2.1.1 List the principal structures of the
|
|
|
- Claribel Anthony
- 5 years ago
- Views:
Transcription
1 physiology List the principal structures of the The principle structures of the respiratory are: Nose/Mouth used for inhalation of oxygen-rich air and expelling carbon dioxide rich air Pharynx - passageway leading from the oral and nasal cavities in the head to the larynx Larynx (voice box) - tubular structure connected to the top of the trachea Trachea (windpipe) - conveys air from the larynx to the two main bronchi, with the lungs and their air sacs as the ultimate destination
2 physiology List the principal structures of the The principle structures of the respiratory are: Bronchi (bronchus singular) - airway in the respiratory tract that conducts air into the lungs. Bronchi will branch into smaller tubes that become bronchioles. Bronchioles - any of the minute branches into which a bronchus divides. Lungs - each of the pair of organs situated within the rib cage, consisting of elastic sacs with branching passages into which air is drawn, so that oxygen can pass into the blood and carbon dioxide be removed. Alveoli - any of the many tiny air sacs in the lungs where the exchange of oxygen and carbon dioxide takes place.
3 2.1.1 List the principal structures of physiology the Pharynx Gas exchange ONLY occurs in the alveoli in the (O2 in, CO2 out) Left Lung
4 physiology Outline the functions of the conducting airways Diaphragm - a dome-shaped, muscular partition separating the thorax from the abdomen in mammals. It plays a major role in breathing, as its contraction increases the volume of the thorax and so inflates the lungs.
5 physiology Tricks to preventing or getting rid of a side cramp (of the diaphragm) Eat mindfully pre-run. Foods that are higher in fat and fiber take longer to digest. That doesn t mean they are bad foods, but if you eat them within one to two hours before a run, they can cause havoc creating stomach upset, stitches, and other problems. Invest in a solid warmup. Going from sitting to running speed can create irregular, rapid-fire breathing patterns, which can translate to you bending over in pain on the side of the road Regulate your breathing. Match your breathing to your strides inhaling for two to four strides and exhaling for the same. The faster the pace, the shorter the sequence (fast pace = one or two strides per breath, slower = three or four strides per breath). This can not only prevent stitches, but also improve the efficiency of your oxygen transport. Slow down and exhale to release the stitch. If you still get another side cramp, implement this strategy and it will go away in seconds (I promise). Slow your pace and exhale as the foot on the opposite side of the cramp strikes the ground. When you exhale, you relax the muscles of your diaphragm. When this happens in unison with your foot striking the ground, the impact forces travel up the body and through your core (your side too) and exacerbate (piss off) the muscles in spasm creating that stitch. When you change the side of the landing forces to the opposite side, the tension causing the stitch releases.
6 physiology Outline the functions of the conducting airways Breathing based on physics Air flows from areas of high pressure to low pressure Inhalation occurs when the air pressure in the lungs is lower than in the atmosphere At rest, inhalation caused by diaphragm contraction Diaphragm pulls downward (contracts) and creates a vacuum in the chest cavity by increasing lung volume. Draws air in due to pressure imbalance
7 physiology Outline the functions of the conducting airways The exhalation process is passive (no energy required) because as the diaphragm relaxes it returns to original position, shrinking lung volume and creating greater pressure in the lungs compared to atmosphere.
8 physiology Outline the functions of the conducting airways BREATHING MOVEMENT S VIDEO
9 physiology Outline the functions of the conducting airways During exercise, more oxygen is needed in the active muscles and more carbon dioxide is being produced. More air needs to be inhaled and exhaled at a faster rate Additional muscles must be recruited to make this happen - external intercostal muscles (chest muscles), abdominals and even shoulders can assist in increasing lung volume Compression also can use the contractions of these muscles to expel air faster thus increasing respiration rate. Uses/needs an incredible amount of energy
10
11 physiology Define respiratory terms Atmospheric pressure pressure exerted by the weight of the atmosphere Intra alveolar (intrapulmonary) pressure pressure of the lungs relative to the atmosphere Pulmonary ventilation - is commonly referred to as breathing. It is the process of air flowing into the lungs during inspiration (inhalation) and out of the lungs during expiration (exhalation). Total Lung Capacity (TLC) the amount of gas contained in the lung at the end of a maximal inhalation Tidal volume (VT) the amount of air moving into and out of the lungs while at rest.
12 physiology Define respiratory terms Vital Capacity (VC) the greatest volume of gas that, following maximum inhalation, can be expelled during a complete, slow, forced exhalation Expiratory reserve volume (ERV) the additional maximal volume of air that can be expelled from the lungs by forced exhalation after normal exhalation (after lowest tidal volume) Inspiratory reserve volume (IRV) - the additional maximal volume of air that can be drawn into the lungs by forced inhalation after normal inhalation (after highest tidal volume) Residual Volume (RV) - volume representing the amount of air left in the lungs after a forced exhalation; this volume cannot be measured, only calculated.
13 physiology Define respiratory terms Total lung capacity can be calculated by adding vital capacity to residual volume of the lungs. During normal, quiet respiration, about 500mL of air is inspired. The same amount of air moves out with expiration. This volume of air is called the tidal volume. When we forcibly take a deep breath, we can take in up to 3100mL above the tidal volume. This additional air is the inspiratory reserve volume. Browne et. al 2001
14 physiology Define respiratory terms We can also forcibly exhale. This is termed the expiratory reserve volume. Forced Expiratory Volume (FEV) Test of dynamic lung function Even after the expiratory reserve volume is expelled, some air is still trapped in the lungs because of pressure. This is called the residual volume. This also allows for uninterrupted gaseous exchange during the breathing cycle.
15 physiology
16 physiology Explain the mechanics of ventilation in the human lungs
17
18 physiology Explain the mechanics of ventilation in the human lungs
19 physiology Explain the mechanics of ventilation in the human lungs
20 physiology Explain the mechanics of ventilation in the human lungs Explain how the role between volume and pressure regulates breathing. Discuss the role of the intercostal muscles.
21 physiology Explain the mechanics of ventilation in the human lungs VE = volume of air being exhaled per minute VT = tidal volume Bf = breathing frequency (breaths per minute) Page 35 VE (L.min -1 ) = VT (L.Breath -1 ) x Bf (breaths.min -1 )
22 physiology Describe the nervous and chemical control of ventilation during exercise Ventilation increases in response to increasing intensity of exercise The main objective is to maintain resting oxygen and carbon dioxide levels in blood This is achieved by increasing breathing rate and depth of breathing Regulation of breathing is quite complex and no single factor is responsible. Carbon dioxide levels in the blood is commonly thought to be the main driving factor.
23 physiology Describe the nervous and chemical control of ventilation during exercise
24 physiology Describe the nervous and chemical control of ventilation during exercise Inspiration is activated via the respiratory center in the medulla of the brain The lungs inflate because motor neurons activate the diaphragm and the external intercostal muscles. Inflation of the lung tissue stimulates stretch receptors in the bronchioles that inhibit inspiration and stimulate expiration. (don t want to stretch too much) Expiration begins with a recoil of the stretched lung tissue and the inspiratory muscles are stimulated to relax. The internal intercostals muscles will be stimulated while inspiratory muscle activation is inhibited.
25 physiology Describe the nervous and chemical control of ventilation during exercise
26 physiology Describe the nervous and chemical control of ventilation during exercise - The chemical state of blood regulates pulmonary ventilation at rest and exercise. - Variations in PO2, O2, CO2 acidity and temperature activate sensors in the brain (medulla) and arterial to adjust ventilation and maintain blood chemistry within narrow limits. PO2 = partial pressure of oxygen. - It is the individual pressure exerted independently by a particular gas within a mixture of gasses.
27 physiology Describe the nervous and chemical control of ventilation during exercise - When we exercise, we experience an increase in depth and rate of respiration to meet the increased oxygen requirement. - The increase in respiration often precedes the actual increased oxygen requirement!!! What?!?! - There are at least 2 components to this increase in respiration that precedes the increased oxygen requirement. 1) The first component is "anticipation of exercise" and may involve activation of the sympathetic nervous in order to prepare the body for activity
28 physiology Describe the nervous and chemical control of ventilation during exercise 2) The second component involves activation of stretch receptors (proprioceptors) in skeletal muscle and joints. - Increased activity of stretch receptors is detected by the medulla and results in increased rate and depth of respiration. - The effect is very rapid and shows the value of stretching/warming up before exercise (ie. in addition to heating up muscles and connective tissues and reducing stretch-related injuries). - This allows the body to properly prepare for exercise and helps control breathing, heart rate, temperature, etc.
29 physiology Describe the nervous and chemical control of ventilation during exercise
30 physiology Describe the nervous and chemical control of ventilation during exercise Carbon dioxide (CO2) diffuses through the alveolar walls much more easily than oxygen CO2 is produced by muscles then sent into bloodstream. CO2 reacts with carbonic anhydrase & H2O (enzyme to speed up reactions) in red blood cells (RBC s) and forms carbonic acid After being further reduced, it is now bicarbonate (HCO3-) which dissolves in blood plasma (discussed in a few slides). Blood ph drops and sensors force us to breathe. This is necessary to transport CO2 out of the body because we don t want gases in the bloodstream All of these reactions are reversed in the lungs so we can transfer and exhale CO2 from our bodies
31 physiology Describe the nervous and chemical control of ventilation during exercise
32 physiology Describe the nervous and chemical control of ventilation during exercise As it is, carbon dioxide excretion is far more easily hindered than is oxygen absorption. Thus breathing is governed not by oxygen, but the carbon dioxide content of the blood.
33 physiology Describe the nervous and chemical control of ventilation during exercise HYPERVENTIALTION An increase in ventilation above what is required Exhale too much CO2 and inhale too much O2 Leads to an increased blood ph Typically caused by a state of panic, dizziness, tingling in the lips, hands or feet, headache, weakness, fainting and seizures are common Hyperventilation video
34 physiology Outline the role of hemoglobin in oxygen transportation
35 physiology Outline the role of Hemoglobin oxygen transportation Hemoglobin is the iron containing oxygen transport protein in the red blood cells. It transports oxygen from the lungs to the rest of the body, such as the muscles, where it releases it s oxygen. Each molecule of hemoglobin can carry 4 oxygen molecules It can also carry CO2 as carboaminohemoglobin back to the lungs for diffusion and expiration.
36 physiology Outline the role of hemoglobin in oxygen transportation Oxygen at the lungs is collected mostly by red blood cells (~95%) where they combine with hemoglobin to form oxy-hemoglobin (O2 saturated hemoglobin) and the rest (~5%) diffuses into blood plasma (O2 has low solubility) This oxygen dissolved in the plasma determines the movement of oxgyen from cells into the blood (pressure gradient) Plasma PO2 determines the loading of hemoglobin at the lungs and the unloading of oxygen at the cells When there is low PO2, hemoglobin gives up its oxygen to the plasma (it now becomes part of the blood) which increases the PO2 of the blood in relation to surrounding cells. Oxygen moves from the blood to the cells. At rest only 25% of the oxygen content of blood is used with rest remaining in circulation.
37 physiology Outline the role of hemoglobin in oxygen transportation Diffusion - The passive movement of molecules or particles along a concentration gradient, or from regions of higher to regions of lower concentration in relation to surface area Ficks Law Gas concentration reflects the amount of gas in a given volume, (determined by the gas partial pressure and solubility) Partial pressure = percentage concentration x total pressure of gas mixture i.e. PC0 2 and PO 2 Gas pressure represents the force exerted by the gas molecules against the surfaces they encounter i.e. breathing
38 physiology Explain the process of gaseous exchange at the alveoli Fick's Law Fick's law is used to measure the rate of diffusion. It states that: The larger the area and difference in concentration and the thinner the surface, the quicker the rate. So, for example, in the lung the surface area is made very large by the presence of many alveoli. The difference in concentration is maintained by breathing, which brings in air with a high oxygen concentration and removes the air with a high carbon dioxide concentration and by a good blood supply. The capillaries surrounding the alveoli take away the oxygenated blood and replace it with blood with a high carbon dioxide concentration. The walls of the alveoli are only one cell thick, so the surface across which diffusion occurs is thin and the rate is high
39
40
41 physiology Describe the significance of carbon dioxide in the control of pulmonary ventilation Physical solution in plasma (7% 10%); establishes the PCO 2 of the blood Loose combination with Hb (20%) Combined with water as bicarbonate (70%)
42
43 20% = Carboaminohaemoglobin
44
45 physiology Describe the significance of carbon dioxide in the control of pulmonary ventilation CO2 combines with water in the red blood cell to form Carbonic acid (CO2+H20=H2CO3) Carbonic acid ionises into Hydrogen ions (H+) and bicarbonate ions (HC03) At the lungs, as blood PCO2 lowers Hydrogen ions and Bicarbonate ions recombine to form carbonic acid which in turn is broken down to C02 and water
46
47 physiology Describe the significance of carbon dioxide in the control of pulmonary ventilation 1. List two functions of the ventilatroy 2. List 2 factors that determine lung filling. 3. List an average tidal volume for men and women. 4. List the average vital capacity for men and women. 5. Compute V E for an individual with a tidal volume of 0.6 L and a breathing rate of 15 breaths per minute. 6. List 2 ways oxygen transports in blood. 7. Name 3 factors that regulate pulmonary ventilation 8. Why do some swimmers hyperventilate on the starting blocks? 9. Use Ficks law to explain the efficiency of the alveoli 10. Explain how training improves the efficiency of the respiratory
48 physiology Describe the significance of carbon dioxide in the control of pulmonary ventilation 1. List two functions of the ventilatroy 2. List 2 factors that determine lung filling. Magnitude of inspiratory movements Pressure gradient between air inside and air outside the lung 3. List an average tidal volume for men and women. 0.4l 1l 4. List the average vital capacity for men and women Men 4-5litres women 3-4litres 5. Compute V E for an individual with a tidal volume of 0.6 L and a breathing rate of 15 breaths per minute. 9.0 L min -1 = L
49 physiology Describe the significance of carbon dioxide in the control of pulmonary ventilation 1. List 2 ways oxygen transports in blood. 2. Name 3 factors that regulate pulmonary ventilation Lung and muscle stretch receptors Chemoreceptors in the aorta, brain and neck 3. Why do some swimmers hyperventilate on the starting blocks? 4. Use Ficks law to explain the efficiency of the alveoli 1. Explain how training improves the efficiency of the respiratory
50
51
52
53
54 Holding breath activities (ethics be careful)
Respiration. The resspiratory system
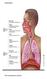 Respiration The resspiratory system The Alveoli The lungs have about 300 million alveoli, with a total crosssec onal area of 50 70 m2.. Each alveolar sac is surrounded by blood capillaries. The walls of
Respiration The resspiratory system The Alveoli The lungs have about 300 million alveoli, with a total crosssec onal area of 50 70 m2.. Each alveolar sac is surrounded by blood capillaries. The walls of
Human Biology Respiratory System
 Human Biology Respiratory System Respiratory System Responsible for process of breathing Works in cooperation with Circulatory system Three types: 1. Internal Respiration 2. External Respiration 3. Cellular
Human Biology Respiratory System Respiratory System Responsible for process of breathing Works in cooperation with Circulatory system Three types: 1. Internal Respiration 2. External Respiration 3. Cellular
Chapter 16 Respiratory System
 Introduction Chapter 16 Respiratory System The respiratory system consists of tubes that filter incoming air and transport it to alveoli where gases are exchanged. Think pair share: what organs are associated
Introduction Chapter 16 Respiratory System The respiratory system consists of tubes that filter incoming air and transport it to alveoli where gases are exchanged. Think pair share: what organs are associated
CHAPTER 3: The respiratory system
 CHAPTER 3: The respiratory system Practice questions - text book pages 56-58 1) When the inspiratory muscles contract, which one of the following statements is true? a. the size of the thoracic cavity
CHAPTER 3: The respiratory system Practice questions - text book pages 56-58 1) When the inspiratory muscles contract, which one of the following statements is true? a. the size of the thoracic cavity
Respiratory System Physiology. Dr. Vedat Evren
 Respiratory System Physiology Dr. Vedat Evren Respiration Processes involved in oxygen transport from the atmosphere to the body tissues and the release and transportation of carbon dioxide produced in
Respiratory System Physiology Dr. Vedat Evren Respiration Processes involved in oxygen transport from the atmosphere to the body tissues and the release and transportation of carbon dioxide produced in
Outline - Respiratory System. Function of the respiratory system Parts of the respiratory system Mechanics of breathing Regulation of breathing
 Respiratory system Function Outline - Respiratory System I. II. III. IV. Respiratory System The function of the respiratory system is to bring in oxygen to the body and remove carbon dioxide. Function
Respiratory system Function Outline - Respiratory System I. II. III. IV. Respiratory System The function of the respiratory system is to bring in oxygen to the body and remove carbon dioxide. Function
 Question 1: Define vital capacity. What is its significance? Vital capacity is the maximum volume of air that can be exhaled after a maximum inspiration. It is about 3.5 4.5 litres in the human body. It
Question 1: Define vital capacity. What is its significance? Vital capacity is the maximum volume of air that can be exhaled after a maximum inspiration. It is about 3.5 4.5 litres in the human body. It
CHAPTER 3: The cardio-respiratory system
 : The cardio-respiratory system Exam style questions - text book pages 44-45 1) Describe the structures involved in gaseous exchange in the lungs and explain how gaseous exchange occurs within this tissue.
: The cardio-respiratory system Exam style questions - text book pages 44-45 1) Describe the structures involved in gaseous exchange in the lungs and explain how gaseous exchange occurs within this tissue.
Physiology of Respiration
 Physiology of Respiration External Respiration = pulmonary ventilation breathing involves 2 processes: inspiration expiration Inspiration an active process involves contraction of diaphragm innervated
Physiology of Respiration External Respiration = pulmonary ventilation breathing involves 2 processes: inspiration expiration Inspiration an active process involves contraction of diaphragm innervated
Chapter 11: Respiratory System Review Assignment
 Name: Date: Mark: / 45 Chapter 11: Respiratory System Review Assignment Multiple Choice = 45 Marks Identify the choice that best completes the statement or answers the question. 1. Which of the following
Name: Date: Mark: / 45 Chapter 11: Respiratory System Review Assignment Multiple Choice = 45 Marks Identify the choice that best completes the statement or answers the question. 1. Which of the following
Lesson 9.1: The Importance of an Organ Delivery System
 Lesson 9.1: The Importance of an Organ Delivery System Animals require a continuous supply of oxygen (O 2 ) for cellular respiration, and they must expel carbon dioxide (CO 2 ), the waste product of this
Lesson 9.1: The Importance of an Organ Delivery System Animals require a continuous supply of oxygen (O 2 ) for cellular respiration, and they must expel carbon dioxide (CO 2 ), the waste product of this
Respiration - Human 1
 Respiration - Human 1 At the end of the lectures on respiration you should be able to, 1. Describe events in the respiratory processes 2. Discuss the mechanism of lung ventilation in human 3. Discuss the
Respiration - Human 1 At the end of the lectures on respiration you should be able to, 1. Describe events in the respiratory processes 2. Discuss the mechanism of lung ventilation in human 3. Discuss the
Structures of the Respiratory System include:
 Respiratory System Structures of the Respiratory System include: ü Oral Cavity ü Nasal Cavity ü Pharynx ü Epiglottis ü Larynx ü Trachea ü Diaphragm ü Lung ü Bronchus ü Bronchioles ü Alveolus ü Pulmonary
Respiratory System Structures of the Respiratory System include: ü Oral Cavity ü Nasal Cavity ü Pharynx ü Epiglottis ü Larynx ü Trachea ü Diaphragm ü Lung ü Bronchus ü Bronchioles ü Alveolus ü Pulmonary
Breathing: The normal rate is about 14 to 20 times a minute. Taking in of air is called Inspiration and the forcing out of air is called Expiration.
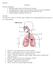 Biology 12 Respiration Divisions of Respiration Breathing: entrance and exit of air into and out of the lungs External Respiration: exchange of gases(o2 and CO2) between air (in alveoli) and blood Internal
Biology 12 Respiration Divisions of Respiration Breathing: entrance and exit of air into and out of the lungs External Respiration: exchange of gases(o2 and CO2) between air (in alveoli) and blood Internal
BIOLOGY 12: UNIT J - CHAPTER 15 - REVIEW WORKSHEET RESPIRATORY SYSTEM
 BIOLOGY 12: UNIT J - CHAPTER 15 - REVIEW WORKSHEET RESPIRATORY SYSTEM A. CHAPTER REVIEW 1. Define the four components of respiration. 2. What happens to the air as it moves along the air passages? What
BIOLOGY 12: UNIT J - CHAPTER 15 - REVIEW WORKSHEET RESPIRATORY SYSTEM A. CHAPTER REVIEW 1. Define the four components of respiration. 2. What happens to the air as it moves along the air passages? What
2. State the volume of air remaining in the lungs after a normal breathing.
 CLASS XI BIOLOGY Breathing And Exchange of Gases 1. Define vital capacity. What is its significance? Answer: Vital Capacity (VC): The maximum volume of air a person can breathe in after a forced expiration.
CLASS XI BIOLOGY Breathing And Exchange of Gases 1. Define vital capacity. What is its significance? Answer: Vital Capacity (VC): The maximum volume of air a person can breathe in after a forced expiration.
Respiratory System Review
 KEY THIS TEST WILL BE COMPLETED IN ONE CLASS PERIOD MONDAY, MARCH 10. 2014 Respiratory System Review Name A. Directions: Fill in the blank with the appropriate vocabulary word or words (several examples
KEY THIS TEST WILL BE COMPLETED IN ONE CLASS PERIOD MONDAY, MARCH 10. 2014 Respiratory System Review Name A. Directions: Fill in the blank with the appropriate vocabulary word or words (several examples
Respiratory system & exercise. Dr. Rehab F Gwada
 Respiratory system & exercise Dr. Rehab F Gwada Objectives of lecture Outline the major anatomical components & important functions of the respiratory system. Describe the mechanics of ventilation. List
Respiratory system & exercise Dr. Rehab F Gwada Objectives of lecture Outline the major anatomical components & important functions of the respiratory system. Describe the mechanics of ventilation. List
GASEOUS EXCHANGE 17 JULY 2013
 GASEOUS EXCHANGE 17 JULY 2013 Lesson Description In this lesson we: Discuss what is gaseous exchange? Consider requirements of an efficient gaseous exchange surface. Look at diversity in gas exchange systems.
GASEOUS EXCHANGE 17 JULY 2013 Lesson Description In this lesson we: Discuss what is gaseous exchange? Consider requirements of an efficient gaseous exchange surface. Look at diversity in gas exchange systems.
I. Gas Exchange Respiratory Surfaces Respiratory Surface:
 I. Gas Exchange Respiratory Surfaces Respiratory Surface: Common characteristics of respiratory surfaces: a) Moist: allows for the RAPID diffusion of dissolved gasses across its surface. Whereas the respiratory
I. Gas Exchange Respiratory Surfaces Respiratory Surface: Common characteristics of respiratory surfaces: a) Moist: allows for the RAPID diffusion of dissolved gasses across its surface. Whereas the respiratory
(Slide 1) Lecture Notes: Respiratory System
 (Slide 1) Lecture Notes: Respiratory System I. (Slide 2) The Respiratory Tract A) Major structures and regions of the respiratory Tract/Route INTO body 1) nose 2) nasal cavity 3) pharynx 4) glottis 5)
(Slide 1) Lecture Notes: Respiratory System I. (Slide 2) The Respiratory Tract A) Major structures and regions of the respiratory Tract/Route INTO body 1) nose 2) nasal cavity 3) pharynx 4) glottis 5)
LAB 7 HUMAN RESPIRATORY LAB. Complete the charts on pgs. 67 and 68 and read directions for using BIOPAC
 66 LAB 7 HUMAN RESPIRATORY LAB Assignments: Due before lab: Quiz: Three Respiratory Interactive Physiology Animations pages 69 73. Complete the charts on pgs. 67 and 68 and read directions for using BIOPAC
66 LAB 7 HUMAN RESPIRATORY LAB Assignments: Due before lab: Quiz: Three Respiratory Interactive Physiology Animations pages 69 73. Complete the charts on pgs. 67 and 68 and read directions for using BIOPAC
Introduction. Respiration. Chapter 10. Objectives. Objectives. The Respiratory System
 Introduction Respiration Chapter 10 The Respiratory System Provides a means of gas exchange between the environment and the body Plays a role in the regulation of acidbase balance during exercise Objectives
Introduction Respiration Chapter 10 The Respiratory System Provides a means of gas exchange between the environment and the body Plays a role in the regulation of acidbase balance during exercise Objectives
PARTS AND STRUCTURE OF THE RESPIRATORY SYSTEM
 PARTS AND STRUCTURE OF THE RESPIRATORY SYSTEM Parts of the Respiratory System The RS can be divided into two parts: 1. Respiratory Tract, (path that air follows). Nasal passage Pharynx Larynx Trachea Bronchi,
PARTS AND STRUCTURE OF THE RESPIRATORY SYSTEM Parts of the Respiratory System The RS can be divided into two parts: 1. Respiratory Tract, (path that air follows). Nasal passage Pharynx Larynx Trachea Bronchi,
Chapter 13 The Respiratory System
 Chapter 13 The Respiratory System by Dr. Jay M. Templin Brooks/Cole - Thomson Learning Atmosphere Tissue cell External respiration Alveoli of lungs 1 Ventilation or gas exchange between the atmosphere
Chapter 13 The Respiratory System by Dr. Jay M. Templin Brooks/Cole - Thomson Learning Atmosphere Tissue cell External respiration Alveoli of lungs 1 Ventilation or gas exchange between the atmosphere
Video. Respiration System. You will use 3 pages of your journal for this lesson. 1. One page for hand written notes onto a journal page
 Respiratory System Video Respiration System You will use 3 pages of your journal for this lesson. 1. One page for hand written notes onto a journal page 2. 2 nd page for diagram 3. 3 rd page for chart
Respiratory System Video Respiration System You will use 3 pages of your journal for this lesson. 1. One page for hand written notes onto a journal page 2. 2 nd page for diagram 3. 3 rd page for chart
Respiration. The ins and outs
 Respiration The ins and outs Functions 1. To bring O 2 into the body and transfer it to the blood stream 2. To remove CO 2 Circulation and respiration work together to achieve these functions Why Do We
Respiration The ins and outs Functions 1. To bring O 2 into the body and transfer it to the blood stream 2. To remove CO 2 Circulation and respiration work together to achieve these functions Why Do We
Then the partial pressure of oxygen is x 760 = 160 mm Hg
 1 AP Biology March 2008 Respiration Chapter 42 Gas exchange occurs across specialized respiratory surfaces. 1) Gas exchange: the uptake of molecular oxygen (O2) from the environment and the discharge of
1 AP Biology March 2008 Respiration Chapter 42 Gas exchange occurs across specialized respiratory surfaces. 1) Gas exchange: the uptake of molecular oxygen (O2) from the environment and the discharge of
Monday, ! Today: Respiratory system! 5/20/14! Transport of Blood! What we ve been covering! Circulatory system! Parts of blood! Heart! tubing!
 Monday, 5.19.14! What we ve been covering! Circulatory system! Parts of blood! Heart! tubing! Transport of Blood! What is transported! Nutrients! Oxygen! Carbon Dioxide! Hormones! Antibodies! What it is/does!
Monday, 5.19.14! What we ve been covering! Circulatory system! Parts of blood! Heart! tubing! Transport of Blood! What is transported! Nutrients! Oxygen! Carbon Dioxide! Hormones! Antibodies! What it is/does!
The physiological functions of respiration and circulation. Mechanics. exercise 7. Respiratory Volumes. Objectives
 exercise 7 Respiratory System Mechanics Objectives 1. To explain how the respiratory and circulatory systems work together to enable gas exchange among the lungs, blood, and body tissues 2. To define respiration,
exercise 7 Respiratory System Mechanics Objectives 1. To explain how the respiratory and circulatory systems work together to enable gas exchange among the lungs, blood, and body tissues 2. To define respiration,
Breathing oxygenates the blood to allow food to be respired
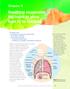 Chapter 6 Breathing oxygenates the blood to allow food to be respired This chapter covers: the structure of the human gas exchange system the mechanism of breathing gas exchange in the alveoli the concept
Chapter 6 Breathing oxygenates the blood to allow food to be respired This chapter covers: the structure of the human gas exchange system the mechanism of breathing gas exchange in the alveoli the concept
Chapter 15. Lecture and Animation Outline
 Chapter 15 Lecture and Animation Outline To run the animations you must be in Slideshow View. Use the buttons on the animation to play, pause, and turn audio/text on or off. Please Note: Once you have
Chapter 15 Lecture and Animation Outline To run the animations you must be in Slideshow View. Use the buttons on the animation to play, pause, and turn audio/text on or off. Please Note: Once you have
The Respiratory System
 Essentials of Human Anatomy & Physiology Elaine N. Marieb Seventh Edition Chapter 13 The Respiratory System Slides 13.1 13.30 Lecture Slides in PowerPoint by Jerry L. Cook Organs of the Respiratory system
Essentials of Human Anatomy & Physiology Elaine N. Marieb Seventh Edition Chapter 13 The Respiratory System Slides 13.1 13.30 Lecture Slides in PowerPoint by Jerry L. Cook Organs of the Respiratory system
Figure 1. A schematic diagram of the human respiratory system.
 Introduction to Respiration In this experiment, you will investigate various aspects of normal breathing, hyperventilation, rebreathing the effect of changing airway resistance and ways in which to measure
Introduction to Respiration In this experiment, you will investigate various aspects of normal breathing, hyperventilation, rebreathing the effect of changing airway resistance and ways in which to measure
Human gas exchange. Question Paper. Save My Exams! The Home of Revision. Cambridge International Examinations. 56 minutes. Time Allowed: Score: /46
 Human gas exchange Question Paper Level Subject Exam oard Topic Sub Topic ooklet O Level iology ambridge International Examinations Respiration Human gas exchange Question Paper Time llowed: 56 minutes
Human gas exchange Question Paper Level Subject Exam oard Topic Sub Topic ooklet O Level iology ambridge International Examinations Respiration Human gas exchange Question Paper Time llowed: 56 minutes
BREATHING AND EXCHANGE OF GASES
 96 BIOLOGY, EXEMPLAR PROBLEMS CHAPTER 17 BREATHING AND EXCHANGE OF GASES MULTIPLE CHOICE QUESTIONS 1. Respiration in insects is called direct because a. The tissues exchange O 2 directly with the air in
96 BIOLOGY, EXEMPLAR PROBLEMS CHAPTER 17 BREATHING AND EXCHANGE OF GASES MULTIPLE CHOICE QUESTIONS 1. Respiration in insects is called direct because a. The tissues exchange O 2 directly with the air in
The Respiratory System. Medical Terminology
 The Respiratory System Medical Terminology The respiratory system is where gas exchange occurs via respiration; inhalation/exhalation. pick up oxygen from inhaled air expels carbon dioxide and water sinus
The Respiratory System Medical Terminology The respiratory system is where gas exchange occurs via respiration; inhalation/exhalation. pick up oxygen from inhaled air expels carbon dioxide and water sinus
RESPIRATORY REGULATION DURING EXERCISE
 RESPIRATORY REGULATION DURING EXERCISE Respiration Respiration delivery of oxygen to and removal of carbon dioxide from the tissue External respiration ventilation and exchange of gases in the lung Internal
RESPIRATORY REGULATION DURING EXERCISE Respiration Respiration delivery of oxygen to and removal of carbon dioxide from the tissue External respiration ventilation and exchange of gases in the lung Internal
1 CHAPTER 17 BREATHING AND EXCHANGE OF GASES https://biologyaipmt.com/
 1 CHAPTER 17 BREATHING AND EXCHANGE OF GASES https://biologyaipmt.com/ CHAPTER 17 BREATHING AND EXCHANGE OF GASES Oxygen (O2) is utilised by the organisms to indirectly break down nutrient molecules like
1 CHAPTER 17 BREATHING AND EXCHANGE OF GASES https://biologyaipmt.com/ CHAPTER 17 BREATHING AND EXCHANGE OF GASES Oxygen (O2) is utilised by the organisms to indirectly break down nutrient molecules like
1. Label a diagram of the respiratory system. Objective sheet 3 Notes
 1. Label a diagram of the respiratory system Objective sheet 3 Notes 2. Functions of the respiratory structures Name Description Function Nasal Cavity Trachea Bronchi (Singular Bronchus) Bronchioles Lungs
1. Label a diagram of the respiratory system Objective sheet 3 Notes 2. Functions of the respiratory structures Name Description Function Nasal Cavity Trachea Bronchi (Singular Bronchus) Bronchioles Lungs
Chapter 17 The Respiratory System: Gas Exchange and Regulation of Breathing
 Chapter 17 The Respiratory System: Gas Exchange and Regulation of Breathing Overview of Pulmonary Circulation o Diffusion of Gases o Exchange of Oxygen and Carbon Dioxide o Transport of Gases in the Blood
Chapter 17 The Respiratory System: Gas Exchange and Regulation of Breathing Overview of Pulmonary Circulation o Diffusion of Gases o Exchange of Oxygen and Carbon Dioxide o Transport of Gases in the Blood
Assignments for Life Processes(Respiration)
 Assignments for Life Processes(Respiration) 1 Question 1 Why do organisms need food? Organisms need food for obtaining energy to perform the vital functions. Question 2 What is a respiratory substrate?
Assignments for Life Processes(Respiration) 1 Question 1 Why do organisms need food? Organisms need food for obtaining energy to perform the vital functions. Question 2 What is a respiratory substrate?
Topic 13: Gas Exchange Ch. 42. Gas Exchange pp Gas Exchange. Gas Exchange in Fish pp Gas Exchange in Fish
 Topic 13: Gas Exchange Ch. 42 Fig. 42.24 Gas Exchange pp.979-989 Gas exchange involves the uptake of oxygen and the discharge of carbon dioxide (i.e. respiration or breathing). It is necessary for cellular
Topic 13: Gas Exchange Ch. 42 Fig. 42.24 Gas Exchange pp.979-989 Gas exchange involves the uptake of oxygen and the discharge of carbon dioxide (i.e. respiration or breathing). It is necessary for cellular
CHAPTER 17 BREATHING AND EXCHANGE OF GASES
 268 BIOLOGY CHAPTER 17 BREATHING AND EXCHANGE OF GASES 17.1 Respiratory Organs 17.2 Mechanism of Breathing 17.3 Exchange of Gases 17.4 Transport of Gases 17.5 Regulation of Respiration 17.6 Disorders of
268 BIOLOGY CHAPTER 17 BREATHING AND EXCHANGE OF GASES 17.1 Respiratory Organs 17.2 Mechanism of Breathing 17.3 Exchange of Gases 17.4 Transport of Gases 17.5 Regulation of Respiration 17.6 Disorders of
Collin County Community College. Lung Physiology
 Collin County Community College BIOL. 2402 Anatomy & Physiology WEEK 9 Respiratory System 1 Lung Physiology Factors affecting Ventillation 1. Airway resistance Flow = Δ P / R Most resistance is encountered
Collin County Community College BIOL. 2402 Anatomy & Physiology WEEK 9 Respiratory System 1 Lung Physiology Factors affecting Ventillation 1. Airway resistance Flow = Δ P / R Most resistance is encountered
SCIENCE 8 RESPIRATION
 SCIENCE 8 RESPIRATION WHEN WE BREATHE, WHAT DO WE BREATHE IN? O2, N2, CO2, O3, NO2 (gas fumes), CO, pollutant, fragrants, toxins, etc. WHAT IS THE PURPOSE OF BREATHING IN? WHAT DOES OUR BODY WANT? O2 WHY?
SCIENCE 8 RESPIRATION WHEN WE BREATHE, WHAT DO WE BREATHE IN? O2, N2, CO2, O3, NO2 (gas fumes), CO, pollutant, fragrants, toxins, etc. WHAT IS THE PURPOSE OF BREATHING IN? WHAT DOES OUR BODY WANT? O2 WHY?
GAS EXCHANGE & PHYSIOLOGY
 GAS EXCHANGE & PHYSIOLOGY Atmospheric Pressure Intra-Alveolar Pressure Inspiration 760 mm HG at Sea Level (= 1 atm) Pressure due to gases (N2, O2, CO2, Misc.) Pressure inside the alveolus (air sac) Phrenic
GAS EXCHANGE & PHYSIOLOGY Atmospheric Pressure Intra-Alveolar Pressure Inspiration 760 mm HG at Sea Level (= 1 atm) Pressure due to gases (N2, O2, CO2, Misc.) Pressure inside the alveolus (air sac) Phrenic
Chapter 13 The Respiratory System
 VI edit Pag 451-499 Chapter 13 The Respiratory System V edit. Pag 459-509 Tissue cell Alveoli of lungs Atmosphere 1 External respiration Ventilation or gas exchange between the atmosphere and air sacs
VI edit Pag 451-499 Chapter 13 The Respiratory System V edit. Pag 459-509 Tissue cell Alveoli of lungs Atmosphere 1 External respiration Ventilation or gas exchange between the atmosphere and air sacs
Respiration. Chapter 39
 Respiration Chapter 39 Impacts, Issues Up in Smoke Smoking immobilizes ciliated cells and kills white blood cells that defend the respiratory system; highly addictive nicotine discourages quitting 39.1
Respiration Chapter 39 Impacts, Issues Up in Smoke Smoking immobilizes ciliated cells and kills white blood cells that defend the respiratory system; highly addictive nicotine discourages quitting 39.1
Then the partial pressure of oxygen is. b) Gases will diffuse down a pressure gradient across a respiratory surface if it is: i) permeable ii) moist
 1 AP Biology March 2008 Respiration Chapter 42 Gas exchange occurs across specialized respiratory surfaces. 1) Gas exchange: Relies on the diffusion of gases down pressure gradients. At sea level, atmosphere
1 AP Biology March 2008 Respiration Chapter 42 Gas exchange occurs across specialized respiratory surfaces. 1) Gas exchange: Relies on the diffusion of gases down pressure gradients. At sea level, atmosphere
IV. FROM AQUATIC TO ATMOSPHERIC BREATHING: THE TRACHEA & THE LUNG
 GAS EXCHANGE AND TRANSPORT I. INTRODUCTION: Heterotrophs oxidize carbon cmpds using O 2 to generate CO 2 & H 2 O. This is cellular respiration II. HOW GAS ENTERS A CELL A. The composition of air: 79% N
GAS EXCHANGE AND TRANSPORT I. INTRODUCTION: Heterotrophs oxidize carbon cmpds using O 2 to generate CO 2 & H 2 O. This is cellular respiration II. HOW GAS ENTERS A CELL A. The composition of air: 79% N
The Breathing System
 The Breathing System Learning Intentions 1. Students should Know how Breathing happens 2. Name and know the functions of the Breathing System 3. Know how the organs work and how they work with other systems
The Breathing System Learning Intentions 1. Students should Know how Breathing happens 2. Name and know the functions of the Breathing System 3. Know how the organs work and how they work with other systems
Animal Systems: The Respiratory System
 Animal Systems: The Respiratory System Tissues, Organs, and Systems of Living Things Cells, Cell Division, and Animal Systems and Plant Systems Cell Specialization Human Systems The Digestive The Circulatory
Animal Systems: The Respiratory System Tissues, Organs, and Systems of Living Things Cells, Cell Division, and Animal Systems and Plant Systems Cell Specialization Human Systems The Digestive The Circulatory
Respiratory System. Part 2
 Respiratory System Part 2 Respiration Exchange of gases between air and body cells Three steps 1. Ventilation 2. External respiration 3. Internal respiration Ventilation Pulmonary ventilation consists
Respiratory System Part 2 Respiration Exchange of gases between air and body cells Three steps 1. Ventilation 2. External respiration 3. Internal respiration Ventilation Pulmonary ventilation consists
Gas Exchange in Animals. Uptake of O2 from environment and discharge of CO2. Respiratory medium! water for aquatic animals, air for terrestial
 Gas Exchange in Animals Uptake of O2 from environment and discharge of CO2 Respiratory medium! water for aquatic animals, air for terrestial Respiratory surface! skin, gills, lungs Circulatory System O2/CO2
Gas Exchange in Animals Uptake of O2 from environment and discharge of CO2 Respiratory medium! water for aquatic animals, air for terrestial Respiratory surface! skin, gills, lungs Circulatory System O2/CO2
respiratory cycle. point in the volumes: 500 milliliters. for men. expiration, up to 1200 milliliters extra makes breathing Respiratory
 10 II. RESPIRATORY VOLUMES, CAPACITIES & PULMONARY FUNCTION TESTS Respiratory volume is the term used for various volumes of air moved by or associated with the lungs at a given point in the respiratory
10 II. RESPIRATORY VOLUMES, CAPACITIES & PULMONARY FUNCTION TESTS Respiratory volume is the term used for various volumes of air moved by or associated with the lungs at a given point in the respiratory
08 Respiration. #79 Respiration realeases energy from food
 08 Respiration #79 Respiration realeases energy from food Respiration is the chemical reactions that break down nutrient molecules in living cells to release energy. In humans, our cells need energy (ATP)
08 Respiration #79 Respiration realeases energy from food Respiration is the chemical reactions that break down nutrient molecules in living cells to release energy. In humans, our cells need energy (ATP)
GASEOUS EXCHANGE IN HUMANS 06 AUGUST 2014
 GASEOUS EXCHANGE IN HUMANS 06 AUGUST 2014 In this lesson we: Lesson Description Look at gaseous exchange in humans in terms of o Ventilation o Inspiration o Expiration o Transport of gases o Homeostatic
GASEOUS EXCHANGE IN HUMANS 06 AUGUST 2014 In this lesson we: Lesson Description Look at gaseous exchange in humans in terms of o Ventilation o Inspiration o Expiration o Transport of gases o Homeostatic
alveoli Chapter 42. Gas Exchange elephant seals gills AP Biology
 alveoli Chapter 42. Gas Exchange gills elephant seals Gas exchange O 2 & CO 2 exchange exchange between environment & cells provides O 2 for aerobic cellular respiration need moist membrane need high
alveoli Chapter 42. Gas Exchange gills elephant seals Gas exchange O 2 & CO 2 exchange exchange between environment & cells provides O 2 for aerobic cellular respiration need moist membrane need high
25/4/2016. Physiology #01 Respiratory system Nayef Garaibeh Rawan Alwaten
 25/4/2016 Physiology #01 Respiratory system Nayef Garaibeh Rawan Alwaten Respiratory System Introduction: - We breath while we are sleeping, talking, working and resting. - Respiratory diseases are abundant
25/4/2016 Physiology #01 Respiratory system Nayef Garaibeh Rawan Alwaten Respiratory System Introduction: - We breath while we are sleeping, talking, working and resting. - Respiratory diseases are abundant
3/24/2009 LAB D.HAMMOUDI.MD. 1. Trachea 2. Thoracic wall 3. Lungs 4. Primary bronchi 5. Diaphragm
 RESPIRATORY PHYSIOLOGY LAB D.HAMMOUDI.MD 1. Trachea 2. Thoracic wall 3. Lungs 4. Primary bronchi 5. Diaphragm 1 KEY WORDS TO KNOW BOYLE S LAW INTERCOSTAL NERVES PHRENIC NERVE DIAPHRAGM EXTERNAL INTERCOSTAL
RESPIRATORY PHYSIOLOGY LAB D.HAMMOUDI.MD 1. Trachea 2. Thoracic wall 3. Lungs 4. Primary bronchi 5. Diaphragm 1 KEY WORDS TO KNOW BOYLE S LAW INTERCOSTAL NERVES PHRENIC NERVE DIAPHRAGM EXTERNAL INTERCOSTAL
Chapter 37: Pulmonary Ventilation. Chad & Angela
 Chapter 37: Pulmonary Ventilation Chad & Angela Respiratory Structures Basic Structures of Respiration Nasal/Oral Cavities Larynx Trachea Bronchi Secondary Bronchi Bronchioles Alveoli Mechanics of Ventilation
Chapter 37: Pulmonary Ventilation Chad & Angela Respiratory Structures Basic Structures of Respiration Nasal/Oral Cavities Larynx Trachea Bronchi Secondary Bronchi Bronchioles Alveoli Mechanics of Ventilation
BREATHING AND EXCHANGE OF GASES
 96 BIOLOGY, EXEMPLAR PROBLEMS CHAPTER 17 BREATHING AND EXCHANGE OF GASES MULTIPLE CHOICE QUESTIONS 1. Respiration in insects is called direct because a. The cell exchange O 2 directly with the air in the
96 BIOLOGY, EXEMPLAR PROBLEMS CHAPTER 17 BREATHING AND EXCHANGE OF GASES MULTIPLE CHOICE QUESTIONS 1. Respiration in insects is called direct because a. The cell exchange O 2 directly with the air in the
practices makes perfect
 Human Respiratory system Chapter 1: Respiration PMR 03, 08 1. The human respiratory system consists of: a... b... c.. d... e. Our body has.. lungs (right & left). f. Each lung consists of the, and alveoli.
Human Respiratory system Chapter 1: Respiration PMR 03, 08 1. The human respiratory system consists of: a... b... c.. d... e. Our body has.. lungs (right & left). f. Each lung consists of the, and alveoli.
Gaseous exchange. Grade 11
 z Gaseous exchange Grade 11 z Terminology 1. Breathing 2. Gaseous exchange 3. Diffusion 4. Spongy mesophyll cells 5. Tracheae 6. Gills 7. Alveoli 8. Larynx 9. Diaphragm 10. Endothelium 1. Pleura 2. Squamous
z Gaseous exchange Grade 11 z Terminology 1. Breathing 2. Gaseous exchange 3. Diffusion 4. Spongy mesophyll cells 5. Tracheae 6. Gills 7. Alveoli 8. Larynx 9. Diaphragm 10. Endothelium 1. Pleura 2. Squamous
Respiratory Pulmonary Ventilation
 Respiratory Pulmonary Ventilation Pulmonary Ventilation Pulmonary ventilation is the act of breathing and the first step in the respiratory process. Pulmonary ventilation brings in air with a new supply
Respiratory Pulmonary Ventilation Pulmonary Ventilation Pulmonary ventilation is the act of breathing and the first step in the respiratory process. Pulmonary ventilation brings in air with a new supply
AP Biology. Chapter 42. Gas Exchange. Optimizing gas exchange. Gas exchange. Gas exchange in many forms. Evolution of gas exchange structures
 alveoli Chapter 42. Gas Exchange gills elephant seals Gas exchange & C exchange exchange between environment & cells provides for aerobic cellular respiration need moist membrane need high surface area
alveoli Chapter 42. Gas Exchange gills elephant seals Gas exchange & C exchange exchange between environment & cells provides for aerobic cellular respiration need moist membrane need high surface area
(A) The partial pressure in the lungs is higher than in the blood, and oxygen diffuses out of the lungs passively.
 DAT Biology - Problem Drill 12: The Respiratory System Question No. 1 of 10 1. Which statement about the partial pressure of oxygen inside the lungs is correct? Question #01 (A) The partial pressure in
DAT Biology - Problem Drill 12: The Respiratory System Question No. 1 of 10 1. Which statement about the partial pressure of oxygen inside the lungs is correct? Question #01 (A) The partial pressure in
Pop Quiz. What produces mucus, HCl and pepsinogen in the stomach? List a water soluable vitamin What is a ruminant stomach?
 Pop Quiz What produces mucus, HCl and pepsinogen in the stomach? List a water soluable vitamin What is a ruminant stomach? Respiratory System Review Cellular respiration: obtain glucose and oxygen, get
Pop Quiz What produces mucus, HCl and pepsinogen in the stomach? List a water soluable vitamin What is a ruminant stomach? Respiratory System Review Cellular respiration: obtain glucose and oxygen, get
system. and then into the tissues. Diffusion of wastes such as Carbon Dioxide from tissues into blood and out of blood into the lungs.
 Respiratory System 1.Exchange Why do of we gases breathe? into the Think blood of all and the tissues. reasons Diffusion why we of Oxygen need a respiratory into blood from the lungs system. and then into
Respiratory System 1.Exchange Why do of we gases breathe? into the Think blood of all and the tissues. reasons Diffusion why we of Oxygen need a respiratory into blood from the lungs system. and then into
Respiratory Lecture Test Questions Set 3
 Respiratory Lecture Test Questions Set 3 1. The pressure of a gas: a. is inversely proportional to its volume b. is unaffected by temperature changes c. is directly proportional to its volume d. does not
Respiratory Lecture Test Questions Set 3 1. The pressure of a gas: a. is inversely proportional to its volume b. is unaffected by temperature changes c. is directly proportional to its volume d. does not
inquiry question How does the respiratory system contribute to energy production for movement? UNCORRECTED PAGE PROOFS
 inquiry question How does the respiratory system contribute to energy production for movement? chapter 7 Structure and functions of the respiratory system The respiratory system is the starting point for
inquiry question How does the respiratory system contribute to energy production for movement? chapter 7 Structure and functions of the respiratory system The respiratory system is the starting point for
82 Respiratory Tract NOTES
 82 Respiratory Tract NOTES RESPIRATORY TRACT The respiratory tract conducts air to the lungs where gaseous exchange occurs. It is separated into air-conducting and respiratory (where gas exchange occurs)
82 Respiratory Tract NOTES RESPIRATORY TRACT The respiratory tract conducts air to the lungs where gaseous exchange occurs. It is separated into air-conducting and respiratory (where gas exchange occurs)
Page 1. Chapter 33: Respiration O 2 CO 2
 Chapter 33: Respiration O 2 CO 2 Features of Respiratory Systems: 1) Moist surface (to dissolve gas) 2) Thin cells lining surface 3) Large surface area contacting environment Facilitate Diffusion Methods
Chapter 33: Respiration O 2 CO 2 Features of Respiratory Systems: 1) Moist surface (to dissolve gas) 2) Thin cells lining surface 3) Large surface area contacting environment Facilitate Diffusion Methods
Gas Exchange Respiratory Systems
 alveoli gills Gas Exchange Respiratory Systems elephant seals 2008-2009 Why do we need a respiratory system? respiration for respiration Need O 2 in for aerobic cellular respiration make ATP Need CO 2
alveoli gills Gas Exchange Respiratory Systems elephant seals 2008-2009 Why do we need a respiratory system? respiration for respiration Need O 2 in for aerobic cellular respiration make ATP Need CO 2
AP Biology. Gas Exchange Respiratory Systems. Gas exchange. Why do we need a respiratory system? Optimizing gas exchange. Gas exchange in many forms
 alveoli Gas Exchange Respiratory Systems gills elephant seals 2008-2009 Why do we need a respiratory system? Need O 2 in food respiration for respiration for aerobic cellular respiration make ATP Need
alveoli Gas Exchange Respiratory Systems gills elephant seals 2008-2009 Why do we need a respiratory system? Need O 2 in food respiration for respiration for aerobic cellular respiration make ATP Need
Circulatory And Respiration
 Circulatory And Respiration Composition Of Blood Blood Heart 200mmHg 120mmHg Aorta Artery Arteriole 50mmHg Capillary Bed Venule Vein Vena Cava Heart Differences Between Arteries and Veins Veins transport
Circulatory And Respiration Composition Of Blood Blood Heart 200mmHg 120mmHg Aorta Artery Arteriole 50mmHg Capillary Bed Venule Vein Vena Cava Heart Differences Between Arteries and Veins Veins transport
Respiratory system. Role. Ventilation consists of 4 (5) steps : oxygen delivery and carbon dioxide elimination ph balance sound and voice formation
 Respiratory system Role oxygen delivery and carbon dioxide elimination ph balance sound and voice formation Ventilation consists of 4 (5) steps : 1. pulmonary ventilation gas exchange between lungs and
Respiratory system Role oxygen delivery and carbon dioxide elimination ph balance sound and voice formation Ventilation consists of 4 (5) steps : 1. pulmonary ventilation gas exchange between lungs and
Airway: the tubes through which air flows between atmosphere and alveoli. Upper airway. Lower airway
 Respiration Yu Yanqin ( 虞燕琴 ), PhD Dept. of fph Physiology Zhejiang University, School of Medicine Respiration Definition: the bodily processes involved in exchange of oxygen (O 2 ) and carbon dioxide
Respiration Yu Yanqin ( 虞燕琴 ), PhD Dept. of fph Physiology Zhejiang University, School of Medicine Respiration Definition: the bodily processes involved in exchange of oxygen (O 2 ) and carbon dioxide
Respiratory Physiology Gaseous Exchange
 Respiratory Physiology Gaseous Exchange Session Objectives. What you will cover Basic anatomy of the lung including airways Breathing movements Lung volumes and capacities Compliance and Resistance in
Respiratory Physiology Gaseous Exchange Session Objectives. What you will cover Basic anatomy of the lung including airways Breathing movements Lung volumes and capacities Compliance and Resistance in
You Might Also Like. I look forward helping you focus your instruction while saving tons of time. Kesler Science Station Lab Activities 40%+ Savings!
 Thanks Connect Thank you for downloading my product. I truly appreciate your support and look forward to hearing your feedback. You can connect with me and find many free activities and strategies over
Thanks Connect Thank you for downloading my product. I truly appreciate your support and look forward to hearing your feedback. You can connect with me and find many free activities and strategies over
Physiology Unit 4 RESPIRATORY PHYSIOLOGY
 Physiology Unit 4 RESPIRATORY PHYSIOLOGY In Physiology Today Respiration External respiration ventilation gas exchange Internal respiration cellular respiration gas exchange Respiratory Cycle Inspiration
Physiology Unit 4 RESPIRATORY PHYSIOLOGY In Physiology Today Respiration External respiration ventilation gas exchange Internal respiration cellular respiration gas exchange Respiratory Cycle Inspiration
Breathing. Physics of Breathing 11/14/2011. Function of Respiratory Tract. Structure of Respiratory Tract. Parts of the Respiratory Tract
 Breathing Function of Respiratory Tract The respiratory tract is a series of spaces and semirigid tubes designed to convey air into and out of the respiratory organs (lungs). Parts of the Respiratory Tract
Breathing Function of Respiratory Tract The respiratory tract is a series of spaces and semirigid tubes designed to convey air into and out of the respiratory organs (lungs). Parts of the Respiratory Tract
P215 Respiratory System, Part 2
 P15 Respiratory System, Part Gas Exchange Oxygen and Carbon Dioxide constant need for oxygen constant production of carbon dioxide exchange (and movement) lung alveoli pulmonary arteries pulmonary capillaries
P15 Respiratory System, Part Gas Exchange Oxygen and Carbon Dioxide constant need for oxygen constant production of carbon dioxide exchange (and movement) lung alveoli pulmonary arteries pulmonary capillaries
The Human Respiratory System
 The Human Respiratory System Maryam Maheri Kiana Kayoda, Nazalia, Emerald Bocobo NPB 101 L section 008 TA: Ashneel Krishna 2/26/2015 Introduction: The respiratory system allows gas exchange between cells
The Human Respiratory System Maryam Maheri Kiana Kayoda, Nazalia, Emerald Bocobo NPB 101 L section 008 TA: Ashneel Krishna 2/26/2015 Introduction: The respiratory system allows gas exchange between cells
Chapter 22 Gas Exchange
 Chapter 22 Gas Exchange PowerPoint Lectures for Biology: Concepts & Connections, Sixth Edition Campbell, Reece, Taylor, Simon, and Dickey Lecture by Edward J. Zalisko Introduction: Surviving in Thin Air
Chapter 22 Gas Exchange PowerPoint Lectures for Biology: Concepts & Connections, Sixth Edition Campbell, Reece, Taylor, Simon, and Dickey Lecture by Edward J. Zalisko Introduction: Surviving in Thin Air
The Continuing Adventures of Mr. O Too
 The Continuing Adventures of Mr. O Too When last we heard from Mr. O Too, he was traveling from the lungs to the leg muscles of an athlete. The unit one observation was a very general overview of the basic
The Continuing Adventures of Mr. O Too When last we heard from Mr. O Too, he was traveling from the lungs to the leg muscles of an athlete. The unit one observation was a very general overview of the basic
Respiratory system. Premedical - Biology
 Respiratory system Premedical - Biology Composition of atmosphere Nitrogen (N 2 ) 840 ppmv (78.084%) Oxygen (O 2 ) 209,460 ppmv (20.946%) Carbon dioxide (CO 2 ) 387 ppmv (0.0387%) Argon (Ar), Neon (Ne),
Respiratory system Premedical - Biology Composition of atmosphere Nitrogen (N 2 ) 840 ppmv (78.084%) Oxygen (O 2 ) 209,460 ppmv (20.946%) Carbon dioxide (CO 2 ) 387 ppmv (0.0387%) Argon (Ar), Neon (Ne),
Lung Volumes and Capacities
 Lung Volumes and Capacities Normally the volume of air entering the lungs during a single inspiration is approximately equal to the volume leaving on the subsequent expiration and is called the tidal volume.
Lung Volumes and Capacities Normally the volume of air entering the lungs during a single inspiration is approximately equal to the volume leaving on the subsequent expiration and is called the tidal volume.
The Respiratory System
 Respiration and Excretion Name Date Class The Respiratory System This section describes the parts of the respiratory system and how they work to help you breathe and speak. Use Target Reading Skills As
Respiration and Excretion Name Date Class The Respiratory System This section describes the parts of the respiratory system and how they work to help you breathe and speak. Use Target Reading Skills As
Chapter 1: Respiration
 Chapter 1: Respiration Respiration Human Breathing Mechanism Transport of oxygen Importance of a healthy respiratory system Respiratory system lungs inhalation exhalation Diffusion of oxygen by blood Transport
Chapter 1: Respiration Respiration Human Breathing Mechanism Transport of oxygen Importance of a healthy respiratory system Respiratory system lungs inhalation exhalation Diffusion of oxygen by blood Transport
UNIT 9 - RESPIRATORY SYSTEM LECTURE NOTES
 UNIT 9 - RESPIRATORY SYSTEM LECTURE NOTES 9.01 GENERAL FUNCTIONS OF THE RESPIRATORY SYSTEM A. Brings oxygenated air to the alveoli B. Removes air containing carbon dioxide C. Filters, warms, and humidifies
UNIT 9 - RESPIRATORY SYSTEM LECTURE NOTES 9.01 GENERAL FUNCTIONS OF THE RESPIRATORY SYSTEM A. Brings oxygenated air to the alveoli B. Removes air containing carbon dioxide C. Filters, warms, and humidifies
REVISION: GASEOUS EXCHANGE 24 SEPTEMBER 2014 Lesson Description
 REVISION: GASEOUS EXCHANGE 24 SEPTEMBER 2014 Lesson Description In this lesson, we revise: Gaseous Exchange in Plants & Animals Gaseous Exchange in Humans Excretion in Humans Focus on the Kidney Gaseous
REVISION: GASEOUS EXCHANGE 24 SEPTEMBER 2014 Lesson Description In this lesson, we revise: Gaseous Exchange in Plants & Animals Gaseous Exchange in Humans Excretion in Humans Focus on the Kidney Gaseous
The Human Body. Everyone Needs Healthy Systems. Blood Vessels
 The Human Body Everyone Needs Healthy Systems There are several systems that make up the human body. Although their functions differ, they all work together to keep your body running smoothly. Some of
The Human Body Everyone Needs Healthy Systems There are several systems that make up the human body. Although their functions differ, they all work together to keep your body running smoothly. Some of
Department of Biology Work Sheet Respiratory system,9 class
 I. Name the following : Department of Biology Work Sheet Respiratory system,9 class 1. A muscular sheet separating the thoracic and abdominal cavities. 2. A respiratory tube supported by cartilaginous
I. Name the following : Department of Biology Work Sheet Respiratory system,9 class 1. A muscular sheet separating the thoracic and abdominal cavities. 2. A respiratory tube supported by cartilaginous
REVISION: GASEOUS EXCHANGE & EXCRETION 11 SEPTEMBER 2013
 REVISION: GASEOUS EXCHANGE & EXCRETION 11 SEPTEMBER 2013 Lesson Description In this lesson we: Revise gaseous exchange in different animals and examine the structure of the kidney Key Concepts Important
REVISION: GASEOUS EXCHANGE & EXCRETION 11 SEPTEMBER 2013 Lesson Description In this lesson we: Revise gaseous exchange in different animals and examine the structure of the kidney Key Concepts Important
BIOLOGY 12 - RESPIRATION - CHAPTER NOTES
 BIOLOGY 12 - RESPIRATION - CHAPTER NOTES We often think of respiration as just breathing. In fact, breathing is just one part of this physiological process. As biologists, we divide respiration up into
BIOLOGY 12 - RESPIRATION - CHAPTER NOTES We often think of respiration as just breathing. In fact, breathing is just one part of this physiological process. As biologists, we divide respiration up into
The Respiratory System
 Name Date Class The Respiratory System This section describes the parts of the respiratory system and how they work to help you breathe and speak. Use Target Reading Skills As you read, complete the flowchart
Name Date Class The Respiratory System This section describes the parts of the respiratory system and how they work to help you breathe and speak. Use Target Reading Skills As you read, complete the flowchart
Lab 17. The Respiratory System. Laboratory Objectives
 Lab 17 The Respiratory System Laboratory Objectives Identify and describe the anatomical structures of the respiratory system. Describe the relationship between volume and pressure. Describe changes in
Lab 17 The Respiratory System Laboratory Objectives Identify and describe the anatomical structures of the respiratory system. Describe the relationship between volume and pressure. Describe changes in
Lectures on Medical Biophysics Department of Biophysics, Medical Faculty, Masaryk University in Brno. Biophysics of breathing.
 Lectures on Medical Biophysics Department of Biophysics, Medical Faculty, Masaryk University in Brno Biophysics of breathing. Spirometry 1 Lecture outline Mechanisms of gas exchange between organism and
Lectures on Medical Biophysics Department of Biophysics, Medical Faculty, Masaryk University in Brno Biophysics of breathing. Spirometry 1 Lecture outline Mechanisms of gas exchange between organism and
