Respiration Lab Instructions
|
|
|
- Junior Harrington
- 5 years ago
- Views:
Transcription
1 Respiration Lab Instructions This laboratory investigation can be performed in any order. Be sure to read all instructions for each section before performing the experiment. PART 1 STUDENT WET SPIROMETER The spirometer has long been the workhorse of the pulmonary scientist. It is a simple and currently very useful instrument which was devised over 100 years ago by John Hutchinson. He wanted an accurate method for measuring what he termed ''vital capacity" of human lungs, which is the largest amount of air that can be exhaled following maximal inspiration. THE WET SPIROMETER The conventional wet spirometer is a water filled reservoir penetrated by an airpipe positioned with its opening above the water level. A smaller canister, called a bell, is placed inside the reservoir, trapping a small volume of air above the pipe. The subject breathes into the spirometer through a flexible tube attached to the airpipe. When the subject exhales into the spirometer, the volume of exhausted gas enters the bell and raises it in the reservoir. Conversely, when the subject inhales air from a partly filled bell, the bell moves downward (WE WILL NOT BE DOING THIS!). The amount of bell movement corresponds to the volume of gas exchanged, which can be recorded on chart paper or measure on a calibrated scale attached to the spirometer. The respiratory cycle can be divided into four distinct volumes or stages that are: 1. Residual volume (RV) or functional residual capacity is the volume of air that is always left in the lungs after exhaling to the fullest extent. 2. Tidal volume (TV) is the volume of air inhaled or exhaled during a normal breath. 3. Inspiratory reserve volume (IRV) is the maximum volume of air that can be inhaled during normal breathing (tidal volume). 4. Expiratory reserve volume (ERV) is the maximum volume of air that can be expelled in excess of the air exhaled in normal breathing (tidal volume) Materials Needed Student Cardboard Mouthpiece Student wet spirometer apparatus Nose plug Alcohol wipe
2 Experiment 1 Measuring Tidal Volume (TV) Tidal Volume (TV): Amount of air either inhaled or exhaled during a single breath. This volume is usually around 400 or 500 ml in males at rest, but can be considerably greater in large or athletic individuals and is increased markedly during exercise. 1. Student should SIT by the spirometer, breathing quietly in and out of the mouth with the nose plug in place. 2. Student places mouthpiece of the spirometer between the lips (making a tight seal) and exhales in a normal, unforced way, into the spirometer. 3. The volume should be read and recorded from the scale by the partner. (NOTE: The spirometer measures in Liters, but your data needs to be measured in ml) 4. Remove the mouthpiece holder from the tube until the spirometer is reset to 0. DO NOT PRESS ON THE DRUM WITH THE MOUTHPIECE HOLDER STILL IN PLACE - YOU WILL BE CLEANING UP A LOT OF WATER!!!! 5. Repeat the experiment twice (for a total of three recordings), making sure that the pointer Experiment 2 Measuring Expiratory Reserve Volume (ERV) Expiratory Reserve Volume (ERV): Amount of air that can be forcefully expelled in excess of normal exhalation at rest. The Expiratory Reserve Volume is approximately 1,100 ml in young adult males. 1. Student should STAND, breathing normally in and out of the mouth for a minute or so with the nose plug in place. 2. After a normal exhalation, student puts the mouthpiece between the lips, and forcibly exhales all the additional air possible. 3. The volume should be read and recorded from the scale by the partner. (NOTE: The spirometer measures in Liters, but your data needs to be measured in ml) 4. Remove the mouthpiece holder from the tube until the spirometer is reset to Repeat the experiment twice (for a total of three recordings), making sure that the pointer
3 Experiment 3 Measuring Inspiratory Reserve Volume (IRV) Inspiratory Reserve Volume (IRV): Amount of air inhaled in excess of normal restful inspiration. Among young adult males this volume is approximately 3,000 ml. 1. STANDING, the student breathes normally for a minute in and out of the mouth with the nose plug in place, then breathes in as deeply as possible. With the mouthpiece inserted, the student then exhales normally, without forcing the air out. 2. The volume should be read and recorded from the scale by the partner. (NOTE: The spirometer measures in Liters, but your data needs to be measured in ml) 3. The IRV reading is obtained by subtracting the student s TV from the reading recorded on the spirometer. 4. Remove the mouthpiece holder from the tube until the spirometer is reset to Repeat the experiment twice (for a total of three recordings), making sure that the pointer Experiment 4 Measuring Vital Capacity (VC) Vital Capacity (VC) which is the maximum amount of air that can be inhaled or exhaled and can be calculated using the following equation: VC = TV+ IRV + ERV Normal VC is roughly 4,500 ml. 1. The student, STANDING with the nose plug in place, slowly and deeply breathes in and out for three complete breaths, then breathes in as deeply as possible, places the spirometer mouthpiece in position, and breathes out as forcibly as possible. 2. The volume should be read and recorded from the scale by the partner. (NOTE: The spirometer measures in Liters, but your data needs to be measured in ml) 3. Remove the mouthpiece holder from the tube until the spirometer is reset to Repeat the experiment twice (for a total of three recordings), making sure that the pointer CLEAN UP: Make sure the mouthpiece holder is removed from the tube, and the spirometer is reset to 0. Throw away the cardboard mouthpiece and wipe the nose plug with an alcohol wipe and discard trash.
4 Use the following to complete Table 2 on your Student Sheet Inspiratory Capacity (IC): The amount of air which can be inhaled after normal expiration (IC = IRV + TV). Normal IC is roughly 3000 ml. Functional Residual Capacity (FRC) is the volume of air present in the lungs at the end of passive expiration. (ERV + RV). Normal is roughly ml. Residual Volume (RV): Amount of air remaining in the lungs after maximum forced expiration. This volume is normally about 1,200 ml in young adult males at rest. The residual volume exists because the normal healthy lung is never fully collapsed. Total Lung Capacity (TLC): volume of air contained in the lungs at the end of a maximal inspiration (TV+ IRV + ERV + RV). For a normal male it is roughly 6000 ml.
5 PART 2 LUNG MODEL Materials Needed Lung Model Procedure 1. Draw and label the model on your student sheet when it is at rest. 2. With your index finger and thumb, gently pull down the tab. Draw the model on your student sheet. 3. Gently push the tab into the cavity (towards the top of the bottle). Draw the model on your student sheet. 4. Go to this website tory-system/mechanics-of-breathing to answer questions 1-3 on your student sheet.
6 PART 3 Changing the Amount of Gas Exchange During Breathing Materials Needed Pulse Oximeter Hyperventilation vs Hypoventilation 1. To complete the introduction table on your student sheet, you will click on the links below. a. Hyperventilation link: b. Hypoventilation link:
7 Part A. Resting Breathing Rate Table 1 1. Place the pulse oximeter on your index finger. 2. Have your partner watch the clock for 30 seconds while your count the number of times you inhale. 3. Immediately record your Oxygen Saturation levels from the pulse oximeter. 4. Repeat two more times. 5. Calculate the average number of breaths and oxygen saturation levels. 6. Multiply the average number of breaths by two to get the average resting breathing rate per minute. 7. Record your observations of how you feel. Part B. Breathing Rate and Hyperventilation Table 2 1. Place the pulse oximeter on your index finger. 2. Have your partner watch the clock for 15 seconds, while you count the number of times you breathe if you hyperventilate (breath fast and deep) for 15s while seated at your desk. 3. Immediately record your Oxygen Saturation levels from the pulse oximeter. 4. Repeat two more times. 5. Calculate the average number of breaths and oxygen saturation levels. 6. Multiply the average number of breaths by four to get the average breathing rate per minute while hyperventilation. Part C. Breathing Rate and Hypoventilation Table 3 1. Place the pulse oximeter on your index finger. 2. Have your partner watch the clock for 15 seconds, while you count the number of times you breathe if you hypoventilate (breath slow and shallow) for 15s while seated at your desk. 3. Immediately record your Oxygen Saturation levels from the pulse oximeter. 4. Repeat two more times. 5. Calculate the average number of breaths and oxygen saturation levels. 6. Multiply the average number of breaths by four to get the average breathing rate per minute while hypoventilating.
Cornell Institute for. Biology Teachers. Respirometry Part I: Lung Volumes and Capacities. Lab issue/rev. date: 12/12/96. Title:
 Cornell Institute for Biology Teachers Copyright Cornell Institute for Biology Teachers, 1999. This work may be copied by the original recipient from CIBT to provide copies for users working under the
Cornell Institute for Biology Teachers Copyright Cornell Institute for Biology Teachers, 1999. This work may be copied by the original recipient from CIBT to provide copies for users working under the
You Are Really Full of Hot Air!
 You Are Really Full of Hot Air! Student Information Page 5B Activity Introduction: You re just full of hot air! How many times has someone said this to you when they didn t quite believe what you were
You Are Really Full of Hot Air! Student Information Page 5B Activity Introduction: You re just full of hot air! How many times has someone said this to you when they didn t quite believe what you were
Pulmonary Function I (modified by C. S. Tritt, April 10, 2006) Volumes and Capacities
 I. Introduction Pulmonary Function I (modified by C. S. Tritt, April 10, 2006) Volumes and Capacities The volume of air a person inhales (inspires) and exhales (expires) can be measured with a spirometer
I. Introduction Pulmonary Function I (modified by C. S. Tritt, April 10, 2006) Volumes and Capacities The volume of air a person inhales (inspires) and exhales (expires) can be measured with a spirometer
Fashionable, don t you think?
 Fashionable, don t you think? 1. Passageway 2. Structure 3. Passageway 4. What is the name of the structure labeled with # 9 in the model at left? 5. What is the name of the structure labeled with # 11
Fashionable, don t you think? 1. Passageway 2. Structure 3. Passageway 4. What is the name of the structure labeled with # 9 in the model at left? 5. What is the name of the structure labeled with # 11
Lab 3. The Respiratory System (designed by Heather E. M. Liwanag with T.M. Williams)
 Name Lab Partners Lab 3. The Respiratory System (designed by Heather E. M. Liwanag with T.M. Williams) Part 1. Lung Volumes and Capacities Objectives 1. Obtain graphical representation of lung capacities
Name Lab Partners Lab 3. The Respiratory System (designed by Heather E. M. Liwanag with T.M. Williams) Part 1. Lung Volumes and Capacities Objectives 1. Obtain graphical representation of lung capacities
Physiology of the Respiratory System
 Biology 212: Anatomy and Physiology II Physiology of the Respiratory System References: Saladin, KS: Anatomy and Physiology, The Unity of Form and Function 8 th (2018). Required reading before beginning
Biology 212: Anatomy and Physiology II Physiology of the Respiratory System References: Saladin, KS: Anatomy and Physiology, The Unity of Form and Function 8 th (2018). Required reading before beginning
LAB 7 HUMAN RESPIRATORY LAB. Complete the charts on pgs. 67 and 68 and read directions for using BIOPAC
 66 LAB 7 HUMAN RESPIRATORY LAB Assignments: Due before lab: Quiz: Three Respiratory Interactive Physiology Animations pages 69 73. Complete the charts on pgs. 67 and 68 and read directions for using BIOPAC
66 LAB 7 HUMAN RESPIRATORY LAB Assignments: Due before lab: Quiz: Three Respiratory Interactive Physiology Animations pages 69 73. Complete the charts on pgs. 67 and 68 and read directions for using BIOPAC
Respiratory Physiology
 Respiratory Physiology Background Information: When inspiring, the pleura attached to the internal chest wall is pulled outward as the thoracic cavity expands. The pleural cavity [space between the outer
Respiratory Physiology Background Information: When inspiring, the pleura attached to the internal chest wall is pulled outward as the thoracic cavity expands. The pleural cavity [space between the outer
Part 1: Inspiratory and expiratory pressures
 BIOEN 327 Autumn 2013 Experimental procedures Throughout these experiments, record in your notebook the purpose of the experiments, the methods you used, and the results. Where possible, make predictions
BIOEN 327 Autumn 2013 Experimental procedures Throughout these experiments, record in your notebook the purpose of the experiments, the methods you used, and the results. Where possible, make predictions
The physiological functions of respiration and circulation. Mechanics. exercise 7. Respiratory Volumes. Objectives
 exercise 7 Respiratory System Mechanics Objectives 1. To explain how the respiratory and circulatory systems work together to enable gas exchange among the lungs, blood, and body tissues 2. To define respiration,
exercise 7 Respiratory System Mechanics Objectives 1. To explain how the respiratory and circulatory systems work together to enable gas exchange among the lungs, blood, and body tissues 2. To define respiration,
Human Respiration Laboratory Experiment By
 Human Respiration Laboratory Experiment By Alison L., Thurow, Brittany Baierlein, Rachel C. Holsinger and Robin L. Cooper Department of Biology, University of Kentucky, Lexington, KY 40506 0225, USA. Purpose:
Human Respiration Laboratory Experiment By Alison L., Thurow, Brittany Baierlein, Rachel C. Holsinger and Robin L. Cooper Department of Biology, University of Kentucky, Lexington, KY 40506 0225, USA. Purpose:
Lung Volumes and Capacities
 Lung Volumes and Capacities Experiment 19 Measurement of lung volumes provides a tool for understanding normal function of the lungs as well as disease states. The breathing cycle is initiated by expansion
Lung Volumes and Capacities Experiment 19 Measurement of lung volumes provides a tool for understanding normal function of the lungs as well as disease states. The breathing cycle is initiated by expansion
Restrictive and Obstructive Airway Diseases
 iworx Physiology Lab Experiment Experiment HS-8-1 Restrictive and Obstructive Airway Diseases Note: The lab presented here is intended for evaluation purposes only. iworx users should refer to the User
iworx Physiology Lab Experiment Experiment HS-8-1 Restrictive and Obstructive Airway Diseases Note: The lab presented here is intended for evaluation purposes only. iworx users should refer to the User
Respiratory System Lab
 Respiratory System Lab Note: Review the safety materials and wear goggles when working with chemicals. Read the entire exercise before you begin. Take time to organize the materials you will need and set
Respiratory System Lab Note: Review the safety materials and wear goggles when working with chemicals. Read the entire exercise before you begin. Take time to organize the materials you will need and set
LAB 3: RESPIRATORY MECHANICS
 BIOEN 327 Autumn 2012 LAB 3: RESPIRATORY MECHANICS Pressures throughout the cardiovascular system are important for the health of the body and of the system itself. Today we explore pulmonary pressures
BIOEN 327 Autumn 2012 LAB 3: RESPIRATORY MECHANICS Pressures throughout the cardiovascular system are important for the health of the body and of the system itself. Today we explore pulmonary pressures
Lung Volumes and Capacities
 BIOL242 Lung Volumes and Capacities Measurement of lung volumes provides a tool for understanding normal function of the lungs as well as disease states. The breathing cycle is initiated by expansion of
BIOL242 Lung Volumes and Capacities Measurement of lung volumes provides a tool for understanding normal function of the lungs as well as disease states. The breathing cycle is initiated by expansion of
Biology 347 General Physiology Lab Basic Pulmonary Functions: Respirometry and Factors that Effect Respiration
 Biology 347 General Physiology Lab Basic Pulmonary Functions: Respirometry and Factors that Effect Respiration Objectives Students will measure breathing parameters in a resting subject. Students will
Biology 347 General Physiology Lab Basic Pulmonary Functions: Respirometry and Factors that Effect Respiration Objectives Students will measure breathing parameters in a resting subject. Students will
Experiment HS-2: Breathing and Gravity
 Experiment HS-2: Breathing and Gravity Background Over a long time, the amount of oxygen (O 2 ) taken up and carbon dioxide (CO 2 ) given off at the tissues is matched with the amount of O 2 taken up and
Experiment HS-2: Breathing and Gravity Background Over a long time, the amount of oxygen (O 2 ) taken up and carbon dioxide (CO 2 ) given off at the tissues is matched with the amount of O 2 taken up and
Respiration. Exercise 1A: Breathing in Resting Volunteers Aim: To measure breathing parameters in a resting individual.
 Respiration Background The amount of air that moves in or out of the lungs during any one breathing cycle is called the tidal volume. Above and beyond normal inspiration, it is possible to breathe in additional
Respiration Background The amount of air that moves in or out of the lungs during any one breathing cycle is called the tidal volume. Above and beyond normal inspiration, it is possible to breathe in additional
April KHALED MOUSA BACHA. Physiology #2. Dr. Nayef AL-Gharaibeh. Pulmonary volumes & capacities
 25 th April Physiology #2 Pulmonary volumes & capacities Dr. Nayef AL-Gharaibeh KHALED MOUSA BACHA We will start this lecture by explaining an important concept from the previous one: Intrapleural pressure
25 th April Physiology #2 Pulmonary volumes & capacities Dr. Nayef AL-Gharaibeh KHALED MOUSA BACHA We will start this lecture by explaining an important concept from the previous one: Intrapleural pressure
Respiratory System Review
 KEY THIS TEST WILL BE COMPLETED IN ONE CLASS PERIOD MONDAY, MARCH 10. 2014 Respiratory System Review Name A. Directions: Fill in the blank with the appropriate vocabulary word or words (several examples
KEY THIS TEST WILL BE COMPLETED IN ONE CLASS PERIOD MONDAY, MARCH 10. 2014 Respiratory System Review Name A. Directions: Fill in the blank with the appropriate vocabulary word or words (several examples
Lesson 12 New Procedure PULMONARY FUNCTION I
 Physiology Lessons for use with the Biopac Student Lab Lesson 12 New Procedure PULMONARY FUNCTION I Volumes and Capacities For Windows 98SE, Me, 2000 Pro, XP or Mac OS X 10.3-10.4 Richard Pflanzer, Ph.D.
Physiology Lessons for use with the Biopac Student Lab Lesson 12 New Procedure PULMONARY FUNCTION I Volumes and Capacities For Windows 98SE, Me, 2000 Pro, XP or Mac OS X 10.3-10.4 Richard Pflanzer, Ph.D.
TV = Tidal volume (500ml) IRV = Inspiratory reserve volume (3,000 ml)
 By: Amin alajlouni Lec: 2nd record Date: 29/10/2017 First of all, this is my first sheet so excuse any mistakes I might make and let's start: As we said before in our last lecture about lung capacities
By: Amin alajlouni Lec: 2nd record Date: 29/10/2017 First of all, this is my first sheet so excuse any mistakes I might make and let's start: As we said before in our last lecture about lung capacities
3/24/2009 LAB D.HAMMOUDI.MD. 1. Trachea 2. Thoracic wall 3. Lungs 4. Primary bronchi 5. Diaphragm
 RESPIRATORY PHYSIOLOGY LAB D.HAMMOUDI.MD 1. Trachea 2. Thoracic wall 3. Lungs 4. Primary bronchi 5. Diaphragm 1 KEY WORDS TO KNOW BOYLE S LAW INTERCOSTAL NERVES PHRENIC NERVE DIAPHRAGM EXTERNAL INTERCOSTAL
RESPIRATORY PHYSIOLOGY LAB D.HAMMOUDI.MD 1. Trachea 2. Thoracic wall 3. Lungs 4. Primary bronchi 5. Diaphragm 1 KEY WORDS TO KNOW BOYLE S LAW INTERCOSTAL NERVES PHRENIC NERVE DIAPHRAGM EXTERNAL INTERCOSTAL
Paul V. Jennemann Maryland Radon Laboratory, Inc Corporate Court, Suite E Ellicott City, MD 21042
 RADON VS PROGENY Paul V. Jennemann Maryland Radon Laboratory, Inc. 3220 Corporate Court, Suite E Ellicott City, MD 21042 1. INTRODUCTION Any one who has taken a radon training course should be familiar
RADON VS PROGENY Paul V. Jennemann Maryland Radon Laboratory, Inc. 3220 Corporate Court, Suite E Ellicott City, MD 21042 1. INTRODUCTION Any one who has taken a radon training course should be familiar
Circulation and Respiration: Vital Signs Student Version
 Circulation and Respiration: Vital Signs Student Version In this lab, you will learn about the circulatory and respiratory systems. You will test the capacity of your lungs, measure your blood pressure
Circulation and Respiration: Vital Signs Student Version In this lab, you will learn about the circulatory and respiratory systems. You will test the capacity of your lungs, measure your blood pressure
Lung Capacity. Science and Engineering Practices: S.1A.1; S.1A.2; S.1A.4; S.1A.5; S.1A.7
 SC Academic Standards: NGSS DCI: Science and Engineering Practices: S.1A.1; S.1A.2; S.1A.4; S.1A.5; S.1A.7 Crosscutting Concepts: Patterns; Cause and Effect: Mechanism and Explanation; Systems and Systems
SC Academic Standards: NGSS DCI: Science and Engineering Practices: S.1A.1; S.1A.2; S.1A.4; S.1A.5; S.1A.7 Crosscutting Concepts: Patterns; Cause and Effect: Mechanism and Explanation; Systems and Systems
Respiratory/Pulmonary Laboratory Experimentation
 Respiratory/Pulmonary Laboratory Experimentation Introduction Anatomy Review The respiratory system has the dubious honor of being the system that permits the transport of gases from the environment inside
Respiratory/Pulmonary Laboratory Experimentation Introduction Anatomy Review The respiratory system has the dubious honor of being the system that permits the transport of gases from the environment inside
Cardiopulmonary Physical Therapy. Haneul Lee, DSc, PT
 Cardiopulmonary Physical Therapy Haneul Lee, DSc, PT OBJECTIVE 1. Explain the principle physiological function of the pulmonary system 2. Outline the major anatomical components of the respiratory system.
Cardiopulmonary Physical Therapy Haneul Lee, DSc, PT OBJECTIVE 1. Explain the principle physiological function of the pulmonary system 2. Outline the major anatomical components of the respiratory system.
The Respiratory System
 Essentials of Human Anatomy & Physiology Elaine N. Marieb Seventh Edition Chapter 13 The Respiratory System Slides 13.1 13.30 Lecture Slides in PowerPoint by Jerry L. Cook Organs of the Respiratory system
Essentials of Human Anatomy & Physiology Elaine N. Marieb Seventh Edition Chapter 13 The Respiratory System Slides 13.1 13.30 Lecture Slides in PowerPoint by Jerry L. Cook Organs of the Respiratory system
The Respiration System in Humans. Madeline Pitman. Group Members: Kathryn Hillegass Michelle Liu Noelle Owen. Section 62 Danielle Cooper
 1 The Respiration System in Humans Madeline Pitman Group Members: Kathryn Hillegass Michelle Liu Noelle Owen Section 62 Danielle Cooper August 11, 2014 2 A. Introduction Experiment Goals The experiment
1 The Respiration System in Humans Madeline Pitman Group Members: Kathryn Hillegass Michelle Liu Noelle Owen Section 62 Danielle Cooper August 11, 2014 2 A. Introduction Experiment Goals The experiment
CHAPTER 3: The respiratory system
 CHAPTER 3: The respiratory system Practice questions - text book pages 56-58 1) When the inspiratory muscles contract, which one of the following statements is true? a. the size of the thoracic cavity
CHAPTER 3: The respiratory system Practice questions - text book pages 56-58 1) When the inspiratory muscles contract, which one of the following statements is true? a. the size of the thoracic cavity
CHAPTER 3: The cardio-respiratory system
 : The cardio-respiratory system Exam style questions - text book pages 44-45 1) Describe the structures involved in gaseous exchange in the lungs and explain how gaseous exchange occurs within this tissue.
: The cardio-respiratory system Exam style questions - text book pages 44-45 1) Describe the structures involved in gaseous exchange in the lungs and explain how gaseous exchange occurs within this tissue.
Collin County Community College. Lung Physiology
 Collin County Community College BIOL. 2402 Anatomy & Physiology WEEK 9 Respiratory System 1 Lung Physiology Factors affecting Ventillation 1. Airway resistance Flow = Δ P / R Most resistance is encountered
Collin County Community College BIOL. 2402 Anatomy & Physiology WEEK 9 Respiratory System 1 Lung Physiology Factors affecting Ventillation 1. Airway resistance Flow = Δ P / R Most resistance is encountered
Chapter 37: Pulmonary Ventilation. Chad & Angela
 Chapter 37: Pulmonary Ventilation Chad & Angela Respiratory Structures Basic Structures of Respiration Nasal/Oral Cavities Larynx Trachea Bronchi Secondary Bronchi Bronchioles Alveoli Mechanics of Ventilation
Chapter 37: Pulmonary Ventilation Chad & Angela Respiratory Structures Basic Structures of Respiration Nasal/Oral Cavities Larynx Trachea Bronchi Secondary Bronchi Bronchioles Alveoli Mechanics of Ventilation
BREATHING AND EXCHANGE OF GASES
 96 BIOLOGY, EXEMPLAR PROBLEMS CHAPTER 17 BREATHING AND EXCHANGE OF GASES MULTIPLE CHOICE QUESTIONS 1. Respiration in insects is called direct because a. The cell exchange O 2 directly with the air in the
96 BIOLOGY, EXEMPLAR PROBLEMS CHAPTER 17 BREATHING AND EXCHANGE OF GASES MULTIPLE CHOICE QUESTIONS 1. Respiration in insects is called direct because a. The cell exchange O 2 directly with the air in the
ALVEOLAR - BLOOD GAS EXCHANGE 1
 ALVEOLAR - BLOOD GAS EXCHANGE 1 Summary: These notes examine the general means by which ventilation is regulated in terrestrial mammals. It then moves on to a discussion of what happens when someone over
ALVEOLAR - BLOOD GAS EXCHANGE 1 Summary: These notes examine the general means by which ventilation is regulated in terrestrial mammals. It then moves on to a discussion of what happens when someone over
BREATHING AND EXCHANGE OF GASES
 96 BIOLOGY, EXEMPLAR PROBLEMS CHAPTER 17 BREATHING AND EXCHANGE OF GASES MULTIPLE CHOICE QUESTIONS 1. Respiration in insects is called direct because a. The tissues exchange O 2 directly with the air in
96 BIOLOGY, EXEMPLAR PROBLEMS CHAPTER 17 BREATHING AND EXCHANGE OF GASES MULTIPLE CHOICE QUESTIONS 1. Respiration in insects is called direct because a. The tissues exchange O 2 directly with the air in
Chapter 53: Clinical Center Single-Breath Carbon Monoxide Diffusing Capacity (DLCO) MOP 53.1 Introduction
 Chapter 53: Clinical Center Single-Breath Carbon Monoxide Diffusing Capacity (DLCO) MOP 53.1 Introduction The DLCO will determine the degree of pulmonary impairment in participants enrolled in the PVDOMICS
Chapter 53: Clinical Center Single-Breath Carbon Monoxide Diffusing Capacity (DLCO) MOP 53.1 Introduction The DLCO will determine the degree of pulmonary impairment in participants enrolled in the PVDOMICS
Measuring Lung Capacity
 Name Class Date Chapter 37 Circulatory and Respiratory Systems Measuring Lung Capacity Introduction The amount of air that you move in and out of your lungs depends on how quickly you are breathing. The
Name Class Date Chapter 37 Circulatory and Respiratory Systems Measuring Lung Capacity Introduction The amount of air that you move in and out of your lungs depends on how quickly you are breathing. The
Regulation of Breathing
 Regulation of Breathing Introduction Breathing involves a complex interaction between many important respiratory organs and the blood. Air is brought into the lungs through the active process of inhalation,
Regulation of Breathing Introduction Breathing involves a complex interaction between many important respiratory organs and the blood. Air is brought into the lungs through the active process of inhalation,
Respiratory Response to Physiologic Challenges. Evaluation copy
 Respiratory Response to Physiologic Challenges Computer 20 The respiratory cycle of inspiration and expiration is controlled by complex mechanisms involving neurons in the cerebral cortex, brain stem,
Respiratory Response to Physiologic Challenges Computer 20 The respiratory cycle of inspiration and expiration is controlled by complex mechanisms involving neurons in the cerebral cortex, brain stem,
TITLE: Pulse Oximetry COMPETENCY #: Resp #1 NEW COMPETENCY REVISION DATE: 10/18/12 EMPLOYEE NAME. DATE INITIAL RE-EVALUATION ANNUAL (if required) PRN
 : Pulse Oximetry COMPETENCY #: Resp #1 NEW COMPETENCY REVISION : 10/18/12 INITIAL RE-EVALUATION ANNUAL (if required) PRN 1. Verifies physician order. 2. Gathers equipment and supplies. 3. Knocks on door
: Pulse Oximetry COMPETENCY #: Resp #1 NEW COMPETENCY REVISION : 10/18/12 INITIAL RE-EVALUATION ANNUAL (if required) PRN 1. Verifies physician order. 2. Gathers equipment and supplies. 3. Knocks on door
 Question 1: Define vital capacity. What is its significance? Vital capacity is the maximum volume of air that can be exhaled after a maximum inspiration. It is about 3.5 4.5 litres in the human body. It
Question 1: Define vital capacity. What is its significance? Vital capacity is the maximum volume of air that can be exhaled after a maximum inspiration. It is about 3.5 4.5 litres in the human body. It
respiratory cycle. point in the volumes: 500 milliliters. for men. expiration, up to 1200 milliliters extra makes breathing Respiratory
 10 II. RESPIRATORY VOLUMES, CAPACITIES & PULMONARY FUNCTION TESTS Respiratory volume is the term used for various volumes of air moved by or associated with the lungs at a given point in the respiratory
10 II. RESPIRATORY VOLUMES, CAPACITIES & PULMONARY FUNCTION TESTS Respiratory volume is the term used for various volumes of air moved by or associated with the lungs at a given point in the respiratory
Unit 15 Manual Resuscitators
 15-1 Unit 15 Manual Resuscitators GOAL On completion of this unit, the student should comprehend the proper operation of self-inflating resuscitation bags, flow-inflating resuscitation bags and gas-powered
15-1 Unit 15 Manual Resuscitators GOAL On completion of this unit, the student should comprehend the proper operation of self-inflating resuscitation bags, flow-inflating resuscitation bags and gas-powered
Activity 2: Examining the Effect of Changing Airway Resistance on Respiratory Volumes
 1 BGYC34 PhysioEx Lab 7 Respiratory Systems Mechanics Marking Scheme Part 1 Complete PhysioEx lab #7. Hand-in all of the pages associated with the lab. Note that there are 5 activities to be completed.
1 BGYC34 PhysioEx Lab 7 Respiratory Systems Mechanics Marking Scheme Part 1 Complete PhysioEx lab #7. Hand-in all of the pages associated with the lab. Note that there are 5 activities to be completed.
Figure 1. A schematic diagram of the human respiratory system.
 Introduction to Respiration In this experiment, you will investigate various aspects of normal breathing, hyperventilation, rebreathing the effect of changing airway resistance and ways in which to measure
Introduction to Respiration In this experiment, you will investigate various aspects of normal breathing, hyperventilation, rebreathing the effect of changing airway resistance and ways in which to measure
Stikstofuitwas en Heliumdilutie. Eric Derom Universitair Ziekenhuis Gent
 Stikstofuitwas en Heliumdilutie Eric Derom Universitair Ziekenhuis Gent Background Overview Helium-dilution technique Principle of Technique Equipment Procedure and Calculations Quality Control Nitrogen
Stikstofuitwas en Heliumdilutie Eric Derom Universitair Ziekenhuis Gent Background Overview Helium-dilution technique Principle of Technique Equipment Procedure and Calculations Quality Control Nitrogen
2. State the volume of air remaining in the lungs after a normal breathing.
 CLASS XI BIOLOGY Breathing And Exchange of Gases 1. Define vital capacity. What is its significance? Answer: Vital Capacity (VC): The maximum volume of air a person can breathe in after a forced expiration.
CLASS XI BIOLOGY Breathing And Exchange of Gases 1. Define vital capacity. What is its significance? Answer: Vital Capacity (VC): The maximum volume of air a person can breathe in after a forced expiration.
Respiration - Human 1
 Respiration - Human 1 At the end of the lectures on respiration you should be able to, 1. Describe events in the respiratory processes 2. Discuss the mechanism of lung ventilation in human 3. Discuss the
Respiration - Human 1 At the end of the lectures on respiration you should be able to, 1. Describe events in the respiratory processes 2. Discuss the mechanism of lung ventilation in human 3. Discuss the
The Human Respiratory System. Mary McKenna. Lab Partners: Jennifer Daciolas-Semon Veronika Mach Colette Roblee
 1 The Human Respiratory System Mary McKenna Lab Partners: Jennifer Daciolas-Semon Veronika Mach Colette Roblee TA: Pearl Chen NPB 101L Section 1 November 25, 2014 2 Introduction The average human will
1 The Human Respiratory System Mary McKenna Lab Partners: Jennifer Daciolas-Semon Veronika Mach Colette Roblee TA: Pearl Chen NPB 101L Section 1 November 25, 2014 2 Introduction The average human will
Respiratory system & exercise. Dr. Rehab F Gwada
 Respiratory system & exercise Dr. Rehab F Gwada Objectives of lecture Outline the major anatomical components & important functions of the respiratory system. Describe the mechanics of ventilation. List
Respiratory system & exercise Dr. Rehab F Gwada Objectives of lecture Outline the major anatomical components & important functions of the respiratory system. Describe the mechanics of ventilation. List
Mechanisms of Breathing. Vital Capacity
 Mechanisms of Breathing Mechanics of Breathing Two muscles are involved in the mechanics of breathing: Diaphragm = large sheet of muscle located beneath the lungs that is the primary muscle in breathing
Mechanisms of Breathing Mechanics of Breathing Two muscles are involved in the mechanics of breathing: Diaphragm = large sheet of muscle located beneath the lungs that is the primary muscle in breathing
Measuring Lung Capacity
 Measuring Lung Capacity 1 Name Measuring Lung Capacity Background Information: We need a constant supply of oxygen in order to stay alive. We use oxygen to break down food to release energy and produce
Measuring Lung Capacity 1 Name Measuring Lung Capacity Background Information: We need a constant supply of oxygen in order to stay alive. We use oxygen to break down food to release energy and produce
Physiology of Respiration
 Physiology of Respiration External Respiration = pulmonary ventilation breathing involves 2 processes: inspiration expiration Inspiration an active process involves contraction of diaphragm innervated
Physiology of Respiration External Respiration = pulmonary ventilation breathing involves 2 processes: inspiration expiration Inspiration an active process involves contraction of diaphragm innervated
2.1.1 List the principal structures of the
 physiology 2.1.1 List the principal structures of the The principle structures of the respiratory are: Nose/Mouth used for inhalation of oxygen-rich air and expelling carbon dioxide rich air Pharynx -
physiology 2.1.1 List the principal structures of the The principle structures of the respiratory are: Nose/Mouth used for inhalation of oxygen-rich air and expelling carbon dioxide rich air Pharynx -
Capnography in the Veterinary Technician Toolbox. Katie Pinner BS, LVT Bush Advanced Veterinary Imaging Richmond, VA
 Capnography in the Veterinary Technician Toolbox Katie Pinner BS, LVT Bush Advanced Veterinary Imaging Richmond, VA What are Respiration and Ventilation? Respiration includes all those chemical and physical
Capnography in the Veterinary Technician Toolbox Katie Pinner BS, LVT Bush Advanced Veterinary Imaging Richmond, VA What are Respiration and Ventilation? Respiration includes all those chemical and physical
iworx Sample Lab Experiment HE-4: Respiratory Exchange Ratio (RER)
 Experiment HE-4: Respiratory Exchange Ratio (RER) Before Starting 1. Read the procedures for the experiment completely before beginning the experiment. Have a good understanding of how to perform the experiment
Experiment HE-4: Respiratory Exchange Ratio (RER) Before Starting 1. Read the procedures for the experiment completely before beginning the experiment. Have a good understanding of how to perform the experiment
Respiratory System Physiology. Dr. Vedat Evren
 Respiratory System Physiology Dr. Vedat Evren Respiration Processes involved in oxygen transport from the atmosphere to the body tissues and the release and transportation of carbon dioxide produced in
Respiratory System Physiology Dr. Vedat Evren Respiration Processes involved in oxygen transport from the atmosphere to the body tissues and the release and transportation of carbon dioxide produced in
Physiology - lecture 3
 Physiology - lecture 3 Residual Volume (RV):the amount of gas remaining in the lung at the end of a maximal exhalation Tidal Volume (TV):the volume of gas inhaled and exhaled during one respiratory cycle.
Physiology - lecture 3 Residual Volume (RV):the amount of gas remaining in the lung at the end of a maximal exhalation Tidal Volume (TV):the volume of gas inhaled and exhaled during one respiratory cycle.
Hypoxia Following Rapid Decompression to 18,288 m (60,000 ft) Attributable to Alveolar Hypoventilation
 Hypoxia Following Rapid Decompression to 18,288 m (60,000 ft) Attributable to Alveolar Hypoventilation Desmond M Connolly PhD QinetiQ Aircrew Systems Senior Medical Officer Timothy J D Oyly BSc Amanda
Hypoxia Following Rapid Decompression to 18,288 m (60,000 ft) Attributable to Alveolar Hypoventilation Desmond M Connolly PhD QinetiQ Aircrew Systems Senior Medical Officer Timothy J D Oyly BSc Amanda
Important Notices. Mouthpiece. Used properly, POWERbreathe can be used safely by almost anyone without any harmful side effects.
 Mouthpiece Valve lower chamber tensioner knob End Cap load calibrated spring Important Notices Used properly, POWERbreathe can be used safely by almost anyone without any harmful side effects. 1. If you
Mouthpiece Valve lower chamber tensioner knob End Cap load calibrated spring Important Notices Used properly, POWERbreathe can be used safely by almost anyone without any harmful side effects. 1. If you
STATIC BIOMECHANICS OF THE MAMMALIAN RESPIRATORY SYSTEM 1
 STATIC BIOMECHANICS OF THE MAMMALIAN RESPIRATORY SYSTEM 1 Summary: We begin a consideration of breathing in mammals. We will start with the definitions of a series of sub- volumes of the total volume of
STATIC BIOMECHANICS OF THE MAMMALIAN RESPIRATORY SYSTEM 1 Summary: We begin a consideration of breathing in mammals. We will start with the definitions of a series of sub- volumes of the total volume of
Introduction. Respiration. Chapter 10. Objectives. Objectives. The Respiratory System
 Introduction Respiration Chapter 10 The Respiratory System Provides a means of gas exchange between the environment and the body Plays a role in the regulation of acidbase balance during exercise Objectives
Introduction Respiration Chapter 10 The Respiratory System Provides a means of gas exchange between the environment and the body Plays a role in the regulation of acidbase balance during exercise Objectives
For more information about how to cite these materials visit
 Author(s): Louis D Alecy, 2009 License: Unless otherwise noted, this material is made available under the terms of the Creative Commons Attribution Non-commercial Share Alike 3.0 License: http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by-nc-sa/3.0/
Author(s): Louis D Alecy, 2009 License: Unless otherwise noted, this material is made available under the terms of the Creative Commons Attribution Non-commercial Share Alike 3.0 License: http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by-nc-sa/3.0/
Measuring Carbon Dioxide in Breath
 Measuring Carbon Dioxide in Breath OBJECTIVES 1. Measure the partial pressure of carbon dioxide in your breath 2. Estimate the volume of air you exhale per day 3. Estimate the volume and mass of CO2 you
Measuring Carbon Dioxide in Breath OBJECTIVES 1. Measure the partial pressure of carbon dioxide in your breath 2. Estimate the volume of air you exhale per day 3. Estimate the volume and mass of CO2 you
Observations of the Properties of the Human Respiratory System. April Ramos Dela Fuente. Bill Keenen; Tommy Kham; Grace Park
 P a g e 1 Observations of the Properties of the Human Respiratory System April Ramos Dela Fuente Bill Keenen; Tommy Kham; Grace Park NPB 101L - Section 06 - Ailsa Dalgliesh 11/25/14 P a g e 2 INTRODUCTION
P a g e 1 Observations of the Properties of the Human Respiratory System April Ramos Dela Fuente Bill Keenen; Tommy Kham; Grace Park NPB 101L - Section 06 - Ailsa Dalgliesh 11/25/14 P a g e 2 INTRODUCTION
SOTM LAB: B7 12/99. DEVELOPERS OF LAB H Johnson JD896, B Nostro JD531, R Norton JD829, V Dunham JD877, E Shirley JD535
 SOTM LAB: B7 12/99 I. TEACHER NOTES & GUIDELINES TITLE OF LAB: Investigating Breathing Volumes DEVELOPERS OF LAB H Johnson JD896, B Nostro JD531, R Norton JD829, V Dunham JD877, E Shirley JD535 OVERVIEW
SOTM LAB: B7 12/99 I. TEACHER NOTES & GUIDELINES TITLE OF LAB: Investigating Breathing Volumes DEVELOPERS OF LAB H Johnson JD896, B Nostro JD531, R Norton JD829, V Dunham JD877, E Shirley JD535 OVERVIEW
Honors Physiology The Respiratory System
 Honors Physiology Name: The Respiratory System Objective: To create a model of our respiratory system, understanding the relationship between structure and function. Warm Up Questions: 1. What is the function
Honors Physiology Name: The Respiratory System Objective: To create a model of our respiratory system, understanding the relationship between structure and function. Warm Up Questions: 1. What is the function
Yanal. Jumana Jihad. Jamil Nazzal. 0 P a g e
 2 Yanal Jumana Jihad Jamil Nazzal 0 P a g e note: this sheet was written and corrected according to the records from section 2 so you may find differences in the arrangement of topics from the records
2 Yanal Jumana Jihad Jamil Nazzal 0 P a g e note: this sheet was written and corrected according to the records from section 2 so you may find differences in the arrangement of topics from the records
Lesson: Sponge Bob and Party Blowers: How Much Air Can You Exhale?
 Lesson: Sponge Bob and Party Blowers: How Much Air Can You Exhale? Teacher: Unit Theme/Course: Date: Timing: Kaylan Duthie Human Respiration 7 th Grade Life Science November 15 th and 16 th 2 Days Rationale/Goal:
Lesson: Sponge Bob and Party Blowers: How Much Air Can You Exhale? Teacher: Unit Theme/Course: Date: Timing: Kaylan Duthie Human Respiration 7 th Grade Life Science November 15 th and 16 th 2 Days Rationale/Goal:
Human Respiration and Regulation. Jean Liu. Group Bernard (Group 1): Megan Bailey, Katharine Chew, David Ma. Section 12, TA Justin Van Hoorebeke
 1 Human Respiration and Regulation Jean Liu Group Bernard (Group 1): Megan Bailey, Katharine Chew, David Ma Section 12, TA Justin Van Hoorebeke November 28, 2014 2 Introduction The respiratory system is
1 Human Respiration and Regulation Jean Liu Group Bernard (Group 1): Megan Bailey, Katharine Chew, David Ma Section 12, TA Justin Van Hoorebeke November 28, 2014 2 Introduction The respiratory system is
Respiratory system. Role. Ventilation consists of 4 (5) steps : oxygen delivery and carbon dioxide elimination ph balance sound and voice formation
 Respiratory system Role oxygen delivery and carbon dioxide elimination ph balance sound and voice formation Ventilation consists of 4 (5) steps : 1. pulmonary ventilation gas exchange between lungs and
Respiratory system Role oxygen delivery and carbon dioxide elimination ph balance sound and voice formation Ventilation consists of 4 (5) steps : 1. pulmonary ventilation gas exchange between lungs and
The Human Respiratory System
 The Human Respiratory System Maryam Maheri Kiana Kayoda, Nazalia, Emerald Bocobo NPB 101 L section 008 TA: Ashneel Krishna 2/26/2015 Introduction: The respiratory system allows gas exchange between cells
The Human Respiratory System Maryam Maheri Kiana Kayoda, Nazalia, Emerald Bocobo NPB 101 L section 008 TA: Ashneel Krishna 2/26/2015 Introduction: The respiratory system allows gas exchange between cells
PULMONARY FUNCTION TESTING CORE
 PULMONARY FUNCTION TESTING CORE NHLBI Pulmonary Vascular Disease Phenomics Program Funded by the National Heart, Lung, and Blood Institute of the National Institutes of Health with support from the Pulmonary
PULMONARY FUNCTION TESTING CORE NHLBI Pulmonary Vascular Disease Phenomics Program Funded by the National Heart, Lung, and Blood Institute of the National Institutes of Health with support from the Pulmonary
Breathing oxygenates the blood to allow food to be respired
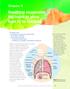 Chapter 6 Breathing oxygenates the blood to allow food to be respired This chapter covers: the structure of the human gas exchange system the mechanism of breathing gas exchange in the alveoli the concept
Chapter 6 Breathing oxygenates the blood to allow food to be respired This chapter covers: the structure of the human gas exchange system the mechanism of breathing gas exchange in the alveoli the concept
EasyWarePro Message Numbers
 Application Note CB 06/2016 EasyWarePro Message Numbers Important note: this application note is only valid beginning from EOPC V1.9.0.18 and EOP / Lab V1.9.0.19. Compared to the previous released version
Application Note CB 06/2016 EasyWarePro Message Numbers Important note: this application note is only valid beginning from EOPC V1.9.0.18 and EOP / Lab V1.9.0.19. Compared to the previous released version
EasyWarePro Message Numbers
 Application Note CB 10/2018 EasyWarePro Message Numbers Important note: this application note is only valid beginning from EOPC V1.9.0.18 and EOP / Lab V1.9.0.19. Compared to the previous released version
Application Note CB 10/2018 EasyWarePro Message Numbers Important note: this application note is only valid beginning from EOPC V1.9.0.18 and EOP / Lab V1.9.0.19. Compared to the previous released version
Department of Biology Work Sheet Respiratory system,9 class
 I. Name the following : Department of Biology Work Sheet Respiratory system,9 class 1. A muscular sheet separating the thoracic and abdominal cavities. 2. A respiratory tube supported by cartilaginous
I. Name the following : Department of Biology Work Sheet Respiratory system,9 class 1. A muscular sheet separating the thoracic and abdominal cavities. 2. A respiratory tube supported by cartilaginous
BIOLOGY 12: UNIT J - CHAPTER 15 - REVIEW WORKSHEET RESPIRATORY SYSTEM
 BIOLOGY 12: UNIT J - CHAPTER 15 - REVIEW WORKSHEET RESPIRATORY SYSTEM A. CHAPTER REVIEW 1. Define the four components of respiration. 2. What happens to the air as it moves along the air passages? What
BIOLOGY 12: UNIT J - CHAPTER 15 - REVIEW WORKSHEET RESPIRATORY SYSTEM A. CHAPTER REVIEW 1. Define the four components of respiration. 2. What happens to the air as it moves along the air passages? What
Breathing. Physics of Breathing 11/14/2011. Function of Respiratory Tract. Structure of Respiratory Tract. Parts of the Respiratory Tract
 Breathing Function of Respiratory Tract The respiratory tract is a series of spaces and semirigid tubes designed to convey air into and out of the respiratory organs (lungs). Parts of the Respiratory Tract
Breathing Function of Respiratory Tract The respiratory tract is a series of spaces and semirigid tubes designed to convey air into and out of the respiratory organs (lungs). Parts of the Respiratory Tract
Airway: the tubes through which air flows between atmosphere and alveoli. Upper airway. Lower airway
 Respiration Yu Yanqin ( 虞燕琴 ), PhD Dept. of fph Physiology Zhejiang University, School of Medicine Respiration Definition: the bodily processes involved in exchange of oxygen (O 2 ) and carbon dioxide
Respiration Yu Yanqin ( 虞燕琴 ), PhD Dept. of fph Physiology Zhejiang University, School of Medicine Respiration Definition: the bodily processes involved in exchange of oxygen (O 2 ) and carbon dioxide
iworx Sample Lab Experiment HE-5: Resting Metabolic Rate (RMR)
 Experiment HE-5: Resting Metabolic Rate (RMR) Before Starting 1. Read the procedures for the experiment completely before beginning the experiment. Have a good understanding of how to perform the experiment
Experiment HE-5: Resting Metabolic Rate (RMR) Before Starting 1. Read the procedures for the experiment completely before beginning the experiment. Have a good understanding of how to perform the experiment
iworx Sample Lab Experiment HE-5: Resting Metabolic Rate (RMR)
 Experiment HE-5: Resting Metabolic Rate (RMR) Before Starting 1. Read the procedures for the experiment completely before beginning the experiment. Have a good understanding of how to perform the experiment
Experiment HE-5: Resting Metabolic Rate (RMR) Before Starting 1. Read the procedures for the experiment completely before beginning the experiment. Have a good understanding of how to perform the experiment
Lung Squeeze: Coughing your lungs out...or not!
 Lung Squeeze: Coughing your lungs out...or not! Introduction: Lung squeeze is a condition that is practically unique to Breath-Hold Diving. Scuba divers are not really aware of it and, sadly, most doctors
Lung Squeeze: Coughing your lungs out...or not! Introduction: Lung squeeze is a condition that is practically unique to Breath-Hold Diving. Scuba divers are not really aware of it and, sadly, most doctors
Lectures on Medical Biophysics Department of Biophysics, Medical Faculty, Masaryk University in Brno. Biophysics of breathing.
 Lectures on Medical Biophysics Department of Biophysics, Medical Faculty, Masaryk University in Brno Biophysics of breathing. Spirometry 1 Lecture outline Mechanisms of gas exchange between organism and
Lectures on Medical Biophysics Department of Biophysics, Medical Faculty, Masaryk University in Brno Biophysics of breathing. Spirometry 1 Lecture outline Mechanisms of gas exchange between organism and
Biology 13A Lab #12: The Respiratory System
 Biology 13A Lab #12: The Respiratory System Lab #12 Table of Contents: Expected Learning Outcomes.... 94 Introduction...... 95 Activity 1: Structures of the Respiratory System 96 Activity 2: Measuring
Biology 13A Lab #12: The Respiratory System Lab #12 Table of Contents: Expected Learning Outcomes.... 94 Introduction...... 95 Activity 1: Structures of the Respiratory System 96 Activity 2: Measuring
Name Date of Data Collection. Class Period Lab Days/Period Teacher. Measuring Lung Capacity
 Measuring Lung Capacity Background: The amount of air that you move in and out of your lungs while breathing normally is referred to as TIDAL VOLUME. While it is possible to inhale and exhale more forcefully
Measuring Lung Capacity Background: The amount of air that you move in and out of your lungs while breathing normally is referred to as TIDAL VOLUME. While it is possible to inhale and exhale more forcefully
DEMONSTRATION OF A NEW TYPE OF. pulmonary complications. diagrammatically in Figure 1. In comparing the lung volume of one person
 EFFECT OF LAPAROTOMY ON LUNG VOLUME. DEMONSTRATION OF A NEW TYPE OF PULMONARY COLLAPSE By HENRY K BEECHER' (From the Surgical Sernices and Metabolism Laboratory of the Massachusetts General Hospital, Boston)
EFFECT OF LAPAROTOMY ON LUNG VOLUME. DEMONSTRATION OF A NEW TYPE OF PULMONARY COLLAPSE By HENRY K BEECHER' (From the Surgical Sernices and Metabolism Laboratory of the Massachusetts General Hospital, Boston)
AUTOVENT 4000 VENTILATOR
 OVERVIEW AUTOVENT 4000 Only properly trained and approved Escambia County Bureau of Public Safety Paramedics are to use the AutoVent 4000 ventilator manufactured by LSP to transport patients already on
OVERVIEW AUTOVENT 4000 Only properly trained and approved Escambia County Bureau of Public Safety Paramedics are to use the AutoVent 4000 ventilator manufactured by LSP to transport patients already on
Using Vernier Equipment to Convert Didactically Taught Human Respiration Lab to Inquiry Based Human Respiration Lab
 Using Vernier Equipment to Convert Didactically Taught Human Respiration Lab to Inquiry Based Human Respiration Lab Timothy J. Bradshaw 1, Samuel P. Carmichael II 2, Jason A. Collett 3, Alma F. Ferrier
Using Vernier Equipment to Convert Didactically Taught Human Respiration Lab to Inquiry Based Human Respiration Lab Timothy J. Bradshaw 1, Samuel P. Carmichael II 2, Jason A. Collett 3, Alma F. Ferrier
Human Biology Respiratory System
 Human Biology Respiratory System Respiratory System Responsible for process of breathing Works in cooperation with Circulatory system Three types: 1. Internal Respiration 2. External Respiration 3. Cellular
Human Biology Respiratory System Respiratory System Responsible for process of breathing Works in cooperation with Circulatory system Three types: 1. Internal Respiration 2. External Respiration 3. Cellular
Respiratory Physiology 2
 Respiratory Physiology 2 Session Objectives. What you will cover Gaseous Exchange Control of Breathing Rate Your objectives are State the function of support structures and epithelia of the bronchial tree
Respiratory Physiology 2 Session Objectives. What you will cover Gaseous Exchange Control of Breathing Rate Your objectives are State the function of support structures and epithelia of the bronchial tree
Selecting and Connecting Breathing Systems
 Selecting and Connecting Breathing Year Group: BVSc3 + Document number: CSL_A03 Equipment for this station: Equipment list: Pen Paper Calculator T-piece (in CSL a strip of white tape is around this system)
Selecting and Connecting Breathing Year Group: BVSc3 + Document number: CSL_A03 Equipment for this station: Equipment list: Pen Paper Calculator T-piece (in CSL a strip of white tape is around this system)
Breeze Suite Quick Start Operator Manual. An Introduction to Pulmonary Function Testing
 Breeze Suite Quick Start Operator Manual An Introduction to Pulmonary Function Testing The MedGraphics Breeze Suite Quick Start Operator Manual is Part No. 142143-001 Rev A. Caution: Federal (USA) law
Breeze Suite Quick Start Operator Manual An Introduction to Pulmonary Function Testing The MedGraphics Breeze Suite Quick Start Operator Manual is Part No. 142143-001 Rev A. Caution: Federal (USA) law
bespoke In general health and rehabilitation Breath-by-breath multi-functional respiratory gas analyser In human performance
 Introduction Expired Gas Analysis or indirect calorimetry, can be used to measure ventilation and the fractions of oxygen and carbon dioxide in expired air. From these measurements, the body's oxygen consumption
Introduction Expired Gas Analysis or indirect calorimetry, can be used to measure ventilation and the fractions of oxygen and carbon dioxide in expired air. From these measurements, the body's oxygen consumption
The Human Respiratory System Yuki Yang Aug.14, 2012
 The Human Respiratory System Yuki Yang Aug.14, 2012 Introduction The human respiratory system is responsible for gas exchange between the environment and body tissues.(sherwood,461) The organs involved
The Human Respiratory System Yuki Yang Aug.14, 2012 Introduction The human respiratory system is responsible for gas exchange between the environment and body tissues.(sherwood,461) The organs involved
1.2 The structure and functions of the cardio-respiratory system Learning objectives
 1.2 The structure and functions of the cardio-respiratory system Learning objectives To understand the functions of the circulatory system. To be able to identify the differences between veins, arteries
1.2 The structure and functions of the cardio-respiratory system Learning objectives To understand the functions of the circulatory system. To be able to identify the differences between veins, arteries
Susan Blonshine, RRT, RPFT, AE-C, FAARC
 Susan Blonshine, RRT, RPFT, AE-C, FAARC 1 The measurement of TLC to distinguish between restrictive and obstructive processes. The evaluation of the pathophysiology of obstructive lung diseases that may
Susan Blonshine, RRT, RPFT, AE-C, FAARC 1 The measurement of TLC to distinguish between restrictive and obstructive processes. The evaluation of the pathophysiology of obstructive lung diseases that may
