Waves- how are they formed and how do they affect the coast?
|
|
|
- Barnard Ray
- 5 years ago
- Views:
Transcription
1 Question 7 Coasts Waves- how are they formed and how do they affect the coast? Waves are caused by friction between the wind and water causing the water to swell. The size and energy of a wave is influenced by: how long the wind has been blowing the strength of the wind how far the wave has travelled (the fetch) Swash: The wave breaking on the beach Backwash: The wave going back out to sea under the force of gravity. Prevailing wind: The most common wind direction. Constructive Waves Destructive Waves They are created in calm weather and are less powerful than destructive waves. They break on the shore and deposit material, building up beaches. They have a swash that is stronger than the backwash. They have a long wavelength, and are low in height. Destructive waves are created in storm conditions. They are created from big, strong waves when the wind is powerful and has been blowing for a long time. They occur when wave energy is high and the wave has travelled over a long fetch. They tend to erode the coast. They have a stronger backwash than swash. They have a short wave length and are high and steep.
2 Coastal processes- weathering When rocks and surface materials are broken down through the actions of the atmosphere we call it weathering. Weathering weakens rocks at the coast and makes them more likely to be affected by mass movement and erosion It is a sub aerial process Chemical: when weak acids for example rain dissolves the rocks. Physical : Freeze thaw weathering- due to temperature, frost, water etc. freeze thaw weathering is when the constant freezing of water and then melting again causes cracks in the rocks. Biological: when rocks are broken up by living things e.g. plant routes or burrowing animals. Coastal Processes - Erosion Hydraulic action. Air may become trapped in joints and cracks on a cliff face. When a wave breaks, the trapped air is compressed which weakens the cliff and causes erosion. Abrasion. Bits of rock and sand in waves grind down cliff surfaces like sandpaper. Attrition. Waves smash rocks and pebbles on the shore into each other, and they break and become smoother. Solution. Acids contained in sea water will dissolve some types of rock such as chalk or limestone Coastal Transport Traction: Pebbles and larger sediment are rolled along the sea bed. Saltation: Load is bounced along the sea bed, eg small pieces of shingle or large sand grains. Currents cannot keep the larger and heavier sediment afloat for long periods. Suspension: Small particles are carried in water, eg silts and clays, which can make the water look cloudy. Currents pick up large amounts of sediment in suspension during a storm, when strong winds generate high energy waves. Solution: Minerals are dissolved in sea water and carried in solution. The load is not visible. Load can come from cliffs made from chalk or limestone, and calcium carbonate is carried along in solution. Coastal Deposition When the sea loses energy, it drops the beach material / sediment, rock particles and pebbles it has been carrying. This is called deposition. Deposition happens when the swash is stronger than the backwash and is associated with constructive waves. Deposition is likely to occur when: waves enter an area of shallow water. waves enter a sheltered area, eg a cove or bay. there is little wind. there is a good supply of material
3 Longshore Drift - Transport The continual swash and backwash that carries material along the coast is called longshore drift. Mass Movement Headlands and bays Landforms from Erosion Soft rock Hard rock Found when you have alternating bands of hard and soft rock such as clay between limestone and chalk. As the waves attack the cliff the soft rock such as clay erodes faster. This forms a horse shoe shape in the cliff called a bay. You find headlines on either side of the bay. Cliff erosion and wave cut platforms Cliffs and wave-cut platforms The process of cliff erosion. 1. Weather weakens the top of the cliff. 2. The sea attacks the base of the cliff forming a wave-cut notch through abrasion and hydraulic action. 3. As erosion continues the notch increases in size undermining the cliff. This causes the cliff to collapse. 4. The backwash carries the rubble towards the sea forming a wave-cut platform. 5. The process repeats and the cliff continues to retreat. 6. Wave cut platforms. Wave cut platforms are the platforms at the bottom of a cliff, formed during cliff erosion.
4 Caves, arches, stacks and stumps. Hydraulic action is the principle process taking place here. The water works its way in through a crack in the cliff, and over a period of time a cave is formed due to continued erosion (hydraulic action and abrasion.) When the cave breaks through to the other side of the headland it becomes an arch. Eventually, the top of the arch will be undermined and collapse forming a stack. The base of the stack will continue to be eroded until it collapses to forma stump. For this process: Tell the story of the feature requested plus all the features before. For example a Stack = Crack>Cave>Arch>Stack Landforms from deposition: Beaches: formed from the deposition of eroded material from elsewhere along the coastline. Spits: 1) Longshore drift moves material along the coastline. 2) There is a sharpe change in direction of the coast e.g. river or bay. 3) A spit forms when the material is deposited. 4) Over time, the spit grows and develops a hook if the prevailing wind changes direction. Waves cannot get past a spit, which creates a sheltered area where silt is deposited and mud flats or salt marshes form. Bars (lagoon): A spit that extends from headland to headland. The water trapped behind forms a lagoon. Salt marshes: often formed in the sheltered area in a spit or a bar.
5 Mass Movement Rocks loosed by weathering move down a slope under the influence of gravity. The rocks can slide or slump Sliding Large chunks of rock slide down a slope quickly without warning. This can make it very dangerous to walk along the cliff. Slumping Common where cliffs are made from clay Clay becomes saturated during heavy rainfall The extra weight/pressure acting on the cliff causes it to move. The clay flows down towards the sea as part of a mud or debris flow As it moves it rotates About CASE STUDY: The impact of rising sea levels: The Maldives Located in the Indian Ocean Small country made up of over 1000 islands Lowest Country in the world Highest point is 2.4 metres above sea level Ideal holiday destination with 30% of GDP coming from tourism What is happening? Sea level is rising between 30cm and 1.4m over the next 100 years Temperatures rise therefore: Polar ice sheets are melting along with mountain glaciers Water is getting in oceans is getting warmer and expanding
6 Impacts on the Maldives Coral reefs will die as they bleach due to deep water and lack of sunlight Ecosystem connected to reefs will die out - marine life 400,000 people forced out of homes environmental refugees Will need international aid to cope with the rise in sea levels Global Impacts of global warming 100million people will be displaced. Many small islands in the Indian and Pacific Oceans will be lost under water. Netherlands is at risk because 27% of the nation is below sea level. Cities like London and New York will have to spend billions on flood defense schemes. Jobs in the tourist industry will be lost and will be hit by mass unemployment. Younger generation will leave the Maldives. Places like the Fens in England could be lost. Risk that entire Island chain will be lost under water. CASE STUDY: The impacts of cliff erosion, Christchurch Bay. Key Facts South Coast of England, near Bournemouth. Eroding at a rate of 1-2 metres per year. 16km stretch of coastline. Difficult to protect it all. Tourism is big business and provider of jobs. Densely populated with resorts such as Barton-on-sea. Why is it eroding rapidly? 1- Marine processes weaken base of cliff. Hydraulic action and abrasion. 2- Sub aerial processes attack cliff top weathering, slumping, sliding. 3- Geology- permeable sand lies on top of impermeable clay and is saturated during heavy rains. This can make cliff top heavier and unstable. 4 - Fetch, 3000 miles distance as waves travel across the Atlantic gaining destructive power from the prevailing wind. 5 - Human activity- building, walking and tourist activity. Christchurch bay is a honey pot attraction. Impacts Social Homes close to the cliff go down in value and are uninsurable. Often worth only 1 Insurance companies refuse to cover coastal erosion because it is an act of god or charge high premiums. Risk of loss of life due to sudden erosion/sliding of homes or walkers along cliff top. People lose homes if they fall into the sea. environmental refugees
7 Economic - Impacts Roads and railways under threat and need protecting at great expense or rerouting. Tourists may be put off due to danger or lose of key attractions therefore it would lead to a decline in business for shops, cafes and hotels. Barton Golf Course has had to be expanded inland to protect the green and rebuild after cliff erosion. Environmental - Impacts Cliff collapse makes the area look unattractive and damage to buildings can leave materials littering the coastline. Some areas are eroding but are not protected because they are areas of special scientific interest. Bird nesting sites and green land are being lost. Coastal Management Britain's coastline is falling into the sea, as a result many areas are protected by sea defences. There are two main forms of coastal Management, hard engineering and soft engineering. Type of defence - hard engineering Building a sea wall A wall built on the edge of the coastline. Pros and cons Advantages Protects the base of cliffs, land and buildings against erosion. Can prevent coastal flooding in some areas. Strong and durable. Made of reinforced concrete. Building groynes A wooden barrier built at right angles to the beach. Disadvantages Expensive to build. 10k per metre. Curved sea walls reflect the energy of the waves back to the sea. This means that the waves remain powerful. Over time the wall may begin to erode. The cost of maintenance is high with the wall having to be replaced every years. Advantages Prevents the movement of beach material along the coast by longshore drift. Allows the build up of a beach. Beaches are a natural defence against erosion and an attraction for tourists. Disadvantages Can be seen as unattractive as they are unnatural features at right angles. Costly to build and maintain, 100k per groyne. Wooden groynes will rot over time.
8 Rock armour or boulder barriers Large boulders are piled up on the beach. Advantages Strong rocks such as granite absorb the energy of waves. Allows the build-up of a beach a natural defence. Disadvantages Can be expensive to obtain and transport the boulders. Cost 1500 per metre. Have to be transported from places such as Norway. Soft engineering (Beach nourishment, Dune regeneration, Marsh creation, Managed retreat) Beach replenishment This replaces beach or cliff material that has been removed by erosion or longshore drift. The main advantage is that beaches are a natural defence against erosion and coastal flooding. Beaches also attract tourists. It is a relatively inexpensive option but requires constant maintenance to replace the beach material as it is washed away. Managed retreat Areas of the coast are allowed to erode and flood naturally. Usually this will be areas considered to be of low value - eg places not being used for housing or farmland. The advantages are that it encourages the development of beaches (a natural defence) and salt marshes (important for the environment) and cost is low. Managed retreat is a cheap option, but people will need to be compensated for loss of buildings and farmland. Alkborough flats tidal defence scheme Location Humber Estuary, Lincolnshire, 440 hectares of agricultural land on the south bank of the River Humber Why does Alkborough need a flood scheme? The effects of climate change are expected to increase high tide levels in the Humber Estuary 300,000 people who live in the area and are at risk of flooding.
9 What are they doing to reduce flood risk? The Environment Agency took charge to protect the area. Opened in September 2006 and is one of the largest flood storage schemes in Europe. It allows flood water from the Humber estuary to spill out of the river during the highest tides to fill the low lying land. By flooding the Alkborough flats they protect places such as Hull. The site s capacity is so great that it could reduce high tide levels in the upper estuary by as much as 150mm -15cm. It is a way of managing rising sea levels through soft engineering It has been designed by the Environment Agency to: The Environment Agency took charge to protect the area. Opened in September 2006 and is one of the largest flood storage schemes in Europe. It allows flood water from the Humber estuary to spill out of the river during the highest tides to fill the low lying land. By flooding the Alkborough flats they protect places such as Hull. The site s capacity is so great that it could reduce high tide levels in the upper estuary by as much as 150mm -15cm. It is a way of managing rising sea levels through soft engineering Coastal habitats: Studland bay nature reserve Location: Dorset, England along the South Coast. Near Swanage. 1.5 million visitors each year. Grass covered dunes, heath and scrub. It is managed by the National Trust. Habitats Sand Dunes develop as the wind deposits sand on low lying areas forming hills. Dunes grow around obstacles such as driftwood. Unique ecosystem marram grass and Lime grass close to shore and heather further inland. Marram grass holds the dunes together. It is the richest 1000 hectares for butterflies, wildlife, birds in the country. Ecosystem- the relationship between plants. animals and the environment. Key problems Increase in tourists and cars. Vegetation is vulnerable and takes years to establish. if it is destroyed then the ecosystem will collapse. Home to rare species of plants and birds that could be lost forever. e.g. Dartford Warblers and Sand Lizards.
10 Key problems- continued Beach gets overcrowded and littered by tourists. Visitors need somewhere to park and can park on the verge damaging the area. Visitors also require additional facilities such as paths and toilets. As a result more space is given over to development with habitat lost forever. Visitors litter and cause fire hazards with BBQ's and cigarettes ends. Solutions Marram grass planted to stabilise the dunes and areas fenced off to allow it to grow. Bird watching hides constructed so animals can be viewed without disturbing them. Car parking spaces have been controlled and limited and vehicles have been banned from the beach. Fire beaters placed in the dunes to control risk of fire. Boardwalks laid and signs placed to educate tourists and prevent footpath erosion.
Coastal Change and Conflict
 Coastal Change and Conflict Outline of the Topic Contrasting Coasts why do all coasts not look the same? Geology of the coast the impact rock structure has on the coastline Waves Constructive and destructive
Coastal Change and Conflict Outline of the Topic Contrasting Coasts why do all coasts not look the same? Geology of the coast the impact rock structure has on the coastline Waves Constructive and destructive
Define the key terms: - Abrasion - Attrition - Hydraulic action - Solution. Y11 Coasts
 Define the key terms: - Abrasion - Attrition - Hydraulic action - Solution Abrasion caused by waves picking up material which is forced against the cliff face wearing it away Attrition where stones and
Define the key terms: - Abrasion - Attrition - Hydraulic action - Solution Abrasion caused by waves picking up material which is forced against the cliff face wearing it away Attrition where stones and
1.1 Coastal processes produce landforms
 1.1 Coastal processes produce landforms Types of wave: destructive and constructive Destructive Carry out erosion Tall Powerful High frequency Backwash greater than the swash Take sediment from beach to
1.1 Coastal processes produce landforms Types of wave: destructive and constructive Destructive Carry out erosion Tall Powerful High frequency Backwash greater than the swash Take sediment from beach to
Coastal Processes and Landforms
 Coastal Processes and Landforms These icons indicate that teacher s notes or useful web addresses are available in the Notes Page. This icon indicates that the slide contains activities created in Flash.
Coastal Processes and Landforms These icons indicate that teacher s notes or useful web addresses are available in the Notes Page. This icon indicates that the slide contains activities created in Flash.
Label the diagram below with long fetch and short fetch:
 Coastal Processes Coasts are shaped by the sea and the action of waves. The processes that take place are erosion, transportation and deposition. The power of waves is one of the most significant forces
Coastal Processes Coasts are shaped by the sea and the action of waves. The processes that take place are erosion, transportation and deposition. The power of waves is one of the most significant forces
Coasts. 1. Coastal Processes. 1.1 Coastal erosion. 1.2 Sediment transport. Coastal Processes and Landforms. i. Hydraulic action
 Coasts Coastal Processes and Landforms 1. Coastal Processes 1.1 Coastal erosion i. Hydraulic action When waves strike against a rock surface, the waves trap air in the rock joints. This air is compressed
Coasts Coastal Processes and Landforms 1. Coastal Processes 1.1 Coastal erosion i. Hydraulic action When waves strike against a rock surface, the waves trap air in the rock joints. This air is compressed
The Sea Geography Notes JC-Learn. JC-Learn. Geography Notes The Sea. 1 P a g e
 JC-Learn Geography Notes The Sea 1 P a g e The Sea *Here, you can choose to study the chapter on glaciation or the one on the sea, or even both, because whenever these topics come up in the Junior Cert
JC-Learn Geography Notes The Sea 1 P a g e The Sea *Here, you can choose to study the chapter on glaciation or the one on the sea, or even both, because whenever these topics come up in the Junior Cert
Identify one factor which influences wave strength (1 Mark) Factors which affect wave strength
 Coasts revision Identify one factor which influences wave strength (1 Mark) Factors which affect wave strength Identify one factor which influences wave strength (1 Mark) Factors which affect wave strength
Coasts revision Identify one factor which influences wave strength (1 Mark) Factors which affect wave strength Identify one factor which influences wave strength (1 Mark) Factors which affect wave strength
Coastal Processes and Landforms
 Coastal Processes and Landforms These icons indicate that teacher s notes or useful web addresses are available in the Notes Page. This icon indicates that the slide contains activities created in Flash.
Coastal Processes and Landforms These icons indicate that teacher s notes or useful web addresses are available in the Notes Page. This icon indicates that the slide contains activities created in Flash.
GCSE GEOGARPHY OCR B REVISION GUIDE Coasts
 GCSE GEOGARPHY OCR B REVISION GUIDE Coasts Definition: The interface between land and sea. Coastal regions cover only 10% of the inhabited land space, yet they are home to more than 60% of the world s
GCSE GEOGARPHY OCR B REVISION GUIDE Coasts Definition: The interface between land and sea. Coastal regions cover only 10% of the inhabited land space, yet they are home to more than 60% of the world s
COASTAL SYSTEMS WAVE ENERGY
 WAVE ENERGY The energy of a wave determines its ability to erode and transport material on the coast Wave energy depends on the fetch, the distance the wind has blown the wave Wind strength and wind duration
WAVE ENERGY The energy of a wave determines its ability to erode and transport material on the coast Wave energy depends on the fetch, the distance the wind has blown the wave Wind strength and wind duration
COASTS (P.38-45) Management: Hard engineering: Groynes Sea walls Gabions Soft Engineering: Beach replenishment Dune regeneration
 COASTS (P.38-45) Processes: Types of wave Weathering Mass Movement Erosion Transport Deposition Landforms: Cracks Caves Arches Stacks/stumps Headlands/bays Coves Spits Tombolos Beaches Sand dunes Management:
COASTS (P.38-45) Processes: Types of wave Weathering Mass Movement Erosion Transport Deposition Landforms: Cracks Caves Arches Stacks/stumps Headlands/bays Coves Spits Tombolos Beaches Sand dunes Management:
Constructive waves build beaches. Each wave is low. As the wave breaks it carries material up the beach in its. material will then be deposited as
 Constructive waves Constructive waves build beaches. Each wave is low. As the wave breaks it carries material up the beach in its swash. The beach material will then be deposited as the backwash soaks
Constructive waves Constructive waves build beaches. Each wave is low. As the wave breaks it carries material up the beach in its swash. The beach material will then be deposited as the backwash soaks
Holderness Coast: A multi-use area
 Holderness Coast: A multi-use area A multi use areas is n area which offers a range of social, economic and environmental activities. Flamborough Head stunning scenery and birds attracts tourists to visit.
Holderness Coast: A multi-use area A multi use areas is n area which offers a range of social, economic and environmental activities. Flamborough Head stunning scenery and birds attracts tourists to visit.
1.5 How do ocean waves and currents change the face of coastal areas? (Chapter 3)
 1.5 How do ocean waves and currents change the face of coastal areas? (Chapter 3) 1. Hydraulic Action/Pressure - air being forced into crack in rocks. 2. Corrosion (Solution) Minerals such as calcium carbonate
1.5 How do ocean waves and currents change the face of coastal areas? (Chapter 3) 1. Hydraulic Action/Pressure - air being forced into crack in rocks. 2. Corrosion (Solution) Minerals such as calcium carbonate
The Physical and Human Causes of Erosion. The Holderness Coast
 The Physical and Human Causes of Erosion The Holderness Coast By The British Geographer Situation The Holderness coast is located on the east coast of England and is part of the East Riding of Yorkshire;
The Physical and Human Causes of Erosion The Holderness Coast By The British Geographer Situation The Holderness coast is located on the east coast of England and is part of the East Riding of Yorkshire;
1.5 Understand how ocean waves and currents change the face of coastal areas. (Chapter 3)
 1.5 Understand how ocean waves and currents change the face of coastal areas. (Chapter 3) 1. Hydraulic Action/Pressure - air being forced into crack in rocks. 2. Corrosion (Solution) Minerals such as calcium
1.5 Understand how ocean waves and currents change the face of coastal areas. (Chapter 3) 1. Hydraulic Action/Pressure - air being forced into crack in rocks. 2. Corrosion (Solution) Minerals such as calcium
Section 1: Waves. There are two distinct types of wave at the coastline: constructive and destructive waves.
 Coastal Erosion EARTH SCIENCE GEOLOGY COASTAL EROSION Section 1: Waves How do waves form? Waves are generated by the competing forces of surface friction. The wind transfers energy from air to water and
Coastal Erosion EARTH SCIENCE GEOLOGY COASTAL EROSION Section 1: Waves How do waves form? Waves are generated by the competing forces of surface friction. The wind transfers energy from air to water and
General Coastal Notes + Landforms! 1
 General Coastal Notes + Landforms! 1 Types of Coastlines: Type Description Primary Coast which is essentially in the same condition when sea level stabilized Coastline after the last ice age, younger.
General Coastal Notes + Landforms! 1 Types of Coastlines: Type Description Primary Coast which is essentially in the same condition when sea level stabilized Coastline after the last ice age, younger.
Coastal Processes Day Criccieth
 Coastal Processes Rivers (Conwy) Rivers (Peris) Urban Studies Lowland Glaciation Tourism and National Parks Soils Sand Dunes Upland Glaciation Rural Settlements The Centre and Staff Fieldwork Equipment
Coastal Processes Rivers (Conwy) Rivers (Peris) Urban Studies Lowland Glaciation Tourism and National Parks Soils Sand Dunes Upland Glaciation Rural Settlements The Centre and Staff Fieldwork Equipment
Name: Form: 2.To know the difference between Constructive and Destructive wave # $
 Name: Form: Landforms and landscape processes: COASTS 1. To know what factors affect the strength of waves # $ 2.To know the difference between Constructive and Destructive wave # $ 3. To be able to draw
Name: Form: Landforms and landscape processes: COASTS 1. To know what factors affect the strength of waves # $ 2.To know the difference between Constructive and Destructive wave # $ 3. To be able to draw
GCSE Geography. Unit One: The Coastal Zone. Question 7.
 GCSE Geography Unit One: The Coastal Zone. Question 7. The Coastal Zone Section of Topic Pages: Notes? Understanding? COASTAL PROCESSES: Weathering: mechanical & chemical. Mass movement: sliding & slumping.
GCSE Geography Unit One: The Coastal Zone. Question 7. The Coastal Zone Section of Topic Pages: Notes? Understanding? COASTAL PROCESSES: Weathering: mechanical & chemical. Mass movement: sliding & slumping.
Overview. Beach Features. Coastal Regions. Other Beach Profile Features. CHAPTER 10 The Coast: Beaches and Shoreline Processes.
 Overview CHAPTER 10 The Coast: Beaches and Shoreline Processes Coastal regions constantly change. The beach is a dominant coastal feature. Wave activity continually modifies the beach and coastal areas.
Overview CHAPTER 10 The Coast: Beaches and Shoreline Processes Coastal regions constantly change. The beach is a dominant coastal feature. Wave activity continually modifies the beach and coastal areas.
Chesil Beach, Dorset UK High energy, shingle coastline. Brighton Beach, Sussex UK Pebble beach
 Beaches: Depositional landform Extends from the highest high tide to the lowest low tide. Very important temporary store in coastal system. Accretion: sediment returning to the visible portion of a beach
Beaches: Depositional landform Extends from the highest high tide to the lowest low tide. Very important temporary store in coastal system. Accretion: sediment returning to the visible portion of a beach
COASTAL MANAGEMENT AND PROTECTION METHODS! 1
 COASTAL MANAGEMENT AND PROTECTION METHODS! 1 Strategy What it does Cons Pros Examples SOFT ENGINEERING: The use of ecological principles and practices to reduce erosion and achieve the stabilization and
COASTAL MANAGEMENT AND PROTECTION METHODS! 1 Strategy What it does Cons Pros Examples SOFT ENGINEERING: The use of ecological principles and practices to reduce erosion and achieve the stabilization and
Nearshore Sediment Transport What influences the loss of sediment on Beaches? - Waves - Winds - Tidal Currents - River discharge - Runoff
 Tides & Beaches Nearshore Sediment Transport What influences the loss of sediment on Beaches? - Waves - Winds - Tidal Currents - River discharge - Runoff Oceans Ocean Topography Physical Structure of the
Tides & Beaches Nearshore Sediment Transport What influences the loss of sediment on Beaches? - Waves - Winds - Tidal Currents - River discharge - Runoff Oceans Ocean Topography Physical Structure of the
There are many different kinds of beaches which are generally characterized by the dominance of waves, tides, rivers and currents, and in particular
 Fig. 11-11, p. 253 There are many different kinds of beaches which are generally characterized by the dominance of waves, tides, rivers and currents, and in particular differ by the amount of energy, which
Fig. 11-11, p. 253 There are many different kinds of beaches which are generally characterized by the dominance of waves, tides, rivers and currents, and in particular differ by the amount of energy, which
AQA(B) GCSE GEOGRAPHY REVISION BOOKLET
 Name: Form: Geography Teacher: AQA(B) GCSE GEOGRAPHY REVISION BOOKLET UNIT 1 THE COASTAL ENVIRONMENT Dr K Hutchinson (Chesterton Community College, Cambridge) Miss E Johns (Hitchin Girls School, Hitchin)
Name: Form: Geography Teacher: AQA(B) GCSE GEOGRAPHY REVISION BOOKLET UNIT 1 THE COASTAL ENVIRONMENT Dr K Hutchinson (Chesterton Community College, Cambridge) Miss E Johns (Hitchin Girls School, Hitchin)
GCSE Geography Coastal Revision Guide. Improve that grade!
 GCSE Geography Coastal Revision Guide Improve that grade! What am I revising? Unit 1: Managing places in the 21st century Section A The Coastal Environment With over four billion people living in coastal
GCSE Geography Coastal Revision Guide Improve that grade! What am I revising? Unit 1: Managing places in the 21st century Section A The Coastal Environment With over four billion people living in coastal
Sustainable Decision Making (SDM) (Foundation and Higher Tier)
 GENERAL CERTIFICATE OF SECONDARY EDUCATION GEOGRAPHY B Sustainable Decision Making (SDM) (Foundation and Higher Tier) B561/01/02/RB RESOURCE BOOKLET *B523590611* This resource booklet should be available
GENERAL CERTIFICATE OF SECONDARY EDUCATION GEOGRAPHY B Sustainable Decision Making (SDM) (Foundation and Higher Tier) B561/01/02/RB RESOURCE BOOKLET *B523590611* This resource booklet should be available
Coastal management has lagged behind the growth in population leading to problems with pollution
 Fifty percent of the population of the industrialized world lives within 100 km of a coast. Coastal management has lagged behind the growth in population leading to problems with pollution and natural
Fifty percent of the population of the industrialized world lives within 100 km of a coast. Coastal management has lagged behind the growth in population leading to problems with pollution and natural
TITLE: COASTAL EROSION AND LANDFORMS.
 TITLE: COASTAL EROSION AND LANDFORMS. AIM: What are the factors that influence the formation of coastal features along Fishing Pond beach Trinidad? LOCATION OF FIELD STUDY: The study was carried out in
TITLE: COASTAL EROSION AND LANDFORMS. AIM: What are the factors that influence the formation of coastal features along Fishing Pond beach Trinidad? LOCATION OF FIELD STUDY: The study was carried out in
The Dynamic Coast. Right Place Resources. A presentation about the interaction between the dynamic coast and people
 The Dynamic Coast Houses threatened by coastal erosion in California Right Place Resources A presentation about the interaction between the dynamic coast and people For the rest of the presentations in
The Dynamic Coast Houses threatened by coastal erosion in California Right Place Resources A presentation about the interaction between the dynamic coast and people For the rest of the presentations in
Lecture Outlines PowerPoint. Chapter 15 Earth Science, 12e Tarbuck/Lutgens
 Lecture Outlines PowerPoint Chapter 15 Earth Science, 12e Tarbuck/Lutgens 2009 Pearson Prentice Hall This work is protected by United States copyright laws and is provided solely for the use of instructors
Lecture Outlines PowerPoint Chapter 15 Earth Science, 12e Tarbuck/Lutgens 2009 Pearson Prentice Hall This work is protected by United States copyright laws and is provided solely for the use of instructors
1 Shoreline Erosion and Deposition
 CHAPTER 12 1 Shoreline Erosion and Deposition SECTION Agents of Erosion and Deposition BEFORE YOU READ After you read this section, you should be able to answer these questions: What is a shoreline? How
CHAPTER 12 1 Shoreline Erosion and Deposition SECTION Agents of Erosion and Deposition BEFORE YOU READ After you read this section, you should be able to answer these questions: What is a shoreline? How
1 Shoreline Erosion and Deposition
 CHAPTER 12 1 Shoreline Erosion and Deposition SECTION Agents of Erosion and Deposition BEFORE YOU READ After you read this section, you should be able to answer these questions: What is a shoreline? How
CHAPTER 12 1 Shoreline Erosion and Deposition SECTION Agents of Erosion and Deposition BEFORE YOU READ After you read this section, you should be able to answer these questions: What is a shoreline? How
Marine Ecosystems. Aquatic Ecosystems Section 2
 Marine Ecosystems Marine ecosystems are located mainly in coastal areas and in the open ocean. Organisms that live in coastal areas adapt to changes in water level and salinity. Organisms that live in
Marine Ecosystems Marine ecosystems are located mainly in coastal areas and in the open ocean. Organisms that live in coastal areas adapt to changes in water level and salinity. Organisms that live in
Earth Science Chapter 16 Section 3 Review
 Name: Class: Date: Earth Science Chapter 16 Section 3 Review Multiple Choice Identify the choice that best completes the statement or answers the question. 1. The movement of water that parallels the shore
Name: Class: Date: Earth Science Chapter 16 Section 3 Review Multiple Choice Identify the choice that best completes the statement or answers the question. 1. The movement of water that parallels the shore
Essentials of Oceanography Eleventh Edition
 Chapter Chapter 1 10 Clickers Lecture Essentials of Oceanography Eleventh Edition The Coast: Beaches and Shoreline Processes Alan P. Trujillo Harold V. Thurman Chapter Overview Coastal regions have distinct
Chapter Chapter 1 10 Clickers Lecture Essentials of Oceanography Eleventh Edition The Coast: Beaches and Shoreline Processes Alan P. Trujillo Harold V. Thurman Chapter Overview Coastal regions have distinct
Shore - place where ocean meets land Coast - refers to the larger zone affected by the processes that occur at this boundary.
 Waves, Beaches, and Coasts Shore - place where ocean meets land Coast - refers to the larger zone affected by the processes that occur at this boundary. Waves: energy moving through water The height of
Waves, Beaches, and Coasts Shore - place where ocean meets land Coast - refers to the larger zone affected by the processes that occur at this boundary. Waves: energy moving through water The height of
SHOREHAM BEACH LOCAL NATURE RESERVE
 SHOREHAM BEACH LOCAL NATURE RESERVE Coastal Geography Education Programme 2014-15 S. Savage 2014 COASTAL GEOGRAPHY OPPORTUNITIES Shoreham Beach Shoreham Beach is a shingle spit formed over many centuries
SHOREHAM BEACH LOCAL NATURE RESERVE Coastal Geography Education Programme 2014-15 S. Savage 2014 COASTAL GEOGRAPHY OPPORTUNITIES Shoreham Beach Shoreham Beach is a shingle spit formed over many centuries
Reading Material. Inshore oceanography, Anikouchine and Sternberg The World Ocean, Prentice-Hall
 Reading Material Inshore oceanography, Anikouchine and Sternberg The World Ocean, Prentice-Hall BEACH PROCESSES AND COASTAL ENVIRONMENTS COASTAL FEATURES Cross section Map view Terminology for Coastal
Reading Material Inshore oceanography, Anikouchine and Sternberg The World Ocean, Prentice-Hall BEACH PROCESSES AND COASTAL ENVIRONMENTS COASTAL FEATURES Cross section Map view Terminology for Coastal
Shorelines Earth - Chapter 20 Stan Hatfield Southwestern Illinois College
 Shorelines Earth - Chapter 20 Stan Hatfield Southwestern Illinois College The Shoreline A Dynamic Interface The shoreline is a dynamic interface (common boundary) among air, land, and the ocean. The shoreline
Shorelines Earth - Chapter 20 Stan Hatfield Southwestern Illinois College The Shoreline A Dynamic Interface The shoreline is a dynamic interface (common boundary) among air, land, and the ocean. The shoreline
The Study of Coastal Erosion on the Happisburgh Coast
 PT-YR: Coastal and Ocean Engineering ENGI.8751 Undergraduate Student Forum Faculty of Engineering and Applied Science, Memorial University, St. john s, NL, Canada March, 2013 Paper Code. (PT-2013 - Roberts)
PT-YR: Coastal and Ocean Engineering ENGI.8751 Undergraduate Student Forum Faculty of Engineering and Applied Science, Memorial University, St. john s, NL, Canada March, 2013 Paper Code. (PT-2013 - Roberts)
4/20/17. #30 - Coastlines - General Principles Coastlines - Overview
 Writing Assignment Due one week from today by 11:59 pm See main class web pages for detailed instructions Essays will be submitted in Illinois Compass (instructions later) Pick one: Earthquakes, tsunamis,
Writing Assignment Due one week from today by 11:59 pm See main class web pages for detailed instructions Essays will be submitted in Illinois Compass (instructions later) Pick one: Earthquakes, tsunamis,
Chapter. The Dynamic Ocean
 Chapter The Dynamic Ocean An ocean current is the mass of ocean water that flows from one place to another. 16.1 The Composition of Seawater Surface Circulation Surface Currents Surface currents are movements
Chapter The Dynamic Ocean An ocean current is the mass of ocean water that flows from one place to another. 16.1 The Composition of Seawater Surface Circulation Surface Currents Surface currents are movements
Chapter 10 Lecture Outline. The Restless Oceans
 Chapter 10 Lecture Outline The Restless Oceans Focus Question 10.1 How does the Coriolis effect influence ocean currents? The Ocean s Surface Circulation Ocean currents Masses of water that flow from one
Chapter 10 Lecture Outline The Restless Oceans Focus Question 10.1 How does the Coriolis effect influence ocean currents? The Ocean s Surface Circulation Ocean currents Masses of water that flow from one
NAME: DATE: Geography: Sea Action. Geography. Sea Action
 Geography Sea Action It is not necessary to carry out all the activities contained in this unit. Please see Teachers Notes for explanations, additional activities, and tips and suggestions. Theme All students:
Geography Sea Action It is not necessary to carry out all the activities contained in this unit. Please see Teachers Notes for explanations, additional activities, and tips and suggestions. Theme All students:
Oceans and Coasts. Chapter 18
 Oceans and Coasts Chapter 18 Exploring the oceans The ocean floor Sediments thicken and the age of the seafloor increases from ridge to shore The continental shelf off the northeast United States Constituent
Oceans and Coasts Chapter 18 Exploring the oceans The ocean floor Sediments thicken and the age of the seafloor increases from ridge to shore The continental shelf off the northeast United States Constituent
4/20/17. #31 - Coastal Erosion. Coastal Erosion - Overview
 Writing Assignment Due Monday by 11:59 pm #31 - Coastal Erosion Beach front property! Great View! Buy now at a great price! See main class web pages for detailed instructions Essays will be submitted in
Writing Assignment Due Monday by 11:59 pm #31 - Coastal Erosion Beach front property! Great View! Buy now at a great price! See main class web pages for detailed instructions Essays will be submitted in
Studland Bay Context and Learning Aims
 Studland Bay Enquiry 7: How are coastal processes affecting Studland Bay? Context and Learning Aims Pupils will be supported in and outside of the classroom to: Identify; describe and explain the physical
Studland Bay Enquiry 7: How are coastal processes affecting Studland Bay? Context and Learning Aims Pupils will be supported in and outside of the classroom to: Identify; describe and explain the physical
Chapter - Oceans and Coasts
 Chapter - Oceans and Coasts Discussion: What do oceans contribute to the environment of Earth? How do Earth s major systems relate to the oceans? Oceans and Coasts Oceans are important - Thermal regulation
Chapter - Oceans and Coasts Discussion: What do oceans contribute to the environment of Earth? How do Earth s major systems relate to the oceans? Oceans and Coasts Oceans are important - Thermal regulation
Chapter 20 Lecture. Earth: An Introduction to Physical Geology. Eleventh Edition. Shorelines. Tarbuck and Lutgens Pearson Education, Inc.
 Chapter 20 Lecture Earth: An Introduction to Physical Geology Eleventh Edition Shorelines Tarbuck and Lutgens The Shoreline: A Dynamic Interface The Coastal Zone The shoreline is constantly modified by
Chapter 20 Lecture Earth: An Introduction to Physical Geology Eleventh Edition Shorelines Tarbuck and Lutgens The Shoreline: A Dynamic Interface The Coastal Zone The shoreline is constantly modified by
Chapter 22, Section 1 - Ocean Currents. Section Objectives
 Chapter 22, Section 1 - Ocean Currents Section Objectives Intro Surface Currents Factors Affecting Ocean Currents Global Wind Belts (you should draw and label a diagram of the global wind belts) The Coriolis
Chapter 22, Section 1 - Ocean Currents Section Objectives Intro Surface Currents Factors Affecting Ocean Currents Global Wind Belts (you should draw and label a diagram of the global wind belts) The Coriolis
Directed Reading. Section: Ocean Currents. a(n). FACTORS THAT AFFECT SURFACE CURRENTS
 Skills Worksheet Directed Reading Section: Ocean Currents 1. A horizontal movement of water in a well-defined pattern is called a(n). 2. What are two ways that oceanographers identify ocean currents? 3.
Skills Worksheet Directed Reading Section: Ocean Currents 1. A horizontal movement of water in a well-defined pattern is called a(n). 2. What are two ways that oceanographers identify ocean currents? 3.
CHAPTER 11.1 THE WORLD OCEAN MARINE BIOMES NOTES
 CHAPTER 11.1 THE WORLD OCEAN MARINE BIOMES NOTES 1. The world ocean can be divided into zones both and. The,, and zones that apply to large lakes also apply to the ocean. 2. In addition to the depth zones,
CHAPTER 11.1 THE WORLD OCEAN MARINE BIOMES NOTES 1. The world ocean can be divided into zones both and. The,, and zones that apply to large lakes also apply to the ocean. 2. In addition to the depth zones,
LAB: WHERE S THE BEACH
 Name: LAB: WHERE S THE BEACH Introduction When you build a sandcastle on the beach, you don't expect it to last forever. You spread out your towel to sunbathe, but you know you can't stay in the same spot
Name: LAB: WHERE S THE BEACH Introduction When you build a sandcastle on the beach, you don't expect it to last forever. You spread out your towel to sunbathe, but you know you can't stay in the same spot
Australian Coastal Councils Conference
 Australian Coastal Councils Conference Kiama March 2019 Where Has My Beach Gone? (and what can I do about it?) Dr Andrew McCowan Water Technology Where Has My Beach Gone? Where Has My Beach Gone? Where
Australian Coastal Councils Conference Kiama March 2019 Where Has My Beach Gone? (and what can I do about it?) Dr Andrew McCowan Water Technology Where Has My Beach Gone? Where Has My Beach Gone? Where
The Movement of Ocean Water. Currents
 The Movement of Ocean Water Currents Ocean Current movement of ocean water that follows a regular pattern influenced by: weather Earth s rotation position of continents Surface current horizontal movement
The Movement of Ocean Water Currents Ocean Current movement of ocean water that follows a regular pattern influenced by: weather Earth s rotation position of continents Surface current horizontal movement
Site: London Bridge. Some further information about London Bridge can be found at the Parks Victoria website
 Site: London Bridge About London Bridge London Bridge is located at the Portsea Back Beach which is approximately 3 kilometres south of Portsea. This site provides students with excellent examples of coastal
Site: London Bridge About London Bridge London Bridge is located at the Portsea Back Beach which is approximately 3 kilometres south of Portsea. This site provides students with excellent examples of coastal
The Composition of Seawater
 The Composition of Seawater Salinity Salinity is the total amount of solid material dissolved in water. Most of the salt in seawater is sodium chloride, common table salt. Element Percent Element Percent
The Composition of Seawater Salinity Salinity is the total amount of solid material dissolved in water. Most of the salt in seawater is sodium chloride, common table salt. Element Percent Element Percent
Seven Sisters Coastline
 Seven Sisters Coastline What are the Seven Sisters made of? The cliffs at the Seven Sisters Country Park are composed of sedimentary chalk limestone, What is chalk limestone? Chalk is made up of the calcite
Seven Sisters Coastline What are the Seven Sisters made of? The cliffs at the Seven Sisters Country Park are composed of sedimentary chalk limestone, What is chalk limestone? Chalk is made up of the calcite
OCEANS. Main Ideas. Lesson 2: Ocean Currents Ocean Currents help distribute heat around Earth.
 Oceans Chapter 10 OCEANS Main Ideas Lesson 2: Ocean Currents Ocean Currents help distribute heat around Earth. Lesson 3: The Ocean Shore The shore is shaped by the movement of water and sand. OCEANS SO
Oceans Chapter 10 OCEANS Main Ideas Lesson 2: Ocean Currents Ocean Currents help distribute heat around Earth. Lesson 3: The Ocean Shore The shore is shaped by the movement of water and sand. OCEANS SO
The Case of the Disappearing Shoreline
 Name The Case of the Disappearing Shoreline Humans change the earth's climate in many ways. One change is the increase of carbon dioxide in the atmosphere. As we burn more fossil fuels, we release more
Name The Case of the Disappearing Shoreline Humans change the earth's climate in many ways. One change is the increase of carbon dioxide in the atmosphere. As we burn more fossil fuels, we release more
Chapter 12: Coasts (after a brief review of Tides)
 Chapter 12: Coasts (after a brief review of Tides) 1 Questions from previous classes: What happens when a wave meets a current? wave = people walking current = bus If wave goes with the current, the wave
Chapter 12: Coasts (after a brief review of Tides) 1 Questions from previous classes: What happens when a wave meets a current? wave = people walking current = bus If wave goes with the current, the wave
SALINITY. It's the amount of dissolved salts the water contains.
 AQUATIC ECOSYSTEMS SALINITY The types of organisms in an aquatic ecosystem depend upon the water s Salinity. It's the amount of dissolved salts the water contains. Salinity determines the two main aquatic
AQUATIC ECOSYSTEMS SALINITY The types of organisms in an aquatic ecosystem depend upon the water s Salinity. It's the amount of dissolved salts the water contains. Salinity determines the two main aquatic
Habitat Fact Sheets. Rocky habitats are dominated by seaweeds and often mussels, which rely on the rocks for attachment.
 Habitat Fact Sheets Habitats in the Gulf of Maine serve many important roles for the environment and for humans as well. These include: cycling nutrients, filtering pollution, trapping sediments, storing
Habitat Fact Sheets Habitats in the Gulf of Maine serve many important roles for the environment and for humans as well. These include: cycling nutrients, filtering pollution, trapping sediments, storing
COASTAL ENVIRONMENTS. 454 lecture 12
 COASTAL ENVIRONMENTS Repeated movement of sediment & water constructs a beach profile reflecting the balance between average daily or seasonal wave forces and resistance of landmass to wave action Coasts
COASTAL ENVIRONMENTS Repeated movement of sediment & water constructs a beach profile reflecting the balance between average daily or seasonal wave forces and resistance of landmass to wave action Coasts
/50. Physical Geology Shorelines
 Physical Geology Shorelines Multiple Guess: (You know the drill 2 points each) 1. The path of movement of a water particle in a wave at sea is 1. circular 2. horizontal 3. vertical 4. elliptical 5. none
Physical Geology Shorelines Multiple Guess: (You know the drill 2 points each) 1. The path of movement of a water particle in a wave at sea is 1. circular 2. horizontal 3. vertical 4. elliptical 5. none
Geography Revision Weekend Snowdonia. Sample Itinerary
 Geography Revision Weekend Snowdonia Sample Itinerary Name Bore da Good morning Prynhawn da Good afternoon Noswaith dda Good evening Nos da Goodnight Helô Hello Sut mae? How are you? Croeso Welcome Hwyl
Geography Revision Weekend Snowdonia Sample Itinerary Name Bore da Good morning Prynhawn da Good afternoon Noswaith dda Good evening Nos da Goodnight Helô Hello Sut mae? How are you? Croeso Welcome Hwyl
SUBJECT: EARTH SCIENCE PAPER: THE DYNAMIC EARTH. Code : 27 COASTAL PROCESSES AND LANDFORMS PROF. A. BALASUBRAMANIAN
 SUBJECT: EARTH SCIENCE PAPER: THE DYNAMIC EARTH Code : 27 TOPIC: COASTAL PROCESSES AND LANDFORMS BY PROF. A. BALASUBRAMANIAN Objectives After attending this module, the user would be able to understand
SUBJECT: EARTH SCIENCE PAPER: THE DYNAMIC EARTH Code : 27 TOPIC: COASTAL PROCESSES AND LANDFORMS BY PROF. A. BALASUBRAMANIAN Objectives After attending this module, the user would be able to understand
Controlling Coastal erosion
 Controlling Coastal erosion Coastal Erosion Rates in the U.S. Coastal Erosion and Stabilization Economic pressures demanding the stabilization of beaches and coastlines are immense Coastal Erosion and
Controlling Coastal erosion Coastal Erosion Rates in the U.S. Coastal Erosion and Stabilization Economic pressures demanding the stabilization of beaches and coastlines are immense Coastal Erosion and
3/9/2013. Build house on cliff for a view of the ocean - be one with said view Pearson Education, Inc. Shorelines: summary in haiku form
 Introduction to Environmental Geology, 5e Edward A. Keller Shorelines: summary in haiku form Chapter 11 Coastal Processes Lecture Presentation prepared by X. Mara Chen, Salisbury University Build house
Introduction to Environmental Geology, 5e Edward A. Keller Shorelines: summary in haiku form Chapter 11 Coastal Processes Lecture Presentation prepared by X. Mara Chen, Salisbury University Build house
* Appalachian Mountains -the mountain range in the Eastern U.S. which terminates in north-central Alabama
 MR. SAND TEACHER'S MANUAL INTRODUCTION: Although Mr. Sand is a cartoon presentation that is attractive to children (of all ages), the material is technically accurate and quite significant to our understanding
MR. SAND TEACHER'S MANUAL INTRODUCTION: Although Mr. Sand is a cartoon presentation that is attractive to children (of all ages), the material is technically accurate and quite significant to our understanding
Oceans Humans both depend on it and threaten it with their activities
 Oceans Humans both depend on it and threaten it with their activities Oceans Water covers nearly ¾ of the Earth s surface More than 50% of the world s population lives within an hour of the coast Oceans
Oceans Humans both depend on it and threaten it with their activities Oceans Water covers nearly ¾ of the Earth s surface More than 50% of the world s population lives within an hour of the coast Oceans
OCEANOGRAPHY STUDY GUIDE
 OCEANOGRAPHY STUDY GUIDE Chapter 2 Section 1 1. Most abundant salt in ocean. Sodium chloride; NaCl 2. Amount of Earth covered by Water 71% 3. Four oceans: What are they? Atlantic, Pacific, Arctic, Indian
OCEANOGRAPHY STUDY GUIDE Chapter 2 Section 1 1. Most abundant salt in ocean. Sodium chloride; NaCl 2. Amount of Earth covered by Water 71% 3. Four oceans: What are they? Atlantic, Pacific, Arctic, Indian
The Sand Beaches of New Hampshire and Maine
 The Sand Beaches of New Hampshire and Maine Beach Preservation and Erosion Control Photographs provided by Joe Kelly and Steve Adams Cover photo: Reid State Park, ME Introduction The sand beaches of New
The Sand Beaches of New Hampshire and Maine Beach Preservation and Erosion Control Photographs provided by Joe Kelly and Steve Adams Cover photo: Reid State Park, ME Introduction The sand beaches of New
Figure 1. Schematic illustration of the major environments on Mustang Island.
 STOP #1: PACKERY CHANNEL BEACH TO BAY We will start this field guide near the north jetty of Packery Channel and hike across the island to Corpus Christi Bay (fig. 1). The island emerges from the Gulf
STOP #1: PACKERY CHANNEL BEACH TO BAY We will start this field guide near the north jetty of Packery Channel and hike across the island to Corpus Christi Bay (fig. 1). The island emerges from the Gulf
Deep-water orbital waves
 What happens when waves approach shore? Deep-water orbital waves Fig. 9.16, p. 211 Wave motion is influenced by water depth and shape of the shoreline wave buildup zone surf zone beach Wave base deepwater
What happens when waves approach shore? Deep-water orbital waves Fig. 9.16, p. 211 Wave motion is influenced by water depth and shape of the shoreline wave buildup zone surf zone beach Wave base deepwater
Geology of the Hawaiian Islands
 Geology of the Hawaiian Islands Class 24 8 April 2004 Any Questions? Rise and fall of sea level and its effect on Hawai`i Sea level Has fluctuated up and down many times in the geologic past Evidence?
Geology of the Hawaiian Islands Class 24 8 April 2004 Any Questions? Rise and fall of sea level and its effect on Hawai`i Sea level Has fluctuated up and down many times in the geologic past Evidence?
Nevis. Wise practices for coping with
 Wise practices for coping with Nevis Caribbean Sea Nevis Historical and Conservation Society Department of Physical Planning, Natural Resources and Environment, Fisheries Division University of Puerto
Wise practices for coping with Nevis Caribbean Sea Nevis Historical and Conservation Society Department of Physical Planning, Natural Resources and Environment, Fisheries Division University of Puerto
Beach profile surveys and morphological change, Otago Harbour entrance to Karitane May 2014 to June 2015
 Beach profile surveys and morphological change, Otago Harbour entrance to Karitane May 2014 to June 2015 Prepared for Port Otago Ltd Martin Single September 2015 Shore Processes and Management Ltd Contact
Beach profile surveys and morphological change, Otago Harbour entrance to Karitane May 2014 to June 2015 Prepared for Port Otago Ltd Martin Single September 2015 Shore Processes and Management Ltd Contact
INTRODUCTION SEAS AND OCEANS: A PRECIOUS RESOURCE KEY FACTS
 6 ~ SEAS FOR LIFE INTRODUCTION SEAS AND OCEANS: A PRECIOUS RESOURCE We all benefit from our seas and oceans. In addition to the more traditional uses like transport, fishing, aquaculture, tourism and recreation,
6 ~ SEAS FOR LIFE INTRODUCTION SEAS AND OCEANS: A PRECIOUS RESOURCE We all benefit from our seas and oceans. In addition to the more traditional uses like transport, fishing, aquaculture, tourism and recreation,
Montserrat. Wise practices for coping with. i b bea n Se a
 Wise practices for coping with Montserrat Car i b bea n Se a Fisheries Division, Montserrat Physical Planning Department, Montserrat University of Puerto Rico, Sea Grant College Program Caribbean Development
Wise practices for coping with Montserrat Car i b bea n Se a Fisheries Division, Montserrat Physical Planning Department, Montserrat University of Puerto Rico, Sea Grant College Program Caribbean Development
Ch19&21 Test. Multiple Choice Identify the choice that best completes the statement or answers the question.
 Ch19&21 Test Multiple Choice Identify the choice that best completes the statement or answers the question. 1. A large body of saline water that may be surrounded by land is a(n) a. submersible. c. global
Ch19&21 Test Multiple Choice Identify the choice that best completes the statement or answers the question. 1. A large body of saline water that may be surrounded by land is a(n) a. submersible. c. global
WHAT ARE ECOSYSTEMS? Dr. V. N. Nayak Professor of Marine Biology (Retd)
 WHAT ARE ECOSYSTEMS? Dr. V. N. Nayak Professor of Marine Biology (Retd) An ECOSYSTEM is an interacting system of plant, animals, and humans and the surrounding environment. An ecosystem contains living
WHAT ARE ECOSYSTEMS? Dr. V. N. Nayak Professor of Marine Biology (Retd) An ECOSYSTEM is an interacting system of plant, animals, and humans and the surrounding environment. An ecosystem contains living
Montessori for Everyone 2013 Types of Coastlines
 Coast The coast is the part of the land that borders the sea. It is subject to constant change, as the result of the waves and deposits carried by water onto the land. Coastline The coastline is where
Coast The coast is the part of the land that borders the sea. It is subject to constant change, as the result of the waves and deposits carried by water onto the land. Coastline The coastline is where
Imagine that you can see a side view of a wave as it approaches a beach. Describe how the wave changes as the wave approaches the beach.
 Geology 101 Name Reading Guide for Ch. 19: Shores and Coastal Processes (p. 612) Waves, Currents, and Tides (p. 614) Waves and Currents (p. 614) Imagine that you can see a side view of a wave as it approaches
Geology 101 Name Reading Guide for Ch. 19: Shores and Coastal Processes (p. 612) Waves, Currents, and Tides (p. 614) Waves and Currents (p. 614) Imagine that you can see a side view of a wave as it approaches
Anguilla. Wise practices for coping with. i b bea n Se a
 Wise practices for coping with Anguilla Car i b bea n Se a Department of Fisheries and Marine Resources, Anguilla Department of Physical Planning, Anguilla University of Puerto Rico, Sea Grant College
Wise practices for coping with Anguilla Car i b bea n Se a Department of Fisheries and Marine Resources, Anguilla Department of Physical Planning, Anguilla University of Puerto Rico, Sea Grant College
BEACH PROCESSES AND COASTAL ENVIRONMENTS
 BEACH PROCESSES AND COASTAL ENVIRONMENTS COASTAL FEATURES Cross section Map view TOPICS: Terminology Waves Beach Morphology Barriers Coastal Migration Tides Tidal Flats and Marshes Sediment Budgets Human
BEACH PROCESSES AND COASTAL ENVIRONMENTS COASTAL FEATURES Cross section Map view TOPICS: Terminology Waves Beach Morphology Barriers Coastal Migration Tides Tidal Flats and Marshes Sediment Budgets Human
OECS Regional Engineering Workshop September 29 October 3, 2014
 B E A C H E S. M A R I N A S. D E S I G N. C O N S T R U C T I O N. OECS Regional Engineering Workshop September 29 October 3, 2014 Coastal Erosion and Sea Defense: Introduction to Coastal Dynamics David
B E A C H E S. M A R I N A S. D E S I G N. C O N S T R U C T I O N. OECS Regional Engineering Workshop September 29 October 3, 2014 Coastal Erosion and Sea Defense: Introduction to Coastal Dynamics David
Questions # 4 7 refer to Figure # 2 (page 321, Fig )
 Shoreline Community College OCEANOGRAPHY 101 Fall 2006 Sample Exam # 3 Instructor: Linda Khandro Questions # 1 3 refer to Figure # 1 (page 284, Fig 11.7) 1. At which position is the moon in its new moon
Shoreline Community College OCEANOGRAPHY 101 Fall 2006 Sample Exam # 3 Instructor: Linda Khandro Questions # 1 3 refer to Figure # 1 (page 284, Fig 11.7) 1. At which position is the moon in its new moon
Beaches Unit (4.5 pts)
 T. James Noyes, El Camino College Beaches Unit (Topic 6A) page 1 Name: Section: Beaches Unit (4.5 pts) Beaches and Shorelines Are Always Changing Waves are slowly and inexorably altering the shoreline,
T. James Noyes, El Camino College Beaches Unit (Topic 6A) page 1 Name: Section: Beaches Unit (4.5 pts) Beaches and Shorelines Are Always Changing Waves are slowly and inexorably altering the shoreline,
Coastal Processes and Landforms: Teachers Notes
 Coastal Processes and Landforms: Teachers Notes This is the one of three programmes produced by Pumpkin Interactive about coasts and coastal management. This programme is concerned with coastal processes
Coastal Processes and Landforms: Teachers Notes This is the one of three programmes produced by Pumpkin Interactive about coasts and coastal management. This programme is concerned with coastal processes
Anatomy of Coastal Regions
 The Coast I. BEACH ANATOMY Anatomy of Coastal Regions Terms for different parts of beaches and coastal regions Are all about ENERGY- ie, where the ocean s energy Mostly through tides and waves, and shape
The Coast I. BEACH ANATOMY Anatomy of Coastal Regions Terms for different parts of beaches and coastal regions Are all about ENERGY- ie, where the ocean s energy Mostly through tides and waves, and shape
Exemplar for Internal Assessment Resource Geography Level 3. Resource title: The Coastal Environment Kaikoura
 Exemplar for internal assessment resource Geography 3.5A for Achievement Standard 91430 Exemplar for Internal Assessment Resource Geography Level 3 Resource title: The Coastal Environment Kaikoura This
Exemplar for internal assessment resource Geography 3.5A for Achievement Standard 91430 Exemplar for Internal Assessment Resource Geography Level 3 Resource title: The Coastal Environment Kaikoura This
Dynamic Shoreline. Why do we care? Loss of land Damage to structures Recreation
 Dynamic Shoreline Why do we care? Loss of land Damage to structures Recreation Coastal Water Movement Waves provide the energy Through breaking As waves shoal Speed decreases Height increases Wavelength
Dynamic Shoreline Why do we care? Loss of land Damage to structures Recreation Coastal Water Movement Waves provide the energy Through breaking As waves shoal Speed decreases Height increases Wavelength
Marginal Marine Environments
 Marginal Marine Environments Delta: discrete shoreline protuberances formed where rivers enter oceans, semi-enclosed seas, lakes or lagoons and supply sediment more rapidly than it can be redistributed
Marginal Marine Environments Delta: discrete shoreline protuberances formed where rivers enter oceans, semi-enclosed seas, lakes or lagoons and supply sediment more rapidly than it can be redistributed
Murlough. Dunes open access, some restricted areas Woodland open access, some restricted areas
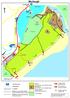 A2 Belfast Road Dundrum Murlough P3 N Dundrum Bay boathouse Ballykinler MOD Firing Range P4 P5 Downshire Bridge inlet floods at high tide Murlough Farm Private PNT Murlough House Private Seals agricultural
A2 Belfast Road Dundrum Murlough P3 N Dundrum Bay boathouse Ballykinler MOD Firing Range P4 P5 Downshire Bridge inlet floods at high tide Murlough Farm Private PNT Murlough House Private Seals agricultural
St Vincent. Grenadines. Wise practices for coping with. and the. i b bea n Se a
 Wise practices for coping with St Vincent Car i b bea n Se a and the Grenadines Bequia Community High School, Bequia, St Vincent and the Grenadines Ministry of Agriculture, Lands and Fisheries, St Vincent
Wise practices for coping with St Vincent Car i b bea n Se a and the Grenadines Bequia Community High School, Bequia, St Vincent and the Grenadines Ministry of Agriculture, Lands and Fisheries, St Vincent
