Surf and Swash Zone Hydrodynamics
|
|
|
- Walter Horn
- 6 years ago
- Views:
Transcription
1 Surf and Swash Zone Hydrodynamics D. Howell Peregrine School of Mathematics, University Walk, Bristol BS8 1TW, England. phone: fax: Ib A. Svendsen Centre for Applied Coastal Research, University of Delaware, Newark, DE 19716, U.S.A. phone: fax: Award #: N Peregrine's home page. Svendsen's homepage (8 reprints available) The home page of the SASME project. LONG-TERM GOALS Improve understanding of the hydrodynamics of the near-shore motions on beaches, with particular reference to the zone where the incident waves break, form surf, and run-up on the beach to give a fluctuating shoreline. This includes the waves and currents that the breaking waves, surf and run-up generate together with necessary details of the motions beneath the waves. Particular attention is directed to improving theoretical models of these motions. OBJECTIVES The main topics for study are: (a) the turbulence generated by breaking waves and bores. A rational, non-empirical, approach to modelling unsteady spilling breakers and bores is a major target. (b) the modelling of surf in the presence of co-existing long waves. (c) improved, and perhaps simplified, modelling of the swash zone. (d) understanding the currents, eddies and long waves generated by the incident waves, especially for irregular non-uniform waves over non-uniform bed topography. APPROACH This grant is to enhance cooperation between the P.I.s and their respective groups in working towards the above goals. The P.I.s meet each other each year and their more junior associates can make extended visits to each other's institution. In both groups the emphasis is on developing mathematical models through to practical numerical programs, including significant interaction with field and experimental results. WORK COMPLETED / RESULTS After some unsatisfactory experience with the accuracy of our existing numerical shallow-water codes when applied to two horizontal dimensions, O. Bokhove and M.D. Patterson have developed 1
2 Report Documentation Page Form Approved OMB No Public reporting burden for the collection of information is estimated to average 1 hour per response, including the time for reviewing instructions, searching existing data sources, gathering and maintaining the data needed, and completing and reviewing the collection of information. Send comments regarding this burden estimate or any other aspect of this collection of information, including suggestions for reducing this burden, to Washington Headquarters Services, Directorate for Information Operations and Reports, 1215 Jefferson Davis Highway, Suite 1204, Arlington VA Respondents should be aware that notwithstanding any other provision of law, no person shall be subject to a penalty for failing to comply with a collection of information if it does not display a currently valid OMB control number. 1. REPORT DATE SEP TITLE AND SUBTITLE Surf and Swash Zone Hydrodynamics 2. REPORT TYPE 3. DATES COVERED to a. CONTRACT NUMBER 5b. GRANT NUMBER 5c. PROGRAM ELEMENT NUMBER 6. AUTHOR(S) 5d. PROJECT NUMBER 5e. TASK NUMBER 5f. WORK UNIT NUMBER 7. PERFORMING ORGANIZATION NAME(S) AND ADDRESS(ES) School of Mathematics, University Walk,,Bristol BS8 1TW, England,,, 8. PERFORMING ORGANIZATION REPORT NUMBER 9. SPONSORING/MONITORING AGENCY NAME(S) AND ADDRESS(ES) 10. SPONSOR/MONITOR S ACRONYM(S) 12. DISTRIBUTION/AVAILABILITY STATEMENT Approved for public release; distribution unlimited 13. SUPPLEMENTARY NOTES 14. ABSTRACT 11. SPONSOR/MONITOR S REPORT NUMBER(S) 15. SUBJECT TERMS 16. SECURITY CLASSIFICATION OF: 17. LIMITATION OF ABSTRACT a. REPORT unclassified b. ABSTRACT unclassified c. THIS PAGE unclassified Same as Report (SAR) 18. NUMBER OF PAGES 7 19a. NAME OF RESPONSIBLE PERSON Standard Form 298 (Rev. 8-98) Prescribed by ANSI Std Z39-18
3 and tested several numerical shallow-water codes for time-domain modeling of breaking waves in the surf zone, trying out various schemes suggested in both the gas dynamics and oceanographic community. Breaking waves in the surf zone are modeled as bores or discontinuities, that are mathematically similar to shocks in gas dynamics. We are especially interested in the bores for two reasons. 1) We have developed ideas that give an alternative approach to the understanding, interpretation and prediction of wave genrated currents (Peregrine 1998, 1999 and Bokhove & Peregrine 1998), and wish to investigate it further. 2) The swash zone over which the shoreline moves with each wave is an importnat region where we are developing the fundamental work of Brocchini & Peregrine (1996). This works aims at improving wave averaged models which at present often have a very simplistic swash zone boundary condition, i.e. that the water depth is zero, a result that is only true in averaged models at the utmost extremity of the runup. The results of our assessment of shallow water numerical schemes are summarized in Bokhove, Patterson & Peregrine (2000), and a full review paper is in preparation. In essence, three schemes have been shown to give good improvements and to be worthy of further study. In brief, they are the convex essentially non-oscillatory scheme of Liu & Osher (1998), the central difference scheme of Jiang & Tadmor (1998) and the essentially non-oscillatory scheme of Shu & Osher (1989). The first two schemes appear to be distinctly more computationally efficient than the last one. In many schemes for hyperbolic partial differential equations such as we are solving there are often problems with 'source' terms. In our case, these correspond to friction terms, which give little trouble and the effects of varying depth where we did have trouble. However, a neat logical way of overcoming that defect has been found. A more severe problem, which has become notorious in swash modelling, is that of the shoreline boundary condition, and the development of various instabilities and inaccuracies. This has been investigated in detail and useful results have emerged. (a) (b) Figure 1. (a) Still from a video of colored water advancing through a matrix of a mixture of two sizes of glass marbles. The air-water interface is near the top. (b) A sketch to indicate that flow paths near the larger marbles offer less resistance. 2
4 In addition, particular focus has been given to the modelling of the moving shoreline in the case where the beach is made of coarse materials so that there is easy flow into the beach and the interior flow is at high Reynolds number. A number of fundamental aspects of this problem appeared to be poorly modelled in the literature. Several measurements have been made for especially simplified flows, in order to obtain better insight into these problems. An initial report is given in Patterson, Peregrine & Loveless (2000). Of particular interest is the effect of mixed sizes in sediment. An experiment with the porous medium made up of a mixture of glass marbles, of diameters 20mm and 8mm diameter, with advancing colored water is shown in figure 1. The larger elements within the matrix provide a low resistance path for advancing water, which shows up as a bulge in the advancing air-water interface. Long-term work to improve the modelling of strong turbulence at a free surface, such as occurs in a splashing breaker, has lead to the submission of two papers: Brocchini & Peregrine (2000a,b) and to the organization of a Euromech meeting on 'Strong turbulence at free surfaces'. Both principal investigators took major roles in this meeting at Genoa, Italy in September The work at the Center for Applied Coastal Research (CACR), University of Delaware has included development of a reference version of the quasi-3d circulation model SHORECIRC(SC) and a detailed manual describing both this model and how to operate it (with Haas, Zhao, and others). Model and manual have been made available for selected nearshore scientists for further testing and comments. Work has started on the analysis of how errors in how particularly the cross-shore boundary conditions influences the solution inside the modelling domain (Chen). The purpose is to clarify if it is possible by extending the model domain in the longshore direction to relax on the accuracy required for the boundary values along cross-shore boundaries, because such boundary conditions are hard to obtain in practical applications. Indications are this will be possible but work in ongoing. Finally, modelling of rip currents has been continued with particular emphasis of the vertical variation of the currents (Haas). A spectacular result is the finding that offshore of the rip channels rip currents quickly develop into currents mainly flowing in the surface. There is a strong variation over the vertical in the direction of the currents. Personnel Exchanges Name Position Visit dates Home Place of visit institution I.A.Svendsen Professor March 2000 CACR U. of Bristol M.Brocchini Professor June 2000 U. of Genoa U. of Bristol CACR WORK IN PROGRESS Earlier work by Bird (1999) on two-dimensional wave groups approaching a beach showed interesting features that indicated that the relative phase of waves in such modulation had a substantial effect on the evolution of such groups. This is now being investigated further. B. Mapp is making good progress in studying how robust the phenomenon is when considered with a threedimensional model. The work is mainly based on using the Davey-Stewartson modulation equations. 3
5 Bokhove and Patterson continue to develop the numerical shallow water code and with emphasis on the generation of unsteady currents such as eddies and rip currents, and on including the effects of porous beds. The work with Brocchini on averaging over the swash zone is being continued with the assistance of R. Archetti to examine the effect of frictional terms which are at their most influential in the swash zone. R.Moraes, at Bristol, is working on detailed hydrodynamic models for the interaction of waves and currents that allow investigation of the effect of strong current gradients. This also gives comparisons with corresponding experimetnal work recently completed at Delaware: Chawla (1999). Svendsen and his group at CACR, U. of Delaware are continuing the development of the quasi-3d circulation model SHORECIRC(SC). This includes developing boundary conditions for the shoreline (in collaboration with Brocchini and his colleagues) that can be used in various models, with different numerical grids and a variety of physical situations. The effects of errors in the specified cross-shore boundary conditions are analyzed and model development is taking place to extend applications to deeper water. Work also continues on analysis of the hydrodynamical mechanisms of rip currents, and a version of the model for generalized curvilinear coordinates is being developed. Finally application to sediment transport and comparison to laboratory measurements of both hydrodynamics and sediment motion and to field data from Duck, North Carolina (in collaboration with Kaihatu, NRL, Stennis. MS), is in progress. IMPACT/APPLICATIONS In all areas mentioned under OBJECTIVES major improvements in modelling are arriving. (a) At a wave-resolving scale the improvements in modelling two horizontal dimensions now give a capability to investigate many features due to three-dimensional wave fields or bed topography. (b) The development of averaged models for the swash region gives a valuable tool for the land-sea boundary which is an area where sediment erosion or deposition are of special significance. (c) presently the best models for the surf zone include 'rollers' to model the breakers. The parameters describing these rollers are obtained from best fits to data. We are gaining understanding of the hydrodynamic feedback between the foot and crest of a breaker such that a more deterministic model that includes breaker initiation, merging and decay can be created. (d) Quantification of the changes of circulation and generation of vorticity by bores gives a new and simpler way of assessing currents from observation of the wave field, in addition they promise new insights into horizontal mixing and transport properties of the surf zone currents. RELATED PROJECTS Related projects in Bristol are: "Surf and swash zone mechanics" (the "SASME project"), PI Peregrine. (sponsor E.U. MAST). "Probabilistic Design Tools for Vertical Breakwaters" ("PROVERBS"), PI Peregrine. (sponsor E.U.). 4
6 "The optimisation of crest level design of sloping coastal structures through prototype monitoring and modelling" ("OPTICREST"), PI Peregrine. (Sponsor E.U.). "Effects of surface currents on the patterns and breaking of surface waves with reference to remote sensing", PI Peregrine. (Sponsor: the U.K.'s Defence Evaluation and Research Agency (DERA). Related projects at Delaware are: "The generation of rip currents and circulation around coastal structures" (Sponsor:NOAA, Sea Grant. "Modelling nearshore waves, currents, and IG wave motion" PI: Svendsen (Sponsor: ONR). "Development and verification of a comprehensive community model for physical processes in the nearshore ocean". PI's Kirby, Svendsen, (at UD, and others outside UD)(Sponsor: NOPP). "A computational model for the hydrodynamical and littoral processes at the large-scale sediment transport facility at WES" PI: Svendsen (Sponsor: ARO). Several of the twelve other groups in the SASME project cooperate with Bristol. This includes contacts with experimental groups e.g. at the Universities of Cantabria, Edinburgh, Florence, and Plymouth. Similar interactions occur with those running complex computer programs (e.g. Danish Hydraulic Institute [DHI], and Delft Hydraulics). Interactions occur between Delaware and the groups conducting hydrodynamic field experiments at Duck, North Carolina (Scripps, Naval Postgraduate School, Oregon State University and others). Close interaction continues between Delaware and the researchers at the Dept. of Mathematical Modelling (IMM) at DTU in Denmark (Per Madsen and his group) and at the University of Genova (Brocchini). REFERENCES / PUBLICATIONS Bird, C.C. (1999). Nonlinear interactions of water waves, wave groups and beaches. Ph.D. thesis, Univ. of Bristol Bokhove, O., Patterson, M.D. & Peregrine, D.H. (2000). Breaking shallow water wave simulations in the surf and swash zone. Proc. 27th Internat. Conf. Coastal Engnrs. ASCE, Sydney, to appear. Brocchini, M. & Peregrine, D.H. (1996). Integral flow properties of the swash zone and averaging. J. Fluid Mech., 317, Brocchini, M & Peregrine D.H. (2000a). The dynamics of strong turbulence at free surfaces. Part 1. Description. Submitted to J. Fluid Mech. Brocchini, M & Peregrine D.H. (2000b). The dynamics of strong turbulence at free surfaces. Part 2. The boundary conditions. Submitted to J. Fluid Mech. Brocchini, M., Bellotti, G. & Svendsen, I.A. (2000). Swash zone modelling for wave-averaged solvers: An example of implementation. Ph.D. Thesis, University of Delaware. 5
7 Chawla, A. (1999). An experimental of study on the dynamics of wave breaking and blocking on opposing currents. Ph.D. Thesis, University of Delaware. Chawla, A. & Kirby, J.T. (1998). Experimental study of wave breaking and blocking on opposing currents. Proc. 26th Internat. Conf. Coastal Engnrs. ASCE, Copenhagen, Donato, A.N., Peregrine, D.H. & Stocker, J. (1999). The focussing of surface waves by internal waves. J. Fluid Mech., 384, Patterson, M.D., Peregrine, D.H. & Loveless, J. (2000). Water wave interaction with coarse sediment. Proc. 27th Internat. Conf. Coastal Engnrs. ASCE, Sydney, to appear. Peregrine, D.H. (1998). Surf zone currents. Theor. & Computational Fluid Dynamics, 10, Peregrine, D.H. (1999). Large-scale vorticity generation by breakers in shallow and deep water. European J.Mech. B/Fluids. 18, Peregrine, D.H. & Bokhove, O. (1998). Vorticity and surf zone currents. Proc. 26th Internat. Conf. Coastal Engnrs. ASCE, Copenhagen. Prasad, R., Bellotti, G., Svendsen, I.A. & Brocchini, M. (2000). Boundary at shorelines. Journal paper in preparation. Stocker, J.R. & Peregrine D.H. (1999). The current-modified nonlinear Schrödinger equation. J. Fluid Mech., 399, Wood, D.J. & Peregrine, D.H. (2000). Study of wave impact against a wall with pressure-impulse theory: Part 1, Trapped air. J. Waterway, Port, Coastal & Ocean Engng., ASCE. 126, Wood, D.J. & Peregrine, D.H. (2000). Study of wave impact against a wall with pressure-impulse theory: Part 2: A porous berm. J. Waterway, Port, Coastal & Ocean Engng., ASCE. 126, Walkden, M., Wood, D.J., Bruce, T. & Peregrine, D.H. (2000). Impulsive seaward loads on caisson breakwaters. J. Waterway, Port, Coastal & Ocean Engng., ASCE. in press. 6
Surf and Swash Zone Hydrodynamics
 Surf and Swash Zone Hydrodynamics D. Howell Peregrine School of Mathematics, University Walk, Bristol BS8 1TW, England. phone: 44-117-928-7971 fax: 44-117-928-7999 email: d.h.peregrine@bris.ac.uk Ib A.
Surf and Swash Zone Hydrodynamics D. Howell Peregrine School of Mathematics, University Walk, Bristol BS8 1TW, England. phone: 44-117-928-7971 fax: 44-117-928-7999 email: d.h.peregrine@bris.ac.uk Ib A.
Kelly Legault, Ph.D., P.E. USACE SAJ
 Kelly Legault, Ph.D., P.E. USACE SAJ Report Documentation Page Form Approved OMB No. 0704-0188 Public reporting burden for the collection of information is estimated to average 1 hour per response, including
Kelly Legault, Ph.D., P.E. USACE SAJ Report Documentation Page Form Approved OMB No. 0704-0188 Public reporting burden for the collection of information is estimated to average 1 hour per response, including
Waves, Turbulence and Boundary Layers
 Waves, Turbulence and Boundary Layers George L. Mellor Program in Atmospheric and Oceanic Sciences Princeton University Princeton NJ 8544-71 phone: (69) 258-657 fax: (69) 258-285 email: glm@splash.princeton.edu
Waves, Turbulence and Boundary Layers George L. Mellor Program in Atmospheric and Oceanic Sciences Princeton University Princeton NJ 8544-71 phone: (69) 258-657 fax: (69) 258-285 email: glm@splash.princeton.edu
RIP CURRENTS. Award # N
 RIP CURRENTS Graham Symonds School of Geography and Oceanography University College, University of New South Wales, Australian Defence Force Academy, Canberra, 2600 AUSTRALIA Phone: 61-6-2688289 Fax: 61-6-2688313
RIP CURRENTS Graham Symonds School of Geography and Oceanography University College, University of New South Wales, Australian Defence Force Academy, Canberra, 2600 AUSTRALIA Phone: 61-6-2688289 Fax: 61-6-2688313
Unsteady Wave-Driven Circulation Cells Relevant to Rip Currents and Coastal Engineering
 Unsteady Wave-Driven Circulation Cells Relevant to Rip Currents and Coastal Engineering Andrew Kennedy Dept of Civil and Coastal Engineering 365 Weil Hall University of Florida Gainesville, FL 32611 phone:
Unsteady Wave-Driven Circulation Cells Relevant to Rip Currents and Coastal Engineering Andrew Kennedy Dept of Civil and Coastal Engineering 365 Weil Hall University of Florida Gainesville, FL 32611 phone:
STUDIES OF FINITE AMPLITUDE SHEAR WAVE INSTABILITIES. James T. Kirby. Center for Applied Coastal Research. University of Delaware.
 STUDIES OF FINITE AMPLITUDE SHEAR WAVE INSTABILITIES James T. Kirby Center for Applied Coastal Research University of Delaware Newark, DE 19716 phone: (32) 831-2438, fax: (32) 831-1228, email: kirby@coastal.udel.edu
STUDIES OF FINITE AMPLITUDE SHEAR WAVE INSTABILITIES James T. Kirby Center for Applied Coastal Research University of Delaware Newark, DE 19716 phone: (32) 831-2438, fax: (32) 831-1228, email: kirby@coastal.udel.edu
Characterizing The Surf Zone With Ambient Noise Measurements
 Characterizing The Surf Zone With Ambient Noise Measurements LONG-TERM GOAL Grant Deane Marine Physical Laboratory Scripps Institution of Oceanography La Jolla, CA 93093-0213 phone: (619) 534-0536 fax:
Characterizing The Surf Zone With Ambient Noise Measurements LONG-TERM GOAL Grant Deane Marine Physical Laboratory Scripps Institution of Oceanography La Jolla, CA 93093-0213 phone: (619) 534-0536 fax:
BRRAKING WAVE FORCES ON WALLS
 CETN-III-38 3/88 BRRAKING WAVE FORCES ON WALLS PURPOSE: To introduce the Goda method as an alternative to the Minikin method for the determination of breaking wave forces on semirigid wall structures.
CETN-III-38 3/88 BRRAKING WAVE FORCES ON WALLS PURPOSE: To introduce the Goda method as an alternative to the Minikin method for the determination of breaking wave forces on semirigid wall structures.
Global Ocean Internal Wave Database
 Global Ocean Internal Wave Database Victor Klemas Graduate College of Marine Studies University of Delaware Newark, DE 19716 phone: (302) 831-8256 fax: (302) 831-6838 email: klemas@udel.edu Quanan Zheng
Global Ocean Internal Wave Database Victor Klemas Graduate College of Marine Studies University of Delaware Newark, DE 19716 phone: (302) 831-8256 fax: (302) 831-6838 email: klemas@udel.edu Quanan Zheng
Rip Currents Onshore Submarine Canyons: NCEX Analysis
 Rip Currents Onshore Submarine Canyons: NCEX Analysis Dr. Thomas C. Lippmann Civil and Environmental Engineering & Geodetic Science, Byrd Polar Research Center, 1090 Carmack Rd., Ohio State University,
Rip Currents Onshore Submarine Canyons: NCEX Analysis Dr. Thomas C. Lippmann Civil and Environmental Engineering & Geodetic Science, Byrd Polar Research Center, 1090 Carmack Rd., Ohio State University,
High Frequency Acoustical Propagation and Scattering in Coastal Waters
 High Frequency Acoustical Propagation and Scattering in Coastal Waters David M. Farmer Graduate School of Oceanography (educational) University of Rhode Island Narragansett, RI 02882 Phone: (401) 874-6222
High Frequency Acoustical Propagation and Scattering in Coastal Waters David M. Farmer Graduate School of Oceanography (educational) University of Rhode Island Narragansett, RI 02882 Phone: (401) 874-6222
Internal Waves in Straits Experiment Progress Report
 DISTRIBUTION STATEMENT A: Approved for public release; distribution is unlimited. Internal Waves in Straits Experiment Progress Report Jody Klymak School of Earth and Ocean Sciences University of Victoria
DISTRIBUTION STATEMENT A: Approved for public release; distribution is unlimited. Internal Waves in Straits Experiment Progress Report Jody Klymak School of Earth and Ocean Sciences University of Victoria
AN EXPERIMENTAL INVESTIGATION OF SPILLING BREAKERS
 AN EXPERIMENTAL INVESTIGATION OF SPILLING BREAKERS Prof. James H. Duncan Department of Mechanical Engineering University of Maryland College Park, Maryland 20742-3035 phone: (301) 405-5260, fax: (301)
AN EXPERIMENTAL INVESTIGATION OF SPILLING BREAKERS Prof. James H. Duncan Department of Mechanical Engineering University of Maryland College Park, Maryland 20742-3035 phone: (301) 405-5260, fax: (301)
( max)o Wind Waves 10 Short Swell (large wave steepness) 25 Long Swell (small wave steepness) 75
 CEPi-I-18 REvKn, 3188 IRREGULAR WAVE DIFFRACTION BY GODA'S KETHOD PURPOSE : To provide a simplified method for determining random wave diffraction coefficients for a semi-infinite breakwater. GENERAL :
CEPi-I-18 REvKn, 3188 IRREGULAR WAVE DIFFRACTION BY GODA'S KETHOD PURPOSE : To provide a simplified method for determining random wave diffraction coefficients for a semi-infinite breakwater. GENERAL :
Determination of Nearshore Wave Conditions and Bathymetry from X-Band Radar Systems
 Determination of Nearshore Wave Conditions and Bathymetry from X-Band Radar Systems Okey G. Nwogu Dept. of Naval Architecture and Marine Engineering University of Michigan Ann Arbor, MI 48109 Phone: (734)
Determination of Nearshore Wave Conditions and Bathymetry from X-Band Radar Systems Okey G. Nwogu Dept. of Naval Architecture and Marine Engineering University of Michigan Ann Arbor, MI 48109 Phone: (734)
Next Generation Modeling for Deep Water Wave Breaking and Langmuir Circulation
 Next Generation Modeling for Deep Water Wave Breaking and Langmuir Circulation Eric D. Skyllingstad College of Oceanic and Atmospheric Sciences, Oregon State University Corvallis, OR 97331, Phone: (541)
Next Generation Modeling for Deep Water Wave Breaking and Langmuir Circulation Eric D. Skyllingstad College of Oceanic and Atmospheric Sciences, Oregon State University Corvallis, OR 97331, Phone: (541)
High-Frequency Scattering from the Sea Surface and Multiple Scattering from Bubbles
 High-Frequency Scattering from the Sea Surface and Multiple Scattering from Bubbles Peter H. Dahl Applied Physics Laboratory College of Ocean and Fisheries Sciences University of Washington Seattle, Washington
High-Frequency Scattering from the Sea Surface and Multiple Scattering from Bubbles Peter H. Dahl Applied Physics Laboratory College of Ocean and Fisheries Sciences University of Washington Seattle, Washington
Waves, Bubbles, Noise, and Underwater Communications
 Waves, Bubbles, Noise, and Underwater Communications Grant B. Deane Marine Physical Laboratory, Scripps Institution of Oceanography UCSD, La Jolla, CA 92093-0238 phone: (858) 534-0536 fax: (858) 534-7641
Waves, Bubbles, Noise, and Underwater Communications Grant B. Deane Marine Physical Laboratory, Scripps Institution of Oceanography UCSD, La Jolla, CA 92093-0238 phone: (858) 534-0536 fax: (858) 534-7641
Rogue Wave Statistics and Dynamics Using Large-Scale Direct Simulations
 Rogue Wave Statistics and Dynamics Using Large-Scale Direct Simulations Dick K.P. Yue Center for Ocean Engineering Department of Mechanical Engineering Massachusetts Institute of Technology Cambridge,
Rogue Wave Statistics and Dynamics Using Large-Scale Direct Simulations Dick K.P. Yue Center for Ocean Engineering Department of Mechanical Engineering Massachusetts Institute of Technology Cambridge,
Air-Sea Interaction Spar Buoy Systems
 DISTRIBUTION STATEMENT A: Distribution approved for public release; distribution is unlimited Air-Sea Interaction Spar Buoy Systems Hans C. Graber CSTARS - University of Miami 11811 SW 168 th Street, Miami,
DISTRIBUTION STATEMENT A: Distribution approved for public release; distribution is unlimited Air-Sea Interaction Spar Buoy Systems Hans C. Graber CSTARS - University of Miami 11811 SW 168 th Street, Miami,
Determination Of Nearshore Wave Conditions And Bathymetry From X-Band Radar Systems
 Determination Of Nearshore Wave Conditions And Bathymetry From X-Band Radar Systems Okey G. Nwogu Dept. of Naval Architecture and Marine Engineering University of Michigan Ann Arbor, MI 489 phone: (734)
Determination Of Nearshore Wave Conditions And Bathymetry From X-Band Radar Systems Okey G. Nwogu Dept. of Naval Architecture and Marine Engineering University of Michigan Ann Arbor, MI 489 phone: (734)
Relevant courses: Functional Analysis, Hydrodynamic Instability, Computational Aspects and Application of Spectral Methods.
 Curriculum Vitae for Henrik Bredmose Name: Henrik Bredmose Date of Birth: December 23, 1974 Married to Malene Brandt Children: Freja Bredmose Brandt Nationality: Danish Member of DCAMM since 1999 Adress:
Curriculum Vitae for Henrik Bredmose Name: Henrik Bredmose Date of Birth: December 23, 1974 Married to Malene Brandt Children: Freja Bredmose Brandt Nationality: Danish Member of DCAMM since 1999 Adress:
Three Dimensional Modeling of Breaking
 Three Dimensional Modeling of Breaking Robert A. Dalrymple Dept of Civil Engineering The Johns Hopkins University 3400 North Charles Street Baltimore, MD 21218 phone: (410) 516-7923 fax: (410) 516-7473
Three Dimensional Modeling of Breaking Robert A. Dalrymple Dept of Civil Engineering The Johns Hopkins University 3400 North Charles Street Baltimore, MD 21218 phone: (410) 516-7923 fax: (410) 516-7473
TITLE: Assessing the Hydrodynamic Performance of Fouling-Release Surfaces (ONR Research Contract # N WR )
 TITLE: Assessing the Hydrodynamic Performance of Fouling-Release Surfaces (ONR Research Contract # N00014-07-WR-2-0213) INVESTIGATOR: Associate Professor Michael P. Schultz, Naval Architecture & Ocean
TITLE: Assessing the Hydrodynamic Performance of Fouling-Release Surfaces (ONR Research Contract # N00014-07-WR-2-0213) INVESTIGATOR: Associate Professor Michael P. Schultz, Naval Architecture & Ocean
Surface Wave Processes on the Continental Shelf and Beach
 Surface Wave Processes on the Continental Shelf and Beach Thomas H. C. Herbers Department of Oceanography, Code OC/He Naval Postgraduate School Monterey, California 93943-5122 phone: (831) 656-2917 fax:
Surface Wave Processes on the Continental Shelf and Beach Thomas H. C. Herbers Department of Oceanography, Code OC/He Naval Postgraduate School Monterey, California 93943-5122 phone: (831) 656-2917 fax:
The Continued Development of the Third-Generation Shallow Water Wave Model "Swan"
 The Continued Development of the Third-Generation Shallow Water Wave Model "Swan" Leo Holthuijsen Department. Of Civil Engineering Delft University of Technology Stevinweg 1, 2628 CN, Delft the Netherlands
The Continued Development of the Third-Generation Shallow Water Wave Model "Swan" Leo Holthuijsen Department. Of Civil Engineering Delft University of Technology Stevinweg 1, 2628 CN, Delft the Netherlands
Internal Waves and Mixing in the Aegean Sea
 Internal Waves and Mixing in the Aegean Sea Michael C. Gregg Applied Physics Laboratory, University of Washington 1013 NE 40 th St. Seattle, WA 98105-6698 phone: (206) 543-1353 fax: (206) 543-6785 email:
Internal Waves and Mixing in the Aegean Sea Michael C. Gregg Applied Physics Laboratory, University of Washington 1013 NE 40 th St. Seattle, WA 98105-6698 phone: (206) 543-1353 fax: (206) 543-6785 email:
Examples of Carter Corrected DBDB-V Applied to Acoustic Propagation Modeling
 Naval Research Laboratory Stennis Space Center, MS 39529-5004 NRL/MR/7182--08-9100 Examples of Carter Corrected DBDB-V Applied to Acoustic Propagation Modeling J. Paquin Fabre Acoustic Simulation, Measurements,
Naval Research Laboratory Stennis Space Center, MS 39529-5004 NRL/MR/7182--08-9100 Examples of Carter Corrected DBDB-V Applied to Acoustic Propagation Modeling J. Paquin Fabre Acoustic Simulation, Measurements,
Wave Breaking, Infragravity Waves, And Sediment Transport In The Nearshore
 Wave Breaking, Infragravity Waves, And Sediment Transport In The Nearshore Dr. Thomas C. Lippmann Center for Coastal Studies Scripps Institution of Oceanography University of California, San Diego La Jolla,
Wave Breaking, Infragravity Waves, And Sediment Transport In The Nearshore Dr. Thomas C. Lippmann Center for Coastal Studies Scripps Institution of Oceanography University of California, San Diego La Jolla,
Nearshore Wave-Topography Interactions
 LONG-TERM GOAL Nearshore Wave-Topography Interactions Rob Holman College of Oceanic and Atmospheric Sciences Oregon State University 104 Ocean Admin Bldg Corvallis, OR 97331-5503 phone: (541) 737-2914
LONG-TERM GOAL Nearshore Wave-Topography Interactions Rob Holman College of Oceanic and Atmospheric Sciences Oregon State University 104 Ocean Admin Bldg Corvallis, OR 97331-5503 phone: (541) 737-2914
Long-Term Autonomous Measurement of Ocean Dissipation with EPS-MAPPER
 Long-Term Autonomous Measurement of Ocean Dissipation with EPS-MAPPER Neil S. Oakey Bedford Institute of Oceanography Dartmouth, Nova Scotia Canada B2Y 4A2 phone: (902) 426-3147 fax: (902) 426-7827 e-mail:
Long-Term Autonomous Measurement of Ocean Dissipation with EPS-MAPPER Neil S. Oakey Bedford Institute of Oceanography Dartmouth, Nova Scotia Canada B2Y 4A2 phone: (902) 426-3147 fax: (902) 426-7827 e-mail:
Acoustic Focusing in Shallow Water and Bubble Radiation Effects
 Acoustic Focusing in Shallow Water and Bubble Radiation Effects Grant B. Deane Marine Physical Laboratory, Scripps Institution of Oceanography UCSD, La Jolla, CA 92093-0238 Phone: (858) 534-0536 fax: (858)
Acoustic Focusing in Shallow Water and Bubble Radiation Effects Grant B. Deane Marine Physical Laboratory, Scripps Institution of Oceanography UCSD, La Jolla, CA 92093-0238 Phone: (858) 534-0536 fax: (858)
MODELING OF CLIMATE CHANGE IMPACTS ON COASTAL STRUCTURES - CONTRIBUTION TO THEIR RE-DESIGN
 Proceedings of the 14 th International Conference on Environmental Science and Technology Rhodes, Greece, 3-5 September 2015 MODELING OF CLIMATE CHANGE IMPACTS ON COASTAL STRUCTURES - CONTRIBUTION TO THEIR
Proceedings of the 14 th International Conference on Environmental Science and Technology Rhodes, Greece, 3-5 September 2015 MODELING OF CLIMATE CHANGE IMPACTS ON COASTAL STRUCTURES - CONTRIBUTION TO THEIR
Imaging the Lung Under Pressure
 DISTRIBUTION STATEMENT A: Approved for public release; distribution is unlimited. Imaging the Lung Under Pressure Peter L. Tyack, Andreas Fahlman, Michael Moore, and Darlene Ketten Woods Hole Oceanographic
DISTRIBUTION STATEMENT A: Approved for public release; distribution is unlimited. Imaging the Lung Under Pressure Peter L. Tyack, Andreas Fahlman, Michael Moore, and Darlene Ketten Woods Hole Oceanographic
REPORT DOCUMENTATION PAGE
 REPORT DOCUMENTATION PAGE Form Approved OMB No. 0704-0188 Public reporting burden for this collection of information is estimated to average 1 hour per response, including the time for reviewing instructions,
REPORT DOCUMENTATION PAGE Form Approved OMB No. 0704-0188 Public reporting burden for this collection of information is estimated to average 1 hour per response, including the time for reviewing instructions,
Near Shore Wave Processes
 Near Shore Wave Processes Edward B. Thornton Oceanography Department Naval Postgraduate School Monterey, CA 93943-5000 phone: (831) 656-2847 fax: (831) 656-2712 email: thornton@nps.navy.mil Timothy P.
Near Shore Wave Processes Edward B. Thornton Oceanography Department Naval Postgraduate School Monterey, CA 93943-5000 phone: (831) 656-2847 fax: (831) 656-2712 email: thornton@nps.navy.mil Timothy P.
Interactions of Waves and River Plume and their Effects on Sediment Transport at River Mouth
 DISTRIBUTION STATEMENT A. Approved for public release; distribution is unlimited. Interactions of Waves and River Plume and their Effects on Sediment Transport at River Mouth Tian-Jian Hsu and Fengyan
DISTRIBUTION STATEMENT A. Approved for public release; distribution is unlimited. Interactions of Waves and River Plume and their Effects on Sediment Transport at River Mouth Tian-Jian Hsu and Fengyan
Waves, Bubbles, Noise and Underwater Communications
 DISTRIBUTION STATEMENT A: Approved for public release; distribution is unlimited. Waves, Bubbles, Noise and Underwater Communications Grant B. Deane Marine Physical Laboratory Scripps Institution of Oceanography
DISTRIBUTION STATEMENT A: Approved for public release; distribution is unlimited. Waves, Bubbles, Noise and Underwater Communications Grant B. Deane Marine Physical Laboratory Scripps Institution of Oceanography
Optical Imaging of the Nearshore
 Optical Imaging of the Nearshore Rob Holman COAS-OSU 104 Ocean Admin Bldg Corvallis, OR 97331-5503 phone: (541) 737-2914 fax: (541) 737-2064 email: holman@coas.oregonstate.edu Award #: N00014-02-1-0154
Optical Imaging of the Nearshore Rob Holman COAS-OSU 104 Ocean Admin Bldg Corvallis, OR 97331-5503 phone: (541) 737-2914 fax: (541) 737-2064 email: holman@coas.oregonstate.edu Award #: N00014-02-1-0154
Marine Mammal Acoustic Tracking from Adapting HARP Technologies
 DISTRIBUTION STATEMENT A: Approved for public release; distribution is unlimited. Marine Mammal Acoustic Tracking from Adapting HARP Technologies Sean M. Wiggins and John A. Hildebrand Marine Physical
DISTRIBUTION STATEMENT A: Approved for public release; distribution is unlimited. Marine Mammal Acoustic Tracking from Adapting HARP Technologies Sean M. Wiggins and John A. Hildebrand Marine Physical
Development and Verification of a Comprehensive Community Model for Physical Processes in the Nearshore Ocean
 Development and Verification of a Comprehensive Community Model for Physical Processes in the Nearshore Ocean James T. Kirby, John Allen, Thomas Drake, Steve Elgar, Robert T. Guza, Dan Hanes, Tom Herbers,
Development and Verification of a Comprehensive Community Model for Physical Processes in the Nearshore Ocean James T. Kirby, John Allen, Thomas Drake, Steve Elgar, Robert T. Guza, Dan Hanes, Tom Herbers,
AFT'LICATION OF M3vABLE-RED F'HYSICAL MODHIS To FBED1crslWM-INDUCED ERmIoN
 CETN-II-18 6189 AFT'LICATION OF M3vABLE-RED F'HYSICAL MODHIS To FBED1crslWM-INDUCED ERmIoN PURKSE: This note provides guidance and nomograms for determining if twodimensional, movable-bed physical models
CETN-II-18 6189 AFT'LICATION OF M3vABLE-RED F'HYSICAL MODHIS To FBED1crslWM-INDUCED ERmIoN PURKSE: This note provides guidance and nomograms for determining if twodimensional, movable-bed physical models
Shoreline Change Modeling Using One-Line Models: Application and Comparison of GenCade, Unibest, and Litpack
 Shoreline Change Modeling Using One-Line Models: Application and Comparison of GenCade, Unibest, and Litpack by Kimberly E. Townsend, Robert C. Thomas, and Ashley E. Frey PURPOSE: The purpose of this Coastal
Shoreline Change Modeling Using One-Line Models: Application and Comparison of GenCade, Unibest, and Litpack by Kimberly E. Townsend, Robert C. Thomas, and Ashley E. Frey PURPOSE: The purpose of this Coastal
INCORPORATION OF RANDOM WAVE EFFECTS INTO A QUASI-3D NEARSHORE CIRCULATION MODEL. James M. Kaihatu, Fengyan Shi, James T. Kirby and Ib A.
 INCORPORATION OF RANDOM WAVE EFFECTS INTO A QUASI-3D NEARSHORE CIRCULATION MODEL James M. Kaihatu, Fengyan Shi, James T. Kirby and Ib A. Svendsen Abstract A coupled wave-hydrodynamic modeling system, comprised
INCORPORATION OF RANDOM WAVE EFFECTS INTO A QUASI-3D NEARSHORE CIRCULATION MODEL James M. Kaihatu, Fengyan Shi, James T. Kirby and Ib A. Svendsen Abstract A coupled wave-hydrodynamic modeling system, comprised
Waves, Currents, & Bathymetric Evolution Near An Inlet
 DISTRIBUTION STATEMENT A. Approved for public release; distribution is unlimited. Waves, Currents, & Bathymetric Evolution Near An Inlet Britt Raubenheimer Woods Hole Oceanographic Institution, MS12 Woods
DISTRIBUTION STATEMENT A. Approved for public release; distribution is unlimited. Waves, Currents, & Bathymetric Evolution Near An Inlet Britt Raubenheimer Woods Hole Oceanographic Institution, MS12 Woods
Development of Low Volume Shape Memory Alloy Variable Ballast System for AUV Use
 Development of Low Volume Shape Memory Alloy Variable Ballast System for AUV Use Dr. Graeme J Rae Ocean Engineering Program Division of Marine and Environmental Systems Florida Institute of Technology
Development of Low Volume Shape Memory Alloy Variable Ballast System for AUV Use Dr. Graeme J Rae Ocean Engineering Program Division of Marine and Environmental Systems Florida Institute of Technology
Beach Wizard: Development of an Operational Nowcast, Short-Term Forecast System for Nearshore Hydrodynamics and Bathymetric Evolution
 Beach Wizard: Development of an Operational Nowcast, Short-Term Forecast System for Nearshore Hydrodynamics and Bathymetric Evolution Ad Reniers Civil Engineering and Geosciences, Delft University of Technology
Beach Wizard: Development of an Operational Nowcast, Short-Term Forecast System for Nearshore Hydrodynamics and Bathymetric Evolution Ad Reniers Civil Engineering and Geosciences, Delft University of Technology
Remote Monitoring of Dolphins and Whales in the High Naval Activity Areas in Hawaiian Waters
 DISTRIBUTION STATEMENT A: Approved for public release; distribution is unlimited. Remote Monitoring of Dolphins and Whales in the High Naval Activity Areas in Hawaiian Waters Whitlow W. L. Au and Marc
DISTRIBUTION STATEMENT A: Approved for public release; distribution is unlimited. Remote Monitoring of Dolphins and Whales in the High Naval Activity Areas in Hawaiian Waters Whitlow W. L. Au and Marc
Observations of Velocity Fields Under Moderately Forced Wind Waves
 Observations of Velocity Fields Under Moderately Forced Wind Waves Timothy P. Stanton Oceanography Department, Code OC/ST Naval Postgraduate School Monterey, CA 93943-5000 phone: (831) 656 3144 fax: (831)
Observations of Velocity Fields Under Moderately Forced Wind Waves Timothy P. Stanton Oceanography Department, Code OC/ST Naval Postgraduate School Monterey, CA 93943-5000 phone: (831) 656 3144 fax: (831)
Quantification of the Effects of Turbulence in Wind on the Flutter Stability of Suspension Bridges
 Quantification of the Effects of Turbulence in Wind on the Flutter Stability of Suspension Bridges T. Abbas 1 and G. Morgenthal 2 1 PhD candidate, Graduate College 1462, Department of Civil Engineering,
Quantification of the Effects of Turbulence in Wind on the Flutter Stability of Suspension Bridges T. Abbas 1 and G. Morgenthal 2 1 PhD candidate, Graduate College 1462, Department of Civil Engineering,
Numerical modeling of refraction and diffraction
 Numerical modeling of refraction and diffraction L. Balas, A. inan Civil Engineering Department, Gazi University, Turkey Abstract A numerical model which simulates the propagation of waves over a complex
Numerical modeling of refraction and diffraction L. Balas, A. inan Civil Engineering Department, Gazi University, Turkey Abstract A numerical model which simulates the propagation of waves over a complex
Rip Currents Onshore Submarine Canyons: NCEX Analysis
 Rip Currents Onshore Submarine Canyons: NCEX Analysis Dr. Thomas C. Lippmann Civil and Environmental Engineering & Geodetic Science, Byrd Polar Research Center, 1090 Carmack Rd., Ohio State University,
Rip Currents Onshore Submarine Canyons: NCEX Analysis Dr. Thomas C. Lippmann Civil and Environmental Engineering & Geodetic Science, Byrd Polar Research Center, 1090 Carmack Rd., Ohio State University,
Understanding the Dynamics of Shallow-Water Oceanographic Moorings
 Understanding the Dynamics of Shallow-Water Oceanographic Moorings Mark A. Grosenbaugh Department of Applied Ocean Physics & Engineering Woods Hole Oceanographic Institution Woods Hole, MA 02543 phone:
Understanding the Dynamics of Shallow-Water Oceanographic Moorings Mark A. Grosenbaugh Department of Applied Ocean Physics & Engineering Woods Hole Oceanographic Institution Woods Hole, MA 02543 phone:
Surface Wave Processes on the Continental Shelf and Beach
 DISTRIBUTION STATEMENT A: Approved for public release; distribution is unlimited. Surface Wave Processes on the Continental Shelf and Beach Thomas H. C. Herbers Department of Oceanography, Code OC/He Naval
DISTRIBUTION STATEMENT A: Approved for public release; distribution is unlimited. Surface Wave Processes on the Continental Shelf and Beach Thomas H. C. Herbers Department of Oceanography, Code OC/He Naval
Observations of Near-Bottom Currents with Low-Cost SeaHorse Tilt Current Meters
 DISTRIBUTION STATEMENT A. Approved for public release; distribution is unlimited. Observations of Near-Bottom Currents with Low-Cost SeaHorse Tilt Current Meters Vitalii A. Sheremet Graduate School of
DISTRIBUTION STATEMENT A. Approved for public release; distribution is unlimited. Observations of Near-Bottom Currents with Low-Cost SeaHorse Tilt Current Meters Vitalii A. Sheremet Graduate School of
Three Dimensional Shallow Water Adaptive Hydraulics (ADH-SW3): Waterborne Vessels
 Three Dimensional Shallow Water Adaptive Hydraulics (ADH-SW3): Waterborne Vessels by Gaurav Savant and Corey J. Trahan PURPOSE: This Coastal and Hydraulics Engineering Technical Note (CHETN) describes
Three Dimensional Shallow Water Adaptive Hydraulics (ADH-SW3): Waterborne Vessels by Gaurav Savant and Corey J. Trahan PURPOSE: This Coastal and Hydraulics Engineering Technical Note (CHETN) describes
NONLINEAR INTERNAL WAVES IN THE SOUTH CHINA SEA
 25 th ACRS 2004 Chiang Mai, Thailand xxx NONLINEAR INTERNAL WAVES IN THE SOUTH CHINA SEA Ming-Kuang Hsu Professor, Kuang Wu Institute of Technology, Taipei, Taiwan, R.O.C. Hsumk@kwit.edu.tw Antony K. Liu
25 th ACRS 2004 Chiang Mai, Thailand xxx NONLINEAR INTERNAL WAVES IN THE SOUTH CHINA SEA Ming-Kuang Hsu Professor, Kuang Wu Institute of Technology, Taipei, Taiwan, R.O.C. Hsumk@kwit.edu.tw Antony K. Liu
Undertow - Zonation of Flow in Broken Wave Bores
 Nearshore Circulation Undertow and Rip Cells Undertow - Zonation of Flow in Broken Wave Bores In the wave breaking process, the landward transfer of water, associated with bore and surface roller decay
Nearshore Circulation Undertow and Rip Cells Undertow - Zonation of Flow in Broken Wave Bores In the wave breaking process, the landward transfer of water, associated with bore and surface roller decay
WAVE BREAKING AND DISSIPATION IN THE NEARSHORE
 WAVE BREAKING AND DISSIPATION IN THE NEARSHORE LONG-TERM GOALS Dr. Thomas C. Lippmann Center for Coastal Studies Scripps Institution of Oceanography University of California, San Diego 9500 Gilman Dr.
WAVE BREAKING AND DISSIPATION IN THE NEARSHORE LONG-TERM GOALS Dr. Thomas C. Lippmann Center for Coastal Studies Scripps Institution of Oceanography University of California, San Diego 9500 Gilman Dr.
PREDICTION OF ERODED VERSUS ACCRETED BEACHES
 CETN-II-2 6/88 PREDICTION OF ERODED VERSUS ACCRETED BEACHES PURPOSE: To present revised procedures for predicting whether a beach profile of a specified sand size will tend to erode or accrete under incident
CETN-II-2 6/88 PREDICTION OF ERODED VERSUS ACCRETED BEACHES PURPOSE: To present revised procedures for predicting whether a beach profile of a specified sand size will tend to erode or accrete under incident
Undertow - Zonation of Flow in Broken Wave Bores
 Lecture 22 Nearshore Circulation Undertow - Zonation of Flow in Broken Wave Bores In the wave breaking process, the landward transfer of water, associated with bore and surface roller decay within the
Lecture 22 Nearshore Circulation Undertow - Zonation of Flow in Broken Wave Bores In the wave breaking process, the landward transfer of water, associated with bore and surface roller decay within the
Shoreline Evolution Due to Oblique Waves in Presence of Submerged Breakwaters. Nima Zakeri (Corresponding Author), Mojtaba Tajziehchi
 Shoreline Evolution Due to Oblique Waves in Presence of Submerged Breakwaters Nima Zakeri (Corresponding Author), Mojtaba Tajziehchi Department of Civil Engineering, Faculty of Engineering, University
Shoreline Evolution Due to Oblique Waves in Presence of Submerged Breakwaters Nima Zakeri (Corresponding Author), Mojtaba Tajziehchi Department of Civil Engineering, Faculty of Engineering, University
AFRL-RX-WP-TP
 AFRL-RX-WP-TP-2012-0215 REVERSE PRESSURE CAPABLE FINGER SEAL (PREPRINT) Nathan Gibson and Joe Yanof Honeywell International, Inc. JANUARY 2012. See additional restrictions described on inside pages STINFO
AFRL-RX-WP-TP-2012-0215 REVERSE PRESSURE CAPABLE FINGER SEAL (PREPRINT) Nathan Gibson and Joe Yanof Honeywell International, Inc. JANUARY 2012. See additional restrictions described on inside pages STINFO
PHYSICAL AND NUMERICAL MODELLING OF WAVE FIELD IN FRONT OF THE CONTAINER TERMINAL PEAR - PORT OF RIJEKA (ADRIATIC SEA)
 PHYSICAL AND NUMERICAL MODELLING OF WAVE FIELD IN FRONT OF THE CONTAINER TERMINAL PEAR - PORT OF RIJEKA (ADRIATIC SEA) DALIBOR CAREVIĆ (1), GORAN LONČAR (1), VLADIMIR ANDROČEC (1) & MARIN PALADIN (1) 1.
PHYSICAL AND NUMERICAL MODELLING OF WAVE FIELD IN FRONT OF THE CONTAINER TERMINAL PEAR - PORT OF RIJEKA (ADRIATIC SEA) DALIBOR CAREVIĆ (1), GORAN LONČAR (1), VLADIMIR ANDROČEC (1) & MARIN PALADIN (1) 1.
CROSS-SHORE SEDIMENT PROCESSES
 The University of the West Indies Organization of American States PROFESSIONAL DEVELOPMENT PROGRAMME: COASTAL INFRASTRUCTURE DESIGN, CONSTRUCTION AND MAINTENANCE A COURSE IN COASTAL DEFENSE SYSTEMS I CHAPTER
The University of the West Indies Organization of American States PROFESSIONAL DEVELOPMENT PROGRAMME: COASTAL INFRASTRUCTURE DESIGN, CONSTRUCTION AND MAINTENANCE A COURSE IN COASTAL DEFENSE SYSTEMS I CHAPTER
Hyperspectral Optical Properties, Remote Sensing, and Underwater Visibility
 Hyperspectral Optical Properties, Remote Sensing, and Underwater Visibility Robert A. Maffione Hydro-Optics, Biology, and Instrumentation Laboratories P.O. Box 859 Moss Landing, California 95039 Phone:
Hyperspectral Optical Properties, Remote Sensing, and Underwater Visibility Robert A. Maffione Hydro-Optics, Biology, and Instrumentation Laboratories P.O. Box 859 Moss Landing, California 95039 Phone:
Study of Passing Ship Effects along a Bank by Delft3D-FLOW and XBeach1
 Study of Passing Ship Effects along a Bank by Delft3D-FLOW and XBeach1 Minggui Zhou 1, Dano Roelvink 2,4, Henk Verheij 3,4 and Han Ligteringen 2,3 1 School of Naval Architecture, Ocean and Civil Engineering,
Study of Passing Ship Effects along a Bank by Delft3D-FLOW and XBeach1 Minggui Zhou 1, Dano Roelvink 2,4, Henk Verheij 3,4 and Han Ligteringen 2,3 1 School of Naval Architecture, Ocean and Civil Engineering,
PhD student, January 2010-December 2013
 Numerical modeling of wave current interactions ata a local scaleand and studyof turbulence closuremodel effects MARIA JOÃO TELES PhD student, January 2010-December 2013 Supervisor: António Pires-Silva,
Numerical modeling of wave current interactions ata a local scaleand and studyof turbulence closuremodel effects MARIA JOÃO TELES PhD student, January 2010-December 2013 Supervisor: António Pires-Silva,
Calculation of the Internal Blast Pressures for Tunnel Magazine Tests
 Calculation of the Internal Blast Pressures for Tunnel Magazine Tests by Kevin Hager Naval Facilities Engineering Service Center Pt Hueneme, CA and Naury Birnbaum Century Dynamics, Inc. San Ramon, CA ABSTRACT
Calculation of the Internal Blast Pressures for Tunnel Magazine Tests by Kevin Hager Naval Facilities Engineering Service Center Pt Hueneme, CA and Naury Birnbaum Century Dynamics, Inc. San Ramon, CA ABSTRACT
ISOLATION OF NON-HYDROSTATIC REGIONS WITHIN A BASIN
 ISOLATION OF NON-HYDROSTATIC REGIONS WITHIN A BASIN Bridget M. Wadzuk 1 (Member, ASCE) and Ben R. Hodges 2 (Member, ASCE) ABSTRACT Modeling of dynamic pressure appears necessary to achieve a more robust
ISOLATION OF NON-HYDROSTATIC REGIONS WITHIN A BASIN Bridget M. Wadzuk 1 (Member, ASCE) and Ben R. Hodges 2 (Member, ASCE) ABSTRACT Modeling of dynamic pressure appears necessary to achieve a more robust
Evaluation of Delft3D Performance in Nearshore Flows
 Naval Research Laboratory Stennis Space Center, MS 39529-5004 NRL/MR/7320--06-8984 Evaluation of Delft3D Performance in Nearshore Flows Y. Larry Hsu James D. Dykes Richard A. Allard Ocean Dynamics and
Naval Research Laboratory Stennis Space Center, MS 39529-5004 NRL/MR/7320--06-8984 Evaluation of Delft3D Performance in Nearshore Flows Y. Larry Hsu James D. Dykes Richard A. Allard Ocean Dynamics and
Salmon: Introduction to ocean waves
 10 Breakers, bores and longshore currents There is lots more to say about linear, shallow-water waves, but now we want to say something about the more general, nonlinear case. To keep the math as simple
10 Breakers, bores and longshore currents There is lots more to say about linear, shallow-water waves, but now we want to say something about the more general, nonlinear case. To keep the math as simple
COASTAL MORPHODYNAMICS
 COASTAL MORPHODYNAMICS PATRICIA CHARDÓN-MALDONADO, PHD, EIT Miguel Canals, Jack A. Puleo, Alec Torres-Freyermuth & Jens Figlus March 9, 2017 OUTLINE INTRODUCTION Meteorological Phenomena Forcing Conditions
COASTAL MORPHODYNAMICS PATRICIA CHARDÓN-MALDONADO, PHD, EIT Miguel Canals, Jack A. Puleo, Alec Torres-Freyermuth & Jens Figlus March 9, 2017 OUTLINE INTRODUCTION Meteorological Phenomena Forcing Conditions
Development and Implementation of a Relocatable Coastal and Nearshore Modeling System
 Development and Implementation of a Relocatable Coastal and Nearshore Modeling System James M. Kaihatu Zachry Department of Civil Engineering, Texas A&M University 3136 TAMU College Station, TX 77843-3136
Development and Implementation of a Relocatable Coastal and Nearshore Modeling System James M. Kaihatu Zachry Department of Civil Engineering, Texas A&M University 3136 TAMU College Station, TX 77843-3136
A Review of the Bed Roughness Variable in MIKE 21 FLOW MODEL FM, Hydrodynamic (HD) and Sediment Transport (ST) modules
 A Review of the Bed Roughness Variable in MIKE 1 FLOW MODEL FM, Hydrodynamic (HD) and Sediment Transport (ST) modules by David Lambkin, University of Southampton, UK 1 Bed roughness is considered a primary
A Review of the Bed Roughness Variable in MIKE 1 FLOW MODEL FM, Hydrodynamic (HD) and Sediment Transport (ST) modules by David Lambkin, University of Southampton, UK 1 Bed roughness is considered a primary
High-Resolution Measurement-Based Phase-Resolved Prediction of Ocean Wavefields
 DISTRIBUTION STATEMENT A. Approved for public release; distribution is unlimited. High-Resolution Measurement-Based Phase-Resolved Prediction of Ocean Wavefields Dick K.P. Yue Center for Ocean Engineering
DISTRIBUTION STATEMENT A. Approved for public release; distribution is unlimited. High-Resolution Measurement-Based Phase-Resolved Prediction of Ocean Wavefields Dick K.P. Yue Center for Ocean Engineering
Seafloor Ripple Measurements at the Martha s Vineyard Coastal Observatory
 Seafloor Ripple Measurements at the Martha s Vineyard Coastal Observatory Alex E. Hay Dalhousie University Department of Oceanography Halifax, N.S. Canada B3H 4J1 Phone: (902) 494-6657 Fax: (902) 494-2885
Seafloor Ripple Measurements at the Martha s Vineyard Coastal Observatory Alex E. Hay Dalhousie University Department of Oceanography Halifax, N.S. Canada B3H 4J1 Phone: (902) 494-6657 Fax: (902) 494-2885
Surface Wave Processes on the Continental Shelf and Beach
 Surface Wave Processes on the Continental Shelf and Beach Thomas H. C. Herbers Department of Oceanography, Code OC/He Naval Postgraduate School Monterey, California 93943-5122 phone: (831) 656-2917 fax:
Surface Wave Processes on the Continental Shelf and Beach Thomas H. C. Herbers Department of Oceanography, Code OC/He Naval Postgraduate School Monterey, California 93943-5122 phone: (831) 656-2917 fax:
Surfzone Bubbles: Model Development, Testing and Extension to Sedimentary/Chemical/Biological Processes
 DISTRIBUTION STATEMENT A. Approved for public release; distribution is unlimited. Surfzone Bubbles: Model Development, Testing and Extension to Sedimentary/Chemical/Biological Processes James T. Kirby
DISTRIBUTION STATEMENT A. Approved for public release; distribution is unlimited. Surfzone Bubbles: Model Development, Testing and Extension to Sedimentary/Chemical/Biological Processes James T. Kirby
DEVELOPMENT OF PRIMARY FRAGMENTATION SEPARATION DISTANCES FOR CASED CYLINDRICAL MUNITIONS
 DEVELOPMENT OF PRIMARY FRAGMENTATION SEPARATION DISTANCES FOR CASED CYLINDRICAL MUNITIONS by William H. Zehrt, Jr., P. E. and Michelle M. Crull, PhD, P. E. U. S. Army Engineering and Support Center, Huntsville
DEVELOPMENT OF PRIMARY FRAGMENTATION SEPARATION DISTANCES FOR CASED CYLINDRICAL MUNITIONS by William H. Zehrt, Jr., P. E. and Michelle M. Crull, PhD, P. E. U. S. Army Engineering and Support Center, Huntsville
IMAGE-BASED STUDY OF BREAKING AND BROKEN WAVE CHARACTERISTICS IN FRONT OF THE SEAWALL
 IMAGE-BASED STUDY OF BREAKING AND BROKEN WAVE CHARACTERISTICS IN FRONT OF THE SEAWALL Weijie Liu 1 and Yoshimitsu Tajima 1 This study aims to study the breaking and broken wave characteristics in front
IMAGE-BASED STUDY OF BREAKING AND BROKEN WAVE CHARACTERISTICS IN FRONT OF THE SEAWALL Weijie Liu 1 and Yoshimitsu Tajima 1 This study aims to study the breaking and broken wave characteristics in front
An Investigation of the Influence of Waves on Sediment Processes in Skagit Bay
 DISTRIBUTION STATEMENT A. Approved for public release; distribution is unlimited. An Investigation of the Influence of Waves on Sediment Processes in Skagit Bay Geoffrey W. Cowles School for Marine Science
DISTRIBUTION STATEMENT A. Approved for public release; distribution is unlimited. An Investigation of the Influence of Waves on Sediment Processes in Skagit Bay Geoffrey W. Cowles School for Marine Science
Using SolidWorks & CFD to Create The Next Generation Airlocks
 Using SolidWorks & CFD to Create The Next Generation Airlocks Matthew Gaffney Mechanical Engineer Geo-Centers, INC US Army Natick Soldier Center Natick, MA 01760 508-233-5557 Matthew.gaffney@natick.army.mil
Using SolidWorks & CFD to Create The Next Generation Airlocks Matthew Gaffney Mechanical Engineer Geo-Centers, INC US Army Natick Soldier Center Natick, MA 01760 508-233-5557 Matthew.gaffney@natick.army.mil
DoD Coral Reef Protection and Management Program
 DoD Coral Reef Protection and Management Program PROJECT TEAM U.S. NAVY TOM EGELAND (ASN(I&E)) LORRI SCHWARTZ (NAVFAC) ALEX VIANA (NFESC) STEVE SMITH (NFESC) BOSTON UNIV. MARINE PRG. PHILLIP LOBEL MINDY
DoD Coral Reef Protection and Management Program PROJECT TEAM U.S. NAVY TOM EGELAND (ASN(I&E)) LORRI SCHWARTZ (NAVFAC) ALEX VIANA (NFESC) STEVE SMITH (NFESC) BOSTON UNIV. MARINE PRG. PHILLIP LOBEL MINDY
Distributed Integrated Ocean Prediction System (DIOPS) / SWAN Rapid Transition Program
 Distributed Integrated Ocean Prediction System (DIOPS) / SWAN Rapid Transition Program Richard A. Allard Naval Research Laboratory Stennis Space Center, MS 39529 phone: (228) 688-4894 fax: (228) 688-4759
Distributed Integrated Ocean Prediction System (DIOPS) / SWAN Rapid Transition Program Richard A. Allard Naval Research Laboratory Stennis Space Center, MS 39529 phone: (228) 688-4894 fax: (228) 688-4759
Nearshore Morphodynamics. Bars and Nearshore Bathymetry. Sediment packages parallel to shore, that store beach sediment
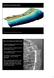 Nearshore Morphodynamics http://coastal.er.usgs.gov/bier/images/chandeleur-xbeach-lg.jpg Bars and Nearshore Bathymetry Sediment packages parallel to shore, that store beach sediment Can be up to 50 km
Nearshore Morphodynamics http://coastal.er.usgs.gov/bier/images/chandeleur-xbeach-lg.jpg Bars and Nearshore Bathymetry Sediment packages parallel to shore, that store beach sediment Can be up to 50 km
M2.50-cal. Multishot Capabilities at the US Army Research Laboratory
 ARL-TN-0694 SEP 2015 US Army Research Laboratory M2.50-cal. Multishot Capabilities at the US Army Research Laboratory by Todd Brinkman Approved for public release; distribution is unlimited. NOTICES Disclaimers
ARL-TN-0694 SEP 2015 US Army Research Laboratory M2.50-cal. Multishot Capabilities at the US Army Research Laboratory by Todd Brinkman Approved for public release; distribution is unlimited. NOTICES Disclaimers
ASIAEX Horizontal Internal Wave Array
 ASIAEX Horizontal Internal Wave Array Timothy F. Duda Applied Ocean Physics and Engineering Department, MS 11 Woods Hole Oceanographic Institution, Woods Hole, MA 02543 Phone: (508) 289-2495 Fax: (508)
ASIAEX Horizontal Internal Wave Array Timothy F. Duda Applied Ocean Physics and Engineering Department, MS 11 Woods Hole Oceanographic Institution, Woods Hole, MA 02543 Phone: (508) 289-2495 Fax: (508)
NUMERICAL SIMULATION OF SEDIMENT PATHWAYS AT AN IDEALIZED INLET AND EBB SHOAL
 In: Proceedings Coastal Sediments 03. 2003. CD-ROM Published by World Scientific Publishing Corp. and East Meets West Productions, Corpus Christi, Texas, USA. ISBN 981-238-422-7. NUMERICAL SIMULATION OF
In: Proceedings Coastal Sediments 03. 2003. CD-ROM Published by World Scientific Publishing Corp. and East Meets West Productions, Corpus Christi, Texas, USA. ISBN 981-238-422-7. NUMERICAL SIMULATION OF
Data Analysis: Plankton Distribution in Internal Waves in Massachusetts Bay
 Data Analysis: Plankton Distribution in Internal Waves in Massachusetts Bay Jesús Pineda MS 34 Biology Department Woods Hole Oceanographic Institution Woods Hole, MA 02543 phone: (508) 289-2274 fax: (508)
Data Analysis: Plankton Distribution in Internal Waves in Massachusetts Bay Jesús Pineda MS 34 Biology Department Woods Hole Oceanographic Institution Woods Hole, MA 02543 phone: (508) 289-2274 fax: (508)
First Year Morphological Evolution of an Artificial Berm at Fort Myers Beach, Florida
 University of South Florida Scholar Commons Geology Faculty Publications Geology 1-2012 First Year Morphological Evolution of an Artificial Berm at Fort Myers Beach, Florida Katherine Brutsche University
University of South Florida Scholar Commons Geology Faculty Publications Geology 1-2012 First Year Morphological Evolution of an Artificial Berm at Fort Myers Beach, Florida Katherine Brutsche University
PARAMETRIZATION OF WAVE TRANSFORMATION ABOVE SUBMERGED BAR BASED ON PHYSICAL AND NUMERICAL TESTS
 Proceedings of the 6 th International Conference on the Application of Physical Modelling in Coastal and Port Engineering and Science (Coastlab16) Ottawa, Canada, May 10-13, 2016 Copyright : Creative Commons
Proceedings of the 6 th International Conference on the Application of Physical Modelling in Coastal and Port Engineering and Science (Coastlab16) Ottawa, Canada, May 10-13, 2016 Copyright : Creative Commons
Navy Shipbuilding Industrial Base
 Navy Shipbuilding Industrial Base May 11, 2011 David J. Berteau Senior Adviser and Director, Defense-Industrial Initiatives Report Documentation Page Form Approved OMB No. 0704-0188 Public reporting burden
Navy Shipbuilding Industrial Base May 11, 2011 David J. Berteau Senior Adviser and Director, Defense-Industrial Initiatives Report Documentation Page Form Approved OMB No. 0704-0188 Public reporting burden
Plankton Distribution in Internal Waves in Massachusetts Bay
 Plankton Distribution in Internal Waves in Massachusetts Bay Jesús Pineda MS 34 Biology Department Woods Hole Oceanographic Institution Woods Hole, MA 02543 phone: (508) 289-2274 fax: (508) 457-2134 email:
Plankton Distribution in Internal Waves in Massachusetts Bay Jesús Pineda MS 34 Biology Department Woods Hole Oceanographic Institution Woods Hole, MA 02543 phone: (508) 289-2274 fax: (508) 457-2134 email:
The Influence of Breaking at the Ocean Surface on Oceanic Radiance and Imaging
 The Influence of Breaking at the Ocean Surface on Oceanic Radiance and Imaging W. Kendall Melville Scripps Institution of Oceanography, University of California, San Diego 9500 Gilman Drive La Jolla, CA
The Influence of Breaking at the Ocean Surface on Oceanic Radiance and Imaging W. Kendall Melville Scripps Institution of Oceanography, University of California, San Diego 9500 Gilman Drive La Jolla, CA
Anthropogenic Noise and the Marine Environment
 Anthropogenic Noise and the Marine Environment R. Hillson and H.-J. Shyu Information Technology Division Introduction: The impact of anthropogenic noise on the marine environment is a subject of increasing
Anthropogenic Noise and the Marine Environment R. Hillson and H.-J. Shyu Information Technology Division Introduction: The impact of anthropogenic noise on the marine environment is a subject of increasing
AIRFLOW GENERATION IN A TUNNEL USING A SACCARDO VENTILATION SYSTEM AGAINST THE BUOYANCY EFFECT PRODUCED BY A FIRE
 - 247 - AIRFLOW GENERATION IN A TUNNEL USING A SACCARDO VENTILATION SYSTEM AGAINST THE BUOYANCY EFFECT PRODUCED BY A FIRE J D Castro a, C W Pope a and R D Matthews b a Mott MacDonald Ltd, St Anne House,
- 247 - AIRFLOW GENERATION IN A TUNNEL USING A SACCARDO VENTILATION SYSTEM AGAINST THE BUOYANCY EFFECT PRODUCED BY A FIRE J D Castro a, C W Pope a and R D Matthews b a Mott MacDonald Ltd, St Anne House,
HYDRODYNAMICS AND MORPHODYNAMICS IN THE SURF ZONE OF A DISSIPATIVE BEACH
 HYDRODYNAMICS AND MORPHODYNAMICS IN THE SURF ZONE OF A DISSIPATIVE BEACH Leo C. van Rijn, Dirk Jan R. Walstra, Bart T. Grasmeijer and Kees Kleinhout Abstract: Two profile models have been compared with
HYDRODYNAMICS AND MORPHODYNAMICS IN THE SURF ZONE OF A DISSIPATIVE BEACH Leo C. van Rijn, Dirk Jan R. Walstra, Bart T. Grasmeijer and Kees Kleinhout Abstract: Two profile models have been compared with
WAVE RUNUP ON COMPOSITE-SLOPE AND CONCAVE BEACHES ABSTRACT
 CHAPTER 168 WAVE RUNUP ON COMPOSITE-SLOPE AND CONCAVE BEACHES R. H. Mayer 1 and D. L. Kriebel 1 ABSTRACT Laboratory experiments were carried out for regular and irregular wave runup over non-uniform beach
CHAPTER 168 WAVE RUNUP ON COMPOSITE-SLOPE AND CONCAVE BEACHES R. H. Mayer 1 and D. L. Kriebel 1 ABSTRACT Laboratory experiments were carried out for regular and irregular wave runup over non-uniform beach
STUDY ON TSUNAMI PROPAGATION INTO RIVERS
 ABSTRACT STUDY ON TSUNAMI PROPAGATION INTO RIVERS Min Roh 1, Xuan Tinh Nguyen 2, Hitoshi Tanaka 3 When tsunami wave propagation from the narrow river mouth, water surface is raised and fluctuated by long
ABSTRACT STUDY ON TSUNAMI PROPAGATION INTO RIVERS Min Roh 1, Xuan Tinh Nguyen 2, Hitoshi Tanaka 3 When tsunami wave propagation from the narrow river mouth, water surface is raised and fluctuated by long
