UNIQUE CHARACTERISTICS OF THE PULMONARY CIRCULATION THE PULMONARY CIRCULATION MUST, AT ALL TIMES, ACCEPT THE ENTIRE CARDIAC OUTPUT
|
|
|
- Gertrude Bates
- 6 years ago
- Views:
Transcription
1 UNIQUE CHARACTERISTICS OF THE PULMONARY CIRCULATION THE PULMONARY CIRCULATION MUST, AT ALL TIMES, ACCEPT THE ENTIRE CARDIAC OUTPUT
2 UNIQUE CHARACTERISTICS OF THE PULMONARY CIRCULATION THE PULMONARY CIRCULATION MUST, AT ALL TIMES, ACCEPT THE ENTIRE CARDIAC OUTPUT THE PULMONARY CIRCULATION IS SUBSERVED BY A VENTRICLE THAT CANNOT GENERATE HIGH PRESSURE
3 UNIQUE CHARACTERISTICS OF THE PULMONARY CIRCULATION THE PULMONARY CIRCULATION MUST, AT ALL TIMES, ACCEPT THE ENTIRE CARDIAC OUTPUT THE PULMONARY CIRCULATION IS SUBSERVED BY A VENTRICLE THAT CANNOT GENERATE HIGH PRESSURE VASCULAR RESISTANCE IN THE PULMONARY CIRCULATION IS ONE- TENTH THAT OF THE SYSTEMIC CIRCULATION
4 UNIQUE CHARACTERISTICS OF THE PULMONARY CIRCULATION THE PULMONARY CIRCULATION MUST, AT ALL TIMES, ACCEPT THE ENTIRE CARDIAC OUTPUT THE PULMONARY CIRCULATION IS SUBSERVED BY A VENTRICLE THAT CANNOT GENERATE HIGH PRESSURE VASCULAR RESISTANCE IN THE PULMONARY CIRCULATION IS ONE- TENTH THAT OF THE SYSTEMIC CIRCULATION WITHIN THE PULMONARY CIRCULATION, BLOOD FLOW MUST BE DIRECTED TO WELL VENTILATED (OXYGENATED) ALVEOLI, THAT IS, VENTILATION MUST BE MATCHED WITH PERFUSION
5 PO 2 = 40 mm Hg PO 2 = 90 mm Hg
6
7 ALVEOLAR HYPOXIA!! Decreased O 2 tension PO 2 IS MAINTAINED BLOOD FLOW IS DIVERTED
8 If the hypoxic reflex fails or if there are no well ventilated lung units to divert to PO 2 will fall Decreased O 2 tension
9 Ventilation Perfusion V/Q Matching
10 How much oxygen is in the alveolus? What is normal? To answer this question we need to review the alveolar gas equation: P A O 2 = F i O 2 (P B -P H 2O ) P a CO 2 / R Where: P A O 2 = alveolar oxygen tension F i O 2 = the fraction of inspired oxygen P B -P H 2O = barometric water vapor pressure P a CO 2 = arterial carbon dioxide tension R = the respiratory quotient
11 How much oxygen is in the alveolus? What is normal? To answer this question we need to review the alveolar gas equation: P A O 2 = F i O 2 (P B -P H 2O ) P a CO 2 / R So: P A O 2 = 0.21 (760 mm Hg 47mm Hg) 40mm Hg/ 0.8 Thus: P A O 2 = 99 mm Hg normal P A O 2 is approximately 99 mm Hg The Sprague modification of the alveolar gas equation (room air only): P a CO 2 x1.25
12 How much oxygen is in the alveolus? How much is in the arterial blood? What is the alveolar arterial oxygen difference (A-aDO 2 ) What are normal blood gas values? ph = 7.35 to 7.45 units PCO 2 = 35 to 45 mm Hg PO 2 = >85 to 90 So what is the normal A-aDO 2? 10 to 15 mm Hg ON ROOM AIR
13 Case # 1: How do you approach the problem? The answer begins with Dalton s gas laws: #1; the pressure of a mixture of gasses equals the sum of the partial pressures of the constituent gasses. #2; so long as no chemical change occurs, each gas in a mixture of gasses is absorbed by a given volume of solvent in proportion not to the local pressure of the mixture, but to the partial pressure of that gas.
14 Case # 1: What does that mean? #1; the pressure of a mixture of gasses equals the sum of the partial pressures of the constituent gasses. In the alveolus, the mixture of gasses contains nitrogen, water vapor, trace gasses, oxygen and carbon dioxide. At the end of a breath, the pressure in the alveolus = atmospheric pressure. So.. P B =PN 2 + P H 2O + P trace gasses + PO 2 + PCO 2 Or.. PO 2 + PCO 2 = a constant
15 Case # 1: What does that mean? If PO 2 + PCO 2 = a constant, then what can we conclude would occur if the alveoli are inadequately ventilated? In the case of alveolar hypoventilation, what happens to the PCO 2? How do we detect this? If PO 2 + PCO 2 = a constant, then what happens if PCO 2 increases? How do you determine if the increase in PCO 2 explains the measured decrease in PO 2?
16 SOLVE THE ALVEOLAR GAS EQUATION! P A O 2 = F i O 2 (P B -P H 2O ) P a CO 2 / R So: P A O 2 = 0.21 (760 mm Hg 47mm Hg) 60mm Hg/ 0.8 Thus, under the best possible conditions: P A O 2 = 74 mm Hg The animal s : P a O 2 = 66 mm Hg, so what is the AaDO 2? The AaDO 2 = or 8 mm Hg So what can you do to save the animal?
17 Case # 2: How do you approach the problem? The answer begins with the alveolar gas equation: P A O 2 = F i O 2 (P B -P H 2O ) P a CO 2 / R So: P A O 2 = 0.21 (760 mm Hg 47mm Hg) 50 mm Hg/ 0.8 P A O 2 = 87 mm Hg The animal s : P a O 2 = 50 mm Hg, so what is the AaDO 2? The AaDO 2 = or 37 mm Hg Does decreased alveolar ventilation explain some or all of the observed reduction in P a O 2?
18 Something else is going on here! How would you figure it out? Maybe we have a problem with the distribution of blood flow in the lung, i.e., ventilation and perfusion are poorly matched. How would you approach that question?
19 The concept of VENOUS ADMIXTURE Venous admixture is said to occur when blood passes through the lung without being properly oxygenated. To let us use this idea, I propose that you consider Venous admixture to be divided into two types. These are termed V/Q MISMATCH and SHUNT Lets see which applies to our case
20 optimal V/Q = 1 V/Q = 1
21 COMPENSATION V/Q = 1 V/Q = 1
22 V/Q MISMATCH V/Q > 1 V/Q < 1 WHAT IF BLOOD FLOW DIVERSION FAILS?
23 Ventilation Perfusion V/Q Matching
24 Ventilation Perfusion V/Q Mismatch V Q
25 How would confirm that this is the mechanism responsible for the reduced oxygen tension in this case? What therapy would you employ? Provide a small amount of supplemental oxygen for the animal.
26 V/Q MISMATCH Response to supplemental oxygen A B V/Q > 1 V/Q < 1
27 alveolus A arterial point alveolus B
28 Case # 3: How do you approach the problem? Do you need the alveolar gas equation: P A O 2 = F i O 2 (P B -P H 2O ) P a CO 2 / R Does decreased alveolar ventilation explain some or all of the observed reduction in P a O 2?
29 Something else is going on here! How would you figure it out? Maybe we have a problem with the distribution of blood flow in the lung, i.e., ventilation and perfusion are poorly matched. How would you approach that question?
30 The concept of VENOUS ADMIXTURE Venous admixture is said to occur when blood passes through the lung without being properly oxygenated. To let us use this idea, I propose that you consider venous admixture to be divided into two types. These are termed V/Q MISMATCH and SHUNT Lets see which applies to our case
31 optimal V/Q = 1 V/Q = 1
32 COMPENSATION
33 SHUNT V/Q > 1 V/Q < 0 WHAT IF BLOOD FLOW DIVERSION FAILS?
34 How would confirm that this is the mechanism responsible for the reduced oxygen tension in this case? What therapy would you employ? Provide supplemental oxygen for the animal - 80% oxygen via mechanical ventilator.
35 Response to supplemental oxygen A B V/Q > 1 V/Q < 0
36 alveolus A arterial point alveolus B
37 Oh great, what do you do now? Can we convert shunt to V/Q mismatch? If so, how? Positive end expiratory pressure AKA; PEEP
38 SHUNT Response to PEEP and supplemental oxygen SHUNT is converted to V/Q mismatch A B V/Q > 1 V/Q < 1
39 RESPONSE TO SUPPLIMENTAL OXYGEN WHY PEEP IS SO VALUABLE alveolus A alveolus A alveolus B arterial point alveolus B arterial point SHUNT V/Q MISMATCH (SHUNT + PEEP)
I Physical Principles of Gas Exchange
 Respiratory Gases Exchange Dr Badri Paudel, M.D. 2 I Physical Principles of Gas Exchange 3 Partial pressure The pressure exerted by each type of gas in a mixture Diffusion of gases through liquids Concentration
Respiratory Gases Exchange Dr Badri Paudel, M.D. 2 I Physical Principles of Gas Exchange 3 Partial pressure The pressure exerted by each type of gas in a mixture Diffusion of gases through liquids Concentration
Lung Volumes and Capacities
 Lung Volumes and Capacities Normally the volume of air entering the lungs during a single inspiration is approximately equal to the volume leaving on the subsequent expiration and is called the tidal volume.
Lung Volumes and Capacities Normally the volume of air entering the lungs during a single inspiration is approximately equal to the volume leaving on the subsequent expiration and is called the tidal volume.
Section Two Diffusion of gases
 Section Two Diffusion of gases Lecture 5: Partial pressure and the composition of gasses in air. Factors affecting diffusion of gases. Ventilation perfusion ratio effect on alveolar gas concentration.
Section Two Diffusion of gases Lecture 5: Partial pressure and the composition of gasses in air. Factors affecting diffusion of gases. Ventilation perfusion ratio effect on alveolar gas concentration.
Respiration (revised 2006) Pulmonary Mechanics
 Respiration (revised 2006) Pulmonary Mechanics PUL 1. Diagram how pleural pressure, alveolar pressure, airflow, and lung volume change during a normal quiet breathing cycle. Identify on the figure the
Respiration (revised 2006) Pulmonary Mechanics PUL 1. Diagram how pleural pressure, alveolar pressure, airflow, and lung volume change during a normal quiet breathing cycle. Identify on the figure the
RESPIRATORY GAS EXCHANGE
 RESPIRATORY GAS EXCHANGE Alveolar PO 2 = 105 mmhg; Pulmonary artery PO 2 = 40 mmhg PO 2 gradient across respiratory membrane 65 mmhg (105 mmhg 40 mmhg) Results in pulmonary vein PO 2 ~100 mmhg Partial
RESPIRATORY GAS EXCHANGE Alveolar PO 2 = 105 mmhg; Pulmonary artery PO 2 = 40 mmhg PO 2 gradient across respiratory membrane 65 mmhg (105 mmhg 40 mmhg) Results in pulmonary vein PO 2 ~100 mmhg Partial
Respiratory Medicine. A-A Gradient & Alveolar Gas Equation Laboratory Diagnostics. Alveolar Gas Equation. See online here
 Respiratory Medicine A-A Gradient & Alveolar Gas Equation Laboratory Diagnostics See online here Alveolar gas equation helps to calculate the partial pressure of oxygen in alveoli and A-a gradient is the
Respiratory Medicine A-A Gradient & Alveolar Gas Equation Laboratory Diagnostics See online here Alveolar gas equation helps to calculate the partial pressure of oxygen in alveoli and A-a gradient is the
PICU Resident Self-Study Tutorial The Basic Physics of Oxygen Transport. I was told that there would be no math!
 Physiology of Oxygen Transport PICU Resident Self-Study Tutorial I was told that there would be no math! INTRODUCTION Christopher Carroll, MD Although cells rely on oxygen for aerobic metabolism and viability,
Physiology of Oxygen Transport PICU Resident Self-Study Tutorial I was told that there would be no math! INTRODUCTION Christopher Carroll, MD Although cells rely on oxygen for aerobic metabolism and viability,
Pulmonary Circulation Linda Costanzo Ph.D.
 Pulmonary Circulation Linda Costanzo Ph.D. OBJECTIVES: After studying this lecture, the student should understand: 1. The differences between pressures in the pulmonary and systemic circulations. 2. How
Pulmonary Circulation Linda Costanzo Ph.D. OBJECTIVES: After studying this lecture, the student should understand: 1. The differences between pressures in the pulmonary and systemic circulations. 2. How
Chapter 17 The Respiratory System: Gas Exchange and Regulation of Breathing
 Chapter 17 The Respiratory System: Gas Exchange and Regulation of Breathing Overview of Pulmonary Circulation o Diffusion of Gases o Exchange of Oxygen and Carbon Dioxide o Transport of Gases in the Blood
Chapter 17 The Respiratory System: Gas Exchange and Regulation of Breathing Overview of Pulmonary Circulation o Diffusion of Gases o Exchange of Oxygen and Carbon Dioxide o Transport of Gases in the Blood
660 mm Hg (normal, 100 mm Hg, room air) Paco, (arterial Pc02) 36 mm Hg (normal, 40 mm Hg) % saturation 50% (normal, 95%-100%)
 148 PHYSIOLOGY CASES AND PROBLEMS Case 26 Carbon Monoxide Poisoning Herman Neiswander is a 65-year-old retired landscape architect in northern Wisconsin. One cold January morning, he decided to warm his
148 PHYSIOLOGY CASES AND PROBLEMS Case 26 Carbon Monoxide Poisoning Herman Neiswander is a 65-year-old retired landscape architect in northern Wisconsin. One cold January morning, he decided to warm his
Rodney Shandukani 14/03/2012
 Rodney Shandukani 14/03/2012 OXYGEN THERAPY Aerobic metabolism accounts for 90% of Oxygen consumption by tissues. generates ATP by oxidative phosphorylation. Oxygen cascade: Oxygen exerts a partial pressure,
Rodney Shandukani 14/03/2012 OXYGEN THERAPY Aerobic metabolism accounts for 90% of Oxygen consumption by tissues. generates ATP by oxidative phosphorylation. Oxygen cascade: Oxygen exerts a partial pressure,
Section Three Gas transport
 Section Three Gas transport Lecture 6: Oxygen transport in blood. Carbon dioxide in blood. Objectives: i. To describe the carriage of O2 in blood. ii. iii. iv. To explain the oxyhemoglobin dissociation
Section Three Gas transport Lecture 6: Oxygen transport in blood. Carbon dioxide in blood. Objectives: i. To describe the carriage of O2 in blood. ii. iii. iv. To explain the oxyhemoglobin dissociation
Respiratory Physiology. Adeyomoye O.I
 Respiratory Physiology By Adeyomoye O.I Outline Introduction Hypoxia Dyspnea Control of breathing Ventilation/perfusion ratios Respiratory/barometric changes in exercise Intra-pulmonary & intra-pleural
Respiratory Physiology By Adeyomoye O.I Outline Introduction Hypoxia Dyspnea Control of breathing Ventilation/perfusion ratios Respiratory/barometric changes in exercise Intra-pulmonary & intra-pleural
Respiratory physiology II.
 Respiratory physiology II. Learning objectives: 29. Pulmonary gas exchange. 30. Oxygen transport in the blood. 31. Carbon-dioxide transport in the blood. 1 Pulmonary gas exchange The transport mechanism
Respiratory physiology II. Learning objectives: 29. Pulmonary gas exchange. 30. Oxygen transport in the blood. 31. Carbon-dioxide transport in the blood. 1 Pulmonary gas exchange The transport mechanism
AIIMS, New Delhi. Dr. K. K. Deepak, Prof. & HOD, Physiology AIIMS, New Delhi Dr. Geetanjali Bade, Asst. Professor AIIMS, New Delhi
 Course : PG Pathshala-Biophysics Paper 13 : Physiological Biophysics Module 17 : Gas transport and pulmonary circulation Principal Investigator: Co-Principal Investigator: Paper Coordinator: Content Writer:
Course : PG Pathshala-Biophysics Paper 13 : Physiological Biophysics Module 17 : Gas transport and pulmonary circulation Principal Investigator: Co-Principal Investigator: Paper Coordinator: Content Writer:
Respiratory System. Prepared by: Dorota Marczuk-Krynicka, MD, PhD
 Respiratory System Prepared by: Dorota Marczuk-Krynicka, MD, PhD Lungs: Ventilation Perfusion Gas Exchange - Diffusion 1. Airways and Airway Resistance (AWR) 2. Mechanics of Breathing and Lung (Elastic)
Respiratory System Prepared by: Dorota Marczuk-Krynicka, MD, PhD Lungs: Ventilation Perfusion Gas Exchange - Diffusion 1. Airways and Airway Resistance (AWR) 2. Mechanics of Breathing and Lung (Elastic)
CHAPTER 6. Oxygen Transport. Copyright 2008 Thomson Delmar Learning
 CHAPTER 6 Oxygen Transport Normal Blood Gas Value Ranges Table 6-1 OXYGEN TRANSPORT Oxygen Dissolved in the Blood Plasma Dissolve means that the gas maintains its precise molecular structure About.003
CHAPTER 6 Oxygen Transport Normal Blood Gas Value Ranges Table 6-1 OXYGEN TRANSPORT Oxygen Dissolved in the Blood Plasma Dissolve means that the gas maintains its precise molecular structure About.003
Respiratory System Physiology. Dr. Vedat Evren
 Respiratory System Physiology Dr. Vedat Evren Respiration Processes involved in oxygen transport from the atmosphere to the body tissues and the release and transportation of carbon dioxide produced in
Respiratory System Physiology Dr. Vedat Evren Respiration Processes involved in oxygen transport from the atmosphere to the body tissues and the release and transportation of carbon dioxide produced in
RESPIRATORY PHYSIOLOGY. Anaesthesiology Block 18 (GNK 586) Prof Pierre Fourie
 RESPIRATORY PHYSIOLOGY Anaesthesiology Block 18 (GNK 586) Prof Pierre Fourie Outline Ventilation Diffusion Perfusion Ventilation-Perfusion relationship Work of breathing Control of Ventilation 2 This image
RESPIRATORY PHYSIOLOGY Anaesthesiology Block 18 (GNK 586) Prof Pierre Fourie Outline Ventilation Diffusion Perfusion Ventilation-Perfusion relationship Work of breathing Control of Ventilation 2 This image
VENTILATION AND PERFUSION IN HEALTH AND DISEASE. Dr.HARIPRASAD VS
 VENTILATION AND PERFUSION IN HEALTH AND DISEASE Dr.HARIPRASAD VS Ventilation Total ventilation - total rate of air flow in and out of the lung during normal tidal breathing. Alveolar ventilation -represents
VENTILATION AND PERFUSION IN HEALTH AND DISEASE Dr.HARIPRASAD VS Ventilation Total ventilation - total rate of air flow in and out of the lung during normal tidal breathing. Alveolar ventilation -represents
By: Aseel Jamil Al-twaijer. Lec : physical principles of gas exchange
 By: Aseel Jamil Al-twaijer Lec : physical principles of gas exchange Date:30 /10/2017 this lecture is about the exchange of gases between the blood and the alveoli. I might add some external definitions
By: Aseel Jamil Al-twaijer Lec : physical principles of gas exchange Date:30 /10/2017 this lecture is about the exchange of gases between the blood and the alveoli. I might add some external definitions
Collin County Community College. Lung Physiology
 Collin County Community College BIOL. 2402 Anatomy & Physiology WEEK 9 Respiratory System 1 Lung Physiology Factors affecting Ventillation 1. Airway resistance Flow = Δ P / R Most resistance is encountered
Collin County Community College BIOL. 2402 Anatomy & Physiology WEEK 9 Respiratory System 1 Lung Physiology Factors affecting Ventillation 1. Airway resistance Flow = Δ P / R Most resistance is encountered
medical physiology :: Pulmonary Physiology in a Nutshell by:
 medical physiology :: Pulmonary Physiology in a Nutshell by: Johan H Koeslag Medical Physiology Stellenbosch University PO Box 19063 Tygerberg, 7505. South Africa Mail me INTRODUCTION The lungs are not
medical physiology :: Pulmonary Physiology in a Nutshell by: Johan H Koeslag Medical Physiology Stellenbosch University PO Box 19063 Tygerberg, 7505. South Africa Mail me INTRODUCTION The lungs are not
Physical Chemistry of Gases: Gas Exchange Linda Costanzo, Ph.D.
 Physical Chemistry of Gases: Gas Exchange Linda Costanzo, Ph.D. OBJECTIVES: After studying this lecture, the student should understand: 1. Application of the gas laws to pulmonary physiology. 2. How to
Physical Chemistry of Gases: Gas Exchange Linda Costanzo, Ph.D. OBJECTIVES: After studying this lecture, the student should understand: 1. Application of the gas laws to pulmonary physiology. 2. How to
Pulmonary Circulation
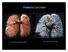 Pulmonary Circulation resin cast of pulmonary arteries resin cast of pulmonary veins Blood Flow to the Lungs Pulmonary Circulation Systemic Circulation Blood supply to the conducting zone provided by the
Pulmonary Circulation resin cast of pulmonary arteries resin cast of pulmonary veins Blood Flow to the Lungs Pulmonary Circulation Systemic Circulation Blood supply to the conducting zone provided by the
Chapter 4: Ventilation Test Bank MULTIPLE CHOICE
 Instant download and all chapters Test Bank Respiratory Care Anatomy and Physiology Foundations for Clinical Practice 3rd Edition Will Beachey https://testbanklab.com/download/test-bank-respiratory-care-anatomy-physiologyfoundations-clinical-practice-3rd-edition-will-beachey/
Instant download and all chapters Test Bank Respiratory Care Anatomy and Physiology Foundations for Clinical Practice 3rd Edition Will Beachey https://testbanklab.com/download/test-bank-respiratory-care-anatomy-physiologyfoundations-clinical-practice-3rd-edition-will-beachey/
Unit II Problem 4 Physiology: Diffusion of Gases and Pulmonary Circulation
 Unit II Problem 4 Physiology: Diffusion of Gases and Pulmonary Circulation - Physical principles of gases: Pressure of a gas is caused by the movement of its molecules against a surface (more concentration
Unit II Problem 4 Physiology: Diffusion of Gases and Pulmonary Circulation - Physical principles of gases: Pressure of a gas is caused by the movement of its molecules against a surface (more concentration
Gas exchange. Tissue cells CO2 CO 2 O 2. Pulmonary capillary. Tissue capillaries
 Gas exchange Pulmonary gas exchange Tissue gas exchange CO 2 O 2 O 2 Tissue cells CO2 CO 2 Pulmonary capillary O 2 O 2 CO 2 Tissue capillaries Physical principles of gas exchange Diffusion: continuous
Gas exchange Pulmonary gas exchange Tissue gas exchange CO 2 O 2 O 2 Tissue cells CO2 CO 2 Pulmonary capillary O 2 O 2 CO 2 Tissue capillaries Physical principles of gas exchange Diffusion: continuous
Let s talk about Capnography
 Let s talk about Capnography This is one of a series of articles by Keith Simpson BVSc MRCVS MIET (Electronics) discussing the practical aspects of some common monitoring techniques. Capnometry is the
Let s talk about Capnography This is one of a series of articles by Keith Simpson BVSc MRCVS MIET (Electronics) discussing the practical aspects of some common monitoring techniques. Capnometry is the
P215 Respiratory System, Part 2
 P15 Respiratory System, Part Gas Exchange Oxygen and Carbon Dioxide constant need for oxygen constant production of carbon dioxide exchange (and movement) lung alveoli pulmonary arteries pulmonary capillaries
P15 Respiratory System, Part Gas Exchange Oxygen and Carbon Dioxide constant need for oxygen constant production of carbon dioxide exchange (and movement) lung alveoli pulmonary arteries pulmonary capillaries
Circulatory And Respiration
 Circulatory And Respiration Composition Of Blood Blood Heart 200mmHg 120mmHg Aorta Artery Arteriole 50mmHg Capillary Bed Venule Vein Vena Cava Heart Differences Between Arteries and Veins Veins transport
Circulatory And Respiration Composition Of Blood Blood Heart 200mmHg 120mmHg Aorta Artery Arteriole 50mmHg Capillary Bed Venule Vein Vena Cava Heart Differences Between Arteries and Veins Veins transport
The physiological functions of respiration and circulation. Mechanics. exercise 7. Respiratory Volumes. Objectives
 exercise 7 Respiratory System Mechanics Objectives 1. To explain how the respiratory and circulatory systems work together to enable gas exchange among the lungs, blood, and body tissues 2. To define respiration,
exercise 7 Respiratory System Mechanics Objectives 1. To explain how the respiratory and circulatory systems work together to enable gas exchange among the lungs, blood, and body tissues 2. To define respiration,
Essential Skills Course Acute Care Module. Respiratory Day 2 (Arterial Blood Gases) Pre course Workbook
 Essential Skills Course Acute Care Module Respiratory Day 2 (Arterial Blood Gases) Pre course Workbook Acknowledgements This pre course workbook has been complied and updated with reference to the original
Essential Skills Course Acute Care Module Respiratory Day 2 (Arterial Blood Gases) Pre course Workbook Acknowledgements This pre course workbook has been complied and updated with reference to the original
Yanal. Jumana Jihad. Jamil Nazzal. 0 P a g e
 2 Yanal Jumana Jihad Jamil Nazzal 0 P a g e note: this sheet was written and corrected according to the records from section 2 so you may find differences in the arrangement of topics from the records
2 Yanal Jumana Jihad Jamil Nazzal 0 P a g e note: this sheet was written and corrected according to the records from section 2 so you may find differences in the arrangement of topics from the records
Chapter 13 The Respiratory System
 Chapter 13 The Respiratory System by Dr. Jay M. Templin Brooks/Cole - Thomson Learning Atmosphere Tissue cell External respiration Alveoli of lungs 1 Ventilation or gas exchange between the atmosphere
Chapter 13 The Respiratory System by Dr. Jay M. Templin Brooks/Cole - Thomson Learning Atmosphere Tissue cell External respiration Alveoli of lungs 1 Ventilation or gas exchange between the atmosphere
Vienna, Austria May 2005 MONITORING GAS EXCHANGE: FROM THEORY TO CLINICAL APPLICATION
 EUROANESTHESIA 2005 Vienna, Austria 28-31 May 2005 MONITORING GAS EXCHANGE: FROM THEORY TO CLINICAL APPLICATION 5RC2 OLA STENQVIST Department of Anaesthesia and Intensive Care Sahlgrenska University Hospital
EUROANESTHESIA 2005 Vienna, Austria 28-31 May 2005 MONITORING GAS EXCHANGE: FROM THEORY TO CLINICAL APPLICATION 5RC2 OLA STENQVIST Department of Anaesthesia and Intensive Care Sahlgrenska University Hospital
- How do the carotid bodies sense arterial blood gases? o The carotid bodies weigh 25mg, yet they have their own artery. This means that they have
 - How do the carotid bodies sense arterial blood gases? o The carotid bodies weigh 25mg, yet they have their own artery. This means that they have the highest blood flow of all organs, which makes them
- How do the carotid bodies sense arterial blood gases? o The carotid bodies weigh 25mg, yet they have their own artery. This means that they have the highest blood flow of all organs, which makes them
TV = Tidal volume (500ml) IRV = Inspiratory reserve volume (3,000 ml)
 By: Amin alajlouni Lec: 2nd record Date: 29/10/2017 First of all, this is my first sheet so excuse any mistakes I might make and let's start: As we said before in our last lecture about lung capacities
By: Amin alajlouni Lec: 2nd record Date: 29/10/2017 First of all, this is my first sheet so excuse any mistakes I might make and let's start: As we said before in our last lecture about lung capacities
Table of Contents. By Adam Hollingworth
 By Adam Hollingworth Table of Contents Oxygen Cascade... 2 Diffusion... 2 Laws of Diffusion... 2 Diffusion & Perfusion Limitations... 3 Oxygen Uptake Along Pulmon Capillary... 4 Measurement of Diffusing
By Adam Hollingworth Table of Contents Oxygen Cascade... 2 Diffusion... 2 Laws of Diffusion... 2 Diffusion & Perfusion Limitations... 3 Oxygen Uptake Along Pulmon Capillary... 4 Measurement of Diffusing
Physiological Basis of Mechanical Ventilation
 Physiological Basis of Mechanical Ventilation Wally Carlo, M.D. University of Alabama at Birmingham Department of Pediatrics Division of Neonatology wcarlo@peds.uab.edu Fine Tuning Mechanical Ventilation
Physiological Basis of Mechanical Ventilation Wally Carlo, M.D. University of Alabama at Birmingham Department of Pediatrics Division of Neonatology wcarlo@peds.uab.edu Fine Tuning Mechanical Ventilation
Respiratory System. Part 2
 Respiratory System Part 2 Respiration Exchange of gases between air and body cells Three steps 1. Ventilation 2. External respiration 3. Internal respiration Ventilation Pulmonary ventilation consists
Respiratory System Part 2 Respiration Exchange of gases between air and body cells Three steps 1. Ventilation 2. External respiration 3. Internal respiration Ventilation Pulmonary ventilation consists
The Physiologic Basis of DLCO testing. Brian Graham Division of Respirology, Critical Care and Sleep Medicine University of Saskatchewan
 The Physiologic Basis of DLCO testing Brian Graham Division of Respirology, Critical Care and Sleep Medicine University of Saskatchewan Objectives Review gas transport from inhaled gas to the rest of the
The Physiologic Basis of DLCO testing Brian Graham Division of Respirology, Critical Care and Sleep Medicine University of Saskatchewan Objectives Review gas transport from inhaled gas to the rest of the
 Question 1: Define vital capacity. What is its significance? Vital capacity is the maximum volume of air that can be exhaled after a maximum inspiration. It is about 3.5 4.5 litres in the human body. It
Question 1: Define vital capacity. What is its significance? Vital capacity is the maximum volume of air that can be exhaled after a maximum inspiration. It is about 3.5 4.5 litres in the human body. It
Respiratory Anatomy and Physiology. Respiratory Anatomy. Function of the Respiratory System
 Respiratory Anatomy and Physiology Michaela Dixon Clinical Development Nurse PICU BRHFC Respiratory Anatomy Function of the Respiratory System - In conjunction with the cardiovascular system, to supply
Respiratory Anatomy and Physiology Michaela Dixon Clinical Development Nurse PICU BRHFC Respiratory Anatomy Function of the Respiratory System - In conjunction with the cardiovascular system, to supply
82 Respiratory Tract NOTES
 82 Respiratory Tract NOTES RESPIRATORY TRACT The respiratory tract conducts air to the lungs where gaseous exchange occurs. It is separated into air-conducting and respiratory (where gas exchange occurs)
82 Respiratory Tract NOTES RESPIRATORY TRACT The respiratory tract conducts air to the lungs where gaseous exchange occurs. It is separated into air-conducting and respiratory (where gas exchange occurs)
ALVEOLAR - BLOOD GAS EXCHANGE 1
 ALVEOLAR - BLOOD GAS EXCHANGE 1 Summary: These notes examine the general means by which ventilation is regulated in terrestrial mammals. It then moves on to a discussion of what happens when someone over
ALVEOLAR - BLOOD GAS EXCHANGE 1 Summary: These notes examine the general means by which ventilation is regulated in terrestrial mammals. It then moves on to a discussion of what happens when someone over
Chapter 23. Gas Exchange and Transportation
 Chapter 23 Gas Exchange and Transportation What is air? Mixture of gasses 78.6 % nitrogen 20.9% oxygen 0.04% carbon dioxide 0 4% water vapor depending on temperature and humidity and minor gases argon,
Chapter 23 Gas Exchange and Transportation What is air? Mixture of gasses 78.6 % nitrogen 20.9% oxygen 0.04% carbon dioxide 0 4% water vapor depending on temperature and humidity and minor gases argon,
CHAPTER 3: The respiratory system
 CHAPTER 3: The respiratory system Practice questions - text book pages 56-58 1) When the inspiratory muscles contract, which one of the following statements is true? a. the size of the thoracic cavity
CHAPTER 3: The respiratory system Practice questions - text book pages 56-58 1) When the inspiratory muscles contract, which one of the following statements is true? a. the size of the thoracic cavity
Under pressure pushing down
 Under pressure pushing down on me When Dalton was conducting his studies, which led him to the atomic-molecular theory of matter, he also included studies of the behaviour of gases. These led him to propose,
Under pressure pushing down on me When Dalton was conducting his studies, which led him to the atomic-molecular theory of matter, he also included studies of the behaviour of gases. These led him to propose,
The Safe Use and Prescription of Medical Oxygen. Luke Howard
 The Safe Use and Prescription of Medical Oxygen Luke Howard Consultant Respiratory Physician Imperial College Healthcare NHS Trust & Co-Chair, British Thoracic Society Emergency Oxygen Guideline Group
The Safe Use and Prescription of Medical Oxygen Luke Howard Consultant Respiratory Physician Imperial College Healthcare NHS Trust & Co-Chair, British Thoracic Society Emergency Oxygen Guideline Group
DOWNLOAD OR READ : VENTILATION BLOOD FLOW AND DIFFUSION PDF EBOOK EPUB MOBI
 DOWNLOAD OR READ : VENTILATION BLOOD FLOW AND DIFFUSION PDF EBOOK EPUB MOBI Page 1 Page 2 ventilation blood flow and diffusion ventilation blood flow and pdf ventilation blood flow and diffusion Title:
DOWNLOAD OR READ : VENTILATION BLOOD FLOW AND DIFFUSION PDF EBOOK EPUB MOBI Page 1 Page 2 ventilation blood flow and diffusion ventilation blood flow and pdf ventilation blood flow and diffusion Title:
PROBLEM SET 9. SOLUTIONS April 23, 2004
 Harvard-MIT Division of Health Sciences and Technology HST.542J: Quantitative Physiology: Organ Transport Systems Instructors: Roger Mark and Jose Venegas MASSACHUSETTS INSTITUTE OF TECHNOLOGY Departments
Harvard-MIT Division of Health Sciences and Technology HST.542J: Quantitative Physiology: Organ Transport Systems Instructors: Roger Mark and Jose Venegas MASSACHUSETTS INSTITUTE OF TECHNOLOGY Departments
exchange of carbon dioxide and of oxygen between the blood and the air in
 M. M. HENRY WILLIAMS, JR.*Cardiorespiratory Laboratory, Grasslands WILLIAMS, JR.* Hospital, Valhalla, New York SOME APPLICATIONS OF PULMONARY PHYSIOLOGY TO CLINICAL MEDICINE During the past ten years a
M. M. HENRY WILLIAMS, JR.*Cardiorespiratory Laboratory, Grasslands WILLIAMS, JR.* Hospital, Valhalla, New York SOME APPLICATIONS OF PULMONARY PHYSIOLOGY TO CLINICAL MEDICINE During the past ten years a
Control of Respiration. Central Control of Ventilation
 Central Control of Goal: maintain sufficient ventilation with minimal energy Process steps: mechanics + aerodynamics Points of Regulation Breathing rate and depth, coughing, swallowing, breath holding
Central Control of Goal: maintain sufficient ventilation with minimal energy Process steps: mechanics + aerodynamics Points of Regulation Breathing rate and depth, coughing, swallowing, breath holding
Respiratory System Study Guide, Chapter 16
 Part I. Clinical Applications Name: Respiratory System Study Guide, Chapter 16 Lab Day/Time: 1. A person with ketoacidosis may hyperventilate. Explain why this occurs, and explain why this hyperventilation
Part I. Clinical Applications Name: Respiratory System Study Guide, Chapter 16 Lab Day/Time: 1. A person with ketoacidosis may hyperventilate. Explain why this occurs, and explain why this hyperventilation
Tter person TERM PAPER. Date: 30/4/ MEDICAL VENTILATOR
 Tter person TERM PAPER BM 600 Nuruddin Bahar Date: 30/4/2012 09002040 MEDICAL VENTILATOR It is an artificial ventilating device which is used to mechanically move breathable air in and out of lungs at
Tter person TERM PAPER BM 600 Nuruddin Bahar Date: 30/4/2012 09002040 MEDICAL VENTILATOR It is an artificial ventilating device which is used to mechanically move breathable air in and out of lungs at
Respiratory Physiology Gaseous Exchange
 Respiratory Physiology Gaseous Exchange Session Objectives. What you will cover Basic anatomy of the lung including airways Breathing movements Lung volumes and capacities Compliance and Resistance in
Respiratory Physiology Gaseous Exchange Session Objectives. What you will cover Basic anatomy of the lung including airways Breathing movements Lung volumes and capacities Compliance and Resistance in
GAS EXCHANGE & PHYSIOLOGY
 GAS EXCHANGE & PHYSIOLOGY Atmospheric Pressure Intra-Alveolar Pressure Inspiration 760 mm HG at Sea Level (= 1 atm) Pressure due to gases (N2, O2, CO2, Misc.) Pressure inside the alveolus (air sac) Phrenic
GAS EXCHANGE & PHYSIOLOGY Atmospheric Pressure Intra-Alveolar Pressure Inspiration 760 mm HG at Sea Level (= 1 atm) Pressure due to gases (N2, O2, CO2, Misc.) Pressure inside the alveolus (air sac) Phrenic
Respiratory Lecture Test Questions Set 3
 Respiratory Lecture Test Questions Set 3 1. The pressure of a gas: a. is inversely proportional to its volume b. is unaffected by temperature changes c. is directly proportional to its volume d. does not
Respiratory Lecture Test Questions Set 3 1. The pressure of a gas: a. is inversely proportional to its volume b. is unaffected by temperature changes c. is directly proportional to its volume d. does not
Blood Gas Interpretation
 Blood Gas Interpretation Pa O2 Saturation (SaO 2 ) Oxygen Therapy Monitoring Oxygen content (O( 2 Ct) Venous Oximetry Mixed venous oxygen saturation SvO 2 Surrogate for Systemic oxygen delivery and
Blood Gas Interpretation Pa O2 Saturation (SaO 2 ) Oxygen Therapy Monitoring Oxygen content (O( 2 Ct) Venous Oximetry Mixed venous oxygen saturation SvO 2 Surrogate for Systemic oxygen delivery and
Gas exchange and ventilation perfusion relationships in the lung
 ERJ Express. Published on July 28, 214 as doi: 1.1183/931936.3714 REVIEW IN PRESS CORRECTED PROOF Gas exchange and ventilation perfusion relationships in the lung Johan Petersson 1,2 and Robb W. Glenny
ERJ Express. Published on July 28, 214 as doi: 1.1183/931936.3714 REVIEW IN PRESS CORRECTED PROOF Gas exchange and ventilation perfusion relationships in the lung Johan Petersson 1,2 and Robb W. Glenny
Chapter 23. Gas Exchange and Transportation
 Chapter 23 Gas Exchange and Transportation What is air? Mixture of gasses 78.6 % nitrogen 20.9% oxygen 0.04% carbon dioxide 0 4% water vapor depending on temperature and humidity other minor gases argon,
Chapter 23 Gas Exchange and Transportation What is air? Mixture of gasses 78.6 % nitrogen 20.9% oxygen 0.04% carbon dioxide 0 4% water vapor depending on temperature and humidity other minor gases argon,
Capnography in the Veterinary Technician Toolbox. Katie Pinner BS, LVT Bush Advanced Veterinary Imaging Richmond, VA
 Capnography in the Veterinary Technician Toolbox Katie Pinner BS, LVT Bush Advanced Veterinary Imaging Richmond, VA What are Respiration and Ventilation? Respiration includes all those chemical and physical
Capnography in the Veterinary Technician Toolbox Katie Pinner BS, LVT Bush Advanced Veterinary Imaging Richmond, VA What are Respiration and Ventilation? Respiration includes all those chemical and physical
HCO - 3 H 2 CO 3 CO 2 + H H H + Breathing rate is regulated by blood ph and C02. CO2 and Bicarbonate act as a ph Buffer in the blood
 Breathing rate is regulated by blood ph and C02 breathing reduces plasma [CO2]; plasma [CO2] increases breathing. When C02 levels are high, breating rate increases to blow off C02 In low C02 conditions,
Breathing rate is regulated by blood ph and C02 breathing reduces plasma [CO2]; plasma [CO2] increases breathing. When C02 levels are high, breating rate increases to blow off C02 In low C02 conditions,
2. State the volume of air remaining in the lungs after a normal breathing.
 CLASS XI BIOLOGY Breathing And Exchange of Gases 1. Define vital capacity. What is its significance? Answer: Vital Capacity (VC): The maximum volume of air a person can breathe in after a forced expiration.
CLASS XI BIOLOGY Breathing And Exchange of Gases 1. Define vital capacity. What is its significance? Answer: Vital Capacity (VC): The maximum volume of air a person can breathe in after a forced expiration.
Exam Key. NROSCI/BIOSC 1070 and MSNBIO 2070 Exam # 2 October 28, 2016 Total POINTS: % of grade in class
 NROSCI/BIOSC 1070 and MSNBIO 2070 Exam # 2 October 28, 2016 Total POINTS: 100 20% of grade in class 1) An arterial blood sample for a patient at sea level is obtained, and the following physiological values
NROSCI/BIOSC 1070 and MSNBIO 2070 Exam # 2 October 28, 2016 Total POINTS: 100 20% of grade in class 1) An arterial blood sample for a patient at sea level is obtained, and the following physiological values
Some major points on the Effects of Hypoxia
 Some major points on the Effects of Hypoxia Source: Kings College London http://www.kcl.ac.uk/teares/gktvc/vc/dental/year1/lectures/rbmsmajorpoints/effectsofhypoxia.htm Cells obtain their energy from oxygen.
Some major points on the Effects of Hypoxia Source: Kings College London http://www.kcl.ac.uk/teares/gktvc/vc/dental/year1/lectures/rbmsmajorpoints/effectsofhypoxia.htm Cells obtain their energy from oxygen.
For more information about how to cite these materials visit
 Author(s): John G. Younger, M.D., 2009 License: Unless otherwise noted, this material is made available under the terms of the Creative Commons Attribution Share Alike 3.0 License: http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by-sa/3.0/
Author(s): John G. Younger, M.D., 2009 License: Unless otherwise noted, this material is made available under the terms of the Creative Commons Attribution Share Alike 3.0 License: http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by-sa/3.0/
birth: a transition better guidelines better outcomes the birth experience a challenging transition the fountains of life: 2/8/2018
 better guidelines better outcomes neonatal resuscitation Anne G. Wlodaver, MD neonatology OU medical center the birth experience a challenging transition birth requires major and sudden transitions some
better guidelines better outcomes neonatal resuscitation Anne G. Wlodaver, MD neonatology OU medical center the birth experience a challenging transition birth requires major and sudden transitions some
CHAPTER 3: The cardio-respiratory system
 : The cardio-respiratory system Exam style questions - text book pages 44-45 1) Describe the structures involved in gaseous exchange in the lungs and explain how gaseous exchange occurs within this tissue.
: The cardio-respiratory system Exam style questions - text book pages 44-45 1) Describe the structures involved in gaseous exchange in the lungs and explain how gaseous exchange occurs within this tissue.
Chapter 16 Respiration. Respiration. Steps in Respiration. Functions of the respiratory system
 Chapter 16 Respiration Functions of the respiratory system Respiration The term respiration includes 3 separate functions: Ventilation: Breathing. Gas exchange: Occurs between air and blood in the lungs.
Chapter 16 Respiration Functions of the respiratory system Respiration The term respiration includes 3 separate functions: Ventilation: Breathing. Gas exchange: Occurs between air and blood in the lungs.
Capnography. The Other Vital Sign. 3 rd Edition J. D Urbano, RCP, CRT Capnography The Other Vital Sign 3 rd Edition
 The Other Vital Sign 3 rd Edition Send questions or comments to: J. D Urbano, RCP, CRT BreathSounds jdurbano@breathsounds.org Visit Our Website: http://www.breathsounds.org Join Our Forum: http://www.breathsounds.org/reportroom/
The Other Vital Sign 3 rd Edition Send questions or comments to: J. D Urbano, RCP, CRT BreathSounds jdurbano@breathsounds.org Visit Our Website: http://www.breathsounds.org Join Our Forum: http://www.breathsounds.org/reportroom/
SIMULATION OF THE HUMAN LUNG. Noah D. Syroid, Volker E. Boehm, and Dwayne R. Westenskow
 SMULATON OF THE HUMAN LUNG Noah D. Syroid, Volker E. Boehm, and Dwayne R. Westenskow Abstract A human lung simulator was implemented using a model based on the Fick principle. The simulator is designed
SMULATON OF THE HUMAN LUNG Noah D. Syroid, Volker E. Boehm, and Dwayne R. Westenskow Abstract A human lung simulator was implemented using a model based on the Fick principle. The simulator is designed
RESPIRATORY REGULATION DURING EXERCISE
 RESPIRATORY REGULATION DURING EXERCISE Respiration Respiration delivery of oxygen to and removal of carbon dioxide from the tissue External respiration ventilation and exchange of gases in the lung Internal
RESPIRATORY REGULATION DURING EXERCISE Respiration Respiration delivery of oxygen to and removal of carbon dioxide from the tissue External respiration ventilation and exchange of gases in the lung Internal
Respiratory Physiology. ED Primary Teaching
 Respiratory Physiology ED Primary Teaching Functions of the respiratory system Gas exchange with O2 and CO2 Surfactant production Defence - IgA and macrophages Filer - pollutants and thromboembolism Metabolises
Respiratory Physiology ED Primary Teaching Functions of the respiratory system Gas exchange with O2 and CO2 Surfactant production Defence - IgA and macrophages Filer - pollutants and thromboembolism Metabolises
Ch. 14 The Behavior of Gases
 Ch. 14 The Behavior of Gases 14.1 PROPERTIES OF GASES Compressibility Compressibility: a measure of how much the volume of matter decreases under pressure Gases are easily compressed because of the spaces
Ch. 14 The Behavior of Gases 14.1 PROPERTIES OF GASES Compressibility Compressibility: a measure of how much the volume of matter decreases under pressure Gases are easily compressed because of the spaces
Respiration. The resspiratory system
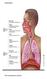 Respiration The resspiratory system The Alveoli The lungs have about 300 million alveoli, with a total crosssec onal area of 50 70 m2.. Each alveolar sac is surrounded by blood capillaries. The walls of
Respiration The resspiratory system The Alveoli The lungs have about 300 million alveoli, with a total crosssec onal area of 50 70 m2.. Each alveolar sac is surrounded by blood capillaries. The walls of
Respiration - Human 1
 Respiration - Human 1 At the end of the lectures on respiration you should be able to, 1. Describe events in the respiratory processes 2. Discuss the mechanism of lung ventilation in human 3. Discuss the
Respiration - Human 1 At the end of the lectures on respiration you should be able to, 1. Describe events in the respiratory processes 2. Discuss the mechanism of lung ventilation in human 3. Discuss the
Mechanical Ventilation
 PROCEDURE - Page 1 of 5 Purpose Scope Physician's Order Indications Procedure Mechanical Artificial Ventilation refers to any methods to deliver volumes of gas into a patient's lungs over an extended period
PROCEDURE - Page 1 of 5 Purpose Scope Physician's Order Indications Procedure Mechanical Artificial Ventilation refers to any methods to deliver volumes of gas into a patient's lungs over an extended period
4/18/12 MECHANISM OF RESPIRATION. Every Breath You Take. Fun Facts
 Objectives MECHANISM OF RESPIRATION Dr Badri Paudel Explain how the intrapulmonary and intrapleural pressures vary during ventilation and relate these pressure changes to Boyle s law. Define the terms
Objectives MECHANISM OF RESPIRATION Dr Badri Paudel Explain how the intrapulmonary and intrapleural pressures vary during ventilation and relate these pressure changes to Boyle s law. Define the terms
NROSCI/BIOSC 1070 and MSNBIO 2070 Exam # 2 October 28, 2016 Total POINTS: % of grade in class
 NROSCI/BIOSC 1070 and MSNBIO 2070 Exam # 2 October 28, 2016 Total POINTS: 100 20% of grade in class 1) An arterial blood sample for a patient at sea level is obtained, and the following physiological values
NROSCI/BIOSC 1070 and MSNBIO 2070 Exam # 2 October 28, 2016 Total POINTS: 100 20% of grade in class 1) An arterial blood sample for a patient at sea level is obtained, and the following physiological values
Gases and Respiration. Respiration Overview I
 Respiration Overview I Respiration Overview II Gas Laws Equation of State: PV = nrt Same volumes of different gases have same # of molecules BTPS: body temp, atmospheric pressure, saturated ATPS: ambient
Respiration Overview I Respiration Overview II Gas Laws Equation of State: PV = nrt Same volumes of different gases have same # of molecules BTPS: body temp, atmospheric pressure, saturated ATPS: ambient
Lung Volumes and Ventilation
 Respiratory System ssrisuma@rics.bwh.harvard.edu Lung Volumes and Ventilation Minute ventilation Volume of an inspired or expired air per minute = tidal volume (V T ) x respiratory rate Dead space ventilation
Respiratory System ssrisuma@rics.bwh.harvard.edu Lung Volumes and Ventilation Minute ventilation Volume of an inspired or expired air per minute = tidal volume (V T ) x respiratory rate Dead space ventilation
Respiratory Physiology
 chapter 4 Respiratory Physiology I. LUNG VOLUMES AND CAPACITIES A. Lung volumes (Figure 4-1) 1. Tidal volume (TV) is the volume inspired or expired with each normal breath. 2. Inspiratory reserve volume
chapter 4 Respiratory Physiology I. LUNG VOLUMES AND CAPACITIES A. Lung volumes (Figure 4-1) 1. Tidal volume (TV) is the volume inspired or expired with each normal breath. 2. Inspiratory reserve volume
Human gas exchange. Question Paper. Save My Exams! The Home of Revision. Cambridge International Examinations. 56 minutes. Time Allowed: Score: /46
 Human gas exchange Question Paper Level Subject Exam oard Topic Sub Topic ooklet O Level iology ambridge International Examinations Respiration Human gas exchange Question Paper Time llowed: 56 minutes
Human gas exchange Question Paper Level Subject Exam oard Topic Sub Topic ooklet O Level iology ambridge International Examinations Respiration Human gas exchange Question Paper Time llowed: 56 minutes
Blood gas adventures at various altitudes. Friedrich Luft Experimental and Clinical Research Center, Berlin-Buch
 Blood gas adventures at various altitudes Friedrich Luft Experimental and Clinical Research Center, Berlin-Buch Mount Everest 8848 M Any point in bird watching here? Respiration is gas exchange: the process
Blood gas adventures at various altitudes Friedrich Luft Experimental and Clinical Research Center, Berlin-Buch Mount Everest 8848 M Any point in bird watching here? Respiration is gas exchange: the process
Dalton s Law How is the total pressure of a mixture of gases related to the partial pressures of the component gases?
 Dalton s Law Chapter 4 The Behavior of Gases 4. Properties of Gases 4. The Gas Laws 4. Ideal Gases Dalton s Law How is the total pressure of a mixture of gases related to the partial pressures of the component
Dalton s Law Chapter 4 The Behavior of Gases 4. Properties of Gases 4. The Gas Laws 4. Ideal Gases Dalton s Law How is the total pressure of a mixture of gases related to the partial pressures of the component
Alveolus and Respiratory Membrane
 Alveolus and Respiratory Membrane thin membrane where gas exchange occurs in the lungs, simple squamous epithelium (Squamous cells have the appearance of thin, flat plates. They fit closely together in
Alveolus and Respiratory Membrane thin membrane where gas exchange occurs in the lungs, simple squamous epithelium (Squamous cells have the appearance of thin, flat plates. They fit closely together in
1.2 The structure and functions of the cardio-respiratory system Learning objectives
 1.2 The structure and functions of the cardio-respiratory system Learning objectives To understand the functions of the circulatory system. To be able to identify the differences between veins, arteries
1.2 The structure and functions of the cardio-respiratory system Learning objectives To understand the functions of the circulatory system. To be able to identify the differences between veins, arteries
Module Two. Objectives: Objectives cont. Objectives cont. Objectives cont.
 Transition to the New National EMS Education Standards: EMT-B B to EMT Module Two Objectives: Upon completion, each participant will do the following to a degree of accuracy that meets the Ntl EMS Education
Transition to the New National EMS Education Standards: EMT-B B to EMT Module Two Objectives: Upon completion, each participant will do the following to a degree of accuracy that meets the Ntl EMS Education
These two respiratory media (air & water) impose rather different constraints on oxygen uptake:
 Topic 19: OXYGEN UPTAKE AND TRANSPORT (lectures 29-30) OBJECTIVES: 1. Be able to compare air vs. water as a respiratory medium with respect to oxygen content, diffusion coefficient, viscosity and water
Topic 19: OXYGEN UPTAKE AND TRANSPORT (lectures 29-30) OBJECTIVES: 1. Be able to compare air vs. water as a respiratory medium with respect to oxygen content, diffusion coefficient, viscosity and water
PHYSIOLOGICAL REVIEW
 PHYSIOLOGICAL REVIEW Coordination of Ventilation and Perfusion* Richard M. Peters, M.D. N either ventilation of areas of the lung that are inadequately perfused with blood returning from the systemic venous
PHYSIOLOGICAL REVIEW Coordination of Ventilation and Perfusion* Richard M. Peters, M.D. N either ventilation of areas of the lung that are inadequately perfused with blood returning from the systemic venous
Respiratory Lecture Test Questions Set 1
 Respiratory Lecture Test Questions Set 1 1. The term "respiration" in its most complete meaning is: a. breathing b. oxygen transport c. carbon dioxide transport d. cellular energy production e. all of
Respiratory Lecture Test Questions Set 1 1. The term "respiration" in its most complete meaning is: a. breathing b. oxygen transport c. carbon dioxide transport d. cellular energy production e. all of
respiratory cycle. point in the volumes: 500 milliliters. for men. expiration, up to 1200 milliliters extra makes breathing Respiratory
 10 II. RESPIRATORY VOLUMES, CAPACITIES & PULMONARY FUNCTION TESTS Respiratory volume is the term used for various volumes of air moved by or associated with the lungs at a given point in the respiratory
10 II. RESPIRATORY VOLUMES, CAPACITIES & PULMONARY FUNCTION TESTS Respiratory volume is the term used for various volumes of air moved by or associated with the lungs at a given point in the respiratory
Office. Hypoxia. Or this. Or even this. Hypoxia E-1. COL Brian W. Smalley DO, MSPH, CPE
 Hypoxia Office COL Brian W. Smalley DO, MSPH, CPE Or this Or even this Hypoxia State of oxygen deficiency in the blood cells and tissues sufficient to cause impairment of function 4 Types Hypoxic Hypemic
Hypoxia Office COL Brian W. Smalley DO, MSPH, CPE Or this Or even this Hypoxia State of oxygen deficiency in the blood cells and tissues sufficient to cause impairment of function 4 Types Hypoxic Hypemic
Animal Physiology Prof. Mainak Das Department of Biological Sciences and Bioengineering Indian Institute of Technology, Kanpur. Module - 01 Lecture 28
 Animal Physiology Prof. Mainak Das Department of Biological Sciences and Bioengineering Indian Institute of Technology, Kanpur Module - 01 Lecture 28 Welcome back, so we are in to the Animal Physiology
Animal Physiology Prof. Mainak Das Department of Biological Sciences and Bioengineering Indian Institute of Technology, Kanpur Module - 01 Lecture 28 Welcome back, so we are in to the Animal Physiology
Under ideal conditions, the rates at which different gases diffuse (spread out) are proportional to their molar masses.
 Chemistry Ms. Ye Name Date Block Graham s Law of Diffusion- Under ideal conditions, the rates at which different gases diffuse (spread out) are proportional to their molar masses. In other words, gas molecules
Chemistry Ms. Ye Name Date Block Graham s Law of Diffusion- Under ideal conditions, the rates at which different gases diffuse (spread out) are proportional to their molar masses. In other words, gas molecules
VOLUNTARY BREATHHOLDING. I. PULMONARY GAS
 VOLUNTARY BREATHHOLDING. I. PULMONARY GAS EXCHANGE DURING BREATHHOLDING'1 By CHARLES D. STEVENS, EUGENE B. FERRIS, JOSEPH P. WEBB, GEORGE L. ENGEL, AND MYRTLE LOGAN (From the Departments of Internal Medicine
VOLUNTARY BREATHHOLDING. I. PULMONARY GAS EXCHANGE DURING BREATHHOLDING'1 By CHARLES D. STEVENS, EUGENE B. FERRIS, JOSEPH P. WEBB, GEORGE L. ENGEL, AND MYRTLE LOGAN (From the Departments of Internal Medicine
Explain how the structure of the gas exchange system of an insect ensures that there is a large surface area for gas exchange.
 1 Gas exchange takes place by diffusion. surfacearea differenceinconcentration diffusion lengthof diffusionpath a The diagram shows part of an insect tracheal system. i Explain how the structure of the
1 Gas exchange takes place by diffusion. surfacearea differenceinconcentration diffusion lengthof diffusionpath a The diagram shows part of an insect tracheal system. i Explain how the structure of the
Chapter 13 The Respiratory System
 VI edit Pag 451-499 Chapter 13 The Respiratory System V edit. Pag 459-509 Tissue cell Alveoli of lungs Atmosphere 1 External respiration Ventilation or gas exchange between the atmosphere and air sacs
VI edit Pag 451-499 Chapter 13 The Respiratory System V edit. Pag 459-509 Tissue cell Alveoli of lungs Atmosphere 1 External respiration Ventilation or gas exchange between the atmosphere and air sacs
