Background on Schistosomiasis in the Latin American and Caribbean Region in the Context of Neglected Tropical Diseases Control
|
|
|
- Rosalyn Ramsey
- 6 years ago
- Views:
Transcription
1 Report: PAHO/WHO Preparatory Meeting on Epidemiological Data Needed to Plan Elimination of Schistosomiasis in the Caribbean (Grenada, December 2007) 1
2 Table of Contents Preface...1 Background...1 Summary of Presentations...2 Background and Objectives of Schistosomiasis Control at the Global and Regional Levels...2 Background on Schistosomiasis in the Latin American and Caribbean Region in the Context of Neglected Tropical Diseases Control...2 World Health Assembly Resolution and Role of PAHO/WHO...3 Successful Control and Elimination Programs in other WHO Regions and in Brazil...4 Schistosomiasis in Brazil...4 Successful Schistosomiasis Control Program in Africa...4 Situation Analysis of Schistosomiasis in Endemic Countries and Formerly-Endemic Countries...6 Suriname...6 St. Lucia...6 Puerto Rico...7 Issues on Surveillance, Endemicity, and Morbidity...7 Surveillance System for Communicable Disease and NTDs in the Caribbean...7 Challenges of Detection and Measurement of Schistosomiasis Morbidity...9 Cuba...9 Recommendations Action Points Suggested for Action by PAHO/WHO Next Steps Acknowledgements References Annexes Annex I: Agenda Annex II: List of Participants
3 Preface The purpose of this meeting was to meet and interchange with national authorities and Schistosomiasis specialists to gauge the level of interest, and estimate the time frame and resources needed for elimination of Schistosomiasis in the Caribbean. More specifically, this meeting aimed to identify and understand the existing Schistosomiasis surveillance and control program actions in endemic countries and formerly-endemic countries in the Caribbean. Furthermore, this meeting aimed to gather existing data useful to map the current prevalence of Schistosomiasis and Praziquantel treatment coverage in endemic countries, and to identify the necessary epidemiological and ecological data still needed to plan for Schistosomiasis elimination in the Caribbean. Background Schistosomiasis is a global health problem in the developing world, approximately 200 million people are infected and more than 650 million live in endemic areas. Schistosomiasis is a disease of the poor who live in conditions that favor transmission. Schistosomiasis is also an insidious disease, poorly recognized at early ages and disabling to men and women during their most productive years. Rarely fatal, but strongly linked to diarrhea, pain, fatigue, hemoglobin deficit, under nutrition, and reduced exercise tolerance; Schistosomiasis effects are not negligible for those who are infected and live in endemic areas where recurring infections are possible. Schistosomiasis is caused by schistosomes, which are parasitic trematode worms. Five species infect humans: Schistosoma mansoni, Schistosoma japonicum, Schistosoma mekongi, Schistosoma intercalatum, and Schistosoma haematobium. Schistosoma infections occur through direct contact with fresh water that harbors free-swimming larval forms of the parasite. Free-swimming larva, known as cercariae, are able to penetrate human skin to cause infection. S. mansoni remains endemic in parts of Brazil, Venezuela, and the Caribbean. Schistosomiasis causes deep acute and chronic morbidity among infected people. Acute Schistosomiasis occurs days after contact with contaminated water. The clinical presentation of acute Schistosomiasis includes fever, headache, generalized myalgias, right-upper quadrant pain and bloody diarrhea. Up to 70 percent of people infected with S. mansoni also report respiratory symptoms. Chronic Schistosomiasis can be presented through gastrointestinal, liver, neurologic, and/or genitourinary pathologies. Schistosomes can live inside their host for years. Schistosomiasis results from the host s immune response to schistosome eggs for their antigens trigger a granulomatous reaction. Granulomas destroy the ova but result in fibrotic depositions in the host tissues. These develop at sites where eggs accumulate the most: intestine and liver for S. mansoni and S. japonicum infections and the genitourinary tract for S. haematobium. Neural pathologies are also known to occur when
4 schistosome eggs accumulate in the host s central nervous system. Higher prevalence of epilepsy and transverse myelitis are observed in communities where Schistosomiasis is endemic. Schistosomiasis is one of ten tropical diseases targeted for control by the Special Program for Research and Training in Tropical Diseases of the United Nations Development Program, the World Bank, and the World Health Organization. Control and elimination of Schistosomiasis and other Neglected Tropical Diseases is essential to ensure the promotion and protection of international human rights treaties and the right to the highest attainable standard of physical and mental health. The 54 th World Health Assembly set a goal of annually treating at least 75 percent of school-age children at risk of infection with Soil-Transmitted Helminths (STHs) and schistosomes and the World Health Organization s Global Plan to Combat Neglected Tropical Diseases includes Schistosomiasis as one of the neglected diseases that will initially be targeted with intensified efforts. [ADD PHOTO OF CD-ROMS] Summary of Presentations Background and Objectives of Schistosomiasis Control at the Global and Regional Levels Background on Schistosomiasis in the Latin American and Caribbean Region in the Context of Neglected Tropical Diseases Control [B. M.Rebollo Background am.pdf] Disability Adjusted Life Years (DALYs) are a useful unit that takes morbidity into account. DALYs measure the years of life that are lost due to disability and/or premature death. The group of diseases known as Neglected Tropical Diseases (NTDs) is responsible for the lost of 56.6 million DALYs. Among them, Schistosomiasis causes the loss of 10.4 million DALYs. NTDs are labeled as such because they are not perceived as a significant problem. These diseases are commonly left out of public health agendas and receive limited funding. NTDs are not usually subjected to mandatory notification or cause epidemiological emergencies. In addition, these diseases are not lucrative for the private sector, thus they generate limited interest for drug and vaccine development. In Latin American and the Caribbean NTDs cause high burden of morbidity and disability. Coinfections are common and result in a higher combined burden of disease. NTDs keep people in poverty and impede the achievement of the United Nation s Millennium Development Goals. Schistosomiasis is endemic in up to eight countries; these are Santa Lucia, Suriname, Guadalupe, Martinique, Dominican Republic, Puerto Rico, Venezuela, and Brazil. It is estimated that 1-3 million 2
5 people are infected, the majority of which reside in NE Brazil and Venezuela. Moreover, it has been estimated that 25 million or more are at risk of disease. Despite these estimates, it is thought that prevalence and morbidity have decreased in historically endemic countries. New studies are needed to determine the actual epidemiological situation of Schistosomiasis in Latin America and the Caribbean. Children, adolescents, pregnant women and some agricultural workers are at greater risk of being infected by schistosomes. Since co-infection with soil-transmitted helminths is common, this allows a multi-disease focus strategy for prevention and control. Schistosomiasis is currently being evaluated for potential elimination in the Caribbean. World Health Assembly Resolution and Role of PAHO/WHO [C. M.Reboya-S.Ault & PAHO-WHO am.pdf] The hallmark clinical manifestation of Schistosomiasis and soil-transmitted helminths infections is blood and nutrients loss. Blood loss leads to iron deficiency anemia, which greatly contributes to growth retardation, stunting, wasting, reduced cognition, and poor school performance and attendance. In 2001, the World Health Assembly s resolution was approved by consensus of WHO member states. Resolution endorses regular antihelminthic treatment of high-risk groups living in areas where soil-transmitted helminths have public health consequences. Resolution mainly targets school-age children (SAC), ages 6-15, in addition to other groups at-risk such as: women of child bearing age, indigenous populations, ethnic minorities, shanty-town dwellers, AIDS patients, orphans and elderly, institutionalized population and certain occupational groups. In addition to endorsing administration of antihelminthic therapy, Resolution also endorses implementation of plans for basic sanitation and adequate safe water supply. It also promotes access to safe water, sanitation and health education through intersectoral cooperation. WHA endorses that any development activity that favors the emergence or spread of parasitic diseases is accompanied by preventive measures. To support WHA PAHO/WHO must provide advocacy in public forums and facilitate development of partnerships. PAHO/WHO also provides technical cooperation to Ministries of Health and other implementing partners. Technical cooperation includes surveys, resistance monitoring, drug donations when possible, procurements training, and resource mobilization. PAHO/WHO also aids in collection of SAC coverage data reported annually to WHO Geneva. Furthermore, PAHO can monitor and evaluate, and promote operational research and sustainability. 3
6 Successful Control and Elimination Programs in other WHO Regions and in Brazil Schistosomiasis in Brazil [D. N.Katz BRAZIL am.pdf] Schistosomiasis presents a difficult public health problem in Brazil. The prevalence estimates range between two and a half to six million infected people. Schistosomiasis severe form of infection yields 900 admissions to hospitals per year. This produces large medical care expenses and reduces productivity by 30 percent. Between 2002 and 2005, 129 patients were seen with severe forms of Schistosomiasis: 75 patients were observed with hepatosplenic forms and 54 patients with neuroschistosomiasis. Schistosomiasis control has been proven difficult in Brazil due to the wide distribution of intermediate hosts and the complexity of the transmission cycle. Low availability of dwellings with potable water and sewerage systems, and insufficient health education of the population at risk of infection also halt the advance of Schistosomiasis control. Additionally, the low sensitivity of diagnostic methods and cure rate of drugs add to the problem. Other local issues that have negatively impacted the control of Schistosomiasis in Brazil include unsatisfactory involvement of the municipalities, insufficient assistance provided to control activities, and inadequate use of data obtained through control programs. Despite the high prevalence of Schistosomiasis, Brazil has taken measures that have contributed to the reduction of the morbidity and mortality of the diseases. About 12.5 million treatments have been administered between 1977 and In addition, the risk of infection has been reduced through environmental sanitation. 934,449 dwellings received benefits regarding sanitary improvements between 1977 and Since the rural population has decreased from 69 percent in 1940 to 21 percent in 1999 the risk of exposure due to migration has also decreased. Moreover, there have been improvements of diagnosis and therapy. Chemotherapy aids greatly in reducing the burden of Schistosomiasis infection. It decreases the intensity of infection and prevalence, reverses the enlargement of liver and spleen and resolves anemia. Furthermore, chemotherapy resolves hepatic fibrosis, prevents the rise of cases with hepatosplenic form, and eliminates blood in feces. Successful Schistosomiasis Control Program in Africa [E. C.Macpherson AFRICA am.pdf] In Africa and Latin America, environmental conditions favor the growth of Schistosomiasis intermediate snail host, Biomphalaria and Schistosoma mansoni is or has the potential to become a public health problem in many areas. These areas commonly feature altitude less than 2000 meters and rainfall greater than 900 mm per year. 4
7 Large water bodies such as lakes, rivers, irrigated lands, and dams are also key for Schistosomiasis transmission and epidemiology, particularly in Africa. Heterogeneity of host factors including: genetic and immunological make-up, nutritional status, and age and gender, vastly influence the likelihood of exposure, transmission, infection, disease and outcome. Human behavior and socioeconomic status greatly increase the risk of exposure particularly in poor communities. Mathematical models of transmission dynamics show that mean intensity of infection is a key parameter in determining transmission and rates of infection over time. The prevalence of eggs found in feces peaks between the ages of 15 and 20. There is also, a strong association between water contact and rate of re-infection. This association is strongest between the ages of 8 and 11. Control measures concentrate on reducing morbidity and mortality through chemotherapy, and on the use to molluscicides to reduce snail populations. Additionally, prevention of contamination of potential transmission sites and exposure protection are essential for Schistosomiasis control. Other control measures include, access to safe water, and ventilated improved pit latrines. A single dose of Praziquantel is safe and efficient. School based strategies have been shown to reduce transmission and morbidity through the reduction of bladder and kidney pathology. Political support at the local village, district, national, and international levels is essential for the success of control programs. Integration with other control programs and assessment of the safety of drug combinations are also important factors that must be taken into account. Evidence of the effectiveness of targeted mass community-based treatment has been seen in Egypt. Between 1988 and 2001, Egypt has vastly reduced the prevalence of both Schistosoma mansoni and Schistosoma hematobium. The main objectives of the Schistosomiasis Control Initiative (SCI) are to encourage the development of a sustainable Schistosomiasis control programme in sub-saharan Africa and to reach at least 75 percent of school-aged children and other high risk groups with chemotherapy. SCI also aims to reduce Schistosomiasis related morbidity in high risk groups, to reduce prevalence and intensity of schistosomiasis infections and to reduce the burden due to intestinal helminths in the targeted situations. In 2002, the National Bilharzia control program in Uganda aimed to reduce morbidity due to Schistosomiasis and Soil-Transmitted Helminths by mass annual distribution of Praziquantel and Albendazole to school-aged children and to high-risk communities in endemic areas. The program was integrated with STHs and vitamin A campaigns. After three rounds of chemotherapy, hookworm prevalence was reduced to close to zero. In total, SCI has administrated over 43 million treatments for Schistosomiasis and STH in 6 sub- Saharan countries. It is estimated that over 20 million people have been cured from these infections. Regular annual treatments will be required to prevent re-infection. 5
8 Situation Analysis of Schistosomiasis in Endemic Countries and Formerly- Endemic Countries Suriname [F. D.Panchoe SURINAME pm.pdf] Schistosomiasis cases were first confirmed in Suriname in The only species of schistosome is Schistosoma mansoni. In Suriname, Schistosomiasis only occurs in coastal areas associated with shell ridges. Various studies have been performed to determine the prevalence rate; in 1974 prevalence rates as high as 45 percent were reported in Saramacca. Between 1973 and 1983 a phase 1 control program was launched in Saramacca to reduce Schistosomiasis prevalence. Surveys were conducted from 1997 to 2001 to determine prevalence rates in Saramacca, Commewijne, Paramaribo, and Wanica en Coronie. The highest prevalence shown in this study was 5 percent in Saramacca. Although at low prevalence rates, schistosomiasis is still endemic in Suriname. Prevalence varies between certain areas and age groups. General prevalence in study areas ranges from 0.3 to 4.7 percent, and it is significantly higher in the age group. High prevalence is also associated with occupational activities such as fishing and agriculture. Suriname recommendations for Schistosomiasis control and elimination include intense information campaigns, adequate treatment of infected people, and monitoring of people living in endemic areas through stool samples. Additionally surveillance, reduction of water contamination, and avoidance of contact with contaminated water are key elements for Schistosomiasis control. This will be accomplished by better disposal of feces and construction of latrines. Reporting systems at the local and national level, reinforcement of infrastructure in order to trace Schistosoma infections, and improving health worker s tools and education are also included in the recommendations. St. Lucia [G. A.Jaima ST. LUCIA pm.pdf] The majority of St. Lucia s rivers are located in the Southern area of the island; therefore this area is affected by Schistosomiasis the most. Past records show that Schistosomiasis in St. Lucia has been reduced but it is still more prevalent than Malaria. Schistosoma mansoni is the most identified parasite in St. Lucia with an incidence rate of 6 cases per 100,000 in Socio-economic status, environmental conditions and life style characteristics like contact with water, mode of fecal disposal and river activities are contributor factors of infection. Since 1995, 106 cases have been reported. Although the risk of Schistosomiasis is low in St. Lucia, it is still important to check the prevalence of the diseases with a screening program. Control strategies should be placed for the elimination of the disease. The priorities for the control strategies are health education, supply of drinking water, access to adequate healthcare facilities, prompt diagnosis and treatment, management of the environment and control of intermediate hosts. 6
9 Puerto Rico [H. G.Hillyer PUERTO RICO pm.pdf] First cases of Schistosomiasis in Puerto Rico were reported in Since then the prevalence of Schistosomiasis in Puerto Rico has fluctuated between 9.9 percent in the 1940s and 10 to 30 percent positive in the 1950s. In the 1950s the areas with highest prevalence were Jayuya, Cieba, Rio Piedras, Patillas, Guayama, and Caguas. In 1957 it was noted that the snail population was directly related to infection prevalence, and that multiparasitism was a common feature. Recent studies have shown that there are no new serologic or parasitological cases in children. Also shown was an age specific decrease. Also, no new clinical cases have been detected. For these reasons, Puerto Rico is on good grounds to eliminate Schistosomiasis. Antibody detection assays such as FAST-ELISA and IMMUNO-BLOT feature high specificity and sensitivity. These assays are useful for monitoring areas where transmission is low. As worm burden and egg load decrease, microscopy methods become insensitive, therefore antibody detection assays are the best screening tool. Immunodiagnostic technology is also cost-effective. Issues on Surveillance, Endemicity, and Morbidity Surveillance System for Communicable Disease and NTDs in the Caribbean [I. C.Frederickson CAREC am.pdf] The Caribbean Epidemiology Centre (CAREC) serves 21 member countries in the English-Speaking Caribbean. CAREC is public health information, service and consulting organization dedicated to improving the capability of member countries in epidemiology, laboratory technology and related public health disciplines through technical cooperation, service, training, and research. CAREC is divided into two divisions: laboratory and epidemiology. The mission of the laboratory division is to strengthen National Laboratory capabilities by providing microbiology reference and referral services. In addition, the laboratory division provides training and appropriate research for surveillance and control of communicable diseases. Its major program areas are vaccine preventable diseases, vector-borne diseases, HIV/AIDS/STDs, diarrheal diseases including food-borne illness, mycobacterial diseases, antibiotic resistance monitoring and quality assurance. The epidemiology division collects, collates, and analyses data obtained via national surveillance systems on communicable and chronic diseases, and injury data. Analyzed data and findings are widely disseminated for policy and program formulation, decision-making, public health action, and evaluation of control measures. 7
10 CAREC and CAREC member countries have developed and promoted a regional Communicable Diseases surveillance system. The purpose is to generate information for policy development, planning, and evaluation. Data collected includes weekly reporting of syndromes, hospital ward notifications, four-weekly reporting of specific diseases, outbreak reports, quarterly and annual HIV/AIDS/STI reports, quarterly tuberculosis reports, and annual leprosy reports. Laboratory surveillance data is also collected. Neglected Tropical Diseases (NTDs) are not detected in the present surveillance system. NTDs have low priority politically and therefore there is no funding. The current challenge is to determine the present status of these diseases in areas where they were historically important. There are different surveillance method options for NTDs surveillance. Some of these include active case detection using surveys, passive case detection using clinics and hospitals, and snail surveillance. Methods of active case detection include using combined surveys for Helminths or other communicable diseases and selecting sensitive, more specific, populations. Passive surveillance through screening of samples from patients admitted into hospital and clinics for reasons other than Schistosomiasis, or through screening of blood bank samples. Snail surveillance is important in order to determine if the habitat is still suitable for snails. Surveillance of NTDs in the Caribbean is going to require external assistance and funding. 8
11 Challenges of Detection and Measurement of Schistosomiasis Morbidity [J. C.King MORBIDITY DETECTION am.pdf] Schistosomiasis causes low mortality but daily morbidity. Morbidity due to hepatosplenomegaly and hematuria are only the tip of the disease/disability iceberg. Lasting pain, diarrhea, and under nutrition are strongly associated with Schistosomiasis and contribute to its morbidity. The health burden due to Schistosomiasis is changing based on a better appreciation of the impact of sub-clinical morbidities. Schistosomiasis burden can be measured through infection prevalence rates, infection intensity, mortality, specific morbidity, and most of all disability. The impetus for earlier DALY rankings was to quantify disability in order to provide a utilitarian comparison across all possible disease control strategies. Schistosomiasis means hemoglobin deficits. Anemia does not have to be severe in order to be disabling, mild chronic disease anemia is significant in terms of its duration, income and birth outcomes. Schistosomiasis reduces average Hemoglobin levels to less than 12 gm/dl. These levels are associated with 3 to 5 percent reduction in work output, and 60 percent reduction in peak workload capacity. Furthermore, under nutrition does not have to be severe to be disabling, even minimal disability is highly significant in a rural poverty setting where undernutrition has multiple causes. Current strategies for Schistosomiasis control include annual drug treatments. Annual drug treatments reduce most forms of severe morbidity, but do not reverse all chronic morbidity and do not reliably reduce transmission. The next challenge is reducing transmission of Schistosomiasis and preventing infection. Molecular monitoring of pre-patency in snails is a large-scale application needed for Schistosomiasis control. Advantages of molecular monitoring include greater specificity of schistosomes species identification, greater sensitivity for detection of snail infection, increased ability to detect effective water contamination by schistosomes eggs. Molecular monitoring provides greater statistical power to detect significant increases or decreases in transmission. Molecular monitoring also decreases the dependence on participation by local population, and is amenable to automation and highthroughput testing. Aside from Schistosomiasis/snail control programs, it is important to explore integrated NTD control. Cuba [K. F. Nunez CUBA pm.pdf] In 1985 the first case of imported Schistosomiasis was recorded in Cuba. By 1999, 90 cases of imported Schistosomiasis had been recorded. However, no autochthonous human cases have been reported in Cuba. Cuba may be at high risk for introduction of Schistosomiasis because it hosts different species of Biomphalaria snails. Three species of snails have been considered as potential host for Schistosoma 9
12 mansoni, these are widely distributed in the country. Furthermore, due to Cubas s geographical location, the island is a frequent stop for migratory birds that seek refuge, and even a nesting place. Birds migrate from North America to the South and then back. Dissemination of eggs or young snails by migratory birds could introduce Biomphalaria glabarata to Cuba. Moreover, the existence of human cases in the Caribbean and South American countries that have increased collaboration with Cuba increases the risk of introduction. To prevent introduction of Schistosomiasis the following recommendations should be considered: strengthening of the Cuban epidemiological surveillance system for Schistosomiasis, increases systematic surveys of Biomphalaria snails, prompt treatment and control of imported cases, and stronger measures to avoid contamination of artificial lakes with sewers. Recommendations 1. The group agreed that Schistosomiasis is an important public health problem in the Latin American and the Caribbean but the scope of the problem is unrecognized. 2. Due to the similarities between the distribution and diagnosis of Schistosomiasis and STH, the group concluded that their surveillance and control efforts should be coordinated. 3. The group proposed the formation of a Regional Alliance for Schistosomiasis elimination and STH control in the Caribbean, for which PAHO could serve as Secretariat. 4. The first task of the Regional Alliance is to conduct mapping of Schistosomiasis distribution in the Caribbean. 5. It was concluded that this proposal be presented to the Chief Medical Officers Council meeting at the next CHRC meeting in Suriname scheduled for April 2008 for their approval. 6. It was recommended that PAHO takes the lead in coordinating the formation of the Regional Alliance and future activities, including the development of timelines and priorities. 7. The participants of the meeting pledged their full support to fulfill these recommendations. Action Points Suggested for Action by PAHO/WHO 1. Collection of additional epidemiological and environmental, historical, and current data. 2. Obtain locations of primary schools and numbers of students in endemic countries. 3. of low Obtain protocols for Schistosomiasis and STH surveillance from other areas endenmicity, or develop such protocols. 10
13 Next Steps Coordinate two new meetings. The following were proposed: A meeting in Suriname: The main objective is to sensitize the CMOs (Chief Medical Officers of Health) of the Caribbean of our plans to eliminate Schistosomiasis in conjunction with the control of soil-transmitted Helminths. The CMOs of CARICOM (Caribbean Community) meet annually in March or April ahead of the annual Caribbean Health Research Council (CHRC) meeting. This year the meeting is in Suriname. A meeting in Brazil: Dr. Katz invited the group to attend an International Symposium on Schistosomiasis in August 2008 in Salvador, Bahia, Brazil where the topic should also be discussed Acknowledgements St. Georges University, WINDREF, ECC 11
14 References Global Plan to Combat Neglected Tropical Diseases World Health Organization King CH, Dickman K, Tisch DJ. Reassessment of the cost of chronic helmintic infection: a meta-analysis of disabilityrelated outcomes in endemic schistosomiasis. Lancet Apr 30-May 6;365(9470): Lammie PJ, Lindo JF, Secor WE, Vasquez J, Ault SK, Eberhard ML. Eliminating lymphatic filariasis, onchocerciasis, and schistosomiasis from the Americas: breaking a historical legacy of slavery. PLoS Negl Trop Dis Nov 7;1(2):e71. Ross AG, Bartley PB, Sleigh AC, Olds GR, Li Y, Williams GM, McManus DP. Schistosomiasis. N Engl J Med Apr 18; 346 (16):
15 Annexes Annex I: Agenda Day 1: Thursday, 13 December 2007 Introduction 08:30 9:00 Registration of Participants 09:00 09-:45 Opening Session and Remarks of Officials, Chaired by C. Macpherson, SGU/WINDREF Welcome and Introduction of Meeting Participants (C. Macpherson) Minister of Health Grenada Hon. Senator Ann David-Antoine Provost of St. George s University Allan Pensick CAREC, PAHO/WHO Christian Fredrickson Programme on Neglected Tropical Diseases Maria Rebollo 09:45 10:00 Review of Workshop objectives (M. Rebollo, PAHO HQ and C Macpherson, ` SGU/WINDREF) Background and Objectives of Schistosomiasis Control and the Global and Regional Levels 10:00-10:15 Objectives of World Health Assembly Resolution with respect to schistosomiasis control (M. Rebollo) 10:15-10:25 Background on schistosomiasis control in LAC Region in the context of the NTDs (M. Rebollo) 10:25 10:30 Background on schistosomiasis control in the Caribbean in the work of CAREC (C. Macpherson) 10:30-10:45 Coffee/Tea Break Successful Control and Elimination Programs in other WHO regions and in Brazil (ChairL J. Lindo, UWI) 10:45 11:15 Schistosomiasis control in Brazil (N. Katz, FIOCRUZ, Brazil) 11:15 11:45 Successful schistosomiasis control and elimination programs in Africa (C. Macpherson, SGU/WINDREF) 11:45 12:15 Discussion of the morning presentations (coordinator: J. Lindo) 12:15-13:30 Lunch (1.25 hours) Situation Analysis of Schistosomiasis in Endemic Countries and Formerly-Endemic Countries (national officials or country representatives) (Chair: C. Frederickson, CAREC) 13:30 14:15 Situation analysis of schistosomiasis in Suriname 14:15 15:00 Situation analysis of schistosomiasis in St. Lucia 15:00 15:45 Presentation of surveillance systems for schistosomiasis in formerly-endemic countries: the case of Puerto Rico (G. Hillyer, CDC) 15:45 16:00 Discussion of the afternoon presentations (coordinatior: C. Frederickson, CAREC) 16:00 16:20 Coffee/Tea Break 16:20 17:00 Observations/comments of CDC staff on situation analysis in countries collaborating with CDC globally (P.Wilkins, W. Secor) 19:30 21:00 Social Event and Cocktails Day 2: Friday, 14 December 2007 Issues on Surveillance, Endemicity, and Morbidity (Chair: C. King, Case Western) 13
16 9:00 9:20 Surveillance systems for communicable diseases and NTDs in Caribbean (C. Fredrickson, CAREC) 9:20 9:45 Comments on schistosomiasis surveillance in areas of low endemicity (N.Katz, FIOCRUZ; P.Wilkins and W. Secor, CDC; G.Hillyar, UPR) 9:45 10:15 Challenge of detection and measurement of schistosomiasis morbidity (C.King, Case Western) 10:15 10:30 Discussion 10:30 10:45 Coffee/Tea Break Data Gaps and Resources Needed to Fill the Gaps (Chair: W. Secor, CDC) 10:45 12:00 Round Table Discussion by Participants: Identification and Listing of Data Gaps and Resources Needed to Fill the Data Gaps (coordinator: W.Secor, CDC; notetakers: C.Fredrickson, M.Rebollo) 12:00 13:30 Lunch 13:30 14:30 Round Table Discussion by Participants: Identification and Listing of Data Gaps Resources Needed to fill the Data Gaps, continued from prior to lunch 14:30 15:30 Informal Panel on Institutional Resources Available to Address Data Gaps in the Region (coordinators: N. Katz) F.A. Nunez, IPK P. Wilkins, CDC J. Lindo, UWI G. Hillyer, UPR C. Macpherson, SGU N. Katz, FIOCRUZ C. King, Case Western 15:30 15:45 Coffee/Tea Break 15:45 16:45 Discussion for Development of Conclusions and Recommendations (coordinators: CDC) 16:45 17:45 Preparation of Conclusions, Recommendations and Next Actions (prepared by C. Macpherson with M. Rebollo, C. Fredrickson) 17:45 18:00 Presentation of Conclusions, Recommendations and Next Actions (C.Macpherson) 18:00 Closure (M.Rebollo, C.Macpherson) 14
17 Annex II: List of Participants Naftale Katz, PhD Full Researcher, WHO Expert Centro de Pesquisas René Rachou/CPqRR FIOCRUZ Rene Rachou Research Center/CPqRR The Oswaldo Cruz Foundation Minas Gerais, Brazil. Fidel Nuñez, M.D., PhD Head of Parasitology Department, Institute for Tropical Medicine, Pedro Kourí, Habana, Cuba John Lindo, PhD Senior Lecturer and Consultant Parasitologist, The University of the West Indies, Kingston 7, Jamaica George Hillyer, PhD Professor and Director, Laboratory of Parasite Immunology and Pathology, Department of Pathology and Lab, UPR, Puerto Rico Alina Jaima St Lucia Dayanand Panchoe, M.D. Head of Parasitology Department Bureau of Public Health Ministry of Health, Suriname Christian Frederickson PhD, MPH, MPM Communicable Disease Advisor, Regional Coordinator for Integrated Vector Management and Pesticides, Caribbean Epidemiology Centre, PAHO/WHO, Trinidad and Tobago Charles King Professor of International Health Center for Global Health and Diseases Case Western University School of Medicine Cleveland, Ohio, USA Maria Rebollo Polo Consultant PAHO/WHO Washington, DC, USA William Evan Secor Research Microbiologist, Centers for Disease Control; Division of Parasitic Diseases; National Center for Zoonotic, Vector-borne & Enteric Diseases CCID/CDC USA Patricia Wilkins, PhD Chief, Reference Diagnostic Service; Associate Director of Laboratory Science; Division of Parasitic Diseases; National Center for Zoonotic, Vector-borne & Enteric Diseases CCID/CDC USA Omowale Amuleru-Marshall, M.A., M.Ed, PhD, MPH Professor and Chair, Department of Public Health and Preventive Medicine, School of Medicine, St Georges University, Grenada, West Indies Molara Aléxis St. Georges University Grenada, West Indies E. Francis Martin St. Georges University Grenada, West Indies Trevor Paul Noel, MPH Deputy Director Windward Island Research and Education Foundations (WINDREF) Alla F. Sverdlik USA Samina Rutrecht, PhD St. Georges University Grenada, West Indies Ravindra Sharma St. Georges University Grenada, West Indies Raymond Sis St. Georges University Grenada, West Indies Shenandoa Toote, BS Medical Student, St Georges University Grenada 15
18 Jeff Donowitz Medical Student, St Georges University, Grenada, West Indies. Ann David-Antoine St. Georges University Grenada Claris Charles, St. Georges University Calum N.L.Macpherson, PhD Vice Provost, International Program Development; Professor & Dean, Graduate Studies, St. George's University, St. George s, Grenada, West Indies Meg Conlon St Georges University IRB Administrator, Office of Research Graduate Studies Program, WINDREF/Bioethics Department. Grenada, West Indies 16
Schistosomiasis: Challenges and Opportunities
 Schistosomiasis: Challenges and Opportunities Charles H. King MD Center for Global Health and Diseases Case Western Reserve University Cleveland, Ohio and Schistosomiasis Consortium for Research and Elimination,
Schistosomiasis: Challenges and Opportunities Charles H. King MD Center for Global Health and Diseases Case Western Reserve University Cleveland, Ohio and Schistosomiasis Consortium for Research and Elimination,
Schistosomiasis. World Health Day 2014 SMALL BITE: Fact sheet. Key facts
 Fact sheet Key facts is an acute and chronic disease caused by parasitic worms. At least 249 million people required preventive treatment for schistosomiasis in 2012. The number of people reported to have
Fact sheet Key facts is an acute and chronic disease caused by parasitic worms. At least 249 million people required preventive treatment for schistosomiasis in 2012. The number of people reported to have
Department of Pure and Applied Zoology, Federal University of Agriculture, Abeokuta, Nigeria
 DEVELOPING NEW BEHAVIOURAL CHANGE INTERVENTIONS FOR SCHISTOSOMIASIS CONTROL Department of Pure and Applied Zoology, Federal University of Agriculture, Abeokuta, Nigeria SCHISTOSOMIASIS Disease of poverty
DEVELOPING NEW BEHAVIOURAL CHANGE INTERVENTIONS FOR SCHISTOSOMIASIS CONTROL Department of Pure and Applied Zoology, Federal University of Agriculture, Abeokuta, Nigeria SCHISTOSOMIASIS Disease of poverty
Lymphatic filariasis (LF) in the Americas: progress on preventive chemotherapy, 2013
 Lymphatic filariasis (LF) in the Americas: progress Four countries with people at risk of infection (, Dominican Republic, Guyana and Haiti); 12 million people requiring preventive 7.1 million people treated
Lymphatic filariasis (LF) in the Americas: progress Four countries with people at risk of infection (, Dominican Republic, Guyana and Haiti); 12 million people requiring preventive 7.1 million people treated
Schistosomiasis. Epidemiology. Global epidemiology
 Schistosomiasis Introduction Epidemiology Risk for Travellers Transmission Signs and Symptoms Treatment Prevention References Reading List Introduction Schistosomiasis, or bilharzia, is caused by worms
Schistosomiasis Introduction Epidemiology Risk for Travellers Transmission Signs and Symptoms Treatment Prevention References Reading List Introduction Schistosomiasis, or bilharzia, is caused by worms
ESCMID Online Lecture Library. by author
 Schistosoma epidemiology & diagnosis José Manuel Correia da Costa INSA National Institute of Health Dr. Ricardo Jorge Brindley PJ & Hotez PJ (2013) Break Out: Urogenital Schistosomiasis and Schistosoma
Schistosoma epidemiology & diagnosis José Manuel Correia da Costa INSA National Institute of Health Dr. Ricardo Jorge Brindley PJ & Hotez PJ (2013) Break Out: Urogenital Schistosomiasis and Schistosoma
WRAIR- GEIS 'Operational Clinical Infectious Disease' Course
 Schistosomiasis WRAIR- GEIS 'Operational Clinical Infectious Disease' Course The opinions or assertions contained herein are the private views of the author, and are not to be construed as official, or
Schistosomiasis WRAIR- GEIS 'Operational Clinical Infectious Disease' Course The opinions or assertions contained herein are the private views of the author, and are not to be construed as official, or
10/14/2009. Helminths: Trematoda - non-segmented flat worms. The schistosomes: Schistosoma mansoni Schistosoma haematobium. Schistosoma mekongi
 Helminths: Trematoda - non-segmented flat worms The schistosomes: Schistosoma mansoni Schistosoma haematobium Schistosoma japonicum Schistosoma mekongi 1 Japan is schistosome-free as of 1976 2 Aquatic
Helminths: Trematoda - non-segmented flat worms The schistosomes: Schistosoma mansoni Schistosoma haematobium Schistosoma japonicum Schistosoma mekongi 1 Japan is schistosome-free as of 1976 2 Aquatic
Helminths: Schistosoma mansoni. Schistosoma japonicum 10/14/2009. Trematoda - non-segmented flat worms
 Helminths: Trematoda - non-segmented flat worms The schistosomes: Schistosoma mansoni Schistosoma haematobium Schistosoma japonicum Schistosoma mekongi Aquatic freshwater snails are the intermediate hosts
Helminths: Trematoda - non-segmented flat worms The schistosomes: Schistosoma mansoni Schistosoma haematobium Schistosoma japonicum Schistosoma mekongi Aquatic freshwater snails are the intermediate hosts
Schistosomiasis / Bilharzia
 Schistosomiasis / Bilharzia An update for registered healthcare practitioners April 2017 Aims of resource:- To raise awareness of Schistosomiasis/Bilharzia infection with registered healthcare practitioners
Schistosomiasis / Bilharzia An update for registered healthcare practitioners April 2017 Aims of resource:- To raise awareness of Schistosomiasis/Bilharzia infection with registered healthcare practitioners
PARASITOLOGY CASE HISTORY 11 (HISTOLOGY) (Lynne S. Garcia)
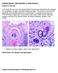 PARASITOLOGY CASE HISTORY 11 (HISTOLOGY) (Lynne S. Garcia) A 37-year-old man from the United Arab Emirates was admitted to the hospital for complaints of upper and lower abdominal pain. The greater omentum
PARASITOLOGY CASE HISTORY 11 (HISTOLOGY) (Lynne S. Garcia) A 37-year-old man from the United Arab Emirates was admitted to the hospital for complaints of upper and lower abdominal pain. The greater omentum
NEWSLETTER. ACTION AGAINST WORMS FROM ANIMATION TO REALITY IN THIS ISSUE: NOVEMBER 2008 ISSUE 12
 ACTION AGAINST WORMS NOVEMBER 2008 ISSUE 12 IN THIS ISSUE: A child taking praziquantel tablets during a deworming campaign in Madagascar, 2008. From animation to reality Prevalence of schistosomiasis Action
ACTION AGAINST WORMS NOVEMBER 2008 ISSUE 12 IN THIS ISSUE: A child taking praziquantel tablets during a deworming campaign in Madagascar, 2008. From animation to reality Prevalence of schistosomiasis Action
A Road Safety Decade - The Case for Action
 A Road Safety Decade - The Case for Action Presentation by Dmitry Sambuk International Coordinator, Make Roads Campaign, FIA Foundation Monday 12 May 2009, Minsk, Republic of Belarus World Report on Road
A Road Safety Decade - The Case for Action Presentation by Dmitry Sambuk International Coordinator, Make Roads Campaign, FIA Foundation Monday 12 May 2009, Minsk, Republic of Belarus World Report on Road
Hussein et al., World J. Biol. Med. Science Volume 2 (3), 74-80, 2015
 Indexed, Abstracted and Cited: ISRA Journal Impact Factor, International Impact Factor Services (IIFS), Directory of Research Journals Indexing (DRJI), International Institute of Organized Research and
Indexed, Abstracted and Cited: ISRA Journal Impact Factor, International Impact Factor Services (IIFS), Directory of Research Journals Indexing (DRJI), International Institute of Organized Research and
Acknowledgements. Schistosomiasis Epidemiology
 Pulmonary Arterial Hypertension and Schistosomiasis Rubin M. Tuder, M. D. Brian Graham, M.D. Program in Translational Lung Program Division of Pulmonary Sciences and Critical Care Medicine, Department
Pulmonary Arterial Hypertension and Schistosomiasis Rubin M. Tuder, M. D. Brian Graham, M.D. Program in Translational Lung Program Division of Pulmonary Sciences and Critical Care Medicine, Department
Spatially explicit modeling of schistosomiasis transmission dynamics: applications to Senegal
 Spatially explicit modeling of schistosomiasis transmission dynamics: applications to Senegal Lorenzo Mari Dipartimento di Elettronica, Informazione e Bioingegneria Politecnico di Milano mailto: lorenzo.mari@polimi.it
Spatially explicit modeling of schistosomiasis transmission dynamics: applications to Senegal Lorenzo Mari Dipartimento di Elettronica, Informazione e Bioingegneria Politecnico di Milano mailto: lorenzo.mari@polimi.it
Creative brief for Radio Skits for Uganda Schistosomiasis Prevention Campaign
 Creative brief for Radio Skits for Uganda Schistosomiasis Prevention Campaign Priority Audiences: 1) Adults who are at high risk of Schistosomiasis. These include parents of children who are also at risk.
Creative brief for Radio Skits for Uganda Schistosomiasis Prevention Campaign Priority Audiences: 1) Adults who are at high risk of Schistosomiasis. These include parents of children who are also at risk.
fñxv tä TÜà väx Challenges in prevention and control of schistosomiasis in the Sudan Mutamad A.Amin* and Durria Mansour Elhussin* Background
 fñxv tä TÜà väx Challenges in prevention and control of schistosomiasis in the Sudan Mutamad A.Amin* and Durria Mansour Elhussin* Background The World Health Organization (WHO) estimated that 200 million
fñxv tä TÜà väx Challenges in prevention and control of schistosomiasis in the Sudan Mutamad A.Amin* and Durria Mansour Elhussin* Background The World Health Organization (WHO) estimated that 200 million
Chapter 25. Schistosomiasis
 Chapter 25. Schistosomiasis The eradication of schistosomiasis (often referred to as bilharziasis or snail fever) or its elimination by multiple, integrated intervention techniques is beyond the human
Chapter 25. Schistosomiasis The eradication of schistosomiasis (often referred to as bilharziasis or snail fever) or its elimination by multiple, integrated intervention techniques is beyond the human
MDB Road Safety Initiative: A Development Priority
 MDB Road Safety Initiative: A Development Priority Every six seconds, someone is killed or maimed on the world s roads. Over 90 percent of these injuries occur in low- and middle-income countries. The
MDB Road Safety Initiative: A Development Priority Every six seconds, someone is killed or maimed on the world s roads. Over 90 percent of these injuries occur in low- and middle-income countries. The
[black box of sprorocyst/rediae]
![[black box of sprorocyst/rediae] [black box of sprorocyst/rediae]](/thumbs/88/114695814.jpg) Digeneans: All life cycles involve a mollusc and a vertebrate All life cycles are similar but different All life cycles are a variation of one theme. Adult-egg-miracidium-[black box of sprorocyst/rediae]
Digeneans: All life cycles involve a mollusc and a vertebrate All life cycles are similar but different All life cycles are a variation of one theme. Adult-egg-miracidium-[black box of sprorocyst/rediae]
The prevalence of schistosomiasis among school children in Zagazig district, Sharkyia Governorate, Egypt
 Middle East Journal of Applied Sciences Volume : 05 Issue : 04 Oct.-Dec. 2015 Pages: 1267-1272 The prevalence of schistosomiasis among school children in Zagazig district, Sharkyia Governorate, Egypt 1
Middle East Journal of Applied Sciences Volume : 05 Issue : 04 Oct.-Dec. 2015 Pages: 1267-1272 The prevalence of schistosomiasis among school children in Zagazig district, Sharkyia Governorate, Egypt 1
The challenges of eliminating tuberculosis
 The challenges of eliminating tuberculosis Christopher Dye World Health Organization Pre 2015: dynamics and control of TB Drug resistance as part of the TB challenge Post 2015: TB elimination and sustainable
The challenges of eliminating tuberculosis Christopher Dye World Health Organization Pre 2015: dynamics and control of TB Drug resistance as part of the TB challenge Post 2015: TB elimination and sustainable
Health Education as Intervention in Promotion of Knowledge, Attitudes and Practices among School Pupils as Regards Schistosomiasis
 EUROPEAN ACADEMIC RESEARCH Vol. II, Issue 9/ December 2014 ISSN 2286-4822 www.euacademic.org Impact Factor: 3.1 (UIF) DRJI Value: 5.9 (B+) Health Education as Intervention in Promotion of Knowledge, Attitudes
EUROPEAN ACADEMIC RESEARCH Vol. II, Issue 9/ December 2014 ISSN 2286-4822 www.euacademic.org Impact Factor: 3.1 (UIF) DRJI Value: 5.9 (B+) Health Education as Intervention in Promotion of Knowledge, Attitudes
Healthy Swimming: Prevention of Recreational Water Illnesses (RWIs)
 Healthy Swimming: Prevention of Recreational Water Illnesses (RWIs) Q u e s t i o n s a n d A n s w e r s f o r A q u a t i c s F a c i l i t y S t a f f The following information about recreational water
Healthy Swimming: Prevention of Recreational Water Illnesses (RWIs) Q u e s t i o n s a n d A n s w e r s f o r A q u a t i c s F a c i l i t y S t a f f The following information about recreational water
Road safety. REGIONAL COMMITTEE Provisional Agenda item 8.5. SEA/RC70/11 Malé, Maldives 6 10 September July Seventieth Session
 REGIONAL COMMITTEE Provisional Agenda item 8.5 Seventieth Session SEA/RC70/11 Malé, Maldives 6 10 September 2017 21 July 2017 Road safety Road traffic injuries constitute a major public health burden with
REGIONAL COMMITTEE Provisional Agenda item 8.5 Seventieth Session SEA/RC70/11 Malé, Maldives 6 10 September 2017 21 July 2017 Road safety Road traffic injuries constitute a major public health burden with
Presentation and Diagnosis of Imported Schistosomiasis: Relevance of Eosinophilia, Microscopy for Ova, and Serology
 Presentation and Diagnosis of Imported Schistosomiasis: Relevance of Eosinophilia, Microscopy for Ova, and Serology Wouter F.W. Bierman, José C.F.M.Wetsteyn, and Tom van Gool Background: In nonendemic
Presentation and Diagnosis of Imported Schistosomiasis: Relevance of Eosinophilia, Microscopy for Ova, and Serology Wouter F.W. Bierman, José C.F.M.Wetsteyn, and Tom van Gool Background: In nonendemic
Investigation of Intestinal Schistosomiasis among School Children in Nteje Town, Oyi Local Government Area of Anambra State
 Jan 2016 Vol 3, No.1 Investigation of Intestinal Schistosomiasis among School Children in Nteje Town, Oyi Local Government Area of Anambra State Anyaegbunam, Lucy C Department of Biological Sciences,Chukwuemeka
Jan 2016 Vol 3, No.1 Investigation of Intestinal Schistosomiasis among School Children in Nteje Town, Oyi Local Government Area of Anambra State Anyaegbunam, Lucy C Department of Biological Sciences,Chukwuemeka
General Description. Cause. Transmission Mode. Epidemiology of Schistosomiasis
 General Description Schistosomiasis, also known as bilharziasis, is a human disease caused by a zoonotic parasite that infects a wide range of animals, including cattle, dogs, pigs, and rodents. It most
General Description Schistosomiasis, also known as bilharziasis, is a human disease caused by a zoonotic parasite that infects a wide range of animals, including cattle, dogs, pigs, and rodents. It most
INTERNATIONAL JOURNAL OF WOMEN'S HEALTH AND REPRODUCTION SCIENCES
 Letter to the Editor INTERNATIONAL JOURNAL OF WOMEN'S HEALTH AND REPRODUCTION SCIENCES http://www.ijwhr.net doi: 10.15296/ijwhr.2014.17 Pathogenic Effects of Genital Schistosomiasis on Men and Women Health
Letter to the Editor INTERNATIONAL JOURNAL OF WOMEN'S HEALTH AND REPRODUCTION SCIENCES http://www.ijwhr.net doi: 10.15296/ijwhr.2014.17 Pathogenic Effects of Genital Schistosomiasis on Men and Women Health
The Increased Risk of Schistosomiasis Caused by High Frequency of Rainfall and Open-Defecation Habit in Indonesia
 International Proceedings of Chemical, Biological and Environmental Engineering, V0l. 93 (2016) DOI: 10.7763/IPCBEE. 2016. V93. 2 The Increased Risk of Schistosomiasis Caused by High Frequency of Rainfall
International Proceedings of Chemical, Biological and Environmental Engineering, V0l. 93 (2016) DOI: 10.7763/IPCBEE. 2016. V93. 2 The Increased Risk of Schistosomiasis Caused by High Frequency of Rainfall
The Canadian Tuberculosis Prevention and Control Strategy: Targeting our Efforts
 The Canadian Tuberculosis Prevention and Control Strategy: Targeting our Efforts Andrea Saunders Tuberculosis Prevention and Control Public Health Agency of Canada The Global Burden of Tuberculosis 1 in
The Canadian Tuberculosis Prevention and Control Strategy: Targeting our Efforts Andrea Saunders Tuberculosis Prevention and Control Public Health Agency of Canada The Global Burden of Tuberculosis 1 in
BIO Parasitology Spring 2009
 BIO 475 - Parasitology Spring 2009 Stephen M. Shuster Northern Arizona University http://www4.nau.edu/isopod Lecture 13 Important Orders a. Echinostomatiformes b. Strigeiformes c. Opisthorchiformes d.
BIO 475 - Parasitology Spring 2009 Stephen M. Shuster Northern Arizona University http://www4.nau.edu/isopod Lecture 13 Important Orders a. Echinostomatiformes b. Strigeiformes c. Opisthorchiformes d.
Joint External Evaluation (JEE)
 Joint External Evaluation (JEE) Zoonotic Diseases Action Package Conference Da Nang, Viet Nam 29-30 August 2017 Background & rationale The IHR Review Committee on Second Extensions for Establishing National
Joint External Evaluation (JEE) Zoonotic Diseases Action Package Conference Da Nang, Viet Nam 29-30 August 2017 Background & rationale The IHR Review Committee on Second Extensions for Establishing National
SCHISTOSOMIASIS CONTROL AND ELIMINATION: NEXT STEPS
 SCHISTOSOMIASIS CONTROL AND ELIMINATION: NEXT STEPS Sunday the 5 th November, Sheraton Inner Harbour Hotel, Baltimore, UK. MEETING REPORT 1. WELCOME BY DAVID ROLLINSON, DIRECTOR OF THE GSA Prof. David
SCHISTOSOMIASIS CONTROL AND ELIMINATION: NEXT STEPS Sunday the 5 th November, Sheraton Inner Harbour Hotel, Baltimore, UK. MEETING REPORT 1. WELCOME BY DAVID ROLLINSON, DIRECTOR OF THE GSA Prof. David
ZERO DRAFT OF THE BRASILIA DECLARATION ON ROAD SAFETY (VERSION PROPOSED BY BRAZIL DATED 26 MARCH 2015)
 ZERO DRAFT OF THE BRASILIA DECLARATION ON ROAD SAFETY (VERSION PROPOSED BY BRAZIL DATED 26 MARCH 2015) Second Global High-Level Conference on Road Safety: Time for Results Brasilia, 18-19 November 2015
ZERO DRAFT OF THE BRASILIA DECLARATION ON ROAD SAFETY (VERSION PROPOSED BY BRAZIL DATED 26 MARCH 2015) Second Global High-Level Conference on Road Safety: Time for Results Brasilia, 18-19 November 2015
Zhang Shuguang. The Development of Community Sports Facilities in China: Effects of the Olympic Games
 Zhang Shuguang The Development of Community Sports Facilities in China: Effects of the Olympic Games Zhang Shuguang China Sport Information Center, Beijing, P.R. China With the influences of the 2008 Beijing
Zhang Shuguang The Development of Community Sports Facilities in China: Effects of the Olympic Games Zhang Shuguang China Sport Information Center, Beijing, P.R. China With the influences of the 2008 Beijing
SECTION 1. The current state of global road safety
 SECTION 1 The current state of global road safety The number of road traffic deaths each year has not increased but remains unacceptably high at 1.24 million per year. Many countries have successfully
SECTION 1 The current state of global road safety The number of road traffic deaths each year has not increased but remains unacceptably high at 1.24 million per year. Many countries have successfully
The current status of Schistosoma mansoni among biomphalaria snails in Kabaka s lake, Kampala Uganda
 Research Journal of Agriculture and Environmental Management Vol. 6(2), pp. 031-035, March, 2017 Available online at http://www.apexjournal.org ISSN 2315-8719 2017 Apex Journal International Full Length
Research Journal of Agriculture and Environmental Management Vol. 6(2), pp. 031-035, March, 2017 Available online at http://www.apexjournal.org ISSN 2315-8719 2017 Apex Journal International Full Length
Walking and Cycling Action Plan Summary. A Catalyst for Change The Regional Transport Strategy for the west of Scotland
 Walking and Cycling Action Plan Summary A Catalyst for Change The Regional Transport Strategy for the west of Scotland 2007-2021 Strathclyde Partnership for Transport Contents Purpose...2 Issues, Constraints
Walking and Cycling Action Plan Summary A Catalyst for Change The Regional Transport Strategy for the west of Scotland 2007-2021 Strathclyde Partnership for Transport Contents Purpose...2 Issues, Constraints
Filariasis. Nematoda Systemic round worms
 Filariasis Nematoda Systemic round worms Filaria -a roundworm -Adult filaria live in body cavities, lymphatics, and subcutaneous tissues -embryos (microfilaria) live in blood or dermis -all require an
Filariasis Nematoda Systemic round worms Filaria -a roundworm -Adult filaria live in body cavities, lymphatics, and subcutaneous tissues -embryos (microfilaria) live in blood or dermis -all require an
INTERGOVERNMENTAL OCEANOGRAPHIC COMMISSION (of UNESCO) Tenth Session of the IOC Sub-Commission for the Caribbean and Adjacent Regions (IOCARIBE)
 IOC/SC-IOCARIBE-X/3s Paris, 1 June 2009 Original: English INTERGOVERNMENTAL OCEANOGRAPHIC COMMISSION (of UNESCO) Tenth Session of the IOC Sub-Commission for the Caribbean and Adjacent Regions (IOCARIBE)
IOC/SC-IOCARIBE-X/3s Paris, 1 June 2009 Original: English INTERGOVERNMENTAL OCEANOGRAPHIC COMMISSION (of UNESCO) Tenth Session of the IOC Sub-Commission for the Caribbean and Adjacent Regions (IOCARIBE)
Plan B Supporting Data for Chapter 7
 Plan B 4.0 - Supporting Data for Chapter 7 World Population, 1950-2008 GRAPH: World Population, 1950-2008 World Population, 1950-2008, with Projections to 2050 GRAPH: World Population, 1950-2008, with
Plan B 4.0 - Supporting Data for Chapter 7 World Population, 1950-2008 GRAPH: World Population, 1950-2008 World Population, 1950-2008, with Projections to 2050 GRAPH: World Population, 1950-2008, with
THE RIGHT TO THE CITY: BRIDGING THE URBAN DIVIDE
 The Fifth Session of the World Urban Forum, Rio de Janeiro, Brazil 19 26 March 2010 THE RIGHT TO THE CITY: BRIDGING THE URBAN DIVIDE World Urban Forum Unit 1 2 VIDEO CLIP WUF 5 TOTAL ATTENDANCE 13,795
The Fifth Session of the World Urban Forum, Rio de Janeiro, Brazil 19 26 March 2010 THE RIGHT TO THE CITY: BRIDGING THE URBAN DIVIDE World Urban Forum Unit 1 2 VIDEO CLIP WUF 5 TOTAL ATTENDANCE 13,795
Proposal for cooperation between GRASP and the CMS Gorilla Agreement
 Proposal for cooperation between GRASP and the CMS Gorilla Agreement Background Great Apes Survival Partnership The Great Apes Survival Partnership (GRASP) was founded in 2001 at the World Summit on Sustainable
Proposal for cooperation between GRASP and the CMS Gorilla Agreement Background Great Apes Survival Partnership The Great Apes Survival Partnership (GRASP) was founded in 2001 at the World Summit on Sustainable
Enhancing the Success of Road Safety Initiatives
 Enhancing the Success of Road Safety Initiatives Cessie Petchi Working for a world free of road crash death and injury About GRSP Founded in 1999 in response to recognition of the road safety issue as
Enhancing the Success of Road Safety Initiatives Cessie Petchi Working for a world free of road crash death and injury About GRSP Founded in 1999 in response to recognition of the road safety issue as
Implementation of a Drowning Surveillance System for Ohio Public Pools
 Implementation of a Drowning Surveillance System for Ohio Public Pools Amanda M. Zabala, MPH CDC/CSTE Applied Epidemiology Fellow Waterborne Ohio Department of Health Bureau of Environmental Health & Radiation
Implementation of a Drowning Surveillance System for Ohio Public Pools Amanda M. Zabala, MPH CDC/CSTE Applied Epidemiology Fellow Waterborne Ohio Department of Health Bureau of Environmental Health & Radiation
Working in low oxygen-controlled atmospheres. Risks and Prevention Measures Dr Michel Falcy, INRS FRANCE
 Working in low oxygen-controlled atmospheres Risks and Prevention Measures Dr Michel Falcy, INRS FRANCE Use of low O 2 -controlled atmospheres Nitrogenrefrigerated lorries Cryogenic facilities (sperm banks)
Working in low oxygen-controlled atmospheres Risks and Prevention Measures Dr Michel Falcy, INRS FRANCE Use of low O 2 -controlled atmospheres Nitrogenrefrigerated lorries Cryogenic facilities (sperm banks)
Current Leprosy Situation in Myanmar. Dr. Oke Soe Deputy Director(Leprosy) Department of Public Health
 Current Leprosy Situation in Myanmar Dr. Oke Soe Deputy Director(Leprosy) Department of Public Health Demographic Information The Republic of the Union of Myanmar Area Sq:km - 676,578 Population - 51486253
Current Leprosy Situation in Myanmar Dr. Oke Soe Deputy Director(Leprosy) Department of Public Health Demographic Information The Republic of the Union of Myanmar Area Sq:km - 676,578 Population - 51486253
Moving towards the elimination of sleeping sickness
 Moving towards the elimination of sleeping sickness Dr. Jose Ramon Franco, Department of Control of Neglected Tropical Diseases 1 Cases THA, 1940-2013 60'000 50'000 40'000 30'000 20'000 10'000 0 2 1940
Moving towards the elimination of sleeping sickness Dr. Jose Ramon Franco, Department of Control of Neglected Tropical Diseases 1 Cases THA, 1940-2013 60'000 50'000 40'000 30'000 20'000 10'000 0 2 1940
Regional Inception Workshop NATIONAL TARGET SETTING TO ACHIEVE LAND DEGRADATION NEUTRALITY in Latin America and The Caribbean
 Regional Inception Workshop NATIONAL TARGET SETTING TO ACHIEVE LAND DEGRADATION NEUTRALITY in Latin America and The Caribbean Buenos Aires, Argentina, 20-21 July 2016 Workshop Report Contents 1. Introduction...
Regional Inception Workshop NATIONAL TARGET SETTING TO ACHIEVE LAND DEGRADATION NEUTRALITY in Latin America and The Caribbean Buenos Aires, Argentina, 20-21 July 2016 Workshop Report Contents 1. Introduction...
Demographic, Social and Health Indicators for Countries of the Eastern Mediterranean
 Demographic, Social and Health Indicators for Countries of the Eastern Mediterranean 2013 WHO-EM/HST/213/E Overall functionality of health information systems in the Region Satisfactory Functional but
Demographic, Social and Health Indicators for Countries of the Eastern Mediterranean 2013 WHO-EM/HST/213/E Overall functionality of health information systems in the Region Satisfactory Functional but
Treatment of Schistosomiasis in Africa
 Treatment of Schistosomiasis in Africa Junyi Mei Junyi is finishing her B.Sc. in Anatomy and Cell Biology and looks forward to working at a medical research lab this summer. She is interested in global
Treatment of Schistosomiasis in Africa Junyi Mei Junyi is finishing her B.Sc. in Anatomy and Cell Biology and looks forward to working at a medical research lab this summer. She is interested in global
Risk of spread after introduction of the virus in to wild boar population
 Available tools for the prevention and control of diseases in wildlife, with focus on ASF in wild boar in infected country: hunting biosecurity and wild boar carcass disposal Marius Masiulis FAO international
Available tools for the prevention and control of diseases in wildlife, with focus on ASF in wild boar in infected country: hunting biosecurity and wild boar carcass disposal Marius Masiulis FAO international
The development of Emergency Aquatic Animal Disease Response Arrangements
 Working together for animal health The development of Emergency Aquatic Animal Disease Response Arrangements 1. What are emergency response arrangements? Australia has a number of emergency response arrangements
Working together for animal health The development of Emergency Aquatic Animal Disease Response Arrangements 1. What are emergency response arrangements? Australia has a number of emergency response arrangements
Mission of the Community Veterinary Emergency Team to LITHUANIA
 Mission of the Community Veterinary Emergency Team to LITHUANIA SCOPE of the mission: African Swine Fever in wild boar in Lithuania at the border with Belarus (27 31 January 2014) Terms of Reference To
Mission of the Community Veterinary Emergency Team to LITHUANIA SCOPE of the mission: African Swine Fever in wild boar in Lithuania at the border with Belarus (27 31 January 2014) Terms of Reference To
Molecular Diagnostics Market - Global Industry Analysis, Size, Share, Growth Trends & Forecast to 2021
 Published on Market Research Reports Inc. (https://www.marketresearchreports.com) Home > Molecular Diagnostics Market - Global Industry Analysis, Size, Share, Growth Trends & Forecast to 2021 Molecular
Published on Market Research Reports Inc. (https://www.marketresearchreports.com) Home > Molecular Diagnostics Market - Global Industry Analysis, Size, Share, Growth Trends & Forecast to 2021 Molecular
Implementation of International Health Regulation (2005) in the African Region
 Implementation of International Health Regulation (2005) in the African Region CAPSCA Second Global Coordination Meeting and Second Regional Steering Committee Meeting, 10-13 October 2011, Abuja/Nigeria
Implementation of International Health Regulation (2005) in the African Region CAPSCA Second Global Coordination Meeting and Second Regional Steering Committee Meeting, 10-13 October 2011, Abuja/Nigeria
Council CNL(14)45 The management approach to salmon fisheries in Norway (Tabled by Norway)
 Agenda Item 6.2 Agenda Item 6.2 For Information Council CNL(14)45 The management approach to salmon fisheries in Norway (Tabled by Norway) 1983 1985 1987 1989 1991 1993 1995 1997 1999 2001 2003 2005 2007
Agenda Item 6.2 Agenda Item 6.2 For Information Council CNL(14)45 The management approach to salmon fisheries in Norway (Tabled by Norway) 1983 1985 1987 1989 1991 1993 1995 1997 1999 2001 2003 2005 2007
AREAS BEYOND NATIONAL JURISDICTION: INDIAN OCEAN DEVELOPING COASTAL STATES TUNA MANAGEMENT WORKSHOP
 AREAS BEYOND NATIONAL JURISDICTION: INDIAN OCEAN DEVELOPING COASTAL STATES TUNA MANAGEMENT WORKSHOP The goal of this workshop is to create a better understanding of among Indian Ocean Developing Coastal
AREAS BEYOND NATIONAL JURISDICTION: INDIAN OCEAN DEVELOPING COASTAL STATES TUNA MANAGEMENT WORKSHOP The goal of this workshop is to create a better understanding of among Indian Ocean Developing Coastal
The use of risk management as best practice to reduce outbreaks of recreational water illnesses in disinfected swimming facilities and spas
 The use of risk management as best practice to reduce outbreaks of recreational water illnesses in disinfected swimming facilities and spas Roy Vore, Ph.D., NSPF I, CPO Vore & Associates, LLC Email: Roy.D.Vore@gmail.com
The use of risk management as best practice to reduce outbreaks of recreational water illnesses in disinfected swimming facilities and spas Roy Vore, Ph.D., NSPF I, CPO Vore & Associates, LLC Email: Roy.D.Vore@gmail.com
Active Travel Strategy Dumfries and Galloway
 Active Travel Strategy Dumfries and Galloway Our Active Travel Strategy The agreed Interventions for Dumfries and Galloway Council s Local Transport Strategy includes an action to Develop an Active Travel
Active Travel Strategy Dumfries and Galloway Our Active Travel Strategy The agreed Interventions for Dumfries and Galloway Council s Local Transport Strategy includes an action to Develop an Active Travel
EGYPT: a national decade of action for road safety
 EGYPT: a national decade of action for road safety 2011 2020 Egypt EGYPT Population: 75 497 913 Income group: Middle Gross national income per capita: $1 580 INSTITUTIONAL FRAMEWORK Lead agency Funded
EGYPT: a national decade of action for road safety 2011 2020 Egypt EGYPT Population: 75 497 913 Income group: Middle Gross national income per capita: $1 580 INSTITUTIONAL FRAMEWORK Lead agency Funded
Practicing Proactive Silica Dust Housekeeping by: Nilfisk, Inc.
 Practicing Proactive Silica Dust Housekeeping by: Nilfisk, Inc. Page 1 Overview 1 2 3 4 What is Silica Dust? Silica Dust Events and NEW OSHA Standard Who s at Risk? Proper Engineering Controls and Housekeeping
Practicing Proactive Silica Dust Housekeeping by: Nilfisk, Inc. Page 1 Overview 1 2 3 4 What is Silica Dust? Silica Dust Events and NEW OSHA Standard Who s at Risk? Proper Engineering Controls and Housekeeping
INVITED CONTRIBUTION
 INVITED CONTRIBUTION 1 INVITED CONTRIBUTION Intramural Aspects of Schistosomiasis Control DONALD B. McMULLEN l INTRODUCTION Work in different parts of the world has tended to solidify a '''one world" concept
INVITED CONTRIBUTION 1 INVITED CONTRIBUTION Intramural Aspects of Schistosomiasis Control DONALD B. McMULLEN l INTRODUCTION Work in different parts of the world has tended to solidify a '''one world" concept
WHY BICYCLES FOR EDUCATION?
 WHY BICYCLES FOR EDUCATION? 28% 59% 126,104 WITH A BICYCLE, STUDENT ATTENDANCE INCREASES UP TO 28% WITH A BICYCLE, ACADEMIC PERFORMANCE INCREASES UP TO 59% NUMBER OF STUDENTS MOBILIZED WITH BUFFALO BICYCLES
WHY BICYCLES FOR EDUCATION? 28% 59% 126,104 WITH A BICYCLE, STUDENT ATTENDANCE INCREASES UP TO 28% WITH A BICYCLE, ACADEMIC PERFORMANCE INCREASES UP TO 59% NUMBER OF STUDENTS MOBILIZED WITH BUFFALO BICYCLES
Reducing Disease Risks Caused by Pathogens Associated with Columbia
 Reducing Disease Risks Caused by Pathogens Associated with Columbia River Hatcheries Jerri Bartholomew Department of Microbiology Oregon State University, Corvallis, OR Pathogen Transmission and Hatchery
Reducing Disease Risks Caused by Pathogens Associated with Columbia River Hatcheries Jerri Bartholomew Department of Microbiology Oregon State University, Corvallis, OR Pathogen Transmission and Hatchery
Journal of Chemical and Pharmaceutical Research, 2016, 8(10): Research Article
 Available online www.jocpr.com Journal of Chemical and Pharmaceutical Research, 2016, 8(10):204-208 Research Article ISSN : 0975-7384 CODEN(USA) : JCPRC5 Epidemiological Behavior of Schistosomiasis in
Available online www.jocpr.com Journal of Chemical and Pharmaceutical Research, 2016, 8(10):204-208 Research Article ISSN : 0975-7384 CODEN(USA) : JCPRC5 Epidemiological Behavior of Schistosomiasis in
2. Context. Existing framework. The context. The challenge. Transport Strategy
 Transport Strategy Providing quality connections Contents 1. Introduction 2. Context 3. Long-term direction 4. Three-year priorities 5. Strategy tree Wellington City Council July 2006 1. Introduction Wellington
Transport Strategy Providing quality connections Contents 1. Introduction 2. Context 3. Long-term direction 4. Three-year priorities 5. Strategy tree Wellington City Council July 2006 1. Introduction Wellington
Rio Grande County Births and Deaths 2015
 Rio Grande County Births and Deaths 2015 Selected birth characteristics: County residents, 2015... 2 Selected birth characteristics by age group of mother: County residents, 2015... 3 Selected birth characteristics
Rio Grande County Births and Deaths 2015 Selected birth characteristics: County residents, 2015... 2 Selected birth characteristics by age group of mother: County residents, 2015... 3 Selected birth characteristics
The impact of global warming and snail susceptibility to schistosomiasis
 The impact of global warming and snail susceptibility to schistosomiasis Matty Knight The George Washington University, Washington DC University of the District of Columbia, Washington DC Life cycle of
The impact of global warming and snail susceptibility to schistosomiasis Matty Knight The George Washington University, Washington DC University of the District of Columbia, Washington DC Life cycle of
INTERNATIONAL COUNCIL OF MUSEUMS (ICOM) INTERNATIONAL COMMITTEE FOR EXHIBITION EXCHANGE (ICEE)
 INTERNATIONAL COUNCIL OF MUSEUMS (ICOM) INTERNATIONAL COMMITTEE FOR EXHIBITION EXCHANGE (ICEE) REQUEST FOR PROPOSALS (RFP) TO HOST THE 2018 ICEE ANNUAL CONFERENCE The International Committee for Exhibition
INTERNATIONAL COUNCIL OF MUSEUMS (ICOM) INTERNATIONAL COMMITTEE FOR EXHIBITION EXCHANGE (ICEE) REQUEST FOR PROPOSALS (RFP) TO HOST THE 2018 ICEE ANNUAL CONFERENCE The International Committee for Exhibition
Killingly Public Schools
 Grade 11 Draft: Jan. 2005 Killingly Public Schools Aquaculture/Natural Resources III Tilapia Production CONTENT STANDARD 11 AQ III 1: The students will understand the origin of Tilapia culture, the worldwide
Grade 11 Draft: Jan. 2005 Killingly Public Schools Aquaculture/Natural Resources III Tilapia Production CONTENT STANDARD 11 AQ III 1: The students will understand the origin of Tilapia culture, the worldwide
SAVE THE NATION ASSOCIATION (SNA)
 SAVE THE NATION ASSOCIATION (SNA) A DRAFT DOCUMENT FOR BRASILLIA DECLARATION ON ROAD SAFETY CONTACT PERSONS: MESGANAW BIMREW, EXECUTIVE DIRECTOR CELL PHONE: +251920717744, EMAIL: mesganaw21@yahoo.com SEIFU
SAVE THE NATION ASSOCIATION (SNA) A DRAFT DOCUMENT FOR BRASILLIA DECLARATION ON ROAD SAFETY CONTACT PERSONS: MESGANAW BIMREW, EXECUTIVE DIRECTOR CELL PHONE: +251920717744, EMAIL: mesganaw21@yahoo.com SEIFU
Effective Management Practices to Reduce the Incidence of Ascites in Broilers
 Effective Management Practices to Reduce the Incidence of Ascites in Broilers December 2009 Summary Introduction Ascites is a multi-factorial syndrome caused by interactions between physiological, environmental
Effective Management Practices to Reduce the Incidence of Ascites in Broilers December 2009 Summary Introduction Ascites is a multi-factorial syndrome caused by interactions between physiological, environmental
Planning for tennis in your Local Government Area. A resource from Tennis Australia
 Planning for tennis in your Local Government Area A resource from Tennis Australia Part 1 July 2016 ABOUT THIS RESOURCE This resource forms part of Tennis Australia's Local Government Engagement Program.
Planning for tennis in your Local Government Area A resource from Tennis Australia Part 1 July 2016 ABOUT THIS RESOURCE This resource forms part of Tennis Australia's Local Government Engagement Program.
FMD CONTROL IN EASTERN EUROPE
 FMD CONTROL IN EASTERN EUROPE 26TH CONFERENCE OF THE OIE REGIONAL COMMISSION FOR EUROPE BERN, SWITZERLAND, 22-26 SEPTEMBER 2014 Prof. Kazimieras Lukauskas, OIE Regional Representative in Moscow Dr. Askar
FMD CONTROL IN EASTERN EUROPE 26TH CONFERENCE OF THE OIE REGIONAL COMMISSION FOR EUROPE BERN, SWITZERLAND, 22-26 SEPTEMBER 2014 Prof. Kazimieras Lukauskas, OIE Regional Representative in Moscow Dr. Askar
SUSTAINABLE HUNTING - Building Capacity for Sustainable Hunting of Migratory Birds in Mediterranean Third Countries LIFE04 TCY/INT/000054
 SUSTAINABLE HUNTING - Building Capacity for Sustainable Hunting of Migratory Birds in Mediterranean Third Countries LIFE04 TCY/INT/000054 Project description Environmental issues Beneficiaries Administrative
SUSTAINABLE HUNTING - Building Capacity for Sustainable Hunting of Migratory Birds in Mediterranean Third Countries LIFE04 TCY/INT/000054 Project description Environmental issues Beneficiaries Administrative
TRAFFIC CRASHES IN WORK ZONES: AN OVERVIEW OF THE BRAZILIAN FEDERAL HIGHWAYS
 TRAFFIC CRASHES IN WORK ZONES: AN OVERVIEW OF THE BRAZILIAN FEDERAL HIGHWAYS Camila Belleza Maciel Barreto LabTrans/UFSC Florianópolis, Brazil Phone: + 55 48 32256960 E-mail: camilabmaciel@gmail.com Amir
TRAFFIC CRASHES IN WORK ZONES: AN OVERVIEW OF THE BRAZILIAN FEDERAL HIGHWAYS Camila Belleza Maciel Barreto LabTrans/UFSC Florianópolis, Brazil Phone: + 55 48 32256960 E-mail: camilabmaciel@gmail.com Amir
Cryptosporidium Incident Response
 WWA Response Plan Cryptosporidium Incident Response Summary Cryptosporidium ( crypto ) is a diarrheal illness caused by a microscopic parasite that lives in the intestines of humans & animals. For a number
WWA Response Plan Cryptosporidium Incident Response Summary Cryptosporidium ( crypto ) is a diarrheal illness caused by a microscopic parasite that lives in the intestines of humans & animals. For a number
University of Victoria Campus Cycling Plan Terms of Reference. 1.0 Project Description
 University of Victoria Campus Cycling Plan Terms of Reference 1.0 Project Description The Campus Cycling Plan, a first for the University, will provide a comprehensive and coordinated approach to support
University of Victoria Campus Cycling Plan Terms of Reference 1.0 Project Description The Campus Cycling Plan, a first for the University, will provide a comprehensive and coordinated approach to support
The Schistosomiasis Control Initiative (SCI): rationale, development and implementation from
 The Schistosomiasis Control Initiative (SCI): rationale, development and implementation from 2002 2008 1719 A. FENWICK 1 *, J. P. WEBSTER 1, E. BOSQUE-OLIVA 1,L.BLAIR 1,F.M.FLEMING 1, Y. ZHANG 1,A.GARBA
The Schistosomiasis Control Initiative (SCI): rationale, development and implementation from 2002 2008 1719 A. FENWICK 1 *, J. P. WEBSTER 1, E. BOSQUE-OLIVA 1,L.BLAIR 1,F.M.FLEMING 1, Y. ZHANG 1,A.GARBA
Local Government Road Safety Summit - 9 April 2018
 Local Government Road Safety Summit - 9 April 2018 Report on outcomes The Associate Minister of Transport, Hon Julie Anne Genter held the Local Government Road Safety Summit in Wellington on 9 April 2018.
Local Government Road Safety Summit - 9 April 2018 Report on outcomes The Associate Minister of Transport, Hon Julie Anne Genter held the Local Government Road Safety Summit in Wellington on 9 April 2018.
The Global Helmet Vaccine Initiative. A project of AIP Foundation
 The Global Helmet Vaccine Initiative A project of AIP Foundation 1 Helmet = Vaccine Likelihood of Fatality from Road Traffic Crash Likelihood of Severe Head Injury from Road Traffic Crash 42% decrease
The Global Helmet Vaccine Initiative A project of AIP Foundation 1 Helmet = Vaccine Likelihood of Fatality from Road Traffic Crash Likelihood of Severe Head Injury from Road Traffic Crash 42% decrease
Community of Practice on Traumatic Brain Injury
 Community of Practice on Traumatic Brain Injury Second Meeting October 15, 2013, 3:00-4:00 PM ET For audio, please call 866-835-7973. Your phone line is currently muted. Today s Agenda Overview of TBI
Community of Practice on Traumatic Brain Injury Second Meeting October 15, 2013, 3:00-4:00 PM ET For audio, please call 866-835-7973. Your phone line is currently muted. Today s Agenda Overview of TBI
Silencing The Uproar
 Silencing The Uproar Fighting for Lions - One Year Later presented by Joe Hosmer, Al Maki, Melissa Simpson, Matt Eckert, Andrew Bird, CC Jaeger As a result, farmers and ranchers would no longer have any
Silencing The Uproar Fighting for Lions - One Year Later presented by Joe Hosmer, Al Maki, Melissa Simpson, Matt Eckert, Andrew Bird, CC Jaeger As a result, farmers and ranchers would no longer have any
ADDIS ABABA ROAD SAFETY STRATEGY
 ADDIS ABABA ROAD SAFETY STRATEGY (2017-2030) Feb 22, 2017 Presentation: Daniel Molla Overview Addis Ababa Capital City of Ethiopia, Seat of AU Area: 540 km 2 Population 3.4 million Road safety crises 400
ADDIS ABABA ROAD SAFETY STRATEGY (2017-2030) Feb 22, 2017 Presentation: Daniel Molla Overview Addis Ababa Capital City of Ethiopia, Seat of AU Area: 540 km 2 Population 3.4 million Road safety crises 400
Why walk? Introducing Heart Foundation Walking! What is Heart Foundation Walking? Your role. Host Organisation
 An Introduction Why walk? It s an inexpensive form of physical activity It s easy doesn t require special skills or equipment It has psychological and community benefits improves mental health and social
An Introduction Why walk? It s an inexpensive form of physical activity It s easy doesn t require special skills or equipment It has psychological and community benefits improves mental health and social
Pedestrian injuries in San Francisco: distribution, causes, and solutions
 Pedestrian injuries in San Francisco: distribution, causes, and solutions Presentation to the San Francisco Health Commission RAJIV BHATIA, MD, MPH DIRECTOR OF OCCUPATIONAL AND ENVIRONMENTAL HEALTH, SAN
Pedestrian injuries in San Francisco: distribution, causes, and solutions Presentation to the San Francisco Health Commission RAJIV BHATIA, MD, MPH DIRECTOR OF OCCUPATIONAL AND ENVIRONMENTAL HEALTH, SAN
Youth/Adult Delegation to WES Sister Community El Rodeo, El Salvador 2018
 Dates : Wednesday, June 20 Sunday, July 1 June 20 Travel to San Salvador June 21-22 in-country orientation, training and team building June 23- travel to El Rodeo June 23 July 1 - in El Rodeo July 1 return
Dates : Wednesday, June 20 Sunday, July 1 June 20 Travel to San Salvador June 21-22 in-country orientation, training and team building June 23- travel to El Rodeo June 23 July 1 - in El Rodeo July 1 return
POLICY AGENDA For Elder Pedestrian Safety
 POLICY AGENDA For Elder Pedestrian Safety Older adults and people with disabilities often have mobility, cognitive, and sensory limitations that affect their behavior as pedestrians and place them at risk
POLICY AGENDA For Elder Pedestrian Safety Older adults and people with disabilities often have mobility, cognitive, and sensory limitations that affect their behavior as pedestrians and place them at risk
Resource Allocation for Malaria Prevention
 Resource Allocation for Malaria Prevention Final Presentation April 17, 2008 Michele Cataldi Christina Cho Cesar Gutierrez Jeff Hull Phillip Kim Andrew Park Sponsor Contact: Jason Pickering, PhD. Faculty
Resource Allocation for Malaria Prevention Final Presentation April 17, 2008 Michele Cataldi Christina Cho Cesar Gutierrez Jeff Hull Phillip Kim Andrew Park Sponsor Contact: Jason Pickering, PhD. Faculty
Information Paper for SAN (CI-4) Identifying the Spatial Stock Structure of Tropical Pacific Tuna Stocks
 Current knowledge, key uncertainties and future research directions for defining the stock structure of skipjack, yellowfin, bigeye and South Pacific albacore tunas in the Pacific Ocean Information Paper
Current knowledge, key uncertainties and future research directions for defining the stock structure of skipjack, yellowfin, bigeye and South Pacific albacore tunas in the Pacific Ocean Information Paper
European Commission Policy, Promotion & Funding for Cycling Madeleine Kelly-Tychtl Directorate-General for Mobility & Transport
 European Commission Policy, Promotion & Funding for Cycling Madeleine Kelly-Tychtl Directorate-General for Mobility & EC Policy 1. policy 2011 White Paper: Two urban mobility goals Ø Halve the use of conventionally
European Commission Policy, Promotion & Funding for Cycling Madeleine Kelly-Tychtl Directorate-General for Mobility & EC Policy 1. policy 2011 White Paper: Two urban mobility goals Ø Halve the use of conventionally
School of Social and Community Medicine, University of Bristol Division of Global Public Health, UC San Diego
 This work was partially supported through a research grant from Gilead Sciences. Gilead had no influence on the design, analysis and content of the study Presentation based on work by Peter Vickerman,
This work was partially supported through a research grant from Gilead Sciences. Gilead had no influence on the design, analysis and content of the study Presentation based on work by Peter Vickerman,
Jerri Bartholomew and Sarah Bjork*
 The Effects of Flow on the Salmon Parasite Ceratomyxa shasta : Establishing Baseline Information For Assessment of Flow Management Alternatives For Mitigating Effects of Myxozoan Pathogens in the Klamath
The Effects of Flow on the Salmon Parasite Ceratomyxa shasta : Establishing Baseline Information For Assessment of Flow Management Alternatives For Mitigating Effects of Myxozoan Pathogens in the Klamath
National Safe Routes to School Program: Initial Results
 National Safe Routes to School Program: Initial Results Lauren Marchetti National Center for Safe Routes to School 9 th Annual New Partners for Smart Growth Thursday, February 4, 2010 Seattle, WA August
National Safe Routes to School Program: Initial Results Lauren Marchetti National Center for Safe Routes to School 9 th Annual New Partners for Smart Growth Thursday, February 4, 2010 Seattle, WA August
NIHR what s new. HSR UK Conference Dr Louise Wood Director of Science, Research & Evidence Department of Health & Social
 NIHR what s new HSR UK Conference 2018 Dr Louise Wood Director of Science, Research & Evidence Department of Health & Social Care @klouisewood Impact of the first ten years of NIHR History of NIHR establishment
NIHR what s new HSR UK Conference 2018 Dr Louise Wood Director of Science, Research & Evidence Department of Health & Social Care @klouisewood Impact of the first ten years of NIHR History of NIHR establishment
Study conducted by University of North Carolina Department of Exercise and Sports Science,
 THE LEARNING CURVE Little League Seeks to Address Concerns, Answer Questions about Curveballs & Overuse Study conducted by University of North Carolina Department of Exercise and Sports Science, Table
THE LEARNING CURVE Little League Seeks to Address Concerns, Answer Questions about Curveballs & Overuse Study conducted by University of North Carolina Department of Exercise and Sports Science, Table
County Donegal Public Participation Network Work Plan
 County Donegal Public Participation Network Work Plan Introduction The purpose of this document is to present a (DRAFT) Work Plan for County Donegal Public Participation Network which will enable member
County Donegal Public Participation Network Work Plan Introduction The purpose of this document is to present a (DRAFT) Work Plan for County Donegal Public Participation Network which will enable member
