WHAT TO DO WITH ILL OR DEAD FROGS
|
|
|
- Cori Hubbard
- 5 years ago
- Views:
Transcription
1 WHAT TO DO WITH ILL OR DEAD FROGS Lee Berger and Rick Speare School of Public Health, Tropical Medicine & Rehabilitation Sciences, James Cook University, Townsville, Qld, 4811 CONTENTS 1. Introduction Assumptions Basic Information Required on All Specimens Preservation Techniques Ideal Processing Technique Specimens to Collect Dead Frogs Problems with Dead Frogs Processing of Dead Frogs Ill Frogs Severity of Illness Problems with Ill Frogs Benefits of Collector Doing Processing Processing of Ill Frogs Terminal Frogs Non-Terminal Frogs Sending Specimens Terminal Frogs Non-Terminal Frogs... 9
2 7. Transportation of Specimens Amphibian Submission Form How to Make Good Quality Formalin % Neutral Buffered Formalin Chemicals needed Procedure INTRODUCTION At our present stage of knowledge about diseases of frogs, we need all the additional specimens that we can get. Only by thorough studies of more dead and ill frogs will we be able to piece together the overall disease picture. For that reason every ill or dead frog is valuable, and efforts to get the maximum amount of information from each specimen are well worth while. Deciding what to do with an ill or dead frog is a complex process. At the current time, if you find a frog that is ill, do not allow it to die in the wild; collect it and allow it to be used. This document will assist you in deciding what to do with a particular ill or dead frog given the particular circumstances associated with it. If possible, identify a wildlife pathologist available to examine frogs to discuss preferred preservation methods. 2. ASSUMPTIONS More information will be obtained from a post mortem examination done by an experienced pathologist than from one done by a person with little experience in collecting specimens from frogs. Less information will be obtained from a dead frog than from a frog that is processed in the terminal state. Therefore, if a collector has dissecting skills and equipment, examining a terminal frog will provide more information than shipping the frog and having it die in transit. Processing of specimens will depend on: - whether the frogs are ill or dead - if ill, whether they are terminal or non-terminal - time from collection to processing - level of expertise of finder/dispatcher - facilities available
3 Any stage (eggs, tadpoles, metamorphs, juveniles and adults) should be sent if dead, ill or abnormal. Dead or ill cane toads should be treated in the same way as frogs. 3. BASIC INFORMATION REQUIRED ON ALL SPECIMENS To make the most of every specimen, please record and pass on the following information: - Species of frog - Date and time - Where found - be very detailed. Use map if helpful - Brief description of area where specimen was found - Why you think it is abnormal. In this include details on appearance and behaviour - Whether other frogs were ill or dead - What proportion of population was affected - Is finding ill or dead frogs a common occurrence? If "yes", please provide details on locations, dates, signs, and species. The submission form at the end of this document can be used to record this information. 4. PRESERVATION TECHNIQUES Once a frog dies, its tissues start to degenerate (post mortem degeneration). The rate of degeneration is dependent on ambient temperature. If a frog is dead, action has to be swift to get the maximum amount of information possible from the specimen. Post mortem change decreases the amount of histological information as well as the chances of isolating an infectious agent. Post mortem degeneration can be stopped by: - chemicals called fixatives (alcohol, formalin, or glutaraldehyde), or - freezing (though this is not ideal) Preserving agents, while protecting the tissues from post mortem degeneration, also kill infectious agents. So if viruses or bacteria are present, once the tissue is preserved, the infectious agent cannot be grown. This is the major disadvantage of preserving specimens. Infectious agents in tissues are best protected by freezing the whole specimen, or pieces of certain tissues.
4 Fixatives stop post mortem degeneration and protect the histology Fixatives kill infectious agents Freezing protects infectious agents and keeps them alive, also toxicology can be done. Freezing stops post mortem degeneration, but ice crystals damage the tissues for histology 4.1 IDEAL PROCESSING TECHNIQUE The ideal solution to get the maximum amount of data is to: - necropsy the frog using an aseptic technique - cut organs into pieces: o preserve parts of organs in 10% buffered neutral formalin for histology (please remember that fresh well buffered formalin is best). o preserve small parts of organs in 2.5% glutaraldehyde for transmission electron microscopy; this enhances the possibility of identifying intracellular pathogens, and is very important when looking for a new infectious agent. - freeze the remainder of organs at -70 o C for isolation of infectious agents. Freezing at -20 o C is better than leaving in the fridge at 4 o C. Obviously this option requires skill, knowledge and access to the correct chemicals. 4.2 SPECIMENS TO COLLECT Specimens for disease investigation are mainly collected for 4 reasons: 1. Histopathology - to observe the pattern of changes in cells in tissues and visualisation of some infectious organisms. Organs affected by disease can be identified. For histopathology, tissues have to be preserved in formalin or alcohol based liquids. Please try to use quality fixatives, e.g. fresh well buffered formalin, as this enables follow-up electron microscopy to be used. 2. Identification of agent - if disease is caused by an infectious agent, fresh or frozen specimens may allow the micro-organism to be isolated, grown in-vitro, identified using antigen detection techniques, or identified using molecular biological techniques. 3. Transmission electron microscopy - if an infectious agent is present, it may be identified using TEM even if the micro-organism cannot be isolated. To get the
5 best result, tissues are preserved in glutaraldehyde (if glutaraldehyde is not available, use formalin). 4. Toxicology - frozen tissues are necessary. Liver, kidney, fat and stomach contents are considered likely to have concentrated levels of toxins. For histology, collect the following in 10% formalin: - Any abnormal changes or lesions - Skin - Skeletal muscle - Liver - Kidney - Spleen - Lung - Heart - Stomach - Intestine - Urinary bladder - Eye - Brain - Bone of femur - Gonads For isolation of infectious agents or toxicology, collect the following organs and freeze: - Any lesions - Liver - Kidney - Lung - Skeletal muscle - Brain
6 - Stomach contents - Fat bodies - Remainder of carcase. To detect chytridiomycosis by PCR, swab ventral skin see separate instructions for molecular diagnosis. 5. DEAD FROGS Dead frogs can be handled in three ways: - Frozen whole - Preserved whole in formalin or alcohol after opening the belly - Necropsy for gross examination and removal of individual organs 5.1 PROBLEMS WITH DEAD FROGS The main problem is that post mortem degeneration in dead frogs is very rapid; the higher the temperature, the greater the rate of degeneration. The aim is to get the maximum amount of information from the frog before it decays any further. 5.2 PROCESSING OF DEAD FROGS If a post mortem can be done immediately by someone with experience and the right chemicals, then do a post mortem, divide organs if possible into two, put specimens for histology in 10% buffered neutral formalin, freeze the other half of the organs, freeze the carcase. 6. ILL FROGS The key question here is mainly for people that have found a terminal (almost dead) frog, and are trying to decide whether: - to forward the frog to the laboratory, and run the risk of it dying in transit, and have the lab get a dead frog; or - to kill the frog on site, and process it for subsequent examination by the laboratory. 6.1 SEVERITY OF ILLNESS An "ill" frog for our purposes has at least one of the following: - behaves in an abnormal fashion;
7 - is very thin; - has abnormalities of eyes or skin; - is deformed Ill frogs should be classified into two groups: terminal and non-terminal. Terminal: a frog which will probably die within 24 hours. Signs: not able to move; moves very slowly; very thin; can be turned onto back and does not attempt to right itself. Non-terminal: a frog that is ill, but will probably not die in 24 hours. Signs: attempts to escape; moves actively. 6.2 PROBLEMS WITH ILL FROGS An ill frog may become a dead frog during transit. Terminally ill frogs and toads usually die in transit. Once an amphibian dies, degeneration occurs rapidly. If a frog is terminal, it is better to process it prior to dispatch, or to dispatch it in a cooled container. 6.3 BENEFITS OF COLLECTOR DOING PROCESSING Since more comprehensive information can be obtained from live amphibians, it is better for us to receive live, ill frogs than dead frogs. So the main aim should be to get a live, ill frog to the Amphibian Disease Group. However, after considering the various factors below, the best option for the collector may be to process the frog, and then to send the specimens to us. 6.4 PROCESSING OF ILL FROGS TERMINAL FROGS Collector Has Minimal Dissection Experience If you have minimal scientific facilities and skill: Put frog in plastic bag in freezer to kill it. If there are many ill frogs, some can be fixed and the rest frozen. 10% formalin is preferred, although 70% alcohol can also be used. After euthanasia, cut through the skin and muscle on the belly before placing in fixative. Collector has Dissection Experience If you have appropriate facilities and skill: - Weigh frog
8 - Measure snout-vent length - Anaesthetise with chloroform, or barbiturate - Open ventrally along abdomen - Collect blood from heart using needle, capillary tube or incision - Make smears (dry at room temperature) - Collect into plain tube (store in fridge at 4 o C) - Collect 0.3 ml into EDTA or sequestrene tube for haematology (store in fridge at 4 o C) - Examine internal organs for abnormalities - Divide organs into 2, one part for histology (placed in 10% formalin), and other into sterile tube (for culture of micro-organisms - freeze in fridge at - 20 o C or - 80 o C) - If possible, a small section of the organs and lesions (~1mm thick) should be placed in 2.5% glutaraldehyde at 4 o C for electron microscopy. 25% glutaraldehyde is usually obtained which needs to be diluted in 0.1M phosphate buffered saline shortly before use. After 24 hours the samples should be transferred to phosphate buffered saline. - Fresh tissue specimens should be frozen at -20 o C NON-TERMINAL FROGS If the frog is ill, but it seems likely that it will not die within 24 hours, do the following: - Source a interested pathologist if possible - Place frog in a bag made of cloth - Wet bag - Dispatch so air supply is not restricted (i.e., don't put into airtight bottle or plastic container). 6.5 SENDING SPECIMENS TERMINAL FROGS Full post mortem
9 To be useful, blood specimens should arrive within 2 days of collection. If delivery is impossible within 2 days, the blood tubes should be frozen as for fresh tissue samples. Dispatch frozen samples with dry ice or if not possible, with an ice brick. Dispatch fixed samples in 10% formalin. Frozen Specimens Forward with dry ice or, if not possible, with an ice brick NON-TERMINAL FROGS Forward as livestock. 7. TRANSPORTATION OF SPECIMENS If sending specimens by air, the fresh tissues are regarded as diagnostic specimens and are not classified as dangerous goods. They have to be packed and dispatched according to IATA Regulation 650. Labelled "Diagnostic specimen" on consignment note. If dry ice is included, the package is treated as a Dangerous Good. Label "Diagnostic specimen and dry ice" on consignment note, but no shipping bill required. If 10% formalin is included, since formalin is a dangerous good, the package has to be packed in accordance with Dangerous Goods Regulations. Shipping bill required.
10 8. AMPHIBIAN SUBMISSION FORM SENDER'S NAME AND ADDRESS: TELEPHONE SENDERS ID NUMBER... SPECIES... STAGE... AGE... SEX... LENGTH Snout-vent... WEIGHT... DATE & TIME COLLECTED...DATE SUBMITTED... LOCATION FOUND(lat/long)... TYPE OF ENVIRONMENT... ARE PESTICIDES etc USED?... ABNORMAL BEHAVIOUR... EFFECT OF HANDLING... ABNORMAL APPEARANCE: Skin... Eyes...Orifices... Other... ARE OTHER FROGS ILL?... PROPORTION OF FROGS AFFECTED... IS FINDING ILL/DEAD FROGS A COMMON OCCURRENCE?... EUTHANASED?... HOW?... FIXATIVE USED (if any)?... FROZEN?...WHAT TEMPERATURE?... TIME FROM DEATH TO AUTOPSY/FREEZING... IF CAPTIVE, HAS ANY MEDICATION/DISINFECTANT BEEN USED?... COMMENTS... Thank you for your cooperation.
11 9. HOW TO MAKE GOOD QUALITY FORMALIN 10% NEUTRAL BUFFERED FORMALIN The quality of the histology depends on using good quality fixatives. The ph of the fixative is critical. The best histology is obtained using 10% formalin with a ph about neutral. The following is a formula that will produce 10% formalin of neutral ph. CHEMICALS NEEDED Di-sodium orthophosphate (Na2HPO4) gm Potassium dihydrogen orthophosphate (KH2P04) gm 40% formaldehyde solution ml Distilled water ml PROCEDURE Dissolve salts in small part of the water with heating. Add remaining water, then formaldehyde. Add 1-2 ml of methylene blue solution as a colour indicator.
Errata to Fish Collection Methods and Standards, RIC Errata to Fish Collection Methods and Standards, Version 4.0, RIC 1997
 Errata to Fish Collection Methods and Standards, Version 4.0, RIC 1997 1. Replace all references to Reconnaissance (1:20 000) Fish and Fish Habitat Inventory: Standards and Procedures, RIC draft (1997)
Errata to Fish Collection Methods and Standards, Version 4.0, RIC 1997 1. Replace all references to Reconnaissance (1:20 000) Fish and Fish Habitat Inventory: Standards and Procedures, RIC draft (1997)
Frog Dissection Pre-Lab
 Name: Class: Date: Why are we dissecting a frog? Frog Dissection Pre-Lab Frogs and humans are vertebrates and they have very similar organ systems. Although all of the internal organs are not exactly the
Name: Class: Date: Why are we dissecting a frog? Frog Dissection Pre-Lab Frogs and humans are vertebrates and they have very similar organ systems. Although all of the internal organs are not exactly the
FROG DISSECTION LAB 100 points possible
 FROG DISSECTION LAB 100 points possible Purpose: The purpose of this lab is to enhance lab performance skills, develop dissection techniques, and compare and contrast the digestive system of a frog to
FROG DISSECTION LAB 100 points possible Purpose: The purpose of this lab is to enhance lab performance skills, develop dissection techniques, and compare and contrast the digestive system of a frog to
Tissue-Plus. User Manual. O.C.T. Compound. Optimal Cutting Temperature Embedding Medium for Frozen Tissue Specimens
 Tissue-Plus O.C.T. Compound Optimal Cutting Temperature Embedding Medium for Frozen Tissue Specimens User Manual Embedding Embedding Media Tissue-Plus O.C.T. Compound Tissue-Plus O.C.T. Compound is a water-soluble
Tissue-Plus O.C.T. Compound Optimal Cutting Temperature Embedding Medium for Frozen Tissue Specimens User Manual Embedding Embedding Media Tissue-Plus O.C.T. Compound Tissue-Plus O.C.T. Compound is a water-soluble
Collecting corals for histopathology. A practical guide
 1 Collecting corals for histopathology. A practical guide Thierry M. Work DVM U. S. Geological Survey National Wildlife Health Center Honolulu Field Station 2013 2 Why do histopathology on corals? Coral
1 Collecting corals for histopathology. A practical guide Thierry M. Work DVM U. S. Geological Survey National Wildlife Health Center Honolulu Field Station 2013 2 Why do histopathology on corals? Coral
Chapter 30 Nonvertebrate Chordates, Fishes, and Amphibians Name
 Chapter 30 Nonvertebrate Chordates, Fishes, and Amphibians Name Lab Dissecting a Perch Background Information Fish are the largest group of vertebrates found in fresh and salt water. In fact, over 25,000
Chapter 30 Nonvertebrate Chordates, Fishes, and Amphibians Name Lab Dissecting a Perch Background Information Fish are the largest group of vertebrates found in fresh and salt water. In fact, over 25,000
Yukon Mandatory Cervid Chronic Wasting Disease Surveillance Program
 Yukon Mandatory Cervid Chronic Wasting Disease Surveillance Program Background At the request of the Game Growers Association and implemented by the Yukon Agriculture Branch, Department of Energy, Mines
Yukon Mandatory Cervid Chronic Wasting Disease Surveillance Program Background At the request of the Game Growers Association and implemented by the Yukon Agriculture Branch, Department of Energy, Mines
FORENSICS TIME OF DEATH. Decomposition and Entomology
 FORENSICS TIME OF DEATH Decomposition and Entomology DEATH Manner of Death can be natural, accidental, suicidal, homicidal, or undetermined. The most common manner of death is natural. Mechanism of Death
FORENSICS TIME OF DEATH Decomposition and Entomology DEATH Manner of Death can be natural, accidental, suicidal, homicidal, or undetermined. The most common manner of death is natural. Mechanism of Death
1-634 TEXAS AGRICULTURAL EXTENSION SERVICE THE TEXAS A&M UNIVERSITY SYSTEM. John E. Hutchison, Dilectol, College Statloll, Texas
 1-634 TEXAS AGRICULTURAL EXTENSION SERVICE THE TEXAS A&M UNIVERSITY SYSTEM John E. Hutchison, Dilectol, College Statloll, Texas FIELD DRESSING BIG GAME Wallace G. Klussmann, Charles W. Ramsey, Milo J.
1-634 TEXAS AGRICULTURAL EXTENSION SERVICE THE TEXAS A&M UNIVERSITY SYSTEM John E. Hutchison, Dilectol, College Statloll, Texas FIELD DRESSING BIG GAME Wallace G. Klussmann, Charles W. Ramsey, Milo J.
Fish Dissection. 1. Place the preserved perch on the dissecting tray. Locate the head region. Examine the eyes. 6. What is the name of these flaps?
 Name: Date: Per: Introduction: Fish Dissection In this lab students will work within a group to learn from the dissection of a Perch. Dissection gives the student the opportunity to observe the location
Name: Date: Per: Introduction: Fish Dissection In this lab students will work within a group to learn from the dissection of a Perch. Dissection gives the student the opportunity to observe the location
Rats, bats, and a whole lot more: Expeditions by the Natural Science Research Laboratory,
 Exhibit Date: May-September 2010 Rats, bats, and a whole lot more: Expeditions by the Natural Science Research Laboratory, 1994-2008 The Natural Science Research Laboratory (NSRL) is a division of the
Exhibit Date: May-September 2010 Rats, bats, and a whole lot more: Expeditions by the Natural Science Research Laboratory, 1994-2008 The Natural Science Research Laboratory (NSRL) is a division of the
Perch Dissection Lab
 Perch Dissection Lab Introduction: The fish in the class Osteichthyes have bony skeletons. There are three groups of the bony fish - -- ray-finned fish, lobe-finned fish, and the lung fish. The perch is
Perch Dissection Lab Introduction: The fish in the class Osteichthyes have bony skeletons. There are three groups of the bony fish - -- ray-finned fish, lobe-finned fish, and the lung fish. The perch is
DISSECTION 101 THE FROG
 DISSECTION 101 THE FROG Dissection helps us understand how living things function. Dissection is analytical. Dissection is an adventure. Discussion Frog anatomy is unique in that it does resemble human
DISSECTION 101 THE FROG Dissection helps us understand how living things function. Dissection is analytical. Dissection is an adventure. Discussion Frog anatomy is unique in that it does resemble human
Dead Perch Parts. ACADEMIC STANDARDS: 4 th Grade B. Know that living things are made up of parts that have specific functions.
 Dead Perch Parts Fish Anatomy Adapted from: An original Creek Connections activity created from the Fish Anatomy model. Grade Level: Intermediate or advanced Duration: 30 minutes Setting: classroom Summary:
Dead Perch Parts Fish Anatomy Adapted from: An original Creek Connections activity created from the Fish Anatomy model. Grade Level: Intermediate or advanced Duration: 30 minutes Setting: classroom Summary:
Gas Exchange ACTIVITY OVERVIEW SUMMARY KEY CONCEPTS AND PROCESS SKILLS KEY VOCABULARY. Teacher s Guide B-75 L A B O R ATO R Y
 Gas Exchange 17 40- to 2 50-minute sessions ACTIVITY OVERVIEW L A B O R ATO R Y SUMMARY This activity explores the role of the respiratory system in the regulation of gases in the blood. Students investigate
Gas Exchange 17 40- to 2 50-minute sessions ACTIVITY OVERVIEW L A B O R ATO R Y SUMMARY This activity explores the role of the respiratory system in the regulation of gases in the blood. Students investigate
T H E H U M A N B R A I N
 1 W O R D S allow = let area = place balance =to spread your weight so that you do not fall breathe = to take air into your lungs and send it out again cell = the smallest part of a living thing that can
1 W O R D S allow = let area = place balance =to spread your weight so that you do not fall breathe = to take air into your lungs and send it out again cell = the smallest part of a living thing that can
i. Once enough cells die and begin to break down, life cannot be restarted.
 a. Death is the cessation or end of life. b. It is characterized by irreversible stopping of blood circulation and brain activity. c. When the heart stops beating, oxygen is deprived from body cells and
a. Death is the cessation or end of life. b. It is characterized by irreversible stopping of blood circulation and brain activity. c. When the heart stops beating, oxygen is deprived from body cells and
They are magnificent birds that are perfectly adapted and sorely needed for a healthy ecosystem.
 INTRODUCTION Vultures play a vital ecological role in the environment. They are the clean-up crew of the animal kingdom. They clean the landscape of dead animals that would otherwise spread disease. They
INTRODUCTION Vultures play a vital ecological role in the environment. They are the clean-up crew of the animal kingdom. They clean the landscape of dead animals that would otherwise spread disease. They
Frog Dissection. PreLab: 1. Where do frogs get their energy? Draw a simple food chain to illustrate.
 Name Date Frog Dissection Class # PreLab: Amphibian Reading As members of the class Amphibia, frogs may live some of their adult lives on land, but they must return to water to reproduce. Eggs are laid
Name Date Frog Dissection Class # PreLab: Amphibian Reading As members of the class Amphibia, frogs may live some of their adult lives on land, but they must return to water to reproduce. Eggs are laid
FISH ANATOMY DIAGRAM AND QUESTIONS
 Name Block FISH ANATOMY DIAGRAM AND QUESTIONS External: 1. What percentage of fish are bony fish? 2. What is the operculum s function? 3. The nostrils are used for, not. 4. Which fins keeps the fish level
Name Block FISH ANATOMY DIAGRAM AND QUESTIONS External: 1. What percentage of fish are bony fish? 2. What is the operculum s function? 3. The nostrils are used for, not. 4. Which fins keeps the fish level
First Aid Exercises 1
 First Aid Exercises 1 1 A N S W E R T H E Q U E S T I O N S I N Y O U R O W N W O R D S! What are the emergency numbers you should remember? What kind of information should you give when you call for help?
First Aid Exercises 1 1 A N S W E R T H E Q U E S T I O N S I N Y O U R O W N W O R D S! What are the emergency numbers you should remember? What kind of information should you give when you call for help?
This article is only a small part of the complete Bob Beck Protocol article. Do NOT use without reading the complete Bob Beck Protocol articles first:
 Bob Beck Protocol by R. Webster Kehr, Independent Cancer Research Foundation, Inc. Important Note This article is only a small part of the complete Bob Beck Protocol article. Do NOT use without reading
Bob Beck Protocol by R. Webster Kehr, Independent Cancer Research Foundation, Inc. Important Note This article is only a small part of the complete Bob Beck Protocol article. Do NOT use without reading
STANDARD OPERATING PROCEDURES
 PAGE: 1 of 12 CONTENTS 1.0 SCOPE AND DESCRIPTION 2.0 METHOD SUMMARY 3.0 SAMPLE PRESERVATION, CONTAINERS, HANDLING, AND STORAGE 4.0 INTERFERENCES AND POTENTIAL PROBLEMS 4.1 Length 4.2 Weight 4.3 Aging 4.4
PAGE: 1 of 12 CONTENTS 1.0 SCOPE AND DESCRIPTION 2.0 METHOD SUMMARY 3.0 SAMPLE PRESERVATION, CONTAINERS, HANDLING, AND STORAGE 4.0 INTERFERENCES AND POTENTIAL PROBLEMS 4.1 Length 4.2 Weight 4.3 Aging 4.4
Interactions Between Wild and Farmed Salmonids in Southern British Columbia: Pathogen Transfer
 Interactions Between Wild and Farmed Salmonids in Southern British Columbia: Pathogen Transfer Stewart Johnson, Michael Foreman, Kyle Garver Brent Hargreaves, Simon R.M. Jones and Chrys Neville PICES AGM
Interactions Between Wild and Farmed Salmonids in Southern British Columbia: Pathogen Transfer Stewart Johnson, Michael Foreman, Kyle Garver Brent Hargreaves, Simon R.M. Jones and Chrys Neville PICES AGM
Food Safety for Deer Hunters
 Food Safety for Deer Hunters Enjoy your sport & treat family and friends to safe Venison Venison Care and Handling of the Meat Chilling and Freezing for Safety & Preservation Meat Preservation Low Temperature
Food Safety for Deer Hunters Enjoy your sport & treat family and friends to safe Venison Venison Care and Handling of the Meat Chilling and Freezing for Safety & Preservation Meat Preservation Low Temperature
Appendix F: Ecology F-5C Pile Installation Demonstration Project Analysis of Tissues of Fish Exposed to Pile Driving
 Appendix F: Ecology F-5C Pile Installation Demonstration Project Analysis of Tissues of Fish Exposed to Pile Driving Pile Installation Demonstration Project Analysis of Tissues of Fish Exposed to Pile
Appendix F: Ecology F-5C Pile Installation Demonstration Project Analysis of Tissues of Fish Exposed to Pile Driving Pile Installation Demonstration Project Analysis of Tissues of Fish Exposed to Pile
Marquette University Institutional Animal Care and Use Committee
 Marquette University Institutional Animal Care and Use Committee Guidelines for Use and Maintenance of Guillotines and other Equipment Used for Decapitation This policy is intended to provide guidelines,
Marquette University Institutional Animal Care and Use Committee Guidelines for Use and Maintenance of Guillotines and other Equipment Used for Decapitation This policy is intended to provide guidelines,
Laboratory Standard Operating Procedure: Specimen Preservatives
 I. THIS STANDARD OPERATING PROCEDURE (SOP) IS FOR A: Specific laboratory procedure or experiment Examples: Formalin, Formaldehyde, Caro-Safe, Alcohol. Generic laboratory procedure that covers several chemicals
I. THIS STANDARD OPERATING PROCEDURE (SOP) IS FOR A: Specific laboratory procedure or experiment Examples: Formalin, Formaldehyde, Caro-Safe, Alcohol. Generic laboratory procedure that covers several chemicals
Infutrace is a formaldehyde & phenol vapor reducing agent
 Infutrace is a formaldehyde & phenol vapor reducing agent Is not a fixative. Is non hazardous for shipping, handling, storage and disposal. Produces a significant reduction of formaldehyde and phenol vapors
Infutrace is a formaldehyde & phenol vapor reducing agent Is not a fixative. Is non hazardous for shipping, handling, storage and disposal. Produces a significant reduction of formaldehyde and phenol vapors
Environmental Change and its Effects
 Environmental Change and its Effects 1 of 22 Boardworks Ltd 2011 2 of 22 Boardworks Ltd 2011 What happens when habitats change? 3 of 22 Boardworks Ltd 2011 Adaptive evolution ensures that individuals within
Environmental Change and its Effects 1 of 22 Boardworks Ltd 2011 2 of 22 Boardworks Ltd 2011 What happens when habitats change? 3 of 22 Boardworks Ltd 2011 Adaptive evolution ensures that individuals within
Killingly Public Schools
 Grade 11 Draft: Jan. 2005 Killingly Public Schools Aquaculture/Natural Resources III Tilapia Production CONTENT STANDARD 11 AQ III 1: The students will understand the origin of Tilapia culture, the worldwide
Grade 11 Draft: Jan. 2005 Killingly Public Schools Aquaculture/Natural Resources III Tilapia Production CONTENT STANDARD 11 AQ III 1: The students will understand the origin of Tilapia culture, the worldwide
Introduction. Major impact on commercial food carp production. Worldwide distribution. History. Spring viraemia of carp (SVC)
 Introduction KOI HERPESVIRUS: USING BIOSECURITY AND SURVEILLANCE TO PRODUCE DISEASE FREE FISH David Huchzermeyer Sterkspruit Veterinary Clinic Lydenburg Koi herpesvirus is a recently emerged viral disease
Introduction KOI HERPESVIRUS: USING BIOSECURITY AND SURVEILLANCE TO PRODUCE DISEASE FREE FISH David Huchzermeyer Sterkspruit Veterinary Clinic Lydenburg Koi herpesvirus is a recently emerged viral disease
Pr oject Summar y. Principal Investigators: Walter Cook, Elizabeth Williams, Fred Lindzey, and Ron Grogan. University of Wyoming
 Pr oject Summar y Chronic wasting disease in white-tailed deer in Wyoming: Interaction with livestock, movement patterns, and evaluation of ante-mortem diagnostic tests Principal Investigators: Walter
Pr oject Summar y Chronic wasting disease in white-tailed deer in Wyoming: Interaction with livestock, movement patterns, and evaluation of ante-mortem diagnostic tests Principal Investigators: Walter
/20 Lab #5 The Dissection of the Perch
 /20 Lab #5 The Dissection of the Perch Perch are members of the class Osterichthyes, or bony fishes. They are found in many Canadian waters and are an excellent specimen of boney fish. Food enters the
/20 Lab #5 The Dissection of the Perch Perch are members of the class Osterichthyes, or bony fishes. They are found in many Canadian waters and are an excellent specimen of boney fish. Food enters the
MUDSKIPPER STANDARD OPERATING PROCEDURES
 MUDSKIPPER STANDARD OPERATING PROCEDURES April 1, 2003 - Revised Dec. 2005 HOUSING: Mudskippers may be held in a variety of tanks as long as they meet the following criteria: 1) The tank size is suitable
MUDSKIPPER STANDARD OPERATING PROCEDURES April 1, 2003 - Revised Dec. 2005 HOUSING: Mudskippers may be held in a variety of tanks as long as they meet the following criteria: 1) The tank size is suitable
Internal Anatomy of Fish
 Internal Anatomy of Fish The Systems of a Fish Skeletal System Muscular System Respiratory System Digestive System Circulatory System Nervous System Reproductive System Special Organs Skeletal System
Internal Anatomy of Fish The Systems of a Fish Skeletal System Muscular System Respiratory System Digestive System Circulatory System Nervous System Reproductive System Special Organs Skeletal System
SAULT STE. MARIE, ONTARIO COURSE OUTLINE
 DOC. 3 26 SAULT COLLEGE OF APPLIED ARTS & TECHNOLOGY SAULT STE. MARIE, ONTARIO OUTLINE TITLE: WILDLIFE SURVEYS FOR 312-6 V CODE NO.: SEMESTER PROGRAM: AUTHOR: FISH AND WILDLIFE TECHNOLOGY H. A. COOPER
DOC. 3 26 SAULT COLLEGE OF APPLIED ARTS & TECHNOLOGY SAULT STE. MARIE, ONTARIO OUTLINE TITLE: WILDLIFE SURVEYS FOR 312-6 V CODE NO.: SEMESTER PROGRAM: AUTHOR: FISH AND WILDLIFE TECHNOLOGY H. A. COOPER
Pacific Salmon and their Environment Salmon Anatomy and Dissection (Primary)
 Science Unit: Lesson 14: Pacific Salmon and their Environment Salmon Anatomy and Dissection (Primary) Summary School Year: 2014/2015 Developed for: Developed by: Students watch as an adult dissects a salmon.
Science Unit: Lesson 14: Pacific Salmon and their Environment Salmon Anatomy and Dissection (Primary) Summary School Year: 2014/2015 Developed for: Developed by: Students watch as an adult dissects a salmon.
SURVEILLANCE FOR AMPHIBIAN MASS MORTALITIES IN BRITISH COLUMBIA (SAMM B.C.)
 SURVEILLANCE FOR AMPHIBIAN MASS MORTALITIES IN BRITISH COLUMBIA (SAMM B.C.) In British Columbia, 64% of the frog species and 30% of the salamander species are listed as species of conservation concern.
SURVEILLANCE FOR AMPHIBIAN MASS MORTALITIES IN BRITISH COLUMBIA (SAMM B.C.) In British Columbia, 64% of the frog species and 30% of the salamander species are listed as species of conservation concern.
Focus Fish anatomy and acoustic technology
 NOAA Gray s Reef National Marine Sanctuary Acoustic Fish Tagging Project Activity: Make and Implant a tag (transmitter) into a Snapper or Grouper Species Then Dissect Fish Grades 9-12 Developed by C.J.
NOAA Gray s Reef National Marine Sanctuary Acoustic Fish Tagging Project Activity: Make and Implant a tag (transmitter) into a Snapper or Grouper Species Then Dissect Fish Grades 9-12 Developed by C.J.
School year: 2007/2008
 Science Unit: Lesson 1: Pacific Salmon and Mountain Pine Beetle Fish Anatomy School year: 2007/2008 Developed for: Developed by: Grade level: Duration of lesson: Notes: Irwin Park Elementary School, West
Science Unit: Lesson 1: Pacific Salmon and Mountain Pine Beetle Fish Anatomy School year: 2007/2008 Developed for: Developed by: Grade level: Duration of lesson: Notes: Irwin Park Elementary School, West
Fish Dissection. Background
 Fish Dissection The Fish Dissection program at Hatfield Marine Science Center is a 50-minute hands-on program for 4th through 12th grade students. Students will work in small groups as they examine a variety
Fish Dissection The Fish Dissection program at Hatfield Marine Science Center is a 50-minute hands-on program for 4th through 12th grade students. Students will work in small groups as they examine a variety
Experiment 18 Properties of Gases
 Experiment 18 Properties of Gases E18-1 E18-2 The Task In this experiment you will investigate some of the properties of gases, i.e. how gases flow, their phase changes and chemical reactivity. Skills
Experiment 18 Properties of Gases E18-1 E18-2 The Task In this experiment you will investigate some of the properties of gases, i.e. how gases flow, their phase changes and chemical reactivity. Skills
The University of Newcastle Animal Care and Ethics Committee Methodology Document
 The University of Newcastle Animal Care and Ethics Committee Methodology Document Document Number: ACEC: 22 Document Name: The use of wildlife in research. Date of ACEC Approval: 6 December 2013 Amendment
The University of Newcastle Animal Care and Ethics Committee Methodology Document Document Number: ACEC: 22 Document Name: The use of wildlife in research. Date of ACEC Approval: 6 December 2013 Amendment
Hydrofluoric Acid SOP
 Introduction Hydrofluoric acid (HF) has a number of chemical, physical, and toxicological properties, which make handling this material especially hazardous. Anhydrous HF is a clear, colorless, fuming,
Introduction Hydrofluoric acid (HF) has a number of chemical, physical, and toxicological properties, which make handling this material especially hazardous. Anhydrous HF is a clear, colorless, fuming,
Keele University Institute for Science and Technology in Medicine. Standard Operating Procedure. Title: Transportation of Human Tissue
 Keele University Institute for Science and Technology in Medicine Standard Operating Procedure SOP Number: HTA-36 Version: 1.0 Title: Transportation of Human Tissue Purpose: To provide a standardised approach
Keele University Institute for Science and Technology in Medicine Standard Operating Procedure SOP Number: HTA-36 Version: 1.0 Title: Transportation of Human Tissue Purpose: To provide a standardised approach
SAFETY DATA SHEET OSOM ifob Test Revision Date:July 9, 2015
 Revision Date:July 9, 2015 Section 1 Identification 1.1 Product Name: 1.2 Intended Use: is a rapid qualitative test for the immunochemical detection of fecal occult blood/human hemoglobin (hhb) in human
Revision Date:July 9, 2015 Section 1 Identification 1.1 Product Name: 1.2 Intended Use: is a rapid qualitative test for the immunochemical detection of fecal occult blood/human hemoglobin (hhb) in human
Safety Issues in Healthcare Programs / Healthcare Employment
 Safety Issues in Healthcare Programs / Healthcare Employment Observing all safety procedures in place and recognizing the hazards that may be around you at all times will help to minimize accidents while
Safety Issues in Healthcare Programs / Healthcare Employment Observing all safety procedures in place and recognizing the hazards that may be around you at all times will help to minimize accidents while
4. Instruction in telemetry requires IACUC review if live vertebrates are used in the training session. a. True b. False
 Name: Quiz for Module 5: Field Biology - Mammals Date: 1. The Guidelines for the Capture, Handling, and Care of Mammals as Approved by the American Society of Mammalogists: were prepared by mammalogists
Name: Quiz for Module 5: Field Biology - Mammals Date: 1. The Guidelines for the Capture, Handling, and Care of Mammals as Approved by the American Society of Mammalogists: were prepared by mammalogists
Frog Dissection. External Observation
 Frog Dissection External Observation Use the diagram below to locate and identify the external features of the head. Find the mouth, external nares, tympani (ear drum), eyes, and nictitating membranes
Frog Dissection External Observation Use the diagram below to locate and identify the external features of the head. Find the mouth, external nares, tympani (ear drum), eyes, and nictitating membranes
AQUATIC ANIMAL BIOSECURITY: CHALLENGES AND SOLUTIONS. THE CASE OF KOI HERPESVIRUS
 AQUATIC ANIMAL BIOSECURITY: CHALLENGES AND SOLUTIONS. THE CASE OF KOI HERPESVIRUS David Huchzermeyer and Philippa Colly Sterkspruit Veterinary Clinic Introduction Koi herpesvirus is a recently emerged
AQUATIC ANIMAL BIOSECURITY: CHALLENGES AND SOLUTIONS. THE CASE OF KOI HERPESVIRUS David Huchzermeyer and Philippa Colly Sterkspruit Veterinary Clinic Introduction Koi herpesvirus is a recently emerged
NUMBER: /2007
 PAGE 1 OF 5 Purpose The purpose of this policy is to describe clear guidelines care of bullfrogs (Rana catesbeiana) and leopard frogs (Rana pipiens) held in the Department of Biology animal rooms. Application
PAGE 1 OF 5 Purpose The purpose of this policy is to describe clear guidelines care of bullfrogs (Rana catesbeiana) and leopard frogs (Rana pipiens) held in the Department of Biology animal rooms. Application
What Can the Bones Tell Us? Effects of Death on the Body. Effects of Death on the Body. Forensic Entomology 5/21/18
 What Can the Bones Tell Us? DNA samples can be collected from bone, teeth, and hair to provide clues to a person s identity. Scientists may also be able to gain clues as to a person s past, recent injuries,
What Can the Bones Tell Us? DNA samples can be collected from bone, teeth, and hair to provide clues to a person s identity. Scientists may also be able to gain clues as to a person s past, recent injuries,
Aseptic Techniques. Techniques for Sterile Compounding. Pharmacy Technician Training Systems Passassured, LLC
 Aseptic Techniques Techniques for Sterile Compounding Pharmacy Technician Training Systems Passassured, LLC Aseptic Techniques, Tech for Sterile Compounding PassAssured's Pharmacy Technician Training Program
Aseptic Techniques Techniques for Sterile Compounding Pharmacy Technician Training Systems Passassured, LLC Aseptic Techniques, Tech for Sterile Compounding PassAssured's Pharmacy Technician Training Program
Fishes and Amphibians Objectives
 Fishes and Amphibians Objectives List the four common body parts of chordates. Describe the two main characteristics of vertebrates. Explain the difference between an ectotherm and an endotherm. Describe
Fishes and Amphibians Objectives List the four common body parts of chordates. Describe the two main characteristics of vertebrates. Explain the difference between an ectotherm and an endotherm. Describe
Updated December CHRONIC WASTING DISEASE FAQs
 Updated December 2017 CHRONIC WASTING DISEASE FAQs What is CWD? Chronic wasting disease affects the central nervous system of elk, deer and moose. Most scientists believe CWD is caused by an infectious
Updated December 2017 CHRONIC WASTING DISEASE FAQs What is CWD? Chronic wasting disease affects the central nervous system of elk, deer and moose. Most scientists believe CWD is caused by an infectious
Bt-Cry1Ac & Bt-Cry2A Multi-trait ELISA Kit DAS ELISA for the detection of Bt-Cry1Ac & Bt-Cry2A proteins Catalog number: PSM 14900
 List of contents Lot number Item 480 wells 4800 wells Antibody-coated 96-well microtiter plates 5 strip 50 solid Alkaline phosphatase enzyme conjugate, concentrated 0.550 ml 5 x 1.1 ml Peroxidase enzyme
List of contents Lot number Item 480 wells 4800 wells Antibody-coated 96-well microtiter plates 5 strip 50 solid Alkaline phosphatase enzyme conjugate, concentrated 0.550 ml 5 x 1.1 ml Peroxidase enzyme
DEPARTMENT SCHOOLS OF HEALTH
 PATIENT LIFTING: Work with patients/human subjects may involve lifting and moving of patients. Exposure to physical injury from lifting and moving of patients/human subjects. Avoid unnecessary exposures.
PATIENT LIFTING: Work with patients/human subjects may involve lifting and moving of patients. Exposure to physical injury from lifting and moving of patients/human subjects. Avoid unnecessary exposures.
Fish Dissection Background
 Fish Dissection Background Introduction Living things are similar to and different from each other. For example, when we look at the inside of a fish, we learn that the organ systems of fish are similar
Fish Dissection Background Introduction Living things are similar to and different from each other. For example, when we look at the inside of a fish, we learn that the organ systems of fish are similar
Gynaecomastia. Benign breast conditions information provided by Breast Cancer Care
 Gynaecomastia This booklet tells you about gynaecomastia. It explains what gynaecomastia is, what causes it, how it s diagnosed and what will happen if it needs to be treated or followed up. Benign breast
Gynaecomastia This booklet tells you about gynaecomastia. It explains what gynaecomastia is, what causes it, how it s diagnosed and what will happen if it needs to be treated or followed up. Benign breast
A breath of fresh air
 A breath of fresh air BIG IDEAS You are learning to: Describe the structure of the lungs Explain how the lungs clean themselves Interpret patterns in data Where are the lungs and what do they do? The lungs
A breath of fresh air BIG IDEAS You are learning to: Describe the structure of the lungs Explain how the lungs clean themselves Interpret patterns in data Where are the lungs and what do they do? The lungs
TECHNICAL BULLETIN. TriControls. Control Materials for Liquid QC and Calibration Verification
 i-stat TECHNICAL BULLETIN Tris Materials for Liquid QC and OVERVIEW As part of the READi initiative (Responds, Enhances, And Delivers innovations), Abbott Point of Care (APOC) has released a new set of
i-stat TECHNICAL BULLETIN Tris Materials for Liquid QC and OVERVIEW As part of the READi initiative (Responds, Enhances, And Delivers innovations), Abbott Point of Care (APOC) has released a new set of
4/26/16. Section 1 Understanding Solutions. Solutions and Suspensions. Solutions and Suspensions. Solutions and Suspensions. Solvents and Solutes
 Section 1 Understanding Solutions On a hot day, you may think that a cool glass of plain water would be refreshing. However, if the glass were actually filled with plain water, it would taste stale. This
Section 1 Understanding Solutions On a hot day, you may think that a cool glass of plain water would be refreshing. However, if the glass were actually filled with plain water, it would taste stale. This
Shandon Cryotome Cryostat Series
 Shandon Cryotome Cryostat Series Shandon Cryotome FSE Shandon Cryotome FE Shandon Cryotome SME Analyze Detect Measure Control Shandon Cryotome Cryocassettes Cryocassettes for the Shandon Cryotome FSE /
Shandon Cryotome Cryostat Series Shandon Cryotome FSE Shandon Cryotome FE Shandon Cryotome SME Analyze Detect Measure Control Shandon Cryotome Cryocassettes Cryocassettes for the Shandon Cryotome FSE /
Laboratory Safety Training. Environmental Health and Safety
 Laboratory Safety Training Environmental Health and Safety Why You Need Lab Safety Training Hazardous materials and/or equipment. You need to understand the risks and how to mitigate them. OSU requires
Laboratory Safety Training Environmental Health and Safety Why You Need Lab Safety Training Hazardous materials and/or equipment. You need to understand the risks and how to mitigate them. OSU requires
TAHC Certified CWD Postmortem Sample Collection Recertification. Presenter/Title
 TAHC Certified CWD Postmortem Sample Collection Recertification Presenter/Title How To Complete Your Recertification How to Complete the Recertification Process 1. Review the powerpoint presentation 2.
TAHC Certified CWD Postmortem Sample Collection Recertification Presenter/Title How To Complete Your Recertification How to Complete the Recertification Process 1. Review the powerpoint presentation 2.
Evaluating the Effects of Stressors on Immune Function during Simulated Dives in Marine Mammals
 DISTRIBUTION STATEMENT A. Approved for public release; distribution is unlimited. Evaluating the Effects of Stressors on Immune Function during Simulated Dives in Marine Mammals Tracy Romano and Laura
DISTRIBUTION STATEMENT A. Approved for public release; distribution is unlimited. Evaluating the Effects of Stressors on Immune Function during Simulated Dives in Marine Mammals Tracy Romano and Laura
Wilderness First Responder Course Peak 7 Adventures
 Wilderness First Responder Course Peak 7 Adventures The practice of the healing arts (including Wilderness First Responder) does not lend itself well to a cook book approach. There are endless variations
Wilderness First Responder Course Peak 7 Adventures The practice of the healing arts (including Wilderness First Responder) does not lend itself well to a cook book approach. There are endless variations
Hazardous substances in the workplace
 Overview Hazardous substances in the workplace A systematic approach to managing risks, including: - identifying hazardous substances - assessing risk - controlling risk Maintaining a safe workplace Victorian
Overview Hazardous substances in the workplace A systematic approach to managing risks, including: - identifying hazardous substances - assessing risk - controlling risk Maintaining a safe workplace Victorian
Dogfish Shark Dissection
 Dogfish Shark Dissection Name Date Period Fun Facts: Materials: The teeth of sharks are modified scales embedded in the skin of its mouth Sharks have pits on their face used to detect electric fields Sharks
Dogfish Shark Dissection Name Date Period Fun Facts: Materials: The teeth of sharks are modified scales embedded in the skin of its mouth Sharks have pits on their face used to detect electric fields Sharks
What environmental factors trigger a fruit fly response?
 Big Idea 4 Interactions investigation 12 FRUIT FLY BEHAVIOR What environmental factors trigger a fruit fly response? BACKGROUND Drosophila melanogaster, the common fruit fly, is an organism that has been
Big Idea 4 Interactions investigation 12 FRUIT FLY BEHAVIOR What environmental factors trigger a fruit fly response? BACKGROUND Drosophila melanogaster, the common fruit fly, is an organism that has been
Annex 9 Processes Quality Control. Introduction
 Annex 9 Processes Quality Control Introduction The eradication of screwworms depends on the release and dispersal into the environment of sterile screwworm flies in optimum biological condition providing
Annex 9 Processes Quality Control Introduction The eradication of screwworms depends on the release and dispersal into the environment of sterile screwworm flies in optimum biological condition providing
Essential Skills Course Acute Care Module. Respiratory Day 2 (Arterial Blood Gases) Pre course Workbook
 Essential Skills Course Acute Care Module Respiratory Day 2 (Arterial Blood Gases) Pre course Workbook Acknowledgements This pre course workbook has been complied and updated with reference to the original
Essential Skills Course Acute Care Module Respiratory Day 2 (Arterial Blood Gases) Pre course Workbook Acknowledgements This pre course workbook has been complied and updated with reference to the original
Pop Quiz. What produces mucus, HCl and pepsinogen in the stomach? List a water soluable vitamin What is a ruminant stomach?
 Pop Quiz What produces mucus, HCl and pepsinogen in the stomach? List a water soluable vitamin What is a ruminant stomach? Respiratory System Review Cellular respiration: obtain glucose and oxygen, get
Pop Quiz What produces mucus, HCl and pepsinogen in the stomach? List a water soluable vitamin What is a ruminant stomach? Respiratory System Review Cellular respiration: obtain glucose and oxygen, get
How do forensic scientists determine the time of death?
 How do forensic scientists determine the time of death? The eyes of a victim can hold answers to the time of death, as a thin cloudy film is developed over the eye within 3 hours after death has occurred.
How do forensic scientists determine the time of death? The eyes of a victim can hold answers to the time of death, as a thin cloudy film is developed over the eye within 3 hours after death has occurred.
Circulation and Respiration: Vital Signs Student Version
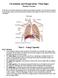 Circulation and Respiration: Vital Signs Student Version In this lab, you will learn about the circulatory and respiratory systems. You will test the capacity of your lungs, measure your blood pressure
Circulation and Respiration: Vital Signs Student Version In this lab, you will learn about the circulatory and respiratory systems. You will test the capacity of your lungs, measure your blood pressure
The Properties of Water
 The Properties of Water Water covers about three fourths of the surface of the earth. It is ubiquitous. It is also one of the simplest, yet most important molecules in living systems. It makes up from
The Properties of Water Water covers about three fourths of the surface of the earth. It is ubiquitous. It is also one of the simplest, yet most important molecules in living systems. It makes up from
Gas Exchange & Circulation
 Why is gas exchange important? Gas Exchange & Circulation Read Ch. 42 start with 42.5: Gas Exchange in Animals Respiration: C 6 H 12 O 6 + O 2! Energy + CO 2 + H 2 O Photosynthesis: Energy + CO 2 + H 2
Why is gas exchange important? Gas Exchange & Circulation Read Ch. 42 start with 42.5: Gas Exchange in Animals Respiration: C 6 H 12 O 6 + O 2! Energy + CO 2 + H 2 O Photosynthesis: Energy + CO 2 + H 2
1.2.7 Furunculosis. Emmett B. Shotts, Jr. College of Veterinary Medicine University of Georgia Athens, GA /
 1.2.7 Furunculosis - 1 1.2.7 Furunculosis Emmett B. Shotts, Jr. College of Veterinary Medicine University of Georgia Athens, GA 30602 404/542-5811 emshotts@alltel.net A. Name of Disease and Etiological
1.2.7 Furunculosis - 1 1.2.7 Furunculosis Emmett B. Shotts, Jr. College of Veterinary Medicine University of Georgia Athens, GA 30602 404/542-5811 emshotts@alltel.net A. Name of Disease and Etiological
Students use wildlife survey study techniques to discover the cause of the drop in a wood duck population.
 Fowl Play Summary Students use wildlife survey study techniques to discover the cause of the drop in a wood duck population. Background Wood ducks spend most of their time in ponds and streams near woods.
Fowl Play Summary Students use wildlife survey study techniques to discover the cause of the drop in a wood duck population. Background Wood ducks spend most of their time in ponds and streams near woods.
Slide 1 of 64. End Show Copyright Pearson Prentice Hall. End Show Copyright Pearson Prentice Hall. Respiration. Slide 5 of 64
 33-3 Form and Function in Chordates Chordates Vertebrate organ systems exhibit a wide range of complexity. This is seen in the different ways that vertebrates feed, breathe, respond, move, and reproduce.
33-3 Form and Function in Chordates Chordates Vertebrate organ systems exhibit a wide range of complexity. This is seen in the different ways that vertebrates feed, breathe, respond, move, and reproduce.
Lung Volumes and Capacities
 Lung Volumes and Capacities Normally the volume of air entering the lungs during a single inspiration is approximately equal to the volume leaving on the subsequent expiration and is called the tidal volume.
Lung Volumes and Capacities Normally the volume of air entering the lungs during a single inspiration is approximately equal to the volume leaving on the subsequent expiration and is called the tidal volume.
PHYLUM CHORDATA: Subphylum vertebrata
 PHYLUM CHORDATA: Subphylum vertebrata There are three basic characteristics that distinguish Phylum Chordata from all other animal phyla: The presence of a flexible, rod-like, internal supporting structure
PHYLUM CHORDATA: Subphylum vertebrata There are three basic characteristics that distinguish Phylum Chordata from all other animal phyla: The presence of a flexible, rod-like, internal supporting structure
Risk of spread after introduction of the virus in to wild boar population
 Available tools for the prevention and control of diseases in wildlife, with focus on ASF in wild boar in infected country: hunting biosecurity and wild boar carcass disposal Marius Masiulis FAO international
Available tools for the prevention and control of diseases in wildlife, with focus on ASF in wild boar in infected country: hunting biosecurity and wild boar carcass disposal Marius Masiulis FAO international
Venepuncture. Clinical Skills. Venepuncture. Dr Brian Jenkins (Clinical Skills Lead) Sian Williams (Clinical Skills Manager)
 Clinical Skills Venepuncture Dr Brian Jenkins (Clinical Skills Lead) Sian Williams (Clinical Skills Manager) Aims and Objectives Aims and Objectives The aim of this module is to facilitate learning regarding
Clinical Skills Venepuncture Dr Brian Jenkins (Clinical Skills Lead) Sian Williams (Clinical Skills Manager) Aims and Objectives Aims and Objectives The aim of this module is to facilitate learning regarding
Risk Assessment Form Cardiff School of Biosciences
 1. General Information Risk Assessment Form Cardiff School of Biosciences IMPORTANT: Before carrying out the assessment, please read the Guidance Notes Department Cardiff School Of Biosciences Building
1. General Information Risk Assessment Form Cardiff School of Biosciences IMPORTANT: Before carrying out the assessment, please read the Guidance Notes Department Cardiff School Of Biosciences Building
Disease emergence and spread related to wildlife trade: aquatic species
 Disease emergence and spread related to wildlife trade: aquatic species Barry Hill President, OIE Aquatic Animal Health Standards Commission Centre for Environment, Fisheries and Aquaculture Science (Cefas)
Disease emergence and spread related to wildlife trade: aquatic species Barry Hill President, OIE Aquatic Animal Health Standards Commission Centre for Environment, Fisheries and Aquaculture Science (Cefas)
Pco2 *20times = 0.6, 2.4, so the co2 carried in the arterial blood in dissolved form is more than the o2 because of its solubility.
 Physiology, sheet #9 Oxygen, is first dissolved in the plasma and the cytosol of the rbc, we have around blood constitutes 7% of our body weight, oxygen, in the capillaries is present in the rbc s and
Physiology, sheet #9 Oxygen, is first dissolved in the plasma and the cytosol of the rbc, we have around blood constitutes 7% of our body weight, oxygen, in the capillaries is present in the rbc s and
These two respiratory media (air & water) impose rather different constraints on oxygen uptake:
 Topic 19: OXYGEN UPTAKE AND TRANSPORT (lectures 29-30) OBJECTIVES: 1. Be able to compare air vs. water as a respiratory medium with respect to oxygen content, diffusion coefficient, viscosity and water
Topic 19: OXYGEN UPTAKE AND TRANSPORT (lectures 29-30) OBJECTIVES: 1. Be able to compare air vs. water as a respiratory medium with respect to oxygen content, diffusion coefficient, viscosity and water
Increase exchange rate by moving medium over respiratory surface
 Ventilation Increase exchange rate by moving medium over respiratory surface Water ~800x heavier than air, potentially expensive ventilation Oxygen per unit mass Air: 1.3 g contains 210 ml O 2 Water: 1000
Ventilation Increase exchange rate by moving medium over respiratory surface Water ~800x heavier than air, potentially expensive ventilation Oxygen per unit mass Air: 1.3 g contains 210 ml O 2 Water: 1000
The Ozark Hellbender: No longer found under the rocks. By: Justine M. Dover
 Picture courtesy of Clint Hale Missouri Department of Conservation The Missourian Ozark Hellbender is a disappearing two foot long salamander living under the rocks of the Ozarks. There are not too many
Picture courtesy of Clint Hale Missouri Department of Conservation The Missourian Ozark Hellbender is a disappearing two foot long salamander living under the rocks of the Ozarks. There are not too many
Wildlife CSI - Panhandle elk mortality study
 Wildlife CSI - Panhandle elk mortality study By Laura Wolf, Wildlife Regional Biologist Monday, September 25, 2017-11:11 AM MDT The Panhandle region placed 172 GPS radio-collars on 6-month old elk calves
Wildlife CSI - Panhandle elk mortality study By Laura Wolf, Wildlife Regional Biologist Monday, September 25, 2017-11:11 AM MDT The Panhandle region placed 172 GPS radio-collars on 6-month old elk calves
What does the % represent on the beakers?
 DISSOLVED OXYGEN VIDEO FAQs What does the % represent on the beakers? What are the glass tubes to beakers for? How is the temperature being kept the same (at 5 o then 35 o )? What is salinity in parts
DISSOLVED OXYGEN VIDEO FAQs What does the % represent on the beakers? What are the glass tubes to beakers for? How is the temperature being kept the same (at 5 o then 35 o )? What is salinity in parts
COLLECTION OF BLOOD. Types of patients
 COLLECTION OF BLOOD Capillary Sampling The specimen of choice for laboratory analysis is generally a venous specimen. For blood gas analysis, the specimen of choice originates from an arterial draw. When
COLLECTION OF BLOOD Capillary Sampling The specimen of choice for laboratory analysis is generally a venous specimen. For blood gas analysis, the specimen of choice originates from an arterial draw. When
Importance of TOD. 1st question at most murder scenes: "How long has this person been dead?
 Death Importance of TOD 1st question at most murder scenes: "How long has this person been dead? It's crucial to know when the crime was committed. it can help narrow the search for a suspect or it can
Death Importance of TOD 1st question at most murder scenes: "How long has this person been dead? It's crucial to know when the crime was committed. it can help narrow the search for a suspect or it can
1.0 PURPOSE The purpose of this procedure is to describe the use of basic aseptic technique.
 1.0 PURPOSE The purpose of this procedure is to describe the use of basic aseptic technique. 2.0 RESPONSIBILITY 2.1 It is the responsibility of each employee working in a laboratory setting to follow this
1.0 PURPOSE The purpose of this procedure is to describe the use of basic aseptic technique. 2.0 RESPONSIBILITY 2.1 It is the responsibility of each employee working in a laboratory setting to follow this
HOW-TO CONDUCT A WEEKLY SAFETY MEETING
 HOW-TO CONDUCT A WEEKLY SAFETY MEETING 1. Hold the meeting on the job, preferably where everyone can sit and relax. 2. Hold the meeting at the beginning of the shift, right after lunch, or after a break.
HOW-TO CONDUCT A WEEKLY SAFETY MEETING 1. Hold the meeting on the job, preferably where everyone can sit and relax. 2. Hold the meeting at the beginning of the shift, right after lunch, or after a break.
Colic Fact Sheet One hell of a belly ache
 Colic Fact Sheet One hell of a belly ache No other word strikes fear in the hearts and minds of horse owners more than the word Colic - it can affect any horse at any time for a multitude of reason. Sadly,
Colic Fact Sheet One hell of a belly ache No other word strikes fear in the hearts and minds of horse owners more than the word Colic - it can affect any horse at any time for a multitude of reason. Sadly,
CspB ELISA Kit DAS ELISA for the detection of CspB protein Catalog number: PSP 35500
 List of contents Lot number Item 480 wells 4800 wells Antibody-coated 96-well microtiter plates 5 strip 50 solid Peroxidase enzyme conjugate, concentrated 0.550 ml 5 x 1.1 ml RUB6 enzyme conjugate diluent
List of contents Lot number Item 480 wells 4800 wells Antibody-coated 96-well microtiter plates 5 strip 50 solid Peroxidase enzyme conjugate, concentrated 0.550 ml 5 x 1.1 ml RUB6 enzyme conjugate diluent
Harbour Porpoise Release Program Newsletter
 Harbour Porpoise Release Program Newsletter Volume 5 Fall 2003 We have come to the end of another successful year for the Harbour Porpoise Release Program. We would like to thank all of you for ensuring
Harbour Porpoise Release Program Newsletter Volume 5 Fall 2003 We have come to the end of another successful year for the Harbour Porpoise Release Program. We would like to thank all of you for ensuring
