ENGINEERING FLUID MECHANICS
|
|
|
- Erin Hutchinson
- 5 years ago
- Views:
Transcription
1 DEPARTMENT of MECHANICAL ENGINEERING FLUID MECHANICS Subject code: 10ME46B Faculty name: Naveen H E QUESTION BANK UNIT-1: FLUID PROPERTIES 1. Define the following: i) density, ii) weight density, iii) specific volume, iv) specific gravity, v) dynamic viscosity vi) kinematic viscosity 2. State the Newton s law of viscosity and give examples of its applications. 3. Define Newtonian and Non-Newtonian fluids. 4. Explain the phenomenon of capillarity. Obtain an expression for capillary rise of a liquid. 5. How does viscosity of a fluid vary with temperature? 6. Define surface tension. Prove that the relationship between surface tension and pressure inside a droplet of liquid in excess of outside pressure is given by 7. An oil film of thickness 1.5mm is used fro lubrication between square plate of size 0.9m x 0.9m and an inclined plane having an angle of inclination The weight of the square plate is N and it slides down the plane with a uniform velocity of 0.2 m/s. find the dynamic viscosity of the oil. 8. Determine the bulk modulus of elasticity of a fluid which is compressed in a cylinder from a volume of m 3 at 70N/cm 2 pressure to a volume of m 3 at 270 N/cm 2 pressure. 9. The surface tension of water in contact with air is given as N/m. The pressure outside the droplet of water of diameter 0.02 mm is atmospheric N/cm 2. Calculate the pressure within the droplet of water. 10. The capillary rise in the glass tube used for measuring water level is not to exceed 0.5 mm. determine its minimum size, given that surface tension for water in contact with air = N/m. UNIT-2: FLUID STATISTICS 1. State and prove the Pascal s law. 2. Differentiate between: i) Absolute and gauge pressure, ii) simple manometer and differential manometer and iii) Piezometer and pressure gauges. 3. Explain briefly the working principle of Bourdon pressure gauge with a neat sketch. 4. Derive an expression for the force exerted on a submerged vertical plane surface by the static liquid and located the position of center of pressure. 5. Prove that the center of pressure of a completely submerged plane surface is always below the center of gravity of the submerged surface or at most coincide with the center of gravity when the plane surface is horizontal.
2 6. An open tank contains water upto a depth of 1.5 m and above it an oil of sp. gr. 0.8 for a depth of 2 m. find the pressure intensity i) at the interface of the two liquids, and ii) at the bottom of the tank. 7. A simple manometer is used to measure the pressure of oil (sp. gr. = 0.8) flowing in a pipe line. Its right limb is open to the atmosphere and left limb is connected to the pipe. The center of the pipe is 9 cm below the level of mercury (sg =13.6) in the right limb. If the difference of mercury level in the two limbs is 15 cm, determine the absolute pressure of the oil in the pipe in N/cm A U- tube differential manometer connects two pressure pipes A and B. Pipe A contains carbon tetrachloride having a specific gravity under a pressure of N/cm 2. And pipe B contains oil o sp. Gr. 0.8 under pressure of N/cm 2. The pipe A lies 2.5 m above pipe B. find the difference of pressure measured by mercury as fluid filling U-tube. 9. Determine the total pressure and center of pressure on an isosceles triangular plate of base 5 m and altitude 5 m when the plate is immersed vertically in an oil of sp. gr The base of the plate is 1m below the free surface of oil
3 UNIT 3: BUOYANCY AND FLUID KINEMATICS
4 Unit 4:- Unit 5: Reciprocating Air Compressor 1. What is meant by single acting compressor? 2. What is meant by double acting compressor? 3. What is meant by single stage compressor? 4. What is meant by multistage compressor? 5. Define isentropic efficiency 6. Define mean effective pressure. How is it related to in power of an I.C engine. 7. What is meant by free air delivered? 8. Explain how flow of air is controlled in a reciprocating compressor? 9. What factors limit the delivery pressure in reciprocating compressor? 10. Name the methods adopted for increasing isothermal efficiency of reciprocating air compressor. 11. Why clearance is necessary and what is its effect on the performance of reciprocating compressor? 12. What is compression ratio? 13. What is meant by inter cooler? 14. Define the terms as applied to reciprocating compressor: Mechanical efficiency, isothermal efficiency, isentropic efficiency.
5 15. What factors limit the delivery pressure in a reciprocating compressor? 16. Name the methods adopted for increasing isothermal efficiency of reciprocating air compressor. 17. What are the factors that affect the volumetric efficiency of a reciprocating compressor? 18. Discuss the effect of clearance upon the performance of an air compressor. 19. Differentiate between prefect inter cooling and imperfect inter cooling. 20. Compare reciprocating and rotary compressor. 21. What is the main advantage of inter cooling in multistage reciprocating compressor? 22. Why clearance is necessary in reciprocating compressor? 23. Differentiate positive and non positive displacement compressor? 24. What is the effect of clearance volume on the power required and work done in a reciprocating air compressor? 25. Drive an expression for the work done by single stage single acting reciprocating air compressor. 26. Drive an expression for the volumetric efficiency of reciprocating air compressors 27. A single stage single acting air compressor is used to compress air from 1 bar and 22 C to 6 bar according to the law PV 1.25 = C. The compressor runs at 125 rpm and the ratio of stroke length to bore of a cylinder is 1.5. If the power required by the compressor is 20 kw, determine the size of the cylinder. 28. A single stage single acting air compressor is used to compress air from bar and 25 C to 7 bar according to law PV 1.3 = C. The bore and stroke of a cylinder are 120mm and 150mm respectively. The compressor runs at 250 rpm.if clearance volume of the cylinder is 5% of stroke volume and the mechanical efficiency of the compressor is 85%, determine volumetric efficiency, power, and mass of air delivered per minute. 29. A two stage singe acting air compressor compresses 2m 3 airs from 1 bar and 20 C to 15 bar. The air from the low pressure compressor is cooled to 25 C in the intercooler. Calculate the minimum power required to run the compressor if, the compression follows PV 1.25 =C and the compressor runs at 400 rpm. 30. The free air delivery of a single cylinder single stage reciprocating air compressor is 2.5m 3 /min. The ambient air is at STP conditions and delivery pressure is 7 bar. The clearance volume is 5% of the stroke volume and law of compression and expansion is pv 1.25 =C. If L=1.2D and compressor runs at 150rpm, determine the size of the cylinders. 31. A multi stage air compressor is to be designed to evaluate the pressure from 1 bar to 120 bar. Such that the single stage pressure ratio not to exceed 4. Find (i) Number of stages (ii). Exact stage pressure ratio (iii) Inter stage pressure. 32. Consider a single acting two stage reciprocating air compressor running at 300rpm. Air is compressed at a rate of 4.5kg/min from 1.013bar and 288K through a pressure ratio of 9 to 1. Both the stages have same pressure ratio and the index of expansion in both stages is 1.3. Assume a complete inter-cooling, find the indicated power and the cylinder swept volume required. Assume that the clearance volumes of both stages are 5% of their respective swept volumes.
6 33. A two-cylinder single-acting air compressor is to deliver 16 kg of air per minute at 7 bar from suction conditions 1 bar and 15 C. Clearance may be taken as 4% of stroke volume and the index for both compression and re expansion as 1.3. Compressor is directly coupled to a four-cylinder four-stroke petrol engine which runs at 2000 r.p.m. with a brake mean effective pressure of 5.5bar. Assuming a stroke-broke ratio of 1.2 for both engine and compressor and a mechanical efficiency of 82% for compressor, calculate the required cylinder dimensions. 34. A two stage air compressor compresses air from 1 bar and 20 C to 42 bar. If the law of compression is pv 1.3 = constant and the inter cooling is perfect. Find per kg of air i). The work done in compression ii). The mass of cooling water necessary for abstracting the heat in the intercooler, if the temperature rise of the cooling water is 25 C. 35. A single stage single acting reciprocating air compressor delivers 14 m 3 of free air per minute from 1 bar to 7 bar. The speed of compressor is 310rpm.Assuming that compression and expansion follow the law pv 1.35 = constant and clearance is 5% of the swept volume, find the diameter and stroke of the compressor. Take stroke length is 1.5 times the bore diameter. 36. A single acting single stage compressor is belt driven from an electric motor at 400rpm. The cylinder diameter is 15 cm and the stroke is 17.5 cm. The air is compressed from 1 bar to 7 bar and the law of compression PV 1.3 = constant. Find the power of the motor, if transmission efficiency is 97% and the mechanical efficiency of the compressor is 90%. Neglect clearance effects. 37. A two-stage double acting air compressor, operating at 200 r.p.m, takes in air at bar and 27 C. The size of the L.P. cylinder is 350 x 380 mm, the stroke of H.P. cylinder is the same as that of the L.P. cylinder and the clearance of both the cylinders is 4%. The L.P. cylinder discharges the air at a pressure of bar. The air passes through the intercooler so that it enters the H.P. cylinder at 27 C and bar, finally it is discharged from the compressor at 15.4 bar. The value of n is both cylinders is 1.3. Cp = kj/kg-k and R = kj/kg-k. Calculate (i). The heat rejected in the inter cooler. (ii).the diameter of H.P. cylinder and (iii). The power required to drive H.P. cylinder. Unit 6: Gas Turbine And propulsion systems 1. How the gas turbine cycles classified? 2. What are essential components required for the operation of gas turbine cycle and explain their functionality. 3. Draw the schematic diagram of open cycle gas turbine unit and explain its working along with its merits and demerits. 4. Explain with neat sketch Closed cycle gas turbine plant 5. Explain with neat sketch differences between open cycle gas turbine plant and closed Cycle turbine plant. 6. Derive the expression for thermal efficiency of a simple gas turbine plant 7. Show that the efficiency of an air standard Brayton cycle is a function of isentropic pressure ratio. 8. What are different operating variables affect the thermal efficiency of gas turbine power plant? Explain.
7 9. Show that the specific output of a simple gas turbine cycle is maximum, when the pressure ratio is such that the compressor and turbine outlet temperatures are equal. 10. What are different parameters influence the performance of gas turbine cycle. Explain. 11. What is the effect of pressure ratio during compression on the performance of gas turbine cycle? 12. Draw the schematic layout of gas turbine cycle with regenerator, intercooler and reheating. Explain salient features. 13. Sketch the ideal regenerative Brayton cycle in two stage compression and expansion with intercooling and reheating. Mark the salient points on T-s diagrams. 14. Derive the thermal efficiency of gas turbine with multi stage compression with intercooling. 15. What is the influence of isentropic efficiency of compressor and turbine on thermal efficiency of gas turbine unit? Explain with suitable diagrams. 16. Explain the working of regenerative gas turbine cycle with p-v and T-s diagrams. 17. The minimum and maximum temperature limits in a gas turbine plant are288 K and 1100 K. The pressure limits are 1 bar and 8 bar. Determine the thermal efficiency and work ratio. 18. In a gas turbine power cycle, the pressure ratio is 6 and the maximum cycle temperature is C. The air enters to the cylinder at 15 0 c and the flow rate of air is 12 kg/s. Determine the power developed and thermal efficiency of cycle. 19. A Brayton cycle works between 1 bar, 300 K and 5 bar, 1250 K. There are two stages of compression with perfect intercooling and two stages of expansion with reheating. The work output of first expansion stage being used to drive the two compressors, where the inter-stage pressure is optimized for the compressor. The air from the first stage turbine is again heated to 1250 K and expanded. Calculate the power output of free power turbine and cycle efficiency without and with perfect heat exchanger and compare them. Also calculate the percentage improvement in the efficiency because of the addition of heat exchangers. 20. A closed cycle gas turbine using Argon as the working fluid has a two compression with perfect inter cooling. The overall pressure ratio is 9 and pressure ratio in each stage is equal. Each stage has an isentropic efficiency of 85%. The turbine is also two stages with equal pressure ratio with inter change reheat to original temperature. Each turbine stage has an isentropic efficiency of 90%. The turbine inlet temperature is 1100K and the compressor inlet is 303K. Find i. Work done per kg of fluid flow ii. Work ratio iii. The overall cycle efficiency. iv. The properties of argon are C p = kJ/kg 0 K, Γ =1.667 and R= kJ/kg 0 K 21. A Gas turbine plant works between the temperature limits of K and 2880 K Isentropic efficiency for compressor and turbines are 0.85 and 0.8 respectively. Determine the optimum pressure ratio for maximum work output and also for maximum Cycle thermal efficiency.
8 22. Compare the maximum work delivered by an air craft gas turbine which works with two stage compression with inter cooling. The compressor pressure ratio is 4 and the temperature limit is 1000 K, for the given ambient condition 1 bar and 301 K. If the temperature and pressure at 6000 m altitude is C and 0.5 bar, find the percentage change in network output, efficiency and exhaust gas temperature if the volume flow rate is 2.5 m 3 /s. 23. In gas turbine plant, operating on joules cycle, maximum and minimum temperatures of C and 27 0 C. The pressure ratio is 4.5. Calculate the specific work output, cycle efficiency and work ratio. Assume isentropic efficiency of compressor and turbine 85%and 90% respectively. What is the heat rate in kj / kw-hr? If the rating of the turbine is 1300kW, what is the mass flow in kg/s. Neglect the mass of fuel C p =1.005 kj/kg 0 K. 24. In gas turbine plant, operating on joules cycle, maximum and minimum temperatures of C and 27 0 C. The pressure ratio is 4.5. Calculate the specific work output, cycle efficiency and work ratio. Assume isentropic efficiency of Compressor and turbine 85%and 90% respectively. What is the heat rate in kj / kw-hr? If the rating of the turbine is 1300kW, what is the mass flow in kg/s. Neglect the mass of fuel. C p =1.005 kj/kg 0K. Unit 7: Refrigeration: 1. Name four important properties of a good refrigerant 2. What is the difference between air conditioning and refrigeration? 3. In a vapour compression refrigeration system, where the highest temperature will occur? 4. The vapour absorption system can use low-grade heat energy in the generator. Is true of false? 6. Name any four commonly used refrigerants. 7. Explain unit of Refrigeration. 8. Why throttle valve is used in place of expansion cylinder for vapour compression refrigerant machine. 9. What are the effects of super heating and sub cooling on.the vapour compression cycle? 10. What are the properties of good refrigerant? 11. Draw neat sketch of simple vapor compression refrigeration system and explain. 12. A refrigeration system of 10.5 tonnes capacity at an evaporator temperature of -12 C and a condenser temperature of 27 C is needed in a food storage locker. The refrigerant Ammonia is sub cooled by 6 C before entering the expansion valve. The compression in the compressor is of adiabatic type. Find 1. Condition of vapor at outlet of the compressor. 2. Condition of vapor at the entrance of the evaporator 3.COP & power required. 13. An ammonia refrigerator produces 30 tonnes of ice from and at 0 C in a day of 24 hours. The temperature range in the compressor is from 25 C to 15 C. The vapour is dry saturated at the end of compression and an expansion valve is used. Calculate the coefficient of performance. The properties of the refrigerant are given in the following table
9 14. A food storage locker requires a refrigerating capacity of 50kW. It works between a condenser temperature of 35 C and an evaporator temperature of -10 C. The refrigerant is ammonia; It is sub-cooled by 5 C before entering the expansion valve and dry saturated vapour leaving the evaporator. Assuming a single cylinder, single acting compressor operating at 1000 rpm with stroke equal to 1.2 times the bore. Determine The power required and cylinder dimensions, the properties of ammonia are, Unit 8: Psychometry:- 1. How are air-conditioning systems classified? 2. How does humidity affect human comfort? 3. What are the various sources of heat gain of an air-conditioned space? 4. What do you mean by the term infiltration in heat load calculations? Define Psychrometry. 5. What is humidification and dehumidification? 6. Define specific humidity. 7. Differentiate absolute humidity and relative humidity. 8. What is effective temperature? 9. Represent the following psychrometric process using skeleton psychrometric chart? 10. Define Relative humidity. 11. Define degree of saturation. 12. What is meant by adiabatic saturation temperature (or) thermodynamic wet bulb temperature? 13. What is dew point temperature? How it is related to dry bulb and wet bulb temperature at the saturation condition? 14. What is meant by dry bulb temperature (DBT)? 15. What is meant by wet bulb temperature (WBT)?
10 16. Define sensible heat and latent heat. 17. Consider a room that contains air at 1 atm., 35 o C and 40 percent relative humidity. Using psychrometric chart, determine (i) the specific humidity (ii) the enthalpy (iii) the wet-bulb temperature (iv) the dew-point temperature, and (v) specific volume of air. 18. An air water vapour mixture at 0.1MPa, 30 o C, 80% RH has a volume of 50m 3. Calculate the specific humidity, dew point, wet bulb temperature, mass of dry air and mass of water vapour. 19. Air at 16 o C and 25% relative humidity passes through a heater and then through a humidifier to reach final dry bulb temperature of 30 o C and 50% relative humidity. Calculative the heat and moisture added to the air. What is the sensible heat factor? 20. Saturated air at 20 o C at a rate of 1.16m 3 /sec is mixed adiabatically with the outside air at 35 o C and 50% relative humidity at a rate of 0.5m 3 /sec. assuming adiabatic mixing condition at 1 atm, determine specific humidity, relative humidity, dry bulb temperature and volume flow rate of the mixture. 21. (a) A sling psychrometer reads 40 O C DBT and 36 O C WBT. Find the humidity ratio, relative humidity, DPT, specific volume of air, density of air, density of water vapour and enthalpy. (b) Saturated air at 21 O C is passed through a drier so that the final relative humidity is 20%. The air is then passed through a cooler until its final temperature is 21 O C without a change in specific humidity. Find (i) The temperature of air after drying process, (ii) the heat rejected in cooling process, (iii) the due point temperature at the end of drying process m 3 of air per minute at 31 o C DBT and 18.5 o C WBT is passed over the cooling coil whose surface temperature is 4.4 o C. The coil cooling capacity is 3.56 tons of refrigeration under the given condition of air. Determine DBT and WBT of the air leaving the cooling coil. 23. A sling psychrometer in a laboratory test recorded the following readings.dry bulb temperature = 35 C, Wet bulb temperature = 25 C Calculate the following (i) specific humidity (ii) relative humidity (iii) vapour density in air (iv) dew point temperature and (v) Enthalpy of mixture per kg of dry air Take atmospheric pressure = bar. 24. An office is to be air-conditioned for 50 staff when the outdoor conditions are 30 C DBT and 75% RH if the quantity of air supplied is 0.4m 3 /min/person, find the following: (i) Capacity of the cooling coil in tonnes of refrigeration (ii) Capacity of the heating coil in kw (iii). Amount of water vapour removed per hour, Assume that required air inlet conditions are 20 C DBT and 60% RH, Air is conditioned first by cooling and dehumidifying and then by heating. (iv). If the heating coil surface temperature is 25 C, find the by-pass factor of the heating coil?
CERTIFICATES OF COMPETENCY IN THE MERCHANT NAVY MARINE ENGINEER OFFICER
 CERTIFICATES OF COMPETENCY IN THE MERCHANT NAVY MARINE ENGINEER OFFICER EXAMINATIONS ADMINISTERED BY THE SCOTTISH QUALIFICATIONS AUTHORITY ON BEHALF OF THE MARITIME AND COASTGUARD AGENCY STCW 95 CHIEF
CERTIFICATES OF COMPETENCY IN THE MERCHANT NAVY MARINE ENGINEER OFFICER EXAMINATIONS ADMINISTERED BY THE SCOTTISH QUALIFICATIONS AUTHORITY ON BEHALF OF THE MARITIME AND COASTGUARD AGENCY STCW 95 CHIEF
EXAM # 2. First Name Last Name CIRCLE YOUR LECTURE BELOW: INSTRUCTIONS
 CIRCLE YOUR LECTURE BELOW: First Name Last Name Div. 1 08:30 am Prof. Chen Div. 2 11:30 am Prof. Braun EXAM # 2 INSTRUCTIONS 1. This is a closed book examination. You are allowed to have two single sheets
CIRCLE YOUR LECTURE BELOW: First Name Last Name Div. 1 08:30 am Prof. Chen Div. 2 11:30 am Prof. Braun EXAM # 2 INSTRUCTIONS 1. This is a closed book examination. You are allowed to have two single sheets
GLOSSARY OF TERMS. Adiabatic Compression Compression process when all heat of compression is retained in the gas being compressed.
 GLOSSARY OF TERMS Absolute pressure Total pressure measured from absolute zero i.e. a perfect vacuum. As a practical matter, gauge pressure plus atmospheric pressure. Absolute temperature Temperature measured
GLOSSARY OF TERMS Absolute pressure Total pressure measured from absolute zero i.e. a perfect vacuum. As a practical matter, gauge pressure plus atmospheric pressure. Absolute temperature Temperature measured
ME1251 THERMAL ENGINEERING UNIT IV AIR COMPRESSORS
 ME1251 THERMAL ENGINEERING UNIT IV AIR COMPRESSORS UNIT-IV 4. 1 CONTENTS TECHNICAL TERMS 4.1 Classification of compressors 4.2 Positive Displacement compressors 4.2.1 Double acting compressor 4.2.2 Diaphragm
ME1251 THERMAL ENGINEERING UNIT IV AIR COMPRESSORS UNIT-IV 4. 1 CONTENTS TECHNICAL TERMS 4.1 Classification of compressors 4.2 Positive Displacement compressors 4.2.1 Double acting compressor 4.2.2 Diaphragm
Irrigation &Hydraulics Department lb / ft to kg/lit.
 CAIRO UNIVERSITY FLUID MECHANICS Faculty of Engineering nd Year CIVIL ENG. Irrigation &Hydraulics Department 010-011 1. FLUID PROPERTIES 1. Identify the dimensions and units for the following engineering
CAIRO UNIVERSITY FLUID MECHANICS Faculty of Engineering nd Year CIVIL ENG. Irrigation &Hydraulics Department 010-011 1. FLUID PROPERTIES 1. Identify the dimensions and units for the following engineering
ENGG. THERMODYNAMICS
 ENGG. THERMODYNAMICS Unit-1 [8 hrs] Introduction To Thermodynamics: Basic concepts of Thermodynamics, Closed & Open Systems, Forms of energy, Properties of a system, State and Equilibrium, Processes and
ENGG. THERMODYNAMICS Unit-1 [8 hrs] Introduction To Thermodynamics: Basic concepts of Thermodynamics, Closed & Open Systems, Forms of energy, Properties of a system, State and Equilibrium, Processes and
Quiz #1 Thermodynamics Spring, 2018 Closed Book, Open Appendices, Closed Notes, CLOSED CALCULATORS
 Quiz #1 Closed Book, Open Appendices, Closed Notes, CLOSED CALCULATORS An astronaut has a mass of 161 lbm on the surface of the earth. Calculate his weight (in lbf) on planet Rigel 4 where g = 20.0 ft/s
Quiz #1 Closed Book, Open Appendices, Closed Notes, CLOSED CALCULATORS An astronaut has a mass of 161 lbm on the surface of the earth. Calculate his weight (in lbf) on planet Rigel 4 where g = 20.0 ft/s
Please welcome for any correction or misprint in the entire manuscript and your valuable suggestions kindly mail us
 Problems of Practices Of Basic and Applied Thermodynamics First Law of Thermodynamics Prepared By Brij Bhooshan Asst. Professor B. S. A. College of Engg. And Technology Mathura, Uttar Pradesh, (India)
Problems of Practices Of Basic and Applied Thermodynamics First Law of Thermodynamics Prepared By Brij Bhooshan Asst. Professor B. S. A. College of Engg. And Technology Mathura, Uttar Pradesh, (India)
Hours / 100 Marks Seat No.
 17421 21415 3 Hours / 100 Marks Seat No. Instructions : (1) All Questions are compulsory. (2) Answer each next main Question on a new page. (3) Illustrate your answers with neat sketches wherever necessary.
17421 21415 3 Hours / 100 Marks Seat No. Instructions : (1) All Questions are compulsory. (2) Answer each next main Question on a new page. (3) Illustrate your answers with neat sketches wherever necessary.
ASSIGNMENT-1 HYDROPOWER PLANT
 ASSIGNMENT-1 HYDROPOWER PLANT Theory 1. Give classification of hydro electric power plant. 2. Write advantages, disadvantages and application of hydro electric power plant. 3. Explain general layout and
ASSIGNMENT-1 HYDROPOWER PLANT Theory 1. Give classification of hydro electric power plant. 2. Write advantages, disadvantages and application of hydro electric power plant. 3. Explain general layout and
Unit 24: Applications of Pneumatics and Hydraulics
 Unit 24: Applications of Pneumatics and Hydraulics Unit code: J/601/1496 QCF level: 4 Credit value: 15 OUTCOME 2 TUTORIAL 11 AIR COMPRESSORS AND DISTRIBUTION SYSTEM The material needed for outcome 2 is
Unit 24: Applications of Pneumatics and Hydraulics Unit code: J/601/1496 QCF level: 4 Credit value: 15 OUTCOME 2 TUTORIAL 11 AIR COMPRESSORS AND DISTRIBUTION SYSTEM The material needed for outcome 2 is
Gas Vapor Injection on Refrigerant Cycle Using Piston Technology
 Purdue University Purdue e-pubs International Refrigeration and Air Conditioning Conference School of Mechanical Engineering 2012 Gas Vapor Injection on Refrigerant Cycle Using Piston Technology Sophie
Purdue University Purdue e-pubs International Refrigeration and Air Conditioning Conference School of Mechanical Engineering 2012 Gas Vapor Injection on Refrigerant Cycle Using Piston Technology Sophie
ASSIGNMENT 2 CHE 3473
 DUE: May 23 ASSIGNMENT 2 CHE 3473 #Problem 1: 3.3 #Problem 2: 3.4 #Problem 3: 3.5 #Problem 4: 3.6 #Problem 5: 3.7 #Problem 6: 3.8 #Problem 7: 3.11 #Problem 8: 3.15 #Problem 9: 3.22 #Problem 10: 3.32 #Problem
DUE: May 23 ASSIGNMENT 2 CHE 3473 #Problem 1: 3.3 #Problem 2: 3.4 #Problem 3: 3.5 #Problem 4: 3.6 #Problem 5: 3.7 #Problem 6: 3.8 #Problem 7: 3.11 #Problem 8: 3.15 #Problem 9: 3.22 #Problem 10: 3.32 #Problem
HW-1: Due by 5:00 pm EDT on Wednesday 13 June 2018 to GradeScope.
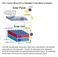 HW-1: Due by 5:00 pm EDT on Wednesday 13 June 2018 to GradeScope. The solar cell/solar panel shown above depict how a semiconductor can transform solar power into electrical power. Consider the solar panel
HW-1: Due by 5:00 pm EDT on Wednesday 13 June 2018 to GradeScope. The solar cell/solar panel shown above depict how a semiconductor can transform solar power into electrical power. Consider the solar panel
Applied Fluid Mechanics
 Applied Fluid Mechanics 1. The Nature of Fluid and the Study of Fluid Mechanics 2. Viscosity of Fluid 3. Pressure Measurement 4. Forces Due to Static Fluid 5. Buoyancy and Stability 6. Flow of Fluid and
Applied Fluid Mechanics 1. The Nature of Fluid and the Study of Fluid Mechanics 2. Viscosity of Fluid 3. Pressure Measurement 4. Forces Due to Static Fluid 5. Buoyancy and Stability 6. Flow of Fluid and
ASSIGNMENT 2 CHE 3473
 DUE: May 21 ASSIGNMENT 2 CHE 3473 #Problem 1 Read Chapter 3. ALL OF IT. Time yourself and report the time. #Problem 2: 3.2 #Problem 3: 3.3 #Problem 4: 3.5 #Problem 5: 3.6 #Problem 6: 3.7 #Problem 7: 3.8
DUE: May 21 ASSIGNMENT 2 CHE 3473 #Problem 1 Read Chapter 3. ALL OF IT. Time yourself and report the time. #Problem 2: 3.2 #Problem 3: 3.3 #Problem 4: 3.5 #Problem 5: 3.6 #Problem 6: 3.7 #Problem 7: 3.8
Enter your parameter set number (1-27)
 1- Helium balloons fly and balloons with air sink. Assume that we want to get a balloon that is just floating in the air, neither rising nor falling, when a small weight is placed hanging in the balloon.
1- Helium balloons fly and balloons with air sink. Assume that we want to get a balloon that is just floating in the air, neither rising nor falling, when a small weight is placed hanging in the balloon.
ASSIGNMENT-1 HYDROPOWER PLANT
 ASSIGNMENT-1 HYDROPOWER PLANT Theory 1. Give classification of hydro electric power plant. 2. Write advantages, disadvantages and application of hydro electric power plant. 3. Explain general layout and
ASSIGNMENT-1 HYDROPOWER PLANT Theory 1. Give classification of hydro electric power plant. 2. Write advantages, disadvantages and application of hydro electric power plant. 3. Explain general layout and
FLUID MECHANICS Time: 1 hour (ECE-301) Max. Marks :30
 B.Tech. [SEM III(ME&CE)] QUIZ TEST-1 (Session : 2013-14) Time: 1 hour (ECE-301) Max. Marks :30 Note: Attempt all questions. PART A Q1. The velocity of the fluid filling a hollow cylinder of radius 0.1
B.Tech. [SEM III(ME&CE)] QUIZ TEST-1 (Session : 2013-14) Time: 1 hour (ECE-301) Max. Marks :30 Note: Attempt all questions. PART A Q1. The velocity of the fluid filling a hollow cylinder of radius 0.1
CHAPTER-2 IMPACT OF JET
 CHAPTER-2 IMPACT OF JET FLUID POWER ENGINEERING (2151903) 1. A jet of water of diameter 5cm moving with a velocity of 25 m/sec impinges on a fixed curved plate tangentially at one end at an angle of 30
CHAPTER-2 IMPACT OF JET FLUID POWER ENGINEERING (2151903) 1. A jet of water of diameter 5cm moving with a velocity of 25 m/sec impinges on a fixed curved plate tangentially at one end at an angle of 30
Earlier Lecture. In the earlier lecture, we have seen Kapitza & Heylandt systems which are the modifications of the Claude System.
 17 1 Earlier Lecture In the earlier lecture, we have seen Kapitza & Heylandt systems which are the modifications of the Claude System. Collins system is an extension of the Claude system to reach lower
17 1 Earlier Lecture In the earlier lecture, we have seen Kapitza & Heylandt systems which are the modifications of the Claude System. Collins system is an extension of the Claude system to reach lower
NEW POLYTECHNIC, KOLHAPUR
 Content: 3.1 Classification of air compressor - Construction and working of single stage and two stage reciprocating air compressors with P-V. diagram. Necessity of multistaging and inter cooling. Construction
Content: 3.1 Classification of air compressor - Construction and working of single stage and two stage reciprocating air compressors with P-V. diagram. Necessity of multistaging and inter cooling. Construction
PHYS 101 Previous Exam Problems
 PHYS 101 Previous Exam Problems CHAPTER 14 Fluids Fluids at rest pressure vs. depth Pascal s principle Archimedes s principle Buoynat forces Fluids in motion: Continuity & Bernoulli equations 1. How deep
PHYS 101 Previous Exam Problems CHAPTER 14 Fluids Fluids at rest pressure vs. depth Pascal s principle Archimedes s principle Buoynat forces Fluids in motion: Continuity & Bernoulli equations 1. How deep
3 1 PRESSURE. This is illustrated in Fig. 3 3.
 P = 3 psi 66 FLUID MECHANICS 150 pounds A feet = 50 in P = 6 psi P = s W 150 lbf n = = 50 in = 3 psi A feet FIGURE 3 1 The normal stress (or pressure ) on the feet of a chubby person is much greater than
P = 3 psi 66 FLUID MECHANICS 150 pounds A feet = 50 in P = 6 psi P = s W 150 lbf n = = 50 in = 3 psi A feet FIGURE 3 1 The normal stress (or pressure ) on the feet of a chubby person is much greater than
SAMPLE RH = P 1. where. P 1 = the partial pressure of the water vapor at the dew point temperature of the mixture of dry air and water vapor
 moisture starts to condense out of the air. The temperature at which this happens is called the dew point temperature, or the saturation temperature. What is commonly called saturation pressure or condensing
moisture starts to condense out of the air. The temperature at which this happens is called the dew point temperature, or the saturation temperature. What is commonly called saturation pressure or condensing
Hours / 100 Marks Seat No.
 17421 15116 3 Hours / 100 Seat No. Instructions (1) All Questions are Compulsory. (2) Answer each next main Question on a new page. (3) Illustrate your answers with neat sketches wherever necessary. (4)
17421 15116 3 Hours / 100 Seat No. Instructions (1) All Questions are Compulsory. (2) Answer each next main Question on a new page. (3) Illustrate your answers with neat sketches wherever necessary. (4)
Actual volumetric efficiency, ƞvol Displacement volume Vd=π/4*D 2 L*N m3/min. pv n = c. FAD=mRT1/p m3/min ƞvol=fad/vd
 Following data relate to a performance test of a single acting 14 cm 10 cm reciprocating compressor are given: suction pressure = 1 bar, suction temperature = 0 C, discharge pressure = 6 bar, discharge
Following data relate to a performance test of a single acting 14 cm 10 cm reciprocating compressor are given: suction pressure = 1 bar, suction temperature = 0 C, discharge pressure = 6 bar, discharge
THERMODYNAMICS, HEAT AND MASS TRANSFER TUTORIAL NO: 1 (SPECIFIC VOLUME, PRESSURE AND TEMPERATURE)
 THERMODYNAMICS, HEAT AND MASS TRANSFER TUTORIAL NO: 1 (SPECIFIC VOLUME, PRESSURE AND TEMPERATURE) 1. A vacuum gauge mounted on a condenser reads 66 cm Hg. What is the absolute pressure in the condenser
THERMODYNAMICS, HEAT AND MASS TRANSFER TUTORIAL NO: 1 (SPECIFIC VOLUME, PRESSURE AND TEMPERATURE) 1. A vacuum gauge mounted on a condenser reads 66 cm Hg. What is the absolute pressure in the condenser
Fundamentals of Compressed Air Systems. Pre-Workshop Assignment
 Page 1 In order to ensure that the Compressed Air Challenge Fundamentals of Compressed Air Systems Training is most useful to you, it will be important for you to bring information about your plant s compressed
Page 1 In order to ensure that the Compressed Air Challenge Fundamentals of Compressed Air Systems Training is most useful to you, it will be important for you to bring information about your plant s compressed
Process Nature of Process
 AP Physics Free Response Practice Thermodynamics 1983B4. The pv-diagram above represents the states of an ideal gas during one cycle of operation of a reversible heat engine. The cycle consists of the
AP Physics Free Response Practice Thermodynamics 1983B4. The pv-diagram above represents the states of an ideal gas during one cycle of operation of a reversible heat engine. The cycle consists of the
Compressors. Basic Classification and design overview
 Compressors Basic Classification and design overview What are compressors? Compressors are mechanical devices that compresses gases. It is widely used in industries and has various applications How they
Compressors Basic Classification and design overview What are compressors? Compressors are mechanical devices that compresses gases. It is widely used in industries and has various applications How they
and its weight (in newtons) when located on a planet with an acceleration of gravity equal to 4.0 ft/s 2.
 1.26. A certain object weighs 300 N at the earth's surface. Determine the mass of the object (in kilograms) and its weight (in newtons) when located on a planet with an acceleration of gravity equal to
1.26. A certain object weighs 300 N at the earth's surface. Determine the mass of the object (in kilograms) and its weight (in newtons) when located on a planet with an acceleration of gravity equal to
CRYOGENICS LIQUID NITROGEN AS A NON- POLLUTING FUEL
 CRYOGENICS LIQUID NITROGEN AS A NON- POLLUTING FUEL 1 INTRODUCTION: In 1997, the University of North Texas (UNT) and University of Washington (UW) independently developed liquid nitrogen powered vehicles
CRYOGENICS LIQUID NITROGEN AS A NON- POLLUTING FUEL 1 INTRODUCTION: In 1997, the University of North Texas (UNT) and University of Washington (UW) independently developed liquid nitrogen powered vehicles
Advanced Management of Compressed Air Systems Pre-Workshop Assignment
 Advanced Management of Compressed Air Systems Page 1 In order to ensure that the Compressed Air Challenge Level II Training is most useful to you, it will be important for you to bring information about
Advanced Management of Compressed Air Systems Page 1 In order to ensure that the Compressed Air Challenge Level II Training is most useful to you, it will be important for you to bring information about
Pressure Measurement
 Pressure Measurement Manometers Sensors, Transducers Ashish J. Modi Lecturer, Dept. of Mech.Engg., Shri S.V.M. inst. Of Technology, Bharuch Pressure Pressure is a force per unit area exerted by a fluid
Pressure Measurement Manometers Sensors, Transducers Ashish J. Modi Lecturer, Dept. of Mech.Engg., Shri S.V.M. inst. Of Technology, Bharuch Pressure Pressure is a force per unit area exerted by a fluid
 Hydrostatic pressure Consider a tank of fluid which contains a very thin plate of (neutrally buoyant) material with area A. This situation is shown in Figure below. If the plate is in equilibrium (it does
Hydrostatic pressure Consider a tank of fluid which contains a very thin plate of (neutrally buoyant) material with area A. This situation is shown in Figure below. If the plate is in equilibrium (it does
. In an elevator accelerating upward (A) both the elevator accelerating upward (B) the first is equations are valid
 IIT JEE Achiever 2014 Ist Year Physics-2: Worksheet-1 Date: 2014-06-26 Hydrostatics 1. A liquid can easily change its shape but a solid cannot because (A) the density of a liquid is smaller than that of
IIT JEE Achiever 2014 Ist Year Physics-2: Worksheet-1 Date: 2014-06-26 Hydrostatics 1. A liquid can easily change its shape but a solid cannot because (A) the density of a liquid is smaller than that of
An Investigation of Liquid Injection in Refrigeration Screw Compressors
 An Investigation of Liquid Injection in Refrigeration Screw Compressors Nikola Stosic, Ahmed Kovacevic and Ian K. Smith Centre for Positive Displacement Compressor Technology, City University, London EC1V
An Investigation of Liquid Injection in Refrigeration Screw Compressors Nikola Stosic, Ahmed Kovacevic and Ian K. Smith Centre for Positive Displacement Compressor Technology, City University, London EC1V
Third measurement MEASUREMENT OF PRESSURE
 1. Pressure gauges using liquids Third measurement MEASUREMENT OF PRESSURE U tube manometers are the simplest instruments to measure pressure with. In Fig.22 there can be seen three kinds of U tube manometers
1. Pressure gauges using liquids Third measurement MEASUREMENT OF PRESSURE U tube manometers are the simplest instruments to measure pressure with. In Fig.22 there can be seen three kinds of U tube manometers
Two-Stage Linear Compressor with Economizer Cycle Where Piston(s) Stroke(s) are Varied to Optimize Energy Efficiency
 Purdue University Purdue e-pubs International Compressor Engineering Conference School of Mechanical Engineering 2006 Two-Stage Linear Compressor with Economizer Cycle Where Piston(s) Stroke(s) are Varied
Purdue University Purdue e-pubs International Compressor Engineering Conference School of Mechanical Engineering 2006 Two-Stage Linear Compressor with Economizer Cycle Where Piston(s) Stroke(s) are Varied
Schedule of Requirements THERMODYNAMICS LABORATORY- CHEMICAL ENGINEERING DEPARTMENT
 S. No 1 Description Calorimeter The Unit should be designed for the accurate determination of the calorific value of liquid and solid hydrocarbons and other fuels. Specifications: A temperature-controlled
S. No 1 Description Calorimeter The Unit should be designed for the accurate determination of the calorific value of liquid and solid hydrocarbons and other fuels. Specifications: A temperature-controlled
PERFORMANCE AND CHARACTERISTICS OF COMPRESSOR/EXPANDER COMBINATION FOR CO 2 CYCLE ABSTRACT
 PERFORMANCE AND CHARACTERISTICS OF COMPRESSOR/EXPANDER COMBINATION FOR CO 2 CYCLE M. FUKUTA, T. YANAGISAWA, S. NAKAYA (b), and Y. OGI Shizuoka University, 3-5-1 Johoku Hamamatsu, 432-8561, Japan Fax +81-53-478-158,
PERFORMANCE AND CHARACTERISTICS OF COMPRESSOR/EXPANDER COMBINATION FOR CO 2 CYCLE M. FUKUTA, T. YANAGISAWA, S. NAKAYA (b), and Y. OGI Shizuoka University, 3-5-1 Johoku Hamamatsu, 432-8561, Japan Fax +81-53-478-158,
Natural Gas Gathering
 Natural Gas Gathering Course No: R04-002 Credit: 4 PDH Jim Piter, P.E. Continuing Education and Development, Inc. 9 Greyridge Farm Court Stony Point, NY 10980 P: (877) 322-5800 F: (877) 322-4774 info@cedengineering.com
Natural Gas Gathering Course No: R04-002 Credit: 4 PDH Jim Piter, P.E. Continuing Education and Development, Inc. 9 Greyridge Farm Court Stony Point, NY 10980 P: (877) 322-5800 F: (877) 322-4774 info@cedengineering.com
Simulator For Performance Prediction Of Reciprocating Compressor Considering Various Losses
 Simulator For Performance Prediction Of Reciprocating Considering Various Losses Aditya S. Bawane 1, Dr. V.K. Bhojwani 2, Mitali B. Deshmukh 3 1 (Mechanical Engineering Department, JSCOE, S.P. Pune University,
Simulator For Performance Prediction Of Reciprocating Considering Various Losses Aditya S. Bawane 1, Dr. V.K. Bhojwani 2, Mitali B. Deshmukh 3 1 (Mechanical Engineering Department, JSCOE, S.P. Pune University,
Vibration-Free Joule-Thomson Cryocoolers for Distributed Microcooling
 Vibration-Free Joule-Thomson Cryocoolers for Distributed Microcooling W. Chen, M. Zagarola Creare Inc. Hanover, NH, USA ABSTRACT This paper reports on an innovative concept for a space-borne Joule-Thomson
Vibration-Free Joule-Thomson Cryocoolers for Distributed Microcooling W. Chen, M. Zagarola Creare Inc. Hanover, NH, USA ABSTRACT This paper reports on an innovative concept for a space-borne Joule-Thomson
Properties of Fluids SPH4C
 Properties of Fluids SPH4C Fluids Liquids and gases are both fluids: a fluid is any substance that flows and takes the shape of its container. Fluids Liquids and gases are both fluids: a fluid is any substance
Properties of Fluids SPH4C Fluids Liquids and gases are both fluids: a fluid is any substance that flows and takes the shape of its container. Fluids Liquids and gases are both fluids: a fluid is any substance
Old-Exam.Questions-Ch-14 T072 T071
 Old-Exam.Questions-Ch-14 T072 Q23. Water is pumped out of a swimming pool at a speed of 5.0 m/s through a uniform hose of radius 1.0 cm. Find the mass of water pumped out of the pool in one minute. (Density
Old-Exam.Questions-Ch-14 T072 Q23. Water is pumped out of a swimming pool at a speed of 5.0 m/s through a uniform hose of radius 1.0 cm. Find the mass of water pumped out of the pool in one minute. (Density
A B isothermal compression at a temperature of 300 K. The work done on the air is 104 J.
 Q1. In an ideal hot air engine, a fixed mass of air is continuously taken through the following four processes: A B isothermal compression at a temperature of 300 K. The work done on the air is 104 J.
Q1. In an ideal hot air engine, a fixed mass of air is continuously taken through the following four processes: A B isothermal compression at a temperature of 300 K. The work done on the air is 104 J.
Chapter 3 Atmospheric Thermodynamics
 Chapter 3 Atmospheric Thermodynamics Spring 2017 Partial Pressure and Dalton Dalton's law of partial pressure: total pressure exerted by a mixture of gases which do not interact chemically is equal to
Chapter 3 Atmospheric Thermodynamics Spring 2017 Partial Pressure and Dalton Dalton's law of partial pressure: total pressure exerted by a mixture of gases which do not interact chemically is equal to
CVEN 311 Fluid Dynamics Fall Semester 2011 Dr. Kelly Brumbelow, Texas A&M University. Final Exam
 CVEN 311 Fluid Dynamics Fall Semester 2011 Dr. Kelly Brumbelow, Texas A&M University Final Exam 8 pages, front & back, not including reference sheets; 21 questions An excerpt from the NCEES Fundamentals
CVEN 311 Fluid Dynamics Fall Semester 2011 Dr. Kelly Brumbelow, Texas A&M University Final Exam 8 pages, front & back, not including reference sheets; 21 questions An excerpt from the NCEES Fundamentals
S.A. Klein and G.F. Nellis Cambridge University Press, 2011
 16-1 A flow nozzle is to be used to determine the mass flow rate of air through a 1.5 inch internal diameter pipe. The air in the line upstream of the meters is at 70 F and 95 psig. The barometric pressure
16-1 A flow nozzle is to be used to determine the mass flow rate of air through a 1.5 inch internal diameter pipe. The air in the line upstream of the meters is at 70 F and 95 psig. The barometric pressure
CHAPTER 31 IDEAL GAS LAWS
 CHAPTER 31 IDEAL GAS LAWS EXERCISE 144, Page 317 1. The pressure of a mass of gas is increased from 150 kpa to 750 kpa at constant temperature. Determine the final volume of the gas, if its initial volume
CHAPTER 31 IDEAL GAS LAWS EXERCISE 144, Page 317 1. The pressure of a mass of gas is increased from 150 kpa to 750 kpa at constant temperature. Determine the final volume of the gas, if its initial volume
Quick Reference Technical Data
 Bulletin 127C 2 Quick Reference Technical Data For over 100 years, The Spencer Turbine Company has specialized in innovative solutions to air and gas handling problems. Spencer's product line includes
Bulletin 127C 2 Quick Reference Technical Data For over 100 years, The Spencer Turbine Company has specialized in innovative solutions to air and gas handling problems. Spencer's product line includes
Selection of gas compressors: part 2
 36 Compressors Selection of gas compressors: part 2 In this multipart series, Eduardo Larralde and Rafael Ocampo aim to provide a comprehensive survey of the current state of the art concerning gas Following
36 Compressors Selection of gas compressors: part 2 In this multipart series, Eduardo Larralde and Rafael Ocampo aim to provide a comprehensive survey of the current state of the art concerning gas Following
A Numerical Simulation of Fluid-Structure Interaction for Refrigerator Compressors Suction and Exhaust System Performance Analysis
 1131, Page 1 A Numerical Simulation of Fluid-Structure Interaction for Refrigerator Compressors Suction and Exhaust System Performance Analysis Shoufei Wu*, Zonghuai Wang Jiaxipera Compressor Co., Ltd.,
1131, Page 1 A Numerical Simulation of Fluid-Structure Interaction for Refrigerator Compressors Suction and Exhaust System Performance Analysis Shoufei Wu*, Zonghuai Wang Jiaxipera Compressor Co., Ltd.,
Figure 1 Schematic of opposing air bearing concept
 Theoretical Analysis of Opposing Air Bearing Concept This concept utilizes air bearings to constrain five degrees of freedom of the optic as shown in the figure below. Three pairs of inherently compensated
Theoretical Analysis of Opposing Air Bearing Concept This concept utilizes air bearings to constrain five degrees of freedom of the optic as shown in the figure below. Three pairs of inherently compensated
HANDBOOK SAFETY DEVICES. Ed SAFETY DEVICES DS-ED 01/ ENG 1
 HANDBOOK Ed. 2017 1 CHAPTER 5 SELECTION CRITERIA FOR SAFETY VALVES CALCULATION OF THE DISCHARGE CAPACITY (Ref. EN 13136:2013) The evaluation of the minimum required discharge capacity of safety valves
HANDBOOK Ed. 2017 1 CHAPTER 5 SELECTION CRITERIA FOR SAFETY VALVES CALCULATION OF THE DISCHARGE CAPACITY (Ref. EN 13136:2013) The evaluation of the minimum required discharge capacity of safety valves
ME 200 Thermodynamics I Spring 2010 (Last) (First) Thermo Number: CIRCLE YOUR LECTURE BELOW
 ME 200 Thermodynamics I Name: Spring 2010 Thermo Number: CIRCLE YOUR LECTURE BELOW Div. 1 8:30 am Div. 2 10:30 am Div. 3 12:30 pm Naik Tree Clark Div. 4 1:30 pm Kim Div. 5 3:30 pm Mathison EXAM 2 INSTRUCTIONS
ME 200 Thermodynamics I Name: Spring 2010 Thermo Number: CIRCLE YOUR LECTURE BELOW Div. 1 8:30 am Div. 2 10:30 am Div. 3 12:30 pm Naik Tree Clark Div. 4 1:30 pm Kim Div. 5 3:30 pm Mathison EXAM 2 INSTRUCTIONS
Offshore Equipment. Yutaek Seo
 Offshore Equipment Yutaek Seo Flash Gas Compressor (East spar) Dehydration NGL recovery Slug catcher Separator Stabilization Booster compressor Gas export compression (Donghae-1 Platform) May 7 th Gas
Offshore Equipment Yutaek Seo Flash Gas Compressor (East spar) Dehydration NGL recovery Slug catcher Separator Stabilization Booster compressor Gas export compression (Donghae-1 Platform) May 7 th Gas
IRC 2011 All Rights Reserved
 1 2 3 The enthalpy of saturated vapor and the enthalpy of saturated liquid is evaluated at the fully accumulated relief device set pressure (P=P set * 1.1 + 14.7). Set Pressure (psig) h fg (Btu/lbm) 150
1 2 3 The enthalpy of saturated vapor and the enthalpy of saturated liquid is evaluated at the fully accumulated relief device set pressure (P=P set * 1.1 + 14.7). Set Pressure (psig) h fg (Btu/lbm) 150
The water supply for a hydroelectric plant is a reservoir with a large surface area. An outlet pipe takes the water to a turbine.
 Fluids 1a. [1 mark] The water supply for a hydroelectric plant is a reservoir with a large surface area. An outlet pipe takes the water to a turbine. State the difference in terms of the velocity of the
Fluids 1a. [1 mark] The water supply for a hydroelectric plant is a reservoir with a large surface area. An outlet pipe takes the water to a turbine. State the difference in terms of the velocity of the
Chapter 4, Problem 30.
 Chapter 4, Problem 30. A well-insulated rigid tank contains 5 kg of a saturated liquid vapor mixture of water at l00 kpa. Initially, three-quarters of the mass is in the liquid phase. An electric resistor
Chapter 4, Problem 30. A well-insulated rigid tank contains 5 kg of a saturated liquid vapor mixture of water at l00 kpa. Initially, three-quarters of the mass is in the liquid phase. An electric resistor
University of Cincinnati
 Mapping the Design Space of a Recuperated, Recompression, Precompression Supercritical Carbon Dioxide Power Cycle with Intercooling, Improved Regeneration, and Reheat Andrew Schroder Mark Turner University
Mapping the Design Space of a Recuperated, Recompression, Precompression Supercritical Carbon Dioxide Power Cycle with Intercooling, Improved Regeneration, and Reheat Andrew Schroder Mark Turner University
AP Physics B Ch 10 Fluids. MULTIPLE CHOICE. Choose the one alternative that best completes the statement or answers the question.
 Name: Period: Date: AP Physics B Ch 10 Fluids 1) The three common phases of matter are A) solid, liquid, and vapor. B) solid, plasma, and gas. C) condensate, plasma, and gas. D) solid, liquid, and gas.
Name: Period: Date: AP Physics B Ch 10 Fluids 1) The three common phases of matter are A) solid, liquid, and vapor. B) solid, plasma, and gas. C) condensate, plasma, and gas. D) solid, liquid, and gas.
INDIAN INSTITUTE OF TECHNOLOGY ROORKEE NPTEL NPTEL ONLINE CERTIFICATION COURSE. Refrigeration and Air-conditioning
 INDIAN INSTITUTE OF TECHNOLOGY ROORKEE NPTEL NPTEL ONLINE CERTIFICATION COURSE Refrigeration and Air-conditioning Lecture-07 Vapour Compression Cycle-1 with Prof. Ravi Kumar Department of Mechanical and
INDIAN INSTITUTE OF TECHNOLOGY ROORKEE NPTEL NPTEL ONLINE CERTIFICATION COURSE Refrigeration and Air-conditioning Lecture-07 Vapour Compression Cycle-1 with Prof. Ravi Kumar Department of Mechanical and
Chapter 13 Fluids. Copyright 2009 Pearson Education, Inc.
 Chapter 13 Fluids Phases of Matter Density and Specific Gravity Pressure in Fluids Atmospheric Pressure and Gauge Pressure Pascal s Principle Units of Chapter 13 Measurement of Pressure; Gauges and the
Chapter 13 Fluids Phases of Matter Density and Specific Gravity Pressure in Fluids Atmospheric Pressure and Gauge Pressure Pascal s Principle Units of Chapter 13 Measurement of Pressure; Gauges and the
COURSE NUMBER: ME 321 Fluid Mechanics I Fluid statics. Course teacher Dr. M. Mahbubur Razzaque Professor Department of Mechanical Engineering BUET
 COURSE NUMBER: ME 321 Fluid Mechanics I Fluid statics Course teacher Dr. M. Mahbubur Razzaque Professor Department of Mechanical Engineering BUET 1 Fluid statics Fluid statics is the study of fluids in
COURSE NUMBER: ME 321 Fluid Mechanics I Fluid statics Course teacher Dr. M. Mahbubur Razzaque Professor Department of Mechanical Engineering BUET 1 Fluid statics Fluid statics is the study of fluids in
MATHEMATICAL MODELING OF PERFORMANCE OF A LIQUD PISTON COMPRESSOR
 9. Pompa Vana Kompressör Kongresi 5-7 Mayıs 2016, İstanbul MATHEMATICAL MODELING OF PERFORMANCE OF A LIQUD PISTON COMPRESSOR Süleyman Doğan Öner Email: oner@ug.bilkent.edu.tr İbrahim Nasuh Yıldıran Email:
9. Pompa Vana Kompressör Kongresi 5-7 Mayıs 2016, İstanbul MATHEMATICAL MODELING OF PERFORMANCE OF A LIQUD PISTON COMPRESSOR Süleyman Doğan Öner Email: oner@ug.bilkent.edu.tr İbrahim Nasuh Yıldıran Email:
Chapter 13 Fluids. Copyright 2009 Pearson Education, Inc.
 Chapter 13 Fluids Phases of Matter Density and Specific Gravity Pressure in Fluids Atmospheric Pressure and Gauge Pressure Pascal s Principle Units of Chapter 13 Measurement of Pressure; Gauges and the
Chapter 13 Fluids Phases of Matter Density and Specific Gravity Pressure in Fluids Atmospheric Pressure and Gauge Pressure Pascal s Principle Units of Chapter 13 Measurement of Pressure; Gauges and the
Unit A-2: List of Subjects
 ES312 Energy Transfer Fundamentals Unit A: Fundamental Concepts ROAD MAP... A-1: Introduction to Thermodynamics A-2: Engineering Properties Unit A-2: List of Subjects Basic Properties and Temperature Pressure
ES312 Energy Transfer Fundamentals Unit A: Fundamental Concepts ROAD MAP... A-1: Introduction to Thermodynamics A-2: Engineering Properties Unit A-2: List of Subjects Basic Properties and Temperature Pressure
CHAPTER 3 AUTOMOTIVE AIR COMPRESSOR
 30 CHAPTER 3 AUTOMOTIVE AIR COMPRESSOR 3.1 INTRODUCTION A machine providing air at a high pressure is called as an air compressor. Air compressors have been used in industry for well over 100 years because
30 CHAPTER 3 AUTOMOTIVE AIR COMPRESSOR 3.1 INTRODUCTION A machine providing air at a high pressure is called as an air compressor. Air compressors have been used in industry for well over 100 years because
Another convenient term is gauge pressure, which is a pressure measured above barometric pressure.
 VACUUM Theory and Applications Vacuum may be defined as the complete emptiness of a given volume. It is impossible to obtain a perfect vacuum, but it is possible to obtain a level of vacuum, defined as
VACUUM Theory and Applications Vacuum may be defined as the complete emptiness of a given volume. It is impossible to obtain a perfect vacuum, but it is possible to obtain a level of vacuum, defined as
Middle East Technical University Department of Mechanical Engineering ME 305 Fluid Mechanics I Fall 2018 Section 4 (Dr.
 Middle East Technical University Department of Mechanical Engineering ME 305 Fluid Mechanics I Fall 2018 Section 4 (Dr. Sert) Study Set 2 Reading Assignments You can find the answers of some of the following
Middle East Technical University Department of Mechanical Engineering ME 305 Fluid Mechanics I Fall 2018 Section 4 (Dr. Sert) Study Set 2 Reading Assignments You can find the answers of some of the following
GAS MIXTURES. Department of Mechanical Engineering
 Chapter 13 GAS MIXTURES Dr Ali Jawarneh Department of Mechanical Engineering Hashemite University it 2 Objectives Develop rules for determining nonreacting gas mixture properties from knowledge of mixture
Chapter 13 GAS MIXTURES Dr Ali Jawarneh Department of Mechanical Engineering Hashemite University it 2 Objectives Develop rules for determining nonreacting gas mixture properties from knowledge of mixture
University of Cincinnati
 Mapping the Design Space of a Recuperated, Recompression, Precompression Supercritical Carbon Dioxide Power Cycle with Intercooling, Improved Regeneration, and Reheat Andrew Schroder Mark Turner University
Mapping the Design Space of a Recuperated, Recompression, Precompression Supercritical Carbon Dioxide Power Cycle with Intercooling, Improved Regeneration, and Reheat Andrew Schroder Mark Turner University
THE COMPARISON OF THEORETICAL TO PRACTICAL CARGO LOADING RATE OF BUTANE - ANALYSIS OF LPG CARRIER RELIQUEFACTION PLANT
 Journal of KONES Powertrain and Transport, Vol. 20, No. 1 2013 THE COMPARISON OF THEORETICAL TO PRACTICAL CARGO LOADING RATE OF BUTANE - ANALYSIS OF LPG CARRIER RELIQUEFACTION PLANT Dariusz Nanowski Gdynia
Journal of KONES Powertrain and Transport, Vol. 20, No. 1 2013 THE COMPARISON OF THEORETICAL TO PRACTICAL CARGO LOADING RATE OF BUTANE - ANALYSIS OF LPG CARRIER RELIQUEFACTION PLANT Dariusz Nanowski Gdynia
Pump Selection and Sizing (ENGINEERING DESIGN GUIDELINE)
 Guidelines for Processing Plant Page : 1 of 64 Feb 2007 (ENGINEERING DESIGN GUIDELINE) Author: A L Ling Checked by: Karl Kolmetz TABLE OF CONTENT INTRODUCTION Scope 5 General Design Consideration Type
Guidelines for Processing Plant Page : 1 of 64 Feb 2007 (ENGINEERING DESIGN GUIDELINE) Author: A L Ling Checked by: Karl Kolmetz TABLE OF CONTENT INTRODUCTION Scope 5 General Design Consideration Type
PHYSICS - CLUTCH CH 17: FLUID MECHANICS.
 !! www.clutchprep.com INTRO TO DENSITY LIQUIDS and GASES are types of. So we use the term to refer generally to both Liquids AND Gases. The DENSITY of a material is a measure of how tight the molecules
!! www.clutchprep.com INTRO TO DENSITY LIQUIDS and GASES are types of. So we use the term to refer generally to both Liquids AND Gases. The DENSITY of a material is a measure of how tight the molecules
Write important assumptions used in derivation of Bernoulli s equation. Apart from an airplane wing, give an example based on Bernoulli s principle
 HW#3 Sum07 #1. Answer in 4 to 5 lines in the space provided for each question: (a) A tank partially filled with water has a balloon well below the free surface and anchored to the bottom by a string. The
HW#3 Sum07 #1. Answer in 4 to 5 lines in the space provided for each question: (a) A tank partially filled with water has a balloon well below the free surface and anchored to the bottom by a string. The
Single- or Two-Stage Compression
 The following article was published in ASHRAE Journal, August 2008. Copyright 2008 American Society of Heating, Refrigerating and Air- Conditioning Engineers, Inc. It is presented for educational purposes
The following article was published in ASHRAE Journal, August 2008. Copyright 2008 American Society of Heating, Refrigerating and Air- Conditioning Engineers, Inc. It is presented for educational purposes
Lecture 26 HYDRAULIC CIRCUIT DESIGN AND ANALYSIS
 Lecture 6 HYDRAULIC CIRCUIT DESIGN AND ANALYSIS Example 1.14 Design a car crushing system. The crushing force required is such that a 15 cm diameter cylinder is required at a working pressure of 16.5 kg/cm.
Lecture 6 HYDRAULIC CIRCUIT DESIGN AND ANALYSIS Example 1.14 Design a car crushing system. The crushing force required is such that a 15 cm diameter cylinder is required at a working pressure of 16.5 kg/cm.
PTRT 2470: Petroleum Data Management 3 - Facilities Test 4 (Spring 2017)
 Use scantron to answer all questions PTRT 2470: Petroleum Data Management 3 - Facilities Test 4 (Spring 2017) 1. The term dehydration of natural gas means A. addition of water vapor B. removal of water
Use scantron to answer all questions PTRT 2470: Petroleum Data Management 3 - Facilities Test 4 (Spring 2017) 1. The term dehydration of natural gas means A. addition of water vapor B. removal of water
SELECTION CRITERIA FOR SAFETY VALVE
 mdmdmdpag 1 di 17 SELECTION CRITERIA FOR SAFETY VALVE CALCULATION OF THE DISCHARGE CAPACITY (Ref. EN 13136:2013) The calculation of the minimum discharge capacity is linked to the system configuration
mdmdmdpag 1 di 17 SELECTION CRITERIA FOR SAFETY VALVE CALCULATION OF THE DISCHARGE CAPACITY (Ref. EN 13136:2013) The calculation of the minimum discharge capacity is linked to the system configuration
Tutorial. BOSfluids. Relief valve
 Tutorial Relief valve The Relief valve tutorial describes the theory and modeling process of a pressure relief valve or safety valve. It covers the algorithm BOSfluids uses to model the valve and a worked
Tutorial Relief valve The Relief valve tutorial describes the theory and modeling process of a pressure relief valve or safety valve. It covers the algorithm BOSfluids uses to model the valve and a worked
Correction of Pressure Drop in Steam and Water System in Performance Test of Boiler
 IOP Conference Series: Earth and Environmental Science PAPER OPEN ACCESS Correction of Pressure Drop in Steam and Water System in Performance Test of Boiler To cite this article: Jinglong Liu et al 2018
IOP Conference Series: Earth and Environmental Science PAPER OPEN ACCESS Correction of Pressure Drop in Steam and Water System in Performance Test of Boiler To cite this article: Jinglong Liu et al 2018
POLISH MARITIME RESEARCH 4(80) 2013 Vol 20; pp /pomr
 POLISH MARITIME RESEARCH 4(80) 2013 Vol 20; pp. 25-33 10.2478/pomr-2013-0037 The influence of efficiency of the cooling system on the thermodynamic parameters and performance of a two - stage VC 20.96
POLISH MARITIME RESEARCH 4(80) 2013 Vol 20; pp. 25-33 10.2478/pomr-2013-0037 The influence of efficiency of the cooling system on the thermodynamic parameters and performance of a two - stage VC 20.96
SAMSON SOLUTIONS Energy and Power (Critical Applications)
 SAMSON SOLUTIONS Energy and Power (Critical Applications) Speakers: Ing. Gianluigi Rossi Ing. Stefano Salvadori Managing Director - SAMSON Italy Head of Sales and Project Department - SAMSON Italy MARKET
SAMSON SOLUTIONS Energy and Power (Critical Applications) Speakers: Ing. Gianluigi Rossi Ing. Stefano Salvadori Managing Director - SAMSON Italy Head of Sales and Project Department - SAMSON Italy MARKET
TESTING AND ANALYZING ON P-V DIAGRAM OF CO 2 ROLLING PISTON EXPANDER
 TESTING AND ANALYZING ON P-V DIAGRAM OF CO 2 ROLLING PISTON EXPANDER ICR07-B2-431 Xianyang ZENG, Yitai MA, Shengchun LIU, Hongli WANG Thermal Energy Research Institute, Tianjin University, Tianjin, 300072,
TESTING AND ANALYZING ON P-V DIAGRAM OF CO 2 ROLLING PISTON EXPANDER ICR07-B2-431 Xianyang ZENG, Yitai MA, Shengchun LIU, Hongli WANG Thermal Energy Research Institute, Tianjin University, Tianjin, 300072,
Basics of Low-temperature Refrigeration
 Published by CERN in the Proceedings of the CAS-CERN Accelerator School: Superconductivity for Accelerators, Erice, Italy, 24 April 4 May 203, edited by R. Bailey, CERN 204 005 (CERN, Geneva, 204) Basics
Published by CERN in the Proceedings of the CAS-CERN Accelerator School: Superconductivity for Accelerators, Erice, Italy, 24 April 4 May 203, edited by R. Bailey, CERN 204 005 (CERN, Geneva, 204) Basics
3. A fluid is forced through a pipe of changing cross section as shown. In which section would the pressure of the fluid be a minimum?
 AP Physics Multiple Choice Practice Fluid Mechanics 1. A cork has weight mg and density 5% of water s density. A string is tied around the cork and attached to the bottom of a water-filled container. The
AP Physics Multiple Choice Practice Fluid Mechanics 1. A cork has weight mg and density 5% of water s density. A string is tied around the cork and attached to the bottom of a water-filled container. The
CHAPTER 3 : AIR COMPRESSOR
 CHAPTER 3 : AIR COMPRESSOR Robotic & Automation Department FACULTY OF MANUFACTURING ENGINEERING, UTeM Learning Objectives Identify types of compressors available Calculate air capacity rating of compressor
CHAPTER 3 : AIR COMPRESSOR Robotic & Automation Department FACULTY OF MANUFACTURING ENGINEERING, UTeM Learning Objectives Identify types of compressors available Calculate air capacity rating of compressor
hydro-pac, inc. Low-Pressure Gas Compressors 1500 to 6000 PSI
 hydro-pac, inc. LX-SERIES Low-Pressure Gas Compressors 1500 to 6000 PSI hydro-pac, inc. LX-SERIES Features Hydro-Pac LX-SERIES Gas Compressors feature: Oil-free non lubricated gas pistons and cylinders
hydro-pac, inc. LX-SERIES Low-Pressure Gas Compressors 1500 to 6000 PSI hydro-pac, inc. LX-SERIES Features Hydro-Pac LX-SERIES Gas Compressors feature: Oil-free non lubricated gas pistons and cylinders
Assumptions 1 At specified conditions, air behaves as an ideal gas. 2 The volume of the tire remains constant.
 PTT 04/ Applied Fluid Mechanics Sem, Session015/016 ASSIGNMENT 1 CHAPTER AND CHAPTER 1. The air in an automobile tire with a volume of 0.0740 m is at 0 C and 140 kpa. Determine the amount of air that must
PTT 04/ Applied Fluid Mechanics Sem, Session015/016 ASSIGNMENT 1 CHAPTER AND CHAPTER 1. The air in an automobile tire with a volume of 0.0740 m is at 0 C and 140 kpa. Determine the amount of air that must
LECTURE 20 FLOW CONTROL VAVLES SELF EVALUATION QUESTIONS AND ANSWERS
 LECTURE 20 FLOW CONTROL VAVLES SELF EVALUATION QUESTIONS AND ANSWERS 1: A cylinder has to exert a forward thrust of 150 kn and a reverse thrust of 15 kn. The effects of using various methods of regulating
LECTURE 20 FLOW CONTROL VAVLES SELF EVALUATION QUESTIONS AND ANSWERS 1: A cylinder has to exert a forward thrust of 150 kn and a reverse thrust of 15 kn. The effects of using various methods of regulating
Investigation to Improve Efficiency of Transcritical R744 Two-Stage Vapor Compression Systems
 Purdue University Purdue e-pubs International efrigeration and Air Conditioning Conference School of Mechanical Engineering 2008 Investigation to Improve Efficiency of Transcritical 744 Two-Stage Vapor
Purdue University Purdue e-pubs International efrigeration and Air Conditioning Conference School of Mechanical Engineering 2008 Investigation to Improve Efficiency of Transcritical 744 Two-Stage Vapor
Influencing Factors Study of the Variable Speed Scroll Compressor with EVI Technology
 Purdue University Purdue e-pubs International Compressor Engineering Conference School of Mechanical Engineering 2016 Influencing Factors Study of the Variable Speed Scroll Compressor with EVI Technology
Purdue University Purdue e-pubs International Compressor Engineering Conference School of Mechanical Engineering 2016 Influencing Factors Study of the Variable Speed Scroll Compressor with EVI Technology
Concept of Fluid. Density. Pressure: Pressure in a Fluid. Pascal s principle. Buoyancy. Archimede s Principle. Forces on submerged surfaces
 FLUID MECHANICS The fluid essential to all life has a beauty of its own. It also helps support the weight of this swimmer. (credit: Terren, Wikimedia Commons) Concept of Fluid Density Pressure: Pressure
FLUID MECHANICS The fluid essential to all life has a beauty of its own. It also helps support the weight of this swimmer. (credit: Terren, Wikimedia Commons) Concept of Fluid Density Pressure: Pressure
1.2 Example 1: A simple hydraulic system
 Note: It is possible to use more than one fluid in the Hydraulic library. This is important because you can model combined cooling and lubrication systems of a library. The hydraulic library assumes a
Note: It is possible to use more than one fluid in the Hydraulic library. This is important because you can model combined cooling and lubrication systems of a library. The hydraulic library assumes a
γ water = 62.4 lb/ft 3 = 9800 N/m 3
 CEE 4 Aut 004, Exam # Work alone. Answer all questions. Total pts: 90. Always make your thought process clear; if it is not, you will not receive partial credit for incomplete or partially incorrect answers.
CEE 4 Aut 004, Exam # Work alone. Answer all questions. Total pts: 90. Always make your thought process clear; if it is not, you will not receive partial credit for incomplete or partially incorrect answers.
Water in the Atmosphere
 Water in the Atmosphere Chapter 24 Solid to Liquid The process of changing state, such as melting ice, requires that energy be transferred in the form of heat. Latent heat is the energy absorbed or released
Water in the Atmosphere Chapter 24 Solid to Liquid The process of changing state, such as melting ice, requires that energy be transferred in the form of heat. Latent heat is the energy absorbed or released
