Civil Air Patrol Auxiliary of the United States Air Force
|
|
|
- Jade Gilmore
- 6 years ago
- Views:
Transcription
1 Mountain Flying Qualification Course Civil Air Patrol Auxiliary of the United States Air Force
2 Physiological Effects of Altitude
3 Physiological Effects of Altitude OXYGEN DEPRIVATION (HYPOXIA) SINUS PRESSURE ULTRAVIOLET RADIATION
4 Definition of Hypoxia Hypoxia is a lack of oxygen at the tissue level of the body due to a decrease of oxygen pressure in inspired air or because of conditions that interfere with the diffusion or absorption of oxygen within the body. Types of Hypoxia Histotoxic Hypoxia Interference of the tissue s ability to absorb or metabolize delivered oxygen Often caused by alcohol, narcotics, or poisons Hypemic Hypoxia Reduction of the blood s ability to carry oxygen Carbon monoxide is most common cause Other causes: anemia, blood loss, and smoking Hypoxic Hypoxia Lack of oxygen in the tissues due to decrease in the partial pressure of oxygen at altitude
5 Causes of Hypoxia Flight at an altitude where there is insufficient partial pressure of oxygen to cause oxygen transfer Ingestion or inspiration of drugs that interfere with the blood s ability to absorb or transport oxygen from the lungs to the cells Malfunction of the circulatory system Positive g forces preventing oxygenated blood from reaching the brain Mechanical malfunction of supplemental oxygen equipment Symptoms of Hypoxia The most common initial symptom is mild euphoria, making the self-detection of hypoxia less likely and more difficult. Every person s symptoms differ in order and severity, but often include: Decreased visual acuity Mental confusion Shallow, rapid breathing Cyanosis (blue) of the fingernails Headache Eventual incapacitation, followed by death
6 Use lowest practical flight level Minimize duration of high-altitude operations Allow acclimatization to higher altitudes Refrain from alcohol and tobacco products Maintain good physical condition Use supplemental oxygen Prevention of Hypoxia Supplemental Oxygen Required for crewmembers when flying between 12,500 and 14,000 MSL for over 30 minutes Required for crewmembers at all times when flying above 14,000 MSL Must be provided to passengers above 15,000 MSL Will have beneficial effects at altitudes well below those required by regulation While the regulations require use of supplemental oxygen in terms of absolute altitude, the physiological effects of hypoxia result from density altitude. Base decisions regarding exposure to hypoxia on calculations of the density altitude at which you are operating.
7 Sinus Pressure Air trapped in sinus cavities and the inner ear must be equalized during climbs and descents to prevent pain and tissue damage. Yawning during ascent is usually sufficient, but use of the Valsalva Maneuver during descent may be required: Close your mouth and keep it closed Pinch your nostrils closed tightly Force your tongue against the roof of your mouth Exhale forcibly through the upper throat into your nasal cavity until pressure is equalized Ultraviolet Radiation Thin air at higher altitudes allows more damaging UV radiation from the sun to reach your cockpit. Protect exposed skin with sunscreen Wear sunglasses which block both UV-A and UV-B radiation.
8 Personal Equipment Wear layers of warm clothing Aircraft heater may be ineffective or inoperative Heater may not distribute air evenly throughout the aircraft May be all you retain following rapid egress from aircraft Carry water in cockpit to prevent dehydration Augment normal aircraft survival gear Mountains become very cold at night, even in the summer Sleeping bag can be a lifesaver, especially if injured High-calorie food necessary in low temperature environment Traveling for water or shelter can be difficult in steep terrain
9 END
Office. Hypoxia. Or this. Or even this. Hypoxia E-1. COL Brian W. Smalley DO, MSPH, CPE
 Hypoxia Office COL Brian W. Smalley DO, MSPH, CPE Or this Or even this Hypoxia State of oxygen deficiency in the blood cells and tissues sufficient to cause impairment of function 4 Types Hypoxic Hypemic
Hypoxia Office COL Brian W. Smalley DO, MSPH, CPE Or this Or even this Hypoxia State of oxygen deficiency in the blood cells and tissues sufficient to cause impairment of function 4 Types Hypoxic Hypemic
To develop understanding of mental and physical standards required for operating an aircraft
 Aeromedical Factors Objective To develop understanding of mental and physical standards required for operating an aircraft Outline Obtaining a medical certificate Causes, symptoms, effects, and corrective
Aeromedical Factors Objective To develop understanding of mental and physical standards required for operating an aircraft Outline Obtaining a medical certificate Causes, symptoms, effects, and corrective
Outline What is it and what to expect Pilot physiology Oxygen equipment per FAA Wave windows Relevant FAR s NCSA Rules
 Northern California Soaring Association 2010 Safety Seminar High Altitude Wave Flight Considerations by Mike Voie, CFIG Outline What is it and what to expect Pilot physiology Oxygen equipment per FAA Wave
Northern California Soaring Association 2010 Safety Seminar High Altitude Wave Flight Considerations by Mike Voie, CFIG Outline What is it and what to expect Pilot physiology Oxygen equipment per FAA Wave
II.A. Aeromedical Factors
 References: FAA-H-8083-3; AIM; AC 67-2 Objectives The student should exhibit knowledge regarding aeromedical factors as required in the PTS. Key Elements Elements Schedule Equipment IP s Actions SP s Actions
References: FAA-H-8083-3; AIM; AC 67-2 Objectives The student should exhibit knowledge regarding aeromedical factors as required in the PTS. Key Elements Elements Schedule Equipment IP s Actions SP s Actions
ALTITUDE PHYSIOLOGY. Physiological Zones of the Atmosphere. Composition of the Air AIR ATTENDANTS COURSE. Sea Level Pressure
 AIR ATTENDANTS COURSE ALTITUDE PHYSIOLOGY Physical Divisions of the Atmosphere 1200 miles 600 miles EXOSPHERE Physiological Zones of the Atmosphere 50 miles IONOSPHERE SPACE EQUIVALENT ZONE: 50,000 feet
AIR ATTENDANTS COURSE ALTITUDE PHYSIOLOGY Physical Divisions of the Atmosphere 1200 miles 600 miles EXOSPHERE Physiological Zones of the Atmosphere 50 miles IONOSPHERE SPACE EQUIVALENT ZONE: 50,000 feet
Physiology of Flight
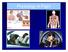 Physiology of Flight Physiology of Flight Physiology of flight: how the human body functions during flight Overview 1. Physiological Divisions of the Atmosphere 2. Hypoxia and Hyperventilation 3. Trapped
Physiology of Flight Physiology of Flight Physiology of flight: how the human body functions during flight Overview 1. Physiological Divisions of the Atmosphere 2. Hypoxia and Hyperventilation 3. Trapped
Oxygen and Respiration
 THRESHOLDS OF OXYGEN REQUIREMENTS SUMMARY Up to 10,000 ft Air only 10,000-33,700 ft Oxygen/Air mixture 33,700-40,000 ft 100% Oxygen Above 40,000 ft 100% Oxygen under pressure HYPOXIC HYPOXIA The term for
THRESHOLDS OF OXYGEN REQUIREMENTS SUMMARY Up to 10,000 ft Air only 10,000-33,700 ft Oxygen/Air mixture 33,700-40,000 ft 100% Oxygen Above 40,000 ft 100% Oxygen under pressure HYPOXIC HYPOXIA The term for
Aerospace Physiology MARYLAND. Cardiopulmonary Physiology. Musculoskeletal Vestibular Neurological. Respiratory Cardiovascular U N I V E R S I T Y O F
 Cardiopulmonary Physiology Respiratory Cardiovascular Musculoskeletal Vestibular Neurological 2003 David L. Akin - All rights reserved http://spacecraft.ssl.umd.edu The Human Circulatory System Lung Measurements
Cardiopulmonary Physiology Respiratory Cardiovascular Musculoskeletal Vestibular Neurological 2003 David L. Akin - All rights reserved http://spacecraft.ssl.umd.edu The Human Circulatory System Lung Measurements
Environmental Considerations
 Environmental Considerations I. Hyperthermia a. Heat stress i. Take extreme caution in hot, humid weather ii. Every year athletes die from heat related causes iii. Body temperature must be obtained by
Environmental Considerations I. Hyperthermia a. Heat stress i. Take extreme caution in hot, humid weather ii. Every year athletes die from heat related causes iii. Body temperature must be obtained by
Review of iterative design approach Respiratory Cardiovascular Musculoskeletal Vestibular Neurological
 Review of iterative design approach Respiratory Cardiovascular Musculoskeletal Vestibular Neurological 2001 David L. Akin - All rights reserved http://spacecraft.ssl.umd.edu Overview of the Design Process
Review of iterative design approach Respiratory Cardiovascular Musculoskeletal Vestibular Neurological 2001 David L. Akin - All rights reserved http://spacecraft.ssl.umd.edu Overview of the Design Process
American College of Occupational and Preventive Medicine 2011 Annual Meeting, Orlando, Florida, November 2, 2011
 Administrative Information Risk Assessment: Low AEROSPACE/ OCCUPATIONAL MEDICINE BAROMETRIC CONCERNS Dr. John Campbell, MFS Environmental Considerations: None Safety Considerations: None Evaluation: 50
Administrative Information Risk Assessment: Low AEROSPACE/ OCCUPATIONAL MEDICINE BAROMETRIC CONCERNS Dr. John Campbell, MFS Environmental Considerations: None Safety Considerations: None Evaluation: 50
O-1. American Osteopathic College of Occupational and Preventive Medicine 2013 Mid Year Educational Conference, Phoenix, Arizona February 14-17, 2013
 Administrative Information Risk Assessment: Low AEROSPACE/ OCCUPATIONAL MEDICINE BAROMETRIC CONCERNS Dr. John Campbell, DO, MPH, MFS Environmental Considerations: None Safety Considerations: None Evaluation:
Administrative Information Risk Assessment: Low AEROSPACE/ OCCUPATIONAL MEDICINE BAROMETRIC CONCERNS Dr. John Campbell, DO, MPH, MFS Environmental Considerations: None Safety Considerations: None Evaluation:
High Altitude Concerns
 High Altitude Concerns 17 March, 2014 PRESENTED BY: John M. Davenport, Lt. Col., USAF, Ret. International Operators Conference Tampa, FL March 17 20, 2014 Welcome Aviators! High Altitude Concerns Question
High Altitude Concerns 17 March, 2014 PRESENTED BY: John M. Davenport, Lt. Col., USAF, Ret. International Operators Conference Tampa, FL March 17 20, 2014 Welcome Aviators! High Altitude Concerns Question
Aviation Medicine Seminar Series
 Aviation Medicine Seminar Series Bruce R. Gilbert, M.D., Ph.D. Associate Clinical Professor of Urology Weill Cornell Medical College Stony Brook University Medical College Head, Section of Male Reproduction
Aviation Medicine Seminar Series Bruce R. Gilbert, M.D., Ph.D. Associate Clinical Professor of Urology Weill Cornell Medical College Stony Brook University Medical College Head, Section of Male Reproduction
RESPIRATION AND EXCRETION
 CHAPTER 13 RESPIRATION AND EXCRETION SECTION 13 1 The Respiratory System (pages 430-438) This section describes the parts of the respiratory system and how they work to help you breathe and speak. Introduction
CHAPTER 13 RESPIRATION AND EXCRETION SECTION 13 1 The Respiratory System (pages 430-438) This section describes the parts of the respiratory system and how they work to help you breathe and speak. Introduction
GLIDING NEW ZEALAND QUALIFIED GLIDER PILOT CERTIFICATE HUMAN FACTORS EXAMINATION. Time Allowed: 1 Hour
 GLIDING NEW ZEALAND QUALIFIED GLIDER PILOT CERTIFICATE HUMAN FACTORS EXAMINATION Time Allowed: 1 Hour INSTRUCTIONS: 1. Do not write on this examination paper. Write only on the answer sheet provided. 2.
GLIDING NEW ZEALAND QUALIFIED GLIDER PILOT CERTIFICATE HUMAN FACTORS EXAMINATION Time Allowed: 1 Hour INSTRUCTIONS: 1. Do not write on this examination paper. Write only on the answer sheet provided. 2.
1 out of every 5,555 of drivers dies in car accidents 1 out of every 7692 pregnant women die from complications 1 out of every 116,666 skydives ended
 1 out of every 5,555 of drivers dies in car accidents 1 out of every 7692 pregnant women die from complications 1 out of every 116,666 skydives ended in a fatality in 2000 1 out of every 126,626 marathon
1 out of every 5,555 of drivers dies in car accidents 1 out of every 7692 pregnant women die from complications 1 out of every 116,666 skydives ended in a fatality in 2000 1 out of every 126,626 marathon
Chapter 9 Airway Respirations Metabolism Oxygen Requirements Respiratory Anatomy Respiratory Anatomy Respiratory Anatomy Diaphragm
 1 Chapter 9 Airway 2 Respirations Every cell of the body requires to survive Oxygen must come in and carbon must go out 3 Metabolism Metabolism--Process where the body s cells convert food to Adequate
1 Chapter 9 Airway 2 Respirations Every cell of the body requires to survive Oxygen must come in and carbon must go out 3 Metabolism Metabolism--Process where the body s cells convert food to Adequate
Cold and Heat Emergencies Video Cold & Heat Emergencies
 CHAPTER 20 Cold and Heat Emergencies Video Cold & Heat Emergencies Lesson Objectives 1. Describe the different types of cold and heat emergencies and what you can do to prevent them. 2. Explain factors
CHAPTER 20 Cold and Heat Emergencies Video Cold & Heat Emergencies Lesson Objectives 1. Describe the different types of cold and heat emergencies and what you can do to prevent them. 2. Explain factors
HUMAN PERFORMANCE AND LIMITATIONS
 1 An overstressed pilot may show the following symptoms: 1. mental blocks, confusion and channelized attention 2. resignation, frustration, rage 3. deterioration in motor coordination 4. high pitch voice
1 An overstressed pilot may show the following symptoms: 1. mental blocks, confusion and channelized attention 2. resignation, frustration, rage 3. deterioration in motor coordination 4. high pitch voice
Breathing Process: Inhalation
 Airway Chapter 6 Breathing Process: Inhalation Active part of breathing Diaphragm and intercostal muscles contract, allowing the lungs to expand. The decrease in pressure allows lungs to fill with air.
Airway Chapter 6 Breathing Process: Inhalation Active part of breathing Diaphragm and intercostal muscles contract, allowing the lungs to expand. The decrease in pressure allows lungs to fill with air.
Human Biology Respiratory System
 Human Biology Respiratory System Respiratory System Responsible for process of breathing Works in cooperation with Circulatory system Three types: 1. Internal Respiration 2. External Respiration 3. Cellular
Human Biology Respiratory System Respiratory System Responsible for process of breathing Works in cooperation with Circulatory system Three types: 1. Internal Respiration 2. External Respiration 3. Cellular
Cold Weather Emergencies
 Cold Weather Emergencies Introduction Medical emergencies can result from exposure to heat or cold. Certain populations are at higher risk for heat and cold emergencies. Children Older people People with
Cold Weather Emergencies Introduction Medical emergencies can result from exposure to heat or cold. Certain populations are at higher risk for heat and cold emergencies. Children Older people People with
Espilat Mountaineering Club
 In the name of God Espilat Mountaineering Club May 2013 MEDICAL PROBLEMS IN HIGH MOUNTAIN ENVIRONMENTS Arya Hamedanchi MD, MPH Level one International Anthropometrist International Certificate of Ski Medicine
In the name of God Espilat Mountaineering Club May 2013 MEDICAL PROBLEMS IN HIGH MOUNTAIN ENVIRONMENTS Arya Hamedanchi MD, MPH Level one International Anthropometrist International Certificate of Ski Medicine
Toolbox Talk. Carbon Monoxide
 Carbon Monoxide Toolbox Talk Carbon monoxide defies all five human senses. You can t see it, smell it, touch it or taste it and you certainly can t hear this potentially deadly gas, which has been called
Carbon Monoxide Toolbox Talk Carbon monoxide defies all five human senses. You can t see it, smell it, touch it or taste it and you certainly can t hear this potentially deadly gas, which has been called
CABIN DEPRESSURIZATION AND SLOW ONSET HYPOXIA CRM, SIMULATOR AND SCENARIO BASED PHYSIOLOGY
 CABIN DEPRESSURIZATION AND SLOW ONSET HYPOXIA CRM, SIMULATOR AND SCENARIO BASED PHYSIOLOGY LESSONS LEARNED FROM 2500 PILOTS TRAINED IN SLOW ONSET HYPOXIA SOUTHERN AEROMEDICAL INSTITUTE DR. PAUL BUZA MEDICAL
CABIN DEPRESSURIZATION AND SLOW ONSET HYPOXIA CRM, SIMULATOR AND SCENARIO BASED PHYSIOLOGY LESSONS LEARNED FROM 2500 PILOTS TRAINED IN SLOW ONSET HYPOXIA SOUTHERN AEROMEDICAL INSTITUTE DR. PAUL BUZA MEDICAL
OXYGEN THERAPY. Teaching plan
 OXYGEN THERAPY Teaching plan To use this lesson for self-study, the learner should read the material, do the activity, and take the test. For group study, the leader may give each learner a copy of the
OXYGEN THERAPY Teaching plan To use this lesson for self-study, the learner should read the material, do the activity, and take the test. For group study, the leader may give each learner a copy of the
Event 203 First Aid Webelos Training Material
 The First Aid competitive event for Camperall will consist of 2 different First Aid components, a scenario challenge and a stretcher course challenge. The stretcher challenge will include constructing
The First Aid competitive event for Camperall will consist of 2 different First Aid components, a scenario challenge and a stretcher course challenge. The stretcher challenge will include constructing
 Question 1: Define vital capacity. What is its significance? Vital capacity is the maximum volume of air that can be exhaled after a maximum inspiration. It is about 3.5 4.5 litres in the human body. It
Question 1: Define vital capacity. What is its significance? Vital capacity is the maximum volume of air that can be exhaled after a maximum inspiration. It is about 3.5 4.5 litres in the human body. It
Page 1. Chapter 33: Respiration O 2 CO 2
 Chapter 33: Respiration O 2 CO 2 Features of Respiratory Systems: 1) Moist surface (to dissolve gas) 2) Thin cells lining surface 3) Large surface area contacting environment Facilitate Diffusion Methods
Chapter 33: Respiration O 2 CO 2 Features of Respiratory Systems: 1) Moist surface (to dissolve gas) 2) Thin cells lining surface 3) Large surface area contacting environment Facilitate Diffusion Methods
Oxygen course notes. PHYSICS OF THE ATMOSPHERE Definition - Envelope of gases surrounding the earth
 Oxygen course notes Aim The aim of this course is to give an understanding of the following as they relate to glider operations at altitudes above 10,000 : 1. the physics of the atmosphere 2. the physiology
Oxygen course notes Aim The aim of this course is to give an understanding of the following as they relate to glider operations at altitudes above 10,000 : 1. the physics of the atmosphere 2. the physiology
ANNEX D: PHYSIOLOGICAL EPISODES
 1. The Navy s definition of a physiological episode (PE) is when a pilot experiences loss in performance related to insufficient oxygen, depressurization, or other factors during flight. For the purposes
1. The Navy s definition of a physiological episode (PE) is when a pilot experiences loss in performance related to insufficient oxygen, depressurization, or other factors during flight. For the purposes
The Physiologic Basis of DLCO testing. Brian Graham Division of Respirology, Critical Care and Sleep Medicine University of Saskatchewan
 The Physiologic Basis of DLCO testing Brian Graham Division of Respirology, Critical Care and Sleep Medicine University of Saskatchewan Objectives Review gas transport from inhaled gas to the rest of the
The Physiologic Basis of DLCO testing Brian Graham Division of Respirology, Critical Care and Sleep Medicine University of Saskatchewan Objectives Review gas transport from inhaled gas to the rest of the
SPQ Module 9 Breathing at Altitude
 SPQ Module 9 Breathing at Altitude For most people traveling 1130 kilometers on foot over a frozen ice cap with no support would be daunting enough without facing the prospect of being short of breath
SPQ Module 9 Breathing at Altitude For most people traveling 1130 kilometers on foot over a frozen ice cap with no support would be daunting enough without facing the prospect of being short of breath
Glider Oxygen Systems
 Glider Oxygen Systems John DeRosa CLGC May 13, 2018 http://aviation.derosaweb.net jhderosa@yahoo.com This document is updated quite often! Be sure to download the latest version! Issue Date: June 4, 2018
Glider Oxygen Systems John DeRosa CLGC May 13, 2018 http://aviation.derosaweb.net jhderosa@yahoo.com This document is updated quite often! Be sure to download the latest version! Issue Date: June 4, 2018
Guide to Cold Stress at Work
 Guide to Cold Stress at Work WCB Website: www.wcb.pe.ca Toll free in Atlantic Canada: 1-800-237-5049 Revised: Jan/06 Cold Stress at Work Working in the cold is part of the job for many Prince Edward Islanders.
Guide to Cold Stress at Work WCB Website: www.wcb.pe.ca Toll free in Atlantic Canada: 1-800-237-5049 Revised: Jan/06 Cold Stress at Work Working in the cold is part of the job for many Prince Edward Islanders.
Sc ienc e 9-Biology Work sheet 8-2 A Single Breat h & Tak ing Care
 Unit 2 Your Living Body Sc ienc e 9-Biology Work sheet 8-2 A Single Breat h & Tak ing Care Name No pen or pencil No Textbook 20 Due Date Show Me Hand In Correct and Hand In Again By Read pages 159-167
Unit 2 Your Living Body Sc ienc e 9-Biology Work sheet 8-2 A Single Breat h & Tak ing Care Name No pen or pencil No Textbook 20 Due Date Show Me Hand In Correct and Hand In Again By Read pages 159-167
REMOTE LOCATION FIRST AID
 LESSON 23 REMOTE LOCATION FIRST AID 23-1 First Aid Differences in Remote Locations Most first aid based on fact that help will arrive within 10 20 minutes of 9-1-1 call Most first aid intended to meet
LESSON 23 REMOTE LOCATION FIRST AID 23-1 First Aid Differences in Remote Locations Most first aid based on fact that help will arrive within 10 20 minutes of 9-1-1 call Most first aid intended to meet
Tioga ISD Athletic Department Heat Policy
 Tioga ISD Athletic Department Heat Policy Practice of competition in hot and humid environmental conditions poses special problems for student-athletes. Heat stress and resulting heat illness is a primary
Tioga ISD Athletic Department Heat Policy Practice of competition in hot and humid environmental conditions poses special problems for student-athletes. Heat stress and resulting heat illness is a primary
SCUBA - self contained underwater breathing apparatus. 5 million sport scuba divers in U.S. 250, ,000 new certifications annually in U.S.
 SCUBA - self contained underwater breathing apparatus 5 million sport scuba divers in US 250,000-400,000 new certifications annually in US Diving occurs in oceans, freshwater lakes, rivers and quarries
SCUBA - self contained underwater breathing apparatus 5 million sport scuba divers in US 250,000-400,000 new certifications annually in US Diving occurs in oceans, freshwater lakes, rivers and quarries
Environmental Injuries: The Winter Athlete. Thomas Moran, MD Primary Care Sports Medicine Fellow University of Chicago - NorthShore
 Environmental Injuries: The Winter Athlete Thomas Moran, MD Primary Care Sports Medicine Fellow University of Chicago - NorthShore Introduction Chicago Marathon >41,000 runners 2006 (36 start,48 high with
Environmental Injuries: The Winter Athlete Thomas Moran, MD Primary Care Sports Medicine Fellow University of Chicago - NorthShore Introduction Chicago Marathon >41,000 runners 2006 (36 start,48 high with
PHYSIOLOGY. Let s look at the route in sequence, starting at the lungs where the blood releases CO2 and takes on oxygen at the pulmonary capillaries.
 PHYSIOLOGY Circulation: Blood circulates around your body to fuel the body with oxygen, the body uses the oxygen and changes it to carbon dioxide (CO2) the blood then carries this back to the lungs where
PHYSIOLOGY Circulation: Blood circulates around your body to fuel the body with oxygen, the body uses the oxygen and changes it to carbon dioxide (CO2) the blood then carries this back to the lungs where
Unit 3: The Physiology of Diving and Nitrox
 Unit 3: The Physiology of Diving and Nitrox Narcosis Decompression Sickness Physiological Effects of High Oxygen Levels Physiological Effects of High Oxygen Levels Student Performance: By the end of the
Unit 3: The Physiology of Diving and Nitrox Narcosis Decompression Sickness Physiological Effects of High Oxygen Levels Physiological Effects of High Oxygen Levels Student Performance: By the end of the
AIR QUALITY. Safety is in the Air AVOIDING CARBON MONOXIDE POISONING WHILE SCUBA DIVING
 AIR QUALITY Safety is in the Air AVOIDING CARBON MONOXIDE POISONING WHILE SCUBA DIVING INTRODUCTION Carbon monoxide poisoning and its influence on diving safety Carbon monoxide (CO) is an odourless, colourless
AIR QUALITY Safety is in the Air AVOIDING CARBON MONOXIDE POISONING WHILE SCUBA DIVING INTRODUCTION Carbon monoxide poisoning and its influence on diving safety Carbon monoxide (CO) is an odourless, colourless
Structures of the Respiratory System include:
 Respiratory System Structures of the Respiratory System include: ü Oral Cavity ü Nasal Cavity ü Pharynx ü Epiglottis ü Larynx ü Trachea ü Diaphragm ü Lung ü Bronchus ü Bronchioles ü Alveolus ü Pulmonary
Respiratory System Structures of the Respiratory System include: ü Oral Cavity ü Nasal Cavity ü Pharynx ü Epiglottis ü Larynx ü Trachea ü Diaphragm ü Lung ü Bronchus ü Bronchioles ü Alveolus ü Pulmonary
Respiration. Chapter 39
 Respiration Chapter 39 Impacts, Issues Up in Smoke Smoking immobilizes ciliated cells and kills white blood cells that defend the respiratory system; highly addictive nicotine discourages quitting 39.1
Respiration Chapter 39 Impacts, Issues Up in Smoke Smoking immobilizes ciliated cells and kills white blood cells that defend the respiratory system; highly addictive nicotine discourages quitting 39.1
Glucose + Oxygen Carbon Dioxide + Water + Energy C6H12O CO2 + 6H20 + energy
 Cell Respiration - A food oxidization process in body cells to produce energy - Occurs (happens) in animal cells and plant cells Notes : Metabolic Reactions in Gaseous Exchange CELL RESPIRATION Photosynthesis
Cell Respiration - A food oxidization process in body cells to produce energy - Occurs (happens) in animal cells and plant cells Notes : Metabolic Reactions in Gaseous Exchange CELL RESPIRATION Photosynthesis
Aerospace Physiology. Lecture #11 Oct. 7, 2014 Cardiopulmonary physiology. Musculoskeletal Vestibular Neurological Environmental Effects MARYLAND
 Lecture #11 Oct. 7, 2014 Cardiopulmonary physiology Respiratory Cardiovascular Musculoskeletal Vestibular Neurological Environmental Effects 1 2014 David L. Akin - All rights reserved http://spacecraft.ssl.umd.edu
Lecture #11 Oct. 7, 2014 Cardiopulmonary physiology Respiratory Cardiovascular Musculoskeletal Vestibular Neurological Environmental Effects 1 2014 David L. Akin - All rights reserved http://spacecraft.ssl.umd.edu
Your web browser (Safari 7) is out of date. For more security, comfort and the best experience on this site: Update your browser Ignore
 Your web browser (Safari 7) is out of date. For more security, comfort and the best experience on this site: Update your browser Ignore ALTITU DE For the complete encyclopedic entry with media resources,
Your web browser (Safari 7) is out of date. For more security, comfort and the best experience on this site: Update your browser Ignore ALTITU DE For the complete encyclopedic entry with media resources,
Acute Mountain Sickness
 Innere Medizin VII / Sportmedizin Acute Mountain Sickness Peter Bärtsch www.klinikum.uni-heidelberg.de/sportmedizin AMS: Clinical Picture Symptoms: - Headache - Loss of appetite, nausea, vomiting - Dizziness
Innere Medizin VII / Sportmedizin Acute Mountain Sickness Peter Bärtsch www.klinikum.uni-heidelberg.de/sportmedizin AMS: Clinical Picture Symptoms: - Headache - Loss of appetite, nausea, vomiting - Dizziness
Possible Outcomes of inadequate climatic cold management:
 COMPOSITE RISK MANAGEMENT (COLD WEATHER INJURY PREVENTION) A comprehensive cold weather injury prevention and management program will follow the principles of composite risk management by identifying hazards,
COMPOSITE RISK MANAGEMENT (COLD WEATHER INJURY PREVENTION) A comprehensive cold weather injury prevention and management program will follow the principles of composite risk management by identifying hazards,
Heat Illness Prevention
 Heat Illness Prevention EGUSD Risk Management (916) 686-7775 The why s and wherefores CCR, Title 8, Subchapter 7. General Safety Orders Group 2. Safe Practices and Personal Protection Article 10. Personal
Heat Illness Prevention EGUSD Risk Management (916) 686-7775 The why s and wherefores CCR, Title 8, Subchapter 7. General Safety Orders Group 2. Safe Practices and Personal Protection Article 10. Personal
Chapter 53: Clinical Center Single-Breath Carbon Monoxide Diffusing Capacity (DLCO) MOP 53.1 Introduction
 Chapter 53: Clinical Center Single-Breath Carbon Monoxide Diffusing Capacity (DLCO) MOP 53.1 Introduction The DLCO will determine the degree of pulmonary impairment in participants enrolled in the PVDOMICS
Chapter 53: Clinical Center Single-Breath Carbon Monoxide Diffusing Capacity (DLCO) MOP 53.1 Introduction The DLCO will determine the degree of pulmonary impairment in participants enrolled in the PVDOMICS
Respiratory physiology II.
 Respiratory physiology II. Learning objectives: 29. Pulmonary gas exchange. 30. Oxygen transport in the blood. 31. Carbon-dioxide transport in the blood. 1 Pulmonary gas exchange The transport mechanism
Respiratory physiology II. Learning objectives: 29. Pulmonary gas exchange. 30. Oxygen transport in the blood. 31. Carbon-dioxide transport in the blood. 1 Pulmonary gas exchange The transport mechanism
Chapter 13 The Respiratory System
 Chapter 13 The Respiratory System by Dr. Jay M. Templin Brooks/Cole - Thomson Learning Atmosphere Tissue cell External respiration Alveoli of lungs 1 Ventilation or gas exchange between the atmosphere
Chapter 13 The Respiratory System by Dr. Jay M. Templin Brooks/Cole - Thomson Learning Atmosphere Tissue cell External respiration Alveoli of lungs 1 Ventilation or gas exchange between the atmosphere
First Aid - immediate care that is given to the victim of an injury or illness until experts can take over - Oftentimes, it s the difference between
 First Aid First Aid - immediate care that is given to the victim of an injury or illness until experts can take over - Oftentimes, it s the difference between life and death or recovery vs permanent disability
First Aid First Aid - immediate care that is given to the victim of an injury or illness until experts can take over - Oftentimes, it s the difference between life and death or recovery vs permanent disability
CHAPTER 6. Oxygen Transport. Copyright 2008 Thomson Delmar Learning
 CHAPTER 6 Oxygen Transport Normal Blood Gas Value Ranges Table 6-1 OXYGEN TRANSPORT Oxygen Dissolved in the Blood Plasma Dissolve means that the gas maintains its precise molecular structure About.003
CHAPTER 6 Oxygen Transport Normal Blood Gas Value Ranges Table 6-1 OXYGEN TRANSPORT Oxygen Dissolved in the Blood Plasma Dissolve means that the gas maintains its precise molecular structure About.003
PHTY 300 Wk 1 Lectures
 PHTY 300 Wk 1 Lectures Arterial Blood Gas Components The test provides information on - Acid base balance - Oxygenation - Hemoglobin levels - Electrolyte blood glucose, lactate, renal function When initially
PHTY 300 Wk 1 Lectures Arterial Blood Gas Components The test provides information on - Acid base balance - Oxygenation - Hemoglobin levels - Electrolyte blood glucose, lactate, renal function When initially
Respiration in Organisms MULTIPLE CHOICE QUESTIONS NCERT
 10 Respiration in Organisms MULTIPLE CHOICE QUESTIONS 1. Sometimes when we do heavy exercise, anaerobic respiration takes place in our muscle cells. What is produced during this process? alcohol and lactic
10 Respiration in Organisms MULTIPLE CHOICE QUESTIONS 1. Sometimes when we do heavy exercise, anaerobic respiration takes place in our muscle cells. What is produced during this process? alcohol and lactic
Life 23 - Respiration in Air Raven & Johnson Ch. 53 (part)
 1 Life 23 - Respiration in Air Raven & Johnson Ch. 53 (part) Objectives 1: Compare the properties of air and water as media for respiration, and the consequences for the evolution of respiratory systems
1 Life 23 - Respiration in Air Raven & Johnson Ch. 53 (part) Objectives 1: Compare the properties of air and water as media for respiration, and the consequences for the evolution of respiratory systems
The physiological functions of respiration and circulation. Mechanics. exercise 7. Respiratory Volumes. Objectives
 exercise 7 Respiratory System Mechanics Objectives 1. To explain how the respiratory and circulatory systems work together to enable gas exchange among the lungs, blood, and body tissues 2. To define respiration,
exercise 7 Respiratory System Mechanics Objectives 1. To explain how the respiratory and circulatory systems work together to enable gas exchange among the lungs, blood, and body tissues 2. To define respiration,
UNDERSTANDING THE PRINCIPLES OF
 AVIATION MEDICINE IN ACTION: UNDERSTANDING THE PRINCIPLES OF AVIATION MEDICINE IN FLYING OPERATIONS MAJ(DR) Dominic TAN Air Force Medical Service Republic of Singapore Air Force 2 WHAT IS AVIATION MEDICINE
AVIATION MEDICINE IN ACTION: UNDERSTANDING THE PRINCIPLES OF AVIATION MEDICINE IN FLYING OPERATIONS MAJ(DR) Dominic TAN Air Force Medical Service Republic of Singapore Air Force 2 WHAT IS AVIATION MEDICINE
Animal Systems: The Respiratory System
 Animal Systems: The Respiratory System Tissues, Organs, and Systems of Living Things Cells, Cell Division, and Animal Systems and Plant Systems Cell Specialization Human Systems The Digestive The Circulatory
Animal Systems: The Respiratory System Tissues, Organs, and Systems of Living Things Cells, Cell Division, and Animal Systems and Plant Systems Cell Specialization Human Systems The Digestive The Circulatory
Hyperbaric Oxygen Therapy
 Hyperbaric Oxygen Therapy WWW.RN.ORG Reviewed September 2017, Expires September 2019 Provider Information and Specifics available on our Website Unauthorized Distribution Prohibited 2017 RN.ORG, S.A.,
Hyperbaric Oxygen Therapy WWW.RN.ORG Reviewed September 2017, Expires September 2019 Provider Information and Specifics available on our Website Unauthorized Distribution Prohibited 2017 RN.ORG, S.A.,
DECOMPRESSION PHYSIOLOGY and SUSCEPTIBILITY
 Chapter 13 DECOMPRESSION PHYSIOLOGY and SUSCEPTIBILITY Decompression Sickness (DCS) is an illness caused by the effects of gas coming out of solution to form bubbles in the body after diving. It is due
Chapter 13 DECOMPRESSION PHYSIOLOGY and SUSCEPTIBILITY Decompression Sickness (DCS) is an illness caused by the effects of gas coming out of solution to form bubbles in the body after diving. It is due
Oxygen Therapy. Respiratory Rehabilitation Program. What is oxygen?
 Respiratory Rehabilitation Program What is oxygen? Oxygen Therapy Oxygen is a colourless, tasteless, odorless gas that you need to live. Oxygen is found in the air you breathe at a concentration of 21%.
Respiratory Rehabilitation Program What is oxygen? Oxygen Therapy Oxygen is a colourless, tasteless, odorless gas that you need to live. Oxygen is found in the air you breathe at a concentration of 21%.
SCENARIO #2 CARBON MONOXIDE INCIDENT IN AN AUTO SHOP
 SCENARIO #2 CARBON MONOXIDE INCIDENT IN AN AUTO SHOP 169 FIGURE 8-8 A 500 gallon ASME propane tank is used to supply an interior space heater at an automobile repair shop. During extremely cold weather,
SCENARIO #2 CARBON MONOXIDE INCIDENT IN AN AUTO SHOP 169 FIGURE 8-8 A 500 gallon ASME propane tank is used to supply an interior space heater at an automobile repair shop. During extremely cold weather,
Cold Weather Safety Program
 Title: Cold Weather Safety program Effective Date: 12/6/2014 Control Number: THG_0052 Revision Number: 1 Date: 10/23/2015 Annual Review Completed: 5/13/2015 Cold Weather Safety Program CONTENTS I. INTRODUCTION
Title: Cold Weather Safety program Effective Date: 12/6/2014 Control Number: THG_0052 Revision Number: 1 Date: 10/23/2015 Annual Review Completed: 5/13/2015 Cold Weather Safety Program CONTENTS I. INTRODUCTION
2. State the volume of air remaining in the lungs after a normal breathing.
 CLASS XI BIOLOGY Breathing And Exchange of Gases 1. Define vital capacity. What is its significance? Answer: Vital Capacity (VC): The maximum volume of air a person can breathe in after a forced expiration.
CLASS XI BIOLOGY Breathing And Exchange of Gases 1. Define vital capacity. What is its significance? Answer: Vital Capacity (VC): The maximum volume of air a person can breathe in after a forced expiration.
Unit II Problem 4 Physiology: Diffusion of Gases and Pulmonary Circulation
 Unit II Problem 4 Physiology: Diffusion of Gases and Pulmonary Circulation - Physical principles of gases: Pressure of a gas is caused by the movement of its molecules against a surface (more concentration
Unit II Problem 4 Physiology: Diffusion of Gases and Pulmonary Circulation - Physical principles of gases: Pressure of a gas is caused by the movement of its molecules against a surface (more concentration
GAS EXCHANGE & PHYSIOLOGY
 GAS EXCHANGE & PHYSIOLOGY Atmospheric Pressure Intra-Alveolar Pressure Inspiration 760 mm HG at Sea Level (= 1 atm) Pressure due to gases (N2, O2, CO2, Misc.) Pressure inside the alveolus (air sac) Phrenic
GAS EXCHANGE & PHYSIOLOGY Atmospheric Pressure Intra-Alveolar Pressure Inspiration 760 mm HG at Sea Level (= 1 atm) Pressure due to gases (N2, O2, CO2, Misc.) Pressure inside the alveolus (air sac) Phrenic
OBTAINING A MEDICAL CERTIFICATE
 Ch 15.qxd 10/24/03 8:46 AM Page 15-1 As a pilot, it is important to stay aware of the mental and physical standards required for the type of flying done. This chapter provides information on medical certification
Ch 15.qxd 10/24/03 8:46 AM Page 15-1 As a pilot, it is important to stay aware of the mental and physical standards required for the type of flying done. This chapter provides information on medical certification
MATERIAL SAFETY DATA SHEET
 Page 1 of 5 1. PRODUCT AND COMPANY IDENTIFICATION PRODUCT NAME: PRODUCT DESCRIPTION: (Sn60/Pb40, Sn63/Pb37, Sn62/Pb36/Ag2) MANUFACTURER Qualitek International, Inc. 315 Fairbank St. Addison, IL 60101 Emergency
Page 1 of 5 1. PRODUCT AND COMPANY IDENTIFICATION PRODUCT NAME: PRODUCT DESCRIPTION: (Sn60/Pb40, Sn63/Pb37, Sn62/Pb36/Ag2) MANUFACTURER Qualitek International, Inc. 315 Fairbank St. Addison, IL 60101 Emergency
Respiration. The ins and outs
 Respiration The ins and outs Functions 1. To bring O 2 into the body and transfer it to the blood stream 2. To remove CO 2 Circulation and respiration work together to achieve these functions Why Do We
Respiration The ins and outs Functions 1. To bring O 2 into the body and transfer it to the blood stream 2. To remove CO 2 Circulation and respiration work together to achieve these functions Why Do We
Directions: The following two questions refer to the diagram below, which shows a group of cells from the respiratory tract.
 Topic 7 Gas exchange in humans Directions: The following two questions refer to the diagram below, which shows a group of cells from the respiratory tract. X Y 1. What is the function of structure X? A.
Topic 7 Gas exchange in humans Directions: The following two questions refer to the diagram below, which shows a group of cells from the respiratory tract. X Y 1. What is the function of structure X? A.
Chapter 22 Gas Exchange
 Chapter 22 Gas Exchange PowerPoint Lectures for Biology: Concepts & Connections, Sixth Edition Campbell, Reece, Taylor, Simon, and Dickey Lecture by Edward J. Zalisko Introduction: Surviving in Thin Air
Chapter 22 Gas Exchange PowerPoint Lectures for Biology: Concepts & Connections, Sixth Edition Campbell, Reece, Taylor, Simon, and Dickey Lecture by Edward J. Zalisko Introduction: Surviving in Thin Air
AEROMEDICAL FACTORS. ATTENTION - One of the error factors that we can try to control if we are aware of them
 AEROMEDICAL FACTORS II-A ATTENTION - One of the error factors that we can try to control if we are aware of them MOTIVATION - Everyone will at some point have a cold, take some kind of drugs or drink alcohol
AEROMEDICAL FACTORS II-A ATTENTION - One of the error factors that we can try to control if we are aware of them MOTIVATION - Everyone will at some point have a cold, take some kind of drugs or drink alcohol
3.6. The Respiratory System
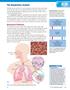 The Respiratory System Whether you are aware of it or not, you breathe in and out 15 times each minute on average. This rate increases automatically if your physical activity increases. With normal breathing,
The Respiratory System Whether you are aware of it or not, you breathe in and out 15 times each minute on average. This rate increases automatically if your physical activity increases. With normal breathing,
1. Label a diagram of the respiratory system. Objective sheet 3 Notes
 1. Label a diagram of the respiratory system Objective sheet 3 Notes 2. Functions of the respiratory structures Name Description Function Nasal Cavity Trachea Bronchi (Singular Bronchus) Bronchioles Lungs
1. Label a diagram of the respiratory system Objective sheet 3 Notes 2. Functions of the respiratory structures Name Description Function Nasal Cavity Trachea Bronchi (Singular Bronchus) Bronchioles Lungs
Biology 13A Lab #12: The Respiratory System
 Biology 13A Lab #12: The Respiratory System Lab #12 Table of Contents: Expected Learning Outcomes.... 94 Introduction...... 95 Activity 1: Structures of the Respiratory System 96 Activity 2: Measuring
Biology 13A Lab #12: The Respiratory System Lab #12 Table of Contents: Expected Learning Outcomes.... 94 Introduction...... 95 Activity 1: Structures of the Respiratory System 96 Activity 2: Measuring
Using the Lifebox oximeter in the neonatal unit. Tutorial 1 the basics
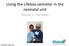 Using the Lifebox oximeter in the neonatal unit Tutorial 1 the basics Lifebox 2014. 2011. All rights reserved The Lifebox Pulse Oximeter In this tutorial you will learn about: The function of a pulse oximeter
Using the Lifebox oximeter in the neonatal unit Tutorial 1 the basics Lifebox 2014. 2011. All rights reserved The Lifebox Pulse Oximeter In this tutorial you will learn about: The function of a pulse oximeter
Physiology of Respiration
 Physiology of Respiration External Respiration = pulmonary ventilation breathing involves 2 processes: inspiration expiration Inspiration an active process involves contraction of diaphragm innervated
Physiology of Respiration External Respiration = pulmonary ventilation breathing involves 2 processes: inspiration expiration Inspiration an active process involves contraction of diaphragm innervated
Outdoor Action Guide to High Altitude: Acclimatization and Illnesses
 Outdoor Action Guide to High Altitude: Acclimatization and Illnesses Last Page update 07/07/1999 by Rick Curtis, Director, Outdoor Action Program Navigation Back to the AEE Wilderness Safety Page OA Guide
Outdoor Action Guide to High Altitude: Acclimatization and Illnesses Last Page update 07/07/1999 by Rick Curtis, Director, Outdoor Action Program Navigation Back to the AEE Wilderness Safety Page OA Guide
What is the Eustachian tube and what does it do?
 Eustachian Tube Dysfunction Eustachian tube dysfunction (ETD) can cause dulled hearing. It is usually a temporary problem that lasts a week or so and most commonly occurs during and after a cold. There
Eustachian Tube Dysfunction Eustachian tube dysfunction (ETD) can cause dulled hearing. It is usually a temporary problem that lasts a week or so and most commonly occurs during and after a cold. There
GEMINI VISITOR S GUIDE VISITOR S VERSION
 Gemini Observatory Northern Operations Center 670 N. A ohoku Place, Hilo, Hawaii 96720 Phone: (808) 974-2500 Fax: (808) 974-2589 Dear Visitor, For your personal safety, please read this entire safety policy
Gemini Observatory Northern Operations Center 670 N. A ohoku Place, Hilo, Hawaii 96720 Phone: (808) 974-2500 Fax: (808) 974-2589 Dear Visitor, For your personal safety, please read this entire safety policy
Assumptions: Rodenator with adequate blast pressure
 Control method: Assumptions: Rodenator with adequate blast pressure This humaneness assessment assumes that blast pressure is adequate throughout the warren to cause death for the majority of rabbits within
Control method: Assumptions: Rodenator with adequate blast pressure This humaneness assessment assumes that blast pressure is adequate throughout the warren to cause death for the majority of rabbits within
The Respiratory System
 Name Date Class The Respiratory System This section describes the parts of the respiratory system and how they work to help you breathe and speak. Use Target Reading Skills As you read, complete the flowchart
Name Date Class The Respiratory System This section describes the parts of the respiratory system and how they work to help you breathe and speak. Use Target Reading Skills As you read, complete the flowchart
Magdalen Court School
 Introduction Working in a cold environment whether it be cold weather, cold water, or an indoor freezer is part of the job for many British Columbia workers. One of the major hazards you face when working
Introduction Working in a cold environment whether it be cold weather, cold water, or an indoor freezer is part of the job for many British Columbia workers. One of the major hazards you face when working
Respiratory Signs: Tachypnea (RR>30/min), Desaturation, Shallow breathing, Use of accessory muscles Breathing sound: Wheezing, Rhonchi, Crepitation.
 Respiratory Signs: Tachypnea (RR>30/min), Desaturation, Shallow breathing, Use of accessory muscles Breathing sound: Wheezing, Rhonchi, Crepitation. Paradoxical breathing Hyper-resonance on percussion:
Respiratory Signs: Tachypnea (RR>30/min), Desaturation, Shallow breathing, Use of accessory muscles Breathing sound: Wheezing, Rhonchi, Crepitation. Paradoxical breathing Hyper-resonance on percussion:
R S A B C CPR. Basic Life Support Flow Chart Check for danger. Check Response. Send for Help. Check Airway. Check for Breathing.
 CPR CPR is the technique of the manual inflation of the lungs with oxygen, and compression of the heart, therefore pumping oxygenated blood around the body, and keeping the vital organs supplied with oxygen.
CPR CPR is the technique of the manual inflation of the lungs with oxygen, and compression of the heart, therefore pumping oxygenated blood around the body, and keeping the vital organs supplied with oxygen.
First Aid Exercises 1
 First Aid Exercises 1 1 A N S W E R T H E Q U E S T I O N S I N Y O U R O W N W O R D S! What are the emergency numbers you should remember? What kind of information should you give when you call for help?
First Aid Exercises 1 1 A N S W E R T H E Q U E S T I O N S I N Y O U R O W N W O R D S! What are the emergency numbers you should remember? What kind of information should you give when you call for help?
Then the partial pressure of oxygen is. b) Gases will diffuse down a pressure gradient across a respiratory surface if it is: i) permeable ii) moist
 1 AP Biology March 2008 Respiration Chapter 42 Gas exchange occurs across specialized respiratory surfaces. 1) Gas exchange: Relies on the diffusion of gases down pressure gradients. At sea level, atmosphere
1 AP Biology March 2008 Respiration Chapter 42 Gas exchange occurs across specialized respiratory surfaces. 1) Gas exchange: Relies on the diffusion of gases down pressure gradients. At sea level, atmosphere
GUIDELINES FOR THE DIVER ** EXAMINATION
 GUIDELINES FOR THE DIVER ** EXAMINATION Dear Diver Enclosed please find the first draft of a recently compiled sample list of Diver ** theory questions. These guidelines are aimed at assisting two groups
GUIDELINES FOR THE DIVER ** EXAMINATION Dear Diver Enclosed please find the first draft of a recently compiled sample list of Diver ** theory questions. These guidelines are aimed at assisting two groups
DIVING HABITS AND PRACTICES:
 Rocky Mountain Aquatics FINAL SCUBA EXAM Please record all answers on the answer sheet provided. DO NOT MAKE ANY MARKS IN THIS TEST BOOKLET. Read all the answers first before making a choice. In some instances
Rocky Mountain Aquatics FINAL SCUBA EXAM Please record all answers on the answer sheet provided. DO NOT MAKE ANY MARKS IN THIS TEST BOOKLET. Read all the answers first before making a choice. In some instances
Gas Exchange in Animals. Uptake of O2 from environment and discharge of CO2. Respiratory medium! water for aquatic animals, air for terrestial
 Gas Exchange in Animals Uptake of O2 from environment and discharge of CO2 Respiratory medium! water for aquatic animals, air for terrestial Respiratory surface! skin, gills, lungs Circulatory System O2/CO2
Gas Exchange in Animals Uptake of O2 from environment and discharge of CO2 Respiratory medium! water for aquatic animals, air for terrestial Respiratory surface! skin, gills, lungs Circulatory System O2/CO2
MATERIAL SAFETY DATA SHEET Date Issued : 04/08/2004 MSDS No : XP692 (Sn63/Pb37) Date Revised : 02/25/2013 Revision No : 4
 Page 1 of 5 1. PRODUCT AND COMPANY IDENTIFICATION PRODUCT NAME: PRODUCT DESCRIPTION: No Clean Solder Paste MANUFACTURER 24 HR. EMERGENCY TELEPHONE NUMBERS Qualitek International, Inc. 1-800-535-5053 Infotrac
Page 1 of 5 1. PRODUCT AND COMPANY IDENTIFICATION PRODUCT NAME: PRODUCT DESCRIPTION: No Clean Solder Paste MANUFACTURER 24 HR. EMERGENCY TELEPHONE NUMBERS Qualitek International, Inc. 1-800-535-5053 Infotrac
Respiratory Physiology
 Respiratory Physiology Background Information: When inspiring, the pleura attached to the internal chest wall is pulled outward as the thoracic cavity expands. The pleural cavity [space between the outer
Respiratory Physiology Background Information: When inspiring, the pleura attached to the internal chest wall is pulled outward as the thoracic cavity expands. The pleural cavity [space between the outer
Chapter 16 Respiratory System
 Introduction Chapter 16 Respiratory System The respiratory system consists of tubes that filter incoming air and transport it to alveoli where gases are exchanged. Think pair share: what organs are associated
Introduction Chapter 16 Respiratory System The respiratory system consists of tubes that filter incoming air and transport it to alveoli where gases are exchanged. Think pair share: what organs are associated
SAFETY DATA SHEET. NC600 No Clean Solder Wire - Sn/Ag/Cu Alloys. MANUFACTURER 24 HR. EMERGENCY TELEPHONE NUMBERS Qualitek International, Inc.
 Page 1 of 5 1. PRODUCT AND COMPANY IDENTIFICATION PRODUCT NAME: PRODUCT DESCRIPTION: NC600 (No Clean Solder Wire) MANUFACTURER 24 HR. EMERGENCY TELEPHONE NUMBERS Qualitek International, Inc. 1-800-535-5053
Page 1 of 5 1. PRODUCT AND COMPANY IDENTIFICATION PRODUCT NAME: PRODUCT DESCRIPTION: NC600 (No Clean Solder Wire) MANUFACTURER 24 HR. EMERGENCY TELEPHONE NUMBERS Qualitek International, Inc. 1-800-535-5053
AIIMS, New Delhi. Dr. K. K. Deepak, Prof. & HOD, Physiology AIIMS, New Delhi Dr. Geetanjali Bade, Asst. Professor AIIMS, New Delhi
 Course : PG Pathshala-Biophysics Paper 13 : Physiological Biophysics Module 17 : Gas transport and pulmonary circulation Principal Investigator: Co-Principal Investigator: Paper Coordinator: Content Writer:
Course : PG Pathshala-Biophysics Paper 13 : Physiological Biophysics Module 17 : Gas transport and pulmonary circulation Principal Investigator: Co-Principal Investigator: Paper Coordinator: Content Writer:
