RESUSCITATION. If baby very floppy and heart rate slow, assist breathing immediately. If baby not breathing adequately by 90 sec, assist breathing
|
|
|
- Marshall Byrd
- 5 years ago
- Views:
Transcription
1 RESUSCITATION Check equipment daily, and before resuscitation Follow Resuscitation Council UK Guidelines DRY AND COVER Cord clamping see Cord clamping below >28 weeks gestation, dry baby, remove wet towels and cover baby with dry towels <28 weeks gestation, do not dry body but place in plastic bag, dry head only and put on hat Cord clamping It is current NLS recommendation that cord is not clamped immediately In uncompromised infants a delay in cord clamping of at least one minute is recommended After discussion in Staffordshire, Shropshire & Black Country resuscitation group it has been decided any time a neonatologist is called for fetal reasons, do not delay cord clamping ASSESS Assess colour, tone, breathing and heart rate If baby very floppy and heart rate slow, assist breathing immediately Reassess every 30 sec throughout resuscitation process If help required, request immediately CHECK AIRWAY If baby not breathing adequately by 90 sec, assist breathing For baby to breathe effectively, airway must be open To open airway, place baby supine with head in neutral position If very floppy, consider chin support or jaw thrust while maintaining the neutral position IMMEDIATE TREATMENT Airway Keep head in neutral position Use T-piece and soft round face mask, extending from nasal bridge to chin Give 5 inflation breaths, sustaining inflation pressure (Table 1) for 2 3 sec for each breath Give PEEP of 5 cm H 2 O Begin inflation breaths in air Table 1: Inflation pressure (avoid using pressure higher than recommended) Term infant 30 cm of water Preterm infant cm of water No chest movement Ask yourself: Is head in neutral position? Is a jaw thrust required? Do you need a second person to help with airway to perform a jaw thrust?
2 Is there an obstruction and do you need to look with a laryngoscope and suck with a largebore device? Consider placing oro-pharyngeal (Guedel) airway under direct vision using laryngoscope Is inflation time long enough? if no chest movement occurs after alternative airway procedures above have been tried (volume given is a function of time and pressure), a larger volume can be delivered if necessary by inflating for a longer time (3 4 sec) Attach saturation monitor to right hand see Saturation monitoring for guidance on saturation targets Endotracheal intubation Indications Severe hypoxia (e.g. terminal apnoea or fresh stillbirth) Stabilisation of airway Extreme prematurity Congenital diaphragmatic hernia Safe insertion of tracheal tube requires skill and experience If you cannot insert a tracheal tube within 30 sec, revert to mask ventilation Breathing Most babies have a good heart rate after birth and establish breathing by 90 sec if not breathing adequately give 5 inflation breaths, preferably using air at pressures in Table 1 heart rate should rapidly increase as oxygenated blood reaches heart Do not move onto ventilation breaths unless you have a heart rate response OR you have seen chest movement Review assessment after inflation breaths Is there a rise in heart rate? Is there chest movement with the breaths you are giving? If no spontaneous breathing, but chest movement has been obtained, perform 30 sec of ventilation breaths, given at a rate of 30 breaths per min (1 sec inspiration) Table 2: Outcome after 30 sec of ventilation breaths Heart rate Breathing Action Increases Not started breathing Provide breaths/min Where available, use PEEP at 5 cm water with T-piece system <60 Obvious chest movement Start chest compressions See below If baby is floppy with slow heart rate and there is chest movement, start cardiac compressions with ventilation breaths immediately after inflation breaths Increase inspired oxygen concentration every 30 sec by 30% e.g % depending on response see Saturation chart
3 Chest compression Use if heart rate approximately <60 beats/min (do not try and count accurately as this will waste time) Figure 1 Figure 2 Start chest compression only after successful inflation of lungs Pictures taken from NLS manual and Resuscitation Council (UK) and reproduced with their permission Ideal hold (figure1/figure 2) Circle chest with both hands so that thumbs of both hands can press on the sternum just below an imaginary line joining the nipples with fingers over baby s spine Alternative hold (less effective) Compress lower sternum with fingers whilst supporting baby s back. The alternative hand position for cardiac compressions can be used when access to the umbilicus for UVC catheterisation is required, as hands around the chest may be awkward
4 Action Compress chest quickly and firmly to reduce the antero-posterior diameter of the chest by about one-third, followed by full re-expansion to allow ventricles to refill remember to relax grip during IPPV, and feel for chest movement during ventilation breaths, as it is easy to lose neutral position when cardiac compressions are started Co-ordinate compression and ventilation to avoid competition. Aim for 3:1 ratio of compressions to ventilations, and 90 compressions and 30 breaths (120 events ) per min Blood If there is evidence of fetal haemorrhage, consider giving O negative emergency blood Resuscitation drugs Always ask about drugs taken recently by, or given to mother Consider drugs only if there is an undetectable or slow heartbeat despite effective lung inflation and effective chest compression Umbilical venous catheter (UVC) preferred venous access Adrenaline 1:10, microgram/kg (0.1 ml/kg) IV If this dose is not effective, consider giving 30 microgram/kg (0.3 ml/kg) after sodium bicarbonate has been given Adrenaline should only be given via the ET tube if venous access is taking time to achieve; it should not delay intravenous access and treatment; the dose is ml/kg of 1 in 10,000. Sodium bicarbonate 4.2% 1 2 mmol/kg (2 4 ml/kg) IV (never give via ET tube) Glucose 10% 2.5 ml/kg IV slowly over 5 min Sodium chloride 0.9% 10 ml/kg IV Naloxone Consider only after ventilation by mask or endotracheal tube has been established with chest movement seen and heart beat >100 beats/min If mother has been given pethidine within 2 4 hr of delivery, give IM naloxone: 100 microgram (0.25 ml) for small prem babies 200 microgram (0.5 ml) for all other babies Do not give naloxone to babies born to mothers who abuse narcotics WHEN TO STOP If no sign of life present after 10 min of continuous good quality resuscitation, outlook is poor with few survivors, majority will have cerebral palsy and learning difficulties If no sustained spontaneous breathing 30 min after a heart rate has been established, majority also have poor prognosis Continue resuscitation until a senior neonatologist advises stopping
5 MONITORING Saturation monitoring Oxygen monitoring is activated when paediatrician/2 nd pair of hands arrives. In the meantime, the person initiating resuscitation carries out all the usual steps in resuscitation Do not stop resuscitation for a saturation probe to be attached Attach saturation monitor to the right hand once five inflation breaths have been given Saturations should spontaneously improve as Table 3 Table 3 Time (min) Acceptable pre-ductal saturations (%) Air to oxygen If inflation breaths have been successful and chest movement seen but heart rate and/or colour/saturations (if available) not improved: in term babies increase oxygen to 30% in preterm babies increase oxygen to 30% If no response, increase by increments of 30% every 30 sec i.e.: Term air /100% Preterm air /100% Reduce oxygen if saturation levels as per Boost recommendations when oxygen saturation levels at 91 95% for preterm <30 weeks or >95% for term at 10 min of life (otherwise Resus Council target sats should be followed to stop babies being too pink too early on and being at risk of O 2 toxicity) Preterm deliveries >26 weeks gestation do not require routine intubation if respiratory effort good these babies can receive PEEP 5cm H 2 0 via mask ventilation with oxygen supplementation as appropriate on the resuscitaire and PEEP support on transfer to NICU If respiratory effort is poor, at any point, or baby s condition deteriorates, intubate and ventilate as per BAPM guidance DOCUMENTATION Make accurate written record of facts (not opinions) as soon as possible after the event Record when you were called, by whom and why condition of baby on arrival what you did and when you did it timing and detail of any response by baby date and time of writing your entry a legible signature COMMUNICATION Inform parents what has happened (the facts)
6 Newborn life support algorithm Dry baby Remove wet towels and cover Start clock or note time Birth AT Assess tone, breathing and heart rate If gasping or not breathing Open airway Give 5 inflation breaths Consider SpO 2 monitoring 30 sec 60 sec ALL STAGES Re-assess If no increase in heart rate, look for chest movement ASK: If chest not moving Re-check head position Consider 2-person airway control and other airway manoeuvres Repeat inflation breaths Consider SpO 2 monitoring Look for a response Acceptable Pre-ductal SpO 2 2 min 60% 3 min 70% 4 min 80% 5 min 85% 10 min 90% No increase in heart rate Look for chest movement When chest moving If heart rate not detectable or slow (<60/min), start chest compressions 3 compressions to each breath DO YOU Re-assess heart rate Every 30 sec If heart rate not detectable or slow (<60/min), consider venous access and drugs NEED HELP?
Learning objectives. First Response Learning Module 2 Based on ILCOR and ANZCOR 2016
 First Response Learning Module 2 Based on ILCOR and ANZCOR 2016 Learning objectives Following completion of the theoretical & practical components of this module, the participant will be able to demonstrate
First Response Learning Module 2 Based on ILCOR and ANZCOR 2016 Learning objectives Following completion of the theoretical & practical components of this module, the participant will be able to demonstrate
First Response Learning Module 2 Based on ILCOR and ANZCOR Victorian Newborn Resuscitation Project Updated March 2018
 First Response Learning Module 2 Based on ILCOR and ANZCOR 2016 Learning objectives Following completion of the theoretical & practical components of this module, the participant will be able to demonstrate
First Response Learning Module 2 Based on ILCOR and ANZCOR 2016 Learning objectives Following completion of the theoretical & practical components of this module, the participant will be able to demonstrate
Nottingham Neonatal Service - Clinical Guidelines
 Title of Guideline (must include the word Guideline (not protocol, policy, procedure etc) Author: Contact Name and Job Title Directorate & Speciality Date of submission 8 th Feb 2018 Explicit definition
Title of Guideline (must include the word Guideline (not protocol, policy, procedure etc) Author: Contact Name and Job Title Directorate & Speciality Date of submission 8 th Feb 2018 Explicit definition
Objectives. Fetal Physiology. Fetal Physiology. Resuscitation and Stabilization of the Newborn. Which Babies Require Resuscitation?
 Objectives Resuscitation and Stabilization of the Newborn June 7, 2018 Angela N. Burton, NNP-BC Henry Ford Health System Review the physiology of fetal / neonatal circulation and first breaths. Review
Objectives Resuscitation and Stabilization of the Newborn June 7, 2018 Angela N. Burton, NNP-BC Henry Ford Health System Review the physiology of fetal / neonatal circulation and first breaths. Review
First Response & Advanced Resuscitation Learning Modules 2 and 3 Based on ILCOR and ANZCOR 2016
 First Response & Advanced Resuscitation Learning Modules 2 and 3 Based on ILCOR and ANZCOR 2016 Learning objectives Following completion of the theoretical & practical components of this module, the participant
First Response & Advanced Resuscitation Learning Modules 2 and 3 Based on ILCOR and ANZCOR 2016 Learning objectives Following completion of the theoretical & practical components of this module, the participant
Operating & troubleshooting a self inflating bag. Victorian Newborn Resuscitation Project Updated February 2012
 Operating & troubleshooting a self inflating bag Six key steps to success Step 1 Choose the correct size self inflating bag for newborn resuscitation: a 240 ml bag Step 2 Choose the correct sized mask
Operating & troubleshooting a self inflating bag Six key steps to success Step 1 Choose the correct size self inflating bag for newborn resuscitation: a 240 ml bag Step 2 Choose the correct sized mask
MINI- COURSE on Management of OXYGEN in babies with RESPIRATORY DISTRESS
 MINI- COURSE on Management of OXYGEN in babies with RESPIRATORY DISTRESS Instructions: Read each sheet and answer any questions as honestly as possible The first sheets have 5 questions to allow you to
MINI- COURSE on Management of OXYGEN in babies with RESPIRATORY DISTRESS Instructions: Read each sheet and answer any questions as honestly as possible The first sheets have 5 questions to allow you to
Unit 15 Manual Resuscitators
 15-1 Unit 15 Manual Resuscitators GOAL On completion of this unit, the student should comprehend the proper operation of self-inflating resuscitation bags, flow-inflating resuscitation bags and gas-powered
15-1 Unit 15 Manual Resuscitators GOAL On completion of this unit, the student should comprehend the proper operation of self-inflating resuscitation bags, flow-inflating resuscitation bags and gas-powered
Cardio Pulmonary Resuscitation (CPR) 1
 CETL 2008 Cardio Pulmonary Resuscitation (CPR) 1 Tracey Gibson, Elaine Cole & Anne McLeod Introduction This presentation has been designed to compliment the CPR lead lecture and seminar presentations within
CETL 2008 Cardio Pulmonary Resuscitation (CPR) 1 Tracey Gibson, Elaine Cole & Anne McLeod Introduction This presentation has been designed to compliment the CPR lead lecture and seminar presentations within
Chapter 9 Airway Respirations Metabolism Oxygen Requirements Respiratory Anatomy Respiratory Anatomy Respiratory Anatomy Diaphragm
 1 Chapter 9 Airway 2 Respirations Every cell of the body requires to survive Oxygen must come in and carbon must go out 3 Metabolism Metabolism--Process where the body s cells convert food to Adequate
1 Chapter 9 Airway 2 Respirations Every cell of the body requires to survive Oxygen must come in and carbon must go out 3 Metabolism Metabolism--Process where the body s cells convert food to Adequate
birth: a transition better guidelines better outcomes the birth experience a challenging transition the fountains of life: 2/8/2018
 better guidelines better outcomes neonatal resuscitation Anne G. Wlodaver, MD neonatology OU medical center the birth experience a challenging transition birth requires major and sudden transitions some
better guidelines better outcomes neonatal resuscitation Anne G. Wlodaver, MD neonatology OU medical center the birth experience a challenging transition birth requires major and sudden transitions some
BASIC LIFE SUPPORT - PAEDIATRIC
 BASIC LIFE SUPPORT - PAEDIATRIC First Issued by/date BKW PCT May 2003 Issue Version Purpose of Issue/Description of Change 3 Policy reviewed. No changes in procedure or legislation since policy revised
BASIC LIFE SUPPORT - PAEDIATRIC First Issued by/date BKW PCT May 2003 Issue Version Purpose of Issue/Description of Change 3 Policy reviewed. No changes in procedure or legislation since policy revised
Basic Life Support Adult
 1/3.4.1 Version 4, 03/2016 Basic Life Support Adult CFR - A EFR Collapse Initiate mobilisation of 3 to 4 practitioners / responders Unresponsive and breathing abnormally or gasping 112 / 999 Go to Primary
1/3.4.1 Version 4, 03/2016 Basic Life Support Adult CFR - A EFR Collapse Initiate mobilisation of 3 to 4 practitioners / responders Unresponsive and breathing abnormally or gasping 112 / 999 Go to Primary
Basic life support updates
 Basic life support 2010 updates Chest compressions. Airway, Breathing (C-A-B) science indicates the following order: 1. Check the patient for responsiveness and breathing. 2. Call for help and get the
Basic life support 2010 updates Chest compressions. Airway, Breathing (C-A-B) science indicates the following order: 1. Check the patient for responsiveness and breathing. 2. Call for help and get the
RCH Simulation Program Skill Stations Initial Responders 1 st 3 mins of resuscitation
 RCH Simulation Program Skill Stations Initial Responders 1 st 3 mins of resuscitation LEARNING OBJECTIVES: By the end of this module, candidates should be able to : (1) Demonstrate resuscitation of an
RCH Simulation Program Skill Stations Initial Responders 1 st 3 mins of resuscitation LEARNING OBJECTIVES: By the end of this module, candidates should be able to : (1) Demonstrate resuscitation of an
PRACTICE GUIDELINE EM004 EMERGENCY CENTRE EQUIPMENT
 PRACTICE GUIDELINE EM004 EMERGENCY CENTRE EQUIPMENT This Practice Guideline sets out the minimum recommended equipment for an Emergency Centre. It should be read in conjunction with Practice Guideline
PRACTICE GUIDELINE EM004 EMERGENCY CENTRE EQUIPMENT This Practice Guideline sets out the minimum recommended equipment for an Emergency Centre. It should be read in conjunction with Practice Guideline
E C C. American Heart Association. Basic Life Support for Healthcare Providers. Written Examinations. March 2011
 E C C American Heart Association Basic Life Support for Healthcare Providers Written Examinations Contents: Examination Memo Student Answer Sheet Version A Exam Version A Answer Key Version A Reference
E C C American Heart Association Basic Life Support for Healthcare Providers Written Examinations Contents: Examination Memo Student Answer Sheet Version A Exam Version A Answer Key Version A Reference
Breathing Process: Inhalation
 Airway Chapter 6 Breathing Process: Inhalation Active part of breathing Diaphragm and intercostal muscles contract, allowing the lungs to expand. The decrease in pressure allows lungs to fill with air.
Airway Chapter 6 Breathing Process: Inhalation Active part of breathing Diaphragm and intercostal muscles contract, allowing the lungs to expand. The decrease in pressure allows lungs to fill with air.
Airways and Resuscitators. CRC 330 Cardiorespiratory Care University of South Alabama
 Airways and Resuscitators CRC 330 Cardiorespiratory Care University of South Alabama Causes of Upper Airway Obstruction CNS depressionanesthesia, drug overdose Cardiac arrest Loss of consciousness Foreign
Airways and Resuscitators CRC 330 Cardiorespiratory Care University of South Alabama Causes of Upper Airway Obstruction CNS depressionanesthesia, drug overdose Cardiac arrest Loss of consciousness Foreign
R S A B C CPR. Basic Life Support Flow Chart Check for danger. Check Response. Send for Help. Check Airway. Check for Breathing.
 CPR CPR is the technique of the manual inflation of the lungs with oxygen, and compression of the heart, therefore pumping oxygenated blood around the body, and keeping the vital organs supplied with oxygen.
CPR CPR is the technique of the manual inflation of the lungs with oxygen, and compression of the heart, therefore pumping oxygenated blood around the body, and keeping the vital organs supplied with oxygen.
Once student shouts for help, instructor says, Here s the barrier device. I am going to get the AED. STOP TEST
 Adult CPR and AED Adult Skills CPR Testing and Checklist AED Skills Testing Checklist Student Name Date of Test Hospital Scenario: You are working in a hospital or clinic, and you see a person who has
Adult CPR and AED Adult Skills CPR Testing and Checklist AED Skills Testing Checklist Student Name Date of Test Hospital Scenario: You are working in a hospital or clinic, and you see a person who has
Breathing Devices. Chapter 8 KNOWLEDGE OBJECTIVES SKILL OBJECTIVES. 6. List four precautions to take when using oxygen.
 KNOWLEDGE OBJECTIVES Chapter 8 Breathing Devices 1. Identify four advantages of using airway breathing devices. 2. Describe how to use a resuscitation mask to ventilate a nonbreathing person. 3. Describe
KNOWLEDGE OBJECTIVES Chapter 8 Breathing Devices 1. Identify four advantages of using airway breathing devices. 2. Describe how to use a resuscitation mask to ventilate a nonbreathing person. 3. Describe
Neonatal tidal volume targeted ventilation
 Neonatal tidal volume targeted ventilation Colin Morley Retired Professor of Neonatal Medicine, Royal Women s Hospital, Melbourne, Australia. Honorary Visiting Fellow, Dept Obstetrics and Gynaecology,
Neonatal tidal volume targeted ventilation Colin Morley Retired Professor of Neonatal Medicine, Royal Women s Hospital, Melbourne, Australia. Honorary Visiting Fellow, Dept Obstetrics and Gynaecology,
B.L.S احیای پایھ کودکان American Heart Association
 B.L.S احیای پایھ 2010 American Heart Association کودکان زنجیره حیاتی کودکان 1.prevention, 2.early CPR, 3.prompt access to the emergency response system, 4.rapid PALS, 5. integrated post cardiac arrest
B.L.S احیای پایھ 2010 American Heart Association کودکان زنجیره حیاتی کودکان 1.prevention, 2.early CPR, 3.prompt access to the emergency response system, 4.rapid PALS, 5. integrated post cardiac arrest
Basic Life Support. Based on UK Resuscitation Guidelines (2010)
 Basic Life Support Based on UK Resuscitation Guidelines (2010) Clinical Skills and Simulation Team With acknowledgements also to Basic Life Support Faculty - SoNMS PowerPoint content last updated 26/05/2015
Basic Life Support Based on UK Resuscitation Guidelines (2010) Clinical Skills and Simulation Team With acknowledgements also to Basic Life Support Faculty - SoNMS PowerPoint content last updated 26/05/2015
https://youtu.be/5r7havfzxek
 CPR https://youtu.be/5r7havfzxek CPR Saves Lives Cardiopulmonary Resuscitation or CPR and defibrillation within 3-5 minutes can save over 50% of cardiac arrest victims CPR followed by AED saves thousands
CPR https://youtu.be/5r7havfzxek CPR Saves Lives Cardiopulmonary Resuscitation or CPR and defibrillation within 3-5 minutes can save over 50% of cardiac arrest victims CPR followed by AED saves thousands
Supplement Study Guide for. Basic Life Support (BLS) for Healthcare Providers
 for Basic Life Support (BLS) for Healthcare Providers Table of Contents Objectives... 3 One Rescuer Adult CPR Sequence... 4 One Rescuer Child CPR Sequence (1 year to Puberty)... Error! Bookmark not defined.
for Basic Life Support (BLS) for Healthcare Providers Table of Contents Objectives... 3 One Rescuer Adult CPR Sequence... 4 One Rescuer Child CPR Sequence (1 year to Puberty)... Error! Bookmark not defined.
BLS. Compressions Airway Breaths. Basic Life Support Quick Reference. Critical Concepts
 BLS Basic Life Support Quick Reference C-A-B Compressions Airway Breaths Critical Concepts High-quality CPR improves a victim s chances of survival. The critical characteristics of high-quality CPR include
BLS Basic Life Support Quick Reference C-A-B Compressions Airway Breaths Critical Concepts High-quality CPR improves a victim s chances of survival. The critical characteristics of high-quality CPR include
E C C. American Heart Association. BLS for Healthcare Providers. Written Exams. January 12, 2012
 E C C American Heart Association BLS for Healthcare Providers Written Exams Contents: Exam Memo Student Answer Sheet Version C Exam Version C Answer Key Version C Reference Sheet Version D Exam Version
E C C American Heart Association BLS for Healthcare Providers Written Exams Contents: Exam Memo Student Answer Sheet Version C Exam Version C Answer Key Version C Reference Sheet Version D Exam Version
2015 Guidelines Summary HeartSine samaritan PAD Automated External Defibrillators
 2015 Guidelines Summary HeartSine samaritan PAD Automated External Defibrillators This document provides a summary of the 2015 guidelines and how the HeartSine samaritan PAD range of products complies
2015 Guidelines Summary HeartSine samaritan PAD Automated External Defibrillators This document provides a summary of the 2015 guidelines and how the HeartSine samaritan PAD range of products complies
Introduction to Conventional Ventilation
 Introduction to Conventional Ventilation Dr Julian Eason Consultant Neonatologist Derriford Hospital Mechanics Inspiration diaphragm lowers and thorax expands Negative intrathoracic/intrapleural pressure
Introduction to Conventional Ventilation Dr Julian Eason Consultant Neonatologist Derriford Hospital Mechanics Inspiration diaphragm lowers and thorax expands Negative intrathoracic/intrapleural pressure
American Heart Association. Basic Life Support for Healthcare Providers
 American Heart Association Basic Life Support for Healthcare Providers Pre course Review Materials Revised Huntsville Hospital Training Center Disclaimer: This document is solely produced by Huntsville
American Heart Association Basic Life Support for Healthcare Providers Pre course Review Materials Revised Huntsville Hospital Training Center Disclaimer: This document is solely produced by Huntsville
Mechanical Ventilation
 Mechanical Ventilation Chapter 4 Mechanical Ventilation Equipment When providing mechanical ventilation for pediatric casualties, it is important to select the appropriately sized bag-valve mask or endotracheal
Mechanical Ventilation Chapter 4 Mechanical Ventilation Equipment When providing mechanical ventilation for pediatric casualties, it is important to select the appropriately sized bag-valve mask or endotracheal
2005 Top Ten Major Changes in Treatment Recommendations *
 2005 Top Ten Major Changes in Treatment Recommendations * This document reviews the top ten new treatment recommendations and guidelines for ASHI s basic life support training programs for professional
2005 Top Ten Major Changes in Treatment Recommendations * This document reviews the top ten new treatment recommendations and guidelines for ASHI s basic life support training programs for professional
Greater Manchester, High Peak and East Cheshire Neonatal Transport Service
 Date / PetCO 2 (kpa) Interventions Greater Manchester, High Peak and East Cheshire Neonatal Transport Service - 19 - END TIDAL CARBON DIOXIDE Transport No:... FIRST 10 END CARBON DIOXIDE MEASUREMENTS (taken
Date / PetCO 2 (kpa) Interventions Greater Manchester, High Peak and East Cheshire Neonatal Transport Service - 19 - END TIDAL CARBON DIOXIDE Transport No:... FIRST 10 END CARBON DIOXIDE MEASUREMENTS (taken
Adult, Child and Infant Exam
 CPR Pro for the Professional Rescuer Adult, Child and Infant Exam Instructions: Read each of the following questions carefully and then place an X over the correct answer on the separate answer sheet provided.
CPR Pro for the Professional Rescuer Adult, Child and Infant Exam Instructions: Read each of the following questions carefully and then place an X over the correct answer on the separate answer sheet provided.
Once student shouts for help, instructor says, Here s the barrier device. I am going to get the AED. STOP TEST
 Adult CPR and AED Adult Skills CPR Testing and Checklist AED Skills Testing Checklist Hospital Scenario: You are working in a hospital or clinic, and you see a person who has suddenly collapsed in the
Adult CPR and AED Adult Skills CPR Testing and Checklist AED Skills Testing Checklist Hospital Scenario: You are working in a hospital or clinic, and you see a person who has suddenly collapsed in the
Great products available through ROI!
 Great products available through ROI! AGREEMENT NUMBER Through May 31, 2019 DISP. FIBER OPTIC LARYNGOSCOPES Blades and handles completely disposable Blades constructed of surgical stainless steel, and
Great products available through ROI! AGREEMENT NUMBER Through May 31, 2019 DISP. FIBER OPTIC LARYNGOSCOPES Blades and handles completely disposable Blades constructed of surgical stainless steel, and
 Introduction Welcome to COMPREHENSIVE BASIC LIFE SUPPORT Course. BLS is the foundation for saving lives after cardiac arrest. You will learn the skills of highquality cardiopulmonary resuscitation (CPR)
Introduction Welcome to COMPREHENSIVE BASIC LIFE SUPPORT Course. BLS is the foundation for saving lives after cardiac arrest. You will learn the skills of highquality cardiopulmonary resuscitation (CPR)
Basic Life Support & Automated External Defibrillation Course. OBJECTIVES
 OBJECTIVES Basic Life Support & Automated External Defibrillation Course www.erc.edu At the end of this course participants should be able to demonstrate: How to assess the collapsed victim. How to perform
OBJECTIVES Basic Life Support & Automated External Defibrillation Course www.erc.edu At the end of this course participants should be able to demonstrate: How to assess the collapsed victim. How to perform
LESSON ASSIGNMENT. Perform Cardiopulmonary Resuscitation on a Child or Infant. After completing this lesson, you should be able to:
 LESSON ASSIGNMENT LESSON 6 Perform Cardiopulmonary Resuscitation on a Child or Infant. TEXT ASSIGNMENT Paragraphs 6-1 through 6-7. LESSON OBJECTIVES After completing this lesson, you should be able to:
LESSON ASSIGNMENT LESSON 6 Perform Cardiopulmonary Resuscitation on a Child or Infant. TEXT ASSIGNMENT Paragraphs 6-1 through 6-7. LESSON OBJECTIVES After completing this lesson, you should be able to:
NOTE: If not used, provider must document reason(s) for deferring mechanical ventilation in a patient with an advanced airway
 APPENDIX: TITLE: Mechanical Ventilator Use REVISED: November 1, 2017 I. Introduction: Mechanical Ventilation is the use of an automated device to deliver positive pressure ventilation to a patient. Proper
APPENDIX: TITLE: Mechanical Ventilator Use REVISED: November 1, 2017 I. Introduction: Mechanical Ventilation is the use of an automated device to deliver positive pressure ventilation to a patient. Proper
Basic Life Support (BLS) for the Healthcare Provider
 Essential Medical Training, LLC Providing Quality, Professional Training Basic Life Support (BLS) for the Healthcare Provider Course Study Guide and Agenda 772-781-9249 office 772-382-0607 fax Email: treasurecoastcpr@gmail.com
Essential Medical Training, LLC Providing Quality, Professional Training Basic Life Support (BLS) for the Healthcare Provider Course Study Guide and Agenda 772-781-9249 office 772-382-0607 fax Email: treasurecoastcpr@gmail.com
Hallowell EMC 2000 and 2002 Veterinary Ventilator Set-up, Use, and Troubleshooting
 Hallowell EMC 2000 and 2002 Veterinary Ventilator Set-up, Use, and Troubleshooting This is a quick reference for setting up, using, and troubleshooting the Hallowell EMC 2000 and 2002 Small Animal Ventilator.
Hallowell EMC 2000 and 2002 Veterinary Ventilator Set-up, Use, and Troubleshooting This is a quick reference for setting up, using, and troubleshooting the Hallowell EMC 2000 and 2002 Small Animal Ventilator.
Other Oxygen Delivery Systems
 53 Oxygen is the most commonly used drug in the NICU. Excessive use of oxygen is linked to BPD and RDP. At the same time, hypoxemia is equally harmful and is associated with increased risk of mortality.
53 Oxygen is the most commonly used drug in the NICU. Excessive use of oxygen is linked to BPD and RDP. At the same time, hypoxemia is equally harmful and is associated with increased risk of mortality.
Using the Lifebox oximeter in the neonatal unit. Tutorial 1 the basics
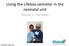 Using the Lifebox oximeter in the neonatal unit Tutorial 1 the basics Lifebox 2014. 2011. All rights reserved The Lifebox Pulse Oximeter In this tutorial you will learn about: The function of a pulse oximeter
Using the Lifebox oximeter in the neonatal unit Tutorial 1 the basics Lifebox 2014. 2011. All rights reserved The Lifebox Pulse Oximeter In this tutorial you will learn about: The function of a pulse oximeter
Code Blue III Simulators. ALS and Emergency Care Simulators
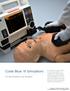 Code Blue III Simulators ALS and Emergency Care Simulators Our Code Blue III system teaches ALS skills using realistic code scenarios. Each step you take is monitored by software providing important feedback,
Code Blue III Simulators ALS and Emergency Care Simulators Our Code Blue III system teaches ALS skills using realistic code scenarios. Each step you take is monitored by software providing important feedback,
Breathing during mask ventilation of preterm infants at birth
 6 Breathing during mask ventilation of preterm infants at birth Corinne J.M. van der Pot Kim Schilleman Stuart B. Hooper Colin J. Morley Frans J. Walther Arjan B. te Pas Submitted Chapter 6 Abstract Objective
6 Breathing during mask ventilation of preterm infants at birth Corinne J.M. van der Pot Kim Schilleman Stuart B. Hooper Colin J. Morley Frans J. Walther Arjan B. te Pas Submitted Chapter 6 Abstract Objective
SimNewB. User Guide.
 EN SimNewB User Guide www.laerdal.com Contents Introduction 4 Items Included & Storage 5 System Overview & Setup 6 Features 7 Airway Features 7 Breathing Features 7 Vascular Features 7 Circulation Features
EN SimNewB User Guide www.laerdal.com Contents Introduction 4 Items Included & Storage 5 System Overview & Setup 6 Features 7 Airway Features 7 Breathing Features 7 Vascular Features 7 Circulation Features
excellence in care Procedure Management of patients with difficult oxygenation. For Review Aug 2015
 Difficult Oxygenation HELI.CLI.12 Purpose This procedure describes the processes and procedures for a lung protective strategy in the mechanical ventilation of patients that are difficult to oxygenate
Difficult Oxygenation HELI.CLI.12 Purpose This procedure describes the processes and procedures for a lung protective strategy in the mechanical ventilation of patients that are difficult to oxygenate
Proceedings of the World Small Animal Veterinary Association Sydney, Australia 2007
 Proceedings of the World Small Animal Sydney, Australia 2007 Hosted by: Next WSAVA Congress NURSES SETTING UP FOR ANAESTHESIA HOW TO PLAN FOR A SAFE ANAESTHETIC Sandra Forysth, BVSc DipACVA Institute of
Proceedings of the World Small Animal Sydney, Australia 2007 Hosted by: Next WSAVA Congress NURSES SETTING UP FOR ANAESTHESIA HOW TO PLAN FOR A SAFE ANAESTHETIC Sandra Forysth, BVSc DipACVA Institute of
Inspire rpap REVOLUTION FROM THE FIRST BREATH
 Inspire rpap TM REVOLUTION FROM THE FIRST BREATH The Inspire rpap The Inspire rpap is a revolutionary, non-invasive system for the initial stabilisation and resuscitation of infants. TM Its innovative,
Inspire rpap TM REVOLUTION FROM THE FIRST BREATH The Inspire rpap The Inspire rpap is a revolutionary, non-invasive system for the initial stabilisation and resuscitation of infants. TM Its innovative,
Basic Life Support (BLS)
 Basic Life Support (BLS) Basic Life Support (BLS) is the foundation for saving lives after cardiac arrest. Participant will learn the skills of high-quality cardiopulmonary resuscitation (CPR) for victims
Basic Life Support (BLS) Basic Life Support (BLS) is the foundation for saving lives after cardiac arrest. Participant will learn the skills of high-quality cardiopulmonary resuscitation (CPR) for victims
STANDARDIZED PROCEDURE NEONATAL INTUBATION (Neonatal)
 I. Definition This procedure is done in order to establish access to the airway in order to assist ventilation by the use of either endotracheal tube (ET tube) and bag, ET tube and continuous positive
I. Definition This procedure is done in order to establish access to the airway in order to assist ventilation by the use of either endotracheal tube (ET tube) and bag, ET tube and continuous positive
ADVANCED FIRST AID. Bibiana Navarro Matillas. Andalusian School of Public Health Guillermo Cañadas de la Fuente. Universidad de Granada
 ADVANCED FIRST AID Bibiana Navarro Matillas. Andalusian School of Public Health Guillermo Cañadas de la Fuente. Universidad de Granada BASIC LIFE SUPPORT 1. Ensure that the scene is safe. 2. Assess the
ADVANCED FIRST AID Bibiana Navarro Matillas. Andalusian School of Public Health Guillermo Cañadas de la Fuente. Universidad de Granada BASIC LIFE SUPPORT 1. Ensure that the scene is safe. 2. Assess the
BLS Guideline 3 COMPRESSIONS
 Australian Resuscitation Advisory Network BLS Guideline 3 COMPRESSIONS Scope Who does this guideline apply to? This guideline applies to all persons are unresponsive to pain and present with absent or
Australian Resuscitation Advisory Network BLS Guideline 3 COMPRESSIONS Scope Who does this guideline apply to? This guideline applies to all persons are unresponsive to pain and present with absent or
O-Two Self-Study Guide. e600 Transport Ventilator Ventilation Modes
 O-Two Self-Study Guide e600 Transport Ventilator Ventilation Modes e600 VENTILATION MODES The e600 ventilator has 13 ventilation modes: Manual Ventilation, Controlled Mandatory Ventilation (CMV), Assist
O-Two Self-Study Guide e600 Transport Ventilator Ventilation Modes e600 VENTILATION MODES The e600 ventilator has 13 ventilation modes: Manual Ventilation, Controlled Mandatory Ventilation (CMV), Assist
VENTILATION STRATEGIES FOR THE CRITICALLY UNWELL
 VENTILATION STRATEGIES FOR THE CRITICALLY UNWELL Dr Nick Taylor Visiting Emergency Specialist Teaching Hospital Karapitiya Senior Specialist and Director ED Training Clinical Lecturer, Australian National
VENTILATION STRATEGIES FOR THE CRITICALLY UNWELL Dr Nick Taylor Visiting Emergency Specialist Teaching Hospital Karapitiya Senior Specialist and Director ED Training Clinical Lecturer, Australian National
Trust Guideline for Neonatal Volume Guarantee Ventilation (VGV)
 A Clinical Guideline For Use in: By: For: Division responsible for document: Key words: Name of document author: Job title of document author: Name of document author s Line Manager: Job title of author
A Clinical Guideline For Use in: By: For: Division responsible for document: Key words: Name of document author: Job title of document author: Name of document author s Line Manager: Job title of author
COALINGA STATE HOSPITAL. Effective Date: August 31, 2006
 COALINGA STATE HOSPITAL NURSING POLICY AND PROCEDURE MANUAL SECTION Emergency Procedures POLICY NUMBER: 702 Effective Date: August 31, 2006 SUBJECT: CARDIOPULMONARY RESUSCITATION (CPR) 1. PURPOSE: To provide
COALINGA STATE HOSPITAL NURSING POLICY AND PROCEDURE MANUAL SECTION Emergency Procedures POLICY NUMBER: 702 Effective Date: August 31, 2006 SUBJECT: CARDIOPULMONARY RESUSCITATION (CPR) 1. PURPOSE: To provide
The aim of this guideline is to describe the indications and procedure for using high flow nasal prong oxygen
 High flow nasal prong HFNP oxygen therapy o Introduction & aim o Indications o Contraindications o Management equipment setup patient management o Weaning o Complications Introduction Humidified high flow
High flow nasal prong HFNP oxygen therapy o Introduction & aim o Indications o Contraindications o Management equipment setup patient management o Weaning o Complications Introduction Humidified high flow
Disclaimer This material is intended for use by trained family members and caregivers of children with tracheostomies who are patients at the Alberta
 Module 12: CPR Disclaimer This material is intended for use by trained family members and caregivers of children with tracheostomies who are patients at the Alberta Children s Hospital. Although reasonable
Module 12: CPR Disclaimer This material is intended for use by trained family members and caregivers of children with tracheostomies who are patients at the Alberta Children s Hospital. Although reasonable
Name: Date: Pd. CPR Questionnaire. 3. Chest compressions are an important part of CPR because they keep flowing to the, and other.
 Name: Date: Pd. CPR Questionnaire 1. What does CPR stand for? 2. What does the ABCD of CPR stand for? A - B - C - D 3. Chest compressions are an important part of CPR because they keep flowing to the,
Name: Date: Pd. CPR Questionnaire 1. What does CPR stand for? 2. What does the ABCD of CPR stand for? A - B - C - D 3. Chest compressions are an important part of CPR because they keep flowing to the,
BASIC LIFE SUPPORT C1
 C1 BASIC LIFE SUPPORT Objectives To understand: The risks to the rescuer during resuscitation How to perform BLS The differences between layperson and in-hospital BLS C2 Risks to the rescuer C3 Eliminate
C1 BASIC LIFE SUPPORT Objectives To understand: The risks to the rescuer during resuscitation How to perform BLS The differences between layperson and in-hospital BLS C2 Risks to the rescuer C3 Eliminate
Newborn Nursing Skills and ALS Simulator LF01400U Instruction Manual
 Newborn Nursing Skills and ALS Simulator LF01400U Instruction Manual Products by Nasco About the Simulator Meeting your neonatal resuscitation program course curriculum, the Life/form Newborn Nursing Skills
Newborn Nursing Skills and ALS Simulator LF01400U Instruction Manual Products by Nasco About the Simulator Meeting your neonatal resuscitation program course curriculum, the Life/form Newborn Nursing Skills
Virginia Office of Emergency Medical Services Scope of Practice - Procedures for EMS Personnel
 Specific tasks in this document shall refer to the Virginia Education Standards. AIRWAY TECHNIQUES Airway Adjuncts Airway Maneuvers Alternate Airway Devices Oropharyngeal Airway Nasopharyngeal Airway Head
Specific tasks in this document shall refer to the Virginia Education Standards. AIRWAY TECHNIQUES Airway Adjuncts Airway Maneuvers Alternate Airway Devices Oropharyngeal Airway Nasopharyngeal Airway Head
ONLINE DATA SUPPLEMENT. First 24 hours: All patients with ARDS criteria were ventilated during 24 hours with low V T (6-8 ml/kg
 APPENDIX 1 Appendix 1. Complete respiratory protocol. First 24 hours: All patients with ARDS criteria were ventilated during 24 hours with low V T (6-8 ml/kg predicted body weight (PBW)) (NEJM 2000; 342
APPENDIX 1 Appendix 1. Complete respiratory protocol. First 24 hours: All patients with ARDS criteria were ventilated during 24 hours with low V T (6-8 ml/kg predicted body weight (PBW)) (NEJM 2000; 342
At the end of this course participants should be able to demonstrate:
 ١ ٢ At the end of this course participants should be able to demonstrate: How to assess the collapsed victim. How to perform chest compression and rescue breathing. How to place an unconscious breathing
١ ٢ At the end of this course participants should be able to demonstrate: How to assess the collapsed victim. How to perform chest compression and rescue breathing. How to place an unconscious breathing
Difficult Oxygenation Distribution: Sydney X Illawarra X Orange X
 HELICOPTER OPERATING PROCEDURE HOP No: C/12 Issued: May 2011 Page: 1 of 5 Revision No: Original Difficult Oxygenation Distribution: Sydney X Illawarra X Orange X TRIM No: 09/300 Document No: D10/9973 X
HELICOPTER OPERATING PROCEDURE HOP No: C/12 Issued: May 2011 Page: 1 of 5 Revision No: Original Difficult Oxygenation Distribution: Sydney X Illawarra X Orange X TRIM No: 09/300 Document No: D10/9973 X
APPLICATION OF POCKET MASK
 Module 10 APPLICATION OF POCKET MASK APPLICATION OF POCKET MASK The pocket mask is a barrier device used to provide rescue breathing. It has a one-way valve that prevents exchange of secretions between
Module 10 APPLICATION OF POCKET MASK APPLICATION OF POCKET MASK The pocket mask is a barrier device used to provide rescue breathing. It has a one-way valve that prevents exchange of secretions between
MANAGEMENT OF COLLAPSED ADULT PATIENT
 MANAGEMENT OF COLLAPSED ADULT PATIENT Author Information Dr. Venugopalan P.P. Chief Emergency Medicine Dy Director, MIMS Academy Malabar Institute of Medical Sciences Ltd. P.O. Govindapuram, Calicut, Kerala
MANAGEMENT OF COLLAPSED ADULT PATIENT Author Information Dr. Venugopalan P.P. Chief Emergency Medicine Dy Director, MIMS Academy Malabar Institute of Medical Sciences Ltd. P.O. Govindapuram, Calicut, Kerala
Response to Basic Emergencies
 UNIT52 Response to Basic Emergencies PROCEDURE ADULT CPR, ONE RESCUER Standard precautions should be followed if at all possible. This means gloves should be worn and a barrier device used. If the victim
UNIT52 Response to Basic Emergencies PROCEDURE ADULT CPR, ONE RESCUER Standard precautions should be followed if at all possible. This means gloves should be worn and a barrier device used. If the victim
Update on chest compressions
 Update on chest compressions Georg M Schmölzer Centre for the Studies of Asphyxia and Resuscitation, Royal Alexandra Hospital, Edmonton, Canada; Dept. of Pediatrics, University of Alberta, Edmonton, Canada
Update on chest compressions Georg M Schmölzer Centre for the Studies of Asphyxia and Resuscitation, Royal Alexandra Hospital, Edmonton, Canada; Dept. of Pediatrics, University of Alberta, Edmonton, Canada
BASIC LIFE SUPPORT CPR: Introduction. Why & When to Do it? CPR... ABCDEF
 BASIC LIFE SUPPORT CPR: Considered when an individual cannot adequately breathe and maintain circulation to vital organs. Introduction Why & When to Do it? Collapsed patients require assistance to maintain
BASIC LIFE SUPPORT CPR: Considered when an individual cannot adequately breathe and maintain circulation to vital organs. Introduction Why & When to Do it? Collapsed patients require assistance to maintain
Cardio Pulmonary Resuscitation
 1 CPR (HLTCPR201B Perform CPR) 2 Action Plan D anger R esponse S end for help A irway B reathing C PR D efibrillation 3 D anger Check for dangers to: Yourself Bystanders Casualty Walk 360 o around the
1 CPR (HLTCPR201B Perform CPR) 2 Action Plan D anger R esponse S end for help A irway B reathing C PR D efibrillation 3 D anger Check for dangers to: Yourself Bystanders Casualty Walk 360 o around the
How to Perform CPR. The CABs of CPR are Circulation, Airway and Breathing. C - Circulation (Chest Compressions)
 How to Perform CPR Learning how to perform cardio-pulmonary resuscitation (CPR) saves lives. While no statistics are available on the exact number of lives sudden cardiac arrest claims per year, approximately
How to Perform CPR Learning how to perform cardio-pulmonary resuscitation (CPR) saves lives. While no statistics are available on the exact number of lives sudden cardiac arrest claims per year, approximately
LV Protocol On SmartMan. Products LV Protocol can be intubated or not Available on ALS (LV) Pro and Pro+ Megacode (LV) Pro and Pro+
 LV Protocol On SmartMan Products LV Protocol can be intubated or not Available on ALS (LV) Pro and Pro+ Megacode (LV) Pro and Pro+ SmartMan Low Volume 10:1 on a Non-Intubated Patient (For CAM, CAMS, ART,
LV Protocol On SmartMan Products LV Protocol can be intubated or not Available on ALS (LV) Pro and Pro+ Megacode (LV) Pro and Pro+ SmartMan Low Volume 10:1 on a Non-Intubated Patient (For CAM, CAMS, ART,
Clinical Skills. Administering Oxygen
 Clinical Skills Administering Oxygen Updated July 2017 Clare Cann Original 2012 Carole Loveridge, Lecturer in Women`s Health Aims and Objectives Aims and Objectives The aim of this module is to facilitate
Clinical Skills Administering Oxygen Updated July 2017 Clare Cann Original 2012 Carole Loveridge, Lecturer in Women`s Health Aims and Objectives Aims and Objectives The aim of this module is to facilitate
SPEMS SKILLS PROFICIENCY CRITERIA Paramedic
 SPEMS SKILLS PROFICIENCY CRITERIA Paramedic The following skills are required at the Paramedic Level: 1. King Airway 2. IV 3. Endotracheal Intubation 4. Adult EZ IO 5. Pedi EZ IO 6. Pleural Decompression
SPEMS SKILLS PROFICIENCY CRITERIA Paramedic The following skills are required at the Paramedic Level: 1. King Airway 2. IV 3. Endotracheal Intubation 4. Adult EZ IO 5. Pedi EZ IO 6. Pleural Decompression
American Heart Association Health Care Provider CPR 2010 Curriculum
 American Heart Association Health Care Provider CPR 2010 Curriculum 1 CPR Overview Compressions are most important part of CPR Push hard and fast Minimize interruptions CAB Assessment Circulation Airway
American Heart Association Health Care Provider CPR 2010 Curriculum 1 CPR Overview Compressions are most important part of CPR Push hard and fast Minimize interruptions CAB Assessment Circulation Airway
NHS. Blackpool Teaching Hospitals. NHS Foundation Trust. Basic Life Support. Page 1
 Blackpool Teaching Hospitals NHS Foundation Trust NHS Basic Life Support Page 1 Page 2 Introduction Why do this course? Because it will help you save lives! It will help you: Assess a collapsed victim;
Blackpool Teaching Hospitals NHS Foundation Trust NHS Basic Life Support Page 1 Page 2 Introduction Why do this course? Because it will help you save lives! It will help you: Assess a collapsed victim;
Minimum equipment list for cardiopulmonary resuscitation Primary dental care
 Minimum equipment list for cardiopulmonary resuscitation Primary dental care Resuscitation Council (UK) 5th Floor Tavistock House North Tavistock Square London WC1H 9HR Tel: 020 7388 4678 Fax: 020 7383
Minimum equipment list for cardiopulmonary resuscitation Primary dental care Resuscitation Council (UK) 5th Floor Tavistock House North Tavistock Square London WC1H 9HR Tel: 020 7388 4678 Fax: 020 7383
AUTOVENT 4000 VENTILATOR
 OVERVIEW AUTOVENT 4000 Only properly trained and approved Escambia County Bureau of Public Safety Paramedics are to use the AutoVent 4000 ventilator manufactured by LSP to transport patients already on
OVERVIEW AUTOVENT 4000 Only properly trained and approved Escambia County Bureau of Public Safety Paramedics are to use the AutoVent 4000 ventilator manufactured by LSP to transport patients already on
If you do not wish to perform rescue breaths, deliver compressions only, until medical assistance arrives.
 Basic Life Support Care and resuscitation of a collapsed adult Basic life support (BLS) is a life saving technique, it involves chest compressions combined with rescue breaths (mouth to mouth). BLS can
Basic Life Support Care and resuscitation of a collapsed adult Basic life support (BLS) is a life saving technique, it involves chest compressions combined with rescue breaths (mouth to mouth). BLS can
Manual: Biphasic Positive Airway Pressure (BiPAP) Ventilation
 RCH@Home Manual: Biphasic Positive Airway Pressure (BiPAP) Ventilation 1. Commonly used terms... 2 1.1 Inspiration... 2 1.2 Expiration... 2 1.3 Breath rate (bpm)... 2 1.4 Ventilation... 2 1.5 Biphasic
RCH@Home Manual: Biphasic Positive Airway Pressure (BiPAP) Ventilation 1. Commonly used terms... 2 1.1 Inspiration... 2 1.2 Expiration... 2 1.3 Breath rate (bpm)... 2 1.4 Ventilation... 2 1.5 Biphasic
Pediatric Basic & Advanced Life Support. Gassem Gohal FAAP FRCPC Pediatric Dep. Head Jazan Faculty of Medicine
 Pediatric Basic & Advanced Life Support Gassem Gohal FAAP FRCPC Pediatric Dep. Head Jazan Faculty of Medicine ObjecGves To be familiar with the systematic assessment of a seriously ill or injured child.
Pediatric Basic & Advanced Life Support Gassem Gohal FAAP FRCPC Pediatric Dep. Head Jazan Faculty of Medicine ObjecGves To be familiar with the systematic assessment of a seriously ill or injured child.
PHTY 300 Wk 1 Lectures
 PHTY 300 Wk 1 Lectures Arterial Blood Gas Components The test provides information on - Acid base balance - Oxygenation - Hemoglobin levels - Electrolyte blood glucose, lactate, renal function When initially
PHTY 300 Wk 1 Lectures Arterial Blood Gas Components The test provides information on - Acid base balance - Oxygenation - Hemoglobin levels - Electrolyte blood glucose, lactate, renal function When initially
RESPIRATORY CARE POLICY AND PROCEDURE MANUAL. a) Persistent hypoxemia despite improved ventilatory pattern and elevated Fl02
 The University of Mississippi AND PROCEDURE MANUAL Effective Date: June 30, 1990 Revised Date: December 2009 MANUAL CODE Page 1 of 5 PREPARED BY: Respiratory Care Policy and Procedure Review Committee
The University of Mississippi AND PROCEDURE MANUAL Effective Date: June 30, 1990 Revised Date: December 2009 MANUAL CODE Page 1 of 5 PREPARED BY: Respiratory Care Policy and Procedure Review Committee
SARASOTA MEMORIAL HOSPITAL NURSING PROCEDURE
 SARASOTA MEMORIAL HOSPITAL NURSING PROCEDURE TITLE: ISSUED FOR: ENDO TRACHEAL SUCTIONING OF THE ADULT PATIENT (suc03) Nursing, Respiratory DATE: REVIEWED: PAGES: 11/82 12/18 1 of 5 RESPONSIBILITY: RN,
SARASOTA MEMORIAL HOSPITAL NURSING PROCEDURE TITLE: ISSUED FOR: ENDO TRACHEAL SUCTIONING OF THE ADULT PATIENT (suc03) Nursing, Respiratory DATE: REVIEWED: PAGES: 11/82 12/18 1 of 5 RESPONSIBILITY: RN,
Cardiac Arrest General
 Date: November 15, 2012 Page 1 of 5 Cardiac Arrest General This protocol should be followed for all adult cardiac arrests. Medical cardiac arrest patients undergoing attempted resuscitation should not
Date: November 15, 2012 Page 1 of 5 Cardiac Arrest General This protocol should be followed for all adult cardiac arrests. Medical cardiac arrest patients undergoing attempted resuscitation should not
American Heart Association. Heartsaver CPR
 American Heart Association Heartsaver CPR Adult Module Pretest February 2001 2001 American Heart Association Heartsaver CPR Course Adult Module Pretest Please do not mark on this examination. Record the
American Heart Association Heartsaver CPR Adult Module Pretest February 2001 2001 American Heart Association Heartsaver CPR Course Adult Module Pretest Please do not mark on this examination. Record the
Chapter 4: Ventilation Test Bank MULTIPLE CHOICE
 Instant download and all chapters Test Bank Respiratory Care Anatomy and Physiology Foundations for Clinical Practice 3rd Edition Will Beachey https://testbanklab.com/download/test-bank-respiratory-care-anatomy-physiologyfoundations-clinical-practice-3rd-edition-will-beachey/
Instant download and all chapters Test Bank Respiratory Care Anatomy and Physiology Foundations for Clinical Practice 3rd Edition Will Beachey https://testbanklab.com/download/test-bank-respiratory-care-anatomy-physiologyfoundations-clinical-practice-3rd-edition-will-beachey/
Endotracheal Suctioning: In Line ETT
 Approved by: Endotracheal Suctioning: In Line ETT Gail Cameron Senior Director Operations, Maternal, Neonatal & Child Health Programs Dr. Paul Byrne Medical Director, Neonatology Neonatal Policy & Procedures
Approved by: Endotracheal Suctioning: In Line ETT Gail Cameron Senior Director Operations, Maternal, Neonatal & Child Health Programs Dr. Paul Byrne Medical Director, Neonatology Neonatal Policy & Procedures
THE AMERICAN SAFETY & HEALTH INSTITUTE ADULT CPR EXAM
 THE AMERICAN SAFETY & HEALTH INSTITUTE ADULT CPR EXAM 1. During an adult victim s assessment, responder should check victim for responsiveness. If no response, responder should first: A. Check for signals
THE AMERICAN SAFETY & HEALTH INSTITUTE ADULT CPR EXAM 1. During an adult victim s assessment, responder should check victim for responsiveness. If no response, responder should first: A. Check for signals
LESSON ASSIGNMENT. Perform Cardiopulmonary Resuscitation on an Adult , Administer External Chest Compressions.
 LESSON ASSIGNMENT LESSON 4 Perform Cardiopulmonary Resuscitation on an Adult. TEXT ASSIGNMENT Paragraphs 4-1 through 4-5. TASKS TAUGHT LESSON OBJECTIVES 081-831-0046, Administer External Chest Compressions.
LESSON ASSIGNMENT LESSON 4 Perform Cardiopulmonary Resuscitation on an Adult. TEXT ASSIGNMENT Paragraphs 4-1 through 4-5. TASKS TAUGHT LESSON OBJECTIVES 081-831-0046, Administer External Chest Compressions.
BASIC LIFE SUPPORT THEORY. Before reading this, you should watch the 5 minute film found on Youtube titled ERC BLS WITH AED
 BASIC LIFE SUPPORT THEORY Before reading this, you should watch the 5 minute film found on Youtube titled ERC BLS WITH AED Objectives By the end of this session you will have an awareness of: Importance
BASIC LIFE SUPPORT THEORY Before reading this, you should watch the 5 minute film found on Youtube titled ERC BLS WITH AED Objectives By the end of this session you will have an awareness of: Importance
Operation and Maintenance of the EPV200 Portable Ventilator
 Operation and Maintenance of the EPV200 Portable Ventilator 1 Applications of the EPV200 The EPV200 Portable Ventilator is a gas powered electronically controlled mechanical ventilator, designed to provide
Operation and Maintenance of the EPV200 Portable Ventilator 1 Applications of the EPV200 The EPV200 Portable Ventilator is a gas powered electronically controlled mechanical ventilator, designed to provide
Children Small Adults Newborns Small Children
 Children Small Adults Newborns Small Children Curt Partain RRT-NPS NICU Respiratory Care Clinical Educator Community Regional Medical Center Fresno, Ca. Oxygen Use: Infants > 35 weeks gestation begin with
Children Small Adults Newborns Small Children Curt Partain RRT-NPS NICU Respiratory Care Clinical Educator Community Regional Medical Center Fresno, Ca. Oxygen Use: Infants > 35 weeks gestation begin with
Endotracheal Tubes - VentiSeal (High Volume Low Pressure)
 Endotracheal Tubes - VentiSeal (High Volume Low Pressure) VentiSeal reduces the risk of vocal cord injury and tracheal necrosis through an optimal volume cuff with ideal pressure distribution and effective
Endotracheal Tubes - VentiSeal (High Volume Low Pressure) VentiSeal reduces the risk of vocal cord injury and tracheal necrosis through an optimal volume cuff with ideal pressure distribution and effective
COMMUNITY SAFETY CONSULTANTS AHA CPR COURSE RECORD SHEET
 Revised 5-31-2018 CSC COURSE #: COMMUNTY SAFETY CONSULTANTS AHA CPR COURSE RECORD SHEET Organization: Address: ZP: Date: Start Time: End Time: Total Hours: Total Days: # of nitial students: # of Renewal
Revised 5-31-2018 CSC COURSE #: COMMUNTY SAFETY CONSULTANTS AHA CPR COURSE RECORD SHEET Organization: Address: ZP: Date: Start Time: End Time: Total Hours: Total Days: # of nitial students: # of Renewal
