[2] Explain how the alveoli create a surface for efficient gaseous exchange
|
|
|
- Blake Anderson
- 5 years ago
- Views:
Transcription
1 1 (a) (i) Name the two types of epithelial tissue found in the lungs and airways.... [2] (ii) The epithelial cells in the lungs are arranged into structures called alveoli. Explain how the alveoli create a surface for efficient gaseous exchange. In your answer you should use appropriate technical terms, spelled correctly.... [5] (b) To improve gaseous exchange, the air in the alveoli is refreshed by ventilation. The air movement created by ventilation can be recorded using suitable apparatus. (i) Name the apparatus used to record these air movements.... [1]
2 Fig. 3.1 shows a trace recorded from this apparatus volume of air in air chamber (dm 3 ) time (s) Fig. 3.1 (ii) Calculate the rate of breathing over the first minute from the trace. answer =... breaths per minute [1] (iii) Using the trace, calculate the rate of oxygen consumption over the first minute. Show your working. answer =... dm 3 min 1 [2] [Total: 11]
3 2 Many teachers use models to demonstrate and explain breathing and lung function in mammals. Fig. 2.1 is a model of the mammalian chest. glass tube rubber bung glass bell jar balloons flexible rubber sheet secured to the sides of the bell jar Fig. 2.1 (a) When the rubber sheet is pulled down the balloons expand. Explain why the balloons expand [3]
4 (b) A teacher used the model in Fig. 2.1 to demonstrate the difference between tidal volume and vital capacity. (i) Explain the meaning of the term tidal volume.... [2] (ii) Suggest how the teacher may have used the model to demonstrate tidal volume.... [2] (iii) Explain the meaning of the term vital capacity.... [2] (iv) Suggest how the teacher may have used the model to demonstrate vital capacity.... [1] [Total: 10]
5 3 In an experiment to measure the rate of diffusion, a student placed cubes of agar jelly containing an indicator into dilute hydrochloric acid. The indicator changes from pink to colourless in acidic conditions. The student used cubes of different sizes and recorded the time taken for the pink colour of each cube to disappear completely. The student s results are recorded in Table 2.1. Length of side of cube (mm) Surface area of cube (mm 2 ) Volume of cube (mm 3 ) Surface area to volume ratio Time taken for pink colour to disappear (s) Rate of diffusion (mm s 1 ) : : : : Table 2.1 (a) (i) Calculate the surface area to volume ratio of the cube with 10 mm sides. Show your working. Answer =... [2] (ii) Using the data in Table 2.1, describe the relationship between the rate of diffusion and the surface area to volume ratio.... [2]
6 (iii) Explain the significance of the relationship between rate of diffusion and the surface area to volume ratio for large plants.... [2] (b) Another student used the same raw data obtained in the experiment but calculated a different rate of diffusion for each cube. This student s results are shown in Table 2.2. Length of side of cube (mm) Time taken for pink colour to disappear (s) Rate of diffusion (mm s 1 ) Table 2.2 In this student s table, the calculation of the rate of diffusion is incorrect. (i) Suggest the method used to calculate the rate of diffusion in Table [1] (ii) State why the method in (b)(i) is not correct.... [1]
7 (c) In mammals, the lungs are adapted to enable efficient gaseous exchange. The table below lists some of the adaptations of the lungs. Complete the table explaining how each adaptation improves efficiency of gaseous exchange. Adaptation How this adaptation improves efficiency of gaseous exchange squamous epithelium large number of alveoli good blood supply good ventilation [4] [Total: 12]
8 4 (a) List three reasons why a large, multicellular animal, such as a mammal, needs a transport system [3] Fig. 1.1, on the insert, shows the nervous pathways that coordinate heart action. Above the diagram is a trace showing the electrical activity associated with one heart beat. (b) (i) State the full name given to a trace showing the electrical activity of the heart.... [1] (ii) Identify the components of the heart labelled A and B on Fig A... B... [2] (c) (i) During the electrical stimulation of the heart, there is a short delay between the excitation of the atria and excitation of the ventricles. Explain why this delay is essential.... [2]
9 (ii) The Purkyne tissue carries the excitation wave down the septum to the apex of the heart. Explain why the excitation wave is carried to the apex.... [2] [Total: 10]
10 5 Fig. 5.1 shows the changes in the volume of air in the lungs of a student at rest during one breath B volume of air (dm 3 ) A X C time (s) Fig. 5.1 (a) (i) Name the measurement represented by the line X.... [1] (ii) What is happening to the elastic fibres in the walls of the alveoli at point A?... [1]
11 (b) Explain what causes the change in the volume of air between points B and C on Fig In your answer you should use appropriate technical terms, spelt correctly [4] (c) Using Fig. 5.1, calculate the breathing rate of this student in breaths per minute. Answer =... breaths per minute [2] (d) About 1 dm 3 of air cannot be expelled from the lungs. This is known as the residual volume. Suggest why it is not possible to expel all the air from the lungs [2] [Total: 10]
(a) (i) Describe how a large difference in oxygen concentration is maintained between a fish gill and the surrounding water.
 1. Answers should be written in continuous prose. Credit will be given for biological accuracy, the organisation and presentation of information and the way in which an answer is expressed. Fick s law
1. Answers should be written in continuous prose. Credit will be given for biological accuracy, the organisation and presentation of information and the way in which an answer is expressed. Fick s law
GASEOUS EXCHANGE 17 JULY 2013
 GASEOUS EXCHANGE 17 JULY 2013 Lesson Description In this lesson we: Discuss what is gaseous exchange? Consider requirements of an efficient gaseous exchange surface. Look at diversity in gas exchange systems.
GASEOUS EXCHANGE 17 JULY 2013 Lesson Description In this lesson we: Discuss what is gaseous exchange? Consider requirements of an efficient gaseous exchange surface. Look at diversity in gas exchange systems.
practices makes perfect
 Human Respiratory system Chapter 1: Respiration PMR 03, 08 1. The human respiratory system consists of: a... b... c.. d... e. Our body has.. lungs (right & left). f. Each lung consists of the, and alveoli.
Human Respiratory system Chapter 1: Respiration PMR 03, 08 1. The human respiratory system consists of: a... b... c.. d... e. Our body has.. lungs (right & left). f. Each lung consists of the, and alveoli.
Directions: The following two questions refer to the diagram below, which shows a group of cells from the respiratory tract.
 Topic 7 Gas exchange in humans Directions: The following two questions refer to the diagram below, which shows a group of cells from the respiratory tract. X Y 1. What is the function of structure X? A.
Topic 7 Gas exchange in humans Directions: The following two questions refer to the diagram below, which shows a group of cells from the respiratory tract. X Y 1. What is the function of structure X? A.
Department of Biology Work Sheet Respiratory system,9 class
 I. Name the following : Department of Biology Work Sheet Respiratory system,9 class 1. A muscular sheet separating the thoracic and abdominal cavities. 2. A respiratory tube supported by cartilaginous
I. Name the following : Department of Biology Work Sheet Respiratory system,9 class 1. A muscular sheet separating the thoracic and abdominal cavities. 2. A respiratory tube supported by cartilaginous
It is a product of proteins broken down in the mammal. It is exchanged for oxygen which is taken into the blood.
 5 The table shows the approximate composition of air breathed out by a mammal. Where does the nitrogen in the air breathed out come from? It is a product of proteins broken down in the mammal. It is a
5 The table shows the approximate composition of air breathed out by a mammal. Where does the nitrogen in the air breathed out come from? It is a product of proteins broken down in the mammal. It is a
1.2 The structure and functions of the cardio-respiratory system Learning objectives
 1.2 The structure and functions of the cardio-respiratory system Learning objectives To understand the functions of the circulatory system. To be able to identify the differences between veins, arteries
1.2 The structure and functions of the cardio-respiratory system Learning objectives To understand the functions of the circulatory system. To be able to identify the differences between veins, arteries
Respiratory Physiology Gaseous Exchange
 Respiratory Physiology Gaseous Exchange Session Objectives. What you will cover Basic anatomy of the lung including airways Breathing movements Lung volumes and capacities Compliance and Resistance in
Respiratory Physiology Gaseous Exchange Session Objectives. What you will cover Basic anatomy of the lung including airways Breathing movements Lung volumes and capacities Compliance and Resistance in
Multicellular Organisms. Sub-Topic 2.7 Animal Transport & Exchange Systems
 Multicellular Organisms Sub-Topic 2.7 Animal Transport & Exchange Systems On completion of this sub-topic I will be able to state that: Rings of cartilage keep the main airways open Oxygen and carbon dioxide
Multicellular Organisms Sub-Topic 2.7 Animal Transport & Exchange Systems On completion of this sub-topic I will be able to state that: Rings of cartilage keep the main airways open Oxygen and carbon dioxide
Glucose + Oxygen Carbon Dioxide + Water + Energy C6H12O CO2 + 6H20 + energy
 Cell Respiration - A food oxidization process in body cells to produce energy - Occurs (happens) in animal cells and plant cells Notes : Metabolic Reactions in Gaseous Exchange CELL RESPIRATION Photosynthesis
Cell Respiration - A food oxidization process in body cells to produce energy - Occurs (happens) in animal cells and plant cells Notes : Metabolic Reactions in Gaseous Exchange CELL RESPIRATION Photosynthesis
CHAPTER 3: The cardio-respiratory system
 : The cardio-respiratory system Exam style questions - text book pages 44-45 1) Describe the structures involved in gaseous exchange in the lungs and explain how gaseous exchange occurs within this tissue.
: The cardio-respiratory system Exam style questions - text book pages 44-45 1) Describe the structures involved in gaseous exchange in the lungs and explain how gaseous exchange occurs within this tissue.
CHAPTER 3: The respiratory system
 CHAPTER 3: The respiratory system Practice questions - text book pages 56-58 1) When the inspiratory muscles contract, which one of the following statements is true? a. the size of the thoracic cavity
CHAPTER 3: The respiratory system Practice questions - text book pages 56-58 1) When the inspiratory muscles contract, which one of the following statements is true? a. the size of the thoracic cavity
Explain how the structure of the gas exchange system of an insect ensures that there is a large surface area for gas exchange.
 1 Gas exchange takes place by diffusion. surfacearea differenceinconcentration diffusion lengthof diffusionpath a The diagram shows part of an insect tracheal system. i Explain how the structure of the
1 Gas exchange takes place by diffusion. surfacearea differenceinconcentration diffusion lengthof diffusionpath a The diagram shows part of an insect tracheal system. i Explain how the structure of the
BREATHING AND EXCHANGE OF GASES
 96 BIOLOGY, EXEMPLAR PROBLEMS CHAPTER 17 BREATHING AND EXCHANGE OF GASES MULTIPLE CHOICE QUESTIONS 1. Respiration in insects is called direct because a. The cell exchange O 2 directly with the air in the
96 BIOLOGY, EXEMPLAR PROBLEMS CHAPTER 17 BREATHING AND EXCHANGE OF GASES MULTIPLE CHOICE QUESTIONS 1. Respiration in insects is called direct because a. The cell exchange O 2 directly with the air in the
Department of Biology Work Sheet Respiratory system
 Department of Biology Work Sheet Respiratory system 1. Name the following : i. A muscular sheet separating the thoracic and abdominal cavities. ii. A respiratory tube supported by cartilaginous rings.
Department of Biology Work Sheet Respiratory system 1. Name the following : i. A muscular sheet separating the thoracic and abdominal cavities. ii. A respiratory tube supported by cartilaginous rings.
Respiration. The resspiratory system
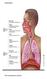 Respiration The resspiratory system The Alveoli The lungs have about 300 million alveoli, with a total crosssec onal area of 50 70 m2.. Each alveolar sac is surrounded by blood capillaries. The walls of
Respiration The resspiratory system The Alveoli The lungs have about 300 million alveoli, with a total crosssec onal area of 50 70 m2.. Each alveolar sac is surrounded by blood capillaries. The walls of
Collin County Community College. Lung Physiology
 Collin County Community College BIOL. 2402 Anatomy & Physiology WEEK 9 Respiratory System 1 Lung Physiology Factors affecting Ventillation 1. Airway resistance Flow = Δ P / R Most resistance is encountered
Collin County Community College BIOL. 2402 Anatomy & Physiology WEEK 9 Respiratory System 1 Lung Physiology Factors affecting Ventillation 1. Airway resistance Flow = Δ P / R Most resistance is encountered
Then the partial pressure of oxygen is. b) Gases will diffuse down a pressure gradient across a respiratory surface if it is: i) permeable ii) moist
 1 AP Biology March 2008 Respiration Chapter 42 Gas exchange occurs across specialized respiratory surfaces. 1) Gas exchange: Relies on the diffusion of gases down pressure gradients. At sea level, atmosphere
1 AP Biology March 2008 Respiration Chapter 42 Gas exchange occurs across specialized respiratory surfaces. 1) Gas exchange: Relies on the diffusion of gases down pressure gradients. At sea level, atmosphere
How Animals Survive (Circulation and Gas Exchange)
 How Animals Survive (Circulation and Gas Exchange) by Flourence Octaviano on February 16, 2018 lesson duration of 30 minutes under Earth and Life Science generated on February 16, 2018 at 12:45 am Tags:
How Animals Survive (Circulation and Gas Exchange) by Flourence Octaviano on February 16, 2018 lesson duration of 30 minutes under Earth and Life Science generated on February 16, 2018 at 12:45 am Tags:
Respiratory System. Part 2
 Respiratory System Part 2 Respiration Exchange of gases between air and body cells Three steps 1. Ventilation 2. External respiration 3. Internal respiration Ventilation Pulmonary ventilation consists
Respiratory System Part 2 Respiration Exchange of gases between air and body cells Three steps 1. Ventilation 2. External respiration 3. Internal respiration Ventilation Pulmonary ventilation consists
 Question 1: Define vital capacity. What is its significance? Vital capacity is the maximum volume of air that can be exhaled after a maximum inspiration. It is about 3.5 4.5 litres in the human body. It
Question 1: Define vital capacity. What is its significance? Vital capacity is the maximum volume of air that can be exhaled after a maximum inspiration. It is about 3.5 4.5 litres in the human body. It
Respiratory Physiology 2
 Respiratory Physiology 2 Session Objectives. What you will cover Gaseous Exchange Control of Breathing Rate Your objectives are State the function of support structures and epithelia of the bronchial tree
Respiratory Physiology 2 Session Objectives. What you will cover Gaseous Exchange Control of Breathing Rate Your objectives are State the function of support structures and epithelia of the bronchial tree
Monday, ! Today: Respiratory system! 5/20/14! Transport of Blood! What we ve been covering! Circulatory system! Parts of blood! Heart! tubing!
 Monday, 5.19.14! What we ve been covering! Circulatory system! Parts of blood! Heart! tubing! Transport of Blood! What is transported! Nutrients! Oxygen! Carbon Dioxide! Hormones! Antibodies! What it is/does!
Monday, 5.19.14! What we ve been covering! Circulatory system! Parts of blood! Heart! tubing! Transport of Blood! What is transported! Nutrients! Oxygen! Carbon Dioxide! Hormones! Antibodies! What it is/does!
Section Two Diffusion of gases
 Section Two Diffusion of gases Lecture 5: Partial pressure and the composition of gasses in air. Factors affecting diffusion of gases. Ventilation perfusion ratio effect on alveolar gas concentration.
Section Two Diffusion of gases Lecture 5: Partial pressure and the composition of gasses in air. Factors affecting diffusion of gases. Ventilation perfusion ratio effect on alveolar gas concentration.
Mammalian systems. Chapter 3 Pages
 Mammalian systems Chapter 3 Pages 75-103 Learning intentions To know that multicellular organisms exist from specialized cells To know how the respiratory system is specialized and organized and how a
Mammalian systems Chapter 3 Pages 75-103 Learning intentions To know that multicellular organisms exist from specialized cells To know how the respiratory system is specialized and organized and how a
BREATHING AND EXCHANGE OF GASES
 96 BIOLOGY, EXEMPLAR PROBLEMS CHAPTER 17 BREATHING AND EXCHANGE OF GASES MULTIPLE CHOICE QUESTIONS 1. Respiration in insects is called direct because a. The tissues exchange O 2 directly with the air in
96 BIOLOGY, EXEMPLAR PROBLEMS CHAPTER 17 BREATHING AND EXCHANGE OF GASES MULTIPLE CHOICE QUESTIONS 1. Respiration in insects is called direct because a. The tissues exchange O 2 directly with the air in
A Liter a Lung Measuring Lung Capacity
 A Liter a Lung Measuring Lung Capacity OBJECTIVE In this investigation, students will compare the actual and expected vital capacities of their classmates. LEVEL Middle Grades Life Science CONNECTIONS
A Liter a Lung Measuring Lung Capacity OBJECTIVE In this investigation, students will compare the actual and expected vital capacities of their classmates. LEVEL Middle Grades Life Science CONNECTIONS
Life 24 - Blood and Circulation Raven & Johnson Ch 52 & 53 (parts)
 1 Life 24 - Blood and Circulation Raven & Johnson Ch 52 & 53 (parts) Objectives 1: Understand the importance of oxygen carrier molecules in respiration 2: Describe the characteristics and locations of
1 Life 24 - Blood and Circulation Raven & Johnson Ch 52 & 53 (parts) Objectives 1: Understand the importance of oxygen carrier molecules in respiration 2: Describe the characteristics and locations of
OB11 Carry out qualitative tests to compare the carbon dioxide levels of inhaled and exhaled air
 Biology: 5. Respiration and Breathing Please remember to photocopy 4 pages onto one sheet by going A3 A4 and using back to back on the photocopier OB9 Syllabus Describe the process of aerobic respiration
Biology: 5. Respiration and Breathing Please remember to photocopy 4 pages onto one sheet by going A3 A4 and using back to back on the photocopier OB9 Syllabus Describe the process of aerobic respiration
The diagram shows an alveolus next to a blood capillary in a lung. (a) (i) Draw a ring around the correct answer to complete the sentence. diffusion.
 BREATHING / GAS EXCHANGE. NAME. Q.Gas exchange takes place in the lungs. The diagram shows an alveolus next to a blood capillary in a lung. The arrows show the movement of two gases, A and B. (a) (i) Draw
BREATHING / GAS EXCHANGE. NAME. Q.Gas exchange takes place in the lungs. The diagram shows an alveolus next to a blood capillary in a lung. The arrows show the movement of two gases, A and B. (a) (i) Draw
ADVANCED SUBSIDIARY GCE G622 APPLIED SCIENCE
 ADVANCED SUBSIDIARY GCE APPLIED SCIENCE Unit 3: Monitoring the activity of the human body TUESDAY 5 JUNE 2007 G622 Afternoon *CUP/T21601* Additional materials: Electronic calculator Ruler (cm/mm) Time:
ADVANCED SUBSIDIARY GCE APPLIED SCIENCE Unit 3: Monitoring the activity of the human body TUESDAY 5 JUNE 2007 G622 Afternoon *CUP/T21601* Additional materials: Electronic calculator Ruler (cm/mm) Time:
Gaseous exchange. Grade 11
 z Gaseous exchange Grade 11 z Terminology 1. Breathing 2. Gaseous exchange 3. Diffusion 4. Spongy mesophyll cells 5. Tracheae 6. Gills 7. Alveoli 8. Larynx 9. Diaphragm 10. Endothelium 1. Pleura 2. Squamous
z Gaseous exchange Grade 11 z Terminology 1. Breathing 2. Gaseous exchange 3. Diffusion 4. Spongy mesophyll cells 5. Tracheae 6. Gills 7. Alveoli 8. Larynx 9. Diaphragm 10. Endothelium 1. Pleura 2. Squamous
3.3.2 Gas Exchange SPECIFICATION
 alevelbiology.co.uk 3.3.2 Gas Exchange SPECIFICATION Adaptations of gas exchange surfaces, shown by gas exchange: Across the body surface of a single-celled organism In the tracheal system of an insect
alevelbiology.co.uk 3.3.2 Gas Exchange SPECIFICATION Adaptations of gas exchange surfaces, shown by gas exchange: Across the body surface of a single-celled organism In the tracheal system of an insect
GASEOUS EXCHANGE IN HUMANS 06 AUGUST 2014
 GASEOUS EXCHANGE IN HUMANS 06 AUGUST 2014 In this lesson we: Lesson Description Look at gaseous exchange in humans in terms of o Ventilation o Inspiration o Expiration o Transport of gases o Homeostatic
GASEOUS EXCHANGE IN HUMANS 06 AUGUST 2014 In this lesson we: Lesson Description Look at gaseous exchange in humans in terms of o Ventilation o Inspiration o Expiration o Transport of gases o Homeostatic
Then the partial pressure of oxygen is x 760 = 160 mm Hg
 1 AP Biology March 2008 Respiration Chapter 42 Gas exchange occurs across specialized respiratory surfaces. 1) Gas exchange: the uptake of molecular oxygen (O2) from the environment and the discharge of
1 AP Biology March 2008 Respiration Chapter 42 Gas exchange occurs across specialized respiratory surfaces. 1) Gas exchange: the uptake of molecular oxygen (O2) from the environment and the discharge of
Chapter 16 Respiratory System
 Introduction Chapter 16 Respiratory System The respiratory system consists of tubes that filter incoming air and transport it to alveoli where gases are exchanged. Think pair share: what organs are associated
Introduction Chapter 16 Respiratory System The respiratory system consists of tubes that filter incoming air and transport it to alveoli where gases are exchanged. Think pair share: what organs are associated
Topic 13: Gas Exchange Ch. 42. Gas Exchange pp Gas Exchange. Gas Exchange in Fish pp Gas Exchange in Fish
 Topic 13: Gas Exchange Ch. 42 Fig. 42.24 Gas Exchange pp.979-989 Gas exchange involves the uptake of oxygen and the discharge of carbon dioxide (i.e. respiration or breathing). It is necessary for cellular
Topic 13: Gas Exchange Ch. 42 Fig. 42.24 Gas Exchange pp.979-989 Gas exchange involves the uptake of oxygen and the discharge of carbon dioxide (i.e. respiration or breathing). It is necessary for cellular
My Question Paper. Copyright WJEC CBAC Ltd. All rights reserved Page 1 of 16
 My Question Paper Copyright WJEC CBAC Ltd. All rights reserved Page 1 of 16 1. Copyright WJEC CBAC Ltd. All rights reserved Page 2 of 16 Copyright WJEC CBAC Ltd. All rights reserved Page 3 of 16 2. The
My Question Paper Copyright WJEC CBAC Ltd. All rights reserved Page 1 of 16 1. Copyright WJEC CBAC Ltd. All rights reserved Page 2 of 16 Copyright WJEC CBAC Ltd. All rights reserved Page 3 of 16 2. The
Systems of distribution
 Systems of distribution Outline Distribution of respiratory gases, and in blood Respiratory systems - transport of oxygen to tissues - radically different designs in mammals, birds, insects Vertebrate
Systems of distribution Outline Distribution of respiratory gases, and in blood Respiratory systems - transport of oxygen to tissues - radically different designs in mammals, birds, insects Vertebrate
IV. FROM AQUATIC TO ATMOSPHERIC BREATHING: THE TRACHEA & THE LUNG
 GAS EXCHANGE AND TRANSPORT I. INTRODUCTION: Heterotrophs oxidize carbon cmpds using O 2 to generate CO 2 & H 2 O. This is cellular respiration II. HOW GAS ENTERS A CELL A. The composition of air: 79% N
GAS EXCHANGE AND TRANSPORT I. INTRODUCTION: Heterotrophs oxidize carbon cmpds using O 2 to generate CO 2 & H 2 O. This is cellular respiration II. HOW GAS ENTERS A CELL A. The composition of air: 79% N
Hyndland Secondary School Biology Department
 Hyndland Secondary School Biology Department Body in Action Homework and Question Booklet 1 Body in Action (a) Movement... 2 Skeleton... 2 Joints... 3 Body in Action (b) The need for Energy... 5 Heart...
Hyndland Secondary School Biology Department Body in Action Homework and Question Booklet 1 Body in Action (a) Movement... 2 Skeleton... 2 Joints... 3 Body in Action (b) The need for Energy... 5 Heart...
BIOLOGY 12: UNIT J - CHAPTER 15 - REVIEW WORKSHEET RESPIRATORY SYSTEM
 BIOLOGY 12: UNIT J - CHAPTER 15 - REVIEW WORKSHEET RESPIRATORY SYSTEM A. CHAPTER REVIEW 1. Define the four components of respiration. 2. What happens to the air as it moves along the air passages? What
BIOLOGY 12: UNIT J - CHAPTER 15 - REVIEW WORKSHEET RESPIRATORY SYSTEM A. CHAPTER REVIEW 1. Define the four components of respiration. 2. What happens to the air as it moves along the air passages? What
Breathing oxygenates the blood to allow food to be respired
 Chapter 6 Breathing oxygenates the blood to allow food to be respired This chapter covers: the structure of the human gas exchange system the mechanism of breathing gas exchange in the alveoli the concept
Chapter 6 Breathing oxygenates the blood to allow food to be respired This chapter covers: the structure of the human gas exchange system the mechanism of breathing gas exchange in the alveoli the concept
Figure 1. A schematic diagram of the human respiratory system.
 Introduction to Respiration In this experiment, you will investigate various aspects of normal breathing, hyperventilation, rebreathing the effect of changing airway resistance and ways in which to measure
Introduction to Respiration In this experiment, you will investigate various aspects of normal breathing, hyperventilation, rebreathing the effect of changing airway resistance and ways in which to measure
G622. APPLIED SCIENCE Monitoring the Activity of the Human Body ADVANCED SUBSIDIARY GCE. Thursday 27 May 2010 Afternoon. Duration: 1 hour 30 minutes
 ADVANCED SUBSIDIARY GCE APPLIED SCIENCE Monitoring the Activity of the Human Body G622 *OCE/17533* Candidates answer on the Question Paper OCR Supplied Materials: None Other Materials Required: Electronic
ADVANCED SUBSIDIARY GCE APPLIED SCIENCE Monitoring the Activity of the Human Body G622 *OCE/17533* Candidates answer on the Question Paper OCR Supplied Materials: None Other Materials Required: Electronic
Lesson: What a Gas! Human Respiration 7 th Grade Life Science November 30 th -31 st. Rationale/Goal:
 Lesson: What a Gas! Teacher: Unit Theme/Course: Date: Timing: Kaylan Duthie Human Respiration 7 th Grade Life Science November 30 th -31 st 1.5 days Rationale/Goal: Students will draw upon a previous lab
Lesson: What a Gas! Teacher: Unit Theme/Course: Date: Timing: Kaylan Duthie Human Respiration 7 th Grade Life Science November 30 th -31 st 1.5 days Rationale/Goal: Students will draw upon a previous lab
Lung Volumes and Capacities
 Lung Volumes and Capacities Normally the volume of air entering the lungs during a single inspiration is approximately equal to the volume leaving on the subsequent expiration and is called the tidal volume.
Lung Volumes and Capacities Normally the volume of air entering the lungs during a single inspiration is approximately equal to the volume leaving on the subsequent expiration and is called the tidal volume.
REVISION: GASEOUS EXCHANGE & EXCRETION 11 SEPTEMBER 2013
 REVISION: GASEOUS EXCHANGE & EXCRETION 11 SEPTEMBER 2013 Lesson Description In this lesson we: Revise gaseous exchange in different animals and examine the structure of the kidney Key Concepts Important
REVISION: GASEOUS EXCHANGE & EXCRETION 11 SEPTEMBER 2013 Lesson Description In this lesson we: Revise gaseous exchange in different animals and examine the structure of the kidney Key Concepts Important
The physiological functions of respiration and circulation. Mechanics. exercise 7. Respiratory Volumes. Objectives
 exercise 7 Respiratory System Mechanics Objectives 1. To explain how the respiratory and circulatory systems work together to enable gas exchange among the lungs, blood, and body tissues 2. To define respiration,
exercise 7 Respiratory System Mechanics Objectives 1. To explain how the respiratory and circulatory systems work together to enable gas exchange among the lungs, blood, and body tissues 2. To define respiration,
Outline - Respiratory System. Function of the respiratory system Parts of the respiratory system Mechanics of breathing Regulation of breathing
 Respiratory system Function Outline - Respiratory System I. II. III. IV. Respiratory System The function of the respiratory system is to bring in oxygen to the body and remove carbon dioxide. Function
Respiratory system Function Outline - Respiratory System I. II. III. IV. Respiratory System The function of the respiratory system is to bring in oxygen to the body and remove carbon dioxide. Function
Alveolus and Respiratory Membrane
 Alveolus and Respiratory Membrane thin membrane where gas exchange occurs in the lungs, simple squamous epithelium (Squamous cells have the appearance of thin, flat plates. They fit closely together in
Alveolus and Respiratory Membrane thin membrane where gas exchange occurs in the lungs, simple squamous epithelium (Squamous cells have the appearance of thin, flat plates. They fit closely together in
Transport in cells. Specification coverage
 3 Transport in cells T F A R What does smelling your best friend s deodorant have in common with making a cup of tea? One thing is that they both involve the movement of particles. Particles spread out
3 Transport in cells T F A R What does smelling your best friend s deodorant have in common with making a cup of tea? One thing is that they both involve the movement of particles. Particles spread out
GCE. Biology. Mark Scheme for the Units. January 2010 HX21/MS/R/10J. Advanced GCE A2 H421 Advanced Subsidiary GCE AS H021 PMT
 GCE Biology Advanced GCE A2 H421 Advanced Subsidiary GCE AS H021 Mark Scheme for the Units January 2010 HX21/MS/R/10J Oxford Cambridge and RSA Examinations F211 Cells, Exchange and Transport 1 (a) 1500
GCE Biology Advanced GCE A2 H421 Advanced Subsidiary GCE AS H021 Mark Scheme for the Units January 2010 HX21/MS/R/10J Oxford Cambridge and RSA Examinations F211 Cells, Exchange and Transport 1 (a) 1500
Chapter 37: Pulmonary Ventilation. Chad & Angela
 Chapter 37: Pulmonary Ventilation Chad & Angela Respiratory Structures Basic Structures of Respiration Nasal/Oral Cavities Larynx Trachea Bronchi Secondary Bronchi Bronchioles Alveoli Mechanics of Ventilation
Chapter 37: Pulmonary Ventilation Chad & Angela Respiratory Structures Basic Structures of Respiration Nasal/Oral Cavities Larynx Trachea Bronchi Secondary Bronchi Bronchioles Alveoli Mechanics of Ventilation
Gas Exchange in Animals. Uptake of O2 from environment and discharge of CO2. Respiratory medium! water for aquatic animals, air for terrestial
 Gas Exchange in Animals Uptake of O2 from environment and discharge of CO2 Respiratory medium! water for aquatic animals, air for terrestial Respiratory surface! skin, gills, lungs Circulatory System O2/CO2
Gas Exchange in Animals Uptake of O2 from environment and discharge of CO2 Respiratory medium! water for aquatic animals, air for terrestial Respiratory surface! skin, gills, lungs Circulatory System O2/CO2
Animal Systems: The Respiratory System
 Animal Systems: The Respiratory System Tissues, Organs, and Systems of Living Things Cells, Cell Division, and Animal Systems and Plant Systems Cell Specialization Human Systems The Digestive The Circulatory
Animal Systems: The Respiratory System Tissues, Organs, and Systems of Living Things Cells, Cell Division, and Animal Systems and Plant Systems Cell Specialization Human Systems The Digestive The Circulatory
REVISION: GASEOUS EXCHANGE 24 SEPTEMBER 2014 Lesson Description
 REVISION: GASEOUS EXCHANGE 24 SEPTEMBER 2014 Lesson Description In this lesson, we revise: Gaseous Exchange in Plants & Animals Gaseous Exchange in Humans Excretion in Humans Focus on the Kidney Gaseous
REVISION: GASEOUS EXCHANGE 24 SEPTEMBER 2014 Lesson Description In this lesson, we revise: Gaseous Exchange in Plants & Animals Gaseous Exchange in Humans Excretion in Humans Focus on the Kidney Gaseous
08 Respiration. #79 Respiration realeases energy from food
 08 Respiration #79 Respiration realeases energy from food Respiration is the chemical reactions that break down nutrient molecules in living cells to release energy. In humans, our cells need energy (ATP)
08 Respiration #79 Respiration realeases energy from food Respiration is the chemical reactions that break down nutrient molecules in living cells to release energy. In humans, our cells need energy (ATP)
Unit II Problem 4 Physiology: Diffusion of Gases and Pulmonary Circulation
 Unit II Problem 4 Physiology: Diffusion of Gases and Pulmonary Circulation - Physical principles of gases: Pressure of a gas is caused by the movement of its molecules against a surface (more concentration
Unit II Problem 4 Physiology: Diffusion of Gases and Pulmonary Circulation - Physical principles of gases: Pressure of a gas is caused by the movement of its molecules against a surface (more concentration
GCE AS MARKING SCHEME
 GCE AS MARKING SCHEME SUMMER 2017 AS (NEW) BIOLOGY - COMPONENT 2 B400U20-1 INTRODUCTION This marking scheme was used by WJEC for the 2017 examination. It was finalised after detailed discussion at examiners'
GCE AS MARKING SCHEME SUMMER 2017 AS (NEW) BIOLOGY - COMPONENT 2 B400U20-1 INTRODUCTION This marking scheme was used by WJEC for the 2017 examination. It was finalised after detailed discussion at examiners'
inquiry question How does the respiratory system contribute to energy production for movement? UNCORRECTED PAGE PROOFS
 inquiry question How does the respiratory system contribute to energy production for movement? chapter 7 Structure and functions of the respiratory system The respiratory system is the starting point for
inquiry question How does the respiratory system contribute to energy production for movement? chapter 7 Structure and functions of the respiratory system The respiratory system is the starting point for
Respiration. Chapter 33
 Respiration Chapter 33 Learning Objectives: Understand the basis of gas exchange and factors that influence diffusion of gases in and out of tissues Compare and contrast different respiratory systems among
Respiration Chapter 33 Learning Objectives: Understand the basis of gas exchange and factors that influence diffusion of gases in and out of tissues Compare and contrast different respiratory systems among
GASEOUS EXCHANGE IN PLANTS & ANIMALS 30 JULY 2014
 GASEOUS EXCHANGE IN PLANTS & ANIMALS 30 JULY 2014 In this lesson, we: Lesson Description Define gaseous exchange o o Look at the requirements for efficient gaseous exchange Study gaseous exchange in various
GASEOUS EXCHANGE IN PLANTS & ANIMALS 30 JULY 2014 In this lesson, we: Lesson Description Define gaseous exchange o o Look at the requirements for efficient gaseous exchange Study gaseous exchange in various
VT PLUS HF performance verification of Bunnell Life-Pulse HFJV (High Frequency Jet Ventilator)
 VT PLUS HF performance verification of Bunnell Life-Pulse HFJV (High Frequency Jet Ventilator) VT PLUS HF provides a special mode for evaluating the performance of high frequency ventilators while connected
VT PLUS HF performance verification of Bunnell Life-Pulse HFJV (High Frequency Jet Ventilator) VT PLUS HF provides a special mode for evaluating the performance of high frequency ventilators while connected
The Respiratory System
 Essentials of Human Anatomy & Physiology Elaine N. Marieb Seventh Edition Chapter 13 The Respiratory System Slides 13.1 13.30 Lecture Slides in PowerPoint by Jerry L. Cook Organs of the Respiratory system
Essentials of Human Anatomy & Physiology Elaine N. Marieb Seventh Edition Chapter 13 The Respiratory System Slides 13.1 13.30 Lecture Slides in PowerPoint by Jerry L. Cook Organs of the Respiratory system
Lectures on Medical Biophysics Department of Biophysics, Medical Faculty, Masaryk University in Brno. Biophysics of breathing.
 Lectures on Medical Biophysics Department of Biophysics, Medical Faculty, Masaryk University in Brno Biophysics of breathing. Spirometry 1 Lecture outline Mechanisms of gas exchange between organism and
Lectures on Medical Biophysics Department of Biophysics, Medical Faculty, Masaryk University in Brno Biophysics of breathing. Spirometry 1 Lecture outline Mechanisms of gas exchange between organism and
 Subject: Transport Code: 2803/01 Session: June Year: 2002 Mark Scheme MAXIMUM MARK 45 ADVICE TO EXAMINERS ON THE ANNOTATION OF SCRIPTS 1. Please ensure that you use the final version of the Mark Scheme.
Subject: Transport Code: 2803/01 Session: June Year: 2002 Mark Scheme MAXIMUM MARK 45 ADVICE TO EXAMINERS ON THE ANNOTATION OF SCRIPTS 1. Please ensure that you use the final version of the Mark Scheme.
Subject: Transport Code: 2803/01. Session: June Year: Mark Scheme
 Subject: Transport Code: 2803/01 Session: June Year: 2002 MAXIMUM MARK 45 ADVICE TO EXAMINERS ON THE ANNOTATION OF SCRIPTS 1. Please ensure that you use the final version of the. You are advised to destroy
Subject: Transport Code: 2803/01 Session: June Year: 2002 MAXIMUM MARK 45 ADVICE TO EXAMINERS ON THE ANNOTATION OF SCRIPTS 1. Please ensure that you use the final version of the. You are advised to destroy
Respiratory System Physiology. Dr. Vedat Evren
 Respiratory System Physiology Dr. Vedat Evren Respiration Processes involved in oxygen transport from the atmosphere to the body tissues and the release and transportation of carbon dioxide produced in
Respiratory System Physiology Dr. Vedat Evren Respiration Processes involved in oxygen transport from the atmosphere to the body tissues and the release and transportation of carbon dioxide produced in
Physiology Unit 4 RESPIRATORY PHYSIOLOGY
 Physiology Unit 4 RESPIRATORY PHYSIOLOGY In Physiology Today Respiration External respiration ventilation gas exchange Internal respiration cellular respiration gas exchange Respiratory Cycle Inspiration
Physiology Unit 4 RESPIRATORY PHYSIOLOGY In Physiology Today Respiration External respiration ventilation gas exchange Internal respiration cellular respiration gas exchange Respiratory Cycle Inspiration
Honors Physiology The Respiratory System
 Honors Physiology Name: The Respiratory System Objective: To create a model of our respiratory system, understanding the relationship between structure and function. Warm Up Questions: 1. What is the function
Honors Physiology Name: The Respiratory System Objective: To create a model of our respiratory system, understanding the relationship between structure and function. Warm Up Questions: 1. What is the function
2.1.1 List the principal structures of the
 physiology 2.1.1 List the principal structures of the The principle structures of the respiratory are: Nose/Mouth used for inhalation of oxygen-rich air and expelling carbon dioxide rich air Pharynx -
physiology 2.1.1 List the principal structures of the The principle structures of the respiratory are: Nose/Mouth used for inhalation of oxygen-rich air and expelling carbon dioxide rich air Pharynx -
Lab 3. The Respiratory System (designed by Heather E. M. Liwanag with T.M. Williams)
 Name Lab Partners Lab 3. The Respiratory System (designed by Heather E. M. Liwanag with T.M. Williams) Part 1. Lung Volumes and Capacities Objectives 1. Obtain graphical representation of lung capacities
Name Lab Partners Lab 3. The Respiratory System (designed by Heather E. M. Liwanag with T.M. Williams) Part 1. Lung Volumes and Capacities Objectives 1. Obtain graphical representation of lung capacities
BIOLOGY INTERACTIVE ASSESSMENT QUESTIONS BASED ON STANDARD PRACTICAL EXERCISES... Biology Part 1 LEARNING VERSION
 INTERACTIVE ASSESSMENT QUESTIONS BASED ON STANDARD PRACTICAL EXERCISES... Biology Part 1 IN THIS ANSWERS ARE IMMEDIATELY AND VISIBLY MARKED, CORRECT ANSWERS ARE INDICATED ON REQUEST, AND END OF SECTION
INTERACTIVE ASSESSMENT QUESTIONS BASED ON STANDARD PRACTICAL EXERCISES... Biology Part 1 IN THIS ANSWERS ARE IMMEDIATELY AND VISIBLY MARKED, CORRECT ANSWERS ARE INDICATED ON REQUEST, AND END OF SECTION
GAS EXCHANGE & CIRCULATION CHAPTER 42 ( )
 Winter 08 1 of 10 GAS EXCHANGE & CIRCULATION CHAPTER 42 (867 891) MOVEMENT OF GASES Both O 2 and CO 2 move by The movement down a If a gas produced in one location, it diffuses away But diffusion is usually
Winter 08 1 of 10 GAS EXCHANGE & CIRCULATION CHAPTER 42 (867 891) MOVEMENT OF GASES Both O 2 and CO 2 move by The movement down a If a gas produced in one location, it diffuses away But diffusion is usually
Circulation and Gas Exchange Chapter 42
 Circulation and Gas Exchange Chapter 42 Circulatory systems link exchange surfaces with cells throughout the body Diffusion is only efficient over small distances In small and/or thin animals, cells can
Circulation and Gas Exchange Chapter 42 Circulatory systems link exchange surfaces with cells throughout the body Diffusion is only efficient over small distances In small and/or thin animals, cells can
I. Gas Exchange Respiratory Surfaces Respiratory Surface:
 I. Gas Exchange Respiratory Surfaces Respiratory Surface: Common characteristics of respiratory surfaces: a) Moist: allows for the RAPID diffusion of dissolved gasses across its surface. Whereas the respiratory
I. Gas Exchange Respiratory Surfaces Respiratory Surface: Common characteristics of respiratory surfaces: a) Moist: allows for the RAPID diffusion of dissolved gasses across its surface. Whereas the respiratory
Lesson 28. Function - Respiratory Pumps in Air Breathers Buccal Force Pump Aspiration Pump - Patterns of Gas Transfer in Chordates
 Lesson 28 Lesson Outline: Evolution of Respiratory Mechanisms - Air Breathers Form - Accessory Air Breathing Organs Facultative vs Obligate - Lungs Function - Respiratory Pumps in Air Breathers Buccal
Lesson 28 Lesson Outline: Evolution of Respiratory Mechanisms - Air Breathers Form - Accessory Air Breathing Organs Facultative vs Obligate - Lungs Function - Respiratory Pumps in Air Breathers Buccal
Respiratory System Review
 KEY THIS TEST WILL BE COMPLETED IN ONE CLASS PERIOD MONDAY, MARCH 10. 2014 Respiratory System Review Name A. Directions: Fill in the blank with the appropriate vocabulary word or words (several examples
KEY THIS TEST WILL BE COMPLETED IN ONE CLASS PERIOD MONDAY, MARCH 10. 2014 Respiratory System Review Name A. Directions: Fill in the blank with the appropriate vocabulary word or words (several examples
Pop Quiz. What produces mucus, HCl and pepsinogen in the stomach? List a water soluable vitamin What is a ruminant stomach?
 Pop Quiz What produces mucus, HCl and pepsinogen in the stomach? List a water soluable vitamin What is a ruminant stomach? Respiratory System Review Cellular respiration: obtain glucose and oxygen, get
Pop Quiz What produces mucus, HCl and pepsinogen in the stomach? List a water soluable vitamin What is a ruminant stomach? Respiratory System Review Cellular respiration: obtain glucose and oxygen, get
What do animals do to survive?
 What do animals do to survive? Section 26-1 All Animals have are carry out Eukaryotic cells with Heterotrophs Essential functions such as No cell walls Feeding Respiration Circulation Excretion Response
What do animals do to survive? Section 26-1 All Animals have are carry out Eukaryotic cells with Heterotrophs Essential functions such as No cell walls Feeding Respiration Circulation Excretion Response
Human gas exchange. Question Paper. Save My Exams! The Home of Revision. Cambridge International Examinations. 56 minutes. Time Allowed: Score: /46
 Human gas exchange Question Paper Level Subject Exam oard Topic Sub Topic ooklet O Level iology ambridge International Examinations Respiration Human gas exchange Question Paper Time llowed: 56 minutes
Human gas exchange Question Paper Level Subject Exam oard Topic Sub Topic ooklet O Level iology ambridge International Examinations Respiration Human gas exchange Question Paper Time llowed: 56 minutes
Using the Lifebox oximeter in the neonatal unit. Tutorial 1 the basics
 Using the Lifebox oximeter in the neonatal unit Tutorial 1 the basics Lifebox 2014. 2011. All rights reserved The Lifebox Pulse Oximeter In this tutorial you will learn about: The function of a pulse oximeter
Using the Lifebox oximeter in the neonatal unit Tutorial 1 the basics Lifebox 2014. 2011. All rights reserved The Lifebox Pulse Oximeter In this tutorial you will learn about: The function of a pulse oximeter
Measuring Lung Capacity
 Measuring Lung Capacity 1 Name Measuring Lung Capacity Background Information: We need a constant supply of oxygen in order to stay alive. We use oxygen to break down food to release energy and produce
Measuring Lung Capacity 1 Name Measuring Lung Capacity Background Information: We need a constant supply of oxygen in order to stay alive. We use oxygen to break down food to release energy and produce
Experiment B-3 Respiration
 1 Experiment B-3 Respiration Objectives To study the diffusion process of oxygen and carbon dioxide between the alveoli and pulmonary capillaries. To determine the percentage of oxygen in exhaled air while
1 Experiment B-3 Respiration Objectives To study the diffusion process of oxygen and carbon dioxide between the alveoli and pulmonary capillaries. To determine the percentage of oxygen in exhaled air while
SCIENCE- NOTES. Q1. Draw the diagram of human respiratory system and explain the function of the following parts:
 SCIENCE- NOTES NAME: RESPIRATION IN ORGANISMS STD.VII DIV: Q1. Draw the diagram of human respiratory system and explain the function of the following parts: i. Nasal cavity ii. Trachea iii. Lungs iv. Bronchioles
SCIENCE- NOTES NAME: RESPIRATION IN ORGANISMS STD.VII DIV: Q1. Draw the diagram of human respiratory system and explain the function of the following parts: i. Nasal cavity ii. Trachea iii. Lungs iv. Bronchioles
1. Label a diagram of the respiratory system. Objective sheet 3 Notes
 1. Label a diagram of the respiratory system Objective sheet 3 Notes 2. Functions of the respiratory structures Name Description Function Nasal Cavity Trachea Bronchi (Singular Bronchus) Bronchioles Lungs
1. Label a diagram of the respiratory system Objective sheet 3 Notes 2. Functions of the respiratory structures Name Description Function Nasal Cavity Trachea Bronchi (Singular Bronchus) Bronchioles Lungs
Lab 17. The Respiratory System. Laboratory Objectives
 Lab 17 The Respiratory System Laboratory Objectives Identify and describe the anatomical structures of the respiratory system. Describe the relationship between volume and pressure. Describe changes in
Lab 17 The Respiratory System Laboratory Objectives Identify and describe the anatomical structures of the respiratory system. Describe the relationship between volume and pressure. Describe changes in
understanding of cell size and shape absorption of food substances in villi rate of diffusion gas exchange in air sacs
 Cell Designer Relation to topics / curriculum link: Prior knowledge and skills needed: diffusion understanding of cell size and shape absorption of food substances in villi rate of diffusion gas exchange
Cell Designer Relation to topics / curriculum link: Prior knowledge and skills needed: diffusion understanding of cell size and shape absorption of food substances in villi rate of diffusion gas exchange
Sc ienc e 9-Biology Work sheet 8-2 A Single Breat h & Tak ing Care
 Unit 2 Your Living Body Sc ienc e 9-Biology Work sheet 8-2 A Single Breat h & Tak ing Care Name No pen or pencil No Textbook 20 Due Date Show Me Hand In Correct and Hand In Again By Read pages 159-167
Unit 2 Your Living Body Sc ienc e 9-Biology Work sheet 8-2 A Single Breat h & Tak ing Care Name No pen or pencil No Textbook 20 Due Date Show Me Hand In Correct and Hand In Again By Read pages 159-167
Introduction to Biological Science - BIOL Gas Exchange
 Gas Exchange A. Influence of concentration gradient on gas diffusion rate 1. You have two tubes of permeable membrane. a. Add an arrow to illustrate concurrent fluid flow in Tubes A and B. Tube A Tube
Gas Exchange A. Influence of concentration gradient on gas diffusion rate 1. You have two tubes of permeable membrane. a. Add an arrow to illustrate concurrent fluid flow in Tubes A and B. Tube A Tube
They selected fully grown leaves from five different plants of each species.
 Q1.Scientists studied three species of plant. They selected fully grown leaves from five different plants of each species. For each leaf they measured: leaf surface area leaf thickness the number of stomata
Q1.Scientists studied three species of plant. They selected fully grown leaves from five different plants of each species. For each leaf they measured: leaf surface area leaf thickness the number of stomata
(Slide 1) Lecture Notes: Respiratory System
 (Slide 1) Lecture Notes: Respiratory System I. (Slide 2) The Respiratory Tract A) Major structures and regions of the respiratory Tract/Route INTO body 1) nose 2) nasal cavity 3) pharynx 4) glottis 5)
(Slide 1) Lecture Notes: Respiratory System I. (Slide 2) The Respiratory Tract A) Major structures and regions of the respiratory Tract/Route INTO body 1) nose 2) nasal cavity 3) pharynx 4) glottis 5)
Preliminary Biology Assessment Task #1. Part 1 is to be completed and handed in before the start of period 1 on Friday 13/05/2016.
 Preliminary Biology Assessment Task #1 Assessment Overview: There are THREE (3) parts to this assessment. Part 1: Research and planning; To be done in own time. Part 1 is to be completed and handed in
Preliminary Biology Assessment Task #1 Assessment Overview: There are THREE (3) parts to this assessment. Part 1: Research and planning; To be done in own time. Part 1 is to be completed and handed in
The Breathing System
 The Breathing System Learning Intentions 1. Students should Know how Breathing happens 2. Name and know the functions of the Breathing System 3. Know how the organs work and how they work with other systems
The Breathing System Learning Intentions 1. Students should Know how Breathing happens 2. Name and know the functions of the Breathing System 3. Know how the organs work and how they work with other systems
COMBINED SCIENCE 0653/6 CO-ORDINATED SCIENCES 0654/6
 Centre Number Candidate Number Candidate Name International General Certificate of Secondary Education UNIVERSITY OF CAMBRIDGE LOCAL EXAMINATIONS SYNDICATE COMBINED SCIENCE 0653/6 CO-ORDINATED SCIENCES
Centre Number Candidate Number Candidate Name International General Certificate of Secondary Education UNIVERSITY OF CAMBRIDGE LOCAL EXAMINATIONS SYNDICATE COMBINED SCIENCE 0653/6 CO-ORDINATED SCIENCES
Structures of the Respiratory System include:
 Respiratory System Structures of the Respiratory System include: ü Oral Cavity ü Nasal Cavity ü Pharynx ü Epiglottis ü Larynx ü Trachea ü Diaphragm ü Lung ü Bronchus ü Bronchioles ü Alveolus ü Pulmonary
Respiratory System Structures of the Respiratory System include: ü Oral Cavity ü Nasal Cavity ü Pharynx ü Epiglottis ü Larynx ü Trachea ü Diaphragm ü Lung ü Bronchus ü Bronchioles ü Alveolus ü Pulmonary
PARTS AND STRUCTURE OF THE RESPIRATORY SYSTEM
 PARTS AND STRUCTURE OF THE RESPIRATORY SYSTEM Parts of the Respiratory System The RS can be divided into two parts: 1. Respiratory Tract, (path that air follows). Nasal passage Pharynx Larynx Trachea Bronchi,
PARTS AND STRUCTURE OF THE RESPIRATORY SYSTEM Parts of the Respiratory System The RS can be divided into two parts: 1. Respiratory Tract, (path that air follows). Nasal passage Pharynx Larynx Trachea Bronchi,
Breathing. Physics of Breathing 11/14/2011. Function of Respiratory Tract. Structure of Respiratory Tract. Parts of the Respiratory Tract
 Breathing Function of Respiratory Tract The respiratory tract is a series of spaces and semirigid tubes designed to convey air into and out of the respiratory organs (lungs). Parts of the Respiratory Tract
Breathing Function of Respiratory Tract The respiratory tract is a series of spaces and semirigid tubes designed to convey air into and out of the respiratory organs (lungs). Parts of the Respiratory Tract
Applied Science SC02 (JUN15SC0201) General Certificate of Education Advanced Subsidiary Examination June Energy Transfer Systems TOTAL
 Centre Number Surname Candidate Number For Examiner s Use Other Names Candidate Signature Examiner s Initials Question Mark Applied Science General Certificate of Education Advanced Subsidiary Examination
Centre Number Surname Candidate Number For Examiner s Use Other Names Candidate Signature Examiner s Initials Question Mark Applied Science General Certificate of Education Advanced Subsidiary Examination
