Geophysical Fluid Dynamics of the Earth. Jeffrey B. Weiss University of Colorado, Boulder
|
|
|
- Drusilla Crawford
- 5 years ago
- Views:
Transcription
1 Geophysical Fluid Dynamics of the Earth Jeffrey B. Weiss University of Colorado, Boulder
2 The Earth is a spinning sphere Coriolis force depends on latitude solar flux depends on latitude Michael Ritter, tbook/title_page.htm l
3 Atmosphere is turbulent global scale forcing: L ~ 10 7 m dissipation: ν air ~ 10-5 m 2 /s jet stream velocity: U ~ 10 2 m/s R atm = 10 14
4 Direct simulation impossible Kolmogorov scale η = 1 mm current global models: ~ 1 o resolution ~ 100 km improvement needed: 10 8 computer speed-up: ~ Moore s Law: 200 years need to be smarter (or very patient)
5 Climate system self-organizes layers: troposphere circulations Hadley cell spatially localized organization ocean vortices spatio-temporal organization El-Niño
6 Radiative forcing IPCC
7 Atmospheric Layers troposphere is weather layer height governed by radiation convection dynamics tropopause dynamics interesting stratosphere stably stratified
8 planetary boundary layer directly feels surface 3d turbulence strong diurnal cycle surface layer lower 10% log wind profile free atmosphere Arya, S.P. Air Pollution Meteorology and Dispersion affected by rotation/stratification
9 ocean mixed layer directly feels atmosphere mixed by wind stabilized by solar heating
10 thermocline m deep ocean below stably stratified slow currents
11 3-cell model Large scale circulations trades westerlies ITCZ deserts frontal zone shifts seasonally NASA JPL
12 wind-driven ocean circulation winds + basins = gyres horizontal large geostrophic component timescales: months geographyalltheway.com
13 serendipitous tracers 1990: 20,000 Nike shoes washed into Pacific Gyre 1992: 29,000 bathtub toys locations from beachcombers
14 thermohaline circulation density driven vertical overturning forcing: small scale intermittent convection uncertain vertical mixing timescale: 1000 yrs large climate impact
15 spatially localized features Coherent structures vortices, jets, fronts rotation and stratification suppress vortex stretching inverse cascade to large scales
16 Spatio-temporal phenomena El Niño, Monsoons, NAO, MJO, PDO, As records lengthen, expect to see more can have extreme multi-scale components NOAA
17 Monsoon seasonal circulation associated with landsea contrast complex intermittency experience the North American Monsoon burst break
18 Balances often find balances between subset of forces provide insight into dynamics departures important even if small asymptotic analysis gives reduced models
19 Hydrostatic Balance aspect ratio α = H/L Froude number Fr = U/NH non-rotating Boussinesq equations for departures about basic state b(z) vertical momentum eqn α 2 Fr 2 << 1 gives hydrostatic balance U 2 /L 2 N 2 << 1 t buoy 2 << t adv 2
20 large scale troposphere N ~ 10-2 /s, H ~ 10 km, L ~ 1000 km, U ~ 10 m/s Fr ~ 0.1 α ~ 0.01 α 2 Fr 2 ~ 10-6 fails at fronts and convection large scale ocean N ~ 10-2 /s, H ~ 1 km, L ~ 1000 km, U ~ 0.1m/s Fr ~ 0.01 α ~ α 2 Fr 2 ~ hydrostatic down to small horizontal scales fails at deep convection sites preconditioning: Fr near unity plumes: H/L large
21 Geostrophic balance Rossby number: Ro = U/ f L horizontal momentum eqn scaling: Ro << 1: geostrophy flow along isobars diagnostic relation
22 upper air map
23 thermal wind combine geostrophic and hydrostatic obtain wind shear midlatitudes heating decreases with latitude eastward wind increases with height jet intensification
24 turbulent cascades compare homogeneous isotropic 3d and 2d energy injection at large scale dissipation at small scale intermediate: inertial scales, only depend on energy flux ε focus on spectra: assume local in k and universal
25 dimensional analysis T requires α = 2/3 L requires β = 5/3 Vallis, Atmospheric and Oceanic Fluid Dynamics, 2006
26 2d cascades In 2d, two inviscid invariants energy E and enstrophy Z in 3d vortex stretching creates enstrophy Z(k) = k 2 E(k) centroid wavenumber width initial narrow E(k) spreads
27 energy cascades to large scales: inverse Vallis, Atmospheric and Oceanic Fluid Dynamics, 2006 similar argument: enstrophy to small scales: direct
28 energy inertial range to large scales enstrophy inertial range to small scales energy inertial ranges same scaling as 3d need mechanism to remove energy at large scales, e.g. Ekman drag enstrophy flux η ~ Z/T ~1/T 3 E(k) ~ η 2/3 k -3 Vallis, Atmospheric and Oceanic Fluid Dynamics, 2006
29 cascades on 2d β-plane vorticity equation on 2d β-plane f = β y Rossby waves dispersion relation
30 scaling small scales advection and turbulence dominate crossover: Rhines scale large scales, β dominates waves inhibit cascades
31 anisotropy of Rossby waves advection freq Uk ~ Rossby wave freq ω turbulence waves Vallis, Atmospheric and Oceanic Fluid Dynamics, 2006
32 ocean jets zonal jets observed to populate ocean instantaneous 18 week avg 200 week avg Maximenko, et al 2005
Lecture 15 General Circulation of the Atmosphere and Ocean
 Lecture 15 General Circulation of the Atmosphere and Ocean Non-rotating model of atmospheric general circulation Hadley (1735) Cell is induced by uneven distribution of solar heating. Conceptual models
Lecture 15 General Circulation of the Atmosphere and Ocean Non-rotating model of atmospheric general circulation Hadley (1735) Cell is induced by uneven distribution of solar heating. Conceptual models
Winds and Ocean Circulations
 Winds and Ocean Circulations AT 351 Lab 5 February 20, 2008 Sea Surface Temperatures 1 Temperature Structure of the Ocean Ocean Currents 2 What causes ocean circulation? The direction of most ocean currents
Winds and Ocean Circulations AT 351 Lab 5 February 20, 2008 Sea Surface Temperatures 1 Temperature Structure of the Ocean Ocean Currents 2 What causes ocean circulation? The direction of most ocean currents
Chapter 6: Atmospheric Pressure, Wind, and Global Circulation
 Discovering Physical Geography Third Edition by Alan Arbogast Chapter 6: Atmospheric Pressure, Wind, and Global Circulation Factors That Influence Air Pressure Air Pressure is the measured weight of air
Discovering Physical Geography Third Edition by Alan Arbogast Chapter 6: Atmospheric Pressure, Wind, and Global Circulation Factors That Influence Air Pressure Air Pressure is the measured weight of air
Summary of Lecture 10, 04 March 2008 Introduce the Hadley circulation and examine global weather patterns. Discuss jet stream dynamics jet streams
 Summary of Lecture 10, 04 March 2008 Introduce the Hadley circulation and examine global weather patterns. Discuss jet stream dynamics jet streams arise because the Coriolis force prevents Hadley-type
Summary of Lecture 10, 04 March 2008 Introduce the Hadley circulation and examine global weather patterns. Discuss jet stream dynamics jet streams arise because the Coriolis force prevents Hadley-type
ATMS 310 Tropical Dynamics
 ATMS 310 Tropical Dynamics Introduction Throughout the semester we have focused on mid-latitude dynamics. This is not to say that the dynamics of other parts of the world, such as the tropics, are any
ATMS 310 Tropical Dynamics Introduction Throughout the semester we have focused on mid-latitude dynamics. This is not to say that the dynamics of other parts of the world, such as the tropics, are any
Global Winds AOSC 200 Tim Canty
 Global Winds AOSC 200 Tim Canty Class Web Site: http://www.atmos.umd.edu/~tcanty/aosc200 Topics for today: Global Wind Patterns Deserts Jet Stream Monsoons Ocean transport Ocean cycles Lecture 16 Oct 24
Global Winds AOSC 200 Tim Canty Class Web Site: http://www.atmos.umd.edu/~tcanty/aosc200 Topics for today: Global Wind Patterns Deserts Jet Stream Monsoons Ocean transport Ocean cycles Lecture 16 Oct 24
Climate & Earth System Science. Introduction to Meteorology & Climate. Chapter 07. Lecture 14. Global Scale Winds. Simple Introductory Examples:
 Climate & Earth System Science Introduction to Meteorology & Climate MAPH 10050 Peter Lynch Peter Lynch Meteorology & Climate Centre School of Mathematical Sciences University College Dublin Meteorology
Climate & Earth System Science Introduction to Meteorology & Climate MAPH 10050 Peter Lynch Peter Lynch Meteorology & Climate Centre School of Mathematical Sciences University College Dublin Meteorology
Chapter 10: Global Wind Systems
 Chapter 10: Global Wind Systems Three-cell model of atmospheric circulation Intertropical Convergence Zone (ITCZ) Typical surface wind patterns Upper-level pressure and winds Climatological sea-level pressure
Chapter 10: Global Wind Systems Three-cell model of atmospheric circulation Intertropical Convergence Zone (ITCZ) Typical surface wind patterns Upper-level pressure and winds Climatological sea-level pressure
McKnight's Physical Geography 11e
 Chapter 2 Lecture McKnight's Physical Geography 11e Lectures Chapter 5 Atmospheric Pressure and Wind Michael Commons Ohio Northern University Atmospheric Pressure and Wind The Nature of Atmospheric Pressure
Chapter 2 Lecture McKnight's Physical Geography 11e Lectures Chapter 5 Atmospheric Pressure and Wind Michael Commons Ohio Northern University Atmospheric Pressure and Wind The Nature of Atmospheric Pressure
Lecture 5: Climate Tapestry. Sea/Land Breeze. Thermal Energy to Kinetic Energy
 Lecture 5: Climate Tapestry JS JP Thermal Energy to Kinetic Energy Hadley Cell Ferrel Cell (driven by eddies) Pressure and Wind Global Wind Patterns Polar Cell L H L H Effect of Earth s Rotation On Winds
Lecture 5: Climate Tapestry JS JP Thermal Energy to Kinetic Energy Hadley Cell Ferrel Cell (driven by eddies) Pressure and Wind Global Wind Patterns Polar Cell L H L H Effect of Earth s Rotation On Winds
SIO20 - Midterm Examination 2 v1 Winter Section A. Circle the letter corresponding to the best answer. (1 point each)
 NAME: Section A. Circle the letter corresponding to the best answer. (1 point each) 1. Rainbows result from: a. refraction and reflection of sunlight by water droplets b. reflection of sunlight by oceans
NAME: Section A. Circle the letter corresponding to the best answer. (1 point each) 1. Rainbows result from: a. refraction and reflection of sunlight by water droplets b. reflection of sunlight by oceans
The Coriolis force, geostrophy, Rossby waves and the westward intensification
 Chapter 3 The Coriolis force, geostrophy, Rossby waves and the westward intensification The oceanic circulation is the result of a certain balance of forces. Geophysical Fluid Dynamics shows that a very
Chapter 3 The Coriolis force, geostrophy, Rossby waves and the westward intensification The oceanic circulation is the result of a certain balance of forces. Geophysical Fluid Dynamics shows that a very
The Air-Sea Interaction. Masanori Konda Kyoto University
 2 The Air-Sea Interaction Masanori Konda Kyoto University 2.1 Feedback between Ocean and Atmosphere Heat and momentum exchange between the ocean and atmosphere Atmospheric circulation Condensation heat
2 The Air-Sea Interaction Masanori Konda Kyoto University 2.1 Feedback between Ocean and Atmosphere Heat and momentum exchange between the ocean and atmosphere Atmospheric circulation Condensation heat
The Monsoon and Its Variability Prof. Sulochana Gadgil Centre for Atmospheric & Oceanic Sciences Indian Institute of Science Bangalore
 The Monsoon and Its Variability Prof. Sulochana Gadgil Centre for Atmospheric & Oceanic Sciences Indian Institute of Science Bangalore Lecture - 04 Background about the Atmosphere and Rotating Systems
The Monsoon and Its Variability Prof. Sulochana Gadgil Centre for Atmospheric & Oceanic Sciences Indian Institute of Science Bangalore Lecture - 04 Background about the Atmosphere and Rotating Systems
Goal: Develop quantitative understanding of ENSO genesis, evolution, and impacts
 The Delayed Oscillator Zebiak and Cane (1987) Model Other Theories Theory of ENSO teleconnections Goal: Develop quantitative understanding of ENSO genesis, evolution, and impacts The delayed oscillator
The Delayed Oscillator Zebiak and Cane (1987) Model Other Theories Theory of ENSO teleconnections Goal: Develop quantitative understanding of ENSO genesis, evolution, and impacts The delayed oscillator
Air moves towards ITCZ in tropics because of rising air - convection. Horizontal extent of Hadley cell is modified by Friction Coriolis Force
 Air moves towards ITCZ in tropics because of rising air - convection Horizontal extent of Hadley cell is modified by Friction Coriolis Force Speed from rotation Objects at rest on Earth move at very different
Air moves towards ITCZ in tropics because of rising air - convection Horizontal extent of Hadley cell is modified by Friction Coriolis Force Speed from rotation Objects at rest on Earth move at very different
Global Circulations. GEOG/ENST 2331 Lecture 15 Ahrens: Chapter 10
 Global Circulations GEOG/ENST 2331 Lecture 15 Ahrens: Chapter 10 Last lecture Microscale (turbulence) Mesoscale (land/sea breeze) Synoptic scale (monsoon) Global scale (3 cell circulation) Three Cell Model
Global Circulations GEOG/ENST 2331 Lecture 15 Ahrens: Chapter 10 Last lecture Microscale (turbulence) Mesoscale (land/sea breeze) Synoptic scale (monsoon) Global scale (3 cell circulation) Three Cell Model
Chapter 2. Turbulence and the Planetary Boundary Layer
 Chapter 2. Turbulence and the Planetary Boundary Layer In the chapter we will first have a qualitative overview of the PBL then learn the concept of Reynolds averaging and derive the Reynolds averaged
Chapter 2. Turbulence and the Planetary Boundary Layer In the chapter we will first have a qualitative overview of the PBL then learn the concept of Reynolds averaging and derive the Reynolds averaged
The Surface Currents OCEA 101
 The Surface Currents OCEA 101 Why should you care? - the surface ocean circulation controls the major ocean biomes - variations in ocean circulation control the supply of nutrients for marine organisms
The Surface Currents OCEA 101 Why should you care? - the surface ocean circulation controls the major ocean biomes - variations in ocean circulation control the supply of nutrients for marine organisms
SIO 210 Problem Set 3 November 4, 2011 Due Nov. 14, 2011
 SIO 210 Problem Set 3 November 4, 2011 Due Nov. 14, 2011 1. At 20 N, both the ocean and the atmosphere carry approximately 2 PW of heat poleward, for a total of about 4 PW (see figure). If (at this latitude)
SIO 210 Problem Set 3 November 4, 2011 Due Nov. 14, 2011 1. At 20 N, both the ocean and the atmosphere carry approximately 2 PW of heat poleward, for a total of about 4 PW (see figure). If (at this latitude)
Wednesday, September 15, 2010 Coriolis force, 3 dimensions (p 65)
 Wednesday, September 15, 2010 Coriolis force, 3 dimensions (p 65) Weather fronts (p 63) General circulation on a rotating Earth (p 65) Geostrophy force balance (p 66) Local effects (no coriolis force)
Wednesday, September 15, 2010 Coriolis force, 3 dimensions (p 65) Weather fronts (p 63) General circulation on a rotating Earth (p 65) Geostrophy force balance (p 66) Local effects (no coriolis force)
Ocean Circulation. Si Hui Lee and Frances Wen. You can access ME at
 Ocean Circulation Si Hui Lee and Frances Wen You can access ME at http://tinyurl.com/oceancirculation Earth - the blue planet - 71% area covered by the oceans - 3/4 of ocean area between 3000-6000m deep
Ocean Circulation Si Hui Lee and Frances Wen You can access ME at http://tinyurl.com/oceancirculation Earth - the blue planet - 71% area covered by the oceans - 3/4 of ocean area between 3000-6000m deep
The Ocean is a Geophysical Fluid Like the Atmosphere. The Physical Ocean. Yet Not Like the Atmosphere. ATS 760 Global Carbon Cycle The Physical Ocean
 The Physical Ocean The Ocean is a Geophysical Fluid Like the Atmosphere Three real forces: Gravity Pressure gradients Friction Two apparent forces: Coriolis and Centrifugal Geostrophic & Hydrostatic balances
The Physical Ocean The Ocean is a Geophysical Fluid Like the Atmosphere Three real forces: Gravity Pressure gradients Friction Two apparent forces: Coriolis and Centrifugal Geostrophic & Hydrostatic balances
3/22/11. General Circulation of the Atmosphere. General Circulation of the Atmosphere
 Chapter 10 General refers to the average air flow, actual winds will vary considerably. Average conditions help identify driving forces. The basic cause of the general circulation is unequal heating of
Chapter 10 General refers to the average air flow, actual winds will vary considerably. Average conditions help identify driving forces. The basic cause of the general circulation is unequal heating of
Lecture 18: El Niño. Atmosphere, Ocean, Climate Dynamics EESS 146B/246B
 Lecture 18: El Niño Atmosphere, Ocean, Climate Dynamics EESS 146B/246B El Niño Transient equatorial motions: Kelvin and Rossby waves. Positive feedback mechanism associated with air-sea coupling. Atmospheric
Lecture 18: El Niño Atmosphere, Ocean, Climate Dynamics EESS 146B/246B El Niño Transient equatorial motions: Kelvin and Rossby waves. Positive feedback mechanism associated with air-sea coupling. Atmospheric
Introduction to Oceanography OCE 1001
 Introduction to Oceanography OCE 1001 Lecture Notes Chantale Bégin & Jessica Fry Version 2.1 10. Ocean Circulation (Trujillo, Chapter 7) Major ocean currents are stable and predictable; they have been
Introduction to Oceanography OCE 1001 Lecture Notes Chantale Bégin & Jessica Fry Version 2.1 10. Ocean Circulation (Trujillo, Chapter 7) Major ocean currents are stable and predictable; they have been
RECTIFICATION OF THE MADDEN-JULIAN OSCILLATION INTO THE ENSO CYCLE
 RECTIFICATION OF THE MADDEN-JULIAN OSCILLATION INTO THE ENSO CYCLE By William S. Kessler and Richard Kleeman Journal of Climate Vol.13, 1999 SWAP, May 2009, Split, Croatia Maristella Berta What does give
RECTIFICATION OF THE MADDEN-JULIAN OSCILLATION INTO THE ENSO CYCLE By William S. Kessler and Richard Kleeman Journal of Climate Vol.13, 1999 SWAP, May 2009, Split, Croatia Maristella Berta What does give
SIO 210 Final examination Wednesday, December 11, PM Sumner auditorium Name:
 SIO 210 Final examination Wednesday, December 11, 2013 2-5 PM Sumner auditorium Name: Turn off all phones, ipods, etc. and put them away. This is a closed book exam. You may use one page of notes, both
SIO 210 Final examination Wednesday, December 11, 2013 2-5 PM Sumner auditorium Name: Turn off all phones, ipods, etc. and put them away. This is a closed book exam. You may use one page of notes, both
Friday, February 8 th. Winds/Coriolis Worksheet: Due Today Lab Worksheet: Finish Questions
 Ocean Currents Friday, February 8 th Winds/Coriolis Worksheet: Due Today Lab Worksheet: Finish Questions Non-rotating Earth Convection cell model Add rotation and add landmasses unequal heating and cooling
Ocean Currents Friday, February 8 th Winds/Coriolis Worksheet: Due Today Lab Worksheet: Finish Questions Non-rotating Earth Convection cell model Add rotation and add landmasses unequal heating and cooling
Meteorology I Pre test for the Second Examination
 Meteorology I Pre test for the Second Examination MULTIPLE CHOICE 1. A primary reason why land areas warm up more rapidly than water areas is that a) on land, all solar energy is absorbed in a shallow
Meteorology I Pre test for the Second Examination MULTIPLE CHOICE 1. A primary reason why land areas warm up more rapidly than water areas is that a) on land, all solar energy is absorbed in a shallow
GFD1 AS509/OC512 Winter Q Dargan Frierson Lab 6 P.B.Rhines Kelvin Waves and other inertial/gravity waves Tues 7 Feb 12.30
 GFD1 AS509/OC512 Winter Q. 2017 Dargan Frierson Lab 6 P.B.Rhines Kelvin Waves and other inertial/gravity waves Tues 7 Feb 12.30 With this lab we return to wave propagation; succeeding labs will look at
GFD1 AS509/OC512 Winter Q. 2017 Dargan Frierson Lab 6 P.B.Rhines Kelvin Waves and other inertial/gravity waves Tues 7 Feb 12.30 With this lab we return to wave propagation; succeeding labs will look at
Chapter 7: Circulation And The Atmosphere
 Chapter 7: Circulation And The Atmosphere Highly integrated wind system Main Circulation Currents: series of deep rivers of air encircling the planet Various perturbations or vortices (hurricanes, tornados,
Chapter 7: Circulation And The Atmosphere Highly integrated wind system Main Circulation Currents: series of deep rivers of air encircling the planet Various perturbations or vortices (hurricanes, tornados,
9/25/2014. Scales of Atmospheric Motion. Scales of Atmospheric Motion. Chapter 7: Circulation of the Atmosphere
 Chapter 7: Circulation of the Atmosphere The Atmosphere: An Introduction to Meteorology, 12 th Lutgens Tarbuck Lectures by: Heather Gallacher, Cleveland State University Scales of Atmospheric Motion Small-
Chapter 7: Circulation of the Atmosphere The Atmosphere: An Introduction to Meteorology, 12 th Lutgens Tarbuck Lectures by: Heather Gallacher, Cleveland State University Scales of Atmospheric Motion Small-
ATMOSPHERIC CIRCULATION. WIND = The horizontal movement of air. Results from the differences in air pressure. Always moves from HIGH to LOW.
 ATMOSPHERIC CIRCULATION WIND = The horizontal movement of air. Results from the differences in air pressure. Always moves from HIGH to LOW. Pressure differences result from variations in temperature. AIR
ATMOSPHERIC CIRCULATION WIND = The horizontal movement of air. Results from the differences in air pressure. Always moves from HIGH to LOW. Pressure differences result from variations in temperature. AIR
Meteorology. Circle the letter that corresponds to the correct answer
 Chapter 7 Worksheet 2 Meteorology Name: Circle the letter that corresponds to the correct answer 1) Which of the following factors contributes to the general subsidence in the latitude zone 20 degrees
Chapter 7 Worksheet 2 Meteorology Name: Circle the letter that corresponds to the correct answer 1) Which of the following factors contributes to the general subsidence in the latitude zone 20 degrees
ESS15 Lecture 12. Review, tropical oceans & El Nino, and the thermohaline ocean circulation. Please see new reading material on website.
 ESS15 Lecture 12 Review, tropical oceans & El Nino, and the thermohaline ocean circulation. Please see new reading material on website. Review. I-clicker exercise: In this graph of Earth s energy imbalances
ESS15 Lecture 12 Review, tropical oceans & El Nino, and the thermohaline ocean circulation. Please see new reading material on website. Review. I-clicker exercise: In this graph of Earth s energy imbalances
Small- and large-scale circulation
 The Earth System - Atmosphere II Small- and large-scale circulation Atmospheric Circulation 1. Global atmospheric circulation can be thought of as a series of deep rivers that encircle the planet. 2. Imbedded
The Earth System - Atmosphere II Small- and large-scale circulation Atmospheric Circulation 1. Global atmospheric circulation can be thought of as a series of deep rivers that encircle the planet. 2. Imbedded
PHYSICAL GEOGRAPHY. By Brett Lucas
 PHYSICAL GEOGRAPHY By Brett Lucas ATMOSPHERIC PRESSURE AND WIND Atmospheric Pressure and Wind Atmospheric Processes The Nature of Wind General Circulation of the Atmosphere Modifications of General Circulation
PHYSICAL GEOGRAPHY By Brett Lucas ATMOSPHERIC PRESSURE AND WIND Atmospheric Pressure and Wind Atmospheric Processes The Nature of Wind General Circulation of the Atmosphere Modifications of General Circulation
Lecture 13 El Niño/La Niña Ocean-Atmosphere Interaction. Idealized 3-Cell Model of Wind Patterns on a Rotating Earth. Previous Lecture!
 Lecture 13 El Niño/La Niña Ocean-Atmosphere Interaction Previous Lecture! Global Winds General Circulation of winds at the surface and aloft Polar Jet Stream Subtropical Jet Stream Monsoons 1 2 Radiation
Lecture 13 El Niño/La Niña Ocean-Atmosphere Interaction Previous Lecture! Global Winds General Circulation of winds at the surface and aloft Polar Jet Stream Subtropical Jet Stream Monsoons 1 2 Radiation
Isaac Newton ( )
 Introduction to Climatology GEOGRAPHY 300 Isaac Newton (1642-1727) Tom Giambelluca University of Hawai i at Mānoa Atmospheric Pressure, Wind, and The General Circulation Philosophiæ Naturalis Principia
Introduction to Climatology GEOGRAPHY 300 Isaac Newton (1642-1727) Tom Giambelluca University of Hawai i at Mānoa Atmospheric Pressure, Wind, and The General Circulation Philosophiæ Naturalis Principia
Week 6-7: Wind-driven ocean circulation. Tally s book, chapter 7
 Week 6-7: Wind-driven ocean circulation Tally s book, chapter 7 Recap so far Our goal (since week 3) has been to understand large-scale ocean circulation and its underlying physics, and to learn how to
Week 6-7: Wind-driven ocean circulation Tally s book, chapter 7 Recap so far Our goal (since week 3) has been to understand large-scale ocean circulation and its underlying physics, and to learn how to
5. El Niño Southern Oscillation
 5. El Niño Southern Oscillation Copyright 2006 Emily Shuckburgh, University of Cambridge. Not to be quoted or reproduced without permission. EFS 5/1 Ocean-Atmosphere Coupling Tropical atmosphere/ocean,
5. El Niño Southern Oscillation Copyright 2006 Emily Shuckburgh, University of Cambridge. Not to be quoted or reproduced without permission. EFS 5/1 Ocean-Atmosphere Coupling Tropical atmosphere/ocean,
Atmospheric Circulation
 Atmospheric Circulation Why do we say Earth's temperature is moderate? It may not look like it, but various processes work to moderate Earth's temperature across the latitudes. Atmospheric circulation
Atmospheric Circulation Why do we say Earth's temperature is moderate? It may not look like it, but various processes work to moderate Earth's temperature across the latitudes. Atmospheric circulation
Gravity waves in stable atmospheric boundary layers
 Gravity waves in stable atmospheric boundary layers Carmen J. Nappo CJN Research Meteorology Knoxville, Tennessee 37919, USA Abstract Gravity waves permeate the stable atmospheric planetary boundary layer,
Gravity waves in stable atmospheric boundary layers Carmen J. Nappo CJN Research Meteorology Knoxville, Tennessee 37919, USA Abstract Gravity waves permeate the stable atmospheric planetary boundary layer,
ESCI 485 Air/sea Interaction Lesson 9 Equatorial Adjustment and El Nino Dr. DeCaria
 ESCI 485 Air/sea Interaction Lesson 9 Equatorial Adjustment and El Nino Dr. DeCaria Reference: El Nino, La Nina, and the Southern Oscillation, Philander THE TWO-LAYER SHALLOW WATER MODEL The ocean can
ESCI 485 Air/sea Interaction Lesson 9 Equatorial Adjustment and El Nino Dr. DeCaria Reference: El Nino, La Nina, and the Southern Oscillation, Philander THE TWO-LAYER SHALLOW WATER MODEL The ocean can
CHAPTER 7 Ocean Circulation
 1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 13 14 CHAPTER 7 Ocean Circulation Words Ocean currents Moving seawater Surface ocean currents Transfer heat from warmer to cooler areas Similar to pattern of major wind belts
1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 13 14 CHAPTER 7 Ocean Circulation Words Ocean currents Moving seawater Surface ocean currents Transfer heat from warmer to cooler areas Similar to pattern of major wind belts
For Class Today How does ocean water circulate? Ocean currents, surface currents, gyres, currents & climate, upwelling, deep ocean circulation
 For Class Today Modified Cornell Notes on section 16.1 (pg. 448-453) **Follow the guide in your ISN and previous notes for help** Heading: How does ocean water circulate? Left hand side categories: Ocean
For Class Today Modified Cornell Notes on section 16.1 (pg. 448-453) **Follow the guide in your ISN and previous notes for help** Heading: How does ocean water circulate? Left hand side categories: Ocean
Atmospheric & Ocean Circulation-
 Atmospheric & Ocean Circulation- Overview: Atmosphere & Climate Atmospheric layers Heating at different latitudes Atmospheric convection cells (Hadley, Ferrel, Polar) Coriolis Force Generation of winds
Atmospheric & Ocean Circulation- Overview: Atmosphere & Climate Atmospheric layers Heating at different latitudes Atmospheric convection cells (Hadley, Ferrel, Polar) Coriolis Force Generation of winds
Monday, October 2, Watch for new assessment (Week 4/5 review) TA s have your tests, please see key (at course website)
 Monday, October 2, 2017 Watch for new assessment (Week 4/5 review) TA s have your tests, please see key (at course website) Homework 3 Due date Wednesday, Oct 11 (8 pm) Be ready to watch another important
Monday, October 2, 2017 Watch for new assessment (Week 4/5 review) TA s have your tests, please see key (at course website) Homework 3 Due date Wednesday, Oct 11 (8 pm) Be ready to watch another important
Chapter 9: Circulation of the Ocean
 Chapter 9: Circulation of the Ocean Tropical gardens on Britain s Scilly Isles. Only 48 kilometers (30 miles) off the coast of Cornwall at 50 N, these scenic islands lie in the path of the warm waters
Chapter 9: Circulation of the Ocean Tropical gardens on Britain s Scilly Isles. Only 48 kilometers (30 miles) off the coast of Cornwall at 50 N, these scenic islands lie in the path of the warm waters
ATS150: Global Climate Change. Oceans and Climate. Icebergs. Scott Denning CSU 1
 The Oceans Wind-Driven Gyre Circulations Icebergs Scott Denning CSU 1 Surface Balance of Forces friction coriolis wind stress resultant current Wind stress accelerates surface water Friction couples surface
The Oceans Wind-Driven Gyre Circulations Icebergs Scott Denning CSU 1 Surface Balance of Forces friction coriolis wind stress resultant current Wind stress accelerates surface water Friction couples surface
Atmosphere Circulation
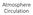 Atmosphere Circulation Winds What Causes Winds? Difference in air pressure due to unequal heating of the atmosphere. Temperatures vary according to the amount of sun it gets. Uneven heating of the Earth
Atmosphere Circulation Winds What Causes Winds? Difference in air pressure due to unequal heating of the atmosphere. Temperatures vary according to the amount of sun it gets. Uneven heating of the Earth
Abrupt marine boundary layer changes revealed by airborne in situ and lidar measurements
 Abrupt marine boundary layer changes revealed by airborne in situ and lidar measurements David A. Rahn 1, Thomas R. Parish 2, and David Leon 2 1 Univeristy of Kansas 2 Univeristy of Wyoming Precision Atmospheric
Abrupt marine boundary layer changes revealed by airborne in situ and lidar measurements David A. Rahn 1, Thomas R. Parish 2, and David Leon 2 1 Univeristy of Kansas 2 Univeristy of Wyoming Precision Atmospheric
Section 1. Global Wind Patterns and Weather. What Do You See? Think About It. Investigate. Learning Outcomes
 Chapter 5 Winds, Oceans, Weather, and Climate Section 1 Global Wind Patterns and Weather What Do You See? Learning Outcomes In this section, you will Determine the effects of Earth s rotation and the uneven
Chapter 5 Winds, Oceans, Weather, and Climate Section 1 Global Wind Patterns and Weather What Do You See? Learning Outcomes In this section, you will Determine the effects of Earth s rotation and the uneven
10% water in the world is tied up in the surface ocean currents. (above the pycnocline) Primary source is wind: Westerlies, Trades, Polar Easterlies
 Oceanography Chapter 9 10% water in the world is tied up in the surface ocean currents. (above the pycnocline) Primary source is wind: Westerlies, Trades, Polar Easterlies Coriolis deflects winds (and
Oceanography Chapter 9 10% water in the world is tied up in the surface ocean currents. (above the pycnocline) Primary source is wind: Westerlies, Trades, Polar Easterlies Coriolis deflects winds (and
OCN 201 Surface Circulation
 OCN 201 Surface Circulation Excess heat in equatorial regions requires redistribution toward the poles 1 In the Northern hemisphere, Coriolis force deflects movement to the right In the Southern hemisphere,
OCN 201 Surface Circulation Excess heat in equatorial regions requires redistribution toward the poles 1 In the Northern hemisphere, Coriolis force deflects movement to the right In the Southern hemisphere,
Trade winds Prevailing westerlies east
 Warm-up Page: 528, 1. What is the major wind belt that is nearest the equator? Trade winds Page: 528, 2. What is the major wind belt that the most of the USA belongs to: Prevailing westerlies Page: 528,
Warm-up Page: 528, 1. What is the major wind belt that is nearest the equator? Trade winds Page: 528, 2. What is the major wind belt that the most of the USA belongs to: Prevailing westerlies Page: 528,
Transport and mixing in the extratropical tropopause region in a high vertical resolution GCM
 Transport and mixing in the extratropical tropopause region in a high vertical resolution GCM (Miyazaki et al. JAS 2010a,2010b) Kazuyuki Miyazaki Royal Netherlands Meteorological Institute (KNMI) Japan
Transport and mixing in the extratropical tropopause region in a high vertical resolution GCM (Miyazaki et al. JAS 2010a,2010b) Kazuyuki Miyazaki Royal Netherlands Meteorological Institute (KNMI) Japan
Wednesday, September 27, 2017 Test Monday, about half-way through grading. No D2L Assessment this week, watch for one next week
 Wednesday, September 27, 2017 Test Monday, about half-way through grading No D2L Assessment this week, watch for one next week Homework 3 Climate Variability (due Monday, October 9) Quick comment on Coriolis
Wednesday, September 27, 2017 Test Monday, about half-way through grading No D2L Assessment this week, watch for one next week Homework 3 Climate Variability (due Monday, October 9) Quick comment on Coriolis
Chapter 10. Thermohaline Circulation
 Chapter 10. Thermohaline Circulation Main References: Schloesser, F., R. Furue, J. P. McCreary, and A. Timmermann, 2012: Dynamics of the Atlantic meridional overturning circulation. Part 1: Buoyancy-forced
Chapter 10. Thermohaline Circulation Main References: Schloesser, F., R. Furue, J. P. McCreary, and A. Timmermann, 2012: Dynamics of the Atlantic meridional overturning circulation. Part 1: Buoyancy-forced
Chapter 6. Atmospheric and Oceanic. Circulations. Circulations
 Chapter 6 Atmospheric and Oceanic Circulations Robert W. Christopherson Charlie Thomsen Winds: Transfer energy and mass (1) Balance energy equatorial energy surplus and polar energy deficit (2) Generate
Chapter 6 Atmospheric and Oceanic Circulations Robert W. Christopherson Charlie Thomsen Winds: Transfer energy and mass (1) Balance energy equatorial energy surplus and polar energy deficit (2) Generate
The atmospheric circulation system
 The atmospheric circulation system Key questions Why does the air move? Are the movements of the winds random across the surface of the Earth, or do they follow regular patterns? What implications do these
The atmospheric circulation system Key questions Why does the air move? Are the movements of the winds random across the surface of the Earth, or do they follow regular patterns? What implications do these
Ocean Currents Unit (4 pts)
 Name: Section: Ocean Currents Unit (Topic 9A-1) page 1 Ocean Currents Unit (4 pts) Ocean Currents An ocean current is like a river in the ocean: water is flowing traveling from place to place. Historically,
Name: Section: Ocean Currents Unit (Topic 9A-1) page 1 Ocean Currents Unit (4 pts) Ocean Currents An ocean current is like a river in the ocean: water is flowing traveling from place to place. Historically,
Air Pressure and Wind
 Air Pressure and Wind 19.1 Understanding Air Pressure Air Pressure Defined Air pressure is the pressure exerted by the weight of air. Air pressure is exerted in all directions down, up, and sideways. The
Air Pressure and Wind 19.1 Understanding Air Pressure Air Pressure Defined Air pressure is the pressure exerted by the weight of air. Air pressure is exerted in all directions down, up, and sideways. The
Standard atmosphere Typical height (m) Pressure (mb)
 Standard atmosphere Pressure (mb) Typical height (ft) Typical height (m) 1013.25 0 0 1000 370 110 850 4780 1460 700 9880 3010 500 18280 5570 300 30050 9160 Whiteman 2000 Pressure decreases exponentially
Standard atmosphere Pressure (mb) Typical height (ft) Typical height (m) 1013.25 0 0 1000 370 110 850 4780 1460 700 9880 3010 500 18280 5570 300 30050 9160 Whiteman 2000 Pressure decreases exponentially
Kathleen Dohan. Wind-Driven Surface Currents. Earth and Space Research, Seattle, WA
 Updates to OSCAR and challenges with capturing the wind-driven currents. Wind-Driven Surface Currents Kathleen Dohan Earth and Space Research, Seattle, WA ENSO OSCAR Surface currents from satellite fields
Updates to OSCAR and challenges with capturing the wind-driven currents. Wind-Driven Surface Currents Kathleen Dohan Earth and Space Research, Seattle, WA ENSO OSCAR Surface currents from satellite fields
DUE TO EXTERNAL FORCES
 17B.6 DNS ON GROWTH OF A VERTICAL VORTEX IN CONVECTION DUE TO EXTERNAL FORCES Ryota Iijima* and Tetsuro Tamura Tokyo Institute of Technology, Yokohama, Japan 1. INTRODUCTION Various types of vertical vortices,
17B.6 DNS ON GROWTH OF A VERTICAL VORTEX IN CONVECTION DUE TO EXTERNAL FORCES Ryota Iijima* and Tetsuro Tamura Tokyo Institute of Technology, Yokohama, Japan 1. INTRODUCTION Various types of vertical vortices,
IX. Upper Ocean Circulation
 IX. Upper Ocean Circulation World Ocean Covers 71% of Earth s surface Contains 97% of surface water Arctic Ocean NH: 61% ocean, 39% land Pacific Ocean Atlantic Ocean Southern Ocean Indian Ocean SH: 81%
IX. Upper Ocean Circulation World Ocean Covers 71% of Earth s surface Contains 97% of surface water Arctic Ocean NH: 61% ocean, 39% land Pacific Ocean Atlantic Ocean Southern Ocean Indian Ocean SH: 81%
Understanding El Nino-Monsoon teleconnections
 Understanding El Nino-Monsoon teleconnections Dr Neena Joseph Mani Earth & Climate Science INSA Anniversary General meeting, Session: Science in IISER Pune 27 th December 2017 Mean State of the equatorial
Understanding El Nino-Monsoon teleconnections Dr Neena Joseph Mani Earth & Climate Science INSA Anniversary General meeting, Session: Science in IISER Pune 27 th December 2017 Mean State of the equatorial
Thorsten Mauritsen *, Gunilla Svensson Stockholm University, Stockholm, Sweden
 J.1 WAVE FLOW SIMULATIONS OVER ARCTIC LEADS Thorsten Mauritsen *, Gunilla Svensson Stockholm University, Stockholm, Sweden Branko Grisogono Department of Geophysics, Faculty of Science, Zagreb, Croatia
J.1 WAVE FLOW SIMULATIONS OVER ARCTIC LEADS Thorsten Mauritsen *, Gunilla Svensson Stockholm University, Stockholm, Sweden Branko Grisogono Department of Geophysics, Faculty of Science, Zagreb, Croatia
Chapter. Air Pressure and Wind
 Chapter Air Pressure and Wind 19.1 Understanding Air Pressure Air Pressure Defined Air pressure is the pressure exerted by the weight of air. 19.1 Understanding Air Pressure Air Pressure Defined Air pressure
Chapter Air Pressure and Wind 19.1 Understanding Air Pressure Air Pressure Defined Air pressure is the pressure exerted by the weight of air. 19.1 Understanding Air Pressure Air Pressure Defined Air pressure
Lecture The Oceans
 Lecture 22 -- The Oceans ATMOSPHERE CIRCULATION AND WINDS Coriolis effect Prevailing winds and vertical circulation Zones of pressure, evap. & ppt. Factors modifying global winds -- Differential heating
Lecture 22 -- The Oceans ATMOSPHERE CIRCULATION AND WINDS Coriolis effect Prevailing winds and vertical circulation Zones of pressure, evap. & ppt. Factors modifying global winds -- Differential heating
Lecture 7. More on BL wind profiles and turbulent eddy structures. In this lecture
 Lecture 7. More on BL wind profiles and turbulent eddy structures In this lecture Stability and baroclinicity effects on PBL wind and temperature profiles Large-eddy structures and entrainment in shear-driven
Lecture 7. More on BL wind profiles and turbulent eddy structures In this lecture Stability and baroclinicity effects on PBL wind and temperature profiles Large-eddy structures and entrainment in shear-driven
ABSTRACT INTRODUCTION
 Numerical investigation of the formation of elevated pollution layers over the Los Angeles air basin Rong Lu, R.P. Turco Department of Atmospheric Sciences, University of California, Los Angeles, 405 Hilgard
Numerical investigation of the formation of elevated pollution layers over the Los Angeles air basin Rong Lu, R.P. Turco Department of Atmospheric Sciences, University of California, Los Angeles, 405 Hilgard
The Asian monsoon anticyclone and water vapor transport
 The Asian monsoon anticyclone and water vapor transport Bill Randel Atmospheric Chemistry Division NCAR Thanks to: Mijeong Park, Louisa Emmons 1 What is the monsoon anticyclone, and why is it interesting?
The Asian monsoon anticyclone and water vapor transport Bill Randel Atmospheric Chemistry Division NCAR Thanks to: Mijeong Park, Louisa Emmons 1 What is the monsoon anticyclone, and why is it interesting?
Ocean circulation and surface buoyancy fluxes: dynamics and energetics!
 Ocean circulation and surface buoyancy fluxes: dynamics and energetics Ross Griffiths with credits: Graham Hughes, Andy Hogg, Kial Stewart, Julia Mullarney, J.Tan Research School of Earth Sciences The
Ocean circulation and surface buoyancy fluxes: dynamics and energetics Ross Griffiths with credits: Graham Hughes, Andy Hogg, Kial Stewart, Julia Mullarney, J.Tan Research School of Earth Sciences The
Lecture 22: Ageostrophic motion and Ekman layers
 Lecture 22: Ageostrophic motion and Ekman layers November 5, 2003 1 Subgeostrophic flow: the Ekman layer Before returning to our discussion of the general circulation of the atmosphere in Chapter 8, we
Lecture 22: Ageostrophic motion and Ekman layers November 5, 2003 1 Subgeostrophic flow: the Ekman layer Before returning to our discussion of the general circulation of the atmosphere in Chapter 8, we
Trade winds How do they affect the tropical oceans? 10/9/13. Take away concepts and ideas. El Niño - Southern Oscillation (ENSO)
 El Niño - Southern Oscillation (ENSO) Ocean-atmosphere interactions Take away concepts and ideas What is El Niño, La Niña? Trade wind and Walker circulation. What is the Southern Oscillation? Tropical
El Niño - Southern Oscillation (ENSO) Ocean-atmosphere interactions Take away concepts and ideas What is El Niño, La Niña? Trade wind and Walker circulation. What is the Southern Oscillation? Tropical
Atmosphere & Weather. Earth Science
 Atmosphere & Weather Earth Science Energy Transfer in the Atmosphere Earth s energy is provided by the SUN! Energy is important to us because it 1. Drives winds and ocean currents. 2. Allows plants to
Atmosphere & Weather Earth Science Energy Transfer in the Atmosphere Earth s energy is provided by the SUN! Energy is important to us because it 1. Drives winds and ocean currents. 2. Allows plants to
Tropical temperature variance and wave-mean flow interactions derived from GPS radio occultation data
 Tropical temperature variance and wave-mean flow interactions derived from GPS radio occultation data Bill Randel 1, Mijeong Park 1, Peter Hitchcock 1 and Joowan Kim 2 1 NCAR, Boulder, CO USA 2 Kongju
Tropical temperature variance and wave-mean flow interactions derived from GPS radio occultation data Bill Randel 1, Mijeong Park 1, Peter Hitchcock 1 and Joowan Kim 2 1 NCAR, Boulder, CO USA 2 Kongju
Wind and Air Pressure
 Wind and Air Pressure When air moves above the surface of the Earth, it is called wind. Wind is caused by differences in air pressure. When a difference in pressure exists, the air will move from areas
Wind and Air Pressure When air moves above the surface of the Earth, it is called wind. Wind is caused by differences in air pressure. When a difference in pressure exists, the air will move from areas
Wind: Small Scale and Local Systems Chapter 9 Part 1
 Wind: Small Scale and Local Systems Chapter 9 Part 1 Atmospheric scales of motion Scales of atmospheric circulations range from meters or less to thousands of kilometers- millions of meters Time scales
Wind: Small Scale and Local Systems Chapter 9 Part 1 Atmospheric scales of motion Scales of atmospheric circulations range from meters or less to thousands of kilometers- millions of meters Time scales
Department of Physics, University of Toronto. Thanks: James Anstey, Stephen Beagley, Erich Becker, Michaela Hegglin, Paul Kushner
 Stratospheric Residual Circulation and Tropopause Structure Thomas Birner Theodore G. Shepherd Department of Physics, University of Toronto Thanks: James Anstey, Stephen Beagley, Erich Becker, Michaela
Stratospheric Residual Circulation and Tropopause Structure Thomas Birner Theodore G. Shepherd Department of Physics, University of Toronto Thanks: James Anstey, Stephen Beagley, Erich Becker, Michaela
(20 points) 1. ENSO is a coupled climate phenomenon in the tropical Pacific that has both regional and global impacts.
 SIO 210 Problem Set 4 Answer key December 1, 2014 Due Dec. 12, 2014 (20 points) 1. ENSO is a coupled climate phenomenon in the tropical Pacific that has both regional and global impacts. (2 points) a)
SIO 210 Problem Set 4 Answer key December 1, 2014 Due Dec. 12, 2014 (20 points) 1. ENSO is a coupled climate phenomenon in the tropical Pacific that has both regional and global impacts. (2 points) a)
Additive effect of two solar forcing mechanisms and influences on. tropical Pacific climate. National Center for Atmospheric Research
 Additive effect of two solar forcing mechanisms and influences on tropical Pacific climate Gerald A. Meehl Julie Arblaster, Fabrizio Sassi, Katja Matthes, and Harry van Loon National Center for Atmospheric
Additive effect of two solar forcing mechanisms and influences on tropical Pacific climate Gerald A. Meehl Julie Arblaster, Fabrizio Sassi, Katja Matthes, and Harry van Loon National Center for Atmospheric
The structure of the Persian Gulf outflow subjected to density variations
 Author(s) 2009. This work is distributed under the Creative Commons Attribution 3.0 License. Ocean Science The structure of the Persian Gulf outflow subjected to density variations A. A. Bidokhti 1 and
Author(s) 2009. This work is distributed under the Creative Commons Attribution 3.0 License. Ocean Science The structure of the Persian Gulf outflow subjected to density variations A. A. Bidokhti 1 and
Interference of the Equatorial Waves on the 2017 Indian Monsoon Northward Progression
 https://www.bing.com/images/search?view=detailv2&ccid=4gaj08ec&id=15b827d717e11e 07790F5BCC0A4E13BBD103123C&thid=OIP.4gaj08EcIqXuIdGNdiwwUAEsDI&q=monsoon+pi ctures&simid=608027853209010910&selectedindex=119&mode=overlay&first=1
https://www.bing.com/images/search?view=detailv2&ccid=4gaj08ec&id=15b827d717e11e 07790F5BCC0A4E13BBD103123C&thid=OIP.4gaj08EcIqXuIdGNdiwwUAEsDI&q=monsoon+pi ctures&simid=608027853209010910&selectedindex=119&mode=overlay&first=1
Gravity wave driven descent of the stratopause following major stratospheric sudden warmings
 Gravity wave driven descent of the stratopause following major stratospheric sudden warmings P. Hitchcock, T. G. Shepherd University of Toronto, Canada Acknowledgements: S. Yoden, G. Manney Introduction:
Gravity wave driven descent of the stratopause following major stratospheric sudden warmings P. Hitchcock, T. G. Shepherd University of Toronto, Canada Acknowledgements: S. Yoden, G. Manney Introduction:
Lesson: Ocean Circulation
 Lesson: Ocean Circulation By Keith Meldahl Corresponding to Chapter 9: Ocean Circulation As this figure shows, there is a connection between the prevailing easterly and westerly winds (discussed in Chapter
Lesson: Ocean Circulation By Keith Meldahl Corresponding to Chapter 9: Ocean Circulation As this figure shows, there is a connection between the prevailing easterly and westerly winds (discussed in Chapter
The impacts of explicitly simulated gravity waves on large-scale circulation in the
 The impacts of explicitly simulated gravity waves on large-scale circulation in the Southern Hemisphere. Linda Mudoni Department of Geological and Atmospheric Sciences October 2003 Introduction In the
The impacts of explicitly simulated gravity waves on large-scale circulation in the Southern Hemisphere. Linda Mudoni Department of Geological and Atmospheric Sciences October 2003 Introduction In the
Local Winds. Please read Ahrens Chapter 10
 Local Winds Please read Ahrens Chapter 10 Scales of Motion Microscale: meters Turbulent eddies Formed by mechanical disturbance or convection Lifetimes of minutes Mesoscale: km s to 100 s of km s Local
Local Winds Please read Ahrens Chapter 10 Scales of Motion Microscale: meters Turbulent eddies Formed by mechanical disturbance or convection Lifetimes of minutes Mesoscale: km s to 100 s of km s Local
MET 200 Lecture 11 Local Winds. Last Lecture: Forces. Review of Forces. Balance of Forces
 MET 200 Lecture 11 Local Winds Last Lecture: Forces Scales of Motion Eddies Sea Breeze Mountain-Valley Circulations Chinook - Snow Eater Drainage Wind - Katabatic Wind 1 2 Review of Forces 1. Pressure
MET 200 Lecture 11 Local Winds Last Lecture: Forces Scales of Motion Eddies Sea Breeze Mountain-Valley Circulations Chinook - Snow Eater Drainage Wind - Katabatic Wind 1 2 Review of Forces 1. Pressure
Full Name: Class: Period: Date:
 Topic/Objective: Essential Question: Full Name: Class: Period: Date: Tutor Use Only: Air Pressure and Wind (Chapter 19) Air Pressure the weight of the atmosphere pushing down on the Earth exerting a force
Topic/Objective: Essential Question: Full Name: Class: Period: Date: Tutor Use Only: Air Pressure and Wind (Chapter 19) Air Pressure the weight of the atmosphere pushing down on the Earth exerting a force
Lornshill Academy. Geography Department Higher Revision Physical Environments - Atmosphere
 Lornshill Academy Geography Department Higher Revision Physical Environments - Atmosphere Physical Environments Atmosphere Global heat budget The earth s energy comes from solar radiation, this incoming
Lornshill Academy Geography Department Higher Revision Physical Environments - Atmosphere Physical Environments Atmosphere Global heat budget The earth s energy comes from solar radiation, this incoming
Airborne measurements of gravity wave breaking at the tropopause
 GEOPHYSICAL RESEARCH LETTERS, VOL. 30, NO. 20, 2070, doi:10.1029/2003gl018207, 2003 Airborne measurements of gravity wave breaking at the tropopause James A. Whiteway, 1,6 Edward G. Pavelin, 2 Reinhold
GEOPHYSICAL RESEARCH LETTERS, VOL. 30, NO. 20, 2070, doi:10.1029/2003gl018207, 2003 Airborne measurements of gravity wave breaking at the tropopause James A. Whiteway, 1,6 Edward G. Pavelin, 2 Reinhold
Gravity Wave and Kelvin Wave Activity in the Tropical Lower Stratosphere. Thomas Birner
 Gravity Wave and Kelvin Wave Activity in the Tropical Lower Stratosphere Thomas Birner with contributions by: Anne (Sasha) Glanville, Jeremiah Sjoberg, Richard Johnson Department of Atmospheric Science,
Gravity Wave and Kelvin Wave Activity in the Tropical Lower Stratosphere Thomas Birner with contributions by: Anne (Sasha) Glanville, Jeremiah Sjoberg, Richard Johnson Department of Atmospheric Science,
Lecture 14. Heat lows and the TCZ
 Lecture 14 Heat lows and the TCZ ITCZ/TCZ and heat lows While the ITCZ/TCZ is associated with a trough at low levels, it must be noted that a low pressure at the surface and cyclonic vorticity at 850 hpa
Lecture 14 Heat lows and the TCZ ITCZ/TCZ and heat lows While the ITCZ/TCZ is associated with a trough at low levels, it must be noted that a low pressure at the surface and cyclonic vorticity at 850 hpa
W3 Global Circulation Systems
 W3 Global Circulation Systems Which regions of Earth receive the most energy from the Sun? If not for global circulation systems There would only be two narrow regions that would support life What
W3 Global Circulation Systems Which regions of Earth receive the most energy from the Sun? If not for global circulation systems There would only be two narrow regions that would support life What
PGF. Pressure Gradient. Wind is horizontal movement of the air or other word air in motion. Forces affecting winds 2/14/2017
 Winds Wind is horizontal movement of the air or other word air in motion. Forces affecting winds 1. Pressure gradient force a. High pressure flows to low pressure b. Pressure gradient = difference in pressure
Winds Wind is horizontal movement of the air or other word air in motion. Forces affecting winds 1. Pressure gradient force a. High pressure flows to low pressure b. Pressure gradient = difference in pressure
AOS 103. Week 4 Discussion
 AOS 103 Week 4 Discussion Starting from an atmospheric HIGH pressure center (e.g. for the subtropical Pacific) North Hemi 1) Deduce/draw/describe the geostrophic wind 2) Deduce/draw/describe the Ekman
AOS 103 Week 4 Discussion Starting from an atmospheric HIGH pressure center (e.g. for the subtropical Pacific) North Hemi 1) Deduce/draw/describe the geostrophic wind 2) Deduce/draw/describe the Ekman
