INTRODUCTION TO LESSON CLUSTER 4
|
|
|
- Steven Powers
- 6 years ago
- Views:
Transcription
1 INTRODUCTION TO LESSON CLUSTER 4 COMPRESSING AND EXPANDING AIR A. Lesson Cluster Goals and Lesson Objectives Goals Students should be able to explain the expansion and compression of gases (e.g., air) in molecular terms. Lesson Objectives Students should be able to: 4.1 Explain that molecules are constantly moving and hitting each other. 4.2 Explain why air in the syringe can be compressed, but water cannot. 4.3 Explain the various concentrations of air molecules at different altitudes. 4.4 Understand how to make a good explanation, using the example of a bicycle tire. B. Key Elements of a Good Description This is the first lesson cluster that focuses primarily on using the kinetic molecular theory to explain observable phenomena. Such explanation, however, will be the primary focus of all the remaining lesson clusters. In general, all good explanations using the kinetic molecular theory should do at least the following: a. Substances: Identify the substance that is responsible for the observable phenomenon that is being explained and describe the macroscopic changes that are taking place in that substance. b. Molecules: Describe the changes in molecules that are responsible for the macroscopic substances. For all of the phenomena in this lesson cluster, the key substances are gases that are being compressed or are expanding. Students should learn to explain both why air and other gases can be compressed and why they "push back" harder when they are compressed.
2 They can be compressed because the molecules of gases are relatively far apart, with lots of empty space between them. They push back harder when they are compressed because when molecules are pushed closer together, more of them hit the walls of the container, so the gas "pushes out" harder. C. Students' Conceptual Learning Constructing a complete molecular explanation for a phenomenon is a difficult process for many students. Some students do not even see why we would consider a discussion of molecules an "explanation," since students are used to explaining things by relating them to familiar ideas and events and the idea of molecules is not familiar or comfortable to them. Even students who are trying to construct molecular explanations for phenomena often find it very difficult. They may have difficulty identifying the key substance that is responsible for the change, focusing, for instance, on the bicycle tire rather than the air inside it. They may not know what is happening to the substance, or to the molecules that it is composed of, or they may not be able to explain the relationship between molecular events and macroscopic phenomena. This unit contains many observable phenomena; the students will need all of these opportunities and lots of help to master this difficult task. This lesson cluster builds in a variety of ways on ideas from earlier lesson clusters. In particular, students will need to use the ideas that all gases are substances made of molecules, and that those molecules are in constant motion, colliding with each other as well as with objects and the walls of whatever container holds a gas. This lesson cluster also introduces several new and different ideas associated with the compressibility of substances. On the macroscopic level, many students have had little experience with the compressibility of gases or the relative incompressibility of solids and liquids. Lesson 4.1 and 4.2 To understand compression or expansion of gases, students should recognize that gases are evenly distributed through the spaces they occupy. Since air is invisible, however, students often postulate that air is distributed unevenly in order to explain a phenomenon. The most common student misconception is that gases (e.g., air) move from one place to another when compressed or expanded. For instance, when air is compressed in a syringe, air stays around the opening of the syringe because air is pushed forward. In contrast, when air expands in the syringe, air stays around the plunger because air is pushed backward. In fact, the constant motion of molecules and their freedom to move any where in the gaseous state assures that they will generally be distributed evenly (actually randomly) throughout the space occupied by a gas. Compression of gases can be understood because of a molecular characteristic that most students are not aware of: Molecules of gases are relatively far apart and the spaces
3 between them are empty. Some students may not think in terms of spaces between molecules. Furthermore, the teacher should emphasize that air consists only of molecules with empty spaces between these molecules. In contrast to gases, solids and liquids cannot be compressed by ordinary means. Molecules of liquids and solids are fairly closely packed and in constant contact with each other, so solids and liquids are much harder to compress. However, students may simply think in terms of observable properties of water vs. air, such as, water is hard or water has more "stuff" in it. At the microscopic level, some may think that molecules are larger or harder in water than in air. Thus, the teacher should emphasize that the difference between the compression of air and water is due to the relative distance between molecules. (Those solids that can be compressed are generally porous, like sponges. It is the air pockets that are easily compressed, not the solid itself.) Lesson 4.3 The concentration of air varies at different altitudes. However, students may think that concentration of air is the same in a valley, at sea level, or in high mountains, and see no relationship to the compression or expansion of air in a syringe. The concentration of air, again, is due to relative spaces between molecules at different altitudes. It is probably not important in this unit to talk about air pressure, or the weight of the atmosphere. We are only using the examples in this lesson as additional ways of talking about how molecules are arranged in gases. The teacher should stress how concentration of air is related to the amount of air that our body needs: We need to breath harder at higher altitudes, because we take in less air with each breath.
4 D. Conceptual Contrasts The chart below contrasts common patterns in student thinking with scientific thinking about some of the important issues for this lesson cluster. Issue Goal Conceptions Students' Conceptions Distribution of gases Gases spread evenly through Distribution of gases is in space the spaces they occupy. uneven before or after expansion or compression. Compression of gases Gases can be compressed. Gases move from one region to another when compressed or expanded. Constant motion All molecules are constantly Molecules may sometimes moving. be still, especially in solids. Spaces between Gases consist of nothing except Molecules have "air" or other molecules molecules with empty spaces things between them. between them.
5 LESSON 4.1 EXPLAINING THINGS WITH MOLECULES PURPOSE: To help students explain that molecules are constantly moving and constantly hitting each other. ADVANCE PREPARATION: For this demonstration you will need a hair dryer, ping pong ball, and an inflated ball. Wind-chimes are optional. MATERIALS LIST: ping pong ball hair dryer inflated ball wind-chimes (optional) TEACHING SUGGESTIONS: 1. Have the students read the first three paragraphs of the lesson and discuss them. 2. Do the demonstrations. You will need a hair dryer with a round nozzle and a ping pong ball. When the hair dryer is pointed straight up it will support the ball in mid air. 3. Have the students answer the questions in the activity book and discuss them.
6 LESSON 4.2 COMPRESSING AIR PURPOSE: To help explain that a gas has molecules that are very far apart with large empty spaces between the molecules. The gas molecules can be pushed together. Liquids cannot be compressed because the molecules of liquids are already close together. MATERIALS LIST: For each group of students: syringe plastic cup water Transparency 7: What happens to air molecules when the plunger is pushed in? TEACHING SUGGESTIONS: If you anticipate that the students will use the syringes for water fights do not distribute the water until it is needed. 1. Introduce the lesson with Activity You might want to review the arrangement and motion of molecules in liquids and gases before the students read the Science Book.
7 Use transparency 7 here: TRANSPARENCY 7: WHAT HAPPENS TO AIR MOLECULES WHEN THE PLUNGER IS PUSHED IN? Bottom Layer Many students believe that air molecules will escape or try to escape when the plunger of a syringe is pushed in. Some think all or most of the molecules are pushed to the opening of the syringe. Overlay Students hold the above misconceptions because they do not understand the idea of compressibility of air. You should point out to students that molecules of air have large, empty spaces between them. This means that when air is compressed, molecules merely move closer together. The molecules remain evenly distributed and are not all at one end of the syringe.
8 LESSON 4.3 BREATHING THICK AIR AND THIN AIR PURPOSE: To help students describe the various concentration of air molecules at different altitudes and to use the kinetic molecular theory to explain compression of gases. ADVANCE PREPARATION: You may want to demonstrate compressed gas by using aerosol cans or a CO2 fire extinguisher. You may be able to find pictures of scuba divers or mountain climbers. MATERIALS LIST: Aerosol can or CO2 fire extinguisher (optional) TEACHING SUGGESTIONS: You can use aerosol cans to demonstrate the force with which compressed gas comes out of the can. Pictures of mountain climbers or deep sea divers using compressed air tanks may be useful in stimulating student interest and discussion. 1. Have the students read the Science Book and discuss the major ideas. 2. Then have the students do the Question Set Other examples of thick air and thin air: a. Commercial airline flights. Some students probably have flown on commercial airline flights; above 10,000 feet the air is too thin to breathe easily. The entire crew and passenger compartments are pressurized to provide people sufficient air to breathe. Federal regulations require that emergency oxygen masks be provided on commercial airliners that fly above 10,000 feet. b. Deep-sea divers This is a good time to review what students have learned in this lesson and draw out any remaining misconceptions.
9 You may have students try to explain, after having heard this explanation, how other phenomena work, such as the commercial airliners discussed at the beginning of this lesson.
10 LESSON 4.4 BICYCLE TIRES PURPOSE: The primary purpose of this lesson is to introduce students to a simple way of checking the quality of their explanations. A good explanation discusses both the substances that are changing and what is happening to the molecules of those substances. Students apply this rule to one situation: Pumping air into the bicycle tire. The rule will be used regularly throughout the rest of the unit. ADVANCE PREPARATION: (optional) You may want to pump up a bicycle tire as a demonstration. MATERIALS LIST: bicycle pump and tire (or entire bicycle) Transparency 8: Where does the air go when you pump it into a tire? Poster 1: To EXPLAIN things, ask TWO QUESTIONS TEACHING SUGGESTIONS: 1. Have students explain what happens when air goes into and out of the bicycle tire. 2. You should model applying the rule to check the quality of the explanations. 3. Discuss other situations with students applying the rule themselves. Use Poster 1 here:
11 Use Transparency 8 here: WHERE DOES THE AIR GO WHEN YOU PUMP IT INTO A TIRE? TRANSPARENCY 8: WHERE DOES THE AIR GO WHEN YOU PUMP IT INTO A TIRE? BOTTOM LAYER: OVERLAY: Many students feel that when you pump air into a tire, the air molecules stay right next to the valve system. They feel air simply goes "into the tire," and do not offer any further explanation. Students' naive ideas should be countered with the overlay. When air is pumped into a tire, the air molecules spread out until they are relatively evenly spaces. Thus, students should understand that the air "goes all over" or spreads evenly throughout the tire. SUGGESTIONS FOR ADDITIONAL ACTIVITIES: 1. Air pressure at sea level is about 15 pounds per square inch, and, the pressure of a gas is inversely proportional to its volume (i.e., doubling the pressure, halves the volume). Have students figure out what the pressure of the gas in a syringe is when the volume is reduces from 5 ml to 2.5 ml, to 1 ml, to 0.5 ml.
12 MATERIALS LIST CLUSTER 4, LESSONS Lesson 4.1: Lesson 4.2: Lesson 4.3: Lesson 4.4: ping pong ball inflated ball hair dryer wind chimes (optional) For each group: syringe plastic cup water Transparency 7 aerosol cans or CO2 fire extinguisher (optional) pictures of scuba divers or mountain climbers (optional) bicycle pump and tire (or entire bicycle - optional) Transparency 8 Poster 1
Chapter 12. Properties of Gases
 Properties of Gases Each state of matter has its own properties. Gases have unique properties because the distance between the particles of a gas is much greater than the distance between the particles
Properties of Gases Each state of matter has its own properties. Gases have unique properties because the distance between the particles of a gas is much greater than the distance between the particles
Practice Packet Unit 8: Gases
 Name: Regents Chemistry: Practice Packet Unit 8: Gases www.chempride.weebly.com Vocabulary: Absolute Zero: Avogadro s Hypothesis: (Normal) Boiling Point: Direct Relationship: Evaporating: Gas: Ideal Gas:
Name: Regents Chemistry: Practice Packet Unit 8: Gases www.chempride.weebly.com Vocabulary: Absolute Zero: Avogadro s Hypothesis: (Normal) Boiling Point: Direct Relationship: Evaporating: Gas: Ideal Gas:
Unit 9: Gas Laws REGENTS CHEMISTRY
 Name: Unit 9: Gas Laws REGENTS CHEMISTRY 1 Name: Unit 9: Gas Laws The concept of an ideal gas is a model to explain the behavior of gases. A real gas is most like an ideal gas when the real gas is at low
Name: Unit 9: Gas Laws REGENTS CHEMISTRY 1 Name: Unit 9: Gas Laws The concept of an ideal gas is a model to explain the behavior of gases. A real gas is most like an ideal gas when the real gas is at low
Unit 9 Packet: Gas Laws Introduction to Gas Laws Notes:
 Name: Unit 9 Packet: Gas Laws Introduction to Gas Laws Notes: Block: In chemistry, the relationships between gas physical properties are described as gas laws. Some of these properties are pressure, volume,
Name: Unit 9 Packet: Gas Laws Introduction to Gas Laws Notes: Block: In chemistry, the relationships between gas physical properties are described as gas laws. Some of these properties are pressure, volume,
Procedure 1: Volume vs. Pressure 1.) Using the lap tops, go to the Physics Education Technology from the University of Colorado at:
 Deriving the Gas Laws Background The gaseous state of matter consists of particles (gas molecules like oxygen, nitrogen, and carbon dioxide) which, according to the kinetic theory of gases, are in constant
Deriving the Gas Laws Background The gaseous state of matter consists of particles (gas molecules like oxygen, nitrogen, and carbon dioxide) which, according to the kinetic theory of gases, are in constant
8.1 Properties of Gases. Goal: Describe the Kinetic Molecular Theory of Gases and the units of measurement used for gases.
 Gases Chapter 8 Chapter 8 8.1 - Properties of Gases 8.2 Pressure and Volume (Boyle s Law) 8.3 Temperature and Volume (Charles Law) 8.4 Temperature and Pressure (Guy-Lussac s Law) 8.5 The Combined Gas Low
Gases Chapter 8 Chapter 8 8.1 - Properties of Gases 8.2 Pressure and Volume (Boyle s Law) 8.3 Temperature and Volume (Charles Law) 8.4 Temperature and Pressure (Guy-Lussac s Law) 8.5 The Combined Gas Low
Gases Chapter 8. Chapter 8
 Gases Chapter 8 Chapter 8 8.1 - Properties of Gases 8.2 Pressure and Volume (Boyle s Law) 8.3 Temperature and Volume (Charles Law) 8.4 Temperature and Pressure (Guy-Lussac s Law) 8.5 The Combined Gas Low
Gases Chapter 8 Chapter 8 8.1 - Properties of Gases 8.2 Pressure and Volume (Boyle s Law) 8.3 Temperature and Volume (Charles Law) 8.4 Temperature and Pressure (Guy-Lussac s Law) 8.5 The Combined Gas Low
Gases. Chapter 8. Chapter 8. Gases Properties of Gases. We are surrounded by gases, but we are often
 Gases Chapter 8 8.1 Properties of Gases Goal: Describe the Kinetic Molecular Theory of Gases and the units of measurement used for gases. Chapter 8 8.1 - Properties of Gases 8.2 Pressure and Volume (Boyle
Gases Chapter 8 8.1 Properties of Gases Goal: Describe the Kinetic Molecular Theory of Gases and the units of measurement used for gases. Chapter 8 8.1 - Properties of Gases 8.2 Pressure and Volume (Boyle
Practice(Packet( Chapter(5:(Gases( Practice(Packet:(Gases( ( Regents Chemistry: Dr. Shanzer ( ( ( ( ( ( ( ( ( ( ( ( ( ( ( ( ( ( ( ( ( ( ( ( ( ( ( (
 PracticePacket:Gases Regents Chemistry: Dr. Shanzer PracticePacket Chapter5:Gases http://drshanzerchemistry.weebly.com Gas Laws Regents Vocabulary 1. Vapor Pressure Table H) the pressure of the vapor above
PracticePacket:Gases Regents Chemistry: Dr. Shanzer PracticePacket Chapter5:Gases http://drshanzerchemistry.weebly.com Gas Laws Regents Vocabulary 1. Vapor Pressure Table H) the pressure of the vapor above
Practice Packet Unit 8: Gases
 Regents Chemistry: Mr. Palermo Practice Packet Unit 8: Gases Vocabulary: Lesson 1: Lesson 2: Lesson 3: Study Guide: 1 Vocabulary For each word, provide a short but specific definition from YOUR OWN BRAIN!
Regents Chemistry: Mr. Palermo Practice Packet Unit 8: Gases Vocabulary: Lesson 1: Lesson 2: Lesson 3: Study Guide: 1 Vocabulary For each word, provide a short but specific definition from YOUR OWN BRAIN!
Chapter 11 The Behavior of Gases
 Chapter 11 The Behavior of Gases 1 Section 11.1 The Properties of Gases Objectives: Explain why gases are easier to compress than solids or liquids are. Describe the three factors that affect gas pressure
Chapter 11 The Behavior of Gases 1 Section 11.1 The Properties of Gases Objectives: Explain why gases are easier to compress than solids or liquids are. Describe the three factors that affect gas pressure
Name Class Date. What are some properties of gases? How do changes of pressure, temperature, or volume affect a gas?
 CHAPTER 3 States of Matter 4 Behavior of Gases SECTION KEY IDEAS As you read this section, keep these questions in mind: What are some properties of gases? How do changes of pressure, temperature, or volume
CHAPTER 3 States of Matter 4 Behavior of Gases SECTION KEY IDEAS As you read this section, keep these questions in mind: What are some properties of gases? How do changes of pressure, temperature, or volume
Practice Packet: Gases. Regents Chemistry: Dr. Shanzer. Practice Packet. Chapter 5: Gases.
 Practice Packet: Gases Regents Chemistry: Dr. Shanzer Practice Packet Chapter 5: Gases http://drshanzerchemistry.weebly.com 8/30/15 The Kinetic Molecular Theory (KMT), Ideal vs Real gases & Avogadro s
Practice Packet: Gases Regents Chemistry: Dr. Shanzer Practice Packet Chapter 5: Gases http://drshanzerchemistry.weebly.com 8/30/15 The Kinetic Molecular Theory (KMT), Ideal vs Real gases & Avogadro s
Notes: Gas Laws (text Ch. 11)
 Name Per. Notes: Gas Laws (text Ch. 11) NOTE: This set of class notes is not complete. We will be filling in information in class. If you are absent, it is your responsibility to get missing information
Name Per. Notes: Gas Laws (text Ch. 11) NOTE: This set of class notes is not complete. We will be filling in information in class. If you are absent, it is your responsibility to get missing information
Gas Pressure. Pressure is the force exerted per unit area by gas molecules as they strike the surfaces around them.
 Chapter 5 Gases Gas Gases are composed of particles that are moving around very fast in their container(s). These particles moves in straight lines until they collides with either the container wall or
Chapter 5 Gases Gas Gases are composed of particles that are moving around very fast in their container(s). These particles moves in straight lines until they collides with either the container wall or
Honors Chemistry - Problem Set Chapter 13 Classify each of these statements as always true, AT; sometimes true, ST; or never true, NT.
 Honors Chemistry - Problem Set Chapter 13 Classify each of these statements as always true, AT; sometimes true, ST; or never true, NT. 1. Atmospheric pressure is 760 mm Hg. 2. The SI unit of pressure is
Honors Chemistry - Problem Set Chapter 13 Classify each of these statements as always true, AT; sometimes true, ST; or never true, NT. 1. Atmospheric pressure is 760 mm Hg. 2. The SI unit of pressure is
Chemistry 20 Unit 2 Gases FITB Notes. Topic A Characteristics of Gases
 Chemistry 20 Unit 2 Gases FITB Notes General Outcome: Topic A Characteristics of Gases We use technologies that were designed with the knowledge of the visible characteristics ( ) of gases ex. SCUBA equipment,
Chemistry 20 Unit 2 Gases FITB Notes General Outcome: Topic A Characteristics of Gases We use technologies that were designed with the knowledge of the visible characteristics ( ) of gases ex. SCUBA equipment,
Name: Chapter 13: Gases
 Name: Chapter 13: Gases Gases and gas behavior is one of the most important and most fun things to learn during your year in chemistry. Here are all of the gas notes and worksheets in two packets. We will
Name: Chapter 13: Gases Gases and gas behavior is one of the most important and most fun things to learn during your year in chemistry. Here are all of the gas notes and worksheets in two packets. We will
4. Using the kinetic molecular theory, explain why a gas can be easily compressed, while a liquid and a solid cannot?
 Name Period HW 1 Worksheet (Goals 1-4) - Kinetic Molecular Theory 1. Describe how gases, liquids, and solids compare using the following table. Solids Liquids Gases Volume (definite or indefinite) Molecular
Name Period HW 1 Worksheet (Goals 1-4) - Kinetic Molecular Theory 1. Describe how gases, liquids, and solids compare using the following table. Solids Liquids Gases Volume (definite or indefinite) Molecular
Talk Science Professional Development
 Talk Science Professional Development Transcript for Grade 5 Scientist Case: The Air, a Gas Investigations 1. The Air, a Gas Investigations Through the Eyes of a Scientist We met Dr. Lindley Winslow in
Talk Science Professional Development Transcript for Grade 5 Scientist Case: The Air, a Gas Investigations 1. The Air, a Gas Investigations Through the Eyes of a Scientist We met Dr. Lindley Winslow in
Students measure the change in pressure by varying the volume of trapped air in a syringe while:
 How Does a Trapped Gas Behave? Teacher Information Objective Students investigate the effect of changes in the volume of a confined gas on pressure at constant temperature. Using the pressure sensor, students
How Does a Trapped Gas Behave? Teacher Information Objective Students investigate the effect of changes in the volume of a confined gas on pressure at constant temperature. Using the pressure sensor, students
States of Matter. The Behavior of Gases
 States of Matter The Behavior of Gases What do you think? Read the two statements below and decide whether you agree or disagree with them. Place an A in the Before column if you agree with the statement
States of Matter The Behavior of Gases What do you think? Read the two statements below and decide whether you agree or disagree with them. Place an A in the Before column if you agree with the statement
Name /74. MULTIPLE CHOICE. Choose the one alternative that best completes the statement or answers the question.
 Ch 11 Gases STUDY GUIDE Accelerated Chemistry SCANTRON Name /74 MULTIPLE CHOICE. Choose the one alternative that best completes the statement or answers the question. 1) Which of the following statements
Ch 11 Gases STUDY GUIDE Accelerated Chemistry SCANTRON Name /74 MULTIPLE CHOICE. Choose the one alternative that best completes the statement or answers the question. 1) Which of the following statements
Guide for Reading. Vocabulary compressibility
 14.1 Properties of Gases Connecting to Your World In organized soccer, there are rules about equipment. For international competitions, the ball s mass must be not more than 450 grams and not less than
14.1 Properties of Gases Connecting to Your World In organized soccer, there are rules about equipment. For international competitions, the ball s mass must be not more than 450 grams and not less than
Kinetic Molecular Theory
 Kinetic Molecular Theory Name Period Unit 7 HW 1 Worksheet (Goals 1 & 2) 1. Describe how gases, liquids, and solids compare using the following table. Volume (definite or indefinite) Molecular Motion (high,
Kinetic Molecular Theory Name Period Unit 7 HW 1 Worksheet (Goals 1 & 2) 1. Describe how gases, liquids, and solids compare using the following table. Volume (definite or indefinite) Molecular Motion (high,
UNIT 2 FLUIDS PHYS:1200 LECTURE 12 FLUIDS (1)
 1 UNIT 2 FLUIDS PHYS:1200 LECTURE 12 FLUIDS (1) Lecture 12 is the first lecture on the new topic of fluids. Thus far we have been discussing the physics of ideal solid objects that do not change their
1 UNIT 2 FLUIDS PHYS:1200 LECTURE 12 FLUIDS (1) Lecture 12 is the first lecture on the new topic of fluids. Thus far we have been discussing the physics of ideal solid objects that do not change their
Gases. Edward Wen, PhD
 Gases Edward Wen, PhD Properties of Gases expand to completely fill their container take the shape of their container low density much less than solid or liquid state compressible when pressure is changed.
Gases Edward Wen, PhD Properties of Gases expand to completely fill their container take the shape of their container low density much less than solid or liquid state compressible when pressure is changed.
Chemistry: It s a gas
 Chemistry: It s a gas Part IV Molar mass of a gas Density of a gas Dalton s Law: high altitudes and scuba diving Kinetic Molecular Theory: fast gases are hot! I have a chemistry test on Friday, there is
Chemistry: It s a gas Part IV Molar mass of a gas Density of a gas Dalton s Law: high altitudes and scuba diving Kinetic Molecular Theory: fast gases are hot! I have a chemistry test on Friday, there is
Chapter 14-Gases. Dr. Walker
 Chapter 14-Gases Dr. Walker State of Matter Gases are one of the four states of matter along with solids, liquids, and plasma Conversion to Gases From liquids Evaporation Example: Boiling water From solids
Chapter 14-Gases Dr. Walker State of Matter Gases are one of the four states of matter along with solids, liquids, and plasma Conversion to Gases From liquids Evaporation Example: Boiling water From solids
Chemistry 51 Chapter 7 PROPERTIES OF GASES. Gases are the least dense and most mobile of the three phases of matter.
 ROERIES OF GASES Gases are the least dense and most mobile of the three phases of matter. articles of matter in the gas phase are spaced far apart from one another and move rapidly and collide with each
ROERIES OF GASES Gases are the least dense and most mobile of the three phases of matter. articles of matter in the gas phase are spaced far apart from one another and move rapidly and collide with each
Chapter 1, Lesson 5: Air, It s Really There
 Chapter 1, Lesson 5: Air, It s Really There Key Concepts In a gas, the particles (atoms and molecules) have weak attractions for one another. They are able to move freely past each other with little interaction
Chapter 1, Lesson 5: Air, It s Really There Key Concepts In a gas, the particles (atoms and molecules) have weak attractions for one another. They are able to move freely past each other with little interaction
Gas volume and pressure are indirectly proportional.
 Section 2 The Gas Laws Key Terms Boyle s law Charles s law combined gas law absolute zero Gay-Lussac s law Scientists have been studying physical properties of gases for hundreds of years In 1662, Robert
Section 2 The Gas Laws Key Terms Boyle s law Charles s law combined gas law absolute zero Gay-Lussac s law Scientists have been studying physical properties of gases for hundreds of years In 1662, Robert
DO NOT, under any circumstances, throw this away! This packet MUST be saved for the final exam.
 Name: Period: Unit 2 Packet Energy and States of Matter Unit 2 Packet Contents Sheet (This Paper!) Unit 2 Objectives Notes: Kinetic Molecular Theory of Gases- 3 pgs (with Behavior of Gases Reading, and
Name: Period: Unit 2 Packet Energy and States of Matter Unit 2 Packet Contents Sheet (This Paper!) Unit 2 Objectives Notes: Kinetic Molecular Theory of Gases- 3 pgs (with Behavior of Gases Reading, and
What happens to the mass and what happens to the weight of the liquid in the cup? decreases stays the same decreases stays the same
 1 cup contains hot liquid. Some of the liquid evaporates. What happens to the mass and what happens to the weight of the liquid in the cup? mass stays the same stays the same weight stays the same stays
1 cup contains hot liquid. Some of the liquid evaporates. What happens to the mass and what happens to the weight of the liquid in the cup? mass stays the same stays the same weight stays the same stays
CHAPTER 11: THE GASEOUS STATE
 CHAPTER 11: THE GASEOUS STATE DO Problems: 1-2, 3b, 4a, 5a, 6b, 7, 8a, 9-14, 17-20, 23-26, 29-42 11.1 Properties of Gases 1. Gases have indefinite shape take the shape of its container 2. Gases can expand
CHAPTER 11: THE GASEOUS STATE DO Problems: 1-2, 3b, 4a, 5a, 6b, 7, 8a, 9-14, 17-20, 23-26, 29-42 11.1 Properties of Gases 1. Gases have indefinite shape take the shape of its container 2. Gases can expand
Chapter 5. Pressure. Atmospheric Pressure. Gases. Force Pressure = Area
 Chapter 5 Gases Water for many homes is supplied by a well The pump removes air from the pipe, decreasing the air pressure in the pipe The pressure then pushes the water up the pipe Pressure Atmospheric
Chapter 5 Gases Water for many homes is supplied by a well The pump removes air from the pipe, decreasing the air pressure in the pipe The pressure then pushes the water up the pipe Pressure Atmospheric
9A Gas volume and pressure are indirectly proportional.
 The Gas Laws Key Terms Boyle s law Charles s law combined gas law absolute zero Gay-Lussac s law Scientists have been studying physical properties of gases for hundreds of years In 1662, Robert Boyle discovered
The Gas Laws Key Terms Boyle s law Charles s law combined gas law absolute zero Gay-Lussac s law Scientists have been studying physical properties of gases for hundreds of years In 1662, Robert Boyle discovered
CP Chapter 13/14 Notes The Property of Gases Kinetic Molecular Theory
 CP Chapter 13/14 Notes The Property of Gases Kinetic Molecular Theory Kinetic Molecular Theory of Gases The word kinetic refers to. Kinetic energy is the an object has because of its motion. Kinetic Molecular
CP Chapter 13/14 Notes The Property of Gases Kinetic Molecular Theory Kinetic Molecular Theory of Gases The word kinetic refers to. Kinetic energy is the an object has because of its motion. Kinetic Molecular
Gas Laws. Essential Learning Outcomes: 1. Change can be measured. 2. Changes can occur within a substance that alters its identity.
 Gas Laws Gas Laws: Gases and pressures affect our lives every day. From the weather we experience to the air we breathe, it all has to do with gases and pressures. Why do we have wind? Why do we have the
Gas Laws Gas Laws: Gases and pressures affect our lives every day. From the weather we experience to the air we breathe, it all has to do with gases and pressures. Why do we have wind? Why do we have the
ACTIVITY 1: Buoyancy Problems. OBJECTIVE: Practice and Reinforce concepts related to Fluid Pressure, primarily Buoyancy
 LESSON PLAN: SNAP, CRACKLE, POP: Submarine Buoyancy, Compression, and Rotational Equilibrium DEVELOPED BY: Bill Sanford, Nansemond Suffolk Academy 2012 NAVAL HISTORICAL FOUNDATION TEACHER FELLOWSHIP ACTIVITY
LESSON PLAN: SNAP, CRACKLE, POP: Submarine Buoyancy, Compression, and Rotational Equilibrium DEVELOPED BY: Bill Sanford, Nansemond Suffolk Academy 2012 NAVAL HISTORICAL FOUNDATION TEACHER FELLOWSHIP ACTIVITY
Unit 14 Gas Laws Funsheets
 Name: Period: Unit 14 Gas Laws Funsheets Part A: Vocabulary and Concepts- Answer the following questions. Refer to your notes and the PowerPoint for help. 1. List 5 different common uses for gases: a.
Name: Period: Unit 14 Gas Laws Funsheets Part A: Vocabulary and Concepts- Answer the following questions. Refer to your notes and the PowerPoint for help. 1. List 5 different common uses for gases: a.
The Kinetic-Molecular Theory of Gases based on the idea that particles are always in motion
 The Kinetic-Molecular Theory of Gases based on the idea that particles are always in motion Five assumptions: 1. Most of the volume occupied dby a gas is empty space 2. Collisions between gas particles
The Kinetic-Molecular Theory of Gases based on the idea that particles are always in motion Five assumptions: 1. Most of the volume occupied dby a gas is empty space 2. Collisions between gas particles
Gases. Name: Class: Date: Matching
 Name: Class: Date: Gases Matching Match each item with the correct statement below. a. Boyle's law d. Graham's law b. Charles's law e. Gay-Lussac's law c. Dalton's law f. ideal gas law 1. For a given mass
Name: Class: Date: Gases Matching Match each item with the correct statement below. a. Boyle's law d. Graham's law b. Charles's law e. Gay-Lussac's law c. Dalton's law f. ideal gas law 1. For a given mass
Worksheet 12 - Partial Pressures and the Kinetic Molecular Theory of Gases
 Worksheet 12 - Partial Pressures and the Kinetic olecular Theory of Gases Dalton's Law of Partial Pressures states that the sums of the pressures of each gas in the mixture add to give the total pressure
Worksheet 12 - Partial Pressures and the Kinetic olecular Theory of Gases Dalton's Law of Partial Pressures states that the sums of the pressures of each gas in the mixture add to give the total pressure
Temperature Temperature
 Temperature Temperature is a measure of how hot or cold an object is compared to another object. indicates that heat flows from the object with a higher temperature to the object with a lower temperature.
Temperature Temperature is a measure of how hot or cold an object is compared to another object. indicates that heat flows from the object with a higher temperature to the object with a lower temperature.
6.9B verify through investigations that thermal energy moves in a predictable pattern from warmer to cooler 6.5B recognize that a limited number of
 6.9B verify through investigations that thermal energy moves in a predictable pattern from warmer to cooler 6.5B recognize that a limited number of elements comprise the largest portion of oceans and atmosphere
6.9B verify through investigations that thermal energy moves in a predictable pattern from warmer to cooler 6.5B recognize that a limited number of elements comprise the largest portion of oceans and atmosphere
Properties of Air. Air Takes Up Space
 Properties of Air Air Takes Up Space Take an empty ziploc bag, open it and pull it through the air like a parachute. Now close it, seal it and try to squish the bag. There s nothing in the bag, right?
Properties of Air Air Takes Up Space Take an empty ziploc bag, open it and pull it through the air like a parachute. Now close it, seal it and try to squish the bag. There s nothing in the bag, right?
Chemistry Chapter 12. Characteristics of Gases. Characteristics of Gases 1/31/2012. Gases and Liquids
 Importance of Gases Chemistry Chapter 12 Gases and Liquids Airbags fill with N 2 gas in an accident. Gas is generated by the decomposition of sodium azide, NaN 3. 2 NaN 3 ---> 2 Na + 3 N 2 THREE STATES
Importance of Gases Chemistry Chapter 12 Gases and Liquids Airbags fill with N 2 gas in an accident. Gas is generated by the decomposition of sodium azide, NaN 3. 2 NaN 3 ---> 2 Na + 3 N 2 THREE STATES
INVESTIGATING GAS LAWS WORKSHEET - SCH 3U
 INESIGAING GAS LAWS WORKSHEE - SCH 3U Review: Convert the following. 30.0 C = K 55 F = C = K 255 cm 3 = L 5500 ml = m 3 799 mm Hg = kpa 155 kpa = lb/in 2 (1) BOYLE S LAW he Relationship between Pressure
INESIGAING GAS LAWS WORKSHEE - SCH 3U Review: Convert the following. 30.0 C = K 55 F = C = K 255 cm 3 = L 5500 ml = m 3 799 mm Hg = kpa 155 kpa = lb/in 2 (1) BOYLE S LAW he Relationship between Pressure
Chapter 13. Gases. Copyright Cengage Learning. All rights reserved 1
 Chapter 13 Gases Copyright Cengage Learning. All rights reserved 1 Section 13.1 Pressure Why study gases? An understanding of real world phenomena. An understanding of how science works. Copyright Cengage
Chapter 13 Gases Copyright Cengage Learning. All rights reserved 1 Section 13.1 Pressure Why study gases? An understanding of real world phenomena. An understanding of how science works. Copyright Cengage
Boyle s law Verifying the relation between air pressure and volume measuring air pressure in a closed container.
 Objective The purpose of this activity is to analyze the relationship between the pressure and volume of a confined gas at constant temperature, create a hypothesis and proceed to test it using the Labdisc
Objective The purpose of this activity is to analyze the relationship between the pressure and volume of a confined gas at constant temperature, create a hypothesis and proceed to test it using the Labdisc
Judith Herzfeld 1996,1998. These exercises are provided here for classroom and study use only. All other uses are copyright protected.
 Judith Herzfeld 1996,1998 These exercises are provided here for classroom and study use only. All other uses are copyright protected. 2.7-110 A yardstick laid on a table with a few inches hanging over
Judith Herzfeld 1996,1998 These exercises are provided here for classroom and study use only. All other uses are copyright protected. 2.7-110 A yardstick laid on a table with a few inches hanging over
Chapter 5: Gases 5.1 Pressure Why study gases? An understanding of real world phenomena. An understanding of how science works.
 Chapter 5: Gases 5.1 Pressure Why study gases? An understanding of real world phenomena. An understanding of how science works. A Gas Uniformly fills any container. Easily compressed. Mixes completely
Chapter 5: Gases 5.1 Pressure Why study gases? An understanding of real world phenomena. An understanding of how science works. A Gas Uniformly fills any container. Easily compressed. Mixes completely
Name Chemistry Pre-AP
 Name Chemistry Pre-AP Notes: Gas Laws and Gas Stoichiometry Period Part 1: The Nature of Gases and The Gas Laws I. Nature of Gases A. Kinetic-Molecular Theory The - theory was developed to account for
Name Chemistry Pre-AP Notes: Gas Laws and Gas Stoichiometry Period Part 1: The Nature of Gases and The Gas Laws I. Nature of Gases A. Kinetic-Molecular Theory The - theory was developed to account for
Lecture Handout 5: Gases (Online Text Chapter 6)
 Lecture Handout 5: Gases (Online Text Chapter 6) I. The Structure of a Gas A. Gases are composed of particles that are flying around very fast in their container(s). 1. The particles travel in straight
Lecture Handout 5: Gases (Online Text Chapter 6) I. The Structure of a Gas A. Gases are composed of particles that are flying around very fast in their container(s). 1. The particles travel in straight
CHM111 Lab Gas Laws Grading Rubric
 Name Team Name CHM111 Lab Gas Laws Grading Rubric Criteria Points possible Points earned Lab Performance Printed lab handout and rubric was brought to lab 3 Safety and proper waste disposal procedures
Name Team Name CHM111 Lab Gas Laws Grading Rubric Criteria Points possible Points earned Lab Performance Printed lab handout and rubric was brought to lab 3 Safety and proper waste disposal procedures
Experiment #12. Gas Laws.
 Goal To observe gas laws in the laboratory. Experiment #12. Gas Laws. Introduction All ideal gases, regardless of molar mass or chemical properties, follow the same gas laws under most conditions. Gas
Goal To observe gas laws in the laboratory. Experiment #12. Gas Laws. Introduction All ideal gases, regardless of molar mass or chemical properties, follow the same gas laws under most conditions. Gas
Quantitative Properties of Gases. 1. Amount (mass or moles) 2. Volume 3. Pressure 4. Temperature
 Chapter 2 Gases Quantitative Properties of Gases 1. Amount (mass or moles) 2. Volume 3. Pressure 4. Temperature Kinetic Molecular Theory: (Video) Smallest particles (atoms, ions or molecules) of a substance
Chapter 2 Gases Quantitative Properties of Gases 1. Amount (mass or moles) 2. Volume 3. Pressure 4. Temperature Kinetic Molecular Theory: (Video) Smallest particles (atoms, ions or molecules) of a substance
Bernoulli s Principle at Work
 Diagram of demonstration Denise Winkler and Kim Brown July 25, 2003 Bernoulli s Principle at Work *Airflow should be straight on the edge of the airfoil. pivot rod airflow counter weight support rod airfoil
Diagram of demonstration Denise Winkler and Kim Brown July 25, 2003 Bernoulli s Principle at Work *Airflow should be straight on the edge of the airfoil. pivot rod airflow counter weight support rod airfoil
THE GAS STATE. Unit 4. CHAPTER KEY TERMS HOME WORK 9.1 Kinetic Molecular Theory States of Matter Solid, Liquid, gas.
 Unit 4 THE GAS STATE CHAPTER KEY TERMS HOME WORK 9. Kinetic Molecular Theory States of Matter Solid, Liquid, gas Page 4 # to 4 9. Boyles Law P α /V PV = Constant P V = P V Pressure Atmospheric Pressure
Unit 4 THE GAS STATE CHAPTER KEY TERMS HOME WORK 9. Kinetic Molecular Theory States of Matter Solid, Liquid, gas Page 4 # to 4 9. Boyles Law P α /V PV = Constant P V = P V Pressure Atmospheric Pressure
You should be able to: Describe Equipment Barometer Manometer. 5.1 Pressure Read and outline 5.1 Define Barometer
 A P CHEMISTRY - Unit 5: Gases Unit 5: Gases Gases are distinguished from other forms of matter, not only by their power of indefinite expansion so as to fill any vessel, however large, and by the great
A P CHEMISTRY - Unit 5: Gases Unit 5: Gases Gases are distinguished from other forms of matter, not only by their power of indefinite expansion so as to fill any vessel, however large, and by the great
Gases Chapter 11 (and 10)
 Gases Chapter 11 (and 10) Warm up 1. What is a gas? 2. What is pressure? 3. What units are used to measure pressure? Properties of Gas Expansion: indefinite shape and volume Fluidity: particle move pass
Gases Chapter 11 (and 10) Warm up 1. What is a gas? 2. What is pressure? 3. What units are used to measure pressure? Properties of Gas Expansion: indefinite shape and volume Fluidity: particle move pass
Kinetic-Molecular Theory
 GASES Chapter Eleven Kinetic-Molecular Theory! Recall that our only previous description of gases stated that gases completely fill and take the shape of their containers.! The Kinetic-Molecular Theory
GASES Chapter Eleven Kinetic-Molecular Theory! Recall that our only previous description of gases stated that gases completely fill and take the shape of their containers.! The Kinetic-Molecular Theory
B. As the gas particles move and strike a surface, they push on that surface 1. If we could measure the total amount of force exerted by gas
 Chapter 5: Gases I. The Structure of a Gas A. Gases are composed of particles that are flying around very fast in their container(s). 1. The particles travel in straight lines until they encounter either
Chapter 5: Gases I. The Structure of a Gas A. Gases are composed of particles that are flying around very fast in their container(s). 1. The particles travel in straight lines until they encounter either
IT S A GAS
 IT S A GAS IT S A GAS The Nature of Gases Gases have some interesting characteristics that have fascinated scientists for 300 years. The first gas to be studied was air & it was a long time before it was
IT S A GAS IT S A GAS The Nature of Gases Gases have some interesting characteristics that have fascinated scientists for 300 years. The first gas to be studied was air & it was a long time before it was
Matter is made up of particles which are in continual random motion Misconception: Only when a substance is in its liquid or gas state do its
 Kinetic Theory of Matter Matter is made up of particles which are in continual random motion Misconception: Only when a substance is in its liquid or gas state do its particles move because in these two
Kinetic Theory of Matter Matter is made up of particles which are in continual random motion Misconception: Only when a substance is in its liquid or gas state do its particles move because in these two
Honors Chemistry Unit 7 Gas Laws Notes
 Honors Chemistry Unit 7 Gas Laws Notes Kinetic Molecular Theory 1. List the five assumptions: Assumption Description Extra Info 1 Basically means: the particles themselves have compared to the space between
Honors Chemistry Unit 7 Gas Laws Notes Kinetic Molecular Theory 1. List the five assumptions: Assumption Description Extra Info 1 Basically means: the particles themselves have compared to the space between
End of Chapter Exercises
 End of Chapter Exercises Exercises 1 12 are conceptual questions that are designed to see if you have understood the main concepts of the chapter. 1. While on an airplane, you take a drink from your water
End of Chapter Exercises Exercises 1 12 are conceptual questions that are designed to see if you have understood the main concepts of the chapter. 1. While on an airplane, you take a drink from your water
STUDENT ACTIVITY: Looking at water solid, liquid or gas
 Activity idea STUDENT ACTIVITY: Looking at water In this activity, students use water to explore its properties as a. By the end of this activity, students should be able to: identify one or more characteristics
Activity idea STUDENT ACTIVITY: Looking at water In this activity, students use water to explore its properties as a. By the end of this activity, students should be able to: identify one or more characteristics
THE BEHAVIOR OF GASES
 14 THE BEHAVIOR OF GASES SECTION 14.1 PROPERTIES OF GASES (pages 413 417) This section uses kinetic theory to explain the properties of gases. This section also explains how gas pressure is affected by
14 THE BEHAVIOR OF GASES SECTION 14.1 PROPERTIES OF GASES (pages 413 417) This section uses kinetic theory to explain the properties of gases. This section also explains how gas pressure is affected by
Kinetic Molecular Theory Gases. Behavior of gases. Postulate two. Postulate one. Postulate three. Postulate four
 Kinetic Molecular Theory Gases Gas particles are so small that their individual volume can be considered to be negligible Gas particles are in constant motion and the collisions of the particles with the
Kinetic Molecular Theory Gases Gas particles are so small that their individual volume can be considered to be negligible Gas particles are in constant motion and the collisions of the particles with the
Name Date Class CHAPTER ASSESSMENT. 1. Equal volumes of gases at the same temperature and pressure contain equal numbers of particles.
 Name ate lass HPTER 14 HPTER SSESSMENT Gases Reviewing Vocabulary Match the definition in olumn with the term in olumn. olumn 1. Equal volumes of gases at the same temperature and pressure contain equal
Name ate lass HPTER 14 HPTER SSESSMENT Gases Reviewing Vocabulary Match the definition in olumn with the term in olumn. olumn 1. Equal volumes of gases at the same temperature and pressure contain equal
When comparing two real gases at the same conditions, the one with the smaller particles is more ideal.
 Gas BASICS Gases are the most fun phases because mostly they are invisible and you have to use your measuring and wits to grasp how perfect they are. You already know that gases follow the Kinetic Molecular
Gas BASICS Gases are the most fun phases because mostly they are invisible and you have to use your measuring and wits to grasp how perfect they are. You already know that gases follow the Kinetic Molecular
CHEM 355 EXPERIMENT 7. Viscosity of gases: Estimation of molecular diameter
 CHEM 355 EXPERIMENT 7 Viscosity of gases: Estimation of molecular diameter Expressed most simply, the viscosity of a fluid (liquid or gas) relates to its resistance to flow. The viscosity of a gas is determined
CHEM 355 EXPERIMENT 7 Viscosity of gases: Estimation of molecular diameter Expressed most simply, the viscosity of a fluid (liquid or gas) relates to its resistance to flow. The viscosity of a gas is determined
Unit 8: Gases and States of Matter
 Unit 8: Gases and States of Matter Gases Particles that have no definite shape or volume. They adapt to the shape and volume of their container. Ideal gases are imaginary gases that comply with all the
Unit 8: Gases and States of Matter Gases Particles that have no definite shape or volume. They adapt to the shape and volume of their container. Ideal gases are imaginary gases that comply with all the
States of Matter. About the. 30 Chapter 2. Matter exists in various physical states, which are determined by the movement of the matter s particles.
 2 States of Matter Matter exists in various physical states, which are determined by the movement of the matter s particles. SECTION 1 Three States of Matter....... 32 2 Behavior of Gases........... 36
2 States of Matter Matter exists in various physical states, which are determined by the movement of the matter s particles. SECTION 1 Three States of Matter....... 32 2 Behavior of Gases........... 36
Can You Smell What I Smell?
 Can You Smell What I Smell? What Will We Do? AND DEVELOPING AN INITIAL MODEL We will develop a model to show what makes up an odor and use the model to explain how an odor gets from one place to another.
Can You Smell What I Smell? What Will We Do? AND DEVELOPING AN INITIAL MODEL We will develop a model to show what makes up an odor and use the model to explain how an odor gets from one place to another.
CP Chapter 13/14 Notes The Property of Gases Kinetic Molecular Theory
 CP Chapter 13/14 Notes The Property of Gases Kinetic Molecular Theory Kinetic Molecular Theory of Gases The word kinetic refers to. Kinetic energy is the an object has because of its motion. Kinetic Molecular
CP Chapter 13/14 Notes The Property of Gases Kinetic Molecular Theory Kinetic Molecular Theory of Gases The word kinetic refers to. Kinetic energy is the an object has because of its motion. Kinetic Molecular
Please do not write on this test. Please use the answer sheet. 1) Please choose all conditions that would allow a gas sample to behave ideally.
 AP Chemistry Test (Chapter 5) Please do not write on this test. Please use the answer sheet. Multiple Choice (50%) 1) Please choose all conditions that would allow a gas sample to behave ideally. I) Nonpolar
AP Chemistry Test (Chapter 5) Please do not write on this test. Please use the answer sheet. Multiple Choice (50%) 1) Please choose all conditions that would allow a gas sample to behave ideally. I) Nonpolar
Chemistry 101 Chapter 5 GAS MIXTURES
 GAS MIXTURES Consider mixing equal volumes of 3 different gases, all at the same temperature and pressure in a container of the same size. 1 L He 1 L N 2 1 L O 2 1 L mixture t = 0 0 C t = 0 0 C t = 0 0
GAS MIXTURES Consider mixing equal volumes of 3 different gases, all at the same temperature and pressure in a container of the same size. 1 L He 1 L N 2 1 L O 2 1 L mixture t = 0 0 C t = 0 0 C t = 0 0
Gases. Unit 10. How do gases behave?
 Gases Unit 10 How do gases behave? Gases are perhaps the most mysterious of all of the phases of matter. For the most part gases are invisible to us, and it was once believed that in the air there is no
Gases Unit 10 How do gases behave? Gases are perhaps the most mysterious of all of the phases of matter. For the most part gases are invisible to us, and it was once believed that in the air there is no
KINETIC THEORY OF GASES
 CHAPTER 18 GASES KINETIC THEORY OF GASES A given amt. of gas will occupy the entire volume of its container. Changes in temp. have a greater effect on the vol. of a gas than on a liquid or solid KINETIC
CHAPTER 18 GASES KINETIC THEORY OF GASES A given amt. of gas will occupy the entire volume of its container. Changes in temp. have a greater effect on the vol. of a gas than on a liquid or solid KINETIC
Temp in Kelvin = (Temp in O C) Temp in o C = (Temp in Kelvin) Perform the following conversions:
 Study: *Questions About Gases WS and More Questions About Gases WS *Go back over your notes taken from the book and in class. *Use your book: Chapter 3 PG 66-97 The Kelvin temperature of a gas (or any
Study: *Questions About Gases WS and More Questions About Gases WS *Go back over your notes taken from the book and in class. *Use your book: Chapter 3 PG 66-97 The Kelvin temperature of a gas (or any
Air exerts a on the walls of its container. Air Pressure is due to the of the molecules in the air as they
 Lesson 1,2: What is Air Pressure? Air exerts a on the walls of its container. This is often called Pressure. Air Pressure is due to the of the molecules in the air as they collide with the walls. Air has.
Lesson 1,2: What is Air Pressure? Air exerts a on the walls of its container. This is often called Pressure. Air Pressure is due to the of the molecules in the air as they collide with the walls. Air has.
Section 8.1 Properties of Gases Goal: Describe the kinetic molecular theory of gases and the units of measurement used for gases.
 Chapter 8 Gases Practice Problems Section 8.1 Properties of Gases Goal: Describe the kinetic molecular theory of gases and the units of measurement used for gases. Summary: In a gas, particles are so far
Chapter 8 Gases Practice Problems Section 8.1 Properties of Gases Goal: Describe the kinetic molecular theory of gases and the units of measurement used for gases. Summary: In a gas, particles are so far
Chemistry Chapter 10 Test
 Chemistry Chapter 10 Test True/False Indicate whether the sentence or statement is true or false. 1. KMT stands for Kinetic Mole Theory. 2. One of the assumptions in the KMT is that the particles are spread
Chemistry Chapter 10 Test True/False Indicate whether the sentence or statement is true or false. 1. KMT stands for Kinetic Mole Theory. 2. One of the assumptions in the KMT is that the particles are spread
Lab Dates. CRHS Academic Chemistry Unit 11 Gas Laws Notes
 Name Period CRHS Academic Chemistry Unit 11 Gas Laws Notes Quiz Date Lab Dates Exam Date Notes, Homework, Exam Reviews and Their KEYS located on CRHS Academic Chemistry Website: https://cincochem.pbworks.com
Name Period CRHS Academic Chemistry Unit 11 Gas Laws Notes Quiz Date Lab Dates Exam Date Notes, Homework, Exam Reviews and Their KEYS located on CRHS Academic Chemistry Website: https://cincochem.pbworks.com
Chapter 3. Solids, Liquids, and Gases
 Chapter 3 Solids, Liquids, and Gases Section 1: States of Matter Learning Objectives: Describe the characteristics of a solid Describe the characteristics of a liquid Describe the characteristics of a
Chapter 3 Solids, Liquids, and Gases Section 1: States of Matter Learning Objectives: Describe the characteristics of a solid Describe the characteristics of a liquid Describe the characteristics of a
Please do not write on this test. Please use the answer sheet.
 AP Chemistry Test (Chapter 5) Multiple Choice (50%) Please do not write on this test. Please use the answer sheet. Form: Snowboard 1) A sample of argon gas is sealed in a rigid metal tank. The temperature
AP Chemistry Test (Chapter 5) Multiple Choice (50%) Please do not write on this test. Please use the answer sheet. Form: Snowboard 1) A sample of argon gas is sealed in a rigid metal tank. The temperature
NOTES: Behavior of Gases
 NOTES: Behavior of Gases Properties of Gases Gases have weight Gases take up space Gases exert pressure Gases fill their containers Gases are mostly empty space The molecules in a gas are separate, very
NOTES: Behavior of Gases Properties of Gases Gases have weight Gases take up space Gases exert pressure Gases fill their containers Gases are mostly empty space The molecules in a gas are separate, very
Solids, Liquids, and Gases
 chapter 14 Solids, Liquids, and Gases section 3 Behavior of Gases What You ll Learn how a gas exerts pressure on its container how changing pressure, temperature, or volume affect a gas Before You Read
chapter 14 Solids, Liquids, and Gases section 3 Behavior of Gases What You ll Learn how a gas exerts pressure on its container how changing pressure, temperature, or volume affect a gas Before You Read
Chapter 10. Physical Characteristics of Gases
 Chapter 10 Physical Characteristics of Gases Kinetic Molecular Theory An understanding of the behavior of atoms that make up matter Ideal gas: an imaginary gas that perfectly fits all assumptions of the
Chapter 10 Physical Characteristics of Gases Kinetic Molecular Theory An understanding of the behavior of atoms that make up matter Ideal gas: an imaginary gas that perfectly fits all assumptions of the
ACFM vs. SCFM vs. ICFM Series of Technical White Papers from Squire-Cogswell
 ACFM vs. SCFM vs. ICFM Series of Technical White Papers from Squire-Cogswell Squire Cogswell / Aeros Instruments, Inc. 1111 Lakeside Drive Gurnee, IL 60031 Phone: (800) 448-0770 Fax: (847) 855-6304 info@squire-cogswell.com
ACFM vs. SCFM vs. ICFM Series of Technical White Papers from Squire-Cogswell Squire Cogswell / Aeros Instruments, Inc. 1111 Lakeside Drive Gurnee, IL 60031 Phone: (800) 448-0770 Fax: (847) 855-6304 info@squire-cogswell.com
End of Chapter Exercises
 End of Chapter Exercises Exercises 1 12 are conceptual questions that are designed to see if you have understood the main concepts of the chapter. 1. While on an airplane, you take a drink from your water
End of Chapter Exercises Exercises 1 12 are conceptual questions that are designed to see if you have understood the main concepts of the chapter. 1. While on an airplane, you take a drink from your water
PARTICLE SPACING PART 1
 PARTICLE SPACING PART 1 Name(s) ACTIVITY #1 COMPRESSIBILITY OF LIQUIDS AND GASES Obtain two syringes. Fill one of the syringes about half full of water. Remove any air bubbles left inside. Fill the second
PARTICLE SPACING PART 1 Name(s) ACTIVITY #1 COMPRESSIBILITY OF LIQUIDS AND GASES Obtain two syringes. Fill one of the syringes about half full of water. Remove any air bubbles left inside. Fill the second
Name: Class: Date: SHORT ANSWER Answer the following questions in the space provided.
 CHAPTER 11 REVIEW Gases SECTION 1 SHORT ANSWER Answer the following questions in the space provided. 1. Pressure =. For a constant force, when the surface area is tripled the pressure is (a) doubled. (b)
CHAPTER 11 REVIEW Gases SECTION 1 SHORT ANSWER Answer the following questions in the space provided. 1. Pressure =. For a constant force, when the surface area is tripled the pressure is (a) doubled. (b)
Flying High. HHJS Science Week Background Information. Forces and Flight
 Flying High HHJS Science Week 2013 Background Information Forces and Flight Flight Background Information Flying is defined as controlled movement through the air. Many things can become airborne but this
Flying High HHJS Science Week 2013 Background Information Forces and Flight Flight Background Information Flying is defined as controlled movement through the air. Many things can become airborne but this
Puff Bottles. Dr Joseph Ireland (2013) Dr Joe. For more activities see Creating Science at
 Puff Bottles Introduction: A child can pretend a balloon is alive, or that they have magic powers over a balloon allowing others to try and sort out the mystery of how the magic happens. This science activity
Puff Bottles Introduction: A child can pretend a balloon is alive, or that they have magic powers over a balloon allowing others to try and sort out the mystery of how the magic happens. This science activity
2.1 Simple Kinetic Molecular Model of Matter
 For more awesome GSE and level resources, visit us at www.savemyexams.co.uk/ 2.1 Simple Kinetic Molecular Model of Matter Question Paper Level IGSE Subject Physics (625) Exam oard Topic Sub Topic ooklet
For more awesome GSE and level resources, visit us at www.savemyexams.co.uk/ 2.1 Simple Kinetic Molecular Model of Matter Question Paper Level IGSE Subject Physics (625) Exam oard Topic Sub Topic ooklet
Chapter 10: Properties of Gases: The Air We Breathe
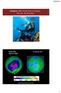 Chapter 10: Properties of Gases: The Air We Breathe South Pole Sept 24, 2006 15 February 2017 http://ozonewatch.gsfc.nasa.gov 1 Chapter Outline 10.1 10.2 10.3 The Properties of Gases Effusion and the Kinetic
Chapter 10: Properties of Gases: The Air We Breathe South Pole Sept 24, 2006 15 February 2017 http://ozonewatch.gsfc.nasa.gov 1 Chapter Outline 10.1 10.2 10.3 The Properties of Gases Effusion and the Kinetic
