Michiel Twiss BScPT, MScPT i.a. Contact:
|
|
|
- Elvin Walters
- 5 years ago
- Views:
Transcription
1 Quest for the Holy Strike Contemporary considerations for the clinical management and prevention of running related injuries: kinematics and kinetics in forefoot and rearfoot strike patterns Michiel Twiss BScPT, MScPT i.a. Contact:
2 Content INTRODUCTION 3 METHODS 4 RESULTS 5 Kinematics of RFS and FFS 5 Kinetics of RFS and FFS 5 DISCUSSION 7 CONCLUSION 9 REFERENCES 11 APPENDIX FIGURES
3 Introduction Running has become increasingly popular with over 17 million finishers in more than races in the United States in 2015 (Chan et al., 2017). However, running entails the risk of running-related injury. Reports on the incidence of lower extremity injuries sustained from long distance running range from 20-80% in runners (van Gent et al., 2007). The most frequent injury site is at the knee with patellofemoral pain syndrome (PFPS) being the most common knee injury followed by iliotibial band syndrome (ITBS or runners knee ), plantar fasciitis and meniscal injuries (Taunton, 2002). Some runners land on their heels (heel-strikers) and some runners land on the forefoot and differences in both kinematics and kinetics during different foot-strike patterns have an effect on injury susceptibility. The purpose of this essay is to determine the influence of different footstrike patterns on prevention and clinical management of running-related injuries by comparing kinematics and kinetics of forefoot and rearfoot strike patterns during running. 3
4 Methods Searching for relevant literature was conducted in Pubmed and Google Scholar using combinations and variants of different terms such as `running`, `runners`, `foot strike pattern`, `forces`, `forefoot`, `rearfoot`, `barefoot`, `shod`, `kinetics`, `kinematics`, `injury prevention`. The choice of relevant articles was narrowed down after reading titles and abstracts. Additional articles were handsearched ensuring comprehensiveness. The literature should help to lead the discussion of this essay. 4
5 Results Two distinct foot strike patterns can be identified among runners: forefoot strike pattern (FFS) and rearfoot strike pattern (RFS). About 85% of shoed runners typically adopt an RFS or heelstrike, i.e. the heel being the first part of the food contacting the ground whereas barefoot or minimalistic-shoewear runners typically adopt a mid- or forefoot strike (Larson et al., 2011). Midfoot striking (MFS) can be considered an intermediate in the continuum of these landing patterns and will not be discussed here as a distinct pattern. Kinematics of RFS and FFS The difference in kinematics between RFS and FFS can be described as follows: At the moment of impact during RFS and FFS the hip and knee are both flexed. At initial contact during RFS, the ankle is dorsiflexed with the runner typically landing in the middle or outside of the heel. In FFS the ankle is plantarflexed with the runner typically landing on the lateral side of the forefoot on the 4th and 5th metatarsal heads or ball of the foot. During the loading response in RFS, the ankle will continue to plantarflex with the forefoot coming down to flat foot. In FFS the ankle will dorsiflex - whilst stretching and loading the plantar fascia, the calf muscles, and Achilles tendon controlling the heel descent. Knee and hip continue to flex in both RFS and FFS. However, in FFS, the knee generally flexes more compared to RFS (Lieberman, 2012). Following flat foot to midstance pronation occurs eversion, dorsiflexion, and arch stretching from heel to toe in RFS with the ankle dorsiflexing. At the same time the lower leg moves forward relative to the foot causing eversion. The foot (flat on the ground) will start to stretch the arch. In FFS pronation occurs in opposite direction from toe to heel. In both RFS and FFS knee and hip extension occur during midstance to toe off with the ankle plantarflexing and lifting the heel of the ground. The arch recoils, flexing the toes causing upward and forward acceleration of the body preparing for the next rearfoot impact. ( Running Barefoot: Biomechanics of Foot Strike, n.d.) Kinetics of RFS and FFS The ground reaction force (GRF) with its corresponding torque and the controlling/counteracting muscle forces and their corresponding torques are the source of joint loading in the lower leg during distinct foot strike patterns. The difference in kinetics of both strike patterns is described below. 5
6 RFS and FFS kinetics at initial contact and loading response At the moment of impact during RFS, the vertical GRF vector lies behind the axis of the ankle joint causing a clockwise ankle moment. In contrast, at the moment of impact during FFS, the GRF vector is in front of the axis of the ankle joint causing an anti-clockwise moment, i.e. the top of the foot will come towards the shank. During the loading response in RFS, a counteracting muscle force is delivered through the eccentric activity of the M. tibialis anterior (TA) controlling any slapping down of the foot and pronation whereas in FFS the counteracting muscle force will be delivered by the eccentric activity of the M. gastrocnemius (GAS) and M. Soleus (SOL) which both control the downward motion of the heel pad (Fig.1). RFS and FFS kinetics at midstance and swing There are significant differences in joint torques when running either RFS or FFS across the stride (midstance and swing). Knee moments are significantly larger and ankle moments are significantly smaller during RFS in comparison to FFS. Furthermore, across the stride during RFS the knee shows greater peak instantaneous power absorption though much smaller peak instantaneous power absorption at the ankle compared to FFS (Stearne, Alderson, Green, Donnelly, & Rubenson, 2014) (Fig. 2). Additional kinetic data from Stearne et al. regarding energy absorption at the individual joints during stance indicate that energy is more or less equally distributed at the ankle and knee during RFS (45.2% at the ankle and 41.1% at the knee). In contrast, in habitual FFS runners, the ankle contributes much more to negative work (energy absorption) compared to the knee (62.4% ankle vs 25.7% knee) and also compared to RFS (62.4% ankle FFS and 45.2% ankle RFS) (Fig. 3). Hip joint moments and power absorption do not show significant differences when comparing both patterns. 6
7 Discussion Comparison of the biomechanics of habitual RFS- with habitual FFS runners shows different strains within the lower limb joints. Habitual RFS runners place more demand on the knee joint in both sagittal and frontal planes compared to FFS whereas habitual FFS runners place more demand on the ankle joint in the sagittal plane (Stearne et al., 2014). Stearne et al. measured vertical forces based on the GRF using inverse dynamics to calculate the net joint moments and energy absorption (power) in both patterns. Given the knee being the predominant site of injury (van Gent et al., 2007) and 85% of shoed runners adopt an RFS pattern (Knorz et al., 2017) these results suggest that habitual RFS runners with knee problems could benefit from switching to an FFS pattern. However, shear forces (AP and ML components) need to be considered. These were not calculated in the study by Stearne. Other research shows that shear forces can amount to relevant levels for previously injured joints with instability and/or pre-existing cartilage damage during running (Knorz et al., 2017): Knorz was able to demonstrate that for the ankle, the knee and the hip moderate but significantly higher shear forces arise during FFS with the exception of the knee in APdirection. Loading rates (LR) in FFS in all three joints remained lower in most directions compared to LR in RFS, with the exception of higher AP-LR at both the ankle and the hip as well as higher ML-LR at the hip during FFS (Fig. 4). Regarding the hip, Knorz et al. write that biomechanical analyses are difficult, `due to the anatomic position of the hip joint close to the center of the body` with data difficult to interpret. Albeit, these findings are consistent with other research revealing that FFS is associated with higher ankle joint stress. For physiotherapists and other healthcare practitioners, this could mean that specific recommendations can be made to runners with unstable ankle joints, tendon pathology or hip problems. These runners may benefit from or switching to RFS. Also, habitual FFS runners switching from FFS to RFS are able to replicate the joint mechanical characteristics demonstrated by habitual RFS runners. Interestingly, style switching did not increase frontal plane knee loads as in habitual RFS runners and it required less positive mechanical average power in the limb at the same running speed of habitual RFS runners (Stearne et al., 2014). Switching to RFS - while maintaining mechanical performance - in injury rehabilitation of abovementioned pathologies may be a useful strategy. As can be seen in Figure 4, because FFS was associated with significantly lower shear forces in the AP-direction in the knee, FFS may be favored for runners with previous specific knee injuries such as ACL-tears or patellofemoral pain syndrome (PFPS). Data from a case series showed that adopting an FFS was beneficial in patients with patellofemoral pain 7
8 (Cheung & Davis, 2011) and another study demonstrated the effectiveness of a two-week gait modification training in reducing vertical impact loads (Chan et al., 2017). According to the authors, the gait retraining group may have shifted to a more midfoot or forefoot strike. Also, at follow up at 12-months, the gait retraining group had a much lower injury rate compared to the controls, 16% to 38% respectively. Several limitations of this study will be discussed below, also with regards to potential future research. 8
9 Conclusion Running is an incredibly popular fitness activity. In particular, running is of low cost and an easy-to-implement intervention to maintain overall fitness and prevent cardiovascular, musculoskeletal and psychological disease. However, running is associated with increased risk of injury. This essay sought after the influence of two distinct strike patterns on running mechanics and tissue loading (at the joint, muscle, tendon and bone level) to determine if the application of one strike pattern over the other might provide beneficial effects with regards to prevention and management of running related injuries. Running mechanics, in general, have been studied for hundreds of years and researchers are still trying to better understand the relationship between running biomechanics and injury (McClay, 2000). Biomechenical research comparing both strike patterns is booming and generally indicates that FFS may lead to higher MPF (shear forces) and RFS seem to lead to higher LR. Higher LR in RFS probably results from the impact peak at initial contact (heel landing) whereas higher shear forces in FFS are a consequence of reduced ground contact time (Knorz et al., 2017). Higher LR is considered an important factor for running injuries (McClay, 2000) with RFS runners being more at more risk for running injuries. Converting to an FFS pattern may positively influence the course of running injuries (Davis, Rice, & Wearing, 2017). Higher shear forces may be detrimental in previously injured joints with instability and/or pre-existing cartilage and thus moderately higher AP and ML components during FFS in the ankle and hip joints (Knorz et al., 2017) should be taken into consideration when managing pre-existing injuries in these joints. Up until recently, kinetic data of running mechanics was only accessible through biomechanical research in the laboratory setting. The developments of wearable technology (GPS watches, tibial accelerometers) now allow for analysis outside the laboratory (Willy, 2017). As mentioned in the discussion, a gait retraining program was proven to be effective in reducing vertical loading rates. The study found a reduction in injury rates for the gait retraining group suggesting that by changing gait style, mechanical loads and injury rates could be influenced. Among several limitations in this study are that the gait retraining group requires a biomechanics laboratory. Furthermore, the study did not assess gait mechanics outside the laboratory thus it is unknown if the participants maintained gait changes after training. Also, the study did not measure volume or intensity (faster or slower running) between both groups thus leaving the interpretation of why injury rates were different open for discussion. An interesting future research project could be to determine if wearable technology could ontrol for these confounding factors and overcome the abovementioned study limitations? GPS watches may be more accurate in measuring training loads parameters such as running speed and total volume compared to self-reported measures. Additional controlling for these confounding factors in the field will be valuable in interpreting biomechanical data obtained in the laboratory. Tibial accelerometers and 9
10 pressure sensitive insoles could also provide additional biomechanical data and real-time feedback could assist in gait retraining. However, additional data provided by wearable technology must be accurate and reliable.thus, further research will be needed to test accuracy, reliability, and validity of wearable technology. 10
11 References C2ST TV. (n.d.). Biomechanics of Running: The Science of Movement - Steven McCaw. Retrieved from Chan, Z. Y. S., Zhang, J. H., Au, I. P. H., An, W. W., Shum, G. L. K., Ng, G. Y. F., & Cheung, R. T. H. (2017). Gait Retraining for the Reduction of Injury Occurrence in Novice Distance Runners: 1-Year Follow-up of a Randomized Controlled Trial. The American Journal of Sports Medicine, Cheung, R. T. H., & Davis, I. S. (2011). Landing pattern modification to improve patellofemoral pain in runners: a case series. The Journal of Orthopaedic and Sports Physical Therapy, 41(12), Davis, I. S., Rice, H. M., & Wearing, S. C. (2017). Why forefoot striking in minimal shoes might positively change the course of running injuries. Journal of Sport and Health Science, 6(2), Knorz, S., Kluge, F., Gelse, K., Schulz-Drost, S., Hotfiel, T., Lochmann, M., Krinner, S. (2017). Three-Dimensional Biomechanical Analysis of Rearfoot and Forefoot Running. Orthopaedic Journal of Sports Medicine, 5(7), Larson, P., Higgins, E., Kaminski, J., Decker, T., Preble, J., Lyons, D., Normile, A. (2011). Foot strike patterns of recreational and sub-elite runners in a long-distance road race. Journal of Sports Sciences, 29(15), Lieberman, D. E. (2012). What we can learn about running from barefoot running: an evolutionary medical perspective. Exercise and Sport Sciences Reviews, 40(2), McClay, I. (2000). The evolution of the study of the mechanics of running. Relationship to injury. Journal of the American Podiatric Medical Association, 90(3),
12 Richards, J. (2008). Biomechanics in clinic and research: an interactive teaching and learning course. Edinburgh ; New York: Churchill Livingstone/Elsevier. Running Barefoot: Biomechanics of Foot Strike. (n.d.). Retrieved December 12, 2017, from Stearne, S. M., Alderson, J. A., Green, B. A., Donnelly, C. J., & Rubenson, J. (2014). Joint kinetics in rearfoot versus forefoot running: implications of switching technique. Medicine and Science in Sports and Exercise, 46(8), Taunton, J. E. (2002). A retrospective case-control analysis of 2002 running injuries. British Journal of Sports Medicine, 36(2), van Gent, R. N., Siem, D., van Middelkoop, M., van Os, A. G., Bierma-Zeinstra, S. M. A., Koes, B. W., & Taunton, J. E. (2007). Incidence and determinants of lower extremity running injuries in long distance runners: a systematic review * COMMENTARY. British Journal of Sports Medicine, 41(8), Willy, R. W. (2017). Innovations and pitfalls in the use of wearable devices in the prevention and rehabilitation of running related injuries. Physical Therapy in Sport: Official Journal of the Association of Chartered Physiotherapists in Sports Medicine, 29,
13 Appendix Figures 1-4 Fig.1 Vertical ground reaction force causing clockwise moment in RFS pattern (left) and anti-clockwise moment in FFS pattern (right) (C2ST TV, n.d.) Fig. 2 Ankle, knee and hip joint moments (A) and instantaneous powers (B) Stearne et al., 2014) across the stride (stance and swing) (Stearne et al., 2014) 13
14 Fig. 3 Distribution of positive and negative work during the stance phase (Stearne et al., 2014) Fig. 4 Maximum peak force (MPF) and loading rates (LR) in RFS and FFS in mean pair differences. (Knorz et al., 2017) 14
Foot Biomechanics Getting Back to the Base
 Foot Biomechanics Getting Back to the Base Christopher J. Mehallo, D.O. Rothman Institute Orthopaedics Objectives Understand basic foot biomechanics during walking and running Understand common sports
Foot Biomechanics Getting Back to the Base Christopher J. Mehallo, D.O. Rothman Institute Orthopaedics Objectives Understand basic foot biomechanics during walking and running Understand common sports
Steffen Willwacher, Katina Fischer, Gert Peter Brüggemann Institute of Biomechanics and Orthopaedics, German Sport University, Cologne, Germany
 P01-3 ID126 SURFACE STIFFNESS AFFECTS JOINT LOADING IN RUNNING Steffen Willwacher, Katina Fischer, Gert Peter Brüggemann Institute of Biomechanics and Orthopaedics, German Sport University, Cologne, Germany
P01-3 ID126 SURFACE STIFFNESS AFFECTS JOINT LOADING IN RUNNING Steffen Willwacher, Katina Fischer, Gert Peter Brüggemann Institute of Biomechanics and Orthopaedics, German Sport University, Cologne, Germany
Running Gait Mechanics. Walking vs Running. Ankle Joint Complex Sagittal Plane. As speed increases, when has walking ended and running begun?
 Running Gait Mechanics Walking vs Running As speed increases, when has walking ended and running begun? Ankle Joint Complex Sagittal Plane 1 Ankle Joint Complex Sagittal Plane Pos. @FS 5 o DF Absorption
Running Gait Mechanics Walking vs Running As speed increases, when has walking ended and running begun? Ankle Joint Complex Sagittal Plane 1 Ankle Joint Complex Sagittal Plane Pos. @FS 5 o DF Absorption
10/22/15. Walking vs Running. Normal Running Mechanics. Treadmill vs. Overground Are they the same? Importance of Gait Analysis.
 2 angle (deg) 1/22/1 Normal Running Mechanics Walking vs Running Irene Davis, PhD, PT, FACSM, FAPTA, FASB Director, Spaulding National Running Center Walking Periods of DOUBLE SUPPORT Running Periods of
2 angle (deg) 1/22/1 Normal Running Mechanics Walking vs Running Irene Davis, PhD, PT, FACSM, FAPTA, FASB Director, Spaulding National Running Center Walking Periods of DOUBLE SUPPORT Running Periods of
As a physiotherapist I see many runners in my practice,
 When rubber meets road Mark Richardson reveals the story that our running shoes can tell us, and how it can help you avoid running injury at a glance This article: Shows you how to analyse the sole of
When rubber meets road Mark Richardson reveals the story that our running shoes can tell us, and how it can help you avoid running injury at a glance This article: Shows you how to analyse the sole of
Normal Gait and Dynamic Function purpose of the foot in ambulation. Normal Gait and Dynamic Function purpose of the foot in ambulation
 Normal Gait and Dynamic Function purpose of the foot in ambulation Edward P. Mulligan, PT, DPT, OCS, SCS, ATC Assistant Professor; Residency Chair UT Southwestern School of Health Professions Department
Normal Gait and Dynamic Function purpose of the foot in ambulation Edward P. Mulligan, PT, DPT, OCS, SCS, ATC Assistant Professor; Residency Chair UT Southwestern School of Health Professions Department
Running injuries - what are the most important factors
 Created as a free resource by Clinical Edge Based on Physio Edge podcast 59 with Greg Lehman, Tom Goom and Dr Christian Barton Get your free trial of online Physio education at Why do runners get injured?
Created as a free resource by Clinical Edge Based on Physio Edge podcast 59 with Greg Lehman, Tom Goom and Dr Christian Barton Get your free trial of online Physio education at Why do runners get injured?
Running from injury 2
 Created as a free resource by Clinical Edge Based on Physio Edge podcast 049 with Dr Rich Willy Get your free trial of online Physio education by clicking here Running injuries & assessment Running assessment
Created as a free resource by Clinical Edge Based on Physio Edge podcast 049 with Dr Rich Willy Get your free trial of online Physio education by clicking here Running injuries & assessment Running assessment
Running Injuries in Adolescents Jeffrey Shilt, M.D. Part 1 Page 1
 Running Injuries in Adolescents Jeffrey Shilt, M.D. Chief Surgical Officer, The Woodlands, Texas Children's Hospital Associate Professor, Orthopedic and Scoliosis Surgery, Baylor College of Medicine Part
Running Injuries in Adolescents Jeffrey Shilt, M.D. Chief Surgical Officer, The Woodlands, Texas Children's Hospital Associate Professor, Orthopedic and Scoliosis Surgery, Baylor College of Medicine Part
ASSESMENT Introduction REPORTS Running Reports Walking Reports Written Report
 ASSESMENT REPORTS Introduction Left panel Avatar Playback Right Panel Patient Gait Parameters Report Tab Click on parameter to view avatar at that point in time 2 Introduction Software will compare gait
ASSESMENT REPORTS Introduction Left panel Avatar Playback Right Panel Patient Gait Parameters Report Tab Click on parameter to view avatar at that point in time 2 Introduction Software will compare gait
Chapter 1 - Injury overview Chapter 2 - Fit for Running Assessment Chapter 3 - Soft Tissue Mobilization... 21
 Table of Contents Introduction Chapter 1 - Injury overview... 6 Chapter 2 - Fit for Running Assessment... 13 Chapter 3 - Soft Tissue Mobilization... 21 Chapter 4 - Dynamic Warm-up... 28 Chapter 5 - Strengthening...
Table of Contents Introduction Chapter 1 - Injury overview... 6 Chapter 2 - Fit for Running Assessment... 13 Chapter 3 - Soft Tissue Mobilization... 21 Chapter 4 - Dynamic Warm-up... 28 Chapter 5 - Strengthening...
Outline. Biomechanics of Running. Biomechanics of Running 3/11/2011. Born to Run : A Biomechanical Analysis of Barefoot vs.
 Born to Run : A Biomechanical Analysis of Barefoot vs. Shod Running Linfield College Alicia Amsberry, Brooke Bekkedahl, & Michelle Weber Outline The Biomechanics of Running Barefoot vs. Shod-Running Vibram
Born to Run : A Biomechanical Analysis of Barefoot vs. Shod Running Linfield College Alicia Amsberry, Brooke Bekkedahl, & Michelle Weber Outline The Biomechanics of Running Barefoot vs. Shod-Running Vibram
Giovanni Alfonso Borelli Father of Biomechanics
 Giovanni Alfonso Borelli Father of Biomechanics 1608-1679 Peter Guy BSc DCh Private practice Whitby and Peterborough Professor Chiropody Faculty Michener Institute of Education at UHN Advisory Board Member
Giovanni Alfonso Borelli Father of Biomechanics 1608-1679 Peter Guy BSc DCh Private practice Whitby and Peterborough Professor Chiropody Faculty Michener Institute of Education at UHN Advisory Board Member
Ankle biomechanics demonstrates excessive and prolonged time to peak rearfoot eversion (see Foot Complex graph). We would not necessarily expect
 Case Study #1 The first case study is a runner presenting with bilateral shin splints with pain and tenderness along the medial aspect of the tibia. The symptoms have increased significantly over the last
Case Study #1 The first case study is a runner presenting with bilateral shin splints with pain and tenderness along the medial aspect of the tibia. The symptoms have increased significantly over the last
Normal and Abnormal Gait
 Normal and Abnormal Gait Adrielle Fry, MD EvergreenHealth, Division of Sport and Spine University of Washington Board Review Course March 6, 2017 What are we going to cover? Definitions and key concepts
Normal and Abnormal Gait Adrielle Fry, MD EvergreenHealth, Division of Sport and Spine University of Washington Board Review Course March 6, 2017 What are we going to cover? Definitions and key concepts
A Comparison of Lower Extremity Joint Work and Initial Loading Rates among Four Different Running Styles
 A Comparison of Lower Extremity Joint Work and Initial Loading Rates among Four Different Running Styles Donald Lee Goss A dissertation submitted to the faculty of the University of North Carolina at Chapel
A Comparison of Lower Extremity Joint Work and Initial Loading Rates among Four Different Running Styles Donald Lee Goss A dissertation submitted to the faculty of the University of North Carolina at Chapel
HVORFOR OPSTÅR LØBESKADER?
 HVORFOR OPSTÅR LØBESKADER? PT, MHSc, PhD Post Doc at Section for Sport Science, Department of Public Health, Aarhus Universitet. Idrætsskader, epidemiologi og statistik OUR RESEARCH GROUP: Research coordinator
HVORFOR OPSTÅR LØBESKADER? PT, MHSc, PhD Post Doc at Section for Sport Science, Department of Public Health, Aarhus Universitet. Idrætsskader, epidemiologi og statistik OUR RESEARCH GROUP: Research coordinator
The Problem. An Innovative Approach to the Injured Runner. Dosage. Mechanics. Structure! Postural Observations. Lower Quarter Assessment
 The Problem An Innovative Approach to the Injured Runner Irene S. Davis, PhD, PT, FAPTA, FACSM Director, Spaulding National Running Center Harvard Medical School Healthy People 2020 Initiative 76% runners
The Problem An Innovative Approach to the Injured Runner Irene S. Davis, PhD, PT, FAPTA, FACSM Director, Spaulding National Running Center Harvard Medical School Healthy People 2020 Initiative 76% runners
Running Medicine: A Clinican s Overview Nicholas Shannon, BApSci (Clin Sci), BChiroSci
 : A Clinican s Overview Nicholas, BApSci (Clin Sci), BChiroSci Private Practice Suite 2.13, 343 Little Collins Street, Melbourne, VIC 3000, Australia : A Clinican s Overview ABSTRACT Background: Running
: A Clinican s Overview Nicholas, BApSci (Clin Sci), BChiroSci Private Practice Suite 2.13, 343 Little Collins Street, Melbourne, VIC 3000, Australia : A Clinican s Overview ABSTRACT Background: Running
My pa;ents are ocen keen to quiz me about it, I expect yours are as well.
 Wed 11am T12 This summer I'm publishing a book on lower limb tendinopathy and this presenta;on is essen;ally a spin-off from my research for the book and my clinical work with novice runners. 1 My pa;ents
Wed 11am T12 This summer I'm publishing a book on lower limb tendinopathy and this presenta;on is essen;ally a spin-off from my research for the book and my clinical work with novice runners. 1 My pa;ents
Joint contact loading in forefoot and rearfoot strike patterns during running
 Graduate Theses and Dissertations Graduate College 211 Joint contact loading in forefoot and rearfoot strike patterns during running Brandon David Rooney Iowa State University Follow this and additional
Graduate Theses and Dissertations Graduate College 211 Joint contact loading in forefoot and rearfoot strike patterns during running Brandon David Rooney Iowa State University Follow this and additional
Foot mechanics & implications on training, posture and movement
 Foot mechanics & implications on training, posture and movement Three Arches Three Arches These arches are not reciprocal. When the foot pronates ALL arches should fall. If the medial arch falls and the
Foot mechanics & implications on training, posture and movement Three Arches Three Arches These arches are not reciprocal. When the foot pronates ALL arches should fall. If the medial arch falls and the
Recent Advances in Orthotic Therapy for. Plantar Fasciitis. An Evidence Based Approach. Lawrence Z. Huppin, D.P.M.
 Recent Advances in Orthotic Therapy for Plantar Fasciitis An Evidence Based Approach Lawrence Z. Huppin, D.P.M. Assistant Clinical Professor, Western University of Health Sciences, College of Podiatric
Recent Advances in Orthotic Therapy for Plantar Fasciitis An Evidence Based Approach Lawrence Z. Huppin, D.P.M. Assistant Clinical Professor, Western University of Health Sciences, College of Podiatric
Running Form Modification: When Self-selected is Not Preferred
 Running Form Modification: When Self-selected is Not Preferred Bryan Heiderscheit, PT, PhD Department of Orthopedics and Rehabilitation Department of Biomedical Engineering University of Wisconsin-Madison
Running Form Modification: When Self-selected is Not Preferred Bryan Heiderscheit, PT, PhD Department of Orthopedics and Rehabilitation Department of Biomedical Engineering University of Wisconsin-Madison
Case Study: Chronic Plantar Heel Pain/Plantar Fasciopathy. CASE STUDY PRESENTATION by Resonance Podiatry and Gait Labs
 Case Study: Chronic Plantar Heel Pain/Plantar Fasciopathy CASE STUDY PRESENTATION by Resonance Podiatry and Gait Labs THE PATIENT 43yo female, professional netball umpire 6 month history right plantar
Case Study: Chronic Plantar Heel Pain/Plantar Fasciopathy CASE STUDY PRESENTATION by Resonance Podiatry and Gait Labs THE PATIENT 43yo female, professional netball umpire 6 month history right plantar
MINIMALIST / BAREFOOT RUNNING
 MINIMALIST / BAREFOOT RUNNING DR GAVIN SHANG SPORTS PHYSICIAN MBBCH (WITS) MPHIL SPORTS MED (UCT/SSISA) BORN TO RUN BAREFOOT RUNNING Tarahumara Indians: Persistence hunting and thermo-regulatory advantage
MINIMALIST / BAREFOOT RUNNING DR GAVIN SHANG SPORTS PHYSICIAN MBBCH (WITS) MPHIL SPORTS MED (UCT/SSISA) BORN TO RUN BAREFOOT RUNNING Tarahumara Indians: Persistence hunting and thermo-regulatory advantage
WalkOn product range. Dynamic Ankle-Foot Orthoses. Information for specialist dealers
 WalkOn product range Dynamic Ankle-Foot Orthoses Information for specialist dealers WalkOn Flex WalkOn WalkOn Trimable WalkOn Reaction WalkOn Reaction plus One range Many different applications The WalkOn
WalkOn product range Dynamic Ankle-Foot Orthoses Information for specialist dealers WalkOn Flex WalkOn WalkOn Trimable WalkOn Reaction WalkOn Reaction plus One range Many different applications The WalkOn
Diabetes and Orthoses. Rob Bradbury Talar Made
 Diabetes and Orthoses Rob Bradbury Talar Made Diabetes High prevalence disease 4-6% in UK (over 2.5 mill diagnosed and a further 0.5 ) 6+% in USA 40% in some parts of Middle East (may be higher in Indian
Diabetes and Orthoses Rob Bradbury Talar Made Diabetes High prevalence disease 4-6% in UK (over 2.5 mill diagnosed and a further 0.5 ) 6+% in USA 40% in some parts of Middle East (may be higher in Indian
Arch Height and Running Shoes: The Best Advice to Give Patients
 Arch Height and Running Shoes: The Best Advice to Give Patients by Thomas C. Michaud, DC Published May 1, 2014 by Dynamic Chiropractic Magazine Because runners with different arch heights are prone to
Arch Height and Running Shoes: The Best Advice to Give Patients by Thomas C. Michaud, DC Published May 1, 2014 by Dynamic Chiropractic Magazine Because runners with different arch heights are prone to
Running head: LOWER EXTREMITY JOINT REACTION FORCES 1. Jamie M. Rogers
 Running head: LOWER EXTREMITY JOINT REACTION FORCES 1 The Effect of Barefoot Running Using Two Running Styles on Lower Extremity Joint Reaction Forces Jamie M. Rogers A Senior Thesis submitted in partial
Running head: LOWER EXTREMITY JOINT REACTION FORCES 1 The Effect of Barefoot Running Using Two Running Styles on Lower Extremity Joint Reaction Forces Jamie M. Rogers A Senior Thesis submitted in partial
Assessments SIMPLY GAIT. Posture and Gait. Observing Posture and Gait. Postural Assessment. Postural Assessment 6/28/2016
 Assessments 2 SIMPLY GAIT Understanding movement Evaluations of factors that help therapist form professional judgments Include health, palpatory, range of motion, postural, and gait assessments Assessments
Assessments 2 SIMPLY GAIT Understanding movement Evaluations of factors that help therapist form professional judgments Include health, palpatory, range of motion, postural, and gait assessments Assessments
Footwear Science Publication details, including instructions for authors and subscription information:
 This article was downloaded by: [Eveline Graf] On: 23 May 2013, At: 04:28 Publisher: Taylor & Francis Informa Ltd Registered in England and Wales Registered Number: 1072954 Registered office: Mortimer
This article was downloaded by: [Eveline Graf] On: 23 May 2013, At: 04:28 Publisher: Taylor & Francis Informa Ltd Registered in England and Wales Registered Number: 1072954 Registered office: Mortimer
A bit of background. Session Schedule 3:00-3:10: Introduction & session overview. Overarching research theme: CPTA
 A Cognitive-Biomechanical Perspective for the Management of Common Chronic Musculoskeletal Conditions Skulpan Asavasopon, PT, PhD Loma Linda University Christopher M. Powers, PT, PhD, FAPTA University
A Cognitive-Biomechanical Perspective for the Management of Common Chronic Musculoskeletal Conditions Skulpan Asavasopon, PT, PhD Loma Linda University Christopher M. Powers, PT, PhD, FAPTA University
Research Paper Review
 Research Paper Review This review is published with the permission of Research Review Service (www.researchreviewservice.com) Barefoot Running: An Evaluation of Current Hypothesis, Future Research and
Research Paper Review This review is published with the permission of Research Review Service (www.researchreviewservice.com) Barefoot Running: An Evaluation of Current Hypothesis, Future Research and
10/24/2016. The Puzzle of Pain NMT and the Dynamic Foot Judith DeLany, LMT. Judith DeLany, LMT. NMTCenter.com. NMTCenter.com
 The Puzzle of Pain NMT and the Dynamic Foot Judith DeLany, LMT NMTCenter.com Judith DeLany, LMT NMTCenter.com Define gait cycle and its periods Consider key elements in gait Discuss foot design Consequences
The Puzzle of Pain NMT and the Dynamic Foot Judith DeLany, LMT NMTCenter.com Judith DeLany, LMT NMTCenter.com Define gait cycle and its periods Consider key elements in gait Discuss foot design Consequences
Running Stretches and Flexibility Exercises
 43 Thames Street, St Albans, Christchurch 8013 Phone: (03) 356 1353. Website: philip-bayliss.com Running Stretches and Flexibility Exercises Running is a complex, highly coordinated process involving the
43 Thames Street, St Albans, Christchurch 8013 Phone: (03) 356 1353. Website: philip-bayliss.com Running Stretches and Flexibility Exercises Running is a complex, highly coordinated process involving the
ATHLETES AND ORTHOTICS. January 29, 2014
 ATHLETES AND ORTHOTICS January 29, 2014 TOPICS TO COVER TODAY Why use an orthotic? What athlete would benefit from wearing orthotics? What device should I use: Custom versus off of the shelf orthotics?
ATHLETES AND ORTHOTICS January 29, 2014 TOPICS TO COVER TODAY Why use an orthotic? What athlete would benefit from wearing orthotics? What device should I use: Custom versus off of the shelf orthotics?
12/4/2010 3:10 / 3:40
 Running Assessment Workshop Anthony Luke MD, MPH, CAQ (Sport Med) UCSF PCSM Conference 2010 Running boom in the 70 s and 90 s Men then women % of women runners Wheelchair Evolution 26.2 miles 42.195 km
Running Assessment Workshop Anthony Luke MD, MPH, CAQ (Sport Med) UCSF PCSM Conference 2010 Running boom in the 70 s and 90 s Men then women % of women runners Wheelchair Evolution 26.2 miles 42.195 km
Lower Extremity Joint Kinematics of Shod, Barefoot, and Simulated Barefoot Treadmill Running
 Original Research Lower Extremity Joint Kinematics of Shod, Barefoot, and Simulated Barefoot Treadmill Running MICHELE LEBLANC and HEIDI FERKRANUS* Exercise Science Department, California Lutheran University,
Original Research Lower Extremity Joint Kinematics of Shod, Barefoot, and Simulated Barefoot Treadmill Running MICHELE LEBLANC and HEIDI FERKRANUS* Exercise Science Department, California Lutheran University,
KICKBIKE Your key to optimum sports performance
 KICKBIKE Your key to optimum sports performance Efficient Running is essential to optimum performance of most sports we play. Whether we want to maximize our speed, maximize our endurance, or both, an
KICKBIKE Your key to optimum sports performance Efficient Running is essential to optimum performance of most sports we play. Whether we want to maximize our speed, maximize our endurance, or both, an
video Purpose Pathological Gait Objectives: Primary, Secondary and Compensatory Gait Deviations in CP AACPDM IC #3 1
 s in CP Disclosure Information AACPDM 71st Annual Meeting September 13-16, 2017 Speaker Names: Sylvia Ounpuu, MSc and Kristan Pierz, MD Differentiating Between, Secondary and Compensatory Mechanisms in
s in CP Disclosure Information AACPDM 71st Annual Meeting September 13-16, 2017 Speaker Names: Sylvia Ounpuu, MSc and Kristan Pierz, MD Differentiating Between, Secondary and Compensatory Mechanisms in
RETRAINING RUNNING GAIT TO PREVENT LOWER EXTREMITY OVERUSE INJURIES: A REVIEW OF LITERATURE
 Retraining running gait to prevent overuse injuries 1 RETRAINING RUNNING GAIT TO PREVENT LOWER EXTREMITY OVERUSE INJURIES: A REVIEW OF LITERATURE Daniel P. Sullivan 1 1 Department of Kinesiology, San José
Retraining running gait to prevent overuse injuries 1 RETRAINING RUNNING GAIT TO PREVENT LOWER EXTREMITY OVERUSE INJURIES: A REVIEW OF LITERATURE Daniel P. Sullivan 1 1 Department of Kinesiology, San José
A Functional Approach to Improving Ankle Dorsiflexion. Knock on Effects
 Keith Thornhill PT A Functional Approach to Improving Ankle Dorsiflexion Today's article is a guest post from Keith Thornhill, current team physiotherapist at Munster Rugby (Ireland). In my experience
Keith Thornhill PT A Functional Approach to Improving Ankle Dorsiflexion Today's article is a guest post from Keith Thornhill, current team physiotherapist at Munster Rugby (Ireland). In my experience
Barefoot Running. Ed Mulligan, PT, DPT, OCS, SCS, ATC. Clinical Orthopedic Rehabilitation Education
 Barefoot Running Ed Mulligan, PT, DPT, OCS, SCS, ATC Clinical Orthopedic Rehabilitation Education Not a new concept Nov 1958 1984 Olympics Interesting Trivia Abebe Bilika won the 1960 Olympic marathon
Barefoot Running Ed Mulligan, PT, DPT, OCS, SCS, ATC Clinical Orthopedic Rehabilitation Education Not a new concept Nov 1958 1984 Olympics Interesting Trivia Abebe Bilika won the 1960 Olympic marathon
Purpose. Outline. Angle definition. Objectives:
 Disclosure Information AACPDM 69 th Annual Meeting October 21-24, 2015 Speaker Names: Sylvia Õunpuu, MSc and Kristan Pierz, MD Gait Analysis Data Interpretation: Understanding Kinematic Relationships Within
Disclosure Information AACPDM 69 th Annual Meeting October 21-24, 2015 Speaker Names: Sylvia Õunpuu, MSc and Kristan Pierz, MD Gait Analysis Data Interpretation: Understanding Kinematic Relationships Within
The importance of physical activity throughout an individual's life is indisputable. As healthcare
 What to Expect When They re Expecting: A Look at Biomechanical Changes in Walking/Running During Pregnancy Jennifer Bruer-Vandeweert, Megan Hotchkiss, Jamie Kronenberg, Kristin Olson Dr. Rumit Singh Kakar,
What to Expect When They re Expecting: A Look at Biomechanical Changes in Walking/Running During Pregnancy Jennifer Bruer-Vandeweert, Megan Hotchkiss, Jamie Kronenberg, Kristin Olson Dr. Rumit Singh Kakar,
MAKAZINAN STEWARDSHIP CONFERENCE 2017
 MAKAZINAN STEWARDSHIP CONFERENCE 2017 Aabdeg g wii enjmendaanaa gaa bi nakaziniiying Have to we remember it past here wear on our feet We have to remember what we wore on our feet in the past. A
MAKAZINAN STEWARDSHIP CONFERENCE 2017 Aabdeg g wii enjmendaanaa gaa bi nakaziniiying Have to we remember it past here wear on our feet We have to remember what we wore on our feet in the past. A
THE EFFECT OF PLANTARFLEXION ANGLE ON LANDING MECHANICS USING A WITHIN-SUBJECTS REAL-TIME FEEDBACK PROTOCOL. K. Michael Rowley
 THE EFFECT OF PLANTARFLEXION ANGLE ON LANDING MECHANICS USING A WITHIN-SUBJECTS REAL-TIME FEEDBACK PROTOCOL by K. Michael Rowley A thesis submitted to the Faculty of the University of Delaware in partial
THE EFFECT OF PLANTARFLEXION ANGLE ON LANDING MECHANICS USING A WITHIN-SUBJECTS REAL-TIME FEEDBACK PROTOCOL by K. Michael Rowley A thesis submitted to the Faculty of the University of Delaware in partial
Does Changing Step Width Alter Lower Extremity Biomechanics During Running?
 University of Tennessee, Knoxville Trace: Tennessee Research and Creative Exchange Masters Theses Graduate School 5-2012 Does Changing Step Width Alter Lower Extremity Biomechanics During Running? Richard
University of Tennessee, Knoxville Trace: Tennessee Research and Creative Exchange Masters Theses Graduate School 5-2012 Does Changing Step Width Alter Lower Extremity Biomechanics During Running? Richard
The Human Foot. The Three Major Sections of the Foot
 The Human Foot You ve heard the phrase I have one foot bigger than the other. A closer truth would be no two feet are alike, and yes in many cases one foot is larger than the other. Handling the challenge
The Human Foot You ve heard the phrase I have one foot bigger than the other. A closer truth would be no two feet are alike, and yes in many cases one foot is larger than the other. Handling the challenge
EDUCATION COURSES. Stride. Initial Swing (high knee) Mid stance Toe off Mid swing Initial contact
 EDUCATION COURSES RUNNING ANALYSIS Our purpose is performance enhancement. Improving speed and acceleration is the key to success in most ground-based sports. The ability to run from 0-5-10-20m as fast
EDUCATION COURSES RUNNING ANALYSIS Our purpose is performance enhancement. Improving speed and acceleration is the key to success in most ground-based sports. The ability to run from 0-5-10-20m as fast
Foot strike patterns and body alignment effects on muscle activity during running.
 University of Louisville ThinkIR: The University of Louisville's Institutional Repository Electronic Theses and Dissertations 3-2016 Foot strike patterns and body alignment effects on muscle activity during
University of Louisville ThinkIR: The University of Louisville's Institutional Repository Electronic Theses and Dissertations 3-2016 Foot strike patterns and body alignment effects on muscle activity during
A comparison of gait biomechanics of flip-flops, sandals, barefoot and shoes
 Zhang et al. Journal of Foot and Ankle Research 2013, 6:45 JOURNAL OF FOOT AND ANKLE RESEARCH RESEARCH Open Access A comparison of gait biomechanics of flip-flops, sandals, barefoot and shoes Xiuli Zhang
Zhang et al. Journal of Foot and Ankle Research 2013, 6:45 JOURNAL OF FOOT AND ANKLE RESEARCH RESEARCH Open Access A comparison of gait biomechanics of flip-flops, sandals, barefoot and shoes Xiuli Zhang
-Elastic strain energy (duty factor decreases at higher speeds). Higher forces act on feet. More tendon stretch. More energy stored in tendon.
 As velocity increases ( ) (i.e. increasing Froude number v 2 / gl) the component of the energy cost of transport associated with: -Internal kinetic energy (limbs accelerated to higher angular velocity).
As velocity increases ( ) (i.e. increasing Froude number v 2 / gl) the component of the energy cost of transport associated with: -Internal kinetic energy (limbs accelerated to higher angular velocity).
University Honors Program. Capstone Approval Page
 Patenaude 1 NORTHERN ILLINOIS UNIVERSITY Differences in Foot-strike Patterns during Jogging: A Literature Review A Thesis Submitted to the University Honors Program In Partial Fulfillment of the Requirements
Patenaude 1 NORTHERN ILLINOIS UNIVERSITY Differences in Foot-strike Patterns during Jogging: A Literature Review A Thesis Submitted to the University Honors Program In Partial Fulfillment of the Requirements
Dynamic/Static Foot. Tissues. Static Foot. Dynamic Foot
 Dynamic/Static Tissues Static Plantar fascia biomechanical windlass mechanism intrinsic muscles stabilize metatarsophalangeal (MP) toe joints Weight on whole foot - MP toe joints straight Plantar fascia
Dynamic/Static Tissues Static Plantar fascia biomechanical windlass mechanism intrinsic muscles stabilize metatarsophalangeal (MP) toe joints Weight on whole foot - MP toe joints straight Plantar fascia
PREVIEW ONLY 12/07/2013. Andrew Ellis. Mark Green. This webinar will begin in the next few minutes. Running Gait Analysis a minimalist approach.
 This webinar will begin in the next few minutes Live webinar technical support Please call 1800 006 293 then press 1 You will need to tell tech support that you are a webinar attendee and do not have an
This webinar will begin in the next few minutes Live webinar technical support Please call 1800 006 293 then press 1 You will need to tell tech support that you are a webinar attendee and do not have an
BIOMECHANICAL EVALUATION OF RUNNING AND SOCCER SHOES: METHODOLOGY AND TESTING PROCEDURES. Ewald M. Hennig
 BIOMECHANICAL EVALUATION OF RUNNING AND SOCCER SHOES: METHODOLOGY AND TESTING PROCEDURES Ewald M. Hennig Biomechanics Laboratory, University Duisburg-Essen, Essen, Germany Running shoes are the footwear,
BIOMECHANICAL EVALUATION OF RUNNING AND SOCCER SHOES: METHODOLOGY AND TESTING PROCEDURES Ewald M. Hennig Biomechanics Laboratory, University Duisburg-Essen, Essen, Germany Running shoes are the footwear,
Footwear Science Publication details, including instructions for authors and subscription information:
 This article was downloaded by: [University of Calgary] On: 22 May 2012, At: 07:35 Publisher: Taylor & Francis Informa Ltd Registered in England and Wales Registered Number: 1072954 Registered office:
This article was downloaded by: [University of Calgary] On: 22 May 2012, At: 07:35 Publisher: Taylor & Francis Informa Ltd Registered in England and Wales Registered Number: 1072954 Registered office:
GROUND REACTION FORCE DOMINANT VERSUS NON-DOMINANT SINGLE LEG STEP OFF
 GROUND REACTION FORCE DOMINANT VERSUS NON-DOMINANT SINGLE LEG STEP OFF Sara Gharabaghli, Rebecca Krogstad, Sara Lynch, Sofia Saavedra, and Tamara Wright California State University, San Marcos, San Marcos,
GROUND REACTION FORCE DOMINANT VERSUS NON-DOMINANT SINGLE LEG STEP OFF Sara Gharabaghli, Rebecca Krogstad, Sara Lynch, Sofia Saavedra, and Tamara Wright California State University, San Marcos, San Marcos,
Journal of Advanced Sport Technology 1(1):22-29
 Journal of Advanced Sport Technology 1(1):22-29 Original Research The effectiveness of a novel Kinesio Taping technique on the ground reaction force components during bilateral drop landing in athletes
Journal of Advanced Sport Technology 1(1):22-29 Original Research The effectiveness of a novel Kinesio Taping technique on the ground reaction force components during bilateral drop landing in athletes
Frontal Plane Moments Do Not Accurately Reflect Ankle Dynamics During Running
 Ankle Dynamics During Running 85 JOURNAL OF APPLIED BIOMECHANICS, 2005, 21, 85-95 2005 Human Kinetics Publishers, Inc. Frontal Plane Moments Do Not Accurately Reflect Ankle Dynamics During Running Kristian
Ankle Dynamics During Running 85 JOURNAL OF APPLIED BIOMECHANICS, 2005, 21, 85-95 2005 Human Kinetics Publishers, Inc. Frontal Plane Moments Do Not Accurately Reflect Ankle Dynamics During Running Kristian
SECTION 4 - POSITIVE CASTING
 4-1 SECTION 4 - POSITIVE CASTING THE SHAPE OF THE SHELL IS DERIVED FROM THE SHAPE OF THE CAST Thermo-forming plastic for orthopedic intervention was originally developed at the University of California
4-1 SECTION 4 - POSITIVE CASTING THE SHAPE OF THE SHELL IS DERIVED FROM THE SHAPE OF THE CAST Thermo-forming plastic for orthopedic intervention was originally developed at the University of California
Gait Analysis at Your Fingertips:
 Gait Analysis at Your Fingertips: Enhancing Observational Gait Analysis Using Mobile Device Technology and the Edinburgh Visual Gait Scale Jon R. Davids, MD; Shriners Hospitals for Children Northern California;
Gait Analysis at Your Fingertips: Enhancing Observational Gait Analysis Using Mobile Device Technology and the Edinburgh Visual Gait Scale Jon R. Davids, MD; Shriners Hospitals for Children Northern California;
Cardiff School of Sport DISSERTATION ASSESSMENT PROFORMA: Empirical 1
 Student name: Cardiff School of Sport DISSERTATION ASSESSMENT PROFORMA: Empirical 1 Rebecca O Brien Student ID: St20001320 Programme: SES Dissertation title: Supervisor: Comments The different mechanical
Student name: Cardiff School of Sport DISSERTATION ASSESSMENT PROFORMA: Empirical 1 Rebecca O Brien Student ID: St20001320 Programme: SES Dissertation title: Supervisor: Comments The different mechanical
An investigation of kinematic and kinetic variables for the description of prosthetic gait using the ENOCH system
 An investigation of kinematic and kinetic variables for the description of prosthetic gait using the ENOCH system K. OBERG and H. LANSHAMMAR* Amputee Training and Research Unit, University Hospital, Fack,
An investigation of kinematic and kinetic variables for the description of prosthetic gait using the ENOCH system K. OBERG and H. LANSHAMMAR* Amputee Training and Research Unit, University Hospital, Fack,
Spasticity in gait. Wessex ACPIN Spasticity Presentation Alison Clarke
 Spasticity in gait Clinicians recognise spasticity but the elements of spasticity contributing to gait patterns are often difficult to identify: Variability of muscle tone Observation/recording General
Spasticity in gait Clinicians recognise spasticity but the elements of spasticity contributing to gait patterns are often difficult to identify: Variability of muscle tone Observation/recording General
Shin Splints and Forefoot Contact Running: A Case Report
 Shin Splints and Forefoot Contact Running: A Case Report Michael 1. Cibulka, MHS, PT, OCS' David R. Sinacore, PhD, PTZ Michael 1. Mueller, PhD, PT3 Copyright 1994. All rights reserved. S hin splints are
Shin Splints and Forefoot Contact Running: A Case Report Michael 1. Cibulka, MHS, PT, OCS' David R. Sinacore, PhD, PTZ Michael 1. Mueller, PhD, PT3 Copyright 1994. All rights reserved. S hin splints are
Joint Impact of Lower Extremities in Obese and Overweight Children. Jenny Patel and Benjamin Sweely Tickle College of Engineering November 16th, 2017
 Joint Impact of Lower Extremities in Obese and Overweight Children Jenny Patel and Benjamin Sweely Tickle College of Engineering November 16th, 2017 Impact 340 Million Children Aged 5-19 in 2016 World
Joint Impact of Lower Extremities in Obese and Overweight Children Jenny Patel and Benjamin Sweely Tickle College of Engineering November 16th, 2017 Impact 340 Million Children Aged 5-19 in 2016 World
Gait. Kinesiology RHS 341 Lecture 12 Dr. Einas Al-Eisa
 Gait Kinesiology RHS 341 Lecture 12 Dr. Einas Al-Eisa Definitions Locomotion = the act of moving from one place to the other Gait = the manner of walking Definitions Walking = a smooth, highly coordinated,
Gait Kinesiology RHS 341 Lecture 12 Dr. Einas Al-Eisa Definitions Locomotion = the act of moving from one place to the other Gait = the manner of walking Definitions Walking = a smooth, highly coordinated,
Plantar fasciitis: identify & overcome
 Plantar fasciitis: identify & overcome The plantar fascia is a band of connective tissue (rather like a ligament) which runs from the heel, along the bottom of the foot to the base of each of the toes.
Plantar fasciitis: identify & overcome The plantar fascia is a band of connective tissue (rather like a ligament) which runs from the heel, along the bottom of the foot to the base of each of the toes.
The Risks and Benefits of Running Barefoot or in Minimalist Shoes: A Systematic Review
 University of Central Florida HIM 1990-2015 Open Access The Risks and Benefits of Running Barefoot or in Minimalist Shoes: A Systematic Review 2013 Kyle Perkins University of Central Florida Find similar
University of Central Florida HIM 1990-2015 Open Access The Risks and Benefits of Running Barefoot or in Minimalist Shoes: A Systematic Review 2013 Kyle Perkins University of Central Florida Find similar
video Outline Pre-requisites of Typical Gait Case Studies Case 1 L5 Myelomeningocele Case 1 L5 Myelomeningocele
 Outline Evaluation of Orthosis Function in Children with Neuromuscular Disorders Using Motion Analysis Outcomes Terminology Methods Typically developing Case examples variety of pathologies Sylvia Õunpuu,
Outline Evaluation of Orthosis Function in Children with Neuromuscular Disorders Using Motion Analysis Outcomes Terminology Methods Typically developing Case examples variety of pathologies Sylvia Õunpuu,
The Lateralized Foot & Ankle Pattern and the Pronated Left Chest
 The Lateralized Foot & Ankle Pattern and the Pronated Left Chest Presented by: James Anderson, MPT, PRC Director of Affiliate Programs, Faculty & Board of Certification Postural Restoration Institute Pronate
The Lateralized Foot & Ankle Pattern and the Pronated Left Chest Presented by: James Anderson, MPT, PRC Director of Affiliate Programs, Faculty & Board of Certification Postural Restoration Institute Pronate
The effects of CrossFit and minimalist footwear on Achilles tendon kinetics during running
 Article The effects of CrossFit and minimalist footwear on Achilles tendon kinetics during running Sinclair, Jonathan Kenneth and Sant, Benjamin Available at http://clok.uclan.ac.uk/16748/ Sinclair, Jonathan
Article The effects of CrossFit and minimalist footwear on Achilles tendon kinetics during running Sinclair, Jonathan Kenneth and Sant, Benjamin Available at http://clok.uclan.ac.uk/16748/ Sinclair, Jonathan
Athlete Profiling. Injury Prevention
 Athlete Profiling Injury Prevention Fraser McKinney Physiotherapist Special interest in: Basketball Athletics Race Walking Research Performance markers (screening / HR assessments / biomechanics) Athlete
Athlete Profiling Injury Prevention Fraser McKinney Physiotherapist Special interest in: Basketball Athletics Race Walking Research Performance markers (screening / HR assessments / biomechanics) Athlete
Comparison of Kinematics and Kinetics During Drop and Drop Jump Performance
 schouweiler, hess UW-L Journal of Undergraduate Research XIII (21) Comparison of Kinematics and Kinetics During Drop and Drop Jump Performance Ryan Schouweiler, Karina Hess Faculty Sponsor: Thomas Kernozek,
schouweiler, hess UW-L Journal of Undergraduate Research XIII (21) Comparison of Kinematics and Kinetics During Drop and Drop Jump Performance Ryan Schouweiler, Karina Hess Faculty Sponsor: Thomas Kernozek,
The Pennsylvania State University. The Graduate School. College of Health and Human Development
 The Pennsylvania State University The Graduate School College of Health and Human Development BIOMECHANICAL DIFFERENCES BETWEEN HEEL-TOE AND FOREFOOT RUNNING A Thesis in Kinesiology by Christopher P. Matarazzo
The Pennsylvania State University The Graduate School College of Health and Human Development BIOMECHANICAL DIFFERENCES BETWEEN HEEL-TOE AND FOREFOOT RUNNING A Thesis in Kinesiology by Christopher P. Matarazzo
The ABC s for Increased Running Speed in the Post-Operative Knee Athlete
 The ABC s for Increased Running Speed in the Post-Operative Knee Athlete Robert A. Panariello MS, PT, ATC, CSCS Professional Orthopedic and Sports Physical Therapy New York, New York Professional Athletic
The ABC s for Increased Running Speed in the Post-Operative Knee Athlete Robert A. Panariello MS, PT, ATC, CSCS Professional Orthopedic and Sports Physical Therapy New York, New York Professional Athletic
Dynamix Ankle Foot Orthoses Range
 The Restyled Dynamix Ankle Foot Orthoses Range Supporting your wellbeing Product Range Introduction Index Product Range Introduction... 3 Puffin - Dynamix Supramalleolar... 4 Penguin - Dynamix Plantarflexion...
The Restyled Dynamix Ankle Foot Orthoses Range Supporting your wellbeing Product Range Introduction Index Product Range Introduction... 3 Puffin - Dynamix Supramalleolar... 4 Penguin - Dynamix Plantarflexion...
The Influence of High Heeled Shoes on Kinematics, Kinetics, and Muscle EMG of Normal Female Gait
 JOURNAL OF APPLIED BIOMECHANICS, 2000, 16, 309-319 2000 by Human Kinetics Publishers, Inc. The Influence of High Heeled Shoes on Kinematics, Kinetics, and Muscle EMG of Normal Female Gait Darren J. Stefanyshyn,
JOURNAL OF APPLIED BIOMECHANICS, 2000, 16, 309-319 2000 by Human Kinetics Publishers, Inc. The Influence of High Heeled Shoes on Kinematics, Kinetics, and Muscle EMG of Normal Female Gait Darren J. Stefanyshyn,
The Starting Point. Prosthetic Alignment in the Transtibial Amputee. Outline. COM Motion in the Coronal Plane
 Prosthetic Alignment in the Transtibial Amputee The Starting Point David C. Morgenroth, MD, Department of Rehabilitation Medicine University of Washington VAPSHCS Outline COM Motion in the Coronal Plane
Prosthetic Alignment in the Transtibial Amputee The Starting Point David C. Morgenroth, MD, Department of Rehabilitation Medicine University of Washington VAPSHCS Outline COM Motion in the Coronal Plane
Slide 1. Slide 2. Slide 3 TYPICAL INJURIES ASSOCIATED WITH RUNNING
 1 THE RELATIONSHIP BETWEEN FOOT STRIKE AND RUNNING INJURIES SUSAN THOMPSON PT, OCS ARLINGTON ORTHOPEDIC ASSOCIATES 2 RUNNING 30 million participants in the US alone. Running is an excellent form of exercise,
1 THE RELATIONSHIP BETWEEN FOOT STRIKE AND RUNNING INJURIES SUSAN THOMPSON PT, OCS ARLINGTON ORTHOPEDIC ASSOCIATES 2 RUNNING 30 million participants in the US alone. Running is an excellent form of exercise,
PLANTAR FASCIITIS. Points of Confusion. TREATING SUBCALCANEAL PAIN: Who gets the best outcomes?
 TREATING SUBCALCANEAL PAIN: Who gets the best outcomes? DOUGLAS H. RICHIE, JR., D.P.M. Seal Beach, California Points of Confusion Pathomechanics of Plantar Fascia overload: Foot Pronation STJ Pronation
TREATING SUBCALCANEAL PAIN: Who gets the best outcomes? DOUGLAS H. RICHIE, JR., D.P.M. Seal Beach, California Points of Confusion Pathomechanics of Plantar Fascia overload: Foot Pronation STJ Pronation
CHAPTER IV FINITE ELEMENT ANALYSIS OF THE KNEE JOINT WITHOUT A MEDICAL IMPLANT
 39 CHAPTER IV FINITE ELEMENT ANALYSIS OF THE KNEE JOINT WITHOUT A MEDICAL IMPLANT 4.1 Modeling in Biomechanics The human body, apart of all its other functions is a mechanical mechanism and a structure,
39 CHAPTER IV FINITE ELEMENT ANALYSIS OF THE KNEE JOINT WITHOUT A MEDICAL IMPLANT 4.1 Modeling in Biomechanics The human body, apart of all its other functions is a mechanical mechanism and a structure,
Mike Prevost, PhD
 A Quick Guide to Transitioning to Running Sandals Mike Prevost, PhD www.shammasandals.com A Quick Guide to Transitioning to Running Sandals Mike Prevost, PhD Nothing has impacted my run gait more than
A Quick Guide to Transitioning to Running Sandals Mike Prevost, PhD www.shammasandals.com A Quick Guide to Transitioning to Running Sandals Mike Prevost, PhD Nothing has impacted my run gait more than
THE EFFECTS OF ORTHOTICS ON LOWER EXTREMITY VARIABILITY DURING RUNNING. Samuel Brethauer
 THE EFFECTS OF ORTHOTICS ON LOWER EXTREMITY VARIABILITY DURING RUNNING. By Samuel Brethauer Submitted to the graduate degree program in Health, Sport, and Exercise Science and the Graduate Faculty of the
THE EFFECTS OF ORTHOTICS ON LOWER EXTREMITY VARIABILITY DURING RUNNING. By Samuel Brethauer Submitted to the graduate degree program in Health, Sport, and Exercise Science and the Graduate Faculty of the
Association between Iliotibial Band Syndrome Status and Running Biomechanics in Women
 University of Tennessee, Knoxville Trace: Tennessee Research and Creative Exchange Doctoral Dissertations Graduate School 8-2013 Association between Iliotibial Band Syndrome Status and Running Biomechanics
University of Tennessee, Knoxville Trace: Tennessee Research and Creative Exchange Doctoral Dissertations Graduate School 8-2013 Association between Iliotibial Band Syndrome Status and Running Biomechanics
COMPENSATORY EFFECTS OF FOOT DEFORMITY:
 COMPENSATORY EFFECTS OF FOOT DEFORMITY: Understanding the Nature of Foot Deformity and Imbalance BY KENDRICK A. WHITNEY, DPM, C.PED. 14 Pedorthic Footcare Association www.pedorthics.org The key to optimizing
COMPENSATORY EFFECTS OF FOOT DEFORMITY: Understanding the Nature of Foot Deformity and Imbalance BY KENDRICK A. WHITNEY, DPM, C.PED. 14 Pedorthic Footcare Association www.pedorthics.org The key to optimizing
What is the optimal design of a rocker shoe
 What is the optimal design of a rocker shoe University of Salford School of Health, Sport and Rehabilitation Sciences Deutsche Sporthochschule Köln J Chapman, S Preece, C Nester, B Braunstein, P Bruggerman
What is the optimal design of a rocker shoe University of Salford School of Health, Sport and Rehabilitation Sciences Deutsche Sporthochschule Köln J Chapman, S Preece, C Nester, B Braunstein, P Bruggerman
RUNNING. Normal Running 10/10/2016. Reliability and Concurrent Validity of a 2D Observational Gait Analysis Tool
 Reliability and Concurrent Validity of a 2D Observational Gait Analysis Tool Kevin Yu, SPT Robert Wayner, PT, DPT Jennifer Smith, PT, DPT RUNNING Stance Phase (Single Limb Support) Initial Contact / Foot
Reliability and Concurrent Validity of a 2D Observational Gait Analysis Tool Kevin Yu, SPT Robert Wayner, PT, DPT Jennifer Smith, PT, DPT RUNNING Stance Phase (Single Limb Support) Initial Contact / Foot
Gait Analyser. Description of Walking Performance
 Gait Analyser Description of Walking Performance This brochure will help you to understand clearly the parameters described in the report of the Gait Analyser, provide you with tips to implement the walking
Gait Analyser Description of Walking Performance This brochure will help you to understand clearly the parameters described in the report of the Gait Analyser, provide you with tips to implement the walking
TITLE: Biomechanical Factors in the Etiology of Tibial Stress Fractures. CONTRACTING ORGANIZATION: University of Delaware Delaware, DE
 AD Award Number: DAMD17-00-1-0515 TITLE: Biomechanical Factors in the Etiology of Tibial Stress Fractures PRINCIPAL INVESTIGATOR: Irene S Davis Ph.D. CONTRACTING ORGANIZATION: University of Delaware Delaware,
AD Award Number: DAMD17-00-1-0515 TITLE: Biomechanical Factors in the Etiology of Tibial Stress Fractures PRINCIPAL INVESTIGATOR: Irene S Davis Ph.D. CONTRACTING ORGANIZATION: University of Delaware Delaware,
Barefoot, Only Better!
 !"$%"&'()*$+(!+", Like Barefoot, Only Better! By Caitlin McCarthy, M.S., John P. Porcari, Ph.D., Tom Kernozek, Ph.D., John Willson, Ph.D., and Carl Foster, AndersB Ph.D., with Mark This study was funded
!"$%"&'()*$+(!+", Like Barefoot, Only Better! By Caitlin McCarthy, M.S., John P. Porcari, Ph.D., Tom Kernozek, Ph.D., John Willson, Ph.D., and Carl Foster, AndersB Ph.D., with Mark This study was funded
Ice skating in all its various forms. Living on the Edge: The Biomechanics of Power Skating
 Living on the Edge: The Biomechanics of Power Skating There are some very specific overuse injury patterns seen in the ice hockey population. 135 By R. Neil Humble, DPM Ice skating in all its various forms
Living on the Edge: The Biomechanics of Power Skating There are some very specific overuse injury patterns seen in the ice hockey population. 135 By R. Neil Humble, DPM Ice skating in all its various forms
Gait analysis through sound
 Invited article Niigata Journal of Health and Welfare Vol. 15, No. 1 Gait analysis through sound Kaoru Abe Graduate School of Health and Welfare, Niigata University of Health and Welfare, Niigata, Japan
Invited article Niigata Journal of Health and Welfare Vol. 15, No. 1 Gait analysis through sound Kaoru Abe Graduate School of Health and Welfare, Niigata University of Health and Welfare, Niigata, Japan
Practical Considerations for Evaluation, Treatment and Injury Reduction. John Salva, MPT
 Practical Considerations for Evaluation, Treatment and Injury Reduction John Salva, MPT john@impactphysio.net Participants will be able to: Identify key biomechanical requirements for running. Be aware
Practical Considerations for Evaluation, Treatment and Injury Reduction John Salva, MPT john@impactphysio.net Participants will be able to: Identify key biomechanical requirements for running. Be aware
Supplementary Figure S1
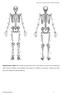 Supplementary Figure S1: Anterior and posterior views of the marker set used in the running gait trials. Forty-six markers were attached to the subject (15 markers on each leg, 4 markers on each arm, and
Supplementary Figure S1: Anterior and posterior views of the marker set used in the running gait trials. Forty-six markers were attached to the subject (15 markers on each leg, 4 markers on each arm, and
WHO ARE WE? Eric Marriott Registered Physiotherapist Master of Physical Therapy, Bachelor of Human Kinetics
 Capilano Golf Club May 26, 2014 WHO ARE WE? Dana Ranahan Registered Physiotherapist B.Sc., B.Sc.P.T., Fellow of the Canadian Academy of Manual and Manipulative Therapy (FCAMT), Diploma Sports Physiotherapy,
Capilano Golf Club May 26, 2014 WHO ARE WE? Dana Ranahan Registered Physiotherapist B.Sc., B.Sc.P.T., Fellow of the Canadian Academy of Manual and Manipulative Therapy (FCAMT), Diploma Sports Physiotherapy,
Orthotic intervention in forefoot and rearfoot strike running patterns
 Clinical Biomechanics 19 (24) 64 7 www.elsevier.com/locate/clinbiomech Orthotic intervention in forefoot and rearfoot strike running patterns Carrie Laughton Stackhouse a, *, Irene McClay Davis b,c, Joseph
Clinical Biomechanics 19 (24) 64 7 www.elsevier.com/locate/clinbiomech Orthotic intervention in forefoot and rearfoot strike running patterns Carrie Laughton Stackhouse a, *, Irene McClay Davis b,c, Joseph
