T he recreational activity of rock climbing continues to grow. Anthropometry of young competitive sport rock climbers ORIGINAL ARTICLE
|
|
|
- Laurel Lewis
- 5 years ago
- Views:
Transcription
1 420 ORIGINAL ARTICLE Anthropometry of young competitive sport rock climbers P B Watts, L M Joubert, A K Lish, J D Mast, B Wilkins... See end of article for authors affiliations... Correspondence to: Professor Watts, 1401 Presque Isle Avenue, Marquette, MI 49855, USA; pwatts@nmu.edu Accepted 2 October Br J Sports Med 2003;37: Background: Adult elite competitive rock climbers are small in stature with low body mass and very low body fat percentage. These characteristics have generated concern that young climbers may attempt body mass reduction to extreme levels with adverse consequences for health and performance. No published anthropometry data for young competitive climbers exist. Objective: To describe the general anthropometric characteristics of junior US competitive rock climbers. Methods: Ninety subjects (mean (SD) age 13.5 (3.0) years) volunteered to participate. All competed at the Junior Competition Climbers Association US National Championship. Anthropometric variables, including height, mass, body mass index (BMI), arm span, biiliocristal and biacromial breadths, skinfold thickness at nine anatomical sites, forearm and hand volumes, and handgrip strength, were measured. Selected variables were expressed as ratio values and as normative age and sex matched centile scores where appropriate. A control group (n = 45) of non-climbing children and youths who participated in a variety of sports activities, including basketball, cross country running, cross country skiing, soccer, and swimming, underwent the same testing procedures in the Exercise Science Laboratory of Northern Michigan University. Results: Mean (SD) self reported climbing ability was (1.20), or about 5.11d on the Yosemite decimal system scale. The mean (SD) experience level was 3.2 (1.9) years, and subjects competed in 10 (5) organised competitions over a 12 month period. Despite similarity in age, there were significant differences (p<0.01) between climbers and control subjects for height, mass, centile scores for height and mass, ratio of arm span to height ( ape index ), biiliocristal/biacromial ratio, sum of seven and sum of nine skinfolds, estimated body fat percentage, and handgrip/mass ratio. Despite significantly lower skinfold sums and estimated body fat percentage, no differences were found between climbers and controls for absolute BMI or BMI expressed as a centile score. Conclusions: Young competitive climbers have similar general anthropometric characteristics to elite adult climbers. These include relatively small stature, low body mass, low sums of skinfolds, and high handgrip to mass ratio. Relative to age matched athletic non-climbers, climbers appear to be more linear in body type with narrow shoulders relative to hips. Differences in body composition exist between climbers and non-climbing athletes despite similar BMI values. T he recreational activity of rock climbing continues to grow in popularity, and the proliferation of indoor climbing walls has fostered informal and formal competitive venues. Study of the climber as an athlete is a relatively new pursuit within the exercise and sport sciences, and early research has focused on physical characteristics that may be associated with high level performance. Watts et al 1 found elite adult competitive climbers to be small in stature with low body mass and very low body fat percentages. Other studies that rated subjects as elite or expert have reported similar results. 2 4 Several studies have reported relatively high hand grip strength/body mass ratios in high level climbers. 15 Although they found high grip strength/mass ratios in elite climbers, Watts et al 1 categorised absolute handgrip strength scores as moderate and suggested that the high strength/ mass ratios were due to the effect of low body mass. The association of high level climbing performance with small stature and low body fat percentage, and the possibility of improving strength/mass ratio through body mass reduction, has raised concern about the potential long term health effects on climbers. Some authors have expressed concern over the effects of extreme body fat reduction, potential for eating disorders, and associated health and performance risks for climbers. 67 Despite anecdotal references to eating disorders and unrealistic weight reduction practices in climbers, no supportive published data in this area are available and no data exist to link the pursuit of excellence in climbing with associated long term health risks. Despite this lack of data, there has been at least one action to discourage manipulation of body mass through imposition of a minimum body mass index (BMI) standard on young competitive climbers. 8 Whether the selected levels of limitation are justifiable or reasonable for this specialised group of athletes is not known because no published anthropometry data for young competitive sport climbers exist. This study attempted to fill a portion of this information void relative to young climbers who perform at high levels. Specifically, its purpose was to evaluate anthropometry data for experienced junior competitive sport climbers between the ages of 9 and 18 years and to compare data for this group with an age matched group of physically active youth who do not climb. METHODS Ninety experienced competitive climbers (52 boys, 38 girls) volunteered and gave informed consent to participate in the study. These subjects were competitors at the United States National Championship of the Junior Competition Climbers Association (JCCA). All data for the climber group (climbers) were collected before competition at the site of the JCCA National Championship in September, Abbreviations: BMI, body mass index; YDS, Yosemite decimal system
2 Anthropometry of rock climbers 421 At the time of data collection, climbers completed a questionnaire to document training volume and self reported climbing ability for best top rope (with the rope anchored above the climber at all times) and red point (where the climber clips the rope into intermediate anchors along the climbing route) ascents. Climbing ability was defined as the most difficult ascent by top rope or red point style, whichever was higher, rated on a modified Yosemite decimal system (YDS) scale. The modified YDS scale for technical free climbing difficulty, where no artificial means are used to aid progress, currently extends from 0 to 15 with letter grades of a, b, c, and d subdividing the numerical categories. Letter subdivisions were assigned values of a = 0.00, b = 0.25, c = 0.50, and d = Thus, a YDS rating of 13b became for the calculation of means. A similar rating conversion has been previously used by Watts et al. 1 A comparison group of 45 age matched volunteers (controls; 30 boys, 15 girls) gave informed consent and underwent the same testing procedures as the climbers. Controls consisted of youths who were physically active in one or more organised sports but did not participate in climbing. They came from a variety of sports and activities including basketball, cross country running, cross country skiing, soccer, and swimming. All control testing was carried out in the Exercise Science Laboratory of Northern Michigan University. Data were expressed in the same way as for climbers to enable comparisons between the two groups. All anthropometry measurements were made in a resting state according to established procedures. 9 A Lafayette anthropometer was used, by a single investigator, to obtain all skeletal dimensions, with measurements made to the nearest millimetre. Standing height was recorded to the nearest half centimetre with the subject barefoot and with the back against a vertical wall. Mass was measured using a Tanita calibrated electronic scale. BMI was calculated as mass/height 2 where mass was expressed in kilograms and height in metres. Height, mass, and BMI were expressed as absolutes and as normative centile scores according to tables published by the US Department of Health and Human Services Centers for Disease Control and Prevention (CDC). 10 Arm span was measured in the standing position with the arms abducted horizontally. The greatest tip to tip distance between the extended fingers was recorded in centimetres. The ratio of arm span to height, known to climbers as the ape index, was calculated as arm span divided by height. Biiliocristal breadth was measured as the distance between the most lateral points on the iliac tubercles. Biacromial breadth was measured as the distance between the most lateral points on the acromion processes. Biiliocristal/ biacromial ratio was calculated as the biiliocristal breadth divided by the biacromial breadth. A lower score for this ratio indicates a more triangular torso. Skinfold thickness was measured to the nearest 0.5 mm with a calibrated Lange caliper at nine anatomical sites by the same trained technician. The nine sites measured were chest, subscapula, midaxilla, suprailiac, iliac crest, abdomen, triceps, thigh, and calf. All measurements were taken on the subject s right side. Percentage body fat (%fat) values were estimated by two different methods. The procedures of Jackson and Pollock 11 use seven skinfold site measurements to estimate body density, with %fat subsequently calculated by the Brozek equation. 4 The sum of the seven skinfolds (S7) used in the Jackson-Pollock equations and the sum of all nine skinfolds (S9) were calculated as variables. %fat was also estimated directly from two skinfold measurements (triceps and calf) by the youth specific equations of Slaughter et al. 13 Forearm and hand volumes were measured to the nearest millilitre by water displacement with the arm in a vertical anatomical position. Hand volume was measured by immersion to the level of a horizontal line between the styloid processes of the radius and ulna. Hand-forearm volume was Figure 1 Distribution of climbing ability (n = 90). YDS, Yosemite decimal system. measured by immersion to the level of the distal edge of the medial epicondyle of the humerus. Forearm volume was calculated as the difference between hand volume and handforearm volume. An adjustable Jaymar hydraulic hand dynamometer was used to record handgrip force, with the subject seated and the elbow flexed to 90. Maximum handgrip forces for each hand were recorded in kilograms as the highest of two trials. Right and left maximum handgrip forces were averaged to provide an average handgrip score. Handgrip/mass ratio was calculated as handgrip divided by total body mass. Jandel Sigma Stat software was used for all statistical analyses. Means (SD) were calculated for measured and calculated variables. Analysis of variance with Tukey post hoc tests were used to test for differences between groups. A p level of 0.05 or less was considered significant for all analyses. RESULTS Mean ages were 13.5 (3.0) and 13.7 (2.7) years for climbers and controls respectively. Climbers had participated in the activity for 3.2 (1.9) years and had competed in 10 (5) organised competitions within a 12 month period. The mean self reported climbing ability for climbers was rated at (1.20), or around 11d on the modified Yosemite YDS scale. Figure 1 presents the overall distribution of abilities among the numerical divisions of the YDS rating system. Table 1 presents means (SD) and minimum-maximum ranges for selected variables of training volume reported by the group of climbers. Control subjects reported a mean sport participation frequency of more than 100 sessions a year and a mean practice/competition time of 7.8 (4.5) hours a week in season. Control subjects also reported a mean of 6.5 (7.0) hours a week of aerobic type exercise as part of or in addition to sports participation. Table 2 presents means (SD) for selected measured variables. Significant differences between climbers and controls are indicated. The wide range of ages in our subjects and consequent variability in growth and developmental stages Table 1 (n=90) Variable Variables of training volume for climbers Mean (SD) Range (min max) Climbing season (months/year) 9.6 (2.9) Climbing sessions (days/week) 3.5 (1.2) Climbing duration (hours/session) 3.3 (1.5) Aerobic exercise (hours/week) 5.9 (5.2)
3 422 Watts, Joubert, Lish, et al Table 2 Means (SD) for selected anthropometric variables of the sample Variable Controls (n=45) Climbers (n=90) Male climbers (n=52) Female climbers (n=38) Height (cm) (14.0) (15.2)* (15.6) (11.9) Height percentile 79.3 (25.3) 50.0 (28.7)* 44.8 (26.0) 54.4 (31.3) Mass (kg) 54.1 (15.0) 47.8 (13.4)* 51.5 (13.6) 40.6 (9.6) Mass percentile 57.8 (25.6) 39.4 (23.5)* 40.8 (23.6) 39.8 (24.6) Height/mass ratio 3.28 (0.78) 3.51 (0.74) 3.33 (0.73) 3.86 (0.64) BMI 19.0 (3.2) 18.6 (2.3) 19.1 (2.2) 17.5 (2.1) BMI percentile 38.7 (29.7) 32.7 (21.5) 36.9 (21.3) 29.2 (21.6) Ape index 0.95 (0.15) 1.01 (0.02)* 1.02 (0.02) 1.01 (0.02) Biliocrist/biacrom ratio 0.74 (0.05) 0.86 (0.08)* 0.87 (0.08) 0.86 (0.08) Σ7 skinfolds (mm) 76.7 (33.4) 50.4 (14.5)* 45.3 (13.0) 56.0 (14.5) Σ9 skinfolds (mm) (45.2) 66.5 (20.5)* 59.3 (19.2) 74.3 (19.6) %Fat Jackson-Pollock 11.3 (6.6) 7.8 (4.4)* 4.4 (2.2) 12.2 (2.6) %Fat Slaughter 18.7 (6.9) 13.0 (3.7)* 11.0 (2.8) 15.9 (2.9) Forearm volume (ml) (266.6) (370.1) (254.8) (190.6) Forearm+hand volume (ml) (426.8) (344.9) (326.8) (235.3) Average HG (kg) 30.7 (13.4) 32.8 (12.8) 36.5 (12.9) 25.1 (6.8) HG/mass ratio 0.55 (0.13) 0.67 (0.12)* 0.70 (0.13) 0.62 (0.08) *Significantly different from controls (p<0.01). Significantly different from controls (p<0.05). BMI, Body mass index; HG, handgrip. make comparison and discussion of absolute data difficult. For this reason we have not compared boys with girls, although these data are presented in the right two columns of table 2. We have also used centile scores and ratio variables when possible. Climbers were significantly smaller in stature and had a lower body mass than the controls (p<0.01; table 2). These significant differences were also evident when data were expressed as normative centile scores (p<0.01; table 2). Height/mass ratio was also higher for climbers (p<0.05; table 2); however, BMI did not differ between the groups. Mean centile scores for BMI were lower for climbers, but this difference was not significant (p = 0.09). Both S7 and S9 skinfold measures were significantly lower for climbers, as were the results of both %fat estimations. The Slaughter equations yielded significantly higher mean %fat estimations than the Jackson-Pollock equations (p<0.01). Figure 2 presents means (SD) for individual skinfold site measurements by group and sex. Mean values were significantly higher for female than male climbers at the triceps, thigh, and calf sites. Mean values were significantly higher for female than male controls at the thigh and calf sites. Skinfold thicknesses were significantly lower for climbers than controls at the chest, iliac crest, abdomen, triceps, thigh, and calf for girls and at the chest, suprailiac, iliac crest, abdomen, triceps, thigh, and calf for boys. Forearm volume, hand+forearm volume, and handgrip force were not significantly different between climbers and controls. The handgrip/mass ratio was significantly higher in climbers. Figure 2 Means (SEM) for individual skinfold measurements by group and sex. *Significantly different from male climbers; p<0.05. Significantly different from male controls; p<0.05. Significantly different from same sex climbers; p<0.05.
4 Anthropometry of rock climbers 423 DISCUSSION Competitive climbing has become increasingly popular among children and youth in recent years. The US Competition Climbing Association (formerly the JCCA) sanctioned over 100 competitions for the year The increased participation of children and youth in competitive climbing highlights the popularity of this sport and increases the interest in research examining this unique population. However, recent published research has focused solely on adult climbers. This study presents the first large sample descriptive data for young competitive climbers. The mean ability level of the group of climbers in this study was (1.20) on the modified YDS scale or around 5.11d with the median at 5.12a on the normal YDS scale. The mean ability for this group of young climbers is lower than previously reported mean abilities of elite adult climbers. Watts et al 1 reported mean ability levels of 5.13c and 5.12c respectively for male (n = 21) and female (n = 18) semifinalists at a 1989 International World Cup competition. The adult subjects of Watts et al, however, were older (men = 26.6 (4.2) years; women = 27.8 (2.0) years) and had more climbing experience (men = 11.2 (4.9) years; women = 8.8 (3.7) years) than the present subjects. Figure 1 illustrates that a large number of these young climbers perform at a comparatively high standard. This is notable considering the large age and experience differences between the present sample and the adult climbers of a decade ago. As in previous studies with adult climbers, the young climbers in this study were found to be relatively small in stature and had low body mass, with means at or below the 50th centile for age and sex matched norms. Climbers were also significantly smaller and lighter than athletic control subjects. The small stature and low body mass in climbers minimises the work requirement of movement along the climbing route. A lighter mass also reduces the force output in muscle that would be required to sustain position and maintain a given hand configuration. This could result in a slower rate of fatigue in smaller climbers than their heavier counterparts. A concern that young climbers may manipulate body mass to extremes in attempts to gain advantage has led one organisation to adopt a set of minimum BMI standards for competitive climbers. 8 The ÖSK BMI limits vary from to for girls and from to for boys between 14 and 18 years of age. We applied these standards to our data and found that 21 of the 90 climbers, or 23.3%, would not have passed the BMI cut off standards of ÖSK. All of these 21 climbers were under 16 years of age. Although this seems like a high percentage, it should be noted that 11 of the 45 control athletes, or 24.4%, would not have passed the ÖSK BMI cut offs. We also found no significant differences between climbers and controls for absolute BMI score or for BMI expressed as a centile score. Despite no BMI related differences between climbers and controls, we did find significant differences for %fat by either estimation method. Our data also indicate that large discrepancies between equations for %fat estimation can occur. The Brozek equation may overestimate %fat in children because it is based on data from older adult cadavers. 20 Still, for our subjects, the Brozek equation yielded lower %fat values than the Slaughter equation. Unresolved questions about the assumptions of tissue densities for children and adolescents, particularly in athletic youth, discourage the application of body fat estimation equations in these populations. Although interpretation of the %fat data is problematic, large differences between the groups were observed for the S7 and S9 skinfold measures. It is also notable that both male and female climbers had lower individual site skinfold means at several sites than their respective controls (fig 2). Watts et al 1 compared individual skinfolds at seven sites between male and female finalists at an international climbing competition and found mean thicknesses for female climbers to exceed values for male climbers at only two sites, the triceps and thigh. The current data for junior climbers differ in this respect, with means for female climbers exceeding those for male climbers at all sites except the chest (fig 2), although these differences were only significant for the triceps, thigh, and calf. The differences in skinfold sums between climbers and controls indicate that the climbers had relatively less body fat. The S7 skinfold means for male and female climbers were 45.3 (13.0) and 56.0 (14.5) mm respectively. Although these values are significantly lower than the controls, they do not necessarily indicate severely low body fat levels. The S7 skinfold values for our subjects are higher than data previously reported for elite adult male (37.8 (6.8) mm) and female (42.5 (8.9) mm) competitive climbers. 1 Sum of skinfold values tend to increase from a point just after puberty to a peak at about 50 years of age. 20 Whether these athletes will follow a reverse of this trend and exhibit the very low body fat levels that have been observed in elite adult climbers will require longitudinal data. Considering the equivalent BMI for climbers and controls and the significant differences in skinfold measures, the climbers appear to be proportionately heavier in lean mass and lower in fat mass than the controls. The fact that the climbers had significantly lower skinfold sums than non-climbers without a difference in BMI suggests that BMI scores are inappropriate for screening subjects for extreme reductions in body weight and body fat. This is supported by Deurenberg et al 21 who found low correlations between BMI and %fat in a large group of subjects aged 7 20 years. Further study in this area is needed. Possession of a long reach relative to height is thought to have a positive influence on climbing performance. Climbers describe the ratio of arm span to height as an ape index and place significance on values over The climbers in this study had significantly higher ape index scores than the controls. Values were similar to those observed by Mermier, et al 18 for adult male ( ) and female ( ) climbers. However, there was no correlation between ape index and climbing ability in our subjects, with r = This low correlation is probably due to the relatively small variability in ape index among the climbers (SD = 0.02). It is also possible that the ape index becomes more important when other traits are equivalent. The higher biiliocristal/biacromial ratio in climbers indicates a less triangular torso than the controls. Most of this difference is accounted for by a narrower biacromial breadth (28.1 (2.5) v 35.7 (4.1) mm) relative to biiliocristal breadth (24.1 (2.6) v 26.2 (2.6) mm) in climbers than controls respectively. This narrower shoulder structure in the climbers could account for a portion of the lower mass observed. Perhaps of more significance is the possibility of a longer arm structure in climbers. The narrow biacromial breadth combined with the relatively large ape index suggests that the climbers had a longer arm component of the total finger tip to tip span distance than the controls. This could have implications for reach distance for a given body position and may be a more important factor than ape index alone. The lack of a significant difference between climbers and controls for handgrip force is supported by our earlier research, which found absolute handgrip strength in elite climbers to rank between the 50th and 75th centiles for age and sex matched norms. 1 When handgrip strength was expressed relative to body mass, as handgrip/mass ratio, climbers rated significantly higher than controls. Scores for boys (0.70 (0.13)) and girls (0.62 (0.08)) in this study compare closely with reported values for elite adult male (0.78 (0.06)) and female (0.66 (0.06)) climbers. 1 Scores for our subjects exceed some handgrip/mass ratios reported for adult climbers. Mermier et al 18 reported grip strength/mass ratios of 0.65
5 424 Watts, Joubert, Lish, et al Take home message Although these accomplished young sport climbers have similar anthropometric characteristics to elite adult climbers, it is notable that they perform at very high levels without the severe reductions in body fat that have been reported for adults. (0.14) and 0.49 (0.10) for adult male and female recreational climbers respectively. Greater development of forearm musculature in the climbers is suggested by our data that indicate no differences in forearm or forearm+hand volumes compared with controls despite significantly smaller stature and lower body mass. In summary, high level young competitive climbers present general anthropometric characteristics similar to elite adult climbers. These include relatively small stature, low body mass, low sum of skinfolds, and high handgrip/mass ratio. Relative to age matched athletic non-climbers, climbers also appear to be more linear in body type with narrow shoulders relative to hips. Body composition differences exist between climbers and non-climbing athletes despite equivalent BMI. ACKNOWLEDGEMENTS This study was supported through funding from a 1999/2000 Peter White Scholar Award and the College of Professional Studies of Northern Michigan University. The authors would also like to acknowledge the support of the Junior Competition Climbers Association and Club Sport, Tigard, Oregon for enabling access to the subjects for this study.... Authors affiliations P B Watts, L M Joubert, A K Lish, J D Mast, B Wilkins, Northern Michigan University, Marquette, MI 49855, USA REFERENCES 1 Watts PB, Martin DT, Durtschi S. Anthropometric profiles of elite male and female competitive sport rock climbers. J Sports Sci 1993;11: Booth J, Marino F, Hill C, et al. Energy cost of sport rock climbing in elite performers. Br J Sports Med 1999;33: Watts PB, Newbury V, Sulentic J. Acute changes in handgrip strength, endurance, and blood lactate with sustained sport rock climbing. J Sports Med Phys Fitness 1996;36: Watts PB, Daggett M, Gallagher P, et al. Metabolic responses during sport rock climbing and the effects of active versus passive recovery. Int J Sports Med 2000;21: Cutts A, Bollen SR. Grip strength and endurance in rock climbers. Proceedings of the Institution of Mechanical Engineers 1993;207: Downing S. Eating disorders: are climbers afflicted? Climbing 1994;15: Steuart K. Walking a thin line. Rock & Ice 1996;73: ÖSK (Öterreichische Sportkletter Kommission). Sportkletterreferat. Langgasse: ÖSK, Norton K, OldsT,eds.Anthropometrica. Sydney: University of New South Wales Press, CDC. Growth charts. Centers for Disease Control and Prevention, National Center for Health Statistics, nhanes/growthcharts/charts.html, Jackson AS, Pollock ML. Practical assessment of body composition. Physician and Sports Medicine 1985;13: Brozek J, Grande F, Anderson J, et al. Densitometric analysis of body composition: revision of some quantitative assumptions. Ann N Y Acad Sci 1963;110: Slaughter MH, Lohman TG, Boileau RA, et al. Skinfold equations for estimating body fatness in children and youth. Hum Biol 1988;60: Billat V, Palleja P, Charlaix T, et al. Energy specificity of rock climbing and aerobic capacity in competitive sport rock climbers. J Sports Med Phys Fitness 1995;35: Doran DA, Grace SR. Physiological and metabolic responses in novice and recreational rock climbers. In: Messenger N, Patterson W, Brook D, eds. The Science of Climbing and Mountaineering (CD-ROM). Champaign, IL: Human Kinetics Software, Grant S, Hynes V, Whittaker A, et al. Anthropometric, strength, endurance and flexibility characteristics of elite and recreational climbers. J Sports Sci 1996;14: Mermier CM, Robergs RA, McMinn SM, et al. Energy expenditure and physiological responses during indoor rock climbing. Br J Sports Med 1997;31: Mermier CM, Janot JM, Parker DL, et al. Physiological and anthropometric determinants of sport climbing performance. Br J Sports Med 2000;34: Watts PB, Drobish KM. Physiological responses to simulated rock climbing at different angles. Med Sci Sports Exerc 1998;30: Plowman SA, Smith DL. Exercise physiology for health, fitness, and performance. Boston: Allyn and Bacon, Deurenberg P, Weststrate JA, Seidell JC. Body mass index as a measure of body fatness: age- and sex-specific prediction formulas. Br J Nutr 1991;65: Br J Sports Med: first published as /bjsm on 26 September Downloaded from on 2 October 2018 by guest. Protected by copyright.
Somatic Profile of Competitive Sport Climbers
 Journal of Human Kinetics volume 29/2011, 107 113 107 Section III Sport, Physical Education & Recreation Somatic Profile of Competitive Sport Climbers by Paweł Tomaszewski 1, Jan Gajewski 1,2, Joanna Lewandowska
Journal of Human Kinetics volume 29/2011, 107 113 107 Section III Sport, Physical Education & Recreation Somatic Profile of Competitive Sport Climbers by Paweł Tomaszewski 1, Jan Gajewski 1,2, Joanna Lewandowska
Heart rate response to a climber s fall in sport climbing
 Proceeding 9th INSHS International Christmas Sport Scientific Conference, 4-6 December 2014. International Network of Sport and Health Science. Szombathely, Hungary Heart rate response to a climber s fall
Proceeding 9th INSHS International Christmas Sport Scientific Conference, 4-6 December 2014. International Network of Sport and Health Science. Szombathely, Hungary Heart rate response to a climber s fall
Vertical hand force and forearm EMG during a High-step Rock-on climbing move with and without added mass
 Northern Michigan University The Commons Conference Papers in Published Proceedings 2005 Vertical hand force and forearm EMG during a High-step Rock-on climbing move with and without added mass Randall
Northern Michigan University The Commons Conference Papers in Published Proceedings 2005 Vertical hand force and forearm EMG during a High-step Rock-on climbing move with and without added mass Randall
Validation of a Step Test in Children Ages 7-11
 Validation of a Step Test in Children Ages 7-11 Emilene Clark Aurora Fry Colleen Smith Tonya Thomas Primary Advisor: Jim Farris, PT, PhD April 20, 2011 Background Exercise Testing Maximal Testing Sub-maximal
Validation of a Step Test in Children Ages 7-11 Emilene Clark Aurora Fry Colleen Smith Tonya Thomas Primary Advisor: Jim Farris, PT, PhD April 20, 2011 Background Exercise Testing Maximal Testing Sub-maximal
Effect of a 7-Week Rock Climbing Class on Physical Fitness and Performance
 Western Michigan University ScholarWorks at WMU Master's Theses Graduate College 6-2015 Effect of a 7-Week Rock Climbing Class on Physical Fitness and Performance Justin Scott Cargo Western Michigan University,
Western Michigan University ScholarWorks at WMU Master's Theses Graduate College 6-2015 Effect of a 7-Week Rock Climbing Class on Physical Fitness and Performance Justin Scott Cargo Western Michigan University,
Physiological and anthropometric determinants of sport climbing performance
 Br J Sports Med 2000;34:359 366 359 Center for Exercise and Applied Human Physiology, University of New Mexico, Albuquerque, New Mexico, USA C M Mermier J M Janot D L Parker JGSwan Correspondence to: C
Br J Sports Med 2000;34:359 366 359 Center for Exercise and Applied Human Physiology, University of New Mexico, Albuquerque, New Mexico, USA C M Mermier J M Janot D L Parker JGSwan Correspondence to: C
FITNESSGRAM Scorecard (for Males , and Adults 18+) Females see last pages
 FITNESSGRAM Scorecard (for Males 14-17+, and Adults 18+) Females see last pages Name: Date: Age: Weight Health Weight: Height: lbs inches Inches 2 : BMI: = (lbs x 703) / inches 2 Skinfold Measures See:
FITNESSGRAM Scorecard (for Males 14-17+, and Adults 18+) Females see last pages Name: Date: Age: Weight Health Weight: Height: lbs inches Inches 2 : BMI: = (lbs x 703) / inches 2 Skinfold Measures See:
INFORMATION SHEET FOR PROSPECTIVE VOLUNTEERS IN THE STUDY
 APPENDICES 126 APPENDIX A INFORMATION SHEET FOR PROSPECTIVE VOLUNTEERS IN THE STUDY PHYSIOLOGICAL AND ANTHROPOMETRICAL COMPARISONS BETWEEN THE TRIATHLETE, RUNNER, CYCLIST AND SWIMMER A study by Jonathan
APPENDICES 126 APPENDIX A INFORMATION SHEET FOR PROSPECTIVE VOLUNTEERS IN THE STUDY PHYSIOLOGICAL AND ANTHROPOMETRICAL COMPARISONS BETWEEN THE TRIATHLETE, RUNNER, CYCLIST AND SWIMMER A study by Jonathan
Changes in a Top-Level Soccer Referee s Training, Match Activities, and Physiology Over an 8-Year Period: A Case Study
 Case Study International Journal of Sports Physiology and Performance, 2011, 6, 281-286 2011 Human Kinetics, Inc. Changes in a Top-Level Soccer Referee s Training, Match Activities, and Physiology Over
Case Study International Journal of Sports Physiology and Performance, 2011, 6, 281-286 2011 Human Kinetics, Inc. Changes in a Top-Level Soccer Referee s Training, Match Activities, and Physiology Over
University of Canberra. This thesis is available in print format from the University of Canberra Library.
 University of Canberra This thesis is available in print format from the University of Canberra Library. If you are the author of this thesis and wish to have the whole thesis loaded here, please contact
University of Canberra This thesis is available in print format from the University of Canberra Library. If you are the author of this thesis and wish to have the whole thesis loaded here, please contact
Montana Hayes. Height: 72 inches (6 0 ) or 1.83 meters Weight: lbs or 70.4 kg BMI: Sum of Three Site Skinfold Calculations
 Montana Hayes Montana is a women s track and field athlete at Concordia University, Nebraska. She competes in the multievents (indoor pentathlon and outdoor heptathlon). In training for these events, Montana
Montana Hayes Montana is a women s track and field athlete at Concordia University, Nebraska. She competes in the multievents (indoor pentathlon and outdoor heptathlon). In training for these events, Montana
An Exploratory Study of Psychomotor Abilities among Cricket Players of Different Level of Achievement
 Research Journal of Physical Education Sciences ISSN 2320 9011 An Exploratory Study of Psychomotor Abilities among Cricket Players of Different Level of Achievement Abstract Baljinder Singh Bal and Ranjeet
Research Journal of Physical Education Sciences ISSN 2320 9011 An Exploratory Study of Psychomotor Abilities among Cricket Players of Different Level of Achievement Abstract Baljinder Singh Bal and Ranjeet
DETERMINANT FACTORS RELATED TO PERFORMANCE IN YOUNG SWIMMERS
 DETERMINANT FACTORS RELATED TO PERFORMANCE IN YOUNG SWIMMERS Luís Rama1 João Santos2, Paulo Gomes2, Francisco Alves3 1Faculdade de Ciências do Desporto e Educação Física, Universidade de Coimbra, Portugal
DETERMINANT FACTORS RELATED TO PERFORMANCE IN YOUNG SWIMMERS Luís Rama1 João Santos2, Paulo Gomes2, Francisco Alves3 1Faculdade de Ciências do Desporto e Educação Física, Universidade de Coimbra, Portugal
University of Canberra. This thesis is available in print format from the University of Canberra Library.
 University of Canberra This thesis is available in print format from the University of Canberra Library. If you are the author of this thesis and wish to have the whole thesis loaded here, please contact
University of Canberra This thesis is available in print format from the University of Canberra Library. If you are the author of this thesis and wish to have the whole thesis loaded here, please contact
Journal of Undergraduate Kinesiology Research
 Physiological responses of rock climbing 1 Journal of Undergraduate Kinesiology Research Official Research Journal of the Department of Kinesiology University of Wisconsin Eau Claire Volume 2 Number 2
Physiological responses of rock climbing 1 Journal of Undergraduate Kinesiology Research Official Research Journal of the Department of Kinesiology University of Wisconsin Eau Claire Volume 2 Number 2
BODY FORM INFLUENCES ON THE DRAG EXPERIENCED BY JUNIOR SWIMMERS. Australia, Perth, Australia
 1 BODY FORM INFLUENCES ON THE DRAG EXPERIENCED BY JUNIOR SWIMMERS Andrew Lyttle 1, Nat Benjanuvatra 2, Brian A Blanksby 2, Bruce C Elliott 2 1 Western Australian Institute of Sport, Perth, Australia 2
1 BODY FORM INFLUENCES ON THE DRAG EXPERIENCED BY JUNIOR SWIMMERS Andrew Lyttle 1, Nat Benjanuvatra 2, Brian A Blanksby 2, Bruce C Elliott 2 1 Western Australian Institute of Sport, Perth, Australia 2
A Comparative Analysis of Motor Fitness Components among Sprinters, Throwers and Jumpers
 Research Journal of Physical Education Sciences ISSN 2320 9011 A Comparative Analysis of Motor Fitness Components among, and Abstract Manjit Singh 1*, Sukhbir Singh 2 and Baljinder Singh Bal 3 1 Department
Research Journal of Physical Education Sciences ISSN 2320 9011 A Comparative Analysis of Motor Fitness Components among, and Abstract Manjit Singh 1*, Sukhbir Singh 2 and Baljinder Singh Bal 3 1 Department
Sex Differences in Growth and Performance of Track and Field Athletes Years
 Journal of Human Kinetics volume 24 2010, 79 85 Section III Sport, Physical Education & Recreation 79 Sex Differences in Growth and Performance of Track and Field Athletes 11 15 Years by Robert M. Malina
Journal of Human Kinetics volume 24 2010, 79 85 Section III Sport, Physical Education & Recreation 79 Sex Differences in Growth and Performance of Track and Field Athletes 11 15 Years by Robert M. Malina
Comparison Level of Handgrip Strength for the Three Categories among Male Athlete s Artificial Wall Climbing and Factors WILL Affect
 Comparison Level of Handgrip Strength for the Three Categories among Male Athlete s Artificial Wall Climbing and Factors WILL Affect Siti NurSarah Salehhodin, Borhannudin Abdullah and Aminuddin Yusoff
Comparison Level of Handgrip Strength for the Three Categories among Male Athlete s Artificial Wall Climbing and Factors WILL Affect Siti NurSarah Salehhodin, Borhannudin Abdullah and Aminuddin Yusoff
JEPonline Journal of Exercise Physiologyonline
 Walking Technique and Estimated VO 2 max Values 21 JEPonline Journal of Exercise Physiologyonline Official Journal of The American Society of Exercise Physiologists (ASEP) ISSN 1097-9751 An International
Walking Technique and Estimated VO 2 max Values 21 JEPonline Journal of Exercise Physiologyonline Official Journal of The American Society of Exercise Physiologists (ASEP) ISSN 1097-9751 An International
A Comparative Study of Running Agility, Jumping Ability and Throwing Ability among Cricket Players
 Research Journal of Physical Education Sciences ISSN 2320 9011 A Comparative Study of Running Agility, Jumping Ability and Throwing Ability among Cricket Players Abstract Karunesh Kumar 1, Manjit Singh
Research Journal of Physical Education Sciences ISSN 2320 9011 A Comparative Study of Running Agility, Jumping Ability and Throwing Ability among Cricket Players Abstract Karunesh Kumar 1, Manjit Singh
Assessment of an International Breaststroke Swimmer Using a Race Readiness Test
 International Journal of Sports Physiology and Performance, 2009, 4, 139-143 2009 Human Kinetics, Inc. Assessment of an International Breaststroke Swimmer Using a Race Readiness Test Kevin G. Thompson
International Journal of Sports Physiology and Performance, 2009, 4, 139-143 2009 Human Kinetics, Inc. Assessment of an International Breaststroke Swimmer Using a Race Readiness Test Kevin G. Thompson
NO ASSOCIATION BETWEEN SKINFOLD THICKNESSES AND RACE PERFORMANCE IN MALE ULTRA-ENDURANCE CYCLISTS IN A 600 KM ULTRA-CYCLING MARATHON
 2009, vol. 10 (2), 91 95 NO ASSOCIATION BETWEEN SKINFOLD THICKNESSES AND RACE PERFORMANCE IN MALE ULTRA-ENDURANCE CYCLISTS IN A 600 KM ULTRA-CYCLING MARATHON DOI: 10.2478/v10038-009-0018-y Beat Knechtle
2009, vol. 10 (2), 91 95 NO ASSOCIATION BETWEEN SKINFOLD THICKNESSES AND RACE PERFORMANCE IN MALE ULTRA-ENDURANCE CYCLISTS IN A 600 KM ULTRA-CYCLING MARATHON DOI: 10.2478/v10038-009-0018-y Beat Knechtle
Monitoring of performance an training in rowers
 Monitoring of performance an training in rowers Jaak Jürimäe Demands of the Sport High maximal oxygen consumption (VO 2max ); Ability to perform at a high percentage of VO 2max for the duration of event;
Monitoring of performance an training in rowers Jaak Jürimäe Demands of the Sport High maximal oxygen consumption (VO 2max ); Ability to perform at a high percentage of VO 2max for the duration of event;
Research nurses trained in the method are responsible for recording all anthropometric measurements from all subjects.
 Anthropometric measures No: 007D 1. Introduction Anthropometric measurements are widely used to predict body density or fat content. A variety of different procedures can be done. For this project waist/hip
Anthropometric measures No: 007D 1. Introduction Anthropometric measurements are widely used to predict body density or fat content. A variety of different procedures can be done. For this project waist/hip
Review Supplement Info Waist-to hip Ratio, Gurth Measurements & Skin Fold
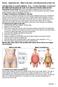 THIS MATERIAL IS A SUPPLEMENTAL TOOL. IT IS NOT INTENDED TO REPLACE INFORMATION PROVIDED IN YOUR TEXT AND/OR STUDENT HAND-BOOKS. Assessing Percent Body Fat: While hydrostatic weighing and the Bod Pod are
THIS MATERIAL IS A SUPPLEMENTAL TOOL. IT IS NOT INTENDED TO REPLACE INFORMATION PROVIDED IN YOUR TEXT AND/OR STUDENT HAND-BOOKS. Assessing Percent Body Fat: While hydrostatic weighing and the Bod Pod are
Optimizing Muscular Strength-to-Weight Ratios in Rock Climbing
 BEAST FINGERS CL IMBIN G RESEARCH MARCH 2018 Optimizing Muscular Strength-to-Weight Ratios in Rock Climbing BY AMAN A N DERSO N A C K N O W L EDG E MENT S We want to thank Dr. Christoph Lutter, and Steven
BEAST FINGERS CL IMBIN G RESEARCH MARCH 2018 Optimizing Muscular Strength-to-Weight Ratios in Rock Climbing BY AMAN A N DERSO N A C K N O W L EDG E MENT S We want to thank Dr. Christoph Lutter, and Steven
Anaerobic and aerobic contributions to 800 m and 8 km season bests
 Short Communication Anaerobic and aerobic contributions to 8 m and 8 km season bests Julia C. Blumkaitis, Christopher L. Sandefur, Christopher A. Fahs, Lindy M. Rossow Objective: Both anaerobic and aerobic
Short Communication Anaerobic and aerobic contributions to 8 m and 8 km season bests Julia C. Blumkaitis, Christopher L. Sandefur, Christopher A. Fahs, Lindy M. Rossow Objective: Both anaerobic and aerobic
Chapter III. Methodology
 Chapter III Methodology 31 Chapter III METHODOLOGY In this chapter, the procedure adopted for the selection of subjects and variables, criterion measures, reliability of the data, administration of the
Chapter III Methodology 31 Chapter III METHODOLOGY In this chapter, the procedure adopted for the selection of subjects and variables, criterion measures, reliability of the data, administration of the
The running economy difference between running barefoot and running shod
 Proceeding 9th INSHS International Christmas Sport Scientific Conference, 4-6 December 2014. International Network of Sport and Health Science. Szombathely, Hungary The running economy difference between
Proceeding 9th INSHS International Christmas Sport Scientific Conference, 4-6 December 2014. International Network of Sport and Health Science. Szombathely, Hungary The running economy difference between
Stride Frequency, Body Fat Percentage, and the Amount of Knee Flexion Affect the Race Time of Male Cross Country Runners
 Stride Frequency, Body Fat Percentage, and the Amount of Knee Flexion Affect the Race Time of Male Cross Country Runners Vineel Mallavarapu 1 and Kevin Finn 2 1 Cedar Falls High School, Cedar Falls, IA
Stride Frequency, Body Fat Percentage, and the Amount of Knee Flexion Affect the Race Time of Male Cross Country Runners Vineel Mallavarapu 1 and Kevin Finn 2 1 Cedar Falls High School, Cedar Falls, IA
Program B-4 Evaluating Physical Development and Nutrition
 Program B-4 Evaluating Physical Development and Nutrition 31 32 I. The Importance of Body Measurement Body measurements are one way we measure a student's physical development. We can evaluate health,
Program B-4 Evaluating Physical Development and Nutrition 31 32 I. The Importance of Body Measurement Body measurements are one way we measure a student's physical development. We can evaluate health,
subjects included in group A were members of other
 Brit. J. Sports Med. - Vol. 11, No. 3, September 1977, pp. 133-137 A STUDY OF TH PHYSICAL WORKING CAPACITY OF GALIC FOOTBALLRS AND HURLRS A.W. S. WATSON, B.Sc., M.Sc., Ph.D., F.R.A.M.I. Department of Physiology,
Brit. J. Sports Med. - Vol. 11, No. 3, September 1977, pp. 133-137 A STUDY OF TH PHYSICAL WORKING CAPACITY OF GALIC FOOTBALLRS AND HURLRS A.W. S. WATSON, B.Sc., M.Sc., Ph.D., F.R.A.M.I. Department of Physiology,
Grandjean,(1) in his opening address at
 AIHA Journal 63:300 304 (2002) Ms. #127 AUTHORS S.A. Lavender a W.S. Marras b R.J. Sabol c a Department of Orthopedic Surgery, Rush-Presbyterian, St. Luke s Medical Center, 1653 W. Congress Parkway, Chicago,
AIHA Journal 63:300 304 (2002) Ms. #127 AUTHORS S.A. Lavender a W.S. Marras b R.J. Sabol c a Department of Orthopedic Surgery, Rush-Presbyterian, St. Luke s Medical Center, 1653 W. Congress Parkway, Chicago,
Study of anthropometric characteristics among the university level archers
 2017; 2(2): 515-519 ISSN: 2456-0057 IJPNPE 2017; 2(2): 515-519 2017 IJPNPE www.journalofsports.com Received: 27-05-2017 Accepted: 28-06-2017 Ritika Physical Education Teacher, Sri Guru Harkrishan Public
2017; 2(2): 515-519 ISSN: 2456-0057 IJPNPE 2017; 2(2): 515-519 2017 IJPNPE www.journalofsports.com Received: 27-05-2017 Accepted: 28-06-2017 Ritika Physical Education Teacher, Sri Guru Harkrishan Public
POSITION-SPECIFIC ANTHROPOMETRIC PROFILES: 2011 WOMEN'S 19 EUROPEAN HANDBALL CHAMPIONSHIP
 POSITION-SPECIFIC ANTHROPOMETRIC PROFILES: 2011 WOMEN'S 19 EUROPEAN HANDBALL CHAMPIONSHIP František URBAN 1, Róbert KANDRÁČ 2, František TÁBORSKÝ 3 1 Member of Union of University Handball Teachers / EHF
POSITION-SPECIFIC ANTHROPOMETRIC PROFILES: 2011 WOMEN'S 19 EUROPEAN HANDBALL CHAMPIONSHIP František URBAN 1, Róbert KANDRÁČ 2, František TÁBORSKÝ 3 1 Member of Union of University Handball Teachers / EHF
Walkable Communities and Adolescent Weight
 Walkable Communities and Adolescent Weight Sandy Slater, PhD Assistant Professor, University of Illinois at Chicago, School of Public Health Research Scientist, UIC Institute for Health Research and Policy
Walkable Communities and Adolescent Weight Sandy Slater, PhD Assistant Professor, University of Illinois at Chicago, School of Public Health Research Scientist, UIC Institute for Health Research and Policy
Energy cost of sport rock climbing in elite performers
 14 Br J Sports Med 1999;33:14 18 Original articles Department of Biomedical Science, The University of Wollongong, Wollongong, NSW 2522, Australia J Booth Human Movement Studies Unit, Charles Sturt University,
14 Br J Sports Med 1999;33:14 18 Original articles Department of Biomedical Science, The University of Wollongong, Wollongong, NSW 2522, Australia J Booth Human Movement Studies Unit, Charles Sturt University,
SPORT INJURIES IN SQUASH
 Original Article SPORT INJURIES IN SQUASH Farshad Okhovatian 1, Ezatolahi AH 2 ABSTRACT Objective: Investigating the squash injuries in the Iranian Squash Federation players. Methodology: We prepared a
Original Article SPORT INJURIES IN SQUASH Farshad Okhovatian 1, Ezatolahi AH 2 ABSTRACT Objective: Investigating the squash injuries in the Iranian Squash Federation players. Methodology: We prepared a
FITNESS TESTING PKG. REPORT AND SPARQ PROTOCOL
 FITNESS TESTING PKG. REPORT AND PROTOCOL BC SOCCER FITNESS TEST PACKAGE INTRODUCTION Over the past 6 years, BC Soccer Provincial Team Programs and the CSA National Training Centre Program West have been
FITNESS TESTING PKG. REPORT AND PROTOCOL BC SOCCER FITNESS TEST PACKAGE INTRODUCTION Over the past 6 years, BC Soccer Provincial Team Programs and the CSA National Training Centre Program West have been
Myths and Science in Cycling
 Myths and Science in Cycling John McDaniel, PhD Kent State University Jim Martin, PhD - U of Utah Steve Elmer, PhD- Michigan Tech Who am I PhD in Exercise Physiology under Dr. Jim Martin at the University
Myths and Science in Cycling John McDaniel, PhD Kent State University Jim Martin, PhD - U of Utah Steve Elmer, PhD- Michigan Tech Who am I PhD in Exercise Physiology under Dr. Jim Martin at the University
The Effect of the Arm Swing on the Heart Rate of Non-Athletes
 The Effect of the Arm Swing on the Heart Rate of Non-Athletes Seekaow Churproong MD*, Buratin Khampirat PhD*, Paraj Ratanajaipan MEng**, Poollarp Tattathongkom BS** * Suranaree University of Technology,
The Effect of the Arm Swing on the Heart Rate of Non-Athletes Seekaow Churproong MD*, Buratin Khampirat PhD*, Paraj Ratanajaipan MEng**, Poollarp Tattathongkom BS** * Suranaree University of Technology,
The following reference pages can be downloaded, given to your learners, who can put them to one side until needed.
 Retail Maths Numeracy skills are needed in many retail activities. Your employees will need to measure, and to work out maths problems daily. Sometimes it is good to have a general reference page for them
Retail Maths Numeracy skills are needed in many retail activities. Your employees will need to measure, and to work out maths problems daily. Sometimes it is good to have a general reference page for them
2012 CALIFORNIA PHYSICAL FITNESS TEST. e-template REFERENCE GUIDE
 2012 CALIFORNIA PHYSICAL FITNESS TEST e-template REFERENCE GUIDE Evalumetrics Inc. January 2012 2012 New e-template Features Starting this year, the e-template contains several new worksheets, with color-coded
2012 CALIFORNIA PHYSICAL FITNESS TEST e-template REFERENCE GUIDE Evalumetrics Inc. January 2012 2012 New e-template Features Starting this year, the e-template contains several new worksheets, with color-coded
Using Hexoskin Wearable Technology to Obtain Body Metrics During Trail Hiking
 Technical Note Using Hexoskin Wearable Technology to Obtain Body Metrics During Trail Hiking JEFF MONTES 1, TORI M. STONE 1, JACOB W. MANNING 2, DAMON MCCUNE 1, DEBRA K. TACAD 1, JOHN C. YOUNG 1, MARK
Technical Note Using Hexoskin Wearable Technology to Obtain Body Metrics During Trail Hiking JEFF MONTES 1, TORI M. STONE 1, JACOB W. MANNING 2, DAMON MCCUNE 1, DEBRA K. TACAD 1, JOHN C. YOUNG 1, MARK
Anthropometric Profile and Special Judo Fitness levels of Indian Judo Players
 ORIGINAL ARTICLE Anthropometric Profile and Special Judo Fitness levels of Indian Judo Players Jayasudha Katralli *, MD; Shivaprasad S. Goudar, MD, MHPE Authors Affiliation: Department of Physiology, J.N.M.C.
ORIGINAL ARTICLE Anthropometric Profile and Special Judo Fitness levels of Indian Judo Players Jayasudha Katralli *, MD; Shivaprasad S. Goudar, MD, MHPE Authors Affiliation: Department of Physiology, J.N.M.C.
INTERACTION OF STEP LENGTH AND STEP RATE DURING SPRINT RUNNING
 INTERACTION OF STEP LENGTH AND STEP RATE DURING SPRINT RUNNING Joseph P. Hunter 1, Robert N. Marshall 1,, and Peter J. McNair 3 1 Department of Sport and Exercise Science, The University of Auckland, Auckland,
INTERACTION OF STEP LENGTH AND STEP RATE DURING SPRINT RUNNING Joseph P. Hunter 1, Robert N. Marshall 1,, and Peter J. McNair 3 1 Department of Sport and Exercise Science, The University of Auckland, Auckland,
Leg Power in Elite Male Fencers: A Comparative Study among the Three Competitive Disciplines
 Leg Power in Elite Male Fencers: A Comparative Study among the Three Competitive Disciplines Gustavo D. Aquilino, Aldo F. Longo, Néstor A. Lentini. Exercise Physiology Laboratory, National Sport High Performance
Leg Power in Elite Male Fencers: A Comparative Study among the Three Competitive Disciplines Gustavo D. Aquilino, Aldo F. Longo, Néstor A. Lentini. Exercise Physiology Laboratory, National Sport High Performance
Women s hockey players have been competing. Prediction of Ice Skating Performance With Off- Ice Testing in Women s Ice Hockey Players
 Journal of Strength and Conditioning Research, 2001, 15(1), 116 122 2001 National Strength & Conditioning Association Prediction of Ice Skating Performance With Off- Ice Testing in Women s Ice Hockey Players
Journal of Strength and Conditioning Research, 2001, 15(1), 116 122 2001 National Strength & Conditioning Association Prediction of Ice Skating Performance With Off- Ice Testing in Women s Ice Hockey Players
Anthropometric and Biomechanical Characteristics on Body Segments of Koreans
 APPLIED HUMAN SCIENCE Journal of Physiological Anthropology Anthropometric and Biomechanical Characteristics on Body Segments of Koreans Se Jin Park 1), Chae-Bogk Kim 2) and Soo Chan Park 1) 1) Ergonomics
APPLIED HUMAN SCIENCE Journal of Physiological Anthropology Anthropometric and Biomechanical Characteristics on Body Segments of Koreans Se Jin Park 1), Chae-Bogk Kim 2) and Soo Chan Park 1) 1) Ergonomics
Journal of Human Sport and Exercise E-ISSN: Universidad de Alicante España
 Journal of Human Sport and Exercise E-ISSN: 1988-5202 jhse@ua.es Universidad de Alicante España KALINA, TOMAS; CACEK, JAN; KMETOVA, LINDA The running economy difference between running barefoot and running
Journal of Human Sport and Exercise E-ISSN: 1988-5202 jhse@ua.es Universidad de Alicante España KALINA, TOMAS; CACEK, JAN; KMETOVA, LINDA The running economy difference between running barefoot and running
APPROACH RUN VELOCITIES OF FEMALE POLE VAULTERS
 APPROACH RUN VELOCITIES OF FEMALE POLE VAULTERS Peter M. McGinnis, Physical Education Department, SUNY College at Cortland, Cortland, New York INTRODUCTION Running speed is an important determinant of
APPROACH RUN VELOCITIES OF FEMALE POLE VAULTERS Peter M. McGinnis, Physical Education Department, SUNY College at Cortland, Cortland, New York INTRODUCTION Running speed is an important determinant of
Activity profiles in adolescent netball: A combination of global positioning system technology and time-motion analysis
 Proceeding Asia Pacific Conference on Performance Analysis of Sport, 21-24 April 2014. Langkawi, Malaysia Activity profiles in adolescent netball: A combination of global positioning system technology
Proceeding Asia Pacific Conference on Performance Analysis of Sport, 21-24 April 2014. Langkawi, Malaysia Activity profiles in adolescent netball: A combination of global positioning system technology
Marathon performance in relation to body fat percentage and training indices in recreational male runners
 Zurich Open Repository and Archive University of Zurich Main Library Strickhofstrasse 39 CH-8057 Zurich www.zora.uzh.ch Year: 2013 Marathon performance in relation to body fat percentage and training indices
Zurich Open Repository and Archive University of Zurich Main Library Strickhofstrasse 39 CH-8057 Zurich www.zora.uzh.ch Year: 2013 Marathon performance in relation to body fat percentage and training indices
The Influence of Heavy Truck Egress Tactics on Ground Reaction Force
 The Influence of Heavy Truck Egress Tactics on Ground Reaction Force Matthew P. Reed Suzanne G. Hoffman Sheila M. Ebert-Hamilton University of Michigan Transportation Research Institute, 2901 Baxter Road,
The Influence of Heavy Truck Egress Tactics on Ground Reaction Force Matthew P. Reed Suzanne G. Hoffman Sheila M. Ebert-Hamilton University of Michigan Transportation Research Institute, 2901 Baxter Road,
The Physical and Physiological Characteristics of 3x3. Results of Medical Study & Scientific Test
 The Physical and Physiological Characteristics of 3x3 Results of Medical Study & Scientific Test Prepared by Dr. Paul Montgomery & Brendan Maloney (Aspetar Orthopaedic Hospital) In cooperation with FIBA
The Physical and Physiological Characteristics of 3x3 Results of Medical Study & Scientific Test Prepared by Dr. Paul Montgomery & Brendan Maloney (Aspetar Orthopaedic Hospital) In cooperation with FIBA
SUPPLEMENTARY INFORMATION
 doi:10.1038/nature17654 Contents Supplementary Text S1. Calculating Locomotor Costs Supplementary Table 1. Estimated ranging costs for humans and other hominoids Supplementary Text S2. Estimating the Costs
doi:10.1038/nature17654 Contents Supplementary Text S1. Calculating Locomotor Costs Supplementary Table 1. Estimated ranging costs for humans and other hominoids Supplementary Text S2. Estimating the Costs
The Influence of Load Carrying Modes on Gait variables of Healthy Indian Women
 The Influence of Load Carrying Modes on Gait variables of Healthy Indian Women *Guha Thakurta A, Iqbal R and De A National Institute of Industrial Engineering, Powai, Vihar Lake, Mumbai-400087, India,
The Influence of Load Carrying Modes on Gait variables of Healthy Indian Women *Guha Thakurta A, Iqbal R and De A National Institute of Industrial Engineering, Powai, Vihar Lake, Mumbai-400087, India,
Coaching Applications. Maturational Timing and Swim Performance in Collegiate Female Swimmers
 Coaching Applications Maturational Timing and Swim Performance in Collegiate Female Swimmers Andrew C. Cornett 1, Sierra Wagner 1, Alan Duski 1, Brian V. Wright 2, and Joel M. Stager 3 1 School of Health
Coaching Applications Maturational Timing and Swim Performance in Collegiate Female Swimmers Andrew C. Cornett 1, Sierra Wagner 1, Alan Duski 1, Brian V. Wright 2, and Joel M. Stager 3 1 School of Health
Chapter III PROCEDURE SELECTION OF SUBJECTS
 69 Chapter III PROCEDURE In this chapter, the selection of subjects, selection of variables, criterion measures, collection of data, reliability of data, administration of tests/procedure of recording
69 Chapter III PROCEDURE In this chapter, the selection of subjects, selection of variables, criterion measures, collection of data, reliability of data, administration of tests/procedure of recording
A CROSS-SECTIONAL ANALYSIS OF SKILL RELATED PHYSICAL FITNESS COMPONENTS OF KAYAKING AND ROWING PLAYERS
 European Journal of Physical Education and Sport Science ISSN: 2501-1235 ISSN-L: 2501-1235 Available on-line at: www.oapub.org/edu doi: 10.5281/zenodo.1050701 Volume 3 Issue 10 2017 A CROSS-SECTIONAL ANALYSIS
European Journal of Physical Education and Sport Science ISSN: 2501-1235 ISSN-L: 2501-1235 Available on-line at: www.oapub.org/edu doi: 10.5281/zenodo.1050701 Volume 3 Issue 10 2017 A CROSS-SECTIONAL ANALYSIS
Sprint Hurdles SPRINT HURDLE RACES: A KINEMATIC ANALYSIS
 Sprint Hurdles SPRINT HURDLE RACES: A KINEMATIC ANALYSIS By Pierre-Jean Vazel, December 2011 In order to prescribe the most effective training possible it is important for coaches to have a sound understanding
Sprint Hurdles SPRINT HURDLE RACES: A KINEMATIC ANALYSIS By Pierre-Jean Vazel, December 2011 In order to prescribe the most effective training possible it is important for coaches to have a sound understanding
POSITION-SPECIFIC ANTHROPOMETRIC PROFILES: 2011 WOMEN'S 17 EUROPEAN HANDBALL CHAMPIONSHIP
 POSITION-SPECIFIC ANTHROPOMETRIC PROFILES: 2011 WOMEN'S 17 EUROPEAN HANDBALL CHAMPIONSHIP František URBAN 1, Róbert KANDRÁČ 2, František TÁBORSKÝ 3 1 Member of the Union of University Handball Teachers
POSITION-SPECIFIC ANTHROPOMETRIC PROFILES: 2011 WOMEN'S 17 EUROPEAN HANDBALL CHAMPIONSHIP František URBAN 1, Róbert KANDRÁČ 2, František TÁBORSKÝ 3 1 Member of the Union of University Handball Teachers
Comparative characteristics of elite New Zealand and South African u/16 rugby players with reference to gamespecific
 original research ARTICLE Comparative characteristics of elite New Zealand and South African u/16 rugby players with reference to gamespecific skills, physical abilities and anthropometric data Emanuel
original research ARTICLE Comparative characteristics of elite New Zealand and South African u/16 rugby players with reference to gamespecific skills, physical abilities and anthropometric data Emanuel
to understand the characteristics which are the result The present study is based on a cross-section sample of
 Brit J. Sports Med. - Vol. 14, Nos 2 & 3, August 1980, pp. 139-144 KINANTHROPOMETRY AND PERFORMANCE OF TOP RANKING INDIAN BASKETBALL PLAYERS H. S. SODHI, PhD Sports Medicine Research Laboratory, Netaii
Brit J. Sports Med. - Vol. 14, Nos 2 & 3, August 1980, pp. 139-144 KINANTHROPOMETRY AND PERFORMANCE OF TOP RANKING INDIAN BASKETBALL PLAYERS H. S. SODHI, PhD Sports Medicine Research Laboratory, Netaii
R ugby league is an international sport played at junior and
 334 ORIGINAL ARTICLE Physiological characteristics of junior and senior rugby league players T J Gabbett...... Correspondence to: Dr Gabbett, Sports Performance Unit, Tasmanian Institute of Sport, PO Box
334 ORIGINAL ARTICLE Physiological characteristics of junior and senior rugby league players T J Gabbett...... Correspondence to: Dr Gabbett, Sports Performance Unit, Tasmanian Institute of Sport, PO Box
Analysis of performance and age of the fastest 100- mile ultra-marathoners worldwide
 CLINICAL SCIENCE Analysis of performance and age of the fastest 100- mile ultra-marathoners worldwide Christoph Alexander Rüst, I Beat Knechtle, I,II Thomas Rosemann, I Romuald Lepers III I University
CLINICAL SCIENCE Analysis of performance and age of the fastest 100- mile ultra-marathoners worldwide Christoph Alexander Rüst, I Beat Knechtle, I,II Thomas Rosemann, I Romuald Lepers III I University
ISO INTERNATIONAL STANDARD. Ergonomics Manual handling Part 1: Lifting and carrying
 INTERNATIONAL STANDARD ISO 11228-1 First edition 2003-05-15 Ergonomics Manual handling Part 1: Lifting and carrying Ergonomie Manutention manuelle Partie 1: Manutention verticale et manutention horizontale
INTERNATIONAL STANDARD ISO 11228-1 First edition 2003-05-15 Ergonomics Manual handling Part 1: Lifting and carrying Ergonomie Manutention manuelle Partie 1: Manutention verticale et manutention horizontale
Predictors of race time in male ironman triathletes: physical characteristics, training, or prerace experience?
 Zurich Open Repository and Archive University of Zurich Main Library Strickhofstrasse 39 CH-8057 Zurich www.zora.uzh.ch Year: 2010 Predictors of race time in male ironman triathletes: physical characteristics,
Zurich Open Repository and Archive University of Zurich Main Library Strickhofstrasse 39 CH-8057 Zurich www.zora.uzh.ch Year: 2010 Predictors of race time in male ironman triathletes: physical characteristics,
Key words: biomechanics, injury, technique, measurement, strength, evaluation
 Becker, T., & Havriluk, R. (2006). Bilateral and anterior-posterior muscular imbalances in swimmers. In J. P. Vilas-Boas, F. Alves, A. Marques (Eds.), Biomechanics and Medicine in Swimming X. Portuguese
Becker, T., & Havriluk, R. (2006). Bilateral and anterior-posterior muscular imbalances in swimmers. In J. P. Vilas-Boas, F. Alves, A. Marques (Eds.), Biomechanics and Medicine in Swimming X. Portuguese
OXYGEN POWER By Jack Daniels, Jimmy Gilbert, 1979
 1 de 6 OXYGEN POWER By Jack Daniels, Jimmy Gilbert, 1979 Appendix A Running is primarily a conditioning sport. It is not a skill sport as is basketball or handball or, to a certain extent, swimming where
1 de 6 OXYGEN POWER By Jack Daniels, Jimmy Gilbert, 1979 Appendix A Running is primarily a conditioning sport. It is not a skill sport as is basketball or handball or, to a certain extent, swimming where
DESIGN BULLETIN #66/2010
 DESIGN BULLETIN #66/2010 Highway Geometric Design Guide Chapter B, Climbing Lane Warrants for Two Lane Undivided and Four Lane Divided Highways - Revised Summary This Design Bulletin is being issued as
DESIGN BULLETIN #66/2010 Highway Geometric Design Guide Chapter B, Climbing Lane Warrants for Two Lane Undivided and Four Lane Divided Highways - Revised Summary This Design Bulletin is being issued as
Is Body Fat a Predictor of Race Time in Female Long-Distance Inline Skaters?
 ORIGINAL ARTICLE Is Body Fat a Predictor of Race Time in Female Long-Distance Inline Skaters? Beat Knechtle* 1,2, MD; Patrizia Knechtle 1 ; Thomas Rosemann 2, MD, PhD; Romuald Lepers 3, PhD Authors Affiliation:
ORIGINAL ARTICLE Is Body Fat a Predictor of Race Time in Female Long-Distance Inline Skaters? Beat Knechtle* 1,2, MD; Patrizia Knechtle 1 ; Thomas Rosemann 2, MD, PhD; Romuald Lepers 3, PhD Authors Affiliation:
Physiological Assessment: Summary Report 11 December 2011
 Physiological Assessment: Summary Report 11 December 211 Katie Parry MD/LD Runner Athlete Test conducted and report compiled by: Dr Andi Drake England Athletics, Leeds Metropolitan University Headingley
Physiological Assessment: Summary Report 11 December 211 Katie Parry MD/LD Runner Athlete Test conducted and report compiled by: Dr Andi Drake England Athletics, Leeds Metropolitan University Headingley
What Length Paddle Should I Use!! Surf Life Saving Australia Level 3 Coaching Research Assignment. June By Richard Duncan
 What Length Paddle Should I Use!! Surf Life Saving Australia Level 3 Coaching Research Assignment June 2006 By Richard Duncan Aims To compare 3 common methods of determining an individuals optimal paddle
What Length Paddle Should I Use!! Surf Life Saving Australia Level 3 Coaching Research Assignment June 2006 By Richard Duncan Aims To compare 3 common methods of determining an individuals optimal paddle
Chapter I examines the anthropometric and physiological factors that. determine success in sport. More specifically it discusses the somatotype
 CHAPTER 1 INTRODUCTION Chapter I examines the anthropometric and physiological factors that determine success in sport. More specifically it discusses the somatotype ratings, VO 2 max and running economy
CHAPTER 1 INTRODUCTION Chapter I examines the anthropometric and physiological factors that determine success in sport. More specifically it discusses the somatotype ratings, VO 2 max and running economy
PHYSICAL FITNESS FOR LAWN BOWLING. by Rob Judson September 2002
 PHYSICAL FITNESS FOR LAWN BOWLING by Rob Judson September 2002 Page 2 General Fitness and Health Lawn bowls imposes lower physical demands than many other sports impose on players. The general physiological
PHYSICAL FITNESS FOR LAWN BOWLING by Rob Judson September 2002 Page 2 General Fitness and Health Lawn bowls imposes lower physical demands than many other sports impose on players. The general physiological
At What Extent Physical Training Can Minimize Gender Differences in Male and Female Trained Swimmers? - A Comparative Analysis
 International Journal of Sports and Physical Education (IJSPE) Volume 3, Issue 1, 2017, PP 24-28 ISSN 2454-6380 http://dx.doi.org/10.20431/2454-6380.0301005 www.arcjournals.org At What Extent Physical
International Journal of Sports and Physical Education (IJSPE) Volume 3, Issue 1, 2017, PP 24-28 ISSN 2454-6380 http://dx.doi.org/10.20431/2454-6380.0301005 www.arcjournals.org At What Extent Physical
Does wearing a wrist guard affect the site of wrist fracture in snow sports?
 Available online at www.sciencedirect.com Procedia Engineering 60 ( 2013 ) 238 242 6 th Asia-Pacific Congress on Sports Technology (APCST) Does wearing a wrist guard affect the site of wrist fracture in
Available online at www.sciencedirect.com Procedia Engineering 60 ( 2013 ) 238 242 6 th Asia-Pacific Congress on Sports Technology (APCST) Does wearing a wrist guard affect the site of wrist fracture in
Measuring Lung Capacity
 Name Class Date Chapter 37 Circulatory and Respiratory Systems Measuring Lung Capacity Introduction The amount of air that you move in and out of your lungs depends on how quickly you are breathing. The
Name Class Date Chapter 37 Circulatory and Respiratory Systems Measuring Lung Capacity Introduction The amount of air that you move in and out of your lungs depends on how quickly you are breathing. The
Vector Rope Trainer Cardiovascular Program Fitness Level: GENERAL
 Cardiovascular Program Fitness Level: GENERAL These are exercise options. Mix and match as preferred during each workout session. Frequency: Two to three days per week Start with 3 minutes of light pace
Cardiovascular Program Fitness Level: GENERAL These are exercise options. Mix and match as preferred during each workout session. Frequency: Two to three days per week Start with 3 minutes of light pace
The Effect of Altitude on Growth of Anthropometric and Motor Performance of 14 Year Old Adolescence
 The Effect of Altitude on Growth of Anthropometric and Motor Performance of 14 Year Old Adolescence Jyan Chandra Gurung* Kadamtala High School, Kadamtala, West Bengal, India. *Corresponding author. Tel:
The Effect of Altitude on Growth of Anthropometric and Motor Performance of 14 Year Old Adolescence Jyan Chandra Gurung* Kadamtala High School, Kadamtala, West Bengal, India. *Corresponding author. Tel:
COMPARISON OF SOME ANTROPOMETRIC AND MORPHOLOGICAL CHARACTERISTICS BETWEEN ICE HOCKEY PLAYERS AND CONTROL GROUP IN KOCAELI
 COMPARISON OF SOME ANTROPOMETRIC AND MORPHOLOGICAL CHARACTERISTICS BETWEEN ICE HOCKEY PLAYERS AND CONTROL GROUP IN KOCAELI Çolak.T.*, Gönener.A**., Bamaç.B.*, Sertbaş.K.**,Taşkıran.Y.**,Özbek.A.*, Bamaç.Y.*
COMPARISON OF SOME ANTROPOMETRIC AND MORPHOLOGICAL CHARACTERISTICS BETWEEN ICE HOCKEY PLAYERS AND CONTROL GROUP IN KOCAELI Çolak.T.*, Gönener.A**., Bamaç.B.*, Sertbaş.K.**,Taşkıran.Y.**,Özbek.A.*, Bamaç.Y.*
EVects of seasonal change in rugby league on the incidence of injury
 144 Department of Orthopaedic and Accident Surgery, Centre, University Hospital, Nottingham NG7 2UH, United Kingdom L Hodgson Phillips Department of Learning Disabilities, University Hospital, Centre,
144 Department of Orthopaedic and Accident Surgery, Centre, University Hospital, Nottingham NG7 2UH, United Kingdom L Hodgson Phillips Department of Learning Disabilities, University Hospital, Centre,
Metabolic production of carbon dioxide in simulated sea states: relevance for hyperbaric escape systems.
 Metabolic production of carbon dioxide in simulated sea states: relevance for hyperbaric escape systems. M. TIPTON, P. NEWTON, T. REILLY Department of Sport & Exercise Science, Institute of Biomedical
Metabolic production of carbon dioxide in simulated sea states: relevance for hyperbaric escape systems. M. TIPTON, P. NEWTON, T. REILLY Department of Sport & Exercise Science, Institute of Biomedical
The physical demands of Super 14 rugby union
 Available online at www.sciencedirect.com Journal of Science and Medicine in Sport 14 (2011) 259 263 Original research The physical demands of Super 14 rugby union Damien Austin a,b,, Tim Gabbett a,c,
Available online at www.sciencedirect.com Journal of Science and Medicine in Sport 14 (2011) 259 263 Original research The physical demands of Super 14 rugby union Damien Austin a,b,, Tim Gabbett a,c,
Steeplechase Hurdle Economy, Mechanics, and Performance
 Brigham Young University BYU ScholarsArchive All Theses and Dissertations 2013-06-27 Steeplechase Hurdle Economy, Mechanics, and Performance Sarah Ingebretsen Brigham Young University - Provo Follow this
Brigham Young University BYU ScholarsArchive All Theses and Dissertations 2013-06-27 Steeplechase Hurdle Economy, Mechanics, and Performance Sarah Ingebretsen Brigham Young University - Provo Follow this
The cycling power profile characteristics of national level junior triathletes
 Southern Cross University epublications@scu School of Health and Human Sciences 01 The cycling power profile characteristics of national level junior triathletes Christopher J. Stevens Southern Cross University
Southern Cross University epublications@scu School of Health and Human Sciences 01 The cycling power profile characteristics of national level junior triathletes Christopher J. Stevens Southern Cross University
ScienceDirect. Long-distance, short-distance: triathlon. One name: two ways.
 Available online at www.sciencedirect.com ScienceDirect Procedia Engineering 112 (2015 ) 244 249 7th Asia-Pacific Congress on Sports Technology, APCST 2015 Long-distance, short-distance: triathlon. One
Available online at www.sciencedirect.com ScienceDirect Procedia Engineering 112 (2015 ) 244 249 7th Asia-Pacific Congress on Sports Technology, APCST 2015 Long-distance, short-distance: triathlon. One
Internet Technology Fundamentals. To use a passing score at the percentiles listed below:
 Internet Technology Fundamentals To use a passing score at the percentiles listed below: PASS candidates with this score or HIGHER: 2.90 High Scores Medium Scores Low Scores Percentile Rank Proficiency
Internet Technology Fundamentals To use a passing score at the percentiles listed below: PASS candidates with this score or HIGHER: 2.90 High Scores Medium Scores Low Scores Percentile Rank Proficiency
APPENDIX A ANTHROPOLOGICAL MEASUREMENT AND LANDMARK DESCRIPTIONS
 APPENDIX A ANTHROPOLOGICAL MEASUREMENT AND LANDMARK DESCRIPTIONS 65 ANTHROPOLOGICAL MEASUREMENT DESCRIPTIONS 66 ACROMIAL HEIGHT Standing surface -- acromion, right. PROCEDURE: Subject is in the anthropometric
APPENDIX A ANTHROPOLOGICAL MEASUREMENT AND LANDMARK DESCRIPTIONS 65 ANTHROPOLOGICAL MEASUREMENT DESCRIPTIONS 66 ACROMIAL HEIGHT Standing surface -- acromion, right. PROCEDURE: Subject is in the anthropometric
Anthropometric Typology of Male and Female Rowers Using K Means Clustering
 Journal of Human Kinetics volume 28/2011, 155 164 155 Section III Sport, Physical Education & Recreation Anthropometric Typology of Male and Female Rowers Using K Means Clustering by Justyna Forjasz 1
Journal of Human Kinetics volume 28/2011, 155 164 155 Section III Sport, Physical Education & Recreation Anthropometric Typology of Male and Female Rowers Using K Means Clustering by Justyna Forjasz 1
The Singapore Copyright Act applies to the use of this document.
 Title Application of GPS technology to create activity profiles of youth international field hockey players in competitive match-play Author(s) Matthew Wylde, Low Chee Yong, Abdul Rashid Aziz, Swarup Mukherjee
Title Application of GPS technology to create activity profiles of youth international field hockey players in competitive match-play Author(s) Matthew Wylde, Low Chee Yong, Abdul Rashid Aziz, Swarup Mukherjee
An Update on the Age of National-level American Swimmers
 Coaching Applications An Update on the Age of National-level American Swimmers Joel Stager 1, Andrew Cornett 2, Dave Tanner 1, and Erica Slaughter 2 1 Counsilman Center for the Science of Swimming, Kinesiology
Coaching Applications An Update on the Age of National-level American Swimmers Joel Stager 1, Andrew Cornett 2, Dave Tanner 1, and Erica Slaughter 2 1 Counsilman Center for the Science of Swimming, Kinesiology
Personal Bicycle Fitting Report Rider Information
 5/19/2011 Retül Notes Report Specialized Dolce PRE-FIT NOTES Courtney is a recreational cyclist coming in today for a fit on her road bike. She enjoys riding with friends and in group rides. She has had
5/19/2011 Retül Notes Report Specialized Dolce PRE-FIT NOTES Courtney is a recreational cyclist coming in today for a fit on her road bike. She enjoys riding with friends and in group rides. She has had
ROSE-HULMAN INSTITUTE OF TECHNOLOGY Department of Mechanical Engineering. Mini-project 3 Tennis ball launcher
 Mini-project 3 Tennis ball launcher Mini-Project 3 requires you to use MATLAB to model the trajectory of a tennis ball being shot from a tennis ball launcher to a player. The tennis ball trajectory model
Mini-project 3 Tennis ball launcher Mini-Project 3 requires you to use MATLAB to model the trajectory of a tennis ball being shot from a tennis ball launcher to a player. The tennis ball trajectory model
Q ATA R F O OT B A L L A N A LY T I C S DA S H B O A R D
 Q ATA R F O OT B A L L A N A LY T I C S DA S H B O A R D DOWNLOAD SAP BO MOBILE APPLICATION (Apple Devices Iphone Ipad, ETC...) Date: 15/08/2018 Version No: 0.2 Contents Opening the Dashboard:... 5 Requiring
Q ATA R F O OT B A L L A N A LY T I C S DA S H B O A R D DOWNLOAD SAP BO MOBILE APPLICATION (Apple Devices Iphone Ipad, ETC...) Date: 15/08/2018 Version No: 0.2 Contents Opening the Dashboard:... 5 Requiring
Western Australian Coaches Conference
 Season Planning Western Australian Coaches Conference Drew McGregor Swimming Queensland Coach Development Season Planning Western Australian Coaches Conference Drew McGregor Swimming Queensland Coach Development
Season Planning Western Australian Coaches Conference Drew McGregor Swimming Queensland Coach Development Season Planning Western Australian Coaches Conference Drew McGregor Swimming Queensland Coach Development
A Nomogram Of Performances In Endurance Running Based On Logarithmic Model Of Péronnet-Thibault
 American Journal of Engineering Research (AJER) e-issn: 2320-0847 p-issn : 2320-0936 Volume-6, Issue-9, pp-78-85 www.ajer.org Research Paper Open Access A Nomogram Of Performances In Endurance Running
American Journal of Engineering Research (AJER) e-issn: 2320-0847 p-issn : 2320-0936 Volume-6, Issue-9, pp-78-85 www.ajer.org Research Paper Open Access A Nomogram Of Performances In Endurance Running
SAL & AIS Talent Identification Findings. Drew McGregor - Coach, AIS Swimming Lachlan Mitchell - PhD Scholar, AIS Physiology
 SAL & AIS Talent Identification Findings Drew McGregor - Coach, AIS Swimming Lachlan Mitchell - PhD Scholar, AIS Physiology Talent vs. Potential What should we be trying to identify? Talent Natural aptitude
SAL & AIS Talent Identification Findings Drew McGregor - Coach, AIS Swimming Lachlan Mitchell - PhD Scholar, AIS Physiology Talent vs. Potential What should we be trying to identify? Talent Natural aptitude
