Chemistry 101 Chapter 5 GAS MIXTURES
|
|
|
- Jeremy Mitchell
- 5 years ago
- Views:
Transcription
1 GAS MIXTURES Consider mixing equal volumes of 3 different gases, all at the same temperature and pressure in a container of the same size. 1 L He 1 L N 2 1 L O 2 1 L mixture t = 0 0 C t = 0 0 C t = 0 0 C t = 0 0 C P(He) = 2 atm P(N 2 ) = 2 atm P(O 2 ) = 2 atm P(mixture) =? P(mixture) = 6 atm NOTE: 1. Each gas in a mixture of gases acts as though it were the only gas in the mixture 2. P(mixture) = P(He) + P(N 2 ) + P(O 2 ) PARTIAL PRESSURES 24
2 DALTON S LAW OF PARTIAL PRESSURES The Total Pressure (P T ) of a mixture of gases is equal to the sum of the partial pressures of the gases in the mixture. P T = P A + P B + P C MOLE FRACTION OF A GAS IN A MIXTURE OF GASES Gas A + Gas B + Gas C = Mixture of gases Total Number of Moles of gas in the Mixture = N N A = number of moles of gas A N B = number of moles of gas B N C = number of moles of gas C N = N A + N B + N C N A N = Mole Fraction of Gas A = X A N B N = Mole Fraction of Gas B = X B N C N = Mole Fraction of Gas C = X C Mole Percent = Mole fraction X 100 N A Example: Mole % of A = x 100 N 25
3 DALTON S LAW OF PARTIAL PRESSURES The Pressure of a sample gas is directly proportional to the number of molecules (expressed as number of moles) of gas. P A N A P B N B P C N C = = = P N P N P N Where: N A, N B, N C = number of moles of gas A, B and C respectively N = total number of moles of gas mixture P A, P B, P C = partial pressures of gas A, B and C respectively P = total pressure of gas mixture Alternately, P A = X A P P B = X B P P C = X C P Examples: 1. Calculate the total pressure (in atm) and partial pressure of each gas in a mixture composed of moles helium gas and moles hydrogen gas in a 5.00 L flask at 10 0 C. N T = mol mol = mol n T = mol n T R T V = L P V = n T R T P = T = 283 K V P =? L atm (0.300 mol )( P = mol K )(283 K ) 5.00 L = atm P He = X He P = P H2 = X H2 P = 26
4 2. The atmosphere in a sealed diving bell contains oxygen and helium. If the gas mixture has atmospheres of oxygen and a total pressure of 3.00 atmospheres, calculate the mass of helium in 1.00 L of gas mixture at 20 0 C. PART A : Calculate the pressure of helium P T = P Oxygen + P Helium P Helium = P T P Oxygen P Helium = 3.00 atm atm = 2.80 atm PART B: Calculate the number of moles of Helium P He = 2.80 atm P V V He = 1.00 L PV = n R T n= T He = 293 K R T n He =? n = (2.80 atm )(1.00 L ) = mol L atm ( mol K )(293 K ) PART C: Calculate the mass of Helium 4.00 g He? g He = moles He x = g He 1 mole He 3. A mixture of 0.25 mol H 2 and 0.45 mol of N 2 are placed in a 1.50 L flask at 27 C. Calculate the partial pressures of each gas and the total pressure. 4. The partial pressure of CH 4 gas is atm and that of O 2 gas is atm in a mixture of the two gases. What is the mole fraction of each gas in the mixture? 27
5 COLLECTING GASES OVER WATER Many gases are commonly collected over water. Consider the collection of Hydrogen gas from the reaction of zinc with hydrochloric acid: Zn(s) + HCl(aq) ZnCl 2 (aq) + H 2 (g) Hydrogen Gas + Water vapor P(H 2 ) P(H 2 O) Atmospheric Pressure =749 mm Hg NOTE: Water level in the tube is the same is at the same height as level in the beaker. Gas Pressure in the tube = P T = P(H 2 ) + P(H 2 O) P(atm) = P T = P(H 2 ) + P(H 2 O) P(atm) = P(H 2 ) + P(H 2 O) P(H 2 O) = is temperature dependent = is given in tables (Table 5.6, page 206) 28
6 Example: 1. An aqueous solution of ammonium nitrite decomposes when heated to give off nitrogen gas and water vapor: NH 4 NO 2 (aq) > 2 H 2 O(g) + N 2 (g) How many grams of NH 4 NO 2 must have reacted if 4.16 L of N 2 gas was collected over water at 19 C and atmospheres of pressure? NH 4 NO 2 (aq) > 2 H 2 O(g) + N 2 (g)? g 4.16 L PART A: Calculate the pressure of dry Nitrogen P T = P(N 2 ) + Pressure of Water Vapor P(N 2 ) = P T Pressure of Water Vapor P T = atm Pressure of Water Vapor =? Table 5.6 at 19 C P(H 2 O) = 16.5mmHg 1 atm 16.5 mm Hg x = atm mm Hg P(N 2 ) = atm atm = atm PART B: Calculate the number of moles of nitrogen P = atm P V V = 4.16 L P V = n R T n = T = 292 K R T n =? n = ( atm )(4.16 L ) = mol L atm ( mol K )(292 K ) PART C: Calculate the mass of NH 4 NO 2 (Stoichiometry) 1 mole NH 4 NO g NH 4 NO 2?g NH 4 NO 2 = moles N 2 x x ¾¾ = 10.5 g 1 mole N 2 1 mole NH 4 NO 2 29
7 2. Helium is collected over water at 25 C and 1.00 atm total pressure. What volume of gas must be collected to obtain g of helium? (At 25 C the vapor pressure of water is 23.8 mmhg) 30
8 KINETIC MOLECULAR THEORY OF IDEAL GASES (Theory of Gas Molecules in Motion) Ideal Gas = A gas that follows the IDEAL GAS LAW (P V = n R T) BASIC IDEA: A GAS CONSISTS OF MOLECULES IN CONSTANT RANDOM MOTION 1 m = mass of molecule Recall: Kinetic Energy = E K = mv 2 v = molecular speed 2 E K = energy of moving molecule POSTULATE 1: The size of molecules is negligible compared to the intermolecular distances Consequence: The Volume of a gas is determined by the distances between the molecules. POSTULATE 2: Molecules move randomly in straight lines in all directions and at various speeds Consequence: The Pressure of a gas is the same in all directions POSTULATE 3: The attractive or repulsive forces between molecules are very weak (negligible) POSTULATE 4: When molecules collide with one another, the collisions are elastic (no energy is lost). This is similar to collisions between billiard balls. POSTULATE 5: The Average Kinetic Energy is directly proportional to the Absolute Temperature 31
9 INTERPRETATION OF THE KINETIC MOLECULAR THEORY OF GASES The PRESSURE of a gas results from: The NUMBER OF COLLISIONS is determined by: BOYLE S LAW Recall: The Temperature is constant; therefore: The COLLISIONS of the molecules with the walls of the container the number of molecules per unit volume average speed of molecules KE ave = constant An Increase Decreases the number Decreases the Decreases In Volume of molecules per frequency of the unit volume collisions Pressure CHARLES LAW Recall: The pressure is constant, therefore: Frequency and force of molecular collisions are constant. An Increase Increases Average Increases the Volume In Temperature Molecular Speed (molecules spread), in order to maintain frequency of collisions unchanged 32
10 MOLECULAR SPEEDS In gases, molecular speeds vary over a wide range Meaning: Different molecules move at different speeds, that are constantly changing, as the molecules collide with one another and the walls of the container It is more convenient to refer to : U = AVERAGE MOLECULAR SPEED = THE SPEED OF A MOLECULE HAVING AVERAGE KINETIC ENERGY (KE AVE ) U = 3 R T M m R = gas constant T = absolute temperature M m = molar mass NOTE: The higher the molar mass, the lower the average molecular speed. (The heavier the molecules, the slower they move) 33
11 DIFFUSION & EFFUSION Diffusion is the process by which a gas spreads through another gas. Effusion is the process by which a gas flows out from a container through a small hole. Oxygen Hydrogen Same Volume, Same Pressure, Same Temperature, Same Size Hole Which Balloon deflates faster? OR Which gas has a higher Rate of Effusion? What is the Ratio between the Rates of Effusion? Rate of Effusion depends on: 1. The cross sectional area of the hole (the same) 2. The number of molecules per unit volume (the same) 3. The average Molecular Speed (U) (different) (the faster they move, the sooner they escape) Recall: U = 3 R T M m NOTE: The Rate of Effusion: is directly proportional to the Average Molecular Speed (U) is inversely proportional to the square root of the Molar Mass 34
12 GRAHAM S LAW OF EFFUSION The Rate of Effusion is inversely proportional to the square root of the Molar Mass Rate of Effusion of H Molar Mass of O 32.0 Rate of Effusion of O Molar Mass of H = = = Conclusion: Hydrogen will effuse 4 times faster than Oxygen Examples: 1. Obtain the ratio of effusion of H 2 and H 2 S under the same conditions. Rate H M (H S) 2 34 Rate H S M (H ) 2 m 2 = = = 2 m If 0.10 mol of I 2 vapor can effuse from an opening in a heated vessel in 52 seconds, how long will it take 0.10 mol of H 2 to effuse under the same condition? Rate H M (I ) Rate I M (H ) m 2 = = = 2 m H 2 effuses 11.2 faster than I 2 It follows that the time t takes H 2 to effuse is 11.2 times shorter: 52 seconds T (H 2 ) = = 4.6 seconds
13 REAL GASES Gases behave according to the Ideal Gas Law, provided: 1. The space occupied by molecules is truly negligible compared to the total gas volume (Postulate 1), 2. The intermolecular forces of attraction are truly negligible (Postulate 3) THIS IS TRUE: at High Temperature, and at Low Pressure Reasons: Molecules are far apart Molecules do not attract IDEAL GAS PV = nrt THIS IS NOT QUITE TRUE: at Low Temperature, and at High Pressure Reasons: Molecules are relatively closer As such: Volume occupied by molecules must be taken into account Intermolecular forces between molecules are not negligible and molecules begin to attract one another 2 n a (P + )(V nb ) = nrt 2 V Van Der Waals Equation for Real Gases NOTE: V (intermolecular space) becomes (V nb) decreased Volume accounts for space occupied by molecules) P becomes a and b n 2 a (P + ) increased Pressure accounts for intermolecular forces of V 2 attraction are constants have different values for different gases 36
You should be able to: Describe Equipment Barometer Manometer. 5.1 Pressure Read and outline 5.1 Define Barometer
 A P CHEMISTRY - Unit 5: Gases Unit 5: Gases Gases are distinguished from other forms of matter, not only by their power of indefinite expansion so as to fill any vessel, however large, and by the great
A P CHEMISTRY - Unit 5: Gases Unit 5: Gases Gases are distinguished from other forms of matter, not only by their power of indefinite expansion so as to fill any vessel, however large, and by the great
Worksheet 12 - Partial Pressures and the Kinetic Molecular Theory of Gases
 Worksheet 12 - Partial Pressures and the Kinetic olecular Theory of Gases Dalton's Law of Partial Pressures states that the sums of the pressures of each gas in the mixture add to give the total pressure
Worksheet 12 - Partial Pressures and the Kinetic olecular Theory of Gases Dalton's Law of Partial Pressures states that the sums of the pressures of each gas in the mixture add to give the total pressure
Chapter 10: Gases. Characteristics of Gases
 Chapter 10: Gases Learning Outcomes: Calculate pressure and convert between pressure units with an emphasis on torr and atmospheres. Calculate P, V, n, or T using the ideal-gas equation. Explain how the
Chapter 10: Gases Learning Outcomes: Calculate pressure and convert between pressure units with an emphasis on torr and atmospheres. Calculate P, V, n, or T using the ideal-gas equation. Explain how the
Chapter 13. Gases. Copyright Cengage Learning. All rights reserved 1
 Chapter 13 Gases Copyright Cengage Learning. All rights reserved 1 Section 13.1 Pressure Why study gases? An understanding of real world phenomena. An understanding of how science works. Copyright Cengage
Chapter 13 Gases Copyright Cengage Learning. All rights reserved 1 Section 13.1 Pressure Why study gases? An understanding of real world phenomena. An understanding of how science works. Copyright Cengage
Chapter 5: Gases 5.1 Pressure Why study gases? An understanding of real world phenomena. An understanding of how science works.
 Chapter 5: Gases 5.1 Pressure Why study gases? An understanding of real world phenomena. An understanding of how science works. A Gas Uniformly fills any container. Easily compressed. Mixes completely
Chapter 5: Gases 5.1 Pressure Why study gases? An understanding of real world phenomena. An understanding of how science works. A Gas Uniformly fills any container. Easily compressed. Mixes completely
Gas Pressure. Pressure is the force exerted per unit area by gas molecules as they strike the surfaces around them.
 Chapter 5 Gases Gas Gases are composed of particles that are moving around very fast in their container(s). These particles moves in straight lines until they collides with either the container wall or
Chapter 5 Gases Gas Gases are composed of particles that are moving around very fast in their container(s). These particles moves in straight lines until they collides with either the container wall or
AP TOPIC 6: Gases. Revised August General properties and kinetic theory
 AP OPIC 6: Gases General properties and kinetic theory Gases are made up of particles that have (relatively) large amounts of energy. A gas has no definite shape or volume and will expand to fill as much
AP OPIC 6: Gases General properties and kinetic theory Gases are made up of particles that have (relatively) large amounts of energy. A gas has no definite shape or volume and will expand to fill as much
temperature and pressure unchanging
 Gas Laws Review I. Variables Used to Describe a Gas A. Pressure (P) kpa, atm, mmhg (torr) -Pressure=force exerted per unit area (force/area) -Generated by collisions within container walls (more collisions=more
Gas Laws Review I. Variables Used to Describe a Gas A. Pressure (P) kpa, atm, mmhg (torr) -Pressure=force exerted per unit area (force/area) -Generated by collisions within container walls (more collisions=more
(for tutoring, homework help, or help with online classes)
 www.tutor-homework.com (for tutoring, homework help, or help with online classes) 1. Which statement is inconsistent with the kinetic theory of an ideal gas? 1. The forces of repulsion between gas molecules
www.tutor-homework.com (for tutoring, homework help, or help with online classes) 1. Which statement is inconsistent with the kinetic theory of an ideal gas? 1. The forces of repulsion between gas molecules
Kinetic Molecular Theory Gases. Behavior of gases. Postulate two. Postulate one. Postulate three. Postulate four
 Kinetic Molecular Theory Gases Gas particles are so small that their individual volume can be considered to be negligible Gas particles are in constant motion and the collisions of the particles with the
Kinetic Molecular Theory Gases Gas particles are so small that their individual volume can be considered to be negligible Gas particles are in constant motion and the collisions of the particles with the
Chapter 13 Gases and Pressure. Pressure and Force. Pressure is the force per unit area on a surface. Force Area. Pressure =
 Chapter 13 Gas Laws Chapter 13 Gases and Pressure Pressure and Force Pressure is the force per unit area on a surface. Pressure = Force Area Chapter 13 Gases and Pressure Gases in the Atmosphere The atmosphere
Chapter 13 Gas Laws Chapter 13 Gases and Pressure Pressure and Force Pressure is the force per unit area on a surface. Pressure = Force Area Chapter 13 Gases and Pressure Gases in the Atmosphere The atmosphere
Chapter 12. The Gaseous State of Matter
 Chapter 12 The Gaseous State of Matter The air in a hot air balloon expands When it is heated. Some of the air escapes from the top of the balloon, lowering the air density inside the balloon, making the
Chapter 12 The Gaseous State of Matter The air in a hot air balloon expands When it is heated. Some of the air escapes from the top of the balloon, lowering the air density inside the balloon, making the
Gas Law Worksheets - WS: Boyle s and Charles Law
 Gas Law Worksheets - WS: Boyle s and Charles Law Boyle s Law states that the volume of a gas varies inversely with its pressure if temperature is held constant. (If one goes up the, other goes down.) We
Gas Law Worksheets - WS: Boyle s and Charles Law Boyle s Law states that the volume of a gas varies inversely with its pressure if temperature is held constant. (If one goes up the, other goes down.) We
Chapter 5. Pressure. Atmospheric Pressure. Gases. Force Pressure = Area
 Chapter 5 Gases Water for many homes is supplied by a well The pump removes air from the pipe, decreasing the air pressure in the pipe The pressure then pushes the water up the pipe Pressure Atmospheric
Chapter 5 Gases Water for many homes is supplied by a well The pump removes air from the pipe, decreasing the air pressure in the pipe The pressure then pushes the water up the pipe Pressure Atmospheric
Chapter 5. Nov 6 1:02 PM
 Chapter 5 Nov 6 1:02 PM Expand to fill their containers Fluid motion (they flow) Have low densities (1/1000 the density of equivalent liquids or solids) Compressible Can Effuse and Diffuse Effuse: The
Chapter 5 Nov 6 1:02 PM Expand to fill their containers Fluid motion (they flow) Have low densities (1/1000 the density of equivalent liquids or solids) Compressible Can Effuse and Diffuse Effuse: The
Chemistry A Molecular Approach. Fourth Edition. Chapter 5. Gases. Copyright 2017, 2014, 2011 Pearson Education, Inc. All Rights Reserved
 Chemistry A Molecular Approach Fourth Edition Chapter 5 Gases Supersonic Skydiving and the Risk of Decompression Gas Gases are composed of particles that are moving around very fast in their container(s).
Chemistry A Molecular Approach Fourth Edition Chapter 5 Gases Supersonic Skydiving and the Risk of Decompression Gas Gases are composed of particles that are moving around very fast in their container(s).
Lecture Handout 5: Gases (Online Text Chapter 6)
 Lecture Handout 5: Gases (Online Text Chapter 6) I. The Structure of a Gas A. Gases are composed of particles that are flying around very fast in their container(s). 1. The particles travel in straight
Lecture Handout 5: Gases (Online Text Chapter 6) I. The Structure of a Gas A. Gases are composed of particles that are flying around very fast in their container(s). 1. The particles travel in straight
CP Chapter 13/14 Notes The Property of Gases Kinetic Molecular Theory
 CP Chapter 13/14 Notes The Property of Gases Kinetic Molecular Theory Kinetic Molecular Theory of Gases The word kinetic refers to. Kinetic energy is the an object has because of its motion. Kinetic Molecular
CP Chapter 13/14 Notes The Property of Gases Kinetic Molecular Theory Kinetic Molecular Theory of Gases The word kinetic refers to. Kinetic energy is the an object has because of its motion. Kinetic Molecular
Section 5.1 Pressure. Why study gases? An understanding of real world phenomena. An understanding of how science works.
 Chapter 5 Gases Section 5.1 Pressure Why study gases? An understanding of real world phenomena. An understanding of how science works. Copyright Cengage Learning. All rights reserved 2 Section 5.1 Pressure
Chapter 5 Gases Section 5.1 Pressure Why study gases? An understanding of real world phenomena. An understanding of how science works. Copyright Cengage Learning. All rights reserved 2 Section 5.1 Pressure
B. As the gas particles move and strike a surface, they push on that surface 1. If we could measure the total amount of force exerted by gas
 Chapter 5: Gases I. The Structure of a Gas A. Gases are composed of particles that are flying around very fast in their container(s). 1. The particles travel in straight lines until they encounter either
Chapter 5: Gases I. The Structure of a Gas A. Gases are composed of particles that are flying around very fast in their container(s). 1. The particles travel in straight lines until they encounter either
To play movie you must be in Slide Show Mode CLICK HERE EXERCISE! EXERCISE! To play movie you must be in Slide Show Mode CLICK HERE
 Boyle s Law Boyle s law Pressure and volume are inversely related (constant T, temperature, and n, # of moles of gas). PV k (kis a constant for a given sample of air at a specific temperature) P V P V
Boyle s Law Boyle s law Pressure and volume are inversely related (constant T, temperature, and n, # of moles of gas). PV k (kis a constant for a given sample of air at a specific temperature) P V P V
Kinetic Molecular Theory imaginary Assumptions of Kinetic Molecular Theory: Problems with KMT:
 AP Chemistry Ms. Ye Name Date Block Kinetic Molecular Theory Explains properties of gases, liquids, and solids in terms of energy using an ideal gas, an imaginary which fits all the assumptions of kinetic
AP Chemistry Ms. Ye Name Date Block Kinetic Molecular Theory Explains properties of gases, liquids, and solids in terms of energy using an ideal gas, an imaginary which fits all the assumptions of kinetic
NOTES: Behavior of Gases
 NOTES: Behavior of Gases Properties of Gases Gases have weight Gases take up space Gases exert pressure Gases fill their containers Gases are mostly empty space The molecules in a gas are separate, very
NOTES: Behavior of Gases Properties of Gases Gases have weight Gases take up space Gases exert pressure Gases fill their containers Gases are mostly empty space The molecules in a gas are separate, very
Unit 8: Gases and States of Matter
 Unit 8: Gases and States of Matter Gases Particles that have no definite shape or volume. They adapt to the shape and volume of their container. Ideal gases are imaginary gases that comply with all the
Unit 8: Gases and States of Matter Gases Particles that have no definite shape or volume. They adapt to the shape and volume of their container. Ideal gases are imaginary gases that comply with all the
States of Matter Review
 States of Matter Review May 13 8:16 PM Physical States of Matter (Phases) Solid Liquid Melting Gas Condensation Freezing Evaporation Deposition Sublimation Sep 13 6:04 PM 1 May 13 8:11 PM Gases Chapter
States of Matter Review May 13 8:16 PM Physical States of Matter (Phases) Solid Liquid Melting Gas Condensation Freezing Evaporation Deposition Sublimation Sep 13 6:04 PM 1 May 13 8:11 PM Gases Chapter
4.) There are no forces of attraction or repulsion between gas particles. This means that
 KINETIC MOLECULAR (K-M) THEORY OF MATTER NOTES - based on the idea that particles of matter are always in motion - assumptions of the K-M Theory 1.) Gases consist of large numbers of tiny particles that
KINETIC MOLECULAR (K-M) THEORY OF MATTER NOTES - based on the idea that particles of matter are always in motion - assumptions of the K-M Theory 1.) Gases consist of large numbers of tiny particles that
Expand to fill their containers, are highly compressible, have extremely low densities.
 Chem150 week6 Handout 1 Gases Characteristics of Gases: Unlike liquids and solids, they Expand to fill their containers, are highly compressible, have extremely low densities. Pressure is the amount of
Chem150 week6 Handout 1 Gases Characteristics of Gases: Unlike liquids and solids, they Expand to fill their containers, are highly compressible, have extremely low densities. Pressure is the amount of
Gilbert Kirss Foster. Chapter 10. Properties of Gases The Air We Breathe
 Gilbert Kirss Foster Chapter 10 Properties of Gases The Air We Breathe Chapter Outline 10.1 The Properties of Gases 10.2 Effusion and the Kinetic Molecular Theory of Gases 10.3 Atmospheric Pressure 10.4
Gilbert Kirss Foster Chapter 10 Properties of Gases The Air We Breathe Chapter Outline 10.1 The Properties of Gases 10.2 Effusion and the Kinetic Molecular Theory of Gases 10.3 Atmospheric Pressure 10.4
Lecture Presentation. Chapter 10. Gases. John D. Bookstaver St. Charles Community College Cottleville, MO Pearson Education, Inc.
 Lecture Presentation Chapter 10 John D. Bookstaver St. Charles Community College Cottleville, MO Characteristics of Unlike liquids and solids, gases Expand to fill their containers. Are highly compressible.
Lecture Presentation Chapter 10 John D. Bookstaver St. Charles Community College Cottleville, MO Characteristics of Unlike liquids and solids, gases Expand to fill their containers. Are highly compressible.
CP Chapter 13/14 Notes The Property of Gases Kinetic Molecular Theory
 CP Chapter 13/14 Notes The Property of Gases Kinetic Molecular Theory Kinetic Molecular Theory of Gases The word kinetic refers to. Kinetic energy is the an object has because of its motion. Kinetic Molecular
CP Chapter 13/14 Notes The Property of Gases Kinetic Molecular Theory Kinetic Molecular Theory of Gases The word kinetic refers to. Kinetic energy is the an object has because of its motion. Kinetic Molecular
GASES. Unit #8. AP Chemistry
 GASES Unit #8 AP Chemistry I. Characteristics of Gases A. Gas Characteristics: 1. Fills its container a. no definite shape b. no definite vol. 2. Easily mixes w/ other gases 3. Exerts pressure on its surroundings
GASES Unit #8 AP Chemistry I. Characteristics of Gases A. Gas Characteristics: 1. Fills its container a. no definite shape b. no definite vol. 2. Easily mixes w/ other gases 3. Exerts pressure on its surroundings
Elements that exist as gases at 25 o C and 1 atmosphere H 2, N 2, O 2, F 2, Cl 2, He, Ne, Ar, Kr, Xe, Rn
 AP Chemistry Chapter 5 Sections 5. 5.9 Note Organizer Pressure, The Gas Laws of Boyle, Charles, and Avogadro, The Ideal Gas Law, Gas Stoichiometry, Dalton s Law of Partial Pressure, The Kinetic olecular
AP Chemistry Chapter 5 Sections 5. 5.9 Note Organizer Pressure, The Gas Laws of Boyle, Charles, and Avogadro, The Ideal Gas Law, Gas Stoichiometry, Dalton s Law of Partial Pressure, The Kinetic olecular
Characteristics of Gases
 Lecture 25-27 Gases Characteristics of Gases Unlike liquids and solids, gases Expand to fill their containers. Are highly compressible. Have extremely low densi@es. Pressure of a gas Force per unit area
Lecture 25-27 Gases Characteristics of Gases Unlike liquids and solids, gases Expand to fill their containers. Are highly compressible. Have extremely low densi@es. Pressure of a gas Force per unit area
CHEMISTRY - CLUTCH CH.5 - GASES.
 !! www.clutchprep.com CONCEPT: UNITS OF PRESSURE Pressure is defined as the force exerted per unit of surface area. Pressure = Force Area The SI unit for Pressure is the, which has the units of. The SI
!! www.clutchprep.com CONCEPT: UNITS OF PRESSURE Pressure is defined as the force exerted per unit of surface area. Pressure = Force Area The SI unit for Pressure is the, which has the units of. The SI
Unit 9 Packet: Gas Laws Introduction to Gas Laws Notes:
 Name: Unit 9 Packet: Gas Laws Introduction to Gas Laws Notes: Block: In chemistry, the relationships between gas physical properties are described as gas laws. Some of these properties are pressure, volume,
Name: Unit 9 Packet: Gas Laws Introduction to Gas Laws Notes: Block: In chemistry, the relationships between gas physical properties are described as gas laws. Some of these properties are pressure, volume,
Ch. 14 The Behavior of Gases
 Ch. 14 The Behavior of Gases 14.1 PROPERTIES OF GASES Compressibility Compressibility: a measure of how much the volume of matter decreases under pressure Gases are easily compressed because of the spaces
Ch. 14 The Behavior of Gases 14.1 PROPERTIES OF GASES Compressibility Compressibility: a measure of how much the volume of matter decreases under pressure Gases are easily compressed because of the spaces
General Properties of Gases
 GASES Chapter 13 Importance of Gases Airbags fill with N 2 gas in an accident. Gas is generated by the decomposition of sodium azide,, NaN 3. 2 NaN 3 ---> > 2 Na + 3 N 2 THREE STATES OF MATTER General
GASES Chapter 13 Importance of Gases Airbags fill with N 2 gas in an accident. Gas is generated by the decomposition of sodium azide,, NaN 3. 2 NaN 3 ---> > 2 Na + 3 N 2 THREE STATES OF MATTER General
2. Calculate the ratio of diffusion rates for carbon monoxide (CO) and carbon dioxide (CO2). υa = MB = 44 = 1.25
 Gas laws worksheet (2-08) (modified 3/17) Answer key Graham s Law 1. Calculate the ratio of effusion rates for nitrogen (N2) and neon (Ne). υa = MB = 20 = 0.845 υb MA 28 2. Calculate the ratio of diffusion
Gas laws worksheet (2-08) (modified 3/17) Answer key Graham s Law 1. Calculate the ratio of effusion rates for nitrogen (N2) and neon (Ne). υa = MB = 20 = 0.845 υb MA 28 2. Calculate the ratio of diffusion
Under ideal conditions, the rates at which different gases diffuse (spread out) are proportional to their molar masses.
 Chemistry Ms. Ye Name Date Block Graham s Law of Diffusion- Under ideal conditions, the rates at which different gases diffuse (spread out) are proportional to their molar masses. In other words, gas molecules
Chemistry Ms. Ye Name Date Block Graham s Law of Diffusion- Under ideal conditions, the rates at which different gases diffuse (spread out) are proportional to their molar masses. In other words, gas molecules
Chemistry: It s a gas
 Chemistry: It s a gas Part IV Molar mass of a gas Density of a gas Dalton s Law: high altitudes and scuba diving Kinetic Molecular Theory: fast gases are hot! I have a chemistry test on Friday, there is
Chemistry: It s a gas Part IV Molar mass of a gas Density of a gas Dalton s Law: high altitudes and scuba diving Kinetic Molecular Theory: fast gases are hot! I have a chemistry test on Friday, there is
Simple Gas Laws. To facilitate comparison of gases, the following standards are used: STP: O C (273 K) and kpa. SATP: 25 C (298 K) and 101.
 Simple Gas Laws To facilitate comparison of gases, the following standards are used: STP: O C (273 K) and 101.3 kpa If assuming 1 mol, V = 22.4L SATP: 25 C (298 K) and 101.3 kpa If assuming 1 mol, V =
Simple Gas Laws To facilitate comparison of gases, the following standards are used: STP: O C (273 K) and 101.3 kpa If assuming 1 mol, V = 22.4L SATP: 25 C (298 K) and 101.3 kpa If assuming 1 mol, V =
Chapter 10: Properties of Gases: The Air We Breathe
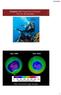 Chapter 10: Properties of Gases: The Air We Breathe Sept, 2006 Sept, 2016 http://ozonewatch.gsfc.nasa.gov 1 Chapter Outline 10.1 The Properties of Gases 10.2 The Kinetic Molecular Theory of Gases* 10.3
Chapter 10: Properties of Gases: The Air We Breathe Sept, 2006 Sept, 2016 http://ozonewatch.gsfc.nasa.gov 1 Chapter Outline 10.1 The Properties of Gases 10.2 The Kinetic Molecular Theory of Gases* 10.3
PSI Chemistry: Gases Multiple Choice Review
 PSI Chemistry: Gases Multiple Choice Review Name Kinetic Molecular Theory 1. According to the kinetic-molecular theory, particles of matterare in constant motion (A) have different shapes (B) have different
PSI Chemistry: Gases Multiple Choice Review Name Kinetic Molecular Theory 1. According to the kinetic-molecular theory, particles of matterare in constant motion (A) have different shapes (B) have different
The Kinetic-Molecular Theory of Gases based on the idea that particles are always in motion
 The Kinetic-Molecular Theory of Gases based on the idea that particles are always in motion Five assumptions: 1. Most of the volume occupied dby a gas is empty space 2. Collisions between gas particles
The Kinetic-Molecular Theory of Gases based on the idea that particles are always in motion Five assumptions: 1. Most of the volume occupied dby a gas is empty space 2. Collisions between gas particles
Chapter 5 Gases. AP CHEMISTRY Chapter 5 Scotch Plains-Fanwood High School Page 1
 Chapter 5 Gases Kinetic Theory All matter is composed of tiny particles that are in continuous, random motion. Gas Pressure = Force Demo: Test tube/h2o beaker Area Demo: Can AP CHEMISTRY Chapter 5 Scotch
Chapter 5 Gases Kinetic Theory All matter is composed of tiny particles that are in continuous, random motion. Gas Pressure = Force Demo: Test tube/h2o beaker Area Demo: Can AP CHEMISTRY Chapter 5 Scotch
Chapter 10: Properties of Gases: The Air We Breathe
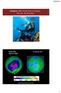 Chapter 10: Properties of Gases: The Air We Breathe South Pole Sept 24, 2006 15 February 2017 http://ozonewatch.gsfc.nasa.gov 1 Chapter Outline 10.1 10.2 10.3 The Properties of Gases Effusion and the Kinetic
Chapter 10: Properties of Gases: The Air We Breathe South Pole Sept 24, 2006 15 February 2017 http://ozonewatch.gsfc.nasa.gov 1 Chapter Outline 10.1 10.2 10.3 The Properties of Gases Effusion and the Kinetic
Behavior of Gases Chapter 12 Assignment & Problem Set
 Behavior of Gases Name Warm-Ups (Show your work for credit) Date 1. Date 2. Date 3. Date 4. Date 5. Date 6. Date 7. Date 8. Behavior of Gases 2 Study Guide: Things You Must Know Vocabulary (know the definition
Behavior of Gases Name Warm-Ups (Show your work for credit) Date 1. Date 2. Date 3. Date 4. Date 5. Date 6. Date 7. Date 8. Behavior of Gases 2 Study Guide: Things You Must Know Vocabulary (know the definition
Chapter 11. Recall: States of Matter. Properties of Gases. Gases
 Chapter 11 Gases Recall: States of Matter Solids and Liquids: are closely related because in each case the particles are interacting with each other Gases: Properties of Gases Gases can be compressed Gases
Chapter 11 Gases Recall: States of Matter Solids and Liquids: are closely related because in each case the particles are interacting with each other Gases: Properties of Gases Gases can be compressed Gases
C h e m i s t r y 1 A : C h a p t e r 5 P a g e 1
 C h e m i s t r y 1 A : C h a p t e r 5 P a g e 1 Chapter 5: Gases Homework: Read Chapter 5. Work out sample/practice exercises Keep up with MasteringChemistry assignments Gas Properties: Ideal Gas: Gases
C h e m i s t r y 1 A : C h a p t e r 5 P a g e 1 Chapter 5: Gases Homework: Read Chapter 5. Work out sample/practice exercises Keep up with MasteringChemistry assignments Gas Properties: Ideal Gas: Gases
Chem 110 General Principles of Chemistry
 CHEM110 Worksheet - Gases Chem 110 General Principles of Chemistry Chapter 9 Gases (pages 337-373) In this chapter we - first contrast gases with liquids and solids and then discuss gas pressure. - review
CHEM110 Worksheet - Gases Chem 110 General Principles of Chemistry Chapter 9 Gases (pages 337-373) In this chapter we - first contrast gases with liquids and solids and then discuss gas pressure. - review
Kinetic-Molecular Theory
 GASES Chapter Eleven Kinetic-Molecular Theory! Recall that our only previous description of gases stated that gases completely fill and take the shape of their containers.! The Kinetic-Molecular Theory
GASES Chapter Eleven Kinetic-Molecular Theory! Recall that our only previous description of gases stated that gases completely fill and take the shape of their containers.! The Kinetic-Molecular Theory
Accelerated Chemistry Study Guide Chapter 13: Gases
 Accelerated Chemistry Study Guide Chapter 13: Gases Terms, definitions, topics Diffusion Kinetic Molecular Theory Atmospheric pressure Barometer Manometer STP Absolute zero Page 1 of 42 Molar volume Partial
Accelerated Chemistry Study Guide Chapter 13: Gases Terms, definitions, topics Diffusion Kinetic Molecular Theory Atmospheric pressure Barometer Manometer STP Absolute zero Page 1 of 42 Molar volume Partial
Practice MC Test unit D (Ch 10) Gas Laws (pg 1 of 10)
 Practice MC Test unit D (Ch 10) Gas Laws (pg 1 of 10) This is practice - Do NOT cheat yourself of finding out what you are capable of doing. Be sure you follow the testing conditions outlined below. DO
Practice MC Test unit D (Ch 10) Gas Laws (pg 1 of 10) This is practice - Do NOT cheat yourself of finding out what you are capable of doing. Be sure you follow the testing conditions outlined below. DO
Honors Chemistry Unit 7 Gas Laws Notes
 Honors Chemistry Unit 7 Gas Laws Notes Kinetic Molecular Theory 1. List the five assumptions: Assumption Description Extra Info 1 Basically means: the particles themselves have compared to the space between
Honors Chemistry Unit 7 Gas Laws Notes Kinetic Molecular Theory 1. List the five assumptions: Assumption Description Extra Info 1 Basically means: the particles themselves have compared to the space between
Name /74. MULTIPLE CHOICE. Choose the one alternative that best completes the statement or answers the question.
 Ch 11 Gases STUDY GUIDE Accelerated Chemistry SCANTRON Name /74 MULTIPLE CHOICE. Choose the one alternative that best completes the statement or answers the question. 1) Which of the following statements
Ch 11 Gases STUDY GUIDE Accelerated Chemistry SCANTRON Name /74 MULTIPLE CHOICE. Choose the one alternative that best completes the statement or answers the question. 1) Which of the following statements
Chapter 6 10/14/13. Gas Law. Volume change with temperature and pressure.
 Chapter 6 10/14/13 Gas Law 1. Properties of a Gas a. Neither definite shape nor volume i. Uniformly fills any container i Exerts pressure on surroundings Volume change with temperature and pressure. b.
Chapter 6 10/14/13 Gas Law 1. Properties of a Gas a. Neither definite shape nor volume i. Uniformly fills any container i Exerts pressure on surroundings Volume change with temperature and pressure. b.
Gases. Chapter 5: Gas Laws Demonstration. September 10, Chapter 5 Gasses.notebook. Dec 18 10:23 AM. Jan 1 4:11 PM. Crushing 55 gallon drum
 Chapter 5: Gases Dec 18 10:23 AM Gas Laws Demonstration Crushing 55 gallon drum Egg in a bottle Student in a bag Boiling Water Charles gas Law Water in a flask Ballon in a bottle Jan 1 4:11 PM 1 5.1 Pressure
Chapter 5: Gases Dec 18 10:23 AM Gas Laws Demonstration Crushing 55 gallon drum Egg in a bottle Student in a bag Boiling Water Charles gas Law Water in a flask Ballon in a bottle Jan 1 4:11 PM 1 5.1 Pressure
Section 8: Gases. The following maps the videos in this section to the Texas Essential Knowledge and Skills for Science TAC (c).
 Section 8: Gases The following maps the videos in this section to the Texas Essential Knowledge and Skills for Science TAC 112.35(c). 8.01 Simple Gas Laws Chemistry (9)(A) 8.02 Ideal Gas Law Chemistry
Section 8: Gases The following maps the videos in this section to the Texas Essential Knowledge and Skills for Science TAC 112.35(c). 8.01 Simple Gas Laws Chemistry (9)(A) 8.02 Ideal Gas Law Chemistry
Chapter 10 Gases. Characteristics of Gases. Pressure. The Gas Laws. The Ideal-Gas Equation. Applications of the Ideal-Gas Equation
 Characteristics of Gases Chapter 10 Gases Pressure The Gas Laws The Ideal-Gas Equation Applications of the Ideal-Gas Equation Gas mixtures and partial pressures Kinetic-Molecular Theory Real Gases: Deviations
Characteristics of Gases Chapter 10 Gases Pressure The Gas Laws The Ideal-Gas Equation Applications of the Ideal-Gas Equation Gas mixtures and partial pressures Kinetic-Molecular Theory Real Gases: Deviations
Section 8.1 Properties of Gases Goal: Describe the kinetic molecular theory of gases and the units of measurement used for gases.
 Chapter 8 Gases Practice Problems Section 8.1 Properties of Gases Goal: Describe the kinetic molecular theory of gases and the units of measurement used for gases. Summary: In a gas, particles are so far
Chapter 8 Gases Practice Problems Section 8.1 Properties of Gases Goal: Describe the kinetic molecular theory of gases and the units of measurement used for gases. Summary: In a gas, particles are so far
Chemistry Chapter 10 Test
 Chemistry Chapter 10 Test True/False Indicate whether the sentence or statement is true or false. 1. KMT stands for Kinetic Mole Theory. 2. One of the assumptions in the KMT is that the particles are spread
Chemistry Chapter 10 Test True/False Indicate whether the sentence or statement is true or false. 1. KMT stands for Kinetic Mole Theory. 2. One of the assumptions in the KMT is that the particles are spread
Basic Concepts of Chemistry Notes for Students [Chapter 10, page 1] D J Weinkauff - Nerinx Hall High School. Chapter 10 Gases
![Basic Concepts of Chemistry Notes for Students [Chapter 10, page 1] D J Weinkauff - Nerinx Hall High School. Chapter 10 Gases Basic Concepts of Chemistry Notes for Students [Chapter 10, page 1] D J Weinkauff - Nerinx Hall High School. Chapter 10 Gases](/thumbs/78/77082586.jpg) Basic Concepts of Chemistry Notes for Students [Chapter 10, page 1] Chapter 10 Gases We have talked a little about gases in Chapter 3 and we dealt briefly with them in our stoichiometric calculations in
Basic Concepts of Chemistry Notes for Students [Chapter 10, page 1] Chapter 10 Gases We have talked a little about gases in Chapter 3 and we dealt briefly with them in our stoichiometric calculations in
Example: 25 C = ( ) K = 298 K. Pressure Symbol: p Units: force per area 1Pa (Pascal) = 1 N/m 2
 Chapter 6: Gases 6.1 Measurements on Gases MH5, Chapter 5.1 Let s look at a certain amount of gas, i.e. trapped inside a balloon. To completely describe the state of this gas one has to specify the following
Chapter 6: Gases 6.1 Measurements on Gases MH5, Chapter 5.1 Let s look at a certain amount of gas, i.e. trapped inside a balloon. To completely describe the state of this gas one has to specify the following
World of Chemistry Notes for Students [Chapter 13, page 1] Chapter 13 Gases
![World of Chemistry Notes for Students [Chapter 13, page 1] Chapter 13 Gases World of Chemistry Notes for Students [Chapter 13, page 1] Chapter 13 Gases](/thumbs/96/127526823.jpg) World of Chemistry Notes for Students [Chapter 3, page ] Chapter 3 Gases ) Sec 3.8 Kinetic Theory of Gases and the Nature of Gases The Kinetic Theory of Matter says that the tiny particles in all forms
World of Chemistry Notes for Students [Chapter 3, page ] Chapter 3 Gases ) Sec 3.8 Kinetic Theory of Gases and the Nature of Gases The Kinetic Theory of Matter says that the tiny particles in all forms
Worksheet 1.7: Gas Laws. Charles Law. Guy-Lassac's Law. Standard Conditions. Abbreviations. Conversions. Gas Law s Equation Symbols
 Name Block Worksheet 1.7: Gas Laws Boyle s Law Charles Law Guy-Lassac's Law Combined Gas Law For a given mass of gas at constant temperature, the volume of a gas varies inversely with pressure PV = k The
Name Block Worksheet 1.7: Gas Laws Boyle s Law Charles Law Guy-Lassac's Law Combined Gas Law For a given mass of gas at constant temperature, the volume of a gas varies inversely with pressure PV = k The
Gases Day 12. Phases of Matter
 Phases of Matter Gases Day 12 Kinetic Molecular Theory ( Ideal Gases ) 1) The molecules of a gas are in continual, and random, motion of varying speeds. 2) The average kinetic energy of the gas molecules
Phases of Matter Gases Day 12 Kinetic Molecular Theory ( Ideal Gases ) 1) The molecules of a gas are in continual, and random, motion of varying speeds. 2) The average kinetic energy of the gas molecules
Unit 8: Kinetic Theory Homework Packet (90 points)
 Name: Key Period: By the end of Unit 8, you should be able to: Kinetic Theory Chapter 13-14 4. Define kinetic theory of gases including collisions 5. Define pressure, including atmospheric pressure, vapor
Name: Key Period: By the end of Unit 8, you should be able to: Kinetic Theory Chapter 13-14 4. Define kinetic theory of gases including collisions 5. Define pressure, including atmospheric pressure, vapor
Behavior of Gases. Gases are mostly The molecules in a gas are separate, very small and very
 Properties of Gases Gases have Gases Gases exert Gases fill their containers Behavior of Gases Gases are mostly The molecules in a gas are separate, very small and very Kinetic Theory of Matter: Gas molecules
Properties of Gases Gases have Gases Gases exert Gases fill their containers Behavior of Gases Gases are mostly The molecules in a gas are separate, very small and very Kinetic Theory of Matter: Gas molecules
Boyle s Law Practice
 Boyle s Law Practice Boyle s Law is an indirect relationship. Most of these problems can be done in your head without showing your work. 1. Herman has 30.0 L of helium gas trapped in a cylinder by a piston.
Boyle s Law Practice Boyle s Law is an indirect relationship. Most of these problems can be done in your head without showing your work. 1. Herman has 30.0 L of helium gas trapped in a cylinder by a piston.
Pressure of the atmosphere varies with elevation and weather conditions. Barometer- device used to measure atmospheric pressure.
 Chapter 12 Section 1 Pressure A gas exerts pressure on its surroundings. Blow up a balloon. The gas we are most familiar with is the atmosphere, a mixture of mostly elemental nitrogen and oxygen. Pressure
Chapter 12 Section 1 Pressure A gas exerts pressure on its surroundings. Blow up a balloon. The gas we are most familiar with is the atmosphere, a mixture of mostly elemental nitrogen and oxygen. Pressure
Completed ALL 2 Warm-up IC Kinetic Molecular Theory Notes. Kinetic Molecular Theory and Pressure Worksheet
 Name: Unit 10- Gas Laws Day Page # Description IC/HW Due Date Completed ALL 2 Warm-up IC 1 3 5 Kinetic Molecular Theory Notes IC 1 6 8 Kinetic Molecular Theory and Pressure Worksheet IC 2 9 10 Gas Law
Name: Unit 10- Gas Laws Day Page # Description IC/HW Due Date Completed ALL 2 Warm-up IC 1 3 5 Kinetic Molecular Theory Notes IC 1 6 8 Kinetic Molecular Theory and Pressure Worksheet IC 2 9 10 Gas Law
Chemistry 51 Chapter 7 PROPERTIES OF GASES. Gases are the least dense and most mobile of the three phases of matter.
 ROERIES OF GASES Gases are the least dense and most mobile of the three phases of matter. articles of matter in the gas phase are spaced far apart from one another and move rapidly and collide with each
ROERIES OF GASES Gases are the least dense and most mobile of the three phases of matter. articles of matter in the gas phase are spaced far apart from one another and move rapidly and collide with each
Kinetic-Molecular Theory of Matter
 Gases Properties of Gases Gas Pressure Gases What gases are important for each of the following: O 2, CO 2 and/or He? A. B. C. D. 1 2 Gases What gases are important for each of the following: O 2, CO 2
Gases Properties of Gases Gas Pressure Gases What gases are important for each of the following: O 2, CO 2 and/or He? A. B. C. D. 1 2 Gases What gases are important for each of the following: O 2, CO 2
Dalton s Law How is the total pressure of a mixture of gases related to the partial pressures of the component gases?
 Dalton s Law Chapter 4 The Behavior of Gases 4. Properties of Gases 4. The Gas Laws 4. Ideal Gases Dalton s Law How is the total pressure of a mixture of gases related to the partial pressures of the component
Dalton s Law Chapter 4 The Behavior of Gases 4. Properties of Gases 4. The Gas Laws 4. Ideal Gases Dalton s Law How is the total pressure of a mixture of gases related to the partial pressures of the component
Name Unit 9 Notes: Gas Laws Period. Complete throughout unit. Due on test day!
 Name Unit 9 Notes: Gas Laws Period Skills: 1. Gases and Entropy 2. Distinguish between Ideal and Real gases 3. Understand KMT and Avogadro s Law 4. Identify and Solve Boyle s Law Problems 5. Identify and
Name Unit 9 Notes: Gas Laws Period Skills: 1. Gases and Entropy 2. Distinguish between Ideal and Real gases 3. Understand KMT and Avogadro s Law 4. Identify and Solve Boyle s Law Problems 5. Identify and
Chapter 9 Gases: Their Properties and Behavior
 Chapter 9 Gases: Their Properties and Behavior 國防醫學院生化學科王明芳老師 2011-11-15 & 2011-11-22 Chapter 9/1 Gases and Gas Pressure Gas mixtures are homogeneous and compressible. Air-the mixture of gases. Molecular
Chapter 9 Gases: Their Properties and Behavior 國防醫學院生化學科王明芳老師 2011-11-15 & 2011-11-22 Chapter 9/1 Gases and Gas Pressure Gas mixtures are homogeneous and compressible. Air-the mixture of gases. Molecular
Chapter 14-Gases. Dr. Walker
 Chapter 14-Gases Dr. Walker State of Matter Gases are one of the four states of matter along with solids, liquids, and plasma Conversion to Gases From liquids Evaporation Example: Boiling water From solids
Chapter 14-Gases Dr. Walker State of Matter Gases are one of the four states of matter along with solids, liquids, and plasma Conversion to Gases From liquids Evaporation Example: Boiling water From solids
Gases. Name: Class: Date: Matching
 Name: Class: Date: Gases Matching Match each item with the correct statement below. a. Boyle's law d. Graham's law b. Charles's law e. Gay-Lussac's law c. Dalton's law f. ideal gas law 1. For a given mass
Name: Class: Date: Gases Matching Match each item with the correct statement below. a. Boyle's law d. Graham's law b. Charles's law e. Gay-Lussac's law c. Dalton's law f. ideal gas law 1. For a given mass
Honors Chemistry - Problem Set Chapter 13 Classify each of these statements as always true, AT; sometimes true, ST; or never true, NT.
 Honors Chemistry - Problem Set Chapter 13 Classify each of these statements as always true, AT; sometimes true, ST; or never true, NT. 1. Atmospheric pressure is 760 mm Hg. 2. The SI unit of pressure is
Honors Chemistry - Problem Set Chapter 13 Classify each of these statements as always true, AT; sometimes true, ST; or never true, NT. 1. Atmospheric pressure is 760 mm Hg. 2. The SI unit of pressure is
States of Matter. Q 7. Calculate the average of kinetic energy, in joules of the molecules in 8.0 g of methane at 27 o C. (IIT JEE Marks)
 Q 1. States of Matter Calculate density of NH 3 at 30 o C and 5 atm pressure Q 2. (IIT JEE 1978 3 Marks) 3.7 g of a gas at 25 o C occupied the same volume as 0.184g of hydrogen at 17 o C and at the same
Q 1. States of Matter Calculate density of NH 3 at 30 o C and 5 atm pressure Q 2. (IIT JEE 1978 3 Marks) 3.7 g of a gas at 25 o C occupied the same volume as 0.184g of hydrogen at 17 o C and at the same
Temperature Temperature
 Temperature Temperature is a measure of how hot or cold an object is compared to another object. indicates that heat flows from the object with a higher temperature to the object with a lower temperature.
Temperature Temperature is a measure of how hot or cold an object is compared to another object. indicates that heat flows from the object with a higher temperature to the object with a lower temperature.
Chemistry Chapter 11 Test Review
 Chemistry Chapter 11 Test Review Multiple Choice Identify the choice that best completes the statement or answers the question. 1. Pressure is the force per unit a. volume. c. length. b. surface area.
Chemistry Chapter 11 Test Review Multiple Choice Identify the choice that best completes the statement or answers the question. 1. Pressure is the force per unit a. volume. c. length. b. surface area.
The Behavior of gases. Section 14.1: Properties of Gases
 The Behavior of gases Section 14.1: Properties of Gases Why do soccer balls explode if you over pump them? What is meant by the term compressibility? Compressibility is a measure of how much the volume
The Behavior of gases Section 14.1: Properties of Gases Why do soccer balls explode if you over pump them? What is meant by the term compressibility? Compressibility is a measure of how much the volume
Chapter 10. Physical Characteristics of Gases
 Chapter 10 Physical Characteristics of Gases Kinetic Molecular Theory An understanding of the behavior of atoms that make up matter Ideal gas: an imaginary gas that perfectly fits all assumptions of the
Chapter 10 Physical Characteristics of Gases Kinetic Molecular Theory An understanding of the behavior of atoms that make up matter Ideal gas: an imaginary gas that perfectly fits all assumptions of the
KINETIC THEORY OF GASES
 CHAPTER 18 GASES KINETIC THEORY OF GASES A given amt. of gas will occupy the entire volume of its container. Changes in temp. have a greater effect on the vol. of a gas than on a liquid or solid KINETIC
CHAPTER 18 GASES KINETIC THEORY OF GASES A given amt. of gas will occupy the entire volume of its container. Changes in temp. have a greater effect on the vol. of a gas than on a liquid or solid KINETIC
Unit 10: Gas Laws. Monday Tuesday Wednesday Thursday Friday. 10 Review for Cumulative Retest. 17 Chem Think Gas Laws Tutorial- Computer Lab-
 Unit 10: Gas Laws Name: Monday Tuesday Wednesday Thursday Friday February 8 Stoichiometry Test Review 9 Stoichiometry Test 10 Review for Cumulative Retest 11 Cumulative Re-Test 12 Pressure & Kinetic Theory
Unit 10: Gas Laws Name: Monday Tuesday Wednesday Thursday Friday February 8 Stoichiometry Test Review 9 Stoichiometry Test 10 Review for Cumulative Retest 11 Cumulative Re-Test 12 Pressure & Kinetic Theory
A. What are the three states of matter chemists work with?
 Chapter 10 and 12 The Behavior of Gases Chapter 10 The States of Matter A. What are the three states of matter chemists work with? Section 10.1 Pg 267 B. We will explain the behavior of gases using the
Chapter 10 and 12 The Behavior of Gases Chapter 10 The States of Matter A. What are the three states of matter chemists work with? Section 10.1 Pg 267 B. We will explain the behavior of gases using the
Substances that are liquids or solids under ordinary conditions may also exist as gases. These are often referred to as vapors. Properties of Gases
 Common Student Misconceptions Students need to be told to always use temperature in Kelvin in gas problems. Students should always use units in gas-law problems to keep track of required conversions. Due
Common Student Misconceptions Students need to be told to always use temperature in Kelvin in gas problems. Students should always use units in gas-law problems to keep track of required conversions. Due
Name Chemistry Pre-AP
 Name Chemistry Pre-AP Notes: Gas Laws and Gas Stoichiometry Period Part 1: The Nature of Gases and The Gas Laws I. Nature of Gases A. Kinetic-Molecular Theory The - theory was developed to account for
Name Chemistry Pre-AP Notes: Gas Laws and Gas Stoichiometry Period Part 1: The Nature of Gases and The Gas Laws I. Nature of Gases A. Kinetic-Molecular Theory The - theory was developed to account for
Student Worksheet for Chemical Gas Laws
 Student Worksheet for Chemical Attempt to work the following practice problems after working through the sample problems in the videos. Answers are given on the last page(s). Relevant Equations Boyle s
Student Worksheet for Chemical Attempt to work the following practice problems after working through the sample problems in the videos. Answers are given on the last page(s). Relevant Equations Boyle s
THE GAS STATE. Unit 4. CHAPTER KEY TERMS HOME WORK 9.1 Kinetic Molecular Theory States of Matter Solid, Liquid, gas.
 Unit 4 THE GAS STATE CHAPTER KEY TERMS HOME WORK 9. Kinetic Molecular Theory States of Matter Solid, Liquid, gas Page 4 # to 4 9. Boyles Law P α /V PV = Constant P V = P V Pressure Atmospheric Pressure
Unit 4 THE GAS STATE CHAPTER KEY TERMS HOME WORK 9. Kinetic Molecular Theory States of Matter Solid, Liquid, gas Page 4 # to 4 9. Boyles Law P α /V PV = Constant P V = P V Pressure Atmospheric Pressure
CHM 111 Unit 5 Sample Questions
 Name: Class: Date: As you work these problems, consider and explain: A. What type of question is it? B. How do you know what type of question it is? C. What information are you looking for? D. What information
Name: Class: Date: As you work these problems, consider and explain: A. What type of question is it? B. How do you know what type of question it is? C. What information are you looking for? D. What information
Unit 9: Gas Laws REGENTS CHEMISTRY
 Name: Unit 9: Gas Laws REGENTS CHEMISTRY 1 Name: Unit 9: Gas Laws The concept of an ideal gas is a model to explain the behavior of gases. A real gas is most like an ideal gas when the real gas is at low
Name: Unit 9: Gas Laws REGENTS CHEMISTRY 1 Name: Unit 9: Gas Laws The concept of an ideal gas is a model to explain the behavior of gases. A real gas is most like an ideal gas when the real gas is at low
Final Gas Law Review
 Name: ate: 1 t which temperature is the vapor pressure of ethanol equal to 80 kpa?. 48. 73. 80. 101 4 Gas Molecular Mass (g/mol) 2 4 17 20 The table shown lists four gases and their molecular mass. Which
Name: ate: 1 t which temperature is the vapor pressure of ethanol equal to 80 kpa?. 48. 73. 80. 101 4 Gas Molecular Mass (g/mol) 2 4 17 20 The table shown lists four gases and their molecular mass. Which
Gases. Edward Wen, PhD
 Gases Edward Wen, PhD Properties of Gases expand to completely fill their container take the shape of their container low density much less than solid or liquid state compressible when pressure is changed.
Gases Edward Wen, PhD Properties of Gases expand to completely fill their container take the shape of their container low density much less than solid or liquid state compressible when pressure is changed.
substitution Rearrangement solving for n/v Convert n to MASS (m) by multiplying BOTH sides by molar mass (M) d = m/v
 3.8.12 A 2.07 L cylinder contains 2.88 mol of Helium gas at 22 C. What the pressure in atmospheres of the gas in the cylinder? How could we find the density of this gas? HW solve the density of the above
3.8.12 A 2.07 L cylinder contains 2.88 mol of Helium gas at 22 C. What the pressure in atmospheres of the gas in the cylinder? How could we find the density of this gas? HW solve the density of the above
Multiple Choice (40%)
 AP Chemistry Test (Chapter 5) Please do not write on this test thank you! Multiple Choice (40%) 1) A sealed rigid container is filled with three ideal gases: A, B and C. The partial pressure of each gas
AP Chemistry Test (Chapter 5) Please do not write on this test thank you! Multiple Choice (40%) 1) A sealed rigid container is filled with three ideal gases: A, B and C. The partial pressure of each gas
To convert to millimeters of mercury, we derive a unit factor related to the equivalent relationship 29.9 in. Hg = 760 mm Hg.
 Example Exercise 11.1 Gas Pressure Conversion Meteorologists state that a falling barometer indicates an approaching storm. Given a barometric pressure of 27.5 in. Hg, express the pressure in each of the
Example Exercise 11.1 Gas Pressure Conversion Meteorologists state that a falling barometer indicates an approaching storm. Given a barometric pressure of 27.5 in. Hg, express the pressure in each of the
8.1 Properties of Gases. Goal: Describe the Kinetic Molecular Theory of Gases and the units of measurement used for gases.
 Gases Chapter 8 Chapter 8 8.1 - Properties of Gases 8.2 Pressure and Volume (Boyle s Law) 8.3 Temperature and Volume (Charles Law) 8.4 Temperature and Pressure (Guy-Lussac s Law) 8.5 The Combined Gas Low
Gases Chapter 8 Chapter 8 8.1 - Properties of Gases 8.2 Pressure and Volume (Boyle s Law) 8.3 Temperature and Volume (Charles Law) 8.4 Temperature and Pressure (Guy-Lussac s Law) 8.5 The Combined Gas Low
Gases Chapter 8. Chapter 8
 Gases Chapter 8 Chapter 8 8.1 - Properties of Gases 8.2 Pressure and Volume (Boyle s Law) 8.3 Temperature and Volume (Charles Law) 8.4 Temperature and Pressure (Guy-Lussac s Law) 8.5 The Combined Gas Low
Gases Chapter 8 Chapter 8 8.1 - Properties of Gases 8.2 Pressure and Volume (Boyle s Law) 8.3 Temperature and Volume (Charles Law) 8.4 Temperature and Pressure (Guy-Lussac s Law) 8.5 The Combined Gas Low
