1. Myxinoides (hagfish) are sister to. what monophyletic group? 2. Which is NOT a characteristic of chordata?
|
|
|
- Primrose Butler
- 5 years ago
- Views:
Transcription
1 1. Myxinoides (hagfish) are sister to a) Verterbrata what monophyletic group? b) Gnathastomata c) Urochordata d) Cephalachordata 2. Which is NOT a characteristic of chordata? a) Pharyngeal pouches b) Notochord c) Exoskeleton d) Myomeres
2 3. Which is an example of a paraphyletic group? a) Gnathostomata b) Agnatha c) Vertebrata d) Chondrichthyes 4. What was the name of the supercontinent that consisted of present day Africa, South America, Australia, and Antarctica? a) Laurentia b) Gondwana c) Pangaea d) Baltica
3 Osteichthyes Systematics and characteristics
4
5 Traditional classification Class Osteichthys About 27,000 species of Bony Fishes Chondrichthyes - cartilaginous fish Osteichthys - bony fish Chondrostei - fish with bone and cartilage Holostei - entirely bony fish Teleostei - final bony fish This series of names implies a gradual increase in bone during evolution -- we now know this was not the case.
6 Phylogenetic placement of bony fishes Osteichthyes is monophyletic group (node 4 on figure) Actinopterygii is sister to Sarcopterygii Sarcopterygii contains Actinistia + Dipnoi + Tetrapoda
7
8 Bony fishes experienced 3 major radiations i Mainly Paleozoic; Bichirs and reedfishes are extant; Mesozoic Gars and bowfin are extant. The primitive sharks appeared in Mesozoic, but no cartilaginous fish survive from the Mesozoic radiation. Cenozoic The extant sharks and rays Sturgeons and paddlefishes Teleosts (~27,000 species today)
9 Bony fish Characteristics of bony fish: Few characters because of diversity of group 1) All have some true bone Skulls have sutures (sharks have a single block of cartilage) Teeth fused to mandibles Swim bladder or lungs usually present 5) Bony operculum present
10 Actinopterygii Ray-finned fishes Exist from late Silurian Characteristics: 1) Scales ganoid, cycloid, ctenoid or no scales. 2) Membranous fins supported by fine bony rays. 3) Caudal fins highly variable. Actinopterygii Contains Polypteriformes (extant bichirs and reedfishes) Polypterus bichir or African rope-fish Have lungs, lobed fins, found in Africa, ganoid scales cover body 1) Spiracle present. 2) Heterocercal tail in some. 3) Ganoid scales. Actinopterygii Contains Acipenseriformes Sturgeons and paddlefish Ganoid Scales on tail, dermal bony plates on back.
11 Accipenser - sturgeons Important economically for meat and Caviar. Huso huso - beluga Largest of the sturgeon group, from Caspian Sea, Up to 3,300 lbs. The finest black caviar in the world comes from this species ($5 per gram).
12 Essay Question Describe the major structures in fish gills and explain how gills efficiently obtain oxygen from the water.
13 Scales Placoid found in sharks, they are modified on the anterior to form teeth, they are composed of a vascular inner core of pulp, a middle layer of dentine and a hard enamel-like outer layer of vitrodentine Ganoid found in gars, bichirs and reedfish, are rhomboid in shape and have a bony basal layer of dentine and outer layer of ganoine, they do not overlap Cycloid found in bowfin, they consist of a surface bony layer and a deeper fibrous layer composed mainly of collagen Ctenoid found in most teleosts, are similar to cycloid scales but they have they have a spiny posterior margin, both cycloid and ctenoid scales grow with the fish so they lay down concentric growth rings and can be used to determine age and growth rates of fish.
14 Scales Placoid Scale Ganoid Scale Cycoid Scale Ctenoid Scale
15 Tails Heterocercal Hypocercal Homocercal
16 Actinopterygii Polydon - paddlefish Includes two species, one in the US (including Texas) and one in China. Weighs up to 200 lbs.
17 Neopterygii Lepisosteiformes (gars) Body covered with Ganoid scales. Swim bladder aids in respiration. Long snout with many teeth, voracious predators on small fish. Restricted to North America. No marine forms (no seagars)
18 Neopterygii Amiiformes (bowfin) Amia Cycloid scales cover body. Predator on smaller fish. Also use swim bladder for respiration. The one living species (Amia calva) is restricted to the Mississippi drainage of North America but fossils are known from Europe.
19 4 important characteristics of gars and dbowfin 1) They are extant members of lineages that are older than Teleost fishes 2) Modified heterocercal tail. 3) Scales ganoid (gars) or Cycloid (bowfin). 4) Swim bladder connected to pharynx aids in respiration.
20 Fig 6-8. Nonteleostean actinopterygian fishes and primitive iti neopterygians Actinopterygians: Bichir Sturgeon Paddlefish Primitive Neopterygians: Gar Bowfin
21 Teleosti There are at least 24 Orders of teleost fishes, comprising ~27,000 species. 1) Tails homocercal in most species. 2) Scales cycloid or ctenoid, NOT ganoid. 3) Swim bladder present in most species.
22 Osteoglossomorpha Worldwide, mostly tropical freshwater Include one of the largest bony fish Arapaima gigas, up to 200kg and 450cm
23 Elopomorpha Tarpons and Eels Worldwide, mostly marine The atlantic ti tarpon is an important game fish American Freshwater Eel Anguilla rostrata Catadromous
24 Clupeomorpha Herrings and Anchovies Worlwide, especially marine
25 Euteleostei Largest clade of teleosts Ostariophysi (catfish and minnows) dominant fishes of freshwater; percent of fish and 80 percent of freshwater two characters Weberian apparatus small bones that connect the swim bladder to the inner ear Presence of fright or alarm substance in the skin (phermones)
26 Ostariophysi com/watch?v=fxw1e Fcm3vw
27 Euteleosti Protacanthopterygii (Salmonids and relatives) This includes the anadromous salmon Paracanthopterygii (cods and anglerfish) About 1200 species
28 Acanthopterygii True spiny-rayed fishes Largest group of extant fish Most species are in the order Perciformes with well over 9300 species
Euteleostei. Basal groups: Ostariophysi
 Chapter 6. Osteichthyes Originated in late Silurian Radiated in Devonian (with other fish groups) Sister taxon to acanthodians Derived Traits (synapomorphies) Lateral line canals Opercular and pectoral
Chapter 6. Osteichthyes Originated in late Silurian Radiated in Devonian (with other fish groups) Sister taxon to acanthodians Derived Traits (synapomorphies) Lateral line canals Opercular and pectoral
OEB 130: BIOLOGY OF FISHES Lecture 4: Overview of ray-finned fish diversity (Actinopterygii)
 OEB 130: BIOLOGY OF FISHES Lecture 4: Overview of ray-finned fish diversity (Actinopterygii) Announcements 1 1. Please review the syllabus for reading and lab information! 2. Please do the readings: for
OEB 130: BIOLOGY OF FISHES Lecture 4: Overview of ray-finned fish diversity (Actinopterygii) Announcements 1 1. Please review the syllabus for reading and lab information! 2. Please do the readings: for
Euteleostomi. Actinopterygii. Class Actinopterygii, Subclass Chondrostei, Order Acipenseriformes, Sturgeon and Paddlefish
 Acipenseriformes: spiracles heterocercal caudal fin Cartilaginous skeleton (secondary) spiral valve Actinopterygii Euteleostomi Class Actinopterygii, Subclass Chondrostei, Order Acipenseriformes, Sturgeon
Acipenseriformes: spiracles heterocercal caudal fin Cartilaginous skeleton (secondary) spiral valve Actinopterygii Euteleostomi Class Actinopterygii, Subclass Chondrostei, Order Acipenseriformes, Sturgeon
ZOOLOGY. FISHES - in practice GENERAL ANATOMY FIN MODIFICATIONS ADAPTATION & MODIFICATION OF FINS POSITION OF PELVIC FINS FISH SKELETON
 ZOOLOGY FISHES - in practice GENERAL ANATOMY Miloslav Petrtýl petrtyl@af.czu.cz The anatomy of Lampanyctodes hectoris (1) operculum (gill cover), (2) lateral line, (3) dorsal fin (4) fat fin, (5) caudal
ZOOLOGY FISHES - in practice GENERAL ANATOMY Miloslav Petrtýl petrtyl@af.czu.cz The anatomy of Lampanyctodes hectoris (1) operculum (gill cover), (2) lateral line, (3) dorsal fin (4) fat fin, (5) caudal
Phylum Chordata Subphylum Vertebrata Superclass Agnatha Class Myxini - hagfishes Class Cephalaspidomorphi - lampreys
 Although it is debatable whether hagfish are vertebrates current classification places the hagfish within the Subphylum Vertebrata. Hagfish and Lampreys are placed in different classes of the Superclass
Although it is debatable whether hagfish are vertebrates current classification places the hagfish within the Subphylum Vertebrata. Hagfish and Lampreys are placed in different classes of the Superclass
FISHES. Agnatha Chondrichthyes Osteichthyes
 FISHES Agnatha Chondrichthyes Osteichthyes General Characteristics! Ectothermic! Vertebrates! Have scales! Swim with fins! Almost all exclusively aquatic! Filter oxygen from water over gills Classes of
FISHES Agnatha Chondrichthyes Osteichthyes General Characteristics! Ectothermic! Vertebrates! Have scales! Swim with fins! Almost all exclusively aquatic! Filter oxygen from water over gills Classes of
Class Osteichthyes. Bony Fish
 Class Osteichthyes Bony Fish General Characteristics of Class internal skeleton ossified (turned to bone) Paired fins made of rays and spines, or lobed fins swim bladder or lung present bony scales (ganoid,
Class Osteichthyes Bony Fish General Characteristics of Class internal skeleton ossified (turned to bone) Paired fins made of rays and spines, or lobed fins swim bladder or lung present bony scales (ganoid,
February 17, Unit 2. Biodiversity. Chordata, the vertebrates
 Unit 2 Biodiversity Chordata, the vertebrates Phylum Chordata Examples: Sea squirts, fish, birds, dinosaurs, humans. General characteristics: 1. Bilaterally symmetrical 2. Coelomate 3. One way digestive
Unit 2 Biodiversity Chordata, the vertebrates Phylum Chordata Examples: Sea squirts, fish, birds, dinosaurs, humans. General characteristics: 1. Bilaterally symmetrical 2. Coelomate 3. One way digestive
Class Actinopterygii - ray-finned fishes Subclass Chondrostei - sturgeons, paddlefish, birchirs Subclass Neopterygii - "modern" ray-finned fishes -
 Class Actinopterygii - ray-finned fishes Subclass Chondrostei - sturgeons, paddlefish, birchirs Subclass Neopterygii - "modern" ray-finned fishes - the most primitive neopterygians are gars and the bowfin
Class Actinopterygii - ray-finned fishes Subclass Chondrostei - sturgeons, paddlefish, birchirs Subclass Neopterygii - "modern" ray-finned fishes - the most primitive neopterygians are gars and the bowfin
Class Myxini Order Myxiniformes Family Myxinidae (hagfishes)
 Class Myxini Order Myxiniformes Family Myxinidae (hagfishes) Lacks jaws Mouth not disk-like barbels present Unpaired fins as continuous fin-fold Branchial skeleton not well developed Eyes degenerate 70-200
Class Myxini Order Myxiniformes Family Myxinidae (hagfishes) Lacks jaws Mouth not disk-like barbels present Unpaired fins as continuous fin-fold Branchial skeleton not well developed Eyes degenerate 70-200
Taxonomy of Fishes. Chapter 18. I. SuperClass Agnatha. A. Class Myxini. Kingdom Animalia. The Fishes
 Taxonomy of Fishes Chapter 18 The Fishes Kingdom Animalia Phylum Chordata SuperClass Agnatha - jawless fish Class Chondrichthyes - cartilagenous fish Class Osteichthyes - bony fish I. SuperClass Agnatha
Taxonomy of Fishes Chapter 18 The Fishes Kingdom Animalia Phylum Chordata SuperClass Agnatha - jawless fish Class Chondrichthyes - cartilagenous fish Class Osteichthyes - bony fish I. SuperClass Agnatha
All members of the Phylum Chordata must have had at one time in their development: 1.Dorsal hollow nerve cord 2.Notochord 3.Pharyngeal gill slits
 Phylum Chordata All members of the Phylum Chordata must have had at one time in their development: 1.Dorsal hollow nerve cord 2.Notochord 3.Pharyngeal gill slits 4.Tail Subphylum Urochordata Tunicates
Phylum Chordata All members of the Phylum Chordata must have had at one time in their development: 1.Dorsal hollow nerve cord 2.Notochord 3.Pharyngeal gill slits 4.Tail Subphylum Urochordata Tunicates
Osteichthyes: Bony Fish
 About 23,000 different species Osteichthyes: Bony Fish AKA: Teleosts Diversity of fishes Anatomical terminology Dorsal Posterior or caudal Anterior Lateral Lateral Ventral Used for relating different parts.eye
About 23,000 different species Osteichthyes: Bony Fish AKA: Teleosts Diversity of fishes Anatomical terminology Dorsal Posterior or caudal Anterior Lateral Lateral Ventral Used for relating different parts.eye
Lecture 8 History of fishes
 Lecture 8 History of fishes Ray Troll Picture = CARD SHARKS Structural Patterns and Trends in Diversification Fish subsumed (since Cope (1889) proposed - Agnatha - jawless fishes and Gnathostome lines
Lecture 8 History of fishes Ray Troll Picture = CARD SHARKS Structural Patterns and Trends in Diversification Fish subsumed (since Cope (1889) proposed - Agnatha - jawless fishes and Gnathostome lines
Chordates 1. Biology 2
 Chordates 1 Biology 2 Kingdom Animals Eukaryotic Multicellular - Many cell types Heterotrophic Feed by ingestion No cell walls Diploid life cycle Phylogenetic Tree Deuterostome Bilateral Symmetry 3 tissues
Chordates 1 Biology 2 Kingdom Animals Eukaryotic Multicellular - Many cell types Heterotrophic Feed by ingestion No cell walls Diploid life cycle Phylogenetic Tree Deuterostome Bilateral Symmetry 3 tissues
Biology 3315 Comparative Vertebrate Morphology Protochordates and Fishes
 Biology 3315 Comparative Vertebrate Morphology Protochordates and Fishes 1. Echinodermata If fossil forms are included, echinoderms are a very diverse assemblage; several classes are now entirely extinct.
Biology 3315 Comparative Vertebrate Morphology Protochordates and Fishes 1. Echinodermata If fossil forms are included, echinoderms are a very diverse assemblage; several classes are now entirely extinct.
8/27/13. Ichthyology BIOL 530, 530L, 529J. Grading. Attendance & General Information. Course Objectives. Text and other Reading.
 Ichthyology BIOL 530, 530L, 529J Dr. Mark Steele Magnolia Hall 4100 Office Hours: Mon & Wed 11-12 or by appointment Justin Hackitt Magnolia Hall 4103 Office Hours: Mon 10-11 or by appointment Course Objectives
Ichthyology BIOL 530, 530L, 529J Dr. Mark Steele Magnolia Hall 4100 Office Hours: Mon & Wed 11-12 or by appointment Justin Hackitt Magnolia Hall 4103 Office Hours: Mon 10-11 or by appointment Course Objectives
Biology 11. Phylum Chordata: Subphylum Vertebrata: The Fishys
 Biology 11 Phylum Chordata: Subphylum Vertebrata: The Fishys Phylum Chordata is typically divided into four subphyla: Higher Chordates We are going to spend the next few classes talking about the Subphylum
Biology 11 Phylum Chordata: Subphylum Vertebrata: The Fishys Phylum Chordata is typically divided into four subphyla: Higher Chordates We are going to spend the next few classes talking about the Subphylum
CHAPTER 16 FISHES STUDY GUIDE 16.1 What Is a Fish? A. Approximately 28,000 living species more than all other species of vertebrates combined B.
 CHAPTER 16 FISHES STUDY GUIDE 16.1 What Is a Fish? A. Approximately 28,000 living species more than all other species of vertebrates combined B. Adaptations that have fitted them to almost every conceivable
CHAPTER 16 FISHES STUDY GUIDE 16.1 What Is a Fish? A. Approximately 28,000 living species more than all other species of vertebrates combined B. Adaptations that have fitted them to almost every conceivable
What is it? Affinities and systematic position of Dipnoi DBS 402B.1 Presidency University, 2015
 What is it? Affinities and systematic position of Dipnoi DBS 402B.1 Presidency University, 2015 What is the question? I ve decided to discuss the controversy, therefore the argument and philosophy of classification/systematics
What is it? Affinities and systematic position of Dipnoi DBS 402B.1 Presidency University, 2015 What is the question? I ve decided to discuss the controversy, therefore the argument and philosophy of classification/systematics
Natural History of Vertebrates Characters Used in Fish Identification (modified )
 Natural History of Vertebrates Characters Used in Fish Identification 1-9-03 (modified 20050118) This lab is designed to familiarize the student with characters used in the identification of fishes. Only
Natural History of Vertebrates Characters Used in Fish Identification 1-9-03 (modified 20050118) This lab is designed to familiarize the student with characters used in the identification of fishes. Only
What is a Fish? Fishes are aquatic vertebrates. Most fishes have paired fins, scales, and gills.
 What is a Fish? Fishes are aquatic vertebrates. Most fishes have paired fins, scales, and gills. Feeding and Digestion Every mode of feeding is seen in fish herbivores, carnivores, parasites, filter feeders,
What is a Fish? Fishes are aquatic vertebrates. Most fishes have paired fins, scales, and gills. Feeding and Digestion Every mode of feeding is seen in fish herbivores, carnivores, parasites, filter feeders,
Fish. Water Dwelling Animals
 Fish Water Dwelling Animals Class Agnatha (Jawless fish) They are believed to be the most primitive and oldest vertebrates. Lamprey and hagfish are the only 2 living members of this class and are placed
Fish Water Dwelling Animals Class Agnatha (Jawless fish) They are believed to be the most primitive and oldest vertebrates. Lamprey and hagfish are the only 2 living members of this class and are placed
radial and indeterminate cleavage Enterocoelous anus from blastopore Bilateral Symmetry Both invertebrates and vertebrates
 Phylum: Chordata Deuterostomes radial and indeterminate cleavage Enterocoelous anus from blastopore Bilateral Symmetry Both invertebrates and vertebrates Contain four anatomical features Phylum: Chordata
Phylum: Chordata Deuterostomes radial and indeterminate cleavage Enterocoelous anus from blastopore Bilateral Symmetry Both invertebrates and vertebrates Contain four anatomical features Phylum: Chordata
Origin and Importance! ! Fish were the first vertebrates to appear on Earth about 500 million years ago.
 2/9/14 Origin and Importance Evolution Marine Fish Fish were the first vertebrates to appear on Earth about 500 million years ago. Fish are the most economically important organism and are a vital source
2/9/14 Origin and Importance Evolution Marine Fish Fish were the first vertebrates to appear on Earth about 500 million years ago. Fish are the most economically important organism and are a vital source
Invertebrate Chordates
 Invertebrate Chordates Chapter 11.2 - Fishes And Invertebrate Chordates... Invertebrate Chordates Lancelets Filter feed and spend most of their time buried in the sand. Only 2 invertebrate chordates Tunicates
Invertebrate Chordates Chapter 11.2 - Fishes And Invertebrate Chordates... Invertebrate Chordates Lancelets Filter feed and spend most of their time buried in the sand. Only 2 invertebrate chordates Tunicates
FI F SH A ND F I F SHES E SUBPHYLUM VERTEBRATA
 FISH AND FISHES SUBPHYLUM VERTEBRATA 24,600 LIVING SPECIES FUN FACTS THAT S MORE THAN TERRESTRIAL ANIMALS! EARTH IS 70% WATER BUT LESS THAN.1% OF THE WATER ON THE PLANET IS FRESHWATER 41% OF FISH SPECIES
FISH AND FISHES SUBPHYLUM VERTEBRATA 24,600 LIVING SPECIES FUN FACTS THAT S MORE THAN TERRESTRIAL ANIMALS! EARTH IS 70% WATER BUT LESS THAN.1% OF THE WATER ON THE PLANET IS FRESHWATER 41% OF FISH SPECIES
Climate Researchers Feeling Heat. By Juliet Eilperin Washington Post Staff Writer Thursday, April 6, 2006; A27
 Biology 2010 April 19, 2006 Readings - From Text (Campbell et al. Biology, 7 th ed.) Chapter 34 pp. 671-707. Climate Researchers Feeling Heat. By Juliet Eilperin Washington Post Staff Writer Thursday,
Biology 2010 April 19, 2006 Readings - From Text (Campbell et al. Biology, 7 th ed.) Chapter 34 pp. 671-707. Climate Researchers Feeling Heat. By Juliet Eilperin Washington Post Staff Writer Thursday,
Is a seahorse a fish, amphibian, or reptile? FISH
 Ch. 30 Loulousis Is a seahorse a fish, amphibian, or reptile? FISH Vertebral Column (Endoskeleton) Gills Single-loop circulation Kidneys Also share all the characteristics of chordates such as notochord,
Ch. 30 Loulousis Is a seahorse a fish, amphibian, or reptile? FISH Vertebral Column (Endoskeleton) Gills Single-loop circulation Kidneys Also share all the characteristics of chordates such as notochord,
Aquatic vertebrates that are characterized by:
 Aquatic vertebrates that are characterized by: Paired fins Used for movement Scales Used for protection Gills Used for exchanging gases Fishes were the first vertebrates to evolve The evolution of jaws
Aquatic vertebrates that are characterized by: Paired fins Used for movement Scales Used for protection Gills Used for exchanging gases Fishes were the first vertebrates to evolve The evolution of jaws
Outline 15: Paleozoic Life
 Outline 15: Paleozoic Life The Evolution of Vertebrates: Fish and Amphibians Phylum Chordata All chordates have a dorsal nerve cord. Chordates with vertebrae are the vertebrates. The vertebrae surround
Outline 15: Paleozoic Life The Evolution of Vertebrates: Fish and Amphibians Phylum Chordata All chordates have a dorsal nerve cord. Chordates with vertebrae are the vertebrates. The vertebrae surround
Outline 15: Paleozoic Life. The Evolution of Vertebrates: Fish and Amphibians
 Outline 15: Paleozoic Life The Evolution of Vertebrates: Fish and Amphibians Phylum Chordata All chordates have a dorsal nerve cord. Chordates with vertebrae are the vertebrates. The vertebrae surround
Outline 15: Paleozoic Life The Evolution of Vertebrates: Fish and Amphibians Phylum Chordata All chordates have a dorsal nerve cord. Chordates with vertebrae are the vertebrates. The vertebrae surround
Morphological Phylogeny of Sturgeons
 Morphological Phylogeny of Sturgeons Biological Classification of Sturgeons and Paddlefishes Kingdom Anamalia Multicellular organism Phylum Chordata Vertebrates Superclass Osteichthyes Bony Fishes Class
Morphological Phylogeny of Sturgeons Biological Classification of Sturgeons and Paddlefishes Kingdom Anamalia Multicellular organism Phylum Chordata Vertebrates Superclass Osteichthyes Bony Fishes Class
Chapter 25: Fishes 1
 Chapter 25: Fishes 1 2 Jawless Fishes (Agnatha) Cartilaginous Fishes (Chondrichthyes) Bony Fishes (Osteichthyes) Lamprey Whale shark Scorpion fish 3 Gills Single-loop Blood Circulation Vertebral column
Chapter 25: Fishes 1 2 Jawless Fishes (Agnatha) Cartilaginous Fishes (Chondrichthyes) Bony Fishes (Osteichthyes) Lamprey Whale shark Scorpion fish 3 Gills Single-loop Blood Circulation Vertebral column
BI 101: Chordate Animals & Biodiversity
 BI 101: Chordate Animals & Biodiversity Final Exam tomorrow Announcements Same time, same place Review Mary s Peak biodiversity results Lab 10 today 1 Deuterostome Development 2 Phylum Chordata Contains
BI 101: Chordate Animals & Biodiversity Final Exam tomorrow Announcements Same time, same place Review Mary s Peak biodiversity results Lab 10 today 1 Deuterostome Development 2 Phylum Chordata Contains
Ray-finned fishes (Actinopterygii)
 Ray-finned fishes (Actinopterygii) Thomas J. Near a, * and Masaki Miya b a Department of Ecology and Evolutionary Biology & Peabody Museum of Natural History, Yale University, New Haven, CT 06520, USA;
Ray-finned fishes (Actinopterygii) Thomas J. Near a, * and Masaki Miya b a Department of Ecology and Evolutionary Biology & Peabody Museum of Natural History, Yale University, New Haven, CT 06520, USA;
5/3/15. Vertebrate Evolution Traces a Long and Diverse History. Construction of Complex Chordate Bodies Begins on a Stiffening Scaffold
 Construction of Complex Chordate Bodies Begins on a Stiffening Scaffold Chordata is the most advanced animal phylum. All chordates have, at some time during development, a notochord. Both invertebrate
Construction of Complex Chordate Bodies Begins on a Stiffening Scaffold Chordata is the most advanced animal phylum. All chordates have, at some time during development, a notochord. Both invertebrate
Readings in Chapter 2, 3, and 7.
 Early Vertebrates Readings in Chapter 2, 3, and 7. Using the Tree of Life Web Project www.tolweb.org org A project to put the entire tree of life, a phylogeny of all life, on the web. Biologists world-wide
Early Vertebrates Readings in Chapter 2, 3, and 7. Using the Tree of Life Web Project www.tolweb.org org A project to put the entire tree of life, a phylogeny of all life, on the web. Biologists world-wide
Reference: Chapter Phylum Chordata! Part Two, Fish
 Reference: Chapter 34.1-34.4 Phylum Chordata! Part Two, Fish 2 Clade Craniata v Evolution of a head (cranium) opened up a completely new way of feeding (for chordates): active predation v Craniates share
Reference: Chapter 34.1-34.4 Phylum Chordata! Part Two, Fish 2 Clade Craniata v Evolution of a head (cranium) opened up a completely new way of feeding (for chordates): active predation v Craniates share
Jawed vertebrates. Classes: Placodermi {extinct} Chondrichthyes? Superclass Gnathostomata. Acanthodii {extinct} Sarcopterygii
 It was found by Dr. Wei Qiwei Jawed vertebrates Superclass Gnathostomata Classes: Placodermi {extinct} Chondrichthyes? Cartilaginous fishes Acanthodii {extinct} 3 Classes with EXTANT members 2 classes
It was found by Dr. Wei Qiwei Jawed vertebrates Superclass Gnathostomata Classes: Placodermi {extinct} Chondrichthyes? Cartilaginous fishes Acanthodii {extinct} 3 Classes with EXTANT members 2 classes
Subphylum Urochordata Subphylum Cephalochordata Subphylum Vertebrata
 Subphylum Urochordata Subphylum Cephalochordata Subphylum Vertebrata The most diverse of all vertebrates My research on fish * PhD Program (Oregon State University) Olfaction
Subphylum Urochordata Subphylum Cephalochordata Subphylum Vertebrata The most diverse of all vertebrates My research on fish * PhD Program (Oregon State University) Olfaction
Question: How does one construct a cladogram from the following indented phylogenetic classification?
 BIOL 461 Cladogram Exercise 2: Indented Classification Skills Not due yet but related to today s exercise Complete on your own paper, include your name. I have used vertebrates because: 1) they are perfectly
BIOL 461 Cladogram Exercise 2: Indented Classification Skills Not due yet but related to today s exercise Complete on your own paper, include your name. I have used vertebrates because: 1) they are perfectly
Chapter 12 Marine Fishes
 Chapter 12 Marine Fishes Marine Protochordates Phylum: Chordata (nerve cord) Subphylum: Protochordata first chordates/primitive Primitive species of marine vertebrates Do not have advanced features (backbone)
Chapter 12 Marine Fishes Marine Protochordates Phylum: Chordata (nerve cord) Subphylum: Protochordata first chordates/primitive Primitive species of marine vertebrates Do not have advanced features (backbone)
CHAPTER. Chordates 24-1
 CHAPTER Chordates 24-1 24-2 Copyright The McGraw-Hill Companies, Inc. Permission required for reproduction or display. Overview Diversity Fish has many usages extending beyond what are actually considered
CHAPTER Chordates 24-1 24-2 Copyright The McGraw-Hill Companies, Inc. Permission required for reproduction or display. Overview Diversity Fish has many usages extending beyond what are actually considered
Figure Figure Phylum Chordata. Possess a dorsal, tubular nerve cord Notochord Pharyngeal gill slits Postanal tail
 Figure 17.2 Figure 18.3 Phylum Chordata Possess a dorsal, tubular nerve cord Notochord Pharyngeal gill slits Postanal tail 1 Other Characteristics of Phylum Chordata Bilateral symmetry Deuterostome, triploblastic,
Figure 17.2 Figure 18.3 Phylum Chordata Possess a dorsal, tubular nerve cord Notochord Pharyngeal gill slits Postanal tail 1 Other Characteristics of Phylum Chordata Bilateral symmetry Deuterostome, triploblastic,
basic fish General Biology:
 Fish form the earliest and the greatest group of all the backboned animals. Fish are cold-blooded vertebrates primarily adapted to living in water. Fish are remarkably various in size, shape, color, physiology,
Fish form the earliest and the greatest group of all the backboned animals. Fish are cold-blooded vertebrates primarily adapted to living in water. Fish are remarkably various in size, shape, color, physiology,
Lecture 3 - Early Fishes
 Lecture 3 - Early Fishes 1. Early Chordates 2. Conodonts 3. Early Vertebrates 4. Jawless fishes 5. Agnatha/ Gnathostomes junction 6. Placoderms 7. Chondrichthyes Cephalochordates (lancelets) Early Chordates
Lecture 3 - Early Fishes 1. Early Chordates 2. Conodonts 3. Early Vertebrates 4. Jawless fishes 5. Agnatha/ Gnathostomes junction 6. Placoderms 7. Chondrichthyes Cephalochordates (lancelets) Early Chordates
Chapter 39. Table of Contents. Section 1 Introduction to Vertebrates. Section 2 Jawless and Cartilaginous Fishes. Section 3 Bony Fishes.
 Fishes Table of Contents Section 1 Introduction to Vertebrates Section 2 Jawless and Cartilaginous Fishes Section 3 Bony Fishes Section 1 Introduction to Vertebrates Objectives Identify the distinguishing
Fishes Table of Contents Section 1 Introduction to Vertebrates Section 2 Jawless and Cartilaginous Fishes Section 3 Bony Fishes Section 1 Introduction to Vertebrates Objectives Identify the distinguishing
AP Biology - Zimmerman Guided Reading Chapter 34
 AP Biology - Zimmerman Guided Reading Chapter 34 1. List the four characteristics of the members of the Phylum Chordata. Name 1. 2. 3. 4. 2. Define the following terms: a. notochord b. Dorsal nerve cord
AP Biology - Zimmerman Guided Reading Chapter 34 1. List the four characteristics of the members of the Phylum Chordata. Name 1. 2. 3. 4. 2. Define the following terms: a. notochord b. Dorsal nerve cord
Lecture Notes Chapter 14
 Lecture Notes Chapter 14 I. Chordata- phylum A. 3 subphyla 1. Urochordata 2. Cephalochordata 3. Vertebrata II. Characteristics of all Chordates (found during some part of the life cycle) A. All have a
Lecture Notes Chapter 14 I. Chordata- phylum A. 3 subphyla 1. Urochordata 2. Cephalochordata 3. Vertebrata II. Characteristics of all Chordates (found during some part of the life cycle) A. All have a
Unit 19.2: Fish. Vocabulary fish spawning swim bladder
 Unit 19.2: Fish Lesson Objectives Describe structure and function in fish. Explain how fish reproduce and develop. Give an overview of the five living classes of fish. Summarize the evolution of fish.
Unit 19.2: Fish Lesson Objectives Describe structure and function in fish. Explain how fish reproduce and develop. Give an overview of the five living classes of fish. Summarize the evolution of fish.
Phylum Chordata. Chief characteristics (some are embryonic):
 Phylum Chordata Vertebrates, sea squirts or tunicates, lancelets such as Amphioxus. Name: "Chord" means "string," referring to the nerve cord and/or notochord. Geologic range: Cambrian to Holocene. Mode
Phylum Chordata Vertebrates, sea squirts or tunicates, lancelets such as Amphioxus. Name: "Chord" means "string," referring to the nerve cord and/or notochord. Geologic range: Cambrian to Holocene. Mode
Superorder Protacanthopterygii
 Superorder Protacanthopterygii Taxonomically problematic group 4 orders: ~12 families, 94 genera, 366 species Disjunct global distribution Highly modified primitive teleosts Pike and pickerel Salmon and
Superorder Protacanthopterygii Taxonomically problematic group 4 orders: ~12 families, 94 genera, 366 species Disjunct global distribution Highly modified primitive teleosts Pike and pickerel Salmon and
Biol Echinoderms & Chordates. But first a few words about Development
 Biol 1309 Echinoderms & Chordates 1 But first a few words about Development Blastula- zygote first develops into a hollow ball of cells Deuterostome - mouth second Protostome - mouth first Cleavage - describes
Biol 1309 Echinoderms & Chordates 1 But first a few words about Development Blastula- zygote first develops into a hollow ball of cells Deuterostome - mouth second Protostome - mouth first Cleavage - describes
Phylum Chordata (Focus will be on Subphylum Vertebrata) Kingdom Animalia Phylum Chordata
 Phylum Chordata (Focus will be on Subphylum Vertebrata) Kingdom Animalia Phylum Chordata - All members have three basic characteristics: 1) a hollow dorsal nerve cord, - spinal cord has small fluid fill
Phylum Chordata (Focus will be on Subphylum Vertebrata) Kingdom Animalia Phylum Chordata - All members have three basic characteristics: 1) a hollow dorsal nerve cord, - spinal cord has small fluid fill
PHYLUM CHORDATA: Subphylum vertebrata
 PHYLUM CHORDATA: Subphylum vertebrata There are three basic characteristics that distinguish Phylum Chordata from all other animal phyla: The presence of a flexible, rod-like, internal supporting structure
PHYLUM CHORDATA: Subphylum vertebrata There are three basic characteristics that distinguish Phylum Chordata from all other animal phyla: The presence of a flexible, rod-like, internal supporting structure
Kingdom Animalia part 2.notebook. April 08, The fun continues... Kingdom Animalia
 The fun continues....... Kingdom Animalia 1 2 Joint legged animals (arthropoda) found from the bottom of the ocean to high above the Earth's surface included insects, arachnid, and crustacean hard external
The fun continues....... Kingdom Animalia 1 2 Joint legged animals (arthropoda) found from the bottom of the ocean to high above the Earth's surface included insects, arachnid, and crustacean hard external
Lab exercise 8: Fish and Amphibians General Zoology Laborarory. Matt Nelson
 Lab exercise 8: Fish and Amphibians General Zoology Laborarory. Matt Nelson Superclass: Agnatha The jawless fish represent the most basal group of Craniata. At one time, the two classes of jawless fish
Lab exercise 8: Fish and Amphibians General Zoology Laborarory. Matt Nelson Superclass: Agnatha The jawless fish represent the most basal group of Craniata. At one time, the two classes of jawless fish
Animal Evolution: Chordate and Vertebrate Evolution and Diversity (Learning Outline)
 Animal Evolution: Chordate and Vertebrate Evolution and Diversity (Learning Outline) 1. Distinguishing features of the phylum Chordata and representative organisms. 2. Highlights of evolutionary steps
Animal Evolution: Chordate and Vertebrate Evolution and Diversity (Learning Outline) 1. Distinguishing features of the phylum Chordata and representative organisms. 2. Highlights of evolutionary steps
6/20/2017. Carcharodon megalodon million YA
 Carcharodon megalodon 10-25 million YA 1 Class Chondrichthyes fishes with cartilaginous skeletons Sublcass Elasmobranchii sharks, skates, and ray 403 shark species and 534 skates and rays living now Subclass
Carcharodon megalodon 10-25 million YA 1 Class Chondrichthyes fishes with cartilaginous skeletons Sublcass Elasmobranchii sharks, skates, and ray 403 shark species and 534 skates and rays living now Subclass
Copyright 2011 Pearson Education, Inc.
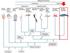 Urochordata (tunicates) Cephalochordata (lancelets) Myxini (hagfishes) Petromyzontiformes (lampreys) Chondrichthyes (sharks, rays) Actinopterygii (ray-finned fish) Actinistia (coelacanths) Dipnoi (lungfishes)
Urochordata (tunicates) Cephalochordata (lancelets) Myxini (hagfishes) Petromyzontiformes (lampreys) Chondrichthyes (sharks, rays) Actinopterygii (ray-finned fish) Actinistia (coelacanths) Dipnoi (lungfishes)
Fishes. a) Fishes are an incredible divers group. The term fish does not denote an actual taxonomic group.
 Fishes 1) Ichthyology the study of fishes a) Fish = one species b) Fishes = more than one species 2) Much of the fascination with fishes comes from the exceptions to general rules. This should give you
Fishes 1) Ichthyology the study of fishes a) Fish = one species b) Fishes = more than one species 2) Much of the fascination with fishes comes from the exceptions to general rules. This should give you
The Animal Kingdom. The Chordates
 The Animal Kingdom The Chordates Phylum Hemichordata Hemichordata (hemi = half; chordata= cord) acorn worm entirely marine adults show 3 of 4 basic characteristics: 1) pharyngial pouches 2) dorsal tubular
The Animal Kingdom The Chordates Phylum Hemichordata Hemichordata (hemi = half; chordata= cord) acorn worm entirely marine adults show 3 of 4 basic characteristics: 1) pharyngial pouches 2) dorsal tubular
Phylum Chordata Featuring Vertebrate Animals
 Phylum Chordata Featuring Vertebrate Animals Prepared by Diana C. Wheat For Linn-Benton Community College Characteristics All have a notochord: a stiff but flexible rod that extends the length of the body
Phylum Chordata Featuring Vertebrate Animals Prepared by Diana C. Wheat For Linn-Benton Community College Characteristics All have a notochord: a stiff but flexible rod that extends the length of the body
Chordates. Bởi: OpenStaxCollege
 Chordates Bởi: OpenStaxCollege Vertebrates are members of the kingdom Animalia and the phylum Chordata ([link]). Recall that animals that possess bilateral symmetry can be divided into two groups protostomes
Chordates Bởi: OpenStaxCollege Vertebrates are members of the kingdom Animalia and the phylum Chordata ([link]). Recall that animals that possess bilateral symmetry can be divided into two groups protostomes
Figure 33.25a Free-living nematode
 Figure 33.25a Free-living nematode Bilateraly symmetrical Pseudocoelomates Body covered with secreated, flexible cuticle. No cilia Only longitudinal muscles. No protonephridia Muscular pharynx Gonochoristic
Figure 33.25a Free-living nematode Bilateraly symmetrical Pseudocoelomates Body covered with secreated, flexible cuticle. No cilia Only longitudinal muscles. No protonephridia Muscular pharynx Gonochoristic
Basic Finfish Features
 1 Vivekanand Bharti Fishery Resources Assessment Division Taxonomy is the practice of identifying different organisms, classifying them into categories and naming them. The whole life (living or extinct)
1 Vivekanand Bharti Fishery Resources Assessment Division Taxonomy is the practice of identifying different organisms, classifying them into categories and naming them. The whole life (living or extinct)
Figure 1: Chordate Characteristics
 I. General Chordate Characteristics Chordates are distinguished as a group by the presence of four embryonic features that may persist into adulthood in some species, but disappear as development progresses
I. General Chordate Characteristics Chordates are distinguished as a group by the presence of four embryonic features that may persist into adulthood in some species, but disappear as development progresses
CHAPTER 12 FISH GUIDED NOTES
 Name Date Period CHAPTER 12 FISH GUIDED NOTES Class Osteichthyes includes all Osteichthyes are cold-blooded vertebrates that breathe through gills and use fins for swimming. Bony fishes share several distinguishing
Name Date Period CHAPTER 12 FISH GUIDED NOTES Class Osteichthyes includes all Osteichthyes are cold-blooded vertebrates that breathe through gills and use fins for swimming. Bony fishes share several distinguishing
FISHES. Aim Describe the distinguishing characteristics of all major groups of fishes.
 Lesson 2 FISHES Aim Describe the distinguishing characteristics of all major groups of fishes. WHAT IS A FISH? There are two common definitions to the term fish. One follows the Greek word Ichthyos and
Lesson 2 FISHES Aim Describe the distinguishing characteristics of all major groups of fishes. WHAT IS A FISH? There are two common definitions to the term fish. One follows the Greek word Ichthyos and
Marine Life. Fishes. Introductory Oceanography Ray Rector - Instructor
 Marine Life Fishes Introductory Oceanography Ray Rector - Instructor MARINE FISHES - Main Concepts 1) Fishes are the oldest group of vertebrates 2) Fish inhabit virtually every marine habitat worldwide
Marine Life Fishes Introductory Oceanography Ray Rector - Instructor MARINE FISHES - Main Concepts 1) Fishes are the oldest group of vertebrates 2) Fish inhabit virtually every marine habitat worldwide
Biology 11 - Chapter 31 Assignment
 Name: Class: Date: Biology 11 - Chapter 31 Assignment True/False Indicate whether the statement is true or false. 1. Echinoderms exhibit their invertebrate heritage by their hard exoskeletons made of calcium
Name: Class: Date: Biology 11 - Chapter 31 Assignment True/False Indicate whether the statement is true or false. 1. Echinoderms exhibit their invertebrate heritage by their hard exoskeletons made of calcium
Marine Fish: Part 1 STUDENT NOTES Date:
 Marine Fish: Part 1 STUDENT NOTES Date: Warm up Is fishes a real word? If so, what does it refer to? Animals are often divided into two groups: Invertebrate: soft-bodied organisms without backbones : all
Marine Fish: Part 1 STUDENT NOTES Date: Warm up Is fishes a real word? If so, what does it refer to? Animals are often divided into two groups: Invertebrate: soft-bodied organisms without backbones : all
Myxiniformes Petromyzontiformes Chondrichthyes Osteichthyes. Before we get to jaws, we need to know something about hard tissues.
 Behold the Gnathostomata: gnathos (jaw) + stoma (mouth) Cephalochordata Urochordata Haikouella Myxiniformes Petromyzontiformes Chondrichthyes Osteichthyes jaws skull proto-vertebrae, true gills, two eyes,
Behold the Gnathostomata: gnathos (jaw) + stoma (mouth) Cephalochordata Urochordata Haikouella Myxiniformes Petromyzontiformes Chondrichthyes Osteichthyes jaws skull proto-vertebrae, true gills, two eyes,
Perch Dissection Lab
 Name: Block: Due Date: Perch Dissection Lab Background The fish in the class Osteichthyes have bony skeletons. There are three groups of the bony fish: ray-finned, lobe-finned, and the lungfish. The perch
Name: Block: Due Date: Perch Dissection Lab Background The fish in the class Osteichthyes have bony skeletons. There are three groups of the bony fish: ray-finned, lobe-finned, and the lungfish. The perch
chapter sixteen Fishes FIRST PAGES What Is a Fish?
 16 chapter sixteen FIRST PAGES Fishes What Is a Fish? In common (and especially older) usage, the term fish has often been used to describe a mixed assortment of water-dwelling animals. We speak of jellyfish,
16 chapter sixteen FIRST PAGES Fishes What Is a Fish? In common (and especially older) usage, the term fish has often been used to describe a mixed assortment of water-dwelling animals. We speak of jellyfish,
Chordates. Chapter 23
 Chordates Chapter 23 Phylum Chordata By the end of the Cambrian period, 540 million years ago, an astonishing variety of animals inhabited Earth s oceans. One of these types of animals gave rise to vertebrates,
Chordates Chapter 23 Phylum Chordata By the end of the Cambrian period, 540 million years ago, an astonishing variety of animals inhabited Earth s oceans. One of these types of animals gave rise to vertebrates,
Animal Diversity. Kingdom Animalia
 7ch11 Animal Diversity Kingdom Animalia Animal Characteristics 1. animals are eukaryotes and are multicellular 2. cells are specialized for different functions (vision,digestion,reproduction) 3. protein,
7ch11 Animal Diversity Kingdom Animalia Animal Characteristics 1. animals are eukaryotes and are multicellular 2. cells are specialized for different functions (vision,digestion,reproduction) 3. protein,
Dorsal hollow nerve chord that forms spinal cord and brain. VERTEBRATES [OVERVIEW - OVERHEAD, similar to fig. 19.1, p. 390]:
![Dorsal hollow nerve chord that forms spinal cord and brain. VERTEBRATES [OVERVIEW - OVERHEAD, similar to fig. 19.1, p. 390]: Dorsal hollow nerve chord that forms spinal cord and brain. VERTEBRATES [OVERVIEW - OVERHEAD, similar to fig. 19.1, p. 390]:](/thumbs/73/69272471.jpg) Phylum Chordata (44,000 species) Dorsal hollow nerve chord that forms spinal cord and brain Notochord at some stage of life cycle Gill slits at some point in life cycle VERTEBRATES [OVERVIEW - OVERHEAD,
Phylum Chordata (44,000 species) Dorsal hollow nerve chord that forms spinal cord and brain Notochord at some stage of life cycle Gill slits at some point in life cycle VERTEBRATES [OVERVIEW - OVERHEAD,
deuterostomes eucoelomates pseudocoelomates acoelomate
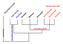 deuterostomes Mollusca Arthropoda Echinodermata Hemichordata Chordata eucoelomates Annelida Rotifera Platyhelminthes Nematoda acoelomate pseudocoelomates Phylum Hemichordata Share characteristics with
deuterostomes Mollusca Arthropoda Echinodermata Hemichordata Chordata eucoelomates Annelida Rotifera Platyhelminthes Nematoda acoelomate pseudocoelomates Phylum Hemichordata Share characteristics with
Classification. Phylum Chordata
 AP Biology Chapter 23 Exercise #17: Chordates: Urochordata & Cephalochordata Lab Guide Chordates show remarkable diversity. Most are vertebrates. All animals that belong to this phylum MUST, at some point
AP Biology Chapter 23 Exercise #17: Chordates: Urochordata & Cephalochordata Lab Guide Chordates show remarkable diversity. Most are vertebrates. All animals that belong to this phylum MUST, at some point
BIOLOGY 11 CHORDATES
 BIOLOGY 11 CHORDATES All chordates share 4 general characteristics: 1. Notochord a dorsal supporting rod located below the nerve cord toward the back in vertebrates, the embryonic notochord is replaced
BIOLOGY 11 CHORDATES All chordates share 4 general characteristics: 1. Notochord a dorsal supporting rod located below the nerve cord toward the back in vertebrates, the embryonic notochord is replaced
Lesson 27. Objectives: At the end of this lesson you should be able to:
 Lesson 27 Lesson Outline: Evolution of Respiratory Mechanisms Cutaneous Exchange Evolution of Respiratory Mechanisms - Water Breathers o Origin of pharyngeal slits from corner of mouth o Origin of skeletal
Lesson 27 Lesson Outline: Evolution of Respiratory Mechanisms Cutaneous Exchange Evolution of Respiratory Mechanisms - Water Breathers o Origin of pharyngeal slits from corner of mouth o Origin of skeletal
- 7 - DESCRIPTION OF SPECIES
 I - 7 - DESCRIPTION OF SPECIES./' Anguilla bicolor McClelland ' Level-finned eel (Figs.i & 2) Length of head 6-8 times in length of body; Diameter of eye 8-10 times, Inter-orbital length 2-2.5 times, Gape
I - 7 - DESCRIPTION OF SPECIES./' Anguilla bicolor McClelland ' Level-finned eel (Figs.i & 2) Length of head 6-8 times in length of body; Diameter of eye 8-10 times, Inter-orbital length 2-2.5 times, Gape
Order Cichliformes, cichlids. Cichlid mouth part diversity
 Order Cichliformes, cichlids South America, Africa, India, one North American species 112 genera, 1300 species, many undescribed Interrupted lateral line Oviparous, Variable forms of parental care Centrarchid
Order Cichliformes, cichlids South America, Africa, India, one North American species 112 genera, 1300 species, many undescribed Interrupted lateral line Oviparous, Variable forms of parental care Centrarchid
Chapter 10. Part 1: Cartilaginous Fishes
 Chapter 10 Part 1: Cartilaginous Fishes Objectives Understand how hagfishes and lampreys differ from all other fishes. Describe how sharks, skates, and rays are related. Differentiate between cartilaginous
Chapter 10 Part 1: Cartilaginous Fishes Objectives Understand how hagfishes and lampreys differ from all other fishes. Describe how sharks, skates, and rays are related. Differentiate between cartilaginous
Teacher Background Information:
 Outcome: 6-1-03: Develop a system to classify common objects or living things into groups and subgroups, and explain the reasoning used in the system s development. Materials: highlighter or writing utensil
Outcome: 6-1-03: Develop a system to classify common objects or living things into groups and subgroups, and explain the reasoning used in the system s development. Materials: highlighter or writing utensil
Fishes are vertebrates that have characteristics allowing them to live and reproduce in water.
 Section 1: are vertebrates that have characteristics allowing them to live and reproduce in water. K What I Know W What I Want to Find Out L What I Learned Essential Questions What are the features of
Section 1: are vertebrates that have characteristics allowing them to live and reproduce in water. K What I Know W What I Want to Find Out L What I Learned Essential Questions What are the features of
Lecture 2 Phylogenetics of Fishes. 1. Phylogenetic systematics. 2. General fish evolution. 3. Molecular systematics & Genetic approaches
 Lecture 2 Phylogenetics of Fishes 1. Phylogenetic systematics 2. General fish evolution 3. Molecular systematics & Genetic approaches Charles Darwin & Alfred Russel Wallace All species are related through
Lecture 2 Phylogenetics of Fishes 1. Phylogenetic systematics 2. General fish evolution 3. Molecular systematics & Genetic approaches Charles Darwin & Alfred Russel Wallace All species are related through
Perch Dissection Lab
 Perch Dissection Lab Introduction: The fish in the class Osteichthyes have bony skeletons. There are three groups of the bony fish - -- ray-finned fish, lobe-finned fish, and the lung fish. The perch is
Perch Dissection Lab Introduction: The fish in the class Osteichthyes have bony skeletons. There are three groups of the bony fish - -- ray-finned fish, lobe-finned fish, and the lung fish. The perch is
The Deuterostomes and the rise of the Vertebrates: from Echinoderms to Man
 The Deuterostomes and the rise of the Vertebrates: from Echinoderms to Man 1 The Deuterostomes Calcarea and Silicea Cnidaria Lophotrochozoa Ecdysozoa Deuterostomia 2 The Ancestral Deuterostome Bilateral
The Deuterostomes and the rise of the Vertebrates: from Echinoderms to Man 1 The Deuterostomes Calcarea and Silicea Cnidaria Lophotrochozoa Ecdysozoa Deuterostomia 2 The Ancestral Deuterostome Bilateral
Materials: Field notebook and pencil INTRODUCTION:
 Field Methods of Fish Biology 2014 Exercise 1: Basic Anatomy and Finding and Measuring Characters *Labs modified from Caillet et al. 1986 and Eric Schultz s Biology of Fishes lab Materials: Field notebook
Field Methods of Fish Biology 2014 Exercise 1: Basic Anatomy and Finding and Measuring Characters *Labs modified from Caillet et al. 1986 and Eric Schultz s Biology of Fishes lab Materials: Field notebook
 CHORDATA SK.M.BASHA Phylum Chordata Vertebrates, sea squirts or tunicates, lancelets such as Amphioxus. Name: "Chord" means "string", referring to the nerve cord and/or notochord. Chief characteristics:
CHORDATA SK.M.BASHA Phylum Chordata Vertebrates, sea squirts or tunicates, lancelets such as Amphioxus. Name: "Chord" means "string", referring to the nerve cord and/or notochord. Chief characteristics:
Increase exchange rate by moving medium over respiratory surface
 Ventilation Increase exchange rate by moving medium over respiratory surface Water ~800x heavier than air, potentially expensive ventilation Oxygen per unit mass Air: 1.3 g contains 210 ml O 2 Water: 1000
Ventilation Increase exchange rate by moving medium over respiratory surface Water ~800x heavier than air, potentially expensive ventilation Oxygen per unit mass Air: 1.3 g contains 210 ml O 2 Water: 1000
Class XI Chapter 4 Animal Kingdom Biology
 Chapter 4 Animal Kingdom Question 1: What are the difficulties that you would face in classification of animals, if common fundamental features are not taken into account? For the classification of living
Chapter 4 Animal Kingdom Question 1: What are the difficulties that you would face in classification of animals, if common fundamental features are not taken into account? For the classification of living
Sharks. The most shark attacks have been in Australia, South Africa, America and Brazil.
 Sharks There are more than 500 different species of shark, including the great white shark, grey reef shark, hammerhead shark and tiger shark. Where do they live? Sharks can be found in every ocean. Grey
Sharks There are more than 500 different species of shark, including the great white shark, grey reef shark, hammerhead shark and tiger shark. Where do they live? Sharks can be found in every ocean. Grey
Fishes and Amphibians Objectives
 Fishes and Amphibians Objectives List the four common body parts of chordates. Describe the two main characteristics of vertebrates. Explain the difference between an ectotherm and an endotherm. Describe
Fishes and Amphibians Objectives List the four common body parts of chordates. Describe the two main characteristics of vertebrates. Explain the difference between an ectotherm and an endotherm. Describe
UNIVERSITY OF SOUTH ALABAMA. GY 112: Earth History. Lectures 28 and 29: Vertebrates. Instructor: Dr. Douglas W. Haywick
 UNIVERSITY OF SOUTH ALABAMA GY 112: Earth History Lectures 28 and 29: Vertebrates Instructor: Dr. Douglas W. Haywick Last Time Plants 1) The first plants (Archean-Proterozoic) 2) Diversification (Paleozoic-Mesozoic)
UNIVERSITY OF SOUTH ALABAMA GY 112: Earth History Lectures 28 and 29: Vertebrates Instructor: Dr. Douglas W. Haywick Last Time Plants 1) The first plants (Archean-Proterozoic) 2) Diversification (Paleozoic-Mesozoic)
AIR-BREATHING DURING ACTIVITY IN THE FISHES AMIA CALVA AND LEPISOSTEUS OCULATUS
 The Journal of Experimental Biology 2, 943 948 (998) Printed in Great Britain The Company of Biologists Limited 998 JEB32 943 AIR-BREATHING DURING ACTIVITY IN THE FISHES AMIA CALVA AND LEPISOSTEUS OCULATUS
The Journal of Experimental Biology 2, 943 948 (998) Printed in Great Britain The Company of Biologists Limited 998 JEB32 943 AIR-BREATHING DURING ACTIVITY IN THE FISHES AMIA CALVA AND LEPISOSTEUS OCULATUS
Vertebrate Animals. DOMAIN- Eukarya KINGDOM- Animalia PHYLUM- Chordata SUBPHYLUM- Vertebrata CLASS- 7 different»orders- 10 Placental mammals
 Vertebrate Animals DOMAIN- Eukarya KINGDOM- Animalia PHYLUM- Chordata SUBPHYLUM- Vertebrata CLASS- 7 different»orders- 10 Placental mammals Characteristics of ALL vertebrates Backbone Endoskeleton Distinct
Vertebrate Animals DOMAIN- Eukarya KINGDOM- Animalia PHYLUM- Chordata SUBPHYLUM- Vertebrata CLASS- 7 different»orders- 10 Placental mammals Characteristics of ALL vertebrates Backbone Endoskeleton Distinct
