11.4 WIND STRESS AND WIND WAVE OBSERVATIONS IN THE PRESENCE OF SWELL 2. METHODS
|
|
|
- Gilbert Booker
- 5 years ago
- Views:
Transcription
1 11.4 WIND STRESS AND WIND WAVE OBSERVATIONS IN THE PRESENCE OF SWELL Douglas Vandemark 1*, W. M. Drennan 2, J. Sun, 3 J. R. French 4 and Hans Graber 2 1 NASA/GSFC, Wallops Island, VA 2 Univ. of Miami, RSMAS, Miami FL 3 NCAR/MMM, Boulder, CO 4 NOAA/ARL, Oak Ridge, TN 1. INTRODUCTION The questions of how wind and ocean waves interact and how this coupling should be parameterized to optimally derive the surface wind stress remain open and central to estimating air-sea coupling at the global and local scales. While much attention has been given to evaluating the effect of the wind-driven waves upon the surface wind stress and air-sea drag coefficient, less emphasis has been given to the more common and more complex mixed sea case. At any given instant, much of the global ocean s wave energy is carried in its swell fields. In fact, the majority of long wave spectra over the seas will exhibit a mixture of locally coupled wind waves and swell that is aligned in some arbitrary fashion with respect to the local wind direction. Recent work (Drennan et al., 1999; Kudryavtsev and Makin, 2004; Larsen et al., 2004; Rutgersson et al., 2001; Smedman et al., 2003) suggests that the swell can and does act to alter the sea drag at light-to-moderate wind conditions. The swell phase speed and direction with respect to the wind vector, the steepness of the swell, and the relative energy of the swell versus the sea are all discussed as factors in this influence. The theoretical work of Kudryavtsev and Makin, (2004) suggests that swell exchanges energy through two mechanisms: the correlation of pressure and wave slope (form drag), and the work of surface turbulent stress against the swell orbital velocity. Observation and theory suggest that it is the case of wind-opposed swell that provides the most substantial increase in the 10 m drag coefficient. An additional point of consideration is the possibility that the wave-induced momentum flux can systematically alter the assumed logarithmic form for the wind profile, perhaps calling into question the use or derivation of a 10 m drag coefficient in some cases. A goal of the present paper is to provide some additional observations for consideration. In particular, the focus will be upon cases where there is a severe drop in the drag coefficient that occurs in conditions of stable boundary conditions and relatively strong swell fields. Data come from Office of Naval Research s Shoaling Waves Experiment (SHOWEX). The primary measurements to be discussed were obtained using a low-flying aircraft that collected both atmospheric and wave field measurements. Another point of interest is to see when observed variability in the drag and short wave statistics covary. This emphasis is driven by the need to use short-wave remote sensing techniques to derive the wind stress information from satellites. 2. METHODS Measurements to be discussed were collected over the western Atlantic within 120 km of Duck NC. All flights occurred between 1997 and 1999, with most data collected in the month of November. Data come from 36 separate flights of the NOAA LongEZ covering a variety of wind and wave conditions. A map of the region, aircraft measurement and buoy locations are shown in Fig. 1. For all data presented herein the aircraft flew at an average altitude of 15 m above the surface. This is a unique vantage point that permits high resolution and high fidelity sensing of the sea surface and air above, much as for a fixed experimental platform. Several recent publications discuss the data products, their derivation, and processing ( French et al., 2000;Mahrt et al., 2001;Sun et al., 2001;Vandemark et al., 2001). Only limited details are discussed below. The aircraft data set used here consists of the friction velocity (u*), bulk Richardson number (Ri), air and sea temperatures, wind velocity scaled to neutral-stability 10 m using the Toga-Coare bulk flux algorithm (U 10N ), wind direction, significant wave height (H s ), mean square slope (mss), mean square slope of low frequency waves (mss l ) and mean square slope of high frequency waves (mss h ). The wave data are derived through a combination of laser altimeter and nadir-looking radar scatterometer measurements ( Vandemark et al., 2001). Low and high frequency limits pertaining to mss are defined as 0.0 to 0.1 Hz for the low regime and 0.1 to 8 Hz for the high. Slope variance for this low frequency estimate is derived directly from the laser altimeter wave elevation and slope data. Normalized radar cross section data at Ka-band is used to extract mss. The high frequency mss estimate is obtained as mss h = mss * Corresponding author: Douglas Vandemark NASA/GSFC, Wallops Island, VA 23337
2 mss l. The friction velocity is derived using the eddy correlation method on the 50 Hz wind velocity component data (u, v, w) collected by the LongEZ. All variables are discussed and validated in the cited works. The processing of the data for the current study involved computing an average value along each successive 15 km ground track in the data set. Only data segments that lie beyond 15 km offshore in cases of offshore flow, or 5 km offshore for onshore flow, are used. This selection is used to provide data that is representative of open ocean conditions in this region (Vickers et al., 2001). Buoy data are also used in this study. First is the National Data Buoy Center s directional wave buoy N44014, located about 100 km to the east of Duck NC. This buoy was over flown frequently in Second are the University of Miami s Air-Sea Interaction System (ASIS) buoys that were located about the SHOWEX site in November of These buoys were used to validate the wind, wave height and flux data from the LongEZ. For this study we are using them to provide directional long wave information. In particular, the wave phase speed (c), direction and rms elevation for both the wind sea and the swell modes observed. samples. The Oost et al. model requires the wind speed, wave height and phase speed of the dominant wave mode and these are provided for each of our observations and averaged versus wind speed bins to create the model line presented. The error bars provide a 95% confidence interval assuming random error in each wind speed bin. As one can see the present observations lie well above the model in the light wind regime but for moderate winds the two results are nearly identical. The model was derived in the North Sea and perhaps similar wave climates and coastal proximity serve to aid this agreement. But the model s incorporation of wave impacts may also be bridging the gap between the two observational data sets to provide a viable model for the drag at moderate winds. Figure 2 Observed air-sea drag coefficient obtained versus wind speed (averaged across 2 ms -1 wind speed bins) for this study with 95% confidence intervals. Dashed line is the model of Oost et al. (2002). Figure 1 Map of the study region east of North Carolina s outer banks. Large symbols denote the buoy locations. Small symbols show center location of each 15 km aircraft data segment used in the study. Data extend as far as 120 km off shore. 3. RESULTS Several statements about the general characteristics of the sea drag observed in this open ocean data set can be made. First, the averaged 10 m drag coefficient data, C d = u * 2 /U 10N 2, agree quite well with the model of Oost et al. (2002) developed for the North Sea. This is shown in Figure 2. The total size of the data here is 665 Second, the light wind data in this set should be treated with caution. Knowledge of the vertical structure of the boundary layer can become quite important in this case and most of the data examined here are acquired at only one nominal altitude above the surface, usually 15 m. Profile uncertainties in both deriving the friction velocity and in understanding the actual depths and characteristics of the inner and outer boundary layer regions in this case point our focus towards the moderate wind speed range. Third, one particularly distinguishing characteristic of the data set is the occurrence of anomalously low C d values on several of the measurement days where the wind speed at altitude registered a moderate level of 4-7 ms -1. We view these as cases of smooth flow. Upon inspection, these days were typically associated with a relatively stable boundary layer. They are also characterized as cases where the wind and swell directions were within 60 degrees of each other and the
3 swell amplitude exceeds that of the sea by a substantial level. Figure 3 Radar-derived slope variance versus friction velocity for a) upper panel is for Nov. 15, 1998; westerly flow and wind-driven seas. b) Lower panel is for Nov. 16, 1998 where easterly winds prevailed for these measurements. Another distinguishing feature for these smooth flow cases is seen when one examines the aircraft s wave slope variance and wind data. It is well known that the short waves generally respond well to local wind variations and this fact was well represented in the present data set. As an example, Figure 3a provides aircraft observations of the Ka-band radar derived mss versus friction velocity for data from Nov where the sea state was predominately westerly, wind driven, and the boundary layer near neutral. A much different observation is seen for the smooth flow cases. Fig 3b shows example data from Nov where the flow reversed to an easterly direction and a low drag coefficient was observed. One can see a clear relationship to the turbulence in the former case and much less in the latter. This lack of correlation is also evident when the data are scattered against the wind speed. Moreover, the level of mss does not tend toward zero in Fig 3b as one expects for very low levels of friction velocity. The general lack of correspondance between the wind and mss was a common feature for these cases. Figure 4 Wind dependence for the 10 m drag coefficient and slope variance estimates. In all cases the upper solid trace is for the overall data set and the lower trace (with error bars) is for the smooth flow cases denoted in Table 1. Dashed line is Oost et al. (2002).
4 Figure 4 and Table 1 provide further detail for the low drag coefficient events that constitute smooth flow cases in our data set. In Figure 4a we reproduce the sea drag results for the overall experiment (Fig. 2) along with the low level drag observations. It is evident that for these cases the level drops 60-70%. The following 3 panels in the figure provide the overall slope variance relationships for the experiment (upper curves on each panel ) as well as the mss vs. wind speed relationship for the smooth flow events only. It is apparent the surface wave roughness is lower for the low drag events as the wind speed increases. This is seen for total, low and high frequency mss estimates. The relative depression in roughness is largest for the high frequency waves, mss h, but the relative decrease from the nominal level is not as large as that for C d. This lack of suppression is consistent with the non-zero levels seen in Fig 3b. Table 1 Average results for the low Cd cases in the data set. Columns represent the date as yymmdd. Variable Samples u * Direction Wind Sea Swell Speed (ms -1 ) U 10N Sea Swell swell:sea (energy ratio) H s (m) Air-sea(degC) Rich. Number While it is known that the drag coefficient, and similarly the roughness length, z o, can depend on numerous factors, the strong depression of the drag coefficient is not found in any usual parameterization that depends for example upon the atmospheric stability, or the sea state (e.g. via inverse wave age (u*/c) and/or wave height). Each of these factors is, in fact, contained within the model of Oost et al. (2002) and others. Upon consideration of the stable flow regimes and the swell we suggest the cases accord most closely with the condition of ultra-smooth flow (Donelan, 1990). We suggest that the results are akin to that seen in the Baltic (Rutgersson et al., 2001; Smedman et al., 2003) where investigations of swell in stable, neutral and unstable boundary layer conditions have been made. The latter paper examines near neutral data and discusses the fact that in mixed seas the sea drag may need to be examined both as a function of the wave age and of the relative wave spectral energy contributions of the sea and the swell. That paper stratifies the condition of E swell :E sea > 4 to be swell dominated. The data for the cases of Table 1 and for ( Smedman et al., 2003) are given in Figure 5. To create these results from Table 1 we adjusted the swell phase velocity by the cosine of the angle with respect to the wind when computing the inverse wage age. Figure 5 Drag levels ( ) for aircraft results of Fig. 4 and Table 1 as given for each of the four days in the Table 1. Diamonds are taken from Fig. 12 of ( Smedman et al., 2003) for swell dominated cases with C d less than 1.e-3. The present results and those of Smedman et al. in Fig. 5 all represent cases of very old waves. The direction of the swell was not available for that study but there are two estimates in their Fig. 12 at old seas where the drag exceeded 1. e-3 in there work and directionality (e.g. opposing-wind swell) may be an issue. Regardless, the data sets shown here do follow a similar course. Present results off the North Carolina coast suggest that the swell is coupling with the atmosphere with a resulting strong decrease in the drag consistent with that seen in the Baltic. 4. SUMMARY Field observations are presented that provide some further support for the effects of swell on the 10 m airsea drag coefficient. The investigation here is preliminary and focused on cases where the drag coefficient dropped to very low levels at moderate wind speeds. Preliminary results indicate the the drag depression is consistent with swell modes traveling in a following-wind (+-70 deg.) direction. The short wave steepness in both the intermediate and cm-scale was
5 reduced for these cases but not with the magnitude seen in the drag. Some common obstacles to further clarification are being addressed. These include self-correlation, isolation of atmospheric stability effects, and perhaps most importantly understanding the influence of the vertical profile on the observed drag and on the inferences that can be drawn using the single level aircraft data for the cases presented. The recent studies cited (e.g. Kudryavtsev and Makin, 2004; Smedman et al., 2003) indicate that the inner (wave) and outer boundary layer structure may be quite different for the case of swell dominance as opposed to well-couple wind waves. Further examination of the aircraft wind and wave cospectra should aid in this effort. Sun, J. L., D. Vandemark, L. Mahrt, D. Vickers, T. Crawford, and C. Vogel, 2001: Momentum transfer over the coastal zone. Journal of Geophysical Research-Atmospheres, 106, Vandemark, D., P. D. Mourad, S. A. Bailey, T. L. Crawford, C. A. Vogel, J. Sun, and B. Chapron, 2001: Measured changes in ocean surface roughness due to atmospheric boundary layer rolls. Journal of Geophysical Research-Oceans, 106, Vickers, D., L. Mahrt, J. L. Sun, and T. Crawford, 2001: Structure of offshore flow. Monthly Weather Review, 129, REFERENCES Donelan, M. A., 1990: Air-sea interaction. The Sea, Ocean Engineering Science, B. Le Mehaute and D. M. Hanes, Eds., John Wiley & Sons, Inc., Drennan, W. M., H. C. Graber, and M. A. Donelan, 1999: Evidence for the effects of swell and unsteady winds on marine wind stress. Journal of Physical Oceanography, 29, French, J. R., G. H. Crescenti, T. L. Crawford, and E. J. Dumas, 2000: LongEZ (N3R) participation in the 1999 shoaling waves experiment (SHOWEX). Data report OAR ARL-20, 51 pp. Kudryavtsev, V. N. and V. K. Makin, 2004: Impact of swell on the marine atmospheric boundary layer. Journal of Physical Oceanography, 34, Larsen, X. G., V. K. Makin, and A. S. Smedman, 2004: Impact of waves on the sea drag: measurements in the Baltic sea and a model interpretation. The Global Atmosphere and Ocean System, 9, Mahrt, L., D. Vickers, J. L. Sun, T. L. Crawford, G. Crescenti, and P. Frederickson, 2001: Surface stress in offshore flow and quasi-frictional decoupling. Journal of Geophysical Research-Atmospheres, 106, Oost, W. A., G. J. Komen, C. M. J. Jacobs, and C. Van Oort, 2002: New evidence for a relation between wind stress and wave age from measurements during ASGAMAGE. Boundary-Layer Meteorology, 103, Rutgersson, A., A. S. Smedman, and U. Hogstrom, 2001: Use of conventional stability parameters during swell. Journal of Geophysical Research- Oceans, 106, Smedman, A. S., X. G. Larsen, U. Hogstrom, K. K. Kahma, and H. Pettersson, 2003: Effect of sea state on the momentum exchange over the sea during neutral conditions. Journal of Geophysical Research-Oceans, 108.
Determination of the Spatial Variation of the Atmosphere and Ocean Wave Fields in Extremely Light Wind Regimes
 Determination of the Spatial Variation of the Atmosphere and Ocean Wave Fields in Extremely Light Wind Regimes Gennaro H. Crescenti U.S. Dept. Commerce / NOAA Air Resources Laboratory Field Research Division
Determination of the Spatial Variation of the Atmosphere and Ocean Wave Fields in Extremely Light Wind Regimes Gennaro H. Crescenti U.S. Dept. Commerce / NOAA Air Resources Laboratory Field Research Division
Air-Sea Interaction Spar Buoy Systems
 DISTRIBUTION STATEMENT A: Distribution approved for public release; distribution is unlimited Air-Sea Interaction Spar Buoy Systems Hans C. Graber CSTARS - University of Miami 11811 SW 168 th Street, Miami,
DISTRIBUTION STATEMENT A: Distribution approved for public release; distribution is unlimited Air-Sea Interaction Spar Buoy Systems Hans C. Graber CSTARS - University of Miami 11811 SW 168 th Street, Miami,
Surface Fluxes and Wind-Wave Interactions in Weak Wind Conditions
 Surface Fluxes and Wind-Wave Interactions in Weak Wind Conditions Jielun Sun Microscale and Mesoscale Meteorology National Center for Atmospheric Research phone: (303) 497-8994 fax: (303) 497-8171 email:
Surface Fluxes and Wind-Wave Interactions in Weak Wind Conditions Jielun Sun Microscale and Mesoscale Meteorology National Center for Atmospheric Research phone: (303) 497-8994 fax: (303) 497-8171 email:
The Influence of Ocean Surface Waves on Offshore Wind Turbine Aerodynamics. Ali Al Sam
 The Influence of Ocean Surface Waves on Offshore Wind Turbine Aerodynamics Ali Al Sam What I m going to wear today? Do I need to leave early to get to work? Taking buss or riding bike? Where will we drink
The Influence of Ocean Surface Waves on Offshore Wind Turbine Aerodynamics Ali Al Sam What I m going to wear today? Do I need to leave early to get to work? Taking buss or riding bike? Where will we drink
Conditions for Offshore Wind Energy Use
 Carl von Ossietzky Universität Oldenburg Institute of Physics Energy Meteorology Group Detlev Heinemann Conditions for Offshore Wind Energy Use Detlev Heinemann ForWind Carl von Ossietzky Universität Oldenburg
Carl von Ossietzky Universität Oldenburg Institute of Physics Energy Meteorology Group Detlev Heinemann Conditions for Offshore Wind Energy Use Detlev Heinemann ForWind Carl von Ossietzky Universität Oldenburg
Review of Equivalent Neutral Winds and Stress
 Review of Equivalent Neutral Winds and Stress Mark A. Bourassa Center for Ocean-Atmospheric Prediction Studies, Geophysical Fluid Dynamics Institute & Department of Earth, Ocean and Atmospheric Science
Review of Equivalent Neutral Winds and Stress Mark A. Bourassa Center for Ocean-Atmospheric Prediction Studies, Geophysical Fluid Dynamics Institute & Department of Earth, Ocean and Atmospheric Science
Wind Stress Working Group 2015 IOVWST Meeting Portland, OR
 Wind Stress Working Group 2015 IOVWST Meeting Portland, OR Summary of Research Topics, Objectives and Questions James B. Edson University of Connecticut SPURS Mooring, Farrar, WHOI Background Motivation
Wind Stress Working Group 2015 IOVWST Meeting Portland, OR Summary of Research Topics, Objectives and Questions James B. Edson University of Connecticut SPURS Mooring, Farrar, WHOI Background Motivation
Observed directional characteristics of the wind, wind stress, and surface waves on the open ocean
 JOURNAL OF GEOPHYSICAL RESEARCH, VOL. 99, NO. C11, PAGES 22,589 22,596, NOVEMBER 15, 1994 Observed directional characteristics of the wind, wind stress, and surface waves on the open ocean Karl F. Rieder
JOURNAL OF GEOPHYSICAL RESEARCH, VOL. 99, NO. C11, PAGES 22,589 22,596, NOVEMBER 15, 1994 Observed directional characteristics of the wind, wind stress, and surface waves on the open ocean Karl F. Rieder
High-Resolution Measurement-Based Phase-Resolved Prediction of Ocean Wavefields
 DISTRIBUTION STATEMENT A. Approved for public release; distribution is unlimited. High-Resolution Measurement-Based Phase-Resolved Prediction of Ocean Wavefields Dick K.P. Yue Center for Ocean Engineering
DISTRIBUTION STATEMENT A. Approved for public release; distribution is unlimited. High-Resolution Measurement-Based Phase-Resolved Prediction of Ocean Wavefields Dick K.P. Yue Center for Ocean Engineering
CHAPTER 6 DISCUSSION ON WAVE PREDICTION METHODS
 CHAPTER 6 DISCUSSION ON WAVE PREDICTION METHODS A critical evaluation of the three wave prediction methods examined in this thesis is presented in this Chapter. The significant wave parameters, Hand T,
CHAPTER 6 DISCUSSION ON WAVE PREDICTION METHODS A critical evaluation of the three wave prediction methods examined in this thesis is presented in this Chapter. The significant wave parameters, Hand T,
Chapter 2. Turbulence and the Planetary Boundary Layer
 Chapter 2. Turbulence and the Planetary Boundary Layer In the chapter we will first have a qualitative overview of the PBL then learn the concept of Reynolds averaging and derive the Reynolds averaged
Chapter 2. Turbulence and the Planetary Boundary Layer In the chapter we will first have a qualitative overview of the PBL then learn the concept of Reynolds averaging and derive the Reynolds averaged
Kathleen Dohan. Wind-Driven Surface Currents. Earth and Space Research, Seattle, WA
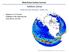 Updates to OSCAR and challenges with capturing the wind-driven currents. Wind-Driven Surface Currents Kathleen Dohan Earth and Space Research, Seattle, WA ENSO OSCAR Surface currents from satellite fields
Updates to OSCAR and challenges with capturing the wind-driven currents. Wind-Driven Surface Currents Kathleen Dohan Earth and Space Research, Seattle, WA ENSO OSCAR Surface currents from satellite fields
Reprocessed QuikSCAT (V04) Wind Vectors with Ku-2011 Geophysical Model Function
 Reprocessed QuikSCAT (V04) Wind Vectors with Ku-2011 Geophysical Model Function Lucrezia Ricciardulli and Frank Wentz Introduction In April 2011, we reprocessed the QuikSCAT ocean wind vectors using a
Reprocessed QuikSCAT (V04) Wind Vectors with Ku-2011 Geophysical Model Function Lucrezia Ricciardulli and Frank Wentz Introduction In April 2011, we reprocessed the QuikSCAT ocean wind vectors using a
EVALUATION OF ENVISAT ASAR WAVE MODE RETRIEVAL ALGORITHMS FOR SEA-STATE FORECASTING AND WAVE CLIMATE ASSESSMENT
 EVALUATION OF ENVISAT ASAR WAVE MODE RETRIEVAL ALGORITHMS FOR SEA-STATE FORECASTING AND WAVE CLIMATE ASSESSMENT F.J. Melger ARGOSS, P.O. Box 61, 8335 ZH Vollenhove, the Netherlands, Email: info@argoss.nl
EVALUATION OF ENVISAT ASAR WAVE MODE RETRIEVAL ALGORITHMS FOR SEA-STATE FORECASTING AND WAVE CLIMATE ASSESSMENT F.J. Melger ARGOSS, P.O. Box 61, 8335 ZH Vollenhove, the Netherlands, Email: info@argoss.nl
3. Observed initial growth of short waves from radar measurements in tanks (Larson and Wright, 1975). The dependence of the exponential amplification
 Geophysica (1997), 33(2), 9-14 Laboratory Measurements of Stress Modulation by Wave Groups M.G. Skafel and M.A. Donelan* National Water Research Institute Canada Centre for Inland Waters Burlington, Ontario,
Geophysica (1997), 33(2), 9-14 Laboratory Measurements of Stress Modulation by Wave Groups M.G. Skafel and M.A. Donelan* National Water Research Institute Canada Centre for Inland Waters Burlington, Ontario,
Jeffrey R. French* NOAA Air Resources Laboratory Atmospheric Turbulence and Diffusion Division Oak Ridge, TN
 9C.4 DIRECT AIRBORNE MEASURMENTS OF MOMENTUM FLUX IN HURRICANES Jeffrey R. French* NOAA Air Resources Laboratory Atmospheric Turbulence and Diffusion Division Oak Ridge, TN William M. Drennan and Jun Zhang
9C.4 DIRECT AIRBORNE MEASURMENTS OF MOMENTUM FLUX IN HURRICANES Jeffrey R. French* NOAA Air Resources Laboratory Atmospheric Turbulence and Diffusion Division Oak Ridge, TN William M. Drennan and Jun Zhang
Wind Flow Validation Summary
 IBHS Research Center Validation of Wind Capabilities The Insurance Institute for Business & Home Safety (IBHS) Research Center full-scale test facility provides opportunities to simulate natural wind conditions
IBHS Research Center Validation of Wind Capabilities The Insurance Institute for Business & Home Safety (IBHS) Research Center full-scale test facility provides opportunities to simulate natural wind conditions
2.5 SHIPBOARD TURBULENCE MEASUREMENTS OF THE MARINE ATMOSPHERIC BOUNDARY LAYER FROM HIRES EXPERIMENT
 2.5 SHIPBOARD TURBULENCE MEASUREMENTS OF THE MARINE ATMOSPHERIC BOUNDARY LAYER FROM HIRES EXPERIMENT John Kalogiros 1*, Q. Wang 2, R. J. Lind 2, T. Herbers 2, and J. Cook 2 1 National Observatory of Athens,
2.5 SHIPBOARD TURBULENCE MEASUREMENTS OF THE MARINE ATMOSPHERIC BOUNDARY LAYER FROM HIRES EXPERIMENT John Kalogiros 1*, Q. Wang 2, R. J. Lind 2, T. Herbers 2, and J. Cook 2 1 National Observatory of Athens,
CHANGE OF THE BRIGHTNESS TEMPERATURE IN THE MICROWAVE REGION DUE TO THE RELATIVE WIND DIRECTION
 JP4.12 CHANGE OF THE BRIGHTNESS TEMPERATURE IN THE MICROWAVE REGION DUE TO THE RELATIVE WIND DIRECTION Masanori Konda* Department of Geophysics, Graduate School of Science, Kyoto University, Japan Akira
JP4.12 CHANGE OF THE BRIGHTNESS TEMPERATURE IN THE MICROWAVE REGION DUE TO THE RELATIVE WIND DIRECTION Masanori Konda* Department of Geophysics, Graduate School of Science, Kyoto University, Japan Akira
Nortek Technical Note No.: TN-021. Chesapeake Bay AWAC Evaluation
 Nortek Technical Note No.: TN-021 Title: Chesapeake Bay AWAC Evaluation Last Edited: October 5, 2004 Authors: Eric Siegel-NortekUSA, Chris Malzone-NortekUSA, Torstein Pedersen- Number of Pages: 12 Chesapeake
Nortek Technical Note No.: TN-021 Title: Chesapeake Bay AWAC Evaluation Last Edited: October 5, 2004 Authors: Eric Siegel-NortekUSA, Chris Malzone-NortekUSA, Torstein Pedersen- Number of Pages: 12 Chesapeake
Mesoscale air-sea interaction and feedback in the western Arabian Sea
 Mesoscale air-sea interaction and feedback in the western Arabian Sea Hyodae Seo (Univ. of Hawaii) Raghu Murtugudde (UMD) Markus Jochum (NCAR) Art Miller (SIO) AMS Air-Sea Interaction Workshop Phoenix,
Mesoscale air-sea interaction and feedback in the western Arabian Sea Hyodae Seo (Univ. of Hawaii) Raghu Murtugudde (UMD) Markus Jochum (NCAR) Art Miller (SIO) AMS Air-Sea Interaction Workshop Phoenix,
An Atlas of Oceanic Internal Solitary Waves (February 2004) by Global Ocean Associates Prepared for Office of Naval Research Code 322 PO
 Overview The is located in the North Atlantic Ocean between southern Ireland and southwest England (Figure 1). The Sea s western edge covers a continental shelf region characterized by rough and irregular
Overview The is located in the North Atlantic Ocean between southern Ireland and southwest England (Figure 1). The Sea s western edge covers a continental shelf region characterized by rough and irregular
PROPAGATION OF LONG-PERIOD WAVES INTO AN ESTUARY THROUGH A NARROW INLET
 PROPAGATION OF LONG-PERIOD WAVES INTO AN ESTUARY THROUGH A NARROW INLET Takumi Okabe, Shin-ichi Aoki and Shigeru Kato Department of Civil Engineering Toyohashi University of Technology Toyohashi, Aichi,
PROPAGATION OF LONG-PERIOD WAVES INTO AN ESTUARY THROUGH A NARROW INLET Takumi Okabe, Shin-ichi Aoki and Shigeru Kato Department of Civil Engineering Toyohashi University of Technology Toyohashi, Aichi,
Development of SAR-Derived Ocean Surface Winds at NOAA/NESDIS
 Development of SAR-Derived Ocean Surface Winds at NOAA/NESDIS Pablo Clemente-Colón, William G. Pichel, NOAA/NESDIS Frank M. Monaldo, Donald R. Thompson The Johns Hopkins University Applied Physics Laboratory
Development of SAR-Derived Ocean Surface Winds at NOAA/NESDIS Pablo Clemente-Colón, William G. Pichel, NOAA/NESDIS Frank M. Monaldo, Donald R. Thompson The Johns Hopkins University Applied Physics Laboratory
Scales of Atmospheric Motion Scale Length Scale (m) Time Scale (sec) Systems/Importance Molecular (neglected)
 Supplement Wind, Fetch and Waves Scales of Atmospheric Motion Scale Length Scale (m) Time Scale (sec) Systems/Importance Molecular 10-7 - 10-2 10-1 (neglected) Coriolis not important Turbulent 10-2 10
Supplement Wind, Fetch and Waves Scales of Atmospheric Motion Scale Length Scale (m) Time Scale (sec) Systems/Importance Molecular 10-7 - 10-2 10-1 (neglected) Coriolis not important Turbulent 10-2 10
RIVET Satellite Remote Sensing and Small Scale Wave Process Analysis
 DISTRIBUTION STATEMENT A. Approved for public release; distribution is unlimited. RIVET Satellite Remote Sensing and Small Scale Wave Process Analysis Hans C. Graber RSMAS Department of Ocean Sciences
DISTRIBUTION STATEMENT A. Approved for public release; distribution is unlimited. RIVET Satellite Remote Sensing and Small Scale Wave Process Analysis Hans C. Graber RSMAS Department of Ocean Sciences
TRIAXYS Acoustic Doppler Current Profiler Comparison Study
 TRIAXYS Acoustic Doppler Current Profiler Comparison Study By Randolph Kashino, Axys Technologies Inc. Tony Ethier, Axys Technologies Inc. Reo Phillips, Axys Technologies Inc. February 2 Figure 1. Nortek
TRIAXYS Acoustic Doppler Current Profiler Comparison Study By Randolph Kashino, Axys Technologies Inc. Tony Ethier, Axys Technologies Inc. Reo Phillips, Axys Technologies Inc. February 2 Figure 1. Nortek
Observations of Velocity Fields Under Moderately Forced Wind Waves
 Observations of Velocity Fields Under Moderately Forced Wind Waves Timothy P. Stanton Oceanography Department, Code OC/ST Naval Postgraduate School Monterey, CA 93943-5000 phone: (831) 656 3144 fax: (831)
Observations of Velocity Fields Under Moderately Forced Wind Waves Timothy P. Stanton Oceanography Department, Code OC/ST Naval Postgraduate School Monterey, CA 93943-5000 phone: (831) 656 3144 fax: (831)
An Investigation of Atmospheric Stability and Its Impact on Scatterometer Winds Across the Gulf Stream
 An Investigation of Atmospheric Stability and Its Impact on Scatterometer Winds Across the Gulf Stream Jim Edson University of Connecticut Doug Vandemark & Amanda Plagge University of New Hampshire CLIMODE
An Investigation of Atmospheric Stability and Its Impact on Scatterometer Winds Across the Gulf Stream Jim Edson University of Connecticut Doug Vandemark & Amanda Plagge University of New Hampshire CLIMODE
Unsteady Wave-Driven Circulation Cells Relevant to Rip Currents and Coastal Engineering
 Unsteady Wave-Driven Circulation Cells Relevant to Rip Currents and Coastal Engineering Andrew Kennedy Dept of Civil and Coastal Engineering 365 Weil Hall University of Florida Gainesville, FL 32611 phone:
Unsteady Wave-Driven Circulation Cells Relevant to Rip Currents and Coastal Engineering Andrew Kennedy Dept of Civil and Coastal Engineering 365 Weil Hall University of Florida Gainesville, FL 32611 phone:
Observed Roughness Lengths for Momentum and Temperature on a Melting Glacier Surface
 5 Observed Roughness Lengths for Momentum and Temperature on a Melting Glacier Surface The roughness lengths for momentum and temperature are calculated on a melting glacier surface. Data from a five level
5 Observed Roughness Lengths for Momentum and Temperature on a Melting Glacier Surface The roughness lengths for momentum and temperature are calculated on a melting glacier surface. Data from a five level
Prediction of Nearshore Waves and Currents: Model Sensitivity, Confidence and Assimilation
 Prediction of Nearshore Waves and Currents: Model Sensitivity, Confidence and Assimilation H. Tuba Özkan-Haller College of Oceanic and Atmospheric Sciences Oregon State University, 104 Ocean Admin Bldg
Prediction of Nearshore Waves and Currents: Model Sensitivity, Confidence and Assimilation H. Tuba Özkan-Haller College of Oceanic and Atmospheric Sciences Oregon State University, 104 Ocean Admin Bldg
A Global Climatology of Wind Wave Interaction
 JUNE 2010 H A N L E Y E T A L. 1263 A Global Climatology of Wind Wave Interaction KIRSTY E. HANLEY AND STEPHEN E. BELCHER Department of Meteorology, University of Reading, Reading, United Kingdom PETER
JUNE 2010 H A N L E Y E T A L. 1263 A Global Climatology of Wind Wave Interaction KIRSTY E. HANLEY AND STEPHEN E. BELCHER Department of Meteorology, University of Reading, Reading, United Kingdom PETER
Are Advanced Wind Flow Models More Accurate? A Test of Four Models
 Are Advanced Wind Flow Models More Accurate? A Test of Four Models Philippe Beaucage, PhD Senior Research Scientist Michael C. Brower, PhD Chief Technical Officer Brazil Wind Power Conference 2012 Albany
Are Advanced Wind Flow Models More Accurate? A Test of Four Models Philippe Beaucage, PhD Senior Research Scientist Michael C. Brower, PhD Chief Technical Officer Brazil Wind Power Conference 2012 Albany
Spectral characteristics of the wind components in the surface Atmospheric Boundary Layer
 Spectral characteristics of the wind components in the surface Atmospheric Boundary Layer COSTAS HELMIS AND DIMOSTHENIS ASIMAKOPOULOS Department of Environmental Physics and Meteorology Faculty of Physics,
Spectral characteristics of the wind components in the surface Atmospheric Boundary Layer COSTAS HELMIS AND DIMOSTHENIS ASIMAKOPOULOS Department of Environmental Physics and Meteorology Faculty of Physics,
Lecture 7. More on BL wind profiles and turbulent eddy structures. In this lecture
 Lecture 7. More on BL wind profiles and turbulent eddy structures In this lecture Stability and baroclinicity effects on PBL wind and temperature profiles Large-eddy structures and entrainment in shear-driven
Lecture 7. More on BL wind profiles and turbulent eddy structures In this lecture Stability and baroclinicity effects on PBL wind and temperature profiles Large-eddy structures and entrainment in shear-driven
Metocean criteria for fatigue assessment. Rafael V. Schiller 5th COPEDI Seminar, Oct 8th 2014.
 Metocean criteria for fatigue assessment Rafael V. Schiller 5th COPEDI Seminar, Oct 8th 2014. Metocean requirements along the lifecycle of a project Metocean criteria for fatigue Analysis techniques and
Metocean criteria for fatigue assessment Rafael V. Schiller 5th COPEDI Seminar, Oct 8th 2014. Metocean requirements along the lifecycle of a project Metocean criteria for fatigue Analysis techniques and
A Comparison of the UK Offshore Wind Resource from the Marine Data Exchange. P. Argyle, S. J. Watson CREST, Loughborough University, UK
 A Comparison of the UK Offshore Wind Resource from the Marine Data Exchange P. Argyle, S. J. Watson CREST, Loughborough University, UK Introduction Offshore wind measurements are scarce and expensive,
A Comparison of the UK Offshore Wind Resource from the Marine Data Exchange P. Argyle, S. J. Watson CREST, Loughborough University, UK Introduction Offshore wind measurements are scarce and expensive,
JCOMM Technical Workshop on Wave Measurements from Buoys
 JCOMM Technical Workshop on Wave Measurements from Buoys Val Swail Chair, JCOMM Expert Team on Wind Waves and Storm Surges Neville Smith Vincent Cardone Peter Janssen Gerbrand Komen Peter Taylor WIND WAVES
JCOMM Technical Workshop on Wave Measurements from Buoys Val Swail Chair, JCOMM Expert Team on Wind Waves and Storm Surges Neville Smith Vincent Cardone Peter Janssen Gerbrand Komen Peter Taylor WIND WAVES
COMPARISON OF CONTEMPORANEOUS WAVE MEASUREMENTS WITH A SAAB WAVERADAR REX AND A DATAWELL DIRECTIONAL WAVERIDER BUOY
 COMPARISON OF CONTEMPORANEOUS WAVE MEASUREMENTS WITH A SAAB WAVERADAR REX AND A DATAWELL DIRECTIONAL WAVERIDER BUOY Scott Noreika, Mark Beardsley, Lulu Lodder, Sarah Brown and David Duncalf rpsmetocean.com
COMPARISON OF CONTEMPORANEOUS WAVE MEASUREMENTS WITH A SAAB WAVERADAR REX AND A DATAWELL DIRECTIONAL WAVERIDER BUOY Scott Noreika, Mark Beardsley, Lulu Lodder, Sarah Brown and David Duncalf rpsmetocean.com
Wave-Phase-Resolved Air-Sea Interaction
 DISTRIBUTION STATEMENT A. Approved for public release; distribution is unlimited. Wave-Phase-Resolved Air-Sea Interaction W. Kendall Melville Scripps Institution of Oceanography (SIO) UC San Diego La Jolla,
DISTRIBUTION STATEMENT A. Approved for public release; distribution is unlimited. Wave-Phase-Resolved Air-Sea Interaction W. Kendall Melville Scripps Institution of Oceanography (SIO) UC San Diego La Jolla,
The relationship between sea level and bottom pressure in an eddy permitting ocean model
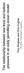 The relationship between sea level and bottom pressure in an eddy permitting ocean model Rory Bingham and Chris Hughes Proudman Oceanographic Laboratory Introduction Motivation: Clearer understanding on
The relationship between sea level and bottom pressure in an eddy permitting ocean model Rory Bingham and Chris Hughes Proudman Oceanographic Laboratory Introduction Motivation: Clearer understanding on
WAVE MECHANICS FOR OCEAN ENGINEERING
 Elsevier Oceanography Series, 64 WAVE MECHANICS FOR OCEAN ENGINEERING P. Boccotti Faculty of Engineering University of Reggio-Calabria Feo di Vito 1-89060 Reggio-Calabria Italy 2000 ELSEVIER Amsterdam
Elsevier Oceanography Series, 64 WAVE MECHANICS FOR OCEAN ENGINEERING P. Boccotti Faculty of Engineering University of Reggio-Calabria Feo di Vito 1-89060 Reggio-Calabria Italy 2000 ELSEVIER Amsterdam
Real Life Turbulence and Model Simplifications. Jørgen Højstrup Wind Solutions/Højstrup Wind Energy VindKraftNet 28 May 2015
 Real Life Turbulence and Model Simplifications Jørgen Højstrup Wind Solutions/Højstrup Wind Energy VindKraftNet 28 May 2015 Contents What is turbulence? Description of turbulence Modelling spectra. Wake
Real Life Turbulence and Model Simplifications Jørgen Højstrup Wind Solutions/Højstrup Wind Energy VindKraftNet 28 May 2015 Contents What is turbulence? Description of turbulence Modelling spectra. Wake
ValidatingWindProfileEquationsduringTropicalStormDebbyin2012
 Global Journal of Researches in Engineering: e Civil And Structural Engineering Volume 4 Issue Version. Year 24 Type: Double Blind Peer Reviewed International Research Journal Publisher: Global Journals
Global Journal of Researches in Engineering: e Civil And Structural Engineering Volume 4 Issue Version. Year 24 Type: Double Blind Peer Reviewed International Research Journal Publisher: Global Journals
DEPARTMENT OF THE NAVY DIVISION NEWPORT OFFICE OF COUNSEL PHONE: FAX: DSN:
 IMAVSBA WARFARE CENTERS NEWPORT DEPARTMENT OF THE NAVY NAVAL UNDERSEA WARFARE CENTER DIVISION NEWPORT OFFICE OF COUNSEL PHONE: 401 832-3653 FAX: 401 832-4432 DSN: 432-3653 Attorney Docket No. 85031 Date:
IMAVSBA WARFARE CENTERS NEWPORT DEPARTMENT OF THE NAVY NAVAL UNDERSEA WARFARE CENTER DIVISION NEWPORT OFFICE OF COUNSEL PHONE: 401 832-3653 FAX: 401 832-4432 DSN: 432-3653 Attorney Docket No. 85031 Date:
Coastal Wave Energy Dissipation: Observations and Modeling
 Coastal Wave Energy Dissipation: Observations and Modeling Jeffrey L Hanson US Army Corps of Engineers Field Research Facility USACE Field Research Facility Kent K. Hathaway US Army Corps of Engineers
Coastal Wave Energy Dissipation: Observations and Modeling Jeffrey L Hanson US Army Corps of Engineers Field Research Facility USACE Field Research Facility Kent K. Hathaway US Army Corps of Engineers
Jackie May* Mark Bourassa. * Current affilitation: QinetiQ-NA
 Jackie May* Mark Bourassa * Current affilitation: QinetiQ-NA Background/Motivation In situ observations (ships and buoys) are used to validate satellite observations Problems with comparing data Sparseness
Jackie May* Mark Bourassa * Current affilitation: QinetiQ-NA Background/Motivation In situ observations (ships and buoys) are used to validate satellite observations Problems with comparing data Sparseness
Refined Source Terms in WAVEWATCH III with Wave Breaking and Sea Spray Forecasts
 DISTRIBUTION STATEMENT A. Approved for public release; distribution is unlimited. Refined Source Terms in WAVEWATCH III with Wave Breaking and Sea Spray Forecasts Michael L. Banner School of Mathematics
DISTRIBUTION STATEMENT A. Approved for public release; distribution is unlimited. Refined Source Terms in WAVEWATCH III with Wave Breaking and Sea Spray Forecasts Michael L. Banner School of Mathematics
SENSOR SYNERGY OF ACTIVE AND PASSIVE MICROWAVE INSTRUMENTS FOR OBSERVATIONS OF MARINE SURFACE WINDS
 SENSOR SYNERGY OF ACTIVE AND PASSIVE MICROWAVE INSTRUMENTS FOR OBSERVATIONS OF MARINE SURFACE WINDS N. Ebuchi Institute of Low Temperature Science, Hokkaido University, N19-W8, Kita-ku, Sapporo 060-0819,
SENSOR SYNERGY OF ACTIVE AND PASSIVE MICROWAVE INSTRUMENTS FOR OBSERVATIONS OF MARINE SURFACE WINDS N. Ebuchi Institute of Low Temperature Science, Hokkaido University, N19-W8, Kita-ku, Sapporo 060-0819,
Currents measurements in the coast of Montevideo, Uruguay
 Currents measurements in the coast of Montevideo, Uruguay M. Fossati, D. Bellón, E. Lorenzo & I. Piedra-Cueva Fluid Mechanics and Environmental Engineering Institute (IMFIA), School of Engineering, Research
Currents measurements in the coast of Montevideo, Uruguay M. Fossati, D. Bellón, E. Lorenzo & I. Piedra-Cueva Fluid Mechanics and Environmental Engineering Institute (IMFIA), School of Engineering, Research
Gravity waves in stable atmospheric boundary layers
 Gravity waves in stable atmospheric boundary layers Carmen J. Nappo CJN Research Meteorology Knoxville, Tennessee 37919, USA Abstract Gravity waves permeate the stable atmospheric planetary boundary layer,
Gravity waves in stable atmospheric boundary layers Carmen J. Nappo CJN Research Meteorology Knoxville, Tennessee 37919, USA Abstract Gravity waves permeate the stable atmospheric planetary boundary layer,
Airborne Remote Sensing of Surface and Internal Wave Processes on the Inner Shelf
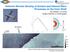 Airborne Remote Sensing of Surface and Internal Wave Processes on the Inner Shelf Ken Melville, Luc Lenain Scripps Institution of Oceanography North Wind/Wave NDBC Station 42040 29.212 N 88.207 W 19 Oct
Airborne Remote Sensing of Surface and Internal Wave Processes on the Inner Shelf Ken Melville, Luc Lenain Scripps Institution of Oceanography North Wind/Wave NDBC Station 42040 29.212 N 88.207 W 19 Oct
Short-period gravity waves over a high-latitude observation site: Rothera, Antarctica
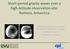 Short-period gravity waves over a high-latitude observation site: Rothera, Antarctica K. Nielsen, D. Broutman, M. Taylor, D. Siskind, S. Eckermann, K. Hoppel, R. Hibbins, M. Jarvis, N. Mitchell, J. Russell
Short-period gravity waves over a high-latitude observation site: Rothera, Antarctica K. Nielsen, D. Broutman, M. Taylor, D. Siskind, S. Eckermann, K. Hoppel, R. Hibbins, M. Jarvis, N. Mitchell, J. Russell
First studies with the high-resolution coupled wave current model CWAM and other aspects of the project Sea State Monitor
 First studies with the high-resolution coupled wave current model CWAM and other aspects of the project Sea State Monitor Jens Kieser, Thomas Bruns German Meteorological Service (Deutscher Wetterdienst,
First studies with the high-resolution coupled wave current model CWAM and other aspects of the project Sea State Monitor Jens Kieser, Thomas Bruns German Meteorological Service (Deutscher Wetterdienst,
Wave energy converter effects on wave and sediment circulation
 Wave energy converter effects on wave and sediment circulation Grace Chang and Craig Jones Integral Consulting Inc. cjones@integral-corp.com; gchang@integral-corp.com Jesse Roberts, Kelley Ruehl, and Chris
Wave energy converter effects on wave and sediment circulation Grace Chang and Craig Jones Integral Consulting Inc. cjones@integral-corp.com; gchang@integral-corp.com Jesse Roberts, Kelley Ruehl, and Chris
PUV Wave Directional Spectra How PUV Wave Analysis Works
 PUV Wave Directional Spectra How PUV Wave Analysis Works Introduction The PUV method works by comparing velocity and pressure time series. Figure 1 shows that pressure and velocity (in the direction of
PUV Wave Directional Spectra How PUV Wave Analysis Works Introduction The PUV method works by comparing velocity and pressure time series. Figure 1 shows that pressure and velocity (in the direction of
Investigating the effect of a wave-dependent momentum flux in a process oriented ocean model
 Boreal Environment Research 14: 3 17 29 ISSN 1239-695 (print) ISSN 1797-2469 (online) helsinki 27 February 29 Investigating the effect of a wave-dependent momentum flux in a process oriented ocean model
Boreal Environment Research 14: 3 17 29 ISSN 1239-695 (print) ISSN 1797-2469 (online) helsinki 27 February 29 Investigating the effect of a wave-dependent momentum flux in a process oriented ocean model
Correlation analysis between UK onshore and offshore wind speeds
 Loughborough University Institutional Repository Correlation analysis between UK onshore and offshore wind speeds This item was submitted to Loughborough University's Institutional Repository by the/an
Loughborough University Institutional Repository Correlation analysis between UK onshore and offshore wind speeds This item was submitted to Loughborough University's Institutional Repository by the/an
E. Agu, M. Kasperski Ruhr-University Bochum Department of Civil and Environmental Engineering Sciences
 EACWE 5 Florence, Italy 19 th 23 rd July 29 Flying Sphere image Museo Ideale L. Da Vinci Chasing gust fronts - wind measurements at the airport Munich, Germany E. Agu, M. Kasperski Ruhr-University Bochum
EACWE 5 Florence, Italy 19 th 23 rd July 29 Flying Sphere image Museo Ideale L. Da Vinci Chasing gust fronts - wind measurements at the airport Munich, Germany E. Agu, M. Kasperski Ruhr-University Bochum
MECHANISM AND COUNTERMEASURES OF WAVE OVERTOPPING FOR LONG-PERIOD SWELL IN COMPLEX BATHYMETRY. Hiroaki Kashima 1 and Katsuya Hirayama 1
 MECHANISM AND COUNTERMEASURES OF WAVE OVERTOPPING FOR LONG-PERIOD SWELL IN COMPLEX BATHYMETRY Hiroaki Kashima 1 and Katsuya Hirayama 1 Recently, coastal disasters due to long-period swells induced by heavy
MECHANISM AND COUNTERMEASURES OF WAVE OVERTOPPING FOR LONG-PERIOD SWELL IN COMPLEX BATHYMETRY Hiroaki Kashima 1 and Katsuya Hirayama 1 Recently, coastal disasters due to long-period swells induced by heavy
A new mechanism of oceanatmosphere coupling in midlatitudes
 A new mechanism of oceanatmosphere coupling in midlatitudes Arnaud Czaja & Nicholas Blunt Imperial College, London Grantham Institute for Climate Change 1. Motivation Two key questions By which mechanism(s)
A new mechanism of oceanatmosphere coupling in midlatitudes Arnaud Czaja & Nicholas Blunt Imperial College, London Grantham Institute for Climate Change 1. Motivation Two key questions By which mechanism(s)
Waves. G. Cowles. General Physical Oceanography MAR 555. School for Marine Sciences and Technology Umass-Dartmouth
 Waves G. Cowles General Physical Oceanography MAR 555 School for Marine Sciences and Technology Umass-Dartmouth Waves Sound Waves Light Waves Surface Waves Radio Waves Tidal Waves Instrument Strings How
Waves G. Cowles General Physical Oceanography MAR 555 School for Marine Sciences and Technology Umass-Dartmouth Waves Sound Waves Light Waves Surface Waves Radio Waves Tidal Waves Instrument Strings How
P2.17 OBSERVATIONS OF STRONG MOUNTAIN WAVES IN THE LEE OF THE MEDICINE BOW MOUNTAINS OF SOUTHEAST WYOMING
 P2.17 OBSERVATIONS OF STRONG MOUNTAIN WAVES IN THE LEE OF THE MEDICINE BOW MOUNTAINS OF SOUTHEAST WYOMING Larry D. Oolman 1, Jeffrey R. French 1, Samuel Haimov 1, David Leon 1, and Vanda Grubišić 2 1 University
P2.17 OBSERVATIONS OF STRONG MOUNTAIN WAVES IN THE LEE OF THE MEDICINE BOW MOUNTAINS OF SOUTHEAST WYOMING Larry D. Oolman 1, Jeffrey R. French 1, Samuel Haimov 1, David Leon 1, and Vanda Grubišić 2 1 University
SURF ZONE HYDRODYNAMICS COMPARISON OF MODELLING AND FIELD DATA
 SURF ZONE HYDRODYNAMICS COMPARISON OF MODELLING AND FIELD DATA Nicholas Grunnet 1, Kévin Martins 2, Rolf Deigaard 3 and Nils Drønen 4 Field data from the NOURTEC project is used for comparison with simulation
SURF ZONE HYDRODYNAMICS COMPARISON OF MODELLING AND FIELD DATA Nicholas Grunnet 1, Kévin Martins 2, Rolf Deigaard 3 and Nils Drønen 4 Field data from the NOURTEC project is used for comparison with simulation
Study of Passing Ship Effects along a Bank by Delft3D-FLOW and XBeach1
 Study of Passing Ship Effects along a Bank by Delft3D-FLOW and XBeach1 Minggui Zhou 1, Dano Roelvink 2,4, Henk Verheij 3,4 and Han Ligteringen 2,3 1 School of Naval Architecture, Ocean and Civil Engineering,
Study of Passing Ship Effects along a Bank by Delft3D-FLOW and XBeach1 Minggui Zhou 1, Dano Roelvink 2,4, Henk Verheij 3,4 and Han Ligteringen 2,3 1 School of Naval Architecture, Ocean and Civil Engineering,
Determination Of Nearshore Wave Conditions And Bathymetry From X-Band Radar Systems
 Determination Of Nearshore Wave Conditions And Bathymetry From X-Band Radar Systems Okey G. Nwogu Dept. of Naval Architecture and Marine Engineering University of Michigan Ann Arbor, MI 489 phone: (734)
Determination Of Nearshore Wave Conditions And Bathymetry From X-Band Radar Systems Okey G. Nwogu Dept. of Naval Architecture and Marine Engineering University of Michigan Ann Arbor, MI 489 phone: (734)
Super-parameterization of boundary layer roll vortices in tropical cyclone models
 DISTRIBUTION STATEMENT A. Approved for public release; distribution is unlimited. Super-parameterization of boundary layer roll vortices in tropical cyclone models PI Isaac Ginis Graduate School of Oceanography
DISTRIBUTION STATEMENT A. Approved for public release; distribution is unlimited. Super-parameterization of boundary layer roll vortices in tropical cyclone models PI Isaac Ginis Graduate School of Oceanography
WAVE FORECASTING FOR OFFSHORE WIND FARMS
 9 th International Workshop on Wave Hindcasting and Forecasting, Victoria, B.C. Canada, September 24-29, 2006 WAVE FORECASTING FOR OFFSHORE WIND FARMS Morten Rugbjerg, Ole René Sørensen and Vagner Jacobsen
9 th International Workshop on Wave Hindcasting and Forecasting, Victoria, B.C. Canada, September 24-29, 2006 WAVE FORECASTING FOR OFFSHORE WIND FARMS Morten Rugbjerg, Ole René Sørensen and Vagner Jacobsen
A study of advection of short wind waves by long waves from surface slope images
 A study of advection of short wind waves by long waves from surface slope images X. Zhang, J. Klinke, and B. Jähne SIO, UCSD, CA 993-02, USA Abstract Spatial and temporal measurements of short wind waves
A study of advection of short wind waves by long waves from surface slope images X. Zhang, J. Klinke, and B. Jähne SIO, UCSD, CA 993-02, USA Abstract Spatial and temporal measurements of short wind waves
CROSS-SHORE SEDIMENT PROCESSES
 The University of the West Indies Organization of American States PROFESSIONAL DEVELOPMENT PROGRAMME: COASTAL INFRASTRUCTURE DESIGN, CONSTRUCTION AND MAINTENANCE A COURSE IN COASTAL DEFENSE SYSTEMS I CHAPTER
The University of the West Indies Organization of American States PROFESSIONAL DEVELOPMENT PROGRAMME: COASTAL INFRASTRUCTURE DESIGN, CONSTRUCTION AND MAINTENANCE A COURSE IN COASTAL DEFENSE SYSTEMS I CHAPTER
Computationally Efficient Determination of Long Term Extreme Out-of-Plane Loads for Offshore Turbines
 Computationally Efficient Determination of Long Term Extreme Out-of-Plane Loads for Offshore Turbines Anand Natarajan Senior Scientist Wind Energy Department, Risø DTU Denmark Introduction IEC 61400-1
Computationally Efficient Determination of Long Term Extreme Out-of-Plane Loads for Offshore Turbines Anand Natarajan Senior Scientist Wind Energy Department, Risø DTU Denmark Introduction IEC 61400-1
On the Interpretation of Scatterometer Winds near Sea Surface Temperature Fronts
 On the Interpretation of Scatterometer Winds near Sea Surface Temperature Fronts Jim Edson University of Connecticut Amanda Plagge & Doug Vandemark University of New Hampshire IOVWST Meeting Utrecht, NL
On the Interpretation of Scatterometer Winds near Sea Surface Temperature Fronts Jim Edson University of Connecticut Amanda Plagge & Doug Vandemark University of New Hampshire IOVWST Meeting Utrecht, NL
Forest Winds in Complex Terrain
 Forest Winds in Complex Terrain Ilda Albuquerque 1 Contents Project Description Motivation Forest Complex Terrain Forested Complex Terrain 2 Project Description WAUDIT (Wind Resource Assessment Audit and
Forest Winds in Complex Terrain Ilda Albuquerque 1 Contents Project Description Motivation Forest Complex Terrain Forested Complex Terrain 2 Project Description WAUDIT (Wind Resource Assessment Audit and
Sea State Analysis. Topics. Module 7 Sea State Analysis 2/22/2016. CE A676 Coastal Engineering Orson P. Smith, PE, Ph.D.
 Sea State Analysis Module 7 Orson P. Smith, PE, Ph.D. Professor Emeritus Module 7 Sea State Analysis Topics Wave height distribution Wave energy spectra Wind wave generation Directional spectra Hindcasting
Sea State Analysis Module 7 Orson P. Smith, PE, Ph.D. Professor Emeritus Module 7 Sea State Analysis Topics Wave height distribution Wave energy spectra Wind wave generation Directional spectra Hindcasting
Influence of rounding corners on unsteady flow and heat transfer around a square cylinder
 Influence of rounding corners on unsteady flow and heat transfer around a square cylinder S. K. Singh Deptt. of Mech. Engg., M. B. M. Engg. College / J. N. V. University, Jodhpur, Rajasthan, India Abstract
Influence of rounding corners on unsteady flow and heat transfer around a square cylinder S. K. Singh Deptt. of Mech. Engg., M. B. M. Engg. College / J. N. V. University, Jodhpur, Rajasthan, India Abstract
Upstream environment for SBI - Modeled and observed biophysical conditions in the northern Bering Sea
 Upstream environment for SBI - Modeled and observed biophysical conditions in the northern Bering Sea Jaclyn Clement 1, Wieslaw Maslowski 1, Lee Cooper 2, Jacqueline Grebmeier 2, Waldemar Walczowski 3,
Upstream environment for SBI - Modeled and observed biophysical conditions in the northern Bering Sea Jaclyn Clement 1, Wieslaw Maslowski 1, Lee Cooper 2, Jacqueline Grebmeier 2, Waldemar Walczowski 3,
Evaluation of Unstructured WAVEWATCH III for Nearshore Application
 Evaluation of Unstructured WAVEWATCH III for Nearshore Application Jane McKee Smith, Tyler Hesser, Mary Anderson Bryant USACE Research and Development Center, Coastal and Hydraulics Lab Aron Roland BGS
Evaluation of Unstructured WAVEWATCH III for Nearshore Application Jane McKee Smith, Tyler Hesser, Mary Anderson Bryant USACE Research and Development Center, Coastal and Hydraulics Lab Aron Roland BGS
IDENTIFICATION OF WIND SEA AND SWELL EVENTS AND SWELL EVENTS PARAMETERIZATION OFF WEST AFRICA. K. Agbéko KPOGO-NUWOKLO
 Workshop: Statistical models of the metocean environment for engineering uses IDENTIFICATION OF WIND SEA AND SWELL EVENTS AND SWELL EVENTS PARAMETERIZATION OFF WEST AFRICA K. Agbéko KPOGO-NUWOKLO IFREMER-
Workshop: Statistical models of the metocean environment for engineering uses IDENTIFICATION OF WIND SEA AND SWELL EVENTS AND SWELL EVENTS PARAMETERIZATION OFF WEST AFRICA K. Agbéko KPOGO-NUWOKLO IFREMER-
APPENDIX G WEATHER DATA SELECTED EXTRACTS FROM ENVIRONMENTAL DATA FOR BCFS VESSEL REPLACEMENT PROGRAM DRAFT REPORT
 APPENDIX G WEATHER DATA SELECTED EXTRACTS FROM ENVIRONMENTAL DATA FOR BCFS VESSEL REPLACEMENT PROGRAM DRAFT REPORT Prepared for: B.C. Ferries Services Inc. Prepared by: George Roddan, P.Eng. Roddan Engineering
APPENDIX G WEATHER DATA SELECTED EXTRACTS FROM ENVIRONMENTAL DATA FOR BCFS VESSEL REPLACEMENT PROGRAM DRAFT REPORT Prepared for: B.C. Ferries Services Inc. Prepared by: George Roddan, P.Eng. Roddan Engineering
WaMoS II Wave Monitoring System
 WaMoS II Wave Monitoring System - An application of WaMoS II at Duck - Katrin Hessner, K. Reichert, J. Dannenberg OceanWaveS GmbH, Germany Kent Hathaway, Don Resio Engineering Research Development Center
WaMoS II Wave Monitoring System - An application of WaMoS II at Duck - Katrin Hessner, K. Reichert, J. Dannenberg OceanWaveS GmbH, Germany Kent Hathaway, Don Resio Engineering Research Development Center
Assessing the quality of Synthetic Aperture Radar (SAR) wind retrieval in coastal zones using multiple Lidars
 Assessing the quality of Synthetic Aperture Radar (SAR) wind retrieval in coastal zones using multiple Lidars Tobias Ahsbahs Merete Badger, Ioanna Karagali, Xiaoli Larsen What is the coastal zone? Coastal
Assessing the quality of Synthetic Aperture Radar (SAR) wind retrieval in coastal zones using multiple Lidars Tobias Ahsbahs Merete Badger, Ioanna Karagali, Xiaoli Larsen What is the coastal zone? Coastal
ANALYSIS OF TURBULENCE STRUCTURE IN THE URBAN BOUNDARY LAYER. Hitoshi Kono and Kae Koyabu University of Hyogo, Japan
 Proceedings of the th Int. Conf. on Harmonisation within ANALYSIS OF TUBULENCE STUCTUE IN THE UBAN BOUNDAY LAYE Hitoshi Kono and Kae Koyabu University of Hyogo, Japan INTODUCTION The surface layer is defined
Proceedings of the th Int. Conf. on Harmonisation within ANALYSIS OF TUBULENCE STUCTUE IN THE UBAN BOUNDAY LAYE Hitoshi Kono and Kae Koyabu University of Hyogo, Japan INTODUCTION The surface layer is defined
Supplementary Material for Satellite Measurements Reveal Persistent Small-Scale Features in Ocean Winds Fig. S1.
 Supplementary Material for Satellite Measurements Reveal Persistent Small-Scale Features in Ocean Winds by D. B. Chelton, M. G. Schlax, M. H. Freilich and Ralph F. Milliff Fig. S1. Global 4-year average
Supplementary Material for Satellite Measurements Reveal Persistent Small-Scale Features in Ocean Winds by D. B. Chelton, M. G. Schlax, M. H. Freilich and Ralph F. Milliff Fig. S1. Global 4-year average
PUBLICATIONS. Journal of Geophysical Research: Oceans. Swell impact on wind stress and atmospheric mixing in a regional coupled atmosphere-wave model
 PUBLICATIONS Journal of Geophysical Research: Oceans RESEARCH ARTICLE Key Points: Adding swell impact on wind stress and atmospheric mixing improves the model performance The influence of swell on wind
PUBLICATIONS Journal of Geophysical Research: Oceans RESEARCH ARTICLE Key Points: Adding swell impact on wind stress and atmospheric mixing improves the model performance The influence of swell on wind
Exploring wave-turbulence interaction through LES modeling
 Exploring wave-turbulence interaction through LES modeling Mireia Udina 1 Jielun Sun 2 M. Rosa Soler 1 Branko Kosović 2 1. Dept. Astronomia i Meteorologia Universitat de Barcelona, Barcelona, Catalunya
Exploring wave-turbulence interaction through LES modeling Mireia Udina 1 Jielun Sun 2 M. Rosa Soler 1 Branko Kosović 2 1. Dept. Astronomia i Meteorologia Universitat de Barcelona, Barcelona, Catalunya
ABNORMALLY HIGH STORM WAVES OBSERVED ON THE EAST COAST OF KOREA
 ABNORMALLY HIGH STORM WAVES OBSERVED ON THE EAST COAST OF KOREA WEON MU JEONG 1 ; SANG-HO OH ; DONGYOUNG LEE 3 ; KYUNG-HO RYU 1 Coastal Engineering Research Department, Korea Ocean Research and Development
ABNORMALLY HIGH STORM WAVES OBSERVED ON THE EAST COAST OF KOREA WEON MU JEONG 1 ; SANG-HO OH ; DONGYOUNG LEE 3 ; KYUNG-HO RYU 1 Coastal Engineering Research Department, Korea Ocean Research and Development
Inter-comparison of wave measurement by accelerometer and GPS wave buoy in shallow water off Cuddalore, east coast of India
 Indian Journal of Geo-Marine Sciences Vol. 43(1), January 2014, pp. 45-49 Inter-comparison of wave measurement by accelerometer and GPS wave buoy in shallow water off Cuddalore, east coast of India Sisir
Indian Journal of Geo-Marine Sciences Vol. 43(1), January 2014, pp. 45-49 Inter-comparison of wave measurement by accelerometer and GPS wave buoy in shallow water off Cuddalore, east coast of India Sisir
The effects of atmospheric stability on coastal wind climates
 Meteorol. Appl. 6, 39 47 (1999) The effects of atmospheric stability on coastal wind climates R J Barthelmie, Department of Wind Energy and Atmospheric Physics, Risø National Laboratory, 4000 Roskilde,
Meteorol. Appl. 6, 39 47 (1999) The effects of atmospheric stability on coastal wind climates R J Barthelmie, Department of Wind Energy and Atmospheric Physics, Risø National Laboratory, 4000 Roskilde,
The Air-Sea Interaction. Masanori Konda Kyoto University
 2 The Air-Sea Interaction Masanori Konda Kyoto University 2.1 Feedback between Ocean and Atmosphere Heat and momentum exchange between the ocean and atmosphere Atmospheric circulation Condensation heat
2 The Air-Sea Interaction Masanori Konda Kyoto University 2.1 Feedback between Ocean and Atmosphere Heat and momentum exchange between the ocean and atmosphere Atmospheric circulation Condensation heat
Quantification of the Effects of Turbulence in Wind on the Flutter Stability of Suspension Bridges
 Quantification of the Effects of Turbulence in Wind on the Flutter Stability of Suspension Bridges T. Abbas 1 and G. Morgenthal 2 1 PhD candidate, Graduate College 1462, Department of Civil Engineering,
Quantification of the Effects of Turbulence in Wind on the Flutter Stability of Suspension Bridges T. Abbas 1 and G. Morgenthal 2 1 PhD candidate, Graduate College 1462, Department of Civil Engineering,
DIRECTION DEPENDENCY OF OFFSHORE TURBULENCE INTENSITY IN THE GERMAN BIGHT
 10 th Wind Energy Conference DEWEK 2010 DIRECTION DEPENDENCY OF OFFSHORE TURBULENCE INTENSITY IN THE GERMAN BIGHT Annette Westerhellweg, Beatriz Canadillas, Thomas Neumann DEWI GmbH, Wilhelmshaven, Germany,
10 th Wind Energy Conference DEWEK 2010 DIRECTION DEPENDENCY OF OFFSHORE TURBULENCE INTENSITY IN THE GERMAN BIGHT Annette Westerhellweg, Beatriz Canadillas, Thomas Neumann DEWI GmbH, Wilhelmshaven, Germany,
NSF funded project , June 2010-May 2015
 NSF funded project 0961545, June 2010-May 2015 Nested Regional Climate Model (nrcm) update The effect of embedding ROMS in a coastal upwelling zone in CCSM4 R. Justin Small (NCAR), Brian Kauffman (NCAR),
NSF funded project 0961545, June 2010-May 2015 Nested Regional Climate Model (nrcm) update The effect of embedding ROMS in a coastal upwelling zone in CCSM4 R. Justin Small (NCAR), Brian Kauffman (NCAR),
Determination of Nearshore Wave Conditions and Bathymetry from X-Band Radar Systems
 Determination of Nearshore Wave Conditions and Bathymetry from X-Band Radar Systems Okey G. Nwogu Dept. of Naval Architecture and Marine Engineering University of Michigan Ann Arbor, MI 48109 Phone: (734)
Determination of Nearshore Wave Conditions and Bathymetry from X-Band Radar Systems Okey G. Nwogu Dept. of Naval Architecture and Marine Engineering University of Michigan Ann Arbor, MI 48109 Phone: (734)
Wave-Current Interaction in Coastal Inlets and River Mouths
 DISTRIBUTION STATEMENT A. Approved for public release; distribution is unlimited. Wave-Current Interaction in Coastal Inlets and River Mouths Tim T. Janssen Department of Geosciences, San Francisco State
DISTRIBUTION STATEMENT A. Approved for public release; distribution is unlimited. Wave-Current Interaction in Coastal Inlets and River Mouths Tim T. Janssen Department of Geosciences, San Francisco State
Variability in the tropical oceans - Monitoring and prediction of El Niño and La Niña -
 Variability in the tropical oceans - Monitoring and prediction of El Niño and La Niña - Jun ichi HIROSAWA Climate Prediction Division Japan Meteorological Agency SST anomaly in Nov. 1997 1 ( ) Outline
Variability in the tropical oceans - Monitoring and prediction of El Niño and La Niña - Jun ichi HIROSAWA Climate Prediction Division Japan Meteorological Agency SST anomaly in Nov. 1997 1 ( ) Outline
Importance of thermal effects and sea surface roughness for offshore wind resource assessment
 Downloaded from orbit.dtu.dk on: Sep 09, 2018 Importance of thermal effects and sea surface roughness for offshore wind resource assessment Lange, B.; Larsen, Søren Ejling; Højstrup, Jørgen; Barthelmie,
Downloaded from orbit.dtu.dk on: Sep 09, 2018 Importance of thermal effects and sea surface roughness for offshore wind resource assessment Lange, B.; Larsen, Søren Ejling; Højstrup, Jørgen; Barthelmie,
Climatology of the 10-m wind along the west coast of South American from 30 years of high-resolution reanalysis
 Climatology of the 10-m wind along the west coast of South American from 30 years of high-resolution reanalysis David A. Rahn and René D. Garreaud Departamento de Geofísica, Facultad de Ciencias Físicas
Climatology of the 10-m wind along the west coast of South American from 30 years of high-resolution reanalysis David A. Rahn and René D. Garreaud Departamento de Geofísica, Facultad de Ciencias Físicas
Wave Energy Atlas in Vietnam
 Wave Energy Atlas in Vietnam Nguyen Manh Hung, Duong Cong Dien 1 1 Institute of Mechanics, 264 Doi Can Str. Hanoi, Vietnam nmhungim@gmail.com; duongdienim@gmail.com Abstract Vietnam has achieved remarkable
Wave Energy Atlas in Vietnam Nguyen Manh Hung, Duong Cong Dien 1 1 Institute of Mechanics, 264 Doi Can Str. Hanoi, Vietnam nmhungim@gmail.com; duongdienim@gmail.com Abstract Vietnam has achieved remarkable
Statistics of wind and wind power over the Mediterranean Sea
 Conférence Méditerranéenne Côtière et Maritime EDITION 2, TANGER, MAROC (2011) Coastal and Maritime Mediterranean Conference Disponible en ligne http://www.paralia.fr Available online Statistics of wind
Conférence Méditerranéenne Côtière et Maritime EDITION 2, TANGER, MAROC (2011) Coastal and Maritime Mediterranean Conference Disponible en ligne http://www.paralia.fr Available online Statistics of wind
