Journal of Coastal Develpopment ISSN : MITIGATION MEASURES FOR GAZA COASTAL EROSION. Received: January 3, 2013 ; Accepted: February 23, 2013
|
|
|
- Marjory Harrison
- 5 years ago
- Views:
Transcription
1 Journal of Coastal Develpopment ISSN : -5 Volume, Number, February, : 5- Acrredited : /Dikti/Kep/9 Original paper MITIGATION MEASURES FOR GAZA COASTAL EROSION Mazen Abualtayef,*, Ahmed Abu Foul, Said Ghabayen, Abdel Fattah Abd Rabou, Ahmed Khaled Seif, Omar Matar Environmental Engineering Department, Islamic University of Gaza, Gaza, Palestine Biology Department, Islamic University of Gaza, Gaza, Palestine Civil Engineering Department, Al Azhar University, Cairo, Egypt Municipality of Khan Younis, Khan Younis, Palestine Received: January, ; Accepted: February, ABSTRACT Coastal erosion is an ongoing hazard affecting Gaza beach, but is worsening due to a wide range of human activities such as the construction of Gaza fishing harbor in The net annual alongshore sediment transport is about 9 m, but can vary significantly depending on the severity of winter storms. According to the observed wave heights and directions, the net waves are cross-shore, therefore vast quantities of sediments may transfer to deep sea. The main objective of this study is to mitigate the erosion problem of Gaza coast. Change detection analysis was used to compute the spatial and temporal change of Gaza shoreline between 9 and. The results show negative rates in general, which means that the erosion was the predominant process. Gaza fishing harbor caused a serious damage to the Beach Camp shoreline. Consequently, several mitigation measures were considered in this study, which are: relocation of Gaza fishing harbor to offshore, groins, detached breakwaters, wide-crested submerged breakwaters and beach nourishment. Several numerical model tests associated with coastal structures are conducted to investigate the influence on morphodynamics. The results show that the relocation of the harbor is the best alternative to stop trapping of the sediments. If for any reason the relocation was not carried out, the wide-crested submerged breakwater alternative is an effective structure for preventing sandy beach erosion. The artificial reef type of submerged breakwaters with beach nourishment is recommended for Gaza beach, because it is an environmentally friendly and improving the ecosystem of marine life. Keywords: Gaza fishing harbor, morphodynamic, artificial reef, remote sensing * Correspondence: Phone: , Fax:+9--, mabualtayef@iugaza.edu.ps INTRODUCTION Development in coastal areas, harbors, breakwaters, jetties and groins, is the focus of considerable research activity by both natural scientists and planners. Compared to many coastlines, that of Eastern Mediterranean coast has been well studied. The primary sediment source is the Nile River. Nile sands have been transported from the outlets of the river to the Palestinian coast by consistent west-to-east and southwest-to-northeast alongshore currents generated by westerly approaching waves (Goldsmith, 9). In recent decades, the coast has been plagued by a serious shortage of sand and by erosion. The sand shortage results from the building of coastal structures that are acting as sediment traps and therefore causing sand shortages on adjacent beaches. Construction of the low Aswan dam in 9 and the high Aswan dam in 9 has almost completely interrupted the Nile River 5
2 Journal of Coastal Develpopment ISSN : -5 Volume, Number, February, : 5- Acrredited : /Dikti/Kep/9 sediment discharge to the sea. Fortunately for Gaza, the Bardawil lagoon sandbar continues to act as a significant source and supplier of sand to Gaza coast (Inman, 9). The coast of Gaza was affected by man-made structures prior to the fishing harbor as shown in Figure. In the early 9s two groins, m long each 5 m apart were built in Gaza City as shown in Figure. Sand accumulation occurred south of the southern groin to a distance of. km. On the other hand, erosion took place north of the northern groin to a distance of. km. The erosion was controlled by a series of nine detached breakwaters built in 9. The detached breakwaters, 5- m long, were built 5 m from the coast line at a depth of m as shown in Figure (Zviely and Klein, ). In 99, the construction of Gaza fishing harbor started and completed in 99. The fishing harbor extends some 5 m into the sea, enabling access to vessels up to m deep. The fishing harbor has locally disturbed the coastal erosion and sedimentation pattern and resulting in sand erosion problems. Furthermore, the building and roads adjacent to the shoreline are facing a stability problem and it is expected to have a serious erosion problem in the coming few years. As a counter-measure to this, the construction waste was deployed in the eroded area, which is working as a beach revetment, to mitigate the severe beach erosion and protecting the hotels. UNRWA has constructed gabions along the Beach Camp with a total length of 5 m to protect the main coastal road. Several short groins have been construction along the Beach Camp for shoreline preservation. However, these mitigations are not effective. Therefore, the significance of the current study is that it not only compares coastal processes before and after the fishing harbor, but it also compares the numerical model s predictive capabilities with the actual impacts. The objectives of the present study were to twofold: to monitor the coastal changes to the north and south of Gaza fishing harbor by using remote sensing techniques, and to compare coastal changes with changes forecast by the numerical model in order to provide long-term protection against erosion. Fig : The two groins built in 9 (Zviely and Klein., ) Fig : The detached breakwaters built in 9 (Zviely and Klein., ) MATERIALS AND METHODS Data in the present study have been collected from analyses of Landsat images from 9 to and combined with sample collection for grain size analyses in order to study the shoreline change for the study area (Fig ). Numerical model runs to predict the morphodynamics and hydrodynamics around the mitigation structures were carried out.
3 Journal of Coastal Develpopment ISSN : -5 Volume, Number, February, : 5- Acrredited : /Dikti/Kep/9 Fig : The study area Satellite images Five satellite Landsat images were obtained for the study area covering path 5 and row. The Landsat multispectral scanner (MSS) sensor images are acquired on June 9 and May 9, Landsat thematic mapper (TM) sensor images are acquired on May 99 and March, and Landsat Enhanced Thematic Mapper Plus (ETM+) sensor image is acquired for June as shown in Figure. The images are of medium quality and free from clouds. The raw MSS images consist of four bands, TM images consist of seven bands and ETM+ images consist of nine bands. The infrared band was selected for the subsequent image processing. The pixel size in each image is shown in Table. The image processing procedures were carried out using ERDAS Imagine and ArcGIS. Figure 5 shows the study area subsets. The images are projected to the Universal Transverse Mercator (UTM), with a spheroid and datum of WGS. Landsat images were geometrically certificated. The rectified images were then used for the image classification. A subset image was created from each image, which covers only the study area on each date. An unsupervised classification algorithm was applied requesting classes and applying iterations, a convergence threshold of.95 and a standard deviation of one. The classified images produced two clusters in each image and the clusters for the terrestrial and sea parts were recorded. To estimate the amount of change between the several dates, we applied a postclassification change detection matrix using ERDAS Imagine. This approach is very useful since the images were classified independently. Areas changed from sea to land and vice versa were recorded. The total area and the location of change between 9 and were measured. Detailed analysis was carried by Abualtayef et al. () for the study area. Table : Satellite images source and resolutions Image source Date Resolution [m m] Landsat MSS Landsat 5 MSS Landsat 5 TM Landsat 5 TM Landsat ETM+ --..
4 Journal of Coastal Develpopment ISSN : -5 Volume, Number, February, : 5- Acrredited : /Dikti/Kep/9 Field study and sample collection The field study included identification of the various landscapes of the area along with the sample collection. Three seabed samples were collected along the Beach Camp coast. Grain size analyses were made using standard sieving techniques at half-phi intervals. The grain size statistical parameters were calculated using the graphical method. Fig. : Landsat satellite images of band- in a) 9, b) 9, c) 99 d) and e) for the study area Since a lack of wave data for Gaza coast, the directional wave observations at Idku station in front of Alexandria s (Egypt) deep waters were considered. The wind conditions at the eastern part of the Mediterranean coast are almost similar. Therefore, the wave condition of Alexandria can be adapted since the wave parameters in deep waters remain the same. The wave recording station is located in a mean water depth of m and yields times daily recordings for a -hour interval (Seif, ). The wave recording of two-year period from to 5 was used in this study. During this period, a total of, measurements were recorded and analyzed. Table shows the breakdown of the measurements and averaged over one year period. For each wave scenario, the significant wave height, peak period, wave direction and duration were analyzed. Numerical model The relocation of fishing harbor to offshore, groins field system, detached breakwaters and wide-crested submerged breakwaters were suggested and examined using the morphodynamic numerical model of nearshore waves, currents, and sediment transport in order to mitigate the coastal erosion. The numerical model was developed by Kuroiwa et al. (99) and recently modified by Seif et al. (). The numerical model consists of four modules to simulate the hydrodynamics and morphodynamics around coastal structures, which are: wave module, nearshore current module, sediment transport module, and beach evolution module. The models were run using the initial bathymetry with a gradient of in 5 for all alternatives except the harbor relocation with a
5 Journal of Coastal Develpopment ISSN : -5 Volume, Number, February, : 5- Acrredited : /Dikti/Kep/9 gradient of in. The grid size was m. The median grain size D 5 was 5 m. The significant wave height, wave period and wave direction at the offshore boundary are shown in Table. The followings are additional conditions for each model test: For the port relocation model test: the computations were performed on an area of. km alongshore and. km cross-shore. The distance from shoreline is m. The water depth in the basin range from 5 to m. The harbor layout and initial bathymetry is shown in Figure (c). For the detached breakwater model test: The computations were performed on an area of. km alongshore and. km cross-shore. The length of the detached breakwater was m,. m crown depth, and the distance from shoreline is 5 m. The test layout and bathymetry is shown in Figure (c). For the submerged breakwaters model test: The computations were performed on an area of. km alongshore and. km crossshore. The length of the submerged breakwater was m,. m crown depth, and the distance from shoreline is m. The test layout and bathymetry is shown in Figure (c). For the groins model test: The computations were performed on an area of. km alongshore and. km cross-shore. The length of the groin was 5 m and m spacing. The test layout and bathymetry is shown in Figure 9(c). Table : The wave scenarios for the study area Significant Peak Wave wave height, period, direction H s [m] T s [s] [deg. North] 9 Wave duration [days] Wave Scenario H.m < H < H < H H > RESULTS AND DISCUSSION Remote sensing findings The coast of Gaza was affected by the manmade structures such as groins, breakwaters and fishing harbor. The construction of fishing harbor has caused an accumulation of sand at the southern fringe of the harbor. The new land (Figure ) is large due to the shape of the main breakwater and become a sediment trap. In addition, the new land is increased by the dumping of construction waste. Change detection results of the remotely sensed images between 9 and for the study area are shown in Table. The study area is extended from Wadi Gaza, km to the south of fishing harbor, to Alsodania area, km to the north of the harbor as shown in Figure. The study findings show that the sediment balance of beach area tended to be negative. This observation is based on the advance of the waterline towards the sea to the south of fishing harbor by an average.5 m year - and based on the treat of the waterline towards the land to the north of fishing harbor by an average.5 m year -. Gaza fishing harbor caused a serious damage to the Beach Camp shoreline, especially after removing six detached breakwaters. The impact of harbor construction has extended to. km to the north and less than. km to the south of harbor. The analyses estimated a 9 m have been added to the beach area in 5 years (Table ) with an annual rate of. m, which represents the highest rate of accretion. However, the erosion is the minimum rate in years. This is due to the dumping of construction waste as a revetment. The revetment protection was active for a short period and the erosion rate was increased after. The annual average erosion rate of m and the annual average accretion rate of m. The change of erosion/accretion rates in various time intervals are shown in Table. The annual sand volume of accretion and erosion was about m for each.
6 Journal of Coastal Develpopment ISSN : -5 Volume, Number, February, : 5- Acrredited : /Dikti/Kep/9 Table : Accretion and erosion rates for the study area Erosion Accretion Image period area [m ] rate [m year - ] area [m ] rate [m year - ] Total 5 Sediment transport rates Since the construction of the Aswan high dam, the Nile no longer brings sediment to the coast, and erosion of Nile delta now constitutes the source for the Nile Littoral Cell (Inman et al., 9). The present study computes the net annual rate of wave-induced alongshore sediment transport range from minimum to maximum m, and the average annual rate of 9 m, northward. Depending on the wave direction, the net waves are cross-shore; therefore, vast quantities of sediments may transfer to deep sea. In the Rafah-Gaza segment, a drastic change from eastward to northward occurs in the direction of the coastline. Mayo (99) claims that large quantities of sediments in this area are out into the deep sea. The net transport remains counterclockwise and gradually increases with distance southward from Gaza. Hence, the wave-induced transport appears to provide the driving force for the net counterclockwise transport of sediments along the Nile Cell, gradually decreasing along the way from the Nile delta about m year - to Gaza about 9 m year - (Carmel et al., 95). Fig. 5: Unsupervised classified images for a) 9, b) 9, c) 99, d), e) for the study area and f) temporal shoreline changes from 9 to
7 Journal of Coastal Develpopment ISSN : -5 Volume, Number, February, : 5- Acrredited : /Dikti/Kep/9 Numerical model results Four numerical tests were carried out, which are relocation of the exiting harbor to offshore, the detached breakwaters, the submersed breakwater and the groin fields in order to mitigate the erosion problem in the Beach Camp coast. The model results are as follows: Offshore fishing harbor model test: Figure (a, b) shows the computed results of wave height distribution and depthaverage current velocity around the offshore harbor, respectively. From these figures, it was found that two vortices are formed between the harbor and shoreline. Clockwise vortex and counter-clockwise vortex are formed at the right side and at the left side, respectively. The strongest currents of. ms - are observed near the harbor s entrance. The wave height decreases toward the shoreline and nearly calm behind the harbor. Figure (c, d) shows the initial bathymetry and computed one after one year beach revolution, respectively. It was found from these figures that slight changes of the morphodynamic were taken place in which the shoreline was advanced and forming two small salients, siltation was accumulated at the harbor s entrance and erosion up to m water depth was taken place near the edge of northern breakwater. In general, no significant morphodynamic changes were taken place within the study area. Detached breakwater model test: Figure shows the computed results of the wave height distribution, the depth-average current velocity and the final bathymetry around the detached breakwater, respectively. From these figures, it was found that the lee of the breakwater was eroded up to 5. m and this will cause a structure failure. The strongest currents of more than. m s - are observed in the study area. The morphodynamic of the area located between the structure and shoreline was severely affected and formed two small salients. The -m contour was retreaded and highly contributed to the erosion amounts. The erosion rate in the study area was about m km - yr -. Submerged breakwaters model test: Figure shows the computed results of the wave height distribution, the current velocity and the final bathymetry around the submerged breakwater. From this figure, it was found that the currents are decreased compared with ones in the previous model tests and the strongest currents are observed over the submersed breakwater and toward the shoreline. The shoreline does not change and the contours of and m are advanced. However, the contour of m was retreated. The annual accretion rate was about m km -. Groins model test: Figure 9 shows the computed results of the wave height distribution, the depth-average current velocity and the final bathymetry around the groin field after one year revolution. From the model results, it was found that the strongest currents are crossshore during the storms. A -m wave height was observed near the head of groins. Although the storm durations are short, they greatly contribute in the majority loss of sediments. The annual erosion rate was about m km -.
8 Journal of Coastal Develpopment ISSN : -5 Volume, Number, February, : 5- Acrredited : /Dikti/Kep/9 (a) X(m) (b) (c) N m/s Y(m) (d) Fig : Gaza offshore fishing harbor after one year beach revolution (a) computed wave height distribution, (b) computed depth-average current velocity, (c) initial bathymetry and (d) computed bathymetry (a) N (b) X(m) m/s Y(m)
9 Journal of Coastal Develpopment ISSN : -5 Volume, Number, February, : 5- Acrredited : /Dikti/Kep/9 (c) (d) Fig. : Detached breakwater after one year beach revolution (a) computed wave height distribution, (b) computed depth-average current velocity at wave height of. m, (c) initial bathymetry and (d) computed bathymetry (a) N (b).. X(m) (c) m/s Y(m) (d) Fig : Submersed breakwater after one year beach revolution (a) computed wave height distribution for. m wave height condition, (b) computed depth-average current velocity for wave height of. m, (c) initial bathymetry and (d) computed bathymetry
10 Journal of Coastal Develpopment ISSN : -5 Volume, Number, February, : 5- Acrredited : /Dikti/Kep/9 (a) N (b) (c) X(m) m/s Y(m) (d) Fig 9: Groins field system after one year beach revolution (a) computed wave height distribution, (b) computed depth-average current velocity at wave height of. m, (c) initial bathymetry and (d) computed bathymetry The environmental impact on the morphodynamic in the study area is presented in Table. The offshore harbor model test shows a positive impact on the environment in which nearly no sand trapping or erosion is taken place at the study area. The incident waves at the deep sea are almost normal to the shoreline and accordingly the cross-shore sediment component will be dominated and less amount of sediment transport will be transported alongshore. Therefore, offshore breakwater will decelerate the cross-shore current and then reducing the amount of sediment to be transported. For the time being, the submersed breakwater (artificial reef type) shows an attractive protection from both morphological and environmental points of view. Table : Environmental impact of various mitigation alternatives Mitigation alternative Annual rate [m km - ] Remarks Relocation of harbor + Accretion Detached Breakwater Erosion Submersed Breakwater + Accretion Groins field system Erosion
11 Journal of Coastal Develpopment ISSN : -5 Volume, Number, February, : 5- Acrredited : /Dikti/Kep/9 Based on the sediment transport, the environmental impact and the numerical model analysis, the recommended alternative is the relocation of harbor. In case the relocation could not be implemented, the submerged artificial reef breakwater would be selected. However, the artificial reef breakwater will transfer the problem to the north. Therefore, combination of nourishment alternative and submerged breakwater is required. The nourishment is used to maintain the shoreline and the erosion at the down-drift side while submerged breakwaters are used as a protection structure. The annual amount of nourishment of m is required at the down-drift side (i.e. m due to trapping of sediments behind the existing harbor and m due to the trapping of sediments behind the artificial reef). CONCLUSIONS The erosion problem along Gaza beach is due to the man-made structures as confirmed by analyzing the historical satellite images from 9 to. These structures include groins built in 9, detached breakwater built in 9 and finally the construction of Gaza fishing harbor in The annual average erosion of.5 m extended. km to the north of harbor and the annual average accretion of.5 m extended to. km to the south of harbor. The numerical model was able to demonstrate the impacts of various wave climates for the suggested beach protection alternatives. Results show that the offshore harbor is the best alternative for Gaza beach restoration in which the erosion problem generator is disappeared. If the relocation could not be implemented, the wide-crested submerged breakwater, artificial reef, is an effective structure for preventing sandy beach erosion due to wave and nearshore current actions, and for the landscape of seaview in front of sandy beaches. The artificial reef type of submerged breakwaters is recommended for Gaza beach, because it is an environmentally friendly and improving the ecosystem of marine life and the fishing industry. The numerical model results show that both groins and detached breakwater have negative environmental impacts. However, the model most runs for short storm which may worsen the situation in case of groins field being selected. REFERENCES Abualtayef, M., Ghabayen, S., Abu Foul, A., Seif, S., Kuroiwa, M., Matsubara, Y., Matar, O.. The impact of Gaza fishing harbor on the Mediterranean coast of Gaza. J. Coast. Dev.(): -. Carmel, Z., Inman, D. and Golik, A. 95. Directional wave measurement at Haifa, Israel, and sediment transport along the Nile littoral cell. Coast. Engineer. 9: -. Goldsmith, V. and Golik, A. 9. Sediment transport model of the southeastern Mediterranean coast. Mar. Geol.,, -5. Inman, D.L., Aubrey, D.G. and Pawka, S.S. 9. Application of nearshore processes to the Nile Delta. In: Proc. of Seminar on Nile Delta Sedimentology, Alexandria, 5-9 Oct. 95 by UNDP/UNESCO Project for Coastal Studies, publ. by the Project under Academy of Scientific Research and Technology, pp Kuroiwa, M., Noda, H. and Matsubara, Y. 99. Application of a quasi- D numerical model to near-shore current. Proc. Int. Conf. Coastal Eng., ICCE,, 5-. Mase, H., Amamori, H. and Takayama, T. 5. Wave prediction model in wavecurrent coexisting field. Proceedings th Canadian Coastal Conference, CD-ROM. Mayo, M. 99. Multi-temporal analysis of sediment transport in the southern Mediterranean by remote sensing. Department of geophysics and planetary sciences. Tel-Aviv University, Israel, M.Sc. Thesis, p. 5
12 Journal of Coastal Develpopment ISSN : -5 Volume, Number, February, : 5- Acrredited : /Dikti/Kep/9 Seif, A., Kuroiwa, M., Abualtayef, M., Mase, H. and Matsubara, Y.. A hydrodynamic model of nearshore waves and wave-induced currents. Int. J. Nav. Archit. Oc. Eng, : -. Seif, A. K.. Numerical simulation of D morphodynamic around Coastal structures using quasi-d nearshore current model. Tottori University, Japan, Doctorate thesis, 5p. Zviely, D. and Klein, M.. The environmental impact of the Gaza Strip coastal constructions. J. Coast. Res., 9(): -.
IMPACTS OF COASTAL PROTECTION STRATEGIES ON THE COASTS OF CRETE: NUMERICAL EXPERIMENTS
 IMPACTS OF COASTAL PROTECTION STRATEGIES ON THE COASTS OF CRETE: NUMERICAL EXPERIMENTS Tsanis, I.K., Saied, U.M., Valavanis V. Department of Environmental Engineering, Technical University of Crete, Chania,
IMPACTS OF COASTAL PROTECTION STRATEGIES ON THE COASTS OF CRETE: NUMERICAL EXPERIMENTS Tsanis, I.K., Saied, U.M., Valavanis V. Department of Environmental Engineering, Technical University of Crete, Chania,
Available online at ScienceDirect. Procedia Engineering 116 (2015 )
 Available online at www.sciencedirect.com ScienceDirect Procedia Engineering 116 (2015 ) 320 325 8th International Conference on Asian and Pacific Coasts (APAC 2015) Department of Ocean Engineering, IIT
Available online at www.sciencedirect.com ScienceDirect Procedia Engineering 116 (2015 ) 320 325 8th International Conference on Asian and Pacific Coasts (APAC 2015) Department of Ocean Engineering, IIT
CHAPTER 8 ASSESSMENT OF COASTAL VULNERABILITY INDEX
 124 CHAPTER 8 ASSESSMENT OF COASTAL VULNERABILITY INDEX 8.1 INTRODUCTION In order to assess the vulnerability of the shoreline considered under this study against the changing environmental conditions,
124 CHAPTER 8 ASSESSMENT OF COASTAL VULNERABILITY INDEX 8.1 INTRODUCTION In order to assess the vulnerability of the shoreline considered under this study against the changing environmental conditions,
SORTING AND SELECTIVE MOVEMENT OF SEDIMENT ON COAST WITH STEEP SLOPE- MASUREMENTS AND PREDICTION
 SORTING AND SELECTIVE MOVEMENT OF SEDIMENT ON COAST WITH STEEP SLOPE- MASUREMENTS AND PREDICTION Toshiro San-nami 1, Takaaki Uda 2, Masumi Serizawa 1 and Toshinori Ishikawa 2 Conveyer belts carrying gravel
SORTING AND SELECTIVE MOVEMENT OF SEDIMENT ON COAST WITH STEEP SLOPE- MASUREMENTS AND PREDICTION Toshiro San-nami 1, Takaaki Uda 2, Masumi Serizawa 1 and Toshinori Ishikawa 2 Conveyer belts carrying gravel
Appendix E Cat Island Borrow Area Analysis
 Appendix E Cat Island Borrow Area Analysis ERDC/CHL Letter Report 1 Cat Island Borrow Area Analysis Multiple borrow area configurations were considered for Cat Island restoration. Borrow area CI1 is located
Appendix E Cat Island Borrow Area Analysis ERDC/CHL Letter Report 1 Cat Island Borrow Area Analysis Multiple borrow area configurations were considered for Cat Island restoration. Borrow area CI1 is located
Inlet Management Study for Pass-A-Grille and Bunces Pass, Pinellas County, Florida
 Inlet Management Study for Pass-A-Grille and Bunces Pass, Pinellas County, Florida Final Report Submitted By Ping Wang, Ph.D., Jun Cheng Ph.D., Zachary Westfall, and Mathieu Vallee Coastal Research Laboratory
Inlet Management Study for Pass-A-Grille and Bunces Pass, Pinellas County, Florida Final Report Submitted By Ping Wang, Ph.D., Jun Cheng Ph.D., Zachary Westfall, and Mathieu Vallee Coastal Research Laboratory
Shoreline changes and reef strengthening at Kavaratti island in Lakshadweep Archipelago - A case study
 Indian Journal of Geo-Marine Sciences Vol. 43(7), July 2014, pp. 1140-1144 Shoreline changes and reef strengthening at Kavaratti island in Lakshadweep Archipelago - A case study T.N.Prakash*, L.Sheela
Indian Journal of Geo-Marine Sciences Vol. 43(7), July 2014, pp. 1140-1144 Shoreline changes and reef strengthening at Kavaratti island in Lakshadweep Archipelago - A case study T.N.Prakash*, L.Sheela
CHAPTER 134 INTRODUCTION
 CHAPTER 134 NEW JETTIES FOR TUNG-KANG FISHING HARBOR, TAIWAN Chi-Fu Su Manager Engineering Department Taiwan Fisheries Consultants, Inc. Taipei, Taiwan INTRODUCTION Tung-Kang Fishing Harbor, which is about
CHAPTER 134 NEW JETTIES FOR TUNG-KANG FISHING HARBOR, TAIWAN Chi-Fu Su Manager Engineering Department Taiwan Fisheries Consultants, Inc. Taipei, Taiwan INTRODUCTION Tung-Kang Fishing Harbor, which is about
MONITORING SEDIMENT TRANSPORT PROCESSES AT MANAVGAT RIVER MOUTH, ANTALYA TURKEY
 COPEDEC VI, 2003 in Colombo, Sri Lanka MONITORING SEDIMENT TRANSPORT PROCESSES AT MANAVGAT RIVER MOUTH, ANTALYA TURKEY Isikhan GULER 1, Aysen ERGIN 2, Ahmet Cevdet YALCINER 3 ABSTRACT Manavgat River, where
COPEDEC VI, 2003 in Colombo, Sri Lanka MONITORING SEDIMENT TRANSPORT PROCESSES AT MANAVGAT RIVER MOUTH, ANTALYA TURKEY Isikhan GULER 1, Aysen ERGIN 2, Ahmet Cevdet YALCINER 3 ABSTRACT Manavgat River, where
SAND ACCUMULATION IN WAVE-SHELTER ZONE OF OHARAI PORT AND CHANGE IN GRAIN SIZE OF SEABED MATERIALS ON NEARBY COAST
 SAND ACCUMULATION IN WAVE-SHELTER ZONE OF OHARAI PORT AND CHANGE IN GRAIN SIZE OF SEABED MATERIALS ON NEARBY COAST Takeo Matsu-ura, Takaaki Uda, Takayuki Kumada and Michio Sumiya Beach changes around facing
SAND ACCUMULATION IN WAVE-SHELTER ZONE OF OHARAI PORT AND CHANGE IN GRAIN SIZE OF SEABED MATERIALS ON NEARBY COAST Takeo Matsu-ura, Takaaki Uda, Takayuki Kumada and Michio Sumiya Beach changes around facing
MULTIDECADAL SHORELINE EVOLUTION DUE TO LARGE-SCALE BEACH NOURISHMENT JAPANESE SAND ENGINE? Abstract
 MULTIDECADAL SHORELINE EVOLUTION DUE TO LARGE-SCALE BEACH NOURISHMENT JAPANESE SAND ENGINE? Masayuki Banno 1, Satoshi Takewaka 2 and Yoshiaki Kuriyama 3 Abstract Beach nourishment is one of the countermeasures
MULTIDECADAL SHORELINE EVOLUTION DUE TO LARGE-SCALE BEACH NOURISHMENT JAPANESE SAND ENGINE? Masayuki Banno 1, Satoshi Takewaka 2 and Yoshiaki Kuriyama 3 Abstract Beach nourishment is one of the countermeasures
Low-crested offshore breakwaters: a functional tool for beach management
 Environmental Problems in Coastal Regions VI 237 Low-crested offshore breakwaters: a functional tool for beach management K. Spyropoulos & E. Andrianis TRITON Consulting Engineers, Greece Abstract Beach
Environmental Problems in Coastal Regions VI 237 Low-crested offshore breakwaters: a functional tool for beach management K. Spyropoulos & E. Andrianis TRITON Consulting Engineers, Greece Abstract Beach
HARBOUR SEDIMENTATION - COMPARISON WITH MODEL
 HARBOUR SEDIMENTATION - COMPARISON WITH MODEL ABSTRACT A mobile-bed model study of Pointe Sapin Harbour, in the Gulf of St. Lawrence, resulted in construction of a detached breakwater and sand trap to
HARBOUR SEDIMENTATION - COMPARISON WITH MODEL ABSTRACT A mobile-bed model study of Pointe Sapin Harbour, in the Gulf of St. Lawrence, resulted in construction of a detached breakwater and sand trap to
Video based assessment of coastal erosion impact on beach attendance. Application to coastal management of Valras beach, France
 Conférence Méditerranéenne Côtière et Maritime EDITION 3, FERRARA, ITALIA (2015) Coastal and Maritime Mediterranean Conference Disponible en ligne http://www.paralia.fr Available online Video based assessment
Conférence Méditerranéenne Côtière et Maritime EDITION 3, FERRARA, ITALIA (2015) Coastal and Maritime Mediterranean Conference Disponible en ligne http://www.paralia.fr Available online Video based assessment
MODELING OF CLIMATE CHANGE IMPACTS ON COASTAL STRUCTURES - CONTRIBUTION TO THEIR RE-DESIGN
 Proceedings of the 14 th International Conference on Environmental Science and Technology Rhodes, Greece, 3-5 September 2015 MODELING OF CLIMATE CHANGE IMPACTS ON COASTAL STRUCTURES - CONTRIBUTION TO THEIR
Proceedings of the 14 th International Conference on Environmental Science and Technology Rhodes, Greece, 3-5 September 2015 MODELING OF CLIMATE CHANGE IMPACTS ON COASTAL STRUCTURES - CONTRIBUTION TO THEIR
SELECTION OF THE PREFERRED MANAGEMENT OPTION FOR STOCKTON BEACH APPLICATION OF 2D COASTAL PROCESSES MODELLING
 SELECTION OF THE PREFERRED MANAGEMENT OPTION FOR STOCKTON BEACH APPLICATION OF 2D COASTAL PROCESSES MODELLING C Allery 1 1 DHI Water and Environment, Sydney, NSW Abstract This paper presents an approach
SELECTION OF THE PREFERRED MANAGEMENT OPTION FOR STOCKTON BEACH APPLICATION OF 2D COASTAL PROCESSES MODELLING C Allery 1 1 DHI Water and Environment, Sydney, NSW Abstract This paper presents an approach
LABORATORY EXPERIMENTS ON EROSION CONTROL PERFORMANCE OF AN L- SHAPED PERMEABLE STRUCTURE. Abstract
 LABORATORY EXPERIMENTS ON EROSION CONTROL PERFORMANCE OF AN L- SHAPED PERMEABLE STRUCTURE Yuuji Maeda 1, Masayuki Unno 2, Masafumi Sato 2, Takao Kurita 2, Takaaki Uda 3 and Shinji Sato 4 Abstract A new
LABORATORY EXPERIMENTS ON EROSION CONTROL PERFORMANCE OF AN L- SHAPED PERMEABLE STRUCTURE Yuuji Maeda 1, Masayuki Unno 2, Masafumi Sato 2, Takao Kurita 2, Takaaki Uda 3 and Shinji Sato 4 Abstract A new
Morphological change on Cua Dai Beach, Vietnam: Part I image analysis
 Morphological change on Cua Dai Beach, Vietnam: Part I image analysis Nguyen Trung Viet 1, Vo Cong Hoang 2,3 and Hitoshi Tanaka 4 Abstract Severe erosion has been occurred on Cua Dai Beach, Hoi An City,
Morphological change on Cua Dai Beach, Vietnam: Part I image analysis Nguyen Trung Viet 1, Vo Cong Hoang 2,3 and Hitoshi Tanaka 4 Abstract Severe erosion has been occurred on Cua Dai Beach, Hoi An City,
USE OF SEGMENTED OFFSHORE BREAKWATERS FOR BEACH EROSION CONTROL
 .. CETN-III-22 4/84 PURPOSE: USE OF SEGMENTED OFFSHORE BREAKWATERS FOR BEACH EROSION CONTROL To provide information on the functional application of and general design considerations for using offshore
.. CETN-III-22 4/84 PURPOSE: USE OF SEGMENTED OFFSHORE BREAKWATERS FOR BEACH EROSION CONTROL To provide information on the functional application of and general design considerations for using offshore
DETACHED BREAKWATERS by Leo C. van Rijn;
 DETACHED BREAKWATERS by Leo C. van Rijn; 1. General A detached breakwater (Figure 1) is defined as a hard shore-parallel structure protecting a section of the shoreline by forming a shield to the waves
DETACHED BREAKWATERS by Leo C. van Rijn; 1. General A detached breakwater (Figure 1) is defined as a hard shore-parallel structure protecting a section of the shoreline by forming a shield to the waves
EVALUATION OF BEACH EROSION UP-DRIFT OF TIDAL INLETS IN SOUTHWEST AND CENTRAL FLORIDA, USA. Mohamed A. Dabees 1 and Brett D.
 EVALUATION OF BEACH EROSION UP-DRIFT OF TIDAL INLETS IN SOUTHWEST AND CENTRAL FLORIDA, USA Mohamed A. Dabees 1 and Brett D. Moore 1 The paper discusses the analysis of up-drift beach erosion near selected
EVALUATION OF BEACH EROSION UP-DRIFT OF TIDAL INLETS IN SOUTHWEST AND CENTRAL FLORIDA, USA Mohamed A. Dabees 1 and Brett D. Moore 1 The paper discusses the analysis of up-drift beach erosion near selected
Cross-shore sediment transports on a cut profile for large scale land reclamations
 Cross-shore sediment transports on a cut profile for large scale land reclamations Martijn Onderwater 1 Dano Roelvink Jan van de Graaff 3 Abstract When building a large scale land reclamation, the safest
Cross-shore sediment transports on a cut profile for large scale land reclamations Martijn Onderwater 1 Dano Roelvink Jan van de Graaff 3 Abstract When building a large scale land reclamation, the safest
Julebæk Strand. Effect full beach nourishment
 Julebæk Strand Effect full beach nourishment Aim of Study This study is a part of the COADAPT funding and the aim of the study is to analyze the effect of beach nourishment. In order to investigate the
Julebæk Strand Effect full beach nourishment Aim of Study This study is a part of the COADAPT funding and the aim of the study is to analyze the effect of beach nourishment. In order to investigate the
Beach Wizard: Development of an Operational Nowcast, Short-Term Forecast System for Nearshore Hydrodynamics and Bathymetric Evolution
 Beach Wizard: Development of an Operational Nowcast, Short-Term Forecast System for Nearshore Hydrodynamics and Bathymetric Evolution Ad Reniers Civil Engineering and Geosciences, Delft University of Technology
Beach Wizard: Development of an Operational Nowcast, Short-Term Forecast System for Nearshore Hydrodynamics and Bathymetric Evolution Ad Reniers Civil Engineering and Geosciences, Delft University of Technology
OECS Regional Engineering Workshop September 29 October 3, 2014
 B E A C H E S. M A R I N A S. D E S I G N. C O N S T R U C T I O N. OECS Regional Engineering Workshop September 29 October 3, 2014 Coastal Erosion and Sea Defense: Introduction to Coastal Dynamics David
B E A C H E S. M A R I N A S. D E S I G N. C O N S T R U C T I O N. OECS Regional Engineering Workshop September 29 October 3, 2014 Coastal Erosion and Sea Defense: Introduction to Coastal Dynamics David
Nearshore Placed Mound Physical Model Experiment
 Nearshore Placed Mound Physical Model Experiment PURPOSE: This technical note describes the migration and dispersion of a nearshore mound subjected to waves in a physical model. The summary includes recommendations
Nearshore Placed Mound Physical Model Experiment PURPOSE: This technical note describes the migration and dispersion of a nearshore mound subjected to waves in a physical model. The summary includes recommendations
BYPASS HARBOURS AT LITTORAL TRANSPORT COASTS
 BYPASS HARBOURS AT LITTORAL TRANSPORT COASTS by K. Mangor 1, I. Brøker 2, R. Deigaard 3 and N. Grunnet 4 ABSTRACT Maintaining sufficient navigation depth in front of the entrance at harbours on littoral
BYPASS HARBOURS AT LITTORAL TRANSPORT COASTS by K. Mangor 1, I. Brøker 2, R. Deigaard 3 and N. Grunnet 4 ABSTRACT Maintaining sufficient navigation depth in front of the entrance at harbours on littoral
Shoreline Evolution Due to Oblique Waves in Presence of Submerged Breakwaters. Nima Zakeri (Corresponding Author), Mojtaba Tajziehchi
 Shoreline Evolution Due to Oblique Waves in Presence of Submerged Breakwaters Nima Zakeri (Corresponding Author), Mojtaba Tajziehchi Department of Civil Engineering, Faculty of Engineering, University
Shoreline Evolution Due to Oblique Waves in Presence of Submerged Breakwaters Nima Zakeri (Corresponding Author), Mojtaba Tajziehchi Department of Civil Engineering, Faculty of Engineering, University
MAR 110 LECTURE #15 Wave Hazards
 1 MAR 110 LECTURE #15 Wave Hazards Rogue Wave Hazard Rogue waves are very large open ocean waves of sometimes can range in height from 60 ft (20m) to120 feet (40m) and thus a significant hazard to large
1 MAR 110 LECTURE #15 Wave Hazards Rogue Wave Hazard Rogue waves are very large open ocean waves of sometimes can range in height from 60 ft (20m) to120 feet (40m) and thus a significant hazard to large
CHAPTER 281 INFLUENCE OF NEARSHORE HARDBOTTOM ON REGIONAL SEDIMENT TRANSPORT
 CHAPTER 281 INFLUENCE OF NEARSHORE HARDBOTTOM ON REGIONAL SEDIMENT TRANSPORT Paul C.-P. Lin, Ph.D., P.E. 1 and R. Harvey Sasso, P.E. 2 ABSTRACT The influence of nearshore hardbottom on longshore and cross-shore
CHAPTER 281 INFLUENCE OF NEARSHORE HARDBOTTOM ON REGIONAL SEDIMENT TRANSPORT Paul C.-P. Lin, Ph.D., P.E. 1 and R. Harvey Sasso, P.E. 2 ABSTRACT The influence of nearshore hardbottom on longshore and cross-shore
The construction of Deepwater Navigation Channel (DNC) in the Bystry arm of the Danube Delta has started in The whole project provides the
 Annex 45 Numerical Studies of Waves, Currents and Sediment Transport at the Marine Part of Deepwater Navigation Channel through the Bystry Arm of the Danube Delta and Model Verification based on Laboratory
Annex 45 Numerical Studies of Waves, Currents and Sediment Transport at the Marine Part of Deepwater Navigation Channel through the Bystry Arm of the Danube Delta and Model Verification based on Laboratory
CHAPTER 179. Performance of a Submerged Breakwater for Shore Protection
 CHAPTER 179 Abstract Performance of a Submerged Breakwater for Shore Protection Albert E. Browder',A. Member, ASCE; Robert G. Dean 2, Member, ASCE; and Renjie Chen 3 A summary is presented of the results
CHAPTER 179 Abstract Performance of a Submerged Breakwater for Shore Protection Albert E. Browder',A. Member, ASCE; Robert G. Dean 2, Member, ASCE; and Renjie Chen 3 A summary is presented of the results
INFLUENCE OF DAMAGED GROINS ON NOURISHED SEASHORE
 INFLUENCE OF DAMAGED GROINS ON NOURISHED SEASHORE Ostrowski R 1., Pruszak Z. 1, Schönhofer J. 1, Szmytkiewicz M. 1, Szmytkiewicz P. 1 The system of timber palisade groins can be very helpful as a measure
INFLUENCE OF DAMAGED GROINS ON NOURISHED SEASHORE Ostrowski R 1., Pruszak Z. 1, Schönhofer J. 1, Szmytkiewicz M. 1, Szmytkiewicz P. 1 The system of timber palisade groins can be very helpful as a measure
ANALYSIS ON PERFORMANCE OF THE EMERGENCY NOURISHMENT PROJECT AT WEST BEACH OF BEIDAIHE, CHINA
 ANALYSIS ON PERFORMANCE OF THE EMERGENCY NOURISHMENT PROJECT AT WEST BEACH OF BEIDAIHE, CHINA Yanxiong Yang 1, Jiabo Zhang 1, Cuiping Kuang 2,*, Yu Zhang 3, Lulu He 2,*, Yi Pan 2 and Shuguang Liu 2 Beach
ANALYSIS ON PERFORMANCE OF THE EMERGENCY NOURISHMENT PROJECT AT WEST BEACH OF BEIDAIHE, CHINA Yanxiong Yang 1, Jiabo Zhang 1, Cuiping Kuang 2,*, Yu Zhang 3, Lulu He 2,*, Yi Pan 2 and Shuguang Liu 2 Beach
Q1. What are the primary causes/contributors to coastal erosion at Westshore and the concept of longshore / littoral drift.
 Q1. What are the primary causes/contributors to coastal erosion at Westshore and the concept of longshore / littoral drift. In order of (timing related) contribution to present problem 1. Beach is too
Q1. What are the primary causes/contributors to coastal erosion at Westshore and the concept of longshore / littoral drift. In order of (timing related) contribution to present problem 1. Beach is too
Investigations and Recommendations for Solutions to the Beach Erosion Problems in the City of Herzliya, Israel
 Investigations and Recommendations for Solutions to the Beach Erosion Problems in the City of Herzliya, Israel Site Inspection Performed 30 April to 6 May 2007 Prepared for: City of Herzliya Office of
Investigations and Recommendations for Solutions to the Beach Erosion Problems in the City of Herzliya, Israel Site Inspection Performed 30 April to 6 May 2007 Prepared for: City of Herzliya Office of
Sustainable Solutions for Coastal Zone Management of Lowland and River Delta Coastlines
 Sustainable Solutions for Coastal Zone Management of Lowland and River Delta Coastlines By Nabil M. Ismail 1, M.ASCE, Robert L. Wiegel 2, Hon. M.ASCE 1] Prof. of Coastal Engineering, Maritime Academy,
Sustainable Solutions for Coastal Zone Management of Lowland and River Delta Coastlines By Nabil M. Ismail 1, M.ASCE, Robert L. Wiegel 2, Hon. M.ASCE 1] Prof. of Coastal Engineering, Maritime Academy,
Chapter 10 Field Survey and Sediment Analysis for the Candidate Site
 Chapter 1 Field Survey and Sediment Analysis for the Candidate Site 1.1 Overview Several kinds of field surveys have been carried out to obtain the necessary information for sediment analysis, planning,
Chapter 1 Field Survey and Sediment Analysis for the Candidate Site 1.1 Overview Several kinds of field surveys have been carried out to obtain the necessary information for sediment analysis, planning,
Beach Nourishment Impact on Beach Safety and Surfing in the North Reach of Brevard County, Florida
 Beach Nourishment Impact on Beach Safety and Surfing in the North Reach of Brevard County, Florida Prepared by John Hearin, Ph.D. Coastal Engineering Vice Chairman Cocoa Beach Chapter Port Canaveral Patrick
Beach Nourishment Impact on Beach Safety and Surfing in the North Reach of Brevard County, Florida Prepared by John Hearin, Ph.D. Coastal Engineering Vice Chairman Cocoa Beach Chapter Port Canaveral Patrick
Physical Modeling of Nearshore Placed Dredged Material Rusty Permenter, Ernie Smith, Michael C. Mohr, Shanon Chader
 Physical Modeling of Nearshore Placed Dredged Material Rusty Permenter, Ernie Smith, Michael C. Mohr, Shanon Chader Research Hydraulic Engineer ERDC-Coastal Hydraulics Laboratory October 25,2012 Study
Physical Modeling of Nearshore Placed Dredged Material Rusty Permenter, Ernie Smith, Michael C. Mohr, Shanon Chader Research Hydraulic Engineer ERDC-Coastal Hydraulics Laboratory October 25,2012 Study
LOCALLY CONCENTRATED SEVERE BEACH EROSION ON SEISHO COAST CAUSED BY TYPHOON T0709
 F-4 Fourth International Conference on Scour and Erosion 2008 LOCALLY CONCENTRATED SEVERE BEACH EROSION ON SEISHO COAST CAUSED BY TYPHOON T0709 Yoshimitsu TAJIMA 1 and Shinji SATO 2 1 Member of JSCE, Associate
F-4 Fourth International Conference on Scour and Erosion 2008 LOCALLY CONCENTRATED SEVERE BEACH EROSION ON SEISHO COAST CAUSED BY TYPHOON T0709 Yoshimitsu TAJIMA 1 and Shinji SATO 2 1 Member of JSCE, Associate
LAB: WHERE S THE BEACH
 Name: LAB: WHERE S THE BEACH Introduction When you build a sandcastle on the beach, you don't expect it to last forever. You spread out your towel to sunbathe, but you know you can't stay in the same spot
Name: LAB: WHERE S THE BEACH Introduction When you build a sandcastle on the beach, you don't expect it to last forever. You spread out your towel to sunbathe, but you know you can't stay in the same spot
IMAGE-BASED FIELD OBSERVATION OF INFRAGRAVITY WAVES ALONG THE SWASH ZONE. Yoshimitsu Tajima 1
 IMAGE-BASED FIELD OBSERVATION OF INFRAGRAVITY WAVES ALONG THE SWASH ZONE Yoshimitsu Tajima 1 This study develops an image-based monitoring techniques for observations of surf zone hydrodynamics especially
IMAGE-BASED FIELD OBSERVATION OF INFRAGRAVITY WAVES ALONG THE SWASH ZONE Yoshimitsu Tajima 1 This study develops an image-based monitoring techniques for observations of surf zone hydrodynamics especially
APPLICATION OF SHORE PROTECTION SCHEMES IN HORNB^K Mads Peder J0rgensen ' Peer Skaarup 2 Karsten Mangor 3 J0rgen Juhl 4
 APPLICATION OF SHORE PROTECTION SCHEMES IN HORNB^K Mads Peder J0rgensen ' Peer Skaarup 2 Karsten Mangor 3 J0rgen Juhl 4 ABSTRACT Hornbask Harbour was built more than a hundred years ago on a sandy coast
APPLICATION OF SHORE PROTECTION SCHEMES IN HORNB^K Mads Peder J0rgensen ' Peer Skaarup 2 Karsten Mangor 3 J0rgen Juhl 4 ABSTRACT Hornbask Harbour was built more than a hundred years ago on a sandy coast
INTRODUCTION TO COASTAL ENGINEERING AND MANAGEMENT
 Advanced Series on Ocean Engineering Volume 16 INTRODUCTION TO COASTAL ENGINEERING AND MANAGEMENT J. William Kamphuis Queen's University, Canada World Scientific Singapore New Jersey London Hong Kong Contents
Advanced Series on Ocean Engineering Volume 16 INTRODUCTION TO COASTAL ENGINEERING AND MANAGEMENT J. William Kamphuis Queen's University, Canada World Scientific Singapore New Jersey London Hong Kong Contents
Currents measurements in the coast of Montevideo, Uruguay
 Currents measurements in the coast of Montevideo, Uruguay M. Fossati, D. Bellón, E. Lorenzo & I. Piedra-Cueva Fluid Mechanics and Environmental Engineering Institute (IMFIA), School of Engineering, Research
Currents measurements in the coast of Montevideo, Uruguay M. Fossati, D. Bellón, E. Lorenzo & I. Piedra-Cueva Fluid Mechanics and Environmental Engineering Institute (IMFIA), School of Engineering, Research
Long Beach Island Holgate Spit Little Egg Inlet Historical Evolution Introduction Longshore Transport Map, Survey and Photo Historic Sequence
 Appendix B Long Beach Island Holgate Spit Little Egg Inlet Historical Evolution Introduction The undeveloped southern end of Long Beach Island (LBI) is referred to as the Holgate spit as it adjoins the
Appendix B Long Beach Island Holgate Spit Little Egg Inlet Historical Evolution Introduction The undeveloped southern end of Long Beach Island (LBI) is referred to as the Holgate spit as it adjoins the
SACO RIVER AND CAMP ELLIS BEACH SACO, MAINE SECTION 111 SHORE DAMAGE MITIGATION PROJECT APPENDIX F ECONOMIC ASSESSMENT
 SACO RIVER AND CAMP ELLIS BEACH SACO, MAINE SECTION 111 SHORE DAMAGE MITIGATION PROJECT APPENDIX F ECONOMIC ASSESSMENT Department of the Army New England District, Corps of Engineers 696 Virginia Road
SACO RIVER AND CAMP ELLIS BEACH SACO, MAINE SECTION 111 SHORE DAMAGE MITIGATION PROJECT APPENDIX F ECONOMIC ASSESSMENT Department of the Army New England District, Corps of Engineers 696 Virginia Road
Inventory of coastal sandy areas protection of infrastructure and planned retreat
 2018-02-28 Inventory of coastal sandy areas protection of infrastructure and planned retreat Johanna Birgander, Thorbjörn Nilsson, Pär Persson Summary To estimate the natural protection around the coast
2018-02-28 Inventory of coastal sandy areas protection of infrastructure and planned retreat Johanna Birgander, Thorbjörn Nilsson, Pär Persson Summary To estimate the natural protection around the coast
Southern California Beach Processes Study
 Southern California Beach Processes Study Torrey Pines Field Site 5th Quarterly Report 31 May 22 to California Resources Agency and California Department of Boating and Waterways R.T. Guza 1, W.C. O Reilly
Southern California Beach Processes Study Torrey Pines Field Site 5th Quarterly Report 31 May 22 to California Resources Agency and California Department of Boating and Waterways R.T. Guza 1, W.C. O Reilly
ALTERNATIVES FOR COASTAL STORM DAMAGE MITIGATION AND FUNCTIONAL DESIGN OF COASTAL STRUCTURES
 The University of the West Indies Organization of American States PROFESSIONAL DEVELOPMENT PROGRAMME: COASTAL INFRASTRUCTURE DESIGN, CONSTRUCTION AND MAINTENANCE A COURSE IN COASTAL DEFENSE SYSTEMS I CHAPTER
The University of the West Indies Organization of American States PROFESSIONAL DEVELOPMENT PROGRAMME: COASTAL INFRASTRUCTURE DESIGN, CONSTRUCTION AND MAINTENANCE A COURSE IN COASTAL DEFENSE SYSTEMS I CHAPTER
USE OF X-BAND RADAR FOR WAVE AND BEACH MORPHOLOGY ANALYSIS
 USE OF X-BAND RADAR FOR WAVE AND BEACH MORPHOLOGY ANALYSIS JAE HYENG LEE ECOH Corporation, 2-6-4, Kitaueno, Taito, Tokyo, 110-0014, Japan SATOSHI TAKEWAKA Institute of Engineering Mechanics and Systems,
USE OF X-BAND RADAR FOR WAVE AND BEACH MORPHOLOGY ANALYSIS JAE HYENG LEE ECOH Corporation, 2-6-4, Kitaueno, Taito, Tokyo, 110-0014, Japan SATOSHI TAKEWAKA Institute of Engineering Mechanics and Systems,
STATUS REPORT FOR THE SUBMERGED REEF BALL TM ARTIFICIAL REEF SUBMERGED BREAKWATER BEACH STABILIZATION PROJECT FOR THE GRAND CAYMAN MARRIOTT HOTEL
 August 23 STATUS REPORT FOR THE SUBMERGED REEF BALL TM ARTIFICIAL REEF SUBMERGED BREAKWATER BEACH STABILIZATION PROJECT FOR THE GRAND CAYMAN MARRIOTT HOTEL performed by Lee E. Harris, Ph.D., P.E. Consulting
August 23 STATUS REPORT FOR THE SUBMERGED REEF BALL TM ARTIFICIAL REEF SUBMERGED BREAKWATER BEACH STABILIZATION PROJECT FOR THE GRAND CAYMAN MARRIOTT HOTEL performed by Lee E. Harris, Ph.D., P.E. Consulting
A process based approach to understand WA s complex coastline Jeff Hansen Ryan Lowe Graham Symonds Laura Segura Gundula Winter
 A process based approach to understand WA s complex coastline Jeff Hansen Ryan Lowe Graham Symonds Laura Segura Gundula Winter WA s coastline is highly variable due to offshore and shore-attached coral
A process based approach to understand WA s complex coastline Jeff Hansen Ryan Lowe Graham Symonds Laura Segura Gundula Winter WA s coastline is highly variable due to offshore and shore-attached coral
Modeling Beach Erosion
 Ocean Lecture & Educator s Night May 16, 2012 Modeling Beach Erosion Below is an overview of the activity Modeling Beach Erosion (New Jersey Sea Grant Consortium, Education Program) to incorporate information
Ocean Lecture & Educator s Night May 16, 2012 Modeling Beach Erosion Below is an overview of the activity Modeling Beach Erosion (New Jersey Sea Grant Consortium, Education Program) to incorporate information
MESSOLOGI LAGOON AREA (GREECE)
 MESSOLOGI LAGOON AREA (GREECE) 20 Contact: Kyriakos SPYROPOULOS TRITON Consulting Engineers 90 Pratinou Str. 11634 Athens (GREECE) Tel: +32 10 729 57 61 Fax: +32 10 724 33 58 e-mail: kspyropoulos@tritonsa.gr
MESSOLOGI LAGOON AREA (GREECE) 20 Contact: Kyriakos SPYROPOULOS TRITON Consulting Engineers 90 Pratinou Str. 11634 Athens (GREECE) Tel: +32 10 729 57 61 Fax: +32 10 724 33 58 e-mail: kspyropoulos@tritonsa.gr
PREDICTION OF BEACH CHANGES AROUND ARTIFICIAL REEF USING BG MODEL
 PREDICTION OF BEACH CHANGES AROUND ARTIFICIAL REEF USING BG MODEL Hiroaki Fujiwara 1, Takaaki Uda 2, Toshiaki Onishi 1, Shiho Miyahara 3 and Masumi Serizawa 3 On the Kaike coast, one of the twelve detached
PREDICTION OF BEACH CHANGES AROUND ARTIFICIAL REEF USING BG MODEL Hiroaki Fujiwara 1, Takaaki Uda 2, Toshiaki Onishi 1, Shiho Miyahara 3 and Masumi Serizawa 3 On the Kaike coast, one of the twelve detached
STORM RESPONSE SIMULATION
 APPENDIX V STORM RESPONSE SIMULATION Final Environmental Impact Statement Village of Bald Head Island Shoreline Protection Project Brunswick County, North Carolina Delft3D Storm Response Simulations With
APPENDIX V STORM RESPONSE SIMULATION Final Environmental Impact Statement Village of Bald Head Island Shoreline Protection Project Brunswick County, North Carolina Delft3D Storm Response Simulations With
HYDRODYNAMICS AND MORPHODYNAMICS IN THE SURF ZONE OF A DISSIPATIVE BEACH
 HYDRODYNAMICS AND MORPHODYNAMICS IN THE SURF ZONE OF A DISSIPATIVE BEACH Leo C. van Rijn, Dirk Jan R. Walstra, Bart T. Grasmeijer and Kees Kleinhout Abstract: Two profile models have been compared with
HYDRODYNAMICS AND MORPHODYNAMICS IN THE SURF ZONE OF A DISSIPATIVE BEACH Leo C. van Rijn, Dirk Jan R. Walstra, Bart T. Grasmeijer and Kees Kleinhout Abstract: Two profile models have been compared with
COASTAL EROSION: INVESTIGATIONS IN THE SOUTHWEST COAST OF SRI LANKA
 COASTAL EROSION: INVESTIGATIONS IN THE SOUTHWEST COAST OF SRI LANKA Wijayawardane I.S.K. 1, Ansaf K.M.M. 2, Ratnasooriya A.H.R. 3, Samarawickrama S.P. 4 1,2 Postgraduate Student, Department of Civil Engineering,
COASTAL EROSION: INVESTIGATIONS IN THE SOUTHWEST COAST OF SRI LANKA Wijayawardane I.S.K. 1, Ansaf K.M.M. 2, Ratnasooriya A.H.R. 3, Samarawickrama S.P. 4 1,2 Postgraduate Student, Department of Civil Engineering,
ALTERNATIVES FOR COASTAL STORM DAMAGE MITIGATION
 ALTERNATIVES FOR COASTAL STORM DAMAGE MITIGATION Dave Basco Old Dominion University, Norfolk, Virginia, USA National Park Service Photo STRUCTURAL (changes to natural, physical system) hardening (seawalls,
ALTERNATIVES FOR COASTAL STORM DAMAGE MITIGATION Dave Basco Old Dominion University, Norfolk, Virginia, USA National Park Service Photo STRUCTURAL (changes to natural, physical system) hardening (seawalls,
SEDIMENT BUDGET OF LIDO OF PELLESTRINA (VENICE) Written by Marcello Di Risio Under the supervision of Giorgio Bellotti and Leopoldo Franco
 SEDIMENT BUDGET OF LIDO OF PELLESTRINA (VENICE) Written by Marcello Di Risio Under the supervision of Giorgio Bellotti and Leopoldo Franco Table of contents: 1. Introduction...3 2. Protection structures
SEDIMENT BUDGET OF LIDO OF PELLESTRINA (VENICE) Written by Marcello Di Risio Under the supervision of Giorgio Bellotti and Leopoldo Franco Table of contents: 1. Introduction...3 2. Protection structures
Nearshore Sediment Transport What influences the loss of sediment on Beaches? - Waves - Winds - Tidal Currents - River discharge - Runoff
 Tides & Beaches Nearshore Sediment Transport What influences the loss of sediment on Beaches? - Waves - Winds - Tidal Currents - River discharge - Runoff Oceans Ocean Topography Physical Structure of the
Tides & Beaches Nearshore Sediment Transport What influences the loss of sediment on Beaches? - Waves - Winds - Tidal Currents - River discharge - Runoff Oceans Ocean Topography Physical Structure of the
SHORELINE ROTATION CAUSED BY LARGE-SCALE EXCAVATION OF REEF FLAT ON SANUR BEACH IN BALI
 SHORELINE ROTATION CAUSED BY LARGE-SCALE EXCAVATION OF REEF FLAT ON SANUR BEACH IN BALI Masatoshi Endo, Akio Kobayashi, Takaaki Uda, Yasuhito Noshi and Susumu Onaka In the southern part of Sanur Beach
SHORELINE ROTATION CAUSED BY LARGE-SCALE EXCAVATION OF REEF FLAT ON SANUR BEACH IN BALI Masatoshi Endo, Akio Kobayashi, Takaaki Uda, Yasuhito Noshi and Susumu Onaka In the southern part of Sanur Beach
Nearshore Dredged Material Placement Pilot Study at Noyo Harbor, CA
 1 Nearshore Dredged Material Placement Pilot Study at Noyo Harbor, CA Noyo Cove N 2011 National Conference on Beach Preservation Technology 9-11, February 2011 Lihwa Lin, Honghai Li, Mitchell Brown US
1 Nearshore Dredged Material Placement Pilot Study at Noyo Harbor, CA Noyo Cove N 2011 National Conference on Beach Preservation Technology 9-11, February 2011 Lihwa Lin, Honghai Li, Mitchell Brown US
COFFS HARBOUR SEDIMENT MODELLING AND INVESTIGATION
 COFFS HARBOUR SEDIMENT MODELLING AND INVESTIGATION Luke McAvoy Undergraduate Engineer (Civil) Griffith School of Engineering, Griffith University, Gold Coast, Australia Daniel Rodger Senior Engineer Water
COFFS HARBOUR SEDIMENT MODELLING AND INVESTIGATION Luke McAvoy Undergraduate Engineer (Civil) Griffith School of Engineering, Griffith University, Gold Coast, Australia Daniel Rodger Senior Engineer Water
SAND BOTTOM EROSION AND CHANGES OF AN ACTIVE LAYER THICKNESS IN THE SURF ZONE OF THE NORDERNEY ISLAND
 SAND BOTTOM EROSION AND CHANGES OF AN ACTIVE LAYER THICKNESS IN THE SURF ZONE OF THE NORDERNEY ISLAND Kos'yan R. 1, Kunz H. 2, Podymov l. 3 1 Prof.Dr.,The Southern Branch of the P.P.Shirshov Institute
SAND BOTTOM EROSION AND CHANGES OF AN ACTIVE LAYER THICKNESS IN THE SURF ZONE OF THE NORDERNEY ISLAND Kos'yan R. 1, Kunz H. 2, Podymov l. 3 1 Prof.Dr.,The Southern Branch of the P.P.Shirshov Institute
BEACH CHANGES CAUSED BY EXTENSION OF OFFSHORE BREAKWATER AND LIMITATIONS OF ARTIFICIAL REEFS CONSTRUCTED AS A MEASURE AGAINST BEACH EROSION
 BEACH CHANGES CAUSED BY EXTENSION OF OFFSHORE BREAKWATER AND LIMITATIONS OF ARTIFICIAL REEFS CONSTRUCTED AS A MEASURE AGAINST BEACH EROSION Yasuhito Noshi 1, Takaaki Uda and Yukiyoshi Hoshigami 3 Beach
BEACH CHANGES CAUSED BY EXTENSION OF OFFSHORE BREAKWATER AND LIMITATIONS OF ARTIFICIAL REEFS CONSTRUCTED AS A MEASURE AGAINST BEACH EROSION Yasuhito Noshi 1, Takaaki Uda and Yukiyoshi Hoshigami 3 Beach
Simulation of hydraulic regime and sediment transport in the Mekong delta coast
 Simulation of hydraulic regime and sediment transport in the Mekong delta coast 1. Introduction Coastal erosion in the Mekong Delta has been recorded in recent years and the erosion rate has been increasing
Simulation of hydraulic regime and sediment transport in the Mekong delta coast 1. Introduction Coastal erosion in the Mekong Delta has been recorded in recent years and the erosion rate has been increasing
STUDY ON TSUNAMI PROPAGATION INTO RIVERS
 ABSTRACT STUDY ON TSUNAMI PROPAGATION INTO RIVERS Min Roh 1, Xuan Tinh Nguyen 2, Hitoshi Tanaka 3 When tsunami wave propagation from the narrow river mouth, water surface is raised and fluctuated by long
ABSTRACT STUDY ON TSUNAMI PROPAGATION INTO RIVERS Min Roh 1, Xuan Tinh Nguyen 2, Hitoshi Tanaka 3 When tsunami wave propagation from the narrow river mouth, water surface is raised and fluctuated by long
THE WAVE CLIMATE IN THE BELGIAN COASTAL ZONE
 THE WAVE CLIMATE IN THE BELGIAN COASTAL ZONE Toon Verwaest, Flanders Hydraulics Research, toon.verwaest@mow.vlaanderen.be Sarah Doorme, IMDC, sarah.doorme@imdc.be Kristof Verelst, Flanders Hydraulics Research,
THE WAVE CLIMATE IN THE BELGIAN COASTAL ZONE Toon Verwaest, Flanders Hydraulics Research, toon.verwaest@mow.vlaanderen.be Sarah Doorme, IMDC, sarah.doorme@imdc.be Kristof Verelst, Flanders Hydraulics Research,
SHORELINE EVOLUTION DUE TO HIGHLY OBLIQUE INCIDENT WAVES AT WALVIS BAY, NAMIBIA
 SHORELINE EVOLUTION DUE TO HIGHLY OBLIQUE INCIDENT WAVES AT WALVIS BAY, NAMIBIA Berry Elfrink, 1 Gordon Prestedge 2, Cesar B.M. Rocha 3, and Jørgen Juhl 4 Abstract: This paper describes the development
SHORELINE EVOLUTION DUE TO HIGHLY OBLIQUE INCIDENT WAVES AT WALVIS BAY, NAMIBIA Berry Elfrink, 1 Gordon Prestedge 2, Cesar B.M. Rocha 3, and Jørgen Juhl 4 Abstract: This paper describes the development
LAKKOPETRA (GREECE) EUROSION Case Study. Contact: Kyriakos SPYROPOULOS. TRITON Consulting Engineers. 90 Pratinou Str Athens (GREECE)
 LAKKOPETRA (GREECE) Contact: Kyriakos SPYROPOULOS TRITON Consulting Engineers 90 Pratinou Str. 11634 Athens (GREECE) Tel: +32 10 729 57 61 Fax: +32 10 724 33 58 e-mail: kspyropoulos@tritonsa.gr 19 1 1.
LAKKOPETRA (GREECE) Contact: Kyriakos SPYROPOULOS TRITON Consulting Engineers 90 Pratinou Str. 11634 Athens (GREECE) Tel: +32 10 729 57 61 Fax: +32 10 724 33 58 e-mail: kspyropoulos@tritonsa.gr 19 1 1.
TRANSPORT OF NEARSHORE DREDGE MATERIAL BERMS
 Proceedings of the 6 th International Conference on the Application of Physical Modelling in Coastal and Port Engineering and Science (Coastlab16) Ottawa, Canada, May 10-13, 2016 Copyright : Creative Commons
Proceedings of the 6 th International Conference on the Application of Physical Modelling in Coastal and Port Engineering and Science (Coastlab16) Ottawa, Canada, May 10-13, 2016 Copyright : Creative Commons
NUMERICAL SIMULATION OF SEDIMENT PATHWAYS AT AN IDEALIZED INLET AND EBB SHOAL
 In: Proceedings Coastal Sediments 03. 2003. CD-ROM Published by World Scientific Publishing Corp. and East Meets West Productions, Corpus Christi, Texas, USA. ISBN 981-238-422-7. NUMERICAL SIMULATION OF
In: Proceedings Coastal Sediments 03. 2003. CD-ROM Published by World Scientific Publishing Corp. and East Meets West Productions, Corpus Christi, Texas, USA. ISBN 981-238-422-7. NUMERICAL SIMULATION OF
Improving predictions of nearshore processes and shoreline dynamics for beaches along Australia s rocky and coral reef coasts
 Improving predictions of nearshore processes and shoreline dynamics for beaches along Australia s rocky and coral reef coasts Ryan Lowe Jeff Hansen, Graham Symonds, Mark Buckley, Andrew Pomeroy, Gundula
Improving predictions of nearshore processes and shoreline dynamics for beaches along Australia s rocky and coral reef coasts Ryan Lowe Jeff Hansen, Graham Symonds, Mark Buckley, Andrew Pomeroy, Gundula
COASTAL MORPHODYNAMICS
 COASTAL MORPHODYNAMICS PATRICIA CHARDÓN-MALDONADO, PHD, EIT Miguel Canals, Jack A. Puleo, Alec Torres-Freyermuth & Jens Figlus March 9, 2017 OUTLINE INTRODUCTION Meteorological Phenomena Forcing Conditions
COASTAL MORPHODYNAMICS PATRICIA CHARDÓN-MALDONADO, PHD, EIT Miguel Canals, Jack A. Puleo, Alec Torres-Freyermuth & Jens Figlus March 9, 2017 OUTLINE INTRODUCTION Meteorological Phenomena Forcing Conditions
Pathways Interns: Annika O Dea, Ian Conery, Andrea Albright
 1 REMOTE SENSING OF COASTAL MORPHODYNAMICS 237 237 237 217 217 217 2 2 2 8 119 27 252 174.59 255 255 255 163 163 163 131 132 122 239 65 53 11 135 12 112 92 56 62 12 13 12 56 48 13 12 111 Kate Brodie Brittany
1 REMOTE SENSING OF COASTAL MORPHODYNAMICS 237 237 237 217 217 217 2 2 2 8 119 27 252 174.59 255 255 255 163 163 163 131 132 122 239 65 53 11 135 12 112 92 56 62 12 13 12 56 48 13 12 111 Kate Brodie Brittany
INVESTIGATION OF THE RIVER MOUTH MORPHOLOGY CHANGES IN SAMEGAWA RIVER INDUCED BY THE 2011 GREAT EAST JAPAN EARTHQUAKE TSUNAMI
 Annual Journal of Hydraulic Engineering, JSCE, Vol.**, 2**, February IVESTIGATIO OF THE RIVER MOUTH MORPHOLOGY CHAGES I SAMEGAWA RIVER IDUCED BY THE 2 GREAT EAST JAPA EARTHQUAKE TSUAMI Mohammad Bagus ADITYAWA,Hitoshi
Annual Journal of Hydraulic Engineering, JSCE, Vol.**, 2**, February IVESTIGATIO OF THE RIVER MOUTH MORPHOLOGY CHAGES I SAMEGAWA RIVER IDUCED BY THE 2 GREAT EAST JAPA EARTHQUAKE TSUAMI Mohammad Bagus ADITYAWA,Hitoshi
Deep-water orbital waves
 What happens when waves approach shore? Deep-water orbital waves Fig. 9.16, p. 211 Wave motion is influenced by water depth and shape of the shoreline wave buildup zone surf zone beach Wave base deepwater
What happens when waves approach shore? Deep-water orbital waves Fig. 9.16, p. 211 Wave motion is influenced by water depth and shape of the shoreline wave buildup zone surf zone beach Wave base deepwater
MIAMI BEACH 32ND STREET HOT SPOT: NUMERICAL MODELING AND DESIGN OPTIMIZATION. Adam Shah - Coastal Engineer Harvey Sasso P.E.
 ABSTRACT MIAMI BEACH 32ND STREET HOT SPOT: NUMERICAL MODELING AND DESIGN OPTIMIZATION Adam Shah - Coastal Engineer Harvey Sasso P.E. - Principal Coastal Systems International, Inc. 464 South Dixie Highway
ABSTRACT MIAMI BEACH 32ND STREET HOT SPOT: NUMERICAL MODELING AND DESIGN OPTIMIZATION Adam Shah - Coastal Engineer Harvey Sasso P.E. - Principal Coastal Systems International, Inc. 464 South Dixie Highway
Prediction of Nearshore Waves and Currents: Model Sensitivity, Confidence and Assimilation
 Prediction of Nearshore Waves and Currents: Model Sensitivity, Confidence and Assimilation H. Tuba Özkan-Haller College of Oceanic and Atmospheric Sciences Oregon State University, 104 Ocean Admin Bldg
Prediction of Nearshore Waves and Currents: Model Sensitivity, Confidence and Assimilation H. Tuba Özkan-Haller College of Oceanic and Atmospheric Sciences Oregon State University, 104 Ocean Admin Bldg
CHANGE IN CARBONATE BEACH TRIGGERED BY CONSTRUCTION OF A BRIDGE ON IRABU ISLAND AND ITS SIMULATION USING BG MODEL
 Proceedings of the 7 th International Conference on Asian and Pacific Coasts (APAC 2013) Bali, Indonesia, September 24-26, 2013 CHANGE IN CARBONATE BEACH TRIGGERED BY CONSTRUCTION OF A BRIDGE ON IRABU
Proceedings of the 7 th International Conference on Asian and Pacific Coasts (APAC 2013) Bali, Indonesia, September 24-26, 2013 CHANGE IN CARBONATE BEACH TRIGGERED BY CONSTRUCTION OF A BRIDGE ON IRABU
VLH Ltd, Nereide Ltd, Saltlake Resorts Ltd Proposed Beach Erosion Protection Works at Bel Ombre Environmental Impact Assessment
 VLH Ltd, Nereide Ltd, Saltlake Resorts Ltd Proposed Beach Erosion Protection Works at Bel Ombre TATO/EIA/01 Issue 15 February 2017 This report takes into account the particular instructions and requirements
VLH Ltd, Nereide Ltd, Saltlake Resorts Ltd Proposed Beach Erosion Protection Works at Bel Ombre TATO/EIA/01 Issue 15 February 2017 This report takes into account the particular instructions and requirements
Wave Breaking and Wave Setup of Artificial Reef with Inclined Crown Keisuke Murakami 1 and Daisuke Maki 2
 Wave Breaking and Wave Setup of Artificial Reef with Inclined Crown Keisuke Murakami 1 and Daisuke Maki 2 Beach protection facilities are sometimes required to harmonize with coastal environments and utilizations.
Wave Breaking and Wave Setup of Artificial Reef with Inclined Crown Keisuke Murakami 1 and Daisuke Maki 2 Beach protection facilities are sometimes required to harmonize with coastal environments and utilizations.
Nearshore Morphodynamics. Bars and Nearshore Bathymetry. Sediment packages parallel to shore, that store beach sediment
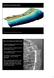 Nearshore Morphodynamics http://coastal.er.usgs.gov/bier/images/chandeleur-xbeach-lg.jpg Bars and Nearshore Bathymetry Sediment packages parallel to shore, that store beach sediment Can be up to 50 km
Nearshore Morphodynamics http://coastal.er.usgs.gov/bier/images/chandeleur-xbeach-lg.jpg Bars and Nearshore Bathymetry Sediment packages parallel to shore, that store beach sediment Can be up to 50 km
ANALYSIS OF MECHANISM OF SAND DEPOSITION INSIDE A FISHING PORT USING BG MODEL
 Proceedings of the 7 th International Conference on Asian and Pacific Coasts (APAC 2013) Bali, Indonesia, September 24-26, 2013 ANALYSIS OF MECHANISM OF SAND DEPOSITION INSIDE A FISHING PORT USING BG MODEL
Proceedings of the 7 th International Conference on Asian and Pacific Coasts (APAC 2013) Bali, Indonesia, September 24-26, 2013 ANALYSIS OF MECHANISM OF SAND DEPOSITION INSIDE A FISHING PORT USING BG MODEL
TITLE: North Carolina s Changing Shorelines. KEYWORDS: erosion - shorelines - mapping - sustainability
 UNC Coastal Studies Institute Teacher Resources 1 TITLE: North Carolina s Changing Shorelines KEYWORDS: erosion - shorelines - mapping - sustainability Changing shorelines impact coastal infrastructure.
UNC Coastal Studies Institute Teacher Resources 1 TITLE: North Carolina s Changing Shorelines KEYWORDS: erosion - shorelines - mapping - sustainability Changing shorelines impact coastal infrastructure.
Chapter 12: Coasts (after a brief review of Tides)
 Chapter 12: Coasts (after a brief review of Tides) 1 Questions from previous classes: What happens when a wave meets a current? wave = people walking current = bus If wave goes with the current, the wave
Chapter 12: Coasts (after a brief review of Tides) 1 Questions from previous classes: What happens when a wave meets a current? wave = people walking current = bus If wave goes with the current, the wave
Directional Wave Spectra from Video Images Data and SWAN Model. Keywords: Directional wave spectra; SWAN; video images; pixels
 Jurnal Teknologi Full paper Directional Wave Spectra from Video Images Data and SWAN Model Muhammad Zikra a*, Noriaki Hashimoto b, Masaru Yamashiro b, Kojiro Suzuki c a Department of Ocean Engineering,
Jurnal Teknologi Full paper Directional Wave Spectra from Video Images Data and SWAN Model Muhammad Zikra a*, Noriaki Hashimoto b, Masaru Yamashiro b, Kojiro Suzuki c a Department of Ocean Engineering,
Chapter 11. Beach Fill and Soft Engineering Structures
 Chapter 11 Beach Fill and Soft Engineering Structures Solutions to Coastal Erosion Soft Structures Hard Structures Retreat No such thing as low cost coastal protection Beach Nourishment Beach Filling Beach
Chapter 11 Beach Fill and Soft Engineering Structures Solutions to Coastal Erosion Soft Structures Hard Structures Retreat No such thing as low cost coastal protection Beach Nourishment Beach Filling Beach
EXISTING AND PLANNED STRATEGIES AND ACTIONS CONNECTED WITH COASTAL PROTECTION IN ASPECT OF PREDICTED SEA LEVEL RISE
 EXISTING AND PLANNED STRATEGIES AND ACTIONS CONNECTED WITH COASTAL PROTECTION IN ASPECT OF PREDICTED SEA LEVEL RISE Andrzej Cieślak Long term coastal protection strategy In 2000 a new 1 Polish long term
EXISTING AND PLANNED STRATEGIES AND ACTIONS CONNECTED WITH COASTAL PROTECTION IN ASPECT OF PREDICTED SEA LEVEL RISE Andrzej Cieślak Long term coastal protection strategy In 2000 a new 1 Polish long term
The morphodynamic responses of artificial embayed beaches to storm events
 Adv. Geosci., 26, 99 103, 2010 doi:10.5194/adgeo-26-99-2010 Author(s) 2010. CC Attribution 3.0 License. Advances in Geosciences The morphodynamic responses of artificial embayed beaches to storm events
Adv. Geosci., 26, 99 103, 2010 doi:10.5194/adgeo-26-99-2010 Author(s) 2010. CC Attribution 3.0 License. Advances in Geosciences The morphodynamic responses of artificial embayed beaches to storm events
SHORE PROTECTION AND HABITAT CREATION AT SHAMROCK ISLAND, TEXAS ABSTRACT
 SHORE PROTECTION AND HABITAT CREATION AT SHAMROCK ISLAND, TEXAS M. Cameron Perry, P.E., and Daniel J. Heilman, P.E. Coastal Engineer Shiner Moseley & Associates., Inc. 555 N. Carancahua Corpus Christi,
SHORE PROTECTION AND HABITAT CREATION AT SHAMROCK ISLAND, TEXAS M. Cameron Perry, P.E., and Daniel J. Heilman, P.E. Coastal Engineer Shiner Moseley & Associates., Inc. 555 N. Carancahua Corpus Christi,
SWASH MODELLING OF A COASTAL PROTECTION SCHEME
 SWASH MODELLING OF A COASTAL PROTECTION SCHEME Mark Klein 1, Andrew Symonds 2, Marcel Zijlema 3, Dan Messiter 4 and Michael Dufour 5 The Beresford shoreline, Australia, is subject to a complex interaction
SWASH MODELLING OF A COASTAL PROTECTION SCHEME Mark Klein 1, Andrew Symonds 2, Marcel Zijlema 3, Dan Messiter 4 and Michael Dufour 5 The Beresford shoreline, Australia, is subject to a complex interaction
Louisiana s 2012 Coastal Master Plan BARRIER SHORELINE MORPHOLOGY MODEL
 Louisiana Coastal Protection & Restorat coastal.louisiana.gov Louisiana s 2012 Coastal Master Plan PREDICTIVE MODELING: committed to our coast BARRIER SHORELINE MORPHOLOGY MODEL Dallon Weathers, University
Louisiana Coastal Protection & Restorat coastal.louisiana.gov Louisiana s 2012 Coastal Master Plan PREDICTIVE MODELING: committed to our coast BARRIER SHORELINE MORPHOLOGY MODEL Dallon Weathers, University
Chapter 10 Lecture Outline. The Restless Oceans
 Chapter 10 Lecture Outline The Restless Oceans Focus Question 10.1 How does the Coriolis effect influence ocean currents? The Ocean s Surface Circulation Ocean currents Masses of water that flow from one
Chapter 10 Lecture Outline The Restless Oceans Focus Question 10.1 How does the Coriolis effect influence ocean currents? The Ocean s Surface Circulation Ocean currents Masses of water that flow from one
Implications of proposed Whanganui Port and lower Whanganui River dredging
 PO Box 637 Wanganui 4540 Attention: Rowan McGregor Dear Rowan 1 Summary We understand that it has been proposed to bring large vessels into the Port at Whanganui requiring the excavation of a channel up
PO Box 637 Wanganui 4540 Attention: Rowan McGregor Dear Rowan 1 Summary We understand that it has been proposed to bring large vessels into the Port at Whanganui requiring the excavation of a channel up
New Jersey Coastal Zone Overview. The New Jersey Beach Profile Network (NJBPN) 3 Dimensional Assessments. Quantifying Shoreline Migration
 New Jersey Coastal Zone Overview The New Jersey Beach Profile Network (NJBPN) Objectives Profile Locations Data Collection Analyzing NJBPN Data Examples 3 Dimensional Assessments Methodology Examples Quantifying
New Jersey Coastal Zone Overview The New Jersey Beach Profile Network (NJBPN) Objectives Profile Locations Data Collection Analyzing NJBPN Data Examples 3 Dimensional Assessments Methodology Examples Quantifying
UC San Diego Scripps Institution of Oceanography Technical Report
 UC San Diego Scripps Institution of Oceanography Technical Report Title Categorizing the Types of Surfing Breaks around Jetty Structures Permalink https://escholarship.org/uc/item/09f405bq Authors Scarfe,
UC San Diego Scripps Institution of Oceanography Technical Report Title Categorizing the Types of Surfing Breaks around Jetty Structures Permalink https://escholarship.org/uc/item/09f405bq Authors Scarfe,
