intestinalhealthinstitute.com Sheila Shea, Director January 15, Sheila Shea
|
|
|
- Damian Hall
- 6 years ago
- Views:
Transcription
1 Gas Revisited I have written about gas many times. One article was published in a local tabloid called the Desert Leaf. It is called Getting It Out Is Not a Gas! ( Another time, I wrote an article for my blog, entitled Inflation and Deflation that I will wrap into this article! Now, I am revisiting this topic again because the gas within people has escalated over the past year. The escalation is that 95-99% of the colonic release is GAS in some people. My clients ask good questions. Where does all the gas come from? If I am not passing it, where is it going? Then I received a raw food book Raw Success by Matt Monarch. He explained his theory of where the gas goes. I will present some ideas on what causes the gas, where the gas goes and a host of other details related to gas. What Does Gas Do? The bottom line is: gas is frequently difficult to get out of the large intestines during a colonic. It can inhibit the release of stool. It forms it own wall. It can be a major obstruction. It can weaken, stretch and twist the gut walls. It can crowd or displace organs. It can restrict the circulatory system through its pressure. It can definitely affect the quality of your life. It reflects a pathogenic microbial overgrowth. Gas is an obstruction. Most clients are confounded when they realize sometimes they have to clear the gas before they clear the solid waste. Gas is a wall the water bumps up against when the water enters the rectum. Sometimes, we clear some waste out then the water will hit a gas pocket and releasing stops. Releasing comes to a standstill until we get the gas out. How do people feel when they are filled with gas whether or not they know it? bloated, distended, inflated, knife pain, tight, tension, about to pop, burning pain, fogged out, low energy, immobilized Most people that report gas or do not know they have excessive gas describe themselves as bloated. Some arrive with incredible pressure in their gut and they do not know what is causing it. Some are overweight and obese with very distended abdomens. Others may be slender but have developed an overgrowth from lifestyle habits. Their abdomens may feel very tight or very puffy to the touch. One female client had a colonic on Wednesday and we used the side position to release her voluminous gas. When she came in today, 2 days later, she said she felt great after the colonic because she had a flat tummy. She had been so bloated, distended and inflated before and was living with it. Page 1
2 Another young woman, overweight, in her twenties said she felt like she could pop or explode. Obviously, those are extremely distressing states and to not lend to relaxation, expression, interaction and quality of life. Gas and Ailments Dr. St. Louis Estes, author of Raw Food and Health, has a chapter on blood gas concepts called Gases. He writes: These gases have a very definite power in undermining health. They deplete the nervous system to such an extent that weakness, loss of memory, vertigo, eye troubles, depression, hysteria and even paralysis occurs where the pressure is so intense that a large blood vessel gives way. Intestinal gases can cause severe contraction of the muscles around the heart and sharp, stubborn pains through the heart areas that may shut off the breath for a few seconds. The great strain on the heart under these circumstances lowers its vitality and changes the heartbeat, making it slower and irregular, or quickened with frequent rapid flutterings and racing throb. Fainting may occur for the sudden congestions due to gas around the heart draws the blood from the brain. Continuous recurrence of this reaction to gas deprives the scalp of its nourishment, and the hair dies and falls out. I have to say that gas can be an obstruction in a your life whether you are at work, having sexual relations with your partner, maintaining an active social life, working out regularly or trying to meditate. You might be uncomfortable, not wanting to focus, move, have sex, socialize or even think. And, interestingly enough, some of you will continue to eat through the discomfort. What Is the Main Cause of Excessive Gas? The subject is excessive gas not the small and normal amount from digestion. According to Elaine Gottschall in her groundbreaking work, Breaking the Vicious Cycle, the excessive gas is caused from a microbial overgrowth. Bacteria and fungi migrate from the large to the small intestines to feed mainly on complex sugars or complex carbohydrates that the person is not breaking down with normal human digestion. The microbes feed on the complex sugars. This kind of digestion is called fermentation digestion. The fermentive by-products are gases, acids and other metabolites that are toxic to the system. In order to heal, we need to stop feeding the pathogens and take in good bacteria or probiotic. How Do We Minimize the Effect of Excessive Gases? Page 2
3 Cleansing and Detoxing: colon hydrotherapy, enemas, detoxes of intestines, liver, parasites Complex carbohydrate free diets: see list Exercising: keep moving Keeping stress-free: good luck Avoiding environmental toxins Combining food properly Chewing Avoiding: eating all day long, late night eating, overeating, overlapping meals Dr Louis Estes, Raw Food and Health According to Dr Estes, cleansing the colon is the number one way to ensure bloodstream and cellular cleanliness. Remember that the colon is the central waste station of the body, the trashcan for all our junk. Colon Hydrotherapy is like taking out the trash. Cleansing the colon empties any gas and waste that may be present and creates a now-empty five-foot long receptacle for the toxins of the body to pour into. Additionally, due to the process of gas diffusion, Colon Hydrotherapy lessens the gas pressure and enables our cells to continually purify. What are the diets for reducing the gas and healing the gut? The diets for reducing the gas and restoring a normal balance of intestinal flora are free of complex sugars. One male, 40 s, had such severe gas it made his life miserable at work and pretty much killed his social life. He was in pain. This situation had been going on 13 years when he came in. He chose to follow the SCD to reduce his gas and heal his gut. It took him about 10 months to begin to see progress. However, there were good signs from the beginning that he was getting progressively better. The moral of this story is that it takes time to heal, to change the patterns, to create the right microbial balance in the gut. The quality to cultivate is patience. (SCD Specific Carbohydrate Diet) Page 3
4 (Gut and Psychology Syndrome) Paleodiet by Lauren Cordain And any other diet that is free of complex sugars Raw fooders and gas Dr Estes writes that raw foodists will create a lot of gas if they do not completely chew their food. I would add that raw foodists are adding a number of raw complex sugars to their diet. Raw or cooked, they are complex sugars and can create gas if the person s enzymes are not breaking them down. Examples are chocolate (37% starch), wild rice, sprouted grains and beans, flax and chia seeds (the mucilage is a polysaccharide or complex sugar), sweet potatoes and parsnips. Onto the original question that clients ask Where does all this gas go? Where does it store itself? We certainly know that it stores in the stomach, small and large intestines. The standard answer is that gas passes out of the colon or we pass gas. Gas also moves upward and we belch it out. Some studies say the gas absorbs through the gut wall, through the blood stream to the lungs where it is exhaled. Some breath tests can be given that let us know what pathogenic bacteria or fungi are creating the gas. That is another explanation of where the gas goes as well as why some people have bad breath. I found another theory in a PDF file or book by Matt Monarch, Raw Success. Matt believes the gas stores in the cells of our body. I quote him here and offer a link to his original article. What is actually happening inside us on a cellular level? Our cells are full of gas. Gas is a result of fermentation. The quality, quantity and combinations of foods we eat determine the amount of fermentative gas released into our system. When this gas is released, our cells absorb it into their structure and it gets locked in through the process of diffusion. Matt defines gas diffusion in this way. Cell membranes are the boundaries between the internal and external environments of a cell. Diffusion across this cellular membrane is the movement of gas molecules from a region of higher concentration to a region of lower concentration. The cells must enlarge to accommodate excessive amounts of incoming pressure from gas. The poorer our eating habits, the more fermentative gases are released in our system, and the more abnormally enlarged our cells become. Page 4
5 The cells are continually working to rid themselves of this gaseous waste. However, with a diet high in complex sugars and refined foods, our inflated cells are constantly subjected to elevated levels of fermentative gas that keep the cells distended. When someone improves his or her diet, the fermentation decreases considerably. The process of detoxification, cells contracting to rid themselves of stored gaseous waste, continues for life especially if one is consistent with an improved diet. Cells cannot release their gaseous waste if a person is chronically constipated in the intestines or the cells. The goal is to relieve the body of this gas. The two most effective ways to accomplish this task are adhering to a healthier diet while undertaking colon hydrotherapy. When you eat a healthier diet, less fermentative gas is produced in your bloodstream during digestion. This lowers the gas pressure on the outside of the cells. Through the process of diffusion, these gases exit the cells and rapidly discharge into the bloodstream into the intestines. Colon Hydrotherapy removes the release of gaseous waste. Cells are free to contract and release any accumulated toxins and gaseous waste with a clean diet such as raw food, the Specific Carbohydrate Diet, the Gut and Psychology Syndrome diet and the Paleodiet. The principle of diffusion works in reverse. The gas passes from a higher concentration in the cells to a lower concentration in the intestines. Now the cells experience less pressure. Colonics remove the build up of solid waste from our colon. And, it can release a build up of toxic gas. The colon equipment has a viewing window where you can look at what is coming out of your colon during the session. In addition to solid waste, you can also see and hear big gas pockets release. That s a loose quote and paraphrase of Matt s theory. I would also add that the bloodstream is the conduit for the gas. When we detoxify we are clearing our cells, our bloodstream and our intestines. It s all one. Educating Colon Hydrotherapists I have a school for colon hydrotherapy. We have had to develop a protocol for getting gas out of the large intestines because it is such a problem. We have a host of techniques we use when the client rests on their side or their back. The issue is so prevalent that students need to be educated and trained in how to deal with it in their practice. Page 5
6 How do I know if I have a gas case? If gas is an issue during the colonic process, I will hear it from the beginning, or I cannot get very much water in or I start to get good releases and then nothing else comes out. The gradations of what clients feel vary. Some do not feel the gas at all yet they have an abundance during the colonic session. Some clients feel some gas yet are shocked to find out how much gas comes out of them during a colonic. Some clients feel very uncomfortable with gas and may release an excessive amount during the colonic. The volume of gas released can be as high as % of what releases from their large intestine during the colonic session. Most people are not eliminating naturally the volume of gas in their intestines. I notice that it does not come out easily during the colonic process while they are laying in the traditional colonic position on their back. I believe the bowels are so stretched and weakened by the continuous gas bloating that their colon muscles do not have the energy to move and release the gas. However, we are able to get the gas out in Left Sims position. I m not sure why. If the gas is prevented from coming out by the weakening and stretching of the walls, so is the ability to eliminate stool. Some individuals have gas and that does come out during the session with all the solid waste. Those individuals have stronger colon muscles and very often, better lifestyle habits meaning diet and exercise. Some of them have done a series of colonics. Their bowels are strengthened and they are able to release more spontaneously and easily. Two clients have reported painful gas a few hours after they received a colonic during which the contents of the large intestines or colon evacuated thoroughly. I have thought about this phenomenon and I speculate that the overgrowth theory in likely in operation. We remove the gas and other waste products during the colonic. However, gas continues to form in the small intestines. The gas will move into the large intestines as the day progresses now that it has been emptied by the colonic. Likely, gas is continuously forming because the fermentation process is so active. If the theory of gas moving into the cells is accurate that might explain why more gas pours into the intestines after a colonic. Diffusion allows the high Page 6
7 volume gas in the cells to move into the intestines which now have a low volume gas. What is the best colonic position to relieve gas? We find that Left Sims position is the best posture to relieve gas. I ask the client to roll onto their left side with knees drawn toward the chest or the left leg stretched straight and the right drawn slightly toward chest. The water pressure going in is slightly higher than the inflows done on the back. May 2009 Newsletter Deflation - Inflation! In this age of the 'economic colonic' I thought it important to write about inflation and deflation. I have written about GAS before and here it is again. Clients come in 'inflated.' It's hard to get anything out of the large intestines or colon because the high volume gas serves as an obstruction. Most clients who experience a release of this excessive gas are not aware that they have this high volume. What I am referring to is that 95% of what is released during the session is GAS, not stool, mucus or particles. The state of being full of gas I call 'inflation.' When this happens, I have the client go from their back to a left side position called Left Sims. We use a slightly higher inflow rate and the gas pours out on each outflow. I 'deflate' the person. Deflation refers to the reduction of gas during the colonic procedure. Gas is the effluent created by pathogenic bacteria and fungi that feed on your consumption of complex sugars. Read foods based on grains, beans, starchy roots such as potatoes, sweet potatoes, yams, and white sugar and milk products. Gas may also be created by bacterial and fungal imbalances caused by antibiotics and steroids. Elaine Gottschall in her book, Breaking the Vicious Cycle, describes the diet and science to alleviate the gas situation. Excessive gas weakens the walls of the gut. Gas can stretch the intestines creating redundancy, or extra lengths, loops, coils and prolapses in the gut. In its most severe form, it can twist the loops of the bowel. Even more reason to avoid creating gas. It will also sap your energy. Your food is not being converted into your energy. It is converted to gas and acids. You wonder why you feel fatigue. Change the diet, add the good bacteria or probiotic and begin to reduce the gas. So when it comes to the gut, what do we want? I would take deflation over Page 7
8 inflation for obvious health reasons. Now, here is another spin on inflation and deflation that is positive and something you can practice on the colonic table as well as every living moment. The breath. Inhalation is the inflation. Exhalation is the deflation. Stay focused on that. The inflation creates spaciousness in the gut and energy. The deflation creates a sense of relaxation. You are exercising your gut. That's a good thing! Page 8
The Human Body. Everyone Needs Healthy Systems. Blood Vessels
 The Human Body Everyone Needs Healthy Systems There are several systems that make up the human body. Although their functions differ, they all work together to keep your body running smoothly. Some of
The Human Body Everyone Needs Healthy Systems There are several systems that make up the human body. Although their functions differ, they all work together to keep your body running smoothly. Some of
Use scientific principles to explain how the sprayer works. You may use diagrams to support your answer.
 4.3 Marking Key This guide includes sample answers, task-specific observable elements, (Appendices 1 and 2), descriptive evaluation rubrics for each competency (Appendices 3 and 4), and non-descriptive
4.3 Marking Key This guide includes sample answers, task-specific observable elements, (Appendices 1 and 2), descriptive evaluation rubrics for each competency (Appendices 3 and 4), and non-descriptive
Animal Systems: The Respiratory System
 Animal Systems: The Respiratory System Tissues, Organs, and Systems of Living Things Cells, Cell Division, and Animal Systems and Plant Systems Cell Specialization Human Systems The Digestive The Circulatory
Animal Systems: The Respiratory System Tissues, Organs, and Systems of Living Things Cells, Cell Division, and Animal Systems and Plant Systems Cell Specialization Human Systems The Digestive The Circulatory
SCIENCE 8 RESPIRATION
 SCIENCE 8 RESPIRATION WHEN WE BREATHE, WHAT DO WE BREATHE IN? O2, N2, CO2, O3, NO2 (gas fumes), CO, pollutant, fragrants, toxins, etc. WHAT IS THE PURPOSE OF BREATHING IN? WHAT DOES OUR BODY WANT? O2 WHY?
SCIENCE 8 RESPIRATION WHEN WE BREATHE, WHAT DO WE BREATHE IN? O2, N2, CO2, O3, NO2 (gas fumes), CO, pollutant, fragrants, toxins, etc. WHAT IS THE PURPOSE OF BREATHING IN? WHAT DOES OUR BODY WANT? O2 WHY?
Multicellular Organisms. Sub-Topic 2.7 Animal Transport & Exchange Systems
 Multicellular Organisms Sub-Topic 2.7 Animal Transport & Exchange Systems On completion of this sub-topic I will be able to state that: Rings of cartilage keep the main airways open Oxygen and carbon dioxide
Multicellular Organisms Sub-Topic 2.7 Animal Transport & Exchange Systems On completion of this sub-topic I will be able to state that: Rings of cartilage keep the main airways open Oxygen and carbon dioxide
Show Me Hand In. Correct and Hand In Again By. Read pages of SP to help you answer the following questions: 1. Name 4 gases contained in air:,
 Name 20 Due Date Show Me Hand In Correct and Hand In Again By Read pages 151-157 of SP to help you answer the following questions: 1. Name 4 gases contained in air:, and. 2. What are two types of solid
Name 20 Due Date Show Me Hand In Correct and Hand In Again By Read pages 151-157 of SP to help you answer the following questions: 1. Name 4 gases contained in air:, and. 2. What are two types of solid
Balancing Active and Receptive Energies: The Practice of Nadi Shodanam
 Balancing Active and Receptive Energies: The Practice of Nadi Shodanam Pranayama Kevin Hoffman Today, and every day. you will breathe 15,000-25,000 times. If you pay attention to your breath, you will
Balancing Active and Receptive Energies: The Practice of Nadi Shodanam Pranayama Kevin Hoffman Today, and every day. you will breathe 15,000-25,000 times. If you pay attention to your breath, you will
08 Respiration. #79 Respiration realeases energy from food
 08 Respiration #79 Respiration realeases energy from food Respiration is the chemical reactions that break down nutrient molecules in living cells to release energy. In humans, our cells need energy (ATP)
08 Respiration #79 Respiration realeases energy from food Respiration is the chemical reactions that break down nutrient molecules in living cells to release energy. In humans, our cells need energy (ATP)
Student Information Document
 Applied Science and Technology 557-306 Secondary Cycle Two, Year One June 2009 Doctors Unlimited A Summer in Colombia Theory Examination Student Information Document Secondary Cycle Two 557-306 Student
Applied Science and Technology 557-306 Secondary Cycle Two, Year One June 2009 Doctors Unlimited A Summer in Colombia Theory Examination Student Information Document Secondary Cycle Two 557-306 Student
A breath of fresh air
 A breath of fresh air BIG IDEAS You are learning to: Describe the structure of the lungs Explain how the lungs clean themselves Interpret patterns in data Where are the lungs and what do they do? The lungs
A breath of fresh air BIG IDEAS You are learning to: Describe the structure of the lungs Explain how the lungs clean themselves Interpret patterns in data Where are the lungs and what do they do? The lungs
Gas Exchange ACTIVITY OVERVIEW SUMMARY KEY CONCEPTS AND PROCESS SKILLS KEY VOCABULARY. Teacher s Guide B-75 L A B O R ATO R Y
 Gas Exchange 17 40- to 2 50-minute sessions ACTIVITY OVERVIEW L A B O R ATO R Y SUMMARY This activity explores the role of the respiratory system in the regulation of gases in the blood. Students investigate
Gas Exchange 17 40- to 2 50-minute sessions ACTIVITY OVERVIEW L A B O R ATO R Y SUMMARY This activity explores the role of the respiratory system in the regulation of gases in the blood. Students investigate
Circulation and Respiration: Vital Signs Student Version
 Circulation and Respiration: Vital Signs Student Version In this lab, you will learn about the circulatory and respiratory systems. You will test the capacity of your lungs, measure your blood pressure
Circulation and Respiration: Vital Signs Student Version In this lab, you will learn about the circulatory and respiratory systems. You will test the capacity of your lungs, measure your blood pressure
Components: Reader with DIGI MATERIAL cross-platform application (ios, Android, Windows, MacOSX) CLIL READERS. Level headwords.
 CirculatorySystem _6 cover.qxp_circulatorysystem _6 cover.qxp 21/9/16 6:56 PM Page 1 Level 6 Components: Reader with DIGI MATERIAL cross-platform application (ios, Android, Windows, MacOSX) Level 1 300
CirculatorySystem _6 cover.qxp_circulatorysystem _6 cover.qxp 21/9/16 6:56 PM Page 1 Level 6 Components: Reader with DIGI MATERIAL cross-platform application (ios, Android, Windows, MacOSX) Level 1 300
Bay Area Scientists in Schools Presentation Plan
 Bay Area Scientists in Schools Presentation Plan Lesson Name Measuring Carbon Dioxide with Vernier Probes Presenter(s) Derek Vigil Currey, Ph.D student in Physics at UCB Grade Level 5th Standards Connection(s)
Bay Area Scientists in Schools Presentation Plan Lesson Name Measuring Carbon Dioxide with Vernier Probes Presenter(s) Derek Vigil Currey, Ph.D student in Physics at UCB Grade Level 5th Standards Connection(s)
Fundamentals of Pistol Marksmanship William Joyner
 Fundamentals of Pistol Marksmanship William Joyner www.bullseyepistol.com In preview, I would like to say that shooting excellent scores with a pistol requires no other elements than those described in
Fundamentals of Pistol Marksmanship William Joyner www.bullseyepistol.com In preview, I would like to say that shooting excellent scores with a pistol requires no other elements than those described in
Introducing the Body Back Buddy TM
 Deep Muscle Massage Introducing the Body Back Buddy TM While in massage school in 1995, I experienced firsthand the numerous benefits of applying direct pressure to tight, sore and knotted muscles... noticeable
Deep Muscle Massage Introducing the Body Back Buddy TM While in massage school in 1995, I experienced firsthand the numerous benefits of applying direct pressure to tight, sore and knotted muscles... noticeable
The Breathing System
 The Breathing System Learning Intentions 1. Students should Know how Breathing happens 2. Name and know the functions of the Breathing System 3. Know how the organs work and how they work with other systems
The Breathing System Learning Intentions 1. Students should Know how Breathing happens 2. Name and know the functions of the Breathing System 3. Know how the organs work and how they work with other systems
Pop Quiz. What produces mucus, HCl and pepsinogen in the stomach? List a water soluable vitamin What is a ruminant stomach?
 Pop Quiz What produces mucus, HCl and pepsinogen in the stomach? List a water soluable vitamin What is a ruminant stomach? Respiratory System Review Cellular respiration: obtain glucose and oxygen, get
Pop Quiz What produces mucus, HCl and pepsinogen in the stomach? List a water soluable vitamin What is a ruminant stomach? Respiratory System Review Cellular respiration: obtain glucose and oxygen, get
Jogging The Course: Informative Guide to Jogging
 Jogging The Course: Informative Guide to Jogging Getting Started: If you re just beginning a jogging program, one of the best ways to start is a run-walk routine. However, if you have had no prior jogging
Jogging The Course: Informative Guide to Jogging Getting Started: If you re just beginning a jogging program, one of the best ways to start is a run-walk routine. However, if you have had no prior jogging
Digestive Anatomy & Physiology
 Digestive Anatomy & Physiology EQS 125 Table of Contents Click on the different sections of the table of contents to jump through this document Equine Digestive Principles... 3 Digestive Terminology...
Digestive Anatomy & Physiology EQS 125 Table of Contents Click on the different sections of the table of contents to jump through this document Equine Digestive Principles... 3 Digestive Terminology...
Monday, ! Today: Respiratory system! 5/20/14! Transport of Blood! What we ve been covering! Circulatory system! Parts of blood! Heart! tubing!
 Monday, 5.19.14! What we ve been covering! Circulatory system! Parts of blood! Heart! tubing! Transport of Blood! What is transported! Nutrients! Oxygen! Carbon Dioxide! Hormones! Antibodies! What it is/does!
Monday, 5.19.14! What we ve been covering! Circulatory system! Parts of blood! Heart! tubing! Transport of Blood! What is transported! Nutrients! Oxygen! Carbon Dioxide! Hormones! Antibodies! What it is/does!
Internal Anatomy of Fish
 Internal Anatomy of Fish The Systems of a Fish Skeletal System Muscular System Respiratory System Digestive System Circulatory System Nervous System Reproductive System Special Organs Skeletal System
Internal Anatomy of Fish The Systems of a Fish Skeletal System Muscular System Respiratory System Digestive System Circulatory System Nervous System Reproductive System Special Organs Skeletal System
The physiological functions of respiration and circulation. Mechanics. exercise 7. Respiratory Volumes. Objectives
 exercise 7 Respiratory System Mechanics Objectives 1. To explain how the respiratory and circulatory systems work together to enable gas exchange among the lungs, blood, and body tissues 2. To define respiration,
exercise 7 Respiratory System Mechanics Objectives 1. To explain how the respiratory and circulatory systems work together to enable gas exchange among the lungs, blood, and body tissues 2. To define respiration,
Before we can understand what dropsy is we must first understand two natural occurring scientific processes namely, Osmosis and Diffusion.
 Dropsy (Ascites) By Duncan Griffiths Before we can understand what dropsy is we must first understand two natural occurring scientific processes namely, Osmosis and Diffusion. Osmosis is the movement of
Dropsy (Ascites) By Duncan Griffiths Before we can understand what dropsy is we must first understand two natural occurring scientific processes namely, Osmosis and Diffusion. Osmosis is the movement of
PARTS AND STRUCTURE OF THE RESPIRATORY SYSTEM
 PARTS AND STRUCTURE OF THE RESPIRATORY SYSTEM Parts of the Respiratory System The RS can be divided into two parts: 1. Respiratory Tract, (path that air follows). Nasal passage Pharynx Larynx Trachea Bronchi,
PARTS AND STRUCTURE OF THE RESPIRATORY SYSTEM Parts of the Respiratory System The RS can be divided into two parts: 1. Respiratory Tract, (path that air follows). Nasal passage Pharynx Larynx Trachea Bronchi,
THE STUDY OF LUNG VELOCITY UNDER DIFFERENT CONDITIONS
 THE STUDY OF LUNG VELOCITY UNDER DIFFERENT CONDITIONS Natasha Chandra Cary Academy ABSTRACT The purpose of this study was to determine which activity made each student have the least lung velocity (L/sec).
THE STUDY OF LUNG VELOCITY UNDER DIFFERENT CONDITIONS Natasha Chandra Cary Academy ABSTRACT The purpose of this study was to determine which activity made each student have the least lung velocity (L/sec).
Hyperventilation. This leaflet is a continuation of the relaxation pack which looks at anxiety and panic attacks
 Hyperventilation This leaflet is a continuation of the relaxation pack which looks at anxiety and panic attacks 21a Hursley Road, Chandlers Ford, Eastleigh, Hants, SO53 2FS Tel no. 02380 240600 E-mail.
Hyperventilation This leaflet is a continuation of the relaxation pack which looks at anxiety and panic attacks 21a Hursley Road, Chandlers Ford, Eastleigh, Hants, SO53 2FS Tel no. 02380 240600 E-mail.
Harmonization exercises II
 Harmonization exercises II Pranayama The Sanskrit word meaning "extension of the prāṇa or breath" or "extension of the life force. Prana - life force, or vital energy Ayāma - to extend or draw out. The
Harmonization exercises II Pranayama The Sanskrit word meaning "extension of the prāṇa or breath" or "extension of the life force. Prana - life force, or vital energy Ayāma - to extend or draw out. The
Alternate Nostril Breathing
 Alternate Nostril Breathing What is Alternate Nostril Breathing? Alternate Nostril Breathing (also called Nadi Shodhana) is the practice of intentionally and in a focused way breathing for a few (or several)
Alternate Nostril Breathing What is Alternate Nostril Breathing? Alternate Nostril Breathing (also called Nadi Shodhana) is the practice of intentionally and in a focused way breathing for a few (or several)
You Might Also Like. I look forward helping you focus your instruction while saving tons of time. Kesler Science Station Lab Activities 40%+ Savings!
 Thanks Connect Thank you for downloading my product. I truly appreciate your support and look forward to hearing your feedback. You can connect with me and find many free activities and strategies over
Thanks Connect Thank you for downloading my product. I truly appreciate your support and look forward to hearing your feedback. You can connect with me and find many free activities and strategies over
Human Biology Respiratory System
 Human Biology Respiratory System Respiratory System Responsible for process of breathing Works in cooperation with Circulatory system Three types: 1. Internal Respiration 2. External Respiration 3. Cellular
Human Biology Respiratory System Respiratory System Responsible for process of breathing Works in cooperation with Circulatory system Three types: 1. Internal Respiration 2. External Respiration 3. Cellular
December 2013 I N S I D E T H I S I S S U E. Merry Christmas to all our friends! 1/ Seasons Greetings. 2/ What s in your hay?
 December 2013 BROOKS PERFORMANCE HORSE FEEDS 1580 HIGHWAY 7 A PORT PERRY ONTARIO L9L 1B5 I N S I D E T H I S I S S U E 1/ Seasons Greetings 2/ What s in your hay? 3/ Minimizing the possibility of impaction
December 2013 BROOKS PERFORMANCE HORSE FEEDS 1580 HIGHWAY 7 A PORT PERRY ONTARIO L9L 1B5 I N S I D E T H I S I S S U E 1/ Seasons Greetings 2/ What s in your hay? 3/ Minimizing the possibility of impaction
INSTRUCTION MANUAL. Automatic Blood Pressure Monitor with Fit Cuff. =Fit Cuff=!"#$% IA1B. Model
 IA1B INSTRUCTION MANUAL Automatic Blood Pressure Monitor with Fit Cuff =Fit Cuff=!"#$% Model IA1B Contents Introduction... 2 Notes on Safety... 3 Know Your Unit... 5 Quick Reference Guide... 7 Initial
IA1B INSTRUCTION MANUAL Automatic Blood Pressure Monitor with Fit Cuff =Fit Cuff=!"#$% Model IA1B Contents Introduction... 2 Notes on Safety... 3 Know Your Unit... 5 Quick Reference Guide... 7 Initial
FIRST AID. Study Topics. At a minimum, the following topics are to be studied for the first aid exam.
 FIRST AID Study Topics At a minimum, the following topics are to be studied for the first aid exam. TOPIC Avoid getting air in stomach during rescue breathing Burns Kinds of Burns & Care Calling for Help
FIRST AID Study Topics At a minimum, the following topics are to be studied for the first aid exam. TOPIC Avoid getting air in stomach during rescue breathing Burns Kinds of Burns & Care Calling for Help
Business Etiquette: Carrying Yourself with Dignity
 Business Etiquette: Carrying Yourself with Dignity Lesson Plan: Sit and Be at Ease Stand and Impress: Look At All That Good Posture Can Do Walk and Command Respect Review Quiz Lesson 3 2 Carrying Yourself
Business Etiquette: Carrying Yourself with Dignity Lesson Plan: Sit and Be at Ease Stand and Impress: Look At All That Good Posture Can Do Walk and Command Respect Review Quiz Lesson 3 2 Carrying Yourself
The Respiratory System
 Respiration and Excretion Name Date Class The Respiratory System This section describes the parts of the respiratory system and how they work to help you breathe and speak. Use Target Reading Skills As
Respiration and Excretion Name Date Class The Respiratory System This section describes the parts of the respiratory system and how they work to help you breathe and speak. Use Target Reading Skills As
WVWCI BIGGEST LOSER WEEK 3: WALKING BASICS DRESS FOR SUCCESS
 DRESS FOR SUCCESS Make sure you dress appropriately for walking. The following items will help you judge what to wear: Wear shoes with proper arch support, a firm heel, and thick, flexible soles that will
DRESS FOR SUCCESS Make sure you dress appropriately for walking. The following items will help you judge what to wear: Wear shoes with proper arch support, a firm heel, and thick, flexible soles that will
Mindfulness Tools. What does it mean to center?
 What does it mean to center? Mindfulness Tools To feel centered is to experience one s psychological center of gravity a solid integration of mind and body. Knowing how to feel centered is as important
What does it mean to center? Mindfulness Tools To feel centered is to experience one s psychological center of gravity a solid integration of mind and body. Knowing how to feel centered is as important
2.1.1 List the principal structures of the
 physiology 2.1.1 List the principal structures of the The principle structures of the respiratory are: Nose/Mouth used for inhalation of oxygen-rich air and expelling carbon dioxide rich air Pharynx -
physiology 2.1.1 List the principal structures of the The principle structures of the respiratory are: Nose/Mouth used for inhalation of oxygen-rich air and expelling carbon dioxide rich air Pharynx -
Lung Volumes and Capacities
 Lung Volumes and Capacities Normally the volume of air entering the lungs during a single inspiration is approximately equal to the volume leaving on the subsequent expiration and is called the tidal volume.
Lung Volumes and Capacities Normally the volume of air entering the lungs during a single inspiration is approximately equal to the volume leaving on the subsequent expiration and is called the tidal volume.
CONTENTS SPECIFICATIONS GENERAL INFORMATION RECOMMENDED USE OPERATING PRINCIPLE TIPS ON TAKING YOUR BLOOD PRESSURE 3-4 BATTERY INSTALLATION
 IFU SBPMON107 CONTENTS SPECIFICATIONS GENERAL INFORMATION RECOMMENDED USE OPERATING PRINCIPLE TIPS ON TAKING YOUR BLOOD PRESSURE BATTERY INSTALLATION CORRECT POSITION FOR MEASUREMENT POSITIONING THE CUFF
IFU SBPMON107 CONTENTS SPECIFICATIONS GENERAL INFORMATION RECOMMENDED USE OPERATING PRINCIPLE TIPS ON TAKING YOUR BLOOD PRESSURE BATTERY INSTALLATION CORRECT POSITION FOR MEASUREMENT POSITIONING THE CUFF
Glucose + Oxygen Carbon Dioxide + Water + Energy C6H12O CO2 + 6H20 + energy
 Cell Respiration - A food oxidization process in body cells to produce energy - Occurs (happens) in animal cells and plant cells Notes : Metabolic Reactions in Gaseous Exchange CELL RESPIRATION Photosynthesis
Cell Respiration - A food oxidization process in body cells to produce energy - Occurs (happens) in animal cells and plant cells Notes : Metabolic Reactions in Gaseous Exchange CELL RESPIRATION Photosynthesis
Assignments for Life Processes(Respiration)
 Assignments for Life Processes(Respiration) 1 Question 1 Why do organisms need food? Organisms need food for obtaining energy to perform the vital functions. Question 2 What is a respiratory substrate?
Assignments for Life Processes(Respiration) 1 Question 1 Why do organisms need food? Organisms need food for obtaining energy to perform the vital functions. Question 2 What is a respiratory substrate?
Marine Fishes. Chapter 8
 Marine Fishes Chapter 8 Fish Gills The construction of the gill is the same in all fish gill arch supports the entire structure, gill rakers are on the forward surface of the gill arch and gill filaments
Marine Fishes Chapter 8 Fish Gills The construction of the gill is the same in all fish gill arch supports the entire structure, gill rakers are on the forward surface of the gill arch and gill filaments
GASEOUS EXCHANGE 17 JULY 2013
 GASEOUS EXCHANGE 17 JULY 2013 Lesson Description In this lesson we: Discuss what is gaseous exchange? Consider requirements of an efficient gaseous exchange surface. Look at diversity in gas exchange systems.
GASEOUS EXCHANGE 17 JULY 2013 Lesson Description In this lesson we: Discuss what is gaseous exchange? Consider requirements of an efficient gaseous exchange surface. Look at diversity in gas exchange systems.
Improving Athlete Performance. Pennsylvania
 Improving Athlete Performance Pennsylvania 1 Learning Objectives and Goals Making healthier choices Leading healthy lifestyles Tracking athlete performance Coaching to improve athlete performance Setting
Improving Athlete Performance Pennsylvania 1 Learning Objectives and Goals Making healthier choices Leading healthy lifestyles Tracking athlete performance Coaching to improve athlete performance Setting
SCRIPT FOR FULL MINDFULNESS PRACTICE BODY SCAN 40 MINUTES
 SCRIPT FOR FULL MINDFULNESS PRACTICE BODY SCAN 40 MINUTES Before we begin, take time to get yourself comfortable. To do the body scan, you can either sit in a chair, or, if you prefer, lie on your back
SCRIPT FOR FULL MINDFULNESS PRACTICE BODY SCAN 40 MINUTES Before we begin, take time to get yourself comfortable. To do the body scan, you can either sit in a chair, or, if you prefer, lie on your back
LESSON 4 BREATHING 4-1. WHAT IS BREATHING?
 LESSON 4 BREATHING 4-1. WHAT IS BREATHING? Basically, breathing is ventilation. Ventilation is the mechanical act of moving air in and out of your lungs. Respiration is commonly confused with ventilation.
LESSON 4 BREATHING 4-1. WHAT IS BREATHING? Basically, breathing is ventilation. Ventilation is the mechanical act of moving air in and out of your lungs. Respiration is commonly confused with ventilation.
Respiratory System Lab
 Respiratory System Lab Note: Review the safety materials and wear goggles when working with chemicals. Read the entire exercise before you begin. Take time to organize the materials you will need and set
Respiratory System Lab Note: Review the safety materials and wear goggles when working with chemicals. Read the entire exercise before you begin. Take time to organize the materials you will need and set
Om Fairy LLC Page 1 This personal yoga practice was created for One Stressed Out Yogi.
 A Restorative Practice for One Stressed Out Yogini. In any of the postures below, if your joints are floating in the air (elbows, knees, ankles, etc.), you can utilize extra props for support, be it a
A Restorative Practice for One Stressed Out Yogini. In any of the postures below, if your joints are floating in the air (elbows, knees, ankles, etc.), you can utilize extra props for support, be it a
RESPIRATION AND EXCRETION
 CHAPTER 13 RESPIRATION AND EXCRETION SECTION 13 1 The Respiratory System (pages 430-438) This section describes the parts of the respiratory system and how they work to help you breathe and speak. Introduction
CHAPTER 13 RESPIRATION AND EXCRETION SECTION 13 1 The Respiratory System (pages 430-438) This section describes the parts of the respiratory system and how they work to help you breathe and speak. Introduction
Biology. Slide 1 of 53. End Show. Copyright Pearson Prentice Hall
 Biology 1 of 53 Chapter 33 Comparing Chordates 2 of 53 This chapter is a good revision of the material we saw during Unit III. 3 of 53 4 of 53 Controlling Body Temperature The control of body temperature
Biology 1 of 53 Chapter 33 Comparing Chordates 2 of 53 This chapter is a good revision of the material we saw during Unit III. 3 of 53 4 of 53 Controlling Body Temperature The control of body temperature
Chapter 1: Respiration
 Chapter 1: Respiration Respiration Human Breathing Mechanism Transport of oxygen Importance of a healthy respiratory system Respiratory system lungs inhalation exhalation Diffusion of oxygen by blood Transport
Chapter 1: Respiration Respiration Human Breathing Mechanism Transport of oxygen Importance of a healthy respiratory system Respiratory system lungs inhalation exhalation Diffusion of oxygen by blood Transport
Respiration. The ins and outs
 Respiration The ins and outs Functions 1. To bring O 2 into the body and transfer it to the blood stream 2. To remove CO 2 Circulation and respiration work together to achieve these functions Why Do We
Respiration The ins and outs Functions 1. To bring O 2 into the body and transfer it to the blood stream 2. To remove CO 2 Circulation and respiration work together to achieve these functions Why Do We
HOW-TO CONDUCT A WEEKLY SAFETY MEETING
 HOW-TO CONDUCT A WEEKLY SAFETY MEETING 1. Hold the meeting on the job, preferably where everyone can sit and relax. 2. Hold the meeting at the beginning of the shift, right after lunch, or after a break.
HOW-TO CONDUCT A WEEKLY SAFETY MEETING 1. Hold the meeting on the job, preferably where everyone can sit and relax. 2. Hold the meeting at the beginning of the shift, right after lunch, or after a break.
table of Contents Foreword: Chapter 1: Chapter 2: Chapter 3: Chapter 4: Chapter 5: Chapter 6: Chapter 7: Chapter 8: Chapter 9: Chapter 10:
 Table of Contents Table of Contents Foreword: You Can Be a Runner... 6 Chapter 1: Why Run?... 8 Chapter 2: What You Need to Get Started... 18 Chapter 3: A Trip to the Running Store... 26 Chapter 4: Setting
Table of Contents Table of Contents Foreword: You Can Be a Runner... 6 Chapter 1: Why Run?... 8 Chapter 2: What You Need to Get Started... 18 Chapter 3: A Trip to the Running Store... 26 Chapter 4: Setting
Cardio Pulmonary Resuscitation
 1 CPR (HLTCPR201B Perform CPR) 2 Action Plan D anger R esponse S end for help A irway B reathing C PR D efibrillation 3 D anger Check for dangers to: Yourself Bystanders Casualty Walk 360 o around the
1 CPR (HLTCPR201B Perform CPR) 2 Action Plan D anger R esponse S end for help A irway B reathing C PR D efibrillation 3 D anger Check for dangers to: Yourself Bystanders Casualty Walk 360 o around the
6 EASY BREATHING TECHNIQUES FOR ENHANCED WEIGHT LOSS
 6 EASY BREATHING TECHNIQUES FOR ENHANCED WEIGHT LOSS NIKA KARAN TABLE OF CONTENTS 1) Introduction 2) The benefits of yoga breathing 3) A short guide to a successful breathing practice 4) Breathing techniques
6 EASY BREATHING TECHNIQUES FOR ENHANCED WEIGHT LOSS NIKA KARAN TABLE OF CONTENTS 1) Introduction 2) The benefits of yoga breathing 3) A short guide to a successful breathing practice 4) Breathing techniques
THAL EQUINE LLC Regional Equine Hospital Horse Owner Education & Resources Santa Fe, New Mexico
 THAL EQUINE LLC Regional Equine Hospital Horse Owner Education & Resources Santa Fe, New Mexico 505-438-6590 www.thalequine.com Colic Surgery: What Horse Owners Should Know Tonight, at midnight, you are
THAL EQUINE LLC Regional Equine Hospital Horse Owner Education & Resources Santa Fe, New Mexico 505-438-6590 www.thalequine.com Colic Surgery: What Horse Owners Should Know Tonight, at midnight, you are
Introducing the Body Back Buddy TM
 Introducing the Body Back Buddy TM While in massage school in 1995, I experienced firsthand the numerous benefits of applying direct pressure to tight, sore and knotted muscles... noticeable relief, more
Introducing the Body Back Buddy TM While in massage school in 1995, I experienced firsthand the numerous benefits of applying direct pressure to tight, sore and knotted muscles... noticeable relief, more
Last night, as I rounded the corner of Burrows and College, my legs felt the
 Last night, as I rounded the corner of Burrows and College, my legs felt the previous 7 miles, and with only ¼ mile left, my breathing was controlled, my blood was flowing, and my heart was pumping. Advances
Last night, as I rounded the corner of Burrows and College, my legs felt the previous 7 miles, and with only ¼ mile left, my breathing was controlled, my blood was flowing, and my heart was pumping. Advances
To keep the body in good health is a duty otherwise we shall not be able to keep our mind strong and clear. - Guatama Buddha
 To keep the body in good health is a duty otherwise we shall not be able to keep our mind strong and clear. - Guatama Buddha Desk Stretches Why Stretch? Stretching allows the muscle to release tension.
To keep the body in good health is a duty otherwise we shall not be able to keep our mind strong and clear. - Guatama Buddha Desk Stretches Why Stretch? Stretching allows the muscle to release tension.
Homeostasis and Negative Feedback Concepts and Breathing Experiments 1
 Homeostasis and Negative Feedback Concepts and Breathing Experiments 1 I. Homeostasis and Negative Feedback Homeostasis refers to the maintenance of relatively constant internal conditions. For example,
Homeostasis and Negative Feedback Concepts and Breathing Experiments 1 I. Homeostasis and Negative Feedback Homeostasis refers to the maintenance of relatively constant internal conditions. For example,
HEAT INJURIES. MANSCEN Safety Office
 HEAT INJURIES MANSCEN Safety Office OBJECTIVES 1. Know Individual risk factors. 2. Proper Acclimatization. 3. Know types of heat injuries, and first aid. 4. Be able to read and obtain WBGT index. A. INDIVIDUAL
HEAT INJURIES MANSCEN Safety Office OBJECTIVES 1. Know Individual risk factors. 2. Proper Acclimatization. 3. Know types of heat injuries, and first aid. 4. Be able to read and obtain WBGT index. A. INDIVIDUAL
16-AND-UNDER (MIDGET) & 18-AND-UNDER (MIDGET) SKILL PROGRESSIONS
 16-AND-UNDER (MIDGET) & 18-AND-UNDER (MIDGET) SKILL PROGRESSIONS At the 16-and-Under (Midget) and 18-and-Under (Midget) levels for boys and girls, players should focus on the skill progressions listed
16-AND-UNDER (MIDGET) & 18-AND-UNDER (MIDGET) SKILL PROGRESSIONS At the 16-and-Under (Midget) and 18-and-Under (Midget) levels for boys and girls, players should focus on the skill progressions listed
Respiration. The resspiratory system
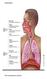 Respiration The resspiratory system The Alveoli The lungs have about 300 million alveoli, with a total crosssec onal area of 50 70 m2.. Each alveolar sac is surrounded by blood capillaries. The walls of
Respiration The resspiratory system The Alveoli The lungs have about 300 million alveoli, with a total crosssec onal area of 50 70 m2.. Each alveolar sac is surrounded by blood capillaries. The walls of
Living with. Chronic Obstructive Pulmonary Disease COPD. Breathing and Relaxation
 Living with Chronic Obstructive Pulmonary Disease COPD Breathing and Relaxation Anatomy and Physiology of COPD Breathing Techniques Positions to Reduce Shortness of Breath Relaxation Exercise Breathing
Living with Chronic Obstructive Pulmonary Disease COPD Breathing and Relaxation Anatomy and Physiology of COPD Breathing Techniques Positions to Reduce Shortness of Breath Relaxation Exercise Breathing
Chapter 9: Safety and First Aid
 Chapter 9: Personal Safety 9.1 Personal Safety Every one has the right to be protected. Violent crime has become a major health problem. Among these crimes are homicide and robbery. Homicide is the killing
Chapter 9: Personal Safety 9.1 Personal Safety Every one has the right to be protected. Violent crime has become a major health problem. Among these crimes are homicide and robbery. Homicide is the killing
Breathing Pattern Disorder
 Breathing Pattern Disorder Information for patients There are many reasons why our breathing can lose its natural rhythm (see diagram). Triggers cause disturbance to our breathing which could lead to unpleasant
Breathing Pattern Disorder Information for patients There are many reasons why our breathing can lose its natural rhythm (see diagram). Triggers cause disturbance to our breathing which could lead to unpleasant
The Respiratory System
 Name Date Class The Respiratory System This section describes the parts of the respiratory system and how they work to help you breathe and speak. Use Target Reading Skills As you read, complete the flowchart
Name Date Class The Respiratory System This section describes the parts of the respiratory system and how they work to help you breathe and speak. Use Target Reading Skills As you read, complete the flowchart
 Index Age: 5 8 Yrs Invocation Prayers 1) Standing: A) Palm Tree Pose (Talasana) B) Ekpadasana C) Cone Pose (Konasana) 2) Sitting: A) Mountain Pose (Parvatasana) B) Cat Pose (Manjarasana) C) Butterfly Pose
Index Age: 5 8 Yrs Invocation Prayers 1) Standing: A) Palm Tree Pose (Talasana) B) Ekpadasana C) Cone Pose (Konasana) 2) Sitting: A) Mountain Pose (Parvatasana) B) Cat Pose (Manjarasana) C) Butterfly Pose
4/16/18. Basic Emotional Energetics. Basic Energetics. Image Copyright 2010 by Steven Horne
 Basic Emotional Energetics Basic Energetics Image Copyright 2010 by Steven Horne 1 Emotion and Energetics Image Copyright 2010 by Steven Horne Emotional Balance Fear - Anxiety (Yellow) Joy, Love, Peace,
Basic Emotional Energetics Basic Energetics Image Copyright 2010 by Steven Horne 1 Emotion and Energetics Image Copyright 2010 by Steven Horne Emotional Balance Fear - Anxiety (Yellow) Joy, Love, Peace,
My Teeth Are Full of Fillings But I ve Never Had A Cavity In My Tongue!
 The Way of Martial Arts MONTHLY INTERACTIVE LESSONS TO HELP IMPROVE YOUR DAILY LIFE B Y M A S T E R E R I C S B A R G E Lesson 10 My Teeth Are Full of Fillings But I ve Never Had A Cavity In My Tongue!
The Way of Martial Arts MONTHLY INTERACTIVE LESSONS TO HELP IMPROVE YOUR DAILY LIFE B Y M A S T E R E R I C S B A R G E Lesson 10 My Teeth Are Full of Fillings But I ve Never Had A Cavity In My Tongue!
1. Label a diagram of the respiratory system. Objective sheet 3 Notes
 1. Label a diagram of the respiratory system Objective sheet 3 Notes 2. Functions of the respiratory structures Name Description Function Nasal Cavity Trachea Bronchi (Singular Bronchus) Bronchioles Lungs
1. Label a diagram of the respiratory system Objective sheet 3 Notes 2. Functions of the respiratory structures Name Description Function Nasal Cavity Trachea Bronchi (Singular Bronchus) Bronchioles Lungs
Mechanisms of Breathing. Vital Capacity
 Mechanisms of Breathing Mechanics of Breathing Two muscles are involved in the mechanics of breathing: Diaphragm = large sheet of muscle located beneath the lungs that is the primary muscle in breathing
Mechanisms of Breathing Mechanics of Breathing Two muscles are involved in the mechanics of breathing: Diaphragm = large sheet of muscle located beneath the lungs that is the primary muscle in breathing
The Petite Player Position Adjustments for Small Hands
 The Petite Player Position Adjustments for Small Hands Molly L. York The Petite Player Position Adjustments for Small Hands Being a petite player with a small stature and petite hand structure can present
The Petite Player Position Adjustments for Small Hands Molly L. York The Petite Player Position Adjustments for Small Hands Being a petite player with a small stature and petite hand structure can present
practices makes perfect
 Human Respiratory system Chapter 1: Respiration PMR 03, 08 1. The human respiratory system consists of: a... b... c.. d... e. Our body has.. lungs (right & left). f. Each lung consists of the, and alveoli.
Human Respiratory system Chapter 1: Respiration PMR 03, 08 1. The human respiratory system consists of: a... b... c.. d... e. Our body has.. lungs (right & left). f. Each lung consists of the, and alveoli.
BIOLOGY 12: UNIT J - CHAPTER 15 - REVIEW WORKSHEET RESPIRATORY SYSTEM
 BIOLOGY 12: UNIT J - CHAPTER 15 - REVIEW WORKSHEET RESPIRATORY SYSTEM A. CHAPTER REVIEW 1. Define the four components of respiration. 2. What happens to the air as it moves along the air passages? What
BIOLOGY 12: UNIT J - CHAPTER 15 - REVIEW WORKSHEET RESPIRATORY SYSTEM A. CHAPTER REVIEW 1. Define the four components of respiration. 2. What happens to the air as it moves along the air passages? What
Structures of the Respiratory System include:
 Respiratory System Structures of the Respiratory System include: ü Oral Cavity ü Nasal Cavity ü Pharynx ü Epiglottis ü Larynx ü Trachea ü Diaphragm ü Lung ü Bronchus ü Bronchioles ü Alveolus ü Pulmonary
Respiratory System Structures of the Respiratory System include: ü Oral Cavity ü Nasal Cavity ü Pharynx ü Epiglottis ü Larynx ü Trachea ü Diaphragm ü Lung ü Bronchus ü Bronchioles ü Alveolus ü Pulmonary
8 Pieces of Brocade. 1. Two hands lifting the sky with finger interlocked to harmonize the triple warmers.
 8 Pieces of Brocade Preparing/standing form: Move left feet one step to the left side, feet with shoulder width, relax and bend knee slightly, stand strict, tongue touch the upper jaw, close lower jaw,
8 Pieces of Brocade Preparing/standing form: Move left feet one step to the left side, feet with shoulder width, relax and bend knee slightly, stand strict, tongue touch the upper jaw, close lower jaw,
Measuring Lung Capacity
 Name Class Date Chapter 37 Circulatory and Respiratory Systems Measuring Lung Capacity Introduction The amount of air that you move in and out of your lungs depends on how quickly you are breathing. The
Name Class Date Chapter 37 Circulatory and Respiratory Systems Measuring Lung Capacity Introduction The amount of air that you move in and out of your lungs depends on how quickly you are breathing. The
YIN&YANG ENERGY LINES
 YIN&YANG ENERGY LINES Karate technique is a combination of intentional creation and distribution of the energy - a physical movement that enables human body the use of its full potential at the time. In
YIN&YANG ENERGY LINES Karate technique is a combination of intentional creation and distribution of the energy - a physical movement that enables human body the use of its full potential at the time. In
Respiratory Pulmonary Ventilation
 Respiratory Pulmonary Ventilation Pulmonary Ventilation Pulmonary ventilation is the act of breathing and the first step in the respiratory process. Pulmonary ventilation brings in air with a new supply
Respiratory Pulmonary Ventilation Pulmonary Ventilation Pulmonary ventilation is the act of breathing and the first step in the respiratory process. Pulmonary ventilation brings in air with a new supply
Silo Gases - the Hidden Danger Silo gas is formed by the natural fermentation of chopped silage shortly after it is placed in the silo.
 Silo Gases - the Hidden Danger Silo gas is formed by the natural fermentation of chopped silage shortly after it is placed in the silo. We have all heard the old saying, a little knowledge is a dangerous
Silo Gases - the Hidden Danger Silo gas is formed by the natural fermentation of chopped silage shortly after it is placed in the silo. We have all heard the old saying, a little knowledge is a dangerous
Chapter 16 Respiratory System
 Introduction Chapter 16 Respiratory System The respiratory system consists of tubes that filter incoming air and transport it to alveoli where gases are exchanged. Think pair share: what organs are associated
Introduction Chapter 16 Respiratory System The respiratory system consists of tubes that filter incoming air and transport it to alveoli where gases are exchanged. Think pair share: what organs are associated
Lesson 28. Function - Respiratory Pumps in Air Breathers Buccal Force Pump Aspiration Pump - Patterns of Gas Transfer in Chordates
 Lesson 28 Lesson Outline: Evolution of Respiratory Mechanisms - Air Breathers Form - Accessory Air Breathing Organs Facultative vs Obligate - Lungs Function - Respiratory Pumps in Air Breathers Buccal
Lesson 28 Lesson Outline: Evolution of Respiratory Mechanisms - Air Breathers Form - Accessory Air Breathing Organs Facultative vs Obligate - Lungs Function - Respiratory Pumps in Air Breathers Buccal
Walking is the best possible exercise.
 Walking Best, safest, and most natural form of exercise Effective form of exercise for all ages Effective form of exercise for all states and levels of health Increases sense of well-being Walking is the
Walking Best, safest, and most natural form of exercise Effective form of exercise for all ages Effective form of exercise for all states and levels of health Increases sense of well-being Walking is the
Unit II Problem 4 Physiology: Diffusion of Gases and Pulmonary Circulation
 Unit II Problem 4 Physiology: Diffusion of Gases and Pulmonary Circulation - Physical principles of gases: Pressure of a gas is caused by the movement of its molecules against a surface (more concentration
Unit II Problem 4 Physiology: Diffusion of Gases and Pulmonary Circulation - Physical principles of gases: Pressure of a gas is caused by the movement of its molecules against a surface (more concentration
Chapter 10 First Aid and Field Sanitation
 Review Questions Chapter 10 First Aid and Field Sanitation 1. True or False. The three reasons for performing first aid are to save lives, prevent further injuries, and prevent infection? 1. True 2. False
Review Questions Chapter 10 First Aid and Field Sanitation 1. True or False. The three reasons for performing first aid are to save lives, prevent further injuries, and prevent infection? 1. True 2. False
Exploring the relationship between Heart Rate (HR) and Ventilation Rate (R) in humans.
 Exploring the relationship between Heart Rate (HR) and Ventilation Rate (R) in humans. The Research Question In this investigation I will be considering the following general research question: Does increased
Exploring the relationship between Heart Rate (HR) and Ventilation Rate (R) in humans. The Research Question In this investigation I will be considering the following general research question: Does increased
This kriya comes from Owner s Manual For The Human Body Kundalini Yoga as Taught by Yogi Bhajan.
 This kriya comes from Owner s Manual For The Human Body Kundalini Yoga as Taught by Yogi Bhajan. There are 47 kriyas in the Owner s Manual, ranging from Routine Maintenance, Brain and Nervous System, Maintaining
This kriya comes from Owner s Manual For The Human Body Kundalini Yoga as Taught by Yogi Bhajan. There are 47 kriyas in the Owner s Manual, ranging from Routine Maintenance, Brain and Nervous System, Maintaining
Recitation question # 05
 Recitation and Lab # 05 The goal of this recitations / labs is to review material related to the CV and respiratory lectures for the second test of this course. Info required to answer this recitation
Recitation and Lab # 05 The goal of this recitations / labs is to review material related to the CV and respiratory lectures for the second test of this course. Info required to answer this recitation
(A) The partial pressure in the lungs is higher than in the blood, and oxygen diffuses out of the lungs passively.
 DAT Biology - Problem Drill 12: The Respiratory System Question No. 1 of 10 1. Which statement about the partial pressure of oxygen inside the lungs is correct? Question #01 (A) The partial pressure in
DAT Biology - Problem Drill 12: The Respiratory System Question No. 1 of 10 1. Which statement about the partial pressure of oxygen inside the lungs is correct? Question #01 (A) The partial pressure in
English Español Português Italiano Deutch Français INSTRUCTION MANUAL FOR DIGITAL BLOOD PRESSURE MONITOR MODEL CH-656C. - Eng 1 -
 English Español Português Italiano Deutch Français INSTRUCTION MANUAL FOR DIGITAL BLOOD PRESSURE MONITOR MODEL CH-656C M - Eng 1 - CLEANING METHOD OF CUFF After cleaning the cuff with a neutral detergent,
English Español Português Italiano Deutch Français INSTRUCTION MANUAL FOR DIGITAL BLOOD PRESSURE MONITOR MODEL CH-656C M - Eng 1 - CLEANING METHOD OF CUFF After cleaning the cuff with a neutral detergent,
MEMBERSHIP OPTIONS. 1 Year. 6 Months. 3 Months. Day Pass
 MEMBERSHIP OPTIONS 1 Year Single Male AED 4,870 AED 4,115 Single Female AED 3,025 AED 2,700 Couple AED 5,630 AED 4,865 Family AED 6,270 AED 5,430 Child (2-15 y.o.) AED 1,300 AED 1,080 6 Months Single Male
MEMBERSHIP OPTIONS 1 Year Single Male AED 4,870 AED 4,115 Single Female AED 3,025 AED 2,700 Couple AED 5,630 AED 4,865 Family AED 6,270 AED 5,430 Child (2-15 y.o.) AED 1,300 AED 1,080 6 Months Single Male
Learn to Breathe. A Simple Technique to Manage Stress. Debra Burdick, LCSW, BCN. Debra E Burdick, LCSW, BCN
 Learn to Breathe A Simple Technique to Manage Stress Debra Burdick, LCSW, BCN www.thebrainlady.com Learn to Breathe A Simple Technique to Manage Stress Mindfulness Paying attention to our breathing is
Learn to Breathe A Simple Technique to Manage Stress Debra Burdick, LCSW, BCN www.thebrainlady.com Learn to Breathe A Simple Technique to Manage Stress Mindfulness Paying attention to our breathing is
The Colic E-Book for Horse Owners Understanding the Risks and How to Avoid Them
 The Colic E-Book for Horse Owners Understanding the Risks and How to Avoid Them By the Crusade Against Equine Colic Presented by SUCCEED Digestive Conditioning Program Originally published as a series
The Colic E-Book for Horse Owners Understanding the Risks and How to Avoid Them By the Crusade Against Equine Colic Presented by SUCCEED Digestive Conditioning Program Originally published as a series
HEAT STRESS Prevention Program
 HEAT STRESS Prevention Program FACTS Although heat-related illness and death are readily preventable, the CDC reports an annual average of 600 Heat related deaths and over 7,000 Heat related illnesses
HEAT STRESS Prevention Program FACTS Although heat-related illness and death are readily preventable, the CDC reports an annual average of 600 Heat related deaths and over 7,000 Heat related illnesses
Michael Pate Utah State University
 Michael Pate Utah State University Objectives To be able to identify types of respiratory hazards To understand different health issues caused by hazards To be able to select the correct protection to
Michael Pate Utah State University Objectives To be able to identify types of respiratory hazards To understand different health issues caused by hazards To be able to select the correct protection to
RSPT 1060 OBJECTIVES OBJECTIVES OBJECTIVES EQUATION OF MOTION. MODULE C Applied Physics Lesson #1 - Mechanics. Ventilation vs.
 RSPT 1060 MODULE C Applied Physics Lesson #1 - Mechanics OBJECTIVES At the end of this module, the student should be able to define the terms and abbreviations used in the module. draw & explain the equation
RSPT 1060 MODULE C Applied Physics Lesson #1 - Mechanics OBJECTIVES At the end of this module, the student should be able to define the terms and abbreviations used in the module. draw & explain the equation
