Respiratory System Physiology. Dr. Vedat Evren
|
|
|
- Spencer Marshall
- 5 years ago
- Views:
Transcription
1 Respiratory System Physiology Dr. Vedat Evren
2 Respiration Processes involved in oxygen transport from the atmosphere to the body tissues and the release and transportation of carbon dioxide produced in the tissues to the atmosphere 3 systems must work in coordination Respiratory system Erythrocytes Circulatory system
3 Respiratory System Airways Lungs Thorax and the muscles of respiration Pulmonary circulation
4 Pulmonary Ventilation Boyle s Law: Gas pressure in closed container is inversely proportional to volume of container Air flow is a result of pressure differences
5 Ventilation Movement of air in and out of lungs Inspiration (inhalation): Breathing in Expiration (exhalation): Breathing out
6 Main Structure
7 Pleura
8 Pleura
9 Pleura
10 Importance of Pleura
11 Airway Structure
12 Alveoli
13 Alveoli
14 Respiratory Epithelium Epithelial and Goblet cells Lines entire airway passage Moisten and protect Mucociliary clearance (1-2 cm/hour upwards) Mucus: 100 ml/day
15 Respiratory Epithelium
16 Pressures Atmospheric pressure: 760 mmhg Intrapleural pressure: 756 mmhg Intrapulmonary pressure: Varies!!! Transpulmonary pressure: Pressure difference between intrapleural and intrapulmonary pressure!!!
17 Inspiration Intrapulmonary pressure must decrease in order to inhale! Thoracic cavity volume increases Lung volume increases IP pressure decreases... (~758 mmhg)
18 Expiration Intrapulmonary pressure must increase in order to exhale Thoracic cavity volume decreases Lung volume decreases (elastic recoiling mostly) IP pressure increases... (~763 mmhg)
19 Pulmonary Air Flow F = P / R Diameter of airways (especially bronchioles) Autonomic innervation Sympathetic Parasympathetic
20 Muscles
21 Intercostal Muscles
22 Respiratory Volumes and Capacities Tidal Volume (TV): 500 ml Inspiratory reserve volume (IRV): 3000 ml Expiratory reserve volume (ERV): 1100 ml Residual volume (RV): 1200 ml
23 Respiratory Volumes and Capacities Inspiratory Capacity: TV + IRV Functional Residual Capacity: ERV + RV Vital Capacity: IRV + TV + ERV Total Lung Capacity: IRV + TV + ERV + RV
24 Surface Tension Remember (!): Properties of water molecule... Surface tension tends to oppose alveoli expansion Pulmonary surfactant reduces surface tension
25 Surfactant Type II alveolar epithelial cells Detergent properties Reduces surface tension Prevents collapse
26 Surfactant
27 Matching Alveolar Air Flow with Blood Flow Pulmonary vessels Vessels can constrict in areas where oxygen flow is low Respiratory passageways Airways can dilate where carbon dioxide levels are high
28 Perfusion Lung blood circulation 5 25 L / minute 24 / 8 mmhg
29 Gas Exchange Partial Pressure Each gas in atmosphere contributes to the entire atmospheric pressure, denoted as P Gases in liquid Gas enters liquid and dissolves in proportion to its partial pressure O 2 and CO 2 Exchange by DIFFUSION PO 2 is 105 mmhg in alveoli and 40 in alveolar capillaries PCO 2 is 45 in alveolar capillaries and 40 in alveoli
30 Partial Pressures Oxygen is 21% of atmosphere 760 mmhg x.21 = 160 mmhg PO2 This mixes with old air already in alveolus to arrive at PO 2 of 105 mmhg
31 Partial Pressures Carbon dioxide is.04% of atmosphere 760 mmhg x.0004 =.3 mm Hg PCO 2 This mixes with high CO 2 levels from residual volume in the alveoli to arrive at PCO 2 of 40 mmhg
32 Partial Pressures
33 Partial Pressures
34 Gas Transport O 2 transport in blood Hemoglobin O 2 binds to the heme group on hemoglobin, with 4 oxygen / Hb PO 2 PO 2 is the most important factor determining whether O 2 and Hb combine or dissociate O 2 - Hb Dissociation curve
35 Oxygen Release
36 Influencing Factors ph CO 2 Temperature DPG
37 DPG 2,3-Bisphosphoglyceric acid Present in erythrocytes 5 mmol/l Binds and stabilizes deoxyhemoglobin (T state) Can t bind to oxyhemoglobin (R state) When there is need for oxygen for the tissues, 2,3DPG increases
38 Curve Shift
39 Curve Shift
40 Carbon Dioxide Transport 7% in plasma 23% in carbamino compounds (bound to globin part of Hb) 70% as Bicarbonate
41 Carbon Dioxide (CO 2 ) + (H 2 O) (H 2 CO 3 ) (H + ) + (HCO 3- ) Enzyme is Carbonic Anhydrase Chloride shift to compensate for bicarbonate moving in and out of RBC
42
43 Controls of Respiration Medullary Rhythmicity Area Medullary Inspiratory Neurons are main control of breathing Pons neurons influence inspiration, with Pneumotaxic area limiting inspiration and Apneustic area prolonging inspiration. Lung stretch receptors limit inspiration from being too deep
44 Controls Medullary Rhythmicity Area Medullary Expiratory Neurons Only active with exercise and forced expiration
45
46 Controls of rate and depth of respiration Arterial PO 2 When PO 2 is VERY low, ventilation increases Arterial PCO 2 The most important regulator of ventilation, small increases in PCO 2, greatly increases ventilation Arterial ph As hydrogen ions increase, alveolar ventilation increases, but hydrogen ions cannot diffuse into CSF as well as CO 2
47 EXERCISE Neural signals (rate & depth) PCO 2 (PO 2 and ph) Cardiac Output Maximal Hb saturation Dilate airways
Physiology Unit 4 RESPIRATORY PHYSIOLOGY
 Physiology Unit 4 RESPIRATORY PHYSIOLOGY In Physiology Today Respiration External respiration ventilation gas exchange Internal respiration cellular respiration gas exchange Respiratory Cycle Inspiration
Physiology Unit 4 RESPIRATORY PHYSIOLOGY In Physiology Today Respiration External respiration ventilation gas exchange Internal respiration cellular respiration gas exchange Respiratory Cycle Inspiration
Respiration - Human 1
 Respiration - Human 1 At the end of the lectures on respiration you should be able to, 1. Describe events in the respiratory processes 2. Discuss the mechanism of lung ventilation in human 3. Discuss the
Respiration - Human 1 At the end of the lectures on respiration you should be able to, 1. Describe events in the respiratory processes 2. Discuss the mechanism of lung ventilation in human 3. Discuss the
Respiratory Lecture Test Questions Set 3
 Respiratory Lecture Test Questions Set 3 1. The pressure of a gas: a. is inversely proportional to its volume b. is unaffected by temperature changes c. is directly proportional to its volume d. does not
Respiratory Lecture Test Questions Set 3 1. The pressure of a gas: a. is inversely proportional to its volume b. is unaffected by temperature changes c. is directly proportional to its volume d. does not
Physiology of Respiration
 Physiology of Respiration External Respiration = pulmonary ventilation breathing involves 2 processes: inspiration expiration Inspiration an active process involves contraction of diaphragm innervated
Physiology of Respiration External Respiration = pulmonary ventilation breathing involves 2 processes: inspiration expiration Inspiration an active process involves contraction of diaphragm innervated
 Question 1: Define vital capacity. What is its significance? Vital capacity is the maximum volume of air that can be exhaled after a maximum inspiration. It is about 3.5 4.5 litres in the human body. It
Question 1: Define vital capacity. What is its significance? Vital capacity is the maximum volume of air that can be exhaled after a maximum inspiration. It is about 3.5 4.5 litres in the human body. It
Chapter 17 The Respiratory System: Gas Exchange and Regulation of Breathing
 Chapter 17 The Respiratory System: Gas Exchange and Regulation of Breathing Overview of Pulmonary Circulation o Diffusion of Gases o Exchange of Oxygen and Carbon Dioxide o Transport of Gases in the Blood
Chapter 17 The Respiratory System: Gas Exchange and Regulation of Breathing Overview of Pulmonary Circulation o Diffusion of Gases o Exchange of Oxygen and Carbon Dioxide o Transport of Gases in the Blood
Respiratory Physiology Gaseous Exchange
 Respiratory Physiology Gaseous Exchange Session Objectives. What you will cover Basic anatomy of the lung including airways Breathing movements Lung volumes and capacities Compliance and Resistance in
Respiratory Physiology Gaseous Exchange Session Objectives. What you will cover Basic anatomy of the lung including airways Breathing movements Lung volumes and capacities Compliance and Resistance in
Respiratory System. Part 2
 Respiratory System Part 2 Respiration Exchange of gases between air and body cells Three steps 1. Ventilation 2. External respiration 3. Internal respiration Ventilation Pulmonary ventilation consists
Respiratory System Part 2 Respiration Exchange of gases between air and body cells Three steps 1. Ventilation 2. External respiration 3. Internal respiration Ventilation Pulmonary ventilation consists
Section Three Gas transport
 Section Three Gas transport Lecture 6: Oxygen transport in blood. Carbon dioxide in blood. Objectives: i. To describe the carriage of O2 in blood. ii. iii. iv. To explain the oxyhemoglobin dissociation
Section Three Gas transport Lecture 6: Oxygen transport in blood. Carbon dioxide in blood. Objectives: i. To describe the carriage of O2 in blood. ii. iii. iv. To explain the oxyhemoglobin dissociation
2. State the volume of air remaining in the lungs after a normal breathing.
 CLASS XI BIOLOGY Breathing And Exchange of Gases 1. Define vital capacity. What is its significance? Answer: Vital Capacity (VC): The maximum volume of air a person can breathe in after a forced expiration.
CLASS XI BIOLOGY Breathing And Exchange of Gases 1. Define vital capacity. What is its significance? Answer: Vital Capacity (VC): The maximum volume of air a person can breathe in after a forced expiration.
Respiratory system & exercise. Dr. Rehab F Gwada
 Respiratory system & exercise Dr. Rehab F Gwada Objectives of lecture Outline the major anatomical components & important functions of the respiratory system. Describe the mechanics of ventilation. List
Respiratory system & exercise Dr. Rehab F Gwada Objectives of lecture Outline the major anatomical components & important functions of the respiratory system. Describe the mechanics of ventilation. List
Chapter 13 The Respiratory System
 Chapter 13 The Respiratory System by Dr. Jay M. Templin Brooks/Cole - Thomson Learning Atmosphere Tissue cell External respiration Alveoli of lungs 1 Ventilation or gas exchange between the atmosphere
Chapter 13 The Respiratory System by Dr. Jay M. Templin Brooks/Cole - Thomson Learning Atmosphere Tissue cell External respiration Alveoli of lungs 1 Ventilation or gas exchange between the atmosphere
Respiration. The resspiratory system
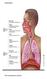 Respiration The resspiratory system The Alveoli The lungs have about 300 million alveoli, with a total crosssec onal area of 50 70 m2.. Each alveolar sac is surrounded by blood capillaries. The walls of
Respiration The resspiratory system The Alveoli The lungs have about 300 million alveoli, with a total crosssec onal area of 50 70 m2.. Each alveolar sac is surrounded by blood capillaries. The walls of
Chapter 16 Respiratory System
 Introduction Chapter 16 Respiratory System The respiratory system consists of tubes that filter incoming air and transport it to alveoli where gases are exchanged. Think pair share: what organs are associated
Introduction Chapter 16 Respiratory System The respiratory system consists of tubes that filter incoming air and transport it to alveoli where gases are exchanged. Think pair share: what organs are associated
Chapter 13 The Respiratory System
 VI edit Pag 451-499 Chapter 13 The Respiratory System V edit. Pag 459-509 Tissue cell Alveoli of lungs Atmosphere 1 External respiration Ventilation or gas exchange between the atmosphere and air sacs
VI edit Pag 451-499 Chapter 13 The Respiratory System V edit. Pag 459-509 Tissue cell Alveoli of lungs Atmosphere 1 External respiration Ventilation or gas exchange between the atmosphere and air sacs
GAS EXCHANGE & PHYSIOLOGY
 GAS EXCHANGE & PHYSIOLOGY Atmospheric Pressure Intra-Alveolar Pressure Inspiration 760 mm HG at Sea Level (= 1 atm) Pressure due to gases (N2, O2, CO2, Misc.) Pressure inside the alveolus (air sac) Phrenic
GAS EXCHANGE & PHYSIOLOGY Atmospheric Pressure Intra-Alveolar Pressure Inspiration 760 mm HG at Sea Level (= 1 atm) Pressure due to gases (N2, O2, CO2, Misc.) Pressure inside the alveolus (air sac) Phrenic
BREATHING AND EXCHANGE OF GASES
 96 BIOLOGY, EXEMPLAR PROBLEMS CHAPTER 17 BREATHING AND EXCHANGE OF GASES MULTIPLE CHOICE QUESTIONS 1. Respiration in insects is called direct because a. The tissues exchange O 2 directly with the air in
96 BIOLOGY, EXEMPLAR PROBLEMS CHAPTER 17 BREATHING AND EXCHANGE OF GASES MULTIPLE CHOICE QUESTIONS 1. Respiration in insects is called direct because a. The tissues exchange O 2 directly with the air in
CHAPTER 3: The respiratory system
 CHAPTER 3: The respiratory system Practice questions - text book pages 56-58 1) When the inspiratory muscles contract, which one of the following statements is true? a. the size of the thoracic cavity
CHAPTER 3: The respiratory system Practice questions - text book pages 56-58 1) When the inspiratory muscles contract, which one of the following statements is true? a. the size of the thoracic cavity
Chapter 22 The Respiratory System
 Chapter 22 The Respiratory System 1 Respiration Pulmonary ventilation (breathing): movement of air into and out of the lungs External respiration: O 2 and CO 2 exchange between the lungs and the blood
Chapter 22 The Respiratory System 1 Respiration Pulmonary ventilation (breathing): movement of air into and out of the lungs External respiration: O 2 and CO 2 exchange between the lungs and the blood
Collin County Community College. Lung Physiology
 Collin County Community College BIOL. 2402 Anatomy & Physiology WEEK 9 Respiratory System 1 Lung Physiology Factors affecting Ventillation 1. Airway resistance Flow = Δ P / R Most resistance is encountered
Collin County Community College BIOL. 2402 Anatomy & Physiology WEEK 9 Respiratory System 1 Lung Physiology Factors affecting Ventillation 1. Airway resistance Flow = Δ P / R Most resistance is encountered
Oxygen and Carbon dioxide Transport. Dr. Laila Al-Dokhi
 Oxygen and Carbon dioxide Transport Dr. Laila Al-Dokhi Objectives 1. Understand the forms of oxygen transport in the blood, the importance of each. 2. Differentiate between O2 capacity, O2 content and
Oxygen and Carbon dioxide Transport Dr. Laila Al-Dokhi Objectives 1. Understand the forms of oxygen transport in the blood, the importance of each. 2. Differentiate between O2 capacity, O2 content and
Outline - Respiratory System. Function of the respiratory system Parts of the respiratory system Mechanics of breathing Regulation of breathing
 Respiratory system Function Outline - Respiratory System I. II. III. IV. Respiratory System The function of the respiratory system is to bring in oxygen to the body and remove carbon dioxide. Function
Respiratory system Function Outline - Respiratory System I. II. III. IV. Respiratory System The function of the respiratory system is to bring in oxygen to the body and remove carbon dioxide. Function
IV. FROM AQUATIC TO ATMOSPHERIC BREATHING: THE TRACHEA & THE LUNG
 GAS EXCHANGE AND TRANSPORT I. INTRODUCTION: Heterotrophs oxidize carbon cmpds using O 2 to generate CO 2 & H 2 O. This is cellular respiration II. HOW GAS ENTERS A CELL A. The composition of air: 79% N
GAS EXCHANGE AND TRANSPORT I. INTRODUCTION: Heterotrophs oxidize carbon cmpds using O 2 to generate CO 2 & H 2 O. This is cellular respiration II. HOW GAS ENTERS A CELL A. The composition of air: 79% N
Respiration (revised 2006) Pulmonary Mechanics
 Respiration (revised 2006) Pulmonary Mechanics PUL 1. Diagram how pleural pressure, alveolar pressure, airflow, and lung volume change during a normal quiet breathing cycle. Identify on the figure the
Respiration (revised 2006) Pulmonary Mechanics PUL 1. Diagram how pleural pressure, alveolar pressure, airflow, and lung volume change during a normal quiet breathing cycle. Identify on the figure the
82 Respiratory Tract NOTES
 82 Respiratory Tract NOTES RESPIRATORY TRACT The respiratory tract conducts air to the lungs where gaseous exchange occurs. It is separated into air-conducting and respiratory (where gas exchange occurs)
82 Respiratory Tract NOTES RESPIRATORY TRACT The respiratory tract conducts air to the lungs where gaseous exchange occurs. It is separated into air-conducting and respiratory (where gas exchange occurs)
(Slide 1) Lecture Notes: Respiratory System
 (Slide 1) Lecture Notes: Respiratory System I. (Slide 2) The Respiratory Tract A) Major structures and regions of the respiratory Tract/Route INTO body 1) nose 2) nasal cavity 3) pharynx 4) glottis 5)
(Slide 1) Lecture Notes: Respiratory System I. (Slide 2) The Respiratory Tract A) Major structures and regions of the respiratory Tract/Route INTO body 1) nose 2) nasal cavity 3) pharynx 4) glottis 5)
2.1.1 List the principal structures of the
 physiology 2.1.1 List the principal structures of the The principle structures of the respiratory are: Nose/Mouth used for inhalation of oxygen-rich air and expelling carbon dioxide rich air Pharynx -
physiology 2.1.1 List the principal structures of the The principle structures of the respiratory are: Nose/Mouth used for inhalation of oxygen-rich air and expelling carbon dioxide rich air Pharynx -
P215 Respiratory System, Part 2
 P15 Respiratory System, Part Gas Exchange Oxygen and Carbon Dioxide constant need for oxygen constant production of carbon dioxide exchange (and movement) lung alveoli pulmonary arteries pulmonary capillaries
P15 Respiratory System, Part Gas Exchange Oxygen and Carbon Dioxide constant need for oxygen constant production of carbon dioxide exchange (and movement) lung alveoli pulmonary arteries pulmonary capillaries
LAB 7 HUMAN RESPIRATORY LAB. Complete the charts on pgs. 67 and 68 and read directions for using BIOPAC
 66 LAB 7 HUMAN RESPIRATORY LAB Assignments: Due before lab: Quiz: Three Respiratory Interactive Physiology Animations pages 69 73. Complete the charts on pgs. 67 and 68 and read directions for using BIOPAC
66 LAB 7 HUMAN RESPIRATORY LAB Assignments: Due before lab: Quiz: Three Respiratory Interactive Physiology Animations pages 69 73. Complete the charts on pgs. 67 and 68 and read directions for using BIOPAC
CHAPTER 3: The cardio-respiratory system
 : The cardio-respiratory system Exam style questions - text book pages 44-45 1) Describe the structures involved in gaseous exchange in the lungs and explain how gaseous exchange occurs within this tissue.
: The cardio-respiratory system Exam style questions - text book pages 44-45 1) Describe the structures involved in gaseous exchange in the lungs and explain how gaseous exchange occurs within this tissue.
Respiratory System Review
 KEY THIS TEST WILL BE COMPLETED IN ONE CLASS PERIOD MONDAY, MARCH 10. 2014 Respiratory System Review Name A. Directions: Fill in the blank with the appropriate vocabulary word or words (several examples
KEY THIS TEST WILL BE COMPLETED IN ONE CLASS PERIOD MONDAY, MARCH 10. 2014 Respiratory System Review Name A. Directions: Fill in the blank with the appropriate vocabulary word or words (several examples
BREATHING AND EXCHANGE OF GASES
 96 BIOLOGY, EXEMPLAR PROBLEMS CHAPTER 17 BREATHING AND EXCHANGE OF GASES MULTIPLE CHOICE QUESTIONS 1. Respiration in insects is called direct because a. The cell exchange O 2 directly with the air in the
96 BIOLOGY, EXEMPLAR PROBLEMS CHAPTER 17 BREATHING AND EXCHANGE OF GASES MULTIPLE CHOICE QUESTIONS 1. Respiration in insects is called direct because a. The cell exchange O 2 directly with the air in the
Chapter 16 Respiration. Respiration. Steps in Respiration. Functions of the respiratory system
 Chapter 16 Respiration Functions of the respiratory system Respiration The term respiration includes 3 separate functions: Ventilation: Breathing. Gas exchange: Occurs between air and blood in the lungs.
Chapter 16 Respiration Functions of the respiratory system Respiration The term respiration includes 3 separate functions: Ventilation: Breathing. Gas exchange: Occurs between air and blood in the lungs.
CHAPTER 17 BREATHING AND EXCHANGE OF GASES
 268 BIOLOGY CHAPTER 17 BREATHING AND EXCHANGE OF GASES 17.1 Respiratory Organs 17.2 Mechanism of Breathing 17.3 Exchange of Gases 17.4 Transport of Gases 17.5 Regulation of Respiration 17.6 Disorders of
268 BIOLOGY CHAPTER 17 BREATHING AND EXCHANGE OF GASES 17.1 Respiratory Organs 17.2 Mechanism of Breathing 17.3 Exchange of Gases 17.4 Transport of Gases 17.5 Regulation of Respiration 17.6 Disorders of
1 CHAPTER 17 BREATHING AND EXCHANGE OF GASES https://biologyaipmt.com/
 1 CHAPTER 17 BREATHING AND EXCHANGE OF GASES https://biologyaipmt.com/ CHAPTER 17 BREATHING AND EXCHANGE OF GASES Oxygen (O2) is utilised by the organisms to indirectly break down nutrient molecules like
1 CHAPTER 17 BREATHING AND EXCHANGE OF GASES https://biologyaipmt.com/ CHAPTER 17 BREATHING AND EXCHANGE OF GASES Oxygen (O2) is utilised by the organisms to indirectly break down nutrient molecules like
Introduction. Respiration. Chapter 10. Objectives. Objectives. The Respiratory System
 Introduction Respiration Chapter 10 The Respiratory System Provides a means of gas exchange between the environment and the body Plays a role in the regulation of acidbase balance during exercise Objectives
Introduction Respiration Chapter 10 The Respiratory System Provides a means of gas exchange between the environment and the body Plays a role in the regulation of acidbase balance during exercise Objectives
Chapter 37: Pulmonary Ventilation. Chad & Angela
 Chapter 37: Pulmonary Ventilation Chad & Angela Respiratory Structures Basic Structures of Respiration Nasal/Oral Cavities Larynx Trachea Bronchi Secondary Bronchi Bronchioles Alveoli Mechanics of Ventilation
Chapter 37: Pulmonary Ventilation Chad & Angela Respiratory Structures Basic Structures of Respiration Nasal/Oral Cavities Larynx Trachea Bronchi Secondary Bronchi Bronchioles Alveoli Mechanics of Ventilation
Gas exchange. Tissue cells CO2 CO 2 O 2. Pulmonary capillary. Tissue capillaries
 Gas exchange Pulmonary gas exchange Tissue gas exchange CO 2 O 2 O 2 Tissue cells CO2 CO 2 Pulmonary capillary O 2 O 2 CO 2 Tissue capillaries Physical principles of gas exchange Diffusion: continuous
Gas exchange Pulmonary gas exchange Tissue gas exchange CO 2 O 2 O 2 Tissue cells CO2 CO 2 Pulmonary capillary O 2 O 2 CO 2 Tissue capillaries Physical principles of gas exchange Diffusion: continuous
HCO - 3 H 2 CO 3 CO 2 + H H H + Breathing rate is regulated by blood ph and C02. CO2 and Bicarbonate act as a ph Buffer in the blood
 Breathing rate is regulated by blood ph and C02 breathing reduces plasma [CO2]; plasma [CO2] increases breathing. When C02 levels are high, breating rate increases to blow off C02 In low C02 conditions,
Breathing rate is regulated by blood ph and C02 breathing reduces plasma [CO2]; plasma [CO2] increases breathing. When C02 levels are high, breating rate increases to blow off C02 In low C02 conditions,
Respiratory Anatomy and Physiology. Respiratory Anatomy. Function of the Respiratory System
 Respiratory Anatomy and Physiology Michaela Dixon Clinical Development Nurse PICU BRHFC Respiratory Anatomy Function of the Respiratory System - In conjunction with the cardiovascular system, to supply
Respiratory Anatomy and Physiology Michaela Dixon Clinical Development Nurse PICU BRHFC Respiratory Anatomy Function of the Respiratory System - In conjunction with the cardiovascular system, to supply
Chapter 23. Gas Exchange and Transportation
 Chapter 23 Gas Exchange and Transportation What is air? Mixture of gasses 78.6 % nitrogen 20.9% oxygen 0.04% carbon dioxide 0 4% water vapor depending on temperature and humidity other minor gases argon,
Chapter 23 Gas Exchange and Transportation What is air? Mixture of gasses 78.6 % nitrogen 20.9% oxygen 0.04% carbon dioxide 0 4% water vapor depending on temperature and humidity other minor gases argon,
Chapter 23. Gas Exchange and Transportation
 Chapter 23 Gas Exchange and Transportation What is air? Mixture of gasses 78.6 % nitrogen 20.9% oxygen 0.04% carbon dioxide 0 4% water vapor depending on temperature and humidity and minor gases argon,
Chapter 23 Gas Exchange and Transportation What is air? Mixture of gasses 78.6 % nitrogen 20.9% oxygen 0.04% carbon dioxide 0 4% water vapor depending on temperature and humidity and minor gases argon,
Human Biology Respiratory System
 Human Biology Respiratory System Respiratory System Responsible for process of breathing Works in cooperation with Circulatory system Three types: 1. Internal Respiration 2. External Respiration 3. Cellular
Human Biology Respiratory System Respiratory System Responsible for process of breathing Works in cooperation with Circulatory system Three types: 1. Internal Respiration 2. External Respiration 3. Cellular
Alveolus and Respiratory Membrane
 Alveolus and Respiratory Membrane thin membrane where gas exchange occurs in the lungs, simple squamous epithelium (Squamous cells have the appearance of thin, flat plates. They fit closely together in
Alveolus and Respiratory Membrane thin membrane where gas exchange occurs in the lungs, simple squamous epithelium (Squamous cells have the appearance of thin, flat plates. They fit closely together in
Respiratory system. Role. Ventilation consists of 4 (5) steps : oxygen delivery and carbon dioxide elimination ph balance sound and voice formation
 Respiratory system Role oxygen delivery and carbon dioxide elimination ph balance sound and voice formation Ventilation consists of 4 (5) steps : 1. pulmonary ventilation gas exchange between lungs and
Respiratory system Role oxygen delivery and carbon dioxide elimination ph balance sound and voice formation Ventilation consists of 4 (5) steps : 1. pulmonary ventilation gas exchange between lungs and
Ch 16: Respiratory System
 Ch 16: Respiratory System SLOs: Explain how intrapulmonary pressures change during breathing Explain surface tension and the role of surfactant in respiratory physiology. Compare and contrast compliance
Ch 16: Respiratory System SLOs: Explain how intrapulmonary pressures change during breathing Explain surface tension and the role of surfactant in respiratory physiology. Compare and contrast compliance
Respiratory System Study Guide, Chapter 16
 Part I. Clinical Applications Name: Respiratory System Study Guide, Chapter 16 Lab Day/Time: 1. A person with ketoacidosis may hyperventilate. Explain why this occurs, and explain why this hyperventilation
Part I. Clinical Applications Name: Respiratory System Study Guide, Chapter 16 Lab Day/Time: 1. A person with ketoacidosis may hyperventilate. Explain why this occurs, and explain why this hyperventilation
The Respiratory System
 Essentials of Human Anatomy & Physiology Elaine N. Marieb Seventh Edition Chapter 13 The Respiratory System Slides 13.1 13.30 Lecture Slides in PowerPoint by Jerry L. Cook Organs of the Respiratory system
Essentials of Human Anatomy & Physiology Elaine N. Marieb Seventh Edition Chapter 13 The Respiratory System Slides 13.1 13.30 Lecture Slides in PowerPoint by Jerry L. Cook Organs of the Respiratory system
RESPIRATION III SEMESTER BOTANY MODULE II
 III SEMESTER BOTANY MODULE II RESPIRATION Lung Capacities and Volumes Tidal volume (TV) air that moves into and out of the lungs with each breath (approximately 500 ml) Inspiratory reserve volume (IRV)
III SEMESTER BOTANY MODULE II RESPIRATION Lung Capacities and Volumes Tidal volume (TV) air that moves into and out of the lungs with each breath (approximately 500 ml) Inspiratory reserve volume (IRV)
Airway: the tubes through which air flows between atmosphere and alveoli. Upper airway. Lower airway
 Respiration Yu Yanqin ( 虞燕琴 ), PhD Dept. of fph Physiology Zhejiang University, School of Medicine Respiration Definition: the bodily processes involved in exchange of oxygen (O 2 ) and carbon dioxide
Respiration Yu Yanqin ( 虞燕琴 ), PhD Dept. of fph Physiology Zhejiang University, School of Medicine Respiration Definition: the bodily processes involved in exchange of oxygen (O 2 ) and carbon dioxide
Respiratory Pulmonary Ventilation
 Respiratory Pulmonary Ventilation Pulmonary Ventilation Pulmonary ventilation is the act of breathing and the first step in the respiratory process. Pulmonary ventilation brings in air with a new supply
Respiratory Pulmonary Ventilation Pulmonary Ventilation Pulmonary ventilation is the act of breathing and the first step in the respiratory process. Pulmonary ventilation brings in air with a new supply
Respiratory Physiology 2
 Respiratory Physiology 2 Session Objectives. What you will cover Gaseous Exchange Control of Breathing Rate Your objectives are State the function of support structures and epithelia of the bronchial tree
Respiratory Physiology 2 Session Objectives. What you will cover Gaseous Exchange Control of Breathing Rate Your objectives are State the function of support structures and epithelia of the bronchial tree
Circulatory And Respiration
 Circulatory And Respiration Composition Of Blood Blood Heart 200mmHg 120mmHg Aorta Artery Arteriole 50mmHg Capillary Bed Venule Vein Vena Cava Heart Differences Between Arteries and Veins Veins transport
Circulatory And Respiration Composition Of Blood Blood Heart 200mmHg 120mmHg Aorta Artery Arteriole 50mmHg Capillary Bed Venule Vein Vena Cava Heart Differences Between Arteries and Veins Veins transport
RESPIRATORY PHYSIOLOGY. Anaesthesiology Block 18 (GNK 586) Prof Pierre Fourie
 RESPIRATORY PHYSIOLOGY Anaesthesiology Block 18 (GNK 586) Prof Pierre Fourie Outline Ventilation Diffusion Perfusion Ventilation-Perfusion relationship Work of breathing Control of Ventilation 2 This image
RESPIRATORY PHYSIOLOGY Anaesthesiology Block 18 (GNK 586) Prof Pierre Fourie Outline Ventilation Diffusion Perfusion Ventilation-Perfusion relationship Work of breathing Control of Ventilation 2 This image
Chapter 23: Respiratory System
 Chapter 23: Respiratory System I. Functions of the Respiratory System A. List and describe the five major functions of the respiratory system: 1. 2. 3. 4. 5. II. Anatomy and Histology of the Respiratory
Chapter 23: Respiratory System I. Functions of the Respiratory System A. List and describe the five major functions of the respiratory system: 1. 2. 3. 4. 5. II. Anatomy and Histology of the Respiratory
Gases and Respiration. Respiration Overview I
 Respiration Overview I Respiration Overview II Gas Laws Equation of State: PV = nrt Same volumes of different gases have same # of molecules BTPS: body temp, atmospheric pressure, saturated ATPS: ambient
Respiration Overview I Respiration Overview II Gas Laws Equation of State: PV = nrt Same volumes of different gases have same # of molecules BTPS: body temp, atmospheric pressure, saturated ATPS: ambient
Section Two Diffusion of gases
 Section Two Diffusion of gases Lecture 5: Partial pressure and the composition of gasses in air. Factors affecting diffusion of gases. Ventilation perfusion ratio effect on alveolar gas concentration.
Section Two Diffusion of gases Lecture 5: Partial pressure and the composition of gasses in air. Factors affecting diffusion of gases. Ventilation perfusion ratio effect on alveolar gas concentration.
BIOLOGY 12: UNIT J - CHAPTER 15 - REVIEW WORKSHEET RESPIRATORY SYSTEM
 BIOLOGY 12: UNIT J - CHAPTER 15 - REVIEW WORKSHEET RESPIRATORY SYSTEM A. CHAPTER REVIEW 1. Define the four components of respiration. 2. What happens to the air as it moves along the air passages? What
BIOLOGY 12: UNIT J - CHAPTER 15 - REVIEW WORKSHEET RESPIRATORY SYSTEM A. CHAPTER REVIEW 1. Define the four components of respiration. 2. What happens to the air as it moves along the air passages? What
Lesson 9.1: The Importance of an Organ Delivery System
 Lesson 9.1: The Importance of an Organ Delivery System Animals require a continuous supply of oxygen (O 2 ) for cellular respiration, and they must expel carbon dioxide (CO 2 ), the waste product of this
Lesson 9.1: The Importance of an Organ Delivery System Animals require a continuous supply of oxygen (O 2 ) for cellular respiration, and they must expel carbon dioxide (CO 2 ), the waste product of this
respiratory cycle. point in the volumes: 500 milliliters. for men. expiration, up to 1200 milliliters extra makes breathing Respiratory
 10 II. RESPIRATORY VOLUMES, CAPACITIES & PULMONARY FUNCTION TESTS Respiratory volume is the term used for various volumes of air moved by or associated with the lungs at a given point in the respiratory
10 II. RESPIRATORY VOLUMES, CAPACITIES & PULMONARY FUNCTION TESTS Respiratory volume is the term used for various volumes of air moved by or associated with the lungs at a given point in the respiratory
Chapter 11: Respiratory System Review Assignment
 Name: Date: Mark: / 45 Chapter 11: Respiratory System Review Assignment Multiple Choice = 45 Marks Identify the choice that best completes the statement or answers the question. 1. Which of the following
Name: Date: Mark: / 45 Chapter 11: Respiratory System Review Assignment Multiple Choice = 45 Marks Identify the choice that best completes the statement or answers the question. 1. Which of the following
4/18/12 MECHANISM OF RESPIRATION. Every Breath You Take. Fun Facts
 Objectives MECHANISM OF RESPIRATION Dr Badri Paudel Explain how the intrapulmonary and intrapleural pressures vary during ventilation and relate these pressure changes to Boyle s law. Define the terms
Objectives MECHANISM OF RESPIRATION Dr Badri Paudel Explain how the intrapulmonary and intrapleural pressures vary during ventilation and relate these pressure changes to Boyle s law. Define the terms
Oxygen, Carbon Dioxide Respiration Gas Transport Chapter 21-23
 nd Lecture Fri 06 Mar 009 Vertebrate Physiology ECOL 437 (MCB/VetSci 437) Univ. of Arizona, spring 009 Kevin Bonine & Kevin Oh Oxygen, Carbon Dioxide Respiration Gas Transport Chapter 1-3 1 Housekeeping,
nd Lecture Fri 06 Mar 009 Vertebrate Physiology ECOL 437 (MCB/VetSci 437) Univ. of Arizona, spring 009 Kevin Bonine & Kevin Oh Oxygen, Carbon Dioxide Respiration Gas Transport Chapter 1-3 1 Housekeeping,
Respiratory Physiology. Adeyomoye O.I
 Respiratory Physiology By Adeyomoye O.I Outline Introduction Hypoxia Dyspnea Control of breathing Ventilation/perfusion ratios Respiratory/barometric changes in exercise Intra-pulmonary & intra-pleural
Respiratory Physiology By Adeyomoye O.I Outline Introduction Hypoxia Dyspnea Control of breathing Ventilation/perfusion ratios Respiratory/barometric changes in exercise Intra-pulmonary & intra-pleural
Physiology: Respiratory System
 In the name of God Physiology: Respiratory System Moradian MD, MPH, PhD candidate Tehran University of Medical Sciences drmoradian@sums.ac.ir 2013 Respiratory Anatomy The primary function of the respiratory
In the name of God Physiology: Respiratory System Moradian MD, MPH, PhD candidate Tehran University of Medical Sciences drmoradian@sums.ac.ir 2013 Respiratory Anatomy The primary function of the respiratory
The physiological functions of respiration and circulation. Mechanics. exercise 7. Respiratory Volumes. Objectives
 exercise 7 Respiratory System Mechanics Objectives 1. To explain how the respiratory and circulatory systems work together to enable gas exchange among the lungs, blood, and body tissues 2. To define respiration,
exercise 7 Respiratory System Mechanics Objectives 1. To explain how the respiratory and circulatory systems work together to enable gas exchange among the lungs, blood, and body tissues 2. To define respiration,
Respiratory System. 1. muscular tube lined by mucous membrane 2. throat 3. nasopharynx, oropharynx, laryngopharynx
 I. Functions of the Respiratory System A. gas exchange B. prevent dehydration C. sound D. olfaction E. ph regulation II. Anatomy of the Respiratory System A. Nose 1. external nares vestibule nasal cavity
I. Functions of the Respiratory System A. gas exchange B. prevent dehydration C. sound D. olfaction E. ph regulation II. Anatomy of the Respiratory System A. Nose 1. external nares vestibule nasal cavity
Recitation question # 05
 Recitation and Lab # 05 The goal of this recitations / labs is to review material related to the CV and respiratory lectures for the second test of this course. Info required to answer this recitation
Recitation and Lab # 05 The goal of this recitations / labs is to review material related to the CV and respiratory lectures for the second test of this course. Info required to answer this recitation
I. Gas Exchange Respiratory Surfaces Respiratory Surface:
 I. Gas Exchange Respiratory Surfaces Respiratory Surface: Common characteristics of respiratory surfaces: a) Moist: allows for the RAPID diffusion of dissolved gasses across its surface. Whereas the respiratory
I. Gas Exchange Respiratory Surfaces Respiratory Surface: Common characteristics of respiratory surfaces: a) Moist: allows for the RAPID diffusion of dissolved gasses across its surface. Whereas the respiratory
Chapter 15. Lecture and Animation Outline
 Chapter 15 Lecture and Animation Outline To run the animations you must be in Slideshow View. Use the buttons on the animation to play, pause, and turn audio/text on or off. Please Note: Once you have
Chapter 15 Lecture and Animation Outline To run the animations you must be in Slideshow View. Use the buttons on the animation to play, pause, and turn audio/text on or off. Please Note: Once you have
I Physical Principles of Gas Exchange
 Respiratory Gases Exchange Dr Badri Paudel, M.D. 2 I Physical Principles of Gas Exchange 3 Partial pressure The pressure exerted by each type of gas in a mixture Diffusion of gases through liquids Concentration
Respiratory Gases Exchange Dr Badri Paudel, M.D. 2 I Physical Principles of Gas Exchange 3 Partial pressure The pressure exerted by each type of gas in a mixture Diffusion of gases through liquids Concentration
RESPIRATORY REGULATION DURING EXERCISE
 RESPIRATORY REGULATION DURING EXERCISE Respiration Respiration delivery of oxygen to and removal of carbon dioxide from the tissue External respiration ventilation and exchange of gases in the lung Internal
RESPIRATORY REGULATION DURING EXERCISE Respiration Respiration delivery of oxygen to and removal of carbon dioxide from the tissue External respiration ventilation and exchange of gases in the lung Internal
Gas Exchange Respiratory Systems
 alveoli gills Gas Exchange Respiratory Systems elephant seals 2008-2009 Why do we need a respiratory system? respiration for respiration Need O 2 in for aerobic cellular respiration make ATP Need CO 2
alveoli gills Gas Exchange Respiratory Systems elephant seals 2008-2009 Why do we need a respiratory system? respiration for respiration Need O 2 in for aerobic cellular respiration make ATP Need CO 2
alveoli Chapter 42. Gas Exchange elephant seals gills AP Biology
 alveoli Chapter 42. Gas Exchange gills elephant seals Gas exchange O 2 & CO 2 exchange exchange between environment & cells provides O 2 for aerobic cellular respiration need moist membrane need high
alveoli Chapter 42. Gas Exchange gills elephant seals Gas exchange O 2 & CO 2 exchange exchange between environment & cells provides O 2 for aerobic cellular respiration need moist membrane need high
Unit II Problem 4 Physiology: Diffusion of Gases and Pulmonary Circulation
 Unit II Problem 4 Physiology: Diffusion of Gases and Pulmonary Circulation - Physical principles of gases: Pressure of a gas is caused by the movement of its molecules against a surface (more concentration
Unit II Problem 4 Physiology: Diffusion of Gases and Pulmonary Circulation - Physical principles of gases: Pressure of a gas is caused by the movement of its molecules against a surface (more concentration
Structures of the Respiratory System include:
 Respiratory System Structures of the Respiratory System include: ü Oral Cavity ü Nasal Cavity ü Pharynx ü Epiglottis ü Larynx ü Trachea ü Diaphragm ü Lung ü Bronchus ü Bronchioles ü Alveolus ü Pulmonary
Respiratory System Structures of the Respiratory System include: ü Oral Cavity ü Nasal Cavity ü Pharynx ü Epiglottis ü Larynx ü Trachea ü Diaphragm ü Lung ü Bronchus ü Bronchioles ü Alveolus ü Pulmonary
AP Biology. Gas Exchange Respiratory Systems. Gas exchange. Why do we need a respiratory system? Optimizing gas exchange. Gas exchange in many forms
 alveoli Gas Exchange Respiratory Systems gills elephant seals 2008-2009 Why do we need a respiratory system? Need O 2 in food respiration for respiration for aerobic cellular respiration make ATP Need
alveoli Gas Exchange Respiratory Systems gills elephant seals 2008-2009 Why do we need a respiratory system? Need O 2 in food respiration for respiration for aerobic cellular respiration make ATP Need
AP Biology. Chapter 42. Gas Exchange. Optimizing gas exchange. Gas exchange. Gas exchange in many forms. Evolution of gas exchange structures
 alveoli Chapter 42. Gas Exchange gills elephant seals Gas exchange & C exchange exchange between environment & cells provides for aerobic cellular respiration need moist membrane need high surface area
alveoli Chapter 42. Gas Exchange gills elephant seals Gas exchange & C exchange exchange between environment & cells provides for aerobic cellular respiration need moist membrane need high surface area
Respiratory/Pulmonary Laboratory Experimentation
 Respiratory/Pulmonary Laboratory Experimentation Introduction Anatomy Review The respiratory system has the dubious honor of being the system that permits the transport of gases from the environment inside
Respiratory/Pulmonary Laboratory Experimentation Introduction Anatomy Review The respiratory system has the dubious honor of being the system that permits the transport of gases from the environment inside
system. and then into the tissues. Diffusion of wastes such as Carbon Dioxide from tissues into blood and out of blood into the lungs.
 Respiratory System 1.Exchange Why do of we gases breathe? into the Think blood of all and the tissues. reasons Diffusion why we of Oxygen need a respiratory into blood from the lungs system. and then into
Respiratory System 1.Exchange Why do of we gases breathe? into the Think blood of all and the tissues. reasons Diffusion why we of Oxygen need a respiratory into blood from the lungs system. and then into
Breathing: The normal rate is about 14 to 20 times a minute. Taking in of air is called Inspiration and the forcing out of air is called Expiration.
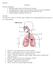 Biology 12 Respiration Divisions of Respiration Breathing: entrance and exit of air into and out of the lungs External Respiration: exchange of gases(o2 and CO2) between air (in alveoli) and blood Internal
Biology 12 Respiration Divisions of Respiration Breathing: entrance and exit of air into and out of the lungs External Respiration: exchange of gases(o2 and CO2) between air (in alveoli) and blood Internal
AIIMS, New Delhi. Dr. K. K. Deepak, Prof. & HOD, Physiology AIIMS, New Delhi Dr. Geetanjali Bade, Asst. Professor AIIMS, New Delhi
 Course : PG Pathshala-Biophysics Paper 13 : Physiological Biophysics Module 17 : Gas transport and pulmonary circulation Principal Investigator: Co-Principal Investigator: Paper Coordinator: Content Writer:
Course : PG Pathshala-Biophysics Paper 13 : Physiological Biophysics Module 17 : Gas transport and pulmonary circulation Principal Investigator: Co-Principal Investigator: Paper Coordinator: Content Writer:
To supply the body with oxygen and dispose of carbon dioxide Respiration four distinct processes must happen
 Respiratory System Consists of the respiratory and conducting zones Respiratory zone Site of gas exchange Consists of bronchioles, alveolar ducts, and alveoli Conducting zone Provides rigid conduits for
Respiratory System Consists of the respiratory and conducting zones Respiratory zone Site of gas exchange Consists of bronchioles, alveolar ducts, and alveoli Conducting zone Provides rigid conduits for
RESPIRATORY GAS EXCHANGE
 RESPIRATORY GAS EXCHANGE Alveolar PO 2 = 105 mmhg; Pulmonary artery PO 2 = 40 mmhg PO 2 gradient across respiratory membrane 65 mmhg (105 mmhg 40 mmhg) Results in pulmonary vein PO 2 ~100 mmhg Partial
RESPIRATORY GAS EXCHANGE Alveolar PO 2 = 105 mmhg; Pulmonary artery PO 2 = 40 mmhg PO 2 gradient across respiratory membrane 65 mmhg (105 mmhg 40 mmhg) Results in pulmonary vein PO 2 ~100 mmhg Partial
Respiratory Lecture Test Questions Set 1
 Respiratory Lecture Test Questions Set 1 1. The term "respiration" in its most complete meaning is: a. breathing b. oxygen transport c. carbon dioxide transport d. cellular energy production e. all of
Respiratory Lecture Test Questions Set 1 1. The term "respiration" in its most complete meaning is: a. breathing b. oxygen transport c. carbon dioxide transport d. cellular energy production e. all of
Breathing and Exchange of Gases
 183 Breathing and Exchange of Gases 1. Skin is an accessory organ of respiration in (a) humans (b) frog (c) rabbit (d) lizard Frog has lungs as its main respiratory organs but during hibernation & aestivation
183 Breathing and Exchange of Gases 1. Skin is an accessory organ of respiration in (a) humans (b) frog (c) rabbit (d) lizard Frog has lungs as its main respiratory organs but during hibernation & aestivation
LECTURE NOTES ANATOMY & PHYSIOLOGY II (A. IMHOLTZ) RESPIRATORY P1 OF 8
 LECTURE NOTES ANATOMY & PHYSIOLOGY II (A. IMHOLTZ) RESPIRATORY P1 OF 8 I. The main functions of the respiratory system include: a. Exchange of O 2 and CO 2. b. Voice production. c. Regulation of plasma
LECTURE NOTES ANATOMY & PHYSIOLOGY II (A. IMHOLTZ) RESPIRATORY P1 OF 8 I. The main functions of the respiratory system include: a. Exchange of O 2 and CO 2. b. Voice production. c. Regulation of plasma
The Human Respiratory System
 The Human Respiratory System Maryam Maheri Kiana Kayoda, Nazalia, Emerald Bocobo NPB 101 L section 008 TA: Ashneel Krishna 2/26/2015 Introduction: The respiratory system allows gas exchange between cells
The Human Respiratory System Maryam Maheri Kiana Kayoda, Nazalia, Emerald Bocobo NPB 101 L section 008 TA: Ashneel Krishna 2/26/2015 Introduction: The respiratory system allows gas exchange between cells
BIOH122 Human Biological Science 2
 BIOH122 Human Biological Science 2 Session 11 Respiratory System 2 Pulmonary Ventilation Bioscience Department Endeavour College of Natural Health endeavour.edu.au Session plan o Pulmonary Ventilation
BIOH122 Human Biological Science 2 Session 11 Respiratory System 2 Pulmonary Ventilation Bioscience Department Endeavour College of Natural Health endeavour.edu.au Session plan o Pulmonary Ventilation
Regulation of Ventilation, Ventilation/ Perfusion Ratio, and Transport of Gases
 M07_LIMM3516_01_SE_C07.indd Page 37 1/28/11 4:38 PM user-s146 Standard Pathophysiology TOPIC Competency Applies fundamental knowledge of the pathophysiology of respiration and perfusion to patient assessment
M07_LIMM3516_01_SE_C07.indd Page 37 1/28/11 4:38 PM user-s146 Standard Pathophysiology TOPIC Competency Applies fundamental knowledge of the pathophysiology of respiration and perfusion to patient assessment
Pulmonary Ventilation
 Pulmonary Ventilation - Goals of respiration: o Provided O 2 to the tissues/remove CO 2 - To achieve these goals, resp. is divided into 4 events: 1. Pulm. Ventilation = exchange of resp. gases between
Pulmonary Ventilation - Goals of respiration: o Provided O 2 to the tissues/remove CO 2 - To achieve these goals, resp. is divided into 4 events: 1. Pulm. Ventilation = exchange of resp. gases between
Then the partial pressure of oxygen is x 760 = 160 mm Hg
 1 AP Biology March 2008 Respiration Chapter 42 Gas exchange occurs across specialized respiratory surfaces. 1) Gas exchange: the uptake of molecular oxygen (O2) from the environment and the discharge of
1 AP Biology March 2008 Respiration Chapter 42 Gas exchange occurs across specialized respiratory surfaces. 1) Gas exchange: the uptake of molecular oxygen (O2) from the environment and the discharge of
Gaseous exchange. Grade 11
 z Gaseous exchange Grade 11 z Terminology 1. Breathing 2. Gaseous exchange 3. Diffusion 4. Spongy mesophyll cells 5. Tracheae 6. Gills 7. Alveoli 8. Larynx 9. Diaphragm 10. Endothelium 1. Pleura 2. Squamous
z Gaseous exchange Grade 11 z Terminology 1. Breathing 2. Gaseous exchange 3. Diffusion 4. Spongy mesophyll cells 5. Tracheae 6. Gills 7. Alveoli 8. Larynx 9. Diaphragm 10. Endothelium 1. Pleura 2. Squamous
Lectures on Medical Biophysics Department of Biophysics, Medical Faculty, Masaryk University in Brno. Biophysics of breathing.
 Lectures on Medical Biophysics Department of Biophysics, Medical Faculty, Masaryk University in Brno Biophysics of breathing. Spirometry 1 Lecture outline Mechanisms of gas exchange between organism and
Lectures on Medical Biophysics Department of Biophysics, Medical Faculty, Masaryk University in Brno Biophysics of breathing. Spirometry 1 Lecture outline Mechanisms of gas exchange between organism and
Respiratory System. Prepared by: Dorota Marczuk-Krynicka, MD, PhD
 Respiratory System Prepared by: Dorota Marczuk-Krynicka, MD, PhD Lungs: Ventilation Perfusion Gas Exchange - Diffusion 1. Airways and Airway Resistance (AWR) 2. Mechanics of Breathing and Lung (Elastic)
Respiratory System Prepared by: Dorota Marczuk-Krynicka, MD, PhD Lungs: Ventilation Perfusion Gas Exchange - Diffusion 1. Airways and Airway Resistance (AWR) 2. Mechanics of Breathing and Lung (Elastic)
Lung Volumes and Ventilation
 Respiratory System ssrisuma@rics.bwh.harvard.edu Lung Volumes and Ventilation Minute ventilation Volume of an inspired or expired air per minute = tidal volume (V T ) x respiratory rate Dead space ventilation
Respiratory System ssrisuma@rics.bwh.harvard.edu Lung Volumes and Ventilation Minute ventilation Volume of an inspired or expired air per minute = tidal volume (V T ) x respiratory rate Dead space ventilation
Lung Volumes and Capacities
 Lung Volumes and Capacities Normally the volume of air entering the lungs during a single inspiration is approximately equal to the volume leaving on the subsequent expiration and is called the tidal volume.
Lung Volumes and Capacities Normally the volume of air entering the lungs during a single inspiration is approximately equal to the volume leaving on the subsequent expiration and is called the tidal volume.
Respiratory Physiology
 chapter 4 Respiratory Physiology I. LUNG VOLUMES AND CAPACITIES A. Lung volumes (Figure 4-1) 1. Tidal volume (TV) is the volume inspired or expired with each normal breath. 2. Inspiratory reserve volume
chapter 4 Respiratory Physiology I. LUNG VOLUMES AND CAPACITIES A. Lung volumes (Figure 4-1) 1. Tidal volume (TV) is the volume inspired or expired with each normal breath. 2. Inspiratory reserve volume
3/24/2009 LAB D.HAMMOUDI.MD. 1. Trachea 2. Thoracic wall 3. Lungs 4. Primary bronchi 5. Diaphragm
 RESPIRATORY PHYSIOLOGY LAB D.HAMMOUDI.MD 1. Trachea 2. Thoracic wall 3. Lungs 4. Primary bronchi 5. Diaphragm 1 KEY WORDS TO KNOW BOYLE S LAW INTERCOSTAL NERVES PHRENIC NERVE DIAPHRAGM EXTERNAL INTERCOSTAL
RESPIRATORY PHYSIOLOGY LAB D.HAMMOUDI.MD 1. Trachea 2. Thoracic wall 3. Lungs 4. Primary bronchi 5. Diaphragm 1 KEY WORDS TO KNOW BOYLE S LAW INTERCOSTAL NERVES PHRENIC NERVE DIAPHRAGM EXTERNAL INTERCOSTAL
Exam Key. NROSCI/BIOSC 1070 and MSNBIO 2070 Exam # 2 October 28, 2016 Total POINTS: % of grade in class
 NROSCI/BIOSC 1070 and MSNBIO 2070 Exam # 2 October 28, 2016 Total POINTS: 100 20% of grade in class 1) An arterial blood sample for a patient at sea level is obtained, and the following physiological values
NROSCI/BIOSC 1070 and MSNBIO 2070 Exam # 2 October 28, 2016 Total POINTS: 100 20% of grade in class 1) An arterial blood sample for a patient at sea level is obtained, and the following physiological values
