You Might Also Like. I look forward helping you focus your instruction while saving tons of time. Kesler Science Station Lab Activities 40%+ Savings!
|
|
|
- Beatrice Nash
- 5 years ago
- Views:
Transcription
1 Thanks Connect Thank you for downloading my product. I truly appreciate your support and look forward to hearing your feedback. You can connect with me and find many free activities and strategies over at my blog KeslerScience.com I look forward helping you focus your instruction while saving tons of time. You Might Also Like All 8 INB Notebook Templates 35% Savings! Kesler Science Station Lab Activities 40%+ Savings! Engaging Lessons for Busy Teachers
2
3 Kesler Science Station Lab Respiratory System If you have never used my Kesler Science Station Labs before please download the FREE Start-Up pack from my TPT store. It will provide you with all of the signage and best practices in order to run the station labs in your classroom. You can read my complete guide to how run effective station labs on my blog. The large directions cards included in this file are intended to be read by the leader of the group once the students get to the station. The smaller task cards can be read by another group member. I prefer that each student do their own lab write-up (included at the end of this file), so that they may use it for reference at a later date. The answer key is provided at the end of the document. Lastly, if any of the internet resources no longer work for some reason please let me know via at chris@keslerscience.com. I cannot guarantee that all resources will be available, but I tried to choose ones that have been around for many years.
4 Kesler Science Station Lab Respiratory System Teacher Directions Explore It! I will spend much of my time at this station making sure students are understanding the concept. You will only need the two diagrams and 3-4 models. Here are two ways to create the models: Organize It! Students should be encouraged to do the Research and Explore station before attempting this one. The key is the last page in this document. #1 #2 I prefer a combo of both methods. Use clay for the top and straws for the bronchus and esophagus so you can have 2 lungs. Illustrate It! Make sure to include colored pencils or crayons at this station. Read It! Print several different copies (I use 6) of the reading passage so that multiple students can read at different paces. Write It! Students should be encouraged to do the Research and Explore station before attempting this one. Research It! The goo.gl link on the task card is case-sensitive. The original link: Assess It! Students should be encouraged to do the Research and Explore station before attempting this one. If I grade anything I usually take a close look at the answers from this station. Watch It! The video is on YouTube and my Google drive. Use YouTube unless your school is blocked. The original link is A Note that URL s are case-sensitive.
5 Write It! Station Directions It is recommended that you have completed at least two of the following stations before working at this station. -Read It! -Explore It! -Watch It! -Research It! Answer each of the task card questions on the lab sheet in complete sentences.
6 Explain the respiratory system including the structures involved and the function of the system. How does the respiratory system work directly with the circulatory system? KeslerScience.com Plants give off oxygen as part of photosynthesis. Explain the impact of this process to humans. KeslerScience.com
7 Assess It! Station Directions It is recommended that you have completed at least two of the following stations before working at this station. -Read It! -Explore It! -Watch It! -Research It! Each member will answer the questions from the task cards on the lab sheet in the Assess It! section.
8 Which is not a part of the respiratory system? How does the diaphragm aide in breathing? A. Alveoli B. Lungs C. Trachea D. Esophagus A. When the diaphragm contracts, the lungs expand and allow oxygen to enter B. When the diaphragm relaxes, the lungs expand and allow oxygen to enter C. The diaphragm does not work with the respiratory system How do plants benefit from human respiration? A. Plants need oxygen to survive B. Plants need water to survive C. Plants need carbon dioxide to survive D. Plants need nitrogen to survive The Respiratory System works directly with the system to exchange oxygen and carbon dioxide in the lungs. A. Muscular B. Endocrine C. Circulatory D. Digestive
9 Read It! Station Directions Each member of the group will read the passage and answer the questions from the task cards on the lab sheet in the Read It! section. It is important to remember that the answers will come directly from the reading passage.
10 Bronchitis Bronchitis is a respiratory disease in which the mucus membrane in the lungs' bronchial passages becomes inflamed. As the irritated membrane swells and grows thicker, it narrows or shuts off the tiny airways in the lungs, resulting in coughing spells that may be accompanied by phlegm and breathlessness. The disease comes in two forms: acute (lasting from one to three weeks) and chronic (lasting at least 3 months of the year for two years in a row). People with asthma may also have asthmatic bronchitis, inflammation of the lining of the bronchial tubes. Acute bronchitis may be responsible for the hacking cough and phlegm production that sometime accompany an upper respiratory infection. In most cases, the infection is viral in origin, but sometimes it's caused by bacteria. If you are otherwise in good health, the mucus membrane should return to normal after you've recovered from the initial lung infection, which usually lasts for several days. Chronic bronchitis is a serious long-term disorder that often requires regular medical treatment. If you are a smoker and come down with acute bronchitis, it will be much harder for you to recover. Every cigarette damages the tiny hair-like structures in your lungs, called cilia, that are responsible for brushing out debris, irritants, and excess mucus. If you continue smoking, the damage to these cilia prevent them from functioning properly, thus increasing your chances of developing chronic bronchitis. In some heavy smokers, the mucus membrane lining the airways stays inflamed and the cilia eventually stop functioning altogether. Clogged with mucus, the lungs are then vulnerable to viral and bacterial infections, which over time distort and permanently damage the lungs' airways. This permanent condition is called COPD (chronic obstructive pulmonary disease). Your doctor can perform a breathing test, called spirometry, to see if you have developed COPD. Chronic bronchitis is one of two main types of a COPD. The other main form of COPD is emphysema. Both forms of COPD make it difficult to breathe. Acute bronchitis is very common. The disorder often can be treated effectively without professional medical assistance. However, if you have severe or persistent symptoms or high fever, or if you cough up blood, you should see your doctor right away.
11 What does the word acute mean from the second paragraph? A. Extended B. Small and cuddly C. Very large D. Short amount of time Why do smokers have a more difficult time getting rid of bronchitis? A. Their lungs shrink over time B. They cough more than other people C. Smoking damages the cilia in the respiratory system D. Smokers are only able to access one lung What are some symptoms of acute bronchitis? Which is the most common respiratory issue? A. Stomachache and vomiting B. High fever and stomach pain C. Coughing up phlegm and difficulty breathing D. Fever and chills A. Chronic bronchitis B. Acute bronchitis C. COPD D. Emphysema
12 Watch It! Station Directions Each member of the group will go to the website listed on task card #1 Complete the task cards in order. Every student will answer the questions from the task cards on the lab sheet in the Watch It! section of the lab sheet.
13 YouTube: G Drive: URL is case-sensitive 1. Click Play on the video. 2. Answer questions from cards #2-4 on your lab sheet. Explain what the process of respiration is. YouTube List at least 6 of the organs or structures which exist in the respiratory system. When we exercise why do we breath harder?
14 Research It! Station Directions Each member of the group will go to the website listed on task card #1 Complete the task cards in order. Every student will answer the questions from the task cards on the lab sheet in the Research It! section.
15 1. Go to Answer the following questions on your lab sheet. 1. Read the first paragraph and summarize the structure (parts) and function of the Respiratory System. 1. Scroll towards the bottom and summarize the transportation of gases in the human body.
16 Explore It! Station Directions One member of the group will read the task cards in order. The group will be responsible for completing each of the tasks that are being read. Each member of the group will then write their conclusions down on the lab sheet in the Explore It! section.
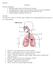
17 Use diagram #1 for the following questions. 1. After looking at the diagram, what role do you think the respiratory system has? 2. What organs and components (parts) make up the respiratory system? The Respiratory System is responsible for exchanging gases in the body. Oxygen is brought in and carbon dioxide is removed. Some of the main organs and components are listed on the following cards. Use diagram #2 to locate them. 1. Lungs the main organ in the system. Each lung expands and contracts as gases are brought in and out of the body. 2. Larynx also called the voice box. It allows the body to produce sounds and speech. 3. Trachea 5-inch long tube that allows air to easily enter and exit the lungs. 1. Bronchi these tubes split off from the trachea and head towards each of the two lungs. 2. Alveoli are tiny sacs within our lungs that allow oxygen and carbon dioxide to move between the lungs and bloodstream. 3. Diaphragm muscle below the lungs. When it contracts the lungs expand allowing air to flow into the lungs.
18 Use the model to answer the following questions. Pick up the model and LIGHTLY pull out and push in the large balloon covering the bottom of the cup. The model is delicate and can break easily if mishandled. Please use care. 1. What happens as you manipulate the balloon? 2. If these were real lungs what gases would be entering and exiting the system? 3. On your lab sheet describe the part of the model that represents each component from the system.
19 Respiratory System Diagram #1
20 Respiratory System Diagram #2
21 Illustrate It! Station Directions Each member of the group will draw a quick sketch on the lab sheet that shows they understand the concept being taught. Use the colored pencils and markers that are provided. The directions for the sketch are provided on the task card at the table.
22 Illustrate It! Station Directions 1. Use the colored pencils to draw a sketch of the Respiratory System. 2. You must label the lungs, oral cavity, nasal cavity, larynx, trachea, bronchus, bronchioles, and diaphragm. (You may use the diagram at the table for help) 3. Off to the side of the diagram list the specific function of the respiratory system.
23
24 Organize It! Station Directions It is recommended that you have completed at least two of the following stations before working at this station. -Read It! -Explore It! -Watch It! -Research It! Use the 6 labels and place them into pairs at the correct place on the diagram. Use the arrows to point to the part. Have your teacher check your work and sign off on your lab sheet.
25 Lungs Alveoli Bronchus Trachea Nasal Cavity Diaphragm The main organ in the respiratory system. Gases are exchanged. Tiny sacs that allow oxygen and carbon dioxide to be exchanged in the lungs Small tubes that branch off from the trachea 5 tube that allows air to flow clearly to and from the lungs Oxygen can enter the human body through this passage Contracts to allow the lungs to expand and let air into them
26
27 Respiratory System Explore It! Task Card #1 1. Name Task Card #6: Lungs Bronchi or Bronchus Task Card #6 1. Trachea Diaphragm Write It! Task Card #1: Task Card #2: Task Card #3:
28 Respiratory System Name Illustrate It! Assess It! #1 #3 Research It! Task Card #1 1. #2 #4 #1 #3 Task Card #2 1. Read It! #2 #4 Organize It!
29 Respiratory System Name Watch It! Task Card #2: Task Card #3: Task Card #4:
30 Respiratory System Answer Key Explore It! Task Card #1 1. Student answers will vary 2. Student answers will vary. They are just exploring at this point. Task Card #6: 2. Oxygen would be entering the lungs and carbon dioxide would be leaving the lungs. 3. Lungs smaller balloons inside Bronchi or Bronchus straws that split off from the main straw Task Card #6 1. The balloons should inflate as the student manipulates the diaphragm. Write It! Trachea The main straw entering the model Diaphragm The balloon that covers the bottom of the bottle/cup Write It! Task Card #1: 1. The respiratory system is necessary so that gases can be exchanged in the human body. Oxygen is breathed in and carbon dioxide is breathed out. Students answers will vary and hopefully they will be more detailed in their answer. 2. The two systems work together because the circulatory system delivers blood to the lungs which is rich in carbon dioxide and needs to be removed from the body. It exchanges the carbon dioxide with oxygen and delivers it throughout the body. 3. Plants and humans depend on each other. We breath out carbon dioxide which plants need for photosynthesis and plants give off oxygen which we use to breath. We depend on them to produce oxygen for survival.
31 Respiratory System Answer Key Illustrate It! The main function of the Respiratory System is exchange gases within the body. Oxygen is delivered to the body and carbon dioxide is removed from it. Assess It! #1 D #3 C Research It! #2 A #4 C Task Card #1 1. The cells of the human body require a constant stream of oxygen to stay alive. The respiratory system provides oxygen to the body s cells while removing carbon dioxide, a waste product that can be lethal if allowed to accumulate. There are 3 major parts of the respiratory system: the airway, the lungs, and the muscles of respiration. The airway, which includes the nose, mouth, pharynx, larynx, trachea, bronchi, and bronchioles, carries air between the lungs and the body s exterior. The lungs act as the functional units of the respiratory system by passing oxygen into the body and carbon dioxide out of the body. Finally, the muscles of respiration, including the diaphragm and intercostal muscles, work together to act as a pump, pushing air into and out of the lungs during breathing. Organize It! See last page of this document for answer diagram Read It! #1 D #3 C #2 C #4 B Task Card #2 1. The 2 major respiratory gases, oxygen and carbon dioxide, are transported through the body in the blood. Blood plasma has the ability to transport some dissolved oxygen and carbon dioxide, but most of the gases transported in the blood are bonded to transport molecules. Hemoglobin is an important transport molecule found in red blood cells that carries almost 99% of the oxygen in the blood. Hemoglobin can also carry a small amount of carbon dioxide from the tissues back to the lungs. However, the vast majority of carbon dioxide is carried in the plasma as bicarbonate ion. When the partial pressure of carbon dioxide is high in the tissues, the enzyme carbonic anhydrase catalyzes a reaction between carbon dioxide and water to form carbonic acid. Carbonic acid then dissociates into hydrogen ion and bicarbonate ion.
32 Respiratory System Answer Key Watch It! Task Card #2: The process of respiration is the exchange of gases that happens within the lungs. Oxygen is breathed in and carbon dioxide is breathed out. The exchange of these gases happens in the lungs. The body system is called the respiratory system. Task Card #3: Nasal cavity, oral cavity, pharynx, lungs, trachea, epiglottis, larynx, bronchi, bronchioles, alveoli Task Card 4: The body needs more oxygen during exercise and therefore breathing is sped up by the body. We can then exchange gases at a faster rate.
33 Nasal Cavity Lungs The main organ in the respiratory system. Gases are exchanged. Diaphragm Oxygen can enter the human body through this passage Contracts to allow the lungs to expand and let air into them Trachea 5 tube that allows air to flow clearly to and from the lungs Bronchus Small tubes that branch off from the trachea Alveoli Tiny sacs that allow oxygen and carbon dioxide to be exchanged in the lungs
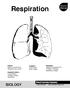
Animal Systems: The Respiratory System
 Animal Systems: The Respiratory System Tissues, Organs, and Systems of Living Things Cells, Cell Division, and Animal Systems and Plant Systems Cell Specialization Human Systems The Digestive The Circulatory
Animal Systems: The Respiratory System Tissues, Organs, and Systems of Living Things Cells, Cell Division, and Animal Systems and Plant Systems Cell Specialization Human Systems The Digestive The Circulatory
PARTS AND STRUCTURE OF THE RESPIRATORY SYSTEM
 PARTS AND STRUCTURE OF THE RESPIRATORY SYSTEM Parts of the Respiratory System The RS can be divided into two parts: 1. Respiratory Tract, (path that air follows). Nasal passage Pharynx Larynx Trachea Bronchi,
PARTS AND STRUCTURE OF THE RESPIRATORY SYSTEM Parts of the Respiratory System The RS can be divided into two parts: 1. Respiratory Tract, (path that air follows). Nasal passage Pharynx Larynx Trachea Bronchi,
Lesson 9.1: The Importance of an Organ Delivery System
 Lesson 9.1: The Importance of an Organ Delivery System Animals require a continuous supply of oxygen (O 2 ) for cellular respiration, and they must expel carbon dioxide (CO 2 ), the waste product of this
Lesson 9.1: The Importance of an Organ Delivery System Animals require a continuous supply of oxygen (O 2 ) for cellular respiration, and they must expel carbon dioxide (CO 2 ), the waste product of this
1. Label a diagram of the respiratory system. Objective sheet 3 Notes
 1. Label a diagram of the respiratory system Objective sheet 3 Notes 2. Functions of the respiratory structures Name Description Function Nasal Cavity Trachea Bronchi (Singular Bronchus) Bronchioles Lungs
1. Label a diagram of the respiratory system Objective sheet 3 Notes 2. Functions of the respiratory structures Name Description Function Nasal Cavity Trachea Bronchi (Singular Bronchus) Bronchioles Lungs
GASEOUS EXCHANGE IN HUMANS 06 AUGUST 2014
 GASEOUS EXCHANGE IN HUMANS 06 AUGUST 2014 In this lesson we: Lesson Description Look at gaseous exchange in humans in terms of o Ventilation o Inspiration o Expiration o Transport of gases o Homeostatic
GASEOUS EXCHANGE IN HUMANS 06 AUGUST 2014 In this lesson we: Lesson Description Look at gaseous exchange in humans in terms of o Ventilation o Inspiration o Expiration o Transport of gases o Homeostatic
Breathing: The normal rate is about 14 to 20 times a minute. Taking in of air is called Inspiration and the forcing out of air is called Expiration.
 Biology 12 Respiration Divisions of Respiration Breathing: entrance and exit of air into and out of the lungs External Respiration: exchange of gases(o2 and CO2) between air (in alveoli) and blood Internal
Biology 12 Respiration Divisions of Respiration Breathing: entrance and exit of air into and out of the lungs External Respiration: exchange of gases(o2 and CO2) between air (in alveoli) and blood Internal
Structures of the Respiratory System include:
 Respiratory System Structures of the Respiratory System include: ü Oral Cavity ü Nasal Cavity ü Pharynx ü Epiglottis ü Larynx ü Trachea ü Diaphragm ü Lung ü Bronchus ü Bronchioles ü Alveolus ü Pulmonary
Respiratory System Structures of the Respiratory System include: ü Oral Cavity ü Nasal Cavity ü Pharynx ü Epiglottis ü Larynx ü Trachea ü Diaphragm ü Lung ü Bronchus ü Bronchioles ü Alveolus ü Pulmonary
Human Biology Respiratory System
 Human Biology Respiratory System Respiratory System Responsible for process of breathing Works in cooperation with Circulatory system Three types: 1. Internal Respiration 2. External Respiration 3. Cellular
Human Biology Respiratory System Respiratory System Responsible for process of breathing Works in cooperation with Circulatory system Three types: 1. Internal Respiration 2. External Respiration 3. Cellular
Respiration. The ins and outs
 Respiration The ins and outs Functions 1. To bring O 2 into the body and transfer it to the blood stream 2. To remove CO 2 Circulation and respiration work together to achieve these functions Why Do We
Respiration The ins and outs Functions 1. To bring O 2 into the body and transfer it to the blood stream 2. To remove CO 2 Circulation and respiration work together to achieve these functions Why Do We
SCIENCE 8 RESPIRATION
 SCIENCE 8 RESPIRATION WHEN WE BREATHE, WHAT DO WE BREATHE IN? O2, N2, CO2, O3, NO2 (gas fumes), CO, pollutant, fragrants, toxins, etc. WHAT IS THE PURPOSE OF BREATHING IN? WHAT DOES OUR BODY WANT? O2 WHY?
SCIENCE 8 RESPIRATION WHEN WE BREATHE, WHAT DO WE BREATHE IN? O2, N2, CO2, O3, NO2 (gas fumes), CO, pollutant, fragrants, toxins, etc. WHAT IS THE PURPOSE OF BREATHING IN? WHAT DOES OUR BODY WANT? O2 WHY?
Video. Respiration System. You will use 3 pages of your journal for this lesson. 1. One page for hand written notes onto a journal page
 Respiratory System Video Respiration System You will use 3 pages of your journal for this lesson. 1. One page for hand written notes onto a journal page 2. 2 nd page for diagram 3. 3 rd page for chart
Respiratory System Video Respiration System You will use 3 pages of your journal for this lesson. 1. One page for hand written notes onto a journal page 2. 2 nd page for diagram 3. 3 rd page for chart
Pop Quiz. What produces mucus, HCl and pepsinogen in the stomach? List a water soluable vitamin What is a ruminant stomach?
 Pop Quiz What produces mucus, HCl and pepsinogen in the stomach? List a water soluable vitamin What is a ruminant stomach? Respiratory System Review Cellular respiration: obtain glucose and oxygen, get
Pop Quiz What produces mucus, HCl and pepsinogen in the stomach? List a water soluable vitamin What is a ruminant stomach? Respiratory System Review Cellular respiration: obtain glucose and oxygen, get
Chapter 11: Respiratory System Review Assignment
 Name: Date: Mark: / 45 Chapter 11: Respiratory System Review Assignment Multiple Choice = 45 Marks Identify the choice that best completes the statement or answers the question. 1. Which of the following
Name: Date: Mark: / 45 Chapter 11: Respiratory System Review Assignment Multiple Choice = 45 Marks Identify the choice that best completes the statement or answers the question. 1. Which of the following
REVISION: GASEOUS EXCHANGE 24 SEPTEMBER 2014 Lesson Description
 REVISION: GASEOUS EXCHANGE 24 SEPTEMBER 2014 Lesson Description In this lesson, we revise: Gaseous Exchange in Plants & Animals Gaseous Exchange in Humans Excretion in Humans Focus on the Kidney Gaseous
REVISION: GASEOUS EXCHANGE 24 SEPTEMBER 2014 Lesson Description In this lesson, we revise: Gaseous Exchange in Plants & Animals Gaseous Exchange in Humans Excretion in Humans Focus on the Kidney Gaseous
Sc ienc e 9-Biology Work sheet 8-2 A Single Breat h & Tak ing Care
 Unit 2 Your Living Body Sc ienc e 9-Biology Work sheet 8-2 A Single Breat h & Tak ing Care Name No pen or pencil No Textbook 20 Due Date Show Me Hand In Correct and Hand In Again By Read pages 159-167
Unit 2 Your Living Body Sc ienc e 9-Biology Work sheet 8-2 A Single Breat h & Tak ing Care Name No pen or pencil No Textbook 20 Due Date Show Me Hand In Correct and Hand In Again By Read pages 159-167
RESPIRATION AND EXCRETION
 CHAPTER 13 RESPIRATION AND EXCRETION SECTION 13 1 The Respiratory System (pages 430-438) This section describes the parts of the respiratory system and how they work to help you breathe and speak. Introduction
CHAPTER 13 RESPIRATION AND EXCRETION SECTION 13 1 The Respiratory System (pages 430-438) This section describes the parts of the respiratory system and how they work to help you breathe and speak. Introduction
A breath of fresh air
 A breath of fresh air BIG IDEAS You are learning to: Describe the structure of the lungs Explain how the lungs clean themselves Interpret patterns in data Where are the lungs and what do they do? The lungs
A breath of fresh air BIG IDEAS You are learning to: Describe the structure of the lungs Explain how the lungs clean themselves Interpret patterns in data Where are the lungs and what do they do? The lungs
The Respiratory System
 Name Date Class The Respiratory System This section describes the parts of the respiratory system and how they work to help you breathe and speak. Use Target Reading Skills As you read, complete the flowchart
Name Date Class The Respiratory System This section describes the parts of the respiratory system and how they work to help you breathe and speak. Use Target Reading Skills As you read, complete the flowchart
Respiratory System Review
 KEY THIS TEST WILL BE COMPLETED IN ONE CLASS PERIOD MONDAY, MARCH 10. 2014 Respiratory System Review Name A. Directions: Fill in the blank with the appropriate vocabulary word or words (several examples
KEY THIS TEST WILL BE COMPLETED IN ONE CLASS PERIOD MONDAY, MARCH 10. 2014 Respiratory System Review Name A. Directions: Fill in the blank with the appropriate vocabulary word or words (several examples
The Breathing System
 The Breathing System Learning Intentions 1. Students should Know how Breathing happens 2. Name and know the functions of the Breathing System 3. Know how the organs work and how they work with other systems
The Breathing System Learning Intentions 1. Students should Know how Breathing happens 2. Name and know the functions of the Breathing System 3. Know how the organs work and how they work with other systems
BIOLOGY 12: UNIT J - CHAPTER 15 - REVIEW WORKSHEET RESPIRATORY SYSTEM
 BIOLOGY 12: UNIT J - CHAPTER 15 - REVIEW WORKSHEET RESPIRATORY SYSTEM A. CHAPTER REVIEW 1. Define the four components of respiration. 2. What happens to the air as it moves along the air passages? What
BIOLOGY 12: UNIT J - CHAPTER 15 - REVIEW WORKSHEET RESPIRATORY SYSTEM A. CHAPTER REVIEW 1. Define the four components of respiration. 2. What happens to the air as it moves along the air passages? What
Glucose + Oxygen Carbon Dioxide + Water + Energy C6H12O CO2 + 6H20 + energy
 Cell Respiration - A food oxidization process in body cells to produce energy - Occurs (happens) in animal cells and plant cells Notes : Metabolic Reactions in Gaseous Exchange CELL RESPIRATION Photosynthesis
Cell Respiration - A food oxidization process in body cells to produce energy - Occurs (happens) in animal cells and plant cells Notes : Metabolic Reactions in Gaseous Exchange CELL RESPIRATION Photosynthesis
Name period date assigned date due date returned
 Name period date assigned date due date returned procedure 1. Take one balloon and stretch it out 2. Take one deep breath and blow into the balloon until you cannot breath out anymore. Do Not Take A Second
Name period date assigned date due date returned procedure 1. Take one balloon and stretch it out 2. Take one deep breath and blow into the balloon until you cannot breath out anymore. Do Not Take A Second
Chapter 16 Respiratory System
 Introduction Chapter 16 Respiratory System The respiratory system consists of tubes that filter incoming air and transport it to alveoli where gases are exchanged. Think pair share: what organs are associated
Introduction Chapter 16 Respiratory System The respiratory system consists of tubes that filter incoming air and transport it to alveoli where gases are exchanged. Think pair share: what organs are associated
The Respiratory System
 Respiration and Excretion Name Date Class The Respiratory System This section describes the parts of the respiratory system and how they work to help you breathe and speak. Use Target Reading Skills As
Respiration and Excretion Name Date Class The Respiratory System This section describes the parts of the respiratory system and how they work to help you breathe and speak. Use Target Reading Skills As
Monday, ! Today: Respiratory system! 5/20/14! Transport of Blood! What we ve been covering! Circulatory system! Parts of blood! Heart! tubing!
 Monday, 5.19.14! What we ve been covering! Circulatory system! Parts of blood! Heart! tubing! Transport of Blood! What is transported! Nutrients! Oxygen! Carbon Dioxide! Hormones! Antibodies! What it is/does!
Monday, 5.19.14! What we ve been covering! Circulatory system! Parts of blood! Heart! tubing! Transport of Blood! What is transported! Nutrients! Oxygen! Carbon Dioxide! Hormones! Antibodies! What it is/does!
Clinical Respiratory System Quiz
 Quiz Description Clinical Respiratory System Quiz Q.1) Q.2) Q.3) Q.4) Q.5) Q.6) What is NOT true about Asthma? It can be triggered by air temperature and allergens. It is the inflammation of the throat.
Quiz Description Clinical Respiratory System Quiz Q.1) Q.2) Q.3) Q.4) Q.5) Q.6) What is NOT true about Asthma? It can be triggered by air temperature and allergens. It is the inflammation of the throat.
Outline - Respiratory System. Function of the respiratory system Parts of the respiratory system Mechanics of breathing Regulation of breathing
 Respiratory system Function Outline - Respiratory System I. II. III. IV. Respiratory System The function of the respiratory system is to bring in oxygen to the body and remove carbon dioxide. Function
Respiratory system Function Outline - Respiratory System I. II. III. IV. Respiratory System The function of the respiratory system is to bring in oxygen to the body and remove carbon dioxide. Function
Respiratory System Homework
 Respiratory System Homework The R S is the body s breathing equipment. Similar to the D system, it takes S from outside the body (G, particularly O ), circulates them through the body to C and T, then
Respiratory System Homework The R S is the body s breathing equipment. Similar to the D system, it takes S from outside the body (G, particularly O ), circulates them through the body to C and T, then
system. and then into the tissues. Diffusion of wastes such as Carbon Dioxide from tissues into blood and out of blood into the lungs.
 Respiratory System 1.Exchange Why do of we gases breathe? into the Think blood of all and the tissues. reasons Diffusion why we of Oxygen need a respiratory into blood from the lungs system. and then into
Respiratory System 1.Exchange Why do of we gases breathe? into the Think blood of all and the tissues. reasons Diffusion why we of Oxygen need a respiratory into blood from the lungs system. and then into
The Respiratory System
 Name Date Class The Respiratory System (pages 564-572) Respiratory System Functions (pages 565-566) Key Concept: The respiratory system moves oxygen from the outside environment into the body. It also
Name Date Class The Respiratory System (pages 564-572) Respiratory System Functions (pages 565-566) Key Concept: The respiratory system moves oxygen from the outside environment into the body. It also
3.6. The Respiratory System
 The Respiratory System Whether you are aware of it or not, you breathe in and out 15 times each minute on average. This rate increases automatically if your physical activity increases. With normal breathing,
The Respiratory System Whether you are aware of it or not, you breathe in and out 15 times each minute on average. This rate increases automatically if your physical activity increases. With normal breathing,
Respiratory System Unit
 Respiratory System Unit An integrative unit including lessons in Science, Art, Math, Health, and Literature 3rd Grade Anatomy Wegner 1 Introduction: The respiratory system allows the human body to take
Respiratory System Unit An integrative unit including lessons in Science, Art, Math, Health, and Literature 3rd Grade Anatomy Wegner 1 Introduction: The respiratory system allows the human body to take
Department of Biology Work Sheet Respiratory system,9 class
 I. Name the following : Department of Biology Work Sheet Respiratory system,9 class 1. A muscular sheet separating the thoracic and abdominal cavities. 2. A respiratory tube supported by cartilaginous
I. Name the following : Department of Biology Work Sheet Respiratory system,9 class 1. A muscular sheet separating the thoracic and abdominal cavities. 2. A respiratory tube supported by cartilaginous
The Respiratory System
 The Respiratory System (pages 112 120) Respiratory System Functions (pages 113 114) Key Concept: The respiratory system moves oxygen from the outside environment into the body. It also removes carbon dioxide
The Respiratory System (pages 112 120) Respiratory System Functions (pages 113 114) Key Concept: The respiratory system moves oxygen from the outside environment into the body. It also removes carbon dioxide
The Respiratory System. Medical Terminology
 The Respiratory System Medical Terminology The respiratory system is where gas exchange occurs via respiration; inhalation/exhalation. pick up oxygen from inhaled air expels carbon dioxide and water sinus
The Respiratory System Medical Terminology The respiratory system is where gas exchange occurs via respiration; inhalation/exhalation. pick up oxygen from inhaled air expels carbon dioxide and water sinus
Page 1. Chapter 33: Respiration O 2 CO 2
 Chapter 33: Respiration O 2 CO 2 Features of Respiratory Systems: 1) Moist surface (to dissolve gas) 2) Thin cells lining surface 3) Large surface area contacting environment Facilitate Diffusion Methods
Chapter 33: Respiration O 2 CO 2 Features of Respiratory Systems: 1) Moist surface (to dissolve gas) 2) Thin cells lining surface 3) Large surface area contacting environment Facilitate Diffusion Methods
Assignments for Life Processes(Respiration)
 Assignments for Life Processes(Respiration) 1 Question 1 Why do organisms need food? Organisms need food for obtaining energy to perform the vital functions. Question 2 What is a respiratory substrate?
Assignments for Life Processes(Respiration) 1 Question 1 Why do organisms need food? Organisms need food for obtaining energy to perform the vital functions. Question 2 What is a respiratory substrate?
Lab 17. The Respiratory System. Laboratory Objectives
 Lab 17 The Respiratory System Laboratory Objectives Identify and describe the anatomical structures of the respiratory system. Describe the relationship between volume and pressure. Describe changes in
Lab 17 The Respiratory System Laboratory Objectives Identify and describe the anatomical structures of the respiratory system. Describe the relationship between volume and pressure. Describe changes in
Chapter 22 Gas Exchange
 Chapter 22 Gas Exchange PowerPoint Lectures for Biology: Concepts & Connections, Sixth Edition Campbell, Reece, Taylor, Simon, and Dickey Lecture by Edward J. Zalisko Introduction: Surviving in Thin Air
Chapter 22 Gas Exchange PowerPoint Lectures for Biology: Concepts & Connections, Sixth Edition Campbell, Reece, Taylor, Simon, and Dickey Lecture by Edward J. Zalisko Introduction: Surviving in Thin Air
(Slide 1) Lecture Notes: Respiratory System
 (Slide 1) Lecture Notes: Respiratory System I. (Slide 2) The Respiratory Tract A) Major structures and regions of the respiratory Tract/Route INTO body 1) nose 2) nasal cavity 3) pharynx 4) glottis 5)
(Slide 1) Lecture Notes: Respiratory System I. (Slide 2) The Respiratory Tract A) Major structures and regions of the respiratory Tract/Route INTO body 1) nose 2) nasal cavity 3) pharynx 4) glottis 5)
BIOLOGY 12 - RESPIRATION - CHAPTER NOTES
 BIOLOGY 12 - RESPIRATION - CHAPTER NOTES We often think of respiration as just breathing. In fact, breathing is just one part of this physiological process. As biologists, we divide respiration up into
BIOLOGY 12 - RESPIRATION - CHAPTER NOTES We often think of respiration as just breathing. In fact, breathing is just one part of this physiological process. As biologists, we divide respiration up into
The Respiratory System
 The Respiratory System Learning Outcomes Identify the following structures in the lungs: windpipe, bronchus, bronchioles and air sacs State the function of the air sacs State the path oxygen takes when
The Respiratory System Learning Outcomes Identify the following structures in the lungs: windpipe, bronchus, bronchioles and air sacs State the function of the air sacs State the path oxygen takes when
Respiration. Chapter 39
 Respiration Chapter 39 Impacts, Issues Up in Smoke Smoking immobilizes ciliated cells and kills white blood cells that defend the respiratory system; highly addictive nicotine discourages quitting 39.1
Respiration Chapter 39 Impacts, Issues Up in Smoke Smoking immobilizes ciliated cells and kills white blood cells that defend the respiratory system; highly addictive nicotine discourages quitting 39.1
Use scientific principles to explain how the sprayer works. You may use diagrams to support your answer.
 4.3 Marking Key This guide includes sample answers, task-specific observable elements, (Appendices 1 and 2), descriptive evaluation rubrics for each competency (Appendices 3 and 4), and non-descriptive
4.3 Marking Key This guide includes sample answers, task-specific observable elements, (Appendices 1 and 2), descriptive evaluation rubrics for each competency (Appendices 3 and 4), and non-descriptive
Lesson 6 Plate Tectonics and Continental Drift PS 2.2 a,e PS 3.1i
 Table of Contents Letter to the Student...................................... 5 Letter to the Family....................................... 6 New York State Performance Standards Correlation Chart.......
Table of Contents Letter to the Student...................................... 5 Letter to the Family....................................... 6 New York State Performance Standards Correlation Chart.......
Respiratory System 1
 Respiratory System 1 Outline Respiratory structures Gills Air-Breathing Animals Amphibians and Reptiles Mammals Birds Structures and Mechanisms of Breathing 2 Copyright The McGraw-Hill Companies, Inc.
Respiratory System 1 Outline Respiratory structures Gills Air-Breathing Animals Amphibians and Reptiles Mammals Birds Structures and Mechanisms of Breathing 2 Copyright The McGraw-Hill Companies, Inc.
I. Gas Exchange Respiratory Surfaces Respiratory Surface:
 I. Gas Exchange Respiratory Surfaces Respiratory Surface: Common characteristics of respiratory surfaces: a) Moist: allows for the RAPID diffusion of dissolved gasses across its surface. Whereas the respiratory
I. Gas Exchange Respiratory Surfaces Respiratory Surface: Common characteristics of respiratory surfaces: a) Moist: allows for the RAPID diffusion of dissolved gasses across its surface. Whereas the respiratory
08 Respiration. #79 Respiration realeases energy from food
 08 Respiration #79 Respiration realeases energy from food Respiration is the chemical reactions that break down nutrient molecules in living cells to release energy. In humans, our cells need energy (ATP)
08 Respiration #79 Respiration realeases energy from food Respiration is the chemical reactions that break down nutrient molecules in living cells to release energy. In humans, our cells need energy (ATP)
OB11 Carry out qualitative tests to compare the carbon dioxide levels of inhaled and exhaled air
 Biology: 5. Respiration and Breathing Please remember to photocopy 4 pages onto one sheet by going A3 A4 and using back to back on the photocopier OB9 Syllabus Describe the process of aerobic respiration
Biology: 5. Respiration and Breathing Please remember to photocopy 4 pages onto one sheet by going A3 A4 and using back to back on the photocopier OB9 Syllabus Describe the process of aerobic respiration
Human gas exchange. Question Paper. Save My Exams! The Home of Revision. Cambridge International Examinations. 56 minutes. Time Allowed: Score: /46
 Human gas exchange Question Paper Level Subject Exam oard Topic Sub Topic ooklet O Level iology ambridge International Examinations Respiration Human gas exchange Question Paper Time llowed: 56 minutes
Human gas exchange Question Paper Level Subject Exam oard Topic Sub Topic ooklet O Level iology ambridge International Examinations Respiration Human gas exchange Question Paper Time llowed: 56 minutes
The Human Body. Everyone Needs Healthy Systems. Blood Vessels
 The Human Body Everyone Needs Healthy Systems There are several systems that make up the human body. Although their functions differ, they all work together to keep your body running smoothly. Some of
The Human Body Everyone Needs Healthy Systems There are several systems that make up the human body. Although their functions differ, they all work together to keep your body running smoothly. Some of
Chapter 1: Respiration
 Chapter 1: Respiration Respiration Human Breathing Mechanism Transport of oxygen Importance of a healthy respiratory system Respiratory system lungs inhalation exhalation Diffusion of oxygen by blood Transport
Chapter 1: Respiration Respiration Human Breathing Mechanism Transport of oxygen Importance of a healthy respiratory system Respiratory system lungs inhalation exhalation Diffusion of oxygen by blood Transport
Multicellular Organisms. Sub-Topic 2.7 Animal Transport & Exchange Systems
 Multicellular Organisms Sub-Topic 2.7 Animal Transport & Exchange Systems On completion of this sub-topic I will be able to state that: Rings of cartilage keep the main airways open Oxygen and carbon dioxide
Multicellular Organisms Sub-Topic 2.7 Animal Transport & Exchange Systems On completion of this sub-topic I will be able to state that: Rings of cartilage keep the main airways open Oxygen and carbon dioxide
practices makes perfect
 Human Respiratory system Chapter 1: Respiration PMR 03, 08 1. The human respiratory system consists of: a... b... c.. d... e. Our body has.. lungs (right & left). f. Each lung consists of the, and alveoli.
Human Respiratory system Chapter 1: Respiration PMR 03, 08 1. The human respiratory system consists of: a... b... c.. d... e. Our body has.. lungs (right & left). f. Each lung consists of the, and alveoli.
25/4/2016. Physiology #01 Respiratory system Nayef Garaibeh Rawan Alwaten
 25/4/2016 Physiology #01 Respiratory system Nayef Garaibeh Rawan Alwaten Respiratory System Introduction: - We breath while we are sleeping, talking, working and resting. - Respiratory diseases are abundant
25/4/2016 Physiology #01 Respiratory system Nayef Garaibeh Rawan Alwaten Respiratory System Introduction: - We breath while we are sleeping, talking, working and resting. - Respiratory diseases are abundant
2/28/18. Respiratory System. 1 Copyright 2016 by Elsevier Inc. All rights reserved. Introduction. Anatomy. Physiology. Respiratory System
 Introduction Respiratory System Chapter 28 Respiration: We inhale air, extract oxygen from it, exhale air Cardiovascular and respiratory systems work together Failure of either system: - Disruption of
Introduction Respiratory System Chapter 28 Respiration: We inhale air, extract oxygen from it, exhale air Cardiovascular and respiratory systems work together Failure of either system: - Disruption of
Then the partial pressure of oxygen is. b) Gases will diffuse down a pressure gradient across a respiratory surface if it is: i) permeable ii) moist
 1 AP Biology March 2008 Respiration Chapter 42 Gas exchange occurs across specialized respiratory surfaces. 1) Gas exchange: Relies on the diffusion of gases down pressure gradients. At sea level, atmosphere
1 AP Biology March 2008 Respiration Chapter 42 Gas exchange occurs across specialized respiratory surfaces. 1) Gas exchange: Relies on the diffusion of gases down pressure gradients. At sea level, atmosphere
2.1.1 List the principal structures of the
 physiology 2.1.1 List the principal structures of the The principle structures of the respiratory are: Nose/Mouth used for inhalation of oxygen-rich air and expelling carbon dioxide rich air Pharynx -
physiology 2.1.1 List the principal structures of the The principle structures of the respiratory are: Nose/Mouth used for inhalation of oxygen-rich air and expelling carbon dioxide rich air Pharynx -
Chapter 42 Part III The Respiratory System
 Biology 120 J. Greg Doheny Chapter 42 Part III The Respiratory System Notes: In this section we will discuss the breathing system, also known as the respiratory system. This should not be confused with
Biology 120 J. Greg Doheny Chapter 42 Part III The Respiratory System Notes: In this section we will discuss the breathing system, also known as the respiratory system. This should not be confused with
Then the partial pressure of oxygen is x 760 = 160 mm Hg
 1 AP Biology March 2008 Respiration Chapter 42 Gas exchange occurs across specialized respiratory surfaces. 1) Gas exchange: the uptake of molecular oxygen (O2) from the environment and the discharge of
1 AP Biology March 2008 Respiration Chapter 42 Gas exchange occurs across specialized respiratory surfaces. 1) Gas exchange: the uptake of molecular oxygen (O2) from the environment and the discharge of
Physical Health and your Respiratory System and Circulatory System
 Physical Health and your Respiratory System and Circulatory System Unit Plan Emily Pritchard Fall 2008 1 P a g e Table of Contents Unit Description... 3 Unit Rationale.. 4 Unit Goals....6 Unit Objectives....7
Physical Health and your Respiratory System and Circulatory System Unit Plan Emily Pritchard Fall 2008 1 P a g e Table of Contents Unit Description... 3 Unit Rationale.. 4 Unit Goals....6 Unit Objectives....7
Anatomy and Physiology Part 11: Of Blood and Breath by: Les Sellnow
 Anatomy and Physiology Part 11: Of Blood and Breath by: Les Sellnow There are few similarities between horses and automobiles, but in a manner of speaking, the horse's circulatory and respiratory systems
Anatomy and Physiology Part 11: Of Blood and Breath by: Les Sellnow There are few similarities between horses and automobiles, but in a manner of speaking, the horse's circulatory and respiratory systems
GASEOUS EXCHANGE 17 JULY 2013
 GASEOUS EXCHANGE 17 JULY 2013 Lesson Description In this lesson we: Discuss what is gaseous exchange? Consider requirements of an efficient gaseous exchange surface. Look at diversity in gas exchange systems.
GASEOUS EXCHANGE 17 JULY 2013 Lesson Description In this lesson we: Discuss what is gaseous exchange? Consider requirements of an efficient gaseous exchange surface. Look at diversity in gas exchange systems.
Unit 8 B: Respiration
 Unit 8 B: Respiration Respiration: Respiration is a chemical reaction that happens in all living cells. It is the way that energy is released from glucose, for our cells to use to keep us functioning.
Unit 8 B: Respiration Respiration: Respiration is a chemical reaction that happens in all living cells. It is the way that energy is released from glucose, for our cells to use to keep us functioning.
Topic 13: Gas Exchange Ch. 42. Gas Exchange pp Gas Exchange. Gas Exchange in Fish pp Gas Exchange in Fish
 Topic 13: Gas Exchange Ch. 42 Fig. 42.24 Gas Exchange pp.979-989 Gas exchange involves the uptake of oxygen and the discharge of carbon dioxide (i.e. respiration or breathing). It is necessary for cellular
Topic 13: Gas Exchange Ch. 42 Fig. 42.24 Gas Exchange pp.979-989 Gas exchange involves the uptake of oxygen and the discharge of carbon dioxide (i.e. respiration or breathing). It is necessary for cellular
In-Home Aides Partners in Quality Care April 2018
 In-Home Aides Partners in Quality Care April 2018 In-Home Aides Partners in Quality Care is a monthly newsletter published for member agencies. Copyright AHHC 2018 - May be reproduced for In- Home Aides.
In-Home Aides Partners in Quality Care April 2018 In-Home Aides Partners in Quality Care is a monthly newsletter published for member agencies. Copyright AHHC 2018 - May be reproduced for In- Home Aides.
SCIENCE- NOTES. Q1. Draw the diagram of human respiratory system and explain the function of the following parts:
 SCIENCE- NOTES NAME: RESPIRATION IN ORGANISMS STD.VII DIV: Q1. Draw the diagram of human respiratory system and explain the function of the following parts: i. Nasal cavity ii. Trachea iii. Lungs iv. Bronchioles
SCIENCE- NOTES NAME: RESPIRATION IN ORGANISMS STD.VII DIV: Q1. Draw the diagram of human respiratory system and explain the function of the following parts: i. Nasal cavity ii. Trachea iii. Lungs iv. Bronchioles
1.2 The structure and functions of the cardio-respiratory system Learning objectives
 1.2 The structure and functions of the cardio-respiratory system Learning objectives To understand the functions of the circulatory system. To be able to identify the differences between veins, arteries
1.2 The structure and functions of the cardio-respiratory system Learning objectives To understand the functions of the circulatory system. To be able to identify the differences between veins, arteries
Gas Exchange Respiratory Systems
 alveoli gills Gas Exchange Respiratory Systems elephant seals 2008-2009 Why do we need a respiratory system? respiration for respiration Need O 2 in for aerobic cellular respiration make ATP Need CO 2
alveoli gills Gas Exchange Respiratory Systems elephant seals 2008-2009 Why do we need a respiratory system? respiration for respiration Need O 2 in for aerobic cellular respiration make ATP Need CO 2
Department of Biology Work Sheet Respiratory system
 Department of Biology Work Sheet Respiratory system 1. Name the following : i. A muscular sheet separating the thoracic and abdominal cavities. ii. A respiratory tube supported by cartilaginous rings.
Department of Biology Work Sheet Respiratory system 1. Name the following : i. A muscular sheet separating the thoracic and abdominal cavities. ii. A respiratory tube supported by cartilaginous rings.
Chapter 9 Airway Respirations Metabolism Oxygen Requirements Respiratory Anatomy Respiratory Anatomy Respiratory Anatomy Diaphragm
 1 Chapter 9 Airway 2 Respirations Every cell of the body requires to survive Oxygen must come in and carbon must go out 3 Metabolism Metabolism--Process where the body s cells convert food to Adequate
1 Chapter 9 Airway 2 Respirations Every cell of the body requires to survive Oxygen must come in and carbon must go out 3 Metabolism Metabolism--Process where the body s cells convert food to Adequate
Respiration. The resspiratory system
 Respiration The resspiratory system The Alveoli The lungs have about 300 million alveoli, with a total crosssec onal area of 50 70 m2.. Each alveolar sac is surrounded by blood capillaries. The walls of
Respiration The resspiratory system The Alveoli The lungs have about 300 million alveoli, with a total crosssec onal area of 50 70 m2.. Each alveolar sac is surrounded by blood capillaries. The walls of
alveoli Chapter 42. Gas Exchange elephant seals gills AP Biology
 alveoli Chapter 42. Gas Exchange gills elephant seals Gas exchange O 2 & CO 2 exchange exchange between environment & cells provides O 2 for aerobic cellular respiration need moist membrane need high
alveoli Chapter 42. Gas Exchange gills elephant seals Gas exchange O 2 & CO 2 exchange exchange between environment & cells provides O 2 for aerobic cellular respiration need moist membrane need high
Respiration BIOLOGY. Visual Learning Company. Reviewers: Stephen Trombulak Ph.D. Professor of Biology Middlebury College
 Instructor s Manual Editors: Brian A. Jerome Ph.D. Stephanie Zak Jerome Assistant Editors: Louise Marrier Lyndsey Canfield Heidi Berry Graphics: Fred Thodal Dean Ladago Reviewers: Stephen Trombulak Ph.D.
Instructor s Manual Editors: Brian A. Jerome Ph.D. Stephanie Zak Jerome Assistant Editors: Louise Marrier Lyndsey Canfield Heidi Berry Graphics: Fred Thodal Dean Ladago Reviewers: Stephen Trombulak Ph.D.
UNIT 9 - RESPIRATORY SYSTEM LECTURE NOTES
 UNIT 9 - RESPIRATORY SYSTEM LECTURE NOTES 9.01 GENERAL FUNCTIONS OF THE RESPIRATORY SYSTEM A. Brings oxygenated air to the alveoli B. Removes air containing carbon dioxide C. Filters, warms, and humidifies
UNIT 9 - RESPIRATORY SYSTEM LECTURE NOTES 9.01 GENERAL FUNCTIONS OF THE RESPIRATORY SYSTEM A. Brings oxygenated air to the alveoli B. Removes air containing carbon dioxide C. Filters, warms, and humidifies
AP Biology. Gas Exchange Respiratory Systems. Gas exchange. Why do we need a respiratory system? Optimizing gas exchange. Gas exchange in many forms
 alveoli Gas Exchange Respiratory Systems gills elephant seals 2008-2009 Why do we need a respiratory system? Need O 2 in food respiration for respiration for aerobic cellular respiration make ATP Need
alveoli Gas Exchange Respiratory Systems gills elephant seals 2008-2009 Why do we need a respiratory system? Need O 2 in food respiration for respiration for aerobic cellular respiration make ATP Need
AP Biology. Chapter 42. Gas Exchange. Optimizing gas exchange. Gas exchange. Gas exchange in many forms. Evolution of gas exchange structures
 alveoli Chapter 42. Gas Exchange gills elephant seals Gas exchange & C exchange exchange between environment & cells provides for aerobic cellular respiration need moist membrane need high surface area
alveoli Chapter 42. Gas Exchange gills elephant seals Gas exchange & C exchange exchange between environment & cells provides for aerobic cellular respiration need moist membrane need high surface area
1 The Respiratory System
 Section 1 The Respiratory System 1 The Respiratory System Objectives After this lesson, students will be able to D.4.1.1 Describe the functions of the respiratory system. D.4.1.2 Identify the structures
Section 1 The Respiratory System 1 The Respiratory System Objectives After this lesson, students will be able to D.4.1.1 Describe the functions of the respiratory system. D.4.1.2 Identify the structures
Chapter 35: Respiratory Systems
 Chapter 35: Respiratory Systems AP Curriculum Alignment Cells are restricted in size by the necessity of maintain a large surface area to volume. The cells of the alveoli, which are the functioning units
Chapter 35: Respiratory Systems AP Curriculum Alignment Cells are restricted in size by the necessity of maintain a large surface area to volume. The cells of the alveoli, which are the functioning units
Directions: The following two questions refer to the diagram below, which shows a group of cells from the respiratory tract.
 Topic 7 Gas exchange in humans Directions: The following two questions refer to the diagram below, which shows a group of cells from the respiratory tract. X Y 1. What is the function of structure X? A.
Topic 7 Gas exchange in humans Directions: The following two questions refer to the diagram below, which shows a group of cells from the respiratory tract. X Y 1. What is the function of structure X? A.
When paramedics rush to the aid of an injured person, they
 Section 37 3 37 3 The Respiratory System 1 FOCUS Objectives 37.3.1 Describe respiration. 37.3.2 Identify the function of the respiratory system. 37.3.3 Describe gas exchange and breathing. 37.3.4 Explain
Section 37 3 37 3 The Respiratory System 1 FOCUS Objectives 37.3.1 Describe respiration. 37.3.2 Identify the function of the respiratory system. 37.3.3 Describe gas exchange and breathing. 37.3.4 Explain
The Continuing Adventures of Mr. O Too
 The Continuing Adventures of Mr. O Too When last we heard from Mr. O Too, he was traveling from the lungs to the leg muscles of an athlete. The unit one observation was a very general overview of the basic
The Continuing Adventures of Mr. O Too When last we heard from Mr. O Too, he was traveling from the lungs to the leg muscles of an athlete. The unit one observation was a very general overview of the basic
The Respiratory System
 Science Unit: Lesson 4: Human Anatomy How Do We Move? The Respiratory System School year: 2007/2008 Developed for: Developed by: Grade level: Duration of lesson: Henderson Annex Elementary School, Vancouver
Science Unit: Lesson 4: Human Anatomy How Do We Move? The Respiratory System School year: 2007/2008 Developed for: Developed by: Grade level: Duration of lesson: Henderson Annex Elementary School, Vancouver
Gaseous exchange. Grade 11
 z Gaseous exchange Grade 11 z Terminology 1. Breathing 2. Gaseous exchange 3. Diffusion 4. Spongy mesophyll cells 5. Tracheae 6. Gills 7. Alveoli 8. Larynx 9. Diaphragm 10. Endothelium 1. Pleura 2. Squamous
z Gaseous exchange Grade 11 z Terminology 1. Breathing 2. Gaseous exchange 3. Diffusion 4. Spongy mesophyll cells 5. Tracheae 6. Gills 7. Alveoli 8. Larynx 9. Diaphragm 10. Endothelium 1. Pleura 2. Squamous
Respiratory/Pulmonary Laboratory Experimentation
 Respiratory/Pulmonary Laboratory Experimentation Introduction Anatomy Review The respiratory system has the dubious honor of being the system that permits the transport of gases from the environment inside
Respiratory/Pulmonary Laboratory Experimentation Introduction Anatomy Review The respiratory system has the dubious honor of being the system that permits the transport of gases from the environment inside
BREATHING AND EXCHANGE OF GASES
 96 BIOLOGY, EXEMPLAR PROBLEMS CHAPTER 17 BREATHING AND EXCHANGE OF GASES MULTIPLE CHOICE QUESTIONS 1. Respiration in insects is called direct because a. The tissues exchange O 2 directly with the air in
96 BIOLOGY, EXEMPLAR PROBLEMS CHAPTER 17 BREATHING AND EXCHANGE OF GASES MULTIPLE CHOICE QUESTIONS 1. Respiration in insects is called direct because a. The tissues exchange O 2 directly with the air in
Gas Exchange ACTIVITY OVERVIEW SUMMARY KEY CONCEPTS AND PROCESS SKILLS KEY VOCABULARY. Teacher s Guide B-75 L A B O R ATO R Y
 Gas Exchange 17 40- to 2 50-minute sessions ACTIVITY OVERVIEW L A B O R ATO R Y SUMMARY This activity explores the role of the respiratory system in the regulation of gases in the blood. Students investigate
Gas Exchange 17 40- to 2 50-minute sessions ACTIVITY OVERVIEW L A B O R ATO R Y SUMMARY This activity explores the role of the respiratory system in the regulation of gases in the blood. Students investigate
Show Me Hand In. Correct and Hand In Again By. Read pages of SP to help you answer the following questions: 1. Name 4 gases contained in air:,
 Name 20 Due Date Show Me Hand In Correct and Hand In Again By Read pages 151-157 of SP to help you answer the following questions: 1. Name 4 gases contained in air:, and. 2. What are two types of solid
Name 20 Due Date Show Me Hand In Correct and Hand In Again By Read pages 151-157 of SP to help you answer the following questions: 1. Name 4 gases contained in air:, and. 2. What are two types of solid
EXPERIMENTING The Respiratory and Circulatory Systems CLIL Course University of Nottingham STUDENT S WORKSHEETS
 EXPERIMENTING The Respiratory and Circulatory Systems CLIL Course University of Nottingham STUDENT S WORKSHEETS M. Antònia Berga Sabaté January March 2009 Worksheet 1 You breathe to take air into your
EXPERIMENTING The Respiratory and Circulatory Systems CLIL Course University of Nottingham STUDENT S WORKSHEETS M. Antònia Berga Sabaté January March 2009 Worksheet 1 You breathe to take air into your
Respiratory Physiology Gaseous Exchange
 Respiratory Physiology Gaseous Exchange Session Objectives. What you will cover Basic anatomy of the lung including airways Breathing movements Lung volumes and capacities Compliance and Resistance in
Respiratory Physiology Gaseous Exchange Session Objectives. What you will cover Basic anatomy of the lung including airways Breathing movements Lung volumes and capacities Compliance and Resistance in
I. Function- Respiration: Breathing: II.Organs: 1. nose/mouth: bronchi: 4. -Cilia is important because:
 Lesson 16.3 NOTES: The Respiratory System (Unlock) Essential Question: -What are the structures and functions of the respiratory system? Learning Target(s): -I can identify structures and explain functions
Lesson 16.3 NOTES: The Respiratory System (Unlock) Essential Question: -What are the structures and functions of the respiratory system? Learning Target(s): -I can identify structures and explain functions
These two respiratory media (air & water) impose rather different constraints on oxygen uptake:
 Topic 19: OXYGEN UPTAKE AND TRANSPORT (lectures 29-30) OBJECTIVES: 1. Be able to compare air vs. water as a respiratory medium with respect to oxygen content, diffusion coefficient, viscosity and water
Topic 19: OXYGEN UPTAKE AND TRANSPORT (lectures 29-30) OBJECTIVES: 1. Be able to compare air vs. water as a respiratory medium with respect to oxygen content, diffusion coefficient, viscosity and water
Living with. Chronic Obstructive Pulmonary Disease COPD. Breathing and Relaxation
 Living with Chronic Obstructive Pulmonary Disease COPD Breathing and Relaxation Anatomy and Physiology of COPD Breathing Techniques Positions to Reduce Shortness of Breath Relaxation Exercise Breathing
Living with Chronic Obstructive Pulmonary Disease COPD Breathing and Relaxation Anatomy and Physiology of COPD Breathing Techniques Positions to Reduce Shortness of Breath Relaxation Exercise Breathing
Introduction THE RESPIRATORY SYSTEM
 Introduction THE RESPIRATORY SYSTEM 1 Lung Capacity The total lung capacity of fully grown healthy lungs is about 5-6 L of air, a person normally inhales and exhales about 0.5 L. Tidal Volume: amount of
Introduction THE RESPIRATORY SYSTEM 1 Lung Capacity The total lung capacity of fully grown healthy lungs is about 5-6 L of air, a person normally inhales and exhales about 0.5 L. Tidal Volume: amount of
It is a product of proteins broken down in the mammal. It is exchanged for oxygen which is taken into the blood.
 5 The table shows the approximate composition of air breathed out by a mammal. Where does the nitrogen in the air breathed out come from? It is a product of proteins broken down in the mammal. It is a
5 The table shows the approximate composition of air breathed out by a mammal. Where does the nitrogen in the air breathed out come from? It is a product of proteins broken down in the mammal. It is a
Introduction. Respiration. Chapter 10. Objectives. Objectives. The Respiratory System
 Introduction Respiration Chapter 10 The Respiratory System Provides a means of gas exchange between the environment and the body Plays a role in the regulation of acidbase balance during exercise Objectives
Introduction Respiration Chapter 10 The Respiratory System Provides a means of gas exchange between the environment and the body Plays a role in the regulation of acidbase balance during exercise Objectives
Ebtihal Al-Remawi. Afnan Ali. Yanal. 1 P a g e
 #1 Ebtihal Al-Remawi Afnan Ali Yanal 1 P a g e 1/15 *before we start: if you are watching the video and have no time for some laughs go to minute (5:28 to 7:02) then go to minute (10:14). I will be adding
#1 Ebtihal Al-Remawi Afnan Ali Yanal 1 P a g e 1/15 *before we start: if you are watching the video and have no time for some laughs go to minute (5:28 to 7:02) then go to minute (10:14). I will be adding
3.3.2 Gas Exchange SPECIFICATION
 alevelbiology.co.uk 3.3.2 Gas Exchange SPECIFICATION Adaptations of gas exchange surfaces, shown by gas exchange: Across the body surface of a single-celled organism In the tracheal system of an insect
alevelbiology.co.uk 3.3.2 Gas Exchange SPECIFICATION Adaptations of gas exchange surfaces, shown by gas exchange: Across the body surface of a single-celled organism In the tracheal system of an insect
The Damages of Smoking
 The Damages of Smoking New Mexico Supercomputing Challenge Final Report April 6, 2016 Team 61 Los Lunas High School Area of Science: Health Team Members: Jen Marie Phifer Aaron Martin Gerald Sanchez Teacher:
The Damages of Smoking New Mexico Supercomputing Challenge Final Report April 6, 2016 Team 61 Los Lunas High School Area of Science: Health Team Members: Jen Marie Phifer Aaron Martin Gerald Sanchez Teacher:
