Introduction to Oxygenation and Aeration Systems
|
|
|
- Calvin Austin
- 5 years ago
- Views:
Transcription
1 Introduction to Oxygenation and Aeration Systems John Little Civil and Environmental Engineering Virginia Tech, Blacksburg, Virginia, USA
2 Acknowledgments Kevin Bierlein, Virginia Tech (PhD) Lee Bryant, Virginia Tech (PhD) and Duke/Eawag (Postdoc) Paul Gantzer, Virginia Tech (MS and PhD) Dan McGinnis, Virginia Tech (MS and PhD) and Eawag (Postdoc) Vickie Singleton (Burris), Virginia Tech (MS and PhD) Johny Wüest, Eawag and EPFL Francisco Rueda, University of Granada Bob Benninger, Western Virginia Water Authority Mark Mobley, Mobley Engineering National Science Foundation CBET CBET DGE (IGERT) CBET Western Virginia Water Authority Tennessee Valley Authority City of Norfolk, Virginia Canton Aargau, Switzerland
3 Presentation Outline Why do we need to add oxygen? Primary oxygenation/aeration systems Oxygen transfer theory Models to predict system performance Sediment oxygen demand Oxidizing iron and manganese Coupled bubble-plume/reservoir model
4 Stratification Oxygen Depletion Hypolimnetic oxygenation to replenish oxygen Figures from Baudirektion Kanton Zürich
5 Why do we need to add oxygen? Hydropower reservoirs Water-storage reservoirs used for drinking water Cold-water fisheries Eutrophication of surface waters
6 Hydropower Reservoirs
7 Drinking Water Treatment Depletion of dissolved oxygen Withdraw water from anoxic hypolimnion Iron, manganese, and hydrogen sulfide from sediment (color, odor) Increased oxidant demand (more chlorine, more DBPs, more corrosion) Increased phosphorus (algal blooms, more coagulant, shorter filter runs)
8 Fish (hypoxia <2.8 mg O 2 /L)
9 Eutrophication - Swan Estuary Perth, Western Australia
10 Salt Wedge Oxygen Depletion
11
12
13 Can we solve the problem by reducing nutrient load? Baudirektion Kanton Zürich
14 Baudirektion Kanton Zürich
15 Baudirektion Kanton Zürich
16 Baudirektion Kanton Zürich
17 Oxygenation and Aeration Systems Four main systems Speece Cone (oxygen) side-stream supersaturation (oxygen) airlift aerator (air) bubble plume (air or oxygen)
18 Courtesy of Rod Jung Speece Cone
19
20 Side-Stream Supersaturation Courtesy of Mark Mobley
21
22 Courtesy of Bob Kortmann Airlift Aerator
23 Courtesy of Bob Kortmann
24 Courtesy of Mark Mobley Bubble Plume
25 Selected Installations Reservoir Type Application Capacity/Cost Camanche Lake Prince Richard B. Russell Upper San Leandro Spring Hollow Carvin s Cove Speece Cone (1 unit) Airlift Aerators (25 units) Bubble Plume ( m) Bubble Plume (2 730 m) Bubble Plume (1 400 m) Bubble Plume (2 600 m) Hydropower Water supply Hydropower Water supply Water supply Water supply Liquid oxygen costs ~ $100/ton 9 tons O 2 /day $1.8M 10 tons O 2 /day $2.8M 200 tons O 2 /day $1.6M 9 tons O 2 /day $450K 0.3 tons O 2 /day $200K 2 tons O 2 /day $450K
26 Hypolimnetic Oxygenation Oxygenation systems Speece Cone (oxygen) side-stream supersaturation (oxygen) airlift aerator (air) bubble plume (air or oxygen) Want to predict performance In each case have gas transfer between individual (discrete) bubbles and water
27 Discrete Bubble Model Tracks individual bubbles rising in water Assumes no coalescence Accounts for changes in bubble volume: change in temperature change in hydrostatic pressure gas transfer of oxygen and nitrogen
28 Discrete Bubble Model J = K (HP C) L i dm dz = K (HP C) L i 4πr v b 2
29 Bubble Rise Velocity 100 Bubble Rise Velocity (cm s -1 ) 10 Tap Water Distilled Water Wüest et al. (1992) Rigid sphere equation Wave equation Bubble Diameter (mm)
30 Mass Transfer Coefficient 0.07 Mass Transfer Coefficient (cm s -1 ) Motarjemi and Jameson (1978) Wüest et al. (1992) Bubble Diameter (mm)
31 Model Validation Oxygen transfer tests in large tank Photographs to determine bubble size as function of gas flow rate Compare model predictions to experimental observations
32 Oxygen Transfer Tests TVA Engineering Lab Tank Height 14 m Tank Diameter 2 m
33 Bubble Size Measurement Water Depth 12.5 m Bubble Diameter 1.9 mm
34 Measured Bubble Size 3.0 Sauter Mean Diameter (mm) Depth = 6.7 meters Depth = 12.5 meters Gas Flow Rate per Unit Length Porous Hose (m 2 h -1 )
35 Oxygen Transfer Tests Nm 3 h Nm 3 h -1 Dissolved Oxygen (g m -3 ) Nm 3 h Time (min)
36 Discrete Bubble Model Validation Dissolved Oxygen (g m -3 ) Observed Predicted Time (min)
37 Model Application Hypolimnetic oxygenation systems airlift aerator (full-lift) [Lake Prince] bubble plume (linear) [Spring Hollow] bubble plume (circular) [Lake Hallwil] Predict oxygen transfer based on: gas (air or oxygen) flow rate initial bubble size
38 Airlift Aerator (full-lift) Lake Prince City of Norfolk Virginia
39 Lake Prince
40 Airlift Aerator
41 Airlift Aerator Model Validation Depth (m) Q air = m 3 s -1 Depth (m) Q air = m 3 s -1 Depth (m) Q air = m 3 s DO (g m -3 ) DO (g m -3 ) DO (g m -3 ) Depth (m) Q air = m 3 s -1 Depth (m) Q air = m 3 s -1 Depth (m) Q air = m 3 s DO (g m -3 ) DO (g m -3 ) DO (g m -3 )
42 Bubble Plume (linear) Spring Hollow Reservoir Western Virginia Water Authority Virginia
43 Spring Hollow Reservoir
44 Observed Oxygen in SHR Elevation (m) DO (mg/l) Julian Day (2001)
45 Oxygenation at Spring Hollow Max depth: 62 m Surface Area: 0.6 km 2 Volume: m 3 DO demand: ~50 kg / day Diffuser length: 620 m Oxygen flow: 20 SCFM (~35Nm 3 /h) Mass addition: ~ 1000 kg/day Efficiency: %
46 Bubble Plume Courtesy of Mark Mobley
47 Observed Temperature Sep 9-Sep Sep Elevation (m) _ Elevation (ft) _ 16-Sep 23-Sep 27-Sep 4-Oct 11-Oct 18-Oct 25-Oct 29-Oct Nov Nov Nov Temperature (C)
48 Observed Dissolved Oxygen Sep 9-Sep Sep Sep Elevation (m) _ Elevation (ft) _ 23-Sep 27-Sep 4-Oct 11-Oct 18-Oct 25-Oct 29-Oct Nov Nov Nov DO (mg/l)
49 Idealized Bubble Plume
50 Plume Model Flux Equations Water Volume Momentum Temperature Salinity Dissolved Gas (O 2 & N 2 ) Gas (O 2 & N 2 ) dq E dz = ρa ρ ρ w w ρp = glw + gλ[ L W(1 λ) ] dm dz df ρ T a dz = ET p dfs E asa dz = ρ 2 dfdi 4rN π = ECai + K L (HiPi C i ) dz v + v 2 dfgi 4rN π = K L (H i P i C i ) dz v + vb b ρ p
51 Plume Model Test Conditions Parameter July 2003 (Air) August 2003 (Oxygen) October 2004 (Oxygen) O 2 in gas supply (%) Entrainment coefficient, α (-) Plume radius ratio, λ (-) Initial plume area (m 2 ) Gas flow rate (Nm 3 hr -1 ) Bubble diameter (mm) Diffuser depth (m)
52 Temperature and DO Contours Depth (m) Depth (m) 2 July ( o C) Distance from Diffuser (m) 2 July (g/m 3 ) Distance from Diffuser (m) Depth (m) Depth (m) 17 August October ( o C) Distance from Diffuser (m) 17 August (g/m 3 ) Distance from Diffuser (m) Depth (m) Depth (m) ( o C) Distance from Diffuser (m) 23 October (g/m 3 ) Distance from Diffuser (m)
53 Plume Boundary Conditions 0 a) 0 b) Depth (m) July Aug Oct Temperature ( ο C) Depth (m) July Aug Oct Dissolved Oxygen (g/m 3 )
54 Linear Plume Model Validation a) b) Depth (m) July Aug Oct 2004 Depth (m) July Aug Oct Plume Temperature ( ο C) Dissolved Oxygen (g/m 3 )
55 Bubble Plume (circular) Lake Hallwil Canton Aargau Switzerland
56 Lake Hallwil M2 30 N M km 20 10
57 Measurements CTD and ADCP
58 Temp ( o C) 24 July Depth (m) Distance from Diffuser (km) Depth (m) September Distance from Diffuser (km) 5.8
59 North velocity (mm/s) Persistent Seiching Depth: m m m m -50 Jun 13 Jun 15 Jun 17 Jun 19
60 DO (g m -3 ) July Depth (m) Distance from Diffuser (km) 0 Depth (m) September Distance from Diffuser (km)
61 Bubble Plume Diffuser
62 Temperature Contours Depth (m) Distance from center line (m) ( o C)
63 Oxygen Contours Depth (m) Distance from centerline (m) (gm -3 ) 0
64 Circular Plume Model Validation Depth (m) DO (g m -3 ) and Temperature ( C) Average Plume DO Predicted DO Average Plume Temperature Predicted Temperature
65 Story so far Why we need oxygenation How various devices work Suite of process models that we can use to predict performance Points to remember: All devices induce mixing in lake/reservoir Lake/reservoir influences performance of oxygenation system (especially bubble plume) Sediment oxygen demand drives oxygen consumption
66 Sediment Oxygen Demand SOD, which typically governs hypolimnetic DO depletion, often assumed constant Some oxygenation systems fail to meet reservoir oxygen demand due to diffuser-induced SOD
67 Carvin s Cove Reservoir Maximum depth (m) 23 Surface area (km 2 ) 2.5 Volume (m 3 ) Avg. length width (m)
68 Oxygenation at Carvin s Cove Dam B C A Diffuser lines Trophic status Eutrophic Oxygen demand (kg/day) ~ 430 Typical stratification period March thru November Diffuser length (m) 1250 (2 625 m diffuser lines)
69 Oxygenation System Photograph by Josh Meltzer Photograph by Josh Meltzer
70 Carvin s Cove Reservoir Soluble Fe Diffuser Installed Aug 1, 05 Off (Jun 15, 06) On (Jul 12, 06) Elevation (m) Jan-00 Jan-01 Jan-02 Jan-03 Jan-04 Jan-05 Jan-06 Jan
71 Carvin s Cove Reservoir Soluble Mn Diffuser Installed Aug 1, 05 Off (Jun 15, 06) On (Jul 12, 06) Elevation (m) Jan-00 Jan-01 Jan-02 Jan-03 Jan-04 Jan-05 Jan-06 Jan-07
72 Observed Temperature Jul 1-Aug 8-Aug 351 x Aug Elevation (m) Sample Location (x) Elevation (ft) 25-Aug 29-Aug 5-Sep 12-Sep 22-Sep 6-Oct Oct 20-Oct Oct Temperature (C) 3-Nov
73 Observed Dissolved Oxygen Jul 1-Aug 8-Aug 351 x Aug Elevation (m) Sample Location (x) Elevation (ft) 25-Aug 29-Aug 5-Sep 12-Sep 22-Sep 6-Oct Oct 20-Oct Oct DO (mg/l) 3-Nov
74 Calculated Oxygen Demand HODmass (kg day -1 ) _ CCR y = 22x SHR y = 6.3x Oxygen Flow Rate (NCMH) Carvins Cove Reservoir Spring Hollow Reservoir
75 Measurements Lander, ADCP and Peepers 1. Profiling lander with microsensors: O 2, temp, redox and ph at SWI 2. In-lab O 2 microsensor measurements of sediment cores: O 2 profile data 3. Acoustic Doppler current profiler: water column velocity profile data 4. Diffusive porewater analyzers (peepers): soluble Fe and Mn profile data Maximum depth (m) 23 Surface area (km 2 ) Volume (m 3 ) Avg. length width (m)
76 Sediment Oxygen Demand Turbulence within bottom boundary layer (BBL) controls diffusive boundary layer (DBL) thickness and sediment-water fluxes 3 2 BBL mixing depth (mm) DBL Sediment oxic zone, z max Fick' s First Flux O 2 (μmol L -1 ) Law of dc = φd dz C = φd Diffusion C δ bulk DBL SWI φ = porosity D = (unity in diffusion coefficient water)
77 Correlation between extent of sediment oxic zone and HOx flow rate 2.5 zmax-flow C3 avg R² = zmax-flow CVCB avg R² = z max (mm) Flow (m 3 hr -1 ) C3 Increased flow directly related to enhanced sediment oxic zone Analogous results from study on hypolimnetic O 2 demand CVCB 77
78 Carvin s Cove Reservoir HOx flow regime for summer Flow (m 3 hr -1 ) C Jun 1-Jul 15-Jul 29-Jul 12-Aug 26-Aug 9-Sep
79 Response of vertical O 2 distribution near the SWI and in the hypolimnion after turning HOx off Depth (m) c b -60 O 2 (μmol L -1 ) J O2 (mmol m -2 d -1 ), C SWI (10-1 μmol L -1 ) a JO2 J CswiC SWI DBL δ DBL HOx turned off DBL thickness, δ DBL (mm) 1E06 Depth (mm) Depth (mm) a SWI SWI /7 8/14 8/21 8/28 9/4 9/11 Time (m/d) 0
80 Variation in Fe and Mn at the SWI in response to HOx operations Soluble Fe 15 Soluble Mn Increased sediment O2 availability 120 d /29 Fe and Mn suppressed near SWI 15 Flow (m3 hr -1) During HOx operation: Depth (cm) a 6/8 7/18 8/27 10/ date (m/d) 4/29 11/15 6/8 7/18 8/27 10/ date (m/d) 11/ b e /29 6/8 7/18 8/27 10/ date (m/d) 11/ /8 7/18 8/27 10/ date (m/d) f /28 8/ date (m/d) 9/6 6/ / / /15 5 c /8 7/28 8/ date (m/d) 9/6 0 Flow (m3 hr -1) Depth (cm) 10 4/29 Flow (m3 hr -1) Depth (cm) 1300 Fe Mn (μmol L-1)
81 Reservoir Dynamics June 1, 06 Carvins Cove Dissolved Oxygen [Oxygenation: 68 NCMH (40 SCFM)] Intakes Open Elevation (m) SCFM increased to 40 SCFM Distance (m)
82 Reservoir Dynamics June 6, 06 Carvins Cove Dissolved Oxygen [Oxygenation: 68 NCMH (40 SCFM)] Intakes Open Elevation (m) Distance (m)
83 Use Si3D for Coupled Model Si3D is a 3-D, free surface hydrodynamic reservoir model Continuity equation for incompressible fluid Navier-Stokes equations for momentum Transport equation for temperature Extensively validated 3D Grid of Spring Hollow Reservoir in Si3D
84 Use Si3D for Coupled Model To couple the plume model with Si3D, sink and source terms were added Plume model predicts entrainment flow rate as well as detrainment flow rate Q d and depth Si3D provides boundary conditions for plume model Cell size = 15 m x 15 m x 1 m
85 Coupled Plume Model Validation Coupled model predictions with plume turned OFF Coupled model predictions with plume turned ON
86 Coupled Plume Model Prediction
87 Current Focus Complex reservoir dynamics coupled reservoir model that includes bubble plume + sediment oxygen demand In-situ oxidation of Fe and Mn and reduction of internal P loading Design and operation of sidestream supersaturation systems Potential control of algal growth with epilimnetic mixing
Hypolimnetic Oxygenation for Indian Creek Reservoir Restoration. Bill Faisst CA/NV AWWA Fall Conference October 22, 2014
 Hypolimnetic Oxygenation for Indian Creek Reservoir Restoration Bill Faisst CA/NV AWWA Fall Conference October 22, 14 Indian Creek Reservoir High desert lake Little runoff ~ acre foot volume Regulatory
Hypolimnetic Oxygenation for Indian Creek Reservoir Restoration Bill Faisst CA/NV AWWA Fall Conference October 22, 14 Indian Creek Reservoir High desert lake Little runoff ~ acre foot volume Regulatory
Interaction between a bubble plume and the near field in a stratified lake
 WATER RESOURCES RESEARCH, VOL. 40,, doi:10.1029/2004wr003038, 2004 Interaction between a bubble plume and the near field in a stratified lake D. F. McGinnis, 1,2 A. Lorke, 3 A. Wüest, 3 A. Stöckli, 4 and
WATER RESOURCES RESEARCH, VOL. 40,, doi:10.1029/2004wr003038, 2004 Interaction between a bubble plume and the near field in a stratified lake D. F. McGinnis, 1,2 A. Lorke, 3 A. Wüest, 3 A. Stöckli, 4 and
CTB3365x Introduction to Water Treatment
 CTB3365x Introduction to Water Treatment D4b Aeration Doris van Halem Did you know that there are not just gasses in your glass of sparkling coke, but also in the tap water you drink? Welcome to the water
CTB3365x Introduction to Water Treatment D4b Aeration Doris van Halem Did you know that there are not just gasses in your glass of sparkling coke, but also in the tap water you drink? Welcome to the water
Modeling of Oxygen Injection Experiment in Savannah Harbor
 593 Modeling of Oxygen Injection Experiment in Savannah Harbor S. Davie 1, H. Moorer 2, H. Rodriguez 1, Y. Plis 1 1 Tetra Tech, Inc., 2110 Powers Ferry Road, Suite 202, Atlanta, GA 30339, PH (770) 850-0949;
593 Modeling of Oxygen Injection Experiment in Savannah Harbor S. Davie 1, H. Moorer 2, H. Rodriguez 1, Y. Plis 1 1 Tetra Tech, Inc., 2110 Powers Ferry Road, Suite 202, Atlanta, GA 30339, PH (770) 850-0949;
Aerobic reoxidation in marine sediments
 Aerobic reoxidation in marine sediments This exercise consists of three small experiments\demonstrations that should be run in parallel. Read the whole description and divide the work between the members
Aerobic reoxidation in marine sediments This exercise consists of three small experiments\demonstrations that should be run in parallel. Read the whole description and divide the work between the members
Wind Regimes 1. 1 Wind Regimes
 Wind Regimes 1 1 Wind Regimes The proper design of a wind turbine for a site requires an accurate characterization of the wind at the site where it will operate. This requires an understanding of the sources
Wind Regimes 1 1 Wind Regimes The proper design of a wind turbine for a site requires an accurate characterization of the wind at the site where it will operate. This requires an understanding of the sources
DRINKING WATER - LAB EXPERIMENTS LAB EXPERIMENTS. Nanofiltration
 DRINKING WATER - LAB EXPERIMENTS LAB EXPERIMENTS Nanofiltration nanofiltration lab experiments Framework This module explains the lab experiment on nanofiltration. Contents This module has the following
DRINKING WATER - LAB EXPERIMENTS LAB EXPERIMENTS Nanofiltration nanofiltration lab experiments Framework This module explains the lab experiment on nanofiltration. Contents This module has the following
Hamurana Stream water movement in Lake Rotorua
 Hamurana Stream water movement in Lake Rotorua NIWA Client Report: HAM2007-031 March 2007 NIWA Project: BOP06211 Hamurana Stream water movement in Lake Rotorua Max Gibbs Eddie Bowman John Nagels Prepared
Hamurana Stream water movement in Lake Rotorua NIWA Client Report: HAM2007-031 March 2007 NIWA Project: BOP06211 Hamurana Stream water movement in Lake Rotorua Max Gibbs Eddie Bowman John Nagels Prepared
Exploring Localized Mixing Dynamics During Wet Weather in a Tidal Fresh Water System
 Exploring Localized Mixing Dynamics During Wet Weather in a Tidal Fresh Water System Ramona McCullough & Phil Duzinski Delaware Estuary Science & Environmental Summit January 27, 2015 Background and objectives
Exploring Localized Mixing Dynamics During Wet Weather in a Tidal Fresh Water System Ramona McCullough & Phil Duzinski Delaware Estuary Science & Environmental Summit January 27, 2015 Background and objectives
PHYS 101 Previous Exam Problems
 PHYS 101 Previous Exam Problems CHAPTER 14 Fluids Fluids at rest pressure vs. depth Pascal s principle Archimedes s principle Buoynat forces Fluids in motion: Continuity & Bernoulli equations 1. How deep
PHYS 101 Previous Exam Problems CHAPTER 14 Fluids Fluids at rest pressure vs. depth Pascal s principle Archimedes s principle Buoynat forces Fluids in motion: Continuity & Bernoulli equations 1. How deep
Lecture 8 questions and answers The Biological Pump
 Lecture 8 questions and answers The Biological Pump (1) How long would it take a particle of about 2micron in size and a density of 1.5 g/cm 3 to get to the bottom of the sea (4000m)? How do particles
Lecture 8 questions and answers The Biological Pump (1) How long would it take a particle of about 2micron in size and a density of 1.5 g/cm 3 to get to the bottom of the sea (4000m)? How do particles
SWI NAPL Recovery. Cemcor Environmental Services. represented by. Contact: Craig Marlow Phone Cell
 SWI NAPL Recovery represented by Cemcor Environmental Services Contact: Craig Marlow Phone 419.867.8966 Cell 419.349.7970 Email cemarlow@att.net Physical mechanisms of SWI Injection in the saturated zone
SWI NAPL Recovery represented by Cemcor Environmental Services Contact: Craig Marlow Phone 419.867.8966 Cell 419.349.7970 Email cemarlow@att.net Physical mechanisms of SWI Injection in the saturated zone
Old-Exam.Questions-Ch-14 T072 T071
 Old-Exam.Questions-Ch-14 T072 Q23. Water is pumped out of a swimming pool at a speed of 5.0 m/s through a uniform hose of radius 1.0 cm. Find the mass of water pumped out of the pool in one minute. (Density
Old-Exam.Questions-Ch-14 T072 Q23. Water is pumped out of a swimming pool at a speed of 5.0 m/s through a uniform hose of radius 1.0 cm. Find the mass of water pumped out of the pool in one minute. (Density
The ventilated filling box containing a vertically distributed source of buoyancy
 University of Wollongong Research Online Faculty of Engineering - Papers (Archive) Faculty of Engineering and Information Sciences 2010 The ventilated filling box containing a vertically distributed source
University of Wollongong Research Online Faculty of Engineering - Papers (Archive) Faculty of Engineering and Information Sciences 2010 The ventilated filling box containing a vertically distributed source
Study on Fire Plume in Large Spaces Using Ground Heating
 Available online at www.sciencedirect.com Procedia Engineering 11 (2011) 226 232 The 5 th Conference on Performance-based Fire and Fire Protection Engineering Study on Fire Plume in Large Spaces Using
Available online at www.sciencedirect.com Procedia Engineering 11 (2011) 226 232 The 5 th Conference on Performance-based Fire and Fire Protection Engineering Study on Fire Plume in Large Spaces Using
Forest Winds in Complex Terrain
 Forest Winds in Complex Terrain Ilda Albuquerque 1 Contents Project Description Motivation Forest Complex Terrain Forested Complex Terrain 2 Project Description WAUDIT (Wind Resource Assessment Audit and
Forest Winds in Complex Terrain Ilda Albuquerque 1 Contents Project Description Motivation Forest Complex Terrain Forested Complex Terrain 2 Project Description WAUDIT (Wind Resource Assessment Audit and
Energy and mass transfer in gas-liquid reactors.
 Energy and mass transfer in gas-liquid reactors. John M Smith School of Engineering (D2) University of Surrey, Guildford GU2 7XH, UK j.smith@surrey.ac.uk 1 Energy and mass transfer in gas-liquid reactors.
Energy and mass transfer in gas-liquid reactors. John M Smith School of Engineering (D2) University of Surrey, Guildford GU2 7XH, UK j.smith@surrey.ac.uk 1 Energy and mass transfer in gas-liquid reactors.
CROSS-SHORE SEDIMENT PROCESSES
 The University of the West Indies Organization of American States PROFESSIONAL DEVELOPMENT PROGRAMME: COASTAL INFRASTRUCTURE DESIGN, CONSTRUCTION AND MAINTENANCE A COURSE IN COASTAL DEFENSE SYSTEMS I CHAPTER
The University of the West Indies Organization of American States PROFESSIONAL DEVELOPMENT PROGRAMME: COASTAL INFRASTRUCTURE DESIGN, CONSTRUCTION AND MAINTENANCE A COURSE IN COASTAL DEFENSE SYSTEMS I CHAPTER
Development of High-speed Gas Dissolution Device
 Development of High-speed Gas Dissolution Device Yoichi Nakano*, Atsushi Suehiro**, Tetsuhiko Fujisato***, Jun Ma**** Kesayoshi Hadano****, Masayuki Fukagawa***** *Ube National College of Technology, Tokiwadai
Development of High-speed Gas Dissolution Device Yoichi Nakano*, Atsushi Suehiro**, Tetsuhiko Fujisato***, Jun Ma**** Kesayoshi Hadano****, Masayuki Fukagawa***** *Ube National College of Technology, Tokiwadai
. In an elevator accelerating upward (A) both the elevator accelerating upward (B) the first is equations are valid
 IIT JEE Achiever 2014 Ist Year Physics-2: Worksheet-1 Date: 2014-06-26 Hydrostatics 1. A liquid can easily change its shape but a solid cannot because (A) the density of a liquid is smaller than that of
IIT JEE Achiever 2014 Ist Year Physics-2: Worksheet-1 Date: 2014-06-26 Hydrostatics 1. A liquid can easily change its shape but a solid cannot because (A) the density of a liquid is smaller than that of
ENVE 301 Environmental Engineering Unit Operations
 ENVE 301 Environmental Engineering Unit Operations Lecture 5 Gas Transfer, Aeration II SPRING 2014 Assist. Prof. A. Evren Tugtas Gas Transfer Examples 2 Example 1: Gas Transfer - Problems Henry s law constant
ENVE 301 Environmental Engineering Unit Operations Lecture 5 Gas Transfer, Aeration II SPRING 2014 Assist. Prof. A. Evren Tugtas Gas Transfer Examples 2 Example 1: Gas Transfer - Problems Henry s law constant
IMPROVING PLANT AERATION USING GAS INFUSION TECHNOLOGY
 IMPROVING PLANT AERATION USING GAS INFUSION TECHNOLOGY AERATION IN WASTEWATER Municipal sewer collection systems-odor Mgmt. Lift and transfer stations Lagoons / Retention Ponds BOD / COD treatment Enhanced
IMPROVING PLANT AERATION USING GAS INFUSION TECHNOLOGY AERATION IN WASTEWATER Municipal sewer collection systems-odor Mgmt. Lift and transfer stations Lagoons / Retention Ponds BOD / COD treatment Enhanced
Workshop 1: Bubbly Flow in a Rectangular Bubble Column. Multiphase Flow Modeling In ANSYS CFX Release ANSYS, Inc. WS1-1 Release 14.
 Workshop 1: Bubbly Flow in a Rectangular Bubble Column 14. 5 Release Multiphase Flow Modeling In ANSYS CFX 2013 ANSYS, Inc. WS1-1 Release 14.5 Introduction This workshop models the dispersion of air bubbles
Workshop 1: Bubbly Flow in a Rectangular Bubble Column 14. 5 Release Multiphase Flow Modeling In ANSYS CFX 2013 ANSYS, Inc. WS1-1 Release 14.5 Introduction This workshop models the dispersion of air bubbles
B. U-Tube Pilot Study
 B. U-Tube Pilot Study Deep U-Tubes offer excellent potential as energy and cost efficient oxygen transfer systems. The depths of 25 to 60 m appear to be most useful for optimal oxygen absorption. U-Tubes
B. U-Tube Pilot Study Deep U-Tubes offer excellent potential as energy and cost efficient oxygen transfer systems. The depths of 25 to 60 m appear to be most useful for optimal oxygen absorption. U-Tubes
Prairie Farm Rehabilitation Administration Paper
 Prairie Farm Rehabilitation Administration Paper Performance Characteristics of Aeration Devices W.C. Mackay *, T.G. Miller *, D.R. Moore 1 & R. Woelcke 1 * Department of Biological Sciences Department,
Prairie Farm Rehabilitation Administration Paper Performance Characteristics of Aeration Devices W.C. Mackay *, T.G. Miller *, D.R. Moore 1 & R. Woelcke 1 * Department of Biological Sciences Department,
Variation of Pressure with Depth in a Fluid *
 OpenStax-CNX module: m42192 1 Variation of Pressure with Depth in a Fluid * OpenStax This work is produced by OpenStax-CNX and licensed under the Creative Commons Attribution License 3.0 Abstract Dene
OpenStax-CNX module: m42192 1 Variation of Pressure with Depth in a Fluid * OpenStax This work is produced by OpenStax-CNX and licensed under the Creative Commons Attribution License 3.0 Abstract Dene
Irrigation &Hydraulics Department lb / ft to kg/lit.
 CAIRO UNIVERSITY FLUID MECHANICS Faculty of Engineering nd Year CIVIL ENG. Irrigation &Hydraulics Department 010-011 1. FLUID PROPERTIES 1. Identify the dimensions and units for the following engineering
CAIRO UNIVERSITY FLUID MECHANICS Faculty of Engineering nd Year CIVIL ENG. Irrigation &Hydraulics Department 010-011 1. FLUID PROPERTIES 1. Identify the dimensions and units for the following engineering
Modelling of bubble plume destratification using DYRESM
 37 IWA Publishing 2005 Journal of Water Supply: Research and Technology AQUA 54.1 2005 Modelling of bubble plume destratification using DYRESM Hengameh Moshfeghi, Amir Etemad-Shahidi and Jorg Imberger
37 IWA Publishing 2005 Journal of Water Supply: Research and Technology AQUA 54.1 2005 Modelling of bubble plume destratification using DYRESM Hengameh Moshfeghi, Amir Etemad-Shahidi and Jorg Imberger
The water supply for a hydroelectric plant is a reservoir with a large surface area. An outlet pipe takes the water to a turbine.
 Fluids 1a. [1 mark] The water supply for a hydroelectric plant is a reservoir with a large surface area. An outlet pipe takes the water to a turbine. State the difference in terms of the velocity of the
Fluids 1a. [1 mark] The water supply for a hydroelectric plant is a reservoir with a large surface area. An outlet pipe takes the water to a turbine. State the difference in terms of the velocity of the
Deep water plume models - What s special about deep water
 Deep water plume models - What s special about deep water Øistein Johansen Senior scientist SINTEF Marine Environmental Technology Deep water blowouts - knowledge basis Present knowledge based on General
Deep water plume models - What s special about deep water Øistein Johansen Senior scientist SINTEF Marine Environmental Technology Deep water blowouts - knowledge basis Present knowledge based on General
The Effects of Stir Speed, Airflow Rate, Diffusers, and Volume on. Water Aeration
 The Effects of Stir Speed, Airflow Rate, Diffusers, and Volume on Water Aeration Cycle 3 - Group B1 Group Leader: David Nguyen Katarina Van Wonterghem Joseph Jimenez Justin Chung CBEMS 140A University
The Effects of Stir Speed, Airflow Rate, Diffusers, and Volume on Water Aeration Cycle 3 - Group B1 Group Leader: David Nguyen Katarina Van Wonterghem Joseph Jimenez Justin Chung CBEMS 140A University
Influence of rounding corners on unsteady flow and heat transfer around a square cylinder
 Influence of rounding corners on unsteady flow and heat transfer around a square cylinder S. K. Singh Deptt. of Mech. Engg., M. B. M. Engg. College / J. N. V. University, Jodhpur, Rajasthan, India Abstract
Influence of rounding corners on unsteady flow and heat transfer around a square cylinder S. K. Singh Deptt. of Mech. Engg., M. B. M. Engg. College / J. N. V. University, Jodhpur, Rajasthan, India Abstract
Fall 2004 Homework Problem Set 9 Due Wednesday, November 24, at start of class
 0.30 Fall 004 Homework Problem Set 9 Due Wednesday, November 4, at start of class Part A. Consider an iron surface which serves as a catalyst for the production of ammonia from nitrogen and hydrogen. The
0.30 Fall 004 Homework Problem Set 9 Due Wednesday, November 4, at start of class Part A. Consider an iron surface which serves as a catalyst for the production of ammonia from nitrogen and hydrogen. The
FIU Digital Commons. Florida International University. Henry O. Briceño Florida International University,
 Florida International University FIU Digital Commons SERC Research Reports Southeast Environmental Research Center 2015 Water Quality Monitoring Project for Demonstration of Canal Remediation Methods Florida
Florida International University FIU Digital Commons SERC Research Reports Southeast Environmental Research Center 2015 Water Quality Monitoring Project for Demonstration of Canal Remediation Methods Florida
Computational Analysis of Oil Spill in Shallow Water due to Wave and Tidal Motion Madhu Agrawal Durai Dakshinamoorthy
 Computational Analysis of Oil Spill in Shallow Water due to Wave and Tidal Motion Madhu Agrawal Durai Dakshinamoorthy 1 OUTLINE Overview of Oil Spill & its Impact Technical Challenges for Modeling Review
Computational Analysis of Oil Spill in Shallow Water due to Wave and Tidal Motion Madhu Agrawal Durai Dakshinamoorthy 1 OUTLINE Overview of Oil Spill & its Impact Technical Challenges for Modeling Review
Measurements of k L a. Steady-State Mass Balance Method:
 Measurements of k a Steady-State Mass Balance Method: In theory, the K a in an apparatus that is operating continuously under steady-state conditions could be evaluated from the flow rates and the concentrations
Measurements of k a Steady-State Mass Balance Method: In theory, the K a in an apparatus that is operating continuously under steady-state conditions could be evaluated from the flow rates and the concentrations
CTB3365x Introduction to Water Treatment
 CTB3365x Introduction to Water Treatment W4e Aeration Merle de Kreuk There is one last thing of the biological part that needs some design. As you know, nitrifyers need oxygen, and also the heterotrophs,
CTB3365x Introduction to Water Treatment W4e Aeration Merle de Kreuk There is one last thing of the biological part that needs some design. As you know, nitrifyers need oxygen, and also the heterotrophs,
Lecture 19 Fluids: density, pressure, Pascal s principle and Buoyancy.
 Lecture 19 Water tower Fluids: density, pressure, Pascal s principle and Buoyancy. Hydraulic press Pascal s vases Barometer What is a fluid? Fluids are substances that flow. substances that take the shape
Lecture 19 Water tower Fluids: density, pressure, Pascal s principle and Buoyancy. Hydraulic press Pascal s vases Barometer What is a fluid? Fluids are substances that flow. substances that take the shape
Water Treatment: Fundamentals and Practical Implications of Bubble Formation
 Water Treatment: Fundamentals and Practical Implications of Bubble Formation Paolo Scardina Thesis submitted to the Faculty of the Virginia Polytechnic Institute and State University In partial fulfillment
Water Treatment: Fundamentals and Practical Implications of Bubble Formation Paolo Scardina Thesis submitted to the Faculty of the Virginia Polytechnic Institute and State University In partial fulfillment
An experimental study of internal wave generation through evanescent regions
 An experimental study of internal wave generation through evanescent regions Allison Lee, Julie Crockett Department of Mechanical Engineering Brigham Young University Abstract Internal waves are a complex
An experimental study of internal wave generation through evanescent regions Allison Lee, Julie Crockett Department of Mechanical Engineering Brigham Young University Abstract Internal waves are a complex
1. All fluids are: A. gases B. liquids C. gases or liquids D. non-metallic E. transparent ans: C
 Chapter 14: FLUIDS 1 All fluids are: A gases B liquids C gases or liquids D non-metallic E transparent 2 Gases may be distinguished from other forms of matter by their: A lack of color B small atomic weights
Chapter 14: FLUIDS 1 All fluids are: A gases B liquids C gases or liquids D non-metallic E transparent 2 Gases may be distinguished from other forms of matter by their: A lack of color B small atomic weights
Comparison of stepped and smooth spillway effects on stream reaeration
 Comparison of stepped and smooth spillway effects on stream reaeration Egemen Aras 1* and Mehmet Berkun 2 1 Gumushane University, Department of Civil Engineering, Gumushane 29100, Turkey 2 Karadeniz Technical
Comparison of stepped and smooth spillway effects on stream reaeration Egemen Aras 1* and Mehmet Berkun 2 1 Gumushane University, Department of Civil Engineering, Gumushane 29100, Turkey 2 Karadeniz Technical
ANSWERS TO QUESTIONS IN THE NOTES AUTUMN 2018
 ANSWERS TO QUESTIONS IN THE NOTES AUTUMN 2018 Section 1.2 Example. The discharge in a channel with bottom width 3 m is 12 m 3 s 1. If Manning s n is 0.013 m -1/3 s and the streamwise slope is 1 in 200,
ANSWERS TO QUESTIONS IN THE NOTES AUTUMN 2018 Section 1.2 Example. The discharge in a channel with bottom width 3 m is 12 m 3 s 1. If Manning s n is 0.013 m -1/3 s and the streamwise slope is 1 in 200,
Large-eddy simulation of a turbulent buoyant helium plume
 Center for Turbulence Research Annual Research Briefs 8 45 Large-eddy simulation of a turbulent buoyant helium plume By G. Blanquart AND H. Pitsch. Motivation and objectives The numerical simulation of
Center for Turbulence Research Annual Research Briefs 8 45 Large-eddy simulation of a turbulent buoyant helium plume By G. Blanquart AND H. Pitsch. Motivation and objectives The numerical simulation of
An Atlas of Oceanic Internal Solitary Waves (February 2004) by Global Ocean Associates Prepared for Office of Naval Research Code 322 PO
 Overview The is located in the North Atlantic Ocean between southern Ireland and southwest England (Figure 1). The Sea s western edge covers a continental shelf region characterized by rough and irregular
Overview The is located in the North Atlantic Ocean between southern Ireland and southwest England (Figure 1). The Sea s western edge covers a continental shelf region characterized by rough and irregular
ZIN Technologies PHi Engineering Support. PHi-RPT CFD Analysis of Large Bubble Mixing. June 26, 2006
 ZIN Technologies PHi Engineering Support PHi-RPT-0002 CFD Analysis of Large Bubble Mixing Proprietary ZIN Technologies, Inc. For nearly five decades, ZIN Technologies has provided integrated products and
ZIN Technologies PHi Engineering Support PHi-RPT-0002 CFD Analysis of Large Bubble Mixing Proprietary ZIN Technologies, Inc. For nearly five decades, ZIN Technologies has provided integrated products and
3. A fluid is forced through a pipe of changing cross section as shown. In which section would the pressure of the fluid be a minimum?
 AP Physics Multiple Choice Practice Fluid Mechanics 1. A cork has weight mg and density 5% of water s density. A string is tied around the cork and attached to the bottom of a water-filled container. The
AP Physics Multiple Choice Practice Fluid Mechanics 1. A cork has weight mg and density 5% of water s density. A string is tied around the cork and attached to the bottom of a water-filled container. The
Laser-Induced Bubbles in Glycerol-Water Mixtures
 Laser-Induced Bubbles in Glycerol-Water Mixtures Allison R. McCarn, Erin M. Englert, and Gary A. Williams Department of Physics and Astronomy, University of California, Los Angeles, California 90095, USA
Laser-Induced Bubbles in Glycerol-Water Mixtures Allison R. McCarn, Erin M. Englert, and Gary A. Williams Department of Physics and Astronomy, University of California, Los Angeles, California 90095, USA
ISOLATION OF NON-HYDROSTATIC REGIONS WITHIN A BASIN
 ISOLATION OF NON-HYDROSTATIC REGIONS WITHIN A BASIN Bridget M. Wadzuk 1 (Member, ASCE) and Ben R. Hodges 2 (Member, ASCE) ABSTRACT Modeling of dynamic pressure appears necessary to achieve a more robust
ISOLATION OF NON-HYDROSTATIC REGIONS WITHIN A BASIN Bridget M. Wadzuk 1 (Member, ASCE) and Ben R. Hodges 2 (Member, ASCE) ABSTRACT Modeling of dynamic pressure appears necessary to achieve a more robust
Effects of a Surface Circulator on Temperature, Dissolved Oxygen, Water Velocity, and. Photosynthetic Yield in Falling Creek Reservoir
 Effects of a Surface Circulator on Temperature, Dissolved Oxygen, Water Velocity, and Photosynthetic Yield in Falling Creek Reservoir Kevin Patrick Elam Thesis submitted to the faculty of the Virginia
Effects of a Surface Circulator on Temperature, Dissolved Oxygen, Water Velocity, and Photosynthetic Yield in Falling Creek Reservoir Kevin Patrick Elam Thesis submitted to the faculty of the Virginia
BASIC PHYSICS APPLIED TO ANAESTHESIOLOGY
 BASIC PHYSICS APPLIED TO ANAESTHESIOLOGY Dr.R.Selvakumar.M.D.D.A.DNB Professor of Anaesthesiology, K.A.P.Viswanatham Govt medical college, Trichy. The current practice of Anaesthesiology demands knowledge
BASIC PHYSICS APPLIED TO ANAESTHESIOLOGY Dr.R.Selvakumar.M.D.D.A.DNB Professor of Anaesthesiology, K.A.P.Viswanatham Govt medical college, Trichy. The current practice of Anaesthesiology demands knowledge
A Tracer Investigation of. Aerated Water Dispersion and Tidal Exchange in. the San Joaquin River and Stockton Ship Channel
 A Tracer Investigation of Aerated Water Dispersion and Tidal Exchange in the San Joaquin River and Stockton Ship Channel Prepared for: Jones & Stokes Sacramento, California Contact: Russ Grimes Prepared
A Tracer Investigation of Aerated Water Dispersion and Tidal Exchange in the San Joaquin River and Stockton Ship Channel Prepared for: Jones & Stokes Sacramento, California Contact: Russ Grimes Prepared
The activated sludge process
 The activated sludge process Most wastewater treatment plants are using the activated sludge process. The heart of such a process mainly consists of an aeration tank, a sedimentation tank or clarifier
The activated sludge process Most wastewater treatment plants are using the activated sludge process. The heart of such a process mainly consists of an aeration tank, a sedimentation tank or clarifier
UTILIZATION OF LEAKY PIPES AS AERATION SYSTEM FOR AQUACULTURE
 UTILIZATION OF LEAKY PIPES AS AERATION SYSTEM FOR AQUACULTURE SAMIR AHMAD ALI ABSTRACT This paper aims to study the possibility of using the leaky pipes as a diffused-air aeration in the aquacultural systems.
UTILIZATION OF LEAKY PIPES AS AERATION SYSTEM FOR AQUACULTURE SAMIR AHMAD ALI ABSTRACT This paper aims to study the possibility of using the leaky pipes as a diffused-air aeration in the aquacultural systems.
1. The principle of fluid pressure that is used in hydraulic brakes or lifts is that:
 University Physics (Prof. David Flory) Chapt_15 Thursday, November 15, 2007 Page 1 Name: Date: 1. The principle of fluid pressure that is used in hydraulic brakes or lifts is that: A) pressure is the same
University Physics (Prof. David Flory) Chapt_15 Thursday, November 15, 2007 Page 1 Name: Date: 1. The principle of fluid pressure that is used in hydraulic brakes or lifts is that: A) pressure is the same
Chapter 9 Fluids and Buoyant Force
 Chapter 9 Fluids and Buoyant Force In Physics, liquids and gases are collectively called fluids. 3/0/018 8:56 AM 1 Fluids and Buoyant Force Formula for Mass Density density mass volume m V water 1000 kg
Chapter 9 Fluids and Buoyant Force In Physics, liquids and gases are collectively called fluids. 3/0/018 8:56 AM 1 Fluids and Buoyant Force Formula for Mass Density density mass volume m V water 1000 kg
AIRFLOW GENERATION IN A TUNNEL USING A SACCARDO VENTILATION SYSTEM AGAINST THE BUOYANCY EFFECT PRODUCED BY A FIRE
 - 247 - AIRFLOW GENERATION IN A TUNNEL USING A SACCARDO VENTILATION SYSTEM AGAINST THE BUOYANCY EFFECT PRODUCED BY A FIRE J D Castro a, C W Pope a and R D Matthews b a Mott MacDonald Ltd, St Anne House,
- 247 - AIRFLOW GENERATION IN A TUNNEL USING A SACCARDO VENTILATION SYSTEM AGAINST THE BUOYANCY EFFECT PRODUCED BY A FIRE J D Castro a, C W Pope a and R D Matthews b a Mott MacDonald Ltd, St Anne House,
Numerical Investigation of Air Bubbles Evolution and Coalescence from Submerged Orifices Based on OpenFOAM
 Numerical Investigation of Air Bubbles Evolution and Coalescence from Submerged Orifices Based on OpenFOAM Pan Feng, He Ying, Li-zhong Mu 2018-7-6 Dalian University of Technology, China Outline Background
Numerical Investigation of Air Bubbles Evolution and Coalescence from Submerged Orifices Based on OpenFOAM Pan Feng, He Ying, Li-zhong Mu 2018-7-6 Dalian University of Technology, China Outline Background
Generating Calibration Gas Standards
 Technical Note 1001 Metronics Inc. Generating Calibration Gas Standards with Dynacal Permeation Devices Permeation devices provide an excellent method of producing known gas concentrations in the PPM and
Technical Note 1001 Metronics Inc. Generating Calibration Gas Standards with Dynacal Permeation Devices Permeation devices provide an excellent method of producing known gas concentrations in the PPM and
Dynamics of bubble rising at small Reynolds numbers
 MATEC Web of Conferences 3, 01004 ( 015) DOI: 10.1051/ matecconf/ 015301004 C Owned by the authors, published by EDP Sciences, 015 Dynamics of bubble rising at small Reynolds numbers Vladimir Arkhipov
MATEC Web of Conferences 3, 01004 ( 015) DOI: 10.1051/ matecconf/ 015301004 C Owned by the authors, published by EDP Sciences, 015 Dynamics of bubble rising at small Reynolds numbers Vladimir Arkhipov
Permeability. Darcy's Law
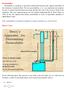 Permeability Permeability is a property of the porous medium that measures the capacity and ability of the formation to transmit fluids. The rock permeability, k, is a very important rock property because
Permeability Permeability is a property of the porous medium that measures the capacity and ability of the formation to transmit fluids. The rock permeability, k, is a very important rock property because
Student name: + is valid for C =. The vorticity
 13.012 Marine Hydrodynamics for Ocean Engineers Fall 2004 Quiz #1 Student name: This is a closed book examination. You are allowed 1 sheet of 8.5 x 11 paper with notes. For the problems in Section A, fill
13.012 Marine Hydrodynamics for Ocean Engineers Fall 2004 Quiz #1 Student name: This is a closed book examination. You are allowed 1 sheet of 8.5 x 11 paper with notes. For the problems in Section A, fill
Properties. terc.ucdavis.edu 8
 Physical Properties 8 Lake surface level Daily since 1900 The lowest lake level on record was 6,220.26 feet on Nov. 30, 1992. Since 1900, lake level has varied by more than 10 feet. Lake level typically
Physical Properties 8 Lake surface level Daily since 1900 The lowest lake level on record was 6,220.26 feet on Nov. 30, 1992. Since 1900, lake level has varied by more than 10 feet. Lake level typically
Experimental Investigation Of Flow Past A Rough Surfaced Cylinder
 (AET- 29th March 214) RESEARCH ARTICLE OPEN ACCESS Experimental Investigation Of Flow Past A Rough Surfaced Cylinder Monalisa Mallick 1, A. Kumar 2 1 (Department of Civil Engineering, National Institute
(AET- 29th March 214) RESEARCH ARTICLE OPEN ACCESS Experimental Investigation Of Flow Past A Rough Surfaced Cylinder Monalisa Mallick 1, A. Kumar 2 1 (Department of Civil Engineering, National Institute
Physics 7b Midterm Exam #1 Fall Name: Disc. Section SID
 Physics 7b Midterm Exam #1 Fall 2004 Name: Disc. Section SID #1 #2 #3 #4 #5 Total M w of O 2 = 32 g/mol, k b =1.38x10-23 J/K, N A =6x10 23 The weight of a 1kg mass on the Earth s surface is 2.2pounds.
Physics 7b Midterm Exam #1 Fall 2004 Name: Disc. Section SID #1 #2 #3 #4 #5 Total M w of O 2 = 32 g/mol, k b =1.38x10-23 J/K, N A =6x10 23 The weight of a 1kg mass on the Earth s surface is 2.2pounds.
Total Dissolved Gas Properties and Processes. by Mike Schneider US Army Corps of Engineers Engineer Research and Development Center
 Total Dissolved Gas Properties and Processes by Mike Schneider US Army Corps of Engineers Engineer Research and Development Center TDG Properties and Processes Scope of Discussion Physical Properties of
Total Dissolved Gas Properties and Processes by Mike Schneider US Army Corps of Engineers Engineer Research and Development Center TDG Properties and Processes Scope of Discussion Physical Properties of
An innovative technology for Coriolis metering under entrained gas conditions
 An innovative technology for Coriolis metering under entrained gas conditions Coriolis mass flowmeters are usually only used for single-phase fluids, i.e. either liquids or gases, since it has been found
An innovative technology for Coriolis metering under entrained gas conditions Coriolis mass flowmeters are usually only used for single-phase fluids, i.e. either liquids or gases, since it has been found
Undertow - Zonation of Flow in Broken Wave Bores
 Nearshore Circulation Undertow and Rip Cells Undertow - Zonation of Flow in Broken Wave Bores In the wave breaking process, the landward transfer of water, associated with bore and surface roller decay
Nearshore Circulation Undertow and Rip Cells Undertow - Zonation of Flow in Broken Wave Bores In the wave breaking process, the landward transfer of water, associated with bore and surface roller decay
IBERIAN SPH 2015 SPH MODELLING FOR AIR ENTRAINMENT IN WAVE BREAKING
 IBERIAN SPH 2015 SPH MODELLING FOR AIR ENTRAINMENT IN WAVE BREAKING DIOGO R.C.B. NEVES OBJECTIVES The work here performed is part of the PhD thesis on Air entrainment in wave breaking: experimental analysis
IBERIAN SPH 2015 SPH MODELLING FOR AIR ENTRAINMENT IN WAVE BREAKING DIOGO R.C.B. NEVES OBJECTIVES The work here performed is part of the PhD thesis on Air entrainment in wave breaking: experimental analysis
Advanced Hydraulics Prof. Dr. Suresh A. Kartha Department of Civil Engineering Indian Institute of Technology, Guwahati
 Advanced Hydraulics Prof. Dr. Suresh A. Kartha Department of Civil Engineering Indian Institute of Technology, Guwahati Module - 4 Hydraulic Jumps Lecture - 1 Rapidly Varied Flow- Introduction Welcome
Advanced Hydraulics Prof. Dr. Suresh A. Kartha Department of Civil Engineering Indian Institute of Technology, Guwahati Module - 4 Hydraulic Jumps Lecture - 1 Rapidly Varied Flow- Introduction Welcome
Temperature, salinity, density, and the oceanic pressure field
 Chapter 2 Temperature, salinity, density, and the oceanic pressure field The ratios of the many components which make up the salt in the ocean are remarkably constant, and salinity, the total salt content
Chapter 2 Temperature, salinity, density, and the oceanic pressure field The ratios of the many components which make up the salt in the ocean are remarkably constant, and salinity, the total salt content
OPTIMIZING THE LENGTH OF AIR SUPPLY DUCT IN CROSS CONNECTIONS OF GOTTHARD BASE TUNNEL. Rehan Yousaf 1, Oliver Scherer 1
 OPTIMIZING THE LENGTH OF AIR SUPPLY DUCT IN CROSS CONNECTIONS OF GOTTHARD BASE TUNNEL Rehan Yousaf 1, Oliver Scherer 1 1 Pöyry Infra Ltd, Zürich, Switzerland ABSTRACT Gotthard Base Tunnel with its 57 km
OPTIMIZING THE LENGTH OF AIR SUPPLY DUCT IN CROSS CONNECTIONS OF GOTTHARD BASE TUNNEL Rehan Yousaf 1, Oliver Scherer 1 1 Pöyry Infra Ltd, Zürich, Switzerland ABSTRACT Gotthard Base Tunnel with its 57 km
Undertow - Zonation of Flow in Broken Wave Bores
 Lecture 22 Nearshore Circulation Undertow - Zonation of Flow in Broken Wave Bores In the wave breaking process, the landward transfer of water, associated with bore and surface roller decay within the
Lecture 22 Nearshore Circulation Undertow - Zonation of Flow in Broken Wave Bores In the wave breaking process, the landward transfer of water, associated with bore and surface roller decay within the
Novelty of Mechanical Surface Aerator Using Flexible Beam to Generate Dissolved Oxygen in Water
 79 UMTAS 2013 Novelty of Mechanical Surface Aerator Using Flexible Beam to Generate Dissolved Oxygen in Water Muhammad Amir Mat Shah 1,* and Badrul Aisham Md Zain 2 Faculty of Mechanical and Manufacturing
79 UMTAS 2013 Novelty of Mechanical Surface Aerator Using Flexible Beam to Generate Dissolved Oxygen in Water Muhammad Amir Mat Shah 1,* and Badrul Aisham Md Zain 2 Faculty of Mechanical and Manufacturing
Bioreactor System ERT 314. Sidang /2011
 Bioreactor System ERT 314 Sidang 1 2010/2011 Chapter 2:Types of Bioreactors Week 4 Flow Patterns in Agitated Tanks The flow pattern in an agitated tank depends on the impeller design, the properties of
Bioreactor System ERT 314 Sidang 1 2010/2011 Chapter 2:Types of Bioreactors Week 4 Flow Patterns in Agitated Tanks The flow pattern in an agitated tank depends on the impeller design, the properties of
EFFECTS OF SIDEWALL OPENINGS ON THE WIND LOADS ON PIPE-FRAMED GREENHOUSES
 The Seventh Asia-Pacific Conference on Wind Engineering, November 8-12, 29, Taipei, Taiwan EFFECTS OF SIDEWALL OPENINGS ON THE WIND LOADS ON PIPE-FRAMED GREENHOUSES Yasushi Uematsu 1, Koichi Nakahara 2,
The Seventh Asia-Pacific Conference on Wind Engineering, November 8-12, 29, Taipei, Taiwan EFFECTS OF SIDEWALL OPENINGS ON THE WIND LOADS ON PIPE-FRAMED GREENHOUSES Yasushi Uematsu 1, Koichi Nakahara 2,
Pressure is defined as force per unit area. Any fluid can exert a force
 Physics Notes Chapter 9 Fluid Mechanics Fluids Fluids are materials that flow, which include both liquids and gases. Liquids have a definite volume but gases do not. In our analysis of fluids it is necessary
Physics Notes Chapter 9 Fluid Mechanics Fluids Fluids are materials that flow, which include both liquids and gases. Liquids have a definite volume but gases do not. In our analysis of fluids it is necessary
The effect of two inclined circular plunging jets on air entrainment in an aeration tank
 Computational Methods in Multiphase Flow III 229 The effect of two inclined circular plunging jets on air entrainment in an aeration tank M. S. Baawain, M. Gamal El-Din & D. W. Smith Department of Civil
Computational Methods in Multiphase Flow III 229 The effect of two inclined circular plunging jets on air entrainment in an aeration tank M. S. Baawain, M. Gamal El-Din & D. W. Smith Department of Civil
Training program on Modelling: A Case study Hydro-dynamic Model of Zanzibar channel
 Training program on Modelling: A Case study Hydro-dynamic Model of Zanzibar channel Mayorga-Adame,C.G., Sanga,I.P.L., Majuto, C., Makame, M.A., Garu,M. INTRODUCTION Hydrodynamic Modeling In understanding
Training program on Modelling: A Case study Hydro-dynamic Model of Zanzibar channel Mayorga-Adame,C.G., Sanga,I.P.L., Majuto, C., Makame, M.A., Garu,M. INTRODUCTION Hydrodynamic Modeling In understanding
Integration of Impact Factors of Gas-Liquid Transfer Rate
 Zhiyong Duan and James L. Martin Department of Civil Engineering Mississippi State University P.O. Box 9546 Mississippi State, MS 39762-9546 662-325-2902 E-mail: zd9@msstate.edu ABSTRACT The gas transfer
Zhiyong Duan and James L. Martin Department of Civil Engineering Mississippi State University P.O. Box 9546 Mississippi State, MS 39762-9546 662-325-2902 E-mail: zd9@msstate.edu ABSTRACT The gas transfer
A numerical Euler-Lagrange method for bubble tower CO2 dissolution modeling
 A numerical Euler-Lagrange method for bubble tower CO2 dissolution modeling Author: Daniel Legendre & Prof. Ron Zevenhoven Åbo Akademi University Thermal and Flow Engineering Laboratory Turku, Finland
A numerical Euler-Lagrange method for bubble tower CO2 dissolution modeling Author: Daniel Legendre & Prof. Ron Zevenhoven Åbo Akademi University Thermal and Flow Engineering Laboratory Turku, Finland
Impact of Dredging the Lower Narrow River on Circulation and Flushing
 Impact of Dredging the Lower Narrow River on Circulation and Flushing Craig Swanson Ph.D. Swanson Environmental Alex Shaw Ocean Engineering, URI Prof. Malcolm L. Spaulding Ocean Engineering, URI 29 January
Impact of Dredging the Lower Narrow River on Circulation and Flushing Craig Swanson Ph.D. Swanson Environmental Alex Shaw Ocean Engineering, URI Prof. Malcolm L. Spaulding Ocean Engineering, URI 29 January
CVEN 311 Fluid Dynamics Fall Semester 2011 Dr. Kelly Brumbelow, Texas A&M University. Final Exam
 CVEN 311 Fluid Dynamics Fall Semester 2011 Dr. Kelly Brumbelow, Texas A&M University Final Exam 8 pages, front & back, not including reference sheets; 21 questions An excerpt from the NCEES Fundamentals
CVEN 311 Fluid Dynamics Fall Semester 2011 Dr. Kelly Brumbelow, Texas A&M University Final Exam 8 pages, front & back, not including reference sheets; 21 questions An excerpt from the NCEES Fundamentals
Tutorial 5 Relative equilibrium
 Tutorial 5 Relative equilibrium 1. n open rectangular tank 3m long and 2m wide is filled with water to a depth of 1.5m. Find the slope of the water surface when the tank moves with an acceleration of 5m/s
Tutorial 5 Relative equilibrium 1. n open rectangular tank 3m long and 2m wide is filled with water to a depth of 1.5m. Find the slope of the water surface when the tank moves with an acceleration of 5m/s
Isotopes and Gases. Isotopes as constraints to air sea gas exchange, gas exchange time scales, the various time scales of carbon (isotope) exchange
 Isotopes and Gases Isotopes as constraints to air sea gas exchange, gas exchange time scales, the various time scales of carbon (isotope) exchange Isotope effects in gas solution and molecular diffusion
Isotopes and Gases Isotopes as constraints to air sea gas exchange, gas exchange time scales, the various time scales of carbon (isotope) exchange Isotope effects in gas solution and molecular diffusion
The Coriolis force, geostrophy, Rossby waves and the westward intensification
 Chapter 3 The Coriolis force, geostrophy, Rossby waves and the westward intensification The oceanic circulation is the result of a certain balance of forces. Geophysical Fluid Dynamics shows that a very
Chapter 3 The Coriolis force, geostrophy, Rossby waves and the westward intensification The oceanic circulation is the result of a certain balance of forces. Geophysical Fluid Dynamics shows that a very
Applications of ELCIRC at LNEC
 stratification in the Guadiana estuary tidal propagation in the Óbidos lagoon Lígia Pinto Anabela Oliveira André B. Fortunato 2 O utline Stratification in the Guadiana estuary The Guadiana estuary Objectives
stratification in the Guadiana estuary tidal propagation in the Óbidos lagoon Lígia Pinto Anabela Oliveira André B. Fortunato 2 O utline Stratification in the Guadiana estuary The Guadiana estuary Objectives
3D NUMERICAL MODELLING OF THE CAPACITY FOR A PARTIALLY PRESSURIZED SPILLWAY
 3D NUMERICAL MODELLING OF THE CAPACITY FOR A PARTIALLY PRESSURIZED SPILLWAY Samuel Vingerhagen 1 & Nils Reidar B. Olsen 1 1 Department of Hydraulic and Environmental Engineering, The Norwegian Univeristy
3D NUMERICAL MODELLING OF THE CAPACITY FOR A PARTIALLY PRESSURIZED SPILLWAY Samuel Vingerhagen 1 & Nils Reidar B. Olsen 1 1 Department of Hydraulic and Environmental Engineering, The Norwegian Univeristy
Section 2 Multiphase Flow, Flowing Well Performance
 Section 2 Multiphase Flow, Flowing Well Performance Multiphase Vertical Flow When producing an oil or gas well, the flow of the fluids up the tubing will be in most cases be 2 phase, liquid and gas. The
Section 2 Multiphase Flow, Flowing Well Performance Multiphase Vertical Flow When producing an oil or gas well, the flow of the fluids up the tubing will be in most cases be 2 phase, liquid and gas. The
Australian Journal of Basic and Applied Sciences. Pressure Distribution of Fluid Flow through Triangular and Square Cylinders
 AENSI Journals Australian Journal of Basic and Applied Sciences ISSN:1991-8178 Journal home page: www.ajbasweb.com Pressure Distribution of Fluid Flow through Triangular and Square Cylinders 1 Nasaruddin
AENSI Journals Australian Journal of Basic and Applied Sciences ISSN:1991-8178 Journal home page: www.ajbasweb.com Pressure Distribution of Fluid Flow through Triangular and Square Cylinders 1 Nasaruddin
Computer Simulation Helps Improve Vertical Column Induced Gas Flotation (IGF) System
 JOURNAL ARTICLES BY FLUENT SOFTWARE USERS JA187 Computer Simulation Helps Improve Vertical Column Induced Gas Flotation (IGF) System Computer simulation has helped NATCO engineers make dramatic improvements
JOURNAL ARTICLES BY FLUENT SOFTWARE USERS JA187 Computer Simulation Helps Improve Vertical Column Induced Gas Flotation (IGF) System Computer simulation has helped NATCO engineers make dramatic improvements
Applications of Bernoulli s principle. Principle states that areas with faster moving fluids will experience less pressure
 Applications of Bernoulli s principle Principle states that areas with faster moving fluids will experience less pressure Artery o When blood flows through narrower regions of arteries, the speed increases
Applications of Bernoulli s principle Principle states that areas with faster moving fluids will experience less pressure Artery o When blood flows through narrower regions of arteries, the speed increases
Assessment and analysis of Googong Reservoir thermistor chain data March - November 2007
 Assessment and analysis of Googong Reservoir thermistor chain data March - November 07 Dr Bradford Sherman CSIRO Land and Water Science Report 39/08 June 08 CSIRO Land and Water Science Report series ISSN:
Assessment and analysis of Googong Reservoir thermistor chain data March - November 07 Dr Bradford Sherman CSIRO Land and Water Science Report 39/08 June 08 CSIRO Land and Water Science Report series ISSN:
AIR-WATER FLOW STRUCTURES AT AN ABRUPT DROP WITH SUPERCRITICAL FLOW
 AIR-WATER FLOW STRUCTURES AT AN ABRUPT DROP WITH SUPERCRITICAL FLOW H. CHANSON and L. TOOMBES Department of Civil Engineering, The University of Queensland, Brisbane QLD 4072, Australia 1. Introduction
AIR-WATER FLOW STRUCTURES AT AN ABRUPT DROP WITH SUPERCRITICAL FLOW H. CHANSON and L. TOOMBES Department of Civil Engineering, The University of Queensland, Brisbane QLD 4072, Australia 1. Introduction
Presented by. Mr.Danish.D.R. M.Tech Coastal Management Institute for Ocean Management Anna University, Chennai Tamil Nadu, India.
 MATHEMATICAL MODEL STUDY OF THE EFFLUENT DISPOSAL FROM A DESALINATION PLANT IN THE MARINE ENVIRONMENT AT TUTICORIN Presented by Mr.Danish.D.R M.Tech Coastal Management Institute for Ocean Management Anna
MATHEMATICAL MODEL STUDY OF THE EFFLUENT DISPOSAL FROM A DESALINATION PLANT IN THE MARINE ENVIRONMENT AT TUTICORIN Presented by Mr.Danish.D.R M.Tech Coastal Management Institute for Ocean Management Anna
Super-parameterization of boundary layer roll vortices in tropical cyclone models
 DISTRIBUTION STATEMENT A. Approved for public release; distribution is unlimited. Super-parameterization of boundary layer roll vortices in tropical cyclone models PI Isaac Ginis Graduate School of Oceanography
DISTRIBUTION STATEMENT A. Approved for public release; distribution is unlimited. Super-parameterization of boundary layer roll vortices in tropical cyclone models PI Isaac Ginis Graduate School of Oceanography
Balloon Calculations
 Balloon Calculations Timothy Paul Smith July 9, 2012 The purpose of this short note is to gather together all the equations and graphs which can be used to calculate the trajectory of a balloon, such as
Balloon Calculations Timothy Paul Smith July 9, 2012 The purpose of this short note is to gather together all the equations and graphs which can be used to calculate the trajectory of a balloon, such as
Well Testing Plan. New York Marginal Well Study. Introduction. I. Tests to be Conducted. II. Testing Procedures
 Well Testing Plan New York Marginal Well Study Introduction The Independent Oil and Gas Association of New York, Inc. (IOGANY) has been awarded funding for a Marginal Well Testing Program from the New
Well Testing Plan New York Marginal Well Study Introduction The Independent Oil and Gas Association of New York, Inc. (IOGANY) has been awarded funding for a Marginal Well Testing Program from the New
Wind tunnel test and numerical simulation of wind pressure on a high-rise building
 Journal of Chongqing University (English Edition) [ISSN 1671-8224] Vol. 9 No. 1 March 2010 Article ID: 1671-8224(2010)01-0047-07 To cite this article: AL ZOUBI Feras, LI Zheng-liang, WEI Qi-ke, SUN Yi.
Journal of Chongqing University (English Edition) [ISSN 1671-8224] Vol. 9 No. 1 March 2010 Article ID: 1671-8224(2010)01-0047-07 To cite this article: AL ZOUBI Feras, LI Zheng-liang, WEI Qi-ke, SUN Yi.
Flow transients in multiphase pipelines
 Flow transients in multiphase pipelines David Wiszniewski School of Mechanical Engineering, University of Western Australia Prof. Ole Jørgen Nydal Multiphase Flow Laboratory, Norwegian University of Science
Flow transients in multiphase pipelines David Wiszniewski School of Mechanical Engineering, University of Western Australia Prof. Ole Jørgen Nydal Multiphase Flow Laboratory, Norwegian University of Science
