URMI MITRA ASSISTANT PROFESSOR, P.G. DEPARTMENT OF ZOOLOGY, BIDHANNAGAR COLLEGE
|
|
|
- Lee Logan
- 6 years ago
- Views:
Transcription
1 FOOT AND ITS MODIFICATIONS IN MOLLUSCA URMI MITRA ASSISTANT PROFESSOR, P.G. DEPARTMENT OF ZOOLOGY, BIDHANNAGAR COLLEGE
2 FOOT AND ITS MODIFICATIONS Foot is a characteristic feature of the phylum Mollusca adapted for locomotion, but can take over the function of reproduction, defence and capturing of the prey. It is regarded as the remnant of the dermo-muscular tube of the ancestral form whose dorsal side becomes degenerated and the ventral side becomes greatly modified for creeping. Foot is innervated by the nerves of the pedal ganglion.
3 Molluscs occupy different niches and thus the foot becomes greatly modified in shape, form and function. The simplest and primitive form of foot in molluscs is considered to be a broad, ventral flat foot adapted for creeping movement. However, foot is absent in some of the molluscs e.g. Ostrea ( class Bivalvia). It is very much reduced in Teredo. True molluscan foot is also absent in aplacophorans. In Neomenia (class Aplacophora), a ventral groove with ciliated ridge serves as a locomotory organ. Reduction or complete loss of foot is also seen in parasitic gastropods. In sedentary and sessile gastropods e.g. Bathysciadium, Vermetus etc. foot is reduced and the ventral sole becomes an effective sucker for attachment to the substratum.
4
5 FOOT AS A CREEPING OR CRAWLING ORGAN: In Monoplacophorans :Neopilina is one of the very few living members of the class Monoplacophora that possess a disc-like foot with a flat creeping sole that occupies the entire ventral side. In Polyplcophorans: Polyplacophorans like Chiton too have a broad, muscular flat foot on the ventral side that helps the animal to adhere to the substratum and creep. In Gastropoda: The foot in Gastropoda usually has an elongated, flat, ventral sole for creeping. Very fine bundles of muscles called as the tarsos muscle are present on the sole of the foot and are responsible not only for locomotion but also for capturing the prey. In higher gastropods, the foot is differentiated into three parts by transverse grooves: a small anterior propodium, large, middle mesopodium and small posterior metapodium. The mesopodium is the locomotory region. Metapodium bears the operculum. However, the propodium is either reduced or absent in most prosobranchs. The foot is variously modified in different gastropods e.g. anterior margin of the foot may form a small tactile process which helps in creeping as is seen in Trochus or the foot may project as a small fleshy process e.g. Turbonilla. Triton has a contractile foot.
6 Patella, the true limpet (prosobranch) is a sluggish animal which creeps slowly when required. It remains firmly attached to the rocks and other objects on the sea shore with the help of the foot. Thus, Patella has a well developed ventral foot with a broad, flat creeping sole to move over the rocks. The foot is surrounded by horse-shoe shaped muscle band known as the pallial muscles for attachment. Acteon and Cypraea possess a foot with very large, broad creeping sole. They move by producing waves of contraction on the foot. Limax, the grey slug is a terrestrial gastropod and bears a long foot on the ventral side with a creeping sole and a pair of longitudinal grooves. The pedal gland just behind the head secretes slime or mucus on which the animal creeps. Like the Limax, Helix, the land snail, too, is a terrestrial gastropod found in moist shady places like the gardens. It creeps very slowly on a self secreted tract of mucus. Haliotis is a herbivorous gastropod that lives attached to rocks and moves very fast, 5m. in a minute. They possess a very large foot that dorsally bears a fold of the skin, the epipodium. The epipodium is an appendage of the foot that gives off numerous sensory epipodal tentacles. Monodonta, and Trochus are also examples of gastropod possessing epipodia as appendages of the foot and beset with tactile papillae that assist them in creeping. In some Gastropods, the foot shows partial regional modification e.g. in Pirulus only the left part of the foot acts as the creeping organ. In Atlanta, the posterior part of the foot is altered into a sucker. In Bullia, the foot is very peculiar as it encircles whole of the body. In Natica, the propodium forms a semicircular flap and is demarcated from rest of the foot by deep transverse grooves. The metapodium is provided with lateral parapodia in Natica. The highly glandular foot of Conus with a long backwardly bent siphon acts as an efficient creeping organ. Caecum is a peculiar gastropod that creeps entirely by the action of the cilia present on the sole of the foot.
7
8 CREEPING MOVEMENT: Creeping commonly occurs by waves of muscular contraction that sweeps over the foot. The sole of the foot is firmly attached to the substratum by the mucus which is sticky and gelatinous. In most of the gastropods, mucus is secreted by the gland cells present in abundance on the sole of the foot. However, in pulmonates, mucus is secreted by the pedal gland situated on the ventral foot. As the muscular wave of contraction is passed forward, the gelatinous mucus liquefies in this region thus allowing the foot to move forward. The muscular contractions may be direct, i.e. passing forwards along the foot from behind or may be retrograde, i.e. passing backwards (anterior to posterior) as is seen in most gastropods, particularly in prosobranchs (refer Pila). The direct waves involve the contraction of the longitudinal and the dorsoventral muscles (from the posterior to the anterior end), while the retrograde waves involve contraction of the transverse muscles followed by the contraction of the longitudinal muscles (from the anterior to the posterior end). The waves may be monotaxic, i.e. a single series of waves traversing the foot, or ditaxic, i.e. distinct coordinated waves on the right and left halves of the foot is responsible for the snails movement. The amplitude of the waves however, is small.
9 Bivalves like Anodonta and Unio have a laterally compressed triangular and ploughshare like or hatchet shaped muscular foot for crawling and ploughing through mud. Foot is actually the extension of the visceral mass. It is antero-ventral in position and ends ventrally in a keel. During locomotion, Unio protrudes out its foot between the two valves of the shell and burrows like a plough-share through the mud or sand by the contraction of the pedal protractor muscles. This results in the flow of blood into the foot which swells up and becomes turgid and anchors the foot in sand or mud. The blood is prevented from returning to the body by sphincter muscle. Now the retractor muscles contract and the body of Unio moves forward. During this action, the blood is forced out of the foot and it becomes narrow. Thus, by alternate contraction and extension of the foot, the animal slowly creeps or burrows. In Bivalves like Nucula, the foot shows a primitive form, possessing a flat ventral sole which is not for creeping. The foot is laterally compressed and directed downward. The two sides of the foot can be folded together producing blade-like edge which is thrust into the sand or mud. The ventral sole then opens to serve as an anchor and the body is drawn down into the substratum. In lepton and some other Bivalves, the foot secondarily acquires a large free extremity with a creeping surface.
10
11 FOOT AS A BURROWING ORGAN: Dentalium ( class Scaphopoda) has a small conical, highly extensible foot adapted for digging and burrowing. The foot in Dentalium and other scaphopods is equipped with pedal haemocoel which acts as a hydrostatic skeleton for extending the foot into the sand. In Siphonodentalium, the foot terminates in a retractile disc having papillae on the margins and is well adapted for digging like Dentalium. The foot In Pholas (class Bivalvia) assumes a short and blunt form, adapted for its burrowing habit. The mantle is closed except for a small pedal aperture through which the small foot can be protruded out to grip the end of the burrow. The foot in Anodonta and Unio can perform the function of burrowing in addition to creeping.
12
13 Solen and Ensis (class Bivalvia) have a large, cylindrical and powerful foot that protrudes out from the anterior end of the shell and is used as a burrowing organ. The Solen burrows like Unio, but very quickly. They can dig about 30cm. in sand in a few seconds. They can also swim forward in jerks by suddenly withdrawing the foot and squirting out water through the siphons. In fast burrowers like Tellina, the foot is large and can be stretched out into a wide sheet of muscle as thin as a blade of a knife as it burrows in the sand. In Mya (soft-shell clam) the foot is feebly developed and is used as a weak burrowing organ. Sigaretus (class Gastropoda) is a burrower and the propodium is well developed and sharply marked off from the mesopodium to act as a digging organ. A dorsal flap-like fold of foot covers the head as a protective, fleshy shield. Tenebridae, a burrowing gastropod extends the anterior extremity of the foot with flow of blood, thus forming an anchor as is seen in bivalves and scaphopoda. In gastropods which crawl about in wet sand e.g. Oliva, the propodium is circular or disc-like modified for burrowing.
14 FOOT AS THE LEAPING ORGAN: o In Trigonia and Cardium (class Bivalvia) the foot is bent upon itself and when the foot suddenly straightens it violently lifts the animal off the ground in a powerful leap. o In Trigona the foot is compressed antero-posteriorly as an elongated keel. o Mytilus (class Bivalvia) has a cylindrical foot that acts as a spring tail. Mytilus remains attached to the substratum by a bunch of byssus thread. o In gastropods like Rostellaria, the foot is reduced, and the operculum becomes sharp like a dagger. The metapodium is not sharply marked off from the rest of the foot. o As the animal digs into the sand, the reduced hook-like foot becomes flexed pulling the animal forward in short sharp leaps. FOOT AS A LOOPING ORGAN: o In Pedipus, the propodium is sharply marked off from the rest of the foot by a groove that helps in the looping movement.
15 FOOT AS A SWIMMING ORGAN: In many Molluscs, the foot becomes modified as a swimming organ. The foot of the swimming gastropods show several adaptive modifications. The common adaptation for swimming is the development of parapodia as lateral lobes of the foot which acts as fins, for example, in Oxygyus and Atlanta (class gastropoda), the propodium is fin like, the mesopodium bears a sucker and the metapodium is produced into a laterally flattened swimming lobe. The shell is laterally compressed and produced into a sharp keel. Carinaria too is a pelagic, marine gastropod where the foot is modified into a fin like swimming organ, its sole forming an adhesive sucker. The shell and metapodium are reduced in Carinaria. In Pterotrachea, the metapodium loses the operculum and becomes reduced to a short, filament like tail for swimming. Creseis, the sea butterfly is a small marine gastropod adapted for pelagic life. The foot develops a pair of large lateral parapodia that functions as fins for swimming. Spiratella is a pelagic gastropod that swims by flapping the parapodia. The foot develops anteriorly into highly muscular wing like projections called the parapodia while the posterior part of the foot is greatly reduced. Aplysia possesses a broad, muscular and ventral foot that bears a pair of lateral fleshy fan-like outgrowths, the parapodia which help in swimming. The posterior part of the foot is usually adhesive and gives rise to a very short and distinct tail. Swimming in Aplysia is achieved in short bursts by the rhythmic waves which pass along the parapodia.
16 In shelled pteropods or sea-butterflies, broad wing like or oar-like parapodia confined to the anterior part of the body, form the largest part of the foot. For example, Limacina swims spirally upwards using the parapodia as oars and drops down by holding them motionless over the head. Naked pteropods are the fastest swimmers among gastropods and rapid sculling motion is brought about by the parapodia which are present on the ventral side. The foot is greatly reduced in Pecten, a marine bivalve. It swims by clapping of the shell-valves. In Cephalopods foot is partly modified into a funnel lying below the head and partly into sucker bearing arms or into tentacle bearing lobes surrounding the mouth. They are eight in Octopus, ten in Loligo and Sepia. The fifth pair of arms in Loligo and Sepia are long, slender and prehensile and are called tentacles bearing suckers only at their expanded ends. Loligo is very active and can swim both forward and backward with the help of fins and funnel. Octopus, the devil-fish inhabits all the seas and closely resembles squids and cuttlefish. They possess eight arms which are alike and slightly webbed at the bases. Each arm bears two rows of sessile suckers. Fins are absent in them. Both Sepia and Octopus dart quickly by forcing out jets of water through the funnel. Sepia also swims about gently by undulating movements of the fins. Amphitretus is an inhabitant of deep sea and the arms are united by a web-like fold, the interbrachial membrane. Female of Argonauta, the paper nautilus usually keeps her trunk in the shell, and when disturbed completely withdraws into it. She sails in the shell, propelling it with her arms. She has one of her arms flattened and expanded at the ends for the secretion and support of the shell. The male Argonauta is a coinhabitant of the females shell.
17 FOOT AS AN ORGAN HELPING REPRODUCTION: In some cephalopods, during the breeding season, one of the arms in males is modified into an intromittent organ for the transference of sperm and is known as the hectocotylised arm. In male Octopus, the third right arm is modified into a spoon-shaped hectocotylized arm. ACCESSORY ORGANS ASSOCIATED WITH THE FOOT: The foot in Molluscs is also a highly glandular organ. Some glands are present on the foot that help in locomotion. The secretions of the glands lubricate the passage during movement e.g. the pedal glands and the mucus secreting glands of the gastropods. In some bivalves, the adult or even the larva possesses a byssus apparatus which helps the animal in adhesion to the substratum. The foot in these animals is much reduced. The byssus gland may be considered homologous to the pedal mucus secreting glands of the gastropods. Mytilus is a common bivalve which remains attached to the rocks by byssus threads. These byssus threads are secreted by the byssus glands in the posterior groove of the much reduced foot. As the secretion of the gland passes out through the aperture, it hardens on contact with the water forming tough, bundle of silky threads which anchors the animal firmly to the substratum. The Organ of Valenciennes in some cephalopod females and Van der Hoeven in Nautilus males are some of the accessory organs associated with the foot.
18
Phylum Mollusca (soft bodied)
 Phylum Mollusca (soft bodied) Most described species in the animal kingdom next to Phylum Arthropoda ~100,000 species... Marine, freshwater and terrestrial. 35,000 fossil species. Most diverse group of
Phylum Mollusca (soft bodied) Most described species in the animal kingdom next to Phylum Arthropoda ~100,000 species... Marine, freshwater and terrestrial. 35,000 fossil species. Most diverse group of
Phylum Mollusca. More than 500,000 known species. Class Polyplacophora. Class Bivalvia. Class Gastropoda. Class Cephalopoda
 Phylum Mollusca Class Polyplacophora Class Gastropoda Class Bivalvia Class Cephalopoda chitons Snails Sea slugs nudibranchs clams Squid Octopus Cuttlefish Nautilus More than 500,000 known species A bag,
Phylum Mollusca Class Polyplacophora Class Gastropoda Class Bivalvia Class Cephalopoda chitons Snails Sea slugs nudibranchs clams Squid Octopus Cuttlefish Nautilus More than 500,000 known species A bag,
Phylum Mollusca. Includes snails and slugs, oysters and clams, and octopuses and squids.
 Mollusks Phylum Mollusca Includes snails and slugs, oysters and clams, and octopuses and squids. Bivalves Nautilus Characteristics Soft-bodied invertebrate Covered with protective mantle that may or may
Mollusks Phylum Mollusca Includes snails and slugs, oysters and clams, and octopuses and squids. Bivalves Nautilus Characteristics Soft-bodied invertebrate Covered with protective mantle that may or may
Chapter 35. Table of Contents. Section 1 Mollusca. Section 2 Annelida. Mollusks and Annelids
 Mollusks and Annelids Table of Contents Section 1 Mollusca Section 2 Annelida Section 1 Mollusca Objectives Describe the key characteristics of mollusks. Describe the body plan of mollusks. Name the characteristics
Mollusks and Annelids Table of Contents Section 1 Mollusca Section 2 Annelida Section 1 Mollusca Objectives Describe the key characteristics of mollusks. Describe the body plan of mollusks. Name the characteristics
I. Evolutionary Perspective. Chapter 12. II. Molluscan Characteristics. A. Regions of Molluscan Body 11/2/10
 I. Evolutionary Perspective Chapter 12 Molluscan Success Some of the world s best predators Large brains Complex sensory structures Rapid locomotion Grasping tentacles Tearing mouthparts Have been around
I. Evolutionary Perspective Chapter 12 Molluscan Success Some of the world s best predators Large brains Complex sensory structures Rapid locomotion Grasping tentacles Tearing mouthparts Have been around
Mollusks Soft-bodied Invertebrates
 Mollusks Soft-bodied Invertebrates Phylum Mollusca Very diverse - more species of molluscs than any other group in the ocean. Phylum includes: Bivalves (2 shells); ex. Clam Gastropods (1 shell, coiled);
Mollusks Soft-bodied Invertebrates Phylum Mollusca Very diverse - more species of molluscs than any other group in the ocean. Phylum includes: Bivalves (2 shells); ex. Clam Gastropods (1 shell, coiled);
Protostomes vs Deuterostomes. Phylum Mollusca
 Protostomes vs Deuterostomes Animals that have a true coelom and complete digestive system can be divided into two main groups. This division is based on the way their embryos develop and the way in which
Protostomes vs Deuterostomes Animals that have a true coelom and complete digestive system can be divided into two main groups. This division is based on the way their embryos develop and the way in which
`Mollusks. may or may not form a hard, calcium carbonate shell. Trochophore Larva
 `Mollusks Phylum Mollusca Soft-bodied invertebrate covered with protective mantle that may or may not form a hard, calcium carbonate shell Includes chitons, snails, slugs, clams, oysters, squid, octopus,
`Mollusks Phylum Mollusca Soft-bodied invertebrate covered with protective mantle that may or may not form a hard, calcium carbonate shell Includes chitons, snails, slugs, clams, oysters, squid, octopus,
Kingdom Animalia Subkingdom Eumetazoa Bilateria Phylum Mollusca
 Kingdom Animalia Subkingdom Eumetazoa Bilateria Phylum Mollusca Professor Andrea Garrison Biology 3A Illustrations 2014 Cengage Learning unless otherwise noted Phylum Mollusca Molluscs (mollis = soft)
Kingdom Animalia Subkingdom Eumetazoa Bilateria Phylum Mollusca Professor Andrea Garrison Biology 3A Illustrations 2014 Cengage Learning unless otherwise noted Phylum Mollusca Molluscs (mollis = soft)
Molluscs. Chapter 16
 Molluscs Chapter 16 Phylum Mollusca Phylum Mollusca includes snails and slugs, oysters and clams, and octopuses and squids. Phylum Mollusca Molluscs have a mesoderm lined body cavity a coelom. They are
Molluscs Chapter 16 Phylum Mollusca Phylum Mollusca includes snails and slugs, oysters and clams, and octopuses and squids. Phylum Mollusca Molluscs have a mesoderm lined body cavity a coelom. They are
 Kingdom: Animalia Phylum:Mollusca Classes: Bivalva, Gastropoda, Cephalopoda http://www.youtube.com/watch?v=0a7j5prl8hc&feature=related http://www2.beavercreek.k12.oh.us/videos/45/pgr45_700k.asf What is
Kingdom: Animalia Phylum:Mollusca Classes: Bivalva, Gastropoda, Cephalopoda http://www.youtube.com/watch?v=0a7j5prl8hc&feature=related http://www2.beavercreek.k12.oh.us/videos/45/pgr45_700k.asf What is
27-4 Mollusks. Slide 1 of 43. End Show. Copyright Pearson Prentice Hall
 1 of 43 What Is a Mollusk? What Is a Mollusk? Mollusks are soft-bodied animals that usually have an internal or external shell. Mollusks include snails, slugs, clams, squids, octopi... They are group together
1 of 43 What Is a Mollusk? What Is a Mollusk? Mollusks are soft-bodied animals that usually have an internal or external shell. Mollusks include snails, slugs, clams, squids, octopi... They are group together
Phylum Mollusca Classes
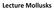 Lecture Mollusks Phylum Mollusca Classes Aculifera with spicules Aplacophora - mollusks without shells Polyplacophora ( Amphineura) chiton, eight plates, intertidal Conchifera with shells Monoplacophora
Lecture Mollusks Phylum Mollusca Classes Aculifera with spicules Aplacophora - mollusks without shells Polyplacophora ( Amphineura) chiton, eight plates, intertidal Conchifera with shells Monoplacophora
Title: May 31 2:42 PM (1 of 23) Phylum Mollusca
 Title: May 31 2:42 PM (1 of 23) Phylum Mollusca Title: May 31 3:25 PM (2 of 23) often referred to as mollusks second largest phylum has 7 classes only looking at 4 bilateral symmetry, true body cavity
Title: May 31 2:42 PM (1 of 23) Phylum Mollusca Title: May 31 3:25 PM (2 of 23) often referred to as mollusks second largest phylum has 7 classes only looking at 4 bilateral symmetry, true body cavity
Mollusks- soft bodied
 Mollusks- soft bodied Objectives Understand the taxonomic relationships and major features of mollusks Learn the external and internal anatomy of the clam and squid Understand the major advantages and
Mollusks- soft bodied Objectives Understand the taxonomic relationships and major features of mollusks Learn the external and internal anatomy of the clam and squid Understand the major advantages and
Phylum Mollusca. Soft-bodied animals. Internal or external shell. Include snails, slugs, clams, squids and octopi
 Phylum Mollusca Soft-bodied animals Internal or external shell Include snails, slugs, clams, squids and octopi Trochophore: free-swimming larval stage of an aquatic mollusk True coeloms Have complex organ
Phylum Mollusca Soft-bodied animals Internal or external shell Include snails, slugs, clams, squids and octopi Trochophore: free-swimming larval stage of an aquatic mollusk True coeloms Have complex organ
Bivalved molluscs filter feeders
 Class Bivalvia Bivalved molluscs have two shells (valves). Mussels, clams, oysters, scallops, shipworms. Mostly sessile filter feeders. No head or radula. Class Bivalvia Part of the mantle is modified
Class Bivalvia Bivalved molluscs have two shells (valves). Mussels, clams, oysters, scallops, shipworms. Mostly sessile filter feeders. No head or radula. Class Bivalvia Part of the mantle is modified
Mollusks Are Soft and Unsegmented
 Mollusks Objectives Understand the taxonomic relationships and major features of mollusks Learn the external and internal anatomy of the clam and squid Understand the major advantages and limitations of
Mollusks Objectives Understand the taxonomic relationships and major features of mollusks Learn the external and internal anatomy of the clam and squid Understand the major advantages and limitations of
Name Date Period. Mollusk Review TORSION HEMOLYMPH SESSILE TROCHOPHORE ADDUCTOR KIDNEY HEMOCOEL MANTLE CHROMATOPHORES VISCERAL MASS
 Name Date Period Mollusk Review MOLLUSK VOCABULARY: Match the word with its definition. TORSION HEMOLYMPH SESSILE TROCHOPHORE ADDUCTOR KIDNEY HEMOCOEL MANTLE CHROMATOPHORES VISCERAL MASS Free-swimming
Name Date Period Mollusk Review MOLLUSK VOCABULARY: Match the word with its definition. TORSION HEMOLYMPH SESSILE TROCHOPHORE ADDUCTOR KIDNEY HEMOCOEL MANTLE CHROMATOPHORES VISCERAL MASS Free-swimming
Life History of Aquatic Organisms (AFI-31306) Lecture: Adaptive radiation in molluscs Martin Lankheet, EZO
 Life History of Aquatic Organisms (AFI-31306) Lecture: Adaptive radiation in molluscs Martin Lankheet, EZO Position in the course THEME Lectures Tutorials Practicals Introduction to Life Life-history trade-offs
Life History of Aquatic Organisms (AFI-31306) Lecture: Adaptive radiation in molluscs Martin Lankheet, EZO Position in the course THEME Lectures Tutorials Practicals Introduction to Life Life-history trade-offs
Copyright The McGraw-Hill Companies, Inc. Permission required for reproduction or display. CHAPTER 17. Annelids 17-1
 CHAPTER 17 Annelids 17-1 Characteristics of the Phylum Annelida Diversity Exhibit segmentation or metamerism Bodies composed of repeated units Each unit contains components of most MAJOR organ systems
CHAPTER 17 Annelids 17-1 Characteristics of the Phylum Annelida Diversity Exhibit segmentation or metamerism Bodies composed of repeated units Each unit contains components of most MAJOR organ systems
Chapter 7. Marine Animals Without a Backbone
 Chapter 7 Marine Animals Without a Backbone Molluscs Characteristics of Phylum: More than 200,000 species Name means "soft body" Basic body plan head, muscular foot and visceral mass in most species Mantle-
Chapter 7 Marine Animals Without a Backbone Molluscs Characteristics of Phylum: More than 200,000 species Name means "soft body" Basic body plan head, muscular foot and visceral mass in most species Mantle-
Phylum Molluska.
 Phylum Molluska www.onacd.ca 3 Main Classes of Mollusks GASTROPODA : includes limpets, snails, slugs and whelks BIVALVIA: includes clams, oysters, muscles, scallops and shipworms CEPHALOPODA: includes
Phylum Molluska www.onacd.ca 3 Main Classes of Mollusks GASTROPODA : includes limpets, snails, slugs and whelks BIVALVIA: includes clams, oysters, muscles, scallops and shipworms CEPHALOPODA: includes
Biology. Slide 1 of 43. End Show. Copyright Pearson Prentice Hall
 Biology 1 of 43 2 of 43 What Is a Mollusk? What are the defining features of mollusks? 3 of 43 What Is a Mollusk? What Is a Mollusk? Mollusks are soft-bodied animals that usually have an internal or external
Biology 1 of 43 2 of 43 What Is a Mollusk? What are the defining features of mollusks? 3 of 43 What Is a Mollusk? What Is a Mollusk? Mollusks are soft-bodied animals that usually have an internal or external
Chapter 28 Mollusks & Annelids. BIOLOGY II Miss. Loulousis
 Chapter 28 Mollusks & Annelids BIOLOGY II Miss. Loulousis Mollusks have a true coelom Snails, slugs, oysters, clams, scallops, octopuses, and squids are all mollusks Annelid earthworm next section Mollusks
Chapter 28 Mollusks & Annelids BIOLOGY II Miss. Loulousis Mollusks have a true coelom Snails, slugs, oysters, clams, scallops, octopuses, and squids are all mollusks Annelid earthworm next section Mollusks
Chapter 10: Mollusca
 Chapter 10: Mollusca Latin: soft 90,000 living spp. 70,000 fossil spp. marine fresh water terrestrial chitons snails nudibranchs clams oysters nautiluses tusk shells slugs sea butterflies mussels squids/cuttlefish
Chapter 10: Mollusca Latin: soft 90,000 living spp. 70,000 fossil spp. marine fresh water terrestrial chitons snails nudibranchs clams oysters nautiluses tusk shells slugs sea butterflies mussels squids/cuttlefish
Mollusks and Annelids. Chapter 23+
 Mollusks and Annelids Chapter 23+ 1 Annelids and Mollusks Coelomates Trochophore larvae Bilateral symmetry More complex organ systems 2 Moving On Up 3 Coelom Coelomates Evolutionary milestone True body
Mollusks and Annelids Chapter 23+ 1 Annelids and Mollusks Coelomates Trochophore larvae Bilateral symmetry More complex organ systems 2 Moving On Up 3 Coelom Coelomates Evolutionary milestone True body
Clam Dissection. Introduction. Taxonomy
 Introduction The phylum Mollusca includes snails, clams, chitons, slugs, limpets, octopi, and squid. As mollusks develop from a fertilized egg to an adult, most pass through a larval stage called the trocophore.
Introduction The phylum Mollusca includes snails, clams, chitons, slugs, limpets, octopi, and squid. As mollusks develop from a fertilized egg to an adult, most pass through a larval stage called the trocophore.
Phylum: Porifera (sponges)
 Phylum: Porifera (sponges) (8,761 known species) General Description: Simplest animals, multicellular No organs or body systems Skeleton composed of spongin (soft) and spicules (hard) Symmetry: Asymmetrical
Phylum: Porifera (sponges) (8,761 known species) General Description: Simplest animals, multicellular No organs or body systems Skeleton composed of spongin (soft) and spicules (hard) Symmetry: Asymmetrical
Each unit contains components of most organ systems. Increased burrowing efficiency by permitting movement of segments
 CHAPTER 17 Annelids Characteristics of the Phylum Annelida Diversity Exhibit segmentation or Bodies composed of units Each unit contains components of most organ systems Increased burrowing efficiency
CHAPTER 17 Annelids Characteristics of the Phylum Annelida Diversity Exhibit segmentation or Bodies composed of units Each unit contains components of most organ systems Increased burrowing efficiency
Figure 32.8 Animal phylogeny based on sequencing of SSU-rRNA
 Figure 32.8 Animal phylogeny based on sequencing of SSU-rRNA Polychaetes Representative Annelids Oligochaetes Marine worms Hirudineans Terrestrial & aquatic Leeches - Aquatic & terrestrial Annelid Circulatory,
Figure 32.8 Animal phylogeny based on sequencing of SSU-rRNA Polychaetes Representative Annelids Oligochaetes Marine worms Hirudineans Terrestrial & aquatic Leeches - Aquatic & terrestrial Annelid Circulatory,
Molluscs. General Introduction. Phylum Mollusca 4/25/2018. Chapter 16. Ancient successful and diverse phylum
 Molluscs Chapter 16 General Introduction Ancient successful and diverse phylum Second largest animal phylum About 50,000 extant species 35,000 fossil species 7 classes Phylum Mollusca Phylum Mollusca includes
Molluscs Chapter 16 General Introduction Ancient successful and diverse phylum Second largest animal phylum About 50,000 extant species 35,000 fossil species 7 classes Phylum Mollusca Phylum Mollusca includes
Stonefly. Gilled Snails
 Mid-Michigan Macroinvertebrates Identification Guide & Descriptions Mayfly Nymphs have 3 tail filaments occasionally 2 tail filaments never paddle or fan-like Feathery gills line the sides of the abdomen
Mid-Michigan Macroinvertebrates Identification Guide & Descriptions Mayfly Nymphs have 3 tail filaments occasionally 2 tail filaments never paddle or fan-like Feathery gills line the sides of the abdomen
Class Polychaeta: Marine Worms
 Class Polychaeta: Marine Worms Animal Phyla Phylum Mollusca (Snails, Clams, Octopods and Allies): Radula: rasping tongue Shell: 3 layers, mostly calcium carbonate Inner-most = nacre = mother of pearl Mantle:
Class Polychaeta: Marine Worms Animal Phyla Phylum Mollusca (Snails, Clams, Octopods and Allies): Radula: rasping tongue Shell: 3 layers, mostly calcium carbonate Inner-most = nacre = mother of pearl Mantle:
Unit 18.2: Mollusks and Annelids
 Unit 18.2: Mollusks and Annelids Lesson Objectives Describe invertebrates in the phylum Mollusca. Summarize the characteristics of annelids. Vocabulary Annelida deposit feeder gills heart mantle Mollusca
Unit 18.2: Mollusks and Annelids Lesson Objectives Describe invertebrates in the phylum Mollusca. Summarize the characteristics of annelids. Vocabulary Annelida deposit feeder gills heart mantle Mollusca
General Molluscan Characteristics
 Phylum Mollusca General Molluscan Characteristics = mollis = soft Bilateral symmetry, secondarily assymetrcial => Soft bodied animals Coelomate and triploblastic Rich fossil record Next to arthropods,
Phylum Mollusca General Molluscan Characteristics = mollis = soft Bilateral symmetry, secondarily assymetrcial => Soft bodied animals Coelomate and triploblastic Rich fossil record Next to arthropods,
scallops Zebra Mussel ctenidium
 7650 species Mostly marine About one thousand species live in fresh water clams scallops Zebra Mussel mussels oysters Zebras on native clams (Unionidae) ctenidium Right valve umbo Adductor muscle Best
7650 species Mostly marine About one thousand species live in fresh water clams scallops Zebra Mussel mussels oysters Zebras on native clams (Unionidae) ctenidium Right valve umbo Adductor muscle Best
ANIMAL FORM AND FUNCTION CEPHALOPODS (PHYLUM MOLLUSCA)
 ANIMAL FORM AND FUNCTION CEPHALOPODS (PHYLUM MOLLUSCA) As part of our continued exploration of the animal kingdom today we will perform a dissection of a squid, which is a member of the Class Cephalopoda
ANIMAL FORM AND FUNCTION CEPHALOPODS (PHYLUM MOLLUSCA) As part of our continued exploration of the animal kingdom today we will perform a dissection of a squid, which is a member of the Class Cephalopoda
Phylum Mollusca. Introduction: Uses and economic value: Problems with mollusks: Intro. Cont. More Intro. Material
 Introduction: Phylum Mollusca ~ 110,000 known species Named for the Latin word Molluscus meaning soft of body. Most are marine, but they can be both aquatic or terrestrial. Live in all areas: arctic to
Introduction: Phylum Mollusca ~ 110,000 known species Named for the Latin word Molluscus meaning soft of body. Most are marine, but they can be both aquatic or terrestrial. Live in all areas: arctic to
Mollusks are soft bodied animals that have an internal or external shell, a similar body plan consisting of four basic parts: a foot, mantle, shell,
 Mollusca Mollusks are soft bodied animals that have an internal or external shell, a similar body plan consisting of four basic parts: a foot, mantle, shell, and visceral mass. Mollusks also possess a
Mollusca Mollusks are soft bodied animals that have an internal or external shell, a similar body plan consisting of four basic parts: a foot, mantle, shell, and visceral mass. Mollusks also possess a
INDICATOR BENTHIC MACROINVERTEBRATE SPECIES AND THEIR CHARACTERISTICS
 Coelenterata (Hydras) Turbellaria (Flatworms) A tube with tentacles Reproduces asexually by budding Movement: sessile, attached or fixed, not free moving Colour: clear to whitish Flattened shape Distinct
Coelenterata (Hydras) Turbellaria (Flatworms) A tube with tentacles Reproduces asexually by budding Movement: sessile, attached or fixed, not free moving Colour: clear to whitish Flattened shape Distinct
Mollusks and Annelids
 Mollusks and Annelids Bởi: OpenStaxCollege The mollusks are a diverse group (85,000 described species) of mostly marine species. They have a variety of forms, ranging from large predatory squid and octopus,
Mollusks and Annelids Bởi: OpenStaxCollege The mollusks are a diverse group (85,000 described species) of mostly marine species. They have a variety of forms, ranging from large predatory squid and octopus,
Mollusca: Class Cephalopoda. Lecture 11
 Mollusca: Class Cephalopoda Lecture 11 Cephalophod Characteristics Characteristics of class All marine Most 6-70 cm up to 20m Architeuthis Shell divided by septa, chambers connected by siphuncle Closed
Mollusca: Class Cephalopoda Lecture 11 Cephalophod Characteristics Characteristics of class All marine Most 6-70 cm up to 20m Architeuthis Shell divided by septa, chambers connected by siphuncle Closed
Phylum Mollusca. By: Christa Jewett, Instructor
 Phylum Mollusca By: Christa Jewett, Instructor For since the creation of the world God s invisible qualities His eternal power and divine nature have been clearly seen, being understood from what has been
Phylum Mollusca By: Christa Jewett, Instructor For since the creation of the world God s invisible qualities His eternal power and divine nature have been clearly seen, being understood from what has been
Have You Wondered? College of Marine Sciences, Shanghai Ocean University
 Have You Wondered? 1. What role sponges play in marine ecosystems? 2. Why some animals are radially symmetrical? 3. If all gelatinous animals are jellyfishes? 4. What flatworms are? 5. What a lophophorate
Have You Wondered? 1. What role sponges play in marine ecosystems? 2. Why some animals are radially symmetrical? 3. If all gelatinous animals are jellyfishes? 4. What flatworms are? 5. What a lophophorate
Molluscs: Gastropod Middle School Student Edition Lab Activity: The Gastropods
 SNIPS AND SNAILS AND GASTROPOD TAILS Molluscs are a clan of closely related animals that includes snails and slugs, clams and oysters, and even squid and octopi. The name comes from the Latin mollus, meaning
SNIPS AND SNAILS AND GASTROPOD TAILS Molluscs are a clan of closely related animals that includes snails and slugs, clams and oysters, and even squid and octopi. The name comes from the Latin mollus, meaning
A. Porifera (sponges): B. Cnidaria (jellies, hydra, sea anemones, and corals):
 Invertebrates Notes A. Porifera (sponges): Porifera literally means. Most sponges are. They are that collect food particles from the water as they pass through flagellated cells called. These cells then
Invertebrates Notes A. Porifera (sponges): Porifera literally means. Most sponges are. They are that collect food particles from the water as they pass through flagellated cells called. These cells then
What Is an Annelid? Annelids are worms with segmented bodies. They have a true coelom that is lined with tissue derived from mesoderm.
 What Is an Annelid? What Is an Annelid? Phylum: Annelidae Annelids are worms with segmented bodies. They have a true coelom that is lined with tissue derived from mesoderm. Three Germ Layers of an Annelid
What Is an Annelid? What Is an Annelid? Phylum: Annelidae Annelids are worms with segmented bodies. They have a true coelom that is lined with tissue derived from mesoderm. Three Germ Layers of an Annelid
Chapter 5 Marine Protozoans and Invertebrates
 Chapter 5 Marine Protozoans and Invertebrates I. The Protozoans A. Kindgom Protista a catch-all category B. Characteristics 1. Mode of nutrition 2. Single-celled or multicellular? 3. Cell structure 4.
Chapter 5 Marine Protozoans and Invertebrates I. The Protozoans A. Kindgom Protista a catch-all category B. Characteristics 1. Mode of nutrition 2. Single-celled or multicellular? 3. Cell structure 4.
What is an insect? An insect is an invertebrate (an animal with no spine) that has three pairs of legs and three
 What is an insect? An insect is an invertebrate (an animal with no spine) that has three pairs of legs and three Small minnow mayfly body divisions. The mouth, antennae, and eyes are located on the head;
What is an insect? An insect is an invertebrate (an animal with no spine) that has three pairs of legs and three Small minnow mayfly body divisions. The mouth, antennae, and eyes are located on the head;
PHYLUM: PLATHYHELMINTHES
 PHYLUM: PLATHYHELMINTHES FLATWORMS Free living (living independently i.e. not attached) Bilaterally symmetrical with a definite front and back, and with left and right sides. Mobile creeping animals. Concentration
PHYLUM: PLATHYHELMINTHES FLATWORMS Free living (living independently i.e. not attached) Bilaterally symmetrical with a definite front and back, and with left and right sides. Mobile creeping animals. Concentration
ZOOLOGY SEGMENTED WORMS (Phylum Annelida)
 ZOOLOGY SEGMENTED WORMS (Phylum Annelida) I. Compared and Contrasted to Phylum Mollusca. A. They are like the molluscs in that they 1. are eucoelomate animals. 2. have specialized sense organs. 3. have
ZOOLOGY SEGMENTED WORMS (Phylum Annelida) I. Compared and Contrasted to Phylum Mollusca. A. They are like the molluscs in that they 1. are eucoelomate animals. 2. have specialized sense organs. 3. have
What is an animal? Introduction to Animals 2. Phylum Mollusca. Phylum Mollusca 4/20/2016
 What is an animal? Introduction to Animals 2 Multicellular chemoorganoheterotrophs Eukaryotes that lack cell walls and chloroplasts Have mitochondria Are motile at some point in their lives Snails, Octopus,
What is an animal? Introduction to Animals 2 Multicellular chemoorganoheterotrophs Eukaryotes that lack cell walls and chloroplasts Have mitochondria Are motile at some point in their lives Snails, Octopus,
Mollusc Adaptation and Diversity
 Mollusc Adaptation and Diversity Grade Level: grades 9-12 Lesson Summary: Students will examine a variety of live and preserved molluscs. They will compare and contrast body forms and try to relate the
Mollusc Adaptation and Diversity Grade Level: grades 9-12 Lesson Summary: Students will examine a variety of live and preserved molluscs. They will compare and contrast body forms and try to relate the
Topic The external and internal anatomy of a clam is typical of bivalves.
 Clam Dissection Topic The external and internal anatomy of a clam is typical of bivalves. Introduction Mollusks are some of the most common marine invertebrates. All mollusks have several characteristic
Clam Dissection Topic The external and internal anatomy of a clam is typical of bivalves. Introduction Mollusks are some of the most common marine invertebrates. All mollusks have several characteristic
Fish. Water Dwelling Animals
 Fish Water Dwelling Animals Class Agnatha (Jawless fish) They are believed to be the most primitive and oldest vertebrates. Lamprey and hagfish are the only 2 living members of this class and are placed
Fish Water Dwelling Animals Class Agnatha (Jawless fish) They are believed to be the most primitive and oldest vertebrates. Lamprey and hagfish are the only 2 living members of this class and are placed
The Education Program at the New Jersey Marine Sciences Consortium SEASHELL HOMES. Following completion of this lesson, students will be able to:
 The Education Program at the New Jersey Marine Sciences Consortium njmsc.org SEASHELL HOMES OVERVIEW OBJECTIVES During this interdisciplinary lesson, students listen to a story about seashells, discuss
The Education Program at the New Jersey Marine Sciences Consortium njmsc.org SEASHELL HOMES OVERVIEW OBJECTIVES During this interdisciplinary lesson, students listen to a story about seashells, discuss
What is an animal? 10/22/17. Bio 242 Laboratory Module 2
 Bio 242 Laboratory Module 2 Theme: Evolution shapes the flow and pattern of information through phylogenetic lineages, evident in the linkage between form and function Objectives -we will track the effects
Bio 242 Laboratory Module 2 Theme: Evolution shapes the flow and pattern of information through phylogenetic lineages, evident in the linkage between form and function Objectives -we will track the effects
Requirements for Animal Life. Phylum Bryozoa. Colonial Bryozoans. A lophophore is a structure used for:
 Requirements for Animal Life Animal phylogeny based on sequencing of SSU-rRNA The demands of 3 unique environments Marine, freshwater, terrestrial Gas exchange Nutrition Distribution and transport Disposal
Requirements for Animal Life Animal phylogeny based on sequencing of SSU-rRNA The demands of 3 unique environments Marine, freshwater, terrestrial Gas exchange Nutrition Distribution and transport Disposal
Henry Guan, Akash Kashyap, and Angus Qian
 Henry Guan, Akash Kashyap, and Angus Qian http://peterbe.mobi/plog/interior-octopus/octopus.jpg Akash Kashyap Overview 85, 000 species Marine, Terrestrial, Freshwater habitats Very Diverse Classes: Chitons,
Henry Guan, Akash Kashyap, and Angus Qian http://peterbe.mobi/plog/interior-octopus/octopus.jpg Akash Kashyap Overview 85, 000 species Marine, Terrestrial, Freshwater habitats Very Diverse Classes: Chitons,
Spiny skinned animals with radial symmetrical body plan. Rays emanating from a common center. Internal skeleton of hardened plates of calcium
 Echinodermata Spiny skinned animals with radial symmetrical body plan. Rays emanating from a common center. Internal skeleton of hardened plates of calcium carbonate. Water vascular system and tube feet
Echinodermata Spiny skinned animals with radial symmetrical body plan. Rays emanating from a common center. Internal skeleton of hardened plates of calcium carbonate. Water vascular system and tube feet
Phylum Platyhelminthes Phylum Nematoda Phylum Mollusca. By: Jerzylin, Beata & Jennifer
 Phylum Platyhelminthes Phylum Nematoda Phylum Mollusca By: Jerzylin, Beata & Jennifer Phylum Platyhelminthes Common Characteristics: Triploblastic Bilateral Symmetry Protostome No true stomach structure
Phylum Platyhelminthes Phylum Nematoda Phylum Mollusca By: Jerzylin, Beata & Jennifer Phylum Platyhelminthes Common Characteristics: Triploblastic Bilateral Symmetry Protostome No true stomach structure
 OCTOPUS Found throughout the world in tropical, warm and cold temperate waters - the octopus is a bottom dweller, spending much of its life in hiding, usually in a hole among rocks. All octopus species
OCTOPUS Found throughout the world in tropical, warm and cold temperate waters - the octopus is a bottom dweller, spending much of its life in hiding, usually in a hole among rocks. All octopus species
Making the Most of Your Monitoring Using Macroinvertebrates
 Making the Most of Your Monitoring Using Macroinvertebrates Benthic Macroinvertebrates What are they? Why are they important? Provide food for fish and other organisms Feed on algae, organic matter, and
Making the Most of Your Monitoring Using Macroinvertebrates Benthic Macroinvertebrates What are they? Why are they important? Provide food for fish and other organisms Feed on algae, organic matter, and
Chapter 10. Part 1: Cartilaginous Fishes
 Chapter 10 Part 1: Cartilaginous Fishes Objectives Understand how hagfishes and lampreys differ from all other fishes. Describe how sharks, skates, and rays are related. Differentiate between cartilaginous
Chapter 10 Part 1: Cartilaginous Fishes Objectives Understand how hagfishes and lampreys differ from all other fishes. Describe how sharks, skates, and rays are related. Differentiate between cartilaginous
Mollusca. BIO2135 Animal Form & Function. Page 1. Phylum Mollusca. Lophotrochozoa. Trochozoans. BIO2135 Animal Form and Function 1 10:29 AM
 Phylum Mollusca 1 10:29 AM Lophotrochozoa Either presence of a U shaped gut and lophophore or Trochophore larval stage Porifera Placozoa Cnidaria Ctenophora Platyhelminthes Gastrotricha Gnathostomulida
Phylum Mollusca 1 10:29 AM Lophotrochozoa Either presence of a U shaped gut and lophophore or Trochophore larval stage Porifera Placozoa Cnidaria Ctenophora Platyhelminthes Gastrotricha Gnathostomulida
Mollusks and Annelids *
 OpenStax-CNX module: m45526 1 Mollusks and Annelids * OpenStax This work is produced by OpenStax-CNX and licensed under the Creative Commons Attribution License 3.0 By the end of this section, you will
OpenStax-CNX module: m45526 1 Mollusks and Annelids * OpenStax This work is produced by OpenStax-CNX and licensed under the Creative Commons Attribution License 3.0 By the end of this section, you will
ANIMAL KINGDOM: PHYLUM MOLLUSCA
 ANIMAL KINGDOM: PHYLUM MOLLUSCA Latin: molluscus - soft Materials: A live snail and snail specimen A set of pictures, labels, and definitions illustrating the external parts of the mollusk A booklet of
ANIMAL KINGDOM: PHYLUM MOLLUSCA Latin: molluscus - soft Materials: A live snail and snail specimen A set of pictures, labels, and definitions illustrating the external parts of the mollusk A booklet of
Dogfish Shark Dissection
 Dogfish Shark Dissection Name Date Period Fun Facts: Materials: The teeth of sharks are modified scales embedded in the skin of its mouth Sharks have pits on their face used to detect electric fields Sharks
Dogfish Shark Dissection Name Date Period Fun Facts: Materials: The teeth of sharks are modified scales embedded in the skin of its mouth Sharks have pits on their face used to detect electric fields Sharks
Shell Honour Created by I & L Weir Queensland, Australia May 2007
 Shell Honour Created by I & L Weir Queensland, Australia May 2007 Q1. What is the meaning of Mollusc? Animal with a soft body usually protected by a shell. E.g. Snails, mussels, oysters and cockles. Q2.
Shell Honour Created by I & L Weir Queensland, Australia May 2007 Q1. What is the meaning of Mollusc? Animal with a soft body usually protected by a shell. E.g. Snails, mussels, oysters and cockles. Q2.
Bivalves: Mollusks that Matter
 Objective Bivalves: Mollusks that Matter Version 6/05 Students will understand the anatomy and physiology of mussels, and understand why they may pose health risks to humans. National Science Education
Objective Bivalves: Mollusks that Matter Version 6/05 Students will understand the anatomy and physiology of mussels, and understand why they may pose health risks to humans. National Science Education
ZOO 2040 Biology of Animals Topic 8. Molluscs
 Phylum Mollusca Second-largest phylum: 50,000-110,000 living species, over 35,000 fossil species. Extremely variable in:! Size (80% are 1000 kg)! Morphology (snails/slugs,
Phylum Mollusca Second-largest phylum: 50,000-110,000 living species, over 35,000 fossil species. Extremely variable in:! Size (80% are 1000 kg)! Morphology (snails/slugs,
CHAPTER 22. Echinoderms 22-1
 CHAPTER 22 Echinoderms 22-1 Phylum Echinodermata: Diversity and Characteristics Characteristics All members have a calcareous skeleton Spiny endoskeleton consists of plates Unique water-vascular system
CHAPTER 22 Echinoderms 22-1 Phylum Echinodermata: Diversity and Characteristics Characteristics All members have a calcareous skeleton Spiny endoskeleton consists of plates Unique water-vascular system
Contents. Foreword 5 About the Authors 7 Contributors 9 Acknowledgements 11
 Contents Foreword 5 About the Authors 7 Contributors 9 Acknowledgements 11 1. Introduction a. The Scheme of this Book 15 b. The Approach to Case Taking 17 c. The Importance of Classification 22 d. Recognising
Contents Foreword 5 About the Authors 7 Contributors 9 Acknowledgements 11 1. Introduction a. The Scheme of this Book 15 b. The Approach to Case Taking 17 c. The Importance of Classification 22 d. Recognising
27/12/2012. Learning Outcome G4
 Learning Outcome G4 Learning Outcome G4 Analyse the increasing complexity of the Phylum Mollusca, the Phylum Echinodermata, and the Phylum Arthropoda Phylum Mollusca, Echinodermata & Arthropoda Students
Learning Outcome G4 Learning Outcome G4 Analyse the increasing complexity of the Phylum Mollusca, the Phylum Echinodermata, and the Phylum Arthropoda Phylum Mollusca, Echinodermata & Arthropoda Students
Point Rating: 3 Size: 10 mm Description: Caddisfly larvae are builders. They make sticky silk from their spit and use it to spin webs for trapping
 Point Rating: 3 Size: 10 mm Description: Caddisfly larvae are builders. They make sticky silk from their spit and use it to spin webs for trapping other insects. Other species use the silk as glue that
Point Rating: 3 Size: 10 mm Description: Caddisfly larvae are builders. They make sticky silk from their spit and use it to spin webs for trapping other insects. Other species use the silk as glue that
Chapter 6 SPONGES. Invertebrates. Sponges. Pore-Bearers. Movement of Water
 Invertebrates Chapter 6 Animals Without Backbones Animals that lack a backbone are called invertebrates. It is estimated that 97% of all species of animals are invertebrates. With the exception of insects,
Invertebrates Chapter 6 Animals Without Backbones Animals that lack a backbone are called invertebrates. It is estimated that 97% of all species of animals are invertebrates. With the exception of insects,
Mollusks. Section 25.3
 Section 25.3 Objectives Evaluate the importance of the coelom to mollusks. Interpret the function of the mantle and its adaptive advantage to mollusks. Analyze the importance of mucus and the muscular
Section 25.3 Objectives Evaluate the importance of the coelom to mollusks. Interpret the function of the mantle and its adaptive advantage to mollusks. Analyze the importance of mucus and the muscular
Introductory List to Local Marine Animals
 Introductory List to Local Marine Animals During your visit to the Huntsman you will have the opportunity to see and investigate many different types of marine animals, especially invertebrates. Below
Introductory List to Local Marine Animals During your visit to the Huntsman you will have the opportunity to see and investigate many different types of marine animals, especially invertebrates. Below
ABCs & Name the parts!
 ABCs & Name the parts! Objective: These two activities are used to introduce the students to the variety of marine life living in European waters while learning their ABCs and practicing their letter writing.
ABCs & Name the parts! Objective: These two activities are used to introduce the students to the variety of marine life living in European waters while learning their ABCs and practicing their letter writing.
2 Mollusks and Annelid Worms
 CHAPTER 15 2 Mollusks and Annelid Worms SECTION Invertebrates BEFORE YOU READ After you read this section, you should be able to answer these questions: What are the four features of mollusks? What are
CHAPTER 15 2 Mollusks and Annelid Worms SECTION Invertebrates BEFORE YOU READ After you read this section, you should be able to answer these questions: What are the four features of mollusks? What are
Unit 19.2: Fish. Vocabulary fish spawning swim bladder
 Unit 19.2: Fish Lesson Objectives Describe structure and function in fish. Explain how fish reproduce and develop. Give an overview of the five living classes of fish. Summarize the evolution of fish.
Unit 19.2: Fish Lesson Objectives Describe structure and function in fish. Explain how fish reproduce and develop. Give an overview of the five living classes of fish. Summarize the evolution of fish.
Symmetry. Asymmetrical- no shape. Radial- same in half when cut any angle. Bilateral- having a distinct right and left side
 Symmetry Asymmetrical- no shape Radial- same in half when cut any angle Bilateral- having a distinct right and left side Invertebrates 95% of Animals No Backbone The simplest animals and they do not have
Symmetry Asymmetrical- no shape Radial- same in half when cut any angle Bilateral- having a distinct right and left side Invertebrates 95% of Animals No Backbone The simplest animals and they do not have
Edible, and. Coral Reefs! Photo: CEDixon
 Spreadable, Edible, and Incredible Coral Reefs! Carrie Dixon Discovery Hall Programs Dauphin Island Sea Lab, AL Photo: CEDixon National Science Content Standards Life Science Content Standard, Grades K-4:
Spreadable, Edible, and Incredible Coral Reefs! Carrie Dixon Discovery Hall Programs Dauphin Island Sea Lab, AL Photo: CEDixon National Science Content Standards Life Science Content Standard, Grades K-4:
Guide to Orders 39 CEPHALOPODS TECHNICAL TERMS AND MEASUREMENTS AND GUIDE TO ORDERS. Order SEPIOIDEA Cuttlefishes
 Guide to Orders 39 CEPHALOPODS All species of octopus, squid and cuttlefish are eaten locally and are of commercial importance, also used as bait for various fish species & lobsters. The Guide to Orders
Guide to Orders 39 CEPHALOPODS All species of octopus, squid and cuttlefish are eaten locally and are of commercial importance, also used as bait for various fish species & lobsters. The Guide to Orders
-8- spinous. nape caudal fin. body depth. pectoral fin. anus. total length Fig. 4
 click for previous page -8-1.3 Illustrated Glossary of Technical Terms and Measurements External Morphology and Measurements spinous dorsal fin soft nape caudal fin interorbital body depth snout lateral
click for previous page -8-1.3 Illustrated Glossary of Technical Terms and Measurements External Morphology and Measurements spinous dorsal fin soft nape caudal fin interorbital body depth snout lateral
Animal Evolution: Chordate and Vertebrate Evolution and Diversity (Learning Outline)
 Animal Evolution: Chordate and Vertebrate Evolution and Diversity (Learning Outline) 1. Distinguishing features of the phylum Chordata and representative organisms. 2. Highlights of evolutionary steps
Animal Evolution: Chordate and Vertebrate Evolution and Diversity (Learning Outline) 1. Distinguishing features of the phylum Chordata and representative organisms. 2. Highlights of evolutionary steps
Origin and Importance! ! Fish were the first vertebrates to appear on Earth about 500 million years ago.
 2/9/14 Origin and Importance Evolution Marine Fish Fish were the first vertebrates to appear on Earth about 500 million years ago. Fish are the most economically important organism and are a vital source
2/9/14 Origin and Importance Evolution Marine Fish Fish were the first vertebrates to appear on Earth about 500 million years ago. Fish are the most economically important organism and are a vital source
STUDIES IN ANIMAL LOCOMOTION
 STUDIES IN ANIMAL LOCOMOTION VIII. THE KINETICS OF LOCOMOTION OF NEREIS DIVERSICOLOR BY J. GRAY Zoological Laboratory, Cambridge (Received 30 March 1938) (With One Plate and Eight Text-figures) THE locomotory
STUDIES IN ANIMAL LOCOMOTION VIII. THE KINETICS OF LOCOMOTION OF NEREIS DIVERSICOLOR BY J. GRAY Zoological Laboratory, Cambridge (Received 30 March 1938) (With One Plate and Eight Text-figures) THE locomotory
Cephalopods Nautilus, Cuttlefish, Octopus, Squid
 Cephalopods Nautilus, Cuttlefish, Octopus, Squid Cephalopod Class They have three (3) hearts cephalo = head pod = foot CHARACTERISTICS Organs two pump blood to the gills and the other pumps blood to the
Cephalopods Nautilus, Cuttlefish, Octopus, Squid Cephalopod Class They have three (3) hearts cephalo = head pod = foot CHARACTERISTICS Organs two pump blood to the gills and the other pumps blood to the
General Characters of Trematodes
 Parasitology Department General Characters of Trematodes By Hala Elwakil, MD Intended Learning Outcomes By the end of this lecture, the student will be able to know: 1. General morphology of trematodes
Parasitology Department General Characters of Trematodes By Hala Elwakil, MD Intended Learning Outcomes By the end of this lecture, the student will be able to know: 1. General morphology of trematodes
External Anatomy Dissection Guide
 External Anatomy Dissection Guide Dissection is the cutting of a dead animal or a plant into separate parts for the purpose of careful and detailed examination and study. The external anatomy is as important
External Anatomy Dissection Guide Dissection is the cutting of a dead animal or a plant into separate parts for the purpose of careful and detailed examination and study. The external anatomy is as important
Chapter 16. Molluscs. Characteristics. Mollusc Diversity
 Copyright The McGraw-Hill Companies, Inc. Permission required for reproduction or display. Chapter 16 Molluscs Characteristics They contain nearly 50,000 living species and 35,000 fossil species. They
Copyright The McGraw-Hill Companies, Inc. Permission required for reproduction or display. Chapter 16 Molluscs Characteristics They contain nearly 50,000 living species and 35,000 fossil species. They
Life Lecture Notes Chapter 13 Mollusca unsegmented bodied critters Valve mantle ii. Bilateral symmetry Gills foot Radula Visceral mass
 Life Lecture Notes Chapter 13 I. Phylum Mollusca a. General Characteristics i. Soft unsegmented bodied critters often covered by a shell called a Valve which is produced by the mantle. ii. Bilateral symmetry
Life Lecture Notes Chapter 13 I. Phylum Mollusca a. General Characteristics i. Soft unsegmented bodied critters often covered by a shell called a Valve which is produced by the mantle. ii. Bilateral symmetry
and Echinoderms Mollusks, Arthropods, Chapter 3 3JZ JCJeEJ O Insects O Mollusks O Echinoderms Diversity and Adaptations Chapter Preview
 Chapter Mollusks, Arthropods, and Echinoderms 3 3JZ JCJeEJ Diversity and Adaptations What are the key characteristics of mollusks, arthropods, and echinoderms? Chapter Preview O Mollusks Discover How Can
Chapter Mollusks, Arthropods, and Echinoderms 3 3JZ JCJeEJ Diversity and Adaptations What are the key characteristics of mollusks, arthropods, and echinoderms? Chapter Preview O Mollusks Discover How Can
Coelomate Worms: Sipunculans, Pogonophorans, Echiurans and Vestimenifera
 Coelomate Worms Coelomate Worms: Sipunculans, Pogonophorans, Echiurans and Vestimenifera Ectoderm Mesoderm Dt Endoderm Coelom Often dismissed as minor or lesser Comprise less than 600 species total Never
Coelomate Worms Coelomate Worms: Sipunculans, Pogonophorans, Echiurans and Vestimenifera Ectoderm Mesoderm Dt Endoderm Coelom Often dismissed as minor or lesser Comprise less than 600 species total Never
Animal Diversity. Kingdom Animalia
 7ch11 Animal Diversity Kingdom Animalia Animal Characteristics 1. animals are eukaryotes and are multicellular 2. cells are specialized for different functions (vision,digestion,reproduction) 3. protein,
7ch11 Animal Diversity Kingdom Animalia Animal Characteristics 1. animals are eukaryotes and are multicellular 2. cells are specialized for different functions (vision,digestion,reproduction) 3. protein,
Chapter 12 Part 2. The Worms Platyhelminthes, Nematoda & Annelida
 Chapter 12 Part 2 The Worms Platyhelminthes, Nematoda & Annelida Phylum: Platyhelminthes Examples: Flatworms, Planaria sp., tapeworms and blood flukes Acoelomate, Invertebrate, Simplest critter w/ bilateral
Chapter 12 Part 2 The Worms Platyhelminthes, Nematoda & Annelida Phylum: Platyhelminthes Examples: Flatworms, Planaria sp., tapeworms and blood flukes Acoelomate, Invertebrate, Simplest critter w/ bilateral
Is a seahorse a fish, amphibian, or reptile? FISH
 Ch. 30 Loulousis Is a seahorse a fish, amphibian, or reptile? FISH Vertebral Column (Endoskeleton) Gills Single-loop circulation Kidneys Also share all the characteristics of chordates such as notochord,
Ch. 30 Loulousis Is a seahorse a fish, amphibian, or reptile? FISH Vertebral Column (Endoskeleton) Gills Single-loop circulation Kidneys Also share all the characteristics of chordates such as notochord,
Echinoderms. Phylum Echinodermata
 Echinoderms Phylum Echinodermata spiny skinned or hedgehog skin sea stars (starfish), sea urchins, sea cucumbers 6000 species radial symmetry in 2 o development bilateral symmetry in larva http://www.biologyreference.com/dn-ep/echinoderm.html
Echinoderms Phylum Echinodermata spiny skinned or hedgehog skin sea stars (starfish), sea urchins, sea cucumbers 6000 species radial symmetry in 2 o development bilateral symmetry in larva http://www.biologyreference.com/dn-ep/echinoderm.html
