a high-rise (78 m) building in the city of Antwerp. CFD simulations are performed for the building with and without second-skin facade concept impleme
|
|
|
- Adam Charles
- 6 years ago
- Views:
Transcription
1 The Seventh International Colloquium on Bluff Body Aerodynamics and Applications (BBAA7) Shanghai, China; September 2-6, 2012 CFD analysis of wind comfort on high-rise building balconies: validation and application H. Montazeri a, B. Blocken a, W.D. Janssen a, T. van Hooff a,b a Building Physics and Services, Eindhoven University of Technology, P.O. Box 513, 5600 MB Eindhoven, The Netherlands, h.montazeri@tue.nl b Division of Building Physics, Katholieke Universiteit Leuven, Kasteelpark Arenberg 40, Leuven, Belgium ABSTRACT: High-rise buildings can cause wind discomfort on the building balconies, necessitating remedial action. In this paper, a new facade concept is evaluated that is intended to significantly improve wind comfort on the balconies of a 78 m high-rise building. The concept consists of a staggered semi-open second-skin facade that partly shields the balconies from the wind. Evaluation of the concept is performed by steady Reynolds-Averaged Navier-Stokes (RANS) CFD simulations with the realizable k-ε turbulence model in combination with the Dutch wind nuisance standard. First, some results of a CFD validation study for buildings with balconies are briefly presented. Next, similar simulations are used to evaluate the new facade concept by comparing the wind comfort at the balconies with and without application of this concept. It is shown that the new facade concept is quite effective in improving wind comfort at the balconies. KEYWORDS: Pedestrian wind environment, wind conditions, Computational Fluid Dynamics (CFD), building balconies 1. INTRODUCTION High-rise buildings can cause high wind speed near ground level and on building balconies, necessitating remedial action. In order to reduce wind discomfort on balconies, different measures can be taken; such as closing the balcony, adding partition walls, etc. Recently a new facade concept was developed by ELD Partnership (ELD 2011). It consists of a staggered semi-open second-skin facade that partly shields the balconies from the wind. It is intended to significantly improve wind comfort on the building balconies. In this paper, the performance of this concept is evaluated by validated CFD simulations and by application of the Dutch wind nuisance standard for a case study with and without application of this new concept. In the past, several CFD studies have been performed to investigate pedestrian-level wind conditions in complex urban environments (e.g. Stathopoulos and Baskaran 1996, Yoshie et al. 2007, Blocken et al. 2012). The use of CFD for complete wind comfort studies however is still relatively scarce, and this especially holds for studies of wind comfort at building balconies. Indeed, most of the previous CFD studies focused on wind comfort at pedestrian level around buildings. To the best of our knowledge, no CFD study has yet been published with focus on wind comfort on building balconies. This paper presents the evaluation of the new second-skin facade concept by ELD Partnership to improve wind comfort at building balconies. First, some results of a CFD validation study for buildings with balconies are briefly presented. Next, the new concept is evaluated for the case of 1674
2 a high-rise (78 m) building in the city of Antwerp. CFD simulations are performed for the building with and without second-skin facade concept implemented. The CFD simulations are performed with the 3D steady Reynolds-Averaged Navier-Stokes (RANS) approach and the realizable k-ε model (Shih et al. 1995). The obtained CFD results are combined with wind speed statistics and a comfort criterion to judge wind comfort on the balconies, according to the Dutch wind nuisance standard. 2. DESCRIPTION OF BUILDING AND URBAN AREA The new high-rise building of the so-called EPA project is located in the northern part of the city of Antwerp, Belgium. It is north-south oriented and surrounded by other high-rise and low-rise buildings (Fig. 1a). It has dimensions L B H = m³. The depth of the balconies on the north, east, south and west side of the tower is 1.32 m, 1.3 m, 1.59 m and 1.56 m, respectively. The facade concept is a second-skin concept, with a first and inner skin that acts as traditional facade and a second outer skin that acts as a wind shield for the balconies. The second skin consists of a staggered semi-open glass facade, as indicated in Figure 1b. It has a permanent solid glass balustrade of 1.2 m high, while above this 1.2 m, solid glass facade panels are applied in a staggered configuration. For the comparison study, a reference high-rise building with only the 1.2 m high balustrade will be considered. Figure 1. (a) High-rise building under study (red) and nearby urban surroundings. (b) Building facade with secondskin staggered facade concept. 3. CFD VALIDATION CFD simulations based on the 3D RANS equations in combination with a turbulence model require validation. Validation can be performed by comparison of the CFD results with either fullscale measurements or wind tunnel data. Experimental data of wind conditions for buildings with balconies are very scarce. In this paper, a unique set of wind tunnel measurements of surface pressures on the facade of a building with balconies is used for validation purposes. 1675
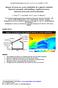
3 The Seventh International Colloquium on Bluff Body Aerodynamics and Applications (BBAA7) Shanghai, China; September 2-6, Wind tunnel measurements Atmospheric boundary layer wind tunnel measurements of wind-induced surface pressure on the facade of a reduced-scale model (1:30) of a medium-rise building were conducted by Chand et al (1998). The incident vertical profile of mean wind speed (i.e. at the location of the test model) can be described by a logarithmic law with aerodynamic roughness length z 0 = m and friction velocity u* = 0.72 m/s. Longitudinal turbulence intensity ranged from 13% near ground level to about 3% at gradient height. The building had dimensions w m d m h m = m 3 (reduced scale, see Fig. 2a) corresponding to full-scale dimensions W m D m H m = m 3. To evaluate the effect of building balconies on mean pressure, the measurements were carried out for an isolated building with and without balconies. Three balconies each with length 0.15 m, width 0.05 m and height 0.03 m were positioned at each floor (Fig. 2a). Surface pressures were measured along three vertical lines on the windward and leeward facade. Each line was in the middle of the balconies and 45 pressure taps were implemented along these lines. Pressure coefficients were related to the incident wind speed at building height (7.1 m/s) Comparison of CFD results and wind tunnel measurements The wind tunnel experiments are reproduced by solving the 3D steady RANS CFD simulations combined with the realizable k-ε model (Shih et al. 1995) and following the best practice guidelines by Franke et al. (2007) and Tominaga et al. (2008a). The computational grid was fully structured and was created using the surface grid extrusion technique presented by van Hooff and Blocken (2010). Figure 2b compares the numerically simulated and measured pressure coefficients at the windward facade of the building with balconies for wind direction 0. It should be noted that in this validation study, only results for the windward facades are considered. It is important to note that steady RANS CFD is deficient in reproducing the wind flow pattern downstream of windward facades (Murakami 1993, Tominaga et al. 2008b). Nevertheless, this approach is used in this paper, because the accuracy of the wind-flow pattern at side and the leeward facades is less important in wind comfort studies. The reason is that wind comfort studies typically focus on high wind speed positions, i.e. where a certain threshold wind speed is exceeded. Other positions do not contribute to the exceedance probabilities. Figure 2b shows that for the windward facades, the trends are well predicted by the CFD simulations. For the building without balconies, the deviations between the experimental and CFD results are generally less than 10%, while for the building with balconies, they are generally less than 20%. Figure 2. (a) Wind tunnel model of building with balconies and three vertical lines for pressure measurements (reduced-scale dimensions in m); (b) Comparison of wind tunnel and CFD results: pressure coefficient C p along vertical line near building edge. 1676
4 4. CASE STUDY: COMPUTATIONAL MODEL AND COMPUTATIONAL PARAMETERS 4.1. Computational geometry and grid A computational model has been made of the tower and its urban surroundings, which are placed in a computational domain with dimensions of m3. The explicitly modeled buildings are the tower itself and the surrounding buildings in a radius of 350 m around the tower. Because of the existing densely built area to the east side of the tower, the buildings placed at that part within a distance of 670 m from the tower are also modeled. The tower is modeled in detail, including staggered facade elements, while the surrounding buildings are included only with their main shape. Special attention was given to the generation of a high-quality and high-resolution grid. The grid was constructed using the surface grid extrusion technique presented by van Hooff and Blocken (2010), which allows a large degree of control over the quality of the grid and its individual cells. It consists of only hexahedral and prismatic cells and does not contain any tetrahedral or pyramid cells. In addition, the grid was constructed following the best practice guidelines by Franke et al. (2007) and Tominaga et al. (2008a). The two grids for building with application of the second-skin facade and the reference building consist of 16,292,495 cells and 15,536,529 cells, respectively (Fig. 3). Figure 3. View from north-east at high-resolution computational grid on surfaces of high-rise building tower and surrounding buildings for (a) building with second-skin facade concept (16,292,495) and (b) reference building (15,536,529) Boundary conditions At the inlet of the domain, neutral atmospheric boundary layer inflow profiles of mean wind speed, turbulent kinetic energy and turbulence dissipation rate are imposed. These profiles are based on the aerodynamic roughness length z0 of the upstream terrain that is not included in the computational domain. At the outlet, zero static pressure is specified. At the sides and the top of the domain, symmetry boundary conditions are imposed (i.e. zero normal velocity and gradients). At the ground surface, the standard wall functions by Launder and Spalding (1974) with the sand-grain roughness modification by Cebeci and Bradshaw (1977). The equivalent sand-grain roughness height ks and roughness constant CS are determined based on their relationship with z0 according to Blocken et al. (2007). At the building surfaces, also standard wall functions are used, with the assumption of smooth walls (ks = 0 m). 1677
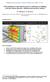
5 The Seventh International Colloquium on Bluff Body Aerodynamics and Applications (BBAA7) Shanghai, China; September 2-6, Solver settings The CFD simulations are performed using the commercial CFD code Fluent The 3D steady RANS equations are solved with the realizable k- turbulence model (Shih et al. 1995). The choice for this turbulence model is based on the recommendations by Franke et al. (2007) and on earlier successful validation studies for pedestrian-level wind conditions with this turbulence model (Blocken and Persoon 2009, Blocken et al. 2012). Pressure velocity-coupling is taken care of by the SIMPLE algorithm. Pressure interpolation is second order. Second-order discretisation schemes are used for both the convection terms and viscous terms of the governing equations. The simulations are performed for the 12 wind directions θ = in 30 intervals. 5. CASE STUDY: CFD SIMULATION RESULTS Figure 4 shows the local amplification factor U/U ref in a horizontal plane at a height of 1.7 m at the 15 th floor of the tower for the two situations and for southwest wind direction. The local amplification factor is defined as the ratio of the local mean wind speed U to the reference wind speed U ref at the same height but in undisturbed (free-stream) conditions. It can be seen that the new concept provides a significantly reduced amplification factor on the balconies two at the windward facades. At the west facade, the amplification factor reduces from a value of about 1.0 to a value of about 0.6. Figure 4. Contours of amplification factor for wind direction 210 in a horizontal plane at a height of 1.7 m above 15 th floor for: (a) the building with application of the second-skin facade concept. (b) The reference building. 6. CASE STUDY: WIND COMFORT ASSESSMENT RESULTS The wind speed amplification factors are used in combination with the Dutch wind nuisance standard for the assessment of wind comfort. For brevity, only some main items of this standard are given here, more details can be found in Willemsen and Wisse (2002, 2007), NEN (2006a, 2006b). The threshold wind speed in the standard is 5 m/s for all activities, while the maximum allowed exceedance probabilities of this threshold vary based on the activity, see Table
6 Table 1: Criteria for wind nuisance according to NEN 8100 (2006a) P(U THR > 5 m/s (in Grade Activity % hours per year) Traversing Strolling Sitting < 2.5 A Good Good Good B Good Good Moderate C Good Moderate Poor D Moderate Poor Poor > 20 E Poor Poor Poor For the wind comfort analysis, the wind statistics of the nearby city of Eindhoven are used. Figure 5 illustrates the exceedance probability of the 5 m/s threshold on the 15 th floor. Because southwest is the prevailing wind direction, the pattern of exceedance probabilities resembles that of the wind speed amplification factor for southwest wind direction (see Fig. 4). Figure 5 clearly shows that the second-skin facade concept improves wind comfort for a large part of the west facade and also for part of the south facade. Figure 5. Contours of exceedance probability in a horizontal plane at a height of 1.7 m above 15 th floor for: (a) the building with application of the second-skin facade concept. (b) The reference building. 7. DISCUSSION Some important limitations of this study are mentioned. The 3D steady RANS equations have been solved with the realizable k-ε model. It is important to note that steady RANS CFD is generally deficient in reproducing the windflow pattern downstream of windward facades (Murakami 1993, Tominaga et al. 2008b). 1679
7 The Seventh International Colloquium on Bluff Body Aerodynamics and Applications (BBAA7) Shanghai, China; September 2-6, 2012 Nevertheless, this approach is used in this paper, because the accuracy of the wind-flow pattern at side and the leeward facades is less important in wind comfort studies. The reason is that wind comfort studies typically focus on high wind speed positions, i.e. where a certain threshold wind speed is (5 m/s in the present study) is exceeded. Other positions do not contribute significantly or do not contribute at all to the exceedance probabilities. No grid-sensitivity analysis was performed. However, the computational grid has been made based on the best practice guidelines by Franke et al. (2007) and Tominaga et al. (2008a) and the grid resolution has been taken either similar or higher than in previous studies for which grid-sensitivity analyses were performed (van Hooff and Blocken 2010, Blocken et al. 2012).. 8. CONCLUSIONS 3D steady RANS CFD simulations have been used in combination with the new Dutch wind nuisance standard to evaluate the performance of a new facade concept. This concept consists of a staggered semi-open second-skin facade that partly shields the balconies from the wind. To achieve this particular purpose, the wind comfort at the balconies with and without application of this concept has been compared. It is shown that the new facade concept is very effective in shielding the balconies and improving the wind comfort. 9. REFERENCES ELD Partnership, Personal communication, B. Blocken, W.D. Janssen, and T. van Hooff, CFD simulation for pedestrian wind comfort and wind safety in urban areas: General decision framework and case study for the Eindhoven University campus, Environmental Modelling & Software, 30 (2012) B. Blocken, T. Stathopoulos, and J. Carmeliet, CFD simulation of the atmospheric boundary layer: wall function problems, Atmospheric Environment, 41 (2007) B. Blocken and J. Persoon, Pedestrian wind comfort around a large football stadium in an urban environment: CFD simulation, validation and application of the new Dutch wind nuisance standard, Journal of Wind Engineering and Industrial Aerodynamics, 97 (2009) T. Cebeci and P. Bradshaw, Momentum Transfer in Boundary Layers, Hemisphere Publishing Corporation, New York, I. Chand, P.K. Bhargava, and N.L.V. Krishak, Effect of balconies on ventilation inducing aeromotive force on low-rise buildings, Building and Environment, 33 (1998) J. Franke, H. Schlünzen, B. Carissimo, Best practice guideline for the CFD simulation of flows in the urban environment, (2007). T. van Hooff and B. Blocken, Coupled urban wind flow and indoor natural ventilation modelling on a high-resolution grid: A case study for the Amsterdam ArenA stadium, Environmental Modelling & Software, 25 (2010) B.E. Launder and D.B. Spalding, The numerical computation of turbulent flows, Computer Methods in Applied Mechanics and Engineering, 3 (1974) NEN, Wind comfort and wind danger in the built environment, NEN8100 (in Dutch) Dutch Standard, 2006a. NEN, Application of mean hourly wind speed statistics for the Netherlands, NPR 6097:2006 (in Dutch), Dutch Practice Guideline, 2006b. S. Murakami, Comparison of various turbulence models applied to a bluff body, Journal of Wind Engineering and Industrial Aerodynamics, (1993) T.H. Shih, W.W. Liou, A. Shabbir, Z. Yang, and J. Zhu, A new k-ε eddy viscosity model for high Reynolds number turbulent flows, Computers & Fluids, 24 (1995)
8 T. Stathopoulos and B.A. Baskaran, Computer simulation of wind environmental conditions around buildings, Engineering Structures, 18 (1996) Y. Tominaga, A. Mochida, R. Yoshie, H. Kataoka, T. Nozu, M. Yoshikawa, and T. Shirasawa, AIJ guidelines for practical applications of CFD to pedestrian wind environment around buildings, Journal of Wind Engineering and Industrial Aerodynamics, 96 (2008a) Y. Tominaga, A. Mochida, S. Murakami, and S. Sawaki, Comparison of various revised k models and LES applied to flow around a high-rise building model with 1:1:2 shape placed within the surface boundary layer, Journal of Wind Engineering and Industrial Aerodynamics, 96 (2008b) E. Willemsen, J.A. Wisse, Accuracy of assessment of wind speed in the built environment, Journal of Wind Engineering and Industrial Aerodynamics, 90 (2002) E. Willemsen, J.A. Wisse, Design for wind comfort in The Netherlands: Procedures, criteria and open research issues. Journal of Wind Engineering and Industrial Aerodynamics, 95 (2007) R. Yoshie, A. Mochida, Y. Tominaga, H. Kataoka, K. Harimoto, T. Nozu, and T. Shirasawa, Cooperative project for CFD prediction of pedestrian wind environment in the Architectural Institute of Japan, Journal of Wind Engineering and Industrial Aerodynamics, 95 (2007)
Improving pedestrian wind comfort around a high rise building in an urban area: a case study by CFD simulations and on-site measurements
 Improving pedestrian wind comfort around a high rise building in an urban area: a case study by CFD simulations and on-site measurements WD Janssen, B Blocken, and T van Hooff Unit Building Physics and
Improving pedestrian wind comfort around a high rise building in an urban area: a case study by CFD simulations and on-site measurements WD Janssen, B Blocken, and T van Hooff Unit Building Physics and
Computational evaluation of pedestrian wind comfort and wind safety around a high-rise building in an urban area
 International Environmental Modelling and Software Society (iemss) 7th Intl. Congress on Env. Modelling and Software, San Diego, CA, USA, Daniel P. Ames, Nigel W.T. Quinn and Andrea E. Rizzoli (Eds.) http://www.iemss.org/society/index.php/iemss-2014-proceedings
International Environmental Modelling and Software Society (iemss) 7th Intl. Congress on Env. Modelling and Software, San Diego, CA, USA, Daniel P. Ames, Nigel W.T. Quinn and Andrea E. Rizzoli (Eds.) http://www.iemss.org/society/index.php/iemss-2014-proceedings
Numerical analysis of surface pressure coefficients for a building with balconies
 Numerical analysis of surface pressure coefficients for a building with balconies Montazeri H., Blocken B. Building Physics and Services, Eindhoven University of Technology, P.O. box 513, 5600 MB Eindhoven,
Numerical analysis of surface pressure coefficients for a building with balconies Montazeri H., Blocken B. Building Physics and Services, Eindhoven University of Technology, P.O. box 513, 5600 MB Eindhoven,
Windsimulaties op de meteorologische microschaal
 Windsimulaties op de meteorologische microschaal dr.ir. Twan van Hooff prof.dr.ir. Bert Blocken Building Physics Section KU Leuven Unit Building Physics and Services TU/e 2015 Twan van Hooff All Rights
Windsimulaties op de meteorologische microschaal dr.ir. Twan van Hooff prof.dr.ir. Bert Blocken Building Physics Section KU Leuven Unit Building Physics and Services TU/e 2015 Twan van Hooff All Rights
Pedestrian wind comfort around buildings: comparison of wind comfort criteria based on whole-flow field data for a complex case study
 Accepted for publication in Building and Environment, October 25, 2012 Pedestrian wind comfort around buildings: comparison of wind comfort criteria based on whole-flow field data for a complex case study
Accepted for publication in Building and Environment, October 25, 2012 Pedestrian wind comfort around buildings: comparison of wind comfort criteria based on whole-flow field data for a complex case study
Surrounding buildings and wind pressure distribution on a high rise building
 Surrounding buildings and wind pressure distribution on a high rise building Conference or Workshop Item Accepted Version Luo, Z. (2008) Surrounding buildings and wind pressure distribution on a high rise
Surrounding buildings and wind pressure distribution on a high rise building Conference or Workshop Item Accepted Version Luo, Z. (2008) Surrounding buildings and wind pressure distribution on a high rise
Accepted for publication in Journal of Wind Engineering and Industrial Aerodynamics, 20 June 2009
 Accepted for publication in Journal of Wind Engineering and Industrial Aerodynamics, 20 June 2009 Pedestrian wind comfort around a large football stadium in an urban environment: CFD simulation, validation
Accepted for publication in Journal of Wind Engineering and Industrial Aerodynamics, 20 June 2009 Pedestrian wind comfort around a large football stadium in an urban environment: CFD simulation, validation
Many elite cyclists therefore try to optimise their position for drag by means of field tests or wind tunnel tests. More recently, also Computational
 The Seventh International Colloquium on Bluff Body Aerodynamics and Applications (BBAA7) Shanghai, China; September 2-6, 2012 RANS and LES simulations of the interference drag of two cyclists B. Blocken
The Seventh International Colloquium on Bluff Body Aerodynamics and Applications (BBAA7) Shanghai, China; September 2-6, 2012 RANS and LES simulations of the interference drag of two cyclists B. Blocken
APPLICATION OF COMPUTATIONAL FLUID DYNAMICS (CFD) IN WIND ANALYSIS OF TALL BUILDINGS. Damith Mohotti, Priyan Mendis, Tuan Ngo
 APPLICATION OF COMPUTATIONAL FLUID DYNAMICS (CFD) IN WIND ANALYSIS OF TALL BUILDINGS Damith Mohotti, Priyan Mendis, Tuan Ngo Department of Infrastructures Engineering, The University of Melbourne, Victoria,
APPLICATION OF COMPUTATIONAL FLUID DYNAMICS (CFD) IN WIND ANALYSIS OF TALL BUILDINGS Damith Mohotti, Priyan Mendis, Tuan Ngo Department of Infrastructures Engineering, The University of Melbourne, Victoria,
Wind tunnel test and numerical simulation of wind pressure on a high-rise building
 Journal of Chongqing University (English Edition) [ISSN 1671-8224] Vol. 9 No. 1 March 2010 Article ID: 1671-8224(2010)01-0047-07 To cite this article: AL ZOUBI Feras, LI Zheng-liang, WEI Qi-ke, SUN Yi.
Journal of Chongqing University (English Edition) [ISSN 1671-8224] Vol. 9 No. 1 March 2010 Article ID: 1671-8224(2010)01-0047-07 To cite this article: AL ZOUBI Feras, LI Zheng-liang, WEI Qi-ke, SUN Yi.
COMPARISONS OF COMPUTATIONAL FLUID DYNAMICS AND
 The Seventh Asia-Pacific Conference on Wind Engineering, November 8-12, 2009, Taipei, Taiwan COMPARISONS OF COMPUTATIONAL FLUID DYNAMICS AND WIND TUNNEL EXPERIMENTS FOR PEDESTRIAN WIND ENVIRONMENTS Chin-Hsien
The Seventh Asia-Pacific Conference on Wind Engineering, November 8-12, 2009, Taipei, Taiwan COMPARISONS OF COMPUTATIONAL FLUID DYNAMICS AND WIND TUNNEL EXPERIMENTS FOR PEDESTRIAN WIND ENVIRONMENTS Chin-Hsien
CFD simulation of wind-induced pressure coefficients on buildings with and without balconies: validation and sensitivity analysis
 Building and Environment, Volume 60, February 2013, Pages 137-149 CFD simulation of wind-induced pressure coefficients on buildings with and without balconies: validation and sensitivity analysis H. Montazeri,
Building and Environment, Volume 60, February 2013, Pages 137-149 CFD simulation of wind-induced pressure coefficients on buildings with and without balconies: validation and sensitivity analysis H. Montazeri,
Impact of eaves on cross-ventilation of a generic isolated leeward sawtooth roof building: windward eaves, leeward eaves and eaves inclination
 Accepted for publication in Building and Environment on May 11, 2015 Impact of eaves on cross-ventilation of a generic isolated leeward sawtooth roof building: windward eaves, leeward eaves and eaves inclination
Accepted for publication in Building and Environment on May 11, 2015 Impact of eaves on cross-ventilation of a generic isolated leeward sawtooth roof building: windward eaves, leeward eaves and eaves inclination
The evolution of the application of CFD on pedestrian wind comfort in engineering practice, a validation study
 EACWE 5 Florence, Italy 19 th 23 rd July 2009 Flying Sphere image Museo Ideale L. Da Vinci The evolution of the application of CFD on pedestrian wind comfort in engineering practice, a validation study
EACWE 5 Florence, Italy 19 th 23 rd July 2009 Flying Sphere image Museo Ideale L. Da Vinci The evolution of the application of CFD on pedestrian wind comfort in engineering practice, a validation study
RESEARCH ON MEASUREMENT AND SIMULATION OF THE WIND ENVIRON- MENT AROUND BUILDINGS IN CAMPUS
 Eleventh International IBPSA Conference Glasgow, Scotland July 27-30, 2009 RESEARCH ON MEASUREMENT AND SIMULATION OF THE WIND ENVIRON- MENT AROUND BUILDINGS IN CAMPUS Bing Wang 1, Borong Lin 1,* 1Deparment
Eleventh International IBPSA Conference Glasgow, Scotland July 27-30, 2009 RESEARCH ON MEASUREMENT AND SIMULATION OF THE WIND ENVIRON- MENT AROUND BUILDINGS IN CAMPUS Bing Wang 1, Borong Lin 1,* 1Deparment
Effect of Diameter on the Aerodynamics of Sepaktakraw Balls, A Computational Study
 ISSN 1750-9823 (print) International Journal of Sports Science and Engineering Vol. 03 (2009) No. 01, pp. 017-021 Effect of Diameter on the Aerodynamics of Sepaktakraw Balls, A Computational Study Zahari
ISSN 1750-9823 (print) International Journal of Sports Science and Engineering Vol. 03 (2009) No. 01, pp. 017-021 Effect of Diameter on the Aerodynamics of Sepaktakraw Balls, A Computational Study Zahari
Validating CFD Simulation Results: Wind flow around a surface mounted cube in a turbulent channel flow
 Validating CFD Simulation Results: Wind flow around a surface mounted cube in a turbulent channel flow ISLAM ABOHELA 1, NEVEEN HAMZA 1, STEVEN DUDEK 1 1 School of Architecture, Planning and Landscape,
Validating CFD Simulation Results: Wind flow around a surface mounted cube in a turbulent channel flow ISLAM ABOHELA 1, NEVEEN HAMZA 1, STEVEN DUDEK 1 1 School of Architecture, Planning and Landscape,
Full scale measurements and simulations of the wind speed in the close proximity of the building skin
 Full scale measurements and simulations of the wind speed in the close proximity of the building skin Radoslav Ponechal 1,* and Peter Juras 1 1 University of Zilina, Faculty of Civil Engineering, Department
Full scale measurements and simulations of the wind speed in the close proximity of the building skin Radoslav Ponechal 1,* and Peter Juras 1 1 University of Zilina, Faculty of Civil Engineering, Department
WIND FLOW CHARACTERISTICS AROUND ROOFTOP SOLAR ARRAY - A NUMERICAL STUDY
 The Eighth Asia-Pacific Conference on Wind Engineering, December 10 14, 2013, Chennai, India WIND FLOW CHARACTERISTICS AROUND ROOFTOP SOLAR ARRAY - A NUMERICAL STUDY D.Ghosh 1, A. K. Mittal 2, S. Behera
The Eighth Asia-Pacific Conference on Wind Engineering, December 10 14, 2013, Chennai, India WIND FLOW CHARACTERISTICS AROUND ROOFTOP SOLAR ARRAY - A NUMERICAL STUDY D.Ghosh 1, A. K. Mittal 2, S. Behera
Assessment of pedestrian wind environment of high-rise complex using CFD simulation
 Assessment of pedestrian wind environment of high-rise complex using CFD simulation Hyungkeun Kim Researcher Department of architectural engineering, Yonsei University vickim@yonsei.ac.kr Taeyeon Kim Professor
Assessment of pedestrian wind environment of high-rise complex using CFD simulation Hyungkeun Kim Researcher Department of architectural engineering, Yonsei University vickim@yonsei.ac.kr Taeyeon Kim Professor
Numerical investigation on the effect of overhang roof around rural house
 Numerical investigation on the effect of overhang roof around rural house *Taksiah A. Majid 1), Shaharudin Shah Zaini 2), Mohd Azmi Ismail 3), Siti Noratikah Che Deraman 4) and Jing Lin Poon 5) 1), 2),
Numerical investigation on the effect of overhang roof around rural house *Taksiah A. Majid 1), Shaharudin Shah Zaini 2), Mohd Azmi Ismail 3), Siti Noratikah Che Deraman 4) and Jing Lin Poon 5) 1), 2),
Cross Comparisons of CFD Prediction for Wind Environment at Pedestrian Level around Buildings
 Cross Comparisons of CFD Prediction for Wind Environment at Pedestrian Level around Buildings Part Comparison of Results for Flow-field around a High-rise Building Located in Surrounding City Blocks Ryuichiro
Cross Comparisons of CFD Prediction for Wind Environment at Pedestrian Level around Buildings Part Comparison of Results for Flow-field around a High-rise Building Located in Surrounding City Blocks Ryuichiro
Modelling the Output of a Flat-Roof Mounted Wind Turbine with an Edge Mounted Lip
 Modelling the Output of a Flat-Roof Mounted Wind Turbine with an Edge Mounted Lip S. J. Wylie 1, S. J. Watson 1, D. G. Infield 2 1 Centre for Renewable Energy Systems Technology, Department of Electronic
Modelling the Output of a Flat-Roof Mounted Wind Turbine with an Edge Mounted Lip S. J. Wylie 1, S. J. Watson 1, D. G. Infield 2 1 Centre for Renewable Energy Systems Technology, Department of Electronic
SCIENCE & TECHNOLOGY
 Pertanika J. Sci. & Technol. 25 (S): 227-238 (2017) SCIENCE & TECHNOLOGY Journal homepage: http://www.pertanika.upm.edu.my/ CFD Analysis on Indoor Temperature and Velocity: Effects of Incident Wind Angle
Pertanika J. Sci. & Technol. 25 (S): 227-238 (2017) SCIENCE & TECHNOLOGY Journal homepage: http://www.pertanika.upm.edu.my/ CFD Analysis on Indoor Temperature and Velocity: Effects of Incident Wind Angle
Determination of the wind pressure distribution on the facade of the triangularly shaped high-rise building structure
 Determination of the wind pressure distribution on the facade of the triangularly shaped high-rise building structure Norbert Jendzelovsky 1,*, Roland Antal 1 and Lenka Konecna 1 1 STU in Bratislava, Faculty
Determination of the wind pressure distribution on the facade of the triangularly shaped high-rise building structure Norbert Jendzelovsky 1,*, Roland Antal 1 and Lenka Konecna 1 1 STU in Bratislava, Faculty
AIRFLOW GENERATION IN A TUNNEL USING A SACCARDO VENTILATION SYSTEM AGAINST THE BUOYANCY EFFECT PRODUCED BY A FIRE
 - 247 - AIRFLOW GENERATION IN A TUNNEL USING A SACCARDO VENTILATION SYSTEM AGAINST THE BUOYANCY EFFECT PRODUCED BY A FIRE J D Castro a, C W Pope a and R D Matthews b a Mott MacDonald Ltd, St Anne House,
- 247 - AIRFLOW GENERATION IN A TUNNEL USING A SACCARDO VENTILATION SYSTEM AGAINST THE BUOYANCY EFFECT PRODUCED BY A FIRE J D Castro a, C W Pope a and R D Matthews b a Mott MacDonald Ltd, St Anne House,
Forest Winds in Complex Terrain
 Forest Winds in Complex Terrain Ilda Albuquerque 1 Contents Project Description Motivation Forest Complex Terrain Forested Complex Terrain 2 Project Description WAUDIT (Wind Resource Assessment Audit and
Forest Winds in Complex Terrain Ilda Albuquerque 1 Contents Project Description Motivation Forest Complex Terrain Forested Complex Terrain 2 Project Description WAUDIT (Wind Resource Assessment Audit and
NUMERICAL INVESTIGATION OF THE FLOW BEHAVIOUR IN A MODERN TRAFFIC TUNNEL IN CASE OF FIRE INCIDENT
 - 277 - NUMERICAL INVESTIGATION OF THE FLOW BEHAVIOUR IN A MODERN TRAFFIC TUNNEL IN CASE OF FIRE INCIDENT Iseler J., Heiser W. EAS GmbH, Karlsruhe, Germany ABSTRACT A numerical study of the flow behaviour
- 277 - NUMERICAL INVESTIGATION OF THE FLOW BEHAVIOUR IN A MODERN TRAFFIC TUNNEL IN CASE OF FIRE INCIDENT Iseler J., Heiser W. EAS GmbH, Karlsruhe, Germany ABSTRACT A numerical study of the flow behaviour
Building Physics and Systems, Technische Universiteit Eindhoven, P.O. box 513, 5600 MB Eindhoven, the Netherlands
 PRE-PRINT of the article: Blocken B, Carmeliet J. 2008. Pedestrian wind conditions at outdoor platforms in a high-rise apartment building: generic sub-configuration validation, wind comfort assessment
PRE-PRINT of the article: Blocken B, Carmeliet J. 2008. Pedestrian wind conditions at outdoor platforms in a high-rise apartment building: generic sub-configuration validation, wind comfort assessment
Wind Flow Model of Area Surrounding the Case Western Reserve University Wind Turbine
 Wind Flow Model of Area Surrounding the Case Western Reserve University Wind Turbine Matheus C. Fernandes 1, David H. Matthiesen PhD *2 1 Case Western Reserve University Dept. of Mechanical Engineering,
Wind Flow Model of Area Surrounding the Case Western Reserve University Wind Turbine Matheus C. Fernandes 1, David H. Matthiesen PhD *2 1 Case Western Reserve University Dept. of Mechanical Engineering,
Wind pressure coefficient determination for greenhouses built in a reclaimed land using CFD technique
 Ref: 1064 Wind pressure coefficient determination for greenhouses built in a reclaimed land using CFD technique Hyun-seob Hwang and In-bok Lee, Department of Rural Systems Engineering, Research Institute
Ref: 1064 Wind pressure coefficient determination for greenhouses built in a reclaimed land using CFD technique Hyun-seob Hwang and In-bok Lee, Department of Rural Systems Engineering, Research Institute
Cooperative roject for CFD rediction of edestrian ind nvironment in the Architectural Institute of Japan
 EACWE4 The Fourth European & African Conference on Wind Engineering J. Náprstek & C. Fischer (eds); ITAM AS CR, Prague, 11-15 July, 2005, Paper #292 Cooperative roject for CFD rediction of edestrian ind
EACWE4 The Fourth European & African Conference on Wind Engineering J. Náprstek & C. Fischer (eds); ITAM AS CR, Prague, 11-15 July, 2005, Paper #292 Cooperative roject for CFD rediction of edestrian ind
Pressure coefficient on flat roofs of rectangular buildings
 Pressure coefficient on flat roofs of rectangular buildings T. Lipecki 1 1 Faculty of Civil Engineering and Architecture, Lublin University of Technology, Poland. t.lipecki@pollub.pl Abstract The paper
Pressure coefficient on flat roofs of rectangular buildings T. Lipecki 1 1 Faculty of Civil Engineering and Architecture, Lublin University of Technology, Poland. t.lipecki@pollub.pl Abstract The paper
Measurement and simulation of the flow field around a triangular lattice meteorological mast
 Measurement and simulation of the flow field around a triangular lattice meteorological mast Matthew Stickland 1, Thomas Scanlon 1, Sylvie Fabre 1, Andrew Oldroyd 2 and Detlef Kindler 3 1. Department of
Measurement and simulation of the flow field around a triangular lattice meteorological mast Matthew Stickland 1, Thomas Scanlon 1, Sylvie Fabre 1, Andrew Oldroyd 2 and Detlef Kindler 3 1. Department of
Numerical Simulation of Wind Effect on a Rooftop Solar Array
 J. Energy Power Sources Vol. 2, No. 8, 2015, pp. 317-322 Received: July 1, 2015, Published: August 30, 2015 Journal of Energy and Power Sources www.ethanpublishing.com Numerical Simulation of Wind Effect
J. Energy Power Sources Vol. 2, No. 8, 2015, pp. 317-322 Received: July 1, 2015, Published: August 30, 2015 Journal of Energy and Power Sources www.ethanpublishing.com Numerical Simulation of Wind Effect
Wind pressure on a single building immersed in a low jet wind profile
 Wind pressure on a single building immersed in a low jet wind profile Conference or Workshop Item Accepted Version Luo, Z. and Hang, J. (2013) Wind pressure on a single building immersed in a low jet wind
Wind pressure on a single building immersed in a low jet wind profile Conference or Workshop Item Accepted Version Luo, Z. and Hang, J. (2013) Wind pressure on a single building immersed in a low jet wind
Roof Mounted Wind Turbines: A Methodology for Assessing Potential Roof Mounting Locations
 PLEA2013-29th Conference, Sustainable Architecture for a Renewable Future, Munich, Germany 10-12 September 2013 Roof Mounted Wind Turbines: A Methodology for Assessing Potential Roof Mounting Locations
PLEA2013-29th Conference, Sustainable Architecture for a Renewable Future, Munich, Germany 10-12 September 2013 Roof Mounted Wind Turbines: A Methodology for Assessing Potential Roof Mounting Locations
AIRFLOW AND TEMPERATURE FIELD CALCULATIONS FOR WINTER SPORTS FACILITIES
 AIRFLOW AND TEMPERATURE FIELD CALCULATIONS FOR WINTER SPORTS FACILITIES Andrea Frisque* Stantec Consulting, Vancouver BC V6B6A3, Canada Rowan, Williams, Davies & Irwin (RWDI), Vancouver, BC, V5Z 1K5, Canada**
AIRFLOW AND TEMPERATURE FIELD CALCULATIONS FOR WINTER SPORTS FACILITIES Andrea Frisque* Stantec Consulting, Vancouver BC V6B6A3, Canada Rowan, Williams, Davies & Irwin (RWDI), Vancouver, BC, V5Z 1K5, Canada**
Wind tunnel tests of a non-typical stadium roof
 Wind tunnel tests of a non-typical stadium roof G. Bosak 1, A. Flaga 1, R. Kłaput 1 and Ł. Flaga 1 1 Wind Engineering Laboratory, Cracow University of Technology, 31-864 Cracow, Poland. liwpk@windlab.pl
Wind tunnel tests of a non-typical stadium roof G. Bosak 1, A. Flaga 1, R. Kłaput 1 and Ł. Flaga 1 1 Wind Engineering Laboratory, Cracow University of Technology, 31-864 Cracow, Poland. liwpk@windlab.pl
CFD Analysis ofwind Turbine Airfoil at Various Angles of Attack
 IOSR Journal of Mechanical and Civil Engineering (IOSR-JMCE) e-issn: 2278-1684,p-ISSN: 2320-334X, Volume 13, Issue 4 Ver. II (Jul. - Aug. 2016), PP 18-24 www.iosrjournals.org CFD Analysis ofwind Turbine
IOSR Journal of Mechanical and Civil Engineering (IOSR-JMCE) e-issn: 2278-1684,p-ISSN: 2320-334X, Volume 13, Issue 4 Ver. II (Jul. - Aug. 2016), PP 18-24 www.iosrjournals.org CFD Analysis ofwind Turbine
CFD SIMULATIONS OF GAS DISPERSION IN VENTILATED ROOMS
 CFD SIMULATIONS OF GAS DISPERSION IN VENTILATED ROOMS T. Gélain, C. Prévost Institut de Radioprotection et de Sûreté Nucléaire (IRSN), Saclay, France Abstract In order to better understand the risks due
CFD SIMULATIONS OF GAS DISPERSION IN VENTILATED ROOMS T. Gélain, C. Prévost Institut de Radioprotection et de Sûreté Nucléaire (IRSN), Saclay, France Abstract In order to better understand the risks due
A study of heat transfer effects on air pollution dispersion in street canyons by numerical simulations
 A study of heat transfer effects on air pollution dispersion in street canyons by numerical simulations N. Moussiopoulos, I. Ossanlis and Ph. Barmpas Aristotle University Thessaloniki, Greece MIMO 3D,
A study of heat transfer effects on air pollution dispersion in street canyons by numerical simulations N. Moussiopoulos, I. Ossanlis and Ph. Barmpas Aristotle University Thessaloniki, Greece MIMO 3D,
Aerodynamic study of a cyclist s moving legs using an innovative approach
 Aerodynamic study of a cyclist s moving legs using an innovative approach Francesco Pozzetti 30 September 2017 Abstract During a period of four weeks in September, I completed a research project in fluid
Aerodynamic study of a cyclist s moving legs using an innovative approach Francesco Pozzetti 30 September 2017 Abstract During a period of four weeks in September, I completed a research project in fluid
Numerical simulation and analysis of aerodynamic drag on a subsonic train in evacuated tube transportation
 Journal of Modern Transportation Volume 20, Number 1, March 2012, Page 44-48 Journal homepage: jmt.swjtu.edu.cn DOI: 10.1007/BF03325776 1 Numerical simulation and analysis of aerodynamic drag on a subsonic
Journal of Modern Transportation Volume 20, Number 1, March 2012, Page 44-48 Journal homepage: jmt.swjtu.edu.cn DOI: 10.1007/BF03325776 1 Numerical simulation and analysis of aerodynamic drag on a subsonic
Numerical Analysis of Wind loads on Tapered Shape Tall Buildings
 IJSTE - International Journal of Science Technology & Engineering Volume 1 Issue 11 May 2015 ISSN (online): 2349-784X Numerical Analysis of Wind loads on Tapered Shape Tall Buildings Ashwin G Hansora Assistant
IJSTE - International Journal of Science Technology & Engineering Volume 1 Issue 11 May 2015 ISSN (online): 2349-784X Numerical Analysis of Wind loads on Tapered Shape Tall Buildings Ashwin G Hansora Assistant
leading edge, where the flow is fully separated. Both for the means and peaks, smooth flow leads to the highest values. A good correlation between cav
 The Seventh International Colloquium on Bluff Body Aerodynamics and Applications (BBAA7) Shanghai, China; September 2-6, 22 Towards a better understanding of pressure equalization Carine van Bentum a,
The Seventh International Colloquium on Bluff Body Aerodynamics and Applications (BBAA7) Shanghai, China; September 2-6, 22 Towards a better understanding of pressure equalization Carine van Bentum a,
The Performance-based Wind Environment Analysis in Campus -Taking University of Shanghai for Science and Technology as an Example
 Journal of Civil Engineering and Construction 2:2 (2013) The Performance-based Wind Environment Analysis in Campus -Taking University of Shanghai for Science and Technology as an Example Miao Ye 1,a, Li
Journal of Civil Engineering and Construction 2:2 (2013) The Performance-based Wind Environment Analysis in Campus -Taking University of Shanghai for Science and Technology as an Example Miao Ye 1,a, Li
NUMERICAL SIMULATION OF STATIC INTERFERENCE EFFECTS FOR SINGLE BUILDINGS GROUP
 NUMERICAL SIMULATION OF STATIC INTERFERENCE EFFECTS FOR SINGLE BUILDINGS GROUP Xing-qian Peng, Chun-hui Zhang 2 and Chang-gui Qiao 2 Professor, College of Civil Engineering, Huaqiao University, Quanzhou,
NUMERICAL SIMULATION OF STATIC INTERFERENCE EFFECTS FOR SINGLE BUILDINGS GROUP Xing-qian Peng, Chun-hui Zhang 2 and Chang-gui Qiao 2 Professor, College of Civil Engineering, Huaqiao University, Quanzhou,
Numerical simulation of topographic effects on wind flow fields over complex terrain
 The Eighth Asia-Pacific Conference on Wind Engineering, December 10 14, 2013, Chennai, India Numerical simulation of topographic effects on wind flow fields over complex terrain B.W. Yan 1, Q.S. LI 2,
The Eighth Asia-Pacific Conference on Wind Engineering, December 10 14, 2013, Chennai, India Numerical simulation of topographic effects on wind flow fields over complex terrain B.W. Yan 1, Q.S. LI 2,
Influence of rounding corners on unsteady flow and heat transfer around a square cylinder
 Influence of rounding corners on unsteady flow and heat transfer around a square cylinder S. K. Singh Deptt. of Mech. Engg., M. B. M. Engg. College / J. N. V. University, Jodhpur, Rajasthan, India Abstract
Influence of rounding corners on unsteady flow and heat transfer around a square cylinder S. K. Singh Deptt. of Mech. Engg., M. B. M. Engg. College / J. N. V. University, Jodhpur, Rajasthan, India Abstract
Workshop 1: Bubbly Flow in a Rectangular Bubble Column. Multiphase Flow Modeling In ANSYS CFX Release ANSYS, Inc. WS1-1 Release 14.
 Workshop 1: Bubbly Flow in a Rectangular Bubble Column 14. 5 Release Multiphase Flow Modeling In ANSYS CFX 2013 ANSYS, Inc. WS1-1 Release 14.5 Introduction This workshop models the dispersion of air bubbles
Workshop 1: Bubbly Flow in a Rectangular Bubble Column 14. 5 Release Multiphase Flow Modeling In ANSYS CFX 2013 ANSYS, Inc. WS1-1 Release 14.5 Introduction This workshop models the dispersion of air bubbles
COMPUTATIONAL FLOW MODEL OF WESTFALL'S LEADING TAB FLOW CONDITIONER AGM-09-R-08 Rev. B. By Kimbal A. Hall, PE
 COMPUTATIONAL FLOW MODEL OF WESTFALL'S LEADING TAB FLOW CONDITIONER AGM-09-R-08 Rev. B By Kimbal A. Hall, PE Submitted to: WESTFALL MANUFACTURING COMPANY September 2009 ALDEN RESEARCH LABORATORY, INC.
COMPUTATIONAL FLOW MODEL OF WESTFALL'S LEADING TAB FLOW CONDITIONER AGM-09-R-08 Rev. B By Kimbal A. Hall, PE Submitted to: WESTFALL MANUFACTURING COMPANY September 2009 ALDEN RESEARCH LABORATORY, INC.
EXPERIMENTAL STUDY OF WIND PRESSURES ON IRREGULAR- PLAN SHAPE BUILDINGS
 BBAA VI International Colloquium on: Bluff Bodies Aerodynamics & Applications Milano, Italy, July, 2-24 8 EXPERIMENTAL STUDY OF WIND PRESSURES ON IRREGULAR- PLAN SHAPE BUILDINGS J. A. Amin and A. K. Ahuja
BBAA VI International Colloquium on: Bluff Bodies Aerodynamics & Applications Milano, Italy, July, 2-24 8 EXPERIMENTAL STUDY OF WIND PRESSURES ON IRREGULAR- PLAN SHAPE BUILDINGS J. A. Amin and A. K. Ahuja
ISOLATION OF NON-HYDROSTATIC REGIONS WITHIN A BASIN
 ISOLATION OF NON-HYDROSTATIC REGIONS WITHIN A BASIN Bridget M. Wadzuk 1 (Member, ASCE) and Ben R. Hodges 2 (Member, ASCE) ABSTRACT Modeling of dynamic pressure appears necessary to achieve a more robust
ISOLATION OF NON-HYDROSTATIC REGIONS WITHIN A BASIN Bridget M. Wadzuk 1 (Member, ASCE) and Ben R. Hodges 2 (Member, ASCE) ABSTRACT Modeling of dynamic pressure appears necessary to achieve a more robust
Centre for Offshore Renewable Energy Engineering, School of Energy, Environment and Agrifood, Cranfield University, Cranfield, MK43 0AL, UK 2
 Fluid Structure Interaction Modelling of A Novel 10MW Vertical-Axis Wind Turbine Rotor Based on Computational Fluid Dynamics and Finite Element Analysis Lin Wang 1*, Athanasios Kolios 1, Pierre-Luc Delafin
Fluid Structure Interaction Modelling of A Novel 10MW Vertical-Axis Wind Turbine Rotor Based on Computational Fluid Dynamics and Finite Element Analysis Lin Wang 1*, Athanasios Kolios 1, Pierre-Luc Delafin
Experimental Investigation Of Flow Past A Rough Surfaced Cylinder
 (AET- 29th March 214) RESEARCH ARTICLE OPEN ACCESS Experimental Investigation Of Flow Past A Rough Surfaced Cylinder Monalisa Mallick 1, A. Kumar 2 1 (Department of Civil Engineering, National Institute
(AET- 29th March 214) RESEARCH ARTICLE OPEN ACCESS Experimental Investigation Of Flow Past A Rough Surfaced Cylinder Monalisa Mallick 1, A. Kumar 2 1 (Department of Civil Engineering, National Institute
FLOW CONSIDERATIONS IN INDUSTRIAL SILENCER DESIGN
 FLOW CONSIDERATIONS IN INDUSTRIAL SILENCER DESIGN George Feng, Kinetics Noise Control, Inc., 3570 Nashua Drive, Mississauga, Ontario Vadim Akishin, Kinetics Noise Control, Inc., 3570 Nashua Drive, Mississauga,
FLOW CONSIDERATIONS IN INDUSTRIAL SILENCER DESIGN George Feng, Kinetics Noise Control, Inc., 3570 Nashua Drive, Mississauga, Ontario Vadim Akishin, Kinetics Noise Control, Inc., 3570 Nashua Drive, Mississauga,
Quantification of the Effects of Turbulence in Wind on the Flutter Stability of Suspension Bridges
 Quantification of the Effects of Turbulence in Wind on the Flutter Stability of Suspension Bridges T. Abbas 1 and G. Morgenthal 2 1 PhD candidate, Graduate College 1462, Department of Civil Engineering,
Quantification of the Effects of Turbulence in Wind on the Flutter Stability of Suspension Bridges T. Abbas 1 and G. Morgenthal 2 1 PhD candidate, Graduate College 1462, Department of Civil Engineering,
Welke daalhouding is het meest aerodynamisch?
 Welke daalhouding is het meest aerodynamisch? Bert Blocken a,b a Faculteit Bouwkunde, Technische Universiteit Eindhoven, Nederland b Departement Burgerlijke Bouwkunde, KU Leuven, België Welke daalhouding
Welke daalhouding is het meest aerodynamisch? Bert Blocken a,b a Faculteit Bouwkunde, Technische Universiteit Eindhoven, Nederland b Departement Burgerlijke Bouwkunde, KU Leuven, België Welke daalhouding
Numerical simulation of aerodynamic performance for two dimensional wind turbine airfoils
 Available online at www.sciencedirect.com Procedia Engineering 31 (2012) 80 86 International Conference on Advances in Computational Modeling and Simulation Numerical simulation of aerodynamic performance
Available online at www.sciencedirect.com Procedia Engineering 31 (2012) 80 86 International Conference on Advances in Computational Modeling and Simulation Numerical simulation of aerodynamic performance
DUE TO EXTERNAL FORCES
 17B.6 DNS ON GROWTH OF A VERTICAL VORTEX IN CONVECTION DUE TO EXTERNAL FORCES Ryota Iijima* and Tetsuro Tamura Tokyo Institute of Technology, Yokohama, Japan 1. INTRODUCTION Various types of vertical vortices,
17B.6 DNS ON GROWTH OF A VERTICAL VORTEX IN CONVECTION DUE TO EXTERNAL FORCES Ryota Iijima* and Tetsuro Tamura Tokyo Institute of Technology, Yokohama, Japan 1. INTRODUCTION Various types of vertical vortices,
Pedestrian Wind Environment around Buildings: Literature Review and Practical Examples
 Pedestrian Wind Environment around Buildings: Literature Review and Practical Examples BERT BLOCKEN 1, * AND JAN CARMELIET 1,2 1 Laboratory of Building Physics Department of Civil Engineering Katholieke
Pedestrian Wind Environment around Buildings: Literature Review and Practical Examples BERT BLOCKEN 1, * AND JAN CARMELIET 1,2 1 Laboratory of Building Physics Department of Civil Engineering Katholieke
Investigations on the Aerodynamic Forces of 2-D Square Lattice Tower Section Using CFD
 J. Energy Power Sources Vol. 1, No. 5, 2014, pp. 270-277 Received: August 14, 2014, Published: November 30, 2014 Journal of Energy and Power Sources www.ethanpublishing.com Investigations on the Aerodynamic
J. Energy Power Sources Vol. 1, No. 5, 2014, pp. 270-277 Received: August 14, 2014, Published: November 30, 2014 Journal of Energy and Power Sources www.ethanpublishing.com Investigations on the Aerodynamic
High Swept-back Delta Wing Flow
 Advanced Materials Research Submitted: 2014-06-25 ISSN: 1662-8985, Vol. 1016, pp 377-382 Accepted: 2014-06-25 doi:10.4028/www.scientific.net/amr.1016.377 Online: 2014-08-28 2014 Trans Tech Publications,
Advanced Materials Research Submitted: 2014-06-25 ISSN: 1662-8985, Vol. 1016, pp 377-382 Accepted: 2014-06-25 doi:10.4028/www.scientific.net/amr.1016.377 Online: 2014-08-28 2014 Trans Tech Publications,
Windcube FCR measurements
 Windcube FCR measurements Principles, performance and recommendations for use of the Flow Complexity Recognition (FCR) algorithm for the Windcube ground-based Lidar Summary: As with any remote sensor,
Windcube FCR measurements Principles, performance and recommendations for use of the Flow Complexity Recognition (FCR) algorithm for the Windcube ground-based Lidar Summary: As with any remote sensor,
AERODYNAMIC FEATURES AS AUXILIARY ARCHITECTURE
 N. Gu, S. Watanabe, H. Erhan, M. Hank Haeusler, W. Huang, R. Sosa (eds.), Rethinking Comprehensive Design: Speculative Counterculture, Proceedings of the 19th International Conference on Computer- Aided
N. Gu, S. Watanabe, H. Erhan, M. Hank Haeusler, W. Huang, R. Sosa (eds.), Rethinking Comprehensive Design: Speculative Counterculture, Proceedings of the 19th International Conference on Computer- Aided
MODELING AND SIMULATION OF VALVE COEFFICIENTS AND CAVITATION CHARACTERISTICS IN A BALL VALVE
 Proceedings of the 37 th International & 4 th National Conference on Fluid Mechanics and Fluid Power FMFP2010 December 16-18, 2010, IIT Madras, Chennai, India FMFP2010 341 MODELING AND SIMULATION OF VALVE
Proceedings of the 37 th International & 4 th National Conference on Fluid Mechanics and Fluid Power FMFP2010 December 16-18, 2010, IIT Madras, Chennai, India FMFP2010 341 MODELING AND SIMULATION OF VALVE
Aerodynamic Measures for the Vortex-induced Vibration of π-shape Composite Girder in Cable-stayed Bridge
 Aerodynamic Measures for the Vortex-induced Vibration of π-shape Composite Girder in Cable-stayed Bridge *Feng Wang 1), Jialing Song 2), Tuo Wu 3), and Muxiong Wei 4) 1), 2, 3), 4) Highway School, Chang
Aerodynamic Measures for the Vortex-induced Vibration of π-shape Composite Girder in Cable-stayed Bridge *Feng Wang 1), Jialing Song 2), Tuo Wu 3), and Muxiong Wei 4) 1), 2, 3), 4) Highway School, Chang
Journal of Engineering Science and Technology Review 9 (5) (2016) Research Article. CFD Simulations of Flow Around Octagonal Shaped Structures
 Jestr Journal of Engineering Science and Technology Review 9 (5) (2016) 72-76 Research Article JOURNAL OF Engineering Science and Technology Review www.jestr.org CFD Simulations of Flow Around Octagonal
Jestr Journal of Engineering Science and Technology Review 9 (5) (2016) 72-76 Research Article JOURNAL OF Engineering Science and Technology Review www.jestr.org CFD Simulations of Flow Around Octagonal
Performance Evaluation of Four-Sided Square Wind Catchers with Different Geometries by Numerical Method
 Article Performance Evaluation of Four-Sided Square Wind Catchers with Different Geometries by Numerical Method Maryam Hossein Ghadiri 1,a, Nik Lukman Nik Ibrahim 1,b, and Mohd Farid Mohamed 2,c 1, 2 Department
Article Performance Evaluation of Four-Sided Square Wind Catchers with Different Geometries by Numerical Method Maryam Hossein Ghadiri 1,a, Nik Lukman Nik Ibrahim 1,b, and Mohd Farid Mohamed 2,c 1, 2 Department
NUMERICAL SIMULATION OF WIND INTERFERENCE EFFECT
 NUMERICAL SIMULATION OF WIND INTERFERENCE EFFECT FOR A STADIUM AND A GYMNASIUM Gang Xu 1, Xing-qian Peng 2, Li Wu 1, Hai Zhu 1 1 Graduate student, College of Civil Engineering, Huaqiao University, Quanzhou,
NUMERICAL SIMULATION OF WIND INTERFERENCE EFFECT FOR A STADIUM AND A GYMNASIUM Gang Xu 1, Xing-qian Peng 2, Li Wu 1, Hai Zhu 1 1 Graduate student, College of Civil Engineering, Huaqiao University, Quanzhou,
CFD Study of Solid Wind Tunnel Wall Effects on Wing Characteristics
 Indian Journal of Science and Technology, Vol 9(45), DOI :10.17485/ijst/2016/v9i45/104585, December 2016 ISSN (Print) : 0974-6846 ISSN (Online) : 0974-5645 CFD Study of Solid Wind Tunnel Wall Effects on
Indian Journal of Science and Technology, Vol 9(45), DOI :10.17485/ijst/2016/v9i45/104585, December 2016 ISSN (Print) : 0974-6846 ISSN (Online) : 0974-5645 CFD Study of Solid Wind Tunnel Wall Effects on
Atmospheric Boundary Layer Simulation Using Wall Function Approach in OpenFoam CFD Software
 Atmospheric Boundary Layer Simulation Using Wall Function Approach in OpenFoam CFD Software Okafor C. Vincent, Ogunoh E. Peter, Ezeokonkwo U. John and Obodoh D. Anosike Abstract The significant development
Atmospheric Boundary Layer Simulation Using Wall Function Approach in OpenFoam CFD Software Okafor C. Vincent, Ogunoh E. Peter, Ezeokonkwo U. John and Obodoh D. Anosike Abstract The significant development
Investigation on 3-D Wing of commercial Aeroplane with Aerofoil NACA 2415 Using CFD Fluent
 Investigation on 3-D of commercial Aeroplane with Aerofoil NACA 2415 Using CFD Fluent Rohit Jain 1, Mr. Sandeep Jain 2, Mr. Lokesh Bajpai 3 1PG Student, 2 Associate Professor, 3 Professor & Head 1 2 3
Investigation on 3-D of commercial Aeroplane with Aerofoil NACA 2415 Using CFD Fluent Rohit Jain 1, Mr. Sandeep Jain 2, Mr. Lokesh Bajpai 3 1PG Student, 2 Associate Professor, 3 Professor & Head 1 2 3
Numerical Fluid Analysis of a Variable Geometry Compressor for Use in a Turbocharger
 Special Issue Turbocharging Technologies 15 Research Report Numerical Fluid Analysis of a Variable Geometry Compressor for Use in a Turbocharger Yuji Iwakiri, Hiroshi Uchida Abstract A numerical fluid
Special Issue Turbocharging Technologies 15 Research Report Numerical Fluid Analysis of a Variable Geometry Compressor for Use in a Turbocharger Yuji Iwakiri, Hiroshi Uchida Abstract A numerical fluid
PERFORMANCE OF A FLAPPED DUCT EXHAUSTING INTO A COMPRESSIBLE EXTERNAL FLOW
 24 TH INTERNATIONAL CONGRESS OF THE AERONAUTICAL SCIENCES PERFORMANCE OF A FLAPPED DUCT EXHAUSTING INTO A COMPRESSIBLE EXTERNAL FLOW P. R. Pratt, J. K. Watterson, E. Benard, S. Hall School of Aeronautical
24 TH INTERNATIONAL CONGRESS OF THE AERONAUTICAL SCIENCES PERFORMANCE OF A FLAPPED DUCT EXHAUSTING INTO A COMPRESSIBLE EXTERNAL FLOW P. R. Pratt, J. K. Watterson, E. Benard, S. Hall School of Aeronautical
ZIN Technologies PHi Engineering Support. PHi-RPT CFD Analysis of Large Bubble Mixing. June 26, 2006
 ZIN Technologies PHi Engineering Support PHi-RPT-0002 CFD Analysis of Large Bubble Mixing Proprietary ZIN Technologies, Inc. For nearly five decades, ZIN Technologies has provided integrated products and
ZIN Technologies PHi Engineering Support PHi-RPT-0002 CFD Analysis of Large Bubble Mixing Proprietary ZIN Technologies, Inc. For nearly five decades, ZIN Technologies has provided integrated products and
MEASUREMENTS ON THE SURFACE WIND PRESSURE CHARACTERISTICS OF TWO SQUARE BUILDINGS UNDER DIFFERENT WIND ATTACK ANGLES AND BUILDING GAPS
 BBAA VI International Colloquium on: Bluff Bodies Aerodynamics & Applications Milano, Italy, July, 2-24 28 MEASUREMENTS ON THE SURFACE WIND PRESSURE CHARACTERISTICS OF TWO SQUARE BUILDINGS UNDER DIFFERENT
BBAA VI International Colloquium on: Bluff Bodies Aerodynamics & Applications Milano, Italy, July, 2-24 28 MEASUREMENTS ON THE SURFACE WIND PRESSURE CHARACTERISTICS OF TWO SQUARE BUILDINGS UNDER DIFFERENT
URBAN ENERGY AND MICROCLIMATE: WIND TUNNEL EXPERIMENTS AND MULTISCALE MODELING
 URBAN ENERGY AND MICROCLIMATE: WIND TUNNEL EXPERIMENTS AND MULTISCALE MODELING Jan Carmeliet 1,2, Jonas Allegrini 1,2, Peter Moonen 1,2, Saba Saneinejad 1, Viktor Dorer 2 1 ETHZ, Chair of Building Physics,
URBAN ENERGY AND MICROCLIMATE: WIND TUNNEL EXPERIMENTS AND MULTISCALE MODELING Jan Carmeliet 1,2, Jonas Allegrini 1,2, Peter Moonen 1,2, Saba Saneinejad 1, Viktor Dorer 2 1 ETHZ, Chair of Building Physics,
Wind Microclimate Assessment
 Australian Catholic University Pedestrian comfort at 115B Victoria Parade Pedestrian comfort at 115B Victoria Parade Quality Information Document 60519200 Client: Australian Catholic University ABN: 15050192660
Australian Catholic University Pedestrian comfort at 115B Victoria Parade Pedestrian comfort at 115B Victoria Parade Quality Information Document 60519200 Client: Australian Catholic University ABN: 15050192660
Influence of wing span on the aerodynamics of wings in ground effect
 Influence of wing span on the aerodynamics of wings in ground effect Sammy Diasinos 1, Tracie J Barber 2 and Graham Doig 2 Abstract A computational fluid dynamics study of the influence of wing span has
Influence of wing span on the aerodynamics of wings in ground effect Sammy Diasinos 1, Tracie J Barber 2 and Graham Doig 2 Abstract A computational fluid dynamics study of the influence of wing span has
Pressure distribution of rotating small wind turbine blades with winglet using wind tunnel
 Journal of Scientific SARAVANAN & Industrial et al: Research PRESSURE DISTRIBUTION OF SMALL WIND TURBINE BLADES WITH WINGLET Vol. 71, June 01, pp. 45-49 45 Pressure distribution of rotating small wind
Journal of Scientific SARAVANAN & Industrial et al: Research PRESSURE DISTRIBUTION OF SMALL WIND TURBINE BLADES WITH WINGLET Vol. 71, June 01, pp. 45-49 45 Pressure distribution of rotating small wind
PRESSURE DISTRIBUTION OF SMALL WIND TURBINE BLADE WITH WINGLETS ON ROTATING CONDITION USING WIND TUNNEL
 International Journal of Mechanical and Production Engineering Research and Development (IJMPERD ) ISSN 2249-6890 Vol.2, Issue 2 June 2012 1-10 TJPRC Pvt. Ltd., PRESSURE DISTRIBUTION OF SMALL WIND TURBINE
International Journal of Mechanical and Production Engineering Research and Development (IJMPERD ) ISSN 2249-6890 Vol.2, Issue 2 June 2012 1-10 TJPRC Pvt. Ltd., PRESSURE DISTRIBUTION OF SMALL WIND TURBINE
Available online at ScienceDirect. Procedia Engineering 161 (2016 )
 Available online at www.sciencedirect.com ScienceDirect Procedia Engineering 161 (216 ) 1845 1851 World Multidisciplinary Civil Engineering-Architecture-Urban Planning Symposium 216, WMCAUS 216 Experimental
Available online at www.sciencedirect.com ScienceDirect Procedia Engineering 161 (216 ) 1845 1851 World Multidisciplinary Civil Engineering-Architecture-Urban Planning Symposium 216, WMCAUS 216 Experimental
Effects of wind incidence angle on wind pressure distribution on square plan tall buildings
 J. Acad. Indus. Res. Vol. 1(12) May 2013 747 RESEARCH ARTICLE ISSN: 2278-5213 Effects of wind incidence angle on wind pressure distribution on square plan tall buildings S.K. Verma 1, A.K. Ahuja 2* and
J. Acad. Indus. Res. Vol. 1(12) May 2013 747 RESEARCH ARTICLE ISSN: 2278-5213 Effects of wind incidence angle on wind pressure distribution on square plan tall buildings S.K. Verma 1, A.K. Ahuja 2* and
3D-simulation of the turbulent wake behind a wind turbine
 Journal of Physics: Conference Series 3D-simulation of the turbulent wake behind a wind turbine To cite this article: Steffen Wußow et al 2007 J. Phys.: Conf. Ser. 75 012033 View the article online for
Journal of Physics: Conference Series 3D-simulation of the turbulent wake behind a wind turbine To cite this article: Steffen Wußow et al 2007 J. Phys.: Conf. Ser. 75 012033 View the article online for
Study on the Influencing Factors of Gas Mixing Length in Nitrogen Displacement of Gas Pipeline Kun Huang 1,a Yan Xian 2,b Kunrong Shen 3,c
 Applied Mechanics and Materials Online: 2013-06-13 ISSN: 1662-7482, Vols. 321-324, pp 299-304 doi:10.4028/www.scientific.net/amm.321-324.299 2013 Trans Tech Publications, Switzerland Study on the Influencing
Applied Mechanics and Materials Online: 2013-06-13 ISSN: 1662-7482, Vols. 321-324, pp 299-304 doi:10.4028/www.scientific.net/amm.321-324.299 2013 Trans Tech Publications, Switzerland Study on the Influencing
Computational Analysis of the S Airfoil Aerodynamic Performance
 Computational Analysis of the 245-3S Airfoil Aerodynamic Performance Luis Velazquez-Araque and Jiří Nožička 2 Department of Mechanical Engineering National University of Táchira, San Cristóbal 5, Venezuela
Computational Analysis of the 245-3S Airfoil Aerodynamic Performance Luis Velazquez-Araque and Jiří Nožička 2 Department of Mechanical Engineering National University of Táchira, San Cristóbal 5, Venezuela
INTERFERENCE EFFECTS OF TWO BUILDINGS ON PEAK WIND PRESSURES
 The Seventh Asia-Pacific Conference on Wind Engineering, November 8-, 9, Taipei, Taiwan INTERFERENCE EFFECTS OF TWO BUILDINGS ON PEAK WIND PRESSURES Wonsul Kim, Yukio Tamura and Akihito Yoshida 3 Ph.D.
The Seventh Asia-Pacific Conference on Wind Engineering, November 8-, 9, Taipei, Taiwan INTERFERENCE EFFECTS OF TWO BUILDINGS ON PEAK WIND PRESSURES Wonsul Kim, Yukio Tamura and Akihito Yoshida 3 Ph.D.
A Study on the Effects of Wind on the Drift Loss of a Cooling Tower
 A Study on the Effects of Wind on the Drift Loss of a Cooling Tower Wanchai Asvapoositkul 1* 1 Department of Mechanical Engineering, Faculty of Engineering, King Mongkut s University of Technology Thonburi
A Study on the Effects of Wind on the Drift Loss of a Cooling Tower Wanchai Asvapoositkul 1* 1 Department of Mechanical Engineering, Faculty of Engineering, King Mongkut s University of Technology Thonburi
Investigation of the Optimal Position of Wind Sensors and Wind Turbines on A Building: A Computational Fluid Dynamics Study
 Indonesian Journal of Electrical Engineering and Computer Science Vol. 8, No. 3, December 2017, pp. 756 ~ 761 DOI: 10.11591/ijeecs.v8.i3.pp756-761 756 Investigation of the Optimal Position of Sensors and
Indonesian Journal of Electrical Engineering and Computer Science Vol. 8, No. 3, December 2017, pp. 756 ~ 761 DOI: 10.11591/ijeecs.v8.i3.pp756-761 756 Investigation of the Optimal Position of Sensors and
Numerical Computations of Wind Turbine Wakes Using Full Rotor Modeling
 2012 2nd International Conference on Power and Energy Systems (ICPES 2012) IPCSIT vol. 56 (2012) (2012) IACSIT Press, Singapore DOI: 10.7763/IPCSIT.2012.V56.21 Numerical Computations of Wind Turbine Wakes
2012 2nd International Conference on Power and Energy Systems (ICPES 2012) IPCSIT vol. 56 (2012) (2012) IACSIT Press, Singapore DOI: 10.7763/IPCSIT.2012.V56.21 Numerical Computations of Wind Turbine Wakes
Study of Passing Ship Effects along a Bank by Delft3D-FLOW and XBeach1
 Study of Passing Ship Effects along a Bank by Delft3D-FLOW and XBeach1 Minggui Zhou 1, Dano Roelvink 2,4, Henk Verheij 3,4 and Han Ligteringen 2,3 1 School of Naval Architecture, Ocean and Civil Engineering,
Study of Passing Ship Effects along a Bank by Delft3D-FLOW and XBeach1 Minggui Zhou 1, Dano Roelvink 2,4, Henk Verheij 3,4 and Han Ligteringen 2,3 1 School of Naval Architecture, Ocean and Civil Engineering,
THE EFFECT OF PLAN SIZE IN WIND CATCHER ON ITS VENTILATION RATE
 THE EFFECT OF PLAN SIZE IN WIND CATCHER ON ITS VENTILATION RATE 1 MARYAM HOSSEIN GHADIRI, 2 MAHMUD DEHNAVI 1 Department of Architecture, Marvdasht Branch, Islamic Azad University, Marvdasht, Iran 2 Department
THE EFFECT OF PLAN SIZE IN WIND CATCHER ON ITS VENTILATION RATE 1 MARYAM HOSSEIN GHADIRI, 2 MAHMUD DEHNAVI 1 Department of Architecture, Marvdasht Branch, Islamic Azad University, Marvdasht, Iran 2 Department
Aerodynamic Performance of Trains with Different Longitudinal Section Lines under Crosswind
 2017 2nd International Conference on Industrial Aerodynamics (ICIA 2017) ISBN: 978-1-60595-481-3 Aerodynamic Performance of Trains with Different Longitudinal Section Lines under Crosswind Taizhong Xie
2017 2nd International Conference on Industrial Aerodynamics (ICIA 2017) ISBN: 978-1-60595-481-3 Aerodynamic Performance of Trains with Different Longitudinal Section Lines under Crosswind Taizhong Xie
AIRFOIL PROFILE OPTIMIZATION OF AN AIR SUCTION EQUIPMENT WITH AN AIR DUCT
 THERMAL SCIENCE, Year 2015, Vol. 19, No. 4, pp. 1217-1222 1217 AIRFOIL PROFILE OPTIMIZATION OF AN AIR SUCTION EQUIPMENT WITH AN AIR DUCT by Li QIU a,b, Rui WANG a,*, Xiao-Dong CHEN b, and De-Peng WANG
THERMAL SCIENCE, Year 2015, Vol. 19, No. 4, pp. 1217-1222 1217 AIRFOIL PROFILE OPTIMIZATION OF AN AIR SUCTION EQUIPMENT WITH AN AIR DUCT by Li QIU a,b, Rui WANG a,*, Xiao-Dong CHEN b, and De-Peng WANG
CFD simulations of the aerodynamic drag of two drafting cyclists
 Accepted for publication in Computers & Fluids on November 21, 2012 CFD simulations of the aerodynamic drag of two drafting cyclists Bert Blocken a,, Thijs Defraeye b, Erwin Koninckx c, Jan Carmeliet d,e,
Accepted for publication in Computers & Fluids on November 21, 2012 CFD simulations of the aerodynamic drag of two drafting cyclists Bert Blocken a,, Thijs Defraeye b, Erwin Koninckx c, Jan Carmeliet d,e,
Study on wind turbine arrangement for offshore wind farms
 Downloaded from orbit.dtu.dk on: Jul 01, 2018 Study on wind turbine arrangement for offshore wind farms Shen, Wen Zhong; Mikkelsen, Robert Flemming Published in: ICOWEOE-2011 Publication date: 2011 Document
Downloaded from orbit.dtu.dk on: Jul 01, 2018 Study on wind turbine arrangement for offshore wind farms Shen, Wen Zhong; Mikkelsen, Robert Flemming Published in: ICOWEOE-2011 Publication date: 2011 Document
The Seventh International Colloquium on Bluff Body Aerodynamics and Applications (BBAA7) Shanghai, China; September 2-6, 2012 Wind tunnel measurements
 The Seventh International Colloquium on Bluff Body Aerodynamics and Applications (BBAA7) Shanghai, China; September 2-6, 2012 Wind tunnel measurements of aeroelastic guyed mast models a, Tomasz Lipecki
The Seventh International Colloquium on Bluff Body Aerodynamics and Applications (BBAA7) Shanghai, China; September 2-6, 2012 Wind tunnel measurements of aeroelastic guyed mast models a, Tomasz Lipecki
Basis of Structural Design
 Basis of Structural Design Course 10 Actions on structures: Wind loads Other loads Course notes are available for download at http://www.ct.upt.ro/users/aurelstratan/ Wind loading: normative references
Basis of Structural Design Course 10 Actions on structures: Wind loads Other loads Course notes are available for download at http://www.ct.upt.ro/users/aurelstratan/ Wind loading: normative references
