Capnography. The Other Vital Sign. 3 rd Edition J. D Urbano, RCP, CRT Capnography The Other Vital Sign 3 rd Edition
|
|
|
- Baldwin Hancock
- 5 years ago
- Views:
Transcription
1 The Other Vital Sign 3 rd Edition
2 Send questions or comments to: J. D Urbano, RCP, CRT BreathSounds jdurbano@breathsounds.org Visit Our Website: Join Our Forum: Registration Always FREE Always SPAM FREE
3 Welcome to the 3 rd Edition of Capnography The Other Vital Sign For many years taking your patients vital has been a standard of practice in all areas of healthcare, from pre-hospital to extended care, and everywhere in between. In today s world of advanced medical education and technology a new vital sign is gaining popularity in patient care settings. Capnography In earlier years capnography was widely misunderstood by healthcare workers. It was believed by many that capnography was intended to estimate their patients P a CO 2. That was never the intention. That misconception has earned capnography a bad-rap in almost all areas of the healthcare community. The purpose of this program is to give you a more accurate understanding of what capnography really is, what kind of information you can learn from it, and how you can use that information to better care for your patient.
4 Capnography refers to the study and measurement of carbon dioxide in exhaled gas. Capnography was first introduced by Karl Luft, a German bioengineer, in 1943 with an infrared CO 2 (carbon dioxide) measuring device he called URAS, or Ultra Rot Absorption Schreiber (Infrared Absorption Writer) It was big, heavy, and very impractical to use. Over the years capnography evolved many times, as did the technology used to measure it. According to a study by the American Society of Anesthesiologists 93% of all avoidable anesthesia related incidents could have been prevented with the use of capnography in conjunction of pulse oxymetry. In 1998 the ASA (American Society of Anesthesiologists) Committee on Standards of Care deemed it mandatory that all patients receiving general anesthesia be continuously monitored for E T CO 2 (End Tidal Carbon Dioxide) Today capnography is successfully used in almost all areas of health care.
5 Carbon dioxide (CO 2 ), one of the waste products of cell metabolism, is created as we burn glucose and oxygen to produce energy in the form of adenosine triphosphate (ATP). The excess CO 2 is carried by the blood to the lungs where it leaves the body during the expiratory phase of respiration. After the expiratory phase is complete the inspiratory phase begins, we take in more oxygen, and that part of the metabolic cycle begins again. There is significance in not only the concentration of CO 2 measured at the end of the expiratory phase, but also in comparison to the concentration of CO 2 in arterial blood.
6 Definitions Capnography A graphical display of CO 2 concentration over time or expired volume. Capnogram CO 2 waveform either plotted against a volume (CO 2 expirogram) or against time (time capnogram). P A CO 2 Partial pressure of carbon dioxide in the alveoli. P a CO 2 Partial pressure of carbon dioxide in arterial blood. P ET CO 2 Partial pressure of carbon dioxide at the end of expiration. P (a-et) CO 2 The difference between P a CO 2 and P ET CO 2. Sometimes called the CO 2 -diff, or CO 2 gradient. P V CO 2 Partial pressure of carbon dioxide in mixed venous blood.
7 To understand capnography you MUST understand that Oxygenation and Ventilation are two entirely different mechanisms that both rely on the respiratory cycle. Oxygenation relies on the inspiratory phase and refers to the amount of oxygen (O 2 ) available and utilized. Ventilation relies on the expiratory phase and refers to the amount of carbon dioxide (CO 2 ) produced during the metabolic cycle of the cells, and exhaled from the body. Oxygenation and ventilation are BOTH needed, in proper proportion, to sustain an adequate and safe quality of life.
8 Oxygenation: The amount of oxygen taken in by the lungs and made available to the cells. Oxygenation relies on the inspiratory phase of the respiratory cycle. There are at lease two ways to check a patients oxygenation status; Invasively an arterial blood gas (ABG) can be obtained which measures, among other things, the PaO 2 (Partial Pressure of Oxygen dissolved in the blood plasma of arterial blood). Non-Invasively a pulse oxymetry can be obtained which measures the amount of oxygen that is bound to the hemoglobin.
9 Ventilation refers to the amount of carbon dioxide in arterial blood and expelled from the body through exhalation. Ventilation relies on the expiratory phase of the respiratory cycle, and can be measured in two ways. Invasively the same arterial blood gas (ABG) sample that measures the PaO 2 also measures the PaCO 2 (Partial Pressure of carbon dioxide dissolved in blood plasma of arterial blood). Non-Invasively the P ET CO 2 (Partial pressure of carbon dioxide in exhaled gas) can be measured. This is measured breath by breath at the end of the expiratory phase.
10 Pre-Hospital Paramedics frequently use carbon dioxide detection devices to assist them in assuring an endotracheal tube is properly placed. Emergency Medicine Capnography is frequently used to assure proper ET tube placement, trend for adequate ventilation during mechanical ventilation, and that the heart rhythm on the monitor is not PEA. Critical Care Medicine In the ICU capnography can be used to trend ventilation during mechanical ventilation, watch for changes in dead space ventilation, and watch the progress of many pulmonary related disease processes. Cardiopulmonary Arrest During CPR capnography can be used as a predictor of survivability, to check for adequate cardiac output during chest compressions, and as an indicator of PEA if a heart rhythm return on the monitor. Procedural Sedation During conscious sedation capnography is a much faster indicator of changes in respiratory status than pulse-oxymetry. It can take several minutes for SaO 2 to change, but E T CO 2 changes almost immediately. Anesthesia Capnography in the OR has been a standard of care since It is used to maintain adequate ventilation, watch for drastic changes in dead space ventilation, and assure the presence of adequate cardiac output during surgery.
11 Methods of Monitoring There are several methods used to detect and monitor carbon dioxide in gas or blood. Infrared Spectrography Most commonly used in the hospital setting Raman Spectrography Mass Spectrography Photo-acoustic Spectrography Molecular Correlation Spectrography (Microstream technology) Chemical Colorimetric Analysis Most commonly used in the pre-hospital setting
12 Infrared spectrography works on the principal that carbon dioxide selectively absorbs a known amount of infrared light of a specific wavelength (4.3 milli-microns). The amount of light absorbed is directly proportional to the concentration of carbon dioxide molecules. A predetermined amount of infrared light is sent from the emitting side of the sensor through a gas sample and collected on the receiving side of the sensor (the receiving side of the CO 2 sensor is an IR detector). The infrared light received is compared to the infrared light transmitted. The difference is then converted by calculations into the partial pressure that you see on the monitor. Some models also calculate the difference into a percentage of total gas concentration. Infrared Spectrography
13 Chemical colorimetric analysis uses a ph-sensitive chemical indicator inside a device that is placed between an endotracheal tube and a breathing circuit, such as a manual respirator or a ventilator circuit. This indicator changes color breath by breath. It turns yellow when it s exposed to a carbon dioxide concentration of 4% or greater, and purple when it s exposed to room air that contains no carbon dioxide. Chemical Colorimetric Analysis CO 2 Not Present These devices are good for quick determination of the presence of CO 2 but are not sensitive to low concentrations of CO 2, as is the case during CPR or other low cardiac output situations. There are also several circumstances which can cause false positive results CO 2 Present
14 The 2 Types of Capnometers Mainstream Sidestream The infrared sensor is in the direct path of the gas source, and connected to the monitor by an electrical wire. The sample of gas is aspirated into the monitor via a lightweight airway adapter and a 6ft length of tubing. The actual sensor is inside the monitor.
15 Mainstream Advantages Mainstream NO sampling tube to become obstructed. No variation due to barometric pressure changes. No variation due to humidity changes. Direct measurement means waveform and readout are in real-time. There is no sampling delay. Suitable for pediatrics and neonates.
16 Mainstream Disadvantages Mainstream The airway adapter sensor puts weight at the end of the endotracheal tube that often needs to be supported. In older models there were minor facial burns reported. The sensor windows can become obstructed with secretions and water rainout. Sensor and airway adapter can be positional difficult to use in unusual positions (prone, etc).
17 Sidestream Advantages Sampling capillary tube and airway adapter is easy to connect. Single patient use sampling No issues with sterilization. Can be used with patient in almost any position (prone, etc ). Can be used on awake patients via a special nasal cannula. CO 2 reading is unaffected by oxygen flow through the nasal cannula.
18 Sidestream Disadvantages The sampling capillary tube can easily become obstructed by water or secretions. Water vapor pressure changes within the sampling tube can affect CO 2 measurement. Waveforms of children are often not clear, deformed. Delay in waveform and readout due to the time it takes the gas sample to travel to the sensor within the unit.
19 I. Phase-I is the onset of expiration which contains only deadspace gas of the upper airway. II. Phase-II is the upward slope that contains a mixture of deadspace gas and alveolar gas. III. Phase-III, also called the alveolar plateau, contains only alveolar gas. o Phase-0 is the onset of inspiration.
20 a. The alpha-angle is the angle between Phase-II and Phase-III of the capnogram. A decreased alpha-angle can indicate partial airway obstructions or V/Q mismatching. b. The beta-angle is the angle between Phase-III and Phase-0 of the capnogram. A decreased beta-angle can indicate CO 2 rebreathing
21 The presence of Phase-IV on a capnogram indicates an unequal emptying between the left and right lung. This can be caused by a unilateral bronchospasm, or a partial airway obstruction within the left or right bronchial tree.
22 Normal values for P ET CO 2 is mmhg. This is for the text-book patient; 35 year, 6 foot, 165 pound, white male in perfect health. In the clinical setting normal P ET CO 2 is considered to be 3 5 mmhg below the P a CO 2 via arterial blood gas measurement. This calculated measurement is the P (a-et) CO 2, also called the CO 2 -diff, or the CO 2 gradient. The P (a-et) CO 2 is directly proportional to the amount of dead-space ventilation (Ventilation that does not participate in gas exchange). There is clinical significance in both measurements The P ET CO 2 and the P (a-et) CO 2. There are numerous conditions and circumstances, acute and chronic, that will effect the P ET CO 2 measurement and the P (a-et) CO 2 measurement. See the tables on the following slides
23 Increased P ET CO 2 : Decreased P ET CO 2 : Decreased Alveolar Ventilation Decreased respiratory rate Decreased tidal volume Increased equipment deadspace Increased Alveolar Ventilation Increased respiratory rate Increased tidal volume Increased CO 2 Production Fever Hypercatabolic state Reduced CO 2 Production Hypothermia Hypocatabolic state Increased Inspired CO 2 Rebreathing CO 2 absorber exhausted External source of CO 2 Increased Alveolar Deadspace Decreased cardiac output Pulmonary embolism High positive end-expiratory pressure (PEEP) during positive pressure ventilation
24 Increased E (a-et) CO 2 : Decreased E (a-et) CO 2 : Emphysema Pulmonary embolism Low cardiac output states Hypovolemia Slightly increases with age Can occur during pregnancy Occurs naturally in young children Young children and infants normally have less dead-space ventilation than adults because their lungs and airways are much smaller in size
25 The above image is a graphical representation of alveolar and deadspace ventilation based on the P ET CO 2 capnogram.
26 Capnography is a very fast indicator of many problems that can arise during artificial ventilation. In most cases capnography responds much faster than pulse-oximetry, which can sometimes take 3 4 minutes to show a change in respiratory status. The measured E T CO 2 alone, while important, is of limited value. In many cases it is the waveform that tells you a lot more about the pulmonary and airway status of your patient.
27 Sudden Loss of P ET CO 2 Airway disconnected ET Tube kinked ET Tube dislodged Airway obstruction Ventilator malfunction
28 Consistently low P ET CO 2 Alveolar hyperventilation Hypothermia Increased dead space ventilation Sedation / Anesthesia
29 Sudden High P ET CO 2 Alveolar hypoventilation Inadequate minute volume Hyperthermia, pain, shivering Respiratory depressant lungs
30 Rising alveolar plateau (Notice the increased alpha-angle) Bronchospasm Mucus plugging Partial airway obstruction Partially kinked ET tube Prolonged expiratory phase
31 Rapidly Decreasing P ET CO 2 Onset of cardiopulmonary arrest Developing pulmonary embolus Increasing dead space ventilation Sudden hypotension / blood loss
32 Rapidly Rising P ET CO 2 Rising body temperature Increased metabolism Progressing alveolar hypoventilation Partial airway obstruction
33 Rapidly Decreasing P ET CO 2 Onset of cardiopulmonary arrest Developing pulmonary embolus Increasing dead space ventilation Sudden hypotension / blood loss
34 This has been the 3 rd edition of the Readers Digest version of Capnography The Other Vital Sign. Thank you very much for spending the time and energy it took to stay awake during this presentation. Use this new found knowledge well, and in good faith. Many thanks to those supreme beings who have allowed me this opportunity to bore you silly with my senseless babbling of information on treating the sick and injured, saving lives, and other such nonsense. Take very good care, and above all Be safe Send questions or comments to: J. D Urbano, RCP, CRT jdurbano@breathsounds.org Visit Our Website: Join Our Forum: (Always FREE)
35 The Other Vital Sign
Capnography in the Veterinary Technician Toolbox. Katie Pinner BS, LVT Bush Advanced Veterinary Imaging Richmond, VA
 Capnography in the Veterinary Technician Toolbox Katie Pinner BS, LVT Bush Advanced Veterinary Imaging Richmond, VA What are Respiration and Ventilation? Respiration includes all those chemical and physical
Capnography in the Veterinary Technician Toolbox Katie Pinner BS, LVT Bush Advanced Veterinary Imaging Richmond, VA What are Respiration and Ventilation? Respiration includes all those chemical and physical
CARBON DIOXIDE METABOLISM AND CAPNOGRAPHY
 CARBON DIOXIDE METABOLISM AND CAPNOGRAPHY CARBON DIOXIDE METABOLISM Production Transportation Elimination Carbon Dioxide production CO 2 is the metabolite produced by the utilization by cells of oxygen
CARBON DIOXIDE METABOLISM AND CAPNOGRAPHY CARBON DIOXIDE METABOLISM Production Transportation Elimination Carbon Dioxide production CO 2 is the metabolite produced by the utilization by cells of oxygen
Let s talk about Capnography
 Let s talk about Capnography This is one of a series of articles by Keith Simpson BVSc MRCVS MIET (Electronics) discussing the practical aspects of some common monitoring techniques. Capnometry is the
Let s talk about Capnography This is one of a series of articles by Keith Simpson BVSc MRCVS MIET (Electronics) discussing the practical aspects of some common monitoring techniques. Capnometry is the
RESPIRATORY PHYSIOLOGY, PHYSICS AND
 Course n : Course 3 Title: RESPIRATORY PHYSIOLOGY, PHYSICS AND PATHOLOGY IN RELATION TO ANAESTHESIA AND INTENSIVE CARE Sub-category: Techniques Topic: Respiratory monitoring Date: May 05-07, 2016 Language:
Course n : Course 3 Title: RESPIRATORY PHYSIOLOGY, PHYSICS AND PATHOLOGY IN RELATION TO ANAESTHESIA AND INTENSIVE CARE Sub-category: Techniques Topic: Respiratory monitoring Date: May 05-07, 2016 Language:
Monitoring, Ventilation & Capnography
 Why do we need to monitor? Monitoring, Ventilation & Capnography Keith Simpson BVSc MRCVS MIET(Electronics) Torquay, Devon. Under anaesthesia animals no longer have the ability to adequately control their
Why do we need to monitor? Monitoring, Ventilation & Capnography Keith Simpson BVSc MRCVS MIET(Electronics) Torquay, Devon. Under anaesthesia animals no longer have the ability to adequately control their
Chapter 4: Ventilation Test Bank MULTIPLE CHOICE
 Instant download and all chapters Test Bank Respiratory Care Anatomy and Physiology Foundations for Clinical Practice 3rd Edition Will Beachey https://testbanklab.com/download/test-bank-respiratory-care-anatomy-physiologyfoundations-clinical-practice-3rd-edition-will-beachey/
Instant download and all chapters Test Bank Respiratory Care Anatomy and Physiology Foundations for Clinical Practice 3rd Edition Will Beachey https://testbanklab.com/download/test-bank-respiratory-care-anatomy-physiologyfoundations-clinical-practice-3rd-edition-will-beachey/
RESPIRATORY REGULATION DURING EXERCISE
 RESPIRATORY REGULATION DURING EXERCISE Respiration Respiration delivery of oxygen to and removal of carbon dioxide from the tissue External respiration ventilation and exchange of gases in the lung Internal
RESPIRATORY REGULATION DURING EXERCISE Respiration Respiration delivery of oxygen to and removal of carbon dioxide from the tissue External respiration ventilation and exchange of gases in the lung Internal
II. Set up the monitor
 I. Introduction Capnography monitors the concentration of CO2 in the respiratory gases, which is a rapid and reliable method to detect life-threatening conditions, such as malposition of endotracheal tubes,
I. Introduction Capnography monitors the concentration of CO2 in the respiratory gases, which is a rapid and reliable method to detect life-threatening conditions, such as malposition of endotracheal tubes,
The physiological functions of respiration and circulation. Mechanics. exercise 7. Respiratory Volumes. Objectives
 exercise 7 Respiratory System Mechanics Objectives 1. To explain how the respiratory and circulatory systems work together to enable gas exchange among the lungs, blood, and body tissues 2. To define respiration,
exercise 7 Respiratory System Mechanics Objectives 1. To explain how the respiratory and circulatory systems work together to enable gas exchange among the lungs, blood, and body tissues 2. To define respiration,
PICU Resident Self-Study Tutorial The Basic Physics of Oxygen Transport. I was told that there would be no math!
 Physiology of Oxygen Transport PICU Resident Self-Study Tutorial I was told that there would be no math! INTRODUCTION Christopher Carroll, MD Although cells rely on oxygen for aerobic metabolism and viability,
Physiology of Oxygen Transport PICU Resident Self-Study Tutorial I was told that there would be no math! INTRODUCTION Christopher Carroll, MD Although cells rely on oxygen for aerobic metabolism and viability,
Mechanical Ventilation
 Mechanical Ventilation Chapter 4 Mechanical Ventilation Equipment When providing mechanical ventilation for pediatric casualties, it is important to select the appropriately sized bag-valve mask or endotracheal
Mechanical Ventilation Chapter 4 Mechanical Ventilation Equipment When providing mechanical ventilation for pediatric casualties, it is important to select the appropriately sized bag-valve mask or endotracheal
I Physical Principles of Gas Exchange
 Respiratory Gases Exchange Dr Badri Paudel, M.D. 2 I Physical Principles of Gas Exchange 3 Partial pressure The pressure exerted by each type of gas in a mixture Diffusion of gases through liquids Concentration
Respiratory Gases Exchange Dr Badri Paudel, M.D. 2 I Physical Principles of Gas Exchange 3 Partial pressure The pressure exerted by each type of gas in a mixture Diffusion of gases through liquids Concentration
CO 2 SOLUTIONS QUICK REFERENCE GUIDE
 SOLUTIONS QUICK REFERENCE GUIDE 2 Solutions Contents Why Measure?.............................................4 Technology Options..........................................5 The Right Solution.............................................6
SOLUTIONS QUICK REFERENCE GUIDE 2 Solutions Contents Why Measure?.............................................4 Technology Options..........................................5 The Right Solution.............................................6
Lung Volumes and Capacities
 Lung Volumes and Capacities Normally the volume of air entering the lungs during a single inspiration is approximately equal to the volume leaving on the subsequent expiration and is called the tidal volume.
Lung Volumes and Capacities Normally the volume of air entering the lungs during a single inspiration is approximately equal to the volume leaving on the subsequent expiration and is called the tidal volume.
VENTILATORS PURPOSE OBJECTIVES
 VENTILATORS PURPOSE To familiarize and acquaint the transfer Paramedic with the skills and knowledge necessary to adequately maintain a ventilator in the interfacility transfer environment. COGNITIVE OBJECTIVES
VENTILATORS PURPOSE To familiarize and acquaint the transfer Paramedic with the skills and knowledge necessary to adequately maintain a ventilator in the interfacility transfer environment. COGNITIVE OBJECTIVES
UNIQUE CHARACTERISTICS OF THE PULMONARY CIRCULATION THE PULMONARY CIRCULATION MUST, AT ALL TIMES, ACCEPT THE ENTIRE CARDIAC OUTPUT
 UNIQUE CHARACTERISTICS OF THE PULMONARY CIRCULATION THE PULMONARY CIRCULATION MUST, AT ALL TIMES, ACCEPT THE ENTIRE CARDIAC OUTPUT UNIQUE CHARACTERISTICS OF THE PULMONARY CIRCULATION THE PULMONARY CIRCULATION
UNIQUE CHARACTERISTICS OF THE PULMONARY CIRCULATION THE PULMONARY CIRCULATION MUST, AT ALL TIMES, ACCEPT THE ENTIRE CARDIAC OUTPUT UNIQUE CHARACTERISTICS OF THE PULMONARY CIRCULATION THE PULMONARY CIRCULATION
By: Aseel Jamil Al-twaijer. Lec : physical principles of gas exchange
 By: Aseel Jamil Al-twaijer Lec : physical principles of gas exchange Date:30 /10/2017 this lecture is about the exchange of gases between the blood and the alveoli. I might add some external definitions
By: Aseel Jamil Al-twaijer Lec : physical principles of gas exchange Date:30 /10/2017 this lecture is about the exchange of gases between the blood and the alveoli. I might add some external definitions
Section Two Diffusion of gases
 Section Two Diffusion of gases Lecture 5: Partial pressure and the composition of gasses in air. Factors affecting diffusion of gases. Ventilation perfusion ratio effect on alveolar gas concentration.
Section Two Diffusion of gases Lecture 5: Partial pressure and the composition of gasses in air. Factors affecting diffusion of gases. Ventilation perfusion ratio effect on alveolar gas concentration.
Mechanical Ventilation
 PROCEDURE - Page 1 of 5 Purpose Scope Physician's Order Indications Procedure Mechanical Artificial Ventilation refers to any methods to deliver volumes of gas into a patient's lungs over an extended period
PROCEDURE - Page 1 of 5 Purpose Scope Physician's Order Indications Procedure Mechanical Artificial Ventilation refers to any methods to deliver volumes of gas into a patient's lungs over an extended period
EMS INTER-FACILITY TRANSPORT WITH MECHANICAL VENTILATOR COURSE OBJECTIVES
 GENERAL PROVISIONS: EMS INTER-FACILITY TRANSPORT WITH MECHANICAL VENTILATOR COURSE OBJECTIVES Individuals providing Inter-facility transport with Mechanical Ventilator must have successfully completed
GENERAL PROVISIONS: EMS INTER-FACILITY TRANSPORT WITH MECHANICAL VENTILATOR COURSE OBJECTIVES Individuals providing Inter-facility transport with Mechanical Ventilator must have successfully completed
Anesthesia monitoring
 Anesthesia monitoring The aim of this anesthesia monitoring teorhetical material is for veterinary assistant to be able to monitore vital signs and any other changes during anesthesia and fill the parameters
Anesthesia monitoring The aim of this anesthesia monitoring teorhetical material is for veterinary assistant to be able to monitore vital signs and any other changes during anesthesia and fill the parameters
Collin County Community College. Lung Physiology
 Collin County Community College BIOL. 2402 Anatomy & Physiology WEEK 9 Respiratory System 1 Lung Physiology Factors affecting Ventillation 1. Airway resistance Flow = Δ P / R Most resistance is encountered
Collin County Community College BIOL. 2402 Anatomy & Physiology WEEK 9 Respiratory System 1 Lung Physiology Factors affecting Ventillation 1. Airway resistance Flow = Δ P / R Most resistance is encountered
Respiration (revised 2006) Pulmonary Mechanics
 Respiration (revised 2006) Pulmonary Mechanics PUL 1. Diagram how pleural pressure, alveolar pressure, airflow, and lung volume change during a normal quiet breathing cycle. Identify on the figure the
Respiration (revised 2006) Pulmonary Mechanics PUL 1. Diagram how pleural pressure, alveolar pressure, airflow, and lung volume change during a normal quiet breathing cycle. Identify on the figure the
Monitoring. Suzie Ward March 2013
 Monitoring Suzie Ward March 2013 Monitoring 1 Oximetry Capnography Oxygen Vapours FRCA Primary Pulse oximetry; how does it work? Is it fast or slow? What are its problems? Graph of light absorption of
Monitoring Suzie Ward March 2013 Monitoring 1 Oximetry Capnography Oxygen Vapours FRCA Primary Pulse oximetry; how does it work? Is it fast or slow? What are its problems? Graph of light absorption of
Name: Oasis: Questions EPCP. Professional Development: ETCO2 Monitoring
 EPCP Professional Development: ET Monitoring Name: Oasis: Questions ET Questions Package 1) Blood entering the pulmonary circuit from the systemic circuit contains on average mmhg. a) 36 b) 46 c) 4 d)
EPCP Professional Development: ET Monitoring Name: Oasis: Questions ET Questions Package 1) Blood entering the pulmonary circuit from the systemic circuit contains on average mmhg. a) 36 b) 46 c) 4 d)
Respiratory Physiology Gaseous Exchange
 Respiratory Physiology Gaseous Exchange Session Objectives. What you will cover Basic anatomy of the lung including airways Breathing movements Lung volumes and capacities Compliance and Resistance in
Respiratory Physiology Gaseous Exchange Session Objectives. What you will cover Basic anatomy of the lung including airways Breathing movements Lung volumes and capacities Compliance and Resistance in
CHAPTER 6. Oxygen Transport. Copyright 2008 Thomson Delmar Learning
 CHAPTER 6 Oxygen Transport Normal Blood Gas Value Ranges Table 6-1 OXYGEN TRANSPORT Oxygen Dissolved in the Blood Plasma Dissolve means that the gas maintains its precise molecular structure About.003
CHAPTER 6 Oxygen Transport Normal Blood Gas Value Ranges Table 6-1 OXYGEN TRANSPORT Oxygen Dissolved in the Blood Plasma Dissolve means that the gas maintains its precise molecular structure About.003
Figure 1. A schematic diagram of the human respiratory system.
 Introduction to Respiration In this experiment, you will investigate various aspects of normal breathing, hyperventilation, rebreathing the effect of changing airway resistance and ways in which to measure
Introduction to Respiration In this experiment, you will investigate various aspects of normal breathing, hyperventilation, rebreathing the effect of changing airway resistance and ways in which to measure
Capnography and Ventilation for the EMS Professional
 Capnography and Ventilation for the EMS Professional Advanced concepts in the ventilation of the acutely ill patient Raymond L. Fowler, M.D., FACEP Associate Professor of Emergency Medicine The University
Capnography and Ventilation for the EMS Professional Advanced concepts in the ventilation of the acutely ill patient Raymond L. Fowler, M.D., FACEP Associate Professor of Emergency Medicine The University
NOTE: If not used, provider must document reason(s) for deferring mechanical ventilation in a patient with an advanced airway
 APPENDIX: TITLE: Mechanical Ventilator Use REVISED: November 1, 2017 I. Introduction: Mechanical Ventilation is the use of an automated device to deliver positive pressure ventilation to a patient. Proper
APPENDIX: TITLE: Mechanical Ventilator Use REVISED: November 1, 2017 I. Introduction: Mechanical Ventilation is the use of an automated device to deliver positive pressure ventilation to a patient. Proper
Using the Lifebox oximeter in the neonatal unit. Tutorial 1 the basics
 Using the Lifebox oximeter in the neonatal unit Tutorial 1 the basics Lifebox 2014. 2011. All rights reserved The Lifebox Pulse Oximeter In this tutorial you will learn about: The function of a pulse oximeter
Using the Lifebox oximeter in the neonatal unit Tutorial 1 the basics Lifebox 2014. 2011. All rights reserved The Lifebox Pulse Oximeter In this tutorial you will learn about: The function of a pulse oximeter
Medical Ventilators. Ryan Sanford Daniel Tajik
 Medical Ventilators Ryan Sanford Daniel Tajik Medical Ventilators Assist patients that have trouble breathing on their own. 2 Oxygen Intake The Respiratory System has the responsibility of providing the
Medical Ventilators Ryan Sanford Daniel Tajik Medical Ventilators Assist patients that have trouble breathing on their own. 2 Oxygen Intake The Respiratory System has the responsibility of providing the
RESPIRATORY MONITORING AND OXIMETRY
 RESPIRATORY MONITORING AND OXIMETRY EE 471 F2016 Prof. Yasser Mostafa Kadah Introduction Respiratory monitoring includes measurement, evaluation, and monitoring of parameters of respiratory system, First
RESPIRATORY MONITORING AND OXIMETRY EE 471 F2016 Prof. Yasser Mostafa Kadah Introduction Respiratory monitoring includes measurement, evaluation, and monitoring of parameters of respiratory system, First
RESPIRATORY GAS EXCHANGE
 RESPIRATORY GAS EXCHANGE Alveolar PO 2 = 105 mmhg; Pulmonary artery PO 2 = 40 mmhg PO 2 gradient across respiratory membrane 65 mmhg (105 mmhg 40 mmhg) Results in pulmonary vein PO 2 ~100 mmhg Partial
RESPIRATORY GAS EXCHANGE Alveolar PO 2 = 105 mmhg; Pulmonary artery PO 2 = 40 mmhg PO 2 gradient across respiratory membrane 65 mmhg (105 mmhg 40 mmhg) Results in pulmonary vein PO 2 ~100 mmhg Partial
MEDICAL EQUIPMENT IV MECHANICAL VENTILATORS. Prof. Yasser Mostafa Kadah
 MEDICAL EQUIPMENT IV - 2013 MECHANICAL VENTILATORS Prof. Yasser Mostafa Kadah Mechanical Ventilator A ventilator is a machine, a system of related elements designed to alter, transmit, and direct energy
MEDICAL EQUIPMENT IV - 2013 MECHANICAL VENTILATORS Prof. Yasser Mostafa Kadah Mechanical Ventilator A ventilator is a machine, a system of related elements designed to alter, transmit, and direct energy
Respiratory Pulmonary Ventilation
 Respiratory Pulmonary Ventilation Pulmonary Ventilation Pulmonary ventilation is the act of breathing and the first step in the respiratory process. Pulmonary ventilation brings in air with a new supply
Respiratory Pulmonary Ventilation Pulmonary Ventilation Pulmonary ventilation is the act of breathing and the first step in the respiratory process. Pulmonary ventilation brings in air with a new supply
Capnography (ICP) Acknowledgement This training package was created by Leonie Wilton. Please direct any questions to your CSO or Team Leader.
 Capnography (ICP) Acknowledgement This training package was created by Leonie Wilton. Please direct any questions to your CSO or Team Leader. Offline Reading Download as PDF Welcome Introduction Basic
Capnography (ICP) Acknowledgement This training package was created by Leonie Wilton. Please direct any questions to your CSO or Team Leader. Offline Reading Download as PDF Welcome Introduction Basic
Respiratory Lecture Test Questions Set 3
 Respiratory Lecture Test Questions Set 3 1. The pressure of a gas: a. is inversely proportional to its volume b. is unaffected by temperature changes c. is directly proportional to its volume d. does not
Respiratory Lecture Test Questions Set 3 1. The pressure of a gas: a. is inversely proportional to its volume b. is unaffected by temperature changes c. is directly proportional to its volume d. does not
Gas exchange. Tissue cells CO2 CO 2 O 2. Pulmonary capillary. Tissue capillaries
 Gas exchange Pulmonary gas exchange Tissue gas exchange CO 2 O 2 O 2 Tissue cells CO2 CO 2 Pulmonary capillary O 2 O 2 CO 2 Tissue capillaries Physical principles of gas exchange Diffusion: continuous
Gas exchange Pulmonary gas exchange Tissue gas exchange CO 2 O 2 O 2 Tissue cells CO2 CO 2 Pulmonary capillary O 2 O 2 CO 2 Tissue capillaries Physical principles of gas exchange Diffusion: continuous
Respiratory Medicine. A-A Gradient & Alveolar Gas Equation Laboratory Diagnostics. Alveolar Gas Equation. See online here
 Respiratory Medicine A-A Gradient & Alveolar Gas Equation Laboratory Diagnostics See online here Alveolar gas equation helps to calculate the partial pressure of oxygen in alveoli and A-a gradient is the
Respiratory Medicine A-A Gradient & Alveolar Gas Equation Laboratory Diagnostics See online here Alveolar gas equation helps to calculate the partial pressure of oxygen in alveoli and A-a gradient is the
Respiratory System Physiology. Dr. Vedat Evren
 Respiratory System Physiology Dr. Vedat Evren Respiration Processes involved in oxygen transport from the atmosphere to the body tissues and the release and transportation of carbon dioxide produced in
Respiratory System Physiology Dr. Vedat Evren Respiration Processes involved in oxygen transport from the atmosphere to the body tissues and the release and transportation of carbon dioxide produced in
UNDERSTANDING NEONATAL WAVEFORM GRAPHICS. Brandon Kuehne, MBA, RRT-NPS, RPFT Director- Neonatal Respiratory Services
 UNDERSTANDING NEONATAL WAVEFORM GRAPHICS Brandon Kuehne, MBA, RRT-NPS, RPFT Director- Neonatal Respiratory Services Disclosures Purpose: To enhance bedside staff s knowledge of ventilation and oxygenation
UNDERSTANDING NEONATAL WAVEFORM GRAPHICS Brandon Kuehne, MBA, RRT-NPS, RPFT Director- Neonatal Respiratory Services Disclosures Purpose: To enhance bedside staff s knowledge of ventilation and oxygenation
Indications for Mechanical Ventilation. Mechanical Ventilation. Indications for Mechanical Ventilation. Modes. Modes: Volume cycled
 Mechanical Ventilation Eric A. Libré, MD VCU School of Medicine Inova Fairfax Hospital and VHC Indications for Mechanical Ventilation Inadequate ventilatory effort Rising pco2 with resp acidosis (7.25)
Mechanical Ventilation Eric A. Libré, MD VCU School of Medicine Inova Fairfax Hospital and VHC Indications for Mechanical Ventilation Inadequate ventilatory effort Rising pco2 with resp acidosis (7.25)
Selecting and Connecting Breathing Systems
 Selecting and Connecting Breathing Year Group: BVSc3 + Document number: CSL_A03 Equipment for this station: Equipment list: Pen Paper Calculator T-piece (in CSL a strip of white tape is around this system)
Selecting and Connecting Breathing Year Group: BVSc3 + Document number: CSL_A03 Equipment for this station: Equipment list: Pen Paper Calculator T-piece (in CSL a strip of white tape is around this system)
Chapter 9 Airway Respirations Metabolism Oxygen Requirements Respiratory Anatomy Respiratory Anatomy Respiratory Anatomy Diaphragm
 1 Chapter 9 Airway 2 Respirations Every cell of the body requires to survive Oxygen must come in and carbon must go out 3 Metabolism Metabolism--Process where the body s cells convert food to Adequate
1 Chapter 9 Airway 2 Respirations Every cell of the body requires to survive Oxygen must come in and carbon must go out 3 Metabolism Metabolism--Process where the body s cells convert food to Adequate
Author: Thomas Sisson, MD, 2009
 Author: Thomas Sisson, MD, 2009 License: Unless otherwise noted, this material is made available under the terms of the Creative Commons Attribution Non-commercial Share Alike 3.0 License: http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by-nc-sa/3.0/
Author: Thomas Sisson, MD, 2009 License: Unless otherwise noted, this material is made available under the terms of the Creative Commons Attribution Non-commercial Share Alike 3.0 License: http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by-nc-sa/3.0/
CHAPTER 3: The respiratory system
 CHAPTER 3: The respiratory system Practice questions - text book pages 56-58 1) When the inspiratory muscles contract, which one of the following statements is true? a. the size of the thoracic cavity
CHAPTER 3: The respiratory system Practice questions - text book pages 56-58 1) When the inspiratory muscles contract, which one of the following statements is true? a. the size of the thoracic cavity
Chapter 17 The Respiratory System: Gas Exchange and Regulation of Breathing
 Chapter 17 The Respiratory System: Gas Exchange and Regulation of Breathing Overview of Pulmonary Circulation o Diffusion of Gases o Exchange of Oxygen and Carbon Dioxide o Transport of Gases in the Blood
Chapter 17 The Respiratory System: Gas Exchange and Regulation of Breathing Overview of Pulmonary Circulation o Diffusion of Gases o Exchange of Oxygen and Carbon Dioxide o Transport of Gases in the Blood
CHAPTER 3: The cardio-respiratory system
 : The cardio-respiratory system Exam style questions - text book pages 44-45 1) Describe the structures involved in gaseous exchange in the lungs and explain how gaseous exchange occurs within this tissue.
: The cardio-respiratory system Exam style questions - text book pages 44-45 1) Describe the structures involved in gaseous exchange in the lungs and explain how gaseous exchange occurs within this tissue.
Completed downloadable Test Bank for Pilbeams Mechanical Ventilation Physiological and Clinical Applications 5th Edition by Cairo
 Completed downloadable Test Bank for Pilbeams Mechanical Ventilation Physiological and Clinical Applications 5th Edition by Cairo Link full download: http://testbankcollection.com/download/pilbeams-mechanicalventilation-physiological-and-clinical-applications-5th-edition-test-bank-cairo
Completed downloadable Test Bank for Pilbeams Mechanical Ventilation Physiological and Clinical Applications 5th Edition by Cairo Link full download: http://testbankcollection.com/download/pilbeams-mechanicalventilation-physiological-and-clinical-applications-5th-edition-test-bank-cairo
Initiation and Management of Airway Pressure Release Ventilation (APRV)
 Initiation and Management of Airway Pressure Release Ventilation (APRV) Eric Kriner RRT Pulmonary Critical Care Clinical Specialist Pulmonary Services Department Medstar Washington Hospital Center Disclosures
Initiation and Management of Airway Pressure Release Ventilation (APRV) Eric Kriner RRT Pulmonary Critical Care Clinical Specialist Pulmonary Services Department Medstar Washington Hospital Center Disclosures
DOWNLOAD OR READ : VENTILATION BLOOD FLOW AND DIFFUSION PDF EBOOK EPUB MOBI
 DOWNLOAD OR READ : VENTILATION BLOOD FLOW AND DIFFUSION PDF EBOOK EPUB MOBI Page 1 Page 2 ventilation blood flow and diffusion ventilation blood flow and pdf ventilation blood flow and diffusion Title:
DOWNLOAD OR READ : VENTILATION BLOOD FLOW AND DIFFUSION PDF EBOOK EPUB MOBI Page 1 Page 2 ventilation blood flow and diffusion ventilation blood flow and pdf ventilation blood flow and diffusion Title:
Circulatory And Respiration
 Circulatory And Respiration Composition Of Blood Blood Heart 200mmHg 120mmHg Aorta Artery Arteriole 50mmHg Capillary Bed Venule Vein Vena Cava Heart Differences Between Arteries and Veins Veins transport
Circulatory And Respiration Composition Of Blood Blood Heart 200mmHg 120mmHg Aorta Artery Arteriole 50mmHg Capillary Bed Venule Vein Vena Cava Heart Differences Between Arteries and Veins Veins transport
Essential Skills Course Acute Care Module. Respiratory Day 2 (Arterial Blood Gases) Pre course Workbook
 Essential Skills Course Acute Care Module Respiratory Day 2 (Arterial Blood Gases) Pre course Workbook Acknowledgements This pre course workbook has been complied and updated with reference to the original
Essential Skills Course Acute Care Module Respiratory Day 2 (Arterial Blood Gases) Pre course Workbook Acknowledgements This pre course workbook has been complied and updated with reference to the original
 Question 1: Define vital capacity. What is its significance? Vital capacity is the maximum volume of air that can be exhaled after a maximum inspiration. It is about 3.5 4.5 litres in the human body. It
Question 1: Define vital capacity. What is its significance? Vital capacity is the maximum volume of air that can be exhaled after a maximum inspiration. It is about 3.5 4.5 litres in the human body. It
RESPIRATORY PHYSIOLOGY. Anaesthesiology Block 18 (GNK 586) Prof Pierre Fourie
 RESPIRATORY PHYSIOLOGY Anaesthesiology Block 18 (GNK 586) Prof Pierre Fourie Outline Ventilation Diffusion Perfusion Ventilation-Perfusion relationship Work of breathing Control of Ventilation 2 This image
RESPIRATORY PHYSIOLOGY Anaesthesiology Block 18 (GNK 586) Prof Pierre Fourie Outline Ventilation Diffusion Perfusion Ventilation-Perfusion relationship Work of breathing Control of Ventilation 2 This image
McHENRY WESTERN LAKE COUNTY EMS SYSTEM FALL 2014 CONTINUING EDUCATION MANDATORY FOR ALL PRIMARY AND PROBATIONARY ALS SYSTEM PROVIDERS.
 McHENRY WESTERN LAKE COUNTY EMS SYSTEM FALL 2014 CONTINUING EDUCATION MANDATORY FOR ALL PRIMARY AND PROBATIONARY ALS SYSTEM PROVIDERS ResQPOD In a cardiac arrest blood flow to the organs stop. Key to survival
McHENRY WESTERN LAKE COUNTY EMS SYSTEM FALL 2014 CONTINUING EDUCATION MANDATORY FOR ALL PRIMARY AND PROBATIONARY ALS SYSTEM PROVIDERS ResQPOD In a cardiac arrest blood flow to the organs stop. Key to survival
Unit II Problem 4 Physiology: Diffusion of Gases and Pulmonary Circulation
 Unit II Problem 4 Physiology: Diffusion of Gases and Pulmonary Circulation - Physical principles of gases: Pressure of a gas is caused by the movement of its molecules against a surface (more concentration
Unit II Problem 4 Physiology: Diffusion of Gases and Pulmonary Circulation - Physical principles of gases: Pressure of a gas is caused by the movement of its molecules against a surface (more concentration
The Physiologic Basis of DLCO testing. Brian Graham Division of Respirology, Critical Care and Sleep Medicine University of Saskatchewan
 The Physiologic Basis of DLCO testing Brian Graham Division of Respirology, Critical Care and Sleep Medicine University of Saskatchewan Objectives Review gas transport from inhaled gas to the rest of the
The Physiologic Basis of DLCO testing Brian Graham Division of Respirology, Critical Care and Sleep Medicine University of Saskatchewan Objectives Review gas transport from inhaled gas to the rest of the
Respiration. The resspiratory system
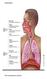 Respiration The resspiratory system The Alveoli The lungs have about 300 million alveoli, with a total crosssec onal area of 50 70 m2.. Each alveolar sac is surrounded by blood capillaries. The walls of
Respiration The resspiratory system The Alveoli The lungs have about 300 million alveoli, with a total crosssec onal area of 50 70 m2.. Each alveolar sac is surrounded by blood capillaries. The walls of
Lab 3. The Respiratory System (designed by Heather E. M. Liwanag with T.M. Williams)
 Name Lab Partners Lab 3. The Respiratory System (designed by Heather E. M. Liwanag with T.M. Williams) Part 1. Lung Volumes and Capacities Objectives 1. Obtain graphical representation of lung capacities
Name Lab Partners Lab 3. The Respiratory System (designed by Heather E. M. Liwanag with T.M. Williams) Part 1. Lung Volumes and Capacities Objectives 1. Obtain graphical representation of lung capacities
S2c Oxygenation & Ventilation
 1 Neonatal/Pediatric Cardiopulmonary Care Assessment of Oxygenation and Ventilation 2 Blood Gases Blood Gas Analysis 3 Infants can make dramatic changes in status very quickly Very difficult to base therapeutic
1 Neonatal/Pediatric Cardiopulmonary Care Assessment of Oxygenation and Ventilation 2 Blood Gases Blood Gas Analysis 3 Infants can make dramatic changes in status very quickly Very difficult to base therapeutic
ALVEOLAR - BLOOD GAS EXCHANGE 1
 ALVEOLAR - BLOOD GAS EXCHANGE 1 Summary: These notes examine the general means by which ventilation is regulated in terrestrial mammals. It then moves on to a discussion of what happens when someone over
ALVEOLAR - BLOOD GAS EXCHANGE 1 Summary: These notes examine the general means by which ventilation is regulated in terrestrial mammals. It then moves on to a discussion of what happens when someone over
Chapter 16 Respiratory System
 Introduction Chapter 16 Respiratory System The respiratory system consists of tubes that filter incoming air and transport it to alveoli where gases are exchanged. Think pair share: what organs are associated
Introduction Chapter 16 Respiratory System The respiratory system consists of tubes that filter incoming air and transport it to alveoli where gases are exchanged. Think pair share: what organs are associated
Corporate Overview and Product Summary
 2008 Corporate Overview and Product Summary Vapotherm Summary: Market leader and originator of High Flow Therapy Founded in 1999 Headquartered in Stevensville, MD Clinical and education leadership in High
2008 Corporate Overview and Product Summary Vapotherm Summary: Market leader and originator of High Flow Therapy Founded in 1999 Headquartered in Stevensville, MD Clinical and education leadership in High
Volumetric Gas Measurements Measurement Site Considerations
 W H I T E P A P E R Volumetric Gas Measurements Measurement Site Considerations ABSTRACT For the measurement of gas exchange (such as carbon dioxide elimination), the choice of the gas and flow measurement
W H I T E P A P E R Volumetric Gas Measurements Measurement Site Considerations ABSTRACT For the measurement of gas exchange (such as carbon dioxide elimination), the choice of the gas and flow measurement
Outline - Respiratory System. Function of the respiratory system Parts of the respiratory system Mechanics of breathing Regulation of breathing
 Respiratory system Function Outline - Respiratory System I. II. III. IV. Respiratory System The function of the respiratory system is to bring in oxygen to the body and remove carbon dioxide. Function
Respiratory system Function Outline - Respiratory System I. II. III. IV. Respiratory System The function of the respiratory system is to bring in oxygen to the body and remove carbon dioxide. Function
OXYGEN THERAPY. (Non-invasive O2 therapy in patient >8yrs)
 OXYGEN THERAPY (Non-invasive O2 therapy in patient >8yrs) Learning aims Indications and precautions for O2 therapy Targets of therapy Standard notation O2 delivery devices Taps, tanks and tubing Notation
OXYGEN THERAPY (Non-invasive O2 therapy in patient >8yrs) Learning aims Indications and precautions for O2 therapy Targets of therapy Standard notation O2 delivery devices Taps, tanks and tubing Notation
How does HFOV work? John F Mills MBBS, FRACP, M Med Sc, PhD Neonatologist Royal Children s Hospital. Synopsis
 How does HFOV work? John F Mills MBBS, FRACP, M Med Sc, PhD Neonatologist Royal Children s Hospital Synopsis Definition of an oscillator Historical perspective Differences between HFOV and CMV Determinants
How does HFOV work? John F Mills MBBS, FRACP, M Med Sc, PhD Neonatologist Royal Children s Hospital Synopsis Definition of an oscillator Historical perspective Differences between HFOV and CMV Determinants
Basics of Mechanical Ventilation. Dr Shrikanth Srinivasan MD,DNB,FNB,EDIC Consultant, Critical Care Medicine Medanta, The Medicity
 Basics of Mechanical Ventilation Dr Shrikanth Srinivasan MD,DNB,FNB,EDIC Consultant, Critical Care Medicine Medanta, The Medicity Overview of topics 1. Goals 2. Settings 3. Modes 4. Advantages and disadvantages
Basics of Mechanical Ventilation Dr Shrikanth Srinivasan MD,DNB,FNB,EDIC Consultant, Critical Care Medicine Medanta, The Medicity Overview of topics 1. Goals 2. Settings 3. Modes 4. Advantages and disadvantages
Selecting the Ventilator and the Mode. Chapter 6
 Selecting the Ventilator and the Mode Chapter 6 Criteria for Ventilator Selection Why does the patient need ventilatory support? Does the ventilation problem require a special mode? What therapeutic goals
Selecting the Ventilator and the Mode Chapter 6 Criteria for Ventilator Selection Why does the patient need ventilatory support? Does the ventilation problem require a special mode? What therapeutic goals
PROBLEM SET 9. SOLUTIONS April 23, 2004
 Harvard-MIT Division of Health Sciences and Technology HST.542J: Quantitative Physiology: Organ Transport Systems Instructors: Roger Mark and Jose Venegas MASSACHUSETTS INSTITUTE OF TECHNOLOGY Departments
Harvard-MIT Division of Health Sciences and Technology HST.542J: Quantitative Physiology: Organ Transport Systems Instructors: Roger Mark and Jose Venegas MASSACHUSETTS INSTITUTE OF TECHNOLOGY Departments
Introduction. Respiration. Chapter 10. Objectives. Objectives. The Respiratory System
 Introduction Respiration Chapter 10 The Respiratory System Provides a means of gas exchange between the environment and the body Plays a role in the regulation of acidbase balance during exercise Objectives
Introduction Respiration Chapter 10 The Respiratory System Provides a means of gas exchange between the environment and the body Plays a role in the regulation of acidbase balance during exercise Objectives
Mechanical Ventilation. Mechanical Ventilation is a Drug!!! is a drug. MV: Indications for use. MV as a Drug: Outline. MV: Indications for use
 Mechanical Ventilation is a Drug!!! Mechanical Ventilation is a drug I am an employee of Philips Healthcare Hospital Respiratory Care Group and they help me pay for my kids education Jim Laging, RRT, RCP
Mechanical Ventilation is a Drug!!! Mechanical Ventilation is a drug I am an employee of Philips Healthcare Hospital Respiratory Care Group and they help me pay for my kids education Jim Laging, RRT, RCP
Monitoring Exhaled Carbon Dioxide
 Monitoring Exhaled Carbon Dioxide Mark S Siobal RRT-ACCS FAARC Introduction Classification and Types of Exhaled CO 2 Monitoring Colorimetric CO 2 Detectors Mainstream CO 2 Monitoring Sidestream CO 2 Monitoring
Monitoring Exhaled Carbon Dioxide Mark S Siobal RRT-ACCS FAARC Introduction Classification and Types of Exhaled CO 2 Monitoring Colorimetric CO 2 Detectors Mainstream CO 2 Monitoring Sidestream CO 2 Monitoring
A CO 2 Waveform Simulator For Evaluation and Testing of Respiratory Gas Analyzers
 2011 ROCKY MOUNTAIN NASA SPACE GRANT CONSORTIUM 1 A CO 2 Waveform Simulator For Evaluation and Testing of Respiratory Gas Analyzers Christina Long, and Joseph Orr, Ph.D. Department of Bioengineering, University
2011 ROCKY MOUNTAIN NASA SPACE GRANT CONSORTIUM 1 A CO 2 Waveform Simulator For Evaluation and Testing of Respiratory Gas Analyzers Christina Long, and Joseph Orr, Ph.D. Department of Bioengineering, University
VENTILATION AND PERFUSION IN HEALTH AND DISEASE. Dr.HARIPRASAD VS
 VENTILATION AND PERFUSION IN HEALTH AND DISEASE Dr.HARIPRASAD VS Ventilation Total ventilation - total rate of air flow in and out of the lung during normal tidal breathing. Alveolar ventilation -represents
VENTILATION AND PERFUSION IN HEALTH AND DISEASE Dr.HARIPRASAD VS Ventilation Total ventilation - total rate of air flow in and out of the lung during normal tidal breathing. Alveolar ventilation -represents
6 th Accredited Advanced Mechanical Ventilation Course for Anesthesiologists. Course Test Results for the accreditation of the acquired knowledge
 6 th Accredited Advanced Mechanical Ventilation Course for Anesthesiologists Course Test Results for the accreditation of the acquired knowledge Q. Concerning the mechanics of the newborn s respiratory
6 th Accredited Advanced Mechanical Ventilation Course for Anesthesiologists Course Test Results for the accreditation of the acquired knowledge Q. Concerning the mechanics of the newborn s respiratory
Errors in Monitoring. BWH Clinical Conference 10/06/04. Copyright 2004, James H Philip, all rights reserved.
 Errors in Monitoring BWH Clinical Conference 10/06/04 Copyright 2004, James H Philip, all rights reserved. Technology Block 2004 10/06/04 James Philip MD Low flow&closed circuit safety&danger 10/06/04
Errors in Monitoring BWH Clinical Conference 10/06/04 Copyright 2004, James H Philip, all rights reserved. Technology Block 2004 10/06/04 James Philip MD Low flow&closed circuit safety&danger 10/06/04
Respiratory system & exercise. Dr. Rehab F Gwada
 Respiratory system & exercise Dr. Rehab F Gwada Objectives of lecture Outline the major anatomical components & important functions of the respiratory system. Describe the mechanics of ventilation. List
Respiratory system & exercise Dr. Rehab F Gwada Objectives of lecture Outline the major anatomical components & important functions of the respiratory system. Describe the mechanics of ventilation. List
Respiratory System Review
 KEY THIS TEST WILL BE COMPLETED IN ONE CLASS PERIOD MONDAY, MARCH 10. 2014 Respiratory System Review Name A. Directions: Fill in the blank with the appropriate vocabulary word or words (several examples
KEY THIS TEST WILL BE COMPLETED IN ONE CLASS PERIOD MONDAY, MARCH 10. 2014 Respiratory System Review Name A. Directions: Fill in the blank with the appropriate vocabulary word or words (several examples
respiratory cycle. point in the volumes: 500 milliliters. for men. expiration, up to 1200 milliliters extra makes breathing Respiratory
 10 II. RESPIRATORY VOLUMES, CAPACITIES & PULMONARY FUNCTION TESTS Respiratory volume is the term used for various volumes of air moved by or associated with the lungs at a given point in the respiratory
10 II. RESPIRATORY VOLUMES, CAPACITIES & PULMONARY FUNCTION TESTS Respiratory volume is the term used for various volumes of air moved by or associated with the lungs at a given point in the respiratory
1. NAME OF THE MEDICINAL PRODUCT. Medicinal Air, Air Liquide 100%, medicinal gas, compressed. 2. QUALITATIVE AND QUANTITATIVE COMPOSITION
 1. NAME OF THE MEDICINAL PRODUCT Medicinal Air, Air Liquide 100%, medicinal gas, compressed. 2. QUALITATIVE AND QUANTITATIVE COMPOSITION Medicinal air 100% at a pressure of 200 bar (15 C). 3. PHARMACEUTICAL
1. NAME OF THE MEDICINAL PRODUCT Medicinal Air, Air Liquide 100%, medicinal gas, compressed. 2. QUALITATIVE AND QUANTITATIVE COMPOSITION Medicinal air 100% at a pressure of 200 bar (15 C). 3. PHARMACEUTICAL
LUNG CLEARANCE INDEX. COR-MAN IN Issue A, Rev INNOVISION ApS Skovvænget 2 DK-5620 Glamsbjerg Denmark
 LUNG CLEARANCE INDEX METHOD COR-MAN-0000-008-IN Issue A, Rev. 3 2013-07-01 INNOVISION ApS Skovvænget 2 DK-5620 Glamsbjerg Denmark Tel.: +45 65 95 91 00 Fax: +45 65 95 78 00 info@innovision.dk www.innovision.dk
LUNG CLEARANCE INDEX METHOD COR-MAN-0000-008-IN Issue A, Rev. 3 2013-07-01 INNOVISION ApS Skovvænget 2 DK-5620 Glamsbjerg Denmark Tel.: +45 65 95 91 00 Fax: +45 65 95 78 00 info@innovision.dk www.innovision.dk
Determination of the Frequency Response of an End Tidal CO2 Analyser
 The ITB Journal Volume 4 Issue 2 Article 5 2003 Determination of the Frequency Response of an End Tidal CO2 Analyser Kabita Shakya Catherine Deegan Fran Hegarty Follow this and additional works at: https://arrow.dit.ie/itbj
The ITB Journal Volume 4 Issue 2 Article 5 2003 Determination of the Frequency Response of an End Tidal CO2 Analyser Kabita Shakya Catherine Deegan Fran Hegarty Follow this and additional works at: https://arrow.dit.ie/itbj
Yanal. Jumana Jihad. Jamil Nazzal. 0 P a g e
 2 Yanal Jumana Jihad Jamil Nazzal 0 P a g e note: this sheet was written and corrected according to the records from section 2 so you may find differences in the arrangement of topics from the records
2 Yanal Jumana Jihad Jamil Nazzal 0 P a g e note: this sheet was written and corrected according to the records from section 2 so you may find differences in the arrangement of topics from the records
Rodney Shandukani 14/03/2012
 Rodney Shandukani 14/03/2012 OXYGEN THERAPY Aerobic metabolism accounts for 90% of Oxygen consumption by tissues. generates ATP by oxidative phosphorylation. Oxygen cascade: Oxygen exerts a partial pressure,
Rodney Shandukani 14/03/2012 OXYGEN THERAPY Aerobic metabolism accounts for 90% of Oxygen consumption by tissues. generates ATP by oxidative phosphorylation. Oxygen cascade: Oxygen exerts a partial pressure,
Gas Exchange Respiratory Systems
 alveoli gills Gas Exchange Respiratory Systems elephant seals 2008-2009 Why do we need a respiratory system? respiration for respiration Need O 2 in for aerobic cellular respiration make ATP Need CO 2
alveoli gills Gas Exchange Respiratory Systems elephant seals 2008-2009 Why do we need a respiratory system? respiration for respiration Need O 2 in for aerobic cellular respiration make ATP Need CO 2
Respiratory Signs: Tachypnea (RR>30/min), Desaturation, Shallow breathing, Use of accessory muscles Breathing sound: Wheezing, Rhonchi, Crepitation.
 Respiratory Signs: Tachypnea (RR>30/min), Desaturation, Shallow breathing, Use of accessory muscles Breathing sound: Wheezing, Rhonchi, Crepitation. Paradoxical breathing Hyper-resonance on percussion:
Respiratory Signs: Tachypnea (RR>30/min), Desaturation, Shallow breathing, Use of accessory muscles Breathing sound: Wheezing, Rhonchi, Crepitation. Paradoxical breathing Hyper-resonance on percussion:
660 mm Hg (normal, 100 mm Hg, room air) Paco, (arterial Pc02) 36 mm Hg (normal, 40 mm Hg) % saturation 50% (normal, 95%-100%)
 148 PHYSIOLOGY CASES AND PROBLEMS Case 26 Carbon Monoxide Poisoning Herman Neiswander is a 65-year-old retired landscape architect in northern Wisconsin. One cold January morning, he decided to warm his
148 PHYSIOLOGY CASES AND PROBLEMS Case 26 Carbon Monoxide Poisoning Herman Neiswander is a 65-year-old retired landscape architect in northern Wisconsin. One cold January morning, he decided to warm his
Physical Chemistry of Gases: Gas Exchange Linda Costanzo, Ph.D.
 Physical Chemistry of Gases: Gas Exchange Linda Costanzo, Ph.D. OBJECTIVES: After studying this lecture, the student should understand: 1. Application of the gas laws to pulmonary physiology. 2. How to
Physical Chemistry of Gases: Gas Exchange Linda Costanzo, Ph.D. OBJECTIVES: After studying this lecture, the student should understand: 1. Application of the gas laws to pulmonary physiology. 2. How to
Respiratory Physiology. Adeyomoye O.I
 Respiratory Physiology By Adeyomoye O.I Outline Introduction Hypoxia Dyspnea Control of breathing Ventilation/perfusion ratios Respiratory/barometric changes in exercise Intra-pulmonary & intra-pleural
Respiratory Physiology By Adeyomoye O.I Outline Introduction Hypoxia Dyspnea Control of breathing Ventilation/perfusion ratios Respiratory/barometric changes in exercise Intra-pulmonary & intra-pleural
Notes on BIPAP/CPAP. M.Berry Emergency physician St Vincent s Hospital, Sydney
 Notes on BIPAP/CPAP M.Berry Emergency physician St Vincent s Hospital, Sydney 2 DEFINITIONS Non-Invasive Positive Pressure Ventilation (NIPPV) Encompasses both CPAP and BiPAP Offers ventilation support
Notes on BIPAP/CPAP M.Berry Emergency physician St Vincent s Hospital, Sydney 2 DEFINITIONS Non-Invasive Positive Pressure Ventilation (NIPPV) Encompasses both CPAP and BiPAP Offers ventilation support
Respiratory Anatomy and Physiology. Respiratory Anatomy. Function of the Respiratory System
 Respiratory Anatomy and Physiology Michaela Dixon Clinical Development Nurse PICU BRHFC Respiratory Anatomy Function of the Respiratory System - In conjunction with the cardiovascular system, to supply
Respiratory Anatomy and Physiology Michaela Dixon Clinical Development Nurse PICU BRHFC Respiratory Anatomy Function of the Respiratory System - In conjunction with the cardiovascular system, to supply
Section Three Gas transport
 Section Three Gas transport Lecture 6: Oxygen transport in blood. Carbon dioxide in blood. Objectives: i. To describe the carriage of O2 in blood. ii. iii. iv. To explain the oxyhemoglobin dissociation
Section Three Gas transport Lecture 6: Oxygen transport in blood. Carbon dioxide in blood. Objectives: i. To describe the carriage of O2 in blood. ii. iii. iv. To explain the oxyhemoglobin dissociation
HCO - 3 H 2 CO 3 CO 2 + H H H + Breathing rate is regulated by blood ph and C02. CO2 and Bicarbonate act as a ph Buffer in the blood
 Breathing rate is regulated by blood ph and C02 breathing reduces plasma [CO2]; plasma [CO2] increases breathing. When C02 levels are high, breating rate increases to blow off C02 In low C02 conditions,
Breathing rate is regulated by blood ph and C02 breathing reduces plasma [CO2]; plasma [CO2] increases breathing. When C02 levels are high, breating rate increases to blow off C02 In low C02 conditions,
Physiology of Respiration
 Physiology of Respiration External Respiration = pulmonary ventilation breathing involves 2 processes: inspiration expiration Inspiration an active process involves contraction of diaphragm innervated
Physiology of Respiration External Respiration = pulmonary ventilation breathing involves 2 processes: inspiration expiration Inspiration an active process involves contraction of diaphragm innervated
Mechanical Ventilation
 Mechanical Ventilation Understanding Modes Rob Chatburn, RRT-NPS, FAARC Research Manager Respiratory Therapy Cleveland Clinic Associate Professor Case Western Reserve University 1 Overview Characteristics
Mechanical Ventilation Understanding Modes Rob Chatburn, RRT-NPS, FAARC Research Manager Respiratory Therapy Cleveland Clinic Associate Professor Case Western Reserve University 1 Overview Characteristics
Anatomy and Physiology Part 11: Of Blood and Breath by: Les Sellnow
 Anatomy and Physiology Part 11: Of Blood and Breath by: Les Sellnow There are few similarities between horses and automobiles, but in a manner of speaking, the horse's circulatory and respiratory systems
Anatomy and Physiology Part 11: Of Blood and Breath by: Les Sellnow There are few similarities between horses and automobiles, but in a manner of speaking, the horse's circulatory and respiratory systems
Test Bank for Pilbeams Mechanical Ventilation Physiological and Clinical Applications 6th Edition by Cairo
 Test Bank for Pilbeams Mechanical Ventilation Physiological and Clinical Applications 6th Edition by Cairo Link full download: http://testbankair.com/download/test-bank-for-pilbeams-mechanicalventilation-physiological-and-clinical-applications-6th-edition-by-cairo/
Test Bank for Pilbeams Mechanical Ventilation Physiological and Clinical Applications 6th Edition by Cairo Link full download: http://testbankair.com/download/test-bank-for-pilbeams-mechanicalventilation-physiological-and-clinical-applications-6th-edition-by-cairo/
