The effect of aging and gender on plantar pressure distribution during the gait in elderly
|
|
|
- Todd Kennedy
- 5 years ago
- Views:
Transcription
1 Acta of Bioengineering and Biomechanics Vol. 20, No. 3, 2018 Original paper DOI: /ABB The effect of aging and gender on plantar pressure distribution during the gait in elderly MARTA GIMUNOVÁ 1,*, MARTIN ZVONAŘ 1, ONDŘEJ MIKESKA 1 Faculty of Sports Studies, Masaryk University, Brno, Czech Republic. Purpose: The effect of age on structural foot characteristics as well as on the plantar pressure distribution has been shown previously. However, the number of studies focused also on gender gait differences of elderly is lacking. The purpose of this study was to compare dynamic gait characteristic in younger and older elderly and to investigate the gender differences as the life-long load and footwear choice differ in males and females. Methods: 61 healthy elderly participants were divided by age and gender into four groups: males 60 69, males 70 79, females and females years old. Plantar pressures were recorded during barefoot walking at naturally chosen speed using Emed-at (Novel GmbH, Germany). Three steps of the left foot of each participant were used for further analysis, furthermore, hallux angle, foot progression angle, and arch index were calculated by the Emed software from obtained footprints. To compare the differences between the analyzed groups, effect size obtained by Cohen s d was used. Results: Comparing the two age male groups, higher mean pressure was found in the age group in region MH4, MH5 and mid-foot, suggesting a greater lateral load and decreased longitudinal arch of the foot. Comparing female groups, the higher mean pressure was found in the older age group in region MH1. In all other regions, the mean pressures were reduced in the older groups. Conclusions: The results suggest that the effect of aging on plantar pressure distribution during the gait is affected by gender and should be considered when evaluating the gait of elderly. Key words: elderly, gait, arch index, pressure distribution, foot progression angle, hallux angle 1. Introduction Differences in fitness between younger and older elderly people were observed due to the reduction of muscle strength, endurance, flexibility and agility. These changes affect not only the physical capacity but also the gait, crucial in the independent performance of normal everyday activities. [12] Furthermore, neurologic gait abnormalities in elderly, e.g., unsteady gait, frontal, hemiparetic, neuropathic, ataxic or spastic gait, were found to be a significant predictor of the risk of non-alzheimer s dementia development [21]. The effect of age on structural foot characteristics as well as on the plantar force and pressure distribution has been shown in previous studies. Aging affects also the risk of falling and adaptations strategies when walking [22], [23]. The analysis of different age groups revealed that the plantar pressure distribution pattern is the most distinct in toddlers, smaller differences were found between adults and seniors [1]. Elderly people tend to have more pronated and flatter feet, reduced range of motion of the ankle and first metatarsophalangeal joint, higher prevalence of hallux valgus, toe deformities, weaken toe plantar flexors and reduced tactile sensitivity [18]. Additionally, in a study by Hessert et al. [6] weight bearing on the lateral side of the foot during heel contact and toe-off phases in elderly people was reported to possibly affect the stability during the gait [6]. Gender-specific differences in the foot shape and structure were also described in previous studies. Foot size, both in absolute and relative dimension, when the stature is considered, is smaller in females [4]. Also, the sexual dimorphism in bones of the foot, e.g., talus, calcaneus, metatarsals or phalanges, has been reported previously facilitating the gender identification in forensic cases [19], [20]. Furthermore, in males, contact * Corresponding author: Marta Gimunová, Faculty of Sports Studies, Masaryk University, Brno, Czech Republic, ul. Kamenice 5, Brno, Czech Republic. Phone: , gimunova@fsps.muni.cz Received: June 6th, 2018 Accepted for publication: September 28th, 2018
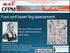
2 140 M. GIMUNOVÁ et al. area, force-time integral under the heel, 1st and 3rd metatarsal head and mean force under the 3rd metatarsal head were observed to be significantly larger compared to females [15]. Additionally, shoes have been identified as a main cause of forefoot disorders in females [24]. Also, during pregnancy increase in foot length, width and decrease in the height of the foot arch was observed [28]. Therefore, the life-long effect of different load (e.g., pregnancy) and footwear choice may result in plantar pressure, hallux angle, foot progression angle and arch index differences of elderly males and females. On the other hand, in a study by Murphy et al. [13] no significant difference between males and females in plantar pressure or normalized mid-foot contact area was found. However, the number of studies focused on gender differences in the gait of adults and elderly is limited. The purpose of this study was to compare dynamic gait characteristic in younger and older elderly and to investigate the gender differences in these two age groups. 2. Materials and methods 61 healthy elderly (21 men, 40 women) participated in this study and, according to age and gender, were divided into four groups: males 60 69, males 70 79, females and females years of age. The mean age [years], height [cm] and body mass [kg] of each group are shown in Table 1. Table 2 shows their foot characteristics: heel width, forefoot width and foot length [cm]. Inclusion criteria included independent walking and no musculoskeletal deformities affecting the gait. Table 1. Participants characteristics n Age Height Body mass Males ± ± ± Males ± 3, ± ± Females ± ± ± 9.82 Females ± ± ± Table 2. Foot characteristics of participants Heel Width Forefoot width Foot length Males ± ± ± 1.43 Males ± ± ± 1.15 Females ± ± ± 1.22 Females ± ± ± 1.34 Plantar pressures were recorded during barefoot walking using the Emed-at (Novel GmbH, Germany), cm platform mounted in a 4.5-meter long path allowing free gait. Participants were asked to walk at their naturally chosen gait speed, as the gait speed sig- Fig. 1. Mask regions of mean pressure and an average pressure distribution picture of males 60 69, males 70 79, females 60 69, and females groups
3 The effect of aging and gender on plantar pressure distribution during the gait in elderly 141 nificantly affect the gait pattern (e.g., Pietraszewski et al. [26]), and three trials of each participant were recorded. For further analysis, three steps of the left foot of each participant were used. Using the Emed-at software, the foot was divided into 10 regions: toe 1, 2, lesser toes, first, second, third, fourth and fifth metatarsal heads, mid-foot and heel, shown in Figure 1 together with the mean pressure distribution picture of each group. Associated variables (hallux angle, foot progression angle and arch index) were calculated subsequently by the Emed software from the obtained foot prints. Informed consent was provided by all participants prior to the data collection session. The study was approved by the local Ethical board. Statistical analysis To compare the differences between groups, effect size obtained by Cohen s d was used. Cohen s d is interpreted as 0.20 small, 0.50 medium, or clinically significant, 0.80 large effect [2]. 3. Results Effect of age The results show significant changes by effect size in plantar pressure in all foot regions, except for the heel in males and MH5 in females. In males, the higher mean pressure was found at age group, compared to the younger group in region MH4, MH5 and mid-foot. Similarly, the effect size analysis of arch index, which provides information about the longitudinal arch of the foot (pes cavus (<0.21), normal foot ( ), pes planus (>0.27)), showed significant foot flattering with age in males. Hallux angle was observed to be significantly higher in the male group, compared to the younger group. In females, the higher mean pressure was found at age group, compared to the younger group in region MH1. In all other regions, the mean pressures were reduced despite the similar body mass in both female groups. For hallux angle, no significant difference between the and female age groups was observed. Foot progression angle increased significantly with age in the female group. The arch index was observed to be significantly lower in the older female group. Table 3 and 4 shows means and standard deviations of analyzed variables for the four groups. Tables 5 and 6 show results of Cohen s d. Effect of gender Hallux valgus prevalence increases with age, observed by increased hallux angle in the male Table 3. Means and standard deviations (SD) of the mean pressure of analyzed foot regions Mean pressure Toe 1 Toe 2 Toes 345 MH1 MH2 MH3 MH4 MH5 Midfoot Heel Males Mean SD Males Mean SD Females Mean SD Females Mean SD Table 4. Means and standard deviations (SD) of analyzed variables Hallux angle Foot progression angle Arch index Males Mean SD Males Mean SD Females Mean SD Females Mean SD group in this study. Comparing the younger male and female group, significantly higher hallux angle was observed in females. In the older groups, no significant difference between males and females was found. On the other hand, foot progression angle increased significantly with age in the female group. Therefore, the gender differences in foot progression angle were observed between the younger elderly only. Gender differences in the arch index were observed in both age groups. The results indicate that greater gender differences may be observed in the younger elderly
4 142 M. GIMUNOVÁ et al. Table 5. Results of Cohen s d and confidence intervals (CI) of mean pressures in analyzed foot regions Males males Females females Toe 1 Cohen s d CI 26.53; ; Toe 2 Cohen s d CI 12.60; ; 8.99 Toe 345 Cohen s d CI 12.71; ; 7.24 MH1 Cohen s d CI 19.37; ; MH2 Cohen s d CI 16.50; ; MH3 Cohen s d CI 20.34; ; MH4 Cohen s d CI 18.72; ; MH5 Cohen s d CI 21.78; ; Midfoot Cohen s d CI 13.61; ; Heel Cohen s d CI 13.99; ; 8.59 Table 6. Results of Cohen s d and confidence intervals (CI) of hallux angle, foot progression angle and arch index Hallux angle Foot progression angle Arch index Cohen s d CI Cohen s d CI Cohen s d CI Males males ,96; 2,32 0, ; , ; 1,05 Females females ; ; ; 0.36 Males females ; ; ; 0.64 Males females ; ; ; 0.24 (hallux angle, foot progression angle, and arch index), as in the older group the effect of gender was observed only in the arch index. 4. Discussion To compare the dynamic gait characteristic in younger (60 69 years of age) and older (70 79 years of age) elderly, and to investigate the possible gender differences in these two age groups, 61 healthy elderly (21 men, 40 women) participated in this study. Effect of age In general, the effect of age was observed by decreased mean plantar pressures in this study. However, in males, higher mean pressure was observed in the older age group (70 79), compared to age group in region MH4, MH5 and mid-foot, suggesting a greater weight-bearing by the lateral side of the foot and decreased longitudinal arch of the foot, both also reported in previous studies [6], [18]. In females, higher mean pressure was found in the age group, compared to age group in region MH1. A similar finding was observed in a study by Menz and Morris [10], where higher loading of MH1 was associated with a reduced range of motion of 1st metatarsal-phalangeal joint (MPJ). In all other regions, the mean pressures were reduced in the older age group despite the similar body mass in both female age groups. A similar finding, i.e., reduced force and pressures under the heel, lateral forefoot and hallux was observed in healthy older people (approximately 68 years old) by Scott et al. [18] and explained mainly by the reduced step length and different foot characteristics in their older age group of elderly. Foot progression angle increased significantly with age in the female group. In previous study by Rosenbaum [17], out-toeing was observed to increase the load on the medial aspect of the mid-foot and forefoot,
5 The effect of aging and gender on plantar pressure distribution during the gait in elderly 143 observed in this group by increased plantar pressures in MH1 region. In contrast to findings of this study, no significant difference in foot progression angle between young and old adults was observed in a previous study where both males and females were observed [8]. The increased foot progression angle may result from external rotation of the hip, femoral or tibial torsion [7]. Hallux valgus may contribute to the instability and risk of falling [9], [1]. Its prevalence increases with age, as observed by increased hallux angle in the male group in this study. No significant difference in hallux angle in younger and older female age groups was observed. The arch index provides information about the foot longitudinal arch development. Effect size analysis of this index shows significant foot flattering with age in males. On the other hand, in females, the higher arch index was observed in the younger group. Effect of gender In our study, greater gender differences were observed in the younger group of elderly (hallux angle, foot progression angle, and arch index). In the older group, the effect of gender was observed only in the arch index. As mentioned above, gender differences in the hallux angle were observed only in the younger age groups, as with age the angle increased in males, which is in accordance with the previous studies reporting the magnitude of hallux angle to be associated with the female gender and age [3], [5], [14]. Females are at special risk, as wearing high heel shoes increase the risk of hallux valgus development and other deleterious effect, e.g., chronic paraspinal muscles fatigue associated with the posture alterations and pain [25], [27]. Gender differences in foot progression angle were also observed in the younger age groups, as it increased significantly with age in females. Similar observation of gender difference in foot progression angle was reported previously in a study by Røislien et al. [16], who found the angle more internally rotated in females and more externally rotated in males. Gender differences in the foot arch index were observed in both age groups. However, no clear trend for this variable was observed. Limitations of this study consist mainly of a relatively small number of participants making the generalization of our findings difficult. In future studies, a large number of elderly participants divided into more precise age groups and the analysis of differences between left and right foot will bring more detailed insight into the effect of aging and gender on gait. 5. Conclusion The dynamic gait characteristic in younger (60 69 years of age) and older (70 79 years of age) male and female elderly were compared. In males of age, greater mean pressure in the region MH4, MH5 and mid-foot observed suggests a greater weight-bearing by the lateral side of the foot and decreased longitudinal arch of the foot. In females, the higher mean pressure was found in a age group in region MH1, probably associated with reduced first MPJ range of motion and with greater foot progression angle. These findings suggest that the effect of aging on plantar pressure distribution during the gait is affected by gender and should be considered by health care professionals when caring after the elderly. References [1] BOSCH K., NAGEL A., WEIGEND L., ROSENBAUM D., From first to last steps in life Pressure patterns of three generations, Clin. Biomech., 2009, 24(8), [2] COHEN J., Statistical power analysis for behavioral sciences, (revised ed.), Academic Press, New York [3] COUGHLIN M.J., CAROLL P.J., Hallux Valgus: Demographics, Etiology, and Radiographic Assessment, Foot Ankle Int., 2007, 28, [4] FESSLER D.M.T., NETTLE D., AFSHAR Y., DE ANDRADE PINHEIRO I., BOLYANATZ A., BORGERHOFF MULDER M., CRAVALHO M., DELGADO T., GRUZD B., OLIVEIRA CORREIA M., KHALTOURINA D., KOROTAYEV A., MARROW J., DE SOUZA L.S., ZBARAUSKAITE A., A Cross-Cultural Investigation of the Role of Foot Size in Physical Attractiveness, Arch. Sex. Behav., 2005, 34(3), [5] HARDY R.H., CLAPHAM J.C.R., Observations on hallux valgus, J. Bone Joint Surg., 1951, 33, [6] HESSERT M.J., VYAS M., LEACH J., HU K., LIPSITZ L.A., NOVAK V., Foot pressure distribution during walking in young and old adults, BMC Geriatr., 2005, 5(8). [7] LINCOLN T.L., SUEN P.W., Common rotational variations in children, J. Am. Acad. Orthop. Surg., 2003, 11(5), [8] MENZ H.B., LATT M.D., TIEDEMANN A., SAN KWAN M.M., LORD S.R., Reliability of the GAITRite walkway system for the quantification of temporo-spatial parameters of gait in young and older people, Gait Posture, 2004, 20, [9] MENZ H.B., LORD S.R., Gait instability in older people with hallux valgus, Foot Ankle Int., 2005, 26, [10] MENZ H.B., MORRIS M.E., Clinical determinants of plantar forces and pressures during walking in older people, Gait Posture, 2006, 24, [11] MICKLE K.J., MUNRO B.J., LORD S.R., MENZ H.B., STEELE J.R., Gait, balance and plantar pressures in older people with toe deformities, Gait Posture, 2011, 34, [12] MILANOVIĆ Z., PANTELIĆ S., TRAJKOVIĆ N., SPORIŠ G., KOSTIĆ R., JAMES N., Age-related decrease in physical activity and functional fitness among elderly men and women, Clin. Interv. Aging, 2013, 8,
6 144 M. GIMUNOVÁ et al. [13] MURPHY D.F., BEYNNON B.D., MICHELSON J.D., VACEK P.M., Efficacy of plantar loading parameters during gait in terms of reliability, variability, effect of gender and relationship between contact area and plantar pressure, Foot Ankle Int., 2005, 26(2), [14] NIX S., SMITH M., VINCENZINO B., Prevalence of hallux valgus in the general population: a systematic review and meta-analysis, J. Foot Ankle Res., 2010, 3, 21. [15] PUTTI A.B., ARNOLD G.P., ABBOUD R.J., Foot pressure differences in men and women, Foot Ankle Surg., 2010, 16(1), [16] RØISLIEN J., SKARE O., GUSTAVSEN M., BROCH N.L., RENNIE L., OPHEIM A., Simultaneous estimation of effects of gender, age and walking speed on kinematic gait data, Gait Posture, 2009, 30, [17] ROSENBAUM D., Foot loading patterns can be changed by deliberately walking with in-toeing or out-toeing gait modifications, Gait Posture, 2013, 38(4), [18] SCOTT G., MENZ H.B., NEWCOMBE L., Age-related differences in foot structure and function, Gait Posture, 2007, 26(1), [19] SMITH S.L., Attribution of foot bones to sex and population groups, J. Forensic Sci., 1997, 42(2), [20] STEEL D.G., The estimation of sex on the basis of the talus and calcaneus, Am. J. Phys. Anthropol., 1976, 45, [21] VERGHESE J., LIPTON R.B., HALL C.B., KUSLANSKY G., KATZ M.J., BUSCHKE H., Abnormality of gait as a predictor of non-alzheimer s dementia, N. Eng. J. Med., 2002, 347, [22] BRIDENBAUGH S.A., KRESSIG R.W., Laboratory Review: The Role of Gait Analysis in Seniors Mobility and Fall Prevention, Gerontol., 2011, 57, [23] CHOI J.S., KANG D.W., SHIN Y.H., TACK G.R., Differences in gait pattern between the elderly and the young during level walking under low illumination, Acta Bioeng. Biomech., 2014, 16, 3 9. [24] FREY C., Foot health and shoewear for women, Clin. Orthop. Relat. Res., 2000, 372, [25] MIKA A., OLEKSY L., MIKOŁAJCZYK E., MARCHEWKA A., MIKA P., Changes of bioelectrical aktivity in cervical paraspinal muscle during gait in low and high heel shoes, Acta Bioeng. Biomech., 2011, 13, [26] PIETRASZEWSKI B., WINIARSKI S., JAROSZCZUK S., Three-dimensional human gait pattern reference data for normal men, Acta Bioeng. Biomech., 2012, 14, [27] YU J., CHEUNG J.T.M., FAN Y., ZHANG Y., LEUNG A.K.L., ZHANG M., Development of a finite element model of female foot for high-heeled shoe design, Clin. Biomech., 2008, 23, Supplement 1, S31 S38. [28] CHIOU W., CHIU H., CHAO A., WANG M., CHEN Y., The influence of body mass on the foot dimensions during pregnancy, Appl. Ergon., 2015, 46,
11/11/2012. Associations of Foot Forces and Pressures to Regional Foot Pain: The Framingham Foot Study. Acknowledgements & Disclosures
 11/11/2012 Associations of Foot Forces and Pressures to Regional Foot Pain: The Jody L. Riskowski, PhD, CSCS Institute for Aging Research (IFAR), Hebrew SeniorLife Harvard Medical School Boston, MA, USA
11/11/2012 Associations of Foot Forces and Pressures to Regional Foot Pain: The Jody L. Riskowski, PhD, CSCS Institute for Aging Research (IFAR), Hebrew SeniorLife Harvard Medical School Boston, MA, USA
Flip-flop footwear with a moulded foot-bed for the treatment of foot pain: a randomised controlled trial
 Flip-flop footwear with a moulded foot-bed for the treatment of foot pain: a randomised controlled trial Dr. Martin Spink, Ms. Angela Searle and Dr. Vivienne Chuter Podiatry department Faculty of Health
Flip-flop footwear with a moulded foot-bed for the treatment of foot pain: a randomised controlled trial Dr. Martin Spink, Ms. Angela Searle and Dr. Vivienne Chuter Podiatry department Faculty of Health
THE INFLUENCE OF SLOW RECOVERY INSOLE ON PLANTAR PRESSURE AND CONTACT AREA DURING WALKING
 March 12, 2015 5:39:44pm WSPC/170-JMMB 1540005 ISSN: 0219-51942nd Reading Journal of Mechanics in Medicine and Biology Vol. 15, No. 2 (2015) 1540005 (6 pages) c World Scientific Publishing Company DOI:
March 12, 2015 5:39:44pm WSPC/170-JMMB 1540005 ISSN: 0219-51942nd Reading Journal of Mechanics in Medicine and Biology Vol. 15, No. 2 (2015) 1540005 (6 pages) c World Scientific Publishing Company DOI:
The Problem. An Innovative Approach to the Injured Runner. Dosage. Mechanics. Structure! Postural Observations. Lower Quarter Assessment
 The Problem An Innovative Approach to the Injured Runner Irene S. Davis, PhD, PT, FAPTA, FACSM Director, Spaulding National Running Center Harvard Medical School Healthy People 2020 Initiative 76% runners
The Problem An Innovative Approach to the Injured Runner Irene S. Davis, PhD, PT, FAPTA, FACSM Director, Spaulding National Running Center Harvard Medical School Healthy People 2020 Initiative 76% runners
A FOOT AXIS FOR COP PATH OF OLDER ADULT SHORT ACCESS-RAMP WALKING STUDY
 A FOOT AXIS FOR COP PATH OF OLDER ADULT SHORT ACCESS-RAMP WALKING STUDY Dr Albert K. Chong and Mei Qichang University of Southern Queensland, Toowoomba, Australia Ningbo University, Ningbo, China A foot
A FOOT AXIS FOR COP PATH OF OLDER ADULT SHORT ACCESS-RAMP WALKING STUDY Dr Albert K. Chong and Mei Qichang University of Southern Queensland, Toowoomba, Australia Ningbo University, Ningbo, China A foot
What is the optimal design of a rocker shoe
 What is the optimal design of a rocker shoe University of Salford School of Health, Sport and Rehabilitation Sciences Deutsche Sporthochschule Köln J Chapman, S Preece, C Nester, B Braunstein, P Bruggerman
What is the optimal design of a rocker shoe University of Salford School of Health, Sport and Rehabilitation Sciences Deutsche Sporthochschule Köln J Chapman, S Preece, C Nester, B Braunstein, P Bruggerman
The Influence of Load Carrying Modes on Gait variables of Healthy Indian Women
 The Influence of Load Carrying Modes on Gait variables of Healthy Indian Women *Guha Thakurta A, Iqbal R and De A National Institute of Industrial Engineering, Powai, Vihar Lake, Mumbai-400087, India,
The Influence of Load Carrying Modes on Gait variables of Healthy Indian Women *Guha Thakurta A, Iqbal R and De A National Institute of Industrial Engineering, Powai, Vihar Lake, Mumbai-400087, India,
New research that enhances our knowledge of foot mechanics as well as the effect of
 The Tissue Stress Model: Justification based on Current Best Evidence New research that enhances our knowledge of foot mechanics as well as the effect of bone alignment on foot mobility during activity
The Tissue Stress Model: Justification based on Current Best Evidence New research that enhances our knowledge of foot mechanics as well as the effect of bone alignment on foot mobility during activity
Impact of heel position on leg muscles during walking
 Original article Niigata Journal of Health and Welfare Vol. 14, No. 1 Impact of heel position on leg muscles during walking Koichi Akaishi Graduate School of Health and Welfare, Niigata University of Health
Original article Niigata Journal of Health and Welfare Vol. 14, No. 1 Impact of heel position on leg muscles during walking Koichi Akaishi Graduate School of Health and Welfare, Niigata University of Health
Diabetes and Orthoses. Rob Bradbury Talar Made
 Diabetes and Orthoses Rob Bradbury Talar Made Diabetes High prevalence disease 4-6% in UK (over 2.5 mill diagnosed and a further 0.5 ) 6+% in USA 40% in some parts of Middle East (may be higher in Indian
Diabetes and Orthoses Rob Bradbury Talar Made Diabetes High prevalence disease 4-6% in UK (over 2.5 mill diagnosed and a further 0.5 ) 6+% in USA 40% in some parts of Middle East (may be higher in Indian
Analysis of Foot Pressure Variation with Change in Stride Length
 IOSR Journal of Dental and Medical Sciences (IOSR-JDMS) e-issn: 2279-853, p-issn: 2279-861.Volume 13, Issue 1 Ver. IV (Oct. 214), PP 46-51 Dr. Charudatta V. Shinde, M.S. MCh ( Orthopaedics ), Dr. Weijie
IOSR Journal of Dental and Medical Sciences (IOSR-JDMS) e-issn: 2279-853, p-issn: 2279-861.Volume 13, Issue 1 Ver. IV (Oct. 214), PP 46-51 Dr. Charudatta V. Shinde, M.S. MCh ( Orthopaedics ), Dr. Weijie
Foot Biomechanics Getting Back to the Base
 Foot Biomechanics Getting Back to the Base Christopher J. Mehallo, D.O. Rothman Institute Orthopaedics Objectives Understand basic foot biomechanics during walking and running Understand common sports
Foot Biomechanics Getting Back to the Base Christopher J. Mehallo, D.O. Rothman Institute Orthopaedics Objectives Understand basic foot biomechanics during walking and running Understand common sports
Customized rocker sole constructions
 Customized rocker sole constructions German guidelines to improve results in daily practice Stief, Thomas Registered Association for the Encouragement of Research and Education Management in Orthopedic
Customized rocker sole constructions German guidelines to improve results in daily practice Stief, Thomas Registered Association for the Encouragement of Research and Education Management in Orthopedic
Arch Height and Running Shoes: The Best Advice to Give Patients
 Arch Height and Running Shoes: The Best Advice to Give Patients by Thomas C. Michaud, DC Published May 1, 2014 by Dynamic Chiropractic Magazine Because runners with different arch heights are prone to
Arch Height and Running Shoes: The Best Advice to Give Patients by Thomas C. Michaud, DC Published May 1, 2014 by Dynamic Chiropractic Magazine Because runners with different arch heights are prone to
REPLACING REDUNDANT STABILOMETRY PARAMETERS WITH RATIO AND MAXIMUM DEVIATION PARAMETERS
 Proceedings of the 12th IASTED International Conference Biomedical Engineering (BioMed 2016) February 15-16, 2016 Innsbruck, Austria REPLACING REDUNDANT STABILOMETRY PARAMETERS WITH RATIO AND MAXIMUM DEVIATION
Proceedings of the 12th IASTED International Conference Biomedical Engineering (BioMed 2016) February 15-16, 2016 Innsbruck, Austria REPLACING REDUNDANT STABILOMETRY PARAMETERS WITH RATIO AND MAXIMUM DEVIATION
Activity Overview. Footprints In The Sand Inquiry MO-BILITY. Activity 2E. Activity Objectives: Activity Description: Activity Background: LESSON 2
 Footprints In The Sand Inquiry Activity 2E Activity Objectives: Working in collaborative groups, students will be able to: assume assigned roles to complete a given task examine the various parts of the
Footprints In The Sand Inquiry Activity 2E Activity Objectives: Working in collaborative groups, students will be able to: assume assigned roles to complete a given task examine the various parts of the
Steffen Willwacher, Katina Fischer, Gert Peter Brüggemann Institute of Biomechanics and Orthopaedics, German Sport University, Cologne, Germany
 P01-3 ID126 SURFACE STIFFNESS AFFECTS JOINT LOADING IN RUNNING Steffen Willwacher, Katina Fischer, Gert Peter Brüggemann Institute of Biomechanics and Orthopaedics, German Sport University, Cologne, Germany
P01-3 ID126 SURFACE STIFFNESS AFFECTS JOINT LOADING IN RUNNING Steffen Willwacher, Katina Fischer, Gert Peter Brüggemann Institute of Biomechanics and Orthopaedics, German Sport University, Cologne, Germany
Comparison of Kinematics and Kinetics During Drop and Drop Jump Performance
 schouweiler, hess UW-L Journal of Undergraduate Research XIII (21) Comparison of Kinematics and Kinetics During Drop and Drop Jump Performance Ryan Schouweiler, Karina Hess Faculty Sponsor: Thomas Kernozek,
schouweiler, hess UW-L Journal of Undergraduate Research XIII (21) Comparison of Kinematics and Kinetics During Drop and Drop Jump Performance Ryan Schouweiler, Karina Hess Faculty Sponsor: Thomas Kernozek,
ATHLETES AND ORTHOTICS. January 29, 2014
 ATHLETES AND ORTHOTICS January 29, 2014 TOPICS TO COVER TODAY Why use an orthotic? What athlete would benefit from wearing orthotics? What device should I use: Custom versus off of the shelf orthotics?
ATHLETES AND ORTHOTICS January 29, 2014 TOPICS TO COVER TODAY Why use an orthotic? What athlete would benefit from wearing orthotics? What device should I use: Custom versus off of the shelf orthotics?
ASSESMENT Introduction REPORTS Running Reports Walking Reports Written Report
 ASSESMENT REPORTS Introduction Left panel Avatar Playback Right Panel Patient Gait Parameters Report Tab Click on parameter to view avatar at that point in time 2 Introduction Software will compare gait
ASSESMENT REPORTS Introduction Left panel Avatar Playback Right Panel Patient Gait Parameters Report Tab Click on parameter to view avatar at that point in time 2 Introduction Software will compare gait
JAPMA Article In Press
 JAPMA Article In Press This article has undergone peer review, copyediting, and author review but is not a final version and may differ from the published version. DOI: http://dx.doi.org/10.7547/15-051
JAPMA Article In Press This article has undergone peer review, copyediting, and author review but is not a final version and may differ from the published version. DOI: http://dx.doi.org/10.7547/15-051
THE ANKLE-HIP TRANSVERSE PLANE COUPLING DURING THE STANCE PHASE OF NORMAL WALKING
 THE ANKLE-HIP TRANSVERSE PLANE COUPLING DURING THE STANCE PHASE OF NORMAL WALKING Thales R. Souza, Rafael Z. Pinto, Renato G. Trede, Nadja C. Pereira, Renata N. Kirkwood and Sérgio T. Fonseca. Movement
THE ANKLE-HIP TRANSVERSE PLANE COUPLING DURING THE STANCE PHASE OF NORMAL WALKING Thales R. Souza, Rafael Z. Pinto, Renato G. Trede, Nadja C. Pereira, Renata N. Kirkwood and Sérgio T. Fonseca. Movement
Figure 1 betois (bending torsion insole system) system with five measuring points and A/D- converter.
 Bending and Torsional Moments - A new measuring system for gait analysis Nora Dawin & Annette Kerkhoff & Klaus Peikenkamp, University of Applied Sciences Münster, Germany Abstract The Laboratory of Biomechanics
Bending and Torsional Moments - A new measuring system for gait analysis Nora Dawin & Annette Kerkhoff & Klaus Peikenkamp, University of Applied Sciences Münster, Germany Abstract The Laboratory of Biomechanics
Dynamix Ankle Foot Orthoses Range
 The Restyled Dynamix Ankle Foot Orthoses Range Supporting your wellbeing Product Range Introduction Index Product Range Introduction... 3 Puffin - Dynamix Supramalleolar... 4 Penguin - Dynamix Plantarflexion...
The Restyled Dynamix Ankle Foot Orthoses Range Supporting your wellbeing Product Range Introduction Index Product Range Introduction... 3 Puffin - Dynamix Supramalleolar... 4 Penguin - Dynamix Plantarflexion...
Gender differences of foot characteristics in older Japanese adults using a 3D foot scanner
 Saghazadeh et al. Journal of Foot and Ankle Research (2015) 8:29 DOI 10.1186/s13047-015-0087-4 JOURNAL OF FOOT AND ANKLE RESEARCH RESEARCH Open Access Gender differences of foot characteristics in older
Saghazadeh et al. Journal of Foot and Ankle Research (2015) 8:29 DOI 10.1186/s13047-015-0087-4 JOURNAL OF FOOT AND ANKLE RESEARCH RESEARCH Open Access Gender differences of foot characteristics in older
Impact Points and Their Effect on Trajectory in Soccer
 Proceedings Impact Points and Their Effect on Trajectory in Soccer Kaoru Kimachi 1, *, Sungchan Hong 2, Shuji Shimonagata 3 and Takeshi Asai 2 1 Doctoral Program of Coaching Science, University of Tsukuba,
Proceedings Impact Points and Their Effect on Trajectory in Soccer Kaoru Kimachi 1, *, Sungchan Hong 2, Shuji Shimonagata 3 and Takeshi Asai 2 1 Doctoral Program of Coaching Science, University of Tsukuba,
INTERACTION OF STEP LENGTH AND STEP RATE DURING SPRINT RUNNING
 INTERACTION OF STEP LENGTH AND STEP RATE DURING SPRINT RUNNING Joseph P. Hunter 1, Robert N. Marshall 1,, and Peter J. McNair 3 1 Department of Sport and Exercise Science, The University of Auckland, Auckland,
INTERACTION OF STEP LENGTH AND STEP RATE DURING SPRINT RUNNING Joseph P. Hunter 1, Robert N. Marshall 1,, and Peter J. McNair 3 1 Department of Sport and Exercise Science, The University of Auckland, Auckland,
Ankle biomechanics demonstrates excessive and prolonged time to peak rearfoot eversion (see Foot Complex graph). We would not necessarily expect
 Case Study #1 The first case study is a runner presenting with bilateral shin splints with pain and tenderness along the medial aspect of the tibia. The symptoms have increased significantly over the last
Case Study #1 The first case study is a runner presenting with bilateral shin splints with pain and tenderness along the medial aspect of the tibia. The symptoms have increased significantly over the last
Anthropometric Characteristics of Feet of Soldiers in the New Zealand Army
 MILITARY MEDICINE, 176, 4:438, 2011 Anthropometric Characteristics of Feet of Soldiers in the New Zealand Army Marian L. Baxter, BPhsEd (Hons) * ; David G. Baxter, DPhil ABSTRACT Lower limb and lower back
MILITARY MEDICINE, 176, 4:438, 2011 Anthropometric Characteristics of Feet of Soldiers in the New Zealand Army Marian L. Baxter, BPhsEd (Hons) * ; David G. Baxter, DPhil ABSTRACT Lower limb and lower back
Relationship between Ground Reaction Force and Stability Level of the Lower Extremity in Runners Background: Objective: Design and Setting:
 Relationship between Ground Reaction Force and Stability Level of the Lower Extremity in Runners Kimitake Sato, Monique Butcher-Mokha Barry University Miami Shores, FL Background: Neuromuscular control
Relationship between Ground Reaction Force and Stability Level of the Lower Extremity in Runners Kimitake Sato, Monique Butcher-Mokha Barry University Miami Shores, FL Background: Neuromuscular control
AN EXPERIMENTAL INVESTIGATION ON GOLF SHOE DESIGN USING FOOT- PRESSURE DISTRIBUTION DURING THE GOLF SWING
 Proceedings of the 4 th BSME-ASME International Conference on Thermal Engineering 27-29 December, 2008, Dhaka, Bangladesh AN EXPERIMENTAL INVESTIGATION ON GOLF SHOE DESIGN USING FOOT- PRESSURE DISTRIBUTION
Proceedings of the 4 th BSME-ASME International Conference on Thermal Engineering 27-29 December, 2008, Dhaka, Bangladesh AN EXPERIMENTAL INVESTIGATION ON GOLF SHOE DESIGN USING FOOT- PRESSURE DISTRIBUTION
Relationship between plantar pressures, physical activity and sedentariness among preschool children
 University of Wollongong Research Online Faculty of Health and Behavioural Sciences - Papers (Archive) Faculty of Science, Medicine and Health 2011 Relationship between plantar pressures, physical activity
University of Wollongong Research Online Faculty of Health and Behavioural Sciences - Papers (Archive) Faculty of Science, Medicine and Health 2011 Relationship between plantar pressures, physical activity
Foot mechanics & implications on training, posture and movement
 Foot mechanics & implications on training, posture and movement Three Arches Three Arches These arches are not reciprocal. When the foot pronates ALL arches should fall. If the medial arch falls and the
Foot mechanics & implications on training, posture and movement Three Arches Three Arches These arches are not reciprocal. When the foot pronates ALL arches should fall. If the medial arch falls and the
Biomechanical evaluation of heel elevation on load transfer experimental measurement and finite element analysis
 Acta Mech. Sin. (2012) 28(1):232 240 DOI 10.1007/s10409-012-0015-9 RESEARCH PAPER Biomechanical evaluation of heel elevation on load transfer experimental measurement and finite element analysis Yan Luximon
Acta Mech. Sin. (2012) 28(1):232 240 DOI 10.1007/s10409-012-0015-9 RESEARCH PAPER Biomechanical evaluation of heel elevation on load transfer experimental measurement and finite element analysis Yan Luximon
An investigation of kinematic and kinetic variables for the description of prosthetic gait using the ENOCH system
 An investigation of kinematic and kinetic variables for the description of prosthetic gait using the ENOCH system K. OBERG and H. LANSHAMMAR* Amputee Training and Research Unit, University Hospital, Fack,
An investigation of kinematic and kinetic variables for the description of prosthetic gait using the ENOCH system K. OBERG and H. LANSHAMMAR* Amputee Training and Research Unit, University Hospital, Fack,
Running Injuries in Adolescents Jeffrey Shilt, M.D. Part 1 Page 1
 Running Injuries in Adolescents Jeffrey Shilt, M.D. Chief Surgical Officer, The Woodlands, Texas Children's Hospital Associate Professor, Orthopedic and Scoliosis Surgery, Baylor College of Medicine Part
Running Injuries in Adolescents Jeffrey Shilt, M.D. Chief Surgical Officer, The Woodlands, Texas Children's Hospital Associate Professor, Orthopedic and Scoliosis Surgery, Baylor College of Medicine Part
Normal Gait and Dynamic Function purpose of the foot in ambulation. Normal Gait and Dynamic Function purpose of the foot in ambulation
 Normal Gait and Dynamic Function purpose of the foot in ambulation Edward P. Mulligan, PT, DPT, OCS, SCS, ATC Assistant Professor; Residency Chair UT Southwestern School of Health Professions Department
Normal Gait and Dynamic Function purpose of the foot in ambulation Edward P. Mulligan, PT, DPT, OCS, SCS, ATC Assistant Professor; Residency Chair UT Southwestern School of Health Professions Department
Normative data of postural sway by using sway meter among young healthy adults
 Normative data of postural sway by using sway meter Original Research Article ISSN: 2394-0026 (P) Normative data of postural sway by using sway meter among young healthy adults Tejal C Nalawade 1*, Shyam
Normative data of postural sway by using sway meter Original Research Article ISSN: 2394-0026 (P) Normative data of postural sway by using sway meter among young healthy adults Tejal C Nalawade 1*, Shyam
WalkOn product range. Dynamic Ankle-Foot Orthoses. Information for specialist dealers
 WalkOn product range Dynamic Ankle-Foot Orthoses Information for specialist dealers WalkOn Flex WalkOn WalkOn Trimable WalkOn Reaction WalkOn Reaction plus One range Many different applications The WalkOn
WalkOn product range Dynamic Ankle-Foot Orthoses Information for specialist dealers WalkOn Flex WalkOn WalkOn Trimable WalkOn Reaction WalkOn Reaction plus One range Many different applications The WalkOn
Defining Flatfoot. 5 Associate Professor, Department of Orthopaedic Surgery, Johns Hopkins Hospital. 456
 01 98-021 1/99/2007-045610 FOOT & ANKLE INTERNATIONAL Copyright O 1999 by the American Orthopaedic Foot and Ankle Soclety, Inc. Defining Flatfoot Jennifer M. Tareco, M.D.,* Nancy H. Miller, M.D.,t Bruce
01 98-021 1/99/2007-045610 FOOT & ANKLE INTERNATIONAL Copyright O 1999 by the American Orthopaedic Foot and Ankle Soclety, Inc. Defining Flatfoot Jennifer M. Tareco, M.D.,* Nancy H. Miller, M.D.,t Bruce
PATHOLOGICAL CONDITIONS REQUIRING THE USE OF CUSTOMIZED LASTS
 ICAMS 2014 5 th International Conference on Advanced Materials and Systems PATHOLOGICAL CONDITIONS REQUIRING THE USE OF CUSTOMIZED LASTS DANIEL PETCU, GHEORGHE BERIJAN INCDTP Division: Leather and Footwear
ICAMS 2014 5 th International Conference on Advanced Materials and Systems PATHOLOGICAL CONDITIONS REQUIRING THE USE OF CUSTOMIZED LASTS DANIEL PETCU, GHEORGHE BERIJAN INCDTP Division: Leather and Footwear
RUNNING SHOE STIFFNESS: THE EFFECT ON WALKING GAIT
 RUNNING SHOE STIFFNESS: THE EFFECT ON WALKING GAIT Stephen N Stanley, Peter J M c Nair, Angela G Walker, & Robert N Marshall Auckland Institute of Technology, Auckland, New Zealand University of Auckland,
RUNNING SHOE STIFFNESS: THE EFFECT ON WALKING GAIT Stephen N Stanley, Peter J M c Nair, Angela G Walker, & Robert N Marshall Auckland Institute of Technology, Auckland, New Zealand University of Auckland,
Journal of Human Sport and Exercise E-ISSN: Universidad de Alicante España
 Journal of Human Sport and Exercise E-ISSN: 1988-5202 jhse@ua.es Universidad de Alicante España KALINA, TOMAS; CACEK, JAN; KMETOVA, LINDA The running economy difference between running barefoot and running
Journal of Human Sport and Exercise E-ISSN: 1988-5202 jhse@ua.es Universidad de Alicante España KALINA, TOMAS; CACEK, JAN; KMETOVA, LINDA The running economy difference between running barefoot and running
Effect of Age and Sex on Gait Characteristics in the Korean Elderly People
 Iran J Public Health, Vol. 47, No.5, May 2018, pp.666-673 Original Article Effect of Age and Sex on Gait Characteristics in the Korean People Yang Sun PARK 1, Ji-Won KIM 2, Yuri KWON 2, Moon-Seok KWON
Iran J Public Health, Vol. 47, No.5, May 2018, pp.666-673 Original Article Effect of Age and Sex on Gait Characteristics in the Korean People Yang Sun PARK 1, Ji-Won KIM 2, Yuri KWON 2, Moon-Seok KWON
Dynamic/Static Foot. Tissues. Static Foot. Dynamic Foot
 Dynamic/Static Tissues Static Plantar fascia biomechanical windlass mechanism intrinsic muscles stabilize metatarsophalangeal (MP) toe joints Weight on whole foot - MP toe joints straight Plantar fascia
Dynamic/Static Tissues Static Plantar fascia biomechanical windlass mechanism intrinsic muscles stabilize metatarsophalangeal (MP) toe joints Weight on whole foot - MP toe joints straight Plantar fascia
The Lateralized Foot & Ankle Pattern and the Pronated Left Chest
 The Lateralized Foot & Ankle Pattern and the Pronated Left Chest Presented by: James Anderson, MPT, PRC Director of Affiliate Programs, Faculty & Board of Certification Postural Restoration Institute Pronate
The Lateralized Foot & Ankle Pattern and the Pronated Left Chest Presented by: James Anderson, MPT, PRC Director of Affiliate Programs, Faculty & Board of Certification Postural Restoration Institute Pronate
Posture influences ground reaction force: implications for crouch gait
 University of Tennessee, Knoxville From the SelectedWorks of Jeffrey A. Reinbolt July 14, 2010 Posture influences ground reaction force: implications for crouch gait H. X. Hoang Jeffrey A. Reinbolt, University
University of Tennessee, Knoxville From the SelectedWorks of Jeffrey A. Reinbolt July 14, 2010 Posture influences ground reaction force: implications for crouch gait H. X. Hoang Jeffrey A. Reinbolt, University
Running Gait Mechanics. Walking vs Running. Ankle Joint Complex Sagittal Plane. As speed increases, when has walking ended and running begun?
 Running Gait Mechanics Walking vs Running As speed increases, when has walking ended and running begun? Ankle Joint Complex Sagittal Plane 1 Ankle Joint Complex Sagittal Plane Pos. @FS 5 o DF Absorption
Running Gait Mechanics Walking vs Running As speed increases, when has walking ended and running begun? Ankle Joint Complex Sagittal Plane 1 Ankle Joint Complex Sagittal Plane Pos. @FS 5 o DF Absorption
video Outline Pre-requisites of Typical Gait Case Studies Case 1 L5 Myelomeningocele Case 1 L5 Myelomeningocele
 Outline Evaluation of Orthosis Function in Children with Neuromuscular Disorders Using Motion Analysis Outcomes Terminology Methods Typically developing Case examples variety of pathologies Sylvia Õunpuu,
Outline Evaluation of Orthosis Function in Children with Neuromuscular Disorders Using Motion Analysis Outcomes Terminology Methods Typically developing Case examples variety of pathologies Sylvia Õunpuu,
The Effect of a Seven Week Exercise Program on Golf Swing Performance and Musculoskeletal Screening Scores
 The Effect of a Seven Week Exercise Program on Golf Swing Performance and Musculoskeletal Screening Scores 2017 Mico Hannes Olivier Bachelor of Sport Science Faculty of Health Sciences and Medicine Bond
The Effect of a Seven Week Exercise Program on Golf Swing Performance and Musculoskeletal Screening Scores 2017 Mico Hannes Olivier Bachelor of Sport Science Faculty of Health Sciences and Medicine Bond
Gait Analyser. Description of Walking Performance
 Gait Analyser Description of Walking Performance This brochure will help you to understand clearly the parameters described in the report of the Gait Analyser, provide you with tips to implement the walking
Gait Analyser Description of Walking Performance This brochure will help you to understand clearly the parameters described in the report of the Gait Analyser, provide you with tips to implement the walking
Biomechanical analysis on force plate of aerobics shoes
 Acta Technica 62 No. 3A/2017, 181 186 c 2017 Institute of Thermomechanics CAS, v.v.i. Biomechanical analysis on force plate of aerobics shoes Yang Yang 1 Abstract. A pair of good shoes is essential to
Acta Technica 62 No. 3A/2017, 181 186 c 2017 Institute of Thermomechanics CAS, v.v.i. Biomechanical analysis on force plate of aerobics shoes Yang Yang 1 Abstract. A pair of good shoes is essential to
Biofeedback Insole can help to Increase Performance and Comfort, and Reduce Injury.
 Biofeedback Insole can help to Increase Performance and Comfort, and Reduce Injury. During independent third party testing for consumer acceptance and evaluation purposes the device was found to provide
Biofeedback Insole can help to Increase Performance and Comfort, and Reduce Injury. During independent third party testing for consumer acceptance and evaluation purposes the device was found to provide
Longitudinal Arch Angle (LAA): Inter-rater reliability comparing Relaxed Calcaneal Stance with Toe Off
 The Foot and Ankle Online Journal Official Publication of the International Foot & Ankle Foundation faoj.org / ISSN 1941-6806 Longitudinal Arch Angle (LAA): Inter-rater reliability comparing Relaxed Calcaneal
The Foot and Ankle Online Journal Official Publication of the International Foot & Ankle Foundation faoj.org / ISSN 1941-6806 Longitudinal Arch Angle (LAA): Inter-rater reliability comparing Relaxed Calcaneal
Barefoot Running. Ed Mulligan, PT, DPT, OCS, SCS, ATC. Clinical Orthopedic Rehabilitation Education
 Barefoot Running Ed Mulligan, PT, DPT, OCS, SCS, ATC Clinical Orthopedic Rehabilitation Education Not a new concept Nov 1958 1984 Olympics Interesting Trivia Abebe Bilika won the 1960 Olympic marathon
Barefoot Running Ed Mulligan, PT, DPT, OCS, SCS, ATC Clinical Orthopedic Rehabilitation Education Not a new concept Nov 1958 1984 Olympics Interesting Trivia Abebe Bilika won the 1960 Olympic marathon
Case Study: Chronic Plantar Heel Pain/Plantar Fasciopathy. CASE STUDY PRESENTATION by Resonance Podiatry and Gait Labs
 Case Study: Chronic Plantar Heel Pain/Plantar Fasciopathy CASE STUDY PRESENTATION by Resonance Podiatry and Gait Labs THE PATIENT 43yo female, professional netball umpire 6 month history right plantar
Case Study: Chronic Plantar Heel Pain/Plantar Fasciopathy CASE STUDY PRESENTATION by Resonance Podiatry and Gait Labs THE PATIENT 43yo female, professional netball umpire 6 month history right plantar
Effect of Taping Therapy and Inner Arch Support on Plantar Lower Body Alignment and Gait
 Korean Journal of Sport Biomechanics 2017; 27(3): 229-238 http://dx.doi.org/10.5103/kjsb.2017.27.3.229 http://e-kjsb.org eissn 2093-9752 ORIGINAL Effect of Taping Therapy and Inner Arch Support on Plantar
Korean Journal of Sport Biomechanics 2017; 27(3): 229-238 http://dx.doi.org/10.5103/kjsb.2017.27.3.229 http://e-kjsb.org eissn 2093-9752 ORIGINAL Effect of Taping Therapy and Inner Arch Support on Plantar
Analysis of foot load during ballet dancers gait
 Acta of Bioengineering and Biomechanics Vol. 16, No. 2, 2014 Original paper DOI: 10.5277/abb140205 Analysis of foot load during ballet dancers gait MARKETA PROCHAZKOVA 1 *, LUCIE TEPLA 1, ZDENEK SVOBODA
Acta of Bioengineering and Biomechanics Vol. 16, No. 2, 2014 Original paper DOI: 10.5277/abb140205 Analysis of foot load during ballet dancers gait MARKETA PROCHAZKOVA 1 *, LUCIE TEPLA 1, ZDENEK SVOBODA
L A B Mask 8 Mask 5 Mask 6 Mask 3 Mask 9 Mask 10 Mask 7 Mask 4 Mask 1 Mask 2 Figure 1. Imprint Index calculation. L = line drawn along medial border o
 The effect of low-dye taping on peak plantar pressures of normal feet during gait Sonia J Russo and Lucy S Chipchase University of South Australia This study investigated whether low-dye anti-pronation
The effect of low-dye taping on peak plantar pressures of normal feet during gait Sonia J Russo and Lucy S Chipchase University of South Australia This study investigated whether low-dye anti-pronation
Giovanni Alfonso Borelli Father of Biomechanics
 Giovanni Alfonso Borelli Father of Biomechanics 1608-1679 Peter Guy BSc DCh Private practice Whitby and Peterborough Professor Chiropody Faculty Michener Institute of Education at UHN Advisory Board Member
Giovanni Alfonso Borelli Father of Biomechanics 1608-1679 Peter Guy BSc DCh Private practice Whitby and Peterborough Professor Chiropody Faculty Michener Institute of Education at UHN Advisory Board Member
The effect of different depths of medial heel skive on plantar pressures
 Bonanno et al. Journal of Foot and Ankle Research 2012, 5:20 JOURNAL OF FOOT AND ANKLE RESEARCH RESEARCH Open Access The effect of different depths of medial on plantar pressures Daniel R Bonanno 1,2*,
Bonanno et al. Journal of Foot and Ankle Research 2012, 5:20 JOURNAL OF FOOT AND ANKLE RESEARCH RESEARCH Open Access The effect of different depths of medial on plantar pressures Daniel R Bonanno 1,2*,
Gender Differences in Hip Joint Kinematics and Kinetics During Side-Step Cutting Maneuver
 ORIGINAL RESEARCH Gender Differences in Hip Joint Kinematics and Kinetics During Side-Step Cutting Maneuver Christine D. Pollard, PhD, PT, Susan M. Sigward, PhD, PT, and Christopher M. Powers, PhD, PT
ORIGINAL RESEARCH Gender Differences in Hip Joint Kinematics and Kinetics During Side-Step Cutting Maneuver Christine D. Pollard, PhD, PT, Susan M. Sigward, PhD, PT, and Christopher M. Powers, PhD, PT
Analysis of Gait Characteristics Changes in Normal Walking and Fast Walking Of the Elderly People
 IOSR Journal of Engineering (IOSRJEN) ISSN (e): 2250-3021, ISSN (p): 2278-8719 Vol. 08, Issue 7 (July. 2018), V (V) 34-41 www.iosrjen.org Analysis of Gait Characteristics Changes in and Of the Elderly
IOSR Journal of Engineering (IOSRJEN) ISSN (e): 2250-3021, ISSN (p): 2278-8719 Vol. 08, Issue 7 (July. 2018), V (V) 34-41 www.iosrjen.org Analysis of Gait Characteristics Changes in and Of the Elderly
Effect of Ankle Dorsiflexion Range of Motion on Rearfoot Motion During Walking
 Effect of Ankle Dorsiflexion Range of Motion on Rearfoot Motion During Walking MARK W. CORNWALL, PhD, PT, CPed* THOMAS G. McPOIL, PhD, PT, ATC* The purpose of this study was to investigate whether the
Effect of Ankle Dorsiflexion Range of Motion on Rearfoot Motion During Walking MARK W. CORNWALL, PhD, PT, CPed* THOMAS G. McPOIL, PhD, PT, ATC* The purpose of this study was to investigate whether the
Analysis of Backward Falls Caused by Accelerated Floor Movements Using a Dummy
 Original Article Analysis of Backward Falls Caused by Accelerated Floor Movements Using a Dummy Hisao NAGATA 1 * and Hisato OHNO 2 1 National Institute of Occupational Safety and Health, 1 4 6 Umezono,
Original Article Analysis of Backward Falls Caused by Accelerated Floor Movements Using a Dummy Hisao NAGATA 1 * and Hisato OHNO 2 1 National Institute of Occupational Safety and Health, 1 4 6 Umezono,
HPW Biomechanics
 HPW Biomechanics hpw@mail.com www.hpwbiomechanics.com ~ via e-mail ~ January 31, 213 To: Attn: From: Subject: I-Roc Debbie Chapman Janet S. Dufek, Ph.D. Research Scientist Additional Footwear Evaluation
HPW Biomechanics hpw@mail.com www.hpwbiomechanics.com ~ via e-mail ~ January 31, 213 To: Attn: From: Subject: I-Roc Debbie Chapman Janet S. Dufek, Ph.D. Research Scientist Additional Footwear Evaluation
Nahid Divandari *, Mahdi Vakili **
 A Study on the relation between height of medial longitudinal arch and sport injuries in lower limb of professional runners by using Navicular Drop and Arch Index clinical tests Nahid Divandari *, Mahdi
A Study on the relation between height of medial longitudinal arch and sport injuries in lower limb of professional runners by using Navicular Drop and Arch Index clinical tests Nahid Divandari *, Mahdi
Changes in speed and efficiency in the front crawl swimming technique at 100m track
 Proceeding 10th INSHS International Christmas Sport Scientific Conference, 4-5 December 2015. International Network of Sport and Health Science. Szombathely, Hungary Changes in speed and efficiency in
Proceeding 10th INSHS International Christmas Sport Scientific Conference, 4-5 December 2015. International Network of Sport and Health Science. Szombathely, Hungary Changes in speed and efficiency in
Changes in Foot Shape after Long-Distance Running
 J. Funct. Morphol. Kinesiol. 2016, 1, 30-38; doi:10.3390/jfmk1010030 Article Journal of Functional Morphology and Kinesiology ISSN 2411-5142 www.mdpi.com/journal/jfmk Changes in Foot Shape after Long-Distance
J. Funct. Morphol. Kinesiol. 2016, 1, 30-38; doi:10.3390/jfmk1010030 Article Journal of Functional Morphology and Kinesiology ISSN 2411-5142 www.mdpi.com/journal/jfmk Changes in Foot Shape after Long-Distance
Running from injury 2
 Created as a free resource by Clinical Edge Based on Physio Edge podcast 049 with Dr Rich Willy Get your free trial of online Physio education by clicking here Running injuries & assessment Running assessment
Created as a free resource by Clinical Edge Based on Physio Edge podcast 049 with Dr Rich Willy Get your free trial of online Physio education by clicking here Running injuries & assessment Running assessment
General Assessment: May I Introduce You to Your Feet?
 General Assessment: May I Introduce You to Your Feet? Knowledge is power. Information is liberating. Education is the premise of progress, in every society, in every family. Kofi Annan Let s get practical
General Assessment: May I Introduce You to Your Feet? Knowledge is power. Information is liberating. Education is the premise of progress, in every society, in every family. Kofi Annan Let s get practical
GROUND REACTION FORCE DOMINANT VERSUS NON-DOMINANT SINGLE LEG STEP OFF
 GROUND REACTION FORCE DOMINANT VERSUS NON-DOMINANT SINGLE LEG STEP OFF Sara Gharabaghli, Rebecca Krogstad, Sara Lynch, Sofia Saavedra, and Tamara Wright California State University, San Marcos, San Marcos,
GROUND REACTION FORCE DOMINANT VERSUS NON-DOMINANT SINGLE LEG STEP OFF Sara Gharabaghli, Rebecca Krogstad, Sara Lynch, Sofia Saavedra, and Tamara Wright California State University, San Marcos, San Marcos,
The Human Foot. The Three Major Sections of the Foot
 The Human Foot You ve heard the phrase I have one foot bigger than the other. A closer truth would be no two feet are alike, and yes in many cases one foot is larger than the other. Handling the challenge
The Human Foot You ve heard the phrase I have one foot bigger than the other. A closer truth would be no two feet are alike, and yes in many cases one foot is larger than the other. Handling the challenge
Footwear Science Publication details, including instructions for authors and subscription information:
 This article was downloaded by: [Eveline Graf] On: 23 May 2013, At: 04:28 Publisher: Taylor & Francis Informa Ltd Registered in England and Wales Registered Number: 1072954 Registered office: Mortimer
This article was downloaded by: [Eveline Graf] On: 23 May 2013, At: 04:28 Publisher: Taylor & Francis Informa Ltd Registered in England and Wales Registered Number: 1072954 Registered office: Mortimer
Treating Foot Pain in Alpine Skiers with
 SPORTS PODIATry Treating Foot Pain in Alpine Skiers with Pes Planus What role should the podiatrist play? 103 By Lawrence Z. Huppin, DPM and Paul R. Scherer, DPM Jakub Gojda Dreamstime The foot plays a
SPORTS PODIATry Treating Foot Pain in Alpine Skiers with Pes Planus What role should the podiatrist play? 103 By Lawrence Z. Huppin, DPM and Paul R. Scherer, DPM Jakub Gojda Dreamstime The foot plays a
Effect of footwear on standing balance in healthy young adult males
 J Musculoskelet Neuronal Interact 2018; 18(1):71-75 Journal of Musculoskeletal and Neuronal Interactions Original Article Effect of footwear on standing balance in healthy young adult males A.H. Alghadir,
J Musculoskelet Neuronal Interact 2018; 18(1):71-75 Journal of Musculoskeletal and Neuronal Interactions Original Article Effect of footwear on standing balance in healthy young adult males A.H. Alghadir,
The clinical assessment of the normal and abnormal foot during locomotion
 The clinical assessment of the normal and abnormal foot during locomotion M. T. MANLEY and E. SOLOMON Department of Biomedical Engineering, University of Cape Town and Groote, Republic of South Africa
The clinical assessment of the normal and abnormal foot during locomotion M. T. MANLEY and E. SOLOMON Department of Biomedical Engineering, University of Cape Town and Groote, Republic of South Africa
Assessment of the influence of jogging on the shape of female foot arches
 Annals of Agricultural and Environmental Medicine 2017, Vol 24, No 4, 596 601 www.aaem.pl ORIGINAL ARTICLE Assessment of the influence of jogging on the shape of female foot arches Agata Maslon 1, Joanna
Annals of Agricultural and Environmental Medicine 2017, Vol 24, No 4, 596 601 www.aaem.pl ORIGINAL ARTICLE Assessment of the influence of jogging on the shape of female foot arches Agata Maslon 1, Joanna
The relationship between the height of the medial longitudinal arch (MLA) and the ankle and knee injuries in professional runners
 Available online at www.sciencedirect.com The Foot 18 (2008) 84 90 The relationship between the height of the medial longitudinal arch (MLA) and the ankle and knee injuries in professional runners Z. Nakhaee
Available online at www.sciencedirect.com The Foot 18 (2008) 84 90 The relationship between the height of the medial longitudinal arch (MLA) and the ankle and knee injuries in professional runners Z. Nakhaee
The study on exercise effects by the change of elastics and angle of the Insole
 The study on exercise effects by the change of elastics and angle of the Insole Lee, Chang-Min, Oh, Yeon-ju, Kim, Jin-Hoon Department of Industrial and Management Engineering Dong-Eui University Gaya-Dong
The study on exercise effects by the change of elastics and angle of the Insole Lee, Chang-Min, Oh, Yeon-ju, Kim, Jin-Hoon Department of Industrial and Management Engineering Dong-Eui University Gaya-Dong
BIOMECHANICAL EVALUATION OF RUNNING AND SOCCER SHOES: METHODOLOGY AND TESTING PROCEDURES. Ewald M. Hennig
 BIOMECHANICAL EVALUATION OF RUNNING AND SOCCER SHOES: METHODOLOGY AND TESTING PROCEDURES Ewald M. Hennig Biomechanics Laboratory, University Duisburg-Essen, Essen, Germany Running shoes are the footwear,
BIOMECHANICAL EVALUATION OF RUNNING AND SOCCER SHOES: METHODOLOGY AND TESTING PROCEDURES Ewald M. Hennig Biomechanics Laboratory, University Duisburg-Essen, Essen, Germany Running shoes are the footwear,
Purpose. Outline. Angle definition. Objectives:
 Disclosure Information AACPDM 69 th Annual Meeting October 21-24, 2015 Speaker Names: Sylvia Õunpuu, MSc and Kristan Pierz, MD Gait Analysis Data Interpretation: Understanding Kinematic Relationships Within
Disclosure Information AACPDM 69 th Annual Meeting October 21-24, 2015 Speaker Names: Sylvia Õunpuu, MSc and Kristan Pierz, MD Gait Analysis Data Interpretation: Understanding Kinematic Relationships Within
FALL-RELATED HIP FRACTURES contribute substantially. Age-Related Changes in Spatial and Temporal Gait Variables
 31 Age-Related Changes in Spatial and Temporal Gait Variables Penny C. Grabiner, BSN, S. Tina Biswas, BSE, Mark D. Grabiner, PhD ABSTRACT. Grabiner PC, Biswas ST, Grabiner MD. Agerelated changes in spatial
31 Age-Related Changes in Spatial and Temporal Gait Variables Penny C. Grabiner, BSN, S. Tina Biswas, BSE, Mark D. Grabiner, PhD ABSTRACT. Grabiner PC, Biswas ST, Grabiner MD. Agerelated changes in spatial
Centre of pressure characteristics in normal, planus and cavus feet
 Buldt et al. Journal of Foot and Ankle Research (2018) 11:3 DOI 10.1186/s13047-018-0245-6 RESEARCH Open Access Centre of pressure characteristics in normal, planus and cavus feet Andrew K. Buldt 1,2*,
Buldt et al. Journal of Foot and Ankle Research (2018) 11:3 DOI 10.1186/s13047-018-0245-6 RESEARCH Open Access Centre of pressure characteristics in normal, planus and cavus feet Andrew K. Buldt 1,2*,
Research Report. Measurements Used to Characterize the Foot and the Medial Longitudinal Arch: Reliability and Validity. Key Words:
 Research Report Measurements Used to Characterize the Foot and the Medial Longitudinal Arch: Reliability and Validity Background and Purpose. Abnormality in the structure of the medial longitudinal arch
Research Report Measurements Used to Characterize the Foot and the Medial Longitudinal Arch: Reliability and Validity Background and Purpose. Abnormality in the structure of the medial longitudinal arch
The running economy difference between running barefoot and running shod
 Proceeding 9th INSHS International Christmas Sport Scientific Conference, 4-6 December 2014. International Network of Sport and Health Science. Szombathely, Hungary The running economy difference between
Proceeding 9th INSHS International Christmas Sport Scientific Conference, 4-6 December 2014. International Network of Sport and Health Science. Szombathely, Hungary The running economy difference between
Foot Anthropometric Profile of High School Students in Bandung
 AMJ. 2018;5(2):93 7 93 Foot Anthropometric Profile of High School Students in Bandung Imam Ramdhani Abdurrahman, 1 Alwin Tahid, 2 Fathurachman 3 1 Faculty of Medicine Universitas Padjadjaran, Indonesia,
AMJ. 2018;5(2):93 7 93 Foot Anthropometric Profile of High School Students in Bandung Imam Ramdhani Abdurrahman, 1 Alwin Tahid, 2 Fathurachman 3 1 Faculty of Medicine Universitas Padjadjaran, Indonesia,
IJSPT ORIGINAL RESEARCH ABSTRACT
 IJSPT ORIGINAL RESEARCH THE USE OF A STATIC MEASURE TO PREDICT FOOT POSTURE AT MIDSUPPORT DURING RUNNING Michael B. Bade, PT, DPT, PhD 1 Timothy L. Chi, SPT 1 Kelly C. Farrell, SPT 1 Amanda J. Gresl, SPT
IJSPT ORIGINAL RESEARCH THE USE OF A STATIC MEASURE TO PREDICT FOOT POSTURE AT MIDSUPPORT DURING RUNNING Michael B. Bade, PT, DPT, PhD 1 Timothy L. Chi, SPT 1 Kelly C. Farrell, SPT 1 Amanda J. Gresl, SPT
Sample Biomechanical Report
 Sample Biomechanical Report To identify the root cause of an injury, and thus determine the optimal treatment for that injury, many pieces of your injury puzzle must be considered. At the Running Injury
Sample Biomechanical Report To identify the root cause of an injury, and thus determine the optimal treatment for that injury, many pieces of your injury puzzle must be considered. At the Running Injury
4/15/17. The Foot Core Paradigm. The Foot Core Concept. A Key to Healthy Feet. International Foot and Ankle Symposium, 2012
 The Foot Core Paradigm A Key to Healthy Feet Irene S. Davis, PhD, PT, FAPTA, FACSM, FASB Director, Spaulding National Running Center Professor, Harvard Medical School The Foot Core Concept International
The Foot Core Paradigm A Key to Healthy Feet Irene S. Davis, PhD, PT, FAPTA, FACSM, FASB Director, Spaulding National Running Center Professor, Harvard Medical School The Foot Core Concept International
Changes in plantar load distribution and gait pattern following foot drop correction in leprosy affected patients
 Lepr Rev (2015) 86, 213 219 Changes in plantar load distribution and gait pattern following foot drop correction in leprosy affected patients MRINMOY KARMAKAR*, JERRY JOSHUA* & NIDHU MAHATO* *Premananda
Lepr Rev (2015) 86, 213 219 Changes in plantar load distribution and gait pattern following foot drop correction in leprosy affected patients MRINMOY KARMAKAR*, JERRY JOSHUA* & NIDHU MAHATO* *Premananda
Grip Force and Heart Rate Responses to Manual Carrying Tasks: Effects of Material, Weight, and Base Area of the Container
 International Journal of Occupational Safety and Ergonomics (JOSE) 2014, Vol. 20, No. 3, 377 383 Grip Force and Heart Rate Responses to Manual Carrying Tasks: Effects of Material, Weight, and Base Area
International Journal of Occupational Safety and Ergonomics (JOSE) 2014, Vol. 20, No. 3, 377 383 Grip Force and Heart Rate Responses to Manual Carrying Tasks: Effects of Material, Weight, and Base Area
A bit of background. Session Schedule 3:00-3:10: Introduction & session overview. Overarching research theme: CPTA
 A Cognitive-Biomechanical Perspective for the Management of Common Chronic Musculoskeletal Conditions Skulpan Asavasopon, PT, PhD Loma Linda University Christopher M. Powers, PT, PhD, FAPTA University
A Cognitive-Biomechanical Perspective for the Management of Common Chronic Musculoskeletal Conditions Skulpan Asavasopon, PT, PhD Loma Linda University Christopher M. Powers, PT, PhD, FAPTA University
Smita Rao PT PhD. Judith F. Baumhauer MD Josh Tome MS Deborah A. Nawoczenski PT PhD
 Smita Rao PT PhD Judith F. Baumhauer MD Josh Tome MS Deborah A. Nawoczenski PT PhD Strong Foot and Ankle Institute Department of Orthopaedics University of Rochester Rochester, NY Center for Foot and Ankle
Smita Rao PT PhD Judith F. Baumhauer MD Josh Tome MS Deborah A. Nawoczenski PT PhD Strong Foot and Ankle Institute Department of Orthopaedics University of Rochester Rochester, NY Center for Foot and Ankle
Palacký Univerzity in Olomouc Faculty of Physical Culture
 Project: Sophisticated biomechanic diagnostics of human movement Registration number: CZ.1.07/2.3.00/09.0209 Palacký Univerzity in Olomouc Faculty of Physical Culture Tento projekt je spolufinancován Evropským
Project: Sophisticated biomechanic diagnostics of human movement Registration number: CZ.1.07/2.3.00/09.0209 Palacký Univerzity in Olomouc Faculty of Physical Culture Tento projekt je spolufinancován Evropským
Case Report: The Infant Flatfoot
 Sergio Puigcerver (1) ; Juan Carlos González (1) ; Roser Part (1) ; Eduardo Brau (1) ; Luis Ramón Mollá (2) (1) Instituto de Biomecánica de Valencia, UPV. Valencia, Spain; ibv@ibv.upv.es ; www.ibv.org
Sergio Puigcerver (1) ; Juan Carlos González (1) ; Roser Part (1) ; Eduardo Brau (1) ; Luis Ramón Mollá (2) (1) Instituto de Biomecánica de Valencia, UPV. Valencia, Spain; ibv@ibv.upv.es ; www.ibv.org
Gait Analysis at Your Fingertips:
 Gait Analysis at Your Fingertips: Enhancing Observational Gait Analysis Using Mobile Device Technology and the Edinburgh Visual Gait Scale Jon R. Davids, MD; Shriners Hospitals for Children Northern California;
Gait Analysis at Your Fingertips: Enhancing Observational Gait Analysis Using Mobile Device Technology and the Edinburgh Visual Gait Scale Jon R. Davids, MD; Shriners Hospitals for Children Northern California;
video Purpose Pathological Gait Objectives: Primary, Secondary and Compensatory Gait Deviations in CP AACPDM IC #3 1
 s in CP Disclosure Information AACPDM 71st Annual Meeting September 13-16, 2017 Speaker Names: Sylvia Ounpuu, MSc and Kristan Pierz, MD Differentiating Between, Secondary and Compensatory Mechanisms in
s in CP Disclosure Information AACPDM 71st Annual Meeting September 13-16, 2017 Speaker Names: Sylvia Ounpuu, MSc and Kristan Pierz, MD Differentiating Between, Secondary and Compensatory Mechanisms in
Clinical Biomechanics
 Clinical Biomechanics 25 (2010) 1047 1052 Contents lists available at ScienceDirect Clinical Biomechanics journal homepage: www.elsevier.com/locate/clinbiomech Gender differences in lower extremity gait
Clinical Biomechanics 25 (2010) 1047 1052 Contents lists available at ScienceDirect Clinical Biomechanics journal homepage: www.elsevier.com/locate/clinbiomech Gender differences in lower extremity gait
The Effects of Simulated Knee Arthrodesis and Temporal Acclimation on Gait Kinematics
 The Effects of Simulated Knee Arthrodesis and Temporal Acclimation on Gait Kinematics Eric M. Lucas, MS 1, Randy Hutchison, PhD 2, Justin Marro, MS 1, Taylor Gambon 1, John D. DesJardins, PhD 1. 1 Clemson
The Effects of Simulated Knee Arthrodesis and Temporal Acclimation on Gait Kinematics Eric M. Lucas, MS 1, Randy Hutchison, PhD 2, Justin Marro, MS 1, Taylor Gambon 1, John D. DesJardins, PhD 1. 1 Clemson
