Anmin Jiang 2 School of Civil Engineering
SUCTION CAISSON FOUNDATIONS FOR OFFSHORE WIND TURBINES
 SUCTION CAISSON FOUNDATIONS FOR OFFSHORE WIND TURBINES Felipe A. Villalobos Oxford University felipe.villalobos@eng.ox.ac.uk Guy T. Houlsby Oxford University guy.houlsby@eng.ox.ac.uk Byron W. Byrne Oxford
SUCTION CAISSON FOUNDATIONS FOR OFFSHORE WIND TURBINES Felipe A. Villalobos Oxford University felipe.villalobos@eng.ox.ac.uk Guy T. Houlsby Oxford University guy.houlsby@eng.ox.ac.uk Byron W. Byrne Oxford
Fatigue Analysis of English-Willow Cricket Bat
 Fatigue Analysis of English-Willow Cricket Bat Mr. Rajshekhar Chimmat 1, Mr. Shreenidhi Kulkarni 2 1M.Tech. Scholar, Dept. of Mechanical Engineering, KLS Gogte Institute of Technology, Belagavi, Karnataka,
Fatigue Analysis of English-Willow Cricket Bat Mr. Rajshekhar Chimmat 1, Mr. Shreenidhi Kulkarni 2 1M.Tech. Scholar, Dept. of Mechanical Engineering, KLS Gogte Institute of Technology, Belagavi, Karnataka,
SETTLEMENT & SLOPE STABILITY ANALYSES
 Appendix A Settlement and Slope Stability Analyses SETTLEMENT & SLOPE STABILITY ANALYSES Saugus RESCO Landfill Saugus, Massachusetts Prepared for: June, 2008 Prepared by: 11 Northeastern Boulevard Salem,
Appendix A Settlement and Slope Stability Analyses SETTLEMENT & SLOPE STABILITY ANALYSES Saugus RESCO Landfill Saugus, Massachusetts Prepared for: June, 2008 Prepared by: 11 Northeastern Boulevard Salem,
Experimental Investigation on Transient Response of Two Stage Pressure Relief Valve
 Experimental Investigation on Transient Response of Two Stage Pressure Relief Valve Prof. Basavaraj V.HUBBALLI 1, Dr. Vilas B.SONDUR 2 1 Jain College of Engineering, Belagavi Karnataka, India, bvhubliabhi@gmail.com
Experimental Investigation on Transient Response of Two Stage Pressure Relief Valve Prof. Basavaraj V.HUBBALLI 1, Dr. Vilas B.SONDUR 2 1 Jain College of Engineering, Belagavi Karnataka, India, bvhubliabhi@gmail.com
Determination of the wind pressure distribution on the facade of the triangularly shaped high-rise building structure
 Determination of the wind pressure distribution on the facade of the triangularly shaped high-rise building structure Norbert Jendzelovsky 1,*, Roland Antal 1 and Lenka Konecna 1 1 STU in Bratislava, Faculty
Determination of the wind pressure distribution on the facade of the triangularly shaped high-rise building structure Norbert Jendzelovsky 1,*, Roland Antal 1 and Lenka Konecna 1 1 STU in Bratislava, Faculty
