Kite Skiing Across Antarctica to Break 3 World Records, in Stunning Photos
|
|
|
- Cuthbert Richardson
- 5 years ago
- Views:
Transcription
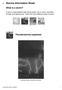
1 Kite Skiing Across Antarctica to Break 3 World Records, in Stunning Photos Blythe Copeland Living / Travel March 22, 2012 credit: Sebastian Copeland Sebastian Copeland is no stranger to cold journeys through Polar terrain: Images he took during a photographic study of Antarctica won him the Photographer of the Year award in 2007, and three years later he released a documentary that followed him on a trek to the North Pole. His most recent trip, though, was even more extreme than usual: Copeland and traveling partner Eric McNair- Landry spent three months on a transcontinental trek of Antarctica, setting not one, but three world records along the way, with help from kites that tapped the wind to make skiing much faster. Here, Copeland shares photos from that trip for a bracing look at one of the world's most powerful - - and little seen - - climates.
2 Copeland and McNair- Landry started the Antarctica Legacy Crossing at the Novolazarevskaya Russian base station on November 5, Less than two months later, on December 27, they checked in at the Pole of Inaccessibility, more than 1,100 miles away. The Pole is aptly named; as Copeland blogged on the day the pair reached it: This marks a first in the history of polar exploration: until today, no team had succeeded in reaching the POI without assistance or motorized transportation. The farthest point from any coast, the POI is effectively the heart of Antarctica, and regarded as the most difficult spot to reach in complete autonomy. A bust of Lenin, and a communications tower is all that remains of the Soviet era base which has been buried by drifting snow since it was abandoned almost fifty years ago.
3 After reaching the Pole of Inaccessibility, Copeland and McNair- Landry set out to claim another record: They became the first travelers to go from that point to the South Pole without help - - and without vehicles. In his blog post recapping day 55 of the trip, Copeland says that this second leg of the journey is believed to have gone 500 to 1000 years without precipitation and writes, We are now traveling a stretch of the globe that has never seen a man until now. In spite of the simplistic human urge to plant a little flag on unconquered land, perhaps to claim some type of ownership or simply to say: I exist - - there is something undeniably exciting, almost mystical, about setting prints where none have been before. In Antarctica especially, it gives the experience the taste of another world. But it wasn't all smooth sailing: Parts of the trip were made even more difficult by rough, windblown snow drifts, called sastrugi. These icy bumps made kite skiing physically tough and also more dangerous, writes Copeland, since the sledges were liable to stop abruptly when "hitting sastrugi from the wrong angle at speed generates enough force to tip it, or flip it."
4 Crossing Antarctica without vehicles also meant that Copeland and McNair- Landry were responsible for hauling their own supplies: 400 pounds each of tents, food, shovels, and other gear. When they couldn't rely on the kites, the men pulled the weight of the loads themselves - - including while they criss- crossed the ice bridges and crevasses of a foot hike up a glacier. The winds that made it possible for the men to travel by kite skiing aren't just your regular breeze: They're katabatic winds, created at the poles when the sun is unable to warm the ground directly. The rays reach the air, instead, and force cold air to sink.
5 As Copeland writes, "Try and visualize the cloud of cold air that shoots down the opening door of a freezer. These winds gain speed as they shoot downhill, sometimes reaching speeds in excess of a hundred miles an hour." On days that provided enough wind for kite skiing, the men could travel the same disance in six minutes using wind power t\hat they could with 60 minutes of walking. Copeland also looked at this trek as a way to draw attention to climate change, pointing out that even though you could never call Antarctica warm, it's still a "formidable player in the implications of climate change both from a geopolitical perspective as well as within its ecosystem." He writes, "But the poles are like great receptacles of what happens remotely: and warming activities conducted thousands of miles away are impacting these fragile systems. Small fluctuations in temperatures are generally visible fastest colder climates, where ice or snow is susceptible to melt."
6 The sastrugi may have been one of the most striking parts of the Antarctica landscape, but the continent has plenty going on under the ice, too. Copeland says that during one kite skiing session, he heard a low, loud noise that sounded like a sonic boom. He and McNair- Landry came up with this explanation: "All we could conclude...is that ice crystals below the surface of the ice form large hollow areas that get covered with blowing snow which freezes over. This creates pockets of air. "The disturbance of running weight over it, as we speed through, settles the ground which spreads and results in creating that sound. The first time it happened, I thought a jet fighter was flying over head!"
7 When they weren't traveling, the men took shelter in these tents, where they were protected from temperatures that dropped to - 40C (on average) and white- out storms. Copeland also spent his off- hours blogging the trip, posting daily updates from the furthest parts of the globe using iridium satellite technology. You can read a full recap of the trip at SebastianCopeland.com Copeland and McNair- Landry reached their final destination - - Hercules Inlet - - two days earlier than they'd expected, and were transported from there to Puntas Arenas, Chile. (On his blog, Copeland writes that McNair- Landry lost 12 pounds and he himself lost but that otherwise, they were in good shape.) Next up: A documentary based on the photos, video, and blog records that the men kept.
9-1: What Causes Climate. 6 th Grade Earth Science
 6 th Grade Earth Science What is Climate? 9-1: What Causes Climate Climate is the long-term average conditions of temperature, precipitation, winds, and clouds in an area. Examples of Climate The Mojave
6 th Grade Earth Science What is Climate? 9-1: What Causes Climate Climate is the long-term average conditions of temperature, precipitation, winds, and clouds in an area. Examples of Climate The Mojave
Read each slide, some slides have information to record on your organizer. Some slides have numbers that go with the question or red and underlined
 Read each slide, some slides have information to record on your organizer. Some slides have numbers that go with the question or red and underlined to use for answering the questions. Essential Question:
Read each slide, some slides have information to record on your organizer. Some slides have numbers that go with the question or red and underlined to use for answering the questions. Essential Question:
Atmosphere & Weather. Earth Science
 Atmosphere & Weather Earth Science Energy Transfer in the Atmosphere Earth s energy is provided by the SUN! Energy is important to us because it 1. Drives winds and ocean currents. 2. Allows plants to
Atmosphere & Weather Earth Science Energy Transfer in the Atmosphere Earth s energy is provided by the SUN! Energy is important to us because it 1. Drives winds and ocean currents. 2. Allows plants to
pole 2 pole TIME IS LIFE
 MIKE HORN t i f e : U h H A t D & Mike Horn May, 2016: Mike Horn embarks on his latest project, the Pole2Pole expedition. The venture will see Mike circling the globe via the two Poles in two years. The
MIKE HORN t i f e : U h H A t D & Mike Horn May, 2016: Mike Horn embarks on his latest project, the Pole2Pole expedition. The venture will see Mike circling the globe via the two Poles in two years. The
Section 2- Migration
 Section 2- Migration Today, most scientists agree that the first people in North America came from Asia. This migration is estimated to have taken place during the last ice age, at least 12,500 years ago.
Section 2- Migration Today, most scientists agree that the first people in North America came from Asia. This migration is estimated to have taken place during the last ice age, at least 12,500 years ago.
3 Global Winds and Local Winds
 CHAPTER 1 3 Global Winds and Local Winds SECTION The Atmosphere BEFORE YOU READ After you read this section, you should be able to answer these questions: What causes wind? What is the Coriolis effect?
CHAPTER 1 3 Global Winds and Local Winds SECTION The Atmosphere BEFORE YOU READ After you read this section, you should be able to answer these questions: What causes wind? What is the Coriolis effect?
THE ATMOSPHERE. WEATHER and CLIMATE. The Atmosphere 10/12/2018 R E M I N D E R S. PART II: People and their. weather. climate?
 R E M I N D E R S Two required essays are due by Oct. 30, 2018. (A third may be used for extra credit in place of a Think Geographically essay.) ESSAY TOPICS (choose any two): Contributions of a noted
R E M I N D E R S Two required essays are due by Oct. 30, 2018. (A third may be used for extra credit in place of a Think Geographically essay.) ESSAY TOPICS (choose any two): Contributions of a noted
Chapter 7 Weather and Climate
 Chapter 7 Weather and Climate *Describe what weather is, what affects it, and where it occurs. *Explain the connection between air pressure and wind. * *Many factors affect a region s weather. * *atmosphere
Chapter 7 Weather and Climate *Describe what weather is, what affects it, and where it occurs. *Explain the connection between air pressure and wind. * *Many factors affect a region s weather. * *atmosphere
Canada s Natural Systems. Canadian Geography 1202
 Canada s Natural Systems Canadian Geography 1202 Canada s Natural Systems Natural System: A system found in nature Here are the four natural systems that we will explore in the next few weeks 1. Canada
Canada s Natural Systems Canadian Geography 1202 Canada s Natural Systems Natural System: A system found in nature Here are the four natural systems that we will explore in the next few weeks 1. Canada
Atmospheric Gases. Earth s Atmosphere extends from earth s surface to outer space. It is made up of a mixture of gases with some solids and liquids.
 Earth s Atmosphere 1-1 I Objectives: Identify the gases in Earthś atmosphere Describe the structures of Earthś atmosphere. Explain what causes air pressure. Atmospheric Gases Earth s Atmosphere extends
Earth s Atmosphere 1-1 I Objectives: Identify the gases in Earthś atmosphere Describe the structures of Earthś atmosphere. Explain what causes air pressure. Atmospheric Gases Earth s Atmosphere extends
By Joel Bender
 By Joel Bender thought I was pretty lucky in 2008, drawing an Alaska 14C I Dall sheep tag. It was a lucky draw and an incredible hunt capped off with a beautiful ram and an adventure with my guide and
By Joel Bender thought I was pretty lucky in 2008, drawing an Alaska 14C I Dall sheep tag. It was a lucky draw and an incredible hunt capped off with a beautiful ram and an adventure with my guide and
9/25/2014. Scales of Atmospheric Motion. Scales of Atmospheric Motion. Chapter 7: Circulation of the Atmosphere
 Chapter 7: Circulation of the Atmosphere The Atmosphere: An Introduction to Meteorology, 12 th Lutgens Tarbuck Lectures by: Heather Gallacher, Cleveland State University Scales of Atmospheric Motion Small-
Chapter 7: Circulation of the Atmosphere The Atmosphere: An Introduction to Meteorology, 12 th Lutgens Tarbuck Lectures by: Heather Gallacher, Cleveland State University Scales of Atmospheric Motion Small-
SPQ Module 9 Breathing at Altitude
 SPQ Module 9 Breathing at Altitude For most people traveling 1130 kilometers on foot over a frozen ice cap with no support would be daunting enough without facing the prospect of being short of breath
SPQ Module 9 Breathing at Altitude For most people traveling 1130 kilometers on foot over a frozen ice cap with no support would be daunting enough without facing the prospect of being short of breath
Thunderstorms explained
 1. Storms Information Sheet What is a storm? A storm is bad weather with strong winds, rain or snow, and often thunder and lightning too. There are many different types of storm. Thunderstorms explained
1. Storms Information Sheet What is a storm? A storm is bad weather with strong winds, rain or snow, and often thunder and lightning too. There are many different types of storm. Thunderstorms explained
Exploring Wind Energy
 2013-2014 Exploring Wind Energy Student Guide SECONDARY Introduction to Wind What is Wind? Wind is simply air in motion. It is produced by the uneven heating of the Earth s surface by energy from the sun.
2013-2014 Exploring Wind Energy Student Guide SECONDARY Introduction to Wind What is Wind? Wind is simply air in motion. It is produced by the uneven heating of the Earth s surface by energy from the sun.
Earth s Atmosphere. Atmospheric Gases. Other Gases. Solids in the Atmosphere
 Earth s Atmosphere 1-1 I Atmospheric Gases Earth s Atmosphere extends from earth s surface to outer space. It is made up of a mixture of gases with some solids and liquids. Other Gases Water Vapor in the
Earth s Atmosphere 1-1 I Atmospheric Gases Earth s Atmosphere extends from earth s surface to outer space. It is made up of a mixture of gases with some solids and liquids. Other Gases Water Vapor in the
Land and sea breezes are an example of which type of heat transfer?
 TEST #7 REVIEW Land and sea breezes are an example of which type of heat transfer? Land and sea breezes are an example of which type of heat transfer? convection The diagram above represents what? The
TEST #7 REVIEW Land and sea breezes are an example of which type of heat transfer? Land and sea breezes are an example of which type of heat transfer? convection The diagram above represents what? The
I. Atmosphere. Maintains a balance between the amount of heat absorbed from the Sun and the amount of heat that escapes back into space.
 Earth s Atmosphere 1-1 I Objectives: Identify the gases in Earthś atmosphere Describe the structures of Earthś atmosphere. Explain what causes air pressure. I. Atmosphere Maintains a balance between the
Earth s Atmosphere 1-1 I Objectives: Identify the gases in Earthś atmosphere Describe the structures of Earthś atmosphere. Explain what causes air pressure. I. Atmosphere Maintains a balance between the
Atmospheric Circulation
 Atmospheric Circulation Why do we say Earth's temperature is moderate? It may not look like it, but various processes work to moderate Earth's temperature across the latitudes. Atmospheric circulation
Atmospheric Circulation Why do we say Earth's temperature is moderate? It may not look like it, but various processes work to moderate Earth's temperature across the latitudes. Atmospheric circulation
Explorer Nears End of Epic Quest From Pole to Pole Playbook...
 Previous post Next post 98 6 1 Tweet Share Explorer Nears End of Epic Quest From Pole to Pole By Kyle Stack Email Author March 7, 2012 2:15 pm Categories: Outdoors, Science Follow @kylestack Johan Enrst
Previous post Next post 98 6 1 Tweet Share Explorer Nears End of Epic Quest From Pole to Pole By Kyle Stack Email Author March 7, 2012 2:15 pm Categories: Outdoors, Science Follow @kylestack Johan Enrst
Notepack 41. Aim: What factors determine the climate of a certain area? Do Now: What is the difference between weather and climate?
 Notepack 41 Aim: What factors determine the climate of a certain area? Do Now: What is the difference between weather and climate? WEATHER VS. CLIMATE Weather atmospheric conditions at a certain location
Notepack 41 Aim: What factors determine the climate of a certain area? Do Now: What is the difference between weather and climate? WEATHER VS. CLIMATE Weather atmospheric conditions at a certain location
The student will be expected to demonstrate an understanding of the cause of winds and how winds affect climate.
 The student will be expected to demonstrate an understanding of the cause of winds and how winds affect climate. In this lesson you will: 2.3.1 Define the term prevailing winds. (k) 2.3.3 State the impact
The student will be expected to demonstrate an understanding of the cause of winds and how winds affect climate. In this lesson you will: 2.3.1 Define the term prevailing winds. (k) 2.3.3 State the impact
Loose Dry Avalanches
 Loose Dry Avalanches Introduction Loose dry avalanches are usually confined to surface layers, and therefore are often small. They contain loose cohesion less dry powdery snow. They start from a point
Loose Dry Avalanches Introduction Loose dry avalanches are usually confined to surface layers, and therefore are often small. They contain loose cohesion less dry powdery snow. They start from a point
READING AND LISTENING. A beach. By John Russell
 READING AND LISTENING http://learnenglish.britishcouncil.org/en/magazine/beach A beach By John Russell life jacket water-sport cliff capsize (v.) paradise float (v.) sanctuary refuge anchor (v.) rock pool
READING AND LISTENING http://learnenglish.britishcouncil.org/en/magazine/beach A beach By John Russell life jacket water-sport cliff capsize (v.) paradise float (v.) sanctuary refuge anchor (v.) rock pool
Wind Patterns on Earth
 Wind Patterns on Earth What causes air to move? Air pressure differences causes air to move. These differences in air pressure at the same altitude is caused by uneven heating of the Earth s surface. With
Wind Patterns on Earth What causes air to move? Air pressure differences causes air to move. These differences in air pressure at the same altitude is caused by uneven heating of the Earth s surface. With
Weather Unit Study Guide
 Weather Unit Study Guide - 2018 Weather vs Climate What does weather measure? The condition of the earth's atmosphere at a particular time and place. How are climate and weather different? Climate is the
Weather Unit Study Guide - 2018 Weather vs Climate What does weather measure? The condition of the earth's atmosphere at a particular time and place. How are climate and weather different? Climate is the
Wind and Wind Patterns
 Wind and Wind Patterns What is Weather? Weather is the condition of Earth s atmosphere at a particular time and place. What is Wind? Wind is air moving across the surface of the Earth. It can move horizontally
Wind and Wind Patterns What is Weather? Weather is the condition of Earth s atmosphere at a particular time and place. What is Wind? Wind is air moving across the surface of the Earth. It can move horizontally
Wind in the Atmosphere
 Lesson 1 Wind in the Atmosphere Essential Question What is wind? By the end of this lesson, you should be able to explain how energy provided by the sun causes atmospheric movement, called wind. 8.10A
Lesson 1 Wind in the Atmosphere Essential Question What is wind? By the end of this lesson, you should be able to explain how energy provided by the sun causes atmospheric movement, called wind. 8.10A
Weather EOG Review Questions
 Weather EOG Review Questions 1. Which statement best describes runoff? A Water vapor cools off and changes into water droplets. B Water in the form of rain, snow, sleet, or hail falls from clouds. C Precipitation
Weather EOG Review Questions 1. Which statement best describes runoff? A Water vapor cools off and changes into water droplets. B Water in the form of rain, snow, sleet, or hail falls from clouds. C Precipitation
Wind Movement and Global and Local Winds
 Wind Movement and Global and Local Winds In previous lessons, you learned that the uneven heating of Earth s surface by the Sun causes some areas to be warmer than others. This uneven heating of land forms
Wind Movement and Global and Local Winds In previous lessons, you learned that the uneven heating of Earth s surface by the Sun causes some areas to be warmer than others. This uneven heating of land forms
4 wild winds AND white water
 94 PoSTcArDS from THe edge 4 wild winds AND white water Above: Being regarded as the most famous lighthouse in the world has meant that eddystone featured extensively on early postcards and you ll see
94 PoSTcArDS from THe edge 4 wild winds AND white water Above: Being regarded as the most famous lighthouse in the world has meant that eddystone featured extensively on early postcards and you ll see
3 Global Winds and Local Winds
 CHAPTER 15 3 Global Winds and Local Winds SECTION The Atmosphere BEFORE YOU READ After you read this section, you should be able to answer these questions: What causes wind? What is the Coriolis effect?
CHAPTER 15 3 Global Winds and Local Winds SECTION The Atmosphere BEFORE YOU READ After you read this section, you should be able to answer these questions: What causes wind? What is the Coriolis effect?
CHAPTER 6 Air-Sea Interaction
 CHAPTER 6 Air-Sea Interaction What causes Earth s seasons? Tilt (23.5 ) responsible for seasons 2011 Pearson Education, Inc. Distribution of Solar Energy Distribution of Solar Energy Atmosphere absorbs
CHAPTER 6 Air-Sea Interaction What causes Earth s seasons? Tilt (23.5 ) responsible for seasons 2011 Pearson Education, Inc. Distribution of Solar Energy Distribution of Solar Energy Atmosphere absorbs
Characters. Photographs by Peg & Datiz, Student Conservationists. Illustrations by George Carrara. Written by Yein Suh
 Written by Yein Suh Photographs by Peg & Datiz, Student Conservationists Illustrations by George Carrara 1 Characters 2 Ms. Lee teaches her class about the Arctic Circle. It is an area around the North
Written by Yein Suh Photographs by Peg & Datiz, Student Conservationists Illustrations by George Carrara 1 Characters 2 Ms. Lee teaches her class about the Arctic Circle. It is an area around the North
Air Masses and Fronts
 Air Masses and Fronts A huge body of air that has similar temperature, humidity, and air pressure at any given height is called an air mass. A single air mass may spread over millions of square kilometers
Air Masses and Fronts A huge body of air that has similar temperature, humidity, and air pressure at any given height is called an air mass. A single air mass may spread over millions of square kilometers
Mount Everest. At 29,028 feet, or 5 miles above sea level, Mount Everest is the highest point on Earth.
 Everest Simulation Introductory Video Storyboard # AUDIO VIDEO 1 TITLE SCREEN (BLACK SCREEN W/ WHITE FONT KEY): 2 At 29,028 feet, or 5 miles above sea level, Mount Everest is the highest point on Earth.
Everest Simulation Introductory Video Storyboard # AUDIO VIDEO 1 TITLE SCREEN (BLACK SCREEN W/ WHITE FONT KEY): 2 At 29,028 feet, or 5 miles above sea level, Mount Everest is the highest point on Earth.
ATOMOSPERIC PRESSURE, WIND & CIRCULATION
 ATOMOSPERIC PRESSURE, WIND & CIRCULATION A. INTRODUCTION Important because: pressure patterns drive wind patterns which in turn drive oceanic circulation patterns o atmospheric & oceanic circulation: major
ATOMOSPERIC PRESSURE, WIND & CIRCULATION A. INTRODUCTION Important because: pressure patterns drive wind patterns which in turn drive oceanic circulation patterns o atmospheric & oceanic circulation: major
Your web browser (Safari 7) is out of date. For more security, comfort and the best experience on this site: Update your browser Ignore
 Your web browser (Safari 7) is out of date. For more security, comfort and the best experience on this site: Update your browser Ignore AVAL ANCHE snowslide For the complete encyclopedic entry with media
Your web browser (Safari 7) is out of date. For more security, comfort and the best experience on this site: Update your browser Ignore AVAL ANCHE snowslide For the complete encyclopedic entry with media
Day 1 What Is Air Pressure? November 28, 2017
 Day 1 What Is Air Pressure? November 28, 2017 Review: What is Climate & Weather? Yesterday we talked about the difference between Climate and weather. So what is Climate? Climate: is the average weather
Day 1 What Is Air Pressure? November 28, 2017 Review: What is Climate & Weather? Yesterday we talked about the difference between Climate and weather. So what is Climate? Climate: is the average weather
Earth s Atmosphere. Air Currents
 CHAPTER 12 Earth s Atmosphere LESSON 3 Air Currents What do you think? Read the two statements below and decide whether you agree or disagree with them. Place an A in the Before column if you agree with
CHAPTER 12 Earth s Atmosphere LESSON 3 Air Currents What do you think? Read the two statements below and decide whether you agree or disagree with them. Place an A in the Before column if you agree with
Warm front and cold front video 3:50
 Construct an explanation of the relationship between air pressure, weather fronts, and air masses and meteorological events such as tornados and thunderstorms Unpacked : Warm front and cold front video
Construct an explanation of the relationship between air pressure, weather fronts, and air masses and meteorological events such as tornados and thunderstorms Unpacked : Warm front and cold front video
Winter Sports (Snow)
 Winter Sports (Snow) Snowy places are a great place to visit if you want to try different activities, but the cold weather means that you need to wrap up warm. Have a look at these two activities that
Winter Sports (Snow) Snowy places are a great place to visit if you want to try different activities, but the cold weather means that you need to wrap up warm. Have a look at these two activities that
Norway Mixed Climbing Project. Climbing under the green light
 Norway Mixed Climbing Project Climbing under the green light A 69 North Mission March 2017 The Project Legendary territory of Vikings, Norway is well known at the present for its stunning Northland landscapes
Norway Mixed Climbing Project Climbing under the green light A 69 North Mission March 2017 The Project Legendary territory of Vikings, Norway is well known at the present for its stunning Northland landscapes
(Some) Fundamentals of Weather
 (Some) Fundamentals of Weather The Weather Channel Weather & Air Quality: Keys: Air motion, clouds, and precipitation. Horizontal: Vertical: Wind Vertical Motions, mixing Wind, mixing dperse Pollutants!!
(Some) Fundamentals of Weather The Weather Channel Weather & Air Quality: Keys: Air motion, clouds, and precipitation. Horizontal: Vertical: Wind Vertical Motions, mixing Wind, mixing dperse Pollutants!!
Horizontal movement of air between cooler and warmer regions. - horizontal movement of air Convection over areas where is
 Winds and Water Chapter 9 continued... Uneven Heating The various materials of the earth absorb and emit energy at different rates Convection Heated air expands; density reduced; air rises Upward movement
Winds and Water Chapter 9 continued... Uneven Heating The various materials of the earth absorb and emit energy at different rates Convection Heated air expands; density reduced; air rises Upward movement
Float & Fly Lesson from a Smallmouth Guru
 http://www.worldfishingnetwork.com/tips/post/a-complete-lesson-in-float-fly-from-the-smallmouthguru-2 SkipperMark Float & Fly Lesson from a Smallmouth Guru Winter is here and for some it can be the most
http://www.worldfishingnetwork.com/tips/post/a-complete-lesson-in-float-fly-from-the-smallmouthguru-2 SkipperMark Float & Fly Lesson from a Smallmouth Guru Winter is here and for some it can be the most
Atmosphere Circulation
 Atmosphere Circulation Winds What Causes Winds? Difference in air pressure due to unequal heating of the atmosphere. Temperatures vary according to the amount of sun it gets. Uneven heating of the Earth
Atmosphere Circulation Winds What Causes Winds? Difference in air pressure due to unequal heating of the atmosphere. Temperatures vary according to the amount of sun it gets. Uneven heating of the Earth
Weather & Atmosphere Study Guide
 Weather & Atmosphere Study Guide 1. Draw a simple water cycle diagram using the following words: Precipitation, Evaporation, Condensation, Transpiration 2. In your own words, explain the difference between
Weather & Atmosphere Study Guide 1. Draw a simple water cycle diagram using the following words: Precipitation, Evaporation, Condensation, Transpiration 2. In your own words, explain the difference between
Wind in the Atmosphere
 Lesson 2 Wind in the Atmosphere ESSENTIAL QUESTION What is wind? By the end of this lesson, you should be able to explain how energy provided by the sun causes atmospheric movement, called wind. p 6.ESS2.2,
Lesson 2 Wind in the Atmosphere ESSENTIAL QUESTION What is wind? By the end of this lesson, you should be able to explain how energy provided by the sun causes atmospheric movement, called wind. p 6.ESS2.2,
EARTH SCIENCE 5.9 (WIND) WEATHER
 EARTH SCIENCE 5.9 (WIND) WEATHER Video Notes Key Points: 1. According to the video, what two factors cause wind: a. b. 2. Fill in the blanks from this quote from the video: Energy from the Sun heats the,
EARTH SCIENCE 5.9 (WIND) WEATHER Video Notes Key Points: 1. According to the video, what two factors cause wind: a. b. 2. Fill in the blanks from this quote from the video: Energy from the Sun heats the,
Water on Earth. How do oceans relate to weather and the atmosphere? Solar Radiation and Convection Currents
 Earth is often called the Blue Planet because so much of its surface (about 71%) is covered by water. Of all the water on Earth, about 96.5% is held in the world s oceans. As you can imagine, these oceans
Earth is often called the Blue Planet because so much of its surface (about 71%) is covered by water. Of all the water on Earth, about 96.5% is held in the world s oceans. As you can imagine, these oceans
Avalanche Problem Essentials Wind Slabs. Development
 1 Avalanche Problem Essentials Wind Slabs This document is part of Decision Making in Avalanche Terrain: a fieldbook for winter backcountry users by Pascal Haegeli, Roger Atkins and Karl Klassen and provides
1 Avalanche Problem Essentials Wind Slabs This document is part of Decision Making in Avalanche Terrain: a fieldbook for winter backcountry users by Pascal Haegeli, Roger Atkins and Karl Klassen and provides
The Wind. Name: by Robert Louis Stevenson. 1 I saw you toss the kites on high. And blow the birds about the sky; And all around I heard you pass,
 The Wind Name: by Robert Louis Stevenson 1 I saw you toss the kites on high And blow the birds about the sky; And all around I heard you pass, Like ladies' skirts across the grass-- Oh wind, a-blowing
The Wind Name: by Robert Louis Stevenson 1 I saw you toss the kites on high And blow the birds about the sky; And all around I heard you pass, Like ladies' skirts across the grass-- Oh wind, a-blowing
STUDENT PACKET # 10. Vocabulary: condensation, convection, convection current, land breeze, sea breeze
 STUDENT PACKET # 10 Name: Date: Student Exploration: Coastal Winds and Clouds Big Idea 7: Earth Systems and Patterns SC.6.E.7.4 Differentiate and show interactions among the geosphere, hydrosphere, cryosphere,
STUDENT PACKET # 10 Name: Date: Student Exploration: Coastal Winds and Clouds Big Idea 7: Earth Systems and Patterns SC.6.E.7.4 Differentiate and show interactions among the geosphere, hydrosphere, cryosphere,
12/14/2015 Idaho Bald Mountain Sidecountry Published by Scott Savage, SAC
 Location: Place Christmas Eve, Bald Mountain Sidecountry State Idaho Date 12/14/2015 Time 1135 Summary 1 skier partially buried and injured due to striking trees Number: Caught 1 Fully Buried 0 Injured
Location: Place Christmas Eve, Bald Mountain Sidecountry State Idaho Date 12/14/2015 Time 1135 Summary 1 skier partially buried and injured due to striking trees Number: Caught 1 Fully Buried 0 Injured
Ice Axe-Boot belay Freedom of the Hills p. 350 Watch:
 Carabiner-Ice Axe Belay Freedom of the Hills pp.358-359 Watch: http://bit.ly/carabinericeaxebelay Also called the stomper belay, the carabiner-ice axe belay provides better security than a boot-axe belay
Carabiner-Ice Axe Belay Freedom of the Hills pp.358-359 Watch: http://bit.ly/carabinericeaxebelay Also called the stomper belay, the carabiner-ice axe belay provides better security than a boot-axe belay
Week 5 - February 23 rd March 1 st. Whistler, Callaghan Valley
 Saturday February 23 Whistler A season pass is a lovely thing. End of the season last year, as Whistler passed to ownership/management of Vail Associates they offered a new Epic ski pass that included
Saturday February 23 Whistler A season pass is a lovely thing. End of the season last year, as Whistler passed to ownership/management of Vail Associates they offered a new Epic ski pass that included
Section 6. The Surface Circulation of the Ocean. What Do You See? Think About It. Investigate. Learning Outcomes
 Chapter 5 Winds, Oceans, Weather, and Climate Section 6 The Surface Circulation of the Ocean What Do You See? Learning Outcomes In this section, you will Understand the general paths of surface ocean currents.
Chapter 5 Winds, Oceans, Weather, and Climate Section 6 The Surface Circulation of the Ocean What Do You See? Learning Outcomes In this section, you will Understand the general paths of surface ocean currents.
Wind Energy. Definition of Wind Energy. Wind energy is energy from moving air.
 Wind Energy Definition of Wind Energy Wind energy is energy from moving air. Air has mass. When it moves, it has kinetic energy. Kinetic energy is the energy of motion. How does wind form? Wind forms when
Wind Energy Definition of Wind Energy Wind energy is energy from moving air. Air has mass. When it moves, it has kinetic energy. Kinetic energy is the energy of motion. How does wind form? Wind forms when
5200 Lawrence Place Hyattsville, Maryland 20781, USA Toll Free: Phone: Fax:
 5200 Lawrence Place Hyattsville, Maryland 20781, USA Toll Free: 1-888-416-0174 Phone: 301-277-3888 Fax: 301-277-3323 www.premierkites.com Congratulations on your purchase of the Osprey sport kite. The
5200 Lawrence Place Hyattsville, Maryland 20781, USA Toll Free: 1-888-416-0174 Phone: 301-277-3888 Fax: 301-277-3323 www.premierkites.com Congratulations on your purchase of the Osprey sport kite. The
Grade 8 Science: Unit 1 Water Systems Chapter 3
 Heat Capacity Grade 8 Science: Unit 1 Water Systems Chapter 3 Heat capacity ( ) is the amount of heat that a substance can hold. has a high heat capacity it can take in a large amount of heat before its
Heat Capacity Grade 8 Science: Unit 1 Water Systems Chapter 3 Heat capacity ( ) is the amount of heat that a substance can hold. has a high heat capacity it can take in a large amount of heat before its
Lesson 7: The Pony Express
 Lesson 7: The Pony Express In the 1850s, mail delivery was not as fast as it is today. Airplanes had not yet been invented, and neither had cars. Railroads had been invented, but the railroad tracks did
Lesson 7: The Pony Express In the 1850s, mail delivery was not as fast as it is today. Airplanes had not yet been invented, and neither had cars. Railroads had been invented, but the railroad tracks did
UNIT 1: WATER SYSTEMS ON EARTH CHAPTER 3
 UNIT 1: WATER SYSTEMS ON EARTH CHAPTER 3 HEAT CAPACITY HEAT CAPACITY (SPECIFIC HEAT CAPACITY) IS THE AMOUNT OF HEAT THAT A SUBSTANCE CAN HOLD WATER HAS A HIGH HEAT CAPACITY IT CAN TAKE IN A LARGE AMOUNT
UNIT 1: WATER SYSTEMS ON EARTH CHAPTER 3 HEAT CAPACITY HEAT CAPACITY (SPECIFIC HEAT CAPACITY) IS THE AMOUNT OF HEAT THAT A SUBSTANCE CAN HOLD WATER HAS A HIGH HEAT CAPACITY IT CAN TAKE IN A LARGE AMOUNT
Taming the Kite! Wineglasses. Wineglasses occur when the top half of the kite fills before the bottom with a twist in the middle.
 Taming the Kite! What goes wrong? Wineglass when launching can happen in light or heavy weather Broaching on a reach usually in heavy weather Death rolls usually in heavy weather Gybing disasters worse
Taming the Kite! What goes wrong? Wineglass when launching can happen in light or heavy weather Broaching on a reach usually in heavy weather Death rolls usually in heavy weather Gybing disasters worse
El Niño Lecture Notes
 El Niño Lecture Notes There is a huge link between the atmosphere & ocean. The oceans influence the atmosphere to affect climate, but the atmosphere also influences the ocean, which can also affect climate.
El Niño Lecture Notes There is a huge link between the atmosphere & ocean. The oceans influence the atmosphere to affect climate, but the atmosphere also influences the ocean, which can also affect climate.
snow winter temperature (noun) (noun) Winter comes after fall. Winter is the opposite of summer. Winter is the coldest time of year.
 WORDS IN CONTEXT DAY 1 (Page 1 of 4) snow Snow is water vapor that has frozen into ice crystals. Snow falls in the form of flakes, not drops. A soft blanket of snow covered the valley. temperature Temperature
WORDS IN CONTEXT DAY 1 (Page 1 of 4) snow Snow is water vapor that has frozen into ice crystals. Snow falls in the form of flakes, not drops. A soft blanket of snow covered the valley. temperature Temperature
Informational/ Explanatory Genre
 Sample Sample 6GRADE Informational/ Explanatory Genre Georgia Center for Assessment All items contained in this Assesslet are the property of the Georgia Center for Assessment. Items may be used for formative
Sample Sample 6GRADE Informational/ Explanatory Genre Georgia Center for Assessment All items contained in this Assesslet are the property of the Georgia Center for Assessment. Items may be used for formative
1.3: CLIMATE GEOGRAPHY. pgs
 1.3: CLIMATE GEOGRAPHY pgs. 76-89 INTRODUCTION WEATHER: Is the combination of temperature, precipitation, cloud cover and wind that we experience EACH DAY. Example: 22 0 C and clear skies. CLIMATE: The
1.3: CLIMATE GEOGRAPHY pgs. 76-89 INTRODUCTION WEATHER: Is the combination of temperature, precipitation, cloud cover and wind that we experience EACH DAY. Example: 22 0 C and clear skies. CLIMATE: The
1 Currents. TAKE A LOOK 2. Read a Map In what direction does the Gulf Stream flow?
 CHAPTER 5 1 Currents SECTION The Movement of Ocean Water BEFORE YOU READ After you read this section, you should be able to answer these questions: What factors affect ocean currents? Why are ocean currents
CHAPTER 5 1 Currents SECTION The Movement of Ocean Water BEFORE YOU READ After you read this section, you should be able to answer these questions: What factors affect ocean currents? Why are ocean currents
Life in the Current. Beyond the Book. FOCUS Book
 FOCUS Book Eddies often form on the edges of a fast-moving ocean current. Make a model of an eddy. Fill a clear plastic bowl with warm tap water. Slowly stir the water to make it swirl. Predict what will
FOCUS Book Eddies often form on the edges of a fast-moving ocean current. Make a model of an eddy. Fill a clear plastic bowl with warm tap water. Slowly stir the water to make it swirl. Predict what will
ì<(sk$m)=bdiiid< +^-Ä-U-Ä-U
 Genre Comprehension Skill Text Features Science Content Nonfiction Cause and Effect Captions Text Boxes Call Outs Glossary Natural Resources Scott Foresman Science 4.10 ì
Genre Comprehension Skill Text Features Science Content Nonfiction Cause and Effect Captions Text Boxes Call Outs Glossary Natural Resources Scott Foresman Science 4.10 ì
Student Teacher School. English Language Arts. Assesslet
 Student Teacher School Sample Sample 6GRADE English Language Arts Assesslet Georgia Center for Assessment All items contained in this assesslet are the property of the Georgia Center for Assessment. Items
Student Teacher School Sample Sample 6GRADE English Language Arts Assesslet Georgia Center for Assessment All items contained in this assesslet are the property of the Georgia Center for Assessment. Items
3 Global Winds and Local Winds
 CHAPTER 6 3 Global Winds and Local Winds SECTION The Atmosphere BEFORE YOU READ After you read this section, you should be able to answer these questions: What causes wind? What is the Coriolis effect?
CHAPTER 6 3 Global Winds and Local Winds SECTION The Atmosphere BEFORE YOU READ After you read this section, you should be able to answer these questions: What causes wind? What is the Coriolis effect?
WINDS Understand the cause of wind and how it affects climate Chapter 4 Pages 59-67
 WINDS Understand the cause of wind and how it affects climate Chapter 4 Pages 59-67 What is Wind? A wind is a horizontal movement of air across a surface. Vertical movements are currents or updrafts and
WINDS Understand the cause of wind and how it affects climate Chapter 4 Pages 59-67 What is Wind? A wind is a horizontal movement of air across a surface. Vertical movements are currents or updrafts and
Yellowstone National Park
 Yellowstone National Park Back Country Photo Tour by Horseback Terry Search of Yellowstone Mountain Guides: Outfitter License #6485 with John & Barbara Gerlach as your wrangler photo guides 2004 Gerlach
Yellowstone National Park Back Country Photo Tour by Horseback Terry Search of Yellowstone Mountain Guides: Outfitter License #6485 with John & Barbara Gerlach as your wrangler photo guides 2004 Gerlach
Social Studies CHAPTER 2: PART 2 CLIMATE AND WEATHER
 Social Studies CHAPTER 2: PART 2 CLIMATE AND WEATHER Climate Weather and Identity Climate and weather have a large influence on how Canadians build their identity. We will study the factors that contribute
Social Studies CHAPTER 2: PART 2 CLIMATE AND WEATHER Climate Weather and Identity Climate and weather have a large influence on how Canadians build their identity. We will study the factors that contribute
THE WIND, THE SUN AND THE RAIN
 THE WIND, THE SUN AND THE RAIN There may be gold and jewels in treasure chests at the bottom of the ocean. A long time ago, ships sank in the ocean, and some people go diving in the ocean to hunt for their
THE WIND, THE SUN AND THE RAIN There may be gold and jewels in treasure chests at the bottom of the ocean. A long time ago, ships sank in the ocean, and some people go diving in the ocean to hunt for their
Oceans and the Global Environment: Lec 2 taking physics and chemistry outdoors. the flowing, waving ocean
 Oceans and the Global Environment: Lec 2 taking physics and chemistry outdoors the flowing, waving ocean Peter Rhines 1 Eric Lindahl 2 Bob Koon 2, Julie Wright 3 www.ocean.washington.edu/courses/has221a-08
Oceans and the Global Environment: Lec 2 taking physics and chemistry outdoors the flowing, waving ocean Peter Rhines 1 Eric Lindahl 2 Bob Koon 2, Julie Wright 3 www.ocean.washington.edu/courses/has221a-08
+ - Water Planet, Water Crisis 2010 Class Notes Topic 2. Water in the earth system Part A: Properties of H 2 O: Why it's so important to us.
 Water Planet, Water Crisis 2010 Class Notes Topic 2. Water in the earth system Part A: Properties of H 2 O: Why it's so important to us. Physical and Chemical properties of H 2 O: Arise from the structure
Water Planet, Water Crisis 2010 Class Notes Topic 2. Water in the earth system Part A: Properties of H 2 O: Why it's so important to us. Physical and Chemical properties of H 2 O: Arise from the structure
T SP P Olympic Winter Games, Sochi, Russia & Olympia the sport biathlon Hopefuls
 T SP P 2014 Olympic Winter Games, Sochi, Russia 2006 & Olympia the sport biathlon. 2014 Hopefuls Biathlon is the most popular winter sport in Europe. And growing in popularity in the U.S. HELP MAKE HISTORY
T SP P 2014 Olympic Winter Games, Sochi, Russia 2006 & Olympia the sport biathlon. 2014 Hopefuls Biathlon is the most popular winter sport in Europe. And growing in popularity in the U.S. HELP MAKE HISTORY
W3 Global Circulation Systems
 W3 Global Circulation Systems Which regions of Earth receive the most energy from the Sun? If not for global circulation systems There would only be two narrow regions that would support life What
W3 Global Circulation Systems Which regions of Earth receive the most energy from the Sun? If not for global circulation systems There would only be two narrow regions that would support life What
In the 1850s, mail delivery was not as fast as it is today. Airplanes had not yet been invented, and neither had cars. Railroads had been invented,
 The Pony Express In the 1850s, mail delivery was not as fast as it is today. Airplanes had not yet been invented, and neither had cars. Railroads had been invented, but the railroad tracks did not run
The Pony Express In the 1850s, mail delivery was not as fast as it is today. Airplanes had not yet been invented, and neither had cars. Railroads had been invented, but the railroad tracks did not run
Name: Date: Day/Period: CGC1P1: Interactions in the Physical Environment. Factors that Affect Climate
 Name: Date: Day/Period: CGC1P1: Interactions in the Physical Environment PART A: Weather and Climate Factors that Affect Climate 1. The words weather and climate are often incorrectly used interchangeably.
Name: Date: Day/Period: CGC1P1: Interactions in the Physical Environment PART A: Weather and Climate Factors that Affect Climate 1. The words weather and climate are often incorrectly used interchangeably.
5200 Lawrence Place Hyattsville, Maryland 20781, USA Toll Free: Phone: Fax:
 5200 Lawrence Place Hyattsville, Maryland 20781, USA Toll Free: 1-888-416-0174 Phone: 301-277-3888 Fax: 301-277-3323 www.premierkites.com Congratulations on your purchase of the Wolf NG sport kite. The
5200 Lawrence Place Hyattsville, Maryland 20781, USA Toll Free: 1-888-416-0174 Phone: 301-277-3888 Fax: 301-277-3323 www.premierkites.com Congratulations on your purchase of the Wolf NG sport kite. The
Ocean Motion. Ocean Currents. Before You Read. Read to Learn
 chapter 18 3 Ocean Motion section 2 Ocean Currents What You ll Learn the Coriolis effect what influences surface currents the temperature of coastal waters about density currents Before You Read Imagine
chapter 18 3 Ocean Motion section 2 Ocean Currents What You ll Learn the Coriolis effect what influences surface currents the temperature of coastal waters about density currents Before You Read Imagine
Greenhouse Effect Activity
 Greenhouse Effect Activity Objectives: The student will: 1. Read and use weather instruments. 2. Collect and record temperature readings. 3. Describe the concept of the greenhouse effect. Materials: Fish
Greenhouse Effect Activity Objectives: The student will: 1. Read and use weather instruments. 2. Collect and record temperature readings. 3. Describe the concept of the greenhouse effect. Materials: Fish
MET 101 Introduction to Meteorology
 MET 101 Introduction to Meteorology MET 101 Griswold 1 MIDTERM EXAM Spring Semester 2015 Thursday, March 12, 2015 Name: Student ID #: Instructions: Closed Book. Time limit is 50 minutes. Total Points Attainable:
MET 101 Introduction to Meteorology MET 101 Griswold 1 MIDTERM EXAM Spring Semester 2015 Thursday, March 12, 2015 Name: Student ID #: Instructions: Closed Book. Time limit is 50 minutes. Total Points Attainable:
Chapter: Atmosphere Section 3: Air Movement
 Table of Contents Chapter: Atmosphere Section 3: Air Movement We will learn about: -Air Movement=Wind -Why different latitudes on Earth will receive different amounts of Solar Energy -The Coriolis Effect
Table of Contents Chapter: Atmosphere Section 3: Air Movement We will learn about: -Air Movement=Wind -Why different latitudes on Earth will receive different amounts of Solar Energy -The Coriolis Effect
What Causes Different Weather?
 What Causes Different Weather? Table of Contents What causes weather?...3 What causes it to rain or snow?...4 What causes flooding?...5 What causes hail?...6 What causes the seasons?...7-8 What causes
What Causes Different Weather? Table of Contents What causes weather?...3 What causes it to rain or snow?...4 What causes flooding?...5 What causes hail?...6 What causes the seasons?...7-8 What causes
9.3. Storing Thermal Energy. Transferring Thermal Energy
 9.3 If you have been to a beach on a hot summer day, you have likely cooled off by going for a dip in the water. The water, which is cooler than you are, removes thermal energy from your body, making you
9.3 If you have been to a beach on a hot summer day, you have likely cooled off by going for a dip in the water. The water, which is cooler than you are, removes thermal energy from your body, making you
Muztagh-Ata 2011 Expedition REPORT
 Muztagh-Ata 2011 Expedition REPORT for Championships of Mountaineering of Baltic States High mountain cathegory Tallinn Route passport Club: Jaan Künnapi Alpinismiklubi ( http://www.jkalpiklubi.ee/ ) Category:
Muztagh-Ata 2011 Expedition REPORT for Championships of Mountaineering of Baltic States High mountain cathegory Tallinn Route passport Club: Jaan Künnapi Alpinismiklubi ( http://www.jkalpiklubi.ee/ ) Category:
100, precipitation Droplets, collide -40 C
 Warm-up 1/8 Page: 556, 1. A cloud droplet must increase in diameter by about times to fall as. 100, precipitation Page: 556, 2. Coalescence is when larger drift downward, then and combine with smaller
Warm-up 1/8 Page: 556, 1. A cloud droplet must increase in diameter by about times to fall as. 100, precipitation Page: 556, 2. Coalescence is when larger drift downward, then and combine with smaller
Animal Survival. Student Page - Grade 4 Prompt for Informative Writing.
 2014-2015 LAUSD INTERIM ASSESSMENTS ELEMENTARY LITERACY GRADE 4 Student Page - Grade 4 Prompt for Informative Writing. Animal Survival Name: Directions: Using what you have learned from reading the articles,
2014-2015 LAUSD INTERIM ASSESSMENTS ELEMENTARY LITERACY GRADE 4 Student Page - Grade 4 Prompt for Informative Writing. Animal Survival Name: Directions: Using what you have learned from reading the articles,
In comparison to depressions, these can be quite boring, at least in terms of the weather they bring.
 Anticyclones In comparison to depressions, these can be quite boring, at least in terms of the weather they bring. In summary, anticyclones; Are larger than low pressure systems, Last longer than low pressure
Anticyclones In comparison to depressions, these can be quite boring, at least in terms of the weather they bring. In summary, anticyclones; Are larger than low pressure systems, Last longer than low pressure
Earth s Atmosphere. Earth s atmosphere is a key factor in allowing life to survive here.
 Chapter 10.2 Earth s Atmosphere Earth s atmosphere is a key factor in allowing life to survive here. This narrow band of air has the right ingredients and maintains the correct temperature, to allow life
Chapter 10.2 Earth s Atmosphere Earth s atmosphere is a key factor in allowing life to survive here. This narrow band of air has the right ingredients and maintains the correct temperature, to allow life
Ocean Current Worksheet
 Ocean Current Worksheet Temperature Affects and Surface Currents: Surface waters of the Earth s oceans are forced to move, primarily by winds. Where winds blow in the same direction for a long period of
Ocean Current Worksheet Temperature Affects and Surface Currents: Surface waters of the Earth s oceans are forced to move, primarily by winds. Where winds blow in the same direction for a long period of
2016/04/03 Alaska Hoodoo Mountains, Eastern Alaska Range Published by Conrad Chapman Eastern Alaska Range Avalanche Center
 2016/04/03 Alaska Hoodoo Mountains, Eastern Alaska Range Published by Conrad Chapman Eastern Alaska Range Avalanche Center Avalanche Details Date: 03 April 2016 Time: 3:00 pm AST Location: Hoodoo Mountains,
2016/04/03 Alaska Hoodoo Mountains, Eastern Alaska Range Published by Conrad Chapman Eastern Alaska Range Avalanche Center Avalanche Details Date: 03 April 2016 Time: 3:00 pm AST Location: Hoodoo Mountains,
Part 2: Specific Skills
 1/12 Part 1: The AMGA Ski Standard Goals The following descriptions are intended to help both candidates better self-assess their skiing skills as well as aid instructors/examiners in assessing skiing
1/12 Part 1: The AMGA Ski Standard Goals The following descriptions are intended to help both candidates better self-assess their skiing skills as well as aid instructors/examiners in assessing skiing
Global Winds and Local Winds
 Global Winds and Local Winds National Science Education Standards ES 1j What is the Coriolis effect? What are the major global wind systems on Earth? What Causes Wind? Wind is moving air caused by differences
Global Winds and Local Winds National Science Education Standards ES 1j What is the Coriolis effect? What are the major global wind systems on Earth? What Causes Wind? Wind is moving air caused by differences
Local Winds. Please read Ahrens Chapter 10
 Local Winds Please read Ahrens Chapter 10 Scales of Motion Microscale: meters Turbulent eddies Formed by mechanical disturbance or convection Lifetimes of minutes Mesoscale: km s to 100 s of km s Local
Local Winds Please read Ahrens Chapter 10 Scales of Motion Microscale: meters Turbulent eddies Formed by mechanical disturbance or convection Lifetimes of minutes Mesoscale: km s to 100 s of km s Local
