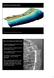
Tsunami-like bore formation in coastal and estuarine environments
|
|
|
- Jacob Blankenship
- 5 years ago
- Views:
Transcription
1 Workshop: an overview on free surface flows Paris, November, 2017 Tsunami-like bore formation in coastal and estuarine environments Philippe Bonneton EPOC/METHYS, CNRS, Bordeaux Univ. Tidal bore Gironde Lavigne Y.
2 Introduction Long waves Tsunamis, tides, infragravity waves, meteorological tsunamis, bore Sumatra 2004 tsunami reaching the coast of Thailand
3 Introduction Long waves Tsunamis, tides, infragravity waves, meteorological tsunamis, 7 min 18 min 30 min 40 min a=2m 50 km Serre Green Naghdi model Tissier, Bonneton et al., JCR2011
4 Introduction Long waves Tsunamis, tides, infragravity waves, meteorological tsunamis, dispersive shock inception 7 min 18 min 30 min 40 min a=2m 50 km bore formation
5 Introduction Tsunami bore Sumatra 2004 tsunami reaching the coast of Thailand references: Grue et al Madsen et al
6 Introduction Tsunami bore 21 st November 2016, Sunaoshi River in Tagajo city, Japan (earthquake 7.4)
7 Introduction Tidal bore Bonneton et al. JGR 2015
8 Introduction Tidal bore Gironde estuary, Saint Pardon, Dordogne Jean-Marc Chauvet, Septembre 2014
9 Introduction Tidal bore Large amplitude spring tide 10 th September 2010 Bonneton et al. JGR 2015
10 Introduction Impact of tsunami-like bores Strong impact on coastal and estuarine environments
11 Introduction Impact of tsunami-like bores Sediment transport and erosion Tidal Bores, Bonneton et al Impact on marine structures and buildings Tsunamis, Arikawa et al. 2013
12 Introduction Conditions for tsunami-like bore formation in coastal and estuarine environments tsunami bore tidal bore
13 Introduction collaborations field measurements Bonneton N., Castelle B., Detandt G., Parisot J-P., Sottolichio A. (EPOC, METHYS team, Bordeaux) Frappart F., Roussel N., Darrozes J. (OMP, Toulouse) Martins K. (Bath University) long wave modeling Ricchuito M., Arpaia L., Filippini A. (INRIA, Bordeaux) Lannes D. (IMB, Bordeaux) Marche F. (IMAG, Montpellier), Tissier M. (TU Delft, Netherlands)
14 Outline Introduction Basic conditions for bore formation in the coastal zone Conditions for tidal bore formation in estuaries Conclusion and perspectives
15 Outline Introduction Basic conditions for bore formation in the coastal zone Conditions for tidal bore formation in estuaries Conclusion and perspectives
16 Basic conditions for bore formation Bore inception? D 0 =150 m L c 4000 m deep ocean Continental shelf the continental shelf is relatively flat D 0, A 0, ω 0 =2π/T 0 LL w0 = ggd 0 ω 0
17 Basic conditions for bore formation µ 0 << 1 ε 0 =O(1) Serre / Green Naghdi equations
18 Basic conditions for bore formation µ 0 << 1 ε 0 =O(1) 7 min 18 min 30 min 40 min a=2m 50 km Serre Green Naghdi model Tissier, Bonneton et al., JCR2011
19 Basic conditions for bore formation µ 0 << 1 ε 0 =O(1) 7 min 18 min 30 min 40 min a=2m 50 km Serre Green Naghdi model Tissier, Bonneton et al., JCR2011
20 Basic conditions for bore formation
21 Basic conditions for bore formation t=0 t=t s /4 t=t s /2 t=3t s /4 t=t s x x s
22 Basic conditions for bore formation D 0 =150 m 4000 m deep ocean L c Continental shelf see Madsen et al 2008
23 Basic conditions for bore formation 150 m 4000 m deep ocean L c Continental shelf
24 Basic conditions for bore formation 150 m 4000 m deep ocean L c Continental shelf
25 Basic conditions for bore formation 150 m 4000 m deep ocean L c Continental shelf Continental shelves D m tsunamis: A 0 2 m, T 0 25 min x s = 460 km tides: T min x s >> L c no tidal bore in open continental shelf water
26 Basic conditions for bore formation 150 m 4000 m deep ocean L c Continental shelf tsunamis: bores may occur in large and shallow (few tens of m) coastal environments: marine coastal plains (e.g.: deltas, alluvial estuaries) or carbonate platforms (e.g.: coral reef systems)
27 Basic conditions for bore formation 150 m 4000 m deep ocean L c Continental shelf tsunamis: bores may occur in large and shallow (few tens of m) coastal environments: marine coastal plains (e.g.: deltas, alluvial estuaries) or carbonate platforms (e.g.: coral reef systems) tides: bores can occur in long shallow alluvial estuaries L 100 km D 0 10 m
28 Basic conditions for bore formation 150 m 4000 m deep ocean L c Continental shelf tsunamis: bores may occur in large and shallow (few tens of m) coastal environments: marine coastal plains (e.g.: deltas, alluvial estuaries) or carbonate platforms (e.g.: coral reef systems) tides: bores can occur in long shallow alluvial estuaries
29 Basic conditions for bore formation 150 m 4000 m deep ocean L c Continental shelf tsunamis: bores may occur in large and shallow (few tens of m) coastal environments: marine coastal plains (e.g.: deltas, alluvial estuaries) or carbonate platforms (e.g.: coral reef systems) tides: bores can occur in long shallow alluvial estuaries in such shallow environments friction plays a significant role
30 Outline Introduction Basic conditions for bore formation in the coastal zone Conditions for tidal bore formation in estuaries Conclusion and perspectives
31 Conditions for tidal bore formation Worldwide tidal bores Severn River - England Amazon River Brazil (Pororoca) Kampar River Sumatra (Bono) Qiantang River China
32 Conditions for tidal bore formation Worldwide tidal bores 3 field campaigns : a unique long-term high-frequency database Gironde/Garonne/Dordogne estuary France Bonneton et al. JGR 2015
33 Conditions for tidal bore formation Worldwide tidal bores 3 field campaigns : a unique long-term high-frequency database Gironde/Garonne/Dordogne estuary France Bonneton et al. JGR 2015
34 Conditions for tidal bore formation Physical criteria Large tidal range (Tr 0 =2A 0 ) Chanson (2012) : Tr 0 > m Small water depth coastal plain alluvial estuaries Large-scale funnel-shaped estuaries Scaling analysis Tide propagation in convergent estuaries : Parker 1991, Lanzoni and Seminara 1998, Toffolon et al First scaling analysis of the tidal bore problem
35 Conditions for tidal bore formation Physical criteria Large tidal range Small water depth coastal plain alluvial estuaries Large-scale funnel-shaped estuaries Scaling analysis Identify the characteristic scales of the problem: morphology of alluvial estuaries tidal wave forcing
36 Conditions for tidal bore formation Alluvial estuary morphology Tide-dominated alluvial estuaries show many morphological similarities all over the world Scheldt estuary along-channel coordinate Savenije 2012
37 Conditions for tidal bore formation Alluvial estuary morphology Pungue estuary Graas et al. 2008
38 Conditions for tidal bore formation Alluvial estuary morphology BB = BB 0 ee xx LL BBB L b0 : convergence length D 0 : characteristic water depth
39 Conditions for tidal bore formation Tidal wave forcing A 0 =Tr 0 /2 (mean spring tidal amplitude) T 0 =12.4 h LL www = ggdd 0 /ω 0 Cf 0 : friction coefficient Q 0 : freshwater discharge
40 Conditions for tidal bore formation Tidal wave forcing A 0 =Tr 0 /2 (mean spring tidal amplitude) T 0 =12.4 h LL www = ggdd 0 /ω 0 Cf 0 : friction coefficient
41 Conditions for tidal bore formation Scaling analysis L b0 D 0 A 0 LL www Cf 0 5 external variables
42 Conditions for tidal bore formation Scaling analysis
43 Conditions for tidal bore formation Scaling analysis
44 Conditions for tidal bore formation Scaling analysis
45 Conditions for tidal bore formation Scaling analysis Tidal wave nonlinearity DD ii > 1.5 Bonneton et al., JGR 2015 necessary condition for tidal bore formation by not a sufficient one
46 Conditions for tidal bore formation Scaling analysis explore the 3D dimensionless external parameter space: (ε 0, δ 0, φ 0 ) Field data: 21 convergent alluvial estuaries Bonneton, P., Filippini, A.G., Arpaia, L., Bonneton, N. and Ricchiuto, M Conditions for tidal bore formation in convergent alluvial estuaries. ECSS, 172, Numerical simulations: 225 runs of a Serre/Green Naghdi model Filippini, A.G., Arpaia, L., Bonneton, P., and Ricchiuto, M Modelling analysis of tidal bore formation in convergent estuaries. in press EJM/B Fluids
47 Conditions for tidal bore formation Field data 1 Chao Phya Thailand 2 Columbia USA 3 Conwy UK 4 Corantijn USA 5 Daly Australia 6 Delaware USA 7 Elbe Germany 8 Gironde France 21 convergent alluvial estuaries 8 tidal bore estuaries 9 Hooghly India 10 Humber UK 11 Limpopo Mozambique D 0, L b0, A 0 =Tr 0 /2, Cf 0 12 Loire France 13 Mae Klong Thailand 14 Maputo Mozambique 15 Ord Australia 16 Pungue Mozambique 17 Qiantang China 18 Scheldt Netherlands 19 Severn UK 20 Tha Chin Thailand 21 Thames UK
48 Conditions for tidal bore formation Field data 1 Chao Phya Thailand 2 Columbia USA 3 Conwy UK 4 Corantijn USA 5 Daly Australia 6 Delaware USA 7 Elbe Germany 8 Gironde France 9 Hooghly India 10 Humber UK 11 Limpopo Mozambique 12 Loire France 13 Mae Klong Thailand 14 Maputo Mozambique 15 Ord Australia 16 Pungue Mozambique 17 Qiantang China 18 Scheldt Netherlands 19 Severn UK 20 Tha Chin Thailand 21 Thames UK Tidal bore estuaries: δ D parameter space (ε 0, φ 0 )
49 Conditions for tidal bore formation Field data ε c (φ 0 ) 1 Chao Phya Thailand 2 Columbia USA 3 Conwy UK 4 Corantijn USA 5 Daly Australia 6 Delaware USA 7 Elbe Germany 8 Gironde France 9 Hooghly India 10 Humber UK 11 Limpopo Mozambique 12 Loire France 13 Mae Klong Thailand 14 Maputo Mozambique 15 Ord Australia 16 Pungue Mozambique 17 Qiantang China 18 Scheldt Netherlands 19 Severn UK 20 Tha Chin Thailand 21 Thames UK Tidal bores occur when ε 0 > ε c (φ 0 )
50 Conditions for tidal bore formation Numerical simulations Numerical investigation of the 2D parameter space (ε 0, φ 0 ) Filippini, A.G., Arpaia, L., Bonneton, P., and Ricchiuto, M., EJM-B / Fluids, 2017 Idealized convergent estuaries fully nonlinear weakly dispersive Boussinesq type equations: Serre/Green Naghdi equations
51 Conditions for tidal bore formation Numerical simulations Numerical investigation of the 2D parameter space (ε 0, φ 0 ) Filippini, A.G., Arpaia, L., Bonneton, P., and Ricchiuto, M., EJM-B / Fluids, 2017 Hybrid FV/FE scheme hyperbolic step 3 rd order upwind MUSCL elliptic step 2 nd order continuous FE
52 Conditions for tidal bore formation Numerical simulations SGN / NLSW ε 0 =0.7, φ 0 = 10 Filippini et al. 2017
53 Conditions for tidal bore formation Numerical simulations SGN / NLSW Filippini et al. 2017
54 Conditions for tidal bore formation Numerical simulations Numerical investigation of the 2D parameter space (ε 0, φ 0 ) model based on the NLSW equations 225 runs with δ 0 = 2
55 Conditions for tidal bore formation Numerical simulations one example on the 225 runs SS mmmmmm = mmmmmm ζ Filippini et al. 2017
56 Conditions for tidal bore formation Numerical simulations δ 0 = 2 SS mmmmmm SS mmmmmm Filippini et al. 2017
57 Conditions for tidal bore formation Numerical simulations rate of change of the tidal range TT rr = TT rr LLLL TT rr (0) TT rr (0) damping amplification Theoretical zero-amplification curve: ε 0 φ 0 = δ 0 (δ ) (Savenije et al. 2008) Filippini et al. 2017
58 Conditions for tidal bore formation Estuary classification a b c d
59 Conditions for tidal bore formation Estuary classification ε c (φ 0 ) Tidal bores occur when ε 0 > ε c (φ 0 )
60 Conclusion Criterion for the formation of tsunami-like bore tsunami bore tidal bore tsunamis: bores may occur in large and shallow coastal environments marine coastal plains with gentle slope (e.g.: deltas, alluvial estuaries) carbonate platforms (e.g.: coral reef systems) tides: bores may occur in long shallow alluvial estuaries
61 Conclusion Conditions for tidal bore formation nonlinear tidal wave transformation is mainly governed by the quadratic friction terms Tidal bores occur when ε 0 > ε c (φ 0 )
62 Perspectives Modelling bore formation from large to small scales using SGN equations application to tidal bores in the Gironde/Garonne estuary t (s)
63 Thank you for your attention
Long wave propagation and bore dynamics in coastal and estuarine environments
 IAHR-APD 2014 Keynote Lecture September 21-24, 2014, Hanoi Long wave propagation and bore dynamics in coastal and estuarine environments Philippe Bonneton EPOC, METHYS team, Bordeaux Univ., CNRS Sumatra
IAHR-APD 2014 Keynote Lecture September 21-24, 2014, Hanoi Long wave propagation and bore dynamics in coastal and estuarine environments Philippe Bonneton EPOC, METHYS team, Bordeaux Univ., CNRS Sumatra
Nearshore Dynamics of Tsunami-like Undular Bores using a Fully Nonlinear Boussinesq Model
 Journal of Coastal Research SI 64 pg - pg ICS2011 (Proceedings) Poland ISSN 0749-0208 Nearshore Dynamics of Tsunami-like Undular Bores using a Fully Nonlinear Boussinesq Model M.Tissier, P. Bonneton, F.
Journal of Coastal Research SI 64 pg - pg ICS2011 (Proceedings) Poland ISSN 0749-0208 Nearshore Dynamics of Tsunami-like Undular Bores using a Fully Nonlinear Boussinesq Model M.Tissier, P. Bonneton, F.
Tidal modulation of wave-setup and wave-induced currents on the Aboré coral reef, New Caledonia
 18th April 2007 Tidal modulation of wave-setup and wave-induced currents on the Aboré coral reef, New Caledonia Philippe BONNETON, Jean-Pierre LEFEBVRE, Patrice BRETEL, Sylvain OUILLON, Pascal DOUILLET
18th April 2007 Tidal modulation of wave-setup and wave-induced currents on the Aboré coral reef, New Caledonia Philippe BONNETON, Jean-Pierre LEFEBVRE, Patrice BRETEL, Sylvain OUILLON, Pascal DOUILLET
MODELING OF CLIMATE CHANGE IMPACTS ON COASTAL STRUCTURES - CONTRIBUTION TO THEIR RE-DESIGN
 Proceedings of the 14 th International Conference on Environmental Science and Technology Rhodes, Greece, 3-5 September 2015 MODELING OF CLIMATE CHANGE IMPACTS ON COASTAL STRUCTURES - CONTRIBUTION TO THEIR
Proceedings of the 14 th International Conference on Environmental Science and Technology Rhodes, Greece, 3-5 September 2015 MODELING OF CLIMATE CHANGE IMPACTS ON COASTAL STRUCTURES - CONTRIBUTION TO THEIR
Impact of the tides, wind and shelf circulation on the Gironde river plume dynamics
 Impact of the tides, wind and shelf circulation on the Gironde river plume dynamics F. Toublanc 1, N. Ayoub 2, P. Marsaleix 3, P. De Mey 2 1 CNES/LEGOS 2 CNRS/LEGOS 3 CNRS/LA, Toulouse, France 5th GODAE
Impact of the tides, wind and shelf circulation on the Gironde river plume dynamics F. Toublanc 1, N. Ayoub 2, P. Marsaleix 3, P. De Mey 2 1 CNES/LEGOS 2 CNRS/LEGOS 3 CNRS/LA, Toulouse, France 5th GODAE
STUDY ON TSUNAMI PROPAGATION INTO RIVERS
 ABSTRACT STUDY ON TSUNAMI PROPAGATION INTO RIVERS Min Roh 1, Xuan Tinh Nguyen 2, Hitoshi Tanaka 3 When tsunami wave propagation from the narrow river mouth, water surface is raised and fluctuated by long
ABSTRACT STUDY ON TSUNAMI PROPAGATION INTO RIVERS Min Roh 1, Xuan Tinh Nguyen 2, Hitoshi Tanaka 3 When tsunami wave propagation from the narrow river mouth, water surface is raised and fluctuated by long
Modeling changes to the historic Lower Columbia River Estuary using Delft3D. Drew Mahedy Lumas Helaire Stefan Talke David Jay May 30, 2014
 Modeling changes to the historic Lower Columbia River Estuary using Delft3D Drew Mahedy Lumas Helaire Stefan Talke David Jay May 30, 2014 Comparison: Historic and Modern LCRE US Coastal Survey, 1868 Historic
Modeling changes to the historic Lower Columbia River Estuary using Delft3D Drew Mahedy Lumas Helaire Stefan Talke David Jay May 30, 2014 Comparison: Historic and Modern LCRE US Coastal Survey, 1868 Historic
A New Generator for Tsunami Wave Generation
 Journal of Energy and Power Engineering 10 (2016) 166-172 doi: 10.17265/1934-8975/2016.03.004 D DAVID PUBLISHING Tetsuya Hiraishi 1, Ryokei Azuma 1, Nobuhito Mori 2, Toshihiro Yasuda 2 and Hajime Mase
Journal of Energy and Power Engineering 10 (2016) 166-172 doi: 10.17265/1934-8975/2016.03.004 D DAVID PUBLISHING Tetsuya Hiraishi 1, Ryokei Azuma 1, Nobuhito Mori 2, Toshihiro Yasuda 2 and Hajime Mase
The impact of ocean bottom morphology on the modelling of long gravity waves from tides and tsunami to climate
 The impact of ocean bottom morphology on the modelling of long gravity waves from tides and tsunami to climate Christian Le Provost and Florent Lyard Laboratoire d Etudes en Géophysique et Océanographie
The impact of ocean bottom morphology on the modelling of long gravity waves from tides and tsunami to climate Christian Le Provost and Florent Lyard Laboratoire d Etudes en Géophysique et Océanographie
Nearshore wave-flow modelling with SWASH
 Nearshore wave-flow modelling with SWASH th Waves Workshop Marcel, Guus and Pieter November, /37 Delft University of Technology Motivation Goal: to develop a model that is capable of simulating wave motion
Nearshore wave-flow modelling with SWASH th Waves Workshop Marcel, Guus and Pieter November, /37 Delft University of Technology Motivation Goal: to develop a model that is capable of simulating wave motion
SEASONDE DETECTION OF TSUNAMI WAVES
 SEASONDE DETECTION OF TSUNAMI WAVES Belinda Lipa, John Bourg, Jimmy Isaacson, Don Barrick, and Laura Pederson 1 I. INTRODUCTION We here report on preliminary results of a study to assess the capability
SEASONDE DETECTION OF TSUNAMI WAVES Belinda Lipa, John Bourg, Jimmy Isaacson, Don Barrick, and Laura Pederson 1 I. INTRODUCTION We here report on preliminary results of a study to assess the capability
NTHMP - Mapping & Modeling Benchmarking Workshop: Tsunami Currents
 NTHMP - Mapping & Modeling Benchmarking Workshop: Tsunami Currents Ahmet Cevdet Yalçıner, Andrey Zaytsev, Utku Kanoğlu Deniz Velioglu, Gozde Guney Dogan, Rozita Kian, Naeimeh Shaghrivand, Betul Aytore
NTHMP - Mapping & Modeling Benchmarking Workshop: Tsunami Currents Ahmet Cevdet Yalçıner, Andrey Zaytsev, Utku Kanoğlu Deniz Velioglu, Gozde Guney Dogan, Rozita Kian, Naeimeh Shaghrivand, Betul Aytore
Tsunami generation, propagation, and devastation. John Fenton
 Tsunami generation, propagation, and devastation John Fenton Tsunami Tsunami is a Japanese term that means "harbour wave". It is used worldwide to describe a large sea wave generated by sea-floor disturbance.
Tsunami generation, propagation, and devastation John Fenton Tsunami Tsunami is a Japanese term that means "harbour wave". It is used worldwide to describe a large sea wave generated by sea-floor disturbance.
SCIENCE OF TSUNAMI HAZARDS
 SCIENCE OF TSUNAMI HAZARDS ISSN 8755-6839 Journal of Tsunami Society International Volume 29 Number 3 2010 ESTIMATION OF EXPECTED MAXIMUM WATER LEVEL DUE TO TIDE AND TSUNAMI INTERACTION ALONG THE COASTAL
SCIENCE OF TSUNAMI HAZARDS ISSN 8755-6839 Journal of Tsunami Society International Volume 29 Number 3 2010 ESTIMATION OF EXPECTED MAXIMUM WATER LEVEL DUE TO TIDE AND TSUNAMI INTERACTION ALONG THE COASTAL
NOAA NTHMP Mapping & Modeling Subcommittee Benchmarking Workshop: Tsunami Current. NEOWAVE Validation
 NOAA NTHMP Mapping & Modeling Subcommittee Benchmarking Workshop: Tsunami Current NEOWAVE Validation Yefei Bai, Yoshiki Yamazaki, and Kwok Fai Cheung Department of Ocean and Resources Engineering University
NOAA NTHMP Mapping & Modeling Subcommittee Benchmarking Workshop: Tsunami Current NEOWAVE Validation Yefei Bai, Yoshiki Yamazaki, and Kwok Fai Cheung Department of Ocean and Resources Engineering University
LONG WAVES OVER THE GREAT BARRIER REEF. Eric Wolanski ABSTRACT
 LONG WAVES OVER THE GREAT BARRIER REEF by Eric Wolanski k ABSTRACT Low-frequency forcing of water currents over the continental shelf f Australia is quite strong and should be taken into account when the
LONG WAVES OVER THE GREAT BARRIER REEF by Eric Wolanski k ABSTRACT Low-frequency forcing of water currents over the continental shelf f Australia is quite strong and should be taken into account when the
Tidally influenced environments. By Alex Tkaczyk, Henrique Menezes, and Isaac Foli
 Tidally influenced environments By Alex Tkaczyk, Henrique Menezes, and Isaac Foli Goals and aims Describe the role of tidal influence in depositional environments. - Deltas - Estuaries Provide an overview
Tidally influenced environments By Alex Tkaczyk, Henrique Menezes, and Isaac Foli Goals and aims Describe the role of tidal influence in depositional environments. - Deltas - Estuaries Provide an overview
LONG WAVE RUN-UP OVER SUBMERGED REEF AND BREAKWATER
 LONG WAVE RUN-UP OVER SUBMERGED REEF AND BREAKWATER A THESIS SUBMITTED TO THE GRADUATE DIVISION OF THE UNIVERSITY OF HAWAIʻI IN PARTIAL FULFILMENT OF THE REQUIREMENTS FOR THE DEGREE OF MASTER OF SCIENCE
LONG WAVE RUN-UP OVER SUBMERGED REEF AND BREAKWATER A THESIS SUBMITTED TO THE GRADUATE DIVISION OF THE UNIVERSITY OF HAWAIʻI IN PARTIAL FULFILMENT OF THE REQUIREMENTS FOR THE DEGREE OF MASTER OF SCIENCE
Coastal Engineering 67 (2012) Contents lists available at SciVerse ScienceDirect. Coastal Engineering
 Coastal Engineering 67 () 54 66 Contents lists available at SciVerse ScienceDirect Coastal Engineering journal homepage: www.elsevier.com/locate/coastaleng A new approach to handle wave breaking in fully
Coastal Engineering 67 () 54 66 Contents lists available at SciVerse ScienceDirect Coastal Engineering journal homepage: www.elsevier.com/locate/coastaleng A new approach to handle wave breaking in fully
Your web browser (Safari 7) is out of date. For more security, comfort and the best experience on this site: Update your browser Ignore
 Your web browser (Safari 7) is out of date. For more security, comfort and the best experience on this site: Update your browser Ignore TIDAL BO RE For the complete encyclopedic entry with media resources,
Your web browser (Safari 7) is out of date. For more security, comfort and the best experience on this site: Update your browser Ignore TIDAL BO RE For the complete encyclopedic entry with media resources,
Clockwise Phase Propagation of Semi-Diurnal Tides in the Gulf of Thailand
 Journal of Oceanography, Vol. 54, pp. 143 to 150. 1998 Clockwise Phase Propagation of Semi-Diurnal Tides in the Gulf of Thailand TETSUO YANAGI 1 and TOSHIYUKI TAKAO 2 1 Research Institute for Applied Mechanics,
Journal of Oceanography, Vol. 54, pp. 143 to 150. 1998 Clockwise Phase Propagation of Semi-Diurnal Tides in the Gulf of Thailand TETSUO YANAGI 1 and TOSHIYUKI TAKAO 2 1 Research Institute for Applied Mechanics,
Tidal analysis and prediction of the flow characteristics around Abu Dhabi Island
 Tidal analysis and prediction of the flow characteristics around Abu Dhabi Island K.A. Mohamed & M.E. El-Dahshan Research Center, Abu Dhabi Water and Electricity Authority Abstract In coastal seas and
Tidal analysis and prediction of the flow characteristics around Abu Dhabi Island K.A. Mohamed & M.E. El-Dahshan Research Center, Abu Dhabi Water and Electricity Authority Abstract In coastal seas and
High Frequency Field Measurements of an Undular Bore Using a 2D LiDAR Scanner
 Article High Frequency Field Measurements of an Undular Bore Using a 2D LiDAR Scanner Kévin Martins 1, *, Philippe Bonneton 2, Frédéric Frappart 3,, Guillaume Detandt 2, Natalie Bonneton 2 and Chris E.
Article High Frequency Field Measurements of an Undular Bore Using a 2D LiDAR Scanner Kévin Martins 1, *, Philippe Bonneton 2, Frédéric Frappart 3,, Guillaume Detandt 2, Natalie Bonneton 2 and Chris E.
Simulation of hydraulic regime and sediment transport in the Mekong delta coast
 Simulation of hydraulic regime and sediment transport in the Mekong delta coast 1. Introduction Coastal erosion in the Mekong Delta has been recorded in recent years and the erosion rate has been increasing
Simulation of hydraulic regime and sediment transport in the Mekong delta coast 1. Introduction Coastal erosion in the Mekong Delta has been recorded in recent years and the erosion rate has been increasing
HYDROSPHERE, OCEANS AND TIDES
 HYDROSPHERE, OCEANS AND TIDES Revision 10x10learning.com 1 Chapter 12. In the Earth s Atmosphere On surface of the Earth Under the ground Hydrosphere comprises of ALL WATER Water Vapour = 0.001% Is very
HYDROSPHERE, OCEANS AND TIDES Revision 10x10learning.com 1 Chapter 12. In the Earth s Atmosphere On surface of the Earth Under the ground Hydrosphere comprises of ALL WATER Water Vapour = 0.001% Is very
An Atlas of Oceanic Internal Solitary Waves (February 2004) by Global Ocean Associates Prepared for Office of Naval Research Code 322 PO
 Overview The is located in the North Atlantic Ocean between southern Ireland and southwest England (Figure 1). The Sea s western edge covers a continental shelf region characterized by rough and irregular
Overview The is located in the North Atlantic Ocean between southern Ireland and southwest England (Figure 1). The Sea s western edge covers a continental shelf region characterized by rough and irregular
Tsunami Waveforms in South China Sea and Runup of Undular Bores
 SCSTW-7, Taichung, 18-22 Nov. 2014 Tsunami Waveforms in South China Sea and Runup of Undular Bores Xi Zhao Hua LIU MOE Key Lab of Hydrodynamics School of NAOCE, Shanghai Jiao Tong University hliu@sjtu.edu.cn
SCSTW-7, Taichung, 18-22 Nov. 2014 Tsunami Waveforms in South China Sea and Runup of Undular Bores Xi Zhao Hua LIU MOE Key Lab of Hydrodynamics School of NAOCE, Shanghai Jiao Tong University hliu@sjtu.edu.cn
Wave Transformation Modeling with Bottom Friction Applied to the Southeast Oahu Reefs. Mary A. Cialone and Jane McKee Smith
 Wave Transformation Modeling with Bottom Friction Applied to the Southeast Oahu Reefs Mary A. Cialone and Jane McKee Smith Outline Objective Study Area STWAVE Friction Formulations Model Validation Summary
Wave Transformation Modeling with Bottom Friction Applied to the Southeast Oahu Reefs Mary A. Cialone and Jane McKee Smith Outline Objective Study Area STWAVE Friction Formulations Model Validation Summary
Waves Part II. non-dispersive (C g =C)
 Waves Part II Previously we discussed Surface Gravity Waves Deep Water Waves Shallow Water Waves C g T 2 C g h dispersive (C g =C/2) Definitions: phase speed C= /T= /k non-dispersive (C g =C) group speed
Waves Part II Previously we discussed Surface Gravity Waves Deep Water Waves Shallow Water Waves C g T 2 C g h dispersive (C g =C/2) Definitions: phase speed C= /T= /k non-dispersive (C g =C) group speed
TIDE-TSUNAMI INTERACTIONS
 TIDE-TSUNAMI INTERACTIONS Zygmunt Kowalik, Tatiana Proshutinsky, Institute of Marine Science, University of Alaska, Fairbanks, AK, USA Andrey Proshutinsky, Woods Hole Oceanographic Institution, Woods Hole,
TIDE-TSUNAMI INTERACTIONS Zygmunt Kowalik, Tatiana Proshutinsky, Institute of Marine Science, University of Alaska, Fairbanks, AK, USA Andrey Proshutinsky, Woods Hole Oceanographic Institution, Woods Hole,
Nearshore Morphodynamics. Bars and Nearshore Bathymetry. Sediment packages parallel to shore, that store beach sediment
 Nearshore Morphodynamics http://coastal.er.usgs.gov/bier/images/chandeleur-xbeach-lg.jpg Bars and Nearshore Bathymetry Sediment packages parallel to shore, that store beach sediment Can be up to 50 km
Nearshore Morphodynamics http://coastal.er.usgs.gov/bier/images/chandeleur-xbeach-lg.jpg Bars and Nearshore Bathymetry Sediment packages parallel to shore, that store beach sediment Can be up to 50 km
Wave research at Department of Oceanography, University of Hawai i
 Wave research at Department of Oceanography, University of Hawai i Hawaii wave climate. Directional waverider buoys around Hawaii. Past and present wave-related research projects. Effect of tides on wave
Wave research at Department of Oceanography, University of Hawai i Hawaii wave climate. Directional waverider buoys around Hawaii. Past and present wave-related research projects. Effect of tides on wave
The events associated with the Great Tsunami of 26 December 2004 Sea Level Variation and Impact on Coastal Region of India
 The events associated with the Great Tsunami of 26 December 2004 Sea Level Variation and Impact on Coastal Region of India Satish R. Shetye National Institute of Oceanography, Goa Tsunamis are shallow-water
The events associated with the Great Tsunami of 26 December 2004 Sea Level Variation and Impact on Coastal Region of India Satish R. Shetye National Institute of Oceanography, Goa Tsunamis are shallow-water
Improving predictions of nearshore processes and shoreline dynamics for beaches along Australia s rocky and coral reef coasts
 Improving predictions of nearshore processes and shoreline dynamics for beaches along Australia s rocky and coral reef coasts Ryan Lowe Jeff Hansen, Graham Symonds, Mark Buckley, Andrew Pomeroy, Gundula
Improving predictions of nearshore processes and shoreline dynamics for beaches along Australia s rocky and coral reef coasts Ryan Lowe Jeff Hansen, Graham Symonds, Mark Buckley, Andrew Pomeroy, Gundula
THE POLARIMETRIC CHARACTERISTICS OF BOTTOM TOPOGRAPHY RELATED FEATURES ON SAR IMAGES
 THE POLARIMETRIC CHARACTERISTICS OF BOTTOM TOPOGRAPHY RELATED FEATURES ON SAR IMAGES Taerim Kim Professor, Ocean System Eng. Dept. Kunsan University Miryong Dong San 68, Kunsan, Jeonbuk, Korea, trkim@kunsan.ac.kr
THE POLARIMETRIC CHARACTERISTICS OF BOTTOM TOPOGRAPHY RELATED FEATURES ON SAR IMAGES Taerim Kim Professor, Ocean System Eng. Dept. Kunsan University Miryong Dong San 68, Kunsan, Jeonbuk, Korea, trkim@kunsan.ac.kr
Tsunamis are not observed via height rather by orbital velocity from shallow-water wave physics
 Modeling of Tsunami Current Flows Presenter: Dr. Don Barrick President, CODAR Ocean Sensors Coauthors: Dr. Belinda Lipa, Chad Whelan RIAM Workshop on Oceanographic Radar Tsunami capability of HF radar
Modeling of Tsunami Current Flows Presenter: Dr. Don Barrick President, CODAR Ocean Sensors Coauthors: Dr. Belinda Lipa, Chad Whelan RIAM Workshop on Oceanographic Radar Tsunami capability of HF radar
Announcements. Project 2 due Nov 7 th Topics for today: Big waves. Tsunamis, seiches and tidal waves. Tsunamis and seiches
 Announcements Project 2 due Nov 7 th Topics for today: Big waves Tsunamis, seiches and tidal waves Tsunamis and seiches Seiche: standing wave that rocks back and forth within an enclosed or semi-enclosed
Announcements Project 2 due Nov 7 th Topics for today: Big waves Tsunamis, seiches and tidal waves Tsunamis and seiches Seiche: standing wave that rocks back and forth within an enclosed or semi-enclosed
NONLINEAR INTERNAL WAVES IN THE SOUTH CHINA SEA
 25 th ACRS 2004 Chiang Mai, Thailand xxx NONLINEAR INTERNAL WAVES IN THE SOUTH CHINA SEA Ming-Kuang Hsu Professor, Kuang Wu Institute of Technology, Taipei, Taiwan, R.O.C. Hsumk@kwit.edu.tw Antony K. Liu
25 th ACRS 2004 Chiang Mai, Thailand xxx NONLINEAR INTERNAL WAVES IN THE SOUTH CHINA SEA Ming-Kuang Hsu Professor, Kuang Wu Institute of Technology, Taipei, Taiwan, R.O.C. Hsumk@kwit.edu.tw Antony K. Liu
PROPAGATION OF LONG-PERIOD WAVES INTO AN ESTUARY THROUGH A NARROW INLET
 PROPAGATION OF LONG-PERIOD WAVES INTO AN ESTUARY THROUGH A NARROW INLET Takumi Okabe, Shin-ichi Aoki and Shigeru Kato Department of Civil Engineering Toyohashi University of Technology Toyohashi, Aichi,
PROPAGATION OF LONG-PERIOD WAVES INTO AN ESTUARY THROUGH A NARROW INLET Takumi Okabe, Shin-ichi Aoki and Shigeru Kato Department of Civil Engineering Toyohashi University of Technology Toyohashi, Aichi,
HARBOUR RESONANCE UNDER IMPACT OF POWERFUL TSUNAMI
 HARBOUR RESONANCE UNDER IMPACT OF POWERFUL TSUNAMI Shentong Lu 1, Jiin-Jen Lee 2, and Xiuying Xing 3 The powerful tsunami events caused by Feb. 27 th, 2010 Chilean earthquake and Mar. 11 th, 2011 Tohoku
HARBOUR RESONANCE UNDER IMPACT OF POWERFUL TSUNAMI Shentong Lu 1, Jiin-Jen Lee 2, and Xiuying Xing 3 The powerful tsunami events caused by Feb. 27 th, 2010 Chilean earthquake and Mar. 11 th, 2011 Tohoku
Testing TELEMAC-2D suitability for tsunami propagation from source to near shore
 Testing TELEMAC-2D suitability for tsunami propagation from source to near shore Alan Cooper, Giovanni Cuomo, Sébastien Bourban, Michael Turnbull, David Roscoe HR Wallingford Ltd, Howbery Park, Wallingford,
Testing TELEMAC-2D suitability for tsunami propagation from source to near shore Alan Cooper, Giovanni Cuomo, Sébastien Bourban, Michael Turnbull, David Roscoe HR Wallingford Ltd, Howbery Park, Wallingford,
ABSTRACT. KEY WORDS: coral reef, storm waves, infragravity waves, power plant, cooling water, field observation. INTRODUCTION FIELD OBSERVATION
 M.W.L. Fluctuations Inside a Cooling Water Tank Set Inside a Coral Reef Julio Monroy Department of Civil Engineering, Kagoshima University -2-4 Korimoto, Kagoshima-shi, Japan 89-65 Ryuchiro Nishi, Michio
M.W.L. Fluctuations Inside a Cooling Water Tank Set Inside a Coral Reef Julio Monroy Department of Civil Engineering, Kagoshima University -2-4 Korimoto, Kagoshima-shi, Japan 89-65 Ryuchiro Nishi, Michio
The construction of Deepwater Navigation Channel (DNC) in the Bystry arm of the Danube Delta has started in The whole project provides the
 Annex 45 Numerical Studies of Waves, Currents and Sediment Transport at the Marine Part of Deepwater Navigation Channel through the Bystry Arm of the Danube Delta and Model Verification based on Laboratory
Annex 45 Numerical Studies of Waves, Currents and Sediment Transport at the Marine Part of Deepwater Navigation Channel through the Bystry Arm of the Danube Delta and Model Verification based on Laboratory
Australian Northwest Shelf
 Overview The Australian Northwest shelf extends roughly 2000 km along the coast of Western Australia (Figure 1). The region is influenced by part of the South Equatorial Current that runs southwest out
Overview The Australian Northwest shelf extends roughly 2000 km along the coast of Western Australia (Figure 1). The region is influenced by part of the South Equatorial Current that runs southwest out
Modeling Historic Columbia River Flood Impacts
 Modeling Historic Columbia River Flood Impacts Columbia River Estuary Workshop May 30, 2014 Present by: Lumas Helaire; Graduate Student, Portland State University Andrew Mahedy; Graduate Student, Portland
Modeling Historic Columbia River Flood Impacts Columbia River Estuary Workshop May 30, 2014 Present by: Lumas Helaire; Graduate Student, Portland State University Andrew Mahedy; Graduate Student, Portland
Currents measurements in the coast of Montevideo, Uruguay
 Currents measurements in the coast of Montevideo, Uruguay M. Fossati, D. Bellón, E. Lorenzo & I. Piedra-Cueva Fluid Mechanics and Environmental Engineering Institute (IMFIA), School of Engineering, Research
Currents measurements in the coast of Montevideo, Uruguay M. Fossati, D. Bellón, E. Lorenzo & I. Piedra-Cueva Fluid Mechanics and Environmental Engineering Institute (IMFIA), School of Engineering, Research
OECS Regional Engineering Workshop September 29 October 3, 2014
 B E A C H E S. M A R I N A S. D E S I G N. C O N S T R U C T I O N. OECS Regional Engineering Workshop September 29 October 3, 2014 Coastal Erosion and Sea Defense: Introduction to Coastal Dynamics David
B E A C H E S. M A R I N A S. D E S I G N. C O N S T R U C T I O N. OECS Regional Engineering Workshop September 29 October 3, 2014 Coastal Erosion and Sea Defense: Introduction to Coastal Dynamics David
Marginal Marine Environments
 Marginal Marine Environments Delta: discrete shoreline protuberances formed where rivers enter oceans, semi-enclosed seas, lakes or lagoons and supply sediment more rapidly than it can be redistributed
Marginal Marine Environments Delta: discrete shoreline protuberances formed where rivers enter oceans, semi-enclosed seas, lakes or lagoons and supply sediment more rapidly than it can be redistributed
TIDAL BORES, AEGIR, EAGRE, MASCARET, POROROCA: THEORY AND OBSERVATIONS
 TIDAL BORES, AEGIR, EAGRE, MASCARET, POROROCA: THEORY AND OBSERVATIONS by Hubert CHANSON Professor, School of Civil Engineering, School of Engineering, The University of Queensland, Brisbane QLD 4072,
TIDAL BORES, AEGIR, EAGRE, MASCARET, POROROCA: THEORY AND OBSERVATIONS by Hubert CHANSON Professor, School of Civil Engineering, School of Engineering, The University of Queensland, Brisbane QLD 4072,
Some basic aspects of internal waves in the ocean & (Tidally driven internal wave generation at the edge of a continental shelf)
 Some basic aspects of internal waves in the ocean & (Tidally driven internal wave generation at the edge of a continental shelf) Weifeng (Gordon) Zhang Applied Ocean Physics & Engineering Department Woods
Some basic aspects of internal waves in the ocean & (Tidally driven internal wave generation at the edge of a continental shelf) Weifeng (Gordon) Zhang Applied Ocean Physics & Engineering Department Woods
R E M I N D E R S. v Two required essays are due by April 9, v Extra Credit: Think Geographically Essays from any five of the textbook s
 R E M I N D E R S v Two required essays are due by April 9, 2019. Ø A third may be used for extra credit in place of a Think Geographically essay. ESSAY TOPICS (choose any two): Contributions of a noted
R E M I N D E R S v Two required essays are due by April 9, 2019. Ø A third may be used for extra credit in place of a Think Geographically essay. ESSAY TOPICS (choose any two): Contributions of a noted
Training program on Modelling: A Case study Hydro-dynamic Model of Zanzibar channel
 Training program on Modelling: A Case study Hydro-dynamic Model of Zanzibar channel Mayorga-Adame,C.G., Sanga,I.P.L., Majuto, C., Makame, M.A., Garu,M. INTRODUCTION Hydrodynamic Modeling In understanding
Training program on Modelling: A Case study Hydro-dynamic Model of Zanzibar channel Mayorga-Adame,C.G., Sanga,I.P.L., Majuto, C., Makame, M.A., Garu,M. INTRODUCTION Hydrodynamic Modeling In understanding
We are long-time and intensive users of COPERNICUS products
 Prevention of river flooding in the French Roussillon Mediterranean Coast SIROCCO academic research group, Laboratoire d Aérologie, CNRS & Toulouse University, France We are long-time and intensive users
Prevention of river flooding in the French Roussillon Mediterranean Coast SIROCCO academic research group, Laboratoire d Aérologie, CNRS & Toulouse University, France We are long-time and intensive users
Coastal management has lagged behind the growth in population leading to problems with pollution
 Fifty percent of the population of the industrialized world lives within 100 km of a coast. Coastal management has lagged behind the growth in population leading to problems with pollution and natural
Fifty percent of the population of the industrialized world lives within 100 km of a coast. Coastal management has lagged behind the growth in population leading to problems with pollution and natural
USING BIOLOGICALLY IMPORTANT PHYSICAL CHARACTERISTICS OF ESTUARIES TO CLASSIFY AUSTRALIAN AND NEW ZEALAND ESTUARIES
 USING BIOLOGICALLY IMPORTANT PHYSICAL CHARACTERISTICS OF ESTUARIES TO CLASSIFY AUSTRALIAN AND NEW ZEALAND ESTUARIES Michael Whelan, Southern Cross University, Australia. Peter Saenger, Southern Cross University,
USING BIOLOGICALLY IMPORTANT PHYSICAL CHARACTERISTICS OF ESTUARIES TO CLASSIFY AUSTRALIAN AND NEW ZEALAND ESTUARIES Michael Whelan, Southern Cross University, Australia. Peter Saenger, Southern Cross University,
Ocean Waves. Capillary. Gravity. Wind generated. Tides Tsunamis Seiches
 Ocean Waves Capillary Wind generated Gravity Tides Tsunamis Seiches Capillary waves are driven by the surface tension produced by electrically polarized water molecule San Pedro Lighthouse Waves are alternate
Ocean Waves Capillary Wind generated Gravity Tides Tsunamis Seiches Capillary waves are driven by the surface tension produced by electrically polarized water molecule San Pedro Lighthouse Waves are alternate
/50. Physical Geology Shorelines
 Physical Geology Shorelines Multiple Guess: (You know the drill 2 points each) 1. The path of movement of a water particle in a wave at sea is 1. circular 2. horizontal 3. vertical 4. elliptical 5. none
Physical Geology Shorelines Multiple Guess: (You know the drill 2 points each) 1. The path of movement of a water particle in a wave at sea is 1. circular 2. horizontal 3. vertical 4. elliptical 5. none
PARAMETRIZATION OF WAVE TRANSFORMATION ABOVE SUBMERGED BAR BASED ON PHYSICAL AND NUMERICAL TESTS
 Proceedings of the 6 th International Conference on the Application of Physical Modelling in Coastal and Port Engineering and Science (Coastlab16) Ottawa, Canada, May 10-13, 2016 Copyright : Creative Commons
Proceedings of the 6 th International Conference on the Application of Physical Modelling in Coastal and Port Engineering and Science (Coastlab16) Ottawa, Canada, May 10-13, 2016 Copyright : Creative Commons
Applications of ELCIRC at LNEC
 stratification in the Guadiana estuary tidal propagation in the Óbidos lagoon Lígia Pinto Anabela Oliveira André B. Fortunato 2 O utline Stratification in the Guadiana estuary The Guadiana estuary Objectives
stratification in the Guadiana estuary tidal propagation in the Óbidos lagoon Lígia Pinto Anabela Oliveira André B. Fortunato 2 O utline Stratification in the Guadiana estuary The Guadiana estuary Objectives
Wave Transformation and Energy Dissipation in the Surf Zone: Comparison Between a Non-linear Model and Field Data.
 Journal of Coastal Research SI 39 pg - pg ICS 2004 (Proccedings) Brazil ISSN 0749-0208 Wave Transformation and Energy Dissipation in the Surf Zone: Comparison Between a Non-linear Model and Field Data.
Journal of Coastal Research SI 39 pg - pg ICS 2004 (Proccedings) Brazil ISSN 0749-0208 Wave Transformation and Energy Dissipation in the Surf Zone: Comparison Between a Non-linear Model and Field Data.
SOME WATER CHARACTERISTICS OF ESTUARIES IN INDONESIA
 SOME WATER CHARACTERISTICS OF ESTUARIES IN INDONESIA by HENK L. UKTOLSEYA 1 ABSTRACT This paper describes the results obtained during several hydro-oceanographical observations of some estuaries in Indonesia
SOME WATER CHARACTERISTICS OF ESTUARIES IN INDONESIA by HENK L. UKTOLSEYA 1 ABSTRACT This paper describes the results obtained during several hydro-oceanographical observations of some estuaries in Indonesia
BCCS TECHNICAL REPORT SERIES
 BCCS TECHNICAL REPORT SERIES Numerical studies of internal solitary wave trains generated at edges in the topography. Berntsen, J., Mathisen, J.-P. and Furnes, G. REPORT No. 21 April 13, Report on Contract
BCCS TECHNICAL REPORT SERIES Numerical studies of internal solitary wave trains generated at edges in the topography. Berntsen, J., Mathisen, J.-P. and Furnes, G. REPORT No. 21 April 13, Report on Contract
COASTAL ENVIRONMENTS. 454 lecture 12
 COASTAL ENVIRONMENTS Repeated movement of sediment & water constructs a beach profile reflecting the balance between average daily or seasonal wave forces and resistance of landmass to wave action Coasts
COASTAL ENVIRONMENTS Repeated movement of sediment & water constructs a beach profile reflecting the balance between average daily or seasonal wave forces and resistance of landmass to wave action Coasts
Transactions on Ecology and the Environment vol 12, 1996 WIT Press, ISSN
 Open boundary condition for unsteady open-channel flow K. Mizumura Civil Engineering Department, Kanazawa Institute of Technology, 7-1 Ogigaoka, Nonoichimachi, Ishikawa Pref. 921, Japan Abstract Initial
Open boundary condition for unsteady open-channel flow K. Mizumura Civil Engineering Department, Kanazawa Institute of Technology, 7-1 Ogigaoka, Nonoichimachi, Ishikawa Pref. 921, Japan Abstract Initial
10 Internal Waves: Reflection and Relation to Normal Modes
 EOSC 579 Lecture 10. Notes date: February 7, 2012 49 10 Internal Waves: Reflection and Relation to Normal Modes This lecture is based on a set of notes written by R. Pawlowicz 10.1 Reflection at a Boundary
EOSC 579 Lecture 10. Notes date: February 7, 2012 49 10 Internal Waves: Reflection and Relation to Normal Modes This lecture is based on a set of notes written by R. Pawlowicz 10.1 Reflection at a Boundary
SWASH MODELLING OF A COASTAL PROTECTION SCHEME
 SWASH MODELLING OF A COASTAL PROTECTION SCHEME Mark Klein 1, Andrew Symonds 2, Marcel Zijlema 3, Dan Messiter 4 and Michael Dufour 5 The Beresford shoreline, Australia, is subject to a complex interaction
SWASH MODELLING OF A COASTAL PROTECTION SCHEME Mark Klein 1, Andrew Symonds 2, Marcel Zijlema 3, Dan Messiter 4 and Michael Dufour 5 The Beresford shoreline, Australia, is subject to a complex interaction
Internal Tides and Solitary Waves in the Northern South China Sea: A Nonhydrostatic Numerical Investigation
 Internal Tides and Solitary Waves in the Northern South China Sea: A Nonhydrostatic Numerical Investigation Ping-Tung Shaw Dept of MEAS, North Carolina State University Box 8208, Raleigh, NC 27695-8208
Internal Tides and Solitary Waves in the Northern South China Sea: A Nonhydrostatic Numerical Investigation Ping-Tung Shaw Dept of MEAS, North Carolina State University Box 8208, Raleigh, NC 27695-8208
Internal Waves in Straits Experiment Progress Report
 DISTRIBUTION STATEMENT A: Approved for public release; distribution is unlimited. Internal Waves in Straits Experiment Progress Report Jody Klymak School of Earth and Ocean Sciences University of Victoria
DISTRIBUTION STATEMENT A: Approved for public release; distribution is unlimited. Internal Waves in Straits Experiment Progress Report Jody Klymak School of Earth and Ocean Sciences University of Victoria
Assessment of flooding on low-elevation reef-lined coasts
 Assessment of flooding on low-elevation reef-lined coasts Ap van Dongeren, Deltares, Delft, The Netherlands With Curt Storlazzi, USGS, Santa Cruz, USA Impact on coral reef-lined islands and coasts Coral
Assessment of flooding on low-elevation reef-lined coasts Ap van Dongeren, Deltares, Delft, The Netherlands With Curt Storlazzi, USGS, Santa Cruz, USA Impact on coral reef-lined islands and coasts Coral
Prof. B.S. Thandaveswara. The periodic rise and fall of the planetary ocean level in response to the gravitational
 37.5 Tides The periodic rise and fall of the planetary ocean level in response to the gravitational interaction of the earth, moon, and sun. The periodic rise and fall of sea level that results from the
37.5 Tides The periodic rise and fall of the planetary ocean level in response to the gravitational interaction of the earth, moon, and sun. The periodic rise and fall of sea level that results from the
Garrett McNamara, Portugal, 30 Jan What is a wave?
 Waves Garrett McNamara, Portugal, 30 Jan 2013 What is a wave? Waves transmit a disturbance / energy from one part of a material to another. The energy is transmitted without substantial movement of the
Waves Garrett McNamara, Portugal, 30 Jan 2013 What is a wave? Waves transmit a disturbance / energy from one part of a material to another. The energy is transmitted without substantial movement of the
An IOOS Operational Wave Observation Plan Supported by NOAA IOOS Program & USACE
 An IOOS Operational Wave Observation Plan Supported by NOAA IOOS Program & USACE R.E. Jensen, W.A. Birkemeier and W. Burnett JCOMM-Workshop on Wave Measurements from Buoys Wave Information to Application
An IOOS Operational Wave Observation Plan Supported by NOAA IOOS Program & USACE R.E. Jensen, W.A. Birkemeier and W. Burnett JCOMM-Workshop on Wave Measurements from Buoys Wave Information to Application
OCN 201 Tides. Tsunamis, Tides and other long waves
 OCN 201 Tides Tsunamis, Tides and other long waves Storm surges Caused by winds and low atmospheric pressure associated with large storms Can raise sea surface by up to 25 ft, bottom contours magnify effect
OCN 201 Tides Tsunamis, Tides and other long waves Storm surges Caused by winds and low atmospheric pressure associated with large storms Can raise sea surface by up to 25 ft, bottom contours magnify effect
Wave behaviour in the inner surf zone
 Wave behaviour in the inner surf zone Hannah POWER 1 and Michael HUGHES 2 Abstract: The inner surf zone is a critical component of models that are used to predict nearshore wave behaviour and beach morphodynamics.
Wave behaviour in the inner surf zone Hannah POWER 1 and Michael HUGHES 2 Abstract: The inner surf zone is a critical component of models that are used to predict nearshore wave behaviour and beach morphodynamics.
Global Ocean Internal Wave Database
 Global Ocean Internal Wave Database Victor Klemas Graduate College of Marine Studies University of Delaware Newark, DE 19716 phone: (302) 831-8256 fax: (302) 831-6838 email: klemas@udel.edu Quanan Zheng
Global Ocean Internal Wave Database Victor Klemas Graduate College of Marine Studies University of Delaware Newark, DE 19716 phone: (302) 831-8256 fax: (302) 831-6838 email: klemas@udel.edu Quanan Zheng
WAVE BREAKING AND DISSIPATION IN THE NEARSHORE
 WAVE BREAKING AND DISSIPATION IN THE NEARSHORE LONG-TERM GOALS Dr. Thomas C. Lippmann Center for Coastal Studies Scripps Institution of Oceanography University of California, San Diego 9500 Gilman Dr.
WAVE BREAKING AND DISSIPATION IN THE NEARSHORE LONG-TERM GOALS Dr. Thomas C. Lippmann Center for Coastal Studies Scripps Institution of Oceanography University of California, San Diego 9500 Gilman Dr.
Airy Wave Theory 1: Wave Length and Celerity
 Airy Wave Theory 1: Wave Length and Celerity Wave Theories Mathematical relationships to describe: (1) the wave form, (2) the water motion (throughout the fluid column) and pressure in waves, and (3) how
Airy Wave Theory 1: Wave Length and Celerity Wave Theories Mathematical relationships to describe: (1) the wave form, (2) the water motion (throughout the fluid column) and pressure in waves, and (3) how
Keywords : tidal bore, mixing and dispersion, sediment process, ecology, review.
 MIXING AND DISPERSION IN TIDAL BORES: A REVIEW Hubert CHANSON Reader in Environmental Fluid Mechanics and Hydraulics, Department of Civil Engineering, The University of Queensland, Brisbane QLD 4072, Australia
MIXING AND DISPERSION IN TIDAL BORES: A REVIEW Hubert CHANSON Reader in Environmental Fluid Mechanics and Hydraulics, Department of Civil Engineering, The University of Queensland, Brisbane QLD 4072, Australia
Sustainable Energy Science and Engineering Center. Ocean Energy. Reference: Renewable Energy by Godfrey Boyle, Oxford University Press, 2004.
 Ocean Energy Reference: Renewable Energy by Godfrey Boyle, Oxford University Press, 2004. Ocean Energy Oceans cover most of the (70%) of the earth s surface and they generate thermal energy from the sun
Ocean Energy Reference: Renewable Energy by Godfrey Boyle, Oxford University Press, 2004. Ocean Energy Oceans cover most of the (70%) of the earth s surface and they generate thermal energy from the sun
An Investigation of the Influence of Waves on Sediment Processes in Skagit Bay
 DISTRIBUTION STATEMENT A. Approved for public release; distribution is unlimited. An Investigation of the Influence of Waves on Sediment Processes in Skagit Bay Geoffrey W. Cowles School for Marine Science
DISTRIBUTION STATEMENT A. Approved for public release; distribution is unlimited. An Investigation of the Influence of Waves on Sediment Processes in Skagit Bay Geoffrey W. Cowles School for Marine Science
OCEANOGRAPHY STUDY GUIDE
 OCEANOGRAPHY STUDY GUIDE Chapter 2 Section 1 1. Most abundant salt in ocean. Sodium chloride; NaCl 2. Amount of Earth covered by Water 71% 3. Four oceans: What are they? Atlantic, Pacific, Arctic, Indian
OCEANOGRAPHY STUDY GUIDE Chapter 2 Section 1 1. Most abundant salt in ocean. Sodium chloride; NaCl 2. Amount of Earth covered by Water 71% 3. Four oceans: What are they? Atlantic, Pacific, Arctic, Indian
APPLICATION OF SOUND PROPAGATION (IN THE PERSIAN GULF AND OMAN SEA)
 APPLICATION OF SOUND PROPAGATION (IN THE PERSIAN GULF AND OMAN SEA) Seyed Majid Mosaddad Department of Physics, Shoushtar Branch, Islamic Azad University, Shoushtar, Iran Email: mosaddad5@gmail.com Abstract
APPLICATION OF SOUND PROPAGATION (IN THE PERSIAN GULF AND OMAN SEA) Seyed Majid Mosaddad Department of Physics, Shoushtar Branch, Islamic Azad University, Shoushtar, Iran Email: mosaddad5@gmail.com Abstract
Berkeley Wave Carpet. Development of a Submerged Pressure Differential Area Wave Energy Converter
 Berkeley Wave Carpet Development of a Submerged Pressure Differential Area Wave Energy Converter Contact: Marcus Lehmann, M.Sc. mlehmann@lbl.gov www.cyclotronroad.org/calwave/ Agenda 1. Development History
Berkeley Wave Carpet Development of a Submerged Pressure Differential Area Wave Energy Converter Contact: Marcus Lehmann, M.Sc. mlehmann@lbl.gov www.cyclotronroad.org/calwave/ Agenda 1. Development History
Effect of Hydrodynamics on Sediment Transport near a Coastal Inlet
 ICHE 2014, Hamburg - Lehfeldt & Kopmann (eds) - 2014 Bundesanstalt für Wasserbau ISBN 978-3-939230-32-8 Effect of Hydrodynamics on Sediment Transport near a Coastal Inlet H. Li, M. Brown, J. Rosati & Z.
ICHE 2014, Hamburg - Lehfeldt & Kopmann (eds) - 2014 Bundesanstalt für Wasserbau ISBN 978-3-939230-32-8 Effect of Hydrodynamics on Sediment Transport near a Coastal Inlet H. Li, M. Brown, J. Rosati & Z.
Cross-shore sediment transports on a cut profile for large scale land reclamations
 Cross-shore sediment transports on a cut profile for large scale land reclamations Martijn Onderwater 1 Dano Roelvink Jan van de Graaff 3 Abstract When building a large scale land reclamation, the safest
Cross-shore sediment transports on a cut profile for large scale land reclamations Martijn Onderwater 1 Dano Roelvink Jan van de Graaff 3 Abstract When building a large scale land reclamation, the safest
Shoreline Evolution Due to Oblique Waves in Presence of Submerged Breakwaters. Nima Zakeri (Corresponding Author), Mojtaba Tajziehchi
 Shoreline Evolution Due to Oblique Waves in Presence of Submerged Breakwaters Nima Zakeri (Corresponding Author), Mojtaba Tajziehchi Department of Civil Engineering, Faculty of Engineering, University
Shoreline Evolution Due to Oblique Waves in Presence of Submerged Breakwaters Nima Zakeri (Corresponding Author), Mojtaba Tajziehchi Department of Civil Engineering, Faculty of Engineering, University
Directed Reading. Section: Ocean Currents. a(n). FACTORS THAT AFFECT SURFACE CURRENTS
 Skills Worksheet Directed Reading Section: Ocean Currents 1. A horizontal movement of water in a well-defined pattern is called a(n). 2. What are two ways that oceanographers identify ocean currents? 3.
Skills Worksheet Directed Reading Section: Ocean Currents 1. A horizontal movement of water in a well-defined pattern is called a(n). 2. What are two ways that oceanographers identify ocean currents? 3.
Waves. G. Cowles. General Physical Oceanography MAR 555. School for Marine Sciences and Technology Umass-Dartmouth
 Waves G. Cowles General Physical Oceanography MAR 555 School for Marine Sciences and Technology Umass-Dartmouth Waves Sound Waves Light Waves Surface Waves Radio Waves Tidal Waves Instrument Strings How
Waves G. Cowles General Physical Oceanography MAR 555 School for Marine Sciences and Technology Umass-Dartmouth Waves Sound Waves Light Waves Surface Waves Radio Waves Tidal Waves Instrument Strings How
Surface Waves NOAA Tech Refresh 20 Jan 2012 Kipp Shearman, OSU
 Surface Waves NOAA Tech Refresh 20 Jan 2012 Kipp Shearman, OSU Outline Surface winds Wind stress Beaufort scale Buoy measurements Surface Gravity Waves Wave characteristics Deep/Shallow water waves Generation
Surface Waves NOAA Tech Refresh 20 Jan 2012 Kipp Shearman, OSU Outline Surface winds Wind stress Beaufort scale Buoy measurements Surface Gravity Waves Wave characteristics Deep/Shallow water waves Generation
Study of Passing Ship Effects along a Bank by Delft3D-FLOW and XBeach1
 Study of Passing Ship Effects along a Bank by Delft3D-FLOW and XBeach1 Minggui Zhou 1, Dano Roelvink 2,4, Henk Verheij 3,4 and Han Ligteringen 2,3 1 School of Naval Architecture, Ocean and Civil Engineering,
Study of Passing Ship Effects along a Bank by Delft3D-FLOW and XBeach1 Minggui Zhou 1, Dano Roelvink 2,4, Henk Verheij 3,4 and Han Ligteringen 2,3 1 School of Naval Architecture, Ocean and Civil Engineering,
Tide transformation in the Guadalquivir estuary (SW Spain) and process-based zonation
 JOURNAL OF GEOPHYSICAL RESEARCH, VOL. 117,, doi:10.1029/2011jc007344, 2012 Tide transformation in the Guadalquivir estuary (SW Spain) and process-based zonation M. Díez-Minguito, 1 A. Baquerizo, 1 M. Ortega-Sánchez,
JOURNAL OF GEOPHYSICAL RESEARCH, VOL. 117,, doi:10.1029/2011jc007344, 2012 Tide transformation in the Guadalquivir estuary (SW Spain) and process-based zonation M. Díez-Minguito, 1 A. Baquerizo, 1 M. Ortega-Sánchez,
FIELD MEASUREMENTS OF SURFACE SUSPENDED SEDIMENT CONCENTRATION IN THE YANGTZE ESTUARY, CHINA
 International Conference on Estuaries and Coasts November 9-11, 2003, Hangzhou, China FIELD MEASUREMENTS OF SURFACE SUSPENDED SEDIMENT CONCENTRATION IN THE YANGTZE ESTUARY, CHINA Qing HE, Zhiying YU, Yuanye
International Conference on Estuaries and Coasts November 9-11, 2003, Hangzhou, China FIELD MEASUREMENTS OF SURFACE SUSPENDED SEDIMENT CONCENTRATION IN THE YANGTZE ESTUARY, CHINA Qing HE, Zhiying YU, Yuanye
ESCI 343 Atmospheric Dynamics II Lesson 10 - Topographic Waves
 ESCI 343 Atmospheric Dynamics II Lesson 10 - Topographic Waves Reference: An Introduction to Dynamic Meteorology (3 rd edition), J.R. Holton Reading: Holton, Section 7.4. STATIONARY WAVES Waves will appear
ESCI 343 Atmospheric Dynamics II Lesson 10 - Topographic Waves Reference: An Introduction to Dynamic Meteorology (3 rd edition), J.R. Holton Reading: Holton, Section 7.4. STATIONARY WAVES Waves will appear
Overview and preview. I. Tides as Waves (really really big) What are the Forces driving these waves? II: Into make-believe.
 The Tides Overview and preview I. Tides as Waves (really really big) What are the Forces driving these waves? II: Into make-believe. Idealized world: no land, deep water, no friction.no problems. Effects
The Tides Overview and preview I. Tides as Waves (really really big) What are the Forces driving these waves? II: Into make-believe. Idealized world: no land, deep water, no friction.no problems. Effects
GEOPHYSICAL RESEARCH LETTERS
 GEOPHYSICAL RESEARCH LETTERS Supporting Information for Observation of deep water microseisms in the North Atlantic Ocean using tide modulations Éric Beucler, 1 Antoine Mocquet, 1 Martin Schimmel, 2 Sébastien
GEOPHYSICAL RESEARCH LETTERS Supporting Information for Observation of deep water microseisms in the North Atlantic Ocean using tide modulations Éric Beucler, 1 Antoine Mocquet, 1 Martin Schimmel, 2 Sébastien
ENVIRONMENTAL, ECOLOGICAL AND CULTURAL IMPACTS OF TIDAL BORES, BENAKS, BONOS AND BURROS
 IWEH. International Workshop on Environmental Hydraulics Theoretical, Experimental and Computational Solutions Valencia, 29 th, 30 th October 2009 ENVIRONMENTAL, ECOLOGICAL AND CULTURAL IMPACTS OF TIDAL
IWEH. International Workshop on Environmental Hydraulics Theoretical, Experimental and Computational Solutions Valencia, 29 th, 30 th October 2009 ENVIRONMENTAL, ECOLOGICAL AND CULTURAL IMPACTS OF TIDAL
What are Waves? Earthquake. Waving flags. Vocal Cords Vibrate
 Waves Ch. 10 What are Waves? All waves are movement of energy through a medium (air, rock, water) Series of vibrations or undulations in a medium Wave types: ocean, sound, light, seismic Vocal Cords Vibrate
Waves Ch. 10 What are Waves? All waves are movement of energy through a medium (air, rock, water) Series of vibrations or undulations in a medium Wave types: ocean, sound, light, seismic Vocal Cords Vibrate
Application of Remote Sensing Image and Mathematical Model for Dispersion of Suspended Solid in the Upper Gulf of Thailand
 Kasetsart J. (Nat. Sci.) 42 : 299-305 (2008) Application of Remote Sensing Image and Mathematical Model for Dispersion of Suspended Solid in the Upper Gulf of Thailand Monton Anongponyoskun 1*, Pramot
Kasetsart J. (Nat. Sci.) 42 : 299-305 (2008) Application of Remote Sensing Image and Mathematical Model for Dispersion of Suspended Solid in the Upper Gulf of Thailand Monton Anongponyoskun 1*, Pramot
Determination Of Nearshore Wave Conditions And Bathymetry From X-Band Radar Systems
 Determination Of Nearshore Wave Conditions And Bathymetry From X-Band Radar Systems Okey G. Nwogu Dept. of Naval Architecture and Marine Engineering University of Michigan Ann Arbor, MI 489 phone: (734)
Determination Of Nearshore Wave Conditions And Bathymetry From X-Band Radar Systems Okey G. Nwogu Dept. of Naval Architecture and Marine Engineering University of Michigan Ann Arbor, MI 489 phone: (734)
Lecture 21: Potpourri
 Lecture 21: Potpourri Lecturer: H. Segur. Write-up: Ali Mashayek and Hélène Scolan June 26, 2009 1 Introduction In this last lecture of the 2009 GFD series, a collection of topics is presented including:
Lecture 21: Potpourri Lecturer: H. Segur. Write-up: Ali Mashayek and Hélène Scolan June 26, 2009 1 Introduction In this last lecture of the 2009 GFD series, a collection of topics is presented including:
