CHAPTER 17 BREATHING AND EXCHANGE OF GASES
|
|
|
- Adelia Blake
- 6 years ago
- Views:
Transcription
1 268 BIOLOGY CHAPTER 17 BREATHING AND EXCHANGE OF GASES 17.1 Respiratory Organs 17.2 Mechanism of Breathing 17.3 Exchange of Gases 17.4 Transport of Gases 17.5 Regulation of Respiration 17.6 Disorders of Respiratory System As you have read earlier, oxygen (O 2 ) is utilised by the organisms to indirectly break down nutrient molecules like glucose and to derive energy for performing various activities. Carbon dioxide (CO 2 ) which is harmful is also released during the above catabolic reactions. It is, therefore, evident that O 2 has to be continuously provided to the cells produced by the cells have to be released out. This process of exchange of O 2 from the atmosphere with CO 2 produced by the cells is called breathing, commonly known as respiration. Place your hands on your chest; you can feel the chest moving up and down. You know that it is due to breathing. How do we breathe? The respiratory organs and the mechanism of breathing are described in the following sections of this chapter RESPIRATORY ORGANS Mechanisms of breathing vary among different groups of animals depending mainly on their habitats and levels of organisation. Lower invertebrates like sponges, coelenterates, flatworms, etc., exchange O 2 with CO 2 by simple diffusion over their entire body surface. Earthworms use their moist cuticle and insects have a network of tubes (tracheal tubes) to transport atmospheric air within the body. Special vascularised structures called gills are used by most of the aquatic arthropods and molluscs whereas vascularised bags called lungs are used by the terrestrial forms for the exchange of gases. Among vertebrates, fishes use gills whereas reptiles, birds and mammals respire through lungs. Amphibians like frogs can respire through their moist skin also. Mammals have a well developed respiratory system.
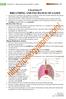
2 BREATHING AND EXCHANGE OF GASES Human Respiratory System We have a pair of external nostrils opening out above the upper lips. It leads to a nasal chamber through the nasal passage. The nasal chamber opens into nasopharynx, which is a portion of pharynx, the common passage for food and air. Nasopharynx opens through glottis of the larynx region into the trachea. Larynx is a cartilaginous box which helps in sound production and hence called the sound box. During swallowing glottis can be covered by a thin elastic cartilaginous flap called epiglottis to prevent the entry of food into the larynx. Trachea is a straight tube extending up to the mid-thoracic cavity, which divides at the level of 5th thoracic vertebra into a right and left primary bronchi. Each bronchi undergoes repeated divisions to form the secondary and tertiary bronchi and bronchioles ending up in very thin terminal bronchioles. The tracheae, primary, secondary and tertiary bronchi, and initial bronchioles are supported by incomplete cartilaginous rings. Each terminal bronchiole gives rise to a number of very thin, irregularwalled and vascularised bag-like structures called alveoli. The branching network of bronchi, bronchioles and alveoli comprise the lungs (Figure 17.1). We have two lungs which are covered by a double layered pleura, with pleural fluid between them. It reduces friction on the lungsurface. The outer pleural membrane is in close contact with the thoracic Epiglottis Larynx Trachea Bronchus Cut end of rib Lung heart Diaphragm Pleural membranes Alveoli Pleural fluid Bronchiole Figure 17.1 Diagrammatic view of human respiratory system (Sectional view of the left lung is also shown)
3 270 BIOLOGY lining whereas the inner pleural membrane is in contact with the lung surface. The part starting with the external nostrils up to the terminal bronchioles constitute the conducting part whereas the alveoli and their ducts form the respiratory or exchange part of the respiratory system. The conducting part transports the atmospheric air to the alveoli, clears it from foreign particles, humidifies and also brings the air to body temperature. Exchange part is the site of actual diffusion of O 2 between blood and atmospheric air. The lungs are situated in the thoracic chamber which is anatomically an air-tight chamber. The thoracic chamber is formed dorsally by the vertebral column, ventrally by the sternum, laterally by the ribs and on the lower side by the dome-shaped diaphragm. The anatomical setup of lungs in thorax is such that any change in the volume of the thoracic cavity will be reflected in the lung (pulmonary) cavity. Such an arrangement is essential for breathing, as we cannot directly alter the pulmonary volume. Respiration involves the following steps: (i) Breathing or pulmonary ventilation by which atmospheric air is drawn in rich alveolar air is released out. (ii) Diffusion of gases (O 2 ) across alveolar membrane. (iii) Transport of gases by the blood. (iv) Diffusion of O 2 between blood and tissues. (v) Utilisation of O 2 by the cells for catabolic reactions and resultant release of CO 2 (cellular respiration as dealt in the Chapter 14 Respiration) MECHANISM OF BREATHING Breathing involves two stages : inspiration during which atmospheric air is drawn in and expiration by which the alveolar air is released out. The movement of air into and out of the lungs is carried out by creating a pressure gradient between the lungs and the atmosphere. Inspiration can occur if the pressure within the lungs (intra-pulmonary pressure) is less than the atmospheric pressure, i.e., there is a negative pressure in the lungs with respect to atmospheric pressure. Similarly, expiration takes place when the intra-pulmonary pressure is higher than the atmospheric pressure. The diaphragm and a specialised set of muscles external and internal intercostals between the ribs, help in generation of such gradients. Inspiration is initiated by the contraction of diaphragm which increases the volume of thoracic chamber in the antero-posterior axis. The contraction of external inter-costal muscles lifts up the ribs and the
4 BREATHING AND EXCHANGE OF GASES 271 sternum causing an increase in the volume of the thoracic chamber in the dorso-ventral axis. The overall increase in the thoracic volume causes a similar increase in pulmonary volume. An increase in pulmonary volume decreases the intra-pulmonary pressure to less than the atmospheric pressure which forces the air from outside to move into the lungs, i.e., inspiration (Figure 17.2a). Relaxation of the diaphragm and the inter-costal muscles returns the diaphragm and sternum to their normal positions and reduce the thoracic volume and thereby the pulmonary volume. This leads to an increase in intra-pulmonary pressure to slightly above the atmospheric pressure causing the expulsion of air from the lungs, i.e., expiration (Figure 17.2b). We have the ability to increase the strength of inspiration and expiration with the help of additional muscles in the abdomen. On an average, a healthy human breathes times/minute. The volume of air involved in breathing movements can be estimated by using a spirometer which helps in clinical assessment of pulmonary functions Respiratory Volumes and Capacities Tidal Volume (TV): Volume of air inspired or expired during a normal respiration. It is approx. 500 ml., i.e., a healthy man can inspire or expire approximately 6000 to 8000 ml of air per minute. Inspiratory Reserve Volume (IRV): Additional volume of air, a person can inspire by a forcible inspiration. This averages 2500 ml to 3000 ml. Expiratory Reserve Volume (ERV): Additional volume of air, a person can expire by a forcible expiration. This averages 1000 ml to 1100 ml. Figure 17.2 Mechanism of breathing showing : (a) inspiration (b) expiration
5 272 BIOLOGY Residual Volume (RV): Volume of air remaining in the lungs even after a forcible expiration. This averages 1100 ml to 1200 ml. By adding up a few respiratory volumes described above, one can derive various pulmonary capacities, which can be used in clinical diagnosis. Inspiratory Capacity (IC): Total volume of air a person can inspire after a normal expiration. This includes tidal volume and inspiratory reserve volume ( TV+IRV). Expiratory Capacity (EC): Total volume of air a person can expire after a normal inspiration. This includes tidal volume and expiratory reserve volume (TV+ERV). Functional Residual Capacity (FRC): Volume of air that will remain in the lungs after a normal expiration. This includes ERV+RV. Vital Capacity (VC): The maximum volume of air a person can breathe in after a forced expiration. This includes ERV, TV and IRV or the maximum volume of air a person can breathe out after a forced inspiration. Total Lung Capacity: Total volume of air accommodated in the lungs at the end of a forced inspiration. This includes RV, ERV, TV and IRV or vital capacity + residual volume EXCHANGE OF GASES Alveoli are the primary sites of exchange of gases. Exchange of gases also occur between blood and tissues. O 2 are exchanged in these sites by simple diffusion mainly based on pressure/concentration gradient. Solubility of the gases as well as the thickness of the membranes involved in diffusion are also some important factors that can affect the rate of diffusion. Pressure contributed by an individual gas in a mixture of gases is called partial pressure and is represented as po 2 for oxygen and pco 2 for carbon dioxide. Partial pressures of these two gases in the atmospheric air and the two sites of diffusion are given in Table 17.1 and in Figure The data given in the table clearly indicates a concentration gradient for oxygen from alveoli to blood and blood to tissues. Similarly, TABLE 17.1 Partial Pressures (in mm Hg) of Oxygen and Carbon dioxide at Different Parts Involved in Diffusion in Comparison to those in Atmosphere Respiratory Atmospheric Alveoli Blood Blood Tissues Gas Air (Deoxygenated) (Oxygenated) O CO
6 BREATHING AND EXCHANGE OF GASES 273 Inspired air Expired air Alveolar air po 2=104 mmhg CO2 O2 pco 2=40 mmhg CO2 O2 Alveolus Pulmonary artery CO2 O2 Pulmonary vein Systemic veins Systemic arteries (carrying deoxygenated blood) (carrying oxygenated blood) CO 2 O 2 po 2 = 40 mm Hg pco = 45 mm Hg 2 CO 2 O 2 Body tissues po 2 = 95 mm Hg pco = 40 mm Hg 2 Figure 17.3 Diagrammatic representation of exchange of gases at the alveolus and the body tissues with blood and transport of oxygen and carbon dioxide a gradient is present for CO 2 in the opposite direction, i.e., from tissues to blood and blood to alveoli. As the solubility of CO 2 is times higher than that of O 2, the amount of CO 2 that can diffuse through the diffusion membrane per unit difference in partial pressure is much higher compared to that of O 2. The diffusion membrane is made up of three major layers (Figure 17.4) namely, the thin squamous epithelium of alveoli, the endothelium of alveolar capillaries and the basement substance in between them. However, its total thickness is much less than a millimetre. Therefore, all the factors in our body are favourable for diffusion of O 2 from alveoli to tissues and that of CO 2 from tissues to alveoli. Alveolar wall (one-celled thick) Air Blood capillary Figure 17.4 Alveolar cavity Basement substance Red blood cell A Diagram of a section of an alveolus with a pulmonary capillary.
7 274 BIOLOGY Percentage saturation of haemoglobin with oxygen 17.4 TRANSPORT OF GASES Blood is the medium of transport for O 2. About 97 per cent of O 2 is transported by RBCs in the blood. The remaining 3 per cent of O 2 is carried in a dissolved state through the plasma. Nearly per cent of CO 2 is transported by RBCs whereas 70 per cent of it is carried as bicarbonate. About 7 per cent of CO 2 is carried in a dissolved state through plasma Transport of Oxygen Haemoglobin is a red coloured iron containing pigment present in the RBCs. O 2 can bind with haemoglobin in a reversible manner to form oxyhaemoglobin. Each haemoglobin molecule can carry a maximum of four molecules of O 2. Binding of oxygen with haemoglobin is primarily related to partial pressure of O 2. Partial pressure of CO 2, hydrogen ion concentration and temperature are the other factors which can interfere with this binding. A sigmoid curve is obtained when percentage saturation of haemoglobin with O 2 is plotted against the po 2. This curve is called the Oxygen dissociation curve (Figure 17.5) and is highly useful in studying the effect of factors like 100 pco 2, H + concentration, etc., on binding of O 2 with haemoglobin. In the alveoli, where there 80 is high po 2, low pco 2, lesser H + concentration and lower temperature, the factors are all favourable for the formation of 60 oxyhaemoglobin, whereas in the tissues, where low po 2, high pco 2, high H + 40 concentration and higher temperature exist, the conditions are favourable for dissociation 20 of oxygen from the oxyhaemoglobin. This clearly indicates that O 2 gets bound to haemoglobin in the lung surface and gets dissociated at the tissues. Every 100 ml of Partial pressure of oxygen (mm Hg) oxygenated blood can deliver around 5 ml of Figure 17.5 Oxygen dissociation curve O 2 to the tissues under normal physiological conditions Transport of Carbon dioxide CO 2 is carried by haemoglobin as carbamino-haemoglobin (about per cent). This binding is related to the partial pressure of CO 2. po 2 is a major factor which could affect this binding. When pco 2 is high and po 2 is low as in the tissues, more binding of carbon dioxide occurs whereas, when the pco 2 is low and po 2 is high as in the alveoli, dissociation
8 BREATHING AND EXCHANGE OF GASES 275 of CO 2 from carbamino-haemoglobin takes place, i.e., CO 2 which is bound to haemoglobin from the tissues is delivered at the alveoli. RBCs contain a very high concentration of the enzyme, carbonic anhydrase and minute quantities of the same is present in the plasma too. This enzyme facilitates the following reaction in both directions. Carbonic Carbonic anhydrase anhydrase CO + HO HCO HCO + H At the tissue site where partial pressure of CO 2 is high due to catabolism, CO 2 diffuses into blood (RBCs and plasma) and forms HCO 3 and H +,. At the alveolar site where pco 2 is low, the reaction proceeds in the opposite direction leading to the formation of CO 2 and H 2 O. Thus, CO 2 trapped as bicarbonate at the tissue level and transported to the alveoli is released out as CO 2 (Figure 17.4). Every 100 ml of deoxygenated blood delivers approximately 4 ml of CO 2 to the alveoli REGULATION OF RESPIRATION Human beings have a significant ability to maintain and moderate the respiratory rhythm to suit the demands of the body tissues. This is done by the neural system. A specialised centre present in the medulla region of the brain called respiratory rhythm centre is primarily responsible for this regulation. Another centre present in the pons region of the brain called pneumotaxic centre can moderate the functions of the respiratory rhythm centre. Neural signal from this centre can reduce the duration of inspiration and thereby alter the respiratory rate. A chemosensitive area is situated adjacent to the rhythm centre which is highly sensitive to CO 2 and hydrogen ions. Increase in these substances can activate this centre, which in turn can signal the rhythm centre to make necessary adjustments in the respiratory process by which these substances can be eliminated. Receptors associated with aortic arch and carotid artery also can recognise changes in CO 2 and H + concentration and send necessary signals to the rhythm centre for remedial actions. The role of oxygen in the regulation of respiratory rhythm is quite insignificant DISORDERS OF RESPIRATORY SYSTEM Asthma is a difficulty in breathing causing wheezing due to inflammation of bronchi and bronchioles. Emphysema is a chronic disorder in which alveolar walls are damaged due to which respiratory surface is decreased. One of the major causes of this is cigarette smoking.
9 276 BIOLOGY Occupational Respiratory Disorders: In certain industries, especially those involving grinding or stone-breaking, so much dust is produced that the defense mechanism of the body cannot fully cope with the situation. Long exposure can give rise to inflammation leading to fibrosis (proliferation of fibrous tissues) and thus causing serious lung damage. Workers in such industries should wear protective masks. SUMMARY Cells utilise oxygen for metabolism and produce energy along with substances like carbon dioxide which is harmful. Animals have evolved different mechanisms for the transport of oxygen to the cells and for the removal of carbon dioxide from there. We have a well developed respiratory system comprising two lungs and associated air passages to perform this function. The first step in respiration is breathing by which atmospheric air is taken in (inspiration) and the alveolar air is released out (expiration). Exchange of O 2 and CO 2 between deoxygenated blood and alveoli, transport of these gases throughout the body by blood, exchange of O 2 between the oxygenated blood and tissues and utilisation of O 2 by the cells (cellular respiration) are the other steps involved. Inspiration and expiration are carried out by creating pressure gradients between the atmosphere and the alveoli with the help of specialised muscles intercostals and diaphragm. Volumes of air involved in these activities can be estimated with the help of spirometer and are of clinical significance. Exchange of O 2 at the alveoli and tissues occur by diffusion. Rate of diffusion is dependent on the partial pressure gradients of O 2 (po 2 ) (pco 2 ), their solubility as well as the thickness of the diffusion surface. These factors in our body facilitate diffusion of O 2 from the alveoli to the deoxygenated blood as well as from the oxygenated blood to the tissues. The factors are favourable for the diffusion of CO 2 in the opposite direction, i.e., from tissues to alveoli. Oxygen is transported mainly as oxyhaemoglobin. In the alveoli where po 2 is higher, O 2 gets bound to haemoglobin which is easily dissociated at the tissues where po 2 is low and pco 2 and H + concentration are high. Nearly 70 per cent of carbon dioxide is transported as bicarbonate (HCO 3 ) with the help of the enzyme carbonic anhydrase per cent of carbon dioxide is carried by haemoglobin as carbamino-haemoglobin. In the tissues where pco 2 is high, it gets bound to blood whereas in the alveoli where pco 2 is low and po 2 is high, it gets removed from the blood. Respiratory rhythm is maintained by the respiratory centre in the medulla region of brain. A pneumotaxic centre in the pons region of the brain and a chemosensitive area in the medulla can alter respiratory mechanism.
10 BREATHING AND EXCHANGE OF GASES 277 EXERCISES 1. Define vital capacity. What is its significance? 2. State the volume of air remaining in the lungs after a normal breathing. 3. Diffusion of gases occurs in the alveolar region only and not in the other parts of respiratory system. Why? 4. What are the major transport mechanisms for CO 2? Explain. 5. What will be the po 2 and pco 2 in the atmospheric air compared to those in the alveolar air? (i) po 2 lesser, pco 2 higher (ii) po 2 higher, pco 2 lesser (iii) po 2 higher, pco 2 higher (iv) po 2 lesser, pco 2 lesser 6. Explain the process of inspiration under normal conditions. 7. How is respiration regulated? 8. What is the effect of pco 2 on oxygen transport? 9. What happens to the respiratory process in a man going up a hill? 10. What is the site of gaseous exchange in an insect? 11. Define oxygen dissociation curve. Can you suggest any reason for its sigmoidal pattern? 12. Have you heard about hypoxia? Try to gather information about it, and discuss with your friends. 13. Distinguish between (a) IRV and ERV (b) Inspiratory capacity and Expiratory capacity. (c) Vital capacity and Total lung capacity. 14. What is Tidal volume? Find out the Tidal volume (approximate value) for a healthy human in an hour.
1 CHAPTER 17 BREATHING AND EXCHANGE OF GASES https://biologyaipmt.com/
 1 CHAPTER 17 BREATHING AND EXCHANGE OF GASES https://biologyaipmt.com/ CHAPTER 17 BREATHING AND EXCHANGE OF GASES Oxygen (O2) is utilised by the organisms to indirectly break down nutrient molecules like
1 CHAPTER 17 BREATHING AND EXCHANGE OF GASES https://biologyaipmt.com/ CHAPTER 17 BREATHING AND EXCHANGE OF GASES Oxygen (O2) is utilised by the organisms to indirectly break down nutrient molecules like
2. State the volume of air remaining in the lungs after a normal breathing.
 CLASS XI BIOLOGY Breathing And Exchange of Gases 1. Define vital capacity. What is its significance? Answer: Vital Capacity (VC): The maximum volume of air a person can breathe in after a forced expiration.
CLASS XI BIOLOGY Breathing And Exchange of Gases 1. Define vital capacity. What is its significance? Answer: Vital Capacity (VC): The maximum volume of air a person can breathe in after a forced expiration.
 Question 1: Define vital capacity. What is its significance? Vital capacity is the maximum volume of air that can be exhaled after a maximum inspiration. It is about 3.5 4.5 litres in the human body. It
Question 1: Define vital capacity. What is its significance? Vital capacity is the maximum volume of air that can be exhaled after a maximum inspiration. It is about 3.5 4.5 litres in the human body. It
BREATHING AND EXCHANGE OF GASES
 96 BIOLOGY, EXEMPLAR PROBLEMS CHAPTER 17 BREATHING AND EXCHANGE OF GASES MULTIPLE CHOICE QUESTIONS 1. Respiration in insects is called direct because a. The tissues exchange O 2 directly with the air in
96 BIOLOGY, EXEMPLAR PROBLEMS CHAPTER 17 BREATHING AND EXCHANGE OF GASES MULTIPLE CHOICE QUESTIONS 1. Respiration in insects is called direct because a. The tissues exchange O 2 directly with the air in
BREATHING AND EXCHANGE OF GASES
 96 BIOLOGY, EXEMPLAR PROBLEMS CHAPTER 17 BREATHING AND EXCHANGE OF GASES MULTIPLE CHOICE QUESTIONS 1. Respiration in insects is called direct because a. The cell exchange O 2 directly with the air in the
96 BIOLOGY, EXEMPLAR PROBLEMS CHAPTER 17 BREATHING AND EXCHANGE OF GASES MULTIPLE CHOICE QUESTIONS 1. Respiration in insects is called direct because a. The cell exchange O 2 directly with the air in the
CHAPTER 3: The respiratory system
 CHAPTER 3: The respiratory system Practice questions - text book pages 56-58 1) When the inspiratory muscles contract, which one of the following statements is true? a. the size of the thoracic cavity
CHAPTER 3: The respiratory system Practice questions - text book pages 56-58 1) When the inspiratory muscles contract, which one of the following statements is true? a. the size of the thoracic cavity
Chapter 16 Respiratory System
 Introduction Chapter 16 Respiratory System The respiratory system consists of tubes that filter incoming air and transport it to alveoli where gases are exchanged. Think pair share: what organs are associated
Introduction Chapter 16 Respiratory System The respiratory system consists of tubes that filter incoming air and transport it to alveoli where gases are exchanged. Think pair share: what organs are associated
Then the partial pressure of oxygen is x 760 = 160 mm Hg
 1 AP Biology March 2008 Respiration Chapter 42 Gas exchange occurs across specialized respiratory surfaces. 1) Gas exchange: the uptake of molecular oxygen (O2) from the environment and the discharge of
1 AP Biology March 2008 Respiration Chapter 42 Gas exchange occurs across specialized respiratory surfaces. 1) Gas exchange: the uptake of molecular oxygen (O2) from the environment and the discharge of
GASEOUS EXCHANGE 17 JULY 2013
 GASEOUS EXCHANGE 17 JULY 2013 Lesson Description In this lesson we: Discuss what is gaseous exchange? Consider requirements of an efficient gaseous exchange surface. Look at diversity in gas exchange systems.
GASEOUS EXCHANGE 17 JULY 2013 Lesson Description In this lesson we: Discuss what is gaseous exchange? Consider requirements of an efficient gaseous exchange surface. Look at diversity in gas exchange systems.
CHAPTER 3: The cardio-respiratory system
 : The cardio-respiratory system Exam style questions - text book pages 44-45 1) Describe the structures involved in gaseous exchange in the lungs and explain how gaseous exchange occurs within this tissue.
: The cardio-respiratory system Exam style questions - text book pages 44-45 1) Describe the structures involved in gaseous exchange in the lungs and explain how gaseous exchange occurs within this tissue.
Then the partial pressure of oxygen is. b) Gases will diffuse down a pressure gradient across a respiratory surface if it is: i) permeable ii) moist
 1 AP Biology March 2008 Respiration Chapter 42 Gas exchange occurs across specialized respiratory surfaces. 1) Gas exchange: Relies on the diffusion of gases down pressure gradients. At sea level, atmosphere
1 AP Biology March 2008 Respiration Chapter 42 Gas exchange occurs across specialized respiratory surfaces. 1) Gas exchange: Relies on the diffusion of gases down pressure gradients. At sea level, atmosphere
Respiratory System Review
 KEY THIS TEST WILL BE COMPLETED IN ONE CLASS PERIOD MONDAY, MARCH 10. 2014 Respiratory System Review Name A. Directions: Fill in the blank with the appropriate vocabulary word or words (several examples
KEY THIS TEST WILL BE COMPLETED IN ONE CLASS PERIOD MONDAY, MARCH 10. 2014 Respiratory System Review Name A. Directions: Fill in the blank with the appropriate vocabulary word or words (several examples
Physiology of Respiration
 Physiology of Respiration External Respiration = pulmonary ventilation breathing involves 2 processes: inspiration expiration Inspiration an active process involves contraction of diaphragm innervated
Physiology of Respiration External Respiration = pulmonary ventilation breathing involves 2 processes: inspiration expiration Inspiration an active process involves contraction of diaphragm innervated
BIOLOGY 12: UNIT J - CHAPTER 15 - REVIEW WORKSHEET RESPIRATORY SYSTEM
 BIOLOGY 12: UNIT J - CHAPTER 15 - REVIEW WORKSHEET RESPIRATORY SYSTEM A. CHAPTER REVIEW 1. Define the four components of respiration. 2. What happens to the air as it moves along the air passages? What
BIOLOGY 12: UNIT J - CHAPTER 15 - REVIEW WORKSHEET RESPIRATORY SYSTEM A. CHAPTER REVIEW 1. Define the four components of respiration. 2. What happens to the air as it moves along the air passages? What
Gaseous exchange. Grade 11
 z Gaseous exchange Grade 11 z Terminology 1. Breathing 2. Gaseous exchange 3. Diffusion 4. Spongy mesophyll cells 5. Tracheae 6. Gills 7. Alveoli 8. Larynx 9. Diaphragm 10. Endothelium 1. Pleura 2. Squamous
z Gaseous exchange Grade 11 z Terminology 1. Breathing 2. Gaseous exchange 3. Diffusion 4. Spongy mesophyll cells 5. Tracheae 6. Gills 7. Alveoli 8. Larynx 9. Diaphragm 10. Endothelium 1. Pleura 2. Squamous
Respiratory System Physiology. Dr. Vedat Evren
 Respiratory System Physiology Dr. Vedat Evren Respiration Processes involved in oxygen transport from the atmosphere to the body tissues and the release and transportation of carbon dioxide produced in
Respiratory System Physiology Dr. Vedat Evren Respiration Processes involved in oxygen transport from the atmosphere to the body tissues and the release and transportation of carbon dioxide produced in
The Respiratory System. Medical Terminology
 The Respiratory System Medical Terminology The respiratory system is where gas exchange occurs via respiration; inhalation/exhalation. pick up oxygen from inhaled air expels carbon dioxide and water sinus
The Respiratory System Medical Terminology The respiratory system is where gas exchange occurs via respiration; inhalation/exhalation. pick up oxygen from inhaled air expels carbon dioxide and water sinus
Breathing oxygenates the blood to allow food to be respired
 Chapter 6 Breathing oxygenates the blood to allow food to be respired This chapter covers: the structure of the human gas exchange system the mechanism of breathing gas exchange in the alveoli the concept
Chapter 6 Breathing oxygenates the blood to allow food to be respired This chapter covers: the structure of the human gas exchange system the mechanism of breathing gas exchange in the alveoli the concept
Respiration - Human 1
 Respiration - Human 1 At the end of the lectures on respiration you should be able to, 1. Describe events in the respiratory processes 2. Discuss the mechanism of lung ventilation in human 3. Discuss the
Respiration - Human 1 At the end of the lectures on respiration you should be able to, 1. Describe events in the respiratory processes 2. Discuss the mechanism of lung ventilation in human 3. Discuss the
Lesson 9.1: The Importance of an Organ Delivery System
 Lesson 9.1: The Importance of an Organ Delivery System Animals require a continuous supply of oxygen (O 2 ) for cellular respiration, and they must expel carbon dioxide (CO 2 ), the waste product of this
Lesson 9.1: The Importance of an Organ Delivery System Animals require a continuous supply of oxygen (O 2 ) for cellular respiration, and they must expel carbon dioxide (CO 2 ), the waste product of this
Human Biology Respiratory System
 Human Biology Respiratory System Respiratory System Responsible for process of breathing Works in cooperation with Circulatory system Three types: 1. Internal Respiration 2. External Respiration 3. Cellular
Human Biology Respiratory System Respiratory System Responsible for process of breathing Works in cooperation with Circulatory system Three types: 1. Internal Respiration 2. External Respiration 3. Cellular
alveoli Chapter 42. Gas Exchange elephant seals gills AP Biology
 alveoli Chapter 42. Gas Exchange gills elephant seals Gas exchange O 2 & CO 2 exchange exchange between environment & cells provides O 2 for aerobic cellular respiration need moist membrane need high
alveoli Chapter 42. Gas Exchange gills elephant seals Gas exchange O 2 & CO 2 exchange exchange between environment & cells provides O 2 for aerobic cellular respiration need moist membrane need high
I. Gas Exchange Respiratory Surfaces Respiratory Surface:
 I. Gas Exchange Respiratory Surfaces Respiratory Surface: Common characteristics of respiratory surfaces: a) Moist: allows for the RAPID diffusion of dissolved gasses across its surface. Whereas the respiratory
I. Gas Exchange Respiratory Surfaces Respiratory Surface: Common characteristics of respiratory surfaces: a) Moist: allows for the RAPID diffusion of dissolved gasses across its surface. Whereas the respiratory
Respiration. The resspiratory system
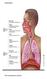 Respiration The resspiratory system The Alveoli The lungs have about 300 million alveoli, with a total crosssec onal area of 50 70 m2.. Each alveolar sac is surrounded by blood capillaries. The walls of
Respiration The resspiratory system The Alveoli The lungs have about 300 million alveoli, with a total crosssec onal area of 50 70 m2.. Each alveolar sac is surrounded by blood capillaries. The walls of
Chapter 13 The Respiratory System
 Chapter 13 The Respiratory System by Dr. Jay M. Templin Brooks/Cole - Thomson Learning Atmosphere Tissue cell External respiration Alveoli of lungs 1 Ventilation or gas exchange between the atmosphere
Chapter 13 The Respiratory System by Dr. Jay M. Templin Brooks/Cole - Thomson Learning Atmosphere Tissue cell External respiration Alveoli of lungs 1 Ventilation or gas exchange between the atmosphere
Breathing: The normal rate is about 14 to 20 times a minute. Taking in of air is called Inspiration and the forcing out of air is called Expiration.
 Biology 12 Respiration Divisions of Respiration Breathing: entrance and exit of air into and out of the lungs External Respiration: exchange of gases(o2 and CO2) between air (in alveoli) and blood Internal
Biology 12 Respiration Divisions of Respiration Breathing: entrance and exit of air into and out of the lungs External Respiration: exchange of gases(o2 and CO2) between air (in alveoli) and blood Internal
Chapter 11: Respiratory System Review Assignment
 Name: Date: Mark: / 45 Chapter 11: Respiratory System Review Assignment Multiple Choice = 45 Marks Identify the choice that best completes the statement or answers the question. 1. Which of the following
Name: Date: Mark: / 45 Chapter 11: Respiratory System Review Assignment Multiple Choice = 45 Marks Identify the choice that best completes the statement or answers the question. 1. Which of the following
AP Biology. Chapter 42. Gas Exchange. Optimizing gas exchange. Gas exchange. Gas exchange in many forms. Evolution of gas exchange structures
 alveoli Chapter 42. Gas Exchange gills elephant seals Gas exchange & C exchange exchange between environment & cells provides for aerobic cellular respiration need moist membrane need high surface area
alveoli Chapter 42. Gas Exchange gills elephant seals Gas exchange & C exchange exchange between environment & cells provides for aerobic cellular respiration need moist membrane need high surface area
Respiration. The ins and outs
 Respiration The ins and outs Functions 1. To bring O 2 into the body and transfer it to the blood stream 2. To remove CO 2 Circulation and respiration work together to achieve these functions Why Do We
Respiration The ins and outs Functions 1. To bring O 2 into the body and transfer it to the blood stream 2. To remove CO 2 Circulation and respiration work together to achieve these functions Why Do We
GASEOUS EXCHANGE IN HUMANS 06 AUGUST 2014
 GASEOUS EXCHANGE IN HUMANS 06 AUGUST 2014 In this lesson we: Lesson Description Look at gaseous exchange in humans in terms of o Ventilation o Inspiration o Expiration o Transport of gases o Homeostatic
GASEOUS EXCHANGE IN HUMANS 06 AUGUST 2014 In this lesson we: Lesson Description Look at gaseous exchange in humans in terms of o Ventilation o Inspiration o Expiration o Transport of gases o Homeostatic
practices makes perfect
 Human Respiratory system Chapter 1: Respiration PMR 03, 08 1. The human respiratory system consists of: a... b... c.. d... e. Our body has.. lungs (right & left). f. Each lung consists of the, and alveoli.
Human Respiratory system Chapter 1: Respiration PMR 03, 08 1. The human respiratory system consists of: a... b... c.. d... e. Our body has.. lungs (right & left). f. Each lung consists of the, and alveoli.
Biology. TOPIC : Breathing and Exchange of Gases. Marks : 120 mks Time : ½ hr
 TOPIC : Breathing and Exchange of Gases Date : Marks : 120 mks Time : ½ hr (1) Read the given statements characterizing certain types of animals. Select the option that correctly exemplifies each of these
TOPIC : Breathing and Exchange of Gases Date : Marks : 120 mks Time : ½ hr (1) Read the given statements characterizing certain types of animals. Select the option that correctly exemplifies each of these
RESPIRATORY SYSTEM OF RABBIT:
 RESPIRATION The term respiration means exchange of gases (particularly oxygen and carbon dioxide) between an organism and its medium. Physiologically, the term respiration may be defined as a biochemical
RESPIRATION The term respiration means exchange of gases (particularly oxygen and carbon dioxide) between an organism and its medium. Physiologically, the term respiration may be defined as a biochemical
1. Label a diagram of the respiratory system. Objective sheet 3 Notes
 1. Label a diagram of the respiratory system Objective sheet 3 Notes 2. Functions of the respiratory structures Name Description Function Nasal Cavity Trachea Bronchi (Singular Bronchus) Bronchioles Lungs
1. Label a diagram of the respiratory system Objective sheet 3 Notes 2. Functions of the respiratory structures Name Description Function Nasal Cavity Trachea Bronchi (Singular Bronchus) Bronchioles Lungs
Chapter 15. Lecture and Animation Outline
 Chapter 15 Lecture and Animation Outline To run the animations you must be in Slideshow View. Use the buttons on the animation to play, pause, and turn audio/text on or off. Please Note: Once you have
Chapter 15 Lecture and Animation Outline To run the animations you must be in Slideshow View. Use the buttons on the animation to play, pause, and turn audio/text on or off. Please Note: Once you have
Outline - Respiratory System. Function of the respiratory system Parts of the respiratory system Mechanics of breathing Regulation of breathing
 Respiratory system Function Outline - Respiratory System I. II. III. IV. Respiratory System The function of the respiratory system is to bring in oxygen to the body and remove carbon dioxide. Function
Respiratory system Function Outline - Respiratory System I. II. III. IV. Respiratory System The function of the respiratory system is to bring in oxygen to the body and remove carbon dioxide. Function
Gas Exchange Respiratory Systems
 alveoli gills Gas Exchange Respiratory Systems elephant seals 2008-2009 Why do we need a respiratory system? respiration for respiration Need O 2 in for aerobic cellular respiration make ATP Need CO 2
alveoli gills Gas Exchange Respiratory Systems elephant seals 2008-2009 Why do we need a respiratory system? respiration for respiration Need O 2 in for aerobic cellular respiration make ATP Need CO 2
Assignments for Life Processes(Respiration)
 Assignments for Life Processes(Respiration) 1 Question 1 Why do organisms need food? Organisms need food for obtaining energy to perform the vital functions. Question 2 What is a respiratory substrate?
Assignments for Life Processes(Respiration) 1 Question 1 Why do organisms need food? Organisms need food for obtaining energy to perform the vital functions. Question 2 What is a respiratory substrate?
Respiratory System. Part 2
 Respiratory System Part 2 Respiration Exchange of gases between air and body cells Three steps 1. Ventilation 2. External respiration 3. Internal respiration Ventilation Pulmonary ventilation consists
Respiratory System Part 2 Respiration Exchange of gases between air and body cells Three steps 1. Ventilation 2. External respiration 3. Internal respiration Ventilation Pulmonary ventilation consists
(Slide 1) Lecture Notes: Respiratory System
 (Slide 1) Lecture Notes: Respiratory System I. (Slide 2) The Respiratory Tract A) Major structures and regions of the respiratory Tract/Route INTO body 1) nose 2) nasal cavity 3) pharynx 4) glottis 5)
(Slide 1) Lecture Notes: Respiratory System I. (Slide 2) The Respiratory Tract A) Major structures and regions of the respiratory Tract/Route INTO body 1) nose 2) nasal cavity 3) pharynx 4) glottis 5)
82 Respiratory Tract NOTES
 82 Respiratory Tract NOTES RESPIRATORY TRACT The respiratory tract conducts air to the lungs where gaseous exchange occurs. It is separated into air-conducting and respiratory (where gas exchange occurs)
82 Respiratory Tract NOTES RESPIRATORY TRACT The respiratory tract conducts air to the lungs where gaseous exchange occurs. It is separated into air-conducting and respiratory (where gas exchange occurs)
AP Biology. Gas Exchange Respiratory Systems. Gas exchange. Why do we need a respiratory system? Optimizing gas exchange. Gas exchange in many forms
 alveoli Gas Exchange Respiratory Systems gills elephant seals 2008-2009 Why do we need a respiratory system? Need O 2 in food respiration for respiration for aerobic cellular respiration make ATP Need
alveoli Gas Exchange Respiratory Systems gills elephant seals 2008-2009 Why do we need a respiratory system? Need O 2 in food respiration for respiration for aerobic cellular respiration make ATP Need
Chapter 1: Respiration
 Chapter 1: Respiration Respiration Human Breathing Mechanism Transport of oxygen Importance of a healthy respiratory system Respiratory system lungs inhalation exhalation Diffusion of oxygen by blood Transport
Chapter 1: Respiration Respiration Human Breathing Mechanism Transport of oxygen Importance of a healthy respiratory system Respiratory system lungs inhalation exhalation Diffusion of oxygen by blood Transport
2.1.1 List the principal structures of the
 physiology 2.1.1 List the principal structures of the The principle structures of the respiratory are: Nose/Mouth used for inhalation of oxygen-rich air and expelling carbon dioxide rich air Pharynx -
physiology 2.1.1 List the principal structures of the The principle structures of the respiratory are: Nose/Mouth used for inhalation of oxygen-rich air and expelling carbon dioxide rich air Pharynx -
The Respiratory System
 Essentials of Human Anatomy & Physiology Elaine N. Marieb Seventh Edition Chapter 13 The Respiratory System Slides 13.1 13.30 Lecture Slides in PowerPoint by Jerry L. Cook Organs of the Respiratory system
Essentials of Human Anatomy & Physiology Elaine N. Marieb Seventh Edition Chapter 13 The Respiratory System Slides 13.1 13.30 Lecture Slides in PowerPoint by Jerry L. Cook Organs of the Respiratory system
Structures of the Respiratory System include:
 Respiratory System Structures of the Respiratory System include: ü Oral Cavity ü Nasal Cavity ü Pharynx ü Epiglottis ü Larynx ü Trachea ü Diaphragm ü Lung ü Bronchus ü Bronchioles ü Alveolus ü Pulmonary
Respiratory System Structures of the Respiratory System include: ü Oral Cavity ü Nasal Cavity ü Pharynx ü Epiglottis ü Larynx ü Trachea ü Diaphragm ü Lung ü Bronchus ü Bronchioles ü Alveolus ü Pulmonary
Respiration. Chapter 39
 Respiration Chapter 39 Impacts, Issues Up in Smoke Smoking immobilizes ciliated cells and kills white blood cells that defend the respiratory system; highly addictive nicotine discourages quitting 39.1
Respiration Chapter 39 Impacts, Issues Up in Smoke Smoking immobilizes ciliated cells and kills white blood cells that defend the respiratory system; highly addictive nicotine discourages quitting 39.1
system. and then into the tissues. Diffusion of wastes such as Carbon Dioxide from tissues into blood and out of blood into the lungs.
 Respiratory System 1.Exchange Why do of we gases breathe? into the Think blood of all and the tissues. reasons Diffusion why we of Oxygen need a respiratory into blood from the lungs system. and then into
Respiratory System 1.Exchange Why do of we gases breathe? into the Think blood of all and the tissues. reasons Diffusion why we of Oxygen need a respiratory into blood from the lungs system. and then into
These two respiratory media (air & water) impose rather different constraints on oxygen uptake:
 Topic 19: OXYGEN UPTAKE AND TRANSPORT (lectures 29-30) OBJECTIVES: 1. Be able to compare air vs. water as a respiratory medium with respect to oxygen content, diffusion coefficient, viscosity and water
Topic 19: OXYGEN UPTAKE AND TRANSPORT (lectures 29-30) OBJECTIVES: 1. Be able to compare air vs. water as a respiratory medium with respect to oxygen content, diffusion coefficient, viscosity and water
Topic 13: Gas Exchange Ch. 42. Gas Exchange pp Gas Exchange. Gas Exchange in Fish pp Gas Exchange in Fish
 Topic 13: Gas Exchange Ch. 42 Fig. 42.24 Gas Exchange pp.979-989 Gas exchange involves the uptake of oxygen and the discharge of carbon dioxide (i.e. respiration or breathing). It is necessary for cellular
Topic 13: Gas Exchange Ch. 42 Fig. 42.24 Gas Exchange pp.979-989 Gas exchange involves the uptake of oxygen and the discharge of carbon dioxide (i.e. respiration or breathing). It is necessary for cellular
Section Two Diffusion of gases
 Section Two Diffusion of gases Lecture 5: Partial pressure and the composition of gasses in air. Factors affecting diffusion of gases. Ventilation perfusion ratio effect on alveolar gas concentration.
Section Two Diffusion of gases Lecture 5: Partial pressure and the composition of gasses in air. Factors affecting diffusion of gases. Ventilation perfusion ratio effect on alveolar gas concentration.
Glucose + Oxygen Carbon Dioxide + Water + Energy C6H12O CO2 + 6H20 + energy
 Cell Respiration - A food oxidization process in body cells to produce energy - Occurs (happens) in animal cells and plant cells Notes : Metabolic Reactions in Gaseous Exchange CELL RESPIRATION Photosynthesis
Cell Respiration - A food oxidization process in body cells to produce energy - Occurs (happens) in animal cells and plant cells Notes : Metabolic Reactions in Gaseous Exchange CELL RESPIRATION Photosynthesis
Introduction. Respiration. Chapter 10. Objectives. Objectives. The Respiratory System
 Introduction Respiration Chapter 10 The Respiratory System Provides a means of gas exchange between the environment and the body Plays a role in the regulation of acidbase balance during exercise Objectives
Introduction Respiration Chapter 10 The Respiratory System Provides a means of gas exchange between the environment and the body Plays a role in the regulation of acidbase balance during exercise Objectives
REVISION: GASEOUS EXCHANGE & EXCRETION 11 SEPTEMBER 2013
 REVISION: GASEOUS EXCHANGE & EXCRETION 11 SEPTEMBER 2013 Lesson Description In this lesson we: Revise gaseous exchange in different animals and examine the structure of the kidney Key Concepts Important
REVISION: GASEOUS EXCHANGE & EXCRETION 11 SEPTEMBER 2013 Lesson Description In this lesson we: Revise gaseous exchange in different animals and examine the structure of the kidney Key Concepts Important
Department of Biology Work Sheet Respiratory system,9 class
 I. Name the following : Department of Biology Work Sheet Respiratory system,9 class 1. A muscular sheet separating the thoracic and abdominal cavities. 2. A respiratory tube supported by cartilaginous
I. Name the following : Department of Biology Work Sheet Respiratory system,9 class 1. A muscular sheet separating the thoracic and abdominal cavities. 2. A respiratory tube supported by cartilaginous
Monday, ! Today: Respiratory system! 5/20/14! Transport of Blood! What we ve been covering! Circulatory system! Parts of blood! Heart! tubing!
 Monday, 5.19.14! What we ve been covering! Circulatory system! Parts of blood! Heart! tubing! Transport of Blood! What is transported! Nutrients! Oxygen! Carbon Dioxide! Hormones! Antibodies! What it is/does!
Monday, 5.19.14! What we ve been covering! Circulatory system! Parts of blood! Heart! tubing! Transport of Blood! What is transported! Nutrients! Oxygen! Carbon Dioxide! Hormones! Antibodies! What it is/does!
Chapter 13 The Respiratory System
 VI edit Pag 451-499 Chapter 13 The Respiratory System V edit. Pag 459-509 Tissue cell Alveoli of lungs Atmosphere 1 External respiration Ventilation or gas exchange between the atmosphere and air sacs
VI edit Pag 451-499 Chapter 13 The Respiratory System V edit. Pag 459-509 Tissue cell Alveoli of lungs Atmosphere 1 External respiration Ventilation or gas exchange between the atmosphere and air sacs
Respiratory Physiology Gaseous Exchange
 Respiratory Physiology Gaseous Exchange Session Objectives. What you will cover Basic anatomy of the lung including airways Breathing movements Lung volumes and capacities Compliance and Resistance in
Respiratory Physiology Gaseous Exchange Session Objectives. What you will cover Basic anatomy of the lung including airways Breathing movements Lung volumes and capacities Compliance and Resistance in
UNIT 9 - RESPIRATORY SYSTEM LECTURE NOTES
 UNIT 9 - RESPIRATORY SYSTEM LECTURE NOTES 9.01 GENERAL FUNCTIONS OF THE RESPIRATORY SYSTEM A. Brings oxygenated air to the alveoli B. Removes air containing carbon dioxide C. Filters, warms, and humidifies
UNIT 9 - RESPIRATORY SYSTEM LECTURE NOTES 9.01 GENERAL FUNCTIONS OF THE RESPIRATORY SYSTEM A. Brings oxygenated air to the alveoli B. Removes air containing carbon dioxide C. Filters, warms, and humidifies
Respiratory system & exercise. Dr. Rehab F Gwada
 Respiratory system & exercise Dr. Rehab F Gwada Objectives of lecture Outline the major anatomical components & important functions of the respiratory system. Describe the mechanics of ventilation. List
Respiratory system & exercise Dr. Rehab F Gwada Objectives of lecture Outline the major anatomical components & important functions of the respiratory system. Describe the mechanics of ventilation. List
IV. FROM AQUATIC TO ATMOSPHERIC BREATHING: THE TRACHEA & THE LUNG
 GAS EXCHANGE AND TRANSPORT I. INTRODUCTION: Heterotrophs oxidize carbon cmpds using O 2 to generate CO 2 & H 2 O. This is cellular respiration II. HOW GAS ENTERS A CELL A. The composition of air: 79% N
GAS EXCHANGE AND TRANSPORT I. INTRODUCTION: Heterotrophs oxidize carbon cmpds using O 2 to generate CO 2 & H 2 O. This is cellular respiration II. HOW GAS ENTERS A CELL A. The composition of air: 79% N
Chapter 17 The Respiratory System: Gas Exchange and Regulation of Breathing
 Chapter 17 The Respiratory System: Gas Exchange and Regulation of Breathing Overview of Pulmonary Circulation o Diffusion of Gases o Exchange of Oxygen and Carbon Dioxide o Transport of Gases in the Blood
Chapter 17 The Respiratory System: Gas Exchange and Regulation of Breathing Overview of Pulmonary Circulation o Diffusion of Gases o Exchange of Oxygen and Carbon Dioxide o Transport of Gases in the Blood
Respiratory Lecture Test Questions Set 3
 Respiratory Lecture Test Questions Set 3 1. The pressure of a gas: a. is inversely proportional to its volume b. is unaffected by temperature changes c. is directly proportional to its volume d. does not
Respiratory Lecture Test Questions Set 3 1. The pressure of a gas: a. is inversely proportional to its volume b. is unaffected by temperature changes c. is directly proportional to its volume d. does not
REVISION: GASEOUS EXCHANGE 24 SEPTEMBER 2014 Lesson Description
 REVISION: GASEOUS EXCHANGE 24 SEPTEMBER 2014 Lesson Description In this lesson, we revise: Gaseous Exchange in Plants & Animals Gaseous Exchange in Humans Excretion in Humans Focus on the Kidney Gaseous
REVISION: GASEOUS EXCHANGE 24 SEPTEMBER 2014 Lesson Description In this lesson, we revise: Gaseous Exchange in Plants & Animals Gaseous Exchange in Humans Excretion in Humans Focus on the Kidney Gaseous
Chapter 22 Gas Exchange
 Chapter 22 Gas Exchange PowerPoint Lectures for Biology: Concepts & Connections, Sixth Edition Campbell, Reece, Taylor, Simon, and Dickey Lecture by Edward J. Zalisko Introduction: Surviving in Thin Air
Chapter 22 Gas Exchange PowerPoint Lectures for Biology: Concepts & Connections, Sixth Edition Campbell, Reece, Taylor, Simon, and Dickey Lecture by Edward J. Zalisko Introduction: Surviving in Thin Air
Gas Exchange in Animals. Uptake of O2 from environment and discharge of CO2. Respiratory medium! water for aquatic animals, air for terrestial
 Gas Exchange in Animals Uptake of O2 from environment and discharge of CO2 Respiratory medium! water for aquatic animals, air for terrestial Respiratory surface! skin, gills, lungs Circulatory System O2/CO2
Gas Exchange in Animals Uptake of O2 from environment and discharge of CO2 Respiratory medium! water for aquatic animals, air for terrestial Respiratory surface! skin, gills, lungs Circulatory System O2/CO2
Respiration. Chapter 33
 Respiration Chapter 33 Learning Objectives: Understand the basis of gas exchange and factors that influence diffusion of gases in and out of tissues Compare and contrast different respiratory systems among
Respiration Chapter 33 Learning Objectives: Understand the basis of gas exchange and factors that influence diffusion of gases in and out of tissues Compare and contrast different respiratory systems among
Chapter 23: Respiratory System
 Chapter 23: Respiratory System I. Functions of the Respiratory System A. List and describe the five major functions of the respiratory system: 1. 2. 3. 4. 5. II. Anatomy and Histology of the Respiratory
Chapter 23: Respiratory System I. Functions of the Respiratory System A. List and describe the five major functions of the respiratory system: 1. 2. 3. 4. 5. II. Anatomy and Histology of the Respiratory
Respiratory System Homework
 Respiratory System Homework The R S is the body s breathing equipment. Similar to the D system, it takes S from outside the body (G, particularly O ), circulates them through the body to C and T, then
Respiratory System Homework The R S is the body s breathing equipment. Similar to the D system, it takes S from outside the body (G, particularly O ), circulates them through the body to C and T, then
Breathing and Exchange of Gases
 183 Breathing and Exchange of Gases 1. Skin is an accessory organ of respiration in (a) humans (b) frog (c) rabbit (d) lizard Frog has lungs as its main respiratory organs but during hibernation & aestivation
183 Breathing and Exchange of Gases 1. Skin is an accessory organ of respiration in (a) humans (b) frog (c) rabbit (d) lizard Frog has lungs as its main respiratory organs but during hibernation & aestivation
Life 23 - Respiration in Air Raven & Johnson Ch. 53 (part)
 1 Life 23 - Respiration in Air Raven & Johnson Ch. 53 (part) Objectives 1: Compare the properties of air and water as media for respiration, and the consequences for the evolution of respiratory systems
1 Life 23 - Respiration in Air Raven & Johnson Ch. 53 (part) Objectives 1: Compare the properties of air and water as media for respiration, and the consequences for the evolution of respiratory systems
Respiratory system. Role. Ventilation consists of 4 (5) steps : oxygen delivery and carbon dioxide elimination ph balance sound and voice formation
 Respiratory system Role oxygen delivery and carbon dioxide elimination ph balance sound and voice formation Ventilation consists of 4 (5) steps : 1. pulmonary ventilation gas exchange between lungs and
Respiratory system Role oxygen delivery and carbon dioxide elimination ph balance sound and voice formation Ventilation consists of 4 (5) steps : 1. pulmonary ventilation gas exchange between lungs and
Introduction THE RESPIRATORY SYSTEM
 Introduction THE RESPIRATORY SYSTEM 1 Lung Capacity The total lung capacity of fully grown healthy lungs is about 5-6 L of air, a person normally inhales and exhales about 0.5 L. Tidal Volume: amount of
Introduction THE RESPIRATORY SYSTEM 1 Lung Capacity The total lung capacity of fully grown healthy lungs is about 5-6 L of air, a person normally inhales and exhales about 0.5 L. Tidal Volume: amount of
GAS EXCHANGE & PHYSIOLOGY
 GAS EXCHANGE & PHYSIOLOGY Atmospheric Pressure Intra-Alveolar Pressure Inspiration 760 mm HG at Sea Level (= 1 atm) Pressure due to gases (N2, O2, CO2, Misc.) Pressure inside the alveolus (air sac) Phrenic
GAS EXCHANGE & PHYSIOLOGY Atmospheric Pressure Intra-Alveolar Pressure Inspiration 760 mm HG at Sea Level (= 1 atm) Pressure due to gases (N2, O2, CO2, Misc.) Pressure inside the alveolus (air sac) Phrenic
25/4/2016. Physiology #01 Respiratory system Nayef Garaibeh Rawan Alwaten
 25/4/2016 Physiology #01 Respiratory system Nayef Garaibeh Rawan Alwaten Respiratory System Introduction: - We breath while we are sleeping, talking, working and resting. - Respiratory diseases are abundant
25/4/2016 Physiology #01 Respiratory system Nayef Garaibeh Rawan Alwaten Respiratory System Introduction: - We breath while we are sleeping, talking, working and resting. - Respiratory diseases are abundant
Human gas exchange. Question Paper. Save My Exams! The Home of Revision. Cambridge International Examinations. 56 minutes. Time Allowed: Score: /46
 Human gas exchange Question Paper Level Subject Exam oard Topic Sub Topic ooklet O Level iology ambridge International Examinations Respiration Human gas exchange Question Paper Time llowed: 56 minutes
Human gas exchange Question Paper Level Subject Exam oard Topic Sub Topic ooklet O Level iology ambridge International Examinations Respiration Human gas exchange Question Paper Time llowed: 56 minutes
Page 1. Chapter 33: Respiration O 2 CO 2
 Chapter 33: Respiration O 2 CO 2 Features of Respiratory Systems: 1) Moist surface (to dissolve gas) 2) Thin cells lining surface 3) Large surface area contacting environment Facilitate Diffusion Methods
Chapter 33: Respiration O 2 CO 2 Features of Respiratory Systems: 1) Moist surface (to dissolve gas) 2) Thin cells lining surface 3) Large surface area contacting environment Facilitate Diffusion Methods
SCIENCE- NOTES. Q1. Draw the diagram of human respiratory system and explain the function of the following parts:
 SCIENCE- NOTES NAME: RESPIRATION IN ORGANISMS STD.VII DIV: Q1. Draw the diagram of human respiratory system and explain the function of the following parts: i. Nasal cavity ii. Trachea iii. Lungs iv. Bronchioles
SCIENCE- NOTES NAME: RESPIRATION IN ORGANISMS STD.VII DIV: Q1. Draw the diagram of human respiratory system and explain the function of the following parts: i. Nasal cavity ii. Trachea iii. Lungs iv. Bronchioles
Physiology Unit 4 RESPIRATORY PHYSIOLOGY
 Physiology Unit 4 RESPIRATORY PHYSIOLOGY In Physiology Today Respiration External respiration ventilation gas exchange Internal respiration cellular respiration gas exchange Respiratory Cycle Inspiration
Physiology Unit 4 RESPIRATORY PHYSIOLOGY In Physiology Today Respiration External respiration ventilation gas exchange Internal respiration cellular respiration gas exchange Respiratory Cycle Inspiration
Alveolus and Respiratory Membrane
 Alveolus and Respiratory Membrane thin membrane where gas exchange occurs in the lungs, simple squamous epithelium (Squamous cells have the appearance of thin, flat plates. They fit closely together in
Alveolus and Respiratory Membrane thin membrane where gas exchange occurs in the lungs, simple squamous epithelium (Squamous cells have the appearance of thin, flat plates. They fit closely together in
Respiratory system. Premedical - Biology
 Respiratory system Premedical - Biology Composition of atmosphere Nitrogen (N 2 ) 840 ppmv (78.084%) Oxygen (O 2 ) 209,460 ppmv (20.946%) Carbon dioxide (CO 2 ) 387 ppmv (0.0387%) Argon (Ar), Neon (Ne),
Respiratory system Premedical - Biology Composition of atmosphere Nitrogen (N 2 ) 840 ppmv (78.084%) Oxygen (O 2 ) 209,460 ppmv (20.946%) Carbon dioxide (CO 2 ) 387 ppmv (0.0387%) Argon (Ar), Neon (Ne),
2/28/18. Respiratory System. 1 Copyright 2016 by Elsevier Inc. All rights reserved. Introduction. Anatomy. Physiology. Respiratory System
 Introduction Respiratory System Chapter 28 Respiration: We inhale air, extract oxygen from it, exhale air Cardiovascular and respiratory systems work together Failure of either system: - Disruption of
Introduction Respiratory System Chapter 28 Respiration: We inhale air, extract oxygen from it, exhale air Cardiovascular and respiratory systems work together Failure of either system: - Disruption of
08 Respiration. #79 Respiration realeases energy from food
 08 Respiration #79 Respiration realeases energy from food Respiration is the chemical reactions that break down nutrient molecules in living cells to release energy. In humans, our cells need energy (ATP)
08 Respiration #79 Respiration realeases energy from food Respiration is the chemical reactions that break down nutrient molecules in living cells to release energy. In humans, our cells need energy (ATP)
Pop Quiz. What produces mucus, HCl and pepsinogen in the stomach? List a water soluable vitamin What is a ruminant stomach?
 Pop Quiz What produces mucus, HCl and pepsinogen in the stomach? List a water soluable vitamin What is a ruminant stomach? Respiratory System Review Cellular respiration: obtain glucose and oxygen, get
Pop Quiz What produces mucus, HCl and pepsinogen in the stomach? List a water soluable vitamin What is a ruminant stomach? Respiratory System Review Cellular respiration: obtain glucose and oxygen, get
Chapter 37: Pulmonary Ventilation. Chad & Angela
 Chapter 37: Pulmonary Ventilation Chad & Angela Respiratory Structures Basic Structures of Respiration Nasal/Oral Cavities Larynx Trachea Bronchi Secondary Bronchi Bronchioles Alveoli Mechanics of Ventilation
Chapter 37: Pulmonary Ventilation Chad & Angela Respiratory Structures Basic Structures of Respiration Nasal/Oral Cavities Larynx Trachea Bronchi Secondary Bronchi Bronchioles Alveoli Mechanics of Ventilation
Animal Systems: The Respiratory System
 Animal Systems: The Respiratory System Tissues, Organs, and Systems of Living Things Cells, Cell Division, and Animal Systems and Plant Systems Cell Specialization Human Systems The Digestive The Circulatory
Animal Systems: The Respiratory System Tissues, Organs, and Systems of Living Things Cells, Cell Division, and Animal Systems and Plant Systems Cell Specialization Human Systems The Digestive The Circulatory
Respiratory System 1
 Respiratory System 1 Outline Respiratory structures Gills Air-Breathing Animals Amphibians and Reptiles Mammals Birds Structures and Mechanisms of Breathing 2 Copyright The McGraw-Hill Companies, Inc.
Respiratory System 1 Outline Respiratory structures Gills Air-Breathing Animals Amphibians and Reptiles Mammals Birds Structures and Mechanisms of Breathing 2 Copyright The McGraw-Hill Companies, Inc.
The physiological functions of respiration and circulation. Mechanics. exercise 7. Respiratory Volumes. Objectives
 exercise 7 Respiratory System Mechanics Objectives 1. To explain how the respiratory and circulatory systems work together to enable gas exchange among the lungs, blood, and body tissues 2. To define respiration,
exercise 7 Respiratory System Mechanics Objectives 1. To explain how the respiratory and circulatory systems work together to enable gas exchange among the lungs, blood, and body tissues 2. To define respiration,
3/24/2009 LAB D.HAMMOUDI.MD. 1. Trachea 2. Thoracic wall 3. Lungs 4. Primary bronchi 5. Diaphragm
 RESPIRATORY PHYSIOLOGY LAB D.HAMMOUDI.MD 1. Trachea 2. Thoracic wall 3. Lungs 4. Primary bronchi 5. Diaphragm 1 KEY WORDS TO KNOW BOYLE S LAW INTERCOSTAL NERVES PHRENIC NERVE DIAPHRAGM EXTERNAL INTERCOSTAL
RESPIRATORY PHYSIOLOGY LAB D.HAMMOUDI.MD 1. Trachea 2. Thoracic wall 3. Lungs 4. Primary bronchi 5. Diaphragm 1 KEY WORDS TO KNOW BOYLE S LAW INTERCOSTAL NERVES PHRENIC NERVE DIAPHRAGM EXTERNAL INTERCOSTAL
BIOLOGY 12 - RESPIRATION - CHAPTER NOTES
 BIOLOGY 12 - RESPIRATION - CHAPTER NOTES We often think of respiration as just breathing. In fact, breathing is just one part of this physiological process. As biologists, we divide respiration up into
BIOLOGY 12 - RESPIRATION - CHAPTER NOTES We often think of respiration as just breathing. In fact, breathing is just one part of this physiological process. As biologists, we divide respiration up into
Section Three Gas transport
 Section Three Gas transport Lecture 6: Oxygen transport in blood. Carbon dioxide in blood. Objectives: i. To describe the carriage of O2 in blood. ii. iii. iv. To explain the oxyhemoglobin dissociation
Section Three Gas transport Lecture 6: Oxygen transport in blood. Carbon dioxide in blood. Objectives: i. To describe the carriage of O2 in blood. ii. iii. iv. To explain the oxyhemoglobin dissociation
Unit II Problem 4 Physiology: Diffusion of Gases and Pulmonary Circulation
 Unit II Problem 4 Physiology: Diffusion of Gases and Pulmonary Circulation - Physical principles of gases: Pressure of a gas is caused by the movement of its molecules against a surface (more concentration
Unit II Problem 4 Physiology: Diffusion of Gases and Pulmonary Circulation - Physical principles of gases: Pressure of a gas is caused by the movement of its molecules against a surface (more concentration
PARTS AND STRUCTURE OF THE RESPIRATORY SYSTEM
 PARTS AND STRUCTURE OF THE RESPIRATORY SYSTEM Parts of the Respiratory System The RS can be divided into two parts: 1. Respiratory Tract, (path that air follows). Nasal passage Pharynx Larynx Trachea Bronchi,
PARTS AND STRUCTURE OF THE RESPIRATORY SYSTEM Parts of the Respiratory System The RS can be divided into two parts: 1. Respiratory Tract, (path that air follows). Nasal passage Pharynx Larynx Trachea Bronchi,
1.2 The structure and functions of the cardio-respiratory system Learning objectives
 1.2 The structure and functions of the cardio-respiratory system Learning objectives To understand the functions of the circulatory system. To be able to identify the differences between veins, arteries
1.2 The structure and functions of the cardio-respiratory system Learning objectives To understand the functions of the circulatory system. To be able to identify the differences between veins, arteries
Respiratory Lecture Test Questions Set 1
 Respiratory Lecture Test Questions Set 1 1. The term "respiration" in its most complete meaning is: a. breathing b. oxygen transport c. carbon dioxide transport d. cellular energy production e. all of
Respiratory Lecture Test Questions Set 1 1. The term "respiration" in its most complete meaning is: a. breathing b. oxygen transport c. carbon dioxide transport d. cellular energy production e. all of
RESPIRATION III SEMESTER BOTANY MODULE II
 III SEMESTER BOTANY MODULE II RESPIRATION Lung Capacities and Volumes Tidal volume (TV) air that moves into and out of the lungs with each breath (approximately 500 ml) Inspiratory reserve volume (IRV)
III SEMESTER BOTANY MODULE II RESPIRATION Lung Capacities and Volumes Tidal volume (TV) air that moves into and out of the lungs with each breath (approximately 500 ml) Inspiratory reserve volume (IRV)
SCIENCE 8 RESPIRATION
 SCIENCE 8 RESPIRATION WHEN WE BREATHE, WHAT DO WE BREATHE IN? O2, N2, CO2, O3, NO2 (gas fumes), CO, pollutant, fragrants, toxins, etc. WHAT IS THE PURPOSE OF BREATHING IN? WHAT DOES OUR BODY WANT? O2 WHY?
SCIENCE 8 RESPIRATION WHEN WE BREATHE, WHAT DO WE BREATHE IN? O2, N2, CO2, O3, NO2 (gas fumes), CO, pollutant, fragrants, toxins, etc. WHAT IS THE PURPOSE OF BREATHING IN? WHAT DOES OUR BODY WANT? O2 WHY?
Directions: The following two questions refer to the diagram below, which shows a group of cells from the respiratory tract.
 Topic 7 Gas exchange in humans Directions: The following two questions refer to the diagram below, which shows a group of cells from the respiratory tract. X Y 1. What is the function of structure X? A.
Topic 7 Gas exchange in humans Directions: The following two questions refer to the diagram below, which shows a group of cells from the respiratory tract. X Y 1. What is the function of structure X? A.
Respiratory Anatomy and Physiology. Respiratory Anatomy. Function of the Respiratory System
 Respiratory Anatomy and Physiology Michaela Dixon Clinical Development Nurse PICU BRHFC Respiratory Anatomy Function of the Respiratory System - In conjunction with the cardiovascular system, to supply
Respiratory Anatomy and Physiology Michaela Dixon Clinical Development Nurse PICU BRHFC Respiratory Anatomy Function of the Respiratory System - In conjunction with the cardiovascular system, to supply
Respiratory Pulmonary Ventilation
 Respiratory Pulmonary Ventilation Pulmonary Ventilation Pulmonary ventilation is the act of breathing and the first step in the respiratory process. Pulmonary ventilation brings in air with a new supply
Respiratory Pulmonary Ventilation Pulmonary Ventilation Pulmonary ventilation is the act of breathing and the first step in the respiratory process. Pulmonary ventilation brings in air with a new supply
