Note! In this lab when you measure, round all measurements to the nearest meter!
|
|
|
- Shannon Davis
- 6 years ago
- Views:
Transcription
1
2 Distance and Displacement Lab Note! In this lab when you measure, round all measurements to the nearest meter! 1. Place a piece of tape where you will begin your walk outside. This tape marks the origin. 2. Walk 10 steps forward and stop. Using the meter stick, have your partner measure the distance you walked. Write that distance here: (don t forget units!) 3. Now turn 180 degrees and walk 5 steps and stop. Using the meter stick, have your partner measure the distance you walked. Write that distance here: (don t forget units!) 4. Now turn 180 degrees and walk 20 steps and stop. Using the meter stick, have your partner measure the distance you walked. Write that distance here: (don t forget units!) 5. Finally, have your partner measure how far you are from the origin. Write that measurement here: This is your measured displacement. 6. Figure out the distance and calculated displacement you walked. Add all measurements to find the distance: Add all forward measurements and subtract all backwards measurements to find the calculated displacement: Did your measured displacement match your calculated displacement? 7. Find your piece of tape again, and walk 10 steps forward and measure how far you walked. Write it here: (don t forget your units!) 8. Turn 90 left, walk 15 steps and measure how far you walked. Write it here: 9. Turn 90 left, walk 10 steps and measure how far you walked. Write it here: 10. Turn 90 left, walk 20 steps and measure how far you walked. Write it here: 11. Have your partner measure how far you are form the origin. Write it here: This is your measured displacement. 12. Now figure out your distance and write it below. Show your work. Add up the measurements you wrote in numbers 7 through 10. Distance = Now figure out your calculated displacement and write it below. Show your work. Add number 7 + number 8 then subtract number 9 and number 10. Calculated Displacement = Does your calculated displacement match your measured displacement? 13. Find your piece of tape again, and walk 20 steps forward. Measure how far you walked and write it here: 14. Turn 90 right and walk 20 steps. Measure how far you walked and write it here: 15. Have your partner measure how far you are from the origin, your measured displacement, and write it here: (Turn this page over and continue.)
3 16. Now figure out your distance and write it below. Show your work. Add number 14 and 15. Distance = Here s a way to figure out your calculated displacement. You can use Pythagoras Theorem! Add the square of number 13 and the square of number 14. Write it here: Now square the distance you measured in number 15 (your measured displacement). Write it here: The two numbers should be equal or nearly so. If you have a calculator, find the square root of the value you found for the sum of the square of #13 and square of #14. This value is your calculated displacement. Does it match your measured displacement (or nearly so)? 17. Now diagram the last walk and indicate displacement with a vector arrow. Show all your measured distances and displacements on the diagram. 18. Show with the same diagram how you used Pythagoras theorem to find your calculated displacement. Label the square of each leg of your triangle on the diagram. 19. Can you explain why Pythagoras Theorem can be used to find the calculated displacement in your last walk? Hint: you made a 90 degree turn on your walk. 19. Explain why displacement is a vector quantity.
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
17
18
19
20
21
22
23 ...Name(s) Speed and the Two-Step Objective: In this lab, you will measure and graph your speed and acceleration as you walk from o another. Step 1: Marking Your Space. You will use the hallway or some other large area to measure a dis string and a meter stick. For our class, we can skip this step because the tiles on the floor are exa Use masking tape to mark a section of tile that equals 20 feet. We will be going into the hallway fo experiment. Do not disturb other classes. Step 2: Speed of a Shuffle Have one person in your group shuffle the length. This means the person s feet should never lea to move you will need to slide your foot in front of the other. This should be a very slow pace. Ano group should time how long it takes (in seconds) to move the 20 feet and record it in the data table. that you can get an average. Step 3: Speed of a Heel-to-Toe Walk This time, you can lift your foot, but must walk by placing one foot exactly at the toe of the other foot with each step. This should also be a fairly slow pace because your steps are tiny. Step 4: Normal Walk For this trial, you can step normally across the length. Try to keep your pace constant. Step 5: Repeat this process by switching to the other person in your group
24 Name of Person Walking: Trial (Person 1) Time to Move 20 ft Shuffle (trial 1) Shuffle (trial 2) Shuffle (trial 3) Average Heel-to-Toe (trial 1) Heel-to-Toe (trial 2) Heel-to-Toe (trial 3) Average Normal Walk (trial 1) Normal Walk (trial 2) Normal Walk (trial 3) Average Name of Person Walking: Trial (Person 1) Time to Move 20 ft Shuffle (trial 1) Shuffle (trial 2) Shuffle (trial 3) Average Heel-to-Toe (trial 1) Heel-to-Toe (trial 2) Heel-to-Toe (trial 3) Average Normal Walk (trial 1) Normal Walk (trial 2) Normal Walk (trial 3) Average Speed (feet/s) Speed (feet/s) ***From this point on, you will be doing the work on you Step 5: Conversions for Fun use the ratio to determin walk (use average) in a minute Now convert your feet per minute to feet per hour (there in an hour) Finally, determine your speed in miles per hour using t 1 mile = 5380 feet. Set up a ratio similar to those above Step 6: Graph your data. Compare the AVERAGE fo walks you and your partner did (shuffle, heel-to-toe, an making a BAR graph. You may want to use different c distinguish between you and your partner.
25
26
27
28
29
30 The moving man Procedure Go to and find The Moving Man simulation under the category of motion. 1. After The Moving Man is open leave the position graph and the velocity graph open but close the acceleration graph by clicking the symbol in the upper righthand corner of the graph. Investigate Moving Man by dragging the dude around with your mouse. This will give you very jumpy data, especially in the acceleration graph why? Now try making the man move using the slider arrows. Use the playback features to look at the graphs. While you make observations, discuss in your group the reasons the graphs look the way they do. 2. Making predictions: on your paper, sketch six of the following graphs. Label them A F. For each of the six scenarios below, in one color, PREDICT what the distance vs. time and velocity vs. time will look like. Don t be afraid to be wrong and don t cheat by looking at Moving Man first! Leave some space for explanations beside or below each graph. A) A man moving from the center of the screen (0 m) to the house (8m) at a slow, steady pace. of the graphs: Explain your reasoning for the appearance
31 B) A man moving from 0 to the house at a faster pace than above. of the graphs: Explain your reasoning for the appearance C) A man standing still at 4 m. of the graphs: Explain your reasoning for the appearance
32 D) A man moving from 0 to the house at a fast pace then moving back to 0 at a slower pace. of the graphs: Explain your reasoning for the appearance 5. Individually write a possible scenario for the following graph. Then compare your scenario with your lab partners to check if it is reasonable. time
33
34
35
36 Name: Date: Hour: Calculations with Velocity and Acceleration Read and solve each of the following problems. Be sure to show all of your work (given, equation, work, and answer with the proper units) Velocity Equations: 1. What distance is traveled by a police car that moves at a constant speed of 2.5 m/s for 20s? Given: v= d= t= Equation & Work: Answer: 2. What is the speed of a horse that travels 45 m in 2 minutes? (remember to convert minutes to seconds) Given: Equation & Work: v= d= t= Answer: 3. How long would it take for a commercial jet to get from St. Louis to New York, a distance of 1,406 km, if it travels at an average velocity of 156 m/s. (You will also need to do some conversions here to match your units) Given: Work: v= d= t= Equation & Answer:
37 Acceleration Equations: 4. A skier takes off from the top of the ski run and reaches a speed of 24 m/s in 4 seconds. What is the skier s acceleration? Given: Work: vi = vf = t = a = Equation & Answer 5. A child on a skateboard is traveling at a velocity of 8 m/s down a hill. At the bottom of the hill, he slows down and comes to a stop in 4 seconds. Calculate the sled s deceleration (negative acceleration). Given: vi = vf = t = a = Answer Equation & Work: 6. A skydiver jumps out of a plane and as he falls he has an acceleration of 9.8 m/s2. How many seconds will it take to reach a speed of 28.5 m/s? Given: vi = vf = t = a = Equation & Work: Answer
38
39
40
Last First Date Per SETTLE LAB: Speed AND Velocity (pp for help) SPEED. Variables. Variables
 DISTANCE Last First Date Per SETTLE LAB: Speed AND Velocity (pp108-111 for help) Pre-Activity NOTES 1. What is speed? SPEED 5-4 - 3-2 - 1 2. What is the formula used to calculate average speed? 3. Calculate
DISTANCE Last First Date Per SETTLE LAB: Speed AND Velocity (pp108-111 for help) Pre-Activity NOTES 1. What is speed? SPEED 5-4 - 3-2 - 1 2. What is the formula used to calculate average speed? 3. Calculate
Add this important safety precaution to your normal laboratory procedures:
 Student Activity Worksheet Speed and Velocity Are You Speeding? Driving Question What is speed and how is it related to velocity? Materials and Equipment For each student or group: Data collection system
Student Activity Worksheet Speed and Velocity Are You Speeding? Driving Question What is speed and how is it related to velocity? Materials and Equipment For each student or group: Data collection system
Jeddah Knowledge International School. Science Revision Pack Answer Key Quarter 3 Grade 10
 Jeddah Knowledge International School Science Revision Pack Answer Key 2016-2017 Quarter 3 Grade 10 Name: Section: ANSWER KEY- SCIENCE GRADE 10, QUARTER 3 1 1. What are the units for mass? A Kilograms
Jeddah Knowledge International School Science Revision Pack Answer Key 2016-2017 Quarter 3 Grade 10 Name: Section: ANSWER KEY- SCIENCE GRADE 10, QUARTER 3 1 1. What are the units for mass? A Kilograms
QUICK WARM UP: Thursday 3/9
 Name: pd: Unit 6, QUICK WARM UP: Thursday 3/9 1) The slope of a distance vs. time graph shows an object s. 2) The slope of a position vs. time graph shows an object s. 3) Can an object have a constant
Name: pd: Unit 6, QUICK WARM UP: Thursday 3/9 1) The slope of a distance vs. time graph shows an object s. 2) The slope of a position vs. time graph shows an object s. 3) Can an object have a constant
Rates and measurement Block 1 Student Activity Sheet
 Block 1 Student Activity Sheet 1. Complete the table below. Use the table, map, and graph to describe the field trip. Can you explain how the bus traveled in terms of distance, time, and speed? Speculate
Block 1 Student Activity Sheet 1. Complete the table below. Use the table, map, and graph to describe the field trip. Can you explain how the bus traveled in terms of distance, time, and speed? Speculate
a. Determine the sprinter's constant acceleration during the first 2 seconds. b. Determine the sprinters velocity after 2 seconds have elapsed.
 AP Physics 1 FR Practice Kinematics 1d 1 The first meters of a 100-meter dash are covered in 2 seconds by a sprinter who starts from rest and accelerates with a constant acceleration. The remaining 90
AP Physics 1 FR Practice Kinematics 1d 1 The first meters of a 100-meter dash are covered in 2 seconds by a sprinter who starts from rest and accelerates with a constant acceleration. The remaining 90
Ball Toss. Vernier Motion Detector
 Experiment 6 When a juggler tosses a ball straight upward, the ball slows down until it reaches the top of its path. The ball then speeds up on its way back down. A graph of its velocity vs. time would
Experiment 6 When a juggler tosses a ball straight upward, the ball slows down until it reaches the top of its path. The ball then speeds up on its way back down. A graph of its velocity vs. time would
Chapter : Linear Motion 2
 Text: Chapter 2.5-2.9 Think and Explain: 4-8 Think and Solve: 2-4 Chapter 2.5-2.9: Linear Motion 2 NAME: Vocabulary: constant acceleration, acceleration due to gravity, free fall Equations: s = d t v =
Text: Chapter 2.5-2.9 Think and Explain: 4-8 Think and Solve: 2-4 Chapter 2.5-2.9: Linear Motion 2 NAME: Vocabulary: constant acceleration, acceleration due to gravity, free fall Equations: s = d t v =
(Lab Interface BLM) Acceleration
 Purpose In this activity, you will study the concepts of acceleration and velocity. To carry out this investigation, you will use a motion sensor and a cart on a track (or a ball on a track, if a cart
Purpose In this activity, you will study the concepts of acceleration and velocity. To carry out this investigation, you will use a motion sensor and a cart on a track (or a ball on a track, if a cart
NAME:... SCHOOL: LINEAR MOTION. Answer ALL questions in this paper in the spaces provided.
 NAME:.... SCHOOL: DATE:... LINEAR MOTION INSTRUCTIONS TO CANDIDATES Answer ALL questions in this paper in the spaces provided. 1. Two forces that act on a moving cyclist are the driving force and the resistive
NAME:.... SCHOOL: DATE:... LINEAR MOTION INSTRUCTIONS TO CANDIDATES Answer ALL questions in this paper in the spaces provided. 1. Two forces that act on a moving cyclist are the driving force and the resistive
Physical Science You will need a calculator today!!
 Physical Science 11.3 You will need a calculator today!! Physical Science 11.3 Speed and Velocity Speed and Velocity Speed The ratio of the distance an object moves to the amount of time the object moves
Physical Science 11.3 You will need a calculator today!! Physical Science 11.3 Speed and Velocity Speed and Velocity Speed The ratio of the distance an object moves to the amount of time the object moves
Phys 201A. Lab 6 - Motion with Constant acceleration Kinematic Equations
 Phys 201A Lab 6 - Motion with Constant acceleration Kinematic Equations Problems: It would be good to list your four kinematic equations below for ready reference. Kinematic equations 1) An amateur bowler
Phys 201A Lab 6 - Motion with Constant acceleration Kinematic Equations Problems: It would be good to list your four kinematic equations below for ready reference. Kinematic equations 1) An amateur bowler
Physics 11 Honours Lesson 3 Distance and Displacement
 Name: Block: Physics 11 Honours Lesson 3 Distance and Displacement In physics, every measured quantity is either a or a. Scalars: For example: Vectors: For example: Note: Vectors are either written in
Name: Block: Physics 11 Honours Lesson 3 Distance and Displacement In physics, every measured quantity is either a or a. Scalars: For example: Vectors: For example: Note: Vectors are either written in
1 An object moves at a constant speed of 6 m/s. This means that the object:
 Slide 1 / 57 1 n object moves at a constant speed of 6 m/s. This means that the object: Increases its speed by 6 m/s every second ecreases its speed by 6 m/s every second oesn t move Has a positive acceleration
Slide 1 / 57 1 n object moves at a constant speed of 6 m/s. This means that the object: Increases its speed by 6 m/s every second ecreases its speed by 6 m/s every second oesn t move Has a positive acceleration
Riverboat Simulator Activity
 Riverboat Simulator Activity Purpose: The purpose of this activity is to analyze the relationship between the two vector components of motion for a river boat as it travels across a river in the presence
Riverboat Simulator Activity Purpose: The purpose of this activity is to analyze the relationship between the two vector components of motion for a river boat as it travels across a river in the presence
Chapter 11 Motion. Displacement-. Always includes Shorter than distance
 Chapter 11 Motion Section 1 - an object s change in position relative to a reference point. Observe objects in to other objects. international unit for. Frame of Reference Frame of reference- a system
Chapter 11 Motion Section 1 - an object s change in position relative to a reference point. Observe objects in to other objects. international unit for. Frame of Reference Frame of reference- a system
Section 1. Objectives:
 Chapter 2 Motion Objectives: Section 1 Use a frame of reference to describe motion Differentiate between Speed and Velocity Calculate the speed of an object Use graphs to describe speed Observing Motion
Chapter 2 Motion Objectives: Section 1 Use a frame of reference to describe motion Differentiate between Speed and Velocity Calculate the speed of an object Use graphs to describe speed Observing Motion
Lab: Relative Velocity (Speed)
 WWW.ARBORSCI.COM Lab: Velocity () By Dr. Joel Bryan OBJECTIVES: Determine average velocity (speed). Predict the relative velocities (speeds) of the two objects traveling in the same and in the opposite
WWW.ARBORSCI.COM Lab: Velocity () By Dr. Joel Bryan OBJECTIVES: Determine average velocity (speed). Predict the relative velocities (speeds) of the two objects traveling in the same and in the opposite
Chapter 11 Motion. Section 1
 Chapter 11 Motion Objectives: Section 1 Use a frame of reference to describe motion Differentiate between Speed and Velocity Calculate the speed of an object Use graphs to describe speed 1 Observing Motion
Chapter 11 Motion Objectives: Section 1 Use a frame of reference to describe motion Differentiate between Speed and Velocity Calculate the speed of an object Use graphs to describe speed 1 Observing Motion
LAB : Using A Spark Timer
 LAB : Using A Spark Timer Read through the whole lab and answer prelab questions prior to lab day. Name: F1 Introduction A spark timer is used to make accurate time and distance measurements for moving
LAB : Using A Spark Timer Read through the whole lab and answer prelab questions prior to lab day. Name: F1 Introduction A spark timer is used to make accurate time and distance measurements for moving
Describing a journey made by an object is very boring if you just use words. As with much of science, graphs are more revealing.
 Distance vs. Time Describing a journey made by an object is very boring if you just use words. As with much of science, graphs are more revealing. Plotting distance against time can tell you a lot about
Distance vs. Time Describing a journey made by an object is very boring if you just use words. As with much of science, graphs are more revealing. Plotting distance against time can tell you a lot about
During the Push What kind of motion does the puck have at this time? Is it speeding up, slowing down, not moving, or moving at a steady speed?
 Elaborate The teacher is giving a demonstration with a hover puck. Make the requested predictions before using your observations to check if you were correct or if you need to make changes.. Predict how
Elaborate The teacher is giving a demonstration with a hover puck. Make the requested predictions before using your observations to check if you were correct or if you need to make changes.. Predict how
Average speed is calculated by taking the total distance travelled and dividing it by the total time:
 Speed Calculations Now that you know your definitions, you ll learn how to calculate some of the quantities. The following formulas are all very similar, but their slight differences are important since
Speed Calculations Now that you know your definitions, you ll learn how to calculate some of the quantities. The following formulas are all very similar, but their slight differences are important since
The bus has to stop a few times. The figure below shows the distance time graph for part of the journey. Time in seconds
 HW Acceleration / 55 Name Q1.A bus is taking some children to school. The bus has to stop a few times. The figure below shows the distance time graph for part of the journey. Time in seconds How far has
HW Acceleration / 55 Name Q1.A bus is taking some children to school. The bus has to stop a few times. The figure below shows the distance time graph for part of the journey. Time in seconds How far has
Compare the scalar of speed and the vector of velocity.
 Review Video QOD 2/14/12: Compare the scalar of speed and the vector of velocity. What are the equations for each? Feb 14 6:51 AM 1 Imagine that you are a race car driver. You push on the accelerator.
Review Video QOD 2/14/12: Compare the scalar of speed and the vector of velocity. What are the equations for each? Feb 14 6:51 AM 1 Imagine that you are a race car driver. You push on the accelerator.
Riverboat Simulator Activity Sheet
 Riverboat Simulator Activity Sheet Purpose: The purpose of this activity is to analyze the relationship between the two vector components of motion for a river boat as it travels across a river in the
Riverboat Simulator Activity Sheet Purpose: The purpose of this activity is to analyze the relationship between the two vector components of motion for a river boat as it travels across a river in the
AP Physics 1 Summer Packet Review of Trigonometry used in Physics
 AP Physics 1 Summer Packet Review of Trigonometry used in Physics For some of you this material will seem pretty familiar and you will complete it quickly. For others, you may not have had much or any
AP Physics 1 Summer Packet Review of Trigonometry used in Physics For some of you this material will seem pretty familiar and you will complete it quickly. For others, you may not have had much or any
HONORS PHYSICS One Dimensional Kinematics
 HONORS PHYSICS One Dimensional Kinematics LESSON OBJECTIVES Be able to... 1. use appropriate metric units and significant figures for given measurements 2. identify aspects of motion such as position,
HONORS PHYSICS One Dimensional Kinematics LESSON OBJECTIVES Be able to... 1. use appropriate metric units and significant figures for given measurements 2. identify aspects of motion such as position,
x 2 = (60 m) 2 + (60 m) 2 x 2 = 3600 m m 2 x = m
 3.1 Track Question a) Distance Traveled is 1600 m. This is length of the path that the person took. The displacement is 0 m. The person begins and ends their journey at the same position. They did not
3.1 Track Question a) Distance Traveled is 1600 m. This is length of the path that the person took. The displacement is 0 m. The person begins and ends their journey at the same position. They did not
Unit 2, Lesson 9: Constant Speed
 Unit 2, Lesson 9: Constant Speed Lesson Goals Use a double number line to find the speed expressed in distance traveled per 1 unit of time. Use per language in the context of constant speed. Understand
Unit 2, Lesson 9: Constant Speed Lesson Goals Use a double number line to find the speed expressed in distance traveled per 1 unit of time. Use per language in the context of constant speed. Understand
Physics 2048 Test 1 Name: Dr. Jeff Saul
 Physics 248 Test 1 Name: Dr. Jeff Saul Group: Spring 22 Date: READ THESE INSTRUCTIONS BEFORE YOU BEGIN Before you start the test, WRITE YOUR NAME ON EVERY PAGE OF THE EXAM. Calculators are permitted, but
Physics 248 Test 1 Name: Dr. Jeff Saul Group: Spring 22 Date: READ THESE INSTRUCTIONS BEFORE YOU BEGIN Before you start the test, WRITE YOUR NAME ON EVERY PAGE OF THE EXAM. Calculators are permitted, but
Gravity: How fast do objects fall? Teacher Version (Grade level: 4 7)
 Gravity: How fast do objects fall? Teacher Version (Grade level: 4 7) *** Experiment with Audacity to be sure you know how to do what s needed for the lab*** Kinematics is the study of how things move
Gravity: How fast do objects fall? Teacher Version (Grade level: 4 7) *** Experiment with Audacity to be sure you know how to do what s needed for the lab*** Kinematics is the study of how things move
Introduction to solving acceleration problems
 Introduction to solving acceleration problems We learned previously that speed is a function of distance and time: s = d t We also learned that velocity is a nearly identical formula. The difference is
Introduction to solving acceleration problems We learned previously that speed is a function of distance and time: s = d t We also learned that velocity is a nearly identical formula. The difference is
The table below shows how the thinking distance and braking distance vary with speed. Thinking distance in m
 Q1.The stopping distance of a car is the sum of the thinking distance and the braking distance. The table below shows how the thinking distance and braking distance vary with speed. Speed in m / s Thinking
Q1.The stopping distance of a car is the sum of the thinking distance and the braking distance. The table below shows how the thinking distance and braking distance vary with speed. Speed in m / s Thinking
MATERIALS: softball, stopwatch, measuring tape, calculator, writing utensil, data table.
 1 PROJECTILE LAB: (SOFTBALL) Name: Partner s Names: Date: PreAP Physics LAB Weight = 1 PURPOSE: To calculate the speed of a softball projectile and its launch angle by measuring only the time and distance
1 PROJECTILE LAB: (SOFTBALL) Name: Partner s Names: Date: PreAP Physics LAB Weight = 1 PURPOSE: To calculate the speed of a softball projectile and its launch angle by measuring only the time and distance
½ 3. 2/3 V (1/3 (1/2V)+1/3(V)+1/3(1/2V))
 TEST 2 Q 1 some HONORS review questions to try Define: displacement, velocity, average velocity, average speed, acceleration. Displacement: change in distance from start (with direction) Velocity: change
TEST 2 Q 1 some HONORS review questions to try Define: displacement, velocity, average velocity, average speed, acceleration. Displacement: change in distance from start (with direction) Velocity: change
PHYSICS 12 NAME: Kinematics and Projectiles Review
 NAME: Kinematics and Projectiles Review (1-3) A ball is thrown into the air, following the path shown in the diagram. At 1, the ball has just left the thrower s hand. At 5, the ball is at its original
NAME: Kinematics and Projectiles Review (1-3) A ball is thrown into the air, following the path shown in the diagram. At 1, the ball has just left the thrower s hand. At 5, the ball is at its original
Although many factors contribute to car accidents, speeding is the
 74 Measuring Speed l a b o r at o ry Although many factors contribute to car accidents, speeding is the most common kind of risky driving. Unsafe speed is involved in about 20% of fatal car accidents in
74 Measuring Speed l a b o r at o ry Although many factors contribute to car accidents, speeding is the most common kind of risky driving. Unsafe speed is involved in about 20% of fatal car accidents in
Physics 2048 Test 1 Fall 2000 Dr. Jeff Saul Name:
 Physics 2048 Test 1 Fall 2000 Dr. Jeff Saul Name: READ THESE INSTRUCTIONS BEFORE YOU BEGIN Before you start the test, WRITE YOUR NAME ON EVERY PAGE OF THE EXAM. Calculators are permitted, but no notes
Physics 2048 Test 1 Fall 2000 Dr. Jeff Saul Name: READ THESE INSTRUCTIONS BEFORE YOU BEGIN Before you start the test, WRITE YOUR NAME ON EVERY PAGE OF THE EXAM. Calculators are permitted, but no notes
One Dimensional Kinematics Challenge Problems
 One Dimensional Kinematics Challenge Problems Problem 1: One-Dimensional Kinematics: Two stones are released from rest at a certain height, one after the other. a) Will the difference between their speeds
One Dimensional Kinematics Challenge Problems Problem 1: One-Dimensional Kinematics: Two stones are released from rest at a certain height, one after the other. a) Will the difference between their speeds
Observing Waves, Their Properties, and Relationships
 Observing Waves, Their Properties, and Relationships Part I: Setting Up the Activity 1. Refer to the material list for materials needed. 2. To successfully conduct this activity, you will need an area
Observing Waves, Their Properties, and Relationships Part I: Setting Up the Activity 1. Refer to the material list for materials needed. 2. To successfully conduct this activity, you will need an area
Force, Motion and Energy Review
 NAME Force, Motion and Energy Review 1 In the picture to the right, two teams of students are playing tug-of-war. Each team is pulling in the opposite direction, but both teams are moving in the same direction.
NAME Force, Motion and Energy Review 1 In the picture to the right, two teams of students are playing tug-of-war. Each team is pulling in the opposite direction, but both teams are moving in the same direction.
at home plate at 1st base at 2nd base at 3rd base back at home distance displacement
 You might need a calculator: The typical baseball diamond is a square 90 ft long on each side. Suppose a player hits a homerun and makes one complete trip from home plate, around the bases, and back to
You might need a calculator: The typical baseball diamond is a square 90 ft long on each side. Suppose a player hits a homerun and makes one complete trip from home plate, around the bases, and back to
Vectors. Wind is blowing 15 m/s East. What is the magnitude of the wind s velocity? What is the direction?
 Physics R Scalar: Vector: Vectors Date: Examples of scalars and vectors: Scalars Vectors Wind is blowing 15 m/s East. What is the magnitude of the wind s velocity? What is the direction? Magnitude: Direction:
Physics R Scalar: Vector: Vectors Date: Examples of scalars and vectors: Scalars Vectors Wind is blowing 15 m/s East. What is the magnitude of the wind s velocity? What is the direction? Magnitude: Direction:
Walk - Run Activity --An S and P Wave Travel Time Simulation ( S minus P Earthquake Location Method)
 Walk - Run Activity --An S and P Wave Travel Time Simulation ( S minus P Earthquake Location Method) L. W. Braile and S. J. Braile (June, 2000) braile@purdue.edu http://web.ics.purdue.edu/~braile Walk
Walk - Run Activity --An S and P Wave Travel Time Simulation ( S minus P Earthquake Location Method) L. W. Braile and S. J. Braile (June, 2000) braile@purdue.edu http://web.ics.purdue.edu/~braile Walk
Introduction to Waves. If you do not have access to equipment, the following experiments can be observed here:
 Introduction to Waves If you do not have access to equipment, the following experiments can be observed here: http://tinyurl.com/lupz3dh 1.1 There is a tray with water in it. This can model throwing a
Introduction to Waves If you do not have access to equipment, the following experiments can be observed here: http://tinyurl.com/lupz3dh 1.1 There is a tray with water in it. This can model throwing a
Velocity signifies the speed of an object AND the direction it is moving.
 Speed and Velocity Speed refers to how far an object travels in a given amount of time, regardless of direction. If a car travels 100 km in 2 hours, it s average speed was 50km/hour. 100km = 50 km/hr 2
Speed and Velocity Speed refers to how far an object travels in a given amount of time, regardless of direction. If a car travels 100 km in 2 hours, it s average speed was 50km/hour. 100km = 50 km/hr 2
Motion in 1 Dimension
 A.P. Physics 1 LCHS A. Rice Unit 1 Displacement, Velocity, & Acceleration: Motion in 1 Dimension In-Class Example Problems and Lecture Notes 1. Freddy the cat started at the 3 meter position. He then walked
A.P. Physics 1 LCHS A. Rice Unit 1 Displacement, Velocity, & Acceleration: Motion in 1 Dimension In-Class Example Problems and Lecture Notes 1. Freddy the cat started at the 3 meter position. He then walked
AP Physics B Summer Homework (Show work)
 #1 NAME: AP Physics B Summer Homework (Show work) #2 Fill in the radian conversion of each angle and the trigonometric value at each angle on the chart. Degree 0 o 30 o 45 o 60 o 90 o 180 o 270 o 360 o
#1 NAME: AP Physics B Summer Homework (Show work) #2 Fill in the radian conversion of each angle and the trigonometric value at each angle on the chart. Degree 0 o 30 o 45 o 60 o 90 o 180 o 270 o 360 o
Standing Waves in a String
 Standing Waves in a String OBJECTIVE To understand the circumstances necessary to produce a standing wave. To observe and define the quantities associated with a standing wave. To determine the wavelength
Standing Waves in a String OBJECTIVE To understand the circumstances necessary to produce a standing wave. To observe and define the quantities associated with a standing wave. To determine the wavelength
Student Outcomes. Lesson Notes. Classwork. Discussion (20 minutes)
 Student Outcomes Students explain a proof of the converse of the Pythagorean Theorem. Students apply the theorem and its converse to solve problems. Lesson Notes Students had their first experience with
Student Outcomes Students explain a proof of the converse of the Pythagorean Theorem. Students apply the theorem and its converse to solve problems. Lesson Notes Students had their first experience with
Eg.#1 A diver steps off a 10. m. high diving board with an initial vertical velocity of zero and experiences an average acceleration 2
 1.3.1 Acceleration due to Gravity Defined as: For many years, it was thought that higher mass objects fall towards the Earth more quickly than lower mass objects. This idea was introduced in approximately
1.3.1 Acceleration due to Gravity Defined as: For many years, it was thought that higher mass objects fall towards the Earth more quickly than lower mass objects. This idea was introduced in approximately
Position and displacement
 /1/14 Position and displacement Objectives Describe motion in 1D using position, distance, and displacement. Analyze motion in 1D using position, distance, and displacement. Correctly use and interpret
/1/14 Position and displacement Objectives Describe motion in 1D using position, distance, and displacement. Analyze motion in 1D using position, distance, and displacement. Correctly use and interpret
1. Which one of the following is a vector quantity? A. time B. speed C. energy D. displacement
 1. Which one of the following is a vector quantity? A. time B. speed C. energy D. displacement 2. A car is travelling at a constant speed of 26.0 m/s down a slope which is 12.0 to the horizontal. What
1. Which one of the following is a vector quantity? A. time B. speed C. energy D. displacement 2. A car is travelling at a constant speed of 26.0 m/s down a slope which is 12.0 to the horizontal. What
Exploration Series. MODEL ROCKET Interactive Physics Simulation Page 01
 MODEL ROCKET ------- Interactive Physics Simulation ------- Page 01 How high will your model rocket fly? At liftoff, the rocket engine is ignited and a thrust force is generated. The rocket accelerates
MODEL ROCKET ------- Interactive Physics Simulation ------- Page 01 How high will your model rocket fly? At liftoff, the rocket engine is ignited and a thrust force is generated. The rocket accelerates
PHYSICS 105. Assignment #3 Due by 10 pm September 29, DISCUSSION SECTION: [ ] D7 W 9 am [ ] D8 W 10 am [ ] HS W 10 am
![PHYSICS 105. Assignment #3 Due by 10 pm September 29, DISCUSSION SECTION: [ ] D7 W 9 am [ ] D8 W 10 am [ ] HS W 10 am PHYSICS 105. Assignment #3 Due by 10 pm September 29, DISCUSSION SECTION: [ ] D7 W 9 am [ ] D8 W 10 am [ ] HS W 10 am](/thumbs/89/98903187.jpg) PHYSICS 105 Assignment #3 Due by 10 pm September 9, 009 NAME: DISCUSSION SECTION: [ ] D7 W 9 am [ ] D8 W 10 am [ ] HS W 10 am [ ] D9 W 11 am [ ] F 1 W 1 pm [ ] F W pm [ ] F3 W 3 pm [ ] F4 W 4 pm [ ] F5
PHYSICS 105 Assignment #3 Due by 10 pm September 9, 009 NAME: DISCUSSION SECTION: [ ] D7 W 9 am [ ] D8 W 10 am [ ] HS W 10 am [ ] D9 W 11 am [ ] F 1 W 1 pm [ ] F W pm [ ] F3 W 3 pm [ ] F4 W 4 pm [ ] F5
1. The graph below shows how the velocity of a toy train moving in a straight line varies over a period of time.
 1. The graph below shows how the velocity of a toy train moving in a straight line varies over a period of time. v/m s 1 B C 0 A D E H t/s F G (a) Describe the motion of the train in the following regions
1. The graph below shows how the velocity of a toy train moving in a straight line varies over a period of time. v/m s 1 B C 0 A D E H t/s F G (a) Describe the motion of the train in the following regions
EXSC 408L Fall '03 Problem Set #2 Linear Motion. Linear Motion
 Problems: 1. Once you have recorded the calibration frame for a data collection, why is it important to make sure the camera does not shut off? hat happens if the camera automatically shuts off after being
Problems: 1. Once you have recorded the calibration frame for a data collection, why is it important to make sure the camera does not shut off? hat happens if the camera automatically shuts off after being
Exam Unit 5: Motion and Forces
 Exam Unit 5: Motion and Forces 1. Aleshia is moving forward at constant speed of 2 m/s. Which statement correctly describes Aleshia s movement? A. Her speed is increasing by 2 m/s every second. B. She
Exam Unit 5: Motion and Forces 1. Aleshia is moving forward at constant speed of 2 m/s. Which statement correctly describes Aleshia s movement? A. Her speed is increasing by 2 m/s every second. B. She
JR. GENIUS EDUCATIONAL SERVICES INC.
 1 Name: 1. Multiple Choice: 25 marks Copy to Scantron Card after finding the answer on the sheet. Fill in the Scantron card in the last 5 min. of the test. Do Short section first. 1. You are riding your
1 Name: 1. Multiple Choice: 25 marks Copy to Scantron Card after finding the answer on the sheet. Fill in the Scantron card in the last 5 min. of the test. Do Short section first. 1. You are riding your
Where are you right now? How fast are you moving? To answer these questions precisely, you
 4.1 Position, Speed, and Velocity Where are you right now? How fast are you moving? To answer these questions precisely, you need to use the concepts of position, speed, and velocity. These ideas apply
4.1 Position, Speed, and Velocity Where are you right now? How fast are you moving? To answer these questions precisely, you need to use the concepts of position, speed, and velocity. These ideas apply
Vocabulary. Page 1. Distance. Displacement. Position. Average Speed. Average Velocity. Instantaneous Speed. Acceleration
 Vocabulary Term Definition Distance Displacement Position Average Speed Average Velocity Instantaneous Speed Acceleration Page 1 Homer walked as follows: Starting at the 0,0 coordinate, he walked 12 meters
Vocabulary Term Definition Distance Displacement Position Average Speed Average Velocity Instantaneous Speed Acceleration Page 1 Homer walked as follows: Starting at the 0,0 coordinate, he walked 12 meters
In addition to reading this assignment, also read Appendices A and B.
 1 Kinematics I Introduction In addition to reading this assignment, also read Appendices A and B. We will be using a motion detector to track the positions of objects with time in several lab exercises
1 Kinematics I Introduction In addition to reading this assignment, also read Appendices A and B. We will be using a motion detector to track the positions of objects with time in several lab exercises
Fall 2008 RED Barcode Here Physics 105, sections 1 and 2 Please write your CID Colton
 Fall 2008 RED Barcode Here Physics 105, sections 1 and 2 Exam 1 Please write your CID Colton 2-3669 3 hour time limit. One 3 5 handwritten note card permitted (both sides). Calculators permitted. No books.
Fall 2008 RED Barcode Here Physics 105, sections 1 and 2 Exam 1 Please write your CID Colton 2-3669 3 hour time limit. One 3 5 handwritten note card permitted (both sides). Calculators permitted. No books.
A child places a car of mass 95 g on the track. She adjusts the controller to a power of 4.2 W so the car accelerates from rest for 0.40 s.
 1 The picture shows a track for racing toy electric cars. A guide pin fits in a groove in the track to keep the car on the track. A small electric motor in the car is controlled, with a hand-controller,
1 The picture shows a track for racing toy electric cars. A guide pin fits in a groove in the track to keep the car on the track. A small electric motor in the car is controlled, with a hand-controller,
Unit Conversion Worksheet
 Name: Period Date: Unit Conversion Worksheet Conversions 1 hour = 3600 seconds 1 mile = 5280 feet 1 yard = 3 feet 1 meter = 3.28 feet 1 km = 0.62 miles 1 light second = 300,000,000 meters 1 kg = 2.2 lbs
Name: Period Date: Unit Conversion Worksheet Conversions 1 hour = 3600 seconds 1 mile = 5280 feet 1 yard = 3 feet 1 meter = 3.28 feet 1 km = 0.62 miles 1 light second = 300,000,000 meters 1 kg = 2.2 lbs
Student Exploration: Uniform Circular Motion
 Name: Date: Student Exploration: Uniform Circular Motion Vocabulary: acceleration, centripetal acceleration, centripetal force, Newton s first law, Newton s second law, uniform circular motion, vector,
Name: Date: Student Exploration: Uniform Circular Motion Vocabulary: acceleration, centripetal acceleration, centripetal force, Newton s first law, Newton s second law, uniform circular motion, vector,
Page 2. Indicate with ticks ( ) in the table below which of the quantities are vectors and which are scalars. Velocity Speed Distance Displacement
 Q1.(a) Indicate with ticks ( ) in the table below which of the quantities are vectors and which are scalars. Velocity Speed Distance Displacement vector scalar (b) A tennis ball is thrown vertically downwards
Q1.(a) Indicate with ticks ( ) in the table below which of the quantities are vectors and which are scalars. Velocity Speed Distance Displacement vector scalar (b) A tennis ball is thrown vertically downwards
During part of the journey the car is driven at a constant speed for five minutes.
 Q1.The figure below shows the horizontal forces acting on a car. (a) Which one of the statements describes the motion of the car? Tick one box. It will be slowing down. It will be stationary. It will have
Q1.The figure below shows the horizontal forces acting on a car. (a) Which one of the statements describes the motion of the car? Tick one box. It will be slowing down. It will be stationary. It will have
1. A rabbit can cover a distance of 80 m in 5 s. What is the speed of the rabbit?
 Chapter Problems Motion at Constant Speed Class Work. A rabbit can cover a distance of 80 m in 5 s. What is the speed of the rabbit?. During the first 50 s a truck traveled at constant speed of 5 m/s.
Chapter Problems Motion at Constant Speed Class Work. A rabbit can cover a distance of 80 m in 5 s. What is the speed of the rabbit?. During the first 50 s a truck traveled at constant speed of 5 m/s.
The CBL cannot get accurate data closer than about 0.5 meters, so your graphs will be distorted anywhere the y-values are less than 0.5 meters.
 Name Hour Hiker Lab In this lab, you will be given a graph and you must try to walk in a manner so that the graph of your distance vs. time looks like the given graph. You will need: 1. A TI83 graphics
Name Hour Hiker Lab In this lab, you will be given a graph and you must try to walk in a manner so that the graph of your distance vs. time looks like the given graph. You will need: 1. A TI83 graphics
Figure 1. The distance the train travels between A and B is not the same as the displacement of the train.
 THE DISTANCE-TIME RELATIONSHIP Q1. A train travels from town A to town B. Figure 1 shows the route taken by the train. Figure 1 has been drawn to scale. Figure 1 (a) The distance the train travels between
THE DISTANCE-TIME RELATIONSHIP Q1. A train travels from town A to town B. Figure 1 shows the route taken by the train. Figure 1 has been drawn to scale. Figure 1 (a) The distance the train travels between
A position graph will give the location of an object at a certain time.
 Calculus 3.4 Notes A position graph will give the location of an object at a certain time. At t = 4, the car is 20 miles away from where it started. A position function is usually written as or. If the
Calculus 3.4 Notes A position graph will give the location of an object at a certain time. At t = 4, the car is 20 miles away from where it started. A position function is usually written as or. If the
1. At what speed must you throw a ball vertically in order to reach the top of a building, 12m tall? Vectors
 Physics R Date: 1. At what speed must you throw a ball vertically in order to reach the top of a building, 12m tall? Scalar: Vectors Vectors Scalars Vector: Wind is blowing 15 m/s East. What is the magnitude
Physics R Date: 1. At what speed must you throw a ball vertically in order to reach the top of a building, 12m tall? Scalar: Vectors Vectors Scalars Vector: Wind is blowing 15 m/s East. What is the magnitude
3. Approximately how far will an object near Earth's surface fall in 3.0 seconds? m m m m
 Page 1 of 5 Sub work 10-10-02 Name 12-OCT-03 1. A car travels a distance of 98 meters in 10. seconds. What is the average speed of the car during this 10.-second interval? 1. 4.9 m/s 3. 49 m/s/ 2. 9.8
Page 1 of 5 Sub work 10-10-02 Name 12-OCT-03 1. A car travels a distance of 98 meters in 10. seconds. What is the average speed of the car during this 10.-second interval? 1. 4.9 m/s 3. 49 m/s/ 2. 9.8
REAL LIFE GRAPHS M.K. HOME TUITION. Mathematics Revision Guides Level: GCSE Higher Tier
 Mathematics Revision Guides Real Life Graphs Page 1 of 19 M.K. HOME TUITION Mathematics Revision Guides Level: GCSE Higher Tier REAL LIFE GRAPHS Version: 2.1 Date: 20-10-2015 Mathematics Revision Guides
Mathematics Revision Guides Real Life Graphs Page 1 of 19 M.K. HOME TUITION Mathematics Revision Guides Level: GCSE Higher Tier REAL LIFE GRAPHS Version: 2.1 Date: 20-10-2015 Mathematics Revision Guides
7.3.2 Distance Time Graphs
 7.3.2 Distance Time Graphs 35 minutes 39 marks Page 1 of 11 Q1. A cyclist goes on a long ride. The graph shows how the distance travelled changes with time during the ride. (i) Between which two points
7.3.2 Distance Time Graphs 35 minutes 39 marks Page 1 of 11 Q1. A cyclist goes on a long ride. The graph shows how the distance travelled changes with time during the ride. (i) Between which two points
MoLE Gas Laws Activities
 MoLE Gas Laws Activities To begin this assignment you must be able to log on to the Internet using Internet Explorer (Microsoft) 4.5 or higher. If you do not have the current version of the browser, go
MoLE Gas Laws Activities To begin this assignment you must be able to log on to the Internet using Internet Explorer (Microsoft) 4.5 or higher. If you do not have the current version of the browser, go
Midterm Exam: Making a Study Guide
 Name: Class: Physics Teacher: Mr. Szopiak Date: Midterm Exam: Making a Study Guide This worksheet will help you and your classmates put together a pretty comprehensive guide to your midterm studying. Your
Name: Class: Physics Teacher: Mr. Szopiak Date: Midterm Exam: Making a Study Guide This worksheet will help you and your classmates put together a pretty comprehensive guide to your midterm studying. Your
5. The magnitude of a vector cannot be smaller than the magnitude of any of its components. TRUE FALSE
 Physics 1 Exam 2 Practice S14 Name: Show work for ANY credit. Box answers. Assume 3 significant figures! Ignore air resistance. NEATNESS COUNTS. Conceptual Questions. (2 points each) 1. A 100 g ball rolls
Physics 1 Exam 2 Practice S14 Name: Show work for ANY credit. Box answers. Assume 3 significant figures! Ignore air resistance. NEATNESS COUNTS. Conceptual Questions. (2 points each) 1. A 100 g ball rolls
CHAPTER 10: LINEAR KINEMATICS OF HUMAN MOVEMENT
 CHAPTER 10: LINEAR KINEMATICS OF HUMAN MOVEMENT 1. Vector mechanics apply to which of the following? A. displacement B. velocity C. speed D. both displacement and velocity 2. If velocity is constant, then
CHAPTER 10: LINEAR KINEMATICS OF HUMAN MOVEMENT 1. Vector mechanics apply to which of the following? A. displacement B. velocity C. speed D. both displacement and velocity 2. If velocity is constant, then
Name Date PD. Pythagorean Theorem
 Name Date PD Pythagorean Theorem Vocabulary: Hypotenuse the side across from the right angle, it will be the longest side Legs are the sides adjacent to the right angle His theorem states: a b c In any
Name Date PD Pythagorean Theorem Vocabulary: Hypotenuse the side across from the right angle, it will be the longest side Legs are the sides adjacent to the right angle His theorem states: a b c In any
Preview. Vibrations and Waves Section 1. Section 1 Simple Harmonic Motion. Section 2 Measuring Simple Harmonic Motion. Section 3 Properties of Waves
 Vibrations and Waves Section 1 Preview Section 1 Simple Harmonic Motion Section 2 Measuring Simple Harmonic Motion Section 3 Properties of Waves Section 4 Wave Interactions Vibrations and Waves Section
Vibrations and Waves Section 1 Preview Section 1 Simple Harmonic Motion Section 2 Measuring Simple Harmonic Motion Section 3 Properties of Waves Section 4 Wave Interactions Vibrations and Waves Section
Float a Big Stick. To investigate how objects float by analyzing forces acting on a floating stick
 Chapter 19: Liquids Flotation 53 Float a Big Stick Purpose To investigate how objects float by analyzing forces acting on a floating stick Required Equipment/Supplies Experiment vernier calipers 250-mL
Chapter 19: Liquids Flotation 53 Float a Big Stick Purpose To investigate how objects float by analyzing forces acting on a floating stick Required Equipment/Supplies Experiment vernier calipers 250-mL
Ch. 2 & 3 Velocity & Acceleration
 Ch. 2 & 3 Velocity & Acceleration Objective: Student will be able to Compare Velocity to Speed Identify what is acceleration Calculate velocity and acceleration from an equation and from slope of a graph.
Ch. 2 & 3 Velocity & Acceleration Objective: Student will be able to Compare Velocity to Speed Identify what is acceleration Calculate velocity and acceleration from an equation and from slope of a graph.
77.1 Apply the Pythagorean Theorem
 Right Triangles and Trigonometry 77.1 Apply the Pythagorean Theorem 7.2 Use the Converse of the Pythagorean Theorem 7.3 Use Similar Right Triangles 7.4 Special Right Triangles 7.5 Apply the Tangent Ratio
Right Triangles and Trigonometry 77.1 Apply the Pythagorean Theorem 7.2 Use the Converse of the Pythagorean Theorem 7.3 Use Similar Right Triangles 7.4 Special Right Triangles 7.5 Apply the Tangent Ratio
Motion Graphing Packet
 Name: Motion Graphing Packet This packet covers two types of motion graphs Distance vs. Time Graphs Velocity vs. Time Graphs Describing the motion of an object is occasionally hard to do with words. Sometimes
Name: Motion Graphing Packet This packet covers two types of motion graphs Distance vs. Time Graphs Velocity vs. Time Graphs Describing the motion of an object is occasionally hard to do with words. Sometimes
Projectile Motion (8/24/11) (approx. completion time for just parts A & B: 1.5 h; for entire lab: 2.3 h)
 Projectile Motion (//) (approx. completion time for just parts A & B:. h; for entire lab:. h) EQUIPMENT NEEDED: Mini Launcher and steel ball plumb bob pushrod meter stick carbon paper white paper C-clamp
Projectile Motion (//) (approx. completion time for just parts A & B:. h; for entire lab:. h) EQUIPMENT NEEDED: Mini Launcher and steel ball plumb bob pushrod meter stick carbon paper white paper C-clamp
Force and Motion Test Review
 Name: Period: Force and Motion Test Review 1. I can tell you that force is.. 2. Force is measured in units called. 3. Unbalanced forces acting on an object will MOST LIKELY cause the object to A. remain
Name: Period: Force and Motion Test Review 1. I can tell you that force is.. 2. Force is measured in units called. 3. Unbalanced forces acting on an object will MOST LIKELY cause the object to A. remain
Movement and Position
 Movement and Position Syllabus points: 1.2 plot and interpret distance-time graphs 1.3 know and use the relationship between average speed, distance moved and 1.4 describe experiments to investigate the
Movement and Position Syllabus points: 1.2 plot and interpret distance-time graphs 1.3 know and use the relationship between average speed, distance moved and 1.4 describe experiments to investigate the
Standard Grade Physics Measuring Motion Name: Class: Teacher:
 Standard Grade Physics Measuring Motion Text and page layout copyright Martin Cunningham 25. Majority of clipart copyright www.clipart.com 25. EAT FRUIT F R U Name: Class: Teacher: !+-..( #-/ #-/.. / )#
Standard Grade Physics Measuring Motion Text and page layout copyright Martin Cunningham 25. Majority of clipart copyright www.clipart.com 25. EAT FRUIT F R U Name: Class: Teacher: !+-..( #-/ #-/.. / )#
Solving Quadratic Equations (FAL)
 Objective: Students will be able to (SWBAT) solve quadratic equations with real coefficient that have complex solutions, in order to (IOT) make sense of a real life situation and interpret the results
Objective: Students will be able to (SWBAT) solve quadratic equations with real coefficient that have complex solutions, in order to (IOT) make sense of a real life situation and interpret the results
D) 83 m D) Acceleration remains the same and speed increases. C) 216 m B) 6.0 m shorter A) 4.5 s A) 15 km/hr C) 47 m C) 20 m/sec B) 20 m/sec
 1. A truck, initially traveling at a speed of 22 meters per second, increases speed at a constant rate of 2.4 meters per second 2 for 3.2 seconds. What is the total distance traveled by the truck during
1. A truck, initially traveling at a speed of 22 meters per second, increases speed at a constant rate of 2.4 meters per second 2 for 3.2 seconds. What is the total distance traveled by the truck during
Figure 1. What is the difference between distance and displacement?
 Q1.A train travels from town A to town B. Figure 1 shows the route taken by the train. Figure 1 has been drawn to scale. Figure 1 (a) The distance the train travels between A and B is not the same as the
Q1.A train travels from town A to town B. Figure 1 shows the route taken by the train. Figure 1 has been drawn to scale. Figure 1 (a) The distance the train travels between A and B is not the same as the
Activity 1: Walking Graphs. Answer the following questions based on your experiences in the Student Activity: Walk This Way.
 I. Foundations for Functions 3.1 Interpreting Distance versus Graphs: Activity 1 Activity 1: Walking Graphs Answer the following questions based on your experiences in the Student Activity: Walk This Way.
I. Foundations for Functions 3.1 Interpreting Distance versus Graphs: Activity 1 Activity 1: Walking Graphs Answer the following questions based on your experiences in the Student Activity: Walk This Way.
PHYSICS REVIEW SHEET 2010 MID-TERM EXAM
 PHYSICS REVIEW SHEET 2010 MID-TERM EXAM Concepts And Definitions Definitions of fact, hypothesis, law, theory Explain the scientific method Difference between average and instantaneous speed and speed
PHYSICS REVIEW SHEET 2010 MID-TERM EXAM Concepts And Definitions Definitions of fact, hypothesis, law, theory Explain the scientific method Difference between average and instantaneous speed and speed
Unit 2 Review: Projectile Motion
 Name: Unit 2 Review: Projectile Motion Date: 1. A projectile is fired from a gun near the surface of Earth. The initial velocity of the projectile has a vertical component of 98 meters per second and a
Name: Unit 2 Review: Projectile Motion Date: 1. A projectile is fired from a gun near the surface of Earth. The initial velocity of the projectile has a vertical component of 98 meters per second and a
INSTRUMENT INSTRUMENTAL ERROR (of full scale) INSTRUMENTAL RESOLUTION. Tutorial simulation. Tutorial simulation
 Lab 1 Standing Waves on a String Learning Goals: To distinguish between traveling and standing waves To recognize how the wavelength of a standing wave is measured To recognize the necessary conditions
Lab 1 Standing Waves on a String Learning Goals: To distinguish between traveling and standing waves To recognize how the wavelength of a standing wave is measured To recognize the necessary conditions
The Pythagorean Theorem Diamond in the Rough
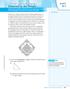 The Pythagorean Theorem SUGGESTED LEARNING STRATEGIES: Shared Reading, Activating Prior Knowledge, Visualization, Interactive Word Wall Cameron is a catcher trying out for the school baseball team. He
The Pythagorean Theorem SUGGESTED LEARNING STRATEGIES: Shared Reading, Activating Prior Knowledge, Visualization, Interactive Word Wall Cameron is a catcher trying out for the school baseball team. He
EF 151 Final Exam - Spring, 2017 Page 3 Copy 223
 EF 151 Final Exam - Spring, 2017 Page 3 Copy 223 Name: Section: 1. Enter your EXAM ID from your seating label. If you don t know your exam ID, enter 000. 0 1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 Digit #1 Digit #2 Digit #3
EF 151 Final Exam - Spring, 2017 Page 3 Copy 223 Name: Section: 1. Enter your EXAM ID from your seating label. If you don t know your exam ID, enter 000. 0 1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 Digit #1 Digit #2 Digit #3
